
Sample records for conjugates promote cytotoxicity
-
Preparation of Conjugates of Cytotoxic Lupane Triterpenes with Biotin.
Soural, Miroslav; Hodon, Jiri; Dickinson, Niall J; Sidova, Veronika; Gurska, Sona; Dzubak, Petr; Hajduch, Marian; Sarek, Jan; Urban, Milan
2015-12-16
To better understand the mechanism of action of antitumor triterpenes, we are developing methods to identify their molecular targets. A promising method is based on combination of quantitative proteomics with SILAC and uses active compounds anchored to magnetic beads via biotin-streptavidin interaction. We developed a simple and fast solid-phase synthetic technique to connect terpenes to biotin through a linker. Betulinic acid was biotinylated from three different conjugation sites for use as a standard validation tool since many molecular targets of this triterpene are already known. Then, a set of four other cytotoxic triterpenoids was biotinylated. Biotinylated terpenes were similarly cytotoxic to their nonbiotinylated parents, which suggests that the target identification should not be influenced by linker or biotin. The developed solid-phase synthetic approach is the first attempt to use solid-phase synthesis to connect active triterpenes to biotin and is applicable as a general procedure for routine conjugation of triterpenes with other molecules of choice.
-
Comparative evaluation of cytotoxicity of a glucosamine-TBA conjugate and a chitosan-TBA conjugate.
Guggi, Davide; Langoth, Nina; Hoffer, Martin H; Wirth, Michael; Bernkop-Schnürch, Andreas
2004-07-08
D-glucosamine and chitosan were modified by the immobilization of thiol groups utilizing 2-iminothiolane. The toxicity profile of the resulting D-glucosamine-TBA (4-thiobutylamidine) conjugate, of chitosan-TBA conjugate and of the corresponding unmodified controls was evaluated in vitro. On the one hand, the cell membrane damaging effect of 0.025% solutions of the test compounds was investigated via red blood cell lysis test. On the other hand, the cytotoxity of 0.025, 0.25 and 0.5% solutions of the test compounds was evaluated on L-929 mouse fibroblast cells utilizing two different bioassays: the MTT assay (3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide), which assess the mitochondrial metabolic activity of the cells, and the BrdU-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, which measures the incorporation in the DNA of 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine and consequently the cell proliferation. Results of the red blood cell lysis test showed that both thiolated compounds displayed a lower membrane damaging effect causing a significantly lower haemoglobine release than the unmodified compounds. Data obtained by the MTT assay and the BrdU assay revealed a concentration dependent relative cytotoxicity for all tested compounds. The covalent linkage of the TBA-substructure to D-glucosamine did not cause a significant increase in cytotoxicity, whereas at higher concentrations a slightly enhanced cytotoxic effect was caused by the derivatisation of chitosan. In conclusion, the -TBA derivatives show a comparable toxicity profile to the corresponding unmodified compounds, which should not compromise their future use as save pharmaceutical excipients.
-
In vitro cytotoxicity of alpha conjugates for human pancreatic cancer cell lines
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Qu, C.; Li, Y.; Rizvi, M.A.; Allen, B.; Samra, J.; Smith, R.
2003-01-01
Targeted Alpha therapy (TAT) can inhibit the growth of micrometastases by selectively killing isolated and preangiogenic clusters of cancer cells. The aim of this study is to demonstrate the cytotoxicity of different alpha conjugates in vitro to human metastatic pancreatic cancer cell lines (CAPAN-1, CFPAN-1 and PANC-1). We are labeling the C595 and J591 (non-specific controls) monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) with 213 Bi were performed according to the standard methods in our laboratory. 213 Bi-C595 is specifically cytotoxic to CAPAN-1, CFPAN-1 and PANC-1cell lines in a concentration-dependent fashion. While non-specific alpha conjugates only killed very small fractions of pancreatic cancer cells. These alpha conjugates might be useful agents for the treatment of micro-metastases in pancreatic cancer patients with over-expression of the targeted receptors
-
Multistage model for the action of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in multicellular conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Macken, C.A.; Perelson, A.S.
1984-01-01
The authors propose a multistage stochastic model to explain data on the kinetics of target cell lysis by cytotoxic T lymphocytes in multicellular conjugates. A novel feature of this model is that the authors explicitly consider both the lethal hitting stage and the target cell disintegration stage of the cytolytic process. Further, the authors allow for the possibility that target cell disintegration is itself a complex process composed of many events. The comparison of this model with the data of other investigators suggests that cytotoxic T cells deliver lethal hits at random to undamage target cells. Having received a lethal hit, the target cell disintegrates over a variable length of time. The disintegration times of target cells from different conjugates appear to be randomly distributed and to be consistent with a model in which disintegration occurs by at least two major, sequential, rate-limiting events. For conjugates containing one lymphocyte and multiple target cells, the mean rate at which a lethally hit target cell disintegrates is found to be independent of the total number of target cells in the conjugate. This model predicts that in such multicellular conjugates, individual target cells lyse one by one, on average at approximately 30-min intervals, thus agreeing closely with previously reported experimental observations. 35 references, 3 figures, 2 tables
-
Commandeur, J.N.M.; Boogaard, P.J.; Mulder, G.J.; Vermeulen, N.P.E.
1991-01-01
The mutagenicity, cytotoxicity and metabolism of two regioisomic l-cysteine- and N-acetyl-l-cysteine-S-conjugates of trichloroethylene were studied. The 1,2-dichlorovinyl(1,2-DCV) isomers of both the cysteine conjugate and the mercapturate were much stronger mutagens in the Ames test with Salmonella
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Szlachcic A
2016-08-01
Full Text Available Anna Szlachcic, Malgorzata Zakrzewska, Michal Lobocki, Piotr Jakimowicz, Jacek Otlewski Department of Protein Engineering, Faculty of Biotechnology, University of Wroclaw, Wroclaw, Poland Abstract: Fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs are attractive candidate cancer therapy targets as they are overexpressed in multiple types of tumors, such as breast, prostate, bladder, and lung cancer. In this study, a natural ligand of FGFR, an engineered variant of fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1V, was conjugated to a potent cytotoxic drug, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE, and used as a targeting agent for cancer cells overexpressing FGFRs, similar to antibodies in antibody–drug conjugates. The FGF1V–valine–citrulline–MMAE conjugate showed a favorable stability profile, bound FGFRs on the cell surface specifically, and efficiently released the drug (MMAE upon cleavage by the lysosomal protease cathepsin B. Importantly, the conjugate showed a prominent cytotoxic effect toward cell lines expressing FGFR. FGF1V–vcMMAE was highly cytotoxic at concentrations even an order of magnitude lower than those found for free MMAE. This effect was FGFR-specific as cells lacking FGFR did not show any increased mortality. Keywords: fibroblast growth factor 1, FGF receptor, targeted cancer therapy, cytotoxic conjugates, FGFR-dependent cancer, MMAE, auristatin
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Yang, Liu, E-mail: yqliu@lzu.edu.c [Lanzhou Jiaotong University (China). Environmental and Municipal Engineering School; Chun-Yan Zhaob; Ying-Qian Liu [Lanzhou University (China). School of Pharmacy
2011-07-01
A series of novel conjugates of camptothecin and 5-fluorouracil were first synthesized and their cytotoxic activities against two human tumor cell lines (SGC-7901 and A-549) as well as in vitro pharmacokinetic determination of lactone stability were studied. Among these compounds, most tested conjugates showed comparable or superior cytotoxic activities to 2, but less potent compared with 1. Particularly, conjugates 10b and 10d were highly active against A-549 with IC{sub 50} values of 0.45 and 0.38 {mu}mol L{sup -1}, respectively. Also, the in vitro pharmacokinetic determination of lactone levels of representative compound 10b showed that the biological life span of their lactone forms in human and mouse plasma significantly increased compared with their mother compound 1. Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) method was then applied for developing linear models to predict the cytotoxic activities of these derivatives that have not yet been synthesized or experimentally tested. In addition, molecular docking was used to clarify the binding mode of these derivatives to human DNA topoisomerase I. The important hydrogen-bonding interactions were observed between these derivatives and their receptor. The results from molecular modeling and QSAR study can guide the design of novel conjugates with higher antitumor activity. (author)
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Sun, Hua; Yue, Partick Y. K.; Wang, Shao Rong
2016-01-01
showed that these conjugates are more potent in both cytotoxic and antiangiogenic assays than their corresponding parent molecules, and are also selectively more active against melanoma cells B16 and metastatic B16BL6 than the two other cancer cell lines (A549 and MCF-7) tested. The predicted...
-
Selective cytotoxicity of an oxygen-radical-generating enzyme conjugated to a monoclonal antibody.
Battelli, M G; Abbondanza, A; Tazzari, P L; Dinota, A; Rizzi, S; Grassi, G; Gobbi, M; Stirpe, F
1988-07-01
The monoclonal antibody 8A, which recognizes a human plasma cell-associated antigen, was covalently linked to xanthine oxidase in a conjugate maintaining both immunological and enzymatic properties. A significant degree of target cell lysis was obtained at an enzyme concentration that was ineffective on non-target cells and on myeloid staminal cells (CFU-GM). The cytotoxic activity was abolished by an excess of antibody, by allopurinol and by superoxide dismutase and catalase. A possible use of the conjugate for bone marrow purging in multiple myeloma patients is suggested.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Altuntas, T. Gul; Zager, Richard A.; Kharasch, Evan D.
2003-01-01
Fluoromethyl-2,2-difluoro-1-(trifluoromethyl)vinyl ether (FDVE) is a fluorinated alkene formed by degradation of the volatile anesthetic sevoflurane in anesthesia machines. FDVE is nephrotoxic in rats but not humans. Rat FDVE nephrotoxicity is attributed to FDVE glutathione conjugation and bioactivation of subsequent FDVE-cysteine S-conjugates, in part by renal β-lyase. Although FDVE conjugation and metabolism occur in both rats and humans, the mechanism for selective toxicity in rats and lack of effect in humans is incompletely elucidated. This investigation measured FDVE S-conjugate cytotoxicity in cultured human proximal tubular HK-2 cells, and compared this with known cytotoxic S-conjugates. HK-2 cells were incubated with FDVE and its GSH, cysteine S-mercapturic acid, cysteine S-sulfoxide, and mercapturic acid sulfoxide conjugates (0.1-2.7 mM) for 24 h. Cytotoxicity was determined by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, total LDH, and the ability of viable cells to reduce a tetrazolium-based compound (MTT). FDVE was cytotoxic only at concentrations ≥0.9 mM. No increase in LDH release was observed with either FDVE-GSH conjugate. The FDVE-cysteine conjugates S-(1,1-difluoro-2-fluoromethoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl) ethyl)-L-cysteine (DFEC) and (Z)-S-(1-fluoro-2-fluoromethoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl) vinyl)-L-cysteine ((Z)-FFVC) caused significant differences in LDH release and MTT reduction only at 2.7 mM; (Z)-FFVC was slightly more cytotoxic. Both S-(1,1-difluoro-2-fluoromethoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl) ethyl)-L-cysteine sulfoxide (DFEC-SO) and (Z)-N-acetyl-S-(1-fluoro-2-fluoromethoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl) vinyl)-L-cysteine sulfoxide ((Z)-N-Ac-FFVC-SO) caused slightly greater changes in LDH release or total LDH than the corresponding equimolar DFEC and (Z)-N-acetyl-S-(1-fluoro-2-fluoromethoxy-2-(trifluoromethyl) vinyl)-L-cysteine ((Z)-N-Ac-FFVC) conjugates. In contrast to FDVE S-conjugates, S-(1,2-dichlorovinyl)-L-cysteine was markedly cytotoxic, at concentrations as low as 0
-
Roy, Jyoti; Nguyen, Trung Xuan; Kanduluru, Ananda Kumar; Venkatesh, Chelvam; Lv, Wei; Reddy, P V Narasimha; Low, Philip S; Cushman, Mark
2015-04-09
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is overexpressed in most prostate cancer cells while being present at low or undetectable levels in normal cells. This difference provides an opportunity to selectively deliver cytotoxic drugs to prostate cancer cells while sparing normal cells that lack PSMA, thus improving potencies and reducing toxicities. PSMA has high affinity for 2-[3-(1,3-dicarboxypropyl)ureido]pentanedioic acid (DUPA) (Ki = 8 nM). After binding to a DUPA-drug conjugate, PSMA internalizes, unloads the conjugate, and returns to the surface. In the present studies, an indenoisoquinoline topoisomerase I inhibitor was conjugated to DUPA via a peptide linker and a drug-release segment that facilitates intracellular cleavage to liberate the drug cargo. The DUPA-indenoisoquinoline conjugate exhibited an IC50 in the low nanomolar range in 22RV1 cell cultures and induced a complete cessation of tumor growth with no toxicity, as determined by loss of body weight and death of treated mice.
