
Sample records for streptococcal conjugative shuttle
-
Jain, S K; Gill, M S; Pawar, H S; Suresh, Sarasija
2014-09-01
Curcumin-diclofenac conjugate as been synthesized by esterification of phenolic group of curcumin with the acid moiety of diclofenac, and characterized by mass spectrometry, NMR, FTIR, DSC, thermogravimetric analysis and X-ray diffraction analysis. The relative solubility of curcumin-diclofenac conjugate, curcumin and diclofenac; stability of curcumin-diclofenac conjugate in intestinal extract; permeability study of curcumin-diclofenac conjugate using the everted rat intestinal sac method; stability of curcumin-diclofenac conjugate in gastrointestinal fluids and in vitro efficacy have been evaluated. In vivo bioavailability of curcumin-diclofenac conjugate and curcumin in Sprague-Dawley rats, and antiarthritic activity of curcumin-diclofenac conjugate, curcumin and diclofenac in modified streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis model in Balb/c mice to mimic rheumatoid arthritis in humans have also been studied. In all of the above studies, curcumin-diclofenac conjugate exhibited enhanced stability as compared to curcumin; its activity was twice that of diclofenac in inhibiting thermal protein denaturation taken as a measure of in vitro antiinflammatory activity; it enhanced the bioavailability of curcumin by more than five folds, and significantly (Parthritis in streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis model as compared to both diclofenac and curcumin.
-
Conjugate gradient optimization programs for shuttle reentry
Powers, W. F.; Jacobson, R. A.; Leonard, D. A.
1972-01-01
Two computer programs for shuttle reentry trajectory optimization are listed and described. Both programs use the conjugate gradient method as the optimization procedure. The Phase 1 Program is developed in cartesian coordinates for a rotating spherical earth, and crossrange, downrange, maximum deceleration, total heating, and terminal speed, altitude, and flight path angle are included in the performance index. The programs make extensive use of subroutines so that they may be easily adapted to other atmospheric trajectory optimization problems.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Kenchington, Anna L.; Lamont, Ronald F.
2017-01-01
of specific polyvalent vaccines continues, but testing has challenges and may require surrogate markers or molecular-based techniques to manipulate antigenicity and immunogenicity. Expert commentary: Group B streptococcal vaccination using conjugated polyvalent vaccines against the major disease causing...
-
Conjugal plasmid transfer (pAM beta 1) in Lactobacillus plantarum.
Shrago, A W; Chassy, B M; Dobrogosz, W J
1986-01-01
The streptococcal plasmid pAM beta 1 (erythromycin resistance) was transferred via conjugation from Streptococcus faecalis to Lactobacillus plantarum and was transferred among L. plantarum strains. Streptococcus sanguis Challis was transformed with pAM beta 1 isolated from these transconjugants, and transformants harboring intact pAM beta 1 could conjugate the plasmid back to L. plantarum.
-
Namjoshi, Sarika; Giralt, Ernest; Benson, Heather
2016-01-01
This study demonstrates the effectiveness of a peptide shuttle in delivering diclofenac into and through human epidermis. Diclofenac was conjugated to a novel phenylalanyl-N-methyl-naphthalenylalanine-derived diketopiperazine (DKP) shuttle and to TAT (a classical cell penetrating peptide), and topically applied to human epidermis in vitro. DKP and TAT effectively permeated into and through human epidermis. When conjugated to diclofenac, both DKP and TAT enhanced delivery into and through human epidermis, though DKP was significantly more effective. Penetration of diclofenac through human epidermis (to receptor) was increased by conjugation to the peptide shuttle and cell penetrating peptide with enhancement of 6x by DKP-diclofenac and 3x by TAT-diclofenac. In addition, the amount of diclofenac retained within the epidermis was significantly increased by peptide conjugation. COX-2 inhibition activity of diclofenac was retained when conjugated to DKP. Our study suggests that the peptide shuttle approach may offer a new strategy for targeted delivery of small therapeutic and diagnostic molecules to the skin. PMID:27548780
-
Pulmonary Renal Syndrome After Streptococcal Pharyngitis
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gopi Mara-Koosham PhD
2016-04-01
Full Text Available Pulmonary renal syndrome is a class of small vessel vasculitides that are characterized by the dual presentation of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH and glomerulonephritis. Pulmonary renal syndrome has multiple etiologies, but its development has been rarely reported following infection with group A streptococcus. We present the case of a 36-year-old Native American male who was transferred to our facility due to refractory hypoxic respiratory failure. He had been diagnosed with streptococcal pharyngitis 2 weeks prior to admission. Given the presence of hemoptysis, bronchoscopy was performed and was consistent with DAH. Urinalysis demonstrated hematuria and proteinuria, in the setting of elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen. Additionally, antistreptolysin O titer was positive. Given the constellation of laboratory findings and history of streptococcal pharyngitis, the patient was diagnosed with PRS secondary to streptococcal infection. High-dose methylprednisolone was initiated with concomitant plasmapheresis. He was extubated successfully after his respiratory status improved and was eventually discharged home after making a full recovery within 2 weeks after admission. This case illustrates the importance of clinically relevant sequelae of streptococcal infection as well as the appropriate treatment of PRS secondary to streptococcal pharyngitis with plasmapheresis and intravenous corticosteroids.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yousuf Mohammed
Full Text Available This study demonstrates the effectiveness of a peptide shuttle in delivering diclofenac into and through human epidermis. Diclofenac was conjugated to a novel phenylalanyl-N-methyl-naphthalenylalanine-derived diketopiperazine (DKP shuttle and to TAT (a classical cell penetrating peptide, and topically applied to human epidermis in vitro. DKP and TAT effectively permeated into and through human epidermis. When conjugated to diclofenac, both DKP and TAT enhanced delivery into and through human epidermis, though DKP was significantly more effective. Penetration of diclofenac through human epidermis (to receptor was increased by conjugation to the peptide shuttle and cell penetrating peptide with enhancement of 6x by DKP-diclofenac and 3x by TAT-diclofenac. In addition, the amount of diclofenac retained within the epidermis was significantly increased by peptide conjugation. COX-2 inhibition activity of diclofenac was retained when conjugated to DKP. Our study suggests that the peptide shuttle approach may offer a new strategy for targeted delivery of small therapeutic and diagnostic molecules to the skin.
-
Tics, OCD and Streptococcal Infection (PANDAS
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J Gordon Millichap
2008-07-01
Full Text Available Forty matched pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections (PANDAS case-control pairs were prospectively evaluated clinically and with testing for group A b-hemolytic streptococcus for an average of 2 years, in a study at University of Rochester School of Medicine, New York; and WHO Streptococcal Reference Laboratory, Minneapolis, MN.
-
Jain, S. K.; Gill, M. S.; Pawar, H. S.; Suresh, Sarasija
2014-01-01
Curcumin-diclofenac conjugate as been synthesized by esterification of phenolic group of curcumin with the acid moiety of diclofenac, and characterized by mass spectrometry, NMR, FTIR, DSC, thermogravimetric analysis and X-ray diffraction analysis. The relative solubility of curcumin-diclofenac conjugate, curcumin and diclofenac; stability of curcumin-diclofenac conjugate in intestinal extract; permeability study of curcumin-diclofenac conjugate using the everted rat intestinal sac method; st...
-
Homology among tet determinants in conjugative elements of streptococci
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Smith, M.D.; Hazum, S.; Guild, W.R.
1981-10-01
A mutation to tetracycline sensitivity in a resistant strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae was shown by several criteria to be due to a point mutation in the conjugative o(cat-tet) element found in the chromosomes of strains derived from BM6001, a clinical strain resistant to tetracycline and chloramphenicol. Strains carrying the mutation were transformed back to tetracycline resistance with the high efficiency of a point marker by donor deoxyribonucleic acids from its ancestral strain and from nine other clinical isolates of pneumococcus and by deoxyribonucleic acids from Group D Streptococcus faecalis and Group B Streptococcus agalactiae strains that also carry conjugative tet elements in their chromosomes. It was not transformed to resistance by tet plasmid deoxyribonucleic acids from either gram-negative or gram-positive species, except for one that carried transposon TN916, the conjugative tet element present in the chromosomes of some S. faecalis strains. The results showed that the tet determinants in conjugative elements of several streptococcal species share a high degree of deoxyribonucleic acid sequence homology and suggested that they differ from other tet genes.
-
Association of streptococcal throat infection with mental disorders
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Orlovska, Sonja; Vestergaard, Claus Hostrup; Bech, Bodil Hammer
2017-01-01
IMPORTANCE Streptococcal infection has been linked with the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and tic disorders, a concept termed pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infection (PANDAS). However, previous studies of this association have b...
-
Management of group B streptococcal bacteriuria in pregnancy.
Allen, Victoria M; Yudin, Mark H
2012-05-01
To provide information regarding the management of group B streptococcal (GBS) bacteriuria to midwives, nurses, and physicians who are providing obstetrical care. The outcomes considered were neonatal GBS disease, preterm birth, pyelonephritis, chorioamnionitis, and recurrence of GBS colonization. Medline, PubMed, and the Cochrane database were searched for articles published in English to December 2010 on the topic of GBS bacteriuria in pregnancy. Bacteriuria is defined in this clinical practice guideline as the presence of bacteria in urine, regardless of the number of colony-forming units per mL (CFU/mL). Low colony counts refer to pregnancies in which it is appropriate to treat GBS bacteriuria to optimize maternal and perinatal outcomes, to reduce the occurrences of antibiotic anaphylaxis, and to prevent increases in antibiotic resistance to GBS and non-GBS pathogens. No cost-benefit analysis is provided. 1. Treatment of any bacteriuria with colony counts ≥ 100 000 CFU/mL in pregnancy is an accepted and recommended strategy and includes treatment with appropriate antibiotics. (II-2A) 2. Women with documented group B streptococcal bacteriuria (regardless of level of colony-forming units per mL) in the current pregnancy should be treated at the time of labour or rupture of membranes with appropriate intravenous antibiotics for the prevention of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal disease. (II-2A) 3. Asymptomatic women with urinary group B streptococcal colony counts pregnancy should not be treated with antibiotics for the prevention of adverse maternal and perinatal outcomes such as pyelonephritis, chorioamnionitis, or preterm birth. (II-2E) 4. Women with documented group B streptococcal bacteriuria should not be re-screened by genital tract culture or urinary culture in the third trimester, as they are presumed to be group B streptococcal colonized. (II-2D).
-
Streptococcal acute pharyngitis
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lais Martins Moreira Anjos
2014-07-01
Full Text Available Acute pharyngitis/tonsillitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the posterior pharynx and tonsils, is a common disease. Several viruses and bacteria can cause acute pharyngitis; however, Streptococcus pyogenes (also known as Lancefield group A β-hemolytic streptococci is the only agent that requires an etiologic diagnosis and specific treatment. S. pyogenes is of major clinical importance because it can trigger post-infection systemic complications, acute rheumatic fever, and post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Symptom onset in streptococcal infection is usually abrupt and includes intense sore throat, fever, chills, malaise, headache, tender enlarged anterior cervical lymph nodes, and pharyngeal or tonsillar exudate. Cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, and diarrhea are uncommon, and their presence suggests a viral cause. A diagnosis of pharyngitis is supported by the patient's history and by the physical examination. Throat culture is the gold standard for diagnosing streptococcus pharyngitis. However, it has been underused in public health services because of its low availability and because of the 1- to 2-day delay in obtaining results. Rapid antigen detection tests have been used to detect S. pyogenes directly from throat swabs within minutes. Clinical scoring systems have been developed to predict the risk of S. pyogenes infection. The most commonly used scoring system is the modified Centor score. Acute S. pyogenes pharyngitis is often a self-limiting disease. Penicillins are the first-choice treatment. For patients with penicillin allergy, cephalosporins can be an acceptable alternative, although primary hypersensitivity to cephalosporins can occur. Another drug option is the macrolides. Future perspectives to prevent streptococcal pharyngitis and post-infection systemic complications include the development of an anti-Streptococcus pyogenes vaccine.
-
Synergistic inhibition of Streptococcal biofilm by ribose and xylitol.
Lee, Heon-Jin; Kim, Se Chul; Kim, Jinkyung; Do, Aejin; Han, Se Yeong; Lee, Bhumgey David; Lee, Hyun Ho; Lee, Min Chan; Lee, So Hui; Oh, Taejun; Park, Sangbin; Hong, Su-Hyung
2015-02-01
Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus are the major causative agents of human dental caries. Therefore, the removal or inhibition of these streptococcal biofilms is essential for dental caries prevention. In the present study, we evaluated the effects of ribose treatment alone or in combination with xylitol on streptococcal biofilm formation for both species. Furthermore, we examined the expression of genes responsible for dextran-dependent aggregation (DDAG). In addition, we investigated whether ribose affects the biofilm formation of xylitol-insensitive streptococci, which results from long-term exposure to xylitol. The viability of streptococci biofilms formed in a 24-well polystyrene plate was quantified by fluorescent staining with the LIVE/DEAD bacterial viability and counting kit, which was followed by fluorescence activated cell sorting analysis. The effects of ribose and/or xylitol on the mRNA expression of DDAG-responsible genes, gbpC and dblB, was evaluated by RT-qPCR. Our data showed that ribose and other pentose molecules significantly inhibited streptococcal biofilm formation and the expression of DDAG-responsible genes. In addition, co-treatment with ribose and xylitol decreased streptococcal biofilm formation to a further extent than ribose or xylitol treatment alone in both streptococcal species. Furthermore, ribose attenuated the increase of xylitol-insensitive streptococcal biofilm, which results in the reduced difference of biofilm formation between S. mutans that are sensitive and insensitive to xylitol. These data suggest that pentose may be used as an additive for teeth-protective materials or in sweets. Furthermore, ribose co-treatment with xylitol might help to increase the anti-cariogenic efficacy of xylitol. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Fiehn, N E; Gutschik, E; Larsen, Tove
1995-01-01
The purpose of this study was to isolate streptococcal strains from the oral cavities of streptococcal endocarditis patients and compare these strains biochemically and genetically with the corresponding streptococcal blood isolates. Total identity was observed between the blood and oral cavity...
-
Severe acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis in an infant
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jameela A Kari
2013-01-01
Full Text Available Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (APSGN is very rare below the age of two years. We report a 14-month-old girl who presented with frank hematuria and nephrotic syndrome following group A streptococcal pharyngitis (GAS, which was confirmed by laboratory investigations. The patient underwent a renal biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and was treated with prednisolone. The proteinuria and hematuria resolved completely in eight weeks. Our case demonstrates that APSGN should be considered in evaluating hematuria and nephrotic syndrome in infants and children below two years of age.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
McDonald Stephen P
2009-07-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background There has not been a comprehensive, multi-centre study of streptococcal peritonitis in patients on peritoneal dialysis (PD to date. Methods The predictors, treatment and clinical outcomes of streptococcal peritonitis were examined by binary logistic regression and multilevel, multivariate poisson regression in all Australian PD patients involving 66 centres between 2003 and 2006. Results Two hundred and eighty-seven episodes of streptococcal peritonitis (4.6% of all peritonitis episodes occurred in 256 individuals. Its occurrence was independently predicted by Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander racial origin. Compared with other organisms, streptococcal peritonitis was associated with significantly lower risks of relapse (3% vs 15%, catheter removal (10% vs 23% and permanent haemodialysis transfer (9% vs 18%, as well as a shorter duration of hospitalisation (5 vs 6 days. Overall, 249 (87% patients were successfully treated with antibiotics without experiencing relapse, catheter removal or death. The majority of streptococcal peritonitis episodes were treated with either intraperitoneal vancomycin (most common or first-generation cephalosporins for a median period of 13 days (interquartile range 8–18 days. Initial empiric antibiotic choice did not influence outcomes. Conclusion Streptococcal peritonitis is a not infrequent complication of PD, which is more common in indigenous patients. When treated with either first-generation cephalosporins or vancomycin for a period of 2 weeks, streptococcal peritonitis is associated with lower risks of relapse, catheter removal and permanent haemodialysis transfer than other forms of PD-associated peritonitis.
-
Guttate Psoriasis Following Streptococcal Vulvovaginitis in a Five-year-old Girl.
Hernandez, Melia; Simms-Cendan, Judith; Zendell, Kathleen
2015-10-01
Guttate psoriasis is frequently associated with a preceding pharyngeal or perianal streptococcal infection in children. Despite Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (GABHS) being the most common cause of specific bacterial vulvovaginitis in prepubertal girls, there are no reports of streptococcal vulvovaginitis triggering guttate psoriasis. A five-year-old girl presented with guttate psoriasis following an episode of Streptococcal pyogenes vulvovaginitis. Following antibiotic treatment and bacterial eradication she developed vulvar psoriasis that resolved with high potency topical steroids. Identification of an antecedent streptoccocal infection can help predict the long term prognosis in children with guttate psoriasis. The vulvovaginal area should be considered as a source of GABHS infection in young girls with guttate psoriasis, and cultures should be considered if symptoms are present. Published by Elsevier Inc.
-
Cho, Sung Bin; Lee, Ju Hee; Ahn, Keun Jae; Cho, Suhyun; Park, Yong-Beom; Lee, Soo-Kon; Bang, Dongsik; Lee, Kwang Hoon
2010-01-01
We evaluated the reactivity of sera from Behçet's disease (BD), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), dermatomyositis (DM), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and Takayasu's arteritis (TA) patients against human α-enolase and streptococcal α-enolase, and identified additional streptococcal antigens. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunoblotting were performed using sera from patients with BD, SLE, DM, RA, and TA and healthy volunteers (control) against human α-enolase and streptococcal α-enolase. Immunoblot analysis and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation-time-of-flight mass spectrometry were used to identify and recombine other streptococcal antigens. Specific positive signals against recombinant human α-enolase were detected by IgM ELISA of serum samples from 50% of BD, 14.3% of SLE, 57.1% of DM, 42.9% of RA, and 57.1% of TA patients. Specific positive signals against streptococcal α-enolase were detected from 42.9% of BD, 14.3% of DM, and 14.3% of TA patients. No SLE and RA sera reacted against streptococcal α-enolase antigen. Streptococcal proteins reacting with sera were identified as hypothetical protein (HP) for SLE and DM patients, acid phosphatase (AP) for RA patients, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) for TA patients. We observed that RA patients did not present serum reactivity against either HP or GAPDH though BD, SLE, DM, and TA patients did. Also, AP reacted with sera from BD, SLE, DM, RA, and TA patients.
-
CURRENT ASPECTS OF ACUTE STREPTOCOCCAL TONSILLOPHARYNGITIS DIAGNOSTICS IN CHILDREN
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
D. P. Polyakov
2013-01-01
Full Text Available Acute tonsillopharyngitis in children is one of the most common reasons for medical consultations. The majority of acute pharyngeal inflammatory diseases are viral. The frequency of bacterial tonsillopharyngitis in children (the main causative agent is group A Streptococcus, GAS is about 20–30%. In spite of it antibiotics are prescribed for 95% of patients, thus it is inappropriate. On the other hand misdiagnosis of acute streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis and antibiotics refusal can lead to suppurative and nonsuppurative rheumatic complications. Some prominent trials have shown a poor ability of signs and inflammatory biomarkers to identify tonsillopharyngitis streptococcal vs. viral. So it is impossible to use them as indication for antibiotic. The experience of clinical score use (McIsaac etc. have also demonstrated a poor prognostic value. As a result the throat swab culture is the «gold standard» of acute streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis. It has such limitations as rare microbiology labs, method technology, the price and the delay in obtaining result. An alternative technique is GAS rapid antigen detecting test (RADT for the identification of GAS directly from throat swabs. The world data shows a high sensitivity and specificity of modern RADTs.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Emrah Kara
2015-03-01
Full Text Available Pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections, refers to a disorder in children who manifest symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder and/or tic disorders associated with acute exacerbations. Although autoimmune responses following infections with streptococcus have been hypothesized to be responsible, there is still controversies about the pathophysiology and treatment. In this article, the treatment methods of pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections and the role of otolaryngologist were discussed.
-
Streptococcal Subdural Empyema as a Complication of Varicella
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J Gordon Millichap
2005-01-01
Full Text Available A 3-month-old male infant who presented with a group A streptococcal subdural empyema on day 5 of a varicella skin rash is reported from the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada.
-
Beta-hemolytic Streptococcal Bacteremia
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, Hans Ulrik; Kolmos, Hans Jørn; Frimodt-Møller, Niels
2002-01-01
Bacteremia with beta-hemolytic Streptococci groups A, B, C and G has a mortality rate of approximately 20%. In this study we analyzed the association of various patient risk factors with mortality. Records from 241 patients with beta-hemolytic streptococcal bacteremia were reviewed with particular...... attention to which predisposing factors were predictors of death. A logistic regression model found age, burns, immunosuppressive treatment and iatrogenic procedures prior to the infection to be significant predictors of death, with odds ratios of 1.7 (per decade), 19.7, 3.6 and 6.8, respectively...
-
Streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis – principles ofdiagnosis and treatment
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Marcin Dziekiewicz
2016-06-01
Full Text Available Tonsillopharyngitis is one of the main causes of medical appointments. In fact, a seemingly simple diagnosis and treatment causes various problems and is the reason of many problems and errors, including antibiotic misuse or overuse. The most frequent aetiological agents of pharyngitis relate to viruses. A carefully taken medical history and physical examination can help distinguish patients in whom bacterial (streptococcal aetiology should be suspected. However, signs and symptoms themselves do not usually allow the correct diagnosis to be established. A clinical suspicion of bacterial infection must be confirmed microbiologically. The best practice is a throat culture. Rapid tests for the presence of Streptococcus pyogenes antigen are a convenient alternative. They are characterised by high sensitivity and specificity. The first-line treatment in streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis is phenoxymethylpenicillin used for 10 days. Streptococcus pyogenes is uniformly sensitive to this antibiotic. Cefadroxil is reserved for patients with non-immediate hypersensitivity to penicillin and Streptococcus pyogenes carriers. Macrolides, in turn, should be used only if immediate hypersensitivity occurs. In this case, 3–5-day treatment with azithromycin is a convenient alternative to clarithromycin. It is important to use its high, double doses – the standard dose is ineffective. Treatment of streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis with amoxicillin, amoxicillin with clavulanic acid and cefuroxime axetil is considered inappropriate and harmful. These are relatively broad-spectrum antibiotics, but their overuse is conductive to the spread of pneumococci of reduced penicillin sensitivity.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tania Rivera-Hernandez
2016-06-01
Full Text Available Group A Streptococcus (GAS is an important human pathogen responsible for both superficial infections and invasive diseases. Autoimmune sequelae may occur upon repeated infection. For this reason, development of a vaccine against GAS represents a major challenge, since certain GAS components may trigger autoimmunity. We formulated three combination vaccines containing the following: (i streptolysin O (SLO, interleukin 8 (IL-8 protease (Streptococcus pyogenes cell envelope proteinase [SpyCEP], group A streptococcal C5a peptidase (SCPA, arginine deiminase (ADI, and trigger factor (TF; (ii the conserved M-protein-derived J8 peptide conjugated to ADI; and (iii group A carbohydrate lacking the N-acetylglucosamine side chain conjugated to ADI. We compared these combination vaccines to a “gold standard” for immunogenicity, full-length M1 protein. Vaccines were adjuvanted with alum, and mice were immunized on days 0, 21, and 28. On day 42, mice were challenged via cutaneous or subcutaneous routes. High-titer antigen-specific antibody responses with bactericidal activity were detected in mouse serum samples for all vaccine candidates. In comparison with sham-immunized mice, all vaccines afforded protection against cutaneous challenge. However, only full-length M1 protein provided protection in the subcutaneous invasive disease model.
-
Acute Rheumatic Fever versus Post-Streptococcal Reactive Arthritis
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ashry, K.M.
2009-01-01
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that may develop after a Group A streptococcal infection and can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. A migrating polyarthritis after throat infection with group A β-haemolytic streptococci is classically attributed to acute rheumatic fever (ARF). Sterile non-migratory arthritis may occur as a separate entity, the so called post streptococcal reactive arthritis (PSRA). This study aimed to identify clinical and serological differences of patients with reactive arthritis after infection with Lance field group Aβ-haemolytic streptococci, compared with acute rheumatic fever. Hundred and twenty patients were recruited for the study , they were classified into two groups according to the diagnosis of ARF and PSRA patients consecutively seen in the Rheumatology and the Pediatric wards. Clinical and laboratory data were assessed through a questionnaire. The diagnosis of rheumatic fever was made based on revised modified Jones' criteria, while the diagnosis of post streptococcal reactive arthritis was made based on Deighton criteria; these associated with laboratory data, electrocardiography, chest X-ray, and bi-dimensional echocardiography. Results revealed no significant differences between both groups as regard age where ρ>0.05, while there were a significant difference regarding the date of antecedent upper respiratory tract infection (ρ 0.05). Regarding the cardio logical changes P-R interval by ECG was prolonged in 19 patients (31.67%)and Echo study showed changes in 12 patient (20%) of cases of ARF patient only. On the basis of simple laboratory variables and management, it ws possible to differentiate ARF from PSRA patients. So it could be concluded that these two conditions are actually distinct identities
-
Group B streptococcal metastatic endophthalmitis.
Nagelberg, H P; Petashnick, D E; To, K W; Woodcome, H A
1994-04-15
Reports of invasive Group B Streptococcus infection in adults with underlying medical conditions have been increasing. Ocular infection with this organism is unusual. Metastatic endophthalmitis in adults caused by this organism has been reported rarely and has only been associated with endocarditis. We encountered two cases of Group B streptococcal metastatic endophthalmitis in adults who did not have endocarditis. These cases reflect the increasing incidence of invasive Group B Streptococcus infection with its varying manifestations. Additionally, they emphasize the importance of considering this pathogen as a cause of metastatic endophthalmitis in adults with predisposing illnesses.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hana Rac
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Necrotizing fasciitis is a deep-seated subcutaneous tissue infection that is commonly associated with streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (TSS. Surgical debridement plus penicillin and clindamycin are the current standard of care. We report a case of necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal TSS where linezolid was added after a failure to improve with standard therapy. Briefly after isolation of Streptococcus pyogenes from tissue cultures, the patient underwent two surgical debridement procedures and was changed to standard of care therapy. While the patient was hemodynamically stable, the patient’s wounds, leukocytosis, and thrombocytopenia all progressively worsened. After initiation of linezolid, the patient slowly improved clinically. The present report is the first to highlight the role of linezolid in streptococcal necrotizing fasciitis and TSS not improving with standard therapy.
-
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Odalovic A.
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN is a frequent cause of acute nephritis in children. This case study was done with the aim to point out that the infections caused by Group A streptococci, in spite of antibiotic era, are still present in the population. An 8-year old boy was admitted in our hospital with a two-day history of fewer, tonsillopharyngitis. After hospital admission, patient was treated with penicillin during the period of 10 days, antihypertensive medications (captopril, furosemide, including restricted diet of salt. After the treatment, patient became better. On demission it was found proteinuria and microhematuria PSGN is very serious disease, which leaves severe complications if the valid therapy with penicillin is not used in propriety time, during the recommended period of 10 days.
-
Singer, Harvey S.
2015-01-01
The entity Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal infections (PANDAS) was initially proposed in 1998 (Swedo, et al. 1998). The formal diagnosis required that the affected individual meet five specific criteria: prepubertal onset, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) and/or a tic disorder, the dramatic sudden explosive onset of symptoms, a relapsing and remitting course of symptoms that are temporally associated with Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal (G...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Papageorgiou Konstantinos I
2008-02-01
Full Text Available Abstract Introduction We report a case of optic atrophy, necrotizing anterior scleritis and keratitis presenting in a patient with Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome. Case presentation A 43-year-old woman developed streptococcal toxic shock syndrome secondary to septic arthritis of her right ankle. Streptococcus pyogenes (b-haemolyticus Group A was isolated from blood cultures and joint aspirate. She was referred for ophthalmology review as her right eye became injected and the pupil had become unresponsive to light whilst she was in the Intensive Therapy Unit (ITU. The iris appeared atrophic and was mid-dilated with no direct or consensual response to light. Three zones of sub-epithelial opacification where noted in the cornea. There where extensive posterior synechiae. Indirect ophthalmoscopy showed a pale right disc. The vision was reduced to hand movements (HM. A diagnosis of optic atrophy was made secondary to post-streptococcal uveitis. She subsequently developed a necrotizing anterior scleritis. Conclusion This case illustrates a previously unreported association of optic atrophy, necrotizing anterior scleritis and keratitis in a patient with post-streptococcal uveitis. This patient had developed Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome secondary to septic arthritis. We recommend increased awareness of the potential risks of these patients developing severe ocular involvement.
-
Evolutionary paths of streptococcal and staphylococcal superantigens
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Okumura Kayo
2012-08-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS harbors several superantigens (SAgs in the prophage region of its genome, although speG and smez are not located in this region. The diversity of SAgs is thought to arise during horizontal transfer, but their evolutionary pathways have not yet been determined. We recently completed sequencing the entire genome of S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (SDSE, the closest relative of GAS. Although speG is the only SAg gene of SDSE, speG was present in only 50% of clinical SDSE strains and smez in none. In this study, we analyzed the evolutionary paths of streptococcal and staphylococcal SAgs. Results We compared the sequences of the 12–60 kb speG regions of nine SDSE strains, five speG+ and four speG–. We found that the synteny of this region was highly conserved, whether or not the speG gene was present. Synteny analyses based on genome-wide comparisons of GAS and SDSE indicated that speG is the direct descendant of a common ancestor of streptococcal SAgs, whereas smez was deleted from SDSE after SDSE and GAS split from a common ancestor. Cumulative nucleotide skew analysis of SDSE genomes suggested that speG was located outside segments of steeper slopes than the stable region in the genome, whereas the region flanking smez was unstable, as expected from the results of GAS. We also detected a previously undescribed staphylococcal SAg gene, selW, and a staphylococcal SAg -like gene, ssl, in the core genomes of all Staphylococcus aureus strains sequenced. Amino acid substitution analyses, based on dN/dS window analysis of the products encoded by speG, selW and ssl suggested that all three genes have been subjected to strong positive selection. Evolutionary analysis based on the Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo method showed that each clade included at least one direct descendant. Conclusions Our findings reveal a plausible model for the comprehensive evolutionary pathway of streptococcal and
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
SE Jabbarifar
2005-11-01
Full Text Available Background: Frequent topical fluoride therapy through toothpaste, mouthrinse, professional gels and solutions causes decrease in incidence, pause and repair of dental caries in the enamel. These mechanisms are done through penetration of fluoride ions (F- and their replacement with hydroxyl ions (OH- of hydroxyappatite of enamel, interfere with microbial metabolism of dental plaque and bacteriostatic effect on some cariogenic bacterial strains such as streptococci. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of fluoride mouthrinse and toothpaste on the number of streptococcal colony forming units of dental plaque. Methods: 62 children with 6-7 years old were put in two groups. Samples of dental plaque from each group were collected both before and after use of the fluoride mouthrinse and or toothpaste. The samples were cultured on blood agar to find the number of streptococcal colony forming units (CFU. The mean colony forming unit was compared inter and intra groups before and after application of Fluoride products. Results: The streptococcal CFU of dental plaque before and after use of the mouthrinse and toothpaste respectively was (1240±1367, 1253±1341.5 and (551±716, 898±1151. Statistically, the streptococcal CFU in each group before and after use of the toothpaste and mouthrinse was significantly different. Conclusion: The findings of this study indicated that the fluoride toothpaste and mouthrinse reduce number of streptococcal colony forming units of dental plaque. Also this reduction was not depended on level of (F- Ions, sort of vehicle of fluoride and frequent application of the fluoride mouthrinse and toothpaste. Keywords: fluoride mouthrinse, fluoride toothpaste, colony forming unit (CFU, streptococcus
-
Beşiroğlu, Lütfullah; Ağargün, Mehmet Yücel; Ozbebit, Ozgür; Sözen, Mehmet; Dilek, Imdat; Güleç, Mustafa
2007-01-01
The acronym PANDAS (pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections) has been assigned to a subgroup of patients experiencing pediatric onset obsessive-compulsive symptoms and tics as a result of autoimmune response to group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection. It has been hypothesized that an immune process initiated by infection affects the basal ganglia and causes neuropsychiatric symptoms. In cases with severe neuropsychiatric symptoms, the use of treatment strategies that interrupt the autoimmune process responsible for the pathogenesis of PANDAS, such as therapeutic plasmapheresis or intravenous immunoglobulin, has been proposed. In this paper, we discuss the effect of plasmapheresis treatment in 4 adult cases of obsessive-compulsive disorder and tic disorder triggered by streptococcal infections.
-
Brimberg, Lior; Benhar, Itai; Mascaro-Blanco, Adita; Alvarez, Kathy; Lotan, Dafna; Winter, Christine; Klein, Julia; Moses, Allon E; Somnier, Finn E; Leckman, James F; Swedo, Susan E; Cunningham, Madeleine W; Joel, Daphna
2012-01-01
Group A streptococcal (GAS) infections and autoimmunity are associated with the onset of a spectrum of neuropsychiatric disorders in children, with the prototypical disorder being Sydenham chorea (SC). Our aim was to develop an animal model that resembled the behavioral, pharmacological, and immunological abnormalities of SC and other streptococcal-related neuropsychiatric disorders. Male Lewis rats exposed to GAS antigen exhibited motor symptoms (impaired food manipulation and beam walking) and compulsive behavior (increased induced-grooming). These symptoms were alleviated by the D2 blocker haloperidol and the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor paroxetine, respectively, drugs that are used to treat motor symptoms and compulsions in streptococcal-related neuropsychiatric disorders. Streptococcal exposure resulted in antibody deposition in the striatum, thalamus, and frontal cortex, and concomitant alterations in dopamine and glutamate levels in cortex and basal ganglia, consistent with the known pathophysiology of SC and related neuropsychiatric disorders. Autoantibodies (IgG) of GAS rats reacted with tubulin and caused elevated calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II signaling in SK-N-SH neuronal cells, as previously found with sera from SC and related neuropsychiatric disorders. Our new animal model translates directly to human disease and led us to discover autoantibodies targeted against dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the rat model as well as in SC and other streptococcal-related neuropsychiatric disorders. PMID:22534626
-
Management of guttate psoriasis in patients with associated streptococcal infection
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Karabudak Abuaf O
2012-11-01
Full Text Available Özlem Karabudak Abuaf, Bilal DoganDepartment of Dermatology, GATA Haydarpasa Teaching Hospital, Istanbul, TurkeyAbstract: Psoriasis is a T cell-mediated inflammatory skin disease. It can be provoked or exacerbated by environmental factors, particularly medications and infections. Guttate psoriasis is a distinctive acute form of psoriasis that generally occurs in children and young adults. The association between guttate psoriasis and Streptococcus pyogenes is well established in medical literature; however, the exact mechanism can only be theorized. Treatment guidelines are not established, and it is unclear how necessary antibiotics are for acute state guttate psoriasis. Many dermatologists have recommended using antibiotic therapy or tonsillectomy, especially for patients with recurrent streptococcal infections. This paper briefly summarizes the possible mechanisms of pathogenesis and the recent research results on this topic and examines under what conditions a curative treatment of streptococcal infection by tonsillectomy or antibiotic treatment may benefit psoriasis patients.Keywords: guttate, psoriasis, treatment, Streptococcus pyogenes
-
Yang, Peng; Peng, Xiaomin; Cui, Shujuan; Shao, Junbin; Zhu, Xuping; Zhang, Daitao; Liang, Huijie; Wang, Quanyi
2013-07-30
Streptococcal superantigens (SAgs) are the major virulence factors of infection in humans for group A Streptococcus (GAS) bacteria. A panel consisting of seven duplex real-time PCR assays was developed to simultaneously detect 13 streptococcal SAgs and one internal control which may be important in the control of GAS-mediated diseases. Primer and probe sequences were selected based on the highly conserved region from an alignment of nucleotide sequences of the 13 streptococcal SAgs. The reaction conditions of the duplex real-time PCR were optimized and the specificity of the duplex assays was evaluated using SAg positive strains. The limit of detection of the duplex assays was determined by using 10-fold serial dilutions of the DNA of 13 streptococcal SAgs and compared to a conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for evaluating the duplex assays sensitivity. Using the duplex assays, we were able to differentiate between 13 SAgs from Streptococcus strains and other non-Streptococcus bacteria without cross-reaction. On the other hand, the limit of detection of the duplex assays was at least one or two log dilutions lower than that of the conventional PCR. The panel was highly specific (100%) and the limit of detection of these duplex groups was at least ten times lower than that obtained by using a conventional PCR method.
-
Influence of surface roughness on streptococcal adhesion forces to composite resins
Mei, Li; Busscher, Henk J; van der Mei, Henny C; Ren, Yijin
OBJECTIVE: To determine streptococcal adhesion forces with composite resins with different surface roughness. METHODS: Polishing and grinding were applied to obtain smooth (roughness 20 nm), moderately rough (150 nm) and rough (350 nm) surfaces of two orthodontic, light-cured composites. Adhesion
-
Is neonatal group B streptococcal infection preventable?
LENUS (Irish Health Repository)
Azam, M
2011-05-01
Early onset group B streptococcal (EOGBS) infection causes significant neonatal morbidity and mortality. We determined the incidence of EOGBS at Galway University Hospital (GUH) and examined any "missed opportunities" for preventing neonatal infection between 2004 and 2009. Our obstetric approach is risk-based. The incidence was 0.45\\/1,000 live-births; one death and one with neurological sequelae. A single mother received IAP; however we could not determine any potential for reducing cases of EOGBS by improving current IAP usage.
-
Group C streptococcal sepsis complicating Fournier gangrene.
Marinella, Mark A
2005-09-01
Fournier gangrene is a life-threatening necrotizing fasciitis of the perineal-scrotal area that occurs in diabetic males. Patients typically present with systemic toxicity and significant inflammatory changes in the scrotum and perineum. Most cases of Fournier gangrene are polymicrobic and require urgent surgical debridement and broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy. We describe a case of Fournier gangrene in a young diabetic man that was associated with group C streptococcal bacteremia, an association previously unreported in the literature to our knowledge.
-
Morici, Eleonora; Simoni, Serena; Brenciani, Andrea; Giovanetti, Eleonora; Varaldo, Pietro E; Mingoia, Marina
2017-01-01
To investigate the genetic basis of catQ-mediated chloramphenicol resistance in Streptococcus agalactiae. Two clinical strains of catQ-positive chloramphenicol-resistant S. agalactiae (Sag236 and Sag403) were recently isolated, typed (MLST, PFGE pulsotypes, capsular types) and their antibiotic resistances investigated by phenotypic and genotypic approaches. Several molecular methods (PCR mapping, restriction assays, Southern blotting, sequencing and sequence analysis, conjugal transfer assays) were used to determine the genetic context of catQ and characterize a genetic element detected in the isolates. Sag236 and Sag403 shared the same ST (ST19), but exhibited a different capsular type (III and V, respectively) and pulsotype. Both harboured the macrolide resistance genes mef(I) and erm(TR) and the tetracycline resistance gene tet(M). Accordingly, they were resistant to chloramphenicol, erythromycin and tetracycline. catQ and mef(I) were associated in an IQ module that was indistinguishable in Sag236 and Sag403. In mating assays, chloramphenicol and erythromycin resistance proved transferable, at low frequency, only from Sag236. Transconjugants carried not only catQ and mef(I), but also erm(TR), suggesting a linkage of the three resistance genes in a mobile element, which, though seemingly non-mobile, was also detected in Sag403. The new element (designated ICESag236, ∼110 kb) results from recombination of two integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) originally described in different streptococcal species: S. agalactiae ICESagTR7, carrying erm(TR); and Streptococcus pneumoniae ICESpn529IQ, carrying the prototype IQ module. These findings strengthen the notion that widespread streptococcal ICEs may form mosaics that enhance their diversity and spread, broaden their host range and carry new cargo genes. © The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. All rights reserved. For Permissions
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Abu Sadat Mohammad Sayeem Bin Shahid
Full Text Available Although Streptococcal bacteremia is common in diarrheal children with high morbidity and mortality, no systematic data are available on Streptococcal bacteremia in diarrheal children. We sought to evaluate the factors associated with Streptococcal bacteremia in diarrheal children under five years of age and their outcome.We used an unmatched case-control design to investigate the associated factors with Streptococcal bacteremia in all the diarrheal children under five years of age through electronic medical record system of Dhaka hospital of International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh. We had simultaneously used a retrospective cohort design to further evaluate the outcome of our study children. All the enrolled children had their blood culture done between January 2010 and December 2012. Comparison was made among the children with (cases = 26 and without Streptococcal bacteremia (controls = 78. Controls were selected randomly from hospitalized diarrheal children under five years of age.Cases had proportionately higher deaths compared to controls, but it was statistically insignificant (15% vs. 10%, p = 0.49. The cases more often presented with severe dehydration, fever, respiratory distress, severe sepsis, and abnormal mental status compared to the controls (for all p<0.05. In the logistic regression analysis, after adjusting for potential confounders, it has been found that Streptococcal bacteremia in diarrheal children under five years of age was independently associated with nutritional edema (OR: 5.86, 95% CI = 1.28-26.80, hypoxemia (OR: 19.39, 95% CI = 2.14-175.91, fever (OR: 4.44, 95% CI = 1.13-17.42, delayed capillary refill time (OR: 7.00, 95% CI = 1.36-35.93, and respiratory distress (OR: 2.69, 95% CI = 1.02-7.12.The results of our analyses suggest that diarrheal children under five years of age presenting with nutritional edema, hypoxemia, fever, delayed capillary refill time, and respiratory distress may be at
-
Fronhoffs, S; Luyken, J; Steuer, K; Hansis, M; Vetter, H; Walger, P
2000-10-01
To evaluate the effect of adjunctive C1-esterase inhibitor substitution therapy on clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (TSS). Observational. Medizinische Poliklinik, University of Bonn, Germany. Seven patients with direct or indirect evidence of streptococcal TSS. In addition to conventional and supportive therapy, all patients received 2-3 single doses of C1-esterase inhibitor totaling 6,000-10,000 U within the first 24 h after admission. All patients developed fulminant septic shock, multiorgan failure and/or capillary leak syndrome and necrotizing fasciitis within 10-72 h following the onset of first symptoms. Between 1 and 4 days following administration of C1-esterase inhibitor, a marked shift of fluid from extravascular to intravascular compartments took place in all but one patient, accompanied by a transient intra-alveolar lung edema and rapidly decreasing need for adrenergic agents. Six of seven patients survived. These clinical observations in a small series of patients and the favorable outcome point towards a positive effect of early and high-dose administration of C1-esterase inhibitor as adjunctive therapy in streptococcal TSS. The possible mechanism involved may be the attenuation of capillary leak syndrome (CLS) via early inactivation of complement and contact systems. Controlled studies are needed to establish an improvement of the survival rates of patients with streptococcal TSS following administration of C1-esterase inhibitor.
-
Streptococcal necrotizing myositis: a case report and clinical review.
Hourmozdi, Justin J; Hawley, Dean A; Hadi, Christiane M; Tahir, Bilal; Seupaul, Rawle A
2014-03-01
Streptococcal necrotizing myositis, also known as gangrenous myositis, is a very rare and severe soft tissue infection that predominately involves skeletal muscle and, eventually, superficial fascia and surrounding tissues. The presentation is often nonspecific until the rapidly progressing clinical course becomes apparent. A high morbidity and mortality rate has been reported in the small number of cases since 1900. Despite several attempts to better define the different entities causing necrotizing myositis, no single definitive causal relationship has been defined. A review of the literature is presented here to help clinicians distinguish those with necrotizing myositis from those with nonnecrotizing myositis when the clinician is at all confronted with the suspicion for such an infection. The case presented is that of a 48-year-old woman who had streptococcal necrotizing myositis. She died roughly 72 h after admission. After the patient's death, the clinical team sought consent for autopsy. Hospital staff made contact with family, and information was obtained from the family that the onset of the patient's symptoms was allegedly temporally related to her acquisition of a new tattoo on the right back, where the tattoo process allegedly included injection of cremated ashes of a pet dog. A high level of suspicion for necrotizing myositis must be maintained for a patient with unexplained severe muscle pain and soft tissue swelling accompanied by systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gwendolyn L. Gilbert
2003-01-01
Full Text Available Objective: To compare two protocols for intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis (IAP against neonatal group B streptococcal (GBS sepsis, with respect to staff compliance, in a prospective cohort study in the obstetric units of a community hospital (A and a university teaching hospital (B.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sarah Chuzeville
Full Text Available Genetic exchanges between Streptococci occur frequently and contribute to their genome diversification. Most of sequenced streptococcal genomes carry multiple mobile genetic elements including Integrative and Conjugative Elements (ICEs that play a major role in these horizontal gene transfers. In addition to genes involved in their mobility and regulation, ICEs also carry genes that can confer selective advantages to bacteria. Numerous elements have been described in S. agalactiae especially those integrated at the 3' end of a tRNA(Lys encoding gene. In strain 515 of S. agalactiae, an invasive neonate human pathogen, the ICE (called 515_tRNA(Lys is functional and carries different putative virulence genes including one encoding a putative new CAMP factor in addition to the one previously described. This work demonstrated the functionality of this CAMP factor (CAMP factor II in Lactococcus lactis but also in pathogenic strains of veterinary origin. The search for co-hemolytic factors in a collection of field strains revealed their presence in S. uberis, S. dysgalactiae, but also for the first time in S. equisimilis and S. bovis. Sequencing of these genes revealed the prevalence of a species-specific factor in S. uberis strains (Uberis factor and the presence of a CAMP factor II encoding gene in S. bovis and S. equisimilis. Furthermore, most of the CAMP factor II positive strains also carried an element integrated in the tRNA(Lys gene. This work thus describes a CAMP factor that is carried by a mobile genetic element and has spread to different streptococcal species.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Anand Thangarajan
2012-02-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background The major virulence factors determining the pathogenicity of streptococcal strains include M protein encoded by emm and emm-like (emmL genes and superantigens. In this study, the distribution of emm, emmL and superantigen genes was analyzed among the streptococcal strains isolated from the patients of acute pharyngitis. Methods The streptococcal strains were isolated from the throat swabs of 1040 patients of acute pharyngitis. The emm and emmL genes were PCR amplified from each strain and sequenced to determine the emm types. The dot-blot hybridization was performed to confirm the pathogens as true emm nontypeable strains. The presence of eleven currently known superantigens was determined in all the strains by multiplex PCR. Results Totally, 124 beta-hemolytic streptococcal strains were isolated and they were classified as group A streptococcus (GAS [15.3% (19/124], group C streptococcus (GCS [59.7% (74/124] and group G streptococcus (GGS [25.0% (31/124]. Among 124 strains, only 35 strains were emm typeable and the remaining 89 strains were emm nontypeable. All GAS isolates were typeable, whereas most of the GCS and GGS strains were nontypeable. These nontypeable strains belong to S. anginosus [75.3% (67/89] and S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis [24.7% (22/89]. The emm and emmL types identified in this study include emm12.0 (28.6%, stG643.0 (28.6%, stC46.0 (17.0%, emm30.11 (8.5%, emm3.0 (2.9%, emm48.0 (5.7%, st3343.0 (2.9%, emm107.0 (2.9% and stS104.2 (2.9%. Various superantigen profiles were observed in typeable as well as nontypeable strains. Conclusions Multiplex PCR analysis revealed the presence of superantigens in all the typeable strains irrespective of their emm types. However, the presence of superantigen genes in emm and emmL nontypeable strains has not been previously reported. In this study, presence of at least one or a combination of superantigen coding genes was identified in all the emm and emmL nontypeable
-
Davies, Bethan; Jesty, Robert; Uddin, Shahana; Metaxa, Victoria
2018-04-26
This case describes a 54-year-old woman with exudative eczema, who was admitted to the intensive care unit with a serum sodium concentration of 191 mmol/L, secondary to profound dehydration in the context of group A streptococcal septicaemia. Successful rehydration and electrolyte normalisation was achieved with continuous venovenous haemodiafiltration (CVVHDF), the replacement fluid of which was infused with hypertonic saline to limit the rate of sodium reduction. This case report comments on three areas of interest. First, hypernatraemia of this level is unusual. Second, the infusion of hypertonic saline into the replacement fluid of the CVVHDF filter is not common practice but successfully ensured a controlled reduction in serum sodium concentration while aggressively replacing a 9 L water deficit. Third, the notable physiological reserve demonstrated by the patient: despite an extraordinary serum sodium concentration in the context of overwhelming streptococcal septicaemia, she has made a full cognitive recovery. © BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
-
Structure of the Mature Streptococcal Cysteine Protease Exotoxin mSpeB in Its Active Dimeric Form
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Olsen, Johan G; Dagil, Robert; Niclasen, Louise Meinert
2009-01-01
Invasive infections of Streptococcus pyogenes are dependent on the cysteine protease streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin B. Previous structures of the enzyme have not disclosed the proper active-site configuration. Here, the crystal structure of the mature enzyme is presented to 1.55 A, disclosing...
-
VANDERMEI, HC; NAUMANN, D; BUSSCHER, HJ
1993-01-01
The grouping and identification made by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) of 40 oral streptococcal strains was compared with their known taxonomic positions. Grouping was obtained by cluster analysis on the spectral distances between the first derivative spectra of the strains. Spectra
-
Purification of SUMO conjugating enzymes and kinetic analysis of substrate conjugation
Yunus, Ali A.; Lima, Christopher D.
2009-01-01
SUMO conjugation to protein substrates requires the concerted action of a dedicated E2 ubiquitin conjugation enzyme (Ubc9) and associated E3 ligases. Although Ubc9 can directly recognize and modify substrate lysine residues that occur within a consensus site for SUMO modification, E3 ligases can redirect specificity and enhance conjugation rates during SUMO conjugation in vitro and in vivo. In this chapter, we will describe methods utilized to purify SUMO conjugating enzymes and model substrates which can be used for analysis of SUMO conjugation in vitro. We will also describe methods to extract kinetic parameters during E3-dependent or E3-independent substrate conjugation. PMID:19107417
-
Sumazaki, Makoto; Saito, Fumi; Ogata, Hideaki; Yoshida, Miho; Kubota, Yorichika; Magoshi, Syunsuke; Kaneko, Hironori
2017-07-14
Breast cancer-related lymphedema often causes cellulitis and is one of the most common complications after breast cancer surgery. Streptococci are the major pathogens underlying such cellulitis. Among the streptococci, the importance of the Lancefield groups C and G is underappreciated; most cases involve Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis. Despite having a relatively weak toxicity compared with group A streptococci, Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis is associated with a mortality rate that is as high as that of group A streptococci in cases of invasive infection because Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis mainly affects elderly individuals who already have various comorbidities. An 83-year-old Japanese woman with breast cancer-related lymphedema in her left upper limb was referred to our hospital with high fever and acute pain with erythema in her left arm. She showed septic shock with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Blood culture showed positive results for Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis, confirming a diagnosis of streptococcal toxic-shock syndrome. She survived after successful intensive care. To the best of our knowledge, this case represents the first report of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis-induced streptococcal toxic-shock syndrome in a patient with breast cancer-related lymphedema. Breast cancer-related lymphedema is a common problem, and we must pay attention to invasive streptococcal soft tissue infections, particularly in elderly patients with chronic disease.
-
Nicolini, Humberto; López, Yaumara; Genis-Mendoza, Alma D; Manrique, Viana; Lopez-Canovas, Lilia; Niubo, Esperanza; Hernández, Lázaro; Bobes, María A; Riverón, Ana M; López-Casamichana, Mavil; Flores, Julio; Lanzagorta, Nuria; De la Fuente-Sandoval, Camilo; Santana, Daniel
2015-01-01
Infection with group A Streptococcus (StrepA) can cause post-infectious sequelae, including a spectrum of childhood-onset obsessive-compulsive (OCD) and tic disorders with autoimmune origin (PANDAS, Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal Infections). Until now, no single immunological test has been designed that unequivocally diagnoses these disorders. In this study, we assessed the detection of serum antibodies against human brain enolase (AE), neural tissue (AN) and Streptococcus (AS) as a laboratory tool for the diagnosis of early-onset psychiatric disorders. Serum antibodies against human brain enolase, total brain proteins, and total proteins from StrepA were detected by ELISA in 37 patients with a presumptive diagnosis of PANDAS and in 12 healthy subjects from Mexico and Cuba. The antibody titers against human brain enolase (AE) and Streptococcal proteins (AS) were higher in patients than in control subjects (t-student, tAE=-2.17, P=0.035; tAS=-2.68, P=0.01, n=12 and 37/group, df=47, significance level 0.05), while the neural antibody titers did not differ between the two groups (P(t)=0.05). The number of subjects (titers> meancontrol + CI95) with simultaneous seropositivity to all three antibodies was higher in the patient group (51.4%) than in the control group (8.3%) group (X2=5.27, P=0.022, df=1, n=49). The simultaneous detection of all three of these antibodies could provide valuable information for the etiologic diagnosis of individuals with early-onset obsessive-compulsive disorders associated with streptococcal infection and, consequently, for prescribing suitable therapy.
-
Sharma, Sachin; Vaish, Supriya; Chopra, Saurabh; Singh, Vindyaprakash; Sharma, Priyanka
2012-01-01
Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders associated with Streptococcal infection (PANDAS) is a unique constellation of signs and symptoms that exist in a subset of children with rapid onset or exacerbation of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and/or tic disorders due to an initial autoimmune reaction to a Group A Beta Hemolytic…
-
Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin B (SpeB) boosts the contact system via binding of a-1 antitrypsin
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Meinert Niclasen, Louise; Olsen, Johan G; Dagil, Robert
2011-01-01
The Streptococcus pyogenes cysteine protease SpeB (streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin B) is important for the invasive potential of the bacteria, but its production is down-regulated following systemic infection. This prompted us to investigate if SpeB potentiated the host immune response after sys...
-
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling: the ins and outs of quantitative imaging.
Molenaar, Chris; Weeks, Kate L
2018-05-17
Nucleocytoplasmic protein shuttling is integral to the transmission of signals between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nuclear/cytoplasmic distribution of proteins of interest can be determined via fluorescence microscopy, following labelling of the target protein with fluorophore-conjugated antibodies (immunofluorescence) or by tagging the target protein with an autofluorescent protein, such as green fluorescent protein (GFP). The latter enables live cell imaging, a powerful approach that precludes many of the artefacts associated with indirect immunofluorescence in fixed cells. In this review, we discuss important considerations for the design and implementation of fluorescence microscopy experiments to quantify the nuclear/cytoplasmic distribution of a protein of interest. We summarise the pros and cons of detecting endogenous proteins in fixed cells by immunofluorescence and ectopically-expressed fluorescent fusion proteins in living cells. We discuss the suitability of widefield fluorescence microscopy and of 2D, 3D and 4D imaging by confocal microscopy for different applications, and describe two different methods for quantifying the nuclear/cytoplasmic distribution of a protein of interest from the fluorescent signal. Finally, we discuss the importance of eliminating sources of bias and subjectivity during image acquisition and post-imaging analyses. This is critical for the accurate and reliable quantification of nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
-
Streptococcus infection in human populations continues to be a major cause of morbidity and mortality. To evaluate the effect of genetic background and toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) on antibacterial defense to streptococcal infection, eight genetically diverse strains of mic...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Antonella Macerollo
2013-09-01
Full Text Available Pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcus infections (PANDAS originated from the observational work of Swedo and collaborators, who formalized their definition in 1998 in a set of operational criteria. The application of these criteria, which focuses on tics and obsessive-compulsive symptoms as core symptoms, has encountered difficulties, eventually leading to a high rate of misdiagnosis. In particular, the core feature represented by the association between newly diagnosed infections and neuropsychiatric symptom relapses in youths with this diagnosis could not be demonstrated by longitudinal studies. Exploratory studies aiming to identify clinical or cognitive features that could discriminate PANDAS from other pediatric obsessive-compulsive and tic disorders present methodological limitations, and therefore are not conclusive. Other behavioral features, in addition to obsessive-compulsive symptoms and tics, have been included in pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndromes (PANS and childhood acute neuropsychiatric syndromes (CANS, two new concepts recently proposed in order to define a much broader clinical spectrum encompassing etiologically diverse entities. Given the uncertainties on the clinical definition of PANDAS, it is not surprising that evidence in support of a post-infectious, immune-mediated pathophysiology is also insufficient. Anti-dopamine receptor antibodies might be relevant to both Sydenham’s chorea (SC—the prototypical post-streptococcal neuropsychiatric disorder—and some rare forms of encephalitis targeting the basal ganglia specifically, but studies exploring their association with children fulfilling Swedo’s criteria for PANDAS have been inconclusive. Moreover, we lack evidence in favor of the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis or tonsillectomy in patients fulfilling Swedo’s criteria for PANDAS, whereas a response to immune-mediated treatments like intravenous
-
Abbink, K.; Kortekaas, J.C.; Buise, M.P.; Dokter, J.; Kuppens, S.M.; Hasaart, T.H.M.
2016-01-01
BACKGROUND: The development of toxic shock syndrome (TSS) after an invasive group A streptococcal (GAS) infection in the postpartum period is a much feared complication. The mortality rate of TSS with necrotizing fasciitis is 30 to 50%. CASE DESCRIPTION: We present the case of a woman with atypical
-
History of Space Shuttle Rendezvous
Goodman, John L.
2011-01-01
This technical history is intended to provide a technical audience with an introduction to the rendezvous and proximity operations history of the Space Shuttle Program. It details the programmatic constraints and technical challenges encountered during shuttle development in the 1970s and over thirty years of shuttle missions. An overview of rendezvous and proximity operations on many shuttle missions is provided, as well as how some shuttle rendezvous and proximity operations systems and flight techniques evolved to meet new programmatic objectives. This revised edition provides additional information on Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, Skylab, and Apollo/Soyuz. Some chapters on the Space Shuttle have been updated and expanded. Four special focus chapters have been added to provide more detailed information on shuttle rendezvous. A chapter on the STS-39 mission of April/May 1991 describes the most complex deploy/retrieve mission flown by the shuttle. Another chapter focuses on the Hubble Space Telescope servicing missions. A third chapter gives the reader a detailed look at the February 2010 STS-130 mission to the International Space Station. The fourth chapter answers the question why rendezvous was not completely automated on the Gemini, Apollo, and Space Shuttle vehicles.
-
Kim, Yeon-Hee; Lee, Si Young
2015-02-01
Mitis-salivarius (MS) agar has been used widely in microbial epidemiological studies because oral viridans streptococci can be selectively grown on this medium. Even though the previous findings reported the limited selecting power of MS agar for streptococcus strains, the identities of non-streptococcal strains from human oral samples which can grow on this medium are not clear yet. In this study, we identified non-streptococcal organisms grown on MS agar plates by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene. Eighty bacterial colonies on MS plates were isolated from plaque samples, and bacterial identification was achieved with the rapid ID 32 Strep system and mini API reader. The bacterial colonies identified as non-streptococci by the API system were selected for further identification. The 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR and verified using DNA sequencing analysis for identification. Sequences were compared with those of reference organisms in the genome database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). Among the 11 isolated non-streptococcal strains on MS plates, 3 strains were identified as Actinomyces naeslundii, 7 strains were identified as Actinomyces oris and 1 strain were identified as Actinomyces sp. using Blastn. In this study, we showed that some oral Actinomyces species can grow on Streptococcus-selective MS agar plates. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Inflammasome/IL-1β Responses to Streptococcal Pathogens
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Christopher N. LaRock
2015-10-01
Full Text Available Inflammation mediated by the inflammasome and the cytokine IL-1β are some of the earliest and most important alarms to infection. These pathways are responsive to the virulence factors that pathogens use to subvert immune processes, and thus are typically activated only by microbes with potential to cause severe disease. Among the most serious human infections are those caused by the pathogenic streptococci, in part because these species numerous strategies for immune evasion. Since the virulence factor armament of each pathogen is unique, the role of IL-1β and the pathways leading to its activation varies for each infection. This review summarizes the role of IL-1β during infections caused by streptococcal pathogens, with emphasis on emergent mechanisms and concepts countering paradigms determined for other organisms.
-
Leckman, James F.; King, Robert A.; Gilbert, Donald L.; Coffey, Barbara J.; Singer, Harvey S.; Dure, Leon S., IV; Grantz, Heidi; Katsovich, Liliya; Lin, Haiqun; Lombroso, Paul J.; Kawikova, Ivana; Johnson, Dwight R.; Kurlan, Roger M.; Kaplan, Edward L.