-
Dong, Lifeng; Witkowski, Colette M.; Craig, Michael M.; Greenwade, Molly M.; Joseph, Katherine L.
2009-12-01
Phase contrast and epifluorescence microscopy were utilized to monitor morphological changes in human astrocytoma cells during a time-course exposure to single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) conjugates with different surfactants and to investigate sub-cellular distribution of the nanotube conjugates, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that cytotoxicity of the nanotube/surfactant conjugates is related to the toxicity of surfactant molecules attached on the nanotube surfaces. Both sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS) are toxic to cells. Exposure to CNT/SDS conjugates (0.5 mg/mL) for less than 5 min caused changes in cell morphology resulting in a distinctly spherical shape compared to untreated cells. In contrast, sodium cholate (SC) and CNT/SC did not affect cell morphology, proliferation, or growth. These data indicate that SC is an environmentally friendly surfactant for the purification and dispersion of SWCNTs. Epifluorescence microscopy analysis of CNT/DNA conjugates revealed distribution in the cytoplasm of cells and did not show adverse effects on cell morphology, proliferation, or viability during a 72-h incubation. These observations suggest that the SWCNTs could be used as non-viral vectors for diagnostic and therapeutic molecules across the blood-brain barrier to the brain and the central nervous system.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Azade Taheri
2011-01-01
Full Text Available Methotrexate-human serum albumin conjugates were developed by a simple carbodiimide reaction. Methotrexate-human serum albumin conjugates were then crosslinked with 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl carbodiimide HCl (EDC to form nanoparticles. The size of nanoparticles determined by laser light scattering and TEM was between 90–150 nm. Nanoparticles were very stable at physiologic conditions (PBS pH 7.4, 37∘C and after incubation with serum. The effect of amount of EDC used for crosslinking on the particle size and free amino groups of nanoparticles was examined. The amount of crosslinker showed no significant effect on the size of nanoparticles but free amino groups of nanoparticles were decreased by increasing the crosslinker. The physicochemical interactions between methotrexate and human serum albumin were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC. Nanoparticles were more cytotoxic on T47D cells compared to free methotrexate. Moreover, methotrexate-human serum albumin nanoparticles decreased the IC50 value of methotrexate on T47D cells in comparison with free methotrexate.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Taheri, A.; Atyabi, F.; Nouri, F.S.; Ahadi, F.; Derakhshan, M.A.; Dinarvand, R.; Atyabi, F.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Ostad, S.N.; Dinarvand, R.; Amini, M.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Ostad, S.N.; Mansoori, P.
2011-01-01
Methotrexate-human serum albumin conjugates were developed by a simple carbodiimide reaction. Methotrexate-human serum albumin conjugates were then crosslinked with 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide HCl (EDC) to form nanoparticles. The size of nanoparticles determined by laser light scattering and TEM was between 90 150 nm. Nanoparticles were very stable at physiologic conditions (PBS pH 7.4, 37 degree C) and after incubation with serum. The effect of amount of EDC used for crosslinking on the particle size and free amino groups of nanoparticles was examined. The amount of cross linker showed no significant effect on the size of nanoparticles but free amino groups of nanoparticles were decreased by increasing the cross linker. The physicochemical interactions between methotrexate and human serum albumin were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Nanoparticles were more cytotoxic on T 47 D cells compared to free methotrexate. Moreover, methotrexate-human serum albumin nanoparticles decreased the C50 value of methotrexate on T 47 D cells in comparison with free methotrexate.
-
Wang, Liang; Chan, Judy Y W; Rêgo, Juciane V; Chong, Cheong-Meng; Ai, Nana; Falcão, Cláudio B; Rádis-Baptista, Gandhi; Lee, Simon M Y
2015-06-01
Animal venoms contain a diverse array of proteins and enzymes that are toxic toward various physiological systems. However, there are also some practical medicinal uses for these toxins including use as anti-bacterial and anti-tumor agents. In this study, we identified a nine-residue cryptic oligopeptide, KRFKKFFKK (EVP50) that is repeatedly encoded in tandem within vipericidin sequences. EVP50 displayed in vivo potent lethal toxicity to zebrafish larvae (LD50=6 μM) when the peptide's N-terminus was chemically conjugated to rhodamine B (RhoB). In vitro, RhoB-conjugated EVP50 (RhoB-EVP50) exhibited a concentration-dependent cytotoxic effect toward MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. In MCF-7 cells, the RhoB-EVP50 nonapeptide accumulated inside the cells within minutes. In the cytoplasm, the RhoB-EVP50 induced extracellular calcium influx and intracellular calcium release. Membrane budding was also observed after incubation with micromolar concentrations of the fluorescent EVP50 conjugate. The conjugate's interference with calcium homeostasis, its intracellular accumulation and its induced membrane dysfunction (budding and vacuolization) seem to act in concert to disrupt the cell circuitry. Contrastively, unconjugated EVP50 peptide did not display neither toxic nor cytotoxic activities in our in vivo and in vitro models. The synergic mechanism of toxicity was restricted to the structurally modified encrypted vipericidin nonapeptide. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Methotrexate and epirubicin conjugates as potential antitumor drugs
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Szymon Wojciech Kmiecik
2017-07-01
Full Text Available Introduction: The use of hybrid molecules has become one of the most significant approaches in new cytotoxic drug design. This study describes synthesis and characterization of conjugates consisting of two well-known and characterized chemotherapeutic agents: methotrexate (MTX and epirubicin (EPR. The synthesized conjugates combine two significant anticancer strategies: combinatory therapy and targeted therapy. These two drugs were chosen because they have different mechanisms of action, which can increase the anticancer effect of the obtained conjugates. MTX, which is a folic acid analog, has high cytotoxic properties and can serve as a targeting moiety that can reach folate receptors (FRs overexpresing tumor cells. Combination of nonselective drugs such as EPR with MTX can increase the selectivity of the obtained conjugates, while maintaining the high cytotoxic properties.Materials and methods: Conjugates were purified by RP-HPLC and the structure was investigated by MS and MS/MS methods. The effect of the conjugates on proliferation of LoVo, LoVo/Dx, MCF-7 and MV-4-11 human cancer cell lines was determined by SRB or MTT assay.Results: The conjugation reaction results in the formation of monosubstituted (α, γ and disubstituted MTX derivatives. In vitro proliferation data demonstrate that the conjugates synthesized in our study show lower cytotoxic properties than both chemotherapeutics used alone.Discussion: Epirubicin cytotoxicity was not observed in obtained conjugates. Effective drugs release after internalization needs further investigation.
-
Kiranda, Hanan Karimah; Mahmud, Rozi; Abubakar, Danmaigoro; Zakaria, Zuki Abubakar
2018-01-01
The evolution of nanomaterial in science has brought about a growing increase in nanotechnology, biomedicine, and engineering fields. This study was aimed at fabrication and characterization of conjugated gold-cockle shell-derived calcium carbonate nanoparticles (Au-CSCaCO3NPs) for biomedical application. The synthetic technique employed used gold nanoparticle citrate reduction method and a simple precipitation method coupled with mechanical use of a Programmable roller-ball mill. The synthesized conjugated nanomaterial was characterized for its physicochemical properties using transmission electron microscope (TEM), field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). However, the intricacy of cellular mechanisms can prove challenging for nanomaterial like Au-CSCaCO3NPs and thus, the need for cytotoxicity assessment. The obtained spherical-shaped nanoparticles (light-green purplish) have an average diameter size of 35 ± 16 nm, high carbon and oxygen composition. The conjugated nanomaterial, also possesses a unique spectra for aragonite polymorph and carboxylic bond significantly supporting interactions between conjugated nanoparticles. The negative surface charge and spectra absorbance highlighted their stability. The resultant spherical shaped conjugated Au-CSCaCO3NPs could be a great nanomaterial for biomedical applications.
-
Kızılşahin, Sadi; Nalbantsoy, Ayşe; Yavaşoğlu, N Ülkü Karabay
2015-01-01
The aim of this study was to determine in vitro synergistic efficacy of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), oleic acid (OLA), safflower oil and taxol (Tax) cytotoxicity on human prostate cancer (PC3) cell line. To determine synergistic efficacy of oil combinations, PC3 treated with different doses of compounds alone and combined with 10 μg/mL Tax. The MTT results indicated that OLA-Tax combinations exhibited cytotoxicity against PC3 at doses of 30 nM+10 μg-Tax, 15 nM+5 μg-Tax and 7.5 nM+2.5 μg-Tax. The treatment of OLA or Tax did not show significant inhibition on PC3, while OLA-Tax combinations showed effective cytotoxicity at treated doses. CLA-Tax combinations demonstrated the same effect on PC3 as combined form with 45.72% versus the alone form as 74.51% viability. Cytotoxic synergy between Tax, OLA and CLA shows enhanced cytotoxicity on PC3 which might be used in the therapy of prostate cancer.