2011-01-01
Objective: The objective of this blinded, prospective, longitudinal study was to determine whether new group A beta hemolytic streptococcal (GABHS) infections are temporally associated with exacerbations of tic or obsessive-compulsive (OC) symptoms in children who met published criteria for pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders…
-
Di Pierro, F; Colombo, M; Giuliani, M G; Danza, M L; Basile, I; Bollani, T; Conti, A M; Zanvit, A; Rottoli, A S
2016-11-01
Streptococcus salivarius K12 (BLIS K12) is a probiotic strain strongly antagonistic to the growth of Streptococcus pyogenes, the most important bacterial cause of pharyngeal infections in humans. Shown to colonize the oral cavity and to be safe for human use, BLIS K12 has previously been reported to reduce pharyngo-tonsillitis episodes in children or adults known to have experienced recurrent streptococcal infection. The present study was focussed upon evaluating the role of BLIS K12 in the control of streptococcal disease and acute otitis media in children attending the first year of kindergarten. By randomization, 222 enrolled children attending the first year of kindergarten were divided into a treated group (N = 111) receiving for 6 months a daily treatment with BLIS K12 (Bactoblis®) and a control group (N = 111) who were monitored as untreated controls. During the 6 months of treatment and 3 months of follow-up, the children were evaluated for treatment tolerance, and for episodes of streptococcal pharyngo-tonsillitis, scarlet fever and acute otitis media. During the 6-month trial (N = 111 per group) the incidence of streptococcal pharyngo-tonsillitis, scarlet fever and acute otitis media was approximately 16%, 9% and 44% respectively in the treated group and 48%, 4% and 80% in the control group. During the 3-months follow-up (N = 29 per group) the corresponding rates of infection were 15%, 0% and 12% in the treated group and 26%, 6% and 36% in the controls. No apparent side effects were detected in the treated group either during treatment or follow-up. All of the enrolled children completed the study. The daily administration of BLIS K12 to children attending their first year of kindergarten was associated with a significant reduction in episodes of streptococcal pharyngitis and acute otitis media. No protection against scarlet fever was detected.
-
CERN Shuttles - Enlarged Regular Shuttle Services as from 8/02/2010
2010-01-01
As of Monday 8 February 2010, please note the enhancement of the regular shuttle services: - with now two shuttles dedicated to the transportation within and between both CERN sites, Meyrin and Prevessin with bus stop at more buildings - To and from the Geneva airport every hour (from building 500) to complement the TPG bus Y For timetable details, please click here: http://gs-dep.web.cern.ch/gs-dep/groups/sem/ls/RegularShuttleTimetable_Feb2010.htm GS-SEM
-
Bacterial meningitis: epidemiology, herd protection, clinical characteristics, and risk assessment
Bijlsma, M.W.
2016-01-01
This thesis studied the epidemiology of community-acquired bacterial meningitis after the nationwide implementation of paediatric conjugate vaccines, as well as the long-term epidemiology of invasive meningococcal disease and neonatal group B streptococcal disease in the Netherlands. Furthermore,
-
Sziller, István; Szabó, Miklós; Valek, Andrea; Rigó, Barbara; Ács, Nándor
2014-07-20
At present, there is no obligatory guideline for the prevention of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal disease in Hungary. The aim of the present study was to gain insight into the spontaneously developed preventive strategy of the domestic obstetric divisions and departments in Hungary. Standardized questionnaire was sent out to each of the 71 obstetric divisions and departments in Hungary. Overall, 20 (27.4%) of the chairpersons replied, and thus, 39.9% of the total number of live births in Hungary were included in the study. Despite missing public health guidelines, each of the divisions and departments developed their own strategy to prevent neonatal group B streptococcal disease. In 95% of cases, bacterial culture of the lower vagina was the method of identifying pregnant women at risk. In 5% of the cases intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis was based on risk assessment only. Of the departments using culture-based prophylaxis, 58% departments sampled women after completion of 36th gestational weeks. Antibiotic of choice was penicillin or ampicillin in 100% of cases. Of the study participants, 80% reported on multiple administration of colonized pregnant women after onset of labor or rupture of the membranes. The authors concluded that the rate of participation in the study was low. However, prevention of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal infection is a priority of obstetric care in Hungary. Lack of a nation-wide public health policy did not prevent obstetric institutions in this country to develop their own prevention strategy. In the majority of cases and institutions, the policy is consistent with the widely accepted international standards.
-
Viridans streptococcal shock syndrome during bone marrow transplantation.
Martino, R; Manteiga, R; Sánchez, I; Brunet, S; Sureda, A; Badell, I; Argilés, B; Subirá, M; Bordes, R; Domingo-Albós, A
1995-01-01
Of 320 patients receiving a marrow transplant at the Hospital de Sant Pau between 1986 and 1992, 12% developed viridans streptococcal bacteremia during severe neutropenia. Five of these patients (13%) developed a rapidly progressive fatal shock syndrome characterized by bilateral pulmonary infiltrates, acute respiratory failure (ARDS) and septic shock early in the transplantation course (6 or 7 days posttransplantation). All patients were transplanted for acute leukemia in remission, and 2 received an allogeneic and 3 an autologous transplant. Four of these subjects were younger than 15 years of age and all had received cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation as conditioning regimen for marrow transplantation. All 5 patients died, and postmortem examinations revealed diffuse pulmonary lesions characteristic of the ARDS. These observations contribute to defining the clinical and pathologic characteristics of this serious complication of intensive anticancer treatment.
-
Tati, Swetha; Li, Rui; Puri, Sumant; Kumar, Rohitashw; Davidow, Peter; Edgerton, Mira
2014-01-01
Oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC) is caused by the opportunistic fungi Candida albicans and is prevalent in immunocompromised patients, individuals with dry mouth, or patients with prolonged antibiotic therapies that reduce oral commensal bacteria. Human salivary histatins, including histatin 5 (Hst 5), are small cationic proteins that are the major source of fungicidal activity of saliva. However, Hsts are rapidly degraded in vivo, limiting their usefulness as therapeutic agents despite their lack of toxicity. We constructed a conjugate peptide using spermidine (Spd) linked to the active fragment of Hst 5 (Hst 54-15), based upon our findings that C. albicans spermidine transporters are required for Hst 5 uptake and fungicidal activity. We found that Hst 54-15-Spd was significantly more effective in killing C. albicans and Candida glabrata than Hst 5 alone in both planktonic and biofilm growth and that Hst 54-15-Spd retained high activity in both serum and saliva. Hst 54-15-Spd was not bactericidal against streptococcal oral commensal bacteria and had no hemolytic activity. We tested the effectiveness of Hst 54-15-Spd in vivo by topical application to tongue surfaces of immunocompromised mice with OPC. Mice treated with Hst 54-15-Spd had significant clearance of candidal tongue lesions macroscopically, which was confirmed by a 3- to 5-log fold reduction of C. albicans colonies recovered from tongue tissues. Hst 54-15-Spd conjugates are a new class of peptide-based drugs with high selectivity for fungi and potential as topical therapeutic agents for oral candidiasis.
-
Shuttle Discovery Landing at Edwards
1989-01-01
The STS-29 Space Shuttle Discovery mission lands at NASA's then Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility, Edwards AFB, California, early Saturday morning, 18 March 1989. Touchdown was at 6:35:49 a.m. PST and wheel stop was at 6:36:40 a.m. on runway 22. Controllers chose the concrete runway for the landing in order to make tests of braking and nosewheel steering. The STS-29 mission was very successful, completing the launch of a Tracking and Data Relay communications satellite, as well as a range of scientific experiments. Discovery's five-man crew was led by Commander Michael L. Coats, and included pilot John E. Blaha and mission specialists James P. Bagian, Robert C. Springer, and James F. Buchli. Space Shuttles are the main element of America's Space Transportation System and are used for space research and other space applications. The shuttles are the first vehicles capable of being launched into space and returning to Earth on a routine basis. Space Shuttles are used as orbiting laboratories in which scientists and mission specialists conduct a wide variety of scientific experiments. Crews aboard shuttles place satellites in orbit, rendezvous with satellites to carry out repair missions and return them to space, and retrieve satellites and return them to Earth for refurbishment and reuse. Space Shuttles are true aerospace vehicles. They leave Earth and its atmosphere under rocket power provided by three liquid-propellant main engines with two solid-propellant boosters attached plus an external liquid-fuel tank. After their orbital missions, they streak back through the atmosphere and land like airplanes. The returning shuttles, however, land like gliders, without power and on runways. Other rockets can place heavy payloads into orbit, but, they can only be used once. Space Shuttles are designed to be continually reused. When Space Shuttles are used to transport complete scientific laboratories into space, the laboratories remain inside the payload bay throughout
-
Space Shuttle - A personal view
Mark, H.
1977-01-01
A typical flight profile for the Space Shuttle is reviewed, and the operation of the Spacelab, as well as deployment of a satellite from the Shuttle, is considered. Selection of crews for a Space Shuttle mission, which may include as many as four payload specialists, is also discussed. Since medical requirements and flight training standards need not be as high for payload specialists as for the three members of the flight crew, the Shuttle may provide an opportunity for many scientists to perform experiments in space. Investigations of the critical opalescence of fluids and laser holography are proposed for Shuttle missions; X-ray astronomy is another likely candidate for inclusion in the program.
-
Mascini, EM; Jansze, M; Schellekens, JFP; Musser, JM; Faber, JAJ; Verhoef-Verhage, LAE; Schouls, L; van Leeuwen, WJ; Verhoef, J; van Dijk, H
As part of a nationwide surveillance in The Netherlands during 1994-1997, 53 patients with invasive group A streptococcal (GAS) infections were evaluated for medical history, symptoms, and outcome. Patients' isolates were tested for the production of pyrogenic exotoxins A (SPE-A) and B (SPE-B).
-
Group G streptococcal myositis in a patient with myeloproliferative neoplasm
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Monica Midha, MD MBS
2016-01-01
Full Text Available While many cases of streptococcal infection are due to Lancefield groups A and B, there has been a rise in reported cases of infections due to group G streptococcus. We present a case of an individual with a hematologic malignancy who developed myositis secondary to group G streptococcus, with no clearly identifiable source of infection. The patient was managed with antibiotic therapy rather than surgical intervention due to high surgical risk related to severe thrombocytopenia. Targeted antibiotics initiated early in the course of disease may prevent the need for surgical intervention. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to avoid the high morbidity and mortality of life-threatening infections caused by group G streptococcus.
-
Mazur, Elżbieta; Bochyńska, Ewa; Juda, Marek; Kozioł-Montewka, Maria
2014-01-01
Group A Streptococcus (GAS) pharyngitis is currently the only commonly occurring form of acute pharyngitis for which antibiotic therapy is definitely indicated. Polish guidelines advocate the use of modified Centor score (MCS) to assess the probability of GAS pharyngitis. They advise performing throat culture or rapid antigen detection test (RADT) in children with score 2-3 in MCS and treating with antibiotic only those in whom GAS was detected. Negative RADT results should be confirmed by culture. In children with score 4, the guidelines allow to introduce empiric antibiotic therapy. Phenoxymethyl penicillin is recommended as a drug of choice to treat GAS pharyngitis. The aim of our study was to evaluate the accuracy of strategy recommended by Polish guidelines in identifying those children with acute pharyngitis who require antibiotic treatment. Hence, diagnostic values of score 4 in MCS and RADT were assessed using throat culture as a reference standard. Phenoxymethyl penicillin efficacy in GAS eradication and prevention of post-streptococcal complications were estimated as well. Ninety children between 2 and 15 years of age with acute pharyngitis symptoms suggesting GAS etiology (MCS ≥ 2), participated in our study. At the initial visit MCS was evaluated and two throat swabs were collected to perform RADT and culture. In children with GAS pharyngitis treated with penicillin, microbiological cure was assessed by performing two control throat cultures. Next, children were under observation for 3 months. Positive predictive value of score 4 in MCS turned out to be 48.05% (95% CI: 36.5-59.7%). RADT sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic accuracy proved to be 100%, 96%, and 98%, respectively. GAS eradication rate in children treated with penicillin turned out to be 92.5%. No post-streptococcal sequelae occurred in any child in 3-month observation. Empiric antibiotic therapy in children with score 4 in MCS will result in significant overtreatment of those with
-
[Streptococcal mediastinitis after thyroidectomy. A literature review].
Bures, C; Zielinski, V; Klatte, T; Swietek, N; Kober, F; Tatzgern, E; Bobak-Wieser, R; Gschwandtner, E; Gilhofer, M; Wechsler-Fördös, A; Hermann, M
2015-12-01
Surgical site infections after thyroid surgery are mostly superficial and can be well treated. Streptococcal mediastinitis in contrast is a rare but life-threatening complication. A 57-year-old female patient experienced septic fever, increase of inflammation parameters and erythema 2 days after thyroid surgery for Graves' disease. This process was triggered by a three-compartment infection by group A Streptococcus (GAS) with involvement of the mediastinum. Therapy over 6 weeks including seven wound revisions with the patient under general anesthesia, pathogen-adapted antibiotic treatment and cervical negative pressure treatment managed to control the infection. A total of 21 cases have been published on this phenomenon, 11 of which had a fatal outcome. High fever and surgical site erythema in the early postoperative period after thyroid surgery can be signs of a GAS infection, which might lead to necrotizing, descending, life-threatening mediastinitis. Early diagnosis with support of computed tomography (CT) scans, immediate therapy including wound opening, lavage, intravenous antibiotic treatment with penicillin and clindamycin are vital. If treatment resistance occurs, cervical negative pressure treatment should be considered.
-
Food packages for Space Shuttle
Fohey, M. F.; Sauer, R. L.; Westover, J. B.; Rockafeller, E. F.
1978-01-01
The paper reviews food packaging techniques used in space flight missions and describes the system developed for the Space Shuttle. Attention is directed to bite-size food cubes used in Gemini, Gemini rehydratable food packages, Apollo spoon-bowl rehydratable packages, thermostabilized flex pouch for Apollo, tear-top commercial food cans used in Skylab, polyethylene beverage containers, Skylab rehydratable food package, Space Shuttle food package configuration, duck-bill septum rehydration device, and a drinking/dispensing nozzle for Space Shuttle liquids. Constraints and testing of packaging is considered, a comparison of food package materials is presented, and typical Shuttle foods and beverages are listed.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Luigina Cellini
2013-06-01
Full Text Available In this work, we studied the antimicrobial properties of a nanocomposite system based on a lactose-substituted chitosan and silver nanoparticles: Chitlac-nAg. Twofold serial dilutions of the colloidal Chitlac-nAg solution were both tested on Streptococcus mitis, Streptococcus mutans, and Streptococcus oralis planktonic phase and biofilm growth mode as well as on saliva samples. The minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations of Chitlac-nAg were evaluated together with its effect on sessile cell viability, as well as both on biofilm formation and on preformed biofilm. In respect to the planktonic bacteria, Chitlac-nAg showed an inhibitory/bactericidal effect against all streptococcal strains at 0.1% (v/v, except for S. mitis ATCC 6249 that was inhibited at one step less. On preformed biofilm, Chitlac-nAg at a value of 0.2%, was able to inhibit the bacterial growth on the supernatant phase as well as on the mature biofilm. For S. mitis ATCC 6249, the biofilm inhibitory concentration of Chitlac-nAg was 0.1%. At sub-inhibitory concentrations, the Streptococcal strains adhesion capability on a polystyrene surface showed a general reduction following a concentration-dependent-way; a similar effect was obtained for the metabolic biofilm activity. From these results, Chitlac-nAg seems to be a promising antibacterial and antibiofilm agent able to hinder plaque formation.
-
Semiquantitative bacterial observations with group B streptococcal vulvovaginitis.
Monif, G R
1999-01-01
OBJECTIVE: Group B streptococcal (GBS) vulvovaginitis is a poorly-delineated clinical entity. The purpose of this study is to report semiquantitative data from four cases of GBS vulvovaginitis and to comment on their significance in terms of the in vitro inhibitory capabilities of GBS. METHODOLOGY: Four patients whose clinical presentations were consistent with GBS vulvovaginitis, from whom GBS was isolated and for whom semi-quantitative as well as qualitative microbiologic data existed, were identified. RESULTS: To produce vulvovaginitis, GBS must be at a high multiplicity (10(8) CFU/g of vaginal fluid). Single coisolates were identified in three of the four cases (two cases of Escherichia coli and one case of Staphylococcus aureus). Group B streptococcus does not inhibit either of these bacteria in vitro. CONCLUSION: When the growth requirements for the demonstration of in vitro inhibition for GBS or lack thereof are met in vivo, the in vivo observations are consistent with those projected from the in vitro data. PMID:10524667
-
Palmieri, Claudio; Magi, Gloria; Mingoia, Marina; Bagnarelli, Patrizia; Ripa, Sandro; Varaldo, Pietro E; Facinelli, Bruna
2012-09-01
Mosaic tetracycline resistance determinants are a recently discovered class of hybrids of ribosomal protection tet genes. They may show different patterns of mosaicism, but their final size has remained unaltered. Initially thought to be confined to a small group of anaerobic bacteria, mosaic tet genes were then found to be widespread. In the genus Streptococcus, a mosaic tet gene [tet(O/W/32/O)] was first discovered in Streptococcus suis, an emerging drug-resistant pig and human pathogen. In this study, we report the molecular characterization of a tet(O/W/32/O) gene-carrying mobile element from an S. suis isolate. tet(O/W/32/O) was detected, in tandem with tet(40), in a circular 14,741-bp genetic element (39.1% G+C; 17 open reading frames [ORFs] identified). The novel element, which we designated 15K, also carried the macrolide resistance determinant erm(B) and an aminoglycoside resistance four-gene cluster including aadE (streptomycin) and aphA (kanamycin). 15K appeared to be an unstable genetic element that, in the absence of recombinases, is capable of undergoing spontaneous excision under standard growth conditions. In the integrated form, 15K was found inside a 54,879-bp integrative and conjugative element (ICE) (50.5% G+C; 55 ORFs), which we designated ICESsu32457. An ∼1.3-kb segment that apparently served as the att site for excision of the unstable 15K element was identified. The novel ICE was transferable at high frequency to recipients from pathogenic Streptococcus species (S. suis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Streptococcus agalactiae), suggesting that the multiresistance 15K element can successfully spread within streptococcal populations.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hadley, S.W.; Wilbur, D.S.
1990-01-01
The preparations and conjugations of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorophenyl 5-[125I/131I]iodo-4-pentenoate (7a) and 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorophenyl 3,3-dimethyl-5-[125I/131I]iodo-4-pentenoate (7b) to monoclonal antibodies are reported. Reagents 7a and 7b were prepared in high radiochemical yield by iododestannylation of their corresponding 5-tri-n-butylstannyl precursors. Radioiodinated antibody conjugates were prepared by reaction of 7a or 7b with the protein at basic pH. Evaluation of these conjugates by several in vitro procedures demonstrated that the radiolabel was attached to the antibody in a stable manner and that the conjugates maintained immunoreactivity. Comparative dual-isotope biodistribution studies of a monoclonal antibody Fab fragment conjugate of 7a and 7b with the same Fab fragment labeled with N-succinimidyl p-[131I]iodobenzoate (PIB, p-iodobenzoate, 2) or directly radioiodinated have been carried out in tumor-bearing nude mice. Coinjection of the Fab conjugate of 7a with the Fab conjugate of 2 demonstrated that the biodistributions were similar in most organs, except the neck tissue (thyroid-containing) and the stomach, which contained substantially increased levels of the 7a label. Coinjection of the Fab conjugate of 7a with the Fab fragment radioiodinated by using the chloramine-T method demonstrated that the biodistributions were remarkably similar, suggesting roughly equivalent in vivo deiodination of these labeled antibody fragments. Coinjection of the Fab conjugate of 7a with the Fab conjugate of 7b indicated that there was ∼ a 2-fold reduction in the amount of in vivo deiodination of the 7b conjugate as compared to the 7a conjugate
-
TDRSS S-shuttle unique receiver equipment
Weinberg, A.; Schwartz, J. J.; Spearing, R.
1985-01-01
Beginning with STS-9, the Tracking and Date Relay Satellite system (TDRSS) will start providing S- and Ku-band communications and tracking support to the Space Shuttle and its payloads. The most significant element of this support takes place at the TDRSS White Sands Ground Terminal, which processes the Shuttle return link S- and Ku-band signals. While Ku-band hardware available to other TDRSS users is also applied to Ku-Shuttle, stringent S-Shuttle link margins have precluded the application of the standard TDRSS S-band processing equipment to S-Shuttle. It was therfore found necessary to develop a unique S-Shuttle Receiver that embodies state-of-the-art digital technology and processing techniques. This receiver, developed by Motorola, Inc., enhances link margins by 1.5 dB relative to the standard S-band equipment and its bit error rate performance is within a few tenths of a dB of theory. An overview description of the Space Shuttle Receiver Equipment (SSRE) is presented which includes the presentation of block diagrams and salient design features. Selected, measured performance results are also presented.
-
Microbial analysis of bite marks by sequence comparison of streptococcal DNA.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Darnell M Kennedy
Full Text Available Bite mark injuries often feature in violent crimes. Conventional morphometric methods for the forensic analysis of bite marks involve elements of subjective interpretation that threaten the credibility of this field. Human DNA recovered from bite marks has the highest evidentiary value, however recovery can be compromised by salivary components. This study assessed the feasibility of matching bacterial DNA sequences amplified from experimental bite marks to those obtained from the teeth responsible, with the aim of evaluating the capability of three genomic regions of streptococcal DNA to discriminate between participant samples. Bite mark and teeth swabs were collected from 16 participants. Bacterial DNA was extracted to provide the template for PCR primers specific for streptococcal 16S ribosomal RNA (16S rRNA gene, 16S-23S intergenic spacer (ITS and RNA polymerase beta subunit (rpoB. High throughput sequencing (GS FLX 454, followed by stringent quality filtering, generated reads from bite marks for comparison to those generated from teeth samples. For all three regions, the greatest overlaps of identical reads were between bite mark samples and the corresponding teeth samples. The average proportions of reads identical between bite mark and corresponding teeth samples were 0.31, 0.41 and 0.31, and for non-corresponding samples were 0.11, 0.20 and 0.016, for 16S rRNA, ITS and rpoB, respectively. The probabilities of correctly distinguishing matching and non-matching teeth samples were 0.92 for ITS, 0.99 for 16S rRNA and 1.0 for rpoB. These findings strongly support the tenet that bacterial DNA amplified from bite marks and teeth can provide corroborating information in the identification of assailants.
-
Jadhav, Swati B; Singhal, Rekha S
2013-10-15
Two enzymes, α-amylase and glucoamylase have been individually and co-conjugated to pectin by covalent binding. Both the enzyme systems showed better thermal and pH stability over the free enzyme system with the complete retention of original activities. Mixture of individually conjugated enzymes showed lower inactivation rate constant with longer half life than the co-conjugated enzyme system. Individually conjugated enzymes showed an increase of 56.48 kJ/mole and 38.22 kJ/mole in activation energy for denaturation than the free enzymes and co-conjugated enzymes, respectively. Km as well as Vmax of individually and co-conjugated enzymes was found to be higher than the free enzymes. SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis confirmed the formation of conjugate and co-conjugate as evident by increased molecular weight. Both the enzyme systems were used for starch hydrolysis where individually conjugated enzymes showed highest release of glucose at 60 °C and pH 5.0 as compared to free and co-conjugated enzyme. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Chemical Shuttle Additives in Lithium Ion Batteries
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Patterson, Mary
2013-03-31
The goals of this program were to discover and implement a redox shuttle that is compatible with large format lithium ion cells utilizing LiNi{sub 1/3}Mn{sub 1/3}Co{sub 1/3}O{sub 2} (NMC) cathode material and to understand the mechanism of redox shuttle action. Many redox shuttles, both commercially available and experimental, were tested and much fundamental information regarding the mechanism of redox shuttle action was discovered. In particular, studies surrounding the mechanism of the reduction of the oxidized redox shuttle at the carbon anode surface were particularly revealing. The initial redox shuttle candidate, namely 2-(pentafluorophenyl)-tetrafluoro-1,3,2-benzodioxaborole (BDB) supplied by Argonne National Laboratory (ANL, Lemont, Illinois), did not effectively protect cells containing NMC cathodes from overcharge. The ANL-RS2 redox shuttle molecule, namely 1,4-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-2,5-di-tert-butyl-benzene, which is a derivative of the commercially successful redox shuttle 2,5-di-tert-butyl-1,4-dimethoxybenzene (DDB, 3M, St. Paul, Minnesota), is an effective redox shuttle for cells employing LiFePO{sub 4} (LFP) cathode material. The main advantage of ANL-RS2 over DDB is its larger solubility in electrolyte; however, ANL-RS2 is not as stable as DDB. This shuttle also may be effectively used to rebalance cells in strings that utilize LFP cathodes. The shuttle is compatible with both LTO and graphite anode materials although the cell with graphite degrades faster than the cell with LTO, possibly because of a reaction with the SEI layer. The degradation products of redox shuttle ANL-RS2 were positively identified. Commercially available redox shuttles Li{sub 2}B{sub 12}F{sub 12} (Air Products, Allentown, Pennsylvania and Showa Denko, Japan) and DDB were evaluated and were found to be stable and effective redox shuttles at low C-rates. The Li{sub 2}B{sub 12}F{sub 12} is suitable for lithium ion cells utilizing a high voltage cathode (potential that is higher
-
CERN Shuttles - NEW Regular Shuttle Services as from 11/01/2010
GS Department
2010-01-01
As of Monday 11 January a new regular shuttle service (from Monday to Friday) will be available to facilitate transportation: Within and between both CERN sites, Meyrin and Prevessin; To and from the following LHC points: ATLAS, ALICE, CMS, LHCb. For further details, please consult the timetable for this service. We should also like to take this opportunity to encourage you to use the new regular TPG Y bus service rather than the special on-demand CERN transport service to and from Geneva Airport whenever possible. The TPG buses run from 06:00 to 00:30. For further details, please consult the TPG timetable. Please do not hesitate to give us your feedback on the shuttle services: e-mail to veronique.marchal@cern.ch. In case of problems with the shuttles, please contact 75411. GS-SEM Group Infrastructure and General Services Department
-
Antibiotic Resistance Patterns in Invasive Group B Streptococcal Isolates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mei L. Castor
2008-01-01
Full Text Available Antibiotics are used for both group B streptococcal (GBS prevention and treatment. Active population-based surveillance for invasive GBS disease was conducted in four states during 1996—2003. Of 3813 case-isolates, 91.0% (3471 were serotyped, 77.1% (2937 had susceptibility testing, and 46.6% (3471 had both. All were sensitive to penicillin, ampicillin, cefazolin, cefotaxime, and vancomycin. Clindamycin and erythromycin resistance was 12.7% and 25.6%, respectively, and associated with serotype V (P<.001. Clindamycin resistance increased from 10.5% to 15.0% (X2 for trend 12.70; P<.001; inducible clindamycin resistance was associated with the erm genotype. Erythromycin resistance increased from 15.8% to 32.8% (X2 for trend 55.46; P<.001. While GBS remains susceptible to beta-lactams, resistance to alternative agents such as erythromycin and clindamycin is an increasing concern.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Fernando Machado Vilhena Dias
2008-01-01
Full Text Available CONTEXTO: A síndrome de Tourette (ST caracteriza-se pela presença de tiques motores e pelo menos um tique fônico. Algumas semelhanças clínicas com a coréia reumática ou de Sydenham (CS incentivaram a formulação da hipótese da existência de um grupo de transtornos neuropsiquiátricos associados a processo auto-imune decorrente de infecção estreptocócica (PANDAS. OBJETIVO: Revisar a literatura quanto às evidências em relação à hipótese de que mecanismos auto-imunes pós-estreptocócicos estão envolvidos na etiopatogênese da ST. MÉTODOS: Revisão sistemática na base de dados MedLine com os termos "Tourette", "tic", "PANDAS", "antibodies", "streptococcal" e "rheumatic". RESULTADOS: Retornaram 238 artigos da busca. Selecionaram-se 53 trabalhos, os quais tiveram suas referências bibliográficas também revisadas. São apresentados os resultados de estudos que avaliaram aspectos imunes na ST, incluindo anticorpos antiestreptocócicos e antinúcleos da base, e sua terapêutica imunebaseada, discutindo a validade do conceito de PANDAS. CONCLUSÕES: As evidências ainda não são satisfatórias no que tange a uma base auto-imune pós-estreptocócica para a ST. Um aprimoramento dos métodos investigativos e na seleção das amostras pode trazer maiores contribuições à questão.BACKGROUND: Tourette's syndrome (TS is characterized by the presence of motor tics and at least one phonic tic. Some clinical similarities with Sydenham's chorea (SC lead to the hypothesis of a new group of disorders associated with an autoimmune process due to a streptococcal infection (PANDAS. Objective: To review the literature in search of evidence on the existence of post-streptococcal autoimmune mechanisms involved with the etiopathogenesis of TS. METHODS: A systematic review with the terms "Tourette", "tic", "PANDAS", "antibodies", "streptococcal" and "rheumatic" was carried on using the MedLine. RESULTS: The search found 238 articles. Fifty and
-
Brooks, G A
2002-04-01
Once thought to be the consequence of oxygen lack in contracting skeletal muscle, the glycolytic product lactate is formed and utilized continuously under fully aerobic conditions. "Cell-cell" and "intracellular lactate shuttle" concepts describe the roles of lactate in the delivery of oxidative and gluconeogenic substrates, as well as in cell signalling. Examples of cell-cell shuttles include lactate exchanges between white-glycolytic and red-oxidative fibres within a working muscle bed, between working skeletal muscle and heart, and between tissues of net lactate release and gluconeogenesis. Lactate exchange between astrocytes and neurons that is linked to glutamatergic signalling in the brain is an example of a lactate shuttle supporting cell-cell signalling. Lactate uptake by mitochondria and pyruvate-lactate exchange in peroxisomes are examples of intracellular lactate shuttles. Lactate exchange between sites of production and removal is facilitated by monocarboxylate transport proteins, of which there are several isoforms, and, probably, also by scaffolding proteins. The mitochondrial lactate-pyruvate transporter appears to work in conjunction with mitochondrial lactate dehydrogenase, which permits lactate to be oxidized within actively respiring cells. Hence mitochondria function to establish the concentration and proton gradients necessary for cells with high mitochondrial densities (e.g. cardiocytes) to take up and oxidize lactate. Arteriovenous difference measurements on working cardiac and skeletal muscle beds as well as NMR spectral analyses of these tissues show that lactate is formed and oxidized within the cells of formation in vivo. Glycolysis and lactate oxidation within cells permits high flux rates and the maintenance of redox balance in the cytosol and mitochondria. Other examples of intracellular lactate shuttles include lactate uptake and oxidation in sperm mitochondria and the facilitation of beta-oxidation in peroxisomes by pyruvate
-
NASA Contingency Shuttle Crew Support (CSCS) Medical Operations
Adams, Adrien
2010-01-01
The genesis of the space shuttle began in the 1930's when Eugene Sanger came up with the idea of a recyclable rocket plane that could carry a crew of people. The very first Shuttle to enter space was the Shuttle "Columbia" which launched on April 12 of 1981. Not only was "Columbia" the first Shuttle to be launched, but was also the first to utilize solid fuel rockets for U.S. manned flight. The primary objectives given to "Columbia" were to check out the overall Shuttle system, accomplish a safe ascent into orbit, and to return back to earth for a safe landing. Subsequent to its first flight Columbia flew 27 more missions but on February 1st, 2003 after a highly successful 16 day mission, the Columbia, STS-107 mission, ended in tragedy. With all Shuttle flight successes come failures such as the fatal in-flight accident of STS 107. As a result of the STS 107 accident, and other close-calls, the NASA Space Shuttle Program developed contingency procedures for a rescue mission by another Shuttle if an on-orbit repair was not possible. A rescue mission would be considered for a situation where a Shuttle and the crew were not in immediate danger, but, was unable to return to Earth or land safely. For Shuttle missions to the International Space Station (ISS), plans were developed so the Shuttle crew would remain on board ISS for an extended period of time until rescued by a "rescue" Shuttle. The damaged Shuttle would subsequently be de-orbited unmanned. During the period when the ISS Crew and Shuttle crew are on board simultaneously multiple issues would need to be worked including, but not limited to: crew diet, exercise, psychological support, workload, and ground contingency support
-
Recurrent group A streptococcal vulvovaginitis in adult women: family epidemiology.
Sobel, Jack D; Funaro, Deana; Kaplan, Edward L
2007-03-01
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal (GAS) vulvovaginitis has been reported in prepubertal girls. In adult women, a vaginal carrier state has been described, but vulvovaginitis is rarely reported. We describe 2 cases of recurrent GAS vulvovaginitis in women whose husbands were gastrointestinal carriers of GAS. Characterization of the isolated strains demonstrated that identical emm types of GAS were shared by partners. Treatment of both partners resulted in resolution of vaginitis. On the basis of negative vaginal culture results obtained after treatment of each individual episode of vaginitis, we believe that the female patients were reinfected as a result of exposure to their husbands, with shedding likely to have occurred in bed. These cases reiterate the necessity for adequate screening of the patient's family and contacts in cases of recurrent GAS infection by culturing all potential areas of GAS carriage.
-
Streptococcal Pharyngitis and Appendicitis in Children.
Nielsen, Jason W; Abel, Stuart A; Kenney, Brian
2018-01-01
Several pathologies, including pharyngitis, are associated with abdominal pain that can mimic appendicitis. We sought to further understand the link between appendicitis-like symptoms and streptococcal (strep) pharyngitis. All patients undergoing ultrasound imaging for appendicitis in our emergency department during 2013 were reviewed (n = 1572). A total of 207 patients were identified who underwent both ultrasound for appendicitis and testing for strep pharyngitis. Demographic and outcomes data between rule out appendicitis patients who underwent strep testing and those who did not were compared. Strep testing was more common in younger patients (mean age = 8.26 vs 10.26 years P appendicitis and 35 (16.9%) patients tested positive for strep pharyngitis. No cases of concurrent strep pharyngitis and appendicitis were identified. The negative appendectomy rate in the strep pharyngitis tested group was 38.5% (5/13), compared with 7.7% (23/296) ( P = .003) in the nontested group. The appendicitis rate among the strep tested group was 3.8% (8/207) compared with 20% (273/1365) in the nontested group ( P appendicitis, and had a higher rate of negative appendectomy. A diagnosis of concurrent appendicitis and strep pharyngitis is rare. In cases of patients with sufficient symptoms to warrant testing for strep pharyngitis a diagnosis of appendicitis is less likely and surgical intervention leads to higher negative appendectomy rates.
-
Bacteriophytochromes control conjugation in Agrobacterium fabrum.
Bai, Yingnan; Rottwinkel, Gregor; Feng, Juan; Liu, Yiyao; Lamparter, Tilman
2016-08-01
Bacterial conjugation, the transfer of single stranded plasmid DNA from donor to recipient cell, is mediated through the type IV secretion system. We performed conjugation assays using a transmissible artificial plasmid as reporter. With this assay, conjugation in Agrobacterium fabrum was modulated by the phytochromes Agp1 and Agp2, photoreceptors that are most sensitive in the red region of visible light. In conjugation studies with wild-type donor cells carrying a pBIN-GUSINT plasmid as reporter that lacked the Ti (tumor inducing) plasmid, no conjugation was observed. When either agp1(-) or agp2(-) knockout donor strains were used, plasmid DNA was delivered to the recipient, indicating that both phytochromes suppress conjugation in the wild type donor. In the recipient strains, the loss of Agp1 or Agp2 led to diminished conjugation. When wild type cells with Ti plasmid and pBIN-GUS reporter plasmid were used as donor, a high rate of conjugation was observed. The DNA transfer was down regulated by red or far-red light by a factor of 3.5. With agp1(-) or agp2(-) knockout donor cells, conjugation in the dark was about 10 times lower than with the wild type donor, and with the double knockout donor no conjugation was observed. These results imply that the phytochrome system has evolved to inhibit conjugation in the light. The decrease of conjugation under different temperature correlated with the decrease of phytochrome autophosphorylation. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Polymers for Protein Conjugation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gianfranco Pasut
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Polyethylene glycol (PEG at the moment is considered the leading polymer for protein conjugation in view of its unique properties, as well as to its low toxicity in humans, qualities which have been confirmed by its extensive use in clinical practice. Other polymers that are safe, biodegradable and custom-designed have, nevertheless, also been investigated as potential candidates for protein conjugation. This review will focus on natural polymers and synthetic linear polymers that have been used for protein delivery and the results associated with their use. Genetic fusion approaches for the preparation of protein-polypeptide conjugates will be also reviewed and compared with the best known chemical conjugation ones.
-
Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease: screening during a pregnancy
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Rosella Bruno
2012-12-01
Full Text Available The prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal (GBS disease is based on the screening of all pregnant women at 35-37 weeks’ gestation for vaginal and rectal GBS colonization. The colonized women receive intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis. Our study reports the different rates of maternal GBS colonization between April 2008 and March 2011. We have collected 3430 samples by swabbing both the lower vagina and rectum and we have employed two different laboratory methods: direct agar plating and selective enrichment broth. The rates of maternal GBS colonization increased from 10.5% during 2008-2009, to 12.2% during 2009-2010 and to 14.4% during 2010-2011, when we have introduced the Todd Hewitt broth. Our results show that the use of an enrichment broth improves detection of GBS carriers women.
-
Quantum Shuttle in Phase Space
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Novotny, Tomas; Donarini, Andrea; Jauho, Antti-Pekka
2003-01-01
Abstract: We present a quantum theory of the shuttle instability in electronic transport through a nanostructure with a mechanical degree of freedom. A phase space formulation in terms of the Wigner function allows us to identify a crossover from the tunneling to the shuttling regime, thus...
-
Invasive Group A streptococcal disease in Ireland, 2004 to 2010.
LENUS (Irish Health Repository)
Martin, J
2011-01-01
Invasive group A streptococcal infections (iGAS) are a major clinical and public health challenge. iGAS is a notifiable disease in Ireland since 2004. The aim of this paper is to describe the epidemiology of iGAS in Ireland for the first time over the seven-year period from 2004 to 2010. The Irish national electronic infectious disease reporting system was used by laboratories to enter the source of iGAS isolates, and by departments of public health to enter clinical and epidemiological details. We extracted and analysed data from 1 January 2004 to 31 December 2010. Over the study period, 400 iGAS cases were notified. The annual incidence of iGAS doubled, from 0.8 per 100,000 population in 2004 to 1.6 in 2008, and then remained the same in 2009 and 2010. The reported average annual incidence rates were highest among children up to five years of age (2.3\\/100,000) and adults aged over 60 years (3.2\\/100,000). The most common risk factors associated with iGAS were skin lesions or wounds. Of the 174 people for whom clinical syndrome information was available, 28 (16%) cases presented with streptococcal toxic shock syndrome and 19 (11%) with necrotising fasciitis. Of the 141 cases for whom seven-day outcomes were recorded, 11 people died with iGAS identified as the main cause of death (seven-day case fatality rate 8%). The notification rate of iGAS in Ireland was lower than that reported in the United Kingdom, Nordic countries and North America but higher than southern and eastern European countries. The reasons for lower notification rates in Ireland compared with other countries may be due to a real difference in incidence, possibly due to prescribing practices, or due to artefacts resulting from the specific Irish case definition and\\/or low reporting in the early stages of a new surveillance system. iGAS disease remains an uncommon but potentially severe disease in Ireland. Ongoing surveillance is required in order to undertake appropriate control measures and
-
1999-01-01
Motors, Honda , Toyota , and Nissan ). By learning from and applying the technologies developed elsewhere, NASA could greatly leverage its funding for...assessing risks to the shuttle. The committee believes that this tool has the potential to be very helpful in assessing and comparing the impact of...environmental regulations). Figure 2-2 shows how the S&PU budget compared to the total shuttle budget during four different years since 1985
-
Nakashima, K; Ichiyama, S; Iinuma, Y; Hasegawa, Y; Ohta, M; Ooe, K; Shimizu, Y; Igarashi, H; Murai, T; Shimokata, K
1997-08-01
In a survey of invasive streptococcal infections in Japan, we analyzed isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes collected between 1992 and 1994. Genomic DNA fingerprints produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) were compared by computer-assisted analysis. Conventional serologic M types were subdivided into PFGE types showing close genetic similarity. Among the 42 isolates from patients with invasive diseases, 16 PFGE types were identified and genetic diversity was clearly demonstrated. Identical fingerprints were observed in both invasive and noninvasive isolates. Only 43% of invasive isolates produced streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A (SPE A), and 31% did not contain the speA gene. These findings suggest that the dissemination of a specific clone is not sufficient to explain all cases of these diseases in Japan and pose a question as to the role of SPE A as a major virulent factor. Bacterial factors other than SPE A and host factors should be considered in evaluation of the pathogenesis of the diseases.
-
Fisher, Robert A
1983-01-01
This book appears at a time of intense activity in optical phase conjugation. We chose not to await the maturation of the field, but instead to provide this material in time to be useful in its development. We have tried very hard to elucidate and interrelate the various nonlinear phenomena which can be used for optical phase conjugation.
-
Space Shuttle critical function audit
Sacks, Ivan J.; Dipol, John; Su, Paul
1990-01-01
A large fault-tolerance model of the main propulsion system of the US space shuttle has been developed. This model is being used to identify single components and pairs of components that will cause loss of shuttle critical functions. In addition, this model is the basis for risk quantification of the shuttle. The process used to develop and analyze the model is digraph matrix analysis (DMA). The DMA modeling and analysis process is accessed via a graphics-based computer user interface. This interface provides coupled display of the integrated system schematics, the digraph models, the component database, and the results of the fault tolerance and risk analyses.
-
Brand-new signage for the CERN shuttles
Roberto Cantoni
2010-01-01
If, after reading the title of this article, you're striving to remember what the signs for the CERN shuttles look like, then you just hit the nail on the head: we bet that only a few people can actually do so. In order to make it easier for CERN users to move around the CERN sites, a graphic restyling of the shuttle signage has been implemented. You will start to see the new timetables in the coming days. Larisa Kuchina, a graphic designer in the Communication Group, restyled the shuttle signage to make it more visible and intelligible. “I was inspired by the very clear and user friendly interface of the Geneva Public Transport system (TPG)”, explains Larisa. “Each timetable will also include the corresponding shuttle route. We will soon introduce new road signs for shuttle stops to make sure they are visible from a distance”. There are currently four shuttle lines, serving 28,000 passengers since February 2010: two of them operate between Meyrin and Pr...
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Chen, Chen; Tang, Jiaqi; Dong, Wei
2007-01-01
shock syndrome (STSS), which was originally associated with Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS) in Streptococci. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying STSS are poorly understood. METHODS AND FINDINGS: To elucidate the genetic determinants of STSS caused by SS2, whole genome sequencing of 3 different......BACKGROUND: Streptococcus suis serotype 2 (SS2) is an important zoonotic pathogen, causing more than 200 cases of severe human infection worldwide, with the hallmarks of meningitis, septicemia, arthritis, etc. Very recently, SS2 has been recognized as an etiological agent for streptococcal toxic...
-
Qualidade conjugal: mapeando conceitos
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Clarisse Mosmann
2006-12-01
Full Text Available Apesar da ampla utilização do conceito de qualidade conjugal, identifica-se falta de clareza conceitual acerca das variáveis que o compõem. Esse artigo apresenta revisão da literatura na área com o objetivo de mapear o conceito de qualidade conjugal. Foram analisadas sete principais teorias sobre o tema: Troca Social, Comportamental, Apego, Teoria da Crise, Interacionismo Simbólico. Pelos postulados propostos nas diferentes teorias, podem-se identificar três grupos de variáveis fundamentais na definição da qualidade conjugal: recursos pessoais dos cônjuges, contexto de inserção do casal e processos adaptativos. Neste sentido, a qualidade conjugal é resultado do processo dinâmico e interativo do casal, razão deste caráter multidimensional.
-
Space Shuttle Endeavour launch
1992-01-01
A smooth countdown culminated in a picture-perfect launch as the Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-47) climbed skyward atop a ladder of billowing smoke. Primary payload for the plarned seven-day flight was Spacelab-J science laboratory. The second flight of Endeavour marks a number of historic firsts: the first space flight of an African-American woman, the first Japanese citizen to fly on a Space Shuttle, and the first married couple to fly in space.
-
Space Shuttle Main Engine Public Test Firing
2000-01-01
A new NASA Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) roars to the approval of more than 2,000 people who came to John C. Stennis Space Center in Hancock County, Miss., on July 25 for a flight-certification test of the SSME Block II configuration. The engine, a new and significantly upgraded shuttle engine, was delivered to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for use on future shuttle missions. Spectators were able to experience the 'shake, rattle and roar' of the engine, which ran for 520 seconds - the length of time it takes a shuttle to reach orbit.
-
Current Noise Spectrum of a Quantum Shuttle
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Flindt, Christian; Novotny, T.; Jauho, Antti-Pekka
2005-01-01
We present a method for calculating the full current noise spectrum S(omega) for the class of nano-electromechanical systems (NEMS) that can be described by a Markovian generalized master equation. As a specific example we apply the method to a quantum shuttle. The noise spectrum of the shuttle has...... peaks at integer multiples of the mechanical frequency, which is slightly renormalized. The renormalization explains a previously observed small deviation of the shuttle Current compared to the expected value given by the product of the natural mechanical frequency and the electron charge. For a certain...... parameter range the quantum shuttle exhibits a coexistence regime, where the charges are transported by two different mechanisms: Shuttling and sequential tunneling. In our previous studies we showed that characteristic features in the zero-frequency noise could be quantitatively understood as a slow...
-
Zettl, Alex Karlwalter [Kensington, CA
2012-03-06
A device for storing data using nanoparticle shuttle memory having a nanotube. The nanotube has a first end and a second end. A first electrode is electrically connected to the first end of the nanotube. A second electrode is electrically connected to the second end of the nanotube. The nanotube has an enclosed nanoparticle shuttle. A switched voltage source is electrically connected to the first electrode and the second electrode, whereby a voltage may be controllably applied across the nanotube. A resistance meter is also connected to the first electrode and the second electrode, whereby the electrical resistance across the nanotube can be determined.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Batten, MR; Senior, BW; Kilian, Mogens
2003-01-01
The amino acid sequence requirements in the hinge of human immunoglobulin A1 (IgA1) for cleavage by IgA1 proteases of different species of Streptococcus were investigated. Recombinant IgA1 antibodies were generated with point mutations at proline 227 and threonine 228, the residues lying on either...... side of the peptide bond at which all streptococcal IgA1 proteases cleave wild-type human IgA1. The amino acid substitutions produced no major effect upon the structure of the mutant IgA1 antibodies or their functional ability to bind to Fcalpha receptors. However, the substitutions had a substantial...... effect upon sensitivity to cleavage with some streptococcal IgA1 proteases, with, in some cases, a single point mutation rendering the antibody resistant to a particular IgA1 protease. This effect was least marked with the IgA1 protease from Streptococcus pneumoniae, which showed no absolute requirement...
-
Cross-Conjugated n-Dopable Aromatic Polyketone
Voortman, Thomas P.; Bartesaghi, Davide; Koster, L. Jan Anton; Chiechi, Ryan C.
2015-01-01
This paper describes the synthesis and characterization of a high molecular weight cross-conjugated polyketone synthesized via scalable Friedel Crafts chemistry. Cross-conjugated polyketones are precursors to conjugated polyions; they become orders of magnitude more conductive after a two-electron
-
Intelligent Shuttle Management and Routing Algorithm
Thomas, Toshen M.; Subashanthini, S.
2017-11-01
Nowadays, most of the big Universities and campuses have Shuttle cabs running in them to cater the transportational needs of the students and faculties. While some shuttle services ask for a meagre sum to be paid for the usage, no digital payment system is onboard these vehicles to go truly cashless. Even more troublesome is the fact that sometimes during the day, some of these cabs run with bare number of passengers, which can result in unwanted budget loss to the shuttle operator. The main purpose of this paper is to create a system with two types of applications: A web portal and an Android app, to digitize the Shuttle cab industry. This system can be used for digital cashless payment feature, tracking passengers, tracking cabs and more importantly, manage the number of shuttle cabs in every route to maximize profit. This project is built upon an ASP.NET website connected to a cloud service along with an Android app that tracks and reads the passengers ID using an attached barcode reader along with the current GPS coordinates, and sends these data to the cloud for processing using the phone’s internet connectivity.
-
Shuttle on-orbit contamination and environmental effects
Leger, L. J.; Jacobs, S.; Ehlers, H. K. F.; Miller, E.
1985-01-01
Ensuring the compatibility of the space shuttle system with payloads and payload measurements is discussed. An extensive set of quantitative requirements and goals was developed and implemented by the space shuttle program management. The performance of the Shuttle system as measured by these requirements and goals was assessed partly through the use of the induced environment contamination monitor on Shuttle flights 2, 3, and 4. Contamination levels are low and generally within the requirements and goals established. Additional data from near-term payloads and already planned contamination measurements will complete the environment definition and allow for the development of contamination avoidance procedures as necessary for any payload.
-
Use of PRA in Shuttle Decision Making Process
Boyer, Roger L.; Hamlin, Teri L.
2010-01-01
How do you use PRA to support an operating program? This presentation will explore how the Shuttle Program Management has used the Shuttle PRA in its decision making process. It will reveal how the PRA has evolved from a tool used to evaluate Shuttle upgrades like Electric Auxiliary Power Unit (EAPU) to a tool that supports Flight Readiness Reviews (FRR) and real-time flight decisions. Specific examples of Shuttle Program decisions that have used the Shuttle PRA as input will be provided including how it was used in the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) manifest decision. It will discuss the importance of providing management with a clear presentation of the analysis, applicable assumptions and limitations, along with estimates of the uncertainty. This presentation will show how the use of PRA by the Shuttle Program has evolved overtime and how it has been used in the decision making process providing specific examples.
-
Block-conjugate-gradient method
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McCarthy, J.F.
1989-01-01
It is shown that by using the block-conjugate-gradient method several, say s, columns of the inverse Kogut-Susskind fermion matrix can be found simultaneously, in less time than it would take to run the standard conjugate-gradient algorithm s times. The method improves in efficiency relative to the standard conjugate-gradient algorithm as the fermion mass is decreased and as the value of the coupling is pushed to its limit before the finite-size effects become important. Thus it is potentially useful for measuring propagators in large lattice-gauge-theory calculations of the particle spectrum
-
Protein carriers of conjugate vaccines
Pichichero, Michael E
2013-01-01
The immunogenicity of polysaccharides as human vaccines was enhanced by coupling to protein carriers. Conjugation transformed the T cell-independent polysaccharide vaccines of the past to T cell-dependent antigenic vaccines that were much more immunogenic and launched a renaissance in vaccinology. This review discusses the conjugate vaccines for prevention of infections caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Specifically, the characteristics of the proteins used in the construction of the vaccines including CRM, tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane complex, and Hemophilus influenzae protein D are discussed. The studies that established differences among and key features of conjugate vaccines including immunologic memory induction, reduction of nasopharyngeal colonization and herd immunity, and antibody avidity and avidity maturation are presented. Studies of dose, schedule, response to boosters, of single protein carriers with single and multiple polysaccharides, of multiple protein carriers with multiple polysaccharides and conjugate vaccines administered concurrently with other vaccines are discussed along with undesirable consequences of conjugate vaccines. The clear benefits of conjugate vaccines in improving the protective responses of the immature immune systems of young infants and the senescent immune systems of the elderly have been made clear and opened the way to development of additional vaccines using this technology for future vaccine products. PMID:23955057
-
Shuttle Columbia Post-landing Tow - with Reflection in Water
1982-01-01
A rare rain allowed this reflection of the Space Shuttle Columbia as it was towed 16 Nov. 1982, to the Shuttle Processing Area at NASA's Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (from 1976 to 1981 and after 1994, the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, following its fifth flight in space. Columbia was launched on mission STS-5 11 Nov. 1982, and landed at Edwards Air Force Base on concrete runway 22. Space Shuttles are the main element of America's Space Transportation System and are used for space research and other space applications. The shuttles are the first vehicles capable of being launched into space and returning to Earth on a routine basis. Space Shuttles are used as orbiting laboratories in which scientists and mission specialists conduct a wide variety of scientific experiments. Crews aboard shuttles place satellites in orbit, rendezvous with satellites to carry out repair missions and return them to space, and retrieve satellites and return them to Earth for refurbishment and reuse. Space Shuttles are true aerospace vehicles. They leave Earth and its atmosphere under rocket power provided by three liquid-propellant main engines withtwo solid-propellant boosters attached plus an external liquid-fuel tank. After their orbital missions, they streak back through the atmosphere and land like airplanes. The returning shuttles, however, land like gliders, without power and on runways. Other rockets can place heavy payloads into orbit, but, they can only be used once. Space Shuttles are designed to be continually reused. When Space Shuttles are used to transport complete scientific laboratories into space, the laboratories remain inside the payload bay throughout the mission. They are then removed after the Space Shuttle returns to Earth and can be reused on future flights. Some of these orbital laboratories, like the Spacelab, provide facilities for several specialists to conduct experiments in such fields as medicine, astronomy, and materials
-
Demirkaya, Sevcan Karakoç; Demirkaya, Mithat; Yusufoğlu, Canan; Akın, Elif
2017-02-01
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common comorbid disease in children with pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections (PANDAS), in which tic-like involuntary movements are frequently seen clinical conditions. In contrast to psychostimulants, atomoxetine is considered as having minimal effects on tics. Here we report two cases with ADHD and PANDAS who were treated with atomoxetine for their ADHD and comorbid tics.
-
Conjugated polymer zwitterions and solar cells comprising conjugated polymer zwitterions
Emrick, Todd; Russell, Thomas; Page, Zachariah; Liu, Yao
2018-06-05
A conjugated polymer zwitterion includes repeating units having structure (I), (II), or a combination thereof ##STR00001## wherein Ar is independently at each occurrence a divalent substituted or unsubstituted C3-30 arylene or heteroarylene group; L is independently at each occurrence a divalent C1-16 alkylene group, C6-30arylene or heteroarylene group, or alkylene oxide group; and R1 is independently at each occurrence a zwitterion. A polymer solar cell including the conjugated polymer zwitterion is also disclosed.
-
Research study of conjugate materials; Conjugate material no chosa kenkyu
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
1998-03-01
The paper reported an introductory research on possibilities of new glass `conjugate materials.` The report took up the structure and synthetic process of conjugate materials to be researched/developed, classified them according to structural elements on molecular, nanometer and cluster levels, and introduced the structures and functions. Further, as glasses with new functions to be proposed, the paper introduced transparent and high-strength glass used for houses and vehicles, light modulation glass which realizes energy saving and optical data processing, and environmentally functional glass which realizes environmental cleaning or high performance biosensor. An initial survey was also conducted on rights of intellectual property to be taken notice of in Japan and abroad in the present situation. Reports were summed up and introduced of Osaka National Research Institute, Electrotechnical Laboratory, and National Industrial Research Institute of Nagoya which are all carrying out leading studies of conjugate materials. 235 refs., 135 figs., 6 tabs.
-
Redox shuttles for safer lithium-ion batteries
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen, Zonghai; Qin, Yan; Amine, Khalil
2009-01-01
Overcharge protection is not only critical for preventing the thermal runaway of lithium-ion batteries during operation, but also important for automatic capacity balancing during battery manufacturing and repair. A redox shuttle is an electrolyte additive that can be used as intrinsic overcharge protection mechanism to enhance the safety characteristics of lithium-ion batteries. The advances on stable redox shuttles are briefly reviewed. Fundamental studies for designing stable redox shuttles are also discussed.
-
Taketa, Kazuhisa; Ohmori, Hiroyuki; Matsumura, Yonesuke; Asahi, Toshihiko; Okimune, Masaaki
1980-01-01
The effect of Picibanil, a streptococcal agent, on the development of liver injury after operations for urogenital cancer was studied retrospectively in the light of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity. The series comprised 32 cases receiving Picibanil and 33 controls with otherwise comparable clinical backgrounds. Picibanil reduced the incidence of postoperative ALT rise over 50 U/l within 6 weeks but increased it thereafter. The increase in ALT activity after 6 weeks was relativel...
-
Batson, B. H.; Seyl, J. W.; Huth, G. K.
1977-01-01
This paper describes an approach for relay of data-modulated subcarriers from Shuttle payloads through the Shuttle Ku-band communications subsystem (and subsequently through a tracking and data relay satellite system to a ground terminal). The novelty is that a channel originally provided for baseband digital data is shown to be suitable for this purpose; the resulting transmission scheme is referred to as a narrowband bent-pipe scheme. Test results demonstrating the validity of the narrowband bent-pipe mode are presented, and limitations on system performance are described.
-
Misonidazole-glutathione conjugates in CHO cells
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Varghese, A.J.; Whitmore, G.F.
1984-01-01
Misonidazole, after reduction to the hydroxylamine derivative, reacts with glutathione (GSH) under physiological conditions. The reaction product has been identified as a mixture of two isomeric conjugates. When water soluble extracts of CHO cells exposed to misonidazole under hypoxic conditions are subjected to HPLC analysis, misonidazole derivatives, having the same chromatographic properties as the GSH-MISO conjugates, were detected. When CHO cells were incubated with misonidazole in the presence of added GSH, a substantial increase in the amount of the conjugate was detected. When extracts of CHO cells exposed to misonidazole under hypoxia were subsequently exposed to GSH, an increased formation of the conjugate was observed. A rearrangement product of the hydroxylamine derivative of misonidazole is postulated as the reactive intermediate responsible for the formation of the conjugate
-
Modelling conjugation with stochastic differential equations
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Philipsen, Kirsten Riber; Christiansen, Lasse Engbo; Hasman, Henrik
2010-01-01
Enterococcus faecium strains in a rich exhaustible media. The model contains a new expression for a substrate dependent conjugation rate. A maximum likelihood based method is used to estimate the model parameters. Different models including different noise structure for the system and observations are compared......Conjugation is an important mechanism involved in the transfer of resistance between bacteria. In this article a stochastic differential equation based model consisting of a continuous time state equation and a discrete time measurement equation is introduced to model growth and conjugation of two...... using a likelihood-ratio test and Akaike's information criterion. Experiments indicating conjugation on the agar plates selecting for transconjugants motivates the introduction of an extended model, for which conjugation on the agar plate is described in the measurement equation. This model is compared...
-
Poly(2-oxazoline)-Antibiotic Conjugates with Penicillins.
Schmidt, Martin; Bast, Livia K; Lanfer, Franziska; Richter, Lena; Hennes, Elisabeth; Seymen, Rana; Krumm, Christian; Tiller, Joerg C
2017-09-20
The conjugation of antibiotics with polymers is rarely done, but it might be a promising alternative to low-molecular-weight derivatization. The two penicillins penicillin G (PenG) and penicillin V (PenV) were attached to the end groups of different water-soluble poly(2-oxazoline)s (POx) via their carboxylic acid function. This ester group was shown to be more stable against hydrolysis than the β-lactam ring of the penicillins. The conjugates are still antimicrobially active and up to 20 times more stable against penicillinase catalyzed hydrolysis. The antibiotic activity of the conjugates against Staphylococcus aureus in the presence of penicillinase is up to 350 times higher compared with the free antibiotics. Conjugates with a second antimicrobial function, a dodecyltrimethylammonium group (DDA-X), at the starting end of the PenG and PenV POx conjugates are more antimicrobially active than the conjugates without DDA-X and show high activity in the presence of penicillinase. For example, the conjugates DDA-X-PEtOx-PenG and DDA-X-PEtOx-PenV are 200 to 350 times more active against S. aureus in the presence of penicillinase and almost as effective as the penicillinase stable cloxacollin (Clox) under these conditions. These conjugates show even greater activity compared to cloxacollin without this enzyme present. Further, both conjugates kill Escherichia coli more effectively than PenG and Clox.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mikić Dragan
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Introduction. Since delay in recognition and effective treatment of necrotizing fasciitis (NF caused by invasive group A streptococcus increases the mortality and disability, the early diagnosis and management of this disease are essential for a better outcome. We presented a patient with a severe form of streptococcal NF of the left upper limb in whom amputation was performed as a life saving procedure. Case report. A 65-year-old man, previously healthy, suffered an injury to his left hand by sting on a fish bone. Two days after that the patient got fever, redness, swelling and pain in his left hand. Clinical examination of the patient after admission indicated NF that spread quickly to the entire left upper limb, left armpit, and the left side of the chest and abdomen. Despite the use of aggressive antibiotic and surgical therapy severe destruction of the skin and subcutaneous tissues developed with the development of gangrene of the left upper limb. In this situation, the team of specialists decided that the patient must be operated on submited to amputation of the left arm, at the shoulder. After amputation and aggressive debridement of soft tissue on the left side of the trunk, the patient completely recovered. β-hemolytic streptococcus group A was isolated from the skin and tissue obtained during the surgery. Conclusion. In the most severe forms of streptococcal NF of the extremities, adequate multidisciplinary treatment, including limb amputation, can save the life of a patient.
-
Shot noise of a quantum shuttle
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Novotny, Tomas; Donarini, Andrea; Flindt, Christian
2004-01-01
We formulate a theory for shot noise in quantum nanoelectromechanical systems. As a specific example, the theory is applied to a quantum shuttle, and the zero-frequency noise, measured by the Fano factor F, is computed. F reaches very low values (Fsimilar or equal to10(-2)) in the shuttling regim...
-
Approximate error conjugation gradient minimization methods
Kallman, Jeffrey S
2013-05-21
In one embodiment, a method includes selecting a subset of rays from a set of all rays to use in an error calculation for a constrained conjugate gradient minimization problem, calculating an approximate error using the subset of rays, and calculating a minimum in a conjugate gradient direction based on the approximate error. In another embodiment, a system includes a processor for executing logic, logic for selecting a subset of rays from a set of all rays to use in an error calculation for a constrained conjugate gradient minimization problem, logic for calculating an approximate error using the subset of rays, and logic for calculating a minimum in a conjugate gradient direction based on the approximate error. In other embodiments, computer program products, methods, and systems are described capable of using approximate error in constrained conjugate gradient minimization problems.
-
CERN Shuttles – TRAM arrival – Two additional shuttles as from 2 May 2011
General Infrastructure Services Department
2011-01-01
With the TRAM’s arrival at CERN and to facilitate mobility inside CERN, the GS Department is reinforcing CERN's shuttle services and will provide users with two additional shuttles from/to Building 33 (CERN Reception) as from Monday 2 May: Circuit No. 5: serving the Meyrin site (approx. every 15 minutes) •\tfrom 7·30 to 9·15 •\tfrom 11·30 to 13·28 (serving restaurants Nos.1 and 2) •\tfrom 16·30 to 18·35 Circuit No. 6: serving the Prevessin site (approx. every 20 minutes) •\tfrom 7·30 to 9·10 •\tfrom 11·30 to 13·28 (serving restaurants Nos. 1, 2 and 3) •\tfrom 16·30 to 18·23 For further details, please consult the timetable for these circuits at the following url: http://gs-dep.web.cern.ch/gs-dep/groups/SEM/ls/ShuttleService/ Please do not hesitate to give us your feedback...
-
STS-62 Space Shuttle mission report
Fricke, Robert W., Jr.
1994-01-01
The STS-62 Space Shuttle Program Mission Report summarizes the Payload activities as well as the Orbiter, External Tank (ET), Solid Rocket Booster (SRB), Redesigned Solid Rocket Motor (RSRM), and the Space Shuttle main engine (SSHE) systems performance during the sixty-first flight of the Space Shuttle Program and sixteenth flight of the Orbiter vehicle Columbia (OV-102). In addition to the Orbiter, the flight vehicle consisted of an ET designated as ET-62; three SSME's which were designated as serial numbers 2031, 2109, and 2029 in positions 1, 2, and 3, respectively; and two SRB's which were designated BI-064. The RSRM's that were installed in each SRB were designated as 360L036A (lightweight) for the left SRB, and 36OWO36B (welterweight) for the right SRB. This STS-62 Space Shuttle Program Mission Report fulfills the Space Shuttle Program requirement as documented in NSTS 07700, Volume 8, Appendix E. That document requires that each major organizational element supporting the Program report the results of its hardware evaluation and mission performance plus identify all related in-flight anomalies. The primary objectives of the STS-62 mission were to perform the operations of the United States Microgravity Payload-2 (USMP-2) and the Office of Aeronautics and Space Technology-2 (OAST-2) payload. The secondary objectives of this flight were to perform the operations of the Dexterous End Effector (DEE), the Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet/A (SSBUV/A), the Limited Duration Space Environment Candidate Material Exposure (LDCE), the Advanced Protein Crystal Growth (APCG), the Physiological Systems Experiments (PSE), the Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG), the Commercial Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (CGBA), the Middeck Zero-Gravity Dynamics Experiment (MODE), the Bioreactor Demonstration System (BDS), the Air Force Maui Optical Site Calibration Test (AMOS), and the Auroral Photography Experiment (APE-B).
-
Li, Chunju; Lin, Qixun; Wang, Jun; Shen, Lijuan; Ma, Guanghui; Su, Zhiguo; Hu, Tao
2012-12-31
Ribonuclease A (RNase A) is a therapeutic enzyme with cytotoxic action against tumor cells. Its clinical application is limited by the short half-life and insufficient stability. Conjugation of albumin can overcome the limitation, whereas dramatically decrease the enzymatic activity of RNase A. Here, three strategies were proposed to prepare the RNase A-bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugates. R-SMCC-B (a conjugate of four RNase A attached with one BSA) and R-PEG-B (a mono-conjugate) were prepared using Sulfo-SMCC (a short bifunctional linker) and mal-PEG-NHS (a bifunctional PEG), respectively. Mal-PEG-NHS and hexadecylamine (HDA) were used to prepare the mono-conjugate, R-HDA-B, where HDA was adopted to bind BSA. The PEG linker can elongate the proximity between RNase A and BSA. In contrast, four RNase A were closely located on BSA in R-SMCC-B. R-SMCC-B showed the lowest K(m) and the highest relative enzymatic activity and k(cat)/K(m) in the three conjugates. Presumably, the tetravalent interaction of RNase A in R-SMCC-B can increase the binding affinity to its substrate. In addition, the slow release of BSA from R-HDA-B may increase the enzymatic activity of R-HDA-B. Our study is expected to provide strategies to develop protein-albumin conjugate with high therapeutic potential. Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Invasive Group A Streptococcal Infection and Vaccine Implications, Auckland, New Zealand
Safar, Atheer; Stewart, Joanna; Trenholme, Adrian; Drinkovic, Dragana; Peat, Briar; Taylor, Susan; Read, Kerry; Roberts, Sally; Voss, Lesley
2011-01-01
We aimed to assess the effect of invasive group A streptococcal (GAS) infection and the potential effects of a multivalent GAS vaccine in New Zealand. During January 2005–December 2006, we conducted prospective population-based laboratory surveillance of Auckland residents admitted to all public hospitals with isolation of GAS from normally sterile sites. Using emm typing, we identified 225 persons with confirmed invasive GAS infection (median 53 years of age; range 0–97 years). Overall incidence was 8.1 cases per 100,00 persons per year (20.4/100,000/year for Maori and Pacific Islanders; 24.4/100,000/year for persons >65 years of age; 33/100,000/year for infants Auckland’s lowest socioeconomic quintile. Twenty-two persons died, for an overall case-fatality rate of 10% (63% for toxic shock syndrome). Seventy-four percent of patients who died had an underlying condition. To the population in our study, the proposed 26-valent vaccine would provide limited benefit. PMID:21749758
-
Chen, Tao; Su, Dian; Gruenhagen, Jason; Gu, Christine; Li, Yi; Yehl, Peter; Chetwyn, Nik P; Medley, Colin D
2016-01-05
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) offer new therapeutic options for advanced cancer patients through precision killing with fewer side effects. The stability and efficacy of ADCs are closely related, emphasizing the urgency and importance of gaining a comprehensive understanding of ADC stability. In this work, a chemical de-conjugation approach was developed to investigate the in-situ stability of the small molecule drug while it is conjugated to the antibody. This method involves chemical-mediated release of the small molecule drug from the ADC and subsequent characterization of the released small molecule drug by HPLC. The feasibility of this technique was demonstrated utilizing a model ADC containing a disulfide linker that is sensitive to the reducing environment within cancer cells. Five reducing agents were screened for use in de-conjugation; tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine (TCEP) was selected for further optimization due to its high efficiency and clean impurity profile. The optimized de-conjugation assay was shown to have excellent specificity and precision. More importantly, it was shown to be stability indicating, enabling the identification and quantification of the small molecule drug and its degradation products under different formulation pHs and storage temperatures. In summary, the chemical de-conjugation strategy demonstrated here offers a powerful tool to assess the in-situ stability of small molecule drugs on ADCs and the resulting information will shed light on ADC formulation/process development and storage condition selection. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Space Shuttle Underside Astronaut Communications Performance Evaluation
Hwu, Shian U.; Dobbins, Justin A.; Loh, Yin-Chung; Kroll, Quin D.; Sham, Catherine C.
2005-01-01
The Space Shuttle Ultra High Frequency (UHF) communications system is planned to provide Radio Frequency (RF) coverage for astronauts working underside of the Space Shuttle Orbiter (SSO) for thermal tile inspection and repairing. This study is to assess the Space Shuttle UHF communication performance for astronauts in the shadow region without line-of-sight (LOS) to the Space Shuttle and Space Station UHF antennas. To insure the RF coverage performance at anticipated astronaut worksites, the link margin between the UHF antennas and Extravehicular Activity (EVA) Astronauts with significant vehicle structure blockage was analyzed. A series of near-field measurements were performed using the NASA/JSC Anechoic Chamber Antenna test facilities. Computational investigations were also performed using the electromagnetic modeling techniques. The computer simulation tool based on the Geometrical Theory of Diffraction (GTD) was used to compute the signal strengths. The signal strength was obtained by computing the reflected and diffracted fields along the propagation paths between the transmitting and receiving antennas. Based on the results obtained in this study, RF coverage for UHF communication links was determined for the anticipated astronaut worksite in the shadow region underneath the Space Shuttle.
-
2007-01-01
Please note that starting from 1 March 2007, the shuttle requests: for official visits or bidders' conferences on the CERN site; towards/from the airport or central Geneva; for long distances, shall be made via Fm.Support@cern.ch or by calling 77777. The radio taxi will still be reachable at 76969. TS/FM Group
-
Photoluminescence in conjugated polymers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Furst, J.E.; Laugesen, R.; Dastoor, P.; McNeill, C.
2002-01-01
Full text: Conjugated polymers combine the electronic and optical properties of semiconductors with the processability of polymers. They contain a sequence of alternate single and double carbon bonds so that the overlap of unhybridised p z orbitals creates a delocalised ρ system which gives semiconducting properties with p-bonding (valence) and p* -antibonding (conduction) bands. Photoluminesence (PL) in conjugated polymers results from the radiative decay of singlet excitons confined to a single chain. The present work is the first in a series of studies in our laboratory that will characterize the optical properties of conjugated polymers. The experiment involves the illumination of thin films of conjugated polymer with UV light (I=360 nm) and observing the subsequent fluorescence using a custom-built, fluorescence spectrometer. Photoluminesence spectra provide basic information about the structure of the polymer film. A typical spectrum is shown in the accompanying figure. The position of the first peak is related to the polymer chain length and resolved multiple vibronic peaks are an indication of film structure and morphology. We will also present results related to the optical degradation of these materials when exposed to air and UV light
-
Bio-Conjugates for Nanoscale Applications
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Villadsen, Klaus
Bio-conjugates for Nanoscale Applications is the title of this thesis, which covers three different projects in chemical bio-conjugation research, namely synthesis and applications of: Lipidated fluorescent peptides, carbohydrate oxime-azide linkers and N-aryl O-R2 oxyamine derivatives. Lipidated...
-
Probabilistic Analysis of Space Shuttle Body Flap Actuator Ball Bearings
Oswald, Fred B.; Jett, Timothy R.; Predmore, Roamer E.; Zaretsky, Erwin V.
2008-01-01
A probabilistic analysis, using the 2-parameter Weibull-Johnson method, was performed on experimental life test data from space shuttle actuator bearings. Experiments were performed on a test rig under simulated conditions to determine the life and failure mechanism of the grease lubricated bearings that support the input shaft of the space shuttle body flap actuators. The failure mechanism was wear that can cause loss of bearing preload. These tests established life and reliability data for both shuttle flight and ground operation. Test data were used to estimate the failure rate and reliability as a function of the number of shuttle missions flown. The Weibull analysis of the test data for the four actuators on one shuttle, each with a 2-bearing shaft assembly, established a reliability level of 96.9 percent for a life of 12 missions. A probabilistic system analysis for four shuttles, each of which has four actuators, predicts a single bearing failure in one actuator of one shuttle after 22 missions (a total of 88 missions for a 4-shuttle fleet). This prediction is comparable with actual shuttle flight history in which a single actuator bearing was found to have failed by wear at 20 missions.
-
Changes to the shuttle circuits
GS Department
2011-01-01
To fit with passengers expectation, there will be some changes to the shuttle circuits as from Monday 10 October. See details on http://cern.ch/ShuttleService (on line on 7 October). Circuit No. 5 is cancelled as circuit No. 1 also stops at Bldg. 33. In order to guarantee shorter travel times, circuit No. 1 will circulate on Meyrin site only and circuit No. 2, with departures from Bldg. 33 and 500, on Prévessin site only. Site Services Section
-
Lima, Igo T.; Risko, Chad; Aziz, Saadullah Gary; Da Silva Filho, Demé trio A Da Silva; Bredas, Jean-Luc
2014-01-01
Donor-acceptor π-conjugated copolymers are of interest for a wide range of electronic applications, including field-effect transistors and solar cells. Here, we present a density functional theory (DFT) study of the impact of varying the conjugation pathway on the geometric, electronic, and optical properties of donor-acceptor systems. We consider both linear ("in series"), traditional conjugation among the donor-acceptor moieties versus structures where the acceptor units are appended orthogonally to the linear, donor-only conjugated backbone. Long-range-corrected hybrid functionals are used in the investigation with the values of the tuned long-range separation parameters providing an estimate of the extent of conjugation as a function of the oligomer architecture. Considerable differences in the electronic and optical properties are determined as a function of the nature of the conjugation pathway, features that should be taken into account in the design of donor-acceptor copolymers.
-
A Shuttle Derived Vehicle launch system
Tewell, J. R.; Buell, D. N.; Ewing, E. S.
1982-01-01
This paper describes a Shuttle Derived Vehicle (SDV) launch system presently being studied for the NASA by Martin Marietta Aerospace which capitalizes on existing Shuttle hardware elements to provide increased accommodations for payload weight, payload volume, or both. The SDV configuration utilizes the existing solid rocket boosters, external tank and the Space Shuttle main engines but replaces the manned orbiter with an unmanned, remotely controlled cargo carrier. This cargo carrier substitution more than doubles the performance capability of the orbiter system and is realistically achievable for minimal cost. The advantages of the SDV are presented in terms of performance and economics. Based on these considerations, it is concluded that an unmanned SDV offers a most attractive complement to the present Space Transportation System.
-
Organometallic B12-DNA conjugate
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hunger, Miriam; Mutti, Elena; Rieder, Alexander
2014-01-01
Design, synthesis, and structural characterization of a B12-octadecanucleotide are presented herein, a new organometallic B12-DNA conjugate. In such covalent conjugates, the natural B12 moiety may be a versatile vector for controlled in vivo delivery of oligonucleotides to cellular targets in hum...
-
The Conjugate Acid-Base Chart.
Treptow, Richard S.
1986-01-01
Discusses the difficulties that beginning chemistry students have in understanding acid-base chemistry. Describes the use of conjugate acid-base charts in helping students visualize the conjugate relationship. Addresses chart construction, metal ions, buffers and pH titrations, and the organic functional groups and nonaqueous solvents. (TW)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kamille Abdool
2015-05-01
Full Text Available We report the case of a 14-year-old boy with a past history of primary generalized seizures, who had been seizure-free for 2 years on sodium valproate and presented with generalized tonic clonic seizures suggestive of breakthrough seizures. Examination revealed hypertension, impetiginous lesions of the lower limbs, microscopic hematuria, elevated antistreptolysin O titre and low complement levels consistent with acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI demonstrated changes consistent with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Hypertension was controlled with intravenous nitroglycerin followed by oral captopril and amlodipine. Brain MRI changes returned normal within 2 weeks. The nephritis went in to remission within 2 months and after 8 months the patient has been seizure free again. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome appeared to have neither short nor intermediate effect on seizure control in this patient. The relationship between posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and seizures is reviewed.
-
Quantum mechanical models for the Fermi shuttle
Sternberg, James; Ovchinnikov, S. Yu.; Macek, J. H.
2009-05-01
Although the Fermi shuttle was originally proposed as an explanation for highly energetic cosmic rays, it is also a mechanism for the production of high energy electrons in atomic collisions [1]. The Fermi shuttle is usually thought of as a classical effect and most models of this process rely on classical or semi-classical approximations. In this work we explore several quantum mechanical models for ion-atom collisions and examine the evidence for the Fermi shuttle in these models. [4pt] [1] B. Sulik, Cs. Koncz, K. Tok'esi, A. Orb'an, and D. Ber'enyi, Phys Rev. Lett. 88 073201 (2002)
-
Fundamental plant biology enabled by the space shuttle.
Paul, Anna-Lisa; Wheeler, Ray M; Levine, Howard G; Ferl, Robert J
2013-01-01
The relationship between fundamental plant biology and space biology was especially synergistic in the era of the Space Shuttle. While all terrestrial organisms are influenced by gravity, the impact of gravity as a tropic stimulus in plants has been a topic of formal study for more than a century. And while plants were parts of early space biology payloads, it was not until the advent of the Space Shuttle that the science of plant space biology enjoyed expansion that truly enabled controlled, fundamental experiments that removed gravity from the equation. The Space Shuttle presented a science platform that provided regular science flights with dedicated plant growth hardware and crew trained in inflight plant manipulations. Part of the impetus for plant biology experiments in space was the realization that plants could be important parts of bioregenerative life support on long missions, recycling water, air, and nutrients for the human crew. However, a large part of the impetus was that the Space Shuttle enabled fundamental plant science essentially in a microgravity environment. Experiments during the Space Shuttle era produced key science insights on biological adaptation to spaceflight and especially plant growth and tropisms. In this review, we present an overview of plant science in the Space Shuttle era with an emphasis on experiments dealing with fundamental plant growth in microgravity. This review discusses general conclusions from the study of plant spaceflight biology enabled by the Space Shuttle by providing historical context and reviews of select experiments that exemplify plant space biology science.
-
REVIEW ARTICLE Conjugated Hyperbilirubinaemia in Early Infancy ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
REVIEW ARTICLE Conjugated Hyperbilirubinaemia in Early Infancy. AOK Johnson. Abstract. Conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia exists when the conjugated serum bilirubin level is more than 2 mg/dl or more than 20 per cent of the total serum bilirubin. It is always pathological in early infancy. The causes are many and diverse ...
-
Shuttle SBUV (SSBUV) Solar Spectral Irradiance V008
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — The Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet (SSBUV) level-2 irradiance data are available for eight space shuttle missions flown between 1989 and 1996. SSBUV, a...
-
AMS gets lift on space shuttle Discovery
2009-01-01
AMS-02, the CERN-recognized experiment that will seek dark matter, missing matter and antimatter in Space aboard the International Space Station (ISS), has recently got the green light to be part of the STS-134 NASA mission in 2010. Installation of AMS detectors in the Prévessin experiment hall.In a recent press release, NASA announced that the last or last-but-one mission of the Space Shuttle programme would be the one that will deliver AMS, the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, to the International Space Station. The Space Shuttle Discovery is due to lift off in July 2010 from Kennedy Space Center and its mission will include the installation of AMS to the exterior of the space station, using both the shuttle and station arms. "It wasn’t easy to get a lift on the Space Shuttle from the Bush administration," says professor Samuel Ting, spokesperson of the experiment, "since during his administration all the funds for space research w...
-
The space shuttle program technologies and accomplishments
Sivolella, Davide
2017-01-01
This book tells the story of the Space Shuttle in its many different roles as orbital launch platform, orbital workshop, and science and technology laboratory. It focuses on the technology designed and developed to support the missions of the Space Shuttle program. Each mission is examined, from both the technical and managerial viewpoints. Although outwardly identical, the capabilities of the orbiters in the late years of the program were quite different from those in 1981. Sivolella traces the various improvements and modifications made to the shuttle over the years as part of each mission story. Technically accurate but with a pleasing narrative style and simple explanations of complex engineering concepts, the book provides details of many lesser known concepts, some developed but never flown, and commemorates the ingenuity of NASA and its partners in making each Space Shuttle mission push the boundaries of what we can accomplish in space. Using press kits, original papers, newspaper and magazine articles...
-
Shuttle sonic boom - Technology and predictions. [environmental impact
Holloway, P. F.; Wilhold, G. A.; Jones, J. H.; Garcia, F., Jr.; Hicks, R. M.
1973-01-01
Because the shuttle differs significantly in both geometric and operational characteristics from conventional supersonic aircraft, estimation of sonic boom characteristics required a new technology base. The prediction procedures thus developed are reviewed. Flight measurements obtained for both the ascent and entry phases of the Apollo 15 and 16 and for the ascent phase only of the Apollo 17 missions are presented which verify the techniques established for application to shuttle. Results of extensive analysis of the sonic boom overpressure characteristics completed to date are presented which indicate that this factor of the shuttle's environmental impact is predictable, localized, of short duration and acceptable. Efforts are continuing to define the shuttle sonic boom characteristics to a fine level of detail based on the final system design.
-
Electron shuttles in biotechnology.
Watanabe, Kazuya; Manefield, Mike; Lee, Matthew; Kouzuma, Atsushi
2009-12-01
Electron-shuttling compounds (electron shuttles [ESs], or redox mediators) are essential components in intracellular electron transfer, while microbes also utilize self-produced and naturally present ESs for extracellular electron transfer. These compounds assist in microbial energy metabolism by facilitating electron transfer between microbes, from electron-donating substances to microbes, and/or from microbes to electron-accepting substances. Artificially supplemented ESs can create new routes of electron flow in the microbial energy metabolism, thereby opening up new possibilities for the application of microbes to biotechnology processes. Typical examples of such processes include halogenated-organics bioremediation, azo-dye decolorization, and microbial fuel cells. Herein we suggest that ESs can be applied widely to create new microbial biotechnology processes.
-
Application of optical phase conjugation to plasma diagnostics (invited)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jahoda, F.C.; Anderson, B.T.; Forman, P.R.; Weber, P.G.
1985-01-01
Several possibilities for plasma diagnostics provided by optical phase conjugation and, in particular, self-pumped phase conjugation in barium titanate (BaTiO 3 ) are discussed. These include placing a plasma within a dye laser cavity equipped with a phase conjugate mirror for intracavity absorption measurements, time differential refractometry with high spatial resolution, and simplified real-time holographic interferometry. The principles of phase conjugation with particular reference to photorefractive media and the special advantages of self-pumped phase conjugation are reviewed prior to the discussion of the applications. Distinctions are made in the applications between those for which photorefractive conjugators are essential and those for which they only offer experimental simplification relative to other types of phase conjugators
-
DIMETHYL ETHER (DME)-FUELED SHUTTLE BUS DEMONSTRATION PROJECT
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Elana M. Chapman; Shirish Bhide; Jennifer Stefanik; Howard Glunt; Andre L. Boehman; Allen Homan; David Klinikowski
2003-04-01
The objectives of this research and demonstration program are to convert a campus shuttle bus to operation on dimethyl ether, a potential ultra-clean alternative diesel fuel. To accomplish this objective, this project includes laboratory evaluation of a fuel conversion strategy, as well as, field demonstration of the DME-fueled shuttle bus. Since DME is a fuel with no lubricity (i.e., it does not possess the lubricating quality of diesel fuel), conventional fuel delivery and fuel injection systems are not compatible with dimethylether. Therefore, to operate a diesel engine on DME one must develop a fuel-tolerant injection system, or find a way to provide the necessary lubricity to the DME. In this project, they have chosen the latter strategy in order to achieve the objective with minimal need to modify the engine. The strategy is to blend DME with diesel fuel, to obtain the necessary lubricity to protect the fuel injection system and to achieve low emissions. The bulk of the efforts over the past year were focused on the conversion of the campus shuttle bus. This process, started in August 2001, took until April 2002 to complete. The process culminated in an event to celebrate the launching of the shuttle bus on DME-diesel operation on April 19, 2002. The design of the system on the shuttle bus was patterned after the system developed in the engine laboratory, but also was subjected to a rigorous failure modes effects analysis with help from Dr. James Hansel of Air Products. The result of this FMEA was the addition of layers of redundancy and over-pressure protection to the system on the shuttle bus. The system became operation in February 2002. Preliminary emissions tests and basic operation of the shuttle bus took place at the Pennsylvania Transportation institute's test track facility near the University Park airport. After modification and optimization of the system on the bus, operation on the campus shuttle route began in early June 2002. However, the
-
Revised estimates for ozone reduction by shuttle operation
Potter, A. E.
1978-01-01
Previous calculations by five different modeling groups of the effect of space shuttle operations on the ozone layer yielded an estimate of 0.2 percent ozone reduction for the Northern Hemisphere at 60 launches per year. Since these calculations were made, the accepted rate constant for the reaction between hydroperoxyl and nitric oxide to yield hydroxyl and nitrogen dioxide, HO2 + NO yields OH + NO2, was revised upward by more than an order of magnitude, with a resultant increase in the predicted ozone reduction for chlorofluoromethanes by a factor of approximately 2. New calculations of the shuttle effect were made with use of the new rate constant data, again by five different modeling groups. The new value of the shuttle effect on the ozone layer was found to be 0.25 percent. The increase resulting from the revised rate constant is considerably less for space shuttle operations than for chlorofluoromethane production, because the new rate constant also increases the calculated rate of downward transport of shuttle exhaust products out of the stratosphere.
-
DIMETHYL ETHER (DME)-FUELED SHUTTLE BUS DEMONSTRATION PROJECT
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Elana M. Chapman; Shirish Bhide; Jennifer Stefanik; Howard Glunt; Andre L. Boehman; Allen Homan; David Klinikowski
2003-04-01
The objectives of this research and demonstration program are to convert a campus shuttle bus to operation on dimethyl ether, a potential ultra-clean alternative diesel fuel. To accomplish this objective, this project includes laboratory evaluation of a fuel conversion strategy, as well as, field demonstration of the DME-fueled shuttle bus. Since DME is a fuel with no lubricity (i.e., it does not possess the lubricating quality of diesel fuel), conventional fuel delivery and fuel injection systems are not compatible with dimethyl ether. Therefore, to operate a diesel engine on DME one must develop a fuel-tolerant injection system, or find a way to provide the necessary lubricity to the DME. In this project, they have chosen the latter strategy in order to achieve the objective with minimal need to modify the engine. Their strategy is to blend DME with diesel fuel, to obtain the necessary lubricity to protect the fuel injection system and to achieve low emissions. The bulk of the efforts over the past year were focused on the conversion of the campus shuttle bus. This process, started in August 2001, took until April 2002 to complete. The process culminated in an event to celebrate the launching of the shuttle bus on DME-diesel operation on April 19, 2002. The design of the system on the shuttle bus was patterned after the system developed in the engine laboratory, but also was subjected to a rigorous failure modes effects analysis (FMEA, referred to by Air Products as a ''HAZOP'' analysis) with help from Dr. James Hansel of Air Products. The result of this FMEA was the addition of layers of redundancy and over-pressure protection to the system on the shuttle bus. The system became operational in February 2002. Preliminary emissions tests and basic operation of the shuttle bus took place at the Pennsylvania Transportation Institute's test track facility near the University Park airport. After modification and optimization of the system on
-
Shuttle bus services quality assessment Tangerang Selatan toward smart city
Fassa, Ferdinand; Sitorus, Fredy Jhon Philip; Adikesuma, Tri Nugraha
2017-11-01
Around the world, shuttle bus operation played the significant role to accommodate transportation for commuting bus passengers. Shuttle Bus services in cities are provided by various bus agencies with kinds of own specific purposes. For instance, at Tangerang Selatan, Indonesia, it was said that shuttle bus In Trans Bintaro is run and operated by private bus companies hire by Bintaro developer. The aim of this research is to identify factors of satisfaction of shuttle bus service in Kota Tangerang Selatan, Indonesia. Several factors are used to analyze sums of 20 parameters performance indicators of Shuttle Bus. A face to face interview using a questionnaire (N=200) was used to collect data on October and March 2017. Likert and diagram Cartesian were used to model the all the parameters. This research succeeded in finding some categories of Shuttle bus service attributes such as accessibility, comfort, and safety. Users agreed that eight indicators in shuttle bus have the excellent achievement, while three indicators on performance remain low and should receive more attention especially punctuality of the bus.
-
Shuttle/TDRSS modelling and link simulation study
Braun, W. R.; Mckenzie, T. M.; Biederman, L.; Lindsey, W. C.
1979-01-01
A Shuttle/TDRSS S-band and Ku-band link simulation package called LinCsim was developed for the evaluation of link performance for specific Shuttle signal designs. The link models were described in detail and the transmitter distortion parameters or user constraints were carefully defined. The overall link degradation (excluding hardware degradations) relative to an ideal BPSK channel were given for various sets of user constraint values. The performance sensitivity to each individual user constraint was then illustrated. The effect of excessive Spacelab clock jitter on the return link BER performance was also investigated as was the problem of subcarrier recovery for the K-band Shuttle return link signal.
-
Puerperal and intrapartum group A streptococcal infection.
Anteby, E Y; Yagel, S; Hanoch, J; Shapiro, M; Moses, A E
1999-01-01
OBJECTIVE: To determine the demographic and clinical variables characteristic of non-epidemic intrapartum or puerperal group A streptococcal (GAS) infection. METHODS: The records of 47 patients diagnosed with intrapartum or puerperal GAS infection over a 6 1/2 year period at Hadassah-University Hospital-Mt. Scopus, Jerusalem were reviewed. Data regarding 25,811 women, the general population of women that delivered during that period, were obtained from their computerized medical records. Frequency distributions, t-test, chi-square, and Spearman's Rank Correlation were used, as appropriate, to analyze and compare demographic and clinical variables associated with development of GAS infection, its clinical course and subsequent development of septic shock. RESULTS: Mean age of mothers with GAS infection was higher than that of our general pregnant population (30.4 versus 27.4 years, P = 0.0019), and a higher proportion of GAS infected patients (30% versus 12%, P < 0.005) experienced PROM. Thirty-one (66%) women had fever as their sole presenting symptom, eight (17%) had fever and abdominal pain, seven (15%) had fever and abnormal vaginal bleeding, and one patient (2%) presented with a rash. Three patients (6%) developed a septic shock. Two of these patients presented with symptoms more than 14 days after delivery. CONCLUSIONS: We describe the characteristics of non-epidemic intrapartum or puerperal GAS infection. Data from our study and review of the literature suggest that some patients who develop septic shock may present later in the puerperium than patients with an uncomplicated GAS infection. PMID:10598916
-
Optimal Wafer Cutting in Shuttle Layout Problems
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nisted, Lasse; Pisinger, David; Altman, Avri
2011-01-01
. The shuttle layout problem is frequently solved in two phases: first, a floorplan of the shuttle is generated. Then, a cutting plan is found which minimizes the overall number of wafers needed to satisfy the demand of each die type. Since some die types require special production technologies, only compatible...
-
Astronaut exposure to space radiation - Space Shuttle experience
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Atwell, W.
1990-01-01
Space Shuttle astronauts are exposed to both the trapped radiation and the galactic cosmic radiation environments. In addition, the sun periodically emits high-energy particles which could pose a serious threat to flight crews. NASA adheres to federal regulations and recommended exposure limits for radiation protection and has established a radiological health and risk assessment program. Using models of the space radiation environment, a Shuttle shielding model, and an anatomical human model, crew exposure estimates are made for each Shuttle flight. The various models are reviewed. Dosimeters are worn by each astronaut and are flown at several fixed locations to obtain inflight measurements. The dosimetry complement is discussed in detail. A comparison between the premission calculations and measurements is presented. Extrapolation of Shuttle experience to long-duration exposure is explored. 14 refs
-
Methotrexate and epirubicin conjugates as potential antitumor drugs
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Szymon Wojciech Kmiecik
2017-07-01
Full Text Available Introduction: The use of hybrid molecules has become one of the most significant approaches in new cytotoxic drug design. This study describes synthesis and characterization of conjugates consisting of two well-known and characterized chemotherapeutic agents: methotrexate (MTX and epirubicin (EPR. The synthesized conjugates combine two significant anticancer strategies: combinatory therapy and targeted therapy. These two drugs were chosen because they have different mechanisms of action, which can increase the anticancer effect of the obtained conjugates. MTX, which is a folic acid analog, has high cytotoxic properties and can serve as a targeting moiety that can reach folate receptors (FRs overexpresing tumor cells. Combination of nonselective drugs such as EPR with MTX can increase the selectivity of the obtained conjugates, while maintaining the high cytotoxic properties.Materials and methods: Conjugates were purified by RP-HPLC and the structure was investigated by MS and MS/MS methods. The effect of the conjugates on proliferation of LoVo, LoVo/Dx, MCF-7 and MV-4-11 human cancer cell lines was determined by SRB or MTT assay.Results: The conjugation reaction results in the formation of monosubstituted (α, γ and disubstituted MTX derivatives. In vitro proliferation data demonstrate that the conjugates synthesized in our study show lower cytotoxic properties than both chemotherapeutics used alone.Discussion: Epirubicin cytotoxicity was not observed in obtained conjugates. Effective drugs release after internalization needs further investigation.
-
Codevelopment of Microbiota and Innate Immunity and the Risk for Group B Streptococcal Disease
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Julia Kolter
2017-11-01
Full Text Available The pathogenesis of neonatal late-onset sepsis (LOD, which manifests between the third day and the third month of life, remains poorly understood. Group B Streptococcus (GBS is the most important cause of LOD in infants without underlying diseases or prematurity and the third most frequent cause of meningitis in the Western world. On the other hand, GBS is a common intestinal colonizer in infants. Accordingly, despite its adaption to the human lower gastrointestinal tract, GBS has retained its potential virulence and its transition from a commensal to a dangerous pathogen is unpredictable in the individual. Several cellular innate immune mechanisms, in particular Toll-like receptors, the inflammasome and the cGAS pathway, are engaged by GBS effectors like nucleic acids. These are likely to impact on the GBS-specific host resistance. Given the long evolution of streptococci as a normal constituent of the human microbiota, the emergence of GBS as the dominant neonatal sepsis cause just about 50 years ago is remarkable. It appears that intensive usage of tetracycline starting in the 1940s has been a selection advantage for the currently dominant GBS clones with superior adhesive and invasive properties. The historical replacement of Group A by Group B streptococci as a leading neonatal pathogen and the higher frequency of other β-hemolytic streptococci in areas with low GBS prevalence suggests the existence of a confined streptococcal niche, where locally competing streptococcal species are subject to environmental and immunological selection pressure. Thus, it seems pivotal to resolve neonatal innate immunity at mucous surfaces and its impact on microbiome composition and quality, i.e., genetic heterogeneity and metabolism, at the microanatomical level. Then, designer pro- and prebiotics, such as attenuated strains of GBS, and oligonucleotide priming of mucosal immunity may unfold their potential and facilitate adaptation of potentially
-
Codevelopment of Microbiota and Innate Immunity and the Risk for Group B Streptococcal Disease.
Kolter, Julia; Henneke, Philipp
2017-01-01
The pathogenesis of neonatal late-onset sepsis (LOD), which manifests between the third day and the third month of life, remains poorly understood. Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is the most important cause of LOD in infants without underlying diseases or prematurity and the third most frequent cause of meningitis in the Western world. On the other hand, GBS is a common intestinal colonizer in infants. Accordingly, despite its adaption to the human lower gastrointestinal tract, GBS has retained its potential virulence and its transition from a commensal to a dangerous pathogen is unpredictable in the individual. Several cellular innate immune mechanisms, in particular Toll-like receptors, the inflammasome and the cGAS pathway, are engaged by GBS effectors like nucleic acids. These are likely to impact on the GBS-specific host resistance. Given the long evolution of streptococci as a normal constituent of the human microbiota, the emergence of GBS as the dominant neonatal sepsis cause just about 50 years ago is remarkable. It appears that intensive usage of tetracycline starting in the 1940s has been a selection advantage for the currently dominant GBS clones with superior adhesive and invasive properties. The historical replacement of Group A by Group B streptococci as a leading neonatal pathogen and the higher frequency of other β-hemolytic streptococci in areas with low GBS prevalence suggests the existence of a confined streptococcal niche, where locally competing streptococcal species are subject to environmental and immunological selection pressure. Thus, it seems pivotal to resolve neonatal innate immunity at mucous surfaces and its impact on microbiome composition and quality, i.e., genetic heterogeneity and metabolism, at the microanatomical level. Then, designer pro- and prebiotics, such as attenuated strains of GBS, and oligonucleotide priming of mucosal immunity may unfold their potential and facilitate adaptation of potentially hazardous streptococci as
-
Shuttle Transportation System Case-Study Development
Ransom, Khadijah
2012-01-01
A case-study collection was developed for NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Using lessons learned and documented by NASA KSC engineers, analysts, and contractors, decades of information related to processing and launching the Space Shuttle was gathered into a single database. The goal was to provide educators with an alternative means to teach real-world engineering processes and to enhance critical thinking, decision making, and problem solving skills. Suggested formats were created to assist both external educators and internal NASA employees to develop and contribute their own case-study reports to share with other educators and students. Via group project, class discussion, or open-ended research format, students will be introduced to the unique decision making process related to Shuttle missions and development. Teaching notes, images, and related documents will be made accessible to the public for presentation of Space Shuttle reports. Lessons investigated included the engine cutoff (ECO) sensor anomaly which occurred during mission STS-114. Students will be presented with general mission infom1ation as well as an explanation of ECO sensors. The project will conclude with the design of a website that allows for distribution of information to the public as well as case-study report submissions from other educators online.
-
Prospective Surveillance of Invasive Group A Streptococcal Disease, Fiji, 2005–2007
Jenney, Adam; Kado, Joseph; Good, Michael F.; Batzloff, Michael; Waqatakirewa, Lepani; Mullholland, E. Kim; Carapetis, Jonathan R.
2009-01-01
We undertook a prospective active surveillance study of invasive group A streptococcal (GAS) disease in Fiji over a 23-month period, 2005–2007. We identified 64 cases of invasive GAS disease, which represents an average annualized all-ages incidence of 9.9 cases/100,000 population per year (95% confidence interval [CI] 7.6–12.6). Rates were highest in those >65 years of age and in those <5 years, particularly in infants, for whom the incidence was 44.9/100,000 (95% CI 18.1–92.5). The case-fatality rate was 32% and was associated with increasing age and underlying coexisting disease, including diabetes and renal disease. Fifty-five of the GAS isolates underwent emm sequence typing; the types were highly diverse, with 38 different emm subtypes and no particular dominant type. Our data support the view that invasive GAS disease is common in developing countries and deserves increased public health attention. PMID:19193265
-
Liquid Hydrogen Consumption During Space Shuttle Program
Partridge, Jonathan K.
2011-01-01
This slide presentation reviews the issue of liquid hydrogen consumption and the points of its loss in prior to the shuttle launch. It traces the movement of the fuel from the purchase to the on-board quantity and the loss that results in 54.6 of the purchased quantity being on board the Shuttle.
-
The Rules and Functions of Nucleocytoplasmic Shuttling Proteins.
Fu, Xuekun; Liang, Chao; Li, Fangfei; Wang, Luyao; Wu, Xiaoqiu; Lu, Aiping; Xiao, Guozhi; Zhang, Ge
2018-05-12
Biological macromolecules are the basis of life activities. There is a separation of spatial dimension between DNA replication and RNA biogenesis, and protein synthesis, which is an interesting phenomenon. The former occurs in the cell nucleus, while the latter in the cytoplasm. The separation requires protein to transport across the nuclear envelope to realize a variety of biological functions. Nucleocytoplasmic transport of protein including import to the nucleus and export to the cytoplasm is a complicated process that requires involvement and interaction of many proteins. In recent years, many studies have found that proteins constantly shuttle between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. These shuttling proteins play a crucial role as transport carriers and signal transduction regulators within cells. In this review, we describe the mechanism of nucleocytoplasmic transport of shuttling proteins and summarize some important diseases related shuttling proteins.
-
AI mass spectrometers for space shuttle health monitoring
Adams, F. W.
1991-01-01
The facility Hazardous Gas Detection System (HGDS) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) is a mass spectrometer based gas analyzer. Two instruments make up the HGDS, which is installed in a prime/backup arrangement, with the option of using both analyzers on the same sample line, or on two different lines simultaneously. It is used for monitoring the Shuttle during fuel loading, countdown, and drainback, if necessary. The use of complex instruments, operated over many shifts, has caused problems in tracking the status of the ground support equipment (GSE) and the vehicle. A requirement for overall system reliability has been a major force in the development of Shuttle GSE, and is the ultimate driver in the choice to pursue artificial intelligence (AI) techniques for Shuttle and Advanced Launch System (ALS) mass spectrometer systems. Shuttle applications of AI are detailed.
-
The flights before the flight - An overview of shuttle astronaut training
Sims, John T.; Sterling, Michael R.
1989-01-01
Space shuttle astronaut training is centered at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. Each astronaut receives many different types of training from many sources. This training includes simulator training in the Shuttle Mission Simulator, in-flight simulator training in the Shuttle Training Aircraft, Extravehicular Activity training in the Weightless Environment Training Facility and a variety of lectures and briefings. Once the training program is completed each shuttle flight crew is well-prepared to perform the normal operations required for their flight and deal with any shuttle system malfunctions that might occur.
-
Shuttle Repair Tools Automate Vehicle Maintenance
2013-01-01
Successfully building, flying, and maintaining the space shuttles was an immensely complex job that required a high level of detailed, precise engineering. After each shuttle landed, it entered a maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) phase. Each system was thoroughly checked and tested, and worn or damaged parts replaced, before the shuttle was rolled out for its next mission. During the MRO period, workers needed to record exactly what needed replacing and why, as well as follow precise guidelines and procedures in making their repairs. That meant traceability, and with it lots of paperwork. In 2007, the number of reports generated during electrical system repairs was getting out of hand-placing among the top three systems in terms of paperwork volume. Repair specialists at Kennedy Space Center were unhappy spending so much time at a desk and so little time actually working on the shuttle. "Engineers weren't spending their time doing technical work," says Joseph Schuh, an electrical engineer at Kennedy. "Instead, they were busy with repetitive, time-consuming processes that, while important in their own right, provided a low return on time invested." The strain of such inefficiency was bad enough that slow electrical repairs jeopardized rollout on several occasions. Knowing there had to be a way to streamline operations, Kennedy asked Martin Belson, a project manager with 30 years experience as an aerospace contractor, to co-lead a team in developing software that would reduce the effort required to document shuttle repairs. The result was System Maintenance Automated Repair Tasks (SMART) software. SMART is a tool for aggregating and applying information on every aspect of repairs, from procedures and instructions to a vehicle s troubleshooting history. Drawing on that data, SMART largely automates the processes of generating repair instructions and post-repair paperwork. In the case of the space shuttle, this meant that SMART had 30 years worth of operations
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sujiet Puthenveetil
Full Text Available Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs are no longer an unknown entity in the field of cancer therapy with the success of marketed ADCs like ADCETRIS and KADCYLA and numerous others advancing through clinical trials. The pursuit of novel cytotoxic payloads beyond the mictotubule inhibitors and DNA damaging agents has led us to the recent discovery of an mRNA splicing inhibitor, thailanstatin, as a potent ADC payload. In our previous work, we observed that the potency of this payload was uniquely tied to the method of conjugation, with lysine conjugates showing much superior potency as compared to cysteine conjugates. However, the ADC field is rapidly shifting towards site-specific ADCs due to their advantages in manufacturability, characterization and safety. In this work we report the identification of a highly efficacious site-specific thailanstatin ADC. The site of conjugation played a critical role on both the in vitro and in vivo potency of these ADCs. During the course of this study, we developed a novel methodology of loading a single site with multiple payloads using an in situ generated multi-drug carrying peptidic linker that allowed us to rapidly screen for optimal conjugation sites. Using this methodology, we were able to identify a double-cysteine mutant ADC delivering four-loaded thailanstatin that was very efficacious in a gastric cancer xenograft model at 3mg/kg and was also shown to be efficacious against T-DM1 resistant and MDR1 overexpressing tumor cell lines.
-
Puthenveetil, Sujiet; He, Haiyin; Loganzo, Frank; Musto, Sylvia; Teske, Jesse; Green, Michael; Tan, Xingzhi; Hosselet, Christine; Lucas, Judy; Tumey, L Nathan; Sapra, Puja; Subramanyam, Chakrapani; O'Donnell, Christopher J; Graziani, Edmund I
2017-01-01
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are no longer an unknown entity in the field of cancer therapy with the success of marketed ADCs like ADCETRIS and KADCYLA and numerous others advancing through clinical trials. The pursuit of novel cytotoxic payloads beyond the mictotubule inhibitors and DNA damaging agents has led us to the recent discovery of an mRNA splicing inhibitor, thailanstatin, as a potent ADC payload. In our previous work, we observed that the potency of this payload was uniquely tied to the method of conjugation, with lysine conjugates showing much superior potency as compared to cysteine conjugates. However, the ADC field is rapidly shifting towards site-specific ADCs due to their advantages in manufacturability, characterization and safety. In this work we report the identification of a highly efficacious site-specific thailanstatin ADC. The site of conjugation played a critical role on both the in vitro and in vivo potency of these ADCs. During the course of this study, we developed a novel methodology of loading a single site with multiple payloads using an in situ generated multi-drug carrying peptidic linker that allowed us to rapidly screen for optimal conjugation sites. Using this methodology, we were able to identify a double-cysteine mutant ADC delivering four-loaded thailanstatin that was very efficacious in a gastric cancer xenograft model at 3mg/kg and was also shown to be efficacious against T-DM1 resistant and MDR1 overexpressing tumor cell lines.
-
General Infrastructure Services Department
2011-01-01
As of Monday 21 February, a new schedule will come into effect for the Airport Shuttle (circuit No. 4) at the end of the afternoon: Last departure at 7:00 pm from Main Buildig, (Bldg. 500) to Airport (instead of 5:10 p.m.); Last departure from Airport to CERN, Main Buildig, (Bldg. 500), at 7:30 p.m. (instead of 5:40 p.m.). Group GS-IS
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
N.V. Nagornaya
2013-11-01
Full Text Available The problem of acute tonsillitis remains relevant in clinical pediatrics. A special role in its etiology belongs to group A β-hemolytic streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes, which is found in every fourth child with acute bacterial tonsillitis. In this article there is presented an analysis of the clinical case of streptococcal tonsillitis in children and the pathogen, epidemiology and prognosis of the disease are described. The authors reviewed the current diagnosis criteria and international treatment approaches. There has been grounded the use of cefuroxime axetil for eradication of Streptococcus pyogenes.
-
Macro Level Simulation Model Of Space Shuttle Processing
2000-01-01
The contents include: 1) Space Shuttle Processing Simulation Model; 2) Knowledge Acquisition; 3) Simulation Input Analysis; 4) Model Applications in Current Shuttle Environment; and 5) Model Applications for Future Reusable Launch Vehicles (RLV's). This paper is presented in viewgraph form.
-
STS-61 Space Shuttle mission report
Fricke, Robert W., Jr.
1994-02-01
The STS-61 Space Shuttle Program Mission Report summarizes the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission as well as the Orbiter, External Tank (ET), Solid Rocket Booster (SRB), Redesigned Solid Rocket Motor (RSRM), and the Space Shuttle main engine (SSME) systems performance during the fifty-ninth flight of the Space Shuttle Program and fifth flight of the Orbiter vehicle Endeavour (OV-105). In addition to the Orbiter, the flight vehicle consisted of an ET designated as ET-60; three SSME's which were designated as serial numbers 2019, 2033, and 2017 in positions 1, 2, and 3, respectively; and two SRB's which were designated BI-063. The RSRM's that were installed in each SRB were designated as 360L023A (lightweight) for the left SRB, and 360L023B (lightweight) for the right SRB. This STS-61 Space Shuttle Program Mission Report fulfills the Space Shuttle Program requirement as documented in NSTS 07700, Volume 8, Appendix E. That document requires that each major organizational element supporting the Program report the results of its hardware evaluation and mission performance plus identify all related in-flight anomalies. The primary objective of the STS-61 mission was to perform the first on-orbit servicing of the Hubble Space Telescope. The servicing tasks included the installation of new solar arrays, replacement of the Wide Field/Planetary Camera I (WF/PC I) with WF/PC II, replacement of the High Speed Photometer (HSP) with the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR), replacement of rate sensing units (RSU's) and electronic control units (ECU's), installation of new magnetic sensing systems and fuse plugs, and the repair of the Goddard High Resolution Spectrometer (GHRS). Secondary objectives were to perform the requirements of the IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC), the IMAX Camera, and the Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) Calibration Test.
-
Wings In Orbit: Scientific and Engineering Legacies of the Space Shuttle
Hale, N. Wayne (Editor); Lulla, Kamlesh (Editor); Lane, Helen W. (Editor); Chapline, Gail (Editor)
2010-01-01
This Space Shuttle book project reviews Wings In Orbit-scientific and engineering legacies of the Space Shuttle. The contents include: 1) Magnificent Flying Machine-A Cathedral to Technology; 2) The Historical Legacy; 3) The Shuttle and its Operations; 4) Engineering Innovations; 5) Major Scientific Discoveries; 6) Social, Cultural, and Educational Legacies; 7) Commercial Aerospace Industries and Spin-offs; and 8) The Shuttle continuum, Role of Human Spaceflight.
-
Stennis Holds Last Planned Space Shuttle Engine Test
2009-01-01
With 520 seconds of shake, rattle and roar on July 29, 2009 NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center marked the end of an era for testing the space shuttle main engines that have powered the nation's Space Shuttle Program for nearly three decades.
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Third Generation PAMAM Dendrimer Conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mohammad Najlah
2017-10-01
Full Text Available The present study compares the use of high generation G3 and low generation G0 Polyamidoamine (PAMAM dendrimers as drug carriers of naproxen (NAP, a poorly water soluble drug. Naproxen was conjugated to G3 in different ratios and to G0 in a 1:1 ratio via a diethylene glycol linker. A lauroyl chain (L, a lipophilic permeability enhancer, was attached to G3 and G0 prodrugs. The G3 and G0 conjugates were more hydrophilic than naproxen as evaluated by the measurement of partitioning between 1-octanol and a phosphate buffer at pH 7.4 and pH 1.2. The unmodified surface PAMAM-NAP conjugates showed significant solubility enhancements of NAP at pH 1.2; however, with the number of NAP conjugated to G3, this was limited to 10 molecules. The lactate dehydrogenase (LDH assay indicated that the G3 dendrimer conjugates had a concentration dependent toxicity towards Caco-2 cells. Attaching naproxen to the surface of the dendrimer increased the IC50 of the resulting prodrugs towards Caco-2 cells. The lauroyl G3 conjugates showed the highest toxicity amongst the PAMAM dendrimer conjugates investigated and were significantly more toxic than the lauroyl-G0-naproxen conjugates. The permeability of naproxen across monolayers of Caco-2 cells was significantly increased by its conjugation to either G3 or G0 PAMAM dendrimers. Lauroyl-G0 conjugates displayed considerably lower cytotoxicity than G3 conjugates and may be preferable for use as a drug carrier for low soluble drugs such as naproxen.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Noorbakhsh S
2010-12-01
% PPV; Anti- streptokinase (cut off level> 332IU/ml had 34% sensitivity; 85% specificity, and 90% PPV; Anti-DNase (cut off level> 140IU/ml had 70% sensitivity; 99% specificity and PPV 90%."n"nConclusion: Patients with tic disorder had a significant high antibody titer against streptococcal infection in comparison with healthy children. It presents possible role for streptococcal infection in tic disorders. Treatment of streptococcal infection is achievable by using of long acting Penicillin in our country. Use of aggressive treatment like plasmaphresis etc needs future RCT studies.
-
CONJUGATED BLOCK-COPOLYMERS FOR ELECTROLUMINESCENT DIODES
Hilberer, A; Gill, R.E; Herrema, J.K; Malliaras, G.G; Wildeman, J.; Hadziioannou, G
In this article we review results obtained in our laboratory on the design and study of new light-emitting polymers. We are interested in the synthesis and characterisation of block copolymers with regularly alternating conjugated and non conjugated sequences. The blocks giving rise to luminescence
-
Tetrafullerene conjugates for all-organic photovoltaics
Fernández, G.; Sánchez, L.; Veldman, D.; Wienk, M.M.; Atienza, C.M.; Guldi, D.M.; Janssen, R.A.J.; Martin, N.
2008-01-01
The synthesis of two new tetrafullerene nanoconjugates in which four C60 units are covalently connected through different -conjugated oligomers (oligo(p-phenylene ethynylene) and oligo(p-phenylene vinylene)) is described. The photovoltaic (PV) response of these C60-based conjugates was evaluated by
-
Shuttles set for US Gulf lift off
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
DeLuca, Marshall
2002-09-01
The author reports on discussions with two US companies about plans for using shuttle tankers to transport oil from platforms in the Gulf of Mexico to US ports as an alternative to pipeline networks. This follows approval by the US Minerals Management Service for FPSOs in the Gulf. The companies are American Shuttle Tankers and Conoco-owned Seahorse Shuttling and Technology. Because the vessels will enter US ports and operate in US waters, they must conform with the US Jones Act: they must be US-built, US-flagged and manned by US crews. They must also be double-hulled. This increases cost and reduces market opportunities for the vessels outside the US. The article also considers the use of articulated tug barges as another option. (UK)
-
The Shuttle Cost and Price model
Leary, Katherine; Stone, Barbara
1983-01-01
The Shuttle Cost and Price (SCP) model was developed as a tool to assist in evaluating major aspects of Shuttle operations that have direct and indirect economic consequences. It incorporates the major aspects of NASA Pricing Policy and corresponds to the NASA definition of STS operating costs. An overview of the SCP model is presented and the cost model portion of SCP is described in detail. Selected recent applications of the SCP model to NASA Pricing Policy issues are presented.
-
Novel Aflatoxin Derivatives and Protein Conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Reinhard Niessner
2007-03-01
Full Text Available Aflatoxins, a group of structurally related mycotoxins, are well known for their toxic and carcinogenic effects in humans and animals. Aflatoxin derivatives and protein conjugates are needed for diverse analytical applications. This work describes a reliable and fast synthesis of novel aflatoxin derivatives, purification by preparative HPLC and characterisation by ESI-MS and one- and two-dimensional NMR. Novel aflatoxin bovine serum albumin conjugates were prepared and characterised by UV absorption and MALDI-MS. These aflatoxin protein conjugates are potentially interesting as immunogens for the generation of aflatoxin selective antibodies with novel specificities.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Maureen U Okwu
2017-04-01
Full Text Available Background: This study aimed to determine the prevalence, antibiotic, and toothpaste sensitivity of oral streptococcal isolates in healthy individuals in the Okada community of Nigeria. Methods: Oral samples were collected from 230 volunteers and were subjected to standard microbiological tests. Antibacterial sensitivity tests were carried out on the streptococcal isolates that were obtained using a disk diffusion technique, and eight kinds of toothpaste (A-H were screened for their antibacterial effects on Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans. Results: The prevalence of oral streptococci found in this study was 26.1% and the predominant species was S. salivarius (13.9%. S. salivarius was highly resistant to cloxacillin (100% and Augmentin (96.9%, whilst resistance to gentamicin and erythromycin was low at 21.9% and 3.1% respectively. S. mutans were completely sensitive to gentamicin whilst resistance to erythromycin was 33.3%. The entire Streptococcus species showed the lowest resistance to erythromycin (20.0%, followed by gentamicin (31.7%. At 100 mg/mL all toothpaste samples had antibacterial effects on S. mutans. At 50 mg/mL all samples except toothpastes G and H inhibited the bacterium. Toothpastes A and E had the lowest minimum inhibitory concentration of 25 mg/mL. Conclusions: Toothpastes A and E were the most effective toothpastes of the eight assessed in this study.
-
Structure Property Relationships in Organic Conjugated Systems
O'Neill, Luke
2008-01-01
A series of pi(п) conjugated oligomers containing 1 to 6 monomer units were studied by absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopies. The results are discussed and examined with regard to the variation of the optical properties with the increase of effective conjugation length. It was found that there was a linear relationship between the positioning of the absorption and photoluminescence maxima plotted against inverse conjugation length. The relationships are in good agreement with the si...
-
Sources and Bioactive Properties of Conjugated Dietary Fatty Acids.
Hennessy, Alan A; Ross, Paul R; Fitzgerald, Gerald F; Stanton, Catherine
2016-04-01
The group of conjugated fatty acids known as conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) isomers have been extensively studied with regard to their bioactive potential in treating some of the most prominent human health malignancies. However, CLA isomers are not the only group of potentially bioactive conjugated fatty acids currently undergoing study. In this regard, isomers of conjugated α-linolenic acid, conjugated nonadecadienoic acid and conjugated eicosapentaenoic acid, to name but a few, have undergone experimental assessment. These studies have indicated many of these conjugated fatty acid isomers commonly possess anti-carcinogenic, anti-adipogenic, anti-inflammatory and immune modulating properties, a number of which will be discussed in this review. The mechanisms through which these bioactivities are mediated have not yet been fully elucidated. However, existing evidence indicates that these fatty acids may play a role in modulating the expression of several oncogenes, cell cycle regulators, and genes associated with energy metabolism. Despite such bioactive potential, interest in these conjugated fatty acids has remained low relative to the CLA isomers. This may be partly attributed to the relatively recent emergence of these fatty acids as bioactives, but also due to a lack of awareness regarding sources from which they can be produced. In this review, we will also highlight the common sources of these conjugated fatty acids, including plants, algae, microbes and chemosynthesis.
-
Preparation and immunological properties of procaine-protein conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Liakopoulou, A.
1981-01-01
Procaine was conjugated to BSA and rat and rabbit Gf using the carbodiimide method and 14 C-procaine as tracer. The composition of the conjugates could be varied depending on the time of incubation and the concentration of procaine in the reaction mixtures. Procaine-BSA conjugates were soluble in water or saline. However, procaine conjugates to rat or rabbit Gf were not readily soluble in saline. These conjugates were good for immunization purposes, but it was cumbersome to work with them when clear solutions were needed, as in the immunochemical procedures used in this study. The immunological properties of the conjugates were studied in rats and rabbits. Rats responded with production of IgGa and precipitating antibodies to the procaine group, but IgE antibodies to the immunogen could not be detected. Furthermore, precipitating antibodies towards the procaine group were raised in rabbits. When BSA was the protein carrier, antibodies to the carrier molecule were also detected in both rats and rabbits. The conjugates of procaine to rat or rabbit Gf did not elicit antibody response to the carrier molecule when used in the homologous species. Hapten inhibition studies suggested that, in the rabbit, antibodies were also produced with specificity directed towards the molecular configuration of the hapten-carrier bond. (author)
-
IRDye78 Conjugates for Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Atif Zaheer
2002-10-01
Full Text Available The detection of human malignancies by near-infrared (NIR fluorescence will require the conjugation of cancer-specific ligands to NIR fluorophores that have optimal photoproperties and pharmacokinetics. IRDye78, a tetra-sulfonated heptamethine indocyanine NIR fluorophore, meets most of the criteria for an in vivo imaging agent, and is available as an N-hydroxysuccinimide ester for conjugation to low-molecular-weight ligands. However, IRDye78 has a high charge-to-mass ratio, complicating purification of conjugates. It also has a potentially labile linkage between fluorophore and ligand. We have developed an ion-pairing purification strategy for IRDye78 that can be performed with a standard C18 column under neutral conditions, thus preserving the stability of fluorophore, ligand, and conjugate. By employing parallel evaporative light scatter and absorbance detectors, all reactants and products are identified, and conjugate purity is maximized. We describe reversible and irreversible conversions of IRDye78 that can occur during sample purification, and describe methods for preserving conjugate stability. Using seven ligands, spanning several classes of small molecules and peptides (neutral, charged, and/or hydrophobic, we illustrate the robustness of these methods, and confirm that IRDye78 conjugates so purified retain bioactivity and permit NIR fluorescence imaging of specific targets.
-
Preconditioning the modified conjugate gradient method ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
In this paper, the convergence analysis of the conventional conjugate Gradient method was reviewed. And the convergence analysis of the modified conjugate Gradient method was analysed with our extension on preconditioning the algorithm. Convergence of the algorithm is a function of the condition number of M-1A.
-
Death of the TonB Shuttle Hypothesis.
Gresock, Michael G; Savenkova, Marina I; Larsen, Ray A; Ollis, Anne A; Postle, Kathleen
2011-01-01
A complex of ExbB, ExbD, and TonB couples cytoplasmic membrane (CM) proton motive force (pmf) to the active transport of large, scarce, or important nutrients across the outer membrane (OM). TonB interacts with OM transporters to enable ligand transport. Several mechanical models and a shuttle model explain how TonB might work. In the mechanical models, TonB remains attached to the CM during energy transduction, while in the shuttle model the TonB N terminus leaves the CM to deliver conformationally stored potential energy to OM transporters. Previous studies suggested that TonB did not shuttle based on the activity of a GFP-TonB fusion that was anchored in the CM by the GFP moiety. When we recreated the GFP-TonB fusion to extend those studies, in our hands it was proteolytically unstable, giving rise to potentially shuttleable degradation products. Recently, we discovered that a fusion of the Vibrio cholerae ToxR cytoplasmic domain to the N terminus of TonB was proteolytically stable. ToxR-TonB was able to be completely converted into a proteinase K-resistant conformation in response to loss of pmf in spheroplasts and exhibited an ability to form a pmf-dependent formaldehyde crosslink to ExbD, both indicators of its location in the CM. Most importantly, ToxR-TonB had the same relative specific activity as wild-type TonB. Taken together, these results provide conclusive evidence that TonB does not shuttle during energy transduction. We had previously concluded that TonB shuttles based on the use of an Oregon Green(®) 488 maleimide probe to assess periplasmic accessibility of N-terminal TonB. Here we show that the probe was permeant to the CM, thus permitting the labeling of the TonB N-terminus. These former results are reinterpreted in the context that TonB does not shuttle, and suggest the existence of a signal transduction pathway from OM to cytoplasm.
-
Cao, Na; Feng, Si-Shen
2008-10-01
To develop a polymer-anticancer drug conjugate, D-alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was employed as a carrier of doxorubicin (DOX) to enhance its therapeutic effects and reduce its side effects. Doxorubicin was chemically conjugated to TPGS. The molecular structure, drug loading efficiency, drug release kinetics and stability of the conjugate were characterized. The cellular uptake, intracellular distribution, and cytotoxicity were accessed by using MCF-7 breast cancer cells and C6 glioma cells as in vitro cell model. The conjugate showed higher cellular uptake efficiency and broader distribution within the cells. Judged by IC(50), the conjugate was found 31.8, 69.6, 84.1% more effective with MCF-7 cells and 43.9, 87.7, 42.2% more effective with C6 cells than the parent drug after 24, 48, 72 h culture, respectively. The in vivo pharmacokinetics and biodistribution were investigated after an i.v. administration at 5 mg DOX/kg body weight in rats. Promisingly, 4.5-fold increase in the half-life and 24-fold increase in the area-under-the-curve (AUC) of DOX were achieved for the TPGS-DOX conjugate compared with the free DOX. The drug level in heart, gastric and intestine was significantly reduced, which is an indication of reduced side effects. Our TPGS-DOX conjugate showed great potential to be a prodrug of higher therapeutic effects and fewer side effects than DOX itself.