-
Marvania, Bhavin; Kakadiya, Rajesh; Christian, Wilson; Chen, Tai-Lin; Wu, Ming-Hsi; Suman, Sharda; Tala, Kiran; Lee, Te-Chang; Shah, Anamik; Su, Tsann-Long
2014-08-18
We synthesized a series of phenyl N-mustard-4-anilinoquinoline conjugates to study their antitumorigenic effects. These agents were prepared by the condensation of 4-[N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenyl isocyanate with 6-amino-4-methylamino or 4-anilinoquinolines. The structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies revealed that the C2-methylquinoline derivatives (18a-o) were generally more cytotoxic than the C2-phenylquinoline conjugates (23a-d) in inhibiting the cell growth of various human tumor cell lines in vitro. However, the methylamino or aniline substituents at C4 of quinoline did not influence the cytotoxic effects. The title conjugates were capable of inducing DNA cross-linking and promoting cell-cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. This study demonstrates that phenyl N-mustard-4-anilinoquinoline conjugates are generally more potent than phenyl N-mustard-4-anilinoquinazoline conjugates against the cell growth of various tumor cell-lines. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
-
Cancer cell specific cytotoxic gene expression mediated by ARF tumor suppressor promoter constructs
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kurayoshi, Kenta; Ozono, Eiko; Iwanaga, Ritsuko; Bradford, Andrew P.; Komori, Hideyuki; Ohtani, Kiyoshi
2014-01-01
Highlights: • ARF promoter showed higher responsiveness to deregulated E2F activity than the E2F1 promoter. • ARF promoter showed higher cancer cell-specificity than E2F1 promoter to drive gene expression. • HSV-TK driven by ARF promoter showed higher cancer cell-specific cytotoxicity than that driven by E2F1 promoter. - Abstract: In current cancer treatment protocols, such as radiation and chemotherapy, side effects on normal cells are major obstacles to radical therapy. To avoid these side effects, a cancer cell-specific approach is needed. One way to specifically target cancer cells is to utilize a cancer specific promoter to express a cytotoxic gene (suicide gene therapy) or a viral gene required for viral replication (oncolytic virotherapy). For this purpose, the selected promoter should have minimal activity in normal cells to avoid side effects, and high activity in a wide variety of cancers to obtain optimal therapeutic efficacy. In contrast to the AFP, CEA and PSA promoters, which have high activity only in a limited spectrum of tumors, the E2F1 promoter exhibits high activity in wide variety of cancers. This is based on the mechanism of carcinogenesis. Defects in the RB pathway and activation of the transcription factor E2F, the main target of the RB pathway, are observed in almost all cancers. Consequently, the E2F1 promoter, which is mainly regulated by E2F, has high activity in wide variety of cancers. However, E2F is also activated by growth stimulation in normal growing cells, suggesting that the E2F1 promoter may also be highly active in normal growing cells. In contrast, we found that the tumor suppressor ARF promoter is activated by deregulated E2F activity, induced by forced inactivation of pRB, but does not respond to physiological E2F activity induced by growth stimulation. We also found that the deregulated E2F activity, which activates the ARF promoter, is detected only in cancer cell lines. These observations suggest that ARF promoter
-
Cancer cell specific cytotoxic gene expression mediated by ARF tumor suppressor promoter constructs
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kurayoshi, Kenta [Department of Bioscience, School of Science and Technology, Kwansei Gakuin University, 2-1 Gakuen, Sanda, Hyogo 669-1337 (Japan); Ozono, Eiko [Centre for Molecular Oncology, Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary, University of London, John Vane Science Centre, Charterhouse Square, London EC1M 6BQ (United Kingdom); Iwanaga, Ritsuko; Bradford, Andrew P. [Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Anschutz Medical Campus, 12800 East 19th Avenue, Aurora, CO 80045 (United States); Komori, Hideyuki [Center for Stem Cell Biology, Life Sciences Institute, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (United States); Ohtani, Kiyoshi, E-mail: btm88939@kwansei.ac.jp [Department of Bioscience, School of Science and Technology, Kwansei Gakuin University, 2-1 Gakuen, Sanda, Hyogo 669-1337 (Japan)
2014-07-18
Highlights: • ARF promoter showed higher responsiveness to deregulated E2F activity than the E2F1 promoter. • ARF promoter showed higher cancer cell-specificity than E2F1 promoter to drive gene expression. • HSV-TK driven by ARF promoter showed higher cancer cell-specific cytotoxicity than that driven by E2F1 promoter. - Abstract: In current cancer treatment protocols, such as radiation and chemotherapy, side effects on normal cells are major obstacles to radical therapy. To avoid these side effects, a cancer cell-specific approach is needed. One way to specifically target cancer cells is to utilize a cancer specific promoter to express a cytotoxic gene (suicide gene therapy) or a viral gene required for viral replication (oncolytic virotherapy). For this purpose, the selected promoter should have minimal activity in normal cells to avoid side effects, and high activity in a wide variety of cancers to obtain optimal therapeutic efficacy. In contrast to the AFP, CEA and PSA promoters, which have high activity only in a limited spectrum of tumors, the E2F1 promoter exhibits high activity in wide variety of cancers. This is based on the mechanism of carcinogenesis. Defects in the RB pathway and activation of the transcription factor E2F, the main target of the RB pathway, are observed in almost all cancers. Consequently, the E2F1 promoter, which is mainly regulated by E2F, has high activity in wide variety of cancers. However, E2F is also activated by growth stimulation in normal growing cells, suggesting that the E2F1 promoter may also be highly active in normal growing cells. In contrast, we found that the tumor suppressor ARF promoter is activated by deregulated E2F activity, induced by forced inactivation of pRB, but does not respond to physiological E2F activity induced by growth stimulation. We also found that the deregulated E2F activity, which activates the ARF promoter, is detected only in cancer cell lines. These observations suggest that ARF promoter
-
Kumar, Kewal; Sagar, Sunil; Esau, Luke; Kaur, Mandeep; Kumar, Vipan
2012-01-01
The present manuscript describes the synthesis of uracil-isatin hybrids via azide-alkyne cycloadditions and their cytotoxic evaluation against three human cancer cell lines viz. HeLa (cervix), MCF-7 (breast) and DU145 (prostate) using MTT assay. The evaluation studies revealed the dependence of cytotoxicity on C-5 substituents of both uracil and isatin as well as the alkyl chain length with compounds 6g and 6k showing IC50 values 18.21 and 13.90 μM respectively against DU145 cell lines. Most of the synthesized conjugates exhibited considerable selectivity against MCF-7 and DU145 cell lines. © 2012 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
-
Kumar, Kewal
2012-12-01
The present manuscript describes the synthesis of uracil-isatin hybrids via azide-alkyne cycloadditions and their cytotoxic evaluation against three human cancer cell lines viz. HeLa (cervix), MCF-7 (breast) and DU145 (prostate) using MTT assay. The evaluation studies revealed the dependence of cytotoxicity on C-5 substituents of both uracil and isatin as well as the alkyl chain length with compounds 6g and 6k showing IC50 values 18.21 and 13.90 μM respectively against DU145 cell lines. Most of the synthesized conjugates exhibited considerable selectivity against MCF-7 and DU145 cell lines. © 2012 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
-
Tubulin Inhibitor-Based Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Cancer Therapy
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hao Chen
2017-08-01
Full Text Available Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs are a class of highly potent biopharmaceutical drugs generated by conjugating cytotoxic drugs with specific monoclonal antibodies through appropriate linkers. Specific antibodies used to guide potent warheads to tumor tissues can effectively reduce undesired side effects of the cytotoxic drugs. An in-depth understanding of antibodies, linkers, conjugation strategies, cytotoxic drugs, and their molecular targets has led to the successful development of several approved ADCs. These ADCs are powerful therapeutics for cancer treatment, enabling wider therapeutic windows, improved pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic properties, and enhanced efficacy. Since tubulin inhibitors are one of the most successful cytotoxic drugs in the ADC armamentarium, this review focuses on the progress in tubulin inhibitor-based ADCs, as well as lessons learned from the unsuccessful ADCs containing tubulin inhibitors. This review should be helpful to facilitate future development of new generations of tubulin inhibitor-based ADCs for cancer therapy.
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Water-soluble Conjugates of Cabazitaxel Hemiesters-Dextran.
Parhizkar, Elahehnaz; Ahmadi, Fatemeh; Daneshamouz, Saeid; Mohammadi-Samani, Soliman; Sakhteman, Amirhossein; Parhizkar, Golnaz
2017-11-24
Cabazitaxel (CTX) is a second- generation taxane derivative, a class of potent anticancer drugs with very low water solubility. CTX is used in patients with resistant prostate cancer unresponsive to the first generation taxane, docetaxel. Currently marketed formulations of CTX contain high concentrations of surfactant and ethanol, which cause severe hypersensitivity reactions in patients. In order to increase its solubility, two hemiester analogs; CTX-succinate and CTX-glutarate were synthesized and characterized. To improve the solubility of hemiesters even more, dextran as a biocompatible polymer was also conjugated to hemiester analogs. MTT assay was performed on MCF-7 cell line to evaluate the cytotoxicity effect of hemiesters and conjugates. Based on the results, hemiester analogs increased water solubility of the drug up to about 3 and 8 fold. Conjugation to dextran enhanced the CTX solubility to more than 1500 fold. These conjugates released the conjugated CTX in less than 24 hours in a pH dependent manner and showed proper hemocompatibility characteristics. The hemiesters had approximately similar cytotoxicity in comparison with CTX and the dextran conjugates showed higher cytotoxicity effect on MCF-7 cell line. Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
-
Comparative cytotoxicity of gold-doxorubicin and InP-doxorubicin conjugates.
Zhang, Xuan; Chibli, Hicham; Kong, Dekun; Nadeau, Jay
2012-07-11
Direct comparisons of different types of nanoparticles for drug delivery have seldom been performed. In this study we compare the physical properties and cellular activity of doxorubicin (Dox) conjugates to gold nanoparticles (Au) and InP quantum dots of comparable diameter. Although the Au particles alone are non-toxic and InP is moderately toxic, Au-Dox is more effective than InP-Dox against the Dox-resistant B16 melanoma cell line. Light exposure does not augment the efficacy of InP-Dox, suggesting that conjugates are breaking down. Electron and confocal microscopy and atomic absorption spectroscopy reveal that over 60% of the Au-Dox conjugates reach the cell nucleus. In contrast, InP-Dox enters cell nuclei to a very limited extent, although liberated Dox from the conjugates does eventually reach the nucleus. These observations are attributed to faster Dox release from Au conjugates under endosomal conditions, greater aggregation of InP-Dox with cytoplasmic proteins, and adherence of InP to membranes. These findings have important implications for design of active drug-nanoparticle conjugates.
-
Karakus, Gulderen; Akin Polat, Zubeyde; Sahin Yaglıoglu, Ayse; Karahan, Mesut; Yenidunya, Ali Fazil
2013-01-01
Poly(maleic anhydride-co-styrene) (MAST) was synthesized by a free-radical polymerization reaction. A bioactive molecule, procainamide hydrochloride (PH), was then conjugated to MAST. The conjugation product was named as MAST/PH. Structural characterization of MAST and MAST/PH was carried out by Fourier Transform Infrared and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy. Their molecular weights were determined by size-exclusion chromatography. A mechanism was then suggested for the conjugation reaction. The results of the cytotoxicity assay, employing a mouse fibroblast cell line (L929), indicated that MAST/PH had no cytotoxicity at concentrations [Formula: see text] 62 μg mL(-1) (p > 0.05). Antiproliferative activities of MAST/PH and PH were determined by the BrdU cell proliferation ELISA assay, using C6 and HeLa cell lines. In the experiment, two anticancer chemotherapy drugs, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil, were included as positive control. Antiproliferative activity results demonstrated that MAST/PH yielded the highest suppression profile (approximately 42%) at 20 μg/ml, while free PH exerted the same activity at 100 μg/ml. Interestingly, both MAST/PH and PH suppressed the proliferation of only one of the cell lines, C6 cells. Both cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil yielded approximately 60% antiproliferative activity on C6 cells at 20 and 100 μg/ml concentrations. Antiangiogenic capacity of both MAST and MAST/PH was also investigated by using the chicken chorioallantoic membrane assay. Results obtained indicated that while MAST/PH could be included into the category of good antiangiogenic substances, the activity score of MAST was within the weak category.
-
Engineering of dendrimer surfaces to enhance transepithelial transport and reduce cytotoxicity.
Jevprasesphant, Rachaneekorn; Penny, Jeffrey; Attwood, David; McKeown, Neil B; D'Emanuele, Antony
2003-10-01
To evaluate the cytotoxicity, permeation, and transport mechanisms of PAMAM dendrimers and surface-modified cationic PAMAM dendrimers using monolayers of the human colon adenocarcinoma cell line, Caco-2. Cytotoxicity was determined using the MTT assay. The effect of dendrimers on monolayer integrity was determined from measurements of transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and [14C]mannitol apparent permeability coefficient (Papp). The Papp of dendrimers through monolayers was measured in both the apical (A)-to-basolateral (B) and B --> A directions at 4 degrees C and 37 degrees C and also in the presence and absence of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) and colchicine. The cytotoxicity and permeation of dendrimers increased with both concentration and generation. The cytotoxicity of cationic dendrimers (G2, G3, G4) was greater than that of anionic dendrimers (G2.5, G3.5) but was reduced by conjugation with lauroyl chloride: the least cytotoxic conjugates were those with six attached lauroyl chains. At 37 degrees C the Papp of cationic dendrimers was higher than that of anionic dendrimers and, in general, increased with the number of attached lipid chains. Cationic dendrimers decreased TEER and significantly increased the Papp of mannitol. Modified dendrimers also reduced TEER and caused a more marked increase in the Papp of mannitol. The Papp values of dendrimers and modified dendrimers were higher in the presence of EDTA, lower in the presence of colchicine, and lower at 4 degrees C than at 37 degrees C. The properties of dendrimers may be significantly modified by surface engineering. Conjugation of cationic PAMAM dendrimers with lauroyl chloride decreased their cytotoxicity and increased their permeation through Caco-2 cell monolayers. Both PAMAM dendrimers and lauroyl-PAMAM dendrimer conjugates can cross epithelial monolayers by paracellular and transcellular pathways.
-
HER2 specific delivery of methotrexate by dendrimer conjugated anti-HER2 mAb
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shukla, Rameshwer; Thomas, Thommey P; Desai, Ankur M; Kotlyar, Alina; Park, Steve J; Baker, James R Jr
2008-01-01
Herceptin, a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to human growth factor receptor-2 (HER2), was covalently attached to a fifth-generation (G5) polyamidoamine dendrimer containing the cytotoxic drug methotrexate. The specific binding and internalization of this conjugate labeled with FITC was clearly demonstrated in cell lines overexpressing HER2 by flow cytometry as well as confocal microscopic analysis. In addition, binding and uptake of antibody conjugated dendrimers was completely blocked by excess non-conjugated herceptin. The dendrimer conjugate was also shown to inhibit the dihydrofolate reductase with similar activity to methotrexate. Co-localization experiments with lysotracker red indicate that antibody conjugate, although internalized efficiently into cells, has an unusually long residence time in the lysosome. Somewhat lower cytotoxicity of the conjugate in comparison to free methotrexate was attributed to the slow release of methotrexate from the conjugate and its long retention in the lysosomal pocket
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Golkar, Nasim; Samani, Soliman Mohammadi; Tamaddon, Ali Mohammad, E-mail: amtamadon@gmail.com [Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Department of Pharmaceutics, School of Pharmacy (Iran, Islamic Republic of)
2016-05-15
Aimed to prepare an enhanced gene delivery system with low cytotoxicity and high transfection efficiency, various cholesterol-conjugated derivates of low generation polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers were prepared. The conjugates were characterized by TNBS assay, FTIR, and {sup 1}H-NMR spectroscopy. Self-assembly of the dendrimer conjugates (G1-Chol, G2-Chol, and G3-Chol) was investigated by pyrene assay. Following formation of the complexes between enhanced green fluorescence protein plasmid and the dendrimer conjugates at various N (primary amine)/P (phosphate) mole ratios, plasmid condensation, biologic stability, cytotoxicity, and protein expression were investigated. The conjugates self-assembled into micellar dispersions with the critical micelle concentration values (<50 µg/ml) depending on the dendrimer generation and cholesterol/amine mole ratio. Cholesterol conjugation resulted in higher resistance of the condensed plasmid DNA in a competition assay with heparin sulfate. Also, the transfection efficiency was determined higher for the cholesterol conjugates than unmodified dendrimers in HepG2 cells, showing the highest for G2-Chol at 40 % degree of cholesterol modification (G2-Chol{sub 40 %}) among various dendrimer generations. Interestingly, such conjugate showed a complete protection of plasmid against serum nucleases. Our results confirmed that the cholesterol conjugation to PAMAM dendrimers of low generations bearing little cytotoxicity improves their several physicochemical and biological characteristics required for an enhanced delivery of plasmid DNA into cells.