-
Meals in orbit. [Space Shuttle food service planning
1980-01-01
Space foods which will be available to the Space Shuttle crew are discussed in view of the research and development of proper nutrition in space that began with the pastelike tube meals of the Mercury and Gemini astronauts. The variety of food types proposed for the Space Shuttle crew which include thermostabilized, intermediate moisture, rehydratable, irradiated, freeze-dried and natural forms are shown to be a result of the successive improvements in the Apollo, Skylab and Apollo Soyuz test project flights. The Space Shuttle crew will also benefit from an increase of caloric content (3,000 cal./day), the convenience of a real oven and a comfortable dining and kitchen area.
-
Holography on the NASA Space Shuttle
Wuerker, R. F.; Heflinger, L. O.; Flannery, J. V.; Kassel, A.; Rollauer, A. M.
1980-01-01
The SL-3 flight on the Space Shuttle will carry a 25 mW He-Ne laser holographic recorder for recording the solution growth of triglycine sulfate (TGS) crystals under low-zero gravity conditions. Three hundred holograms (two orthogonal views) will be taken (on SO-253 film) of each growth experiment. Processing and analysis (i.e., reconstructed imagery, holographic schlieren, reverse reference beam microscopy, and stored beam interferometry) of the holographic records will be done at NASA/MSFC. Other uses of the recorder on the Shuttle have been proposed.
-
The use of the Space Shuttle for land remote sensing
Thome, P. G.
1982-01-01
The use of the Space Shuttle for land remote sensing will grow significantly during the 1980's. The main use will be for general land cover and geological mapping purposes by worldwide users employing specialized sensors such as: high resolution film systems, synthetic aperture radars, and multispectral visible/IR electronic linear array scanners. Because these type sensors have low Space Shuttle load factors, the user's preference will be for shared flights. With this strong preference and given the present prognosis for Space Shuttle flight frequency as a function of orbit inclination, the strongest demand will be for 57 deg orbits. However, significant use will be made of lower inclination orbits. Compared with freeflying satellites, Space Shuttle mission investment requirements will be significantly lower. The use of the Space Shuttle for testing R and D land remote sensors will replace the free-flying satellites for most test programs.
-
Use of Probabilistic Risk Assessment in Shuttle Decision Making Process
Boyer, Roger L.; Hamlin, Teri, L.
2011-01-01
This slide presentation reviews the use of Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) to assist in the decision making for the shuttle design and operation. Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) is a comprehensive, structured, and disciplined approach to identifying and analyzing risk in complex systems and/or processes that seeks answers to three basic questions: (i.e., what can go wrong? what is the likelihood of these occurring? and what are the consequences that could result if these occur?) The purpose of the Shuttle PRA (SPRA) is to provide a useful risk management tool for the Space Shuttle Program (SSP) to identify strengths and possible weaknesses in the Shuttle design and operation. SPRA was initially developed to support upgrade decisions, but has evolved into a tool that supports Flight Readiness Reviews (FRR) and near real-time flight decisions. Examples of the use of PRA for the shuttle are reviewed.
-
Bis-polymer lipid-peptide conjugates and nanoparticles thereof
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Xu, Ting; Dong, He; Shu, Jessica; Dube, Nikhil
2018-04-24
The present invention provides bis-polymer lipid-peptide conjugates containing a hydrophobic block and headgroup containing a helical peptide and two polymer blocks. The conjugates can self-assemble to form helix bundle subunits, which in turn assemble to provide micellar nanocarriers for drug cargos and other agents. Particles containing the conjugates and methods for forming the particles are also disclosed.
-
Adam, D; Scholz, H; Helmerking, M
2001-07-19
Group A Streptococci have remained sensitive to penicillins and other betalactam antibiotics, e. g. cephalosporins. Since the beginning of the 1950s oral penicillin V given three times daily in a dose of 50,000 IU daily has been the drug of choice against Group A streptococcal infection. The German Society for Pediatric Infectious Diseases (DGPI) undertook a large scale multicenter randomized study of culture-proven A-streptococcal tonsillopharyngitis to compare the efficacy and safety of a five day regimen of ceftibuten (9 mg/kg KG, once daily) with 10 days of penicillin V (50,000 I.E./kg KG, divided in three doses), testing for equivalence of clinical and bacteriological efficacy. A one year follow-up served to assess poststreptococcal sequelae like rheumatic fever or glomerulonephritis. The clinical efficacy at the clinical end-point 7-9 days after end of treatment was 86.9% (419/482) for ceftibuten and 88.6% (1,198/1,352) for penicillin V. This result is statistically equivalent (P = 0.0152). Resolution of clinical symptoms was significantly faster in the ceftibuten group (P = 0.043/Fisher-Test) and compliance was significantly superior as well (P (0.001). Eradication of group A streptococci at an early control 2-4 days after end of treatment was not equivalent, 78.49% for ceftibuten and 84.42% for penicillin V (P = 0.5713). Both eradication rates were comparable 7-8 weeks after end of treatment (84.65%, 375/443 ceftibuten vs. 86.82%, 1,067/1,229 penicillin V), the difference not being significant. No cases of poststreptococcal sequelae, e.g. rheumatic fever or glomerulonephritis, attributable to either ceftibuten or penicillin were observed in the course of the study.
-
[Outcome of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis post-streptococcal disease in children].
Jellouli, Manel; Maghraoui, Sondos; Abidi, Kamel; Hammi, Yosra; Goucha, Rim; Naija, Ouns; Zarrouk, Chokri; Gargah, Tahar
2015-11-01
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is a rare form of postinfectious glomerulonephritis. The aim of this study was to describe the outcome of our patients with severe post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. This retrospective study was conducted in the department of pediatrics in Charles-Nicolle Hospital during a period of 13 years (1997-2009). Twenty-seven children were identified. The mean age was 8.7 years. All patients presented renal failure at presentation. The mean serum creatinine at presentation was 376.9 μmol/L. Six patients presented nephrotic syndrome. Twenty-six children had renal biopsies. Renal biopsies showed crescents in 24 cases. Eighteen children received pulse dose of corticosteroids (66.6%) and 6 children (22%) received pulse dose of corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide. Eleven patients required dialysis. At last follow-up, 22 patients (81.5%) had normal kidney function, 2 had renal dysfunction and 3 reached end stage renal disease. The only significant determinant for renal survival was the supportive dialysis (P=0.015). Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis is uncommon. There have been significant advancements in supportive, as well as specific therapy, but the outcome continues to be poor. Copyright © 2015 Association Société de néphrologie. Published by Elsevier SAS. All rights reserved.
-
Space Shuttle GN and C Development History and Evolution
Zimpfer, Douglas; Hattis, Phil; Ruppert, John; Gavert, Don
2011-01-01
Completion of the final Space Shuttle flight marks the end of a significant era in Human Spaceflight. Developed in the 1970 s, first launched in 1981, the Space Shuttle embodies many significant engineering achievements. One of these is the development and operation of the first extensive fly-by-wire human space transportation Guidance, Navigation and Control (GN&C) System. Development of the Space Shuttle GN&C represented first time inclusions of modern techniques for electronics, software, algorithms, systems and management in a complex system. Numerous technical design trades and lessons learned continue to drive current vehicle development. For example, the Space Shuttle GN&C system incorporated redundant systems, complex algorithms and flight software rigorously verified through integrated vehicle simulations and avionics integration testing techniques. Over the past thirty years, the Shuttle GN&C continued to go through a series of upgrades to improve safety, performance and to enable the complex flight operations required for assembly of the international space station. Upgrades to the GN&C ranged from the addition of nose wheel steering to modifications that extend capabilities to control of the large flexible configurations while being docked to the Space Station. This paper provides a history of the development and evolution of the Space Shuttle GN&C system. Emphasis is placed on key architecture decisions, design trades and the lessons learned for future complex space transportation system developments. Finally, some of the interesting flight operations experience is provided to inform future developers of flight experiences.
-
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles, methods of using, and methods of making
Habuchi, Satoshi; Piwonski, Hubert Marek; Michinobu, Tsuyoshi
2017-01-01
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide for conjugated polymer nanoparticle, method of making conjugated polymer nanoparticles, method of using conjugated polymer nanoparticle, polymers, and the like.
-
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles, methods of using, and methods of making
Habuchi, Satoshi
2017-03-16
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide for conjugated polymer nanoparticle, method of making conjugated polymer nanoparticles, method of using conjugated polymer nanoparticle, polymers, and the like.
-
A Dynamic Risk Model for Evaluation of Space Shuttle Abort Scenarios
Henderson, Edward M.; Maggio, Gaspare; Elrada, Hassan A.; Yazdpour, Sabrina J.
2003-01-01
The Space Shuttle is an advanced manned launch system with a respectable history of service and a demonstrated level of safety. Recent studies have shown that the Space Shuttle has a relatively low probability of having a failure that is instantaneously catastrophic during nominal flight as compared with many US and international launch systems. However, since the Space Shuttle is a manned. system, a number of mission abort contingencies exist to primarily ensure the safety of the crew during off-nominal situations and to attempt to maintain the integrity of the Orbiter. As the Space Shuttle ascends to orbit it transverses various intact abort regions evaluated and planned before the flight to ensure that the Space Shuttle Orbiter, along with its crew, may be returned intact either to the original launch site, a transoceanic landing site, or returned from a substandard orbit. An intact abort may be initiated due to a number of system failures but the highest likelihood and most challenging abort scenarios are initiated by a premature shutdown of a Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME). The potential consequences of such a shutdown vary as a function of a number of mission parameters but all of them may be related to mission time for a specific mission profile. This paper focuses on the Dynamic Abort Risk Evaluation (DARE) model process, applications, and its capability to evaluate the risk of Loss Of Vehicle (LOV) due to the complex systems interactions that occur during Space Shuttle intact abort scenarios. In addition, the paper will examine which of the Space Shuttle subsystems are critical to ensuring a successful return of the Space Shuttle Orbiter and crew from such a situation.
-
Nonlinear conjugate gradient methods in micromagnetics
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Fischbacher
2017-04-01
Full Text Available Conjugate gradient methods for energy minimization in micromagnetics are compared. The comparison of analytic results with numerical simulation shows that standard conjugate gradient method may fail to produce correct results. A method that restricts the step length in the line search is introduced, in order to avoid this problem. When the step length in the line search is controlled, conjugate gradient techniques are a fast and reliable way to compute the hysteresis properties of permanent magnets. The method is applied to investigate demagnetizing effects in NdFe12 based permanent magnets. The reduction of the coercive field by demagnetizing effects is μ0ΔH = 1.4 T at 450 K.
-
Usta, M.; Wortelboer, H.M.; Vervoort, J.J.M.; Boersma, M.G.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Bladeren, van P.J.; Cnubben, N.H.P.
2007-01-01
Curcumin, an alpha,beta-unsaturated carbonyl compound, reacts with glutathione, leading to the formation of two monoglutathionyl curcumin conjugates. In the present study, the structures of both glutathione conjugates of curcumin were identified by LC-MS and one- and two-dimensional H-1 NMR
-
A Cluster of Paediatric Invasive Group A Streptococcal and Chicken Pox Infections
LENUS (Irish Health Repository)
Ó Maoldomhnaigh, C
2018-03-01
Group A streptococcus (GAS) causes a variety of acute clinical syndromes from pharyngitis and scarlet fever commonly seen in primary care to more severe life-threatening invasive disease. Invasive GAS, categorised into three groups - necrotising fasciitis, streptococcal toxic shock syndrome and sepsis with or without an identifiable source of infection- is a notifiable disease to the Health Protection Surveillance Centre (HPSC)1. Laboratory criteria for a confirmed case require isolation of GAS from a normally sterile site. The HPSC previously reported a marked increase in the incidence of invasive GAS infections from 1.65\\/100,000 population in 2011 to 3.65\\/100,000 in 20132. The increased incidence was notable also for a 300% increase in the proportion of invasive GAS cases in children. After a slight decrease in incidence in 20153 (2.3\\/100000), we noted a cluster of invasive GAS cases referred to the paediatric infectious disease (PID) department of Children’s University Hospital (CUH), Temple Street, in 2016. We sought to further characterise this cluster of paediatric invasive GAS infections.
-
Stability of the octameric structure affects plasminogen-binding capacity of streptococcal enolase.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Amanda J Cork
Full Text Available Group A Streptococcus (GAS is a human pathogen that has the potential to cause invasive disease by binding and activating human plasmin(ogen. Streptococcal surface enolase (SEN is an octameric α-enolase that is localized at the GAS cell surface. In addition to its glycolytic role inside the cell, SEN functions as a receptor for plasmin(ogen on the bacterial surface, but the understanding of the molecular basis of plasmin(ogen binding is limited. In this study, we determined the crystal and solution structures of GAS SEN and characterized the increased plasminogen binding by two SEN mutants. The plasminogen binding ability of SENK312A and SENK362A is ~2- and ~3.4-fold greater than for the wild-type protein. A combination of thermal stability assays, native mass spectrometry and X-ray crystallography approaches shows that increased plasminogen binding ability correlates with decreased stability of the octamer. We propose that decreased stability of the octameric structure facilitates the access of plasmin(ogen to its binding sites, leading to more efficient plasmin(ogen binding and activation.
-
Selective Covalent Conjugation of Phosphorothioate DNA Oligonucleotides with Streptavidin
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Christof M. Niemeyer
2011-08-01
Full Text Available Protein-DNA conjugates have found numerous applications in the field of diagnostics and nanobiotechnology, however, their intrinsic susceptibility to DNA degradation by nucleases represents a major obstacle for many applications. We here report the selective covalent conjugation of the protein streptavidin (STV with phosphorothioate oligonucleotides (psDNA containing a terminal alkylthiolgroup as the chemically addressable linking unit, using a heterobifunctional NHS-/maleimide crosslinker. The psDNA-STV conjugates were synthesized in about 10% isolated yields. We demonstrate that the terminal alkylthiol group selectively reacts with the maleimide while the backbone sulfur atoms are not engaged in chemical conjugation. The novel psDNA-STV conjugates retain their binding capabilities for both biotinylated macromolecules and the complementary nucleic acid. Moreover, the psDNA-STV conjugate retained its binding capacity for complementary oligomers even after a nuclease digestion step, which effectively degrades deoxyribonucleotide oligomers and thus the binding capability of regular DNA-STV conjugates. The psDNA-STV therefore hold particular promise for applications e.g. in proteome research and novel biosensing devices, where interfering endogenous nucleic acids need to be removed from analytes by nuclease digestion.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, K.T.; Spanggaard, H.; Krebs, Frederik C
2004-01-01
. Electroluminescent devices of the homopolymer itself and of the zinc-porphyrin containing polymer were prepared and the nature of the electroluminescence was characterized. The homopolymer segments were found to optically pump the emission of the zinc-porphyrin dye moities. The homopolymer exhibits blue......Zinc-porphyrin dye molecules were incorporated into the backbone of a conjugated polymer material by a method, which allowed for the incorporation of only one zinc-porphyrin dye molecule into the backbone of each conjugated polymer molecule. The electronic properties of the homopolymer were...
-
Lipid-peptide-polymer conjugates and nanoparticles thereof
Xu, Ting; Dong, He; Shu, Jessica
2015-06-02
The present invention provides a conjugate having a peptide with from about 10 to about 100 amino acids, wherein the peptide adopts a helical structure. The conjugate also includes a first polymer covalently linked to the peptide, and a hydrophobic moiety covalently linked to the N-terminus of the peptide, wherein the hydrophobic moiety comprises a second polymer or a lipid moiety. The present invention also provides helix bundles form by self-assembling the conjugates, and particles formed by self-assembling the helix bundles. Methods of preparing the helix bundles and particles are also provided.
-
Novel β-cyclodextrin-eosin conjugates.
Benkovics, Gábor; Afonso, Damien; Darcsi, András; Béni, Szabolcs; Conoci, Sabrina; Fenyvesi, Éva; Szente, Lajos; Malanga, Milo; Sortino, Salvatore
2017-01-01
Eosin B (EoB) and eosin Y (EoY), two xanthene dye derivatives with photosensitizing ability were prepared in high purity through an improved synthetic route. The dyes were grafted to a 6-monoamino-β-cyclodextrin scaffold under mild reaction conditions through a stable amide linkage using the coupling agent 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium chloride. The molecular conjugates, well soluble in aqueous medium, were extensively characterized by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Preliminary spectroscopic investigations showed that the β-cyclodextrin-EoY conjugate retains both the fluorescence properties and the capability to photogenerate singlet oxygen of the unbound chromophore. In contrast, the corresponding β-cyclodextrin-EoB conjugate did not show either relevant emission or photosensitizing activity probably due to aggregation in aqueous medium, which precludes any response to light excitation.
-
Novel β-cyclodextrin–eosin conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gábor Benkovics
2017-03-01
Full Text Available Eosin B (EoB and eosin Y (EoY, two xanthene dye derivatives with photosensitizing ability were prepared in high purity through an improved synthetic route. The dyes were grafted to a 6-monoamino-β-cyclodextrin scaffold under mild reaction conditions through a stable amide linkage using the coupling agent 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl-4-methylmorpholinium chloride. The molecular conjugates, well soluble in aqueous medium, were extensively characterized by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Preliminary spectroscopic investigations showed that the β-cyclodextrin–EoY conjugate retains both the fluorescence properties and the capability to photogenerate singlet oxygen of the unbound chromophore. In contrast, the corresponding β-cyclodextrin–EoB conjugate did not show either relevant emission or photosensitizing activity probably due to aggregation in aqueous medium, which precludes any response to light excitation.
-
The prevention of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal disease.
Money, Deborah; Allen, Victoria M
2013-10-01
To review the evidence in the literature and to provide recommendations on the management of pregnant women in labour for the prevention of early-onset neonatal group B streptococcal disease. The key revisions in this updated guideline include changed recommendations for regimens for antibiotic prophylaxis, susceptibility testing, and management of women with pre-labour rupture of membranes. Maternal outcomes evaluated included exposure to antibiotics in pregnancy and labour and complications related to antibiotic use. Neonatal outcomes of rates of early-onset group B streptococcal infections are evaluated. Published literature was retrieved through searches of MEDLINE, CINAHL, and The Cochrane Library from January 1980 to July 2012 using appropriate controlled vocabulary and key words (group B streptococcus, antibiotic therapy, infection, prevention). Results were restricted to systematic reviews, randomized control trials/controlled clinical trials, and observational studies. There were no date or language restrictions. Searches were updated on a regular basis and incorporated in the guideline to May 2013. Grey (unpublished) literature was identified through searching the websites of health technology assessment and health technology-related agencies, clinical practice guideline collections, clinical trial registries, and national and international medical specialty societies. The quality of evidence in this document was rated using the criteria described in the Report of the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care (Table 1). The recommendations in this guideline are designed to help clinicians identify and manage pregnancies at risk for neonatal group B streptococcal disease to optimize maternal and perinatal outcomes. No cost-benefit analysis is provided. There is good evidence based on randomized control trial data that in women with pre-labour rupture of membranes at term who are colonized with group B streptococcus, rates of neonatal infection are
-
Photodynamic tissue adhesion with chlorin(e6) protein conjugates.
Khadem, J; Veloso, A A; Tolentino, F; Hasan, T; Hamblin, M R
1999-12-01
To test the hypothesis that a photodynamic laser-activated tissue solder would perform better in sealing scleral incisions when the photosensitizer was covalently linked to the protein than when it was noncovalently mixed. Conjugates and mixtures were prepared between the photosensitizer chlorin(e6) and various proteins (albumin, fibrinogen, and gelatin) in different ratios and used to weld penetrating scleral incisions made in human cadaveric eyes. A blue-green (488-514 nm) argon laser activated the adhesive, and the strength of the closure was measured by increasing the intraocular pressure until the wound showed leakage. Both covalent conjugates and noncovalent mixtures showed a light dose-dependent increase in leaking pressure. A preparation of albumin chlorin(e6) conjugate with additional albumin added (2.5 protein to chlorin(e6) molar ratio) showed significantly higher weld strength than other protein conjugates and mixtures. This is the first report of dye-protein conjugates as tissue solders. These conjugates may have applications in ophthalmology.
-
Structure of a streptococcal adhesion carbohydrate receptor
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cassels, F.J.; Fales, H.M.; London, J.; Carlson, R.W.; van Halbeek, H.
1990-01-01
Interactions between complementary protein and carbohydrate structures on different genera of human oral bacteria have been implicated in the formation of dental plaque. The carbohydrate receptor on Streptococcus sanguis H1 that is specific for the adhesion on Capnocytophaga ochracea ATCC 33596 has been isolated from the streptococcal cell wall, purified, and structurally characterized. The hexasaccharide repeating unit of the polysaccharide was purified by reverse-phase, amino-bonded silica, and gel permeation high performance liquid chromatography. Earlier studies established that the repeating unit was a hexasaccharide composed of rhamnose, galactose, and glucose in the ration of 2:3:1, respectively. In the present study, determination of absolute configuration by gas chromatography of the trimethylsilyl (+)-2-butyl glycosides revealed that the rhamnose residues were of the L configuration while the hexoses were all D. 252Californium plasma desorption mass spectrometry of the native, the acetylated and the reduced and acetylated hexasaccharide determined that the molecular mass of the native hexasaccharide was 959, and that the 2 rhamnose residues were linked to each other at the nonreducing terminus of the linear molecule. Methylation analysis revealed the positions of the glycosidic linkages in the hexasaccharide and showed that a galactose residue was present at the reducing end. The structural characterization of the hexasaccharide was completed by one and two dimensional 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Complete 1H and 13C assignments for each glycosyl residue were established by two-dimensional (1H,1H) correlation spectroscopy, homonuclear Hartmann-Hahn, and (13C,1H) correlation experiments. The configurations of the glycosidic linkages were inferred from the chemical shifts and coupling constants of the anomeric 1H and 13C resonances
-
Space shuttle program: Shuttle Avionics Integration Laboratory. Volume 7: Logistics management plan
1974-01-01
The logistics management plan for the shuttle avionics integration laboratory defines the organization, disciplines, and methodology for managing and controlling logistics support. Those elements requiring management include maintainability and reliability, maintenance planning, support and test equipment, supply support, transportation and handling, technical data, facilities, personnel and training, funding, and management data.
-
Usta, M.; Wortelboer, H.M.; Vervoort, J.; Boersma, M.G.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Bladeren, P.J. van; Cnubben, N.H.P.
2007-01-01
Curcumin, an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound, reacts with glutathione, leading to the formation of two monoglutathionyl curcumin conjugates. In the present study, the structures of both glutathione conjugates of curcumin were identified by LC-MS and one- and two-dimensional 1H NMR analysis, and
-
DENDRIMER CONJUGATES FOR SELECTIVE OF PROTEIN AGGREGATES
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
2004-01-01
Dendrimer conjugates are presented, which are formed between a dendrimer and a protein solubilising substance. Such dendrimer conjugates are effective in the treatment of protein aggregate-related diseases (e.g. prion-related diseases). The protein solubilising substance and the dendrimer together...
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lammerts van Bueren,A.; Higgins, M.; Wang, D.; Burke, R.; Boraston, A.
2007-01-01
The ability of pathogenic bacteria to recognize host glycans is often essential to their virulence. Here we report structure-function studies of previously uncharacterized glycogen-binding modules in the surface-anchored pullulanases from Streptococcus pneumoniae (SpuA) and Streptococcus pyogenes (PulA). Multivalent binding to glycogen leads to a strong interaction with alveolar type II cells in mouse lung tissue. X-ray crystal structures of the binding modules reveal a novel fusion of tandem modules into single, bivalent functional domains. In addition to indicating a structural basis for multivalent attachment, the structure of the SpuA modules in complex with carbohydrate provides insight into the molecular basis for glycogen specificity. This report provides the first evidence that intracellular lung glycogen may be a novel target of pathogenic streptococci and thus provides a rationale for the identification of the streptococcal {alpha}-glucan-metabolizing machinery as virulence factors.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jacob Thomas
Full Text Available Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs are agents of horizontal gene transfer and have major roles in evolution and acquisition of new traits, including antibiotic resistances. ICEs are found integrated in a host chromosome and can excise and transfer to recipient bacteria via conjugation. Conjugation involves nicking of the ICE origin of transfer (oriT by the ICE-encoded relaxase and transfer of the nicked single strand of ICE DNA. For ICEBs1 of Bacillus subtilis, nicking of oriT by the ICEBs1 relaxase NicK also initiates rolling circle replication. This autonomous replication of ICEBs1 is critical for stability of the excised element in growing cells. We found a conserved and previously uncharacterized ICE gene that is required for conjugation and replication of ICEBs1. Our results indicate that this gene, helP (formerly ydcP, encodes a helicase processivity factor that enables the host-encoded helicase PcrA to unwind the double-stranded ICEBs1 DNA. HelP was required for both conjugation and replication of ICEBs1, and HelP and NicK were the only ICEBs1 proteins needed for replication from ICEBs1 oriT. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we measured association of HelP, NicK, PcrA, and the host-encoded single-strand DNA binding protein Ssb with ICEBs1. We found that NicK was required for association of HelP and PcrA with ICEBs1 DNA. HelP was required for association of PcrA and Ssb with ICEBs1 regions distal, but not proximal, to oriT, indicating that PcrA needs HelP to progress beyond nicked oriT and unwind ICEBs1. In vitro, HelP directly stimulated the helicase activity of the PcrA homologue UvrD. Our findings demonstrate that HelP is a helicase processivity factor needed for efficient unwinding of ICEBs1 for conjugation and replication. Homologues of HelP and PcrA-type helicases are encoded on many known and putative ICEs. We propose that these factors are essential for ICE conjugation, replication, and genetic stability.
-
... version Home Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerve Disorders Cranial Nerve Disorders Conjugate Gaze Palsies Horizontal gaze palsy Vertical ... Version. DOCTORS: Click here for the Professional Version Cranial Nerve Disorders Overview of the Cranial Nerves Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia ...
-
Proceedings of the Space Shuttle Environmental Assessment Workshop on Stratospheric Effects
Potter, A. E. (Compiler)
1977-01-01
Various aspects of the potential environmental impact of space shuttle exhaust are explored. Topics include: (1) increased ultraviolet radiation levels in the biosphere due to destruction of atmospheric ozone; (2) climatic changes due to aerosol particles affecting the planetary albedo; (3) space shuttle propellants (including alternate formulations); and (4) measurement of space shuttle exhaust products.
-
Synchronizing a single-electron shuttle to an external drive
Moeckel, Michael J.; Southworth, Darren R.; Weig, Eva M.; Marquardt, Florian
2014-04-01
The nanomechanical single-electron shuttle is a resonant system in which a suspended metallic island oscillates between and impacts at two electrodes. This setup holds promise for one-by-one electron transport and the establishment of an absolute current standard. While the charge transported per oscillation by the nanoscale island will be quantized in the Coulomb blockade regime, the frequency of such a shuttle depends sensitively on many parameters, leading to drift and noise. Instead of considering the nonlinearities introduced by the impact events as a nuisance, here we propose to exploit the resulting nonlinear dynamics to realize a highly precise oscillation frequency via synchronization of the shuttle self-oscillations to an external signal. We link the established phenomenological description of synchronization based on the Adler equation to the microscopic nonlinear dynamics of the electron shuttle by calculating the effective Adler constant analytically in terms of the microscopic parameters.
-
Synchronizing a single-electron shuttle to an external drive
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Moeckel, Michael J; Southworth, Darren R; Weig, Eva M; Marquardt, Florian
2014-01-01
The nanomechanical single-electron shuttle is a resonant system in which a suspended metallic island oscillates between and impacts at two electrodes. This setup holds promise for one-by-one electron transport and the establishment of an absolute current standard. While the charge transported per oscillation by the nanoscale island will be quantized in the Coulomb blockade regime, the frequency of such a shuttle depends sensitively on many parameters, leading to drift and noise. Instead of considering the nonlinearities introduced by the impact events as a nuisance, here we propose to exploit the resulting nonlinear dynamics to realize a highly precise oscillation frequency via synchronization of the shuttle self-oscillations to an external signal. We link the established phenomenological description of synchronization based on the Adler equation to the microscopic nonlinear dynamics of the electron shuttle by calculating the effective Adler constant analytically in terms of the microscopic parameters
-
Steinberg, Florence S.
This 32-page pamphlet contains color photographs and detailed diagrams which illustrate general descriptive comments about living conditions aboard the space shuttle. Described are details of the launch, the cabin, the condition of weightlessness, food, sleep, exercise, atmosphere, personal hygiene, medicine, going EVA (extra-vehicular activity),…
-
Mobile Christian - shuttle flight
2009-01-01
Erin Whittle, 14, (seated) and Brianna Johnson, 14, look on as Louis Stork, 13, attempts a simulated landing of a space shuttle at StenniSphere. The young people were part of a group from Mobile Christian School in Mobile, Ala., that visited StenniSphere on April 21.
-
Synthesis of Mikto-Arm Star Peptide Conjugates.
Koo, Jin Mo; Su, Hao; Lin, Yi-An; Cui, Honggang
2018-01-01
Mikto-arm star peptide conjugates are an emerging class of self-assembling peptide-based structural units that contain three or more auxiliary segments of different chemical compositions and/or functionalities. This group of molecules exhibit interesting self-assembly behavior in solution due to their chemically asymmetric topology. Here we describe the detailed procedure for synthesis of an ABC Mikto-arm star peptide conjugate in which two immiscible entities (a saturated hydrocarbon and a hydrophobic and lipophobic fluorocarbon) are conjugated onto a short β-sheet forming peptide sequence, GNNQQNY, derived from the Sup35 prion, through a lysine junction. Automated and manual Fmoc-solid phase synthesis techniques are used to synthesize the Mikto-arm star peptide conjugates, followed by HPLC purification. We envision that this set of protocols can afford a versatile platform to synthesize a new class of peptidic building units for diverse applications.
-
Fullerene-biomolecule conjugates and their biomedicinal applications.
Yang, Xinlin; Ebrahimi, Ali; Li, Jie; Cui, Quanjun
2014-01-01
Fullerenes are among the strongest antioxidants and are characterized as "radical sponges." The research on biomedicinal applications of fullerenes has achieved significant progress since the landmark publication by Friedman et al in 1993. Fullerene-biomolecule conjugates have become an important area of research during the past 2 decades. By a thorough literature search, we attempt to update the information about the synthesis of different types of fullerene-biomolecule conjugates, including fullerene-containing amino acids and peptides, oligonucleotides, sugars, and esters. Moreover, we also discuss in this review recently reported data on the biological and pharmaceutical utilities of these compounds and some other fullerene derivatives of biomedical importance. While within the fullerene-biomolecule conjugates, in which fullerene may act as both an antioxidant and a carrier, specific targeting biomolecules conjugated to fullerene will undoubtedly strengthen the delivery of functional fullerenes to sites of clinical interest.
-
Gold Nanoparticle Conjugation Enhances the Antiacanthamoebic Effects of Chlorhexidine
Aqeel, Yousuf; Siddiqui, Ruqaiyyah; Anwar, Ayaz; Shah, Muhammad Raza
2015-01-01
Acanthamoeba keratitis is a serious infection with blinding consequences and often associated with contact lens wear. Early diagnosis, followed by aggressive topical application of drugs, is a prerequisite in successful treatment, but even then prognosis remains poor. Several drugs have shown promise, including chlorhexidine gluconate; however, host cell toxicity at physiologically relevant concentrations remains a challenge. Nanoparticles, subcolloidal structures ranging in size from 10 to 100 nm, are effective drug carriers for enhancing drug potency. The overall aim of the present study was to determine whether conjugation with gold nanoparticles enhances the antiacanthamoebic potential of chlorhexidine. Gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles were synthesized. Briefly, gold solution was mixed with chlorhexidine and reduced by adding sodium borohydride, resulting in an intense deep red color, indicative of colloidal gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles. The synthesis was confirmed using UV-visible spectrophotometry that shows a plasmon resonance peak of 500 to 550 nm, indicative of gold nanoparticles. Further characterization using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-mass spectrometry showed a gold-conjugated chlorhexidine complex at m/z 699 ranging in size from 20 to 100 nm, as determined using atomic force microscopy. To determine the amoebicidal and amoebistatic effects, amoebae were incubated with gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles. For controls, amoebae also were incubated with gold and silver nanoparticles alone, chlorhexidine alone, neomycin-conjugated nanoparticles, and neomycin alone. The findings showed that gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles exhibited significant amoebicidal and amoebistatic effects at 5 μM. Amoebicidal effects were observed by parasite viability testing using a Trypan blue exclusion assay and flow-cytometric analysis using propidium iodide, while amoebistatic effects were observed using growth
-
Analytical characterization of polymer-drug conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rizzo, V.; Gigli, M.; Pinciroli, V.
1998-01-01
A few polymeric conjugates of antitumor drugs have been recently developed in view of possible therapeutic advantages: solubilization of sparingly soluble drugs in water, improvement of therapeutic index, organ targeting through a second chemical species bound to the same polymeric chain. In this article it's described the analytical approach used in the characterization of the conjugates for chemical identity, purity and strength of the contained active ingredient. The techniques are: high field NMR and size exclusion chromatography with non-aqueous mobile phase for identity; selective hydrolysis and HPLC for strength and purity. A complete and reliable picture is thus obtained both for qualitative and for quantitative aspects. This is an important step forward in the direction of further development and marketing of polymer-drug conjugates [it
-
Conjugate gradient algorithms using multiple recursions
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Barth, T.; Manteuffel, T.
1996-12-31
Much is already known about when a conjugate gradient method can be implemented with short recursions for the direction vectors. The work done in 1984 by Faber and Manteuffel gave necessary and sufficient conditions on the iteration matrix A, in order for a conjugate gradient method to be implemented with a single recursion of a certain form. However, this form does not take into account all possible recursions. This became evident when Jagels and Reichel used an algorithm of Gragg for unitary matrices to demonstrate that the class of matrices for which a practical conjugate gradient algorithm exists can be extended to include unitary and shifted unitary matrices. The implementation uses short double recursions for the direction vectors. This motivates the study of multiple recursion algorithms.
-
Directional control-response compatibility of joystick steered shuttle cars.
Burgess-Limerick, Robin; Zupanc, Christine M; Wallis, Guy
2012-01-01
Shuttle cars are an unusual class of vehicle operated in underground coal mines, sometimes in close proximity to pedestrians and steering errors may have very serious consequences. A directional control-response incompatibility has previously been described in shuttle cars which are controlled using a steering wheel oriented perpendicular to the direction of travel. Some other shuttle car operators are seated perpendicular to the direction of travel and steer the car via a seat mounted joystick. A virtual simulation was utilised to determine whether the steering arrangement in these vehicles maintains directional control-response compatibility. Twenty-four participants were randomly assigned to either a condition corresponding to this design (consistent direction), or a condition in which the directional steering response was reversed while driving in-bye (visual field compatible). Significantly less accurate steering performance was exhibited by the consistent direction group during the in-bye trials only. Shuttle cars which provide the joystick steering mechanism described here require operators to accommodate alternating compatible and incompatible directional control-response relationships with each change of car direction. A virtual simulation of an underground coal shuttle car demonstrates that the design incorporates a directional control-response incompatibility when driving the vehicle in one direction. This design increases the probability of operator error, with potential adverse safety and productivity consequences.
-
Four-wave mixing and phase conjugation in plasmas
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Federici, J.F.
1989-01-01
Nonlinear optical effects such as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering, Stimulated Raman Scattering, self-focusing, wave-mixing, parametric mixing, etc., have a long history in plasma physics. Recently, four-wave mixing in plasmas and its applications to phase conjugation has been extensively studied. Although four-wave mixing (FWM), using various nonlinear mediums, has many practical applications in the visible regime, no successful attempt has been made to study or demonstrate FWM for wavelengths longer than 10μm. Plasmas as phase conjugate mirrors have received considerable attention since they become more efficient at longer wavelengths (far-infrared to microwave). The purpose of this thesis is to study various fundamental issues which concern the suitability of plasmas for four-wave mixing and phase conjugation. The major contributions of this thesis are the identification and study of thermal and ionization nonlinearities as potential four-wave mixing and phase conjugation mechanisms and the study of the affect of density inhomogeneities on the FWM process. Using a fluid description for the plasma, this thesis demonstrates that collisional heating generates a thermal force which substantially enhances the phase conjugate reflectivity. The prospect of using a novel ionization nonlinearity in weakly ionized plasmas for wave-mixing and phase conjugation is discussed. The ionization nonlinearity arises from localized heating of the plasma by the beat-wave. Wherever, the local temperature is increased, a plasma density grating is produced due to increased electron-impact ionization. Numerical estimates of the phase conjugate reflectivity indicate reflectivities in the range of 10 -4 -10 -3 are possible in a weakly ionized steady-state gas discharge plasma
-
Hu, Shun; Yu, Weili; Hu, Chunyang; Wei, Dong; Shen, Lijuan; Hu, Tao; Yi, Youjin
2017-11-01
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is a serious fatal pathogen that causes tuberculosis (TB). Effective vaccination is urgently needed to deal with the serious threat from TB. Mtb-secreted protein antigens are important virulence determinants of Mtb with poor immunogenicity. Adjuvants and antigen delivery systems are thus highly desired to improve the immunogenicity of protein antigens. Inulin is a biocompatible polysaccharide (PS) adjuvant that can stimulate a strong cellular and humoral immunity. Bacterial capsular PS and haptens have been conjugated with cross-reacting material 197 (CRM 197 ) to improve their immunogenicity. CFP10 and TB10.4 were two Mtb-secreted immunodominant protein antigens. A CFP10-TB10.4 fusion protein (CT) was used as the antigen for covalent conjugation with the CRM 197 -inulin conjugate (CRM-inu). The resultant conjugate (CT-CRM-inu) elicited high CT-specific IgG titers, stimulated splenocyte proliferation and provoked the secretion of Th1-type and Th2-type cytokines. Conjugation with CRM-inu significantly prolonged the systemic circulation of CT and exposure to the immune system. Moreover, CT-CRM-inu showed no apparent toxicity to cardiac, hepatic and renal functions. Thus, conjugation of CT with CRM-inu provided an effective strategy for development of protein-based vaccines against Mtb infection. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Seidlitz, Jakob; Kovacevic, Miro; Latimer, M. Elizabeth; Hommer, Rebecca; Lougee, Lorraine; Grant, Paul
2015-01-01
Abstract Background: The first cases of pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections (PANDAS) were described>15 years ago. Since that time, the literature has been divided between studies that successfully demonstrate an etiologic relationship between Group A streptococcal (GAS) infections and childhood-onset obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and those that fail to find an association. One possible explanation for the conflicting reports is that the diagnostic criteria proposed for PANDAS are not specific enough to describe a unique and homogeneous cohort of patients. To evaluate the validity of the PANDAS criteria, we compared clinical characteristics of PANDAS patients identified in two community practices with a sample of children meeting full research criteria for PANDAS. Methods: A systematic review of clinical records was used to identify the presence or absence of selected symptoms in children evaluated for PANDAS by physicians in Hinsdale, Illinois (n=52) and Bethesda, Maryland (n=40). Results were compared against data from participants in National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) research investigations of PANDAS (n=48). Results: As described in the original PANDAS cohort, males outnumbered females (95:45) by ∼ 2:1, and symptoms began in early childhood (7.3±2.7 years). Clinical presentations were remarkably similar across sites, with all children reporting acute onset of OCD symptoms and multiple comorbidities, including separation anxiety (86–92%), school issues (75–81%), sleep disruptions (71%), tics (60–65%), urinary symptoms (42–81%), and others. Twenty of the community cases (22%) failed to meet PANDAS criteria because of an absence of documentation of GAS infections. Conclusions: The diagnostic criteria for PANDAS can be used by clinicians to accurately identify patients with common clinical features and shared etiology of symptoms. Although difficulties in documenting an association
-
Swedo, Susan E; Seidlitz, Jakob; Kovacevic, Miro; Latimer, M Elizabeth; Hommer, Rebecca; Lougee, Lorraine; Grant, Paul
2015-02-01
The first cases of pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections (PANDAS) were described >15 years ago. Since that time, the literature has been divided between studies that successfully demonstrate an etiologic relationship between Group A streptococcal (GAS) infections and childhood-onset obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and those that fail to find an association. One possible explanation for the conflicting reports is that the diagnostic criteria proposed for PANDAS are not specific enough to describe a unique and homogeneous cohort of patients. To evaluate the validity of the PANDAS criteria, we compared clinical characteristics of PANDAS patients identified in two community practices with a sample of children meeting full research criteria for PANDAS. A systematic review of clinical records was used to identify the presence or absence of selected symptoms in children evaluated for PANDAS by physicians in Hinsdale, Illinois (n=52) and Bethesda, Maryland (n=40). RESULTS were compared against data from participants in National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) research investigations of PANDAS (n=48). As described in the original PANDAS cohort, males outnumbered females (95:45) by ∼ 2:1, and symptoms began in early childhood (7.3±2.7 years). Clinical presentations were remarkably similar across sites, with all children reporting acute onset of OCD symptoms and multiple comorbidities, including separation anxiety (86-92%), school issues (75-81%), sleep disruptions (71%), tics (60-65%), urinary symptoms (42-81%), and others. Twenty of the community cases (22%) failed to meet PANDAS criteria because of an absence of documentation of GAS infections. The diagnostic criteria for PANDAS can be used by clinicians to accurately identify patients with common clinical features and shared etiology of symptoms. Although difficulties in documenting an association between GAS infection and symptom onset/exacerbations may
-
Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour STS-47 Launch
1992-01-01
A smooth countdown culminated in a picture-perfect launch as the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour (STS-47) climbed skyward atop a ladder of billowing smoke on September 12, 1992. The primary payload for the plarned seven-day flight was the Spacelab-J science laboratory. The second flight of Endeavour marks a number of historic firsts: the first space flight of an African-American woman, the first Japanese citizen to fly on a Space Shuttle, and the first married couple to fly in space.
-
O:2-CRM(197) conjugates against Salmonella Paratyphi A.
Micoli, Francesca; Rondini, Simona; Gavini, Massimiliano; Lanzilao, Luisa; Medaglini, Donata; Saul, Allan; Martin, Laura B
2012-01-01
Enteric fevers remain a common and serious disease, affecting mainly children and adolescents in developing countries. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi was believed to cause most enteric fever episodes, but several recent reports have shown an increasing incidence of S. Paratyphi A, encouraging the development of a bivalent vaccine to protect against both serovars, especially considering that at present there is no vaccine against S. Paratyphi A. The O-specific polysaccharide (O:2) of S. Paratyphi A is a protective antigen and clinical data have previously demonstrated the potential of using O:2 conjugate vaccines. Here we describe a new conjugation chemistry to link O:2 and the carrier protein CRM(197), using the terminus 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO), thus leaving the O:2 chain unmodified. The new conjugates were tested in mice and compared with other O:2-antigen conjugates, synthesized adopting previously described methods that use CRM(197) as carrier protein. The newly developed conjugation chemistry yielded immunogenic conjugates with strong serum bactericidal activity against S. Paratyphi A.
-
O:2-CRM(197 conjugates against Salmonella Paratyphi A.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Francesca Micoli
Full Text Available Enteric fevers remain a common and serious disease, affecting mainly children and adolescents in developing countries. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi was believed to cause most enteric fever episodes, but several recent reports have shown an increasing incidence of S. Paratyphi A, encouraging the development of a bivalent vaccine to protect against both serovars, especially considering that at present there is no vaccine against S. Paratyphi A. The O-specific polysaccharide (O:2 of S. Paratyphi A is a protective antigen and clinical data have previously demonstrated the potential of using O:2 conjugate vaccines. Here we describe a new conjugation chemistry to link O:2 and the carrier protein CRM(197, using the terminus 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO, thus leaving the O:2 chain unmodified. The new conjugates were tested in mice and compared with other O:2-antigen conjugates, synthesized adopting previously described methods that use CRM(197 as carrier protein. The newly developed conjugation chemistry yielded immunogenic conjugates with strong serum bactericidal activity against S. Paratyphi A.
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Etrych, Tomáš; Tsukigawa, K.; Nakamura, H.; Chytil, Petr; Fang, J.; Ulbrich, Karel; Otagiri, M.; Maeda, H.
2017-01-01
Roč. 106, 30 August (2017), s. 10-19 ISSN 0928-0987 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GA15-02986S; GA MŠk(CZ) LQ1604; GA MŠk(CZ) ED1.1.00/02.0109 Grant - others:AV ČR,Japan Society for the Promotion of Science(CZ) JSPS-16-05 Program:Bilaterální spolupráce Institutional support: RVO:61389013 Keywords : pirarubicin * PHPMA conjugate * tandem-diblock PHPMA conjugate Subject RIV: FR - Pharmacology ; Medidal Chemistry OBOR OECD: Pharmacology and pharmacy Impact factor: 3.756, year: 2016
-
Integrated circuits based on conjugated polymer monolayer.
Li, Mengmeng; Mangalore, Deepthi Kamath; Zhao, Jingbo; Carpenter, Joshua H; Yan, Hongping; Ade, Harald; Yan, He; Müllen, Klaus; Blom, Paul W M; Pisula, Wojciech; de Leeuw, Dago M; Asadi, Kamal
2018-01-31
It is still a great challenge to fabricate conjugated polymer monolayer field-effect transistors (PoM-FETs) due to intricate crystallization and film formation of conjugated polymers. Here we demonstrate PoM-FETs based on a single monolayer of a conjugated polymer. The resulting PoM-FETs are highly reproducible and exhibit charge carrier mobilities reaching 3 cm 2 V -1 s -1 . The high performance is attributed to the strong interactions of the polymer chains present already in solution leading to pronounced edge-on packing and well-defined microstructure in the monolayer. The high reproducibility enables the integration of discrete unipolar PoM-FETs into inverters and ring oscillators. Real logic functionality has been demonstrated by constructing a 15-bit code generator in which hundreds of self-assembled PoM-FETs are addressed simultaneously. Our results provide the state-of-the-art example of integrated circuits based on a conjugated polymer monolayer, opening prospective pathways for bottom-up organic electronics.
-
METHOD OF CONJUGATED CIRCULAR ARCS TRACING
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
N. Ageyev Vladimir
2017-01-01
Full Text Available The geometric properties of conjugated circular arcs connecting two points on the plane with set directions of tan- gent vectors are studied in the work. It is shown that pairs of conjugated circular arcs with the same conditions in frontier points create one-parameter set of smooth curves tightly filling all the plane. One of the basic properties of this set is the fact that all coupling points of circular arcs are on the circular curve going through the initially given points. The circle radius depends on the direction of tangent vectors. Any point of the circle curve, named auxiliary in this work, determines a pair of conjugated arcs with given boundary conditions. One more condition of the auxiliary circle curve is that it divides the plane into two parts. The arcs going from the initial point are out of the circle limited by this circle curve and the arcs coming to the final point are inside it. These properties are the basis for the method of conjugated circular arcs tracing pro- posed in this article. The algorithm is rather simple and allows to fulfill all the needed plottings using only the divider and ruler. Two concrete examples are considered. The first one is related to the problem of tracing of a pair of conjugated arcs with the minimal curve jump when going through the coupling point. The second one demonstrates the possibility of trac- ing of the smooth curve going through any three points on the plane under condition that in the initial and final points the directions of tangent vectors are given. The proposed methods of conjugated circular arcs tracing can be applied in solving of a wide variety of problems connected with the tracing of cam contours, for example pattern curves in textile industry or in computer-aided-design systems when programming of looms with numeric control.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hansen, Paul Robert
2015-01-01
To produce antibodies against synthetic peptides it is necessary to couple them to a protein carrier. This chapter provides a nonspecialist overview of peptide-carrier conjugation. Furthermore, a protocol for coupling cysteine-containing peptides to bovine serum albumin is outlined....
-
'Secret' Shuttle payloads revealed
Powell, Joel W.
1993-05-01
A secret military payload carried by the orbiter Discovery launched on January 24 1985 is discussed. Secondary payloads on the military Shuttle flights are briefly reviewed. Most of the military middeck experiments were sponsored by the Space Test Program established at the Pentagon to oversee all Defense Department space research projects.
-
Class, Kinship Density, and Conjugal Role Segregation.
Hill, Malcolm D.
1988-01-01
Studied conjugal role segregation in 150 married women from intact families in working-class community. Found that, although involvement in dense kinship networks was associated with conjugal role segregation, respondents' attitudes toward marital roles and phase of family cycle when young children were present were more powerful predictors of…
-
Solar multi-conjugate adaptive optics performance improvement
Zhang, Zhicheng; Zhang, Xiaofang; Song, Jie
2015-08-01
In order to overcome the effect of the atmospheric anisoplanatism, Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics (MCAO), which was developed based on turbulence correction by means of several deformable mirrors (DMs) conjugated to different altitude and by which the limit of a small corrected FOV that is achievable with AO is overcome and a wider FOV is able to be corrected, has been widely used to widen the field-of-view (FOV) of a solar telescope. With the assistance of the multi-threaded Adaptive Optics Simulator (MAOS), we can make a 3D reconstruction of the distorted wavefront. The correction is applied by one or more DMs. This technique benefits from information about atmospheric turbulence at different layers, which can be used to reconstruct the wavefront extremely well. In MAOS, the sensors are either simulated as idealized wavefront gradient sensors, tip-tilt sensors based on the best Zernike fit, or a WFS using physical optics and incorporating user specified pixel characteristics and a matched filter pixel processing algorithm. Only considering the atmospheric anisoplanatism, we focus on how the performance of a solar MCAO system is related to the numbers of DMs and their conjugate heights. We theoretically quantify the performance of the tomographic solar MCAO system. The results indicate that the tomographic AO system can improve the average Strehl ratio of a solar telescope by only employing one or two DMs conjugated to the optimum altitude. And the S.R. has a significant increase when more deformable mirrors are used. Furthermore, we discuss the effects of DM conjugate altitude on the correction achievable by the MCAO system, and present the optimum DM conjugate altitudes.
-
Redox shuttles for overcharge protection of lithium batteries
Amine, Khalil; Chen, Zonghai; Wang, Qingzheng
2010-12-14
The present invention is generally related to electrolytes containing novel redox shuttles for overcharge protection of lithium-ion batteries. The redox shuttles are capable of thousands hours of overcharge tolerance and have a redox potential at about 3-5.5 V vs. Li and particularly about 4.4-4.8 V vs. Li. Accordingly, in one aspect the invention provides electrolytes comprising an alkali metal salt; a polar aprotic solvent; and a redox shuttle additive that is an aromatic compound having at least one aromatic ring with four or more electronegative substituents, two or more oxygen atoms bonded to the aromatic ring, and no hydrogen atoms bonded to the aromatic ring; and wherein the electrolyte solution is substantially non-aqueous. Further there are provided electrochemical devices employing the electrolyte and methods of making the electrolyte.
-
NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot (NSLD) - The application of ATE
Simpkins, Lorenz G.; Jenkins, Henry C.; Mauceri, A. Jack
1990-01-01
The concept of the NASA Shuttle Logistics Depot (NSLD) developed for the Space Shuttle Orbiter Program is described. The function of the NSLD at Cape Canaveral is to perform the acceptance and diagnostic testing of the Shuttle's space-rated line-replaceable units and shop-replaceable units (SRUs). The NSLD includes a comprehensive electronic automatic test station, program development stations, and assorted manufacturing support equipment (including thermal and vibration test equipment, special test equipment, and a card SRU test system). The depot activities also include the establishment of the functions for manufacturing of mechanical parts, soldering, welding, painting, clean room operation, procurement, and subcontract management.
-
Shuttle Planning for Link Closures in Urban Public Transport Networks
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
van der Hurk, Evelien; Koutsopoulos, Haris N.; Wilson, Nigel
2016-01-01
Urban public transport systems must periodically close certain links for maintenance, which can have significant effects on the service provided to passengers. In practice, the effects of closures are mitigated by replacing the closed links with a simple shuttle service. However, alternative...... cost, which includes transfers and frequency-dependent waiting time costs. This model is applied to a shuttle design problem based on a real-world case study of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority network of Boston, Massachusetts. The results show that additional shuttle routes can reduce...
-
Site-Selective Conjugation of Native Proteins with DNA
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Trads, Julie Brender; Tørring, Thomas; Gothelf, Kurt Vesterager
2017-01-01
Conjugation of DNA to proteins is increasingly used in academia and industry to provide proteins with tags for identification or handles for hybridization to other DNA strands. Assay technologies such as immuno-PCR and proximity ligation and the imaging technology DNA-PAINT require DNA-protein....... The introduction of a bioorthogonal handle at a specific position of a protein by recombinant techniques provides an excellent approach to site-specific conjugation, but for many laboratories and for applications where several proteins are to be labeled, the expression of recombinant proteins may be cumbersome...... conjugates. In DNA nanotechnology, the DNA handle is exploited to precisely position proteins by self-assembly. For these applications, site-selective conjugation is almost always desired because fully functional proteins are required to maintain the specificity of antibodies and the activity of enzymes...
-
Conjugated Polymers for Flexible Energy Harvesting and Storage.
Zhang, Zhitao; Liao, Meng; Lou, Huiqing; Hu, Yajie; Sun, Xuemei; Peng, Huisheng
2018-03-01
Since the discovery of conjugated polymers in the 1970s, they have attracted considerable interest in light of their advantages of having a tunable bandgap, high electroactivity, high flexibility, and good processability compared to inorganic conducting materials. The above combined advantages make them promising for effective energy harvesting and storage, which have been widely studied in recent decades. Herein, the key advancements in the use of conjugated polymers for flexible energy harvesting and storage are reviewed. The synthesis, structure, and properties of conjugated polymers are first summarized. Then, their applications in flexible polymer solar cells, thermoelectric generators, supercapacitors, and lithium-ion batteries are described. The remaining challenges are then discussed to highlight the future direction in the development of conjugated polymers. © 2018 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Lipke, Elisabeth; Michalik, Peter
2012-11-01
Sperm conjugation, where two or more sperm are physically united, is a rare but widespread pheno-menon across the animal kingdom. One group well known for its different types of sperm conjugation are spiders. Particularly, haplogyne spiders show a high diversity of sperm traits. Besides individual cleistospermia, primary (synspermia) and secondary (coenospermia, "spermatophore") sperm conjugation occurs. However, the evolution of sperm conjugates and sperm is not understood in this group. Here, we look at how sperm are transferred in Caponiidae (Haplogynae) in pursuit of additional information about the evolution of sperm transfer forms in spiders. Additionally, we investigated the male reproductive system and spermatozoa using light- and transmission electron-microscopy and provide a 3D reconstruction of individual as of well as conjugated spermatozoa. Mature spermatozoa are characterized by an extremely elongated, helical nucleus resulting in the longest spider sperm known to date. At the end of spermiogenesis, synspermia are formed by complete fusion of four spermatids. Thus, synspermia might have evolved early within ecribellate Haplogynae. The fused sperm cells are surrounded by a prominent vesicular area. The function of the vesicular area remains still unknown but might be correlated with the capacitation process inside the female. Further phylogenetic and functional implications of the spermatozoa and sperm conjugation are discussed. Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Design and biological activity of β-sheet breaker peptide conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rocha, Sandra; Cardoso, Isabel; Boerner, Hans; Pereira, Maria Carmo; Saraiva, Maria Joao; Coelho, Manuel
2009-01-01
The sequence LPFFD (iAβ 5 ) prevents amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) fibrillogenesis and neurotoxicity, hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD), as previously demonstrated. In this study iAβ 5 was covalently linked to poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and the activity of conjugates was assessed and compared to the activity of the peptide alone by in vitro studies. The conjugates were characterized by MALDI-TOF. Competition binding assays established that conjugates retained the ability to bind Aβ with similar strength as iAβ 5 . Transmission electron microscopy analysis showed that iAβ 5 conjugates inhibited amyloid fibril formation, which is in agreement with binding properties observed for the conjugates towards Aβ. The conjugates were also able to prevent amyloid-induced cell death, as evaluated by activation of caspase 3. These results demonstrated that the biological activity of iAβ 5 is not affected by the pegylation process.
-
Muscular soreness following prolonged intermittent high-intensity shuttle running.
Thompson, D; Nicholas, C W; Williams, C
1999-05-01
The aim of this study was to examine the impact of prolonged intermittent high-intensity shuttle running on soreness and markers of muscle damage. Sixteen males took part in the study, half of whom were assigned to a running group and half to a resting control group. The exercise protocol involved 90 min of intermittent shuttle running and walking (Loughborough Intermittent Shuttle Test: LIST), reflecting the activity pattern found in multiple-sprint sports such as soccer. Immediately after exercise, there was a significant increase (P < 0.05) in serum activities of creatine kinase and aspartate aminotransferase, and values remained above baseline for 48 h (P < 0.05). Median peak activities of creatine kinase and aspartate aminotransferase occurred 24 h post-exercise and were 774 and 43 U x l(-1), respectively. The intensity of general muscle soreness, and in the specific muscles investigated, was greater than baseline for 72 h after the shuttle test (P < 0.05), peaking 24-48 h post-exercise (P < 0.05). Muscle soreness was not correlated with either creatine kinase or aspartate aminotransferase activity. Soreness was most frequently reported in the hamstrings. Neither soreness nor serum enzyme activity changed in the controls over the 4 day observation period. It appears that unaccustomed performance of prolonged intermittent shuttle running produces a significant increase in both soreness and markers of muscle damage.
-
Schmelcher, Mathias; Powell, Anne M; Camp, Mary J; Pohl, Calvin S; Donovan, David M
2015-10-01
Bovine mastitis results in billion dollar losses annually in the USA alone. Streptococci are among the most relevant causative agents of this disease. Conventional antibiotic therapy is often unsuccessful and contributes to development of antibiotic resistance. Bacteriophage endolysins represent a new class of antimicrobials against these bacteria. In this work, we characterized the endolysins (lysins) of the streptococcal phages λSA2 and B30 and evaluated their potential as anti-mastitis agents. When tested in vitro against live streptococci, both enzymes exhibited near-optimum lytic activities at ionic strengths, pH, and Ca(2+) concentrations consistent with cow milk. When tested in combination in a checkerboard assay, the lysins were found to exhibit strong synergy. The λSA2 lysin displayed high activity in milk against Streptococcus dysgalactiae (reduction of CFU/ml by 3.5 log units at 100 μg/ml), Streptococcus agalactiae (2 log), and Streptococcus uberis (4 log), whereas the B30 lysin was less effective. In a mouse model of bovine mastitis, both enzymes significantly reduced intramammary concentrations of all three streptococcal species (except for B30 vs. S. dysgalactiae), and the effects on mammary gland wet weights and TNFα concentrations were consistent with these findings. Unexpectedly, the synergistic effect determined for the two enzymes in vitro was not observed in the mouse model. Overall, our results illustrate the potential of endolysins for treatment of Streptococcus-induced bovine mastitis.
-
Poulin-Laprade, Dominic; Carraro, Nicolas; Burrus, Vincent
2015-01-01
Nowadays, healthcare systems are challenged by a major worldwide drug resistance crisis caused by the massive and rapid dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and associated emergence of multidrug resistant pathogenic bacteria, in both clinical and environmental settings. Conjugation is the main driving force of gene transfer among microorganisms. This mechanism of horizontal gene transfer mediates the translocation of large DNA fragments between two bacterial cells in direct contact. Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) of the SXT/R391 family (SRIs) and IncA/C conjugative plasmids (ACPs) are responsible for the dissemination of a broad spectrum of antibiotic resistance genes among diverse species of Enterobacteriaceae and Vibrionaceae. The biology, diversity, prevalence and distribution of these two families of conjugative elements have been the subject of extensive studies for the past 15 years. Recently, the transcriptional regulators that govern their dissemination through the expression of ICE- or plasmid-encoded transfer genes have been described. Unrelated repressors control the activation of conjugation by preventing the expression of two related master activator complexes in both types of elements, i.e., SetCD in SXT/R391 ICEs and AcaCD in IncA/C plasmids. Finally, in addition to activating ICE- or plasmid-borne genes, these master activators have been shown to specifically activate phylogenetically unrelated mobilizable genomic islands (MGIs) that also disseminate antibiotic resistance genes and other adaptive traits among a plethora of pathogens such as Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella enterica.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Dominic ePoulin-Laprade
2015-08-01
Full Text Available Nowadays, healthcare systems are challenged by a major worldwide drug resistance crisis caused by the massive and rapid dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and associated emergence of multidrug resistant pathogenic bacteria, in both clinical and environmental settings. Conjugation is the main driving force of gene transfer among microorganisms. This mechanism of horizontal gene transfer mediates the translocation of large DNA fragments between two bacterial cells in direct contact. Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs of the SXT/R391 family (SRIs and IncA/C conjugative plasmids (ACPs are responsible for the dissemination of a broad spectrum of antibiotic resistance genes among diverse species of Enterobacteriaceae and Vibrionaceae. The biology, diversity, prevalence and distribution of these two families of conjugative elements have been the subject of extensive studies for the past 15 years. Recently, the transcriptional regulators that govern their dissemination through the expression of ICE- or plasmid-encoded transfer genes have been described. Unrelated repressors control the activation of conjugation by preventing the expression of two related master activator complexes in both types of elements, i.e. SetCD in SXT/R391 ICEs and AcaCD in IncA/C plasmids. Finally, in addition to activating ICE- or plasmid-borne genes, these master activators have been shown to specifically activate phylogenetically unrelated mobilizable genomic islands (MGIs that also disseminate antibiotic resistance genes and other adaptive traits among a plethora of pathogens such as Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella enterica.
-
A History of Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) Redline Limits Management
Arnold, Thomas M.
2011-01-01
The Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) has several "redlines", which are operational limits designated to preclude a catastrophic shutdown of the SSME. The Space Shuttle Orbiter utilizes a combination of hardware and software to enable or disable the automated redline shutdown capability. The Space Shuttle is launched with the automated SSME redline limits enabled, but there are many scenarios which may result in the manual disabling of the software by the onboard crew. The operational philosophy for manually enabling and disabling the redline limits software has evolved continuously throughout the history of the Space Shuttle Program, due to events such as SSME hardware changes and updates to Space Shuttle contingency abort software. In this paper, the evolution of SSME redline limits management will be fully reviewed, including the operational scenarios which call for manual intervention, and the events that triggered changes to the philosophy. Following this review, improvements to the management of redline limits for future spacecraft will be proposed.
-
Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of gold nanoparticle conjugates with cefotaxime
Titanova, Elena O.; Burygin, Gennady L.
2016-04-01
Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have attracted significant interest as a novel platform for various applications to nanobiotechnology and biomedicine. The conjugates of GNPs with antibiotics and antibodies were also used for selective photothermal killing of protozoa and bacteria. Also the conjugates of some antibiotics with GNPs decreased the number of bacterial growing cells. In this work was made the procedure optimization for conjugation of cefotaxime (a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic) with GNPs (15 nm) and we examined the antimicrobial properties of this conjugate to bacteria culture of E. coli K-12. Addition of cefotaxime solution to colloidal gold does not change their color and extinction spectrum. For physiologically active concentration of cefotaxime (3 μg/mL), it was shown that the optimum pH for the conjugation was more than 9.5. A partial aggregation of the GNPs in saline medium was observed at pH 6.5-7.5. The optimum concentration of K2CO3 for conjugation cefotaxime with GNPs-15 was 5 mM. The optimum concentration of cefotaxime was at 0.36 μg/mL. We found the inhibition of the growth of E. coli K12 upon application cefotaxime-GNP conjugates.
-
Conjugated Polymer Solar Cells
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Paraschuk, Dmitry Y
2006-01-01
This report results from a contract tasking Moscow State University as follows: Conjugated polymers are promising materials for many photonics applications, in particular, for photovoltaic and solar cell devices...
-
Report of the Space Shuttle Management Independent Review Team
1995-02-01
At the request of the NASA Administrator a team was formed to review the Space Shuttle Program and propose a new management system that could significantly reduce operating costs. Composed of a group of people with broad and extensive experience in spaceflight and related areas, the team received briefings from the NASA organizations and most of the supporting contractors involved in the Shuttle Program. In addition, a number of chief executives from the supporting contractors provided advice and suggestions. The team found that the present management system has functioned reasonably well despite its diffuse structure. The team also determined that the shuttle has become a mature and reliable system, and--in terms of a manned rocket-propelled space launch system--is about as safe as today's technology will provide. In addition, NASA has reduced shuttle operating costs by about 25 percent over the past 3 years. The program, however, remains in a quasi-development mode and yearly costs remain higher than required. Given the current NASA-contractor structure and incentives, it is difficult to establish cost reduction as a primary goal and implement changes to achieve efficiencies. As a result, the team sought to create a management structure and associated environment that enables and motivates the Program to further reduce operational costs. Accordingly, the review team concluded that the NASA Space Shuttle Program should (1) establish a clear set of program goals, placing a greater emphasis on cost-efficient operations and user-friendly payload integration; (2) redefine the management structure, separating development and operations and disengaging NASA from the daily operation of the space shuttle; and (3) provide the necessary environment and conditions within the program to pursue these goals.
-
Death of the TonB shuttle hypothesis
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Michael George Gresock
2011-10-01
Full Text Available A complex of ExbB, ExbD, and TonB transduces cytoplasmic membrane (CM proton motive force (pmf to outer membrane (OM transporters so that large, scarce, and important nutrients can be released into the periplasmic space for subsequent transport across the CM. TonB is the component that interacts with the OM transporters and enables ligand transport, and several mechanical models and a shuttle model explain how TonB might work. In the mechanical models, TonB remains attached to the CM during energy transduction, while in the shuttle model the TonB N terminus leaves the CM to deliver conformationally stored potential energy to OM transporters. Previous efforts to test the shuttle model by anchoring TonB to the CM by fusion to a large globular cytoplasmic protein have been hampered by the proteolytic susceptibility of the fusion constructs. Here we confirm that GFP-TonB, tested in a previous study by another laboratory, again gave rise to full-length TonB and slightly larger potentially shuttleable fragments that prevented unambiguous interpretation of the data. Recently, we discovered that a fusion of the Vibrio cholerae ToxR cytoplasmic domain to the N terminus of TonB was proteolytically stable. ToxR-TonB was able to be completely converted into a proteinase K-resistant conformation in response to loss of pmf in spheroplasts and exhibited an ability to form a pmf-dependent formaldehyde crosslink to ExbD, both indicators of its location in the CM. Most importantly, ToxR-TonB had the same relative specific activity as wild-type TonB. Taken together, these results provide the first conclusive evidence that TonB does not shuttle during energy transduction. The interpretations of our previous study, which concluded that TonB shuttled in vivo, were complicated by the fact that the probe used in those studies, Oregon Green® 488 maleimide, was permeant to the CM and could label proteins, including a TonB ∆TMD derivative, confined exclusively to the
-
Shuttle Topography Data Inform Solar Power Analysis
2013-01-01
The next time you flip on a light switch, there s a chance that you could be benefitting from data originally acquired during the Space Shuttle Program. An effort spearheaded by Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) in 2000 put together the first near-global elevation map of the Earth ever assembled, which has found use in everything from 3D terrain maps to models that inform solar power production. For the project, called the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), engineers at JPL designed a 60-meter mast that was fitted onto Shuttle Endeavour. Once deployed in space, an antenna attached to the end of the mast worked in combination with another antenna on the shuttle to simultaneously collect data from two perspectives. Just as having two eyes makes depth perception possible, the SRTM data sets could be combined to form an accurate picture of the Earth s surface elevations, the first hight-detail, near-global elevation map ever assembled. What made SRTM unique was not just its surface mapping capabilities but the completeness of the data it acquired. Over the course of 11 days, the shuttle orbited the Earth nearly 180 times, covering everything between the 60deg north and 54deg south latitudes, or roughly 80 percent of the world s total landmass. Of that targeted land area, 95 percent was mapped at least twice, and 24 percent was mapped at least four times. Following several years of processing, NASA released the data to the public in partnership with NGA. Robert Crippen, a member of the SRTM science team, says that the data have proven useful in a variety of fields. "Satellites have produced vast amounts of remote sensing data, which over the years have been mostly two-dimensional. But the Earth s surface is three-dimensional. Detailed topographic data give us the means to visualize and analyze remote sensing data in their natural three-dimensional structure, facilitating a greater understanding of the features
-
Soluble polymer conjugates for drug delivery.
Minko, Tamara
2005-01-01
The use of water-soluble polymeric conjugates as drug carriers offers several possible advantages. These advantages include: (1) improved drug pharmacokinetics; (2) decreased toxicity to healthy organs; (3) possible facilitation of accumulation and preferential uptake by targeted cells; (4) programmed profile of drug release. In this review, we will consider the main types of useful polymeric conjugates and their role and effectiveness as carriers in drug delivery systems.: © 2005 Elsevier Ltd . All rights reserved.
-
Diffeomorphisms Holder conjugate to Anosov diffeomorphisms
Gogolev, Andrey
2008-01-01
We show by means of a counterexample that a $C^{1+Lip}$ diffeomorphism Holder conjugate to an Anosov diffeomorphism is not necessarily Anosov. The counterexample can bear higher smoothness up to $C^3$. Also we include a result from the 2006 Ph.D. thesis of T. Fisher: a $C^{1+Lip}$ diffeomorphism Holder conjugate to an Anosov diffeomorphism is Anosov itself provided that Holder exponents of the conjugacy and its inverse are sufficiently large.
-
Maltezou, Helen C; Tsagris, Vasilios; Antoniadou, Anastasia; Galani, Labrini; Douros, Constantinos; Katsarolis, Ioannis; Maragos, Antonios; Raftopoulos, Vasilios; Biskini, Panagiota; Kanellakopoulou, Kyriaki; Fretzayas, Andreas; Papadimitriou, Theodoros; Nicolaidou, Polyxeni; Giamarellou, Helen
2008-12-01
To study the performance of the Becton-Dickinson Link 2 Strep A Rapid Test, a rapid antigen detection test (RADT) for diagnosing streptococcal pharyngitis in children presenting to private offices and to the Pediatric Outpatient Clinic of a university hospital, in relation to clinical criteria (fever, tender anterior cervical lymph nodes, tonsillar exudate and absence of cough), and its impact on antibiotic prescription. Children were enrolled in Group A (enrolment by private-practice paediatricians; diagnosis by clinical picture only), Group B (enrolment by private-practice paediatricians; diagnosis by RADT and culture) or Group C (enrolment by hospital-affiliated paediatricians in the Pediatric Outpatient Clinic; diagnosis by RADT and culture). During a 2 year period, 820 children were enrolled [369 (45%) in Group A, 270 (33%) in Group B and 181 (22%) in Group C]. Streptococcal pharyngitis was diagnosed by RADT and culture in 146 (32.4%) of the 451 tested children. The sensitivity, specificity and positive and negative predictive values of the RADT were 83.1%, 93.3%, 82.4% and 93.6%, respectively. A stepwise increase in the sensitivity of the RADT was noted among children with one, two, three or four clinical criteria (60.9% to 95.8%). Paediatricians without access to laboratory tests were more likely to prescribe antibiotics compared with paediatricians with access to tests (72.2% versus 28.2%, P antibiotics more frequently compared with hospital-affiliated paediatricians (55.7% versus 19.9%, P antibiotic administration. Such a strategy has an important impact on limiting throat culture testing and is associated with reduced antibiotic prescription.
-
Conjugate Problems in Convective Heat Transfer: Review
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Abram Dorfman
2009-01-01
Full Text Available A review of conjugate convective heat transfer problems solved during the early and current time of development of this modern approach is presented. The discussion is based on analytical solutions of selected typical relatively simple conjugate problems including steady-state and transient processes, thermal material treatment, and heat and mass transfer in drying. This brief survey is accompanied by the list of almost two hundred publications considering application of different more and less complex analytical and numerical conjugate models for simulating technology processes and industrial devices from aerospace systems to food production. The references are combined in the groups of works studying similar problems so that each of the groups corresponds to one of selected analytical solutions considered in detail. Such structure of review gives the reader the understanding of early and current situation in conjugate convective heat transfer modeling and makes possible to use the information presented as an introduction to this area on the one hand, and to find more complicated publications of interest on the other hand.
-
Improvement of Emulsifying Properties of Wheat Gluten Hydrolysate λ-Carrageenan Conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jin-Shui Wang
2006-01-01
Full Text Available Gluten hydrolysate was prepared through limited enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat gluten resulting from the byproducts of wheat starch. The enzyme applied in the present study was Protamex. Response surface methodology was used to investigate the effects of pH, gluten hydrolysate (GHPλ-carrageenan (C ratio and reaction time on emulsifying properties of the GHP-C conjugate. The regression model for emulsion activity index (EAI was significant at p=0.001, while reaction time had a significant effect on EAI of the conjugate with regression coefficient of 4.25. The interactions of pH and GHP/ C ratio, and GHP/C ratio and reaction time significantly affected the EAI of the conjugate. Both the emulsifying property and nitrogen solubility index (NSI of GHP-C conjugate prepared under the optimal conditions increased more remarkably, compared to the control. The denaturation temperature of GHP-C conjugate obviously increased compared to wheat gluten. The addition of GHP-C conjugate had different effects on dough characteristics. Moreover, this conjugate can delay the increase in the bread crumb firmness during storage. It demonstrated that this conjugate couldimprove the dough characteristics and had anti-staling properties of bread.
-
Tracing the transition of a macro electron shuttle into nonlinear response
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kim, Chulki [Sensor System Research Center, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul 136791 (Korea, Republic of); Prada, Marta [I. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Hamburg, Jungiusstr. 9, Hamburg 20355 (Germany); Qin, Hua [Key Laboratory of Nanodevices, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 398 Ruoshui Road, Industrial Park, Suzhou City, Jiangsu 215123 (China); Kim, Hyun-Seok [Division of Electronics and Electrical Engineering, Dongguk University-Seoul, 100715 Seoul (Korea, Republic of); Blick, Robert H., E-mail: rblick@physnet.uni-hamburg.de [Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1150 University Avenue, Madison, Wisconsin-53706 (United States); Center for Hybrid Nanostructures, Universität Hamburg, Jungiusstr. 11c, Hamburg 20355 (Germany); Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1415 Engineering Dr. Madison, Wisconsin-53706 (United States)
2015-02-09
We present a study on a macroscopic electron shuttle in the transition from linear to nonlinear response. The shuttle consists of a classical mechanical pendulum situated between two capacitor plates. The metallic pendulum enables mechanical transfer of electrons between the plates, hence allowing to directly trace electron shuttling in the time domain. By applying a high voltage to the plates, we drive the system into a controlled nonlinear response, where we observe period doubling.
-
Schedule and complex motion of shuttle bus induced by periodic inflow of passengers
Nagatani, Takashi; Naito, Yuichi
2011-09-01
We have studied the dynamic behavior of a bus in the shuttle bus transportation with a periodic inflow. A bus schedule is closely related to the dynamics. We present the modified circle map model for the dynamics of the shuttle bus. The motion of the shuttle bus depends on the loading parameter and the inflow period. The shuttle bus displays the periodic, quasi-periodic, and chaotic motions with varying both loading parameter and inflow rate.
-
Aerospace News: Space Shuttle Commemoration. Volume 2, No. 7
2011-01-01
The complex space shuttle design was comprised of four components: the external tank, two solid rocket boosters (SRB), and the orbiter vehicle. Six orbiters were used during the life of the program. In order of introduction into the fleet, they were: Enterprise (a test vehicle), Columbia, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour. The space shuttle had the unique ability to launch into orbit, perform on-orbit tasks, return to earth and land on a runway. It was an orbiting laboratory, International Space Station crew delivery and supply replenisher, satellite launcher and payload delivery vehicle, all in one. Except for the external tank, all components of the space shuttle were designed to be reusable for many flights. ATK s reusable solid rocket motors (RSRM) were designed to be flown, recovered, and the metal components reused 20 times. Following each space shuttle launch, the SRBs would parachute into the ocean and be recovered by the Liberty Star and Freedom Star recovery ships. The recovered boosters would then be received at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Hangar AF facility for disassembly and engineering post-flight evaluation. At Hangar AF, the RSRM field joints were demated and the segments prepared to be returned to Utah by railcar. The segments were then shipped to ATK s facilities in Clearfield for additional evaluation prior to washout, disassembly and refurbishment. Later the refurbished metal components would be transported to ATK s Promontory facilities to begin a new cycle. ATK s RSRMs were manufactured in Promontory, Utah. During the Space Shuttle Program, ATK supported NASA s Marshall Space Flight Center whose responsibility was for all propulsion elements on the program, including the main engines and solid rocket motors. On launch day for the space shuttle, ATK s Launch Site Operations employees at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) provided lead engineering support for ground operations and NASA s chief engineer. It was ATK s responsibility
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Matern, S.; Gerok, W.
1977-01-01
Specific radioimmunoassays for separate determinations of serum unconjugated cholic, conjugated cholic and conjugated deoxycholic acids have been developed. Prior to the radioimmunoassay, extraction of serum bile acids was performed with Amberlite XAD-2. Unconjugated cholic acid was separated from glyco- and taurocholic acids by thin-layer chromatography. At 50% displacement of bound labeled glyco[ 3 H]cholic acid using antiserum obtained after immunization with cholic acid-bovine serum albumin-conjugate the cross-reactivity of taurocholic acid was 100%, cholic acid 80%, glycochenodeoxycholic acid 10%, chenodeoxycholic acid 7%, conjugated deoxycholic acid 3%, and conjugated lithocholic acid 3 H]cholic acid was linear on a logit-log plot from 5 to 80 pmol of unlabeled glycocholic acid. Fasting serum conjugated cholic acid in healthy subjects was 0.68 +- 0.34 μmol/l. Unconjugated cholic acid was determined by a solid phase radioimmunoassay using the cholic acid antibody chemically bound to Sepharose. The displacement curve of [ 3 H]cholic acid in the solid phase radioimmunoassay was linear on a logit-log plot from 5 to 200 pmol of unlabeled cholic acid. The coefficient of variation between samples was 5%. Fasting serum conjugated deoxycholic acid concentrations in 10 healthy subjects ranged from 0.18 to 0.92 μmol/l determined by a radioimmunoassay using antiserum obtained after immunization with deoxycholic acid-bovine serum albumin-conjugate. The clinical application of these bile acid radioimmunoassays is shown by an 'oral cholate tolerance test' as a sensitive indicator of liver function and by an 'oral cholyglycine tolerance test' as a useful test for bile acid absorption. (orig.) [de
-
Shayler, David J
2017-01-01
How could the newly authorized space shuttle help in the U.S. quest to build a large research station in Earth orbit? As a means of transporting goods, the shuttle could help supply the parts to the station. But how would the two entitles be physically linked? Docking technologies had to constantly evolve as the designs of the early space stations changed. It was hoped the shuttle would make missions to the Russian Salyut and American Skylab stations, but these were postponed until the Mir station became available, while plans for getting a new U. S. space station underway were stalled. In Linking the Space Shuttle and Space Stations, the author delves into the rich history of the Space Shuttle and its connection to these early space stations, culminating in the nine missions to dock the shuttle to Mir. By 1998, after nearly three decades of planning and operations, shuttle missions to Mir had resulted in: • A proven system to link up the space shuttle to a space station • Equipment and hands-on experienc...
-
2009 Space Shuttle Probabilistic Risk Assessment Overview
Hamlin, Teri L.; Canga, Michael A.; Boyer, Roger L.; Thigpen, Eric B.
2010-01-01
Loss of a Space Shuttle during flight has severe consequences, including loss of a significant national asset; loss of national confidence and pride; and, most importantly, loss of human life. The Shuttle Probabilistic Risk Assessment (SPRA) is used to identify risk contributors and their significance; thus, assisting management in determining how to reduce risk. In 2006, an overview of the SPRA Iteration 2.1 was presented at PSAM 8 [1]. Like all successful PRAs, the SPRA is a living PRA and has undergone revisions since PSAM 8. The latest revision to the SPRA is Iteration 3. 1, and it will not be the last as the Shuttle program progresses and more is learned. This paper discusses the SPRA scope, overall methodology, and results, as well as provides risk insights. The scope, assumptions, uncertainties, and limitations of this assessment provide risk-informed perspective to aid management s decision-making process. In addition, this paper compares the Iteration 3.1 analysis and results to the Iteration 2.1 analysis and results presented at PSAM 8.
-
Vogel, Curtis R; Yang, Qiang
2006-08-21
We present two different implementations of the Fourier domain preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm (FD-PCG) to efficiently solve the large structured linear systems that arise in optimal volume turbulence estimation, or tomography, for multi-conjugate adaptive optics (MCAO). We describe how to deal with several critical technical issues, including the cone coordinate transformation problem and sensor subaperture grid spacing. We also extend the FD-PCG approach to handle the deformable mirror fitting problem for MCAO.
-
Shuttle Planning for Link Closures in Urban Public Transport Networks
van der Hurk, E.; Koutsopoulos, H.; Wilson, N.H.M.; Kroon, L.G.; Maroti, G.
2016-01-01
Urban public transport systems must periodically close certain links for maintenance, which can have significant effects on the service provided to passengers. In practice, the effects of closures are mitigated by replacing the closed links with a simple shuttle service. However, alternative shuttle
-
Preparation and biodistribution study of 99Tcm labelled dextran conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yang Chunhui; Li Hongyu; Liang Jixin; Lu Jia; Luo Hongyi; Zheng Deqiang; Sun Guiquan
2012-01-01
99 Tc m Mannosylated dextran conjugates were prepared through [ 99 Tc m (CO) 3 ] + precursor synthesized by carbonyl Isolink kit. The labelled conjugates were injected sub-dermally into the rear foots of the mice, and the patent blue solution was injected at the same site 10 min before sacrifice. The mice were killed at 1 h and 4 h postinjection, and the samples of different tissues including SLN, 2LN, injection site, liver, spleen, blood were dissected and counted. The uptake in terms was calculated. The results of biodistribution demonstrated that the SLN uptakes of radiopharmaceutical (without mannose in the molecules) were rather low and in vivo excretion of these conjugates were comparatively faster, and the uptake of injection site was also low; on the other hand, the SLN uptakes of radio pharmaceutical (with mannose in their molecules) were much higher than those of their corresponding dextran conjugates without mannose, but the retention in the injection site of these conjugates increased too. The results indicated that the affinity of mannosyl-dextran conjugates to the receptors on the surface of macrophages in the lymph node. In addition, the different relative molecular mass of dextran conjugates also cause different biodistribution results, the major one had higher SLN uptake, the difference was significant (P 99 Tc m (CO) 3 ] + labelled mannosylated dextran conjugates showed promising properties as SLN imaging agent and worth further investigation. (authors)
-
Dynamical localization of two electrons in triple-quantum-dot shuttles
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Qu, Jinxian; Duan, Suqing; Yang, Ning
2012-01-01
The dynamical localization phenomena in two-electron quantum-dot shuttles driven by an ac field have been investigated and analyzed by the Floquet theory. The dynamical localization occurs near the anti-crossings in Floquet eigenenergy spectrum. The oscillation of the quantum-dot shuttles may increase the possibility of the dynamical localization. Especially, even if the two electrons are initialized in two neighbor dots, they can be localized there for appropriate intensity of the driven field. The studies may help the understanding of dynamical localization in electron shuttles and expand the application potential of nanoelectromechanical devices. -- Highlights: ► The dynamical localization in electron shuttle is studied by Floquet theory. ► There is a relation between quasi-energy anti-crossings and dynamical localization. ► The oscillation of quantum dot increases the dynamical localization. ► Even the electrons are initialized in different dots, the localization can occur.
-
A Comparison Between Orion Automated and Space Shuttle Rendezvous Techniques
Ruiz, Jose O,; Hart, Jeremy
2010-01-01
The Orion spacecraft will replace the space shuttle and will be the first human spacecraft since the Apollo program to leave low earth orbit. This vehicle will serve as the cornerstone of a complete space transportation system with a myriad of mission requirements necessitating rendezvous to multiple vehicles in earth orbit, around the moon and eventually beyond . These goals will require a complex and robust vehicle that is, significantly different from both the space shuttle and the command module of the Apollo program. Historically, orbit operations have been accomplished with heavy reliance on ground support and manual crew reconfiguration and monitoring. One major difference with Orion is that automation will be incorporated as a key element of the man-vehicle system. The automated system will consist of software devoted to transitioning between events based on a master timeline. This effectively adds a layer of high level sequencing that moves control of the vehicle from one phase to the next. This type of automated control is not entirely new to spacecraft since the shuttle uses a version of this during ascent and entry operations. During shuttle orbit operations however many of the software modes and hardware switches must be manually configured through the use of printed procedures and instructions voiced from the ground. The goal of the automation scheme on Orion is to extend high level automation to all flight phases. The move towards automation represents a large shift from current space shuttle operations, and so these new systems will be adopted gradually via various safeguards. These include features such as authority-to-proceed, manual down modes, and functional inhibits. This paper describes the contrast between the manual and ground approach of the space shuttle and the proposed automation of the Orion vehicle. I will introduce typical orbit operations that are common to all rendezvous missions and go on to describe the current Orion automation
-
Seismic excitation by space shuttles
Kanamori, H.; Mori, J.; Sturtevant, B.; Anderson, D.L.; Heaton, T.
1992-01-01
Shock waves generated by the space shuttles Columbia (August 13, 1989), Atlantis (April 11, 1991) and Discovery (September 18, 1991) on their return to Edwards Air Force Base, California, were recorded by TERRAscope (Caltech's broadband seismic network), the Caltech-U.S.G.S Southern California Seismic Network (SCSN), and the University of Southern California (USC) Los Angeles Basin Seismic Network. The spatial pattern of the arrival times exhibits hyperbolic shock fronts from which the path, velocity and altitude of the space shuttle could be determined. The shock wave was acoustically coupled to the ground, converted to a seismic wave, and recorded clearly at the broadband TERRAscope stations. The acoustic coupling occurred very differently depending on the conditions of the Earth's surface surrounding the station. For a seismic station located on hard bedrock, the shock wave (N wave) was clearly recorded with little distortion. Aside from the N wave, very little acoustic coupling of the shock wave energy to the ground occurred at these sites. The observed N wave record was used to estimate the overpressure of the shock wave accurately; a pressure change of 0.5 to 2.2 mbars was obtained. For a seismic station located close to the ocean or soft sedimentary basins, a significant amount of shock wave energy was transferred to the ground through acoustic coupling of the shock wave and the oceanic Rayleigh wave. A distinct topography such as a mountain range was found effective to couple the shock wave energy to the ground. Shock wave energy was also coupled to the ground very effectively through large man made structures such as high rise buildings and offshore oil drilling platforms. For the space shuttle Columbia, in particular, a distinct pulse having a period of about 2 to 3 seconds was observed, 12.5 s before the shock wave, with a broadband seismograph in Pasadena. This pulse was probably excited by the high rise buildings in downtown Los Angeles which were
-
Functional properties of nisin–carbohydrate conjugates formed by radiation induced Maillard reaction
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Muppalla, Shobita R.; Sonavale, Rahul; Chawla, Surinder P.; Sharma, Arun
2012-01-01
Nisin–carbohydrate conjugates were prepared by irradiating nisin either with glucose or dextran. Increase in browning and formation of intermediate products was observed with a concomitant decrease in free amino and reducing sugar groups indicating occurrence of the Maillard reaction catalyzed by irradiation. Nisin–carbohydrate conjugates showed a broad spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fluorescence) as well as Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus). Results of antioxidant assays, including that of DPPH radical-scavenging activity and reducing power, showed that the nisin–dextran conjugates possessed better antioxidant potential than nisin–glucose conjugate. These results suggested that it was possible to enhance the functional properties of nisin by preparing radiation induced conjugates suitable for application in food industry. - Highlights: ► Nisin–carbohydrate conjugates were prepared using radiation induced Maillard reaction. ► Conjugation of nisin with dextran/glucose resulted in improvement of antibacterial spectrum. ► Conjugates of nisin with dextran/glucose had significant radical scavenging activity.
-
Cross-conjugation and quantum interference: a general correlation?
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Valkenier, Hennie; Guedon, Constant M.; Markussen, Troels
2014-01-01
We discuss the relationship between the pi-conjugation pattern, molecular length, and charge transport properties of molecular wires, both from an experimental and a theoretical viewpoint. Specifically, we focus on the role of quantum interference in the conductance properties of cross-conjugated...
-
Development of a prototype specialist shuttle vehicle for chipped woodfuel
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2003-06-01
This report gives details of a project to develop and test a specialist chip shuttle vehicle for conveying woodchips out of the forest with the aim of reducing the cost of woodfuel production. The design objectives are described and include the need to allow easy transfer of the chips from the chipper to the shuttle and on into haulage units, good performance and manoeuvrability on and off roads, and high-tip capacity. Estimates of the improved production and reduced woodfuel production costs are discussed along with the anticipated satisfactory operation of the chipper-shuttle combination in a forestry site.
-
Modal Testing of Seven Shuttle Cargo Elements for Space Station
Kappus, Kathy O.; Driskill, Timothy C.; Parks, Russel A.; Patterson, Alan (Technical Monitor)
2001-01-01
From December 1996 to May 2001, the Modal and Control Dynamics Team at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) conducted modal tests on seven large elements of the International Space Station. Each of these elements has been or will be launched as a Space Shuttle payload for transport to the International Space Station (ISS). Like other Shuttle payloads, modal testing of these elements was required for verification of the finite element models used in coupled loads analyses for launch and landing. The seven modal tests included three modules - Node, Laboratory, and Airlock, and four truss segments - P6, P3/P4, S1/P1, and P5. Each element was installed and tested in the Shuttle Payload Modal Test Bed at MSFC. This unique facility can accommodate any Shuttle cargo element for modal test qualification. Flexure assemblies were utilized at each Shuttle-to-payload interface to simulate a constrained boundary in the load carrying degrees of freedom. For each element, multiple-input, multiple-output burst random modal testing was the primary approach with controlled input sine sweeps for linearity assessments. The accelerometer channel counts ranged from 252 channels to 1251 channels. An overview of these tests, as well as some lessons learned, will be provided in this paper.
-
Schedule and complex motion of shuttle bus induced by periodic inflow of passengers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nagatani, Takashi; Naito, Yuichi
2011-01-01
We have studied the dynamic behavior of a bus in the shuttle bus transportation with a periodic inflow. A bus schedule is closely related to the dynamics. We present the modified circle map model for the dynamics of the shuttle bus. The motion of the shuttle bus depends on the loading parameter and the inflow period. The shuttle bus displays the periodic, quasi-periodic, and chaotic motions with varying both loading parameter and inflow rate. -- Highlights: → We studied the dynamic behavior of a bus in the shuttle bus transportation. → We presented the modified circle map model for the bus schedule. → We clarified the dependence of the tour time on both loading parameter and inflow period.
-
Little, Paul; Hobbs, F D Richard; Moore, Michael; Mant, David; Williamson, Ian; McNulty, Cliodna; Cheng, Ying Edith; Leydon, Geraldine; McManus, Richard; Kelly, Joanne; Barnett, Jane; Glasziou, Paul; Mullee, Mark
2013-10-10
To determine the effect of clinical scores that predict streptococcal infection or rapid streptococcal antigen detection tests compared with delayed antibiotic prescribing. Open adaptive pragmatic parallel group randomised controlled trial. Primary care in United Kingdom. Patients aged ≥ 3 with acute sore throat. An internet programme randomised patients to targeted antibiotic use according to: delayed antibiotics (the comparator group for analyses), clinical score, or antigen test used according to clinical score. During the trial a preliminary streptococcal score (score 1, n=1129) was replaced by a more consistent score (score 2, n=631; features: fever during previous 24 hours; purulence; attends rapidly (within three days after onset of symptoms); inflamed tonsils; no cough/coryza (acronym FeverPAIN). Symptom severity reported by patients on a 7 point Likert scale (mean severity of sore throat/difficulty swallowing for days two to four after the consultation (primary outcome)), duration of symptoms, use of antibiotics. For score 1 there were no significant differences between groups. For score 2, symptom severity was documented in 80% (168/207 (81%) in delayed antibiotics group; 168/211 (80%) in clinical score group; 166/213 (78%) in antigen test group). Reported severity of symptoms was lower in the clinical score group (-0.33, 95% confidence interval -0.64 to -0.02; P=0.04), equivalent to one in three rating sore throat a slight versus moderate problem, with a similar reduction for the antigen test group (-0.30, -0.61 to -0.00; P=0.05). Symptoms rated moderately bad or worse resolved significantly faster in the clinical score group (hazard ratio 1.30, 95% confidence interval 1.03 to 1.63) but not the antigen test group (1.11, 0.88 to 1.40). In the delayed antibiotics group, 75/164 (46%) used antibiotics. Use of antibiotics in the clinical score group (60/161) was 29% lower (adjusted risk ratio 0.71, 95% confidence interval 0.50 to 0.95; P=0.02) and in the
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Baran, Erkan T., E-mail: erkantur@metu.edu.tr; Tuzlakoglu, Kadriye, E-mail: kadriye@dep.uminho.pt; Mano, Joao F., E-mail: jmano@dep.uminho.pt; Reis, Rui L., E-mail: rgreis@dep.uminho.pt
2012-08-01
The objective of this study was to investigate the influence of silk fibroin and oxidized starch conjugation on the enzymatic degradation behavior and the cytocompatability of chitosan based biomaterials. The tensile stress of conjugate membranes, which was at 50 Megapascal (MPa) for the lowest fibroin and starch composition (10 weight percent (wt.%)), was decreased significantly with the increased content of fibroin and starch. The weight loss of conjugates in {alpha}-amylase was more notable when the starch concentration was the highest at 30 wt.%. The conjugates were resistant to the degradation by protease and lysozyme except for the conjugates with the lowest starch concentration. After 10 days of cell culture, the proliferation of osteoblast-like cells (SaOS-2) was stimulated significantly by higher fibroin compositions and the DNA synthesis on the conjugate with the highest fibroin (30 wt.%) was about two times more compared to the native chitosan. The light microscopy and the image analysis results showed that the cell area and the lengths were decreased significantly with higher fibroin/chitosan ratio. The study proved that the conjugation of fibroin and starch with the chitosan based biomaterials by the use of non-toxic reductive alkylation crosslinking significantly improved the cytocompatibility and modulated the biodegradation, respectively. - Highlights: Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Silk fibroin, starch and chitosan conjugates were prepared by reductive alkylation. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer The enzymatic biodegradation and the cytocompatibility of conjugates were tested. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer The conjugate with 30% starch composition was degraded by {alpha}-amylase significantly. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Higher starch composition in conjugates prevented protease and lysozyme degradation. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Fibroin incorporation effectively increased the cell proliferation of conjugates.
-
Recent Advances in Conjugated Polymers for Light Emitting Devices
AlSalhi, Mohamad Saleh; Alam, Javed; Dass, Lawrence Arockiasamy; Raja, Mohan
2011-01-01
A recent advance in the field of light emitting polymers has been the discovery of electroluminescent conjugated polymers, that is, kind of fluorescent polymers that emit light when excited by the flow of an electric current. These new generation fluorescent materials may now challenge the domination by inorganic semiconductor materials of the commercial market in light-emitting devices such as light-emitting diodes (LED) and polymer laser devices. This review provides information on unique properties of conjugated polymers and how they have been optimized to generate these properties. The review is organized in three sections focusing on the major advances in light emitting materials, recent literature survey and understanding the desirable properties as well as modern solid state lighting and displays. Recently, developed conjugated polymers are also functioning as roll-up displays for computers and mobile phones, flexible solar panels for power portable equipment as well as organic light emitting diodes in displays, in which television screens, luminous traffic, information signs, and light-emitting wallpaper in homes are also expected to broaden the use of conjugated polymers as light emitting polymers. The purpose of this review paper is to examine conjugated polymers in light emitting diodes (LEDs) in addition to organic solid state laser. Furthermore, since conjugated polymers have been approved as light-emitting organic materials similar to inorganic semiconductors, it is clear to motivate these organic light-emitting devices (OLEDs) and organic lasers for modern lighting in terms of energy saving ability. In addition, future aspects of conjugated polymers in LEDs were also highlighted in this review. PMID:21673938
-
Some aspects of geomagnetically conjugate phenomena
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rycroft, M.J.
1987-12-01
Both charged particles and waves convey information about the thermosphere, ionosphere and magnetosphere from the Northern to the Southern Hemisphere and vice versa, along geomagnetic flux tubes.The interhemispheric travel time of electrons or ions, being dependent upon L-value , pitch angle and energy (which may lie between less than or equal to 1 eV and greater than or equal to 1 MeV) may be many hours, ranging down to less than or equal to 1 s. However, the one-hop propagation time for magnetohydrodynamic or whistler mode waves generally lies between 10/sup 2/s and 1 s. Such times, therefore, give the time scales of transient phenomena that are geomagnetically conjugate and of changes in steady-state plasma processes occurring in geomagnetically conjugate regions. Contrasting examples are presented of conjugate physical phenomena, obtained using satellite, rocket, aircraft and ground-based observations; the latter capitalise upon the rather rare disposition of land - rather than ocean - at each end of a geophysically interesting flux tube. Particular attention is paid to the interactions between whistler mode waves and energetic electrons. Geomagnetic, radio, optical and plasma observations, taken together with model computations, provide a wealth of knowledge on conjugate phenomena and their dependence on conditions in the solar wind, substorms, L-value, etc... Finally, some suggestions are made for future lines of research.
-
Comparative cytotoxicity of gold-doxorubicin and InP-doxorubicin conjugates.
Zhang, Xuan; Chibli, Hicham; Kong, Dekun; Nadeau, Jay
2012-07-11
Direct comparisons of different types of nanoparticles for drug delivery have seldom been performed. In this study we compare the physical properties and cellular activity of doxorubicin (Dox) conjugates to gold nanoparticles (Au) and InP quantum dots of comparable diameter. Although the Au particles alone are non-toxic and InP is moderately toxic, Au-Dox is more effective than InP-Dox against the Dox-resistant B16 melanoma cell line. Light exposure does not augment the efficacy of InP-Dox, suggesting that conjugates are breaking down. Electron and confocal microscopy and atomic absorption spectroscopy reveal that over 60% of the Au-Dox conjugates reach the cell nucleus. In contrast, InP-Dox enters cell nuclei to a very limited extent, although liberated Dox from the conjugates does eventually reach the nucleus. These observations are attributed to faster Dox release from Au conjugates under endosomal conditions, greater aggregation of InP-Dox with cytoplasmic proteins, and adherence of InP to membranes. These findings have important implications for design of active drug-nanoparticle conjugates.
-
Surface chloride salt formation on Space Shuttle exhaust alumina
Cofer, W. R., III; Pellett, G. L.; Sebacher, D. I.; Wakelyn, N. T.
1984-01-01
Aluminum oxide samples from the exhaust of Space Shuttle launches STS-1, STS-4, STS-5, and STS-6 were collected from surfaces on or around the launch pad complex and chemically analyzed. The results indicate that the particulate solid-propellant rocket motor (SRM) alumina was heavily chlorided. Concentrations of water-soluble aluminum (III) ion were large, suggesting that the surface of the SRM alumina particles was rendered soluble by prior reactions with HCl and H2O in the SRM exhaust cloud. These results suggest that Space Shuttle exhaust alumina particles are good sites for nucleation and condensation of atmospheric water. Laboratory experiments conducted at 220 C suggest that partial surface chloriding of alumina may occur in hot Space Shuttle exhaust plumes.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of the antioxidative potential of minoxidil-polyamine conjugates.
Hadjipavlou-Litina, Dimitra; Magoulas, George E; Bariamis, Stavros E; Tsimali, Zinovia; Avgoustakis, Konstantinos; Kontogiorgis, Christos A; Athanassopoulos, Constantinos M; Papaioannou, Dionissios
2013-07-01
A series of conjugates (MNX-CO-PA) of minoxidil (MNX) with the polyamines (PAs) putrescine (PUT), spermidine (SPD) and spermine (SPM) as well as dopamine were produced through activation of MNX with N,N'-carbonyldiimidazole, followed by reaction with dopamine or selectively protected PAs and acid-mediated deprotection. These conjugates together with conjugates of the general type MNX-PA or PA-MNX-PA, readily produced using literature protocols, were tested as antioxidants. The most potent inhibitors of lipid peroxidation were the conjugates MNX-SPM (2, 94%), SPM-MNX-SPM (4, 94%) and MNX-N(4)-SPD (7, 91%) and MNX (91%). The most powerful lipoxygenase (LOX) inhibitors were MNX (IC50 = 20 μM) and the conjugates MNX-N(8)-SPD (9, IC50 = 22.1 μM), MNX-CO-dopamine (11, IC50 = 28 μM) and MNX-N(1)-SPD (8, IC50 = 30 μM). The most interesting conjugates 2, MNX-CO-PUT (5), 8 and 11 as well as MNX were generally found to exhibit weaker (22-36.5%) or no (conjugate 8) anti-inflammatory activity than indomethacin (47%) with the exception of MNX which showed almost equal potency (49%) to indomethacin. The cytocompatibility of conjugates and MNX at the highest concentration of 100 μM showed a survival percentage of 87-107%, with the exception of conjugates with SPM (compound 2) and MNX-CO-SPM (6), which showed considerable cytotoxicity (survival percentage 8-14%). Molecular docking studies were carried on conjugate 9 and the parent compound MNX and were found to be in accordance with our experimental biological results. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tetsuya Sakai
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Group A Streptococcus (GAS, Streptococcus pyogenes causes invasive infections including streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS and local infections. To our knowledge, this is the first report of a case of an invasive GAS infection with pneumonia and pleural empyema (PE followed by STSS (disseminated intravascular coagulation [DIC] and acute renal insufficiency in a healthy male adult. He received combined supportive therapies of PE drainage, anti-DIC agent, hemodialysis, and antimicrobials and eventually made a clinical recovery. GAS isolated from PE was found to have emm1/speA genes, suggestive of a pathogenic strain. Clinicians should be aware of the possibility of this disease entity (pneumonia, PE, and STSS in healthy male adults as well as children and adult women.
-
Anticancer activity of drug conjugates in head and neck cancer cells.
Majumdar, Debatosh; Rahman, Mohammad Aminur; Chen, Zhuo Georgia; Shin, Dong M
2016-06-01
Sexually transmitted oral cancer/head and neck cancer is increasing rapidly. Human papilloma virus (HPV) is playing a role in the pathogenesis of a subset of squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck (SCCHN). Paclitaxel is a widely used anticancer drug for breast, ovarian, testicular, cervical, non-small cell lung, head and neck cancer. However, it is water insoluble and orally inactive. We report the synthesis of water soluble nanosize conjugates of paclitaxel, branched PEG, and EGFR-targeting peptide by employing native chemical ligation. We performed a native chemical ligation between the N-hydroxy succinimide (NHS) ester of paclitaxel succinate and cysteine at pH 6.5 to give the cysteine-conjugated paclitaxel derivative. The thiol functionality of cysteine was activated and subsequently conjugated to multiarm thiol-PEG to obtain the paclitaxel branched PEG conjugate. Finally, we conjugated an EGFR-targeting peptide to obtain conjugates of paclitaxel, branched PEG, and EGFR-targeting peptide. These conjugates show anticancer activity against squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck cells (SCCHN, Tu212).
-
Small angle scattering from protein/sugar conjugates
Jackson, Andrew; White, John
2006-11-01
The Maillard reaction between free amine groups on proteins and sugars is well known. We have examined the effect of the reaction of the casein group of milk proteins with sugars on their nanoscale structure and aggregation. The small angle neutron scattering from beta casein and sodium caseinate and their sugar conjugates have been studied as a function of solution concentration. At high conjugate concentration (greater than ca. 5 mg/ml) the addition of sugar reduces supra-micellar aggregation of the protein whilst at lower concentration, where the protein is expected to be deaggregated already, little effect is seen. Guinier analysis of the scattering data show a radius of gyration of around 75 A˚ for beta casein in solution and around 80 A˚ for the sucrose conjugate.
-
Quantum dot-polymer conjugates for stable luminescent displays.
Ghimire, Sushant; Sivadas, Anjaly; Yuyama, Ken-Ichi; Takano, Yuta; Francis, Raju; Biju, Vasudevanpillai
2018-05-23
The broad absorption of light in the UV-Vis-NIR region and the size-based tunable photoluminescence color of semiconductor quantum dots make these tiny crystals one of the most attractive antennae in solar cells and phosphors in electrooptical devices. One of the primary requirements for such real-world applications of quantum dots is their stable and uniform distribution in optically transparent matrices. In this work, we prepare transparent thin films of polymer-quantum dot conjugates, where CdSe/ZnS quantum dots are uniformly distributed at high densities in a chitosan-polystyrene copolymer (CS-g-PS) matrix. Here, quantum dots in an aqueous solution are conjugated to the copolymer by a phase transfer reaction. With the stable conjugation of quantum dots to the copolymer, we prevent undesired phase separation between the two and aggregation of quantum dots. Furthermore, the conjugate allows us to prepare transparent thin films in which quantum dots are uniformly distributed at high densities. The CS-g-PS copolymer helps us in not only preserving the photoluminescence properties of quantum dots in the film but also rendering excellent photostability to quantum dots at the ensemble and single particle levels, making the conjugate a promising material for photoluminescence-based devices.
-
Free and conjugated dopamine in human ventricular fluid
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sharpless, N.S.; Thal, L.J.; Wolfson, L.I.; Tabaddor, K.; Tyce, G.M.; Waltz, J.M.
1981-01-01
Free dopamine and an acid hydrolyzable conjugate of dopamine were measured in human ventricular fluid specimens with a radioenzymatic assay and by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection. Only trace amounts of free norepinephrine and dopamine were detected in ventricular fluid from patients with movement disorders. When the ventricular fluid was hydrolyzed by heating in HClO 4 or by lyophilization in dilute HClO 4 , however, a substantial amount of free dopamine was released. Values for free plus conjugated dopamine in ventricular fluid from patients who had never taken L-DOPA ranged from 139 to 340 pg/ml when determined by HPLC and from 223 to 428 pg/ml when measured radioenzymatically. The correlation coefficient for values obtained by the two methods in the same sample of CSF was 0.94 (P<0.001). Patients who had been treated with L-DOPA had higher levels of conjugated dopamine in their ventricular CSF which correlated inversely with the time between the last dose of L-DOPA and withdrawal of the ventricular fluid. Additionally, one patient with acute cerebral trauma had elevated levels of free norepinephrine and both free and conjugated dopamine in his ventricular fluid. Conjugation may be an important inactivation pathway for released dopamine in man. (Auth.)
-
Antibody-radioisotope conjugates for tumor localization and treatment
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Larson, S.M.; Carrasquillo, J.A.
1985-01-01
In principle, anti-tumor antibodies can be used to carry radioactivity to tumors for in-vivo diagnosis and treatment of cancer. First, for diagnostic purposes, an antibody that targets a specific antigen (for example, the p97 antigen of human melanoma tumor), is labeled with a tracer amount of radioactivity. When this antibody-radioisotope conjugate is injected into the blood stream, the antibody carries the radioactivity throughout the body and in time, percolates through all the tissues of the body. Because the tumor has specific antigens to which the antibody can bind, the antibody conjugate progressively accumulates in the tumor. Using conventional nuclear medicine imaging equipment, the body of the patient is scanned for radioactivity content, and a map of the distribution of the radioactivity is displayed on photographic film. The tumor shows up as a dense area of radio-activity. These same antibody-radioisotope conjugates may be used for therapy of tumors, except that in this case large amounts of radioactivity are loaded on the antibody. After localization of the conjugate there is sufficient radiation deposited in the tumor of radiotherapy. The success of this approach in the clinic is determined in large measure by the concentration gradient that can be achieved between tissue antibody conjugate in tumor versus normal tissue
-
Conjugal conflict and violence: a review and theoretical paradigm.
Smilkstein, G; Aspy, C B; Quiggins, P A
1994-02-01
Conjugal violence has been described as having multiple etiologies. The variables are so numerous that intervention and research protocols are difficult to effect. This paper proposes a paradigm that establishes conjugal conflict and violence as separate entities. According to the paradigm, conjugal conflict is viewed as "an inevitable part of human association," whereas conjugal violence is determined to be a learned behavioral tactic that is employed as a coping strategy when an individual's conflict threshold potential is exceeded. Evidence will be offered that violence is learned from family of origin and from observing what is common or accepted practice in the community. Use of this paradigm would give primacy to community education programs that advance the concept of conflict resolution through rational discourse.
-
Hsiao, Shih-Chia; Francis, Matthew B.; Bertozzi, Carolyn; Mathies, Richard; Chandra, Ravi; Douglas, Erik; Twite, Amy; Toriello, Nicholas; Onoe, Hiroaki
2016-05-03
The present invention provides conjugates of DNA and cells by linking the DNA to a native functional group on the cell surface. The cells can be without cell walls or can have cell walls. The modified cells can be linked to a substrate surface and used in assay or bioreactors.
-
Hsiao, Shih-Chia; Francis, Matthew B.; Bertozzi, Carolyn; Mathies, Richard; Chandra, Ravi; Douglas, Erik; Twite, Amy; Toriello, Nicholas; Onoe, Hiroaki
2018-05-15
The present invention provides conjugates of DNA and cells by linking the DNA to a native functional group on the cell surface. The cells can be without cell walls or can have cell walls. The modified cells can be linked to a substrate surface and used in assay or bioreactors.
-
Structure and function of nanoparticle-protein conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Aubin-Tam, M-E; Hamad-Schifferli, K
2008-01-01
Conjugation of proteins to nanoparticles has numerous applications in sensing, imaging, delivery, catalysis, therapy and control of protein structure and activity. Therefore, characterizing the nanoparticle-protein interface is of great importance. A variety of covalent and non-covalent linking chemistries have been reported for nanoparticle attachment. Site-specific labeling is desirable in order to control the protein orientation on the nanoparticle, which is crucial in many applications such as fluorescence resonance energy transfer. We evaluate methods for successful site-specific attachment. Typically, a specific protein residue is linked directly to the nanoparticle core or to the ligand. As conjugation often affects the protein structure and function, techniques to probe structure and activity are assessed. We also examine how molecular dynamics simulations of conjugates would complete those experimental techniques in order to provide atomistic details on the effect of nanoparticle attachment. Characterization studies of nanoparticle-protein complexes show that the structure and function are influenced by the chemistry of the nanoparticle ligand, the nanoparticle size, the nanoparticle material, the stoichiometry of the conjugates, the labeling site on the protein and the nature of the linkage (covalent versus non-covalent)
-
Fullerene–biomolecule conjugates and their biomedicinal applications
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yang X
2013-12-01
Full Text Available Xinlin Yang,1 Ali Ebrahimi,1 Jie Li,1,2 Quanjun Cui11Orthopaedic Research Laboratory, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA, USA; 2School of Materials Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, People's Republic of ChinaAbstract: Fullerenes are among the strongest antioxidants and are characterized as "radical sponges." The research on biomedicinal applications of fullerenes has achieved significant progress since the landmark publication by Friedman et al in 1993. Fullerene–biomolecule conjugates have become an important area of research during the past 2 decades. By a thorough literature search, we attempt to update the information about the synthesis of different types of fullerene–biomolecule conjugates, including fullerene-containing amino acids and peptides, oligonucleotides, sugars, and esters. Moreover, we also discuss in this review recently reported data on the biological and pharmaceutical utilities of these compounds and some other fullerene derivatives of biomedical importance. While within the fullerene–biomolecule conjugates, in which fullerene may act as both an antioxidant and a carrier, specific targeting biomolecules conjugated to fullerene will undoubtedly strengthen the delivery of functional fullerenes to sites of clinical interest.Keywords: fullerene, amino acid, peptide, oligonucleotide, sugar, ester
-
The Synthesis of Substituted Piperazine-cholesterol Conjugates for ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
A small library of cholesterol-piperazine conjugates were synthesized by the reaction of cholesteryl chloroformate with a set of substituted piperazines in dichloromethane at room temperature. The conjugates, all obtained in good to excellent yields, were synthesized to be key components of nucleic acid transfection ...
-
Nanostructured conjugated polymers in chemical sensors: synthesis, properties and applications.
Correa, D S; Medeiros, E S; Oliveira, J E; Paterno, L G; Mattoso, Luiz C
2014-09-01
Conjugated polymers are organic materials endowed with a π-electron conjugation along the polymer backbone that present appealing electrical and optical properties for technological applications. By using conjugated polymeric materials in the nanoscale, such properties can be further enhanced. In addition, the use of nanostructured materials makes possible miniaturize devices at the micro/nano scale. The applications of conjugated nanostructured polymers include sensors, actuators, flexible displays, discrete electronic devices, and smart fabric, to name a few. In particular, the use of conjugated polymers in chemical and biological sensors is made feasible owning to their sensitivity to the physicochemical conditions of its surrounding environment, such as chemical composition, pH, dielectric constant, humidity or even temperature. Subtle changes in these conditions bring about variations on the electrical (resistivity and capacitance), optical (absorptivity, luminescence, etc.), and mechanical properties of the conjugated polymer, which can be precisely measured by different experimental methods and ultimately associated with a specific analyte and its concentration. The present review article highlights the main features of conjugated polymers that make them suitable for chemical sensors. An especial emphasis is given to nanostructured sensors systems, which present high sensitivity and selectivity, and find application in beverage and food quality control, pharmaceutical industries, medical diagnosis, environmental monitoring, and homeland security, and other applications as discussed throughout this review.
-
Intense correlation between brain infarction and protein-conjugated acrolein.
Saiki, Ryotaro; Nishimura, Kazuhiro; Ishii, Itsuko; Omura, Tomohiro; Okuyama, Shigeru; Kashiwagi, Keiko; Igarashi, Kazuei
2009-10-01
We recently found that increases in plasma levels of protein-conjugated acrolein and polyamine oxidases, enzymes that produce acrolein, are good markers for stroke. The aim of this study was to determine whether the level of protein-conjugated acrolein is increased and levels of spermine and spermidine, the substrates of acrolein production, are decreased at the locus of infarction. A unilateral infarction was induced in mouse brain by photoinduction after injection of Rose Bengal. The volume of the infarction was analyzed using the public domain National Institutes of Health image program. The level of protein-conjugated acrolein at the locus of infarction and in plasma was measured by Western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively. The levels of polyamines at the locus of infarction and in plasma were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. The level of protein-conjugated acrolein was greatly increased, and levels of spermine and spermidine were decreased at the locus of infarction at 24 hours after the induction of stroke. The size of infarction was significantly decreased by N-acetylcysteine, a scavenger of acrolein. It was also found that the increases in the protein-conjugated acrolein, polyamines, and polyamine oxidases in plasma were observed after the induction of stroke. The results indicate that the induction of infarction is well correlated with the increase in protein-conjugated acrolein at the locus of infarction and in plasma.
-
Quantitative risk analysis of a space shuttle subsystem
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Frank, M.V.
1989-01-01
This paper reports that in an attempt to investigate methods for risk management other than qualitative analysis techniques, NASA has funded pilot study quantitative risk analyses for space shuttle subsystems. The authors performed one such study of two shuttle subsystems with McDonnell Douglas Astronautics Company. The subsystems were the auxiliary power units (APU) on the orbiter, and the hydraulic power units on the solid rocket booster. The technology and results of the APU study are presented in this paper. Drawing from a rich in-flight database as well as from a wealth of tests and analyses, the study quantitatively assessed the risk of APU-initiated scenarios on the shuttle during all phases of a flight mission. Damage states of interest were loss of crew/vehicle, aborted mission, and launch scrub. A quantitative risk analysis approach to deciding on important items for risk management was contrasted with the current NASA failure mode and effects analysis/critical item list approach
-
Optical observations geomagnetically conjugate to sprite-producing lightning discharges
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. A. Marshall
2005-09-01
Full Text Available Theoretical studies have predicted that large positive cloud-to-ground discharges can trigger a runaway avalanche process of relativistic electrons, forming a geomagnetically trapped electron beam. The beam may undergo pitch angle and energy scattering during its traverse of the Earth's magnetosphere, with a small percentage of electrons remaining in the loss cone and precipitating in the magnetically conjugate atmosphere. In particular, N2 1P and N2+1N optical emissions are expected to be observable. In July and August 2003, an attempt was made to detect these optical emissions, called "conjugate sprites", in correlation with sprite observations in Europe near . Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam. Keywords. Ionosphere (Ionsophere-magnetosphere interactions; Ionospheric disturbances; Instruments and techniques
-
Shuttle Orbiter Active Thermal Control Subsystem design and flight experience
Bond, Timothy A.; Metcalf, Jordan L.; Asuncion, Carmelo
1991-01-01
The paper examines the design of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Active Thermal Control Subsystem (ATCS) constructed for providing the vehicle and payload cooling during all phases of a mission and during ground turnaround operations. The operation of the Shuttle ATCS and some of the problems encountered during the first 39 flights of the Shuttle program are described, with special attention given to the major problems encountered with the degradation of the Freon flow rate on the Orbiter Columbia, the Flash Evaporator Subsystem mission anomalies which occurred on STS-26 and STS-34, and problems encountered with the Ammonia Boiler Subsystem. The causes and the resolutions of these problems are discussed.
-
Impact of shuttle environment on prelaunch handling of nickel-hydrogen batteries
Green, R. S.
1986-01-01
Deployment of the American Satellite Company 1 spacecraft for the Space Shuttle Discovery in August 1985 set a new milestone in nickel-hydrogen battery technology. This communications satellite is equipped with two 35 Ah nickel-hydrogen batteries and it is the first such satellite launched into orbit via the Space Shuttle. The prelaunch activities, combined with the environmental constraints onboard the Shuttle, led to the development of a new battery handling procedure. An outline of the prelaunch activities, with particular attention to battery charging, is presented.
-
Minimizing inner product data dependencies in conjugate gradient iteration
Vanrosendale, J.
1983-01-01
The amount of concurrency available in conjugate gradient iteration is limited by the summations required in the inner product computations. The inner product of two vectors of length N requires time c log(N), if N or more processors are available. This paper describes an algebraic restructuring of the conjugate gradient algorithm which minimizes data dependencies due to inner product calculations. After an initial start up, the new algorithm can perform a conjugate gradient iteration in time c*log(log(N)).
-
Covalently bound conjugates of albumin and heparin: Synthesis, fractionation and characterization
Hennink, Wim E.; Feijen, Jan; Ebert, Charles D.; Kim, Sung Wan
1983-01-01
Covalently bound conjugates of human serum albumin and heparin were prepared as compounds which could improve the blood-compatibility of polymer surfaces either by preadsorption or by covalent coupling of the conjugates onto blood contacting surfaces. The conjugates (10–16 weight % of heparin) were
-
Small angle scattering from protein/sugar conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jackson, Andrew; White, John
2006-01-01
The Maillard reaction between free amine groups on proteins and sugars is well known. We have examined the effect of the reaction of the casein group of milk proteins with sugars on their nanoscale structure and aggregation. The small angle neutron scattering from beta casein and sodium caseinate and their sugar conjugates have been studied as a function of solution concentration. At high conjugate concentration (greater than ca. 5mg/ml) the addition of sugar reduces supra-micellar aggregation of the protein whilst at lower concentration, where the protein is expected to be deaggregated already, little effect is seen. Guinier analysis of the scattering data show a radius of gyration of around 75A-bar for beta casein in solution and around 80A-bar for the sucrose conjugate
-
Small angle scattering from protein/sugar conjugates
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jackson, Andrew [Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200 (Australia)]. E-mail: ajj@nist.gov; White, John [Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200 (Australia)
2006-11-15
The Maillard reaction between free amine groups on proteins and sugars is well known. We have examined the effect of the reaction of the casein group of milk proteins with sugars on their nanoscale structure and aggregation. The small angle neutron scattering from beta casein and sodium caseinate and their sugar conjugates have been studied as a function of solution concentration. At high conjugate concentration (greater than ca. 5mg/ml) the addition of sugar reduces supra-micellar aggregation of the protein whilst at lower concentration, where the protein is expected to be deaggregated already, little effect is seen. Guinier analysis of the scattering data show a radius of gyration of around 75A-bar for beta casein in solution and around 80A-bar for the sucrose conjugate.
-
Deciphering conjugative plasmid permissiveness in wastewater microbiomes
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Jacquiod, Samuel Jehan Auguste; Brejnrod, Asker Daniel; Milani, Stefan Morberg
2017-01-01
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are designed to robustly treat polluted water. They are characterized by ceaseless flows of organic, chemical and microbial matter, followed by treatment steps before environmental release. WWTPs are hotspots of horizontal gene transfer between bacteria via...... still remains largely uncharted. Furthermore, current in vitro methods used to assess conjugation in complex microbiomes do not include in situ behaviours of recipient cells, resulting in partial understanding of transfers. We investigated the in vitro conjugation capacities of WWTP microbiomes from...... inlet sewage and outlet treated water using the broad-host range IncP-1 conjugative plasmid, pKJK5. A thorough molecular approach coupling metagenomes to 16S rRNA DNA/cDNA amplicon sequencing was established to characterize microbiomes using the ecological concept of functional response groups. A broad...
-
Cheewatanakornkool, Kamonrak; Niratisai, Sathit; Manchun, Somkamol; Dass, Crispin R; Sriamornsak, Pornsak
2017-10-15
In this paper, pectin was cross-linked by a coupling reaction with either thioglycolic acid or cystamine dihydrochloride to form thiolated pectins. The thiolated pectins were then coupled with doxorubicin (DOX) derivative to obtain thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates by two different methods, disulfide bond formation and disulfide bond exchange. The disulfide bond exchange method provided a simple, fast, and efficient approach for synthesis of thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates, compared to the disulfide bond formation. Characteristics, physicochemical properties, and morphology of thiolated pectins and thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates were determined. DOX content in thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates using low methoxy pectin was found to be higher than that using high methoxy pectin. The in vitro anticancer activity of thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates was significantly higher than that of free DOX, in mouse colon carcinoma and human bone osteosarcoma cells, but insignificantly different from that of free DOX, in human prostate cancer cells. Due to their promising anticancer activity in mouse colon carcinoma cells, the thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates might be suitable for building drug platform for colorectal cancer-targeted delivery of DOX. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Less is More: A Comparison of Antibody-Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates of Different Ratios.