-
Conjugation of curcumin onto alginate enhances aqueous solubility and stability of curcumin.
Dey, Soma; Sreenivasan, K
2014-01-01
Curcumin is a potential drug for various diseases including cancer. Prime limitations associated with curcumin are low water solubility, rapid hydrolytic degradation and poor bioavailability. In order to redress these issues we developed Alginate-Curcumin (Alg-Ccm) conjugate which was characterized by FTIR and (1)H NMR spectroscopy. The conjugate self-assembled in aqueous solution forming micelles with an average hydrodynamic diameter of 459 ± 0.32 nm and negative zeta potential. The spherical micelles were visualized by TEM. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of Alg-Ccm conjugate was determined. A significant enhancement in the aqueous solubility of curcumin was observed upon conjugation with alginate. Formation of micelles improved the stability of curcumin in water at physiological pH. The cytotoxic activity of Alg-Ccm was quantified by MTT assay using L-929 fibroblast cells and it was found to be potentially cytotoxic. Hence, Alg-Ccm could be a promising drug conjugate as well as a nanosized delivery vehicle. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Synthesis, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity evaluation of new cholesterol congeners
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mohamed Ramadan El Sayed Aly
2015-10-01
Full Text Available 3β-Azidocholest-5-ene (3 and (3β-3-(prop-2-yn-1-yloxycholest-5-ene (10 were prepared as substrates to synthesize a variety of three-motif pharmacophoric conjugates through CuAAC. Basically, these conjugates included cholesterol and 1,2,3-triazole moieties, while the third, the pharmacophore, was either a chalcone, a lipophilic residue or a carbohydrate tag. These compounds were successfully prepared in good yields and characterized by NMR, MS and IR spectroscopic techniques. Chalcone conjugate 6c showed the best antimicrobial activity, while the lactoside conjugate 27 showed the best cytotoxic effect in vitro.
-
Gorovits, Boris; Alley, Stephen C; Bilic, Sanela; Booth, Brian; Kaur, Surinder; Oldfield, Phillip; Purushothama, Shobha; Rao, Chetana; Shord, Stacy; Siguenza, Patricia
2013-05-01
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) typically consist of a cytotoxic drug covalently bound to an antibody by a linker. These conjugates have the potential to substantially improve efficacy and reduce toxicity compared with cytotoxic small-molecule drugs. Since ADCs are generally complex heterogeneous mixtures of multiple species, these novel therapeutic products present unique bioanalytical challenges. The growing number of ADCs being developed across the industry suggests the need for alignment of the bioanalytical methods or approaches used to assess the multiple species and facilitate consistent interpretation of the bioanalytical data. With limited clinical data, the current strategies that can be used to provide insight into the relationship between the multiple species and the observed clinical safety and efficacy are still evolving. Considerations of the bioanalytical strategies for ADCs based on the current industry practices that take into account the complexity and heterogeneity of ADCs are discussed.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ke, Hanzhong; Ma, Wanpeng; Wang, Hongda; Cheng, Guoe; Yuan, Han; Wong, Wai-Kwok; Kwong, Daniel W.J.; Tam, Hoi-Lam; Cheah, Kok-Wai; Chan, Chi-Fai; Wong, Ka-Leung
2014-01-01
A novel porphyrin–polypyridyl ruthenium(II) conjugate (TPP–Ru), in which the ruthenium(II) polypyridyl moiety is linked to the β-position of the tetraphenylporphyrin via a Schiff base linkage, has been synthesized and characterized by 1 H NMR, HRMS and UV–visible spectroscopy. The relative singlet oxygen quantum yield and two-photon absorption cross-section of this conjugate, together with its photo-induced DNA cleavage and cytotoxic activities were measured. The results show that the amphiphilic ruthenium(II) polypyridyl–porphyrin conjugate is an effective DNA photocleavage agent, with potential application in one- and two-photon absorption anti-cancer photodynamic therapy. - Highlights: • New porphyrin–ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes (TTP–Ru) have been synthesized. • The TTP–Ru shows substantial two-photon absorption cross-section (σ 2 =391 GM). • The TTP–Ru exhibits a substantial 1 O 2 quantum yield (0.64±0.13). • The TTP–Ru exhibits a strong DNA cleavage activity upon photo-excitation. • The TTP–Ru is available for in vitro imaging and as a photodynamic therapy agent
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ke, Hanzhong, E-mail: kehanz@163.com [Faculty of Material Science and Chemistry, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, Hubei 430074 (China); Ma, Wanpeng; Wang, Hongda; Cheng, Guoe [Faculty of Material Science and Chemistry, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, Hubei 430074 (China); Yuan, Han [Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR (China); Wong, Wai-Kwok, E-mail: wkwong@hkbu.edu.hk [Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR (China); Institute of Advanced Materials, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR (China); Kwong, Daniel W.J. [Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR (China); Tam, Hoi-Lam; Cheah, Kok-Wai [Department of Physics, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR (China); Institute of Advanced Materials, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR (China); Chan, Chi-Fai; Wong, Ka-Leung [Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR (China)
2014-10-15
A novel porphyrin–polypyridyl ruthenium(II) conjugate (TPP–Ru), in which the ruthenium(II) polypyridyl moiety is linked to the β-position of the tetraphenylporphyrin via a Schiff base linkage, has been synthesized and characterized by {sup 1}H NMR, HRMS and UV–visible spectroscopy. The relative singlet oxygen quantum yield and two-photon absorption cross-section of this conjugate, together with its photo-induced DNA cleavage and cytotoxic activities were measured. The results show that the amphiphilic ruthenium(II) polypyridyl–porphyrin conjugate is an effective DNA photocleavage agent, with potential application in one- and two-photon absorption anti-cancer photodynamic therapy. - Highlights: • New porphyrin–ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes (TTP–Ru) have been synthesized. • The TTP–Ru shows substantial two-photon absorption cross-section (σ{sub 2}=391 GM). • The TTP–Ru exhibits a substantial {sup 1}O{sub 2} quantum yield (0.64±0.13). • The TTP–Ru exhibits a strong DNA cleavage activity upon photo-excitation. • The TTP–Ru is available for in vitro imaging and as a photodynamic therapy agent.
-
In vitro cytotoxicity testing of Ubiquicidin 29-41-99mTc
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ocampo, Ivette Z.; Okazaki, Kayo; Dias, Luis Alberto Pereira; Higa, Olga Z.; Silva, Fabiana M. da; Vieira, Daniel P.; Passos, Priscila; Esteves-Pedro, Natalia M.
2015-01-01
The work carried out cytotoxicity tests using a radiopharmaceutical compound produced at IPEN/CNEN-SP to certify its safety through in vitro cytotoxicity tests. Since 2009, the Brazilian regulatory agency (ANVISA) requires that such tests have to be carried out following good laboratory practices (GLP) and in according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) guidelines in order to certify its safety for medical use. Those guidelines comprises series of technical recommendations performed to assure quality of experiments. The study chose Ubiquicidin 29-41, an antimicrobial peptide used to discriminate bacterial infection foci from inflammatory sites. Amounts of UBI 29-41 were conjugated or not to 99m Tc and diluted to equivalent concentrations of 10, 100 and 1000% of the maximum dose (or activity) administered in adults. Possible cytotoxic effects were evaluated in comparison to untreated controls as well as positive and negative damage controls. Both full (radioactive) radiopharmaceuticals, as their precursors (only molecules without conjugation to isotopes) showed no significant cytotoxic effect (cytotoxicity ≤ 10%). The study was conducted for the first time in the country comprising preclinical testing of this radiopharmaceutical in accordance with internationally accepted quality parameters, ensuring the safety of its use and enabling inclusion in the pharmaceutical regulatory agenda. (author)
-
Pavan Kumar, Y; Saha, Puja; Saha, Dhurjhoti; Bessi, Irene; Schwalbe, Harald; Chowdhury, Shantanu; Dash, Jyotirmayee
2016-03-02
The four-stranded G-quadruplex present in the c-MYC P1 promoter has been shown to play a pivotal role in the regulation of c-MYC transcription. Small-molecule compounds capable of inhibiting the c-MYC promoter activity by stabilising the c-MYC G-quadruplex could potentially be used as anticancer agents. In this context, here we report the synthesis of dansyl-guanosine conjugates through one-pot modular click reactions. The dansyl-guanosine conjugates can selectively detect c-MYC G-quadruplex over other biologically relevant quadruplexes and duplex DNA and can be useful as staining reagents for selective visualisation of c-MYC G-quadruplex over duplex DNA by gel electrophoresis. NMR spectroscopic titrations revealed the preferential binding sites of these dansyl ligands to the c-MYC G-quadruplex. A dual luciferase assay and qRT-PCR revealed that a dansyl-bisguanosine ligand represses the c-MYC expression, possibly by stabilising the c-MYC G-quadruplex. © 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Biotin conjugated organic molecules and proteins for cancer therapy: A review.
Maiti, Santanu; Paira, Priyankar
2018-02-10
The main transporter for biotin is sodium dependent multivitamin transporter (SMVT), which is overexpressed in various aggressive cancer cell lines such as ovarian (OV 2008, ID8), leukemia (L1210FR), mastocytoma (P815), colon (Colo-26), breast (4T1, JC, MMT06056), renal (RENCA, RD0995), and lung (M109) cancer cell lines. Furthermore, its overexpression was found higher to that of folate receptor. Therefore, biotin demand in the rapidly growing tumors is higher than normal tissues. Several biotin conjugated organic molecules has been reported here for selective delivery of the drug in cancer cell. Biotin conjugated molecules are showing higher fold of cytotoxicity in biotin positive cancer cell lines than the normal cell. Nanoparticles and polymer surface modified drugs and biotin mediated cancer theranostic strategy was highlighted in this review. The cytotoxicity and selectivity of the drug in cancer cells has enhanced after biotin conjugation. Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Kermanizadeh, Ali; Villadsen, Klaus; Østrem, Ragnhild Garborg
2017-01-01
constructed with the aim of targeting integrins (i.e. vitronectin and/or fibronectin receptors) on activated endothelial cells. The peptide-conjugated liposomes induced only cytotoxicity at the highest concentration in non-activated or activated endothelial cells, as well as in co-culture of endothelial cells...... and macrophages. There was unaltered secretion of cytokines following exposure of peptide-conjugated liposomes to endothelial cells, indicating that the materials were not inflammogenic. Liposomes with a peptide targeting the fibronectin receptor (integrin α5β1) were more effective in targeting of activated....... Therefore, this study demonstrates the feasibility of constructing a peptide-conjugated cationic liposome, which displays targeting to activated endothelial cells at concentrations that are not cytotoxic or inflammogenic to the cells....