Byzova, Nadezhda A; Safenkova, Irina V; Slutskaya, Elvira S; Zherdev, Anatoly V; Dzantiev, Boris B
2017-11-15
This comprehensive study is related to gold nanoparticles (GNPs) conjugated with antibodies. The goal of the study is to determine the minimal concentration of antibodies for conjugate synthesis when the conjugates have high antigen-capturing activity. Two systems were studied: gold nanoparticles conjugated with monoclonal antibodies (mAb-GNP) specific to Helicobacter pylori and gold nanoparticles conjugated with polyclonal antibodies (pAb-GNP) specific to mouse immunoglobulins. Several conjugates were synthesized with different GNP-to-antibody molar ratios (from 1:1 to 1:245) through nondirectional and noncovalent immobilization on a surface of GNPs with a diameter of 25.3 ± 4.6 nm. The maximal antigen-capturing activities and equilibrium constants of the conjugates correlate with the formation of a constant hydrodynamic radius of the conjugates for mAb-GNP (GNP to antibody molar ratio 1:58) and with the stabilizing concentration by flocculation curves for pAb-GNP (GNP to antibody molar ratio 1:116). The application of the conjugates to the lateral flow immunoassay shows that the antibody concentrations used for the conjugation can be reduced (below the stabilizing concentration) without losing activity for the mAb-GNP conjugates. The findings highlight that the optimal concentration of antibodies immobilized on the surface of GNPs is not always equal to the stabilizing concentration determined by the flocculation curve.
-
Conjugation vs hyperconjugation in molecular structure of acrolein
Shishkina, Svitlana V.; Slabko, Anzhelika I.; Shishkin, Oleg V.
2013-01-01
Analysis of geometric parameters of butadiene and acrolein reveals the contradiction between the Csp2-Csp2 bond length in acrolein and classical concept of conjugation degree in the polarized molecules. In this Letter the reasons of this contradiction have been investigated. It is concluded that the Csp2-Csp2 bond length in acrolein is determined by influence of the bonding for it π-π conjugation and antibonding n → σ∗ hyperconjugation between the oxygen lone pair and the antibonding orbital of the single bond. It was shown also this bond length depends on the difference in energy of conjugative and hyperconjugative interactions.
-
The Evolution of the Rendezvous Profile During the Space Shuttle Program
Summa, William R.
2010-01-01
The rendezvous and proximity operations approach design techniques for space shuttle missions has changed significantly during the life of the program in response to new requirements that were not part of the original mission design. The flexibility of the shuttle onboard systems design and the mission planning process has allowed the program to meet these requirements. The design of the space shuttle and the shift from docking to grappling with a robotic ann prevented use of legacy Apollo rendezvous techniques. Over the life of the shuttle program the rendezvous profile has evolved due to several factors, including lowering propellant consumption and increasing flexibility in mission planning. Many of the spacecraft that the shuttle rendezvoused with had unique requirements that drove the creation of mission-unique proximity operations. The dockings to the Russian Mir space station and International Space Station (ISS) required further evolution of rendezvous and proximity operations techniques and additional sensors to enhance crew situational awareness. After the Columbia accident, a Rendezvous Pitch Maneuver (RPM) was added to allow tile photography from ISS. Lessons learned from these rendezvous design changes are applicable to future vehicle designs and operations concepts.
-
Correlation of Space Shuttle Landing Performance with Post-Flight Cardiovascular Dysfunction
McCluskey, R.
2004-01-01
Introduction: Microgravity induces cardiovascular adaptations resulting in orthostatic intolerance on re-exposure to normal gravity. Orthostasis could interfere with performance of complex tasks during the re-entry phase of Shuttle landings. This study correlated measures of Shuttle landing performance with post-flight indicators of orthostatic intolerance. Methods: Relevant Shuttle landing performance parameters routinely recorded at touchdown by NASA included downrange and crossrange distances, airspeed, and vertical speed. Measures of cardiovascular changes were calculated from operational stand tests performed in the immediate post-flight period on mission commanders from STS-41 to STS-66. Stand test data analyzed included maximum standing heart rate, mean increase in maximum heart rate, minimum standing systolic blood pressure, and mean decrease in standing systolic blood pressure. Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated with the null hypothesis that there was no statistically significant linear correlation between stand test results and Shuttle landing performance. A correlation coefficient? 0.5 with a pcorrelations between landing performance and measures of post-flight cardiovascular dysfunction. Discussion: There was no evidence that post-flight cardiovascular stand test data correlated with Shuttle landing performance. This implies that variations in landing performance were not due to space flight-induced orthostatic intolerance.
-
Enhanced photodynamic efficacy of zinc phthalocyanine by conjugating to heptalysine.
Li, Linsen; Luo, Zhipu; Chen, Zhuo; Chen, Jincan; Zhou, Shanyong; Xu, Peng; Hu, Ping; Wang, Jundong; Chen, Naisheng; Huang, Jinling; Huang, Mingdong
2012-11-21
Zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc) is a promising photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy, but faces some challenges: ZnPc is insoluble in water and thus requires either special formulation of ZnPc by, e.g., liposome or Cremophor EL, or chemical modification of Pc ring to enhance its bioavailability and photodynamic efficacy. Here, we conjugated monosubstituted ZnPc-COOH with a series of oligolysine moieties with different numbers of lysine residues (ZnPc-(Lys)(n) (n = 1, 3, 5, 7, 9) to improve the water solubility of the ZnPc conjugates. We measured the photosensitizing efficacies and the cellular uptakes of this series of conjugates on a normal and a cancerous cell line. In addition, we developed a sensitive in situ method to distinguish the difference in photodynamic efficacy among conjugates. Our results showed that ZnPc-(Lys)(7) has the highest photodynamic efficacy compared to the other conjugates investigated.
-
NASA study backs SSTO, urges shuttle phaseout
Asker, James R.
1994-03-01
A brief discusion of a Congressionally ordered NASA study on how to meet future US Government space launch needs is presented. Three options were examined: (1) improvement ofthe Space Shuttle; (2) development of expendable launch vehicles (ELVs); and (3) development of a single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO), manned vehicle that is reusable with advanced technology. After examining the three options, it was determined that the most economical approach to space access through the year 2030 would be to develop the SSTO vehicle and phase out Space Shuttle operations within 15 years and ELVs within 20 years. Other aspects of the study's findings are briefly covered.
-
Radiation dosimetry for the space shuttle program
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jones, K.L.; Richmond, R.G.; Cash, B.L.
1985-01-01
Radiation measurements aboard the Space Shuttle are made to record crew doses for medical records, to verify analytical shielding calculations used in dose predictions and to provide dosimetry support for radiation sensitive payloads and experiments. Low cost systems utilizing thermoluminescent dosimeters, nuclear track detectors and activation foils have been developed to fulfill these requirements. Emphasis has been placed on mission planning and dose prediction. As a result, crew doses both inside the orbiter and during extra-vehicular activities have been reasonable low. Brief descriptions of the space radiation environment, dose prediction models, and radiation measurement systems are provided, along with a summary of the results for the first fourteen Shuttle flights
-
Application of the conjugate-gradient method to ground-water models
Manteuffel, T.A.; Grove, D.B.; Konikow, Leonard F.
1984-01-01
The conjugate-gradient method can solve efficiently and accurately finite-difference approximations to the ground-water flow equation. An aquifer-simulation model using the conjugate-gradient method was applied to a problem of ground-water flow in an alluvial aquifer at the Rocky Mountain Arsenal, Denver, Colorado. For this application, the accuracy and efficiency of the conjugate-gradient method compared favorably with other available methods for steady-state flow. However, its efficiency relative to other available methods depends on the nature of the specific problem. The main advantage of the conjugate-gradient method is that it does not require the use of iteration parameters, thereby eliminating this partly subjective procedure. (USGS)
-
Nonlinear propagation of phase-conjugate focused sound beams in water
Brysev, A. P.; Krutyansky, L. M.; Preobrazhensky, V. L.; Pyl'nov, Yu. V.; Cunningham, K. B.; Hamilton, M. F.
2000-07-01
Nonlinear propagation of phase-conjugate, focused, ultrasound beams is studied. Measurements are presented of harmonic amplitudes along the axis and in the focal plane of the conjugate beam, and of the waveform and spectrum at the focus. A maximum peak pressure of 3.9 MPa was recorded in the conjugate beam. The measurements are compared with simulations based on the KZK equation, and satisfactory agreement is obtained.
-
Effects of thruster firings on the shuttle's plasma and electric field environment
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Machuzak, J.S.; Burke, W.J.; Retterer, J.M.; Hunton, D.E.; Jasperse, J.R.; Smiddy, M.
1993-01-01
Simultaneous plasma and AC/DC electric field measurements taken during the space shuttle mission STS-4 at times of prolonged thruster firings are analyzed and cross correlated. Depending on the orientation of the shuttle's velocity vector to the magnetic field, ion densities and electric field wave spectra were enhanced or decreased. The systematic picture of interactions within the shuttle's plasma/neutral gas environment of Cairns and Gurnett (1991b) is confirmed and extended. Waves are excited by outgassed and thruster-ejected molecules that ionize in close proximity to the shuttle. On time scales significantly less than an ion gyroperiod, the newly created ions act as beams in the background plasma. These beams are sources of VLF waves that propagate near the shuttle and intensify during thruster firings. Plasma density depletions and/or the shuttle's geometry may hinder wave detection in the payload bay. A modified two-stream analysis indicates that beam components propagating at large angles to the magnetic field are unstable to the growth of lower hybrid waves. The beam-excited, lower hybrid waves heat some electrons to sufficient energies to produce impact ionization. Empirical evidence for other wave-growth mechanisms outside the lower-hybrid band is presented. 42 refs., 15 figs., 3 tabs
-
Repenko, Tatjana; Rix, Anne; Ludwanowski, Simon; Go, Dennis; Kiessling, Fabian; Lederle, Wiltrud; Kuehne, Alexander J C
2017-09-07
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles exhibit strong fluorescence and have been applied for biological fluorescence imaging in cell culture and in small animals. However, conjugated polymer particles are hydrophobic and often chemically inert materials with diameters ranging from below 50 nm to several microns. As such, conjugated polymer nanoparticles cannot be excreted through the renal system. This drawback has prevented their application for clinical bio-medical imaging. Here, we present fully conjugated polymer nanoparticles based on imidazole units. These nanoparticles can be bio-degraded by activated macrophages. Reactive oxygen species induce scission of the conjugated polymer backbone at the imidazole unit, leading to complete decomposition of the particles into soluble low molecular weight fragments. Furthermore, the nanoparticles can be surface functionalized for directed targeting. The approach opens a wide range of opportunities for conjugated polymer particles in the fields of medical imaging, drug-delivery, and theranostics.Conjugated polymer nanoparticles have been applied for biological fluorescence imaging in cell culture and in small animals, but cannot readily be excreted through the renal system. Here the authors show fully conjugated polymer nanoparticles based on imidazole units that can be bio-degraded by activated macrophages.
-
Optical observations geomagnetically conjugate to sprite-producing lightning discharges
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. A. Marshall
2005-09-01
Full Text Available Theoretical studies have predicted that large positive cloud-to-ground discharges can trigger a runaway avalanche process of relativistic electrons, forming a geomagnetically trapped electron beam. The beam may undergo pitch angle and energy scattering during its traverse of the Earth's magnetosphere, with a small percentage of electrons remaining in the loss cone and precipitating in the magnetically conjugate atmosphere. In particular, N2 1P and N2+1N optical emissions are expected to be observable. In July and August 2003, an attempt was made to detect these optical emissions, called "conjugate sprites", in correlation with sprite observations in Europe near
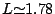 . Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam.
. Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam.
Keywords. Ionosphere (Ionsophere-magnetosphere interactions; Ionospheric disturbances; Instruments and techniques -
Space Shuttle and Hypersonic Entry
Campbell, Charles H.; Gerstenmaier, William H.
2014-01-01
Fifty years of human spaceflight have been characterized by the aerospace operations of the Soyuz, of the Space Shuttle and, more recently, of the Shenzhou. The lessons learned of this past half decade are important and very significant. Particularly interesting is the scenario that is downstream from the retiring of the Space Shuttle. A number of initiatives are, in fact, emerging from in the aftermath of the decision to terminate the Shuttle program. What is more and more evident is that a new era is approaching: the era of the commercial usage and of the commercial exploitation of space. It is probably fair to say, that this is the likely one of the new frontiers of expansion of the world economy. To make a comparison, in the last 30 years our economies have been characterized by the digital technologies, with examples ranging from computers, to cellular phones, to the satellites themselves. Similarly, the next 30 years are likely to be characterized by an exponential increase of usage of extra atmospheric resources, as a result of more economic and efficient way to access space, with aerospace transportation becoming accessible to commercial investments. We are witnessing the first steps of the transportation of future generation that will drastically decrease travel time on our Planet, and significantly enlarge travel envelope including at least the low Earth orbits. The Steve Jobs or the Bill Gates of the past few decades are being replaced by the aggressive and enthusiastic energy of new entrepreneurs. It is also interesting to note that we are now focusing on the aerospace band, that lies on top of the aeronautical shell, and below the low Earth orbits. It would be a mistake to consider this as a known envelope based on the evidences of the flights of Soyuz, Shuttle and Shenzhou. Actually, our comprehension of the possible hypersonic flight regimes is bounded within really limited envelopes. The achievement of a full understanding of the hypersonic flight
-
Space Shuttle Communications Coverage Analysis for Thermal Tile Inspection
Kroll, Quin D.; Hwu, Shian U.; Upanavage, Matthew; Boster, John P.; Chavez, Mark A.
2009-01-01
The space shuttle ultra-high frequency Space-to-Space Communication System has to provide adequate communication coverage for astronauts who are performing thermal tile inspection and repair on the underside of the space shuttle orbiter (SSO). Careful planning and quantitative assessment are necessary to ensure successful system operations and mission safety in this work environment. This study assesses communication systems performance for astronauts who are working in the underside, non-line-of-sight shadow region on the space shuttle. All of the space shuttle and International Space Station (ISS) transmitting antennas are blocked by the SSO structure. To ensure communication coverage at planned inspection worksites, the signal strength and link margin between the SSO/ISS antennas and the extravehicular activity astronauts, whose line-of-sight is blocked by vehicle structure, was analyzed. Investigations were performed using rigorous computational electromagnetic modeling techniques. Signal strength was obtained by computing the reflected and diffracted fields along the signal propagation paths between transmitting and receiving antennas. Radio frequency (RF) coverage was determined for thermal tile inspection and repair missions using the results of this computation. Analysis results from this paper are important in formulating the limits on reliable communication range and RF coverage at planned underside inspection and repair worksites.
-
HAL/S programmer's guide. [for space shuttle program
Newbold, P. M.; Hotz, R. L.
1974-01-01
This programming language was developed for the flight software of the NASA space shuttle program. HAL/S is intended to satisfy virtually all of the flight software requirements of the space shuttle. To achieve this, HAL/s incorporates a wide range of features, including applications-oriented data types and organizations, real time control mechanisms, and constructs for systems programming tasks. As the name indicates, HAL/S is a dialect of the original HAL language previously developed. Changes have been incorporated to simplify syntax, curb excessive generality, or facilitate flight code emission.
-
Shuttle performance enhancement using an uprated OMS engine
Mallini, Charles J.; Boyd, William C.
1988-01-01
The NASA Space Shuttle's Orbital Maneuvering Engine (OME) has been investigated as the basis for an enhancement of Shuttle operational flexibility. The Johnson Space Center has given attention to an upgrading of the OME through the use of a gas generator-driven turbopump to raise engine specific impulse. Hardware tests have demonstrated the projected performance gains, which will yield an enhanced, intact ascent-abort capability, as well an an improved on-orbit payload and altitude capability. Attention is given to the application of these capabilities to the Hubble Space Telescope's deployment.
-
Bromberg, Lev; Raduyk, Svetlana; Hatton, T Alan; Concheiro, Angel; Rodriguez-Valencia, Cosme; Silva, Maite; Alvarez-Lorenzo, Carmen
2009-05-20
Conjugates of linear and branched polyethyleneimine (PEI) and monoamine polyether Jeffamine M-2070 (PO/EO mol ratio 10/31, 2000 Da) were synthesized through polyether activation by cyanuric chloride followed by attachment to PEI and guanidinylation by 1H-pyrazole-carboxamidine hydrochloride. The resulting guanidinylated PEI-polyether conjugates (termed gPEI-Jeffamine) efficiently complexed plasmid DNA, and their polyplexes possessed enhanced colloidal stability in the presence of serum proteins. In vitro studies with mammalian CHO-1, 3T3, and Cos-7 cell lines demonstrated improved transfection efficiency of the pCMVbeta-gal plasmid/gPEI-Jeffamine polyplexes. The guanidinylation of the amino groups of PEI and the conjugation of PEI with the Jeffamine polyether enhanced the conjugates' interaction with genetic material and reduced the cytotoxicity of the polyplexes in experiments with the L929 cell line.
-
Space Shuttle Probabilistic Risk Assessment (SPRA) Iteration 3.2
Boyer, Roger L.
2010-01-01
The Shuttle is a very reliable vehicle in comparison with other launch systems. Much of the risk posed by Shuttle operations is related to fundamental aspects of the spacecraft design and the environments in which it operates. It is unlikely that significant design improvements can be implemented to address these risks prior to the end of the Shuttle program. The model will continue to be used to identify possible emerging risk drivers and allow management to make risk-informed decisions on future missions. Potential uses of the SPRA in the future include: - Calculate risk impact of various mission contingencies (e.g. late inspection, crew rescue, etc.). - Assessing the risk impact of various trade studies (e.g. flow control valves). - Support risk analysis on mission specific events, such as in flight anomalies. - Serve as a guiding star and data source for future NASA programs.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Møller, Thea S B; Liu, Gang; Boysen, Anders
2017-01-01
research suggests that the effect of antibiotic treatment on plasmid conjugation frequencies, and hence the spread of resistance plasmids, may have been overestimated. We addressed the question by quantifying transfer proteins and conjugation frequencies of a blaCTX-M-1 encoding IncI1 resistance plasmid....... The frequency of plasmid conjugation, measured in an antibiotic free environment, increased significantly when the donor was pre-grown in broth containing CTX compared to growth without this drug, regardless of whether blaCTX-M-1 was located on the plasmid or in trans on the chromosome. The results shows...
-
125I Radioimmunoassay of serum ursodeoxycholyl conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hill, A.; Ross, P.E.; Bouchier, I.A.D.
1983-01-01
A radioimmunoassay for serum ursodeoxycholic conjugates using an iodine-125 ligand has been developed. The bile acid was present in normal fasting serum (0.19 +- SD 0.19 μmol/l, n=24) and 2-hour post-prandial serum (0.8 +- SD 0.8 μmol/l, n=16). Gallstone patients undergoing oral ursodeoxycholic acid therapy had significantly higher post-prandial serum levels (21.5 +- SD 14.0 μmol/l, n=15) by radioimmunoassay. Gas liquid chromatography analysis indicated that in normal serum ursodeoxycholic acid was totally conjugated, whereas sera from gallstone patients contained a proportion as the free bile acid (10.2 +- SD 8.1 μmol/l, n=15). Following an oral dose of ursodeoxycholic acid, both unconjugated and conjugated forms of the bile acid appeared in the serum of healthy individuals. (Auth.)
-
Scintillation Reduction using Conjugate-Plane Imaging (Abstract)
Vander Haagen, G. A.
2017-12-01
(Abstract only) All observatories are plagued by atmospheric turbulence exhibited as star scintillation or "twinkle" whether a high altitude adaptive optics research or a 30-cm amateur telescope. It is well known that these disturbances are caused by wind and temperature-driven refractive gradients in the atmosphere and limit the ultimate photometric resolution of land-based facilities. One approach identified by Fuchs (1998) for scintillation noise reduction was to create a conjugate image space at the telescope and focus on the dominant conjugate turbulent layer within that space. When focused on the turbulent layer little or no scintillation exists. This technique is described whereby noise reductions of 6 to 11/1 have been experienced with mathematical and optical bench simulations. Discussed is a proof-of-principle conjugate optical train design for an 80-mm, f7 telescope.
-
NASTRAN analysis of the 1/8-scale space shuttle dynamic model
Bernstein, M.; Mason, P. W.; Zalesak, J.; Gregory, D. J.; Levy, A.
1973-01-01
The space shuttle configuration has more complex structural dynamic characteristics than previous launch vehicles primarily because of the high model density at low frequencies and the high degree of coupling between the lateral and longitudinal motions. An accurate analytical representation of these characteristics is a primary means for treating structural dynamics problems during the design phase of the shuttle program. The 1/8-scale model program was developed to explore the adequacy of available analytical modeling technology and to provide the means for investigating problems which are more readily treated experimentally. The basic objectives of the 1/8-scale model program are: (1) to provide early verification of analytical modeling procedures on a shuttle-like structure, (2) to demonstrate important vehicle dynamic characteristics of a typical shuttle design, (3) to disclose any previously unanticipated structural dynamic characteristics, and (4) to provide for development and demonstration of cost effective prototype testing procedures.
-
Bispecific small molecule-antibody conjugate targeting prostate cancer.
Kim, Chan Hyuk; Axup, Jun Y; Lawson, Brian R; Yun, Hwayoung; Tardif, Virginie; Choi, Sei Hyun; Zhou, Quan; Dubrovska, Anna; Biroc, Sandra L; Marsden, Robin; Pinstaff, Jason; Smider, Vaughn V; Schultz, Peter G
2013-10-29
Bispecific antibodies, which simultaneously target CD3 on T cells and tumor-associated antigens to recruit cytotoxic T cells to cancer cells, are a promising new approach to the treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Here we report a site-specific, semisynthetic method for the production of bispecific antibody-like therapeutics in which a derivative of the prostate-specific membrane antigen-binding small molecule DUPA was selectively conjugated to a mutant αCD3 Fab containing the unnatural amino acid, p-acetylphenylalanine, at a defined site. Homogeneous conjugates were generated in excellent yields and had good solubility. The efficacy of the conjugate was optimized by modifying the linker structure, relative binding orientation, and stoichiometry of the ligand. The optimized conjugate showed potent and selective in vitro activity (EC50 ~ 100 pM), good serum half-life, and potent in vivo activity in prophylactic and treatment xenograft mouse models. This semisynthetic approach is likely to be applicable to the generation of additional bispecific agents using drug-like ligands selective for other cell-surface receptors.
-
Bispecific small molecule–antibody conjugate targeting prostate cancer
Kim, Chan Hyuk; Axup, Jun Y.; Lawson, Brian R.; Yun, Hwayoung; Tardif, Virginie; Choi, Sei Hyun; Zhou, Quan; Dubrovska, Anna; Biroc, Sandra L.; Marsden, Robin; Pinstaff, Jason; Smider, Vaughn V.; Schultz, Peter G.
2013-01-01
Bispecific antibodies, which simultaneously target CD3 on T cells and tumor-associated antigens to recruit cytotoxic T cells to cancer cells, are a promising new approach to the treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Here we report a site-specific, semisynthetic method for the production of bispecific antibody-like therapeutics in which a derivative of the prostate-specific membrane antigen-binding small molecule DUPA was selectively conjugated to a mutant αCD3 Fab containing the unnatural amino acid, p-acetylphenylalanine, at a defined site. Homogeneous conjugates were generated in excellent yields and had good solubility. The efficacy of the conjugate was optimized by modifying the linker structure, relative binding orientation, and stoichiometry of the ligand. The optimized conjugate showed potent and selective in vitro activity (EC50 ∼100 pM), good serum half-life, and potent in vivo activity in prophylactic and treatment xenograft mouse models. This semisynthetic approach is likely to be applicable to the generation of additional bispecific agents using drug-like ligands selective for other cell-surface receptors. PMID:24127589
-
Synthesis and characterization of nido-carborane-cobalamin conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hogenkamp, Harry P.C.; Collins, Douglas A.; Live, David; Benson, Linda M.; Naylor, Stephen
2000-01-01
Three vitamin B 12 (cyanocobalamin) conjugates bearing one nido-carborane molecule or two nido-carborane molecules linked to the propionamide side chains via a four carbon linker have been synthesized. Reaction of o-carboranoylchloride with 1,4-diaminobutane in pyridine produced nido-carboranoyl(4-amidobutyl)amine, which was linked to the b- and d-monocarboxylic acids and the b,d-dicarboxylic acid of cyanocobalamin. Mass spectrometry analysis as well as 11 B nuclear magnetic resonance demonstrated that during the reaction of o-carboranonylchloride with diaminobutane one of the boron atoms was eliminated. In vitro biological activity of the cyanocobalamin-nido-carborane conjugates was assessed by the unsaturated vitamin B 12 binding capacity assay. When compared with 57 Co cyanocobalamin, the biological activity of cyanocobalamin-b-nido-carborane, cyanocobalamin-d-nido-carborane, and cyanocobalamin-b-d-bis-nido-carborane conjugates were 92.93%, 35.75%, and 37.02%, respectively. These findings suggest that the 10 B cobalamin conjugates might be useful agents in treating malignant tumors via neutron capture therapy
-
Shahnaz, G; Perera, G; Sakloetsakun, D; Rahmat, D; Bernkop-Schnürch, A
2010-05-21
This study was aimed at improving the mucoadhesive properties of carboxymethyl dextran by the covalent attachment of cysteine. Mediated by a carbodiimide, l-cysteine was covalently attached to the polymer. The resulting CMD-cysteine conjugate (CMD-(273) conjugate) displayed 273+/-20 micromol thiol groups per gram of polymer (mean+/-S.D.; n=3). Within 2h the viscosity of an aqueous mucus/CMD-(273) conjugate mixture pH 7.4 increased at 37 degrees C by more than 85% compared to a mucus/carboxymethyl dextran mixture indicating enlarged interactions between the mucus and the thiolated polymer. Due to the immobilization of cysteine, the swelling velocity of the polymer was significantly accelerated (ppolymer disintegrated within 15 min, whereas tablets of the CMD-(273) conjugate remained stable for 160 min (means+/-S.D.; n=3). Results from LDH and MTT assays on Caco-2 cells revealed 4.96+/-0.98% cytotoxicity and 94.1+/-0.9% cell viability for the CMD-(273) conjugate, respectively. Controlled release of model compound from CMD-(273) conjugate tablets was observed over 6h. These findings suggest that CMD-(273) conjugate is a promising novel polymer for drug delivery systems providing improved mucoadhesive and cohesive properties, greater stability and biocompatibility. Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Structure Property Relationships in Organic Conjugated Systems
O'Neill, Luke; Lynch, Patrick; McNamara, Mary
2005-01-01
A series of π conjugated oligomers were studied by absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopy. A linear relationship between the positioning of the absorption and photoluminescence maxima plotted against inverse conjugation length is observed. The relationships are in good agreement with the simple particle in a box method, one of the earliest descriptions of the properties of one-dimensional organic molecules. In addition to the electronic transition energies, it was observed that the Sto...
-
Protein carriers of conjugate vaccines: characteristics, development, and clinical trials.
Pichichero, Michael E
2013-12-01
The immunogenicity of polysaccharides as human vaccines was enhanced by coupling to protein carriers. Conjugation transformed the T cell-independent polysaccharide vaccines of the past to T cell-dependent antigenic vaccines that were much more immunogenic and launched a renaissance in vaccinology. This review discusses the conjugate vaccines for prevention of infections caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Specifically, the characteristics of the proteins used in the construction of the vaccines including CRM, tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane complex, and Hemophilus influenzae protein D are discussed. The studies that established differences among and key features of conjugate vaccines including immunologic memory induction, reduction of nasopharyngeal colonization and herd immunity, and antibody avidity and avidity maturation are presented. Studies of dose, schedule, response to boosters, of single protein carriers with single and multiple polysaccharides, of multiple protein carriers with multiple polysaccharides and conjugate vaccines administered concurrently with other vaccines are discussed along with undesirable consequences of conjugate vaccines. The clear benefits of conjugate vaccines in improving the protective responses of the immature immune systems of young infants and the senescent immune systems of the elderly have been made clear and opened the way to development of additional vaccines using this technology for future vaccine products.
-
Space Shuttle dosimetry measurements with RME-III
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hardy, K.A.; Golightly, M.J.; Hardy, A.C.; Atwell, W.; Quam, W.
1991-10-01
A description of the radiation monitoring equipment (RME-III) dosimetry instrument and the results obtained from six Space Shuttle flights are presented. The RME-III is a self-contained, active (real-time), portable dosimeter system developed for the USAF and adapted for utilization in measuring the ionizing radiation environment on the Space Shuttle. This instrument was developed to incorporate the capabilities of two earlier radiation instruments into a single unit and to minimize crew interaction times with longer battery life and expanded memory capacity. Flight data has demonstrated that the RME-III can be used to accurately assess dose from various sources of exposure, such as that encountered in the complex radiation environment of space
-
Demonstration of conjugated dopamine in monkey CSF by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Elchisak, M A; Powers, K H; Ebert, M H
1982-09-01
A method for measuring unconjugated and conjugated dopamine in body tissues and fluids is described. Conjugated dopamine was hydrolyzed in acid to unconjugated dopamine, separated from the sample matrix by alumina chromatography, and assayed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Conjugated dopamine was detected in greater concentrations than unconjugated dopamine in CSF taken from lateral ventricle or thecal sac of the Rhesus monkey. Haloperidol administration did not increase the levels of conjugated dopamine in lumbar CSF.
-
Social behaviour and decision making in bacterial conjugation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Günther eKoraimann
2014-04-01
Full Text Available Bacteria frequently acquire novel genes by HGT (horizontal gene transfer. HGT through the process of bacterial conjugation is highly efficient and depends on the presence of conjugative plasmids (CPs or integrated conjugative elements (ICEs that provide the necessary genes for DNA transmission. This review focuses on recent advancements in our understanding of ssDNA transfer systems and regulatory networks ensuring timely and spatially controlled DNA transfer (tra gene expression. As will become obvious by comparing different systems, by default, tra genes are shut off in cells in which conjugative elements are present. Only when conditions are optimal, donor cells – through epigenetic alleviation of negatively acting roadblocks and direct stimulation of DNA transfer genes – become transfer competent. These transfer competent cells have developmentally transformed into specialized cells capable of secreting ssDNA via a T4S (type IV secretion complex directly into recipient cells. Intriguingly, even under optimal conditions, only a fraction of the population undergoes this transition, a finding that indicates specialization and cooperative, social behavior. Thereby, at the population level, the metabolic burden and other negative consequences of tra gene expression are greatly reduced without compromising the ability to horizontally transfer genes to novel bacterial hosts. This undoubtedly intelligent strategy may explain why conjugative elements – CPs and ICEs – have been successfully kept in and evolved with bacteria to constitute a major driving force of bacterial evolution.
-
Factors contributing to the immunogenicity of meningococcal conjugate vaccines
Bröker, Michael; Berti, Francesco; Costantino, Paolo
2016-01-01
ABSTRACT Various glycoprotein conjugate vaccines have been developed for the prevention of invasive meningococcal disease, having significant advantages over pure polysaccharide vaccines. One of the most important features of the conjugate vaccines is the induction of a T-cell dependent immune response, which enables both the induction of immune memory and a booster response after repeated immunization. The nature of the carrier protein to which the polysaccharides are chemically linked, is often regarded as the main component of the vaccine in determining its immunogenicity. However, other factors can have a significant impact on the vaccine's profile. In this review, we explore the physico-chemical properties of meningococcal conjugate vaccines, which can significantly contribute to the vaccine's immunogenicity. We demonstrate that the carrier is not the sole determining factor of the vaccine's profile, but, moreover, that the conjugate vaccine's immunogenicity is the result of multiple physico-chemical structures and characteristics. PMID:26934310
-
Assembling and supplying the ISS the space shuttle fulfills its mission
Shayler, David J
2017-01-01
The creation and utilization of the International Space Station (ISS) is a milestone in space exploration. But without the Space Shuttle, it would have remained an impossible dream. Assembling and Supplying the ISS is the story of how, between 1998 and 2011, the Shuttle became the platform which enabled the construction and continued operation of the primary scientific research facility in Earth orbit. Fulfilling an objective it had been designed to complete decades before, 37 Shuttle missions carried the majority of the hardware needed to build the ISS and then acted as a ferry and supply train for early resident crews to the station. Building upon the decades of development and experience described in the companion volume Linking the Space Shuttle and Space Stations: Early Docking Technologies from Concept to Implementation, this book explores • a purpose-built hardware processing facility • challenging spacewalking objectives • extensive robotic operations • undocking a unmanned orbiter The experie...
-
Efficient conjugate gradient algorithms for computation of the manipulator forward dynamics
Fijany, Amir; Scheid, Robert E.
1989-01-01
The applicability of conjugate gradient algorithms for computation of the manipulator forward dynamics is investigated. The redundancies in the previously proposed conjugate gradient algorithm are analyzed. A new version is developed which, by avoiding these redundancies, achieves a significantly greater efficiency. A preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm is also presented. A diagonal matrix whose elements are the diagonal elements of the inertia matrix is proposed as the preconditioner. In order to increase the computational efficiency, an algorithm is developed which exploits the synergism between the computation of the diagonal elements of the inertia matrix and that required by the conjugate gradient algorithm.
-
To orbit and back again how the space shuttle flew in space
Sivolella, Davide
2014-01-01
The question may be simple, but the answer is not as easy to give. This book describes the structures and systems used each time the Shuttle was launched, and then follows an imaginary mission, explaining how those structures and systems were used in orbital operations and the return to Earth. Details of how anomalous events were dealt with on individual missions are also provided, as are the recollections of those who built and flew the Shuttle. Highly illustrated with many diagrams, photographs and technical drawings, To Orbit and Back Again • focuses on the engineering aspects of the Shuttle • describes the systems and subsystems in clear, non-technical terms • brings to the fore the design work behind the Space Shuttle and the mission itself. .
-
Functional Hybrid Biomaterials based on Peptide-Polymer Conjugates for Nanomedicine
Shu, Jessica Yo
The focus of this dissertation is the design, synthesis and characterization of hybrid functional biomaterials based on peptide-polymer conjugates for nanomedicine. Generating synthetic materials with properties comparable to or superior than those found in nature has been a "holy grail" for the materials community. Man-made materials are still rather simplistic when compared to the chemical and structural complexity of a cell. Peptide-polymer conjugates have the potential to combine the advantages of the biological and synthetic worlds---that is they can combine the precise chemical structure and diverse functionality of biomolecules with the stability and processibility of synthetic polymers. As a new family of soft matter, they may lead to materials with novel properties that have yet to be realized with either of the components alone. In order for peptide-polymer conjugates to reach their full potential as useful materials, the structure and function of the peptide should be maintained upon polymer conjugation. The success in achieving desirable, functional assemblies relies on fundamentally understanding the interactions between each building block and delicately balancing and manipulating these interactions to achieve targeted assemblies without interfering with designed structures and functionalities. Such fundamental studies of peptide-polymer interactions were investigated as the nature of the polymer (hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic) and the site of its conjugation (end-conjugation vs. side-conjugation) were varied. The fundamental knowledge gained was then applied to the design of amphiphiles that self-assemble to form stable functional micelles. The micelles exhibited exceptional monodispersity and long-term stability, which is atypical of self-assembled systems. Thus such micelles based on amphiphilic peptide-polymer conjugates may meet many current demands in nanomedicine, in particular for drug delivery of hydrophobic anti-cancer therapeutics. Lastly
-
Space Shuttle Status News Conference
2005-01-01
Richard Gilbech, External Tank "Tiger Team" Lead, begins this space shuttle news conference with detailing the two major objectives of the team. The objectives include: 1) Finding the root cause of the foam loss on STS-114; and 2) Near and long term improvements for the external tank. Wayne Hale, Space Shuttle Program Manager, presents a chart to explain the external tank foam loss during STS-114. He gives a possible launch date for STS-121 after there has been a repair to the foam on the External Tank. He further discusses the changes that need to be made to the surrounding areas of the plant in New Orleans, due to Hurricane Katrina. Bill Gerstemaier, NASA Associate Administrator for Space Operations, elaborates on the testing of the external tank foam loss. The discussion ends with questions from the news media about a fix for the foam, replacement of the tiles, foam loss avoidance, the root cause of foam loss and a possible date for a new external tank to be shipped to NASA Kennedy Space Center.
-
Preparation and characterization of microspheres of albumin-heparin conjugates
Kwon, Glen S.; Bae, You Han; Kim, Sung Wan; Cremers, Harry; Cremers, H.F.M.; Feijen, Jan
1991-01-01
Albumin-heparin microspheres have been prepared as a new drug carrier. A soluble albumin-heparin conjugate was synthesized by forming amide bonds between human serum albumin and heparin. After purification the albumin-heparin conjugate was crosslinked in a water-in-oil emulsion to form
-
Phase-conjugate optical coherence tomography
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Erkmen, Baris I.; Shapiro, Jeffrey H.
2006-01-01
Quantum optical coherence tomography (Q-OCT) offers a factor-of-2 improvement in axial resolution and the advantage of even-order dispersion cancellation when it is compared to conventional OCT (C-OCT). These features have been ascribed to the nonclassical nature of the biphoton state employed in the former, as opposed to the classical state used in the latter. Phase-conjugate OCT (PC-OCT) shows that nonclassical light is not necessary to reap Q-OCT's advantages. PC-OCT uses classical-state signal and reference beams, which have a phase-sensitive cross correlation, together with phase conjugation to achieve the axial resolution and even-order dispersion cancellation of Q-OCT with a signal-to-noise ratio that can be comparable to that of C-OCT
-
Modern methods for the synthesis of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zubin, Evgenii M; Oretskaya, Tat'yana S; Romanova, Elena A
2002-01-01
The published data on the methods of chemical solution and solid-phase synthesis of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates are reviewed. The known methods are systematised and their advantages and disadvantages are considered. The approaches to the solution synthesis of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates are systematised according to the type of chemical bonds between the fragments, whereas those to the solid-phase synthesis are classified according to the procedure used for the preparation of conjugates, viz., stepwise elongation of oligonucleotide and peptide chains on the same polymeric support or solid-phase condensation of two presynthesised fragments. The bibliography includes 141 references.
-
Perfect lensing with phase-conjugating surfaces: toward practical realization
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Maslovski, Stanislav; Tretyakov, Sergei
2012-01-01
It is theoretically known that a pair of phase-conjugating surfaces can function as a perfect lens, focusing propagating waves and enhancing evanescent waves. However, the known experimental approaches based on thin sheets of nonlinear materials cannot fully realize the required phase conjugation boundary condition. In this paper, we show that the ideal phase-conjugating surface is, in principle, physically realizable and investigate the necessary properties of nonlinear and nonreciprocal particles which can be used to build a perfect lens system. The physical principle of the lens operation is discussed in detail and directions of possible experimental realizations are outlined. (paper)
-
[Role of proton-motive force in the conjugative DNA transport in Staphylococci].
Gavriliuk, V G; Vinnikov, A I
1997-01-01
Sensitivity of the conjugative process in staphylococci to the action of uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation and inhibitors of electron transport systems have been proved, that testifies to the energy-dependent character of conjugative transport of DNA. Proceeding of the conjugation process depends upon the generation of delta microH+ on the membrane of both the donor and recipient cells. contribution of protonmotive forces to providing for the transfer of plasmids during conjugation to staphylococci has been defined.
-
Launch Vehicle Demonstrator Using Shuttle Assets
Threet, Grady E., Jr.; Creech, Dennis M.; Philips, Alan D.; Water, Eric D.
2011-01-01
The Marshall Space Flight Center Advanced Concepts Office (ACO) has the leading role for NASA s preliminary conceptual launch vehicle design and performance analysis. Over the past several years the ACO Earth-to-Orbit Team has evaluated thousands of launch vehicle concept variations for a multitude of studies including agency-wide efforts such as the Exploration Systems Architecture Study (ESAS), Constellation, Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle (HLLV), Heavy Lift Propulsion Technology (HLPT), Human Exploration Framework Team (HEFT), and Space Launch System (SLS). NASA plans to continue human space exploration and space station utilization. Launch vehicles used for heavy lift cargo and crew will be needed. One of the current leading concepts for future heavy lift capability is an inline one and a half stage concept using solid rocket boosters (SRB) and based on current Shuttle technology and elements. Potentially, the quickest and most cost-effective path towards an operational vehicle of this configuration is to make use of a demonstrator vehicle fabricated from existing shuttle assets and relying upon the existing STS launch infrastructure. Such a demonstrator would yield valuable proof-of-concept data and would provide a working test platform allowing for validated systems integration. Using shuttle hardware such as existing RS-25D engines and partial MPS, propellant tanks derived from the External Tank (ET) design and tooling, and four-segment SRB s could reduce the associated upfront development costs and schedule when compared to a concept that would rely on new propulsion technology and engine designs. There are potentially several other additional benefits to this demonstrator concept. Since a concept of this type would be based on man-rated flight proven hardware components, this demonstrator has the potential to evolve into the first iteration of heavy lift crew or cargo and serve as a baseline for block upgrades. This vehicle could also serve as a demonstration
-
PREPARATION OF CHEMICALLY WELL-DEFINED CARBOHYDRATE DENDRIMER CONJUGATES
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
2004-01-01
A method for the synthesis of dendrimer conjugates having a well-defined chemical structure, comprising one or more carbohydrate moieties and one or more immunomodulating substances coupled to a dendrimer, is presented. First, the carbohydrate is bound to the dendrimer in a chemoselective manner...... conjugates and their use in vaccination, production of antibodies, high throughput screening, diagnostic assays and libraries....
-
Thermal Stability of siRNA Modulates Aptamer- conjugated siRNA Inhibition
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Alexey Berezhnoy
2012-01-01
Full Text Available Oligonucleotide aptamer-mediated in vivo cell targeting of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs is emerging as a useful approach to enhance the efficacy and reduce the adverse effects resulting from siRNA-mediated genetic interference. A current main impediment in aptamer-mediated siRNA targeting is that the activity of the siRNA is often compromised when conjugated to an aptamer, often requiring labor intensive and time consuming design and testing of multiple configurations to identify a conjugate in which the siRNA activity has not been significantly reduced. Here, we show that the thermal stability of the siRNA is an important parameter of siRNA activity in its conjugated form, and that siRNAs with lower melting temperature (Tm are not or are minimally affected when conjugated to the 3′ end of 2′F-pyrimidine-modified aptamers. In addition, the configuration of the aptamer-siRNA conjugate retains activity comparable with the free siRNA duplex when the passenger strand is co-transcribed with the aptamer and 3′ overhangs on the passenger strand are removed. The approach described in this paper significantly reduces the time and effort necessary to screening siRNA sequences that retain biological activity upon aptamer conjugation, facilitating the process of identifying candidate aptamer-siRNA conjugates suitable for in vivo testing.
-
Dual peptide conjugation strategy for improved cellular uptake and mitochondria targeting.
Lin, Ran; Zhang, Pengcheng; Cheetham, Andrew G; Walston, Jeremy; Abadir, Peter; Cui, Honggang
2015-01-21
Mitochondria are critical regulators of cellular function and survival. Delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic agents into mitochondria is a challenging task in modern pharmacology because the molecule to be delivered needs to first overcome the cell membrane barrier and then be able to actively target the intracellular organelle. Current strategy of conjugating either a cell penetrating peptide (CPP) or a subcellular targeting sequence to the molecule of interest only has limited success. We report here a dual peptide conjugation strategy to achieve effective delivery of a non-membrane-penetrating dye 5-carboxyfluorescein (5-FAM) into mitochondria through the incorporation of both a mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) and a CPP into one conjugated molecule. Notably, circular dichroism studies reveal that the combined use of α-helix and PPII-like secondary structures has an unexpected, synergistic contribution to the internalization of the conjugate. Our results suggest that although the use of positively charged MTS peptide allows for improved targeting of mitochondria, with MTS alone it showed poor cellular uptake. With further covalent linkage of the MTS-5-FAM conjugate to a CPP sequence (R8), the dually conjugated molecule was found to show both improved cellular uptake and effective mitochondria targeting. We believe these results offer important insight into the rational design of peptide conjugates for intracellular delivery.
-
Peptide-conjugated micelles as a targeting nanocarrier for gene delivery
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lin, Wen Jen, E-mail: wjlin@ntu.edu.tw; Chien, Wei Hsuan [National Taiwan University, School of Pharmacy, Graduate Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences (China)
2015-09-15
The aim of this study was to develop peptide-conjugated micelles possessing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) targeting ability for gene delivery. A sequence-modified dodecylpeptide, GE11(2R), with enhancing EGF receptor binding affinity, was applied in this study as a targeting ligand. The active targeting micelles were composed of poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)-poly(ethylene glycol) (PLGA-PEG) copolymer conjugated with GE11(2R)-peptide. The particle sizes of peptide-free and peptide-conjugated micelles were 277.0 ± 5.1 and 308.7 ± 14.5 nm, respectively. The peptide-conjugated micelles demonstrated the cellular uptake significantly higher than peptide-free micelles in EGFR high-expressed MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells due to GE11(2R)-peptide specificity. Furthermore, the peptide-conjugated micelles were able to encapsulate plasmid DNA and expressed cellular transfection higher than peptide-free micelles in EGFR high-expressed cells. The EGFR-targeting delivery micelles enhanced DNA internalized into cells and achieved higher cellular transfection in EGFR high-expressed cells.
-
Nanostructured Conjugated Polymers for Energy-Related Applications beyond Solar Cells.
Xie, Jian; Zhao, Cui-E; Lin, Zong-Qiong; Gu, Pei-Yang; Zhang, Qichun
2016-05-20
To meet the ever-increasing requirements for the next generation of sustainable and versatile energy-related devices, conjugated polymers, which have potential advantages over small molecules and inorganic materials, are among the most promising types of green candidates. The properties of conjugated polymers can be tuned through modification of the structure and incorporation of different functional moieties. In addition, superior performances can be achieved as a result of the advantages of nanostructures, such as their large surface areas and the shortened pathways for charge transfer. Therefore, nanostructured conjugated polymers with different properties can be obtained to be applied in different energy-related organic devices. This review focuses on the application and performance of the recently reported nanostructured conjugated polymers for high-performance devices, including rechargeable lithium batteries, microbial fuel cells (MFCs), thermoelectric generators, and photocatalytic systems. The design strategies, reaction mechanisms, advantages, and limitations of nanostructured conjugated polymers are further discussed in each section. Finally, possible routes to improve the performances of the current systems are also included in the conclusion. © 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Balieiro, M. G.; Martini, P. R.; Dossantos, J. R.; Demattos, J. T.
1984-01-01
The ground observations undertaken over the northern position of Minas Gerais State, and part of Distrito Federal from 7 to 12 December 1982, along the Space Shuttle 2 flying orbit 22 of November 1981 are described. Field data related mostly with lithology, geological structures and forest cover, and specific geomorphological and pedological aspects were collected. Ground data are applied to evaluate the SIR-A Experiment, developed in the Space Shuttle-2 mission for natural resources mapping and prospecting.
-
Women experiencing the intergenerationality of conjugal violence
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gilvânia Patrícia do Nascimento Paixão
2015-10-01
Full Text Available Objective: to analyze the family relationship, in childhood and adolescence, of women who experience conjugal violence.Method: qualitative study. Interviews were held with 19 women, who were experiencing conjugal violence, and who were resident in a community in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. The project was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (N. 42/2011.Results: the data was organized using the Discourse of the Collective Subject, identifying the summary central ideas: they witnessed violence between their parents; they suffered repercussions from the violence between their parents: they were angry about the mother's submission to her partner; and they reproduced the conjugal violence. The discourse showed that the women witnessed, in childhood and adolescence, violence between their parents, and were injured both physically and psychologically. As a result of the mother's submission, feelings of anger arose in the children. However, in the adult phase of their own lives, they noticed that their conjugal life resembled that of their parents, reproducing the violence.Conclusion: investment is necessary in strategies designed to break inter-generational violence, and the health professionals are important in this process, as it is a phenomenon with repercussions in health. Because they work in the Family Health Strategy, which focuses on the prevention of harm and illness, health promotion and interdepartmentality, the nurses are essential in the process of preventing and confronting this phenomenon.
-
A nanodiamond-fluorescein conjugate for cell studies
Pedroso-Santana, Seidy; Fleitas-Salazar, Noralvis; Sarabia-Sainz, Andrei; Silva-Campa, Erika; Burgara-Estrella, Alexel; Angulo-Molina, Aracely; Melendrez, Rodrigo; Pedroza-Montero, Martin; Riera, Raul
2018-03-01
The use of nanodiamonds in studies with living systems generally involves the modification of their surfaces with functional groups. Fluorescent molecules can be attached to these groups, so that one can know the exact position of the particles in each moment of the interaction with the cells. Here we modify the surface of detonation nanodiamonds and nitrogen-vacancy center nanodiamonds using carboxylation and hydroxylation procedures. Subsequent reactions with silicates and cysteine, before addition of fluorescein allow to obtain fluorescent nano-conjugates. We used confocal microscopy to observe the position of nanodiamonds interacting with HeLa cells. At 3 h post-incubation the green fluorescence is localized in extracellular rounded like-vesicles assemblies while at 24 h the conjugates can be observed inside the cells. The measurement of the fluorescence emitted by both conjugates allowed to find an enhanced emission of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) when the nitrogen-vacancy center is present. We propose the existence of a fluorescence enhancement by electron transference process. The procedure described in this work allows the functionalization of nanodiamonds with FITC and other molecules using functional surface groups and small size mediators. Also, as was proved in our work, the nanodiamond-fluorescein conjugates can be used to track nanoparticles position within the cell. Localization studies are particularly important for drug delivery applications of nanodiamonds.
-
21 CFR 862.1115 - Urinary bilirubin and its conjugates (nonquantitative) test system.
2010-04-01
... 21 Food and Drugs 8 2010-04-01 2010-04-01 false Urinary bilirubin and its conjugates... Clinical Chemistry Test Systems § 862.1115 Urinary bilirubin and its conjugates (nonquantitative) test system. (a) Identification. A urinary bilirubin and its conjugates (nonquantitative) test system is a...
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kim, Eun-Kyung; Shrestha, Nabeen K. [Department of Chemistry, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791 (Korea, Republic of); Lee, Wonjoo [Department of Chemistry, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791 (Korea, Republic of); Department of Defense Ammunitions, Daeduk College, Daejeon 305-715 (Korea, Republic of); Cai, Gangri, E-mail: caigangri@naver.com [Department of Applied Chemistry, TianJin University of Technology, Tianjin 300384 (China); Department of Chemistry, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791 (Korea, Republic of); Han, Sung-Hwan, E-mail: shhan@hanyang.ac.kr [Department of Chemistry, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791 (Korea, Republic of)
2015-04-01
Manganese dioxide (MnO{sub 2}) thin films are deposited electrochemically on an indium–tin-oxide (ITO) electrode using aqueous bath in presence of conjugated water soluble sulfonated polyaniline (SPAN) or a non-conjugated polyacrylic acid (PAA) polyelectrolyte surfactant. The surface morphology and nature of the electrodeposited MnO{sub 2} films are found to be influenced strongly by the amount and type of polyelectrolyte in the deposition bath. Increasing the SPAN concentration, a porous structure resulting from the reduction of voids between the MnO{sub 2} nano-flakes is obtained. In contrast, by increasing the PAA concentration, dense and spherical MnO{sub 2} nanostructures have been deposited. These results may be caused by initiation of different kinetics and orientation of nucleation of MnO{sub 2} deposits on ITO surface in presence of different types of polyelectrolytes. Cyclic voltammetry study of these films shows the supercapacitor behavior. The porous MnO{sub 2} films grown from the SPAN containing electrolyte demonstrates a specific capacitance of 368.53 F/g at scan rate of 10 mV/s, which is approximately 10 times higher (i.e., 30.29 F/g) than that of the spherical MnO{sub 2} dense films grown from PAA containing electrolyte. - Highlights: • Conjugated/non-conjugated polyelectrolytes were used in deposition of MnO{sub 2}. • The two kinds of MnO{sub 2} film showed entirely different morphology. • Conjugated polyelectrolyte worked as template and also affected the growth rate. • Non-conducting polyelectrolyte could work as template but hindered MnO{sub 2} growth. • The specific capacitance of MnO{sub 2}–S was 10 times higher than MnO{sub 2}–P.
-
Space shuttle operations integration plan
1975-01-01
The Operations Integration Plan is presented, which is to provide functional definition of the activities necessary to develop and integrate shuttle operating plans and facilities to support flight, flight control, and operations. It identifies the major tasks, the organizations responsible, their interrelationships, the sequence of activities and interfaces, and the resultant products related to operations integration.
-
Peptide- and saccharide-conjugated dendrimers for targeted drug delivery: a concise review
Liu, Jie; Gray, Warren D.; Davis, Michael E.; Luo, Ying
2012-01-01
Dendrimers comprise a category of branched materials with diverse functions that can be constructed with defined architectural and chemical structures. When decorated with bioactive ligands made of peptides and saccharides through peripheral chemical groups, dendrimer conjugates are turned into nanomaterials possessing attractive binding properties with the cognate receptors. At the cellular level, bioactive dendrimer conjugates can interact with cells with avidity and selectivity, and this function has particularly stimulated interests in investigating the targeting potential of dendrimer materials for the design of drug delivery systems. In addition, bioactive dendrimer conjugates have so far been studied for their versatile capabilities to enhance stability, solubility and absorption of various types of therapeutics. This review presents a brief discussion on three aspects of the recent studies to use peptide- and saccharide-conjugated dendrimers for drug delivery: (i) synthesis methods, (ii) cell- and tissue-targeting properties and (iii) applications of conjugated dendrimers in drug delivery nanodevices. With more studies to elucidate the structure–function relationship of ligand–dendrimer conjugates in transporting drugs, the conjugated dendrimers hold promise to facilitate targeted delivery and improve drug efficacy for discovery and development of modern pharmaceutics. PMID:23741608
-
Rapid modification of retroviruses using lipid conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mukherjee, Nimisha G; Le Doux, Joseph M; Andrew Lyon, L
2009-01-01
Methods are needed to manipulate natural nanoparticles. Viruses are particularly interesting because they can act as therapeutic cellular delivery agents. Here we examine a new method for rapidly modifying retroviruses that uses lipid conjugates composed of a lipid anchor (1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine), a polyethylene glycol chain, and biotin. The conjugates rapidly and stably modified retroviruses and enabled them to bind streptavidin. The implication of this work for modifying viruses for gene therapy and vaccination protocols is discussed.
-
CONJUGATED POLYMERS AND POLYELECTROLYTES IN SOLAR PHOTOCONVERSION, Final Technical Report
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Schanze, Kirk S [University of Florida
2014-08-05
This DOE-supported program investigated the fundamental properties of conjugated polyelectrolytes, with emphasis placed on studies of excited state energy transport, self-assembly into conjugated polyelectroyte (CPE) based films and colloids, and exciton transport and charge injection in CPE films constructed atop wide bandgap semiconductors. In the most recent grant period we have also extended efforts to examine the properties of low-bandgap donor-acceptor conjugated polyelectrolytes that feature strong visible light absorption and the ability to adsorb to metal-oxide interfaces.
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Water-soluble Conjugates of Cabazitaxel Hemiesters-Dextran.
Parhizkar, Elahehnaz; Ahmadi, Fatemeh; Daneshamouz, Saeid; Mohammadi-Samani, Soliman; Sakhteman, Amirhossein; Parhizkar, Golnaz
2017-11-24
Cabazitaxel (CTX) is a second- generation taxane derivative, a class of potent anticancer drugs with very low water solubility. CTX is used in patients with resistant prostate cancer unresponsive to the first generation taxane, docetaxel. Currently marketed formulations of CTX contain high concentrations of surfactant and ethanol, which cause severe hypersensitivity reactions in patients. In order to increase its solubility, two hemiester analogs; CTX-succinate and CTX-glutarate were synthesized and characterized. To improve the solubility of hemiesters even more, dextran as a biocompatible polymer was also conjugated to hemiester analogs. MTT assay was performed on MCF-7 cell line to evaluate the cytotoxicity effect of hemiesters and conjugates. Based on the results, hemiester analogs increased water solubility of the drug up to about 3 and 8 fold. Conjugation to dextran enhanced the CTX solubility to more than 1500 fold. These conjugates released the conjugated CTX in less than 24 hours in a pH dependent manner and showed proper hemocompatibility characteristics. The hemiesters had approximately similar cytotoxicity in comparison with CTX and the dextran conjugates showed higher cytotoxicity effect on MCF-7 cell line. Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
-
Hemoglobin Detection on a Microfluidic Sensor Chip with a Partially Conjugated Polymer
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Eo, Soo Han; Won, Kwang Jae; Song, Simon; Yoon, Bora; Kim, Jong Man
2010-01-01
The development of efficient chemosensors based on the conjugated polymers has been the central focus of a large number of recent research programs. The presence of extensively delocalized electrons and conformational restrictions of the backbone structures make conjugated polymers attractive sensory materials. In these polymers, molecular recognition events influence electronic absorption and emission properties. Thus, a wide variety of conjugated polymer-based sensors have been investigated. However, the majority of the conjugated polymer sensors described to date have been explored in the form of solutions or thin films. Most biologically interesting target molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, or ions, are only soluble in water. Thus, it is desirable to use water-soluble conjugated polymers as sensor matrices. In general, in order to make water-soluble conjugated polymers tedious procedures are required since most synthetic methods developed for this purpose are incompatible with sidechain functionalities. Accordingly, protecting group strategies are required to prepare polymers with requisite functional groups that foster water solubility
-
Diclofenac in Arabidopsis cells: Rapid formation of conjugates.
Fu, Qiuguo; Ye, Qingfu; Zhang, Jianbo; Richards, Jaben; Borchardt, Dan; Gan, Jay
2017-03-01
Pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) are continuously introduced into the soil-plant system, through practices such as agronomic use of reclaimed water and biosolids containing these trace contaminants. Plants may accumulate PPCPs from soil, serving as a conduit for human exposure. Metabolism likely controls the final accumulation of PPCPs in plants, but is in general poorly understood for emerging contaminants. In this study, we used diclofenac as a model compound, and employed 14 C tracing, and time-of-flight (TOF) and triple quadruple (QqQ) mass spectrometers to unravel its metabolism pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana cells. We further validated the primary metabolites in Arabidopsis seedlings. Diclofenac was quickly taken up into A. thaliana cells. Phase I metabolism involved hydroxylation and successive oxidation and cyclization reactions. However, Phase I metabolites did not accumulate appreciably; they were instead rapidly conjugated with sulfate, glucose, and glutamic acid through Phase II metabolism. In particular, diclofenac parent was directly conjugated with glutamic acid, with acyl-glutamatyl-diclofenac accounting for >70% of the extractable metabolites after 120-h incubation. In addition, at the end of incubation, >40% of the spiked diclofenac was in the non-extractable form, suggesting extensive sequestration into cell matter. The rapid formation of non-extractable residue and dominance of diclofenac-glutamate conjugate uncover previously unknown metabolism pathways for diclofenac. In particular, the rapid conjugation of parent highlights the need to consider conjugates of emerging contaminants in higher plants, and their biological activity and human health implications. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Conjugate Meningococcal Vaccines Development: GSK Biologicals Experience
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jacqueline M. Miller
2011-01-01
Full Text Available Meningococcal diseases are serious threats to global health, and new vaccines specifically tailored to meet the age-related needs of various geographical areas are required. This paper focuses on the meningococcal conjugate vaccines developed by GSK Biologicals. Two combined conjugate vaccines were developed to help protect infants and young children in countries where the incidence of meningococcal serogroup C or serogroup C and Y disease is important: Hib-MenC-TT vaccine, which offers protection against Haemophilus influenzae type b and Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C diseases, is approved in several countries; and Hib-MenCY-TT vaccine, which adds N. meningitidis serogroup Y antigen, is currently in the final stages of development. Additionally, a tetravalent conjugate vaccine (MenACWY-TT designed to help protect against four meningococcal serogroups is presently being evaluated for global use in all age groups. All of these vaccines were shown to be highly immunogenic and to have clinically acceptable safety profiles.
-
Conjugate Meningococcal Vaccines Development: GSK Biologicals Experience
Miller, Jacqueline M.; Mesaros, Narcisa; Van Der Wielen, Marie; Baine, Yaela
2011-01-01
Meningococcal diseases are serious threats to global health, and new vaccines specifically tailored to meet the age-related needs of various geographical areas are required. This paper focuses on the meningococcal conjugate vaccines developed by GSK Biologicals. Two combined conjugate vaccines were developed to help protect infants and young children in countries where the incidence of meningococcal serogroup C or serogroup C and Y disease is important: Hib-MenC-TT vaccine, which offers protection against Haemophilus influenzae type b and Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C diseases, is approved in several countries; and Hib-MenCY-TT vaccine, which adds N. meningitidis serogroup Y antigen, is currently in the final stages of development. Additionally, a tetravalent conjugate vaccine (MenACWY-TT) designed to help protect against four meningococcal serogroups is presently being evaluated for global use in all age groups. All of these vaccines were shown to be highly immunogenic and to have clinically acceptable safety profiles. PMID:21991444
-
Degradable conjugated polymers for the selective sorting of semiconducting carbon nanotubes
Gopalan, Padma; Arnold, Michael Scott; Kansiusarulsamy, Catherine Kanimozhi; Brady, Gerald Joseph; Shea, Matthew John
2018-04-10
Conjugated polymers composed of bi-pyridine units linked to 9,9-dialkyl fluorenyl-2,7-diyl units via imine linkages along the polymer backbone are provided. Also provided are semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes coated with the conjugated polymers and methods of sorting and separating s-SWCNTs from a sample comprising a mixture of s-SWCNTs and metallic single-walled carbon nanotubes using the conjugated polymers.