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jiang X
2012-02-01
Full Text Available Danbo Yang1, Sang Van2, Yingyi Shu1, Xiaoqing Liu1, Yangfeng Ge1, Xinguo Jiang3, Yi Jin2, Lei Yu1,21Biomedical Engineering and Technology Institute, Institutes for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research, East China Normal University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China; 2Biomedical Group, Nitto Denko Technical Corporation, CA, USA; 3School of Pharmacy, Fudan University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of ChinaAim: This work is intended to develop and evaluate a biopolymeric poly(L-γ-glutamyl-glutamine (PGG–docetaxel (DTX conjugate that can spontaneously self-assemble in aqueous solutions to become nanoparticles.Methods: DTX was covalently attached to hydrophilic PGG by direct esterification, and the conjugate was characterized by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, molecular weight gel permeation chromatography, solubility, size distribution and morphology, and hemolysis. Conjugated DTX was found to have 2000 times improved water solubility compared with free DTX. Dynamic light scattering, transmission electron microscopy, and atomic force microscopy revealed the particle size, distribution and morphology of the PGG–DTX conjugate. In addition, the conjugate was further tested for in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo antitumor efficacy on the human non-small cell lung cancer cell line NCI-H460.Results: Conjugated DTX was found to have 2000 times improved water solubility compared with free DTX. The conjugate formed nanoparticles with an average diameter of 30 nm in spherical shape and unimodal particle size distribution. The conjugate exhibited about 2% hemolysis at 10 mg/mL, compared with 56% for Tween 80® at 0.4 mg/mL, and 33% for Cremophor EL® at 10 mg/mL. In addition, the conjugate was further tested for in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo antitumor efficacy on the human non-small cell lung cancer cell line NCI-H460. As expected, conjugated DTX exhibited lower cytotoxicity compared to that of free DTX, in concentration
-
In vitro cytotoxicity testing of Ubiquicidin 29-41-{sup 99m}Tc
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ocampo, Ivette Z.; Okazaki, Kayo; Dias, Luis Alberto Pereira; Higa, Olga Z.; Silva, Fabiana M. da; Vieira, Daniel P., E-mail: dpvieira@ipen.br [Instituto de Pesquisas Energeticas e Nucleares (IPEN/CNEN-SP), Sao Paulo, SP (Brazil); Passos, Priscila; Esteves-Pedro, Natalia M., E-mail: fabiana@biosintesis.com.br [Laboratorio Biosintesis Ltda, Sao Paulo, SP (Brazil)
2015-07-01
The work carried out cytotoxicity tests using a radiopharmaceutical compound produced at IPEN/CNEN-SP to certify its safety through in vitro cytotoxicity tests. Since 2009, the Brazilian regulatory agency (ANVISA) requires that such tests have to be carried out following good laboratory practices (GLP) and in according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) guidelines in order to certify its safety for medical use. Those guidelines comprises series of technical recommendations performed to assure quality of experiments. The study chose Ubiquicidin 29-41, an antimicrobial peptide used to discriminate bacterial infection foci from inflammatory sites. Amounts of UBI{sub 29-41} were conjugated or not to {sup 99m}Tc and diluted to equivalent concentrations of 10, 100 and 1000% of the maximum dose (or activity) administered in adults. Possible cytotoxic effects were evaluated in comparison to untreated controls as well as positive and negative damage controls. Both full (radioactive) radiopharmaceuticals, as their precursors (only molecules without conjugation to isotopes) showed no significant cytotoxic effect (cytotoxicity ≤ 10%). The study was conducted for the first time in the country comprising preclinical testing of this radiopharmaceutical in accordance with internationally accepted quality parameters, ensuring the safety of its use and enabling inclusion in the pharmaceutical regulatory agenda. (author)
-
BF3·Et2O promoted conjugate addition of ethanethiol to electron-deficient alkynes
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
Qing Fa Zhou; Xue Ping Chu; Shen Zhao; Tao Lu; Wei Fang Tang
2012-01-01
An effective method for the synthesis of vinyl thioethers through the conjugate addition of ethanethiol to electron-deficient alkynes promoted by BF3·Et2O has been developed.Electron-deficient internal alkynes react with ethanethiol in this system to yield mainly Z-isomer of vinyl thioether adducts,while electron-deficient terminal alkynes afford mainly E-isomer of vinyl thioether adducts.
-
Mathematical modeling of mutant transferrin-CRM107 molecular conjugates for cancer therapy.
Yoon, Dennis J; Chen, Kevin Y; Lopes, André M; Pan, April A; Shiloach, Joseph; Mason, Anne B; Kamei, Daniel T
2017-03-07
The transferrin (Tf) trafficking pathway is a promising mechanism for use in targeted cancer therapy due to the overexpression of transferrin receptors (TfRs) on cancerous cells. We have previously developed a mathematical model of the Tf/TfR trafficking pathway to improve the efficiency of Tf as a drug carrier. By using diphtheria toxin (DT) as a model toxin, we found that mutating the Tf protein to change its iron release rate improves cellular association and efficacy of the drug. Though this is an improvement upon using wild-type Tf as the targeting ligand, conjugated toxins like DT are unfortunately still highly cytotoxic at off-target sites. In this work, we address this hurdle in cancer research by developing a mathematical model to predict the efficacy and selectivity of Tf conjugates that use an alternative toxin. For this purpose, we have chosen to study a mutant of DT, cross-reacting material 107 (CRM107). First, we developed a mathematical model of the Tf-DT trafficking pathway by extending our Tf/TfR model to include intracellular trafficking via DT and DT receptors. Using this mathematical model, we subsequently investigated the efficacy of several conjugates in cancer cells: DT and CRM107 conjugated to wild-type Tf, as well as to our engineered mutant Tf proteins (K206E/R632A Tf and K206E/R534A Tf). We also investigated the selectivity of mutant Tf-CRM107 against non-neoplastic cells. Through the use of our mathematical model, we predicted that (i) mutant Tf-CRM107 exhibits a greater cytotoxicity than wild-type Tf-CRM107 against cancerous cells, (ii) this improvement was more drastic with CRM107 conjugates than with DT conjugates, and (iii) mutant Tf-CRM107 conjugates were selective against non-neoplastic cells. These predictions were validated with in vitro cytotoxicity experiments, demonstrating that mutant Tf-CRM107 conjugates is indeed a more suitable therapeutic agent. Validation from in vitro experiments also confirmed that such whole
-
ADRIAMYCIN-LOADED ALBUMIN-HEPARIN CONJUGATE MICROSPHERES FOR INTRAPERITONEAL CHEMOTHERAPY
CREMERS, HFM; SEYMOUR, LW; LAM, K; LOS, G; KWON, G; BAE, YH; KIM, SW; FEIJEN, J
1994-01-01
Adriamycin-loaded albumin-heparin conjugate microspheres (ADR-AHCMS) were evaluated as possible intraperitoneal (i.p.) delivery systems for site-specific cytotoxic action. The biocompatibility of the microspheres after intraperitoneal injection was tested first. 1 day after i.p. administration of
-
Li, Chunju; Lin, Qixun; Wang, Jun; Shen, Lijuan; Ma, Guanghui; Su, Zhiguo; Hu, Tao
2012-12-31
Ribonuclease A (RNase A) is a therapeutic enzyme with cytotoxic action against tumor cells. Its clinical application is limited by the short half-life and insufficient stability. Conjugation of albumin can overcome the limitation, whereas dramatically decrease the enzymatic activity of RNase A. Here, three strategies were proposed to prepare the RNase A-bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugates. R-SMCC-B (a conjugate of four RNase A attached with one BSA) and R-PEG-B (a mono-conjugate) were prepared using Sulfo-SMCC (a short bifunctional linker) and mal-PEG-NHS (a bifunctional PEG), respectively. Mal-PEG-NHS and hexadecylamine (HDA) were used to prepare the mono-conjugate, R-HDA-B, where HDA was adopted to bind BSA. The PEG linker can elongate the proximity between RNase A and BSA. In contrast, four RNase A were closely located on BSA in R-SMCC-B. R-SMCC-B showed the lowest K(m) and the highest relative enzymatic activity and k(cat)/K(m) in the three conjugates. Presumably, the tetravalent interaction of RNase A in R-SMCC-B can increase the binding affinity to its substrate. In addition, the slow release of BSA from R-HDA-B may increase the enzymatic activity of R-HDA-B. Our study is expected to provide strategies to develop protein-albumin conjugate with high therapeutic potential. Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Sommerwerk, Sven; Heller, Lucie; Kerzig, Christoph; Kramell, Annemarie E; Csuk, René
2017-02-15
Triterpenoic acids 1-6 exhibited very low or no cytotoxicity at all, but their corresponding 2,3-di-O-acetyl-piperazinyl amides 13-18 showed low EC 50 values for several human tumor cell lines. Their cytotoxicity, however, was also high for the non-malignant mouse fibroblasts NIH 3T3. A significant improvement was achieved by preparing the rhodamine B derivatives 19-24. While rhodamine B is not cytotoxic (up to a concentration of 30μM - cut-off of the assay), the triterpenoid piperazine-spacered rhodamine B derivatives were cytotoxic in nano-molar concentration. Compound 24 (a diacetylated maslinic acid derivative) was most toxic for several human tumor cell lines but less toxic for mouse fibroblasts NIH 3T3. Staining and double-staining experiments revealed 24 to act as a mitocan. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
-
Bromberg, Lev; Raduyk, Svetlana; Hatton, T Alan; Concheiro, Angel; Rodriguez-Valencia, Cosme; Silva, Maite; Alvarez-Lorenzo, Carmen
2009-05-20
Conjugates of linear and branched polyethyleneimine (PEI) and monoamine polyether Jeffamine M-2070 (PO/EO mol ratio 10/31, 2000 Da) were synthesized through polyether activation by cyanuric chloride followed by attachment to PEI and guanidinylation by 1H-pyrazole-carboxamidine hydrochloride. The resulting guanidinylated PEI-polyether conjugates (termed gPEI-Jeffamine) efficiently complexed plasmid DNA, and their polyplexes possessed enhanced colloidal stability in the presence of serum proteins. In vitro studies with mammalian CHO-1, 3T3, and Cos-7 cell lines demonstrated improved transfection efficiency of the pCMVbeta-gal plasmid/gPEI-Jeffamine polyplexes. The guanidinylation of the amino groups of PEI and the conjugation of PEI with the Jeffamine polyether enhanced the conjugates' interaction with genetic material and reduced the cytotoxicity of the polyplexes in experiments with the L929 cell line.
-
Effects of transferrin conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes in lung cancer delivery
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Singh, Rahul Pratap [Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Sharma, Gunjan [Genotoxicology and Cancer Biology Lab, Department of Zoology, Institute of Science, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Sonali [Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Singh, Sanjay [Department of Pharmaceutics, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi 221005 (India); Patne, Shashikant C.U. [Department of Pathology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Pandey, Bajarangprasad L. [Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Koch, Biplob, E-mail: kochbiplob@gmail.com [Genotoxicology and Cancer Biology Lab, Department of Zoology, Institute of Science, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Muthu, Madaswamy S., E-mail: muthubits@rediffmail.com [Department of Pharmaceutics, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi 221005 (India); Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India)
2016-10-01
The aim of this study was to develop multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) which were covalently conjugated with transferrin by carbodiimide chemistry and loaded with docetaxel as a model drug for effective treatment of lung cancer in comparison with the commercial docetaxel injection (Docel™). D-Alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was used as amphiphilic surfactant to improve the aqueous dispersity and biocompatibility of MWCNT. Human lung cancer cells (A549 cells) were employed as an in-vitro model to access cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle analysis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) of the docetaxel/coumarin-6 loaded MWCNT. The cellular uptake results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT showed higher efficiency in comparison with free C6. The IC{sub 50} values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more efficient than Docel™ after 24 h treatment with the A549 cells. Flow cytometry analysis confirmed that cancerous cells appeared significantly (P < 0.05) in the sub-G1 phase for transferrin conjugated MWCNT in comparison with Docel™. Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™. - Highlights: • It shows the development of transferrin conjugated MWCNT formulation of DTX for the effective treatment of lung cancer. • Evaluated the cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle, and ROS level of the DTX/C6 loaded MWCNT. • The IC{sub 50} values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more effective than Docel™. • Safety of the DTX formulations were studied by the measurements of ALP, LDH and total protein count levels in BAL fluid. • Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™ in lung cancer delivery.
-
Effects of transferrin conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes in lung cancer delivery
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Singh, Rahul Pratap; Sharma, Gunjan; Sonali; Singh, Sanjay; Patne, Shashikant C.U.; Pandey, Bajarangprasad L.; Koch, Biplob; Muthu, Madaswamy S.
2016-01-01
The aim of this study was to develop multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) which were covalently conjugated with transferrin by carbodiimide chemistry and loaded with docetaxel as a model drug for effective treatment of lung cancer in comparison with the commercial docetaxel injection (Docel™). D-Alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was used as amphiphilic surfactant to improve the aqueous dispersity and biocompatibility of MWCNT. Human lung cancer cells (A549 cells) were employed as an in-vitro model to access cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle analysis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) of the docetaxel/coumarin-6 loaded MWCNT. The cellular uptake results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT showed higher efficiency in comparison with free C6. The IC_5_0 values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more efficient than Docel™ after 24 h treatment with the A549 cells. Flow cytometry analysis confirmed that cancerous cells appeared significantly (P < 0.05) in the sub-G1 phase for transferrin conjugated MWCNT in comparison with Docel™. Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™. - Highlights: • It shows the development of transferrin conjugated MWCNT formulation of DTX for the effective treatment of lung cancer. • Evaluated the cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle, and ROS level of the DTX/C6 loaded MWCNT. • The IC_5_0 values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more effective than Docel™. • Safety of the DTX formulations were studied by the measurements of ALP, LDH and total protein count levels in BAL fluid. • Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™ in lung cancer delivery.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Martin Kreutz
Full Text Available Antibody-antigen conjugates, which promote antigen-presentation by dendritic cells (DC by means of targeted delivery of antigen to particular DC subsets, represent a powerful vaccination approach. To ensure immunity rather than tolerance induction the co-administration of a suitable adjuvant is paramount. However, co-administration of unlinked adjuvant cannot ensure that all cells targeted by the antibody conjugates are appropriately activated. Furthermore, antigen-presenting cells (APC that do not present the desired antigen are equally strongly activated and could prime undesired responses against self-antigens. We, therefore, were interested in exploring targeted co-delivery of antigen and adjuvant in cis in form of antibody-antigen-adjuvant conjugates for the induction of anti-tumour immunity. In this study, we report on the assembly and characterization of conjugates consisting of DEC205-specific antibody, the model antigen ovalbumin (OVA and CpG oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN. We show that such conjugates are more potent at inducing cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL responses than control conjugates mixed with soluble CpG. However, our study also reveals that the nucleic acid moiety of such antibody-antigen-adjuvant conjugates alters their binding and uptake and allows delivery of the antigen and the adjuvant to cells partially independently of DEC205. Nevertheless, antibody-antigen-adjuvant conjugates are superior to antibody-free antigen-adjuvant conjugates in priming CTL responses and efficiently induce anti-tumour immunity in the murine B16 pseudo-metastasis model. A better understanding of the role of the antibody moiety is required to inform future conjugate vaccination strategies for efficient induction of anti-tumour responses.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dekant, W.; Lash, L.H.; Anders, M.W.
1987-01-01
The bioactivation of S-(2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl)-L-cysteine (CTFC) was studied with purified bovine kidney cysteine conjugate β-lyase and with N-dodecylpyridoxal bromide in cetyltrimethylammonium bromide micelles as a pyridoxal model system. The β-lyase and the pyridoxal model system converted CTFC to chlorofluoroacetic acid and inorganic fluoride, which were identified by 19 F NMR spectrometry. 2-Chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethanethiol and chlorofluorothionoacetyl fluoride were formed as metabolites of CTFC and were trapped with benzyl bromide and diethylamine, respectively, to yield benzyl 2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl sulfide and N,N-diethyl chlorofluorothioacetamide, which were identified by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. The bioactivation mechanism of CTFC therefore involves the initial formation of the unstable thiol 2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethanethiol, which loses hydrogen fluoride to form the acylating agent chlorofluorothionoacetyl fluoride; hydrolysis of the thionoacyl fluoride affords the stable, terminal metabolites chlorofluoroacetic acid and inorganic fluoride. The intermediate acylating agent and chlorofluoroacetic acid may contribute to the cytotoxic effects of CTFC
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Julia M. Tan
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Carbon nanotubes (CNTs have been widely utilized as a novel drug carrier with promising future applications in biomedical therapies due to their distinct characteristics. In the present work, carboxylic acid-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes (f-SWCNTs were used as the starting material to react with anticancer drug, BA to produce f-SWCNTs-BA conjugate via π-π stacking interaction. The conjugate was extensively characterized for drug loading capacity, physicochemical properties, surface morphology, drug releasing characteristics, and cytotoxicity evaluation. The results indicated that the drug loading capacity was determined to be around 20 wt% and this value has been verified by thermogravimetric analysis. The binding of BA onto the surface of f-SWCNTs was confirmed by FTIR and Raman spectroscopies. Powder XRD analysis showed that the structure of the conjugate was unaffected by the loading of BA. The developed conjugate was found to release the drug in a controlled manner with a prolonged release property. According to the preliminary in vitro cytotoxicity studies, the conjugate was not toxic in a standard fibroblast cell line, and anticancer activity was significantly higher in A549 than HepG2 cell line. This study suggests that f-SWCNTs could be developed as an efficient drug carrier to conjugate drugs for pharmaceutical applications in cancer chemotherapies.
-
Zeinali, Majid; Jammalan, Mostafa; Ardestani, Sussan K; Mosaveri, Nader
2009-09-22
Tuberculosis (TB) represents one of the leading killers among all infectious disease. Protection against TB depends on the activation of T-helper type I (Th1) immune response. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have attracted considerable attention because of their potential applications as new nanovehicle. In the current study, tuberculin purified protein derivative (PPD) was conjugated to carboxylated single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs). Cytotoxicity of the carboxylated SWCNT and SWCNT-PPD conjugate was analyzed with MTT assay and by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) generation. Male BALB/c mice were immunized with BCG, PPD, SWCNT-PPD conjugate and PPD in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA). Induction of cellular immune response was analyzed by measuring the levels of Th1 cytokines (IFN-gamma and IL-12) and Th2 cytokines (IL-10 and IL-5). Immunization with non-conjugated PPD or PPD in Freund's adjuvant induced a Th2 cytokine response while immunization with BCG resulted to a mixed Th1/Th2 cytokine response. In contrast, PPD in conjugation with SWCNT generated preferentially a Th1-type cytokine response in the absence of potential cytotoxic effects.
-
Saneja, Ankit; Nayak, Debasis; Srinivas, M; Kumar, Amit; Khare, Vaibhav; Katoch, Archana; Goswami, Anindya; Vishwakarma, Ram A; Sawant, Sanghapal D; Gupta, Prem N
2017-01-15
The overexpression of CD44 in cancer cells reroutes number of oncogenic pathways including the central Pi3K/Akt/NF-kB pathway leading to cancer progression and malignancy. Herein, we developed hyaluronic acid-modified poly(dl-lactic-co-glycolic acid)-poly (ethylene glycol) nanoparticles (PLGA-PEG-HA NPs) for targeted delivery of TTQ (thio-tetrazolyl analog of a clinical candidate, IC87114) to CD44 overexpressing cancer cells. The PLGA-PEG co-polymer was synthesized and characterized by NMR and FTIR. The co-polymer based nanoparticles were prepared by solvent evaporation method and hyaluronic acid (HA) was conjugated on to the nanoparticle surface via EDC/NHS chemistry. The PLGA-PEG-HA NPs had a desirable particle size (AFM). In vitro cytotoxicity and cellular uptake studies demonstrated higher cytotoxicity and enhanced intracellular accumulation of PLGA-PEG-HA NPs compared to PLGA-PEG NPs in high CD44 expressing MiaPaca-2 cells compared to MDA-MB-231 and MCF7 cells. At the molecular level, the PLGA-PEG-HA NPs were found to be inducing premature senescence with increase in senescence associated β-galactosidase activity and senescence specific marker p21 expression through modulation of Pi3K/Akt/NF-kB signaling pathway in MiaPaca-2 cells. These findings collectively indicated that HA-modified nanoparticles might serve as a promising nanocarrier for site-specific drug delivery, and can be explored further to increase the therapeutic efficacy of anticancer drugs via targeting to CD44 over-expressing cancer cells. Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier B.V.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sujiet Puthenveetil
Full Text Available Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs are no longer an unknown entity in the field of cancer therapy with the success of marketed ADCs like ADCETRIS and KADCYLA and numerous others advancing through clinical trials. The pursuit of novel cytotoxic payloads beyond the mictotubule inhibitors and DNA damaging agents has led us to the recent discovery of an mRNA splicing inhibitor, thailanstatin, as a potent ADC payload. In our previous work, we observed that the potency of this payload was uniquely tied to the method of conjugation, with lysine conjugates showing much superior potency as compared to cysteine conjugates. However, the ADC field is rapidly shifting towards site-specific ADCs due to their advantages in manufacturability, characterization and safety. In this work we report the identification of a highly efficacious site-specific thailanstatin ADC. The site of conjugation played a critical role on both the in vitro and in vivo potency of these ADCs. During the course of this study, we developed a novel methodology of loading a single site with multiple payloads using an in situ generated multi-drug carrying peptidic linker that allowed us to rapidly screen for optimal conjugation sites. Using this methodology, we were able to identify a double-cysteine mutant ADC delivering four-loaded thailanstatin that was very efficacious in a gastric cancer xenograft model at 3mg/kg and was also shown to be efficacious against T-DM1 resistant and MDR1 overexpressing tumor cell lines.
-
Puthenveetil, Sujiet; He, Haiyin; Loganzo, Frank; Musto, Sylvia; Teske, Jesse; Green, Michael; Tan, Xingzhi; Hosselet, Christine; Lucas, Judy; Tumey, L Nathan; Sapra, Puja; Subramanyam, Chakrapani; O'Donnell, Christopher J; Graziani, Edmund I
2017-01-01
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are no longer an unknown entity in the field of cancer therapy with the success of marketed ADCs like ADCETRIS and KADCYLA and numerous others advancing through clinical trials. The pursuit of novel cytotoxic payloads beyond the mictotubule inhibitors and DNA damaging agents has led us to the recent discovery of an mRNA splicing inhibitor, thailanstatin, as a potent ADC payload. In our previous work, we observed that the potency of this payload was uniquely tied to the method of conjugation, with lysine conjugates showing much superior potency as compared to cysteine conjugates. However, the ADC field is rapidly shifting towards site-specific ADCs due to their advantages in manufacturability, characterization and safety. In this work we report the identification of a highly efficacious site-specific thailanstatin ADC. The site of conjugation played a critical role on both the in vitro and in vivo potency of these ADCs. During the course of this study, we developed a novel methodology of loading a single site with multiple payloads using an in situ generated multi-drug carrying peptidic linker that allowed us to rapidly screen for optimal conjugation sites. Using this methodology, we were able to identify a double-cysteine mutant ADC delivering four-loaded thailanstatin that was very efficacious in a gastric cancer xenograft model at 3mg/kg and was also shown to be efficacious against T-DM1 resistant and MDR1 overexpressing tumor cell lines.
-
Antibody conjugate radioimmunotherapy of superficial bladder cancer
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Perkins, Alan; Hopper, Melanie; Murray, Andrea; Frier, Malcolm; Bishop, Mike
2002-01-01
The administration of antibody conjugates for cancer therapy is now proving to be of clinical value. We are currently undertaking a programme of clinical studies using the monoclonal antibody C 595 (gG3) which reacts with the MUC1 glycoprotein antigen that is aberrantly expressed in a high proportion of bladder tumours. Radio immuno conjugates of the C 595 antibody have been produced with high radiolabelling efficiency and immuno reactivity using Tc-99 m and In-111 for diagnostic imaging, and disease staging and the cytotoxic radionuclides Cu-67 and Re-188 for therapy of superficial bladder cancer. A Phase I/II therapeutic trail involving the intravesical administration of antibody directly into the bladder has now begun. (author)
-
Mahendran, Gokila; Ponnuchamy, Kumar
2018-05-01
In recent, the conjugation of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with biomolecules has shown great potential especially in disease diagnostics and treatment. Taking this in account, we report the methodology involved in the conjugation of coumarin onto the surface of citrate-capped AuNPs by a simple in situ method. Herein, we systematically performed UV-Vis spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, and zeta potential measurements to characterize citrate-capped AuNPs and bioconjugates. Our results demonstrate in-depth surface chemistry of bioconjugates with improved surface plasmon resonance (529 nm), morphology (near spherical shape), hydrodynamic diameter (25.3 nm) as well as surface charge (- 35 mV). Furthermore, the bioconjugates displayed dose-dependent response in scavenging free radicals and exhibited cytotoxicity against MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines. In addition, phase-contrast microscopic analysis revealed that bioconjugates promote apoptosis in cancer cells in a time-dependent manner. Overall, we ascertain the fact that this kind of bioconjugation of AuNPs with coumarin further enhances the efficacy of inorganic nanomaterials and thus make them a better bio-therapeutic candidate.