-
Firth, David; Bell, Leonard; Squires, Martin; Estdale, Sian; McKee, Colin
2015-09-15
We present the demonstration of a rapid "middle-up" liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS)-based workflow for use in the characterization of thiol-conjugated maleimidocaproyl-monomethyl auristatin F (mcMMAF) and valine-citrulline-monomethyl auristatin E (vcMMAE) antibody-drug conjugates. Deconvoluted spectra were generated following a combination of deglycosylation, IdeS (immunoglobulin-degrading enzyme from Streptococcus pyogenes) digestion, and reduction steps that provide a visual representation of the product for rapid lot-to-lot comparison-a means to quickly assess the integrity of the antibody structure and the applied conjugation chemistry by mass. The relative abundance of the detected ions also offer information regarding differences in drug conjugation levels between samples, and the average drug-antibody ratio can be calculated. The approach requires little material (<100 μg) and, thus, is amenable to small-scale process development testing or as an early component of a complete characterization project facilitating informed decision making regarding which aspects of a molecule might need to be examined in more detail by orthogonal methodologies. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Non-Andersonian conjugate strike-slip faults: Observations, theory, and tectonic implications
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yin, A; Taylor, M H
2008-01-01
Formation of conjugate strike-slip faults is commonly explained by the Anderson fault theory, which predicts a X-shaped conjugate fault pattern with an intersection angle of ∼30 degrees between the maximum compressive stress and the faults. However, major conjugate faults in Cenozoic collisional orogens, such as the eastern Alps, western Mongolia, eastern Turkey, northern Iran, northeastern Afghanistan, and central Tibet, contradict the theory in that the conjugate faults exhibit a V-shaped geometry with intersection angles of 60-75 degrees, which is 30-45 degrees greater than that predicted by the Anderson fault theory. In Tibet and Mongolia, geologic observations can rule out bookshelf faulting, distributed deformation, and temporal changes in stress state as explanations for the abnormal fault patterns. Instead, the GPS-determined velocity field across the conjugate fault zones indicate that the fault formation may have been related to Hagen-Poiseuille flow in map view involving the upper crust and possibly the whole lithosphere based on upper mantle seismicity in southern Tibet and basaltic volcanism in Mongolia. Such flow is associated with two coeval and parallel shear zones having opposite shear sense; each shear zone produce a set of Riedel shears, respectively, and together the Riedel shears exhibit the observed non-Andersonian conjugate strike-slip fault pattern. We speculate that the Hagen-Poiseuille flow across the lithosphere that hosts the conjugate strike-slip zones was produced by basal shear traction related to asthenospheric flow, which moves parallel and away from the indented segment of the collisional fronts. The inferred asthenospheric flow pattern below the conjugate strike-slip fault zones is consistent with the magnitude and orientations of seismic anisotropy observed across the Tibetan and Mongolian conjugate fault zones, suggesting a strong coupling between lithospheric deformation and asthenospheric flow. The laterally moving
-
Non-Andersonian conjugate strike-slip faults: Observations, theory, and tectonic implications
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Yin, A [Department of Earth and Space Sciences and Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA 90025-1567 (United States); Taylor, M H [Department of Geology, University of Kansas, 1475 Jayhawk Blvd., Lawrence, KS 66044 (United States)], E-mail: yin@ess.ucla.edu
2008-07-01
Formation of conjugate strike-slip faults is commonly explained by the Anderson fault theory, which predicts a X-shaped conjugate fault pattern with an intersection angle of {approx}30 degrees between the maximum compressive stress and the faults. However, major conjugate faults in Cenozoic collisional orogens, such as the eastern Alps, western Mongolia, eastern Turkey, northern Iran, northeastern Afghanistan, and central Tibet, contradict the theory in that the conjugate faults exhibit a V-shaped geometry with intersection angles of 60-75 degrees, which is 30-45 degrees greater than that predicted by the Anderson fault theory. In Tibet and Mongolia, geologic observations can rule out bookshelf faulting, distributed deformation, and temporal changes in stress state as explanations for the abnormal fault patterns. Instead, the GPS-determined velocity field across the conjugate fault zones indicate that the fault formation may have been related to Hagen-Poiseuille flow in map view involving the upper crust and possibly the whole lithosphere based on upper mantle seismicity in southern Tibet and basaltic volcanism in Mongolia. Such flow is associated with two coeval and parallel shear zones having opposite shear sense; each shear zone produce a set of Riedel shears, respectively, and together the Riedel shears exhibit the observed non-Andersonian conjugate strike-slip fault pattern. We speculate that the Hagen-Poiseuille flow across the lithosphere that hosts the conjugate strike-slip zones was produced by basal shear traction related to asthenospheric flow, which moves parallel and away from the indented segment of the collisional fronts. The inferred asthenospheric flow pattern below the conjugate strike-slip fault zones is consistent with the magnitude and orientations of seismic anisotropy observed across the Tibetan and Mongolian conjugate fault zones, suggesting a strong coupling between lithospheric deformation and asthenospheric flow. The laterally moving
-
Functional properties of nisin-carbohydrate conjugates formed by radiation induced Maillard reaction
Muppalla, Shobita R.; Sonavale, Rahul; Chawla, Surinder P.; Sharma, Arun
2012-12-01
Nisin-carbohydrate conjugates were prepared by irradiating nisin either with glucose or dextran. Increase in browning and formation of intermediate products was observed with a concomitant decrease in free amino and reducing sugar groups indicating occurrence of the Maillard reaction catalyzed by irradiation. Nisin-carbohydrate conjugates showed a broad spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fluorescence) as well as Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus). Results of antioxidant assays, including that of DPPH radical-scavenging activity and reducing power, showed that the nisin-dextran conjugates possessed better antioxidant potential than nisin-glucose conjugate. These results suggested that it was possible to enhance the functional properties of nisin by preparing radiation induced conjugates suitable for application in food industry.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Li, Nan-Nan; Zheng, Bing-Na [DSAPM Lab and PCFM Lab, Institute of Polymer Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275 (China); Lin, Jian-Tao [DSAPM Lab and PCFM Lab, Institute of Polymer Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275 (China); Guangdong Medical College, Dongguan 523808 (China); Zhang, Li-Ming, E-mail: ceszhlm@mail.sysu.edu.cn [DSAPM Lab and PCFM Lab, Institute of Polymer Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275 (China)
2014-01-01
New heparin–indomethacin conjugate with an ester linkage was prepared by the carbodiimide-mediated condensation reaction, and then characterized by FTIR and {sup 1}HNMR analyses. Due to its amphiphilic character, such a conjugate could self-aggregate into spherical nanoparticles in aqueous system, as confirmed by fluorescence spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy. By the in vitro drug release tests, the resultant conjugate nanoparticles were found to have a sustained and esterase-sensitive release behavior for conjugated indomethacin. In addition, the uptake of these conjugate nanoparticles into human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE1 cells was confirmed by fluorescence microscopy. - Highlights: • New heparin–indomethacin conjugate with an ester linkage was prepared. • Such a conjugate could self-aggregate into spherical nanoparticles in aqueous system. • The resultant conjugate nanoparticles exhibited an esterase-sensitive drug release behavior. • The resultant conjugate nanoparticles showed the cellular uptake ability in CNE1 cells.
-
First-ever evening public engine test of a Space Shuttle Main Engine
2001-01-01
Thousands of people watch the first-ever evening public engine test of a Space Shuttle Main Engine at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. The spectacular test marked Stennis Space Center's 20th anniversary celebration of the first Space Shuttle mission.
-
Threshold couplings of phase-conjugate mirrors with two interaction regions.
Beli, M; Petrovi, M; Sandfuchs, O; Kaiser, F
1998-03-01
Using the grating-action method, we determine the threshold coupling strengths of three generic examples of phase-conjugate mirrors with two interaction regions: the cat conjugator, the mutually incoherent beam coupler, and the interconnected ring mirror.
-
/sup 125/I Radioimmunoassay of serum ursodeoxycholyl conjugates
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hill, A.; Ross, P.E.; Bouchier, I.A.D. (Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, Dundee (UK))
1983-02-07
A radioimmunoassay for serum ursodeoxycholic conjugates using an iodine-125 ligand has been developed. The bile acid was present in normal fasting serum (0.19 +- SD 0.19 ..mu..mol/l, n=24) and 2-hour post-prandial serum (0.8 +- SD 0.8 ..mu..mol/l, n=16). Gallstone patients undergoing oral ursodeoxycholic acid therapy had significantly higher post-prandial serum levels (21.5 +- SD 14.0 ..mu..mol/l, n=15) by radioimmunoassay. Gas liquid chromatography analysis indicated that in normal serum ursodeoxycholic acid was totally conjugated, whereas sera from gallstone patients contained a proportion as the free bile acid (10.2 +- SD 8.1 ..mu..mol/l, n=15). Following an oral dose of ursodeoxycholic acid, both unconjugated and conjugated forms of the bile acid appeared in the serum of healthy individuals.
-
Streptococcal necrotizing fasciitis with toxic shock syndrome and rapid fatal outcome
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kojić Miroslav
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Introduction. Streptococcal necrotizing fasciitis (NF is a serious soft tissue infection with rapid progression of inflammatory process among superficial or deep fascia, systemic host response to infection leading to toxic shock syndrome (TSS, and multiple organ failure. Lethality is high. Case Outline. A 46-year-old male without co-morbidities was admitted to the Emergency Department with redness, swelling and pain on his right lower leg. He became sick two day s ea rlier with m alaise, chills and shivering. On admission he was hypotensive, anuric, with erythematous rash on his face, neck and chest, with acute ren al failure and elevated creatine phosphokinase level. During the next several hours, the changes on his right lower leg rapidly spread to the whole leg, followed by skin destruction and subcutaneo us bleeding, indicating NF. Aggressive antimicrobial, supportive and symptom atic therapy was initiated immediately and on the same evening surgical intervention was performed. Despite these measures, a rapid development of severe TSS, with lethal outcome, occurred in less than 40 hours after the admission. Stre ptococcus pyogenes (group A β-hemolytic Streptococcus was isolated from the throat, skin and tissue obtained duri ng the surgery. Conclusion. Necrotizing fasciitis is a very serious disease with unpre dictable course. For that reason doctors must devote a great deal of a ttention to early, i.e. timely diagnosis of this disease, whose treatment with a multid isciplinary approach is very important.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Manisha Pandey
2016-12-01
Full Text Available The immunobiology underlying the slow acquisition of skin immunity to group A streptococci (GAS, is not understood, but attributed to specific virulence factors impeding innate immunity and significant antigenic diversity of the type-specific M-protein, hindering acquired immunity. We used a number of epidemiologically distinct GAS strains to model the development of acquired immunity. We show that infection leads to antibody responses to the serotype-specific determinants on the M-protein and profound protective immunity; however, memory B cells do not develop and immunity is rapidly lost. Furthermore, antibodies do not develop to a conserved M-protein epitope that is able to induce immunity following vaccination. However, if re-infected with the same strain within three weeks, enduring immunity and memory B-cells (MBCs to type-specific epitopes do develop. Such MBCs can adoptively transfer protection to naïve recipients. Thus, highly protective M-protein-specific MBCs may never develop following a single episode of pyoderma, contributing to the slow acquisition of immunity and to streptococcal endemicity in at-risk populations.
-
Magnetic catechin-dextran conjugate as targeted therapeutic for pancreatic tumour cells.
Vittorio, Orazio; Voliani, Valerio; Faraci, Paolo; Karmakar, Biswajit; Iemma, Francesca; Hampel, Silke; Kavallaris, Maria; Cirillo, Giuseppe
2014-06-01
Catechin-dextran conjugates have recently attracted a lot of attention due to their anticancer activity against a range of cancer cells. Magnetic nanoparticles have the ability to concentrate therapeutically important drugs due to their magnetic-spatial control and provide opportunities for targeted drug delivery. Enhancement of the anticancer efficiency of catechin-dextran conjugate by functionalisation with magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Modification of the coating shell of commercial magnetic nanoparticles (Endorem) composed of dextran with the catechin-dextran conjugate. Catechin-dextran conjugated with Endorem (Endo-Cat) increased the intracellular concentration of the drug and it induced apoptosis in 98% of pancreatic tumour cells placed under magnetic field. The conjugation of catechin-dextran with Endorem enhances the anticancer activity of this drug and provides a new strategy for targeted drug delivery on tumour cells driven by magnetic field. The ability to spatially control the delivery of the catechin-dextran by magnetic field makes it a promising agent for further application in cancer therapy.
-
Fused thiophene-based conjugated polymers and their use in optoelectronic devices
Facchetti, Antonio; Marks, Tobin J.; Takai, Atsuro; Seger, Mark; Chen; , Zhihua
2017-07-18
The present teachings relate to polymeric compounds and their use as organic semiconductors in organic and hybrid optical, optoelectronic, and/or electronic devices such as photovoltaic cells, light emitting diodes, light emitting transistors, and field effect transistors. The disclosed compounds generally include as repeating units at least one annulated thienyl-vinylene-thienyl (TVT) unit and at least one other pi-conjugated unit. The annulated TVT unit can be represented by the formula: ##STR00001## where Cy.sup.1 and Cy.sup.2 can be a five- or six-membered carbocyclic ring. The annulated TVT unit can be optionally substituted at any available ring atom(s), and can be covalently linked to the other pi-conjugated unit via either the thiophene rings or the carbocyclic rings Cy.sup.1 and Cy.sup.2. The other pi-conjugated unit can be a conjugated linear linker including one or more unsaturated bonds, or a conjugated cyclic linker including one or more carbocyclic and/or heterocyclic rings.
-
Functional Requirements for Onboard Management of Space Shuttle Consumables. Volume 2
Graf, P. J.; Herwig, H. A.; Neel, L. W.
1973-01-01
This report documents the results of the study "Functional Requirements for Onboard Management of Space Shuttle Consumables." The study was conducted for the Mission Planning and Analysis Division of the NASA Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center, Houston, Texas, between 3 July 1972 and 16 November 1973. The overall study program objective was two-fold. The first objective was to define a generalized consumable management concept which is applicable to advanced spacecraft. The second objective was to develop a specific consumables management concept for the Space Shuttle vehicle and to generate the functional requirements for the onboard portion of that concept. Consumables management is the process of controlling or influencing the usage of expendable materials involved in vehicle subsystem operation. The report consists of two volumes. Volume I presents a description of the study activities related to general approaches for developing consumable management, concepts for advanced spacecraft applications, and functional requirements for a Shuttle consumables management concept. Volume II presents a detailed description of the onboard consumables management concept proposed for use on the Space Shuttle.
-
Miranda, Jonatan; Arias, Noemi; Fernández-Quintela, Alfredo; del Puy Portillo, María
2014-04-01
Despite its benefits, conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) may cause side effects after long-term administration. Because of this and the controversial efficacy of CLA in humans, alternative biomolecules that may be used as functional ingredients have been studied in recent years. Thus, conjugated linolenic acid (CLNA) has been reported to be a potential anti-obesity molecule which may have additional positive effects related to obesity. According to the results reported in obesity, CLNA needs to be given at higher doses than CLA to be effective. However, because of the few studies conducted so far, it is still difficult to reach clear conclusions about the potential use of these CLNAs in obesity and its related changes (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, or inflammation). Copyright © 2012 SEEN. Published by Elsevier Espana. All rights reserved.
-
Space Shuttle main engine product improvement
Lucci, A. D.; Klatt, F. P.
1985-01-01
The current design of the Space Shuttle Main Engine has passed 11 certification cycles, amassed approximately a quarter million seconds of engine test time in 1200 tests and successfully launched the Space Shuttle 17 times of 51 engine launches through May 1985. Building on this extensive background, two development programs are underway at Rocketdyne to improve the flow of hot gas through the powerhead and evaluate the changes to increase the performance margins in the engine. These two programs, called Phase II+ and Technology Test Bed Precursor program are described. Phase II+ develops a two-tube hot-gas manifold that improves the component environment. The Precursor program will evaluate a larger throat main combustion chamber, conduct combustion stability testing of a baffleless main injector, fabricate an experimental weld-free heat exchanger tube, fabricate and test a high pressure oxidizer turbopump with an improved inlet, and develop and test methods for reducing temperature transients at start and shutdown.
-
Effect of TiO2 on conjugative transfer of RP4 plasmid
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Qian Di; Zhang Buchang; Yang Dong; Chen Zhaoli; Jin Min; Qiu Zhigang; Li Junwen
2013-01-01
Objective: To explore the effect and law of nano-titanium dioxide on the conjugative transfer of RP4 plasmid. Methods: Mating was conducted between Escherichia coli HB101 (RP4) and E. coli K12Rif in saline without stirring under certain conditions and the donor per recipient ratio was 1:1 constantly. The selective LB agar medium plates containing appropriate antibiotics were used to count the number of transconjugants and the conjugative transfer frequency. Results: Nano-titanium dioxide could promote the conjugative transfer of RP4. The nano-titanium dioxide concentration, bacterial concentration, mating temperature and mating time could affect the conjugative transfer of RP4. Conclusion: Nano-titanium dioxide can promote plasmid conjugal transfer in the liquid phase under certain conditions, which may pose a potential hazard to environmental and human health. (authors)
-
Orbital Fitness: An Overview of Space Shuttle Cardiopulmonary Exercise Physiology Findings
Moore, Alan D.
2011-01-01
Limited observations regarding the cardiopulmonary responses to aerobic exercise had been conducted during short-duration spaceflight before the Space Shuttle program. This presentation focuses on the findings regarding changes observed in the cardiopulmonary exercise responses during and following Shuttle flights. During flight, maximum oxygen uptake (VO2max) remained unchanged as did the maximum work rate achievable during cycle exercise testing conducted during the last full flight day. Immediately following flight, the ubiquitous finding, confirmed by investigations conducted during the Spacelab Life Sciences missions 1 and 2 and by NASA Detailed Supplemental Objective studies, indicated that VO2max was reduced; however, the reduction in VO2max was transient and returned to preflight levels within 7 days following return. Studies regarding the influence of aerobic exercise countermeasures performed during flight on postflight performance were mostly limited to the examination of the heart rate (HR) response to submaximal exercise testing on landing day. These studies revealed that exercise HR was elevated in individuals who performed little to no exercise during their missions as compared to individuals who performed regular exercise. In addition, astronauts who performed little to no aerobic exercise during flight demonstrated an increased HR and lowered pulse pressure response to the standard stand test on landing day, indicating a decrease in orthostatic function in these individuals. With regard to exercise modality, four devices were examined during the Shuttle era: two treadmills, a cycle ergometer, and a rowing device. Although there were limited investigations regarding the use of these devices for exercise training aboard the Shuttle, there was no clear consensus reached regarding which proved to be a "superior" device. Each device had a unique operational or physiologic limitation associated with its use. In conclusion, exercise research conducted
-
Yu, Songcheng; Yu, Fei; Zhang, Hongquan; Qu, Lingbo; Wu, Yongjun
2014-06-01
In this study, in order to find out a proper method for conjugation of enrofloxacin to label enzymes, two methods were compared and carbodiimide condensation was proved to be better. The results showed that the binding ratio of enrofloxacin and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) was 8:1 and that of enrofloxacin and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was 5:1. This indicated that conjugate synthesized by carbodiimide condensation was fit for chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA). Furthermore, data revealed that dialysis time was an important parameter for conjugation and 6 days was best. Buffer to dilute conjugate had little effect on CLEIA. The storage condition for conjugates was also studied and it was shown that the conjugate was stable at 4 °C with no additive up to 30 days. These data were valuable for establishing CLEIA to quantify enrofloxacin.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Rhee H
2012-02-01
Full Text Available Hanna Rhee1, Daniel J Cameron21Medicine, San Diego, CA, 2Northern Westchester Hospital, Mount Kisco, NY, USAAbstract: Lyme disease (LD is a complex, multisystemic illness. As the most common vector-borne disease in the United States, LD is caused by bacterial spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, with potential coinfections from agents of anaplasmosis, babesiosis, and ehrlichiosis. Persistent symptoms and clinical signs reflect multiorgan involvement with episodes of active disease and periods of remission, not sparing the coveted central nervous system. The capability of microorganisms to cause and exacerbate various neuropsychiatric pathology is also seen in pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections (PANDAS, a recently described disorder attributed to bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus in which neurologic tics and obsessive-compulsive disorders are sequelae of the infection. In the current overview, LD and PANDAS are juxtaposed through a review of their respective infectious etiologies, clinical presentations, mechanisms of disease development, courses of illness, and treatment options. Future directions related to immunoneuropsychiatry are also discussed.Keywords: neuroborreliosis, infection, obsessive-compulsive disorder, tic disorder, Borrelia burgdorferi, strep throat
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sharma A
2014-05-01
Full Text Available Abhinay Sharma, D Patric Nitsche-SchmitzDepartment of Medical Microbiology, Helmholtz Center for Infection Research, Braunschweig, GermanyAbstract: Acute rheumatic fever is a sequela of Streptococcus pyogenes and potentially of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis infections. Acute rheumatic fever is caused by destructive autoimmunity and inflammation in the extracellular matrix and can lead to rheumatic heart disease, which is the most frequent cardiologic disease that is acquired in youth. Although effective treatments are available, acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease remain serious threats to human health, which affect millions and cause high economic losses. This has motivated the search for a vaccine that prevents the causative streptococcal infections. A variety of potential vaccine candidates have been identified and investigated in the past. Today, new approaches are applied to find alternative candidates. Nevertheless, several obstacles lie in the way of an approved S. pyogenes vaccine for use in humans. Herein, a subjective selection of promising vaccine candidates with respect to the prevention of acute rheumatic fever/rheumatic heart disease and safety regarding immunological side effects is discussed.Keywords: autoimmune disease, side effects, M protein vaccine, molecular mimicry, coiled-coil, collagen binding, PARF
-
2007-01-01
Please note that, to improve the service we provide, a new telephone number - 72500 - has been set up for all shuttle requests concerning: journeys within the CERN site, i.e. official visits or bidders' conferences; journeys to or from the airport or city centre; long-distance journeys. However, it will still be possible to submit requests in writing to Fm.Support@cern. The radio taxi can also still be reached on 76969. The TS/FM group would also like to inform you that details of all light logistics services (transport of persons, distribution and collection of parcels up to 1 tonne, distribution and collection of mail) can be found on the group's website: http://ts-dep.web.cern.ch/ts-dep/groups/fm/fm.htm TS/FM Group 160239
-
Shuttle operations era planning for flight operations
Holt, J. D.; Beckman, D. A.
1984-01-01
The Space Transportation System (STS) provides routine access to space for a wide range of customers in which cargos vary from single payloads on dedicated flights to multiple payloads that share Shuttle resources. This paper describes the flight operations planning process from payload introduction through flight assignment to execution of the payload objectives and the changes that have been introduced to improve that process. Particular attention is given to the factors that influence the amount of preflight preparation necessary to satisfy customer requirements. The partnership between the STS operations team and the customer is described in terms of their functions and responsibilities in the development of a flight plan. A description of the Mission Control Center (MCC) and payload support capabilities completes the overview of Shuttle flight operations.
-
Shuttle Kit Freezer Refrigeration Unit Conceptual Design
Copeland, R. J.
1975-01-01
The refrigerated food/medical sample storage compartment as a kit to the space shuttle orbiter is examined. To maintain the -10 F in the freezer kit, an active refrigeration unit is required, and an air cooled Stirling Cycle refrigerator was selected. The freezer kit contains two subsystems, the refrigeration unit, and the storage volume. The freezer must provide two basic capabilities in one unit. One requirement is to store 215 lbs of food which is consumed in a 30-day period by 7 people. The other requirement is to store 128.3 lbs of medical samples consisting of both urine and feces. The unit can be mounted on the lower deck of the shuttle cabin, and will occupy four standard payload module compartments on the forward bulkhead. The freezer contains four storage compartments.
-
Image Analysis Based on Soft Computing and Applied on Space Shuttle During the Liftoff Process
Dominquez, Jesus A.; Klinko, Steve J.
2007-01-01
Imaging techniques based on Soft Computing (SC) and developed at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) have been implemented on a variety of prototype applications related to the safety operation of the Space Shuttle during the liftoff process. These SC-based prototype applications include detection and tracking of moving Foreign Objects Debris (FOD) during the Space Shuttle liftoff, visual anomaly detection on slidewires used in the emergency egress system for the Space Shuttle at the laJlIlch pad, and visual detection of distant birds approaching the Space Shuttle launch pad. This SC-based image analysis capability developed at KSC was also used to analyze images acquired during the accident of the Space Shuttle Columbia and estimate the trajectory and velocity of the foam that caused the accident.
-
Combining CPT-conjugate neutrino channels at Fermilab
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jansson, Andreas; Parke, Stephen; Saoulidou, Niki; Mena, Olga
2008-01-01
We explore an alternative strategy to determine the neutrino mass hierarchy by making use of possible future neutrino facilities at Fermilab. Here, we use CPT-conjugate neutrino channels, exploiting a ν μ beam from the NuMI beamline and a ν e beam from a beta-beam experimental setup. Both experiments are performed at approximately the same /L. We present different possible accelerator scenarios for the beta-beam neutrino setup and fluxes. This CPT-conjugate neutrino channel scenario can extract the neutrino mass hierarchy down to sin 2 2θ 13 ≅0.02.
-
Research study on antiskid braking systems for the space shuttle
Auselmi, J. A.; Weinberg, L. W.; Yurczyk, R. F.; Nelson, W. G.
1973-01-01
A research project to investigate antiskid braking systems for the space shuttle vehicle was conducted. System from the Concorde, Boeing 747, Boeing 737, and Lockheed L-1011 were investigated. The characteristics of the Boeing 737 system which caused it to be selected are described. Other subjects which were investigated are: (1) trade studies of brake control concepts, (2) redundancy requirements trade study, (3) laboratory evaluation of antiskid systems, and (4) space shuttle hardware criteria.
-
Parallel conjugate gradient algorithms for manipulator dynamic simulation
Fijany, Amir; Scheld, Robert E.
1989-01-01
Parallel conjugate gradient algorithms for the computation of multibody dynamics are developed for the specialized case of a robot manipulator. For an n-dimensional positive-definite linear system, the Classical Conjugate Gradient (CCG) algorithms are guaranteed to converge in n iterations, each with a computation cost of O(n); this leads to a total computational cost of O(n sq) on a serial processor. A conjugate gradient algorithms is presented that provide greater efficiency using a preconditioner, which reduces the number of iterations required, and by exploiting parallelism, which reduces the cost of each iteration. Two Preconditioned Conjugate Gradient (PCG) algorithms are proposed which respectively use a diagonal and a tridiagonal matrix, composed of the diagonal and tridiagonal elements of the mass matrix, as preconditioners. Parallel algorithms are developed to compute the preconditioners and their inversions in O(log sub 2 n) steps using n processors. A parallel algorithm is also presented which, on the same architecture, achieves the computational time of O(log sub 2 n) for each iteration. Simulation results for a seven degree-of-freedom manipulator are presented. Variants of the proposed algorithms are also developed which can be efficiently implemented on the Robot Mathematics Processor (RMP).
-
Target binding improves relaxivity in aptamer-gadolinium conjugates.
Bernard, Elyse D; Beking, Michael A; Rajamanickam, Karunanithi; Tsai, Eve C; Derosa, Maria C
2012-12-01
MRI contrast agents (CA) have been heavily used over the past several decades to enhance the diagnostic value of the obtained images. From a design perspective, two avenues to improve the efficacy of contrast agents are readily evident: optimization of magnetic properties of the CA, and optimization of the pharmacokinetics and distribution of the CA in the patient. Contrast agents consisting of DNA aptamer-gadolinium(III) conjugates provide a single system in which these factors can be addressed simultaneously. In this proof-of-concept study, the 15mer thrombin aptamer was conjugated to diethylenetriaminepentaacetic (DTPA) dianhydride to form a monoamide derivative of the linear open-chain chelate present in the commonly used contrast agent Magnevist(®). The stability of the conjugated DNA aptamer-DTPA-Gd(III) chelate in a transmetallation study using Zn(II) was found to be similar to that reported for DTPA-Gd(III). Relaxivity enhancements of 35 ± 4 and 20 ± 1 % were observed in the presence of thrombin compared to a control protein at fields of 9.4 and 1.5 T, respectively. The inclusion of spacers between the aptamer and the DTPA to eliminate possible steric effects was also investigated but not found to improve the relaxation enhancement achieved in comparison to the unaltered aptamer conjugate.
-
Phase conjugation with random fields and with deterministic and random scatterers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gbur, G.; Wolf, E.
1999-01-01
The theory of distortion correction by phase conjugation, developed since the discovery of this phenomenon many years ago, applies to situations when the field that is conjugated is monochromatic and the medium with which it interacts is deterministic. In this Letter a generalization of the theory is presented that applies to phase conjugation of partially coherent waves interacting with either deterministic or random weakly scattering nonabsorbing media. copyright 1999 Optical Society of America
-
HER2 specific delivery of methotrexate by dendrimer conjugated anti-HER2 mAb
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shukla, Rameshwer; Thomas, Thommey P; Desai, Ankur M; Kotlyar, Alina; Park, Steve J; Baker, James R Jr
2008-01-01
Herceptin, a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to human growth factor receptor-2 (HER2), was covalently attached to a fifth-generation (G5) polyamidoamine dendrimer containing the cytotoxic drug methotrexate. The specific binding and internalization of this conjugate labeled with FITC was clearly demonstrated in cell lines overexpressing HER2 by flow cytometry as well as confocal microscopic analysis. In addition, binding and uptake of antibody conjugated dendrimers was completely blocked by excess non-conjugated herceptin. The dendrimer conjugate was also shown to inhibit the dihydrofolate reductase with similar activity to methotrexate. Co-localization experiments with lysotracker red indicate that antibody conjugate, although internalized efficiently into cells, has an unusually long residence time in the lysosome. Somewhat lower cytotoxicity of the conjugate in comparison to free methotrexate was attributed to the slow release of methotrexate from the conjugate and its long retention in the lysosomal pocket
-
Molecules with linear pi-conjugated pathways between all substituents : Omniconjugation
van der Veen, M.H.; Rispens, M.T; Jonkman, H.T.; Hummelen, J.C.
In this paper, omniconjugation is introduced as a topological phenomenon in pi-conjugated systems. Omniconjugated molecules are defined by the fact that they provide direct and fully pi-conjugated pathways between all subdstituents attached to them. Surprisingly, until now such topologies have never
-
Molecules with Linear π-Conjugated Pathways between All Substituents : Omniconjugation
Veen, Marleen H. van der; Rispens, Minze T.; Jonkman, Harry T.; Hummelen, Jan C.
2004-01-01
In this paper, omniconjugation is introduced as a topological phenomenon in π-conjugated systems. Omniconjugated molecules are defined by the fact that they provide direct and fully π-conjugated pathways between all substituents attached to them. Surprisingly, until now such topologies have never
-
Fractional Consumption of Liquid Hydrogen and Liquid Oxygen During the Space Shuttle Program
Partridge, Jonathan K.
2011-01-01
The Space Shuttle uses the propellants, liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, to meet part of the propulsion requirements from ground to orbit. The Kennedy Space Center procured over 25 million kilograms of liquid hydrogen and over 250 million kilograms of liquid oxygen during the 3D-year Space Shuttle Program. Because of the cryogenic nature of the propellants, approximately 55% of the total purchased liquid hydrogen and 30% of the total purchased liquid oxygen were used in the Space Shuttle Main Engines. The balance of the propellants were vaporized during operations for various purposes. This paper dissects the total consumption of liqUid hydrogen and liqUid oxygen and determines the fraction attributable to each of the various processing and launch operations that occurred during the entire Space Shuttle Program at the Kennedy Space Center.
-
Sequence-specific DNA alkylation by tandem Py-Im polyamide conjugates.
Taylor, Rhys Dylan; Kawamoto, Yusuke; Hashiya, Kaori; Bando, Toshikazu; Sugiyama, Hiroshi
2014-09-01
Tandem N-methylpyrrole-N-methylimidazole (Py-Im) polyamides with good sequence-specific DNA-alkylating activities have been designed and synthesized. Three alkylating tandem Py-Im polyamides with different linkers, which each contained the same moiety for the recognition of a 10 bp DNA sequence, were evaluated for their reactivity and selectivity by DNA alkylation, using high-resolution denaturing gel electrophoresis. All three conjugates displayed high reactivities for the target sequence. In particular, polyamide 1, which contained a β-alanine linker, displayed the most-selective sequence-specific alkylation towards the target 10 bp DNA sequence. The tandem Py-Im polyamide conjugates displayed greater sequence-specific DNA alkylation than conventional hairpin Py-Im polyamide conjugates (4 and 5). For further research, the design of tandem Py-Im polyamide conjugates could play an important role in targeting specific gene sequences. © 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Application of heat-balance integral method to conjugate thermal explosion
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Novozhilov Vasily
2009-01-01
Full Text Available Conjugate thermal explosion is an extension of the classical theory, proposed and studied recently by the author. The paper reports application of heat-balance integral method for developing phase portraits for systems undergoing conjugate thermal explosion. The heat-balance integral method is used as an averaging method reducing partical differential equation problem to the set of first-order ordinary differential equations. The latter reduced problem allows natural interpretation in appropriately chosen phase space. It is shown that, with the help of heat-balance integral technique, conjugate thermal explosion problem can be described with a good accuracy by the set of non-linear first-order differential equations involving complex error function. Phase trajectories are presented for typical regimes emerging in conjugate thermal explosion. Use of heat-balance integral as a spatial averaging method allows efficient description of system evolution to be developed.
-
Lectins as carriers: preparation and purification of a concanavalin A-trypsin conjugate
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shier, W.T.
1985-01-01
The scheme for the preparation and purification of Con A-trypsin demonstrates the presence of Con A in the conjugate by affinity purification and by hemagglutination. The presence of Con A was demonstrated in two additional ways. The conjugate was prepared using trypsin labeled with iodine 125 and unlabeled Con A. The resulting conjugate containing 42,800 cpm/mg protein was used to demonstrate prolonged retention of the conjugated trypsin in mouse footpads. The presence of trypsin was also demonstrated in the conjugate by affinity chromatography and by the esterase activity characteristic of trypsin with tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester as substrate. Con A-trypsin was also assayed for proteolytic activity with a macromolecular substrate azocasein. A comparison of proteolytic activities with these two substrates indicated that 50-80% of the proteolytic activity observed with the small substrate is retained with macromolecular substrates
-
Enhancing the Photoluminescence Emission of Conjugated MEH-PPV by Light Processing
Botiz, Ioan
2014-04-09
We show here that treatment of thin films of conjugated polymers by illumination with light leads to an increase of the intensity of their photoluminescence by up to 42%. The corresponding enhancement of absorbance was much less pronounced. We explain this significant enhancement of photoluminescence by a planarization of the conjugated polymer chains induced by photoexcitations even below the glass transition temperature, possibly due to an increased conjugation length. Interestingly, the photoluminescence remains at the enhanced level for more than 71 h after treatment of the films by illumination with light, likely due to the fact that below the glass transition temperature no restoring force could return the conjugated chains into their initial conformational state. © 2014 American Chemical Society.
-
Conjugation of Inulin Improves Anti-Biofilm Activity of Chitosan.
Zhang, Guiqiang; Liu, Jing; Li, Ruilian; Jiao, Siming; Feng, Cui; Wang, Zhuo A; Du, Yuguang
2018-05-04
Bacteria biofilm helps bacteria prevent phagocytosis during infection and increase resistance to antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive pathogenic bacterium and is tightly associated with biofilm-related infections, which have led to great threat to human health. Chitosan, the only cationic polysaccharide in nature, has been demonstrated to have antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activities, which, however, require a relative high dosage of chitosan. Moreover, poor water solubility further restricts its applications on anti-infection therapy. Inulins are a group of polysaccharides produced by many types of plants, and are widely used in processed foods. Compared to chitosan, inulin is very soluble in water and possesses a mild antibacterial activity against certain pathogenic bacteria. In order to develop an effective strategy to treat biofilm-related infections, we introduce a method by covalent conjugation of inulin to chitosan. The physicochemical characterization of the inulin⁻chitosan conjugate was assayed, and the anti-biofilm activity was evaluated against S. aureus biofilm. The results indicated that, as compared to chitosan, this novel polysaccharide⁻polysaccharide conjugate significantly enhanced activities against S. aureus either in a biofilm or planktonic state. Of note, the conjugate also showed a broad spectrum anti-biofilm activity on different bacteria strains and low cellular toxicity to mammalian cells. These results suggested that chitosan conjugation of inulin was a viable strategy for treatment against biofilm-related infections. This finding may further spread the application of natural polysaccharides on treatments of infectious disease.
-
Feasibility analysis of cislunar flight using the Shuttle Orbiter
Haynes, Davy A.
1991-01-01
A first order orbital mechanics analysis was conducted to examine the possibility of utilizing the Space Shuttle Orbiter to perform payload delivery missions to lunar orbit. In the analysis, the earth orbit of departure was constrained to be that of Space Station Freedom. Furthermore, no enhancements of the Orbiter's thermal protection system were assumed. Therefore, earth orbit insertion maneuvers were constrained to be all propulsive. Only minimal constraints were placed on the lunar orbits and no consideration was given to possible landing sites for lunar surface payloads. The various phases and maneuvers of the mission are discussed for both a conventional (Apollo type) and an unconventional mission profile. The velocity impulses needed, and the propellant masses required are presented for all of the mission maneuvers. Maximum payload capabilities were determined for both of the mission profiles examined. In addition, other issues relating to the feasibility of such lunar shuttle missions are discussed. The results of the analysis indicate that the Shuttle Orbiter would be a poor vehicle for payload delivery missions to lunar orbit.
-
[Relationship between family variables and conjugal adjustment].
Jiménez-Picón, Nerea; Lima-Rodríguez, Joaquín-Salvador; Lima-Serrano, Marta
2018-04-01
To determine whether family variables, such as type of relationship, years of marriage, existence of offspring, number of members of family, stage of family life cycle, transition between stages, perceived social support, and/or stressful life events are related to conjugal adjustment. A cross-sectional and correlational study using questionnaires. Primary care and hospital units of selected centres in the province of Seville, Spain. Consecutive stratified sampling by quotas of 369 heterosexual couples over 18years of age, who maintained a relationship, with or without children, living in Seville. A self-report questionnaire for the sociodemographic variables, and the abbreviated version of the Dyadic Adjustment Scale, Questionnaire MOS Perceived Social Support, and Social Readjustment Rating Scale, were used. Descriptive and inferential statistics were performed with correlation analysis and multivariate regression. Statistically significant associations were found between conjugal adjustment and marriage years (r=-10: Pfamily life cycle (F=2.65; Pfamily life cycle stage (mature-aged stage) on conjugal adjustment (R2=.21; F=9.9; df=356; Prelationship. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Pruksachatkunakorn Chulabhorn
2006-08-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background Most group A streptococcal (GAS vaccine strategies have focused on the surface M protein, a major virulence factor of GAS. The amino-terminus of the M protein elicits antibodies, that are both opsonic and protective, but which are type specific. J14, a chimeric peptide that contains 14 amino acids from the M protein conserved C-region at the carboxy-terminus, offers the possibility of a vaccine which will elicit protective opsonic antibodies against multiple different GAS strains. In this study, we searched for J14 and J14-like sequences and the number of their repeats in the C-region of the M protein from GAS strains isolated from the Northern Thai population. Then, we examined the bactericidal activity of J14, J14.1, J14-R1 and J14-R2 antisera against multiple Thai GAS strains. Results The emm genes of GAS isolates were sequenced and grouped as 14 different J14-types. The most diversity of J14-types was found in the C1-repeat. The J14.1 type was the major sequence in the C2 and C3-repeats. We have shown that antisera raised against the M protein conserved C-repeat region peptides, J14, J14.1, J14-R1 and J14-R2, commonly found in GAS isolates from the Northern Thai population, are able to kill GAS of multiple different emm types derived from an endemic area. The mean percent of bactericidal activities for all J14 and J14-like peptide antisera against GAS isolates were more than 70%. The mean percent of bactericidal activity was highest for J14 antisera followed by J14-R2, J14.1 and J14-R1 antisera. Conclusion Our study demonstrated that antisera raised against the M protein conserved C-repeat region are able to kill multiple different strains of GAS isolated from the Northern Thai population. Therefore, the four conserved "J14" peptides have the potential to be used as GAS vaccine candidates to prevent streptococcal infections in an endemic area.
-
New preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithms for nonlinear unconstrained optimization problems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Al-Bayati, A.; Al-Asadi, N.
1997-01-01
This paper presents two new predilection conjugate gradient algorithms for nonlinear unconstrained optimization problems and examines their computational performance. Computational experience shows that the new proposed algorithms generally imp lone the efficiency of Nazareth's [13] preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm. (authors). 16 refs., 1 tab
-
Orderings for conjugate gradient preconditionings
Ortega, James M.
1991-01-01
The effect of orderings on the rate of convergence of the conjugate gradient method with SSOR or incomplete Cholesky preconditioning is examined. Some results also are presented that help to explain why red/black ordering gives an inferior rate of convergence.
-
Microdosimetry measurements with the RME-III on the space shuttle
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hardy, K.; Golightly, M.J.; Atwell, W.; Quam, W.
1994-01-01
Since December 1988 (STS-27) the USAF Armstrong Laboratory, in conjunction with the NASA Space Radiation Analysis Group, has been conducting microdosimetry measurements on selected high-altitude, high-inclination Space Shuttle mission with the RME-III. The RME-III is a portable, self-contained, active dosimeter system featuring a three-channel tissue equivalent proportional counter (TEPC) which measures particle fluence and computes dose and dose equivalent at operator selected time intervals. The total accumulated absorbed dose and dose equivalent are displayed real time, while the data and the time of the interval dose readings are stored in memory modules for later analysis. Analysis of the time-resolved data permits correlation of the radiation exposure with geographic position, altitude, and spacecraft shielding and orientation. The RME-III has flown on 15 Shuttle missions to date and measurements are in good agreement with other dosimetry measurements made on the Shuttle
-
alpha-Glucosidase-albumin conjugates: effect of chronic administration in mice
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Allen, T.M.; Murray, L.; Bhardwaj, D.; Poznansky, M.J.
1985-01-01
Enzyme albumin conjugates have been proposed as a means of increasing the efficacy of enzyme use in vivo and decreasing immune response to the enzyme. Particulate drug carriers, however, have a pronounced tendency to localize in the mononuclear phagocyte (reticuloendothelial) system. The authors have examined in mice the effect on phagocytic index, tissue distribution and organ size of continued administration of conjugates of alpha-glucosidase with either homologous or heterologous albumin. Mice received 10 X 2-mg injections of bovine serum albumin (BSA) or mouse serum albumin (MSA), either free, polymerized or conjugated with alpha-glucosidase. Experiments involving BSA had to be terminated before the end of the experiment because of anaphylaxis, but these reactions were less severe to the polymerized albumin than to free albumin. Free BSA, BSA polymer and BSA-enzyme conjugates all caused a decrease in phagocytic index after six injections. Mice receiving MSA showed no evidence of anaphylaxis, but mice receiving six or more injections of free MSA, MSA polymer or MSA-enzyme conjugate had significantly decreased phagocytic indices as compared to controls. Phagocytic indices had returned to normal by 7 days after the final injection. Tissue distribution of 125 I-labeled albumin preparations was determined in either naive or chronically injected mice
-
Quantification of residual solvents in antibody drug conjugates using gas chromatography
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Medley, Colin D., E-mail: medley.colin@gene.com [Genentech Inc., Small Molecule Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080 (United States); Kay, Jacob [Research Pharmaceutical Services, 520 Virginia Dr. Fort, Washington, PA (United States); Li, Yi; Gruenhagen, Jason; Yehl, Peter; Chetwyn, Nik P. [Genentech Inc., Small Molecule Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080 (United States)
2014-11-19
Highlights: • Sensitive residual solvents detection in ADCs. • 125 ppm QL for common conjugation solvents. • Generic and validatable method. - Abstract: The detection and quantification of residual solvents present in clinical and commercial pharmaceutical products is necessary from both patient safety and regulatory perspectives. Head-space gas chromatography is routinely used for quantitation of residual solvents for small molecule APIs produced through synthetic processes; however residual solvent analysis is generally not needed for protein based pharmaceuticals produced through cultured cell lines where solvents are not introduced. In contrast, antibody drug conjugates and other protein conjugates where a drug or other molecule is covalently bound to a protein typically use solvents such as N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA), N,N‑dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), or propylene glycol (PG) to dissolve the hydrophobic small molecule drug for conjugation to the protein. The levels of the solvent remaining following the conjugation step are therefore important to patient safety as these parental drug products are introduced directly into the patients bloodstream. We have developed a rapid sample preparation followed by a gas chromatography separation for the detection and quantification of several solvents typically used in these conjugation reactions. This generic method has been validated and can be easily implemented for use in quality control testing for clinical or commercial bioconjugated products.
-
Emulsifying properties of maillard conjugates produced from sodium caseinate and locust bean gum
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. A. Perrechil
2014-06-01
Full Text Available Emulsifying properties of sodium caseinate -locust bean gum Maillard conjugates produced at different temperatures (54 - 96 ºC, protein/polysaccharide ratios (0.3 - 1.0 and reaction times (1 - 24 hours were evaluated. Conjugate formation was confirmed by formation of color and high molecular weight fractions and the decrease of the αs- and β-casein bands. The emulsions stabilized by Maillard conjugates showed good stability. The mean droplet diameter (d32 tended to decrease with the increase of incubation time and temperature, except at extreme conditions (24 hours and 90 ºC or 96 ºC when the partial degradation of the conjugates was probably favored, resulting in phase separation of emulsions. The emulsion viscosity decreased with the increase in the protein/polysaccharide ratio and with the degradation of the conjugates. The conditions used in the experimental design made the optimization of the conjugate production viable, which showed greater emulsifier properties than the pure protein under acid conditions.
-
Space shuttle booster multi-engine base flow analysis
Tang, H. H.; Gardiner, C. R.; Anderson, W. A.; Navickas, J.
1972-01-01
A comprehensive review of currently available techniques pertinent to several prominent aspects of the base thermal problem of the space shuttle booster is given along with a brief review of experimental results. A tractable engineering analysis, capable of predicting the power-on base pressure, base heating, and other base thermal environmental conditions, such as base gas temperature, is presented and used for an analysis of various space shuttle booster configurations. The analysis consists of a rational combination of theoretical treatments of the prominent flow interaction phenomena in the base region. These theories consider jet mixing, plume flow, axisymmetric flow effects, base injection, recirculating flow dynamics, and various modes of heat transfer. Such effects as initial boundary layer expansion at the nozzle lip, reattachment, recompression, choked vent flow, and nonisoenergetic mixing processes are included in the analysis. A unified method was developed and programmed to numerically obtain compatible solutions for the various flow field components in both flight and ground test conditions. Preliminary prediction for a 12-engine space shuttle booster base thermal environment was obtained for a typical trajectory history. Theoretical predictions were also obtained for some clustered-engine experimental conditions. Results indicate good agreement between the data and theoretical predicitons.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jalvandi, Javid; White, Max; Gao, Yuan; Truong, Yen Bach; Padhye, Rajiv; Kyratzis, Ilias Louis
2017-01-01
A range of biodegradable drug-nanofibres composite mats have been reported as drug delivery systems. However, their main disadvantage is the rapid release of the drug immediately after application. This paper reports an improved system based on the incorporation of drug conjugated-chitosan into polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers. The results showed that controlled release of levofloxacin (LVF) could be achieved by covalently binding LVF to low molecular weight chitosan (CS) via a cleavable amide bond and then blending the conjugated CS with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibres prior to electrospinning. PVA/LVF and PVA-CS/LVF nanofibres were fabricated as controls. The conjugated CS-LVF was characterized by FTIR, DSC, TGA and 1 H NMR. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the blended CS-PVA nanofibres had a reduced fibre diameter compared to the controls. Drug release profiles showed that burst release was decreased from 90% in the control PVA/LVF electrospun mats to 27% in the PVA/conjugated CS-LVF mats after 8 h in phosphate buffer at 37 °C. This slower release is due to the cleavable bond between LVF and CS that slowly hydrolysed over time at neutral pH. The results indicate that conjugation of the drug to the polymer backbone is an effective way of minimizing burst release behaviour and achieving sustained release of the drug, LVF. - Highlights: • A novel drug delivery system for controlled release of drug was designed. • Composite PVA/conjugated CS-LVF nanofibres was fabricated by electrospinning. • Conjugated chitosan and composite nanofibres were characterized by various techniques. • Release profiles of drug were significantly improved in composite nanofibres containing drug conjugated chitosan.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jalvandi, Javid, E-mail: Javid.jlv@gmail.com [CSIRO, Manufacturing Flagship, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168 (Australia); School of Fashion and Textiles, College of Design and Social Context, RMIT University, 25 Dawson Street, Brunswick, Victoria 3056 (Australia); White, Max, E-mail: tamrak@bigpond.com [School of Fashion and Textiles, College of Design and Social Context, RMIT University, 25 Dawson Street, Brunswick, Victoria 3056 (Australia); Gao, Yuan, E-mail: Yuan.Gao@csiro.au [CSIRO, Manufacturing Flagship, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168 (Australia); Truong, Yen Bach, E-mail: Yen.truong@csiro.au [CSIRO, Manufacturing Flagship, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168 (Australia); Padhye, Rajiv, E-mail: rajiv.padhye@rmit.edu.au [School of Fashion and Textiles, College of Design and Social Context, RMIT University, 25 Dawson Street, Brunswick, Victoria 3056 (Australia); Kyratzis, Ilias Louis, E-mail: Louis.kyratzis@csiro.au [CSIRO, Manufacturing Flagship, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168 (Australia)
2017-04-01
A range of biodegradable drug-nanofibres composite mats have been reported as drug delivery systems. However, their main disadvantage is the rapid release of the drug immediately after application. This paper reports an improved system based on the incorporation of drug conjugated-chitosan into polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers. The results showed that controlled release of levofloxacin (LVF) could be achieved by covalently binding LVF to low molecular weight chitosan (CS) via a cleavable amide bond and then blending the conjugated CS with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibres prior to electrospinning. PVA/LVF and PVA-CS/LVF nanofibres were fabricated as controls. The conjugated CS-LVF was characterized by FTIR, DSC, TGA and {sup 1}H NMR. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the blended CS-PVA nanofibres had a reduced fibre diameter compared to the controls. Drug release profiles showed that burst release was decreased from 90% in the control PVA/LVF electrospun mats to 27% in the PVA/conjugated CS-LVF mats after 8 h in phosphate buffer at 37 °C. This slower release is due to the cleavable bond between LVF and CS that slowly hydrolysed over time at neutral pH. The results indicate that conjugation of the drug to the polymer backbone is an effective way of minimizing burst release behaviour and achieving sustained release of the drug, LVF. - Highlights: • A novel drug delivery system for controlled release of drug was designed. • Composite PVA/conjugated CS-LVF nanofibres was fabricated by electrospinning. • Conjugated chitosan and composite nanofibres were characterized by various techniques. • Release profiles of drug were significantly improved in composite nanofibres containing drug conjugated chitosan.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rekova, M.; Jedinakova-Krizova, V.
2010-01-01
The aim of the study of labeling of ligand-antibody conjugates was to find optimal conditions of preparing of these conjugates and appropriate radioactivity of selected nuclide for applications in nuclear medicine. Conjugation of the γ-immunoglobulin G (human or bovine IgG, polyclonal antibodies) and bifunctional chelating agent, diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid dianhydride (cDTPAA), was carried out. Various values of the cDTPAA/antibody ratio, the weight concentration of polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies (MEM-97) and buffers were used. Further, the labeling conditions of the DTPA-IgG conjugate by radionuclides 90 Y and 177 Lu were optimized, and the labeling yield and the conjugation ratio of prepared radionuclide-DTPA-IgG conjugates was determined. Optimal incubation time of the immunoglobulin conjugation was obtained at 30 min from mixing of individual components. The labeling yield of radionuclide-DTPA-antibody conjugate higher than 95% was achieved. Higher values of conjugation ratio of radionuclide-DTPA-antibody conjugate were achieved in 0.1 mol L -1 carbonate buffer, pH 8.5, and the 0.1 mol L -1 carbonate buffer is suitable for studied conjugation systems. This study showed that the labeling yield as well as the conjugation ratio of tested systems depend on the amount of antibody substance, bifunctional chelating agent/antibody molar ratio and pH value of the buffer used. (author)
-
Molecularly precise dendrimer-drug conjugates with tunable drug release for cancer therapy.
Zhou, Zhuxian; Ma, Xinpeng; Murphy, Caitlin J; Jin, Erlei; Sun, Qihang; Shen, Youqing; Van Kirk, Edward A; Murdoch, William J
2014-10-06
The structural preciseness of dendrimers makes them perfect drug delivery carriers, particularly in the form of dendrimer-drug conjugates. Current dendrimer-drug conjugates are synthesized by anchoring drug and functional moieties onto the dendrimer peripheral surface. However, functional groups exhibiting the same reactivity make it impossible to precisely control the number and the position of the functional groups and drug molecules anchored to the dendrimer surface. This structural heterogeneity causes variable pharmacokinetics, preventing such conjugates to be translational. Furthermore, the highly hydrophobic drug molecules anchored on the dendrimer periphery can interact with blood components and alter the pharmacokinetic behavior. To address these problems, we herein report molecularly precise dendrimer-drug conjugates with drug moieties buried inside the dendrimers. Surprisingly, the drug release rates of these conjugates were tailorable by the dendrimer generation, surface chemistry, and acidity. © 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Behavioral Health and Performance Operations During the Space Shuttle Program
Beven, G.; Holland, A.; Moomaw, R.; Sipes, W.; Vander Ark, S.
2011-01-01
Prior to the Columbia STS 107 disaster in 2003, the Johnson Space Center s Behavioral Health and Performance Group (BHP) became involved in Space Shuttle Operations on an as needed basis, occasionally acting as a consultant and primarily addressing crew-crew personality conflicts. The BHP group also assisted with astronaut selection at every selection cycle beginning in 1991. Following STS 107, an event that spawned an increased need of behavioral health support to STS crew members and their dependents, BHP services to the Space Shuttle Program were enhanced beginning with the STS 114 Return to Flight mission in 2005. These services included the presence of BHP personnel at STS launches and landings for contingency support, a BHP briefing to the entire STS crew at L-11 months, a private preflight meeting with the STS Commander at L-9 months, and the presence of a BHP consultant at the L-1.5 month Family Support Office briefing to crew and family members. The later development of an annual behavioral health assessment of all active astronauts also augmented BHP s Space Shuttle Program specific services, allowing for private meetings with all STS crew members before and after each mission. The components of each facet of these BHP Space Shuttle Program support services will be presented, along with valuable lessons learned, and with recommendations for BHP involvement in future short duration space missions
-
Two novel plasma diagnostic tools: fiber sensors and phase conjugation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jahoda, F.C.
1985-01-01
A rapidly developing technology (single-mode optical fiber sensors) and recent fundamental research in nonlinear optics (phase conjugation) both offer opportunities for novel plasma diagnostics. Single-mode fiber sensors can replace electrical wire probes for current and magnetic field measurements with advantages in voltage insulation requirements, electromagnetic noise immunity, much greater bandwidth, and some configuration flexibility. Faraday rotation measurements through fibers wound on the ZT-40M RFP have demonstrated quantitative results, but competing linear birefringence effects still hinder independent interpretation. Twisted fiber may solve this problem. Optical phase conjugation (in which a phase reversed copy of a laser beam is generated) allows real time distortion corrections in laser diagnostics. Self-pumped phase conjugation in BaTiO 3 improves the quality of phase conjugation imagery and greatly simplifies experimentation directed toward plasma diagnostics. Our initial applications are a) time-differential refractometry with high spatial resolution and b) intracavity absorption Zeeman spectroscopy
-
Excitons in conjugated polymers: Do we need a paradigma change?
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Beenken, Wichard J.D. [Department of Theoretical Physics I, Ilmenau University of Thechnology (Germany)
2009-12-15
We have previously shown that both, polymer conformation and dynamics are crucial for the exciton transport in conjugated polymers. Thereby we found that the usual Foerster-type hopping transfer model - even if one applies the line-dipole approximation - falls short in one crucial aspect: the nature of the sites the excitons are transferred between is still unclear. We found that the simple model of spectroscopic units defined as segments of the polymer chains separated by structural defects breaking the {pi}-conjugation is only justified for chemical defects like hydrogenated double bonds, or extreme gauche (90 ) torsions between the monomers. Both defects are far too rare in a well-prepared conjugated polymer to explain the mean spectroscopic-unit length of typically 6-7 monomers. Meanwhile, also the concept of dynamical formation of the spectroscopic units, we had previously suggested, has also failed. Thus the question of a paradigma change concerning the exciton transport in conjugated polymers appears on the agenda. (Abstract Copyright [2009], Wiley Periodicals, Inc.)
-
Tran, Phan T.; Goldman, Ellen R.; Mattoussi, Hedi M.; Anderson, George P.; Mauro, J. Matthew
2001-06-01
Colloidal semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) seem suitable for labeling certain biomolecules for use in fluorescent tagging applications, such as fluoro-immunoassays. Compared to organic dye labels, Qds are resistant to photo-degradation, and these luminescent nanoparticles have size-dependent emission spectra spanning a wide range of wavelengths in the visible and near IR. We previously described an electrostatic self-assembly approach for conjugating highly luminescent colloidal CdSe-ZnS core-shell Qds with engineered two-domain recombinant proteins. Here we describe the application of this approach to prepare QD conjugates with the (Beta) 2 immunoglobin G (IgG) binding domain of streptococcal protein G (PG) appended with a basic lucine zipper attachment domain (PG-zb). We also demonstrate that the QD/PG conjugates retain their ability to bind IgG antibodies, and that a specific antibody coupled to QD via the PG functional domain efficiently binds its antigen. These preliminary results indicate that electrostatically self-assembled QD/PG-zb/IgG bioconjugates can be used in fluoro-immunoassays.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Christine Unterweger
2018-03-01
Full Text Available In newborn piglets treatment with long-acting ceftiofur is a common approach to reduce losses due to streptococcal diseases on farms, even if problems start after weaning. The purpose of this study was to examine the influence of a single early-life treatment on Streptococcus (S. suis colonization, transmission, immunoreaction, and drug resistance over an observation period of 14 weeks. In a farm with a history of streptococcal disease and isolation of a S. suis cps 7 mrp+, arcA+ isolate from diseased piglets, half of each litter was treated with a long-acting ceftiofur on day 1. S. suis-isolates were profiled and serum samples were tested for opsonizing antibodies. Treated and untreated pigs did not differ according to average daily weight gains, S. suis-isolation rates and level of opsonizing antibodies. Although the invasive cps 7 strain was not detected in a single piglet over 14 weeks, all animals developed bactericidal activity. No resistance to ceftiofur, but resistance to tetracyclins (100%, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (53% was shown. Our results indicate that early treatment with ceftiofur does not prevent colonization and transmission of S. suis or the induction of bactericidal humoral immunity in nursery and fattening pigs. The necessity of continuous usage should be reconsidered.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Houen, G.; Olsen, D.T.; Hansen, P.R.
2003-01-01
A solid-phase conjugation method utilizing carrier protein bound to an ion exchange matrix was developed. Ovalbumin was adsorbed to an anion exchange matrix using a batch procedure, and the immobilized protein was then derivatized with iodoacetic acid N-hydroxysuccinimid ester. The activated......, and immunization experiments with the eluted conjugates showed that the more substituted conjugates gave rise to the highest titers of glutathione antibodies. Direct immunization with the conjugates adsorbed to the ion exchange matrix was possible and gave rise to high titers of glutathione antibodies. Conjugates...... of ovalbumin and various peptides were prepared in a similar manner and used for production of peptide antisera by direct immunization with the conjugates bound to the ion exchanger. Advantages of the method are its solid-phase nature, allowing fast and efficient reactions and intermediate washings...
-
Conjugated Polymers as Actuators: Modes of Actuation
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Skaarup, Steen
2004-01-01
The physical and chemical properties of conjugated polymers often depend very strongly on the degree of doping with anions or cations. The movement of ions in and out of the polymer matrix as it is redox cycled is also accompanied by mechanical changes. Both the volume and the stiffness can exhibit...... significant differences between the oxidized and reduced states. These effects form the basis of the use of conjugated polymers as actuators (or “artificial muscles”) controllable by a small (1-10 V) voltage. Three basic modes of actuation (bending, linear extension and stiffness change) have been proposed...
-
Conjugated polymers as actuators: modes of actuation
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Skaarup, Steen
2007-01-01
The physical and chemical properties of conjugated polymers often depend very strongly on the degree of doping with anions or cations. The movement of ions in and out of the polymer matrix as it is redox cycled is also accompanied by mechanical changes. Both the volume and the stiffness can exhibit...... significant differences between the oxidized and reduced states. These effects form the basis of the use of conjugated polymers as actuators (or “artificial muscles”) controllable by a small (1-10 V) voltage. Three basic modes of actuation (bending, linear extension and stiffness change) have been proposed...