-
Synthesis and in-vitro cytotoxicity of dendrimer cytostatic conjugates
Scutaru, Ana Maria
2011-01-01
Bendamustine and melphalan are nitrogen mustard derivatives from the group of alkylating agents and are used for the treatment of various cancers such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or breast cancer. However their use is limited by numerous side effects. Therefore, 1,3,5-tris(3-aminopropyl)benzene (G0) and the G1 analogous 1,3,5-tris[3,5-bis(3-aminopropyl)-N-propylbenzamide]benzene were chosen to synthesize cytostatic-dendrimer conjugates and to achieve ‘tumor targeting' through the EP...
-
pH-responsive polymer–drug conjugates as multifunctional micelles for cancer-drug delivery
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kang, Yang; Ha, Wei; Ma, Yuan; Ding, Li-Sheng; Li, Bang-Jing; Liu, Ying-Qian; Fan, Min-Min; Zhang, Sheng
2014-01-01
We developed a novel linear pH-sensitive conjugate methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-4β-aminopodophyllotoxin (mPEG-NPOD-I) by a covalently linked 4β-aminopodophyllotoxin (NPOD) and PEG via imine bond, which was amphiphilic and self-assembled to micelles in an aqueous solution. The mPEG-NPOD-I micelles simultaneously served as an anticancer drug conjugate and as drug carriers. As a drug conjugate, mPEG-NPOD-I showed a significantly faster NPOD release at a mildly acidic pH of 5.0 and 4.0 than a physiological pH of 7.4. Notably, it was confirmed that this drug conjugate could efficiently deliver NPOD to the nuclei of the tumor cells and led to much more cytotoxic effects to A549, Hela, and HepG2 cancer cells than the parent NPOD. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC 50 ) of mPEG-NPOD-I was about one order magnitude lower than that of the NPOD. In vivo, mPEG-NPOD-I reduced the size of the tumors significantly, and the biodistribution studies indicated that this drug conjugate could selectively accumulate in tumor tissues. As drug carriers, the mPEG-NPOD-I micelles encapsulated hydrophobic PTX with drug-loading efficiencies of 57% and drug-loading content of 16%. The loaded PTX also showed pH-triggered fast release behavior, and good additive cytotoxicity effect was observed for the PEG-NPOD-I/PTX. We are convinced that these multifunctional drug conjugate micelles have tremendous potential for targeted cancer therapy. (paper)
-
Intracellular trafficking of new anticancer therapeutics: antibody–drug conjugates
Kalim, Muhammad; Chen, Jie; Wang, Shenghao; Lin, Caiyao; Ullah, Saif; Liang, Keying; Ding, Qian; Chen, Shuqing; Zhan, Jinbiao
2017-01-01
Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) is a milestone in targeted cancer therapy that comprises of monoclonal antibodies chemically linked to cytotoxic drugs. Internalization of ADC takes place via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-mediated endocytosis, and pinocytosis. Conjugation strategies, endocytosis and intracellular trafficking optimization, linkers, and drugs chemistry present a great challenge for researchers to eradicate tumor cells successfully. This inventiveness of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking has given considerable momentum recently to develop specific antibodies and ADCs to treat cancer cells. It is significantly advantageous to emphasize the endocytosis and intracellular trafficking pathways efficiently and to design potent engineered conjugates and biological entities to boost efficient therapies enormously for cancer treatment. Current studies illustrate endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ADC, protein, and linker strategies in unloading and also concisely evaluate practically applicable ADCs. PMID:28814834
-
Intracellular trafficking of new anticancer therapeutics: antibody-drug conjugates.
Kalim, Muhammad; Chen, Jie; Wang, Shenghao; Lin, Caiyao; Ullah, Saif; Liang, Keying; Ding, Qian; Chen, Shuqing; Zhan, Jinbiao
2017-01-01
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is a milestone in targeted cancer therapy that comprises of monoclonal antibodies chemically linked to cytotoxic drugs. Internalization of ADC takes place via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-mediated endocytosis, and pinocytosis. Conjugation strategies, endocytosis and intracellular trafficking optimization, linkers, and drugs chemistry present a great challenge for researchers to eradicate tumor cells successfully. This inventiveness of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking has given considerable momentum recently to develop specific antibodies and ADCs to treat cancer cells. It is significantly advantageous to emphasize the endocytosis and intracellular trafficking pathways efficiently and to design potent engineered conjugates and biological entities to boost efficient therapies enormously for cancer treatment. Current studies illustrate endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ADC, protein, and linker strategies in unloading and also concisely evaluate practically applicable ADCs.
-
Bispecific small molecule-antibody conjugate targeting prostate cancer.
Kim, Chan Hyuk; Axup, Jun Y; Lawson, Brian R; Yun, Hwayoung; Tardif, Virginie; Choi, Sei Hyun; Zhou, Quan; Dubrovska, Anna; Biroc, Sandra L; Marsden, Robin; Pinstaff, Jason; Smider, Vaughn V; Schultz, Peter G
2013-10-29
Bispecific antibodies, which simultaneously target CD3 on T cells and tumor-associated antigens to recruit cytotoxic T cells to cancer cells, are a promising new approach to the treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Here we report a site-specific, semisynthetic method for the production of bispecific antibody-like therapeutics in which a derivative of the prostate-specific membrane antigen-binding small molecule DUPA was selectively conjugated to a mutant αCD3 Fab containing the unnatural amino acid, p-acetylphenylalanine, at a defined site. Homogeneous conjugates were generated in excellent yields and had good solubility. The efficacy of the conjugate was optimized by modifying the linker structure, relative binding orientation, and stoichiometry of the ligand. The optimized conjugate showed potent and selective in vitro activity (EC50 ~ 100 pM), good serum half-life, and potent in vivo activity in prophylactic and treatment xenograft mouse models. This semisynthetic approach is likely to be applicable to the generation of additional bispecific agents using drug-like ligands selective for other cell-surface receptors.
-
Bispecific small molecule–antibody conjugate targeting prostate cancer
Kim, Chan Hyuk; Axup, Jun Y.; Lawson, Brian R.; Yun, Hwayoung; Tardif, Virginie; Choi, Sei Hyun; Zhou, Quan; Dubrovska, Anna; Biroc, Sandra L.; Marsden, Robin; Pinstaff, Jason; Smider, Vaughn V.; Schultz, Peter G.
2013-01-01
Bispecific antibodies, which simultaneously target CD3 on T cells and tumor-associated antigens to recruit cytotoxic T cells to cancer cells, are a promising new approach to the treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Here we report a site-specific, semisynthetic method for the production of bispecific antibody-like therapeutics in which a derivative of the prostate-specific membrane antigen-binding small molecule DUPA was selectively conjugated to a mutant αCD3 Fab containing the unnatural amino acid, p-acetylphenylalanine, at a defined site. Homogeneous conjugates were generated in excellent yields and had good solubility. The efficacy of the conjugate was optimized by modifying the linker structure, relative binding orientation, and stoichiometry of the ligand. The optimized conjugate showed potent and selective in vitro activity (EC50 ∼100 pM), good serum half-life, and potent in vivo activity in prophylactic and treatment xenograft mouse models. This semisynthetic approach is likely to be applicable to the generation of additional bispecific agents using drug-like ligands selective for other cell-surface receptors. PMID:24127589
-
Cao, Na; Feng, Si-Shen
2008-10-01
To develop a polymer-anticancer drug conjugate, D-alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was employed as a carrier of doxorubicin (DOX) to enhance its therapeutic effects and reduce its side effects. Doxorubicin was chemically conjugated to TPGS. The molecular structure, drug loading efficiency, drug release kinetics and stability of the conjugate were characterized. The cellular uptake, intracellular distribution, and cytotoxicity were accessed by using MCF-7 breast cancer cells and C6 glioma cells as in vitro cell model. The conjugate showed higher cellular uptake efficiency and broader distribution within the cells. Judged by IC(50), the conjugate was found 31.8, 69.6, 84.1% more effective with MCF-7 cells and 43.9, 87.7, 42.2% more effective with C6 cells than the parent drug after 24, 48, 72 h culture, respectively. The in vivo pharmacokinetics and biodistribution were investigated after an i.v. administration at 5 mg DOX/kg body weight in rats. Promisingly, 4.5-fold increase in the half-life and 24-fold increase in the area-under-the-curve (AUC) of DOX were achieved for the TPGS-DOX conjugate compared with the free DOX. The drug level in heart, gastric and intestine was significantly reduced, which is an indication of reduced side effects. Our TPGS-DOX conjugate showed great potential to be a prodrug of higher therapeutic effects and fewer side effects than DOX itself.
-
Cai, B.; Spencer, M. J.; Nakamura, G.; Tseng-Ong, L.; Tidball, J. G.
2000-01-01
Previous investigations have shown that cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) contribute to muscle pathology in the dystrophin-null mutant mouse (mdx) model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy through perforin-dependent and perforin-independent mechanisms. We have assessed whether the CTL-mediated pathology includes the promotion of eosinophilia in dystrophic muscle, and thereby provides a secondary mechanism through which CTLs contribute to muscular dystrophy. Quantitative immunohistochemistry confirmed that eosinophilia is a component of the mdx dystrophy. In addition, electron microscopic observations show that eosinophils traverse the basement membrane of mdx muscle fibers and display sites of close apposition of eosinophil and muscle membranes. The close membrane apposition is characterized by impingement of eosinophilic rods of major basic protein into the muscle cell membrane. Transfer of mdx splenocytes and mdx muscle extracts to irradiated C57 mice by intraperitoneal injection resulted in muscle eosinophilia in the recipient mice. Double-mutant mice lacking dystrophin and perforin showed less eosinophilia than was displayed by mdx mice that expressed perforin. Finally, administration of prednisolone, which has been shown previously to reduce the concentration of CTLs in dystrophic muscle, produced a significant reduction in eosinophilia. These findings indicate that eosinophilia is a component of the mdx pathology that is promoted by perforin-dependent cytotoxicity of effector T cells. However, some eosinophilia of mdx muscle is independent of perforin-mediated processes.
-
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Ndamase, AS
2018-02-01
Full Text Available Bisphosphonates have been found to be effective when combined with anticancer drugs for chemotherapy. In this paper, pamidronate and platinum complexes were conjugated to linear poly(amidoamine)s (PAMAM) to improve the drug efficacy. The conjugates...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Azadeh Hashem Nia
2015-04-01
Conclusion: Conjugation of PEI with carbon nanotube les to new vectors with lowered cytotoxicity and higher transfection efficiency. The highest transfection efficiency was obtained with the lowest molecular weight PEI.
-
Bryden, Francesca; Martin, Camille; Letast, Stéphanie; Lles, Eva; Viéitez-Villemin, Inmaculada; Rousseau, Anaïs; Colas, Cyril; Brachet-Botineau, Marie; Allard-Vannier, Emilie; Larbouret, Christel; Viaud-Massuard, Marie-Claude; Joubert, Nicolas
2018-03-14
Herein we describe the synthesis and evaluation of four novel HER2-targeting, cathepsin B-sensitive antibody-drug conjugates bearing a monomethylauristatin E (MMAE) cytotoxic payload, constructed via the conjugation of cleavable linkers to trastuzumab using a site-specific bioconjugation methodology. These linkers vary by both cleavable trigger motif and hydrophilicity, containing one of two cathepsin B sensitive dipeptides (Val-Cit and Val-Ala), and engendered with either hydrophilic or hydrophobic character via application of a PEG 12 spacer. Through evaluation of physical properties, in vitro cytotoxicity, and receptor affinity of the resulting antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), we have demonstrated that while both dipeptide triggers are effective, the increased hydrophobicity of the Val-Ala pair limits its utility within this type of linker. In addition, while PEGylation augments linker hydrophilicity, this change does not translate to more favourable ADC hydrophilicity or potency. While all described structures demonstrated excellent and similar in vitro cytotoxicity, the ADC with the ValCitPABMMAE linker shows the most promising combination of in vitro potency, structural homogeneity, and hydrophilicity, warranting further evaluation into its therapeutic potential.
-
Electron beam irradiation crosslinked hydrogels based on tyramine conjugated gum tragacanth.