-
Functionalized conjugated polyelectrolytes design and biomedical applications
Wang, Shu
2014-01-01
Functionalized Conjugated Polyelectrolytes presents a comprehensive review of these polyelectrolytes and their biomedical applications. Basic aspects like molecular design and optoelectronic properties are covered in the first chapter. Emphasis is placed on the various applications including sensing (chemical and biological), disease diagnosis, cell imaging, drug/gene delivery and disease treatment. This book explores a multi-disciplinary topic of interest to researchers working in the fields of chemistry, materials, biology and medicine. It also offers an integrated perspective on both basic research and application issues. Functionalized conjugated polyelectrolyte materials, which have already drawn considerable interest, will become a major new direction for biomedicine development.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Peiman Eini
2012-04-01
Full Text Available Background: Streptococcus Pyogenes (group A streptococcus, GAS is the most important cause of bacterial pharyngitis in children and adolescents. Acute pharyngitis is one of the most common conditions in all ages but it is most common in children. Over diagnosis of acute pharyngitis represents one of the major causes of antibiotic abuse. The goal of this study is to make an estimate of the frequency of group A streptococcus in sore throat patients in Farshchian hospital emergency department and clinic in Hamadan. Methods: For estimation of the clinical features role in diagnosis of streptococcal sore throat, we took samples of 100 patients with average age of 32.96±29.86 years with sore throat. We took samples from pharynx and used standard methods of bacteriology in order to detect streptococcus. Results: Group A Streptococcus (GAS accounts for 3 percent of all cases of pharyngitis. Clinically, all of the patients had sore throat. The percent breakdowns are as follows: 30% had exudate, 78% had fever, 8% had lymphadenopathy and 7.7 percent of exudative pharyngitis was streptococcal. The cost for unnecessary antibiotic therapy for every single patient who had negative pharynx culture was approximately 32160 Rails. Conclusion: The low frequency of streptococcus pharyngitis in treated patients reveal that diagnosis based on clinical features is not reliable. We recommend use of other diagnostic methods such as Rapid Antigen Detection Tests (RATs. Only reliable and scientific protocols for antibiotic to therapy.
-
New timetable for a Regular morning and evening shuttle
TS Department
2008-01-01
Starting from 31 March 2008, for one month, a new timetable for a regular morning and evening shuttle serving LHC Points 2 and 5 will be put in place. You can find all the corresponding details on the FM group WEB page: http://ts-dep.web.cern.ch/ts-dep/groups/fm/logistique/shuttle_timetable.htm Please note that during April, all other requests for transport from Meyrin and Prévessin to the LHC Points via tel. 76969 during the day (between 8:30 and 17:30) will not be met. TS/FM group Tel. 160239
-
New timetable for a morning and evening regular shuttle
TS Department
2008-01-01
Starting from the 31st of March 2008 and for one month, a new timetable for a morning and evening regular shuttle serving LHC Points 2 and 5, will be put in place. You can find all the corresponding details in the FM group WEB page http://ts-dep.web.cern.ch/ts-dep/groups/fm/logistique/shuttle_timetable.htm Please note that during April, every other request of transfer from Meyrin and Prevessin towards LHC Points reaching the 76969 during the day (between 8:30 and 17:30) will not be satisfied. TS/FM group 160239
-
Grooming the Shuttle for cost-effective access to space
Moore, J. W.
1985-01-01
An assessment is made of the performance of the Space Shuttle-based Space Transportation System (STS) from the initial flights in 1981 to the present, which has involved the launching of 12 satellites and the retrieval of two. It is expected that the STS will soon be able to schedule 24 routine missions/year, upon the achievement of full operational status for the full fleet of four Space Shuttles and the completion of support facilities at both the Kennedy Space Center and Vandenberg Air Force Base. The prospects for space industrialization efforts based on STS are noted.
-
Persistence Mechanisms of Conjugative Plasmids
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Bahl, Martin Iain; Hansen, Lars H.; Sørensen, Søren Johannes
2009-01-01
Are plasmids selfish parasitic DNA molecules or an integrated part of the bacterial genome? This chapter reviews the current understanding of the persistence mechanisms of conjugative plasmids harbored by bacterial cells and populations. The diversity and intricacy of mechanisms affecting the suc...
-
Curcumin-albumin conjugates as an effective anti-cancer agent with immunomodulatory properties.
Aravind, S R; Krishnan, Lissy K
2016-05-01
Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) is an active ingredient in turmeric (Curcuma longa) with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, chemopreventive, chemosensitization, and radiosensitization properties. Conjugation of curcumin (Curc) to albumin (Alb) has been found to increase the aqueous solubility of the drug. The current study aimed to prove the safe use of the Curc-Alb conjugate in animals and to demonstrate that it retains drug action both in vitro and in vivo. Dalton's lymphoma ascites (DLA) cell viability was inhibited by the Curc-Alb conjugate in a dose dependent manner in vitro, as evidenced by the MTT assay. Administration of up to 11.4 mg of conjugated curcumin per kg body weight to healthy animals was non-toxic both in terms of lethality and weight loss. Histological analysis of vital organs (kidney, liver and spleen) also did not show toxic effects. Favorable immuno-modulatory activity was observed after continuous administration of sub-acute doses of the conjugate which caused increase in total leukocyte count, platelet count, and viable cell count in bone marrow, and enhanced proliferation of lymphocyte in vitro upon culture. In vivo studies in the DLA tumor model in mice demonstrated that conjugated drug induces tumor reduction and prevention. Significant tumor reduction was observed when the Curc-Alb conjugate was administered intraperitoneally in DLA-induced mice after 1 day (prevention therapy) and 7 days (reduction therapy) of tumor induction. There was significant reduction in both tumor volume and tumor cell numbers in the treated animals as well as a marked increase in their mean survival time and percent increase in life span. The effect was greater when the conjugate was administered soon after inducing the tumor as compared to when treatment was started after allowing tumor to grow for 7 days. Thus, the results of the present study suggest that curcumin albumin conjugate has immunomodulatory and tumor growth inhibition properties. The study postulates
-
Purdy, Des; O'Keeffe, Triona A T; Elmore, Michael; Herbert, Mike; McLeod, Anne; Bokori-Brown, Monika; Ostrowski, Anna; Minton, Nigel P
2002-10-01
Progress towards understanding the molecular basis of virulence in Clostridium difficile has been hindered by the lack of effective gene transfer systems. We have now, for the first time, developed procedures that may be used to introduce autonomously replicating vectors into this organism through their conjugative, oriT-based mobilization from Escherichia coli donors. Successful transfer was achieved through the use of a plasmid replicon isolated from an indigenous C. difficile plasmid, pCD6, and through the characterization and subsequent circumvention of host restriction/modification (RM) systems. The characterized replicon is the first C. difficile plasmid replicon to be sequenced and encodes a large replication protein (RepA) and a repetitive region composed of a 35 bp iteron sequence repeated seven times. Strain CD6 has two RM systems, CdiCD6I/M.CdiCD6I and CdiCD6II/M. CdiCD6II, with equivalent specificities to Sau96I/M. Sau96I (5'-GGNMCC-3') and MboI/M. MboI (5'-GMATC-3') respectively. A second strain (CD3) possesses a type IIs restriction enzyme, Cdi I, which cleaves the sequence 5'-CATCG-3' between the fourth and fifth nucleotide to give a blunt-ended fragment. This is the first time that an enzyme with this specificity has been reported. The sequential addition of this site to vectors showed that each site caused between a five- and 16-fold reduction in transfer efficiency. The transfer efficiencies achieved with both strains equated to between 1.0 x 10-6 and 5.5 x 10-5 transconjugants per donor.
-
Luleyap, H. Umit; Onatoglu, Dilge; Yilmaz, M. Bertan; Alptekin, Davut; Tahiroglu, Aysegul Y.; Cetiner, Salih; Pazarbasi, Ayfer; Unal, Ilker; Avci, Ayse; Comertpay, Gamze
2013-01-01
Objectives: Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal Infections (PANDAS) is a newly defined disease in neuropsychiatry and occurs with an autoimmune mechanism after Group A Beta Hemolytic Streptococcus (GABHS) infection. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), encoded by TNF-α gene has an important role in the apoptotic mechanisms of autoimmune diseases. Recently, TNF-α polymorphisms and autoimmune/psychiatric disorders have been reported to be related. In this regar...
-
Stochastic Spectral and Conjugate Descent Methods
Kovalev, Dmitry
2018-02-11
The state-of-the-art methods for solving optimization problems in big dimensions are variants of randomized coordinate descent (RCD). In this paper we introduce a fundamentally new type of acceleration strategy for RCD based on the augmentation of the set of coordinate directions by a few spectral or conjugate directions. As we increase the number of extra directions to be sampled from, the rate of the method improves, and interpolates between the linear rate of RCD and a linear rate independent of the condition number. We develop and analyze also inexact variants of these methods where the spectral and conjugate directions are allowed to be approximate only. We motivate the above development by proving several negative results which highlight the limitations of RCD with importance sampling.
-
Stochastic Spectral and Conjugate Descent Methods
Kovalev, Dmitry; Gorbunov, Eduard; Gasanov, Elnur; Richtarik, Peter
2018-01-01
The state-of-the-art methods for solving optimization problems in big dimensions are variants of randomized coordinate descent (RCD). In this paper we introduce a fundamentally new type of acceleration strategy for RCD based on the augmentation of the set of coordinate directions by a few spectral or conjugate directions. As we increase the number of extra directions to be sampled from, the rate of the method improves, and interpolates between the linear rate of RCD and a linear rate independent of the condition number. We develop and analyze also inexact variants of these methods where the spectral and conjugate directions are allowed to be approximate only. We motivate the above development by proving several negative results which highlight the limitations of RCD with importance sampling.
-
Zhou, Kaixin; Xie, Lianyan; Han, Lizhong; Guo, Xiaokui; Wang, Yong; Sun, Jingyong
2017-01-01
ICE Sag37 , a novel integrative and conjugative element carrying multidrug resistance and potential virulence factors, was characterized in a clinical isolate of Streptococcus agalactiae . Two clinical strains of S. agalactiae , Sag37 and Sag158, were isolated from blood samples of new-borns with bacteremia. Sag37 was highly resistant to erythromycin and tetracycline, and susceptible to levofloxacin and penicillin, while Sag158 was resistant to tetracycline and levofloxacin, and susceptible to erythromycin. Transfer experiments were performed and selection was carried out with suitable antibiotic concentrations. Through mating experiments, the erythromycin resistance gene was found to be transferable from Sag37 to Sag158. Sma I-PFGE revealed a new Sma I fragment, confirming the transfer of the fragment containing the erythromycin resistance gene. Whole genome sequencing and sequence analysis revealed a mobile element, ICE Sag37 , which was characterized using several molecular methods and in silico analyses. ICE Sag37 was excised to generate a covalent circular intermediate, which was transferable to S. agalactiae . Inverse PCR was performed to detect the circular form. A serine family integrase mediated its chromosomal integration into rumA , which is a known hotspot for the integration of streptococcal ICEs. The integration site was confirmed using PCR. ICE Sag37 carried genes for resistance to multiple antibiotics, including erythromycin [ erm(B) ], tetracycline [ tet(O) ], and aminoglycosides [ aadE, aphA , and ant(6) ]. Potential virulence factors, including a two-component signal transduction system ( nisK/nisR ), were also observed in ICE Sag37 . S1-PFGE analysis ruled out the existence of plasmids. ICE Sag37 is the first ICE Sa2603 family-like element identified in S. agalactiae carrying both resistance and potential virulence determinants. It might act as a vehicle for the dissemination of multidrug resistance and pathogenicity among S. agalactiae .
-
Shuttle Lesson Learned - Toxicology
James, John T.
2010-01-01
This is a script for a video about toxicology and the space shuttle. The first segment is deals with dust in the space vehicle. The next segment will be about archival samples. Then we'll look at real time on-board analyzers that give us a lot of capability in terms of monitoring for combustion products and the ability to monitor volatile organics on the station. Finally we will look at other issues that are about setting limits and dealing with ground based lessons that pertain to toxicology.
-
Swain, Shasank S; Paidesetty, Sudhir K; Padhy, Rabindra N
2017-03-01
To develop 6 conjugate agents of the moribund antibiotic sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) joined to 6 individual monoterpenes, followed by protocols of medicinal chemistry as potent antibacterials, against multidrug resistant (MDR) human gruesome pathogenic bacteria. Antibacterial activities of the proposed conjugates were ascertained by the 'prediction of activity spectra of substances' (PASS) program. Drug-likeness parameters and toxicity profiles of conjugates were standardized with the Lipinski rule of five, using cheminformatic tools, Molsoft, molinspiration, OSIRIS and ProTox. Antibacterial activities of individual chemicals and conjugates were examined by targeting the bacterial folic acid biosynthesis enzyme, dihydropteroate synthases (DHPSs) of bacteria, Bacillus anthracis, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with 3D structures of DHPSs from protein data bank. According to the PASS program, biological spectral values of conjugate-2, conjugate-5 and conjugate-6 were ascertained effective with 'probably active' or 'Pa' value > 0.5, for anti-infective and antituberculosic activities. Using molecular docking against 5 cited bacterial DHPSs, effective docking scores of 6 monoterpenes in the specified decreasing order (kcal/mol): -9.72 (eugenol against B. anthracis), -9.61 (eugenol against S. pneumoniae), -9. 42 (safrol, against B. anthracis), -9.39 (thymol, against M. tuberculosis), -9.34 (myristicin, against S. pneumoniae) and -9.29 (thymol, against B. anthracis); whereas the lowest docking score of SMZ was -8.46kcal/mol against S. aureus DHPS. Similarly, effective docking scores of conjugates were as specified (kcal/mol.): -10.80 (conjugate-4 consisting SMZ+safrol, against M. tuberculosis), -10.78 (conjugate-5 consisting SMZ+thymol, against M. tuberculosis), -10.60 (conjugate-5 against B. anthracis), -10.26 (conjugate-2 consisting SMZ+ eugenol, against M. tuberculosis), -10.25 (conjugate-5, against S
-
Uptake of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Conjugated with DNA by Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Joseph Harvey
2012-01-01
Full Text Available Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs have been proposed to have great therapeutic potential. SWCNTs conjugated with drugs or genes travel in the systemic circulation to reach target cells or tissues following extravasation from microvessels although the interaction between SWCNT conjugates and the microvascular endothelial cells (ECs remains unknown. We hypothesized that SWCNT-DNA conjugates would be taken up by microvascular ECs and that this process would be facilitated by SWCNTs compared to facilitation by DNA alone. ECs were treated with various concentrations of SWCNT-DNA-FITC conjugates, and the uptake and intracellular distribution of these conjugates were determined by a confocal microscope imaging system followed by quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity. The uptake of SWCNT-DNA-FITC conjugates (2 μg/mL by microvascular ECs was significantly greater than that of DNA-FITC (2 μg/mL, observed at 6 hrs after treatment. For the intracellular distribution, SWCNT-DNA-FITC conjugates were detected in the nucleus of ECs, while DNA-FITC was restricted to the cytoplasm. The fluorescence intensity and distribution of SWCNTs were concentration and time independent. The findings demonstrate that SWCNTs facilitate DNA delivery into microvascular ECs, thus suggesting that SWCNTs serving as drug and gene vehicles have therapeutic potential.
-
Several Guaranteed Descent Conjugate Gradient Methods for Unconstrained Optimization
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
San-Yang Liu
2014-01-01
Full Text Available This paper investigates a general form of guaranteed descent conjugate gradient methods which satisfies the descent condition gkTdk≤-1-1/4θkgk2 θk>1/4 and which is strongly convergent whenever the weak Wolfe line search is fulfilled. Moreover, we present several specific guaranteed descent conjugate gradient methods and give their numerical results for large-scale unconstrained optimization.
-
Conjugation of curcumin onto alginate enhances aqueous solubility and stability of curcumin.
Dey, Soma; Sreenivasan, K
2014-01-01
Curcumin is a potential drug for various diseases including cancer. Prime limitations associated with curcumin are low water solubility, rapid hydrolytic degradation and poor bioavailability. In order to redress these issues we developed Alginate-Curcumin (Alg-Ccm) conjugate which was characterized by FTIR and (1)H NMR spectroscopy. The conjugate self-assembled in aqueous solution forming micelles with an average hydrodynamic diameter of 459 ± 0.32 nm and negative zeta potential. The spherical micelles were visualized by TEM. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of Alg-Ccm conjugate was determined. A significant enhancement in the aqueous solubility of curcumin was observed upon conjugation with alginate. Formation of micelles improved the stability of curcumin in water at physiological pH. The cytotoxic activity of Alg-Ccm was quantified by MTT assay using L-929 fibroblast cells and it was found to be potentially cytotoxic. Hence, Alg-Ccm could be a promising drug conjugate as well as a nanosized delivery vehicle. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Comparison of linoleic and conjugated linoleic acids in enzymatic acidolysis of tristearin
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Yang, Tiankui; Xu, Xuebing; Li, L.T.
2001-01-01
tristearin (SSS) and linoleic (L) or conjugated linoleic (cL) acids (1:6, mol/mol). The other was between tristearin and the mixture of linoleic and conjugated linoleic acids (1:3:3, mol/mol/mol). Acyl incorporation and migration together with triacylglycerol composition of the products were monitored...... with gas chromatography, pancreatic lipase hydrolysis, and high performance liquid chromatography. Both acyl incorporation and migration of linoleic acid were faster than those of conjugated linoleic acid. At 5 h reaction, there were 13.0% LLL, 46.5% LSL, 27.7% LSS, and 5.6% SSS in the product for a system...... between tristearin and linoleic acid; whereas there were 2.4% cLcLcL, 10.4% cLScL, 50.9% cLSS, and 36.2% SSS in the product for a system between tristearin and conjugated linoleic acid. The results suggest that linoleic acid was more reactive than conjugated linoleic acid in the enzymatic acidolysis...
-
Effects of transferrin conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes in lung cancer delivery
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Singh, Rahul Pratap [Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Sharma, Gunjan [Genotoxicology and Cancer Biology Lab, Department of Zoology, Institute of Science, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Sonali [Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Singh, Sanjay [Department of Pharmaceutics, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi 221005 (India); Patne, Shashikant C.U. [Department of Pathology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Pandey, Bajarangprasad L. [Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Koch, Biplob, E-mail: kochbiplob@gmail.com [Genotoxicology and Cancer Biology Lab, Department of Zoology, Institute of Science, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Muthu, Madaswamy S., E-mail: muthubits@rediffmail.com [Department of Pharmaceutics, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi 221005 (India); Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India)
2016-10-01
The aim of this study was to develop multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) which were covalently conjugated with transferrin by carbodiimide chemistry and loaded with docetaxel as a model drug for effective treatment of lung cancer in comparison with the commercial docetaxel injection (Docel™). D-Alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was used as amphiphilic surfactant to improve the aqueous dispersity and biocompatibility of MWCNT. Human lung cancer cells (A549 cells) were employed as an in-vitro model to access cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle analysis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) of the docetaxel/coumarin-6 loaded MWCNT. The cellular uptake results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT showed higher efficiency in comparison with free C6. The IC{sub 50} values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more efficient than Docel™ after 24 h treatment with the A549 cells. Flow cytometry analysis confirmed that cancerous cells appeared significantly (P < 0.05) in the sub-G1 phase for transferrin conjugated MWCNT in comparison with Docel™. Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™. - Highlights: • It shows the development of transferrin conjugated MWCNT formulation of DTX for the effective treatment of lung cancer. • Evaluated the cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle, and ROS level of the DTX/C6 loaded MWCNT. • The IC{sub 50} values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more effective than Docel™. • Safety of the DTX formulations were studied by the measurements of ALP, LDH and total protein count levels in BAL fluid. • Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™ in lung cancer delivery.
-
Effects of transferrin conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes in lung cancer delivery
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Singh, Rahul Pratap; Sharma, Gunjan; Sonali; Singh, Sanjay; Patne, Shashikant C.U.; Pandey, Bajarangprasad L.; Koch, Biplob; Muthu, Madaswamy S.
2016-01-01
The aim of this study was to develop multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) which were covalently conjugated with transferrin by carbodiimide chemistry and loaded with docetaxel as a model drug for effective treatment of lung cancer in comparison with the commercial docetaxel injection (Docel™). D-Alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was used as amphiphilic surfactant to improve the aqueous dispersity and biocompatibility of MWCNT. Human lung cancer cells (A549 cells) were employed as an in-vitro model to access cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle analysis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) of the docetaxel/coumarin-6 loaded MWCNT. The cellular uptake results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT showed higher efficiency in comparison with free C6. The IC_5_0 values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more efficient than Docel™ after 24 h treatment with the A549 cells. Flow cytometry analysis confirmed that cancerous cells appeared significantly (P < 0.05) in the sub-G1 phase for transferrin conjugated MWCNT in comparison with Docel™. Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™. - Highlights: • It shows the development of transferrin conjugated MWCNT formulation of DTX for the effective treatment of lung cancer. • Evaluated the cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle, and ROS level of the DTX/C6 loaded MWCNT. • The IC_5_0 values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more effective than Docel™. • Safety of the DTX formulations were studied by the measurements of ALP, LDH and total protein count levels in BAL fluid. • Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™ in lung cancer delivery.
-
2013-03-28
...-Up Exclusive License: Photosensitizing Antibody-Fluorophore Conjugates for Photoimmunotherapy AGENCY...-205-2010/0-US-01), and entitled ``Photosensitizing Antibody- Fluorophore Conjugates,'' to Aspyrian... invention. The field of use may be limited to ``use of photosensitizing antibody-fluorophore conjugate by...
-
Platelet injectors for Space Shuttle orbit maneuvering engine
Kahl, R. C.; Labotz, R. J.; Bassham, L. B.
1974-01-01
The Space Shuttle Orbit Maneuvering Subsystem Rocket Engine employs a platelet element injector concept. This injector has demonstrated 316-sec vacuum specific impulse performance under simulated altitude conditions when tested with a milled slot/electroformed nickel close-out regenerative chamber and a full 71 area ratio nozzle. To date, over 300 altitude engine tests and 300 stability bomb tests have demonstrated stable, erosion free operation with this concept to test durations of 150 seconds. The injector and chamber also meet the reusable requirements of the shuttle with a cycle life capability in excess of 1000 cycles. An extensive altitude restart program has also demonstrated OMS-engine operation over large variations in the burn and coast times with helium saturated propellants.
-
A Shuttle Upper Atmosphere Mass Spectrometer /SUMS/ experiment
Blanchard, R. C.; Duckett, R. J.; Hinson, E. W.
1982-01-01
A magnetic mass spectrometer is currently being adapted to the Space Shuttle Orbiter to provide repeated high altitude atmosphere data to support in situ rarefied flow aerodynamics research, i.e., in the high velocity, low density flight regime. The experiment, called Shuttle Upper Atmosphere Mass Spectrometer (SUMS), is the first attempt to design mass spectrometer equipment for flight vehicle aerodynamic data extraction. The SUMS experiment will provide total freestream atmospheric quantitites, principally total mass density, above altitudes at which conventional pressure measurements are valid. Experiment concepts, the expected flight profile, tradeoffs in the design of the total system and flight data reduction plans are discussed. Development plans are based upon a SUMS first flight after the Orbiter initial development flights.
-
Treder, Alfred J.; Meldahl, Keith L.
The recorded histories of Shuttle/Orbiter attitude and Inertial Upper Stage (IUS) attitude have been analyzed for all joint flights of the IUS in the Orbiter. This database was studied to determine the behavior of relative alignment between the IUS and Shuttle navigation systems. It is found that the overall accuracy of physical alignment has a Shuttle Orbiter bias component less than 5 arcmin/axis and a short-term stability upper bound of 0.5 arcmin/axis, both at 1 sigma. Summaries of the experienced physical and inertial alginment offsets are shown in this paper, together with alignment variation data, illustrated with some flight histories. Also included is a table of candidate values for some error source groups in an Orbiter/IUS attitude errror model. Experience indicates that the Shuttle is much more accurate and stable as an orbiting launch platform than has so far been advertised. This information will be valuable for future Shuttle payloads, especially those (such as the Aeroassisted Flight Experiment) which carry their own inertial navigation systems, and which could update or initialize their attitude determination systems using the Shuttle as the reference.
-
ACTS/TOS after release from Shuttle Discovery
1993-01-01
The Advanced Communications Technology Satellite (ACTS) with its Transfer Orbit Stage (TOS) is backdropped over the blue ocean following its release from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery. ACTS/TOS deploy was the first major task performed on the almost ten-day mission.
-
Single-particle tracking of quantum dot-conjugated prion proteins inside yeast cells
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tsuji, Toshikazu; Kawai-Noma, Shigeko [Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Graduate School of Biosciences and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, B56, 4259 Nagatsuta, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501 (Japan); Pack, Chan-Gi [Cellular Informatics Laboratory, RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198 (Japan); Terajima, Hideki [Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Graduate School of Biosciences and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, B56, 4259 Nagatsuta, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501 (Japan); Yajima, Junichiro; Nishizaka, Takayuki [Department of Physics, Gakushuin University, 1-5-1 Mejiro, Toshima-ku, Tokyo 171-8588 (Japan); Kinjo, Masataka [Laboratory of Molecular Cell Dynamics, Graduate School of Life Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 001-0021 (Japan); Taguchi, Hideki, E-mail: taguchi@bio.titech.ac.jp [Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Graduate School of Biosciences and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, B56, 4259 Nagatsuta, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501 (Japan)
2011-02-25
Research highlights: {yields} We develop a method to track a quantum dot-conjugated protein in yeast cells. {yields} We incorporate the conjugated quantum dot proteins into yeast spheroplasts. {yields} We track the motions by conventional or 3D tracking microscopy. -- Abstract: Yeast is a model eukaryote with a variety of biological resources. Here we developed a method to track a quantum dot (QD)-conjugated protein in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We chemically conjugated QDs with the yeast prion Sup35, incorporated them into yeast spheroplasts, and tracked the motions by conventional two-dimensional or three-dimensional tracking microscopy. The method paves the way toward the individual tracking of proteins of interest inside living yeast cells.
-
Single-particle tracking of quantum dot-conjugated prion proteins inside yeast cells
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tsuji, Toshikazu; Kawai-Noma, Shigeko; Pack, Chan-Gi; Terajima, Hideki; Yajima, Junichiro; Nishizaka, Takayuki; Kinjo, Masataka; Taguchi, Hideki
2011-01-01
Research highlights: → We develop a method to track a quantum dot-conjugated protein in yeast cells. → We incorporate the conjugated quantum dot proteins into yeast spheroplasts. → We track the motions by conventional or 3D tracking microscopy. -- Abstract: Yeast is a model eukaryote with a variety of biological resources. Here we developed a method to track a quantum dot (QD)-conjugated protein in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We chemically conjugated QDs with the yeast prion Sup35, incorporated them into yeast spheroplasts, and tracked the motions by conventional two-dimensional or three-dimensional tracking microscopy. The method paves the way toward the individual tracking of proteins of interest inside living yeast cells.
-
Nonlinear piezoelectricity in PZT ceramics for generating ultrasonic phase conjugate waves
Yamamoto; Kokubo; Sakai; Takagi
2000-03-01
We have succeeded in the generation of acoustic phase conjugate waves with nonlinear PZT piezoelectric ceramics and applied them to ultrasonic imaging systems. Our aim is to make a phase conjugator with 100% efficiency. For this purpose, it is important to clarify the mechanism of acoustic phase conjugation through nonlinear piezoelectricity. The process is explained by the parametric interaction via the third-order nonlinear piezoelectricity between the incident acoustic wave at angular frequency omega and the pump electric field at 2 omega. We solved the coupling equations including the third-ordered nonlinear piezoelectricity and theoretically derived the amplitude efficiency of the acoustic phase conjugation. We compared the efficiencies between the theoretical and experimental values for PZT ceramics with eight different compositions. Pb[(Zn1/3Nb2/3)(1 - x)Tix]O3 (X = 0.09, PZNT91/9) piezoelectric single crystals have been investigated for high-performance ultrasonic transducer application, because these have large piezoelectric constants, high electrical-mechanical coupling factors and high dielectric constants. We found that they have third-order nonlinear piezoelectric constants much larger than PZT and are hopeful that the material as a phase conjugator has over 100% efficiency.
-
Storage Conditions of Conjugated Reagents Can Impact Results of Immunogenicity Assays
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Robert J. Kubiak
2016-01-01
Full Text Available Consistent performance of anti-drug antibody (ADA assays through all stages of clinical development is critical for the assessment of immunogenicity and interpretation of PK, PD, safety, and efficacy. The electrochemiluminescent assays commonly employed for ADA measurement use drug conjugated with ruthenium and biotin to bind ADA in samples. Here we report an association between high nonspecific ADA responses in certain drug-naïve individuals and the storage buffer of the conjugated reagents used in a monoclonal antibody ADA assay. Ruthenylated reagents stored in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS buffer had increased levels of aggregate and produced variable and high baseline responses in some subjects. Reagents stored in a histidine-sucrose buffer (HSB had lower aggregate levels and produced low sample responses. In contrast to PBS, conjugated reagents formulated in HSB remained low in aggregate content and in sample response variability after 5 freeze/thaw cycles. A reagent monitoring control (RMC serum was prepared for the real-time evaluation of conjugated reagent quality. Using appropriate buffers for storage of conjugated reagents together with RMCs capable of monitoring of reagent aggregation status can help ensure consistent, long-term performance of ADA methods.
-
Intracellular trafficking of new anticancer therapeutics: antibody–drug conjugates
Kalim, Muhammad; Chen, Jie; Wang, Shenghao; Lin, Caiyao; Ullah, Saif; Liang, Keying; Ding, Qian; Chen, Shuqing; Zhan, Jinbiao
2017-01-01
Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) is a milestone in targeted cancer therapy that comprises of monoclonal antibodies chemically linked to cytotoxic drugs. Internalization of ADC takes place via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-mediated endocytosis, and pinocytosis. Conjugation strategies, endocytosis and intracellular trafficking optimization, linkers, and drugs chemistry present a great challenge for researchers to eradicate tumor cells successfully. This inventiveness of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking has given considerable momentum recently to develop specific antibodies and ADCs to treat cancer cells. It is significantly advantageous to emphasize the endocytosis and intracellular trafficking pathways efficiently and to design potent engineered conjugates and biological entities to boost efficient therapies enormously for cancer treatment. Current studies illustrate endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ADC, protein, and linker strategies in unloading and also concisely evaluate practically applicable ADCs. PMID:28814834
-
Intracellular trafficking of new anticancer therapeutics: antibody-drug conjugates.
Kalim, Muhammad; Chen, Jie; Wang, Shenghao; Lin, Caiyao; Ullah, Saif; Liang, Keying; Ding, Qian; Chen, Shuqing; Zhan, Jinbiao
2017-01-01
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is a milestone in targeted cancer therapy that comprises of monoclonal antibodies chemically linked to cytotoxic drugs. Internalization of ADC takes place via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-mediated endocytosis, and pinocytosis. Conjugation strategies, endocytosis and intracellular trafficking optimization, linkers, and drugs chemistry present a great challenge for researchers to eradicate tumor cells successfully. This inventiveness of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking has given considerable momentum recently to develop specific antibodies and ADCs to treat cancer cells. It is significantly advantageous to emphasize the endocytosis and intracellular trafficking pathways efficiently and to design potent engineered conjugates and biological entities to boost efficient therapies enormously for cancer treatment. Current studies illustrate endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ADC, protein, and linker strategies in unloading and also concisely evaluate practically applicable ADCs.
-
Repercussions of imprisonment for conjugal violence: discourses of men
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Anderson Reis de Sousa
Full Text Available ABSTRACT Objective: to know the consequences that men experience related to incarceration by conjugal violence. Methods: qualitative study on 20 men in jail and indicted in criminal processes related to conjugal violence in a Court specialized in Family and Domestic Violence against women. The interviews were classified based on Collective Subject Discourse method, using NVIVO(r software. Results: the collective discourse shows that the experience of preventive imprisonment starts a process of family dismantling, social stigma, financial hardship and psycho-emotional symptoms such as phobia, depression, hypertension, and headaches. Conclusion: due to the physical, mental and social consequences of the conjugal violence-related imprisonment experience, it is urgent to look carefully into the somatization process as well as to the prevention strategies regarding this process.
-
Wingard, Doug
2006-01-01
During the Space Shuttle Columbia Accident Investigation, it was determined that a large chunk of polyurethane insulating foam (= 1.67 lbs) on the External Tank (ET) came loose during Columbia's ascent on 2-1-03. The foam piece struck some of the protective Reinforced Carbon-Carbon (RCC) panels on the leading edge of Columbia's left wing in the mid-wing area. This impact damaged Columbia to the extent that upon re-entry to Earth, superheGed air approaching 3,000 F caused the vehicle to break up, killing all seven astronauts on board. A paper after the Columbia Accident Investigation highlighted thermal analysis testing performed on External Tank TPS materials (1). These materials included BX-250 (now BX-265) rigid polyurethane foam and SLA-561 Super Lightweight Ablator (highly-filled silicone rubber). The large chunk of foam from Columbia originated fiom the left bipod ramp of the ET. The foam in this ramp area was hand-sprayed over the SLA material and various fittings, allowed to dry, and manually shaved into a ramp shape. In Return-to-Flight (RTF) efforts following Columbia, the decision was made to remove the foam in the bipod ramp areas. During RTF efforts, further thermal analysis testing was performed on BX-265 foam by DSC and DMA. Flat panels of foam about 2-in. thick were sprayed on ET tank material (aluminum alloys). The DSC testing showed that foam material very close to the metal substrate cured more slowly than bulk foam material. All of the foam used on the ET is considered fully cured about 21 days after it is sprayed. The RTF culminated in the successful launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on 7-26-05. Although the flight was a success, there was another serious incident of foam loss fiom the ET during Shuttle ascent. This time, a rather large chunk of BX-265 foam (= 0.9 lbs) came loose from the liquid hydrogen (LH2) PAL ramp, although the foam did not strike the Shuttle Orbiter containing the crew. DMA testing was performed on foam samples taken fiom
-
Structural Continuum Modeling of Space Shuttle External Tank Foam Insulation
Steeve, Brian; Ayala, Sam; Purlee, T. Eric; Shaw, Phillip
2006-01-01
This document is a viewgraph presentation reporting on work in modeling the foam insulation of the Space Shuttle External Tank. An analytical understanding of foam mechanics is required to design against structural failure. The Space Shuttle External Tank is covered primarily with closed cell foam to: Prevent ice, Protect structure from ascent aerodynamic and engine plume heating, and Delay break-up during re-entry. It is important that the foam does not shed unacceptable debris during ascent environment. Therefore a modeling of the foam insulation was undertaken.
-
Conjugate heat transfer of laminar film condensation along a horizontal plate
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lee, Euk Soo [Pusan National Univesity, Busan (Korea, Republic of)
2006-03-15
This paper proposes appropriate conjugate parameters and dimensionless temperatures to analysis the conjugate problem of heat conduction in solid wall coupled with laminar film condensation flow adjacent to horizontal flat plate. An efficient methods for some fluids are proposed for its solution. The momentum and energy balance equations are reduced to a nonlinear system of ordinary differential equations with four parameters: the Prandtl number, Pr, Modified Jacob number, Ja{sup *}/Pr, defined by an overall temperature difference, a property ratio {radical}{rho}{sub {iota}}{mu}{sub {iota}} {radical}{rho}{sub {upsilon}}{mu}{sub {upsilon}} and the conjugate parameter {zeta}. The obtained similarity solution reveals the effect of the conjugate parameter, and the results are compared with the simplified solution. The variations of the heat transfer rates as well as the interface temperature and frictions along the plate are shown explicitly.
-
Albumin–Polymer–Drug Conjugates: Long Circulating, High Payload Drug Delivery Vehicles
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Smith, Anton Allen Abbotsford; Zuwala, Kaja; Pilgram, Oliver
2016-01-01
Albumin is an exquisite tool of nature used in biomedicine to achieve long blood residence time for drugs, but the payload it can carry is typically limited to one molecule per protein. In contrast, synthetic macromolecular prodrugs contain multiple copies of drugs per polymer chain but offer only...... a marginal increase in the circulation lifetime of the drugs. We combine the benefits of the two platforms and at the same time overcome their respective limitations. Specifically, we develop the synthesis of albumin–polymer–drug conjugates to obtain long circulating, high payload drug delivery vehicles....... In vivo data validate that albumin endows the conjugate with a blood residence time similar to that of the protein and well exceeding that of the polymer. Therapeutic activity of the conjugates is validated using prodrugs of panobinostat, an HIV latency reversal agent, in which case the conjugates matched...
-
DNA-templated antibody conjugation for targeted drug delivery to cancer cells
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Liu, Tianqiang
2016-01-01
-templated organic synthesis due to the wide existence of the 3-histidine cluster in most wild-type proteins. In this thesis, three projects that relate to targeted drug delivery to cancer cells based on the DTPC method is described. The first project was a delivery system which uses transferrin as the targeting....... The study shows that DNA is a highly useful tool for the assembly of proteins with potential therapeutic applications. The DNA-templated protein conjugation shows a promising application in constructing antibody-toxin conjugates or antibody-drug conjugates. In addition, DNA strands used for antibody...... either antibody engineering or special expression systems and are both time and labor consuming. To avoid the drawbacks caused by conventional chemical modification and recombinant methodologies, an ideal site specific conjugation technique would use natural amino acid residues to the protein by a new...
-
Biotransformation of Flavonoid Conjugates with Fatty Acids and Evaluations of Their Functionalities
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Cynthia Q. Sun
2017-11-01
Full Text Available Enzymatic conjugation with fatty acids including omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω-3 PUFAs derived from fish oil to three citrus fruit-derived flavonoids: grapefruit extract, naringin, and neohesperidin dihydrochalcone were investigated. The conversions were achieved over 85% under the catalysis of lipase Novozyme 435 in acetone at 45°C at semi-preparative scale. The conjugates were purified via solvent partition and silica gel chromatography and achieved 90–98% in purity. The NMR analysis of the conjugates confirmed that the fatty acid carbon chain was linked onto the primary –OH group on the glucose moiety of the flavonoids. The purified flavonoid conjugates alongside their original flavonoids were analyzed for antioxidant activities via 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl scavenging assay, and anti-peroxidation test via peroxide values measured during a 1-week fish oil storage trial. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF assay was conducted with 1, 10, and 100 μM of naringin and grapefruits and their conjugates, respectively, and total VEGF levels were measured at 24 and 48 h, respectively, using ELISA and dot blot analysis. The results from these functionality experiments demonstrated that flavonoid FA conjugates have at least comparable (if not higher antioxidant activity, anti-peroxidation activity, and anti-angiogenic activity.
-
The mitochondrial toxicity of cysteine-S-conjugates: Studies with pentachlorobutadienyl-L-cysteine
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wallin, A.
1990-01-01
Nephrotoxic cysteine conjugates, arising from mercapturate biosynthesis, can perturb the mitochondrial membrane potential and calcium homeostasis in renal epithelial cells. Activation of these cysteine conjugates to reactive species by mitochondrial β-lyases results in covalent binding and mitochondrial damage. PCBC and related cysteine conjugates inhibit ADP-stimulated respiration in mitochondria respiring on alpha-ketoglutrate/malate and succinate indicating that both dehydrogenases may be targets. The respiratory inhibition is blocked by aminooxyacetic acid, an inhibitor of the β-lyase. Hence, metabolic activation is required implying that covalent binding of reactive intermediates may be important to the mitochondrial injury. Binding of 35 S-fragments has been found for 5 conjugates with varying degrees of mitochondrial toxicity. PCBC is more lipophilic and has a higher affinity for cellular membranes than other cysteine conjugates. PCBC rapidly depolarizes the inner membrane potential resulting in an inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and calcium upon sequestration. Consequently, mitochondria and renal epithelial cells exposed to PCBC show a sudden release of calcium upon exposure to PCBC which is followed by a later increase in state 4 respiration leading to an inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation. The primary effect of other cysteine conjugates is an inhibition of the dehydrogenases, thus inhibiting state 3 respiration
-
High Relaxivity Gadolinium Hydroxypyridonate-Viral Capsid Conjugates: Nano-sized MRI Contrast Agents
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Meux, Susan C.; Datta, Ankona; Hooker, Jacob M.; Botta, Mauro; Francis, Matthew B.; Aime, Silvio; Raymond, Kenneth N.
2007-08-29
High relaxivity macromolecular contrast agents based on the conjugation of gadolinium chelates to the interior and exterior surfaces of MS2 viral capsids are assessed. The proton nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion (NMRD) profiles of the conjugates show up to a five-fold increase in relaxivity, leading to a peak relaxivity (per Gd{sup 3+} ion) of 41.6 mM{sup -1}s{sup -1} at 30 MHz for the internally modified capsids. Modification of the exterior was achieved through conjugation to flexible lysines, while internal modification was accomplished by conjugation to relatively rigid tyrosines. Higher relaxivities were obtained for the internally modified capsids, showing that (1) there is facile diffusion of water to the interior of capsids and (2) the rigidity of the linker attaching the complex to the macromolecule is important for obtaining high relaxivity enhancements. The viral capsid conjugated gadolinium hydroxypyridonate complexes appear to possess two inner-sphere water molecules (q = 2) and the NMRD fittings highlight the differences in the local motion for the internal ({tau}{sub RI} = 440 ps) and external ({tau}{sub RI} = 310 ps) conjugates. These results indicate that there are significant advantages of using the internal surface of the capsids for contrast agent attachment, leaving the exterior surface available for the installation of tissue targeting groups.
-
Self-Assembly and Crystallization of Conjugated Block Copolymers
Davidson, Emily Catherine
This dissertation demonstrates the utility of molecular design in conjugated polymers to create diblock copolymers that robustly self-assemble in the melt and confine crystallization upon cooling. This work leverages the model conjugated polymer poly(3-(2'-ethyl)hexylthiophene) (P3EHT), which features a branched side chain, resulting in a dramatically reduced melting temperature (Tm 80°C) relative to the widely-studied poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT) (Tm 200°C). This reduced melting temperature permits an accessible melt phase, without requiring that the segregation strength (chiN) be dramatically increased. Thus, diblock copolymers containing P3EHT demonstrate robust diblock copolymer self-assembly in the melt over a range of compositions and morphologies. Furthermore, confined crystallization in the case of both glassy (polystyrene (PS) matrix block) and soft (polymethylacrylate (PMA) matrix block) confinement is studied, with the finding that even in soft confinement, crystallization is constrained within the diblock microdomains. This success demonstrates the strategy of leveraging molecular design to decrease the driving force for crystallization as a means to achieving robust self-assembly and confined crystallization in conjugated block copolymers. Importantly, despite the relatively flexible nature of P3EHT in the melt, the diblock copolymer phase behavior appears to be significantly impacted by the stiffness (persistence length of 3 nm) of the P3EHT chain compared to the coupled amorphous blocks (persistence length 0.7 nm). In particular, it is shown that the synthesized morphologies are dominated by a very large composition window for lamellar geometries (favored at high P3EHT volume fractions); cylindrical geometries are favored when P3EHT is the minority fraction. This asymmetry of the composition window is attributed to impact of conformational asymmetry (the difference in chain stiffness, as opposed to shape) between conjugated and amorphous blocks
-
Orr, James K.; Peltier, Daryl
2010-01-01
Thsi slide presentation reviews the avionics software system on board the space shuttle, with particular emphasis on the quality and reliability. The Primary Avionics Software System (PASS) provides automatic and fly-by-wire control of critical shuttle systems which executes in redundant computers. Charts given show the number of space shuttle flights vs time, PASS's development history, and other charts that point to the reliability of the system's development. The reliability of the system is also compared to predicted reliability.
-
A self-discharge model of Lithium-Sulfur batteries based on direct shuttle current measurement
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Knap, Vaclav; Stroe, Daniel Loan; Swierczynski, Maciej Jozef
2016-01-01
. A simple but comprehensive mathematical model of the Li-S battery cell self-discharge based on the shuttle current was developed and is presented. The shuttle current values for the model parameterization were obtained from the direct shuttle current measurements. Furthermore, the battery cell depth......-of-discharge values were recomputed in order to account for the influence of the self-discharge and provide a higher accuracy of the model. Finally, the derived model was successfully validated against laboratory experiments at various conditions....
-
Hubble Servicing Challenges Drive Innovation of Shuttle Rendezvous Techniques
Goodman, John L.; Walker, Stephen R.
2009-01-01
Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing, performed by Space Shuttle crews, has contributed to what is arguably one of the most successful astronomy missions ever flown. Both nominal and contingency proximity operations techniques were developed to enable successful servicing, while lowering the risk of damage to HST systems, and improve crew safety. Influencing the development of these techniques were the challenges presented by plume impingement and HST performance anomalies. The design of both the HST and the Space Shuttle was completed before the potential of HST contamination and structural damage by shuttle RCS jet plume impingement was fully understood. Relative navigation during proximity operations has been challenging, as HST was not equipped with relative navigation aids. Since HST reached orbit in 1990, proximity operations design for servicing missions has evolved as insight into plume contamination and dynamic pressure has improved and new relative navigation tools have become available. Servicing missions have provided NASA with opportunities to gain insight into servicing mission design and development of nominal and contingency procedures. The HST servicing experiences and lessons learned are applicable to other programs that perform on-orbit servicing and rendezvous, both human and robotic.
-
Space Shuttle Atlantis is on Launch Pad 39B
2001-01-01
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Atop the mobile launcher platform, Space Shuttle Atlantis arrives on Launch Pad 39B after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. Seen on either side of the orbiters tail are the tail service masts. They support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiters liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft umbilicals. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11- day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the missions spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Stations Service Module.
-
Zhou, Zhan; Zhang, Jing; Zhang, Yan; Ma, Guanghui; Su, Zhiguo
2016-01-20
Conventional preparation strategies for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) result in heterogeneous products with various molecular sizes and species. In this study, we developed a homogeneous preparation strategy by site-specific conjugation of the anticancer drug with an antibody fragment. The model drug doxorubicin (DOX) was coupled to the Fab' fragment of anti-CD20 IgG at its permissive sites through a heterotelechelic PEG linker, generating an antibody fragment-drug conjugate (AFDC). Anti-CD20 IgG was digested and reduced specifically with β-mercaptoethylamine to generate the Fab' fragment with two free mercapto groups in its hinge region. Meanwhile, DOX was conjugated with α-succinimidylsuccinate ω-maleimide polyethylene glycol (NHS-PEG-MAL) to form MAL-PEG-DOX, which was subsequently linked to the free mercapto containing Fab' fragment to form a Fab'-PEG-DOX conjugate. The dual site-specific bioconjugation was achieved through the combination of highly selective reduction of IgG and introduction of heterotelechelic PEG linker. The resulting AFDC provides an utterly homogeneous product, with a definite ratio of one fragment to two drugs. Laser confocal microscopy and cell ELISA revealed that the AFDC could accumulate in the antigen-positive Daudi tumor cell. In addition, the Fab'-PEG-DOX retained appreciable targeting ability and improved antitumor activity, demonstrating an excellent therapeutic effect on the lymphoma mice model for better cure rate and significantly reduced side effects.
-
Side Chain Engineering in Solution-Processable Conjugated Polymers
Mei, Jianguo
2014-01-14
Side chains in conjugated polymers have been primarily utilized as solubilizing groups. However, these side chains have roles that are far beyond. We advocate using side chain engineering to tune a polymer\\'s physical properties, including absorption, emission, energy level, molecular packing, and charge transport. To date, numerous flexible substituents suitable for constructing side chains have been reported. In this Perspective article, we advocate that the side chain engineering approach can advance better designs for next-generation conjugated polymers. © 2013 American Chemical Society.
-
Imaging GABAc Receptors with Ligand-Conjugated Quantum Dots
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ian D. Tomlinson
2007-01-01
Full Text Available We report a methodology for labeling the GABAc receptor on the surface membrane of intact cells. This work builds upon our earlier work with serotonin-conjugated quantum dots and our studies with PEGylated quantum dots to reduce nonspecific binding. In the current approach, a PEGylated derivative of muscimol was synthesized and attached via an amide linkage to quantum dots coated in an amphiphilic polymer derivative of a modified polyacrylamide. These conjugates were used to image GABAC receptors heterologously expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes.
-
Conjugate Gradient like methods and their application to fixed source neutron diffusion problems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Suetomi, Eiichi; Sekimoto, Hiroshi
1989-01-01
This paper presents a number of fast iterative methods for solving systems of linear equations appearing in fixed source problems for neutron diffusion. We employed the conjugate gradient and conjugate residual methods. In order to accelerate the conjugate residual method, we proposed the conjugate residual squared method by transforming the residual polynomial of the conjugate residual method. Since the convergence of these methods depends on the spectrum of coefficient matrix, we employed the incomplete Choleski (IC) factorization and the modified IC (MIC) factorization as preconditioners. These methods were applied to some neutron diffusion problems and compared with the successive overrelaxation (SOR) method. The results of these numerical experiments showed superior convergence characteristics of the conjugate gradient like method with MIC factorization to the SOR method, especially for a problem involving void region. The CPU time of the MICCG, MICCR and MICCRS methods showed no great difference. In order to vectorize the conjugate gradient like methods based on (M)IC factorization, the hyperplane method was used and implemented on the vector computers, the HITAC S-820/80 and ETA10-E (one processor mode). Significant decrease of the CPU times was observed on the S-820/80. Since the scaled conjugate gradient (SCG) method can be vectorized with no manipulation, it was also compared with the above methods. It turned out the SCG method was the fastest with respect to the CPU times on the ETA10-E. These results suggest that one should implement suitable algorithm for different vector computers. (author)
-
Shuttling single metal atom into and out of a metal nanoparticle.
Wang, Shuxin; Abroshan, Hadi; Liu, Chong; Luo, Tian-Yi; Zhu, Manzhou; Kim, Hyung J; Rosi, Nathaniel L; Jin, Rongchao
2017-10-10
It has long been a challenge to dope metal nanoparticles with a specific number of heterometal atoms at specific positions. This becomes even more challenging if the heterometal belongs to the same group as the host metal because of the high tendency of forming a distribution of alloy nanoparticles with different numbers of dopants due to the similarities of metals in outmost electron configuration. Herein we report a new strategy for shuttling a single Ag or Cu atom into a centrally hollow, rod-shaped Au 24 nanoparticle, forming AgAu 24 and CuAu 24 nanoparticles in a highly controllable manner. Through a combined approach of experiment and theory, we explain the shuttling pathways of single dopants into and out of the nanoparticles. This study shows that the single dopant is shuttled into the hollow Au 24 nanoparticle either through the apex or side entry, while shuttling a metal atom out of the Au 25 to form the Au 24 nanoparticle occurs mainly through the side entry.Doping a metal nanocluster with heteroatoms dramatically changes its properties, but it remains difficult to dope with single-atom control. Here, the authors devise a strategy to dope single atoms of Ag or Cu into hollow Au nanoclusters, creating precise alloy nanoparticles atom-by-atom.
-
Information properties of a hologram of mutually conjugate waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rubanov, A.S.; Serebryakova, L.M.
1995-01-01
A theoretical study of information properties of a correlation response to a fragment of an image of a thin referenceless hologram of mutually conjugate waves that is recorded with a phase-conjugating (PC) mirror is reported. It is shown that this hologram reconstructs a full image in reflected light and can be used as an associative storage device and as a selective PC mirror. 7 refs., 1 fig
-
Space Shuttle Orbiter logistics - Managing in a dynamic environment
Renfroe, Michael B.; Bradshaw, Kimberly
1990-01-01
The importance and methods of monitoring logistics vital signs, logistics data sources and acquisition, and converting data into useful management information are presented. With the launch and landing site for the Shuttle Orbiter project at the Kennedy Space Center now totally responsible for its own supportability posture, it is imperative that logistics resource requirements and management be continually monitored and reassessed. Detailed graphs and data concerning various aspects of logistics activities including objectives, inventory operating levels, customer environment, and data sources are provided. Finally, some lessons learned from the Shuttle Orbiter project and logistics options which should be considered by other space programs are discussed.
-
PEMBELAJARAN LARI CEPAT DENGAN MENGGUNAKAN MODIFIKASI SHUTTLE RUN
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Suharjo
2015-09-01
Full Text Available The purpose of this study was to determine "Is Modified Shuttle Run can improve learning outcomes Elementary School fifth grade students Cenggini 02 Subdistrict Balapulang Tegal 2014". This research method is a class action research by using two cycles, each cycle consisting of four stages, namely planning, tindakkan, observation and action planning refleksi..Pada second cycle associated with the results achieved in the first cycle acts as an improvement efforts of the cycle. The subjects of this study were fifth grade students of elementary Negri Cenggini 02. Research conducted includes three domains, namely affective, cognitive and psychomotor addition to the observations made during the process of the learning process takes place. The results showed the affective, cognitive and psychomotor well categorized shows that the learning outcomes quick run using a modified shuttle run a positive impact as seen on mastery learning outcomes of students who exceed the predetermined KKM 75 In the first cycle the average value of students 75 , 71 in the second cycle the average value of 78.60 students, mastery learning in the first cycle reaches 64.29%, while in the second cycle reaches 92.86% mastery learning .mean mastery learning students has increased by 28.57%. It is concluded that learning to run faster by using a modified shuttle run has a positive effect, which can increase student interest and motivation to learn.
-
Development of Tat-Conjugated Dendrimer for Transdermal DNA Vaccine Delivery.
Bahadoran, Azadeh; Moeini, Hassan; Bejo, Mohd Hair; Hussein, Mohd Zobir; Omar, Abdul Rahman
In order to enhance cellular uptake and to facilitate transdermal delivery of DNA vaccine, polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers conjugated with HIV transactivator of transcription (TAT) was developed. First, the plasmid DNA (pIRES-H5/GFP) nanoparticle was formulated using PAMAM dendrimer and TAT peptide and then characterized for surface charge, particle size, DNA encapsulation and protection of the pIRES-H5/GFP DNA plasmid to enzymatic digestion. Subsequently, the potency of the TAT-conjugated dendrimer for gene delivery was evaluated through in vitro transfection into Vero cells followed by gene expression analysis including western blotting, fluorescent microscopy and PCR. The effect of the TAT peptide on cellular uptake of DNA vaccine was studied by qRT-PCR and flow cytometry. Finally, the ability of TAT-conjugated PAMAM dendrimer for transdermal delivery of the DNA plasmid was assessed through artificial membranes followed by qRT-PCR and flow cytometry. TAT-conjugated PAMAM dendrimer showed the ability to form a compact and nanometre-sized polyplexes with the plasmid DNA, having the size range of 105 to 115 nm and a positive charge of +42 to +45 mV over the N/P ratio of 6:1(+/-). In vitro transfection analysis into Vero cells confirms the high potency of TAT-conjugated PAMAM dendrimer to enhance the cellular uptake of DNA vaccine. The permeability value assay through artificial membranes reveals that TAT-conjugated PAMAM has more capacity for transdermal delivery of the DNA compared to unmodified PAMAM dendrimer (Pdendrimer is a promising non-viral vector for transdermal use.This article is open to POST-PUBLICATION REVIEW. Registered readers (see "For Readers") may comment by clicking on ABSTRACT on the issue's contents page.
-
Space Shuttle: Human Capital Challenges Require Management Attention
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
2000-01-01
.... NASA budget data shows that, since 1995, shuttle workforce levels have decreased from about 3,000 to about 1,800 full time equivalent employees NASA based its downsizing efforts on optimistic programmatic assumptions...
-
Rosen, Christian B.; Kodal, Anne L. B.; Nielsen, Jesper S.; Schaffert, David H.; Scavenius, Carsten; Okholm, Anders H.; Voigt, Niels V.; Enghild, Jan J.; Kjems, Jørgen; Tørring, Thomas; Gothelf, Kurt V.
2014-09-01
DNA-protein conjugates are important in bioanalytical chemistry, molecular diagnostics and bionanotechnology, as the DNA provides a unique handle to identify, functionalize or otherwise manipulate proteins. To maintain protein activity, conjugation of a single DNA handle to a specific location on the protein is often needed. However, preparing such high-quality site-specific conjugates often requires genetically engineered proteins, which is a laborious and technically challenging approach. Here we demonstrate a simpler method to create site-selective DNA-protein conjugates. Using a guiding DNA strand modified with a metal-binding functionality, we directed a second DNA strand to the vicinity of a metal-binding site of His6-tagged or wild-type metal-binding proteins, such as serotransferrin, where it subsequently reacted with lysine residues at that site. This method, DNA-templated protein conjugation, facilitates the production of site-selective protein conjugates, and also conjugation to IgG1 antibodies via a histidine cluster in the constant domain.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Khoza, Phindile; Antunes, Edith; Chen, Ji-Yao; Nyokong, Tebello
2013-01-01
This work reports on the synthesis of zinc tetraaminophthalocyanine (ZnTAPc) functionalized with folic acid (FA), forming ZnTAPcFA. The conjugate between FA and ZnTAPc was soluble in water whereas ZnTAPc alone is not. The structure of ZnTAPcFA conjugate was elucidated by 1 H NMR, MALDI-TOF mass and FTIR spectra. Photophysical and photochemical studies of ZnTAPcFA were conducted in DMSO. The increase in fluorescence quantum yield of the conjugate was accompanied by a decrease in the triplet and singlet oxygen quantum yields. The changes in triplet quantum and singlet oxygen quantum yields were marginal when ZnTAPc was simply mixed with FA without a chemical bond. - Highlights: ► A conjugate between folic acid and a zinc tetraaminophthalocyanine was formed. ► The conjugate is water soluble even though the phthalocyanine alone is not. ► The fluorescence quantum yield of the conjugate was enhanced compared to the phthalocyanine alone. ► Triplet quantum yields decreased for the conjugate
-
Hamdani, Afshan Mumtaz; Wani, Idrees Ahmed; Bhat, Naseer Ahmad; Siddiqi, Raushid Ahmad
2018-02-01
This study was undertaken to analyze the effect of conjugation of egg-white lysozyme with guar gum. Lysozyme is an antimicrobial polypeptide that can be used for food preservation. Its antibacterial activity is limited to gram positive bacteria. Conjugation with polysaccharides like guar gum may broaden its activity against gram negatives. Conjugate was developed through Maillard reaction. Assays carried out included sugar estimation, SDS-PAGE, GPC, color, FT-IR, DSC, thermal stability, solubility, emulsifying, foaming and antioxidant activity. In addition, antimicrobial activity of the conjugate was determined against two gram positive (Staphyllococcus aureus and Enterococcus) and two gram negative pathogens (E. coli and Salmonella). Results showed higher functional properties of lysozyme-guar gum conjugate. The antioxidant properties increased from 2.02-35.80% (Inhibition of DPPH) and 1.65-4.93AAE/g (reducing power) upon guar gum conjugation. Conjugate significantly inhibited gram negative bacteria and the antibacterial activity also increased significantly against gram positive pathogens. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Space Shuttle Launch Probability Analysis: Understanding History so We Can Predict the Future
Cates, Grant R.
2014-01-01
The Space Shuttle was launched 135 times and nearly half of those launches required 2 or more launch attempts. The Space Shuttle launch countdown historical data of 250 launch attempts provides a wealth of data that is important to analyze for strictly historical purposes as well as for use in predicting future launch vehicle launch countdown performance. This paper provides a statistical analysis of all Space Shuttle launch attempts including the empirical probability of launch on any given attempt and the cumulative probability of launch relative to the planned launch date at the start of the initial launch countdown. This information can be used to facilitate launch probability predictions of future launch vehicles such as NASA's Space Shuttle derived SLS. Understanding the cumulative probability of launch is particularly important for missions to Mars since the launch opportunities are relatively short in duration and one must wait for 2 years before a subsequent attempt can begin.
-
Zhang, Shuwen; Gong, Yuansheng; Khanal, Som; Lu, Yanjie; Lucey, John A
2017-11-01
Covalent attachment of polysaccharides to proteins (conjugation) via the Maillard reaction has been extensively studied. Conjugation can lead to a significant improvement in protein functionality (e.g., solubility, emulsification, and heat stability). Caseins have previously been successfully conjugated with maltodextrin (Md), but the effect on the detailed acid gelation properties has not been examined. We studied the effect of conjugating sodium caseinate (NaCN) with 3 different sized Md samples via the Maillard reaction in aqueous solutions. The Md samples had dextrose equivalents of 4 to 7, 9 to 12, and 20 to 23 for Md40, Md100, and Md200, respectively. The conjugation reaction was performed in mixtures with 5% NaCN and 5% Md, which were heated at 90°C for 10 h. The degree of conjugation was estimated from the reduction in free amino groups as well as color changes. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-PAGE analysis was performed to confirm conjugation by employing staining of both protein and carbohydrate bands. The molar mass of samples was determined by size-exclusion chromatography coupled with multi-angle laser light scattering. After the conjugation reaction, samples were then gelled by the addition of 0.63% (wt/vol) glucono-δ-lactone at 30°C, such that samples reached pH 4.6 after about 13 h. The rheological properties of samples during acidification was monitored by small-strain dynamic oscillatory rheology. The microstructure of acid gels at pH 4.6 was examined by fluorescence microscopy. Conjugation resulted in a loss of 10.8, 8.8, and 11.9% of the available amino groups in the protein for the NaCN-Md40 conjugates (C40), NaCN-Md100 conjugates (C100), and NaCN-Md100 conjugates (C200), respectively. With a decrease in the size of the type of Md, an increase occurred in the molar mass of the resultant conjugate. The weight average molar masses of NaCN-Md samples were 340, 368, and 425 kDa for the conjugates C40, C100, and C200, respectively. Addition of Md to Na