Tavakol, Moslem; Dehshiri, Saeedeh; Vasheghani-Farahani, Ebrahim
2016-11-05
In the present study, electron beam irradiation was applied to prepare a chemically crosslinked hydrogel based on tyramine conjugated gum tragacanth. Then, the gel content, swelling behavior and cytotoxicity of the hydrogels were evaluated. The gel content of the hydrogels was in the range of 75-85%. Equilibrium swelling degree of the hydrogels decreased from 51 to 14 with increasing polymer concentration and irradiation dose. Moisture retention capability of the hydrogels after 5h incubation at 37°C was in the range of 45-52 that is comparable with of commercial hydrogels. The cytotoxicity analysis showed the good biocompatibility of hydrogels. These results indicated that electron beam irradiation is a promising method to prepare chemically crosslinked tyramine conjugated gum tragacanth hydrogels for biomedical applications. Also, the versatility of electron beam irradiation for crosslinking of a variety of polymers possessing tyramine groups was demonstrated. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
PSMA-targeted bispecific Fab conjugates that engage T cells.
Patterson, James T; Isaacson, Jason; Kerwin, Lisa; Atassi, Ghazi; Duggal, Rohit; Bresson, Damien; Zhu, Tong; Zhou, Heyue; Fu, Yanwen; Kaufmann, Gunnar F
2017-12-15
Bioconjugate formats provide alternative strategies for antigen targeting with bispecific antibodies. Here, PSMA-targeted Fab conjugates were generated using different bispecific formats. Interchain disulfide bridging of an αCD3 Fab enabled installation of either the PSMA-targeting small molecule DUPA (SynFab) or the attachment of an αPSMA Fab (BisFab) by covalent linkage. Optimization of the reducing conditions was critical for selective interchain disulfide reduction and good bioconjugate yield. Activity of αPSMA/CD3 Fab conjugates was tested by in vitro cytotoxicity assays using prostate cancer cell lines. Both bispecific formats demonstrated excellent potency and antigen selectivity. Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Third Generation PAMAM Dendrimer Conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mohammad Najlah
2017-10-01
Full Text Available The present study compares the use of high generation G3 and low generation G0 Polyamidoamine (PAMAM dendrimers as drug carriers of naproxen (NAP, a poorly water soluble drug. Naproxen was conjugated to G3 in different ratios and to G0 in a 1:1 ratio via a diethylene glycol linker. A lauroyl chain (L, a lipophilic permeability enhancer, was attached to G3 and G0 prodrugs. The G3 and G0 conjugates were more hydrophilic than naproxen as evaluated by the measurement of partitioning between 1-octanol and a phosphate buffer at pH 7.4 and pH 1.2. The unmodified surface PAMAM-NAP conjugates showed significant solubility enhancements of NAP at pH 1.2; however, with the number of NAP conjugated to G3, this was limited to 10 molecules. The lactate dehydrogenase (LDH assay indicated that the G3 dendrimer conjugates had a concentration dependent toxicity towards Caco-2 cells. Attaching naproxen to the surface of the dendrimer increased the IC50 of the resulting prodrugs towards Caco-2 cells. The lauroyl G3 conjugates showed the highest toxicity amongst the PAMAM dendrimer conjugates investigated and were significantly more toxic than the lauroyl-G0-naproxen conjugates. The permeability of naproxen across monolayers of Caco-2 cells was significantly increased by its conjugation to either G3 or G0 PAMAM dendrimers. Lauroyl-G0 conjugates displayed considerably lower cytotoxicity than G3 conjugates and may be preferable for use as a drug carrier for low soluble drugs such as naproxen.
-
Simoni, Elena; Bergamini, Christian; Fato, Romana; Tarozzi, Andrea; Bains, Sandip; Motterlini, Roberto; Cavalli, Andrea; Bolognesi, Maria Laura; Minarini, Anna; Hrelia, Patrizia; Lenaz, Giorgio; Rosini, Michela; Melchiorre, Carlo
2010-10-14
Mitochondria-directed antioxidants 2-5 were designed by conjugating curcumin congeners with different polyamine motifs as vehicle tools. The conjugates emerged as efficient antioxidants in mitochondria and fibroblasts and also exerted a protecting role through heme oxygenase-1 activation. Notably, the insertion of a polyamine function into the curcumin-like moiety allowed an efficient intracellular uptake and mitochondria targeting. It also resulted in a significant decrease in the cytotoxicity effects. 2-5 are therefore promising molecules for neuroprotectant lead discovery.
-
Multifunctional adhesive polymers: Preactivated thiolated chitosan-EDTA conjugates.
Netsomboon, Kesinee; Suchaoin, Wongsakorn; Laffleur, Flavia; Prüfert, Felix; Bernkop-Schnürch, Andreas
2017-02-01
The aim of this study was to synthesis preactivated thiolated chitosan-EDTA (Ch-EDTA-cys-2MNA) conjugates exhibiting in particular high mucoadhesive, cohesive and chelating properties. Thiol groups were coupled with chitosan by carbodiimide reaction and further preactivated by attachment with 2-mercaptonicotinic acid (2MNA) via disulfide bond formation. Determinations of primary amino and sulfhydryl groups were performed by TNBS and Ellman's tests, respectively. Cytotoxicity was screened by resazurin assay in Caco-2 cells. Mucoadhesive properties and bivalent cation binding capacity with Mg 2+ and Ca 2+ in comparison to chitosan-EDTA (Ch-EDTA) and thiolated Ch-EDTA (Ch-EDTA-cys) were evaluated. Determination of 2MNA and total sulfhydryl groups indicated that 80% of thiol groups were preactivated. The results from cytotoxicity studies demonstrated that Ch-EDTA-cys and Ch-EDTA-cys-2MNA were not toxic to the cells at the polymer test concentration of 0.25% (w/v) while cell viability decreased by increasing the concentration of Ch-EDTA. Although EDTA molecule was modified by thiolation and preactivation, approximately 50% of chelating properties of the conjugates were maintained compared to Ch-EDTA. Ch-EDTA-cys-2MNA adhered on freshly excised porcine intestinal mucosa up to 6h while Ch-EDTA adhered for just 1h. According to the combination of mucoadhesive and chelating properties of the conjugates synthesized in this study, Ch-EDTA-cys-2MNA might be useful for various mucosal drug delivery systems. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Migita, Satoshi; Wada, Ken-Ichi; Taniguchi, Akiyoshi
2010-10-15
Live cell-based sensors potentially provide functional information about the cytotoxic effect of reagents on various signaling cascades. Cells transfected with a reporter vector derived from a cytotoxic response promoter can be used as intelligent cytotoxicity sensors (i.e., sensor cells). We have combined sensor cells and a microfluidic cell culture system that can achieve several laminar flows, resulting in a reliable high-throughput cytotoxicity detection system. These sensor cells can also be applied to single cell arrays. However, it is difficult to detect a cellular response in a single cell array, due to the heterogeneous response of sensor cells. The objective of this study was cell homogenization with cell cycle synchronization to enhance the response of cell-based biosensors. Our previously established stable sensor cells were brought into cell cycle synchronization under serum-starved conditions and we then investigated the cadmium chloride-induced cytotoxic response at the single cell level. The GFP positive rate of synchronized cells was approximately twice as high as that of the control cells, suggesting that cell homogenization is an important step when using cell-based biosensors with microdevices, such as a single cell array. Copyright 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
-
Recent advances in the construction of antibody-drug conjugates
Chudasama, Vijay; Maruani, Antoine; Caddick, Stephen
2016-02-01
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) comprise antibodies covalently attached to highly potent drugs using a variety of conjugation technologies. As therapeutics, they combine the exquisite specificity of antibodies, enabling discrimination between healthy and diseased tissue, with the cell-killing ability of cytotoxic drugs. This powerful and exciting class of targeted therapy has shown considerable promise in the treatment of various cancers with two US Food and Drug Administration approved ADCs currently on the market (Adcetris and Kadcyla) and approximately 40 currently undergoing clinical evaluation. However, most of these ADCs exist as heterogeneous mixtures, which can result in a narrow therapeutic window and have major pharmacokinetic implications. In order for ADCs to deliver their full potential, sophisticated site-specific conjugation technologies to connect the drug to the antibody are vital. This Perspective discusses the strategies currently used for the site-specific construction of ADCs and appraises their merits and disadvantages.
-
Shahnaz, G; Perera, G; Sakloetsakun, D; Rahmat, D; Bernkop-Schnürch, A
2010-05-21
This study was aimed at improving the mucoadhesive properties of carboxymethyl dextran by the covalent attachment of cysteine. Mediated by a carbodiimide, l-cysteine was covalently attached to the polymer. The resulting CMD-cysteine conjugate (CMD-(273) conjugate) displayed 273+/-20 micromol thiol groups per gram of polymer (mean+/-S.D.; n=3). Within 2h the viscosity of an aqueous mucus/CMD-(273) conjugate mixture pH 7.4 increased at 37 degrees C by more than 85% compared to a mucus/carboxymethyl dextran mixture indicating enlarged interactions between the mucus and the thiolated polymer. Due to the immobilization of cysteine, the swelling velocity of the polymer was significantly accelerated (ppolymer disintegrated within 15 min, whereas tablets of the CMD-(273) conjugate remained stable for 160 min (means+/-S.D.; n=3). Results from LDH and MTT assays on Caco-2 cells revealed 4.96+/-0.98% cytotoxicity and 94.1+/-0.9% cell viability for the CMD-(273) conjugate, respectively. Controlled release of model compound from CMD-(273) conjugate tablets was observed over 6h. These findings suggest that CMD-(273) conjugate is a promising novel polymer for drug delivery systems providing improved mucoadhesive and cohesive properties, greater stability and biocompatibility. Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Uram, Łukasz; Szuster, Magdalena; Filipowicz, Aleksandra; Zaręba, Magdalena; Wałajtys-Rode, Elżbieta; Wołowiec, Stanisław
2017-01-15
In search for soluble derivatives of PAMAM dendrimers as potential carriers for hydrophobic drugs, the conjugates of PAMAM G3 with biotin, further converted into glycodendrimer with d-glucoheptono-1,4-lactone, were prepared. Polyamidoamine dendrimer (PAMAM) of third generation, G3 was functionalized with four biotin equivalents covalently attached to terminal amine nitrogens via amide bond G3 4B . The remaining 28 amine groups were blocked by glucoheptoamide substituents (gh) to give G3 4B28gh or with one fluorescein equivalent (attached by reaction of G3 4B with fluorescein isothiocyanate, FITC) via thiourea bond as FITC followed by exhaustive glucoheptoamidation to get G3 4B27gh1F . As a control the G3 substituted totally with 32 glucoheptoamide residues, G3 gh and its fluorescein labeled analogue G3 31gh1F were synthesized. The glucoheptoamidation of PAMAM G0 dendrimer with glucoheptono-1,4-lactone was performed in order to fully characterize the 1 H NMR spectra of glucoheptoamidated PAMAM dendrimers and to control the derivatization of G3 with glucoheptono-1,4-lactone. Another two derivatives of G3, namely G3 4B28gh1F' and G3 32ghF' , with ester bonded fluorescein were also obtained. Biological properties of obtained dendrimer conjugates were estimated in vitro with human cell lines: normal fibroblast (BJ) and two cancer glioblastoma (U-118 MG) and squamous carcinoma (SCC-15), including cytotoxicity by reduction of XTT and neutral red (NR) assays. Cellular uptake of dendrimer conjugates was evaluated with confocal microscopy. Obtained results confirmed, that biotinylated bioconjugates have always lower cytotoxicity and 3-4 times higher cellular uptake than non-biotinylated dendrimer conjugates in all cell lines. Comparison of various cell lines revealed different dose-dependent cell responses and the lower cytotoxicity of examined dendrimer conjugates for normal fibroblasts and squamous carcinoma, as compared with much higher cytotoxic effects seen in
-
Clement, Sandhya; Deng, Wei; Camilleri, Elizabeth; Wilson, Brian C.; Goldys, Ewa M.
2016-01-01
Singlet oxygen is a primary cytotoxic agent in photodynamic therapy. We show that CeF3 nanoparticles, pure as well as conjugated through electrostatic interaction with the photosensitizer verteporfin, are able to generate singlet oxygen as a result of UV light and 8?keV X-ray irradiation. The X-ray stimulated singlet oxygen quantum yield was determined to be 0.79???0.05 for the conjugate with 31 verteporfin molecules per CeF3 nanoparticle, the highest conjugation level used. From this result ...
-
Antibody drug conjugates - Trojan horses in the war on cancer.
Iyer, U; Kadambi, V J
2011-01-01
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) consist of an antibody attached to a cytotoxic drug by means of a linker. ADCs provide a way to couple the specificity of a monoclonal antibody (mAb) to the cytotoxicity of a small-molecule drug and, therefore, are promising new therapies for cancer. ADCs are prodrugs that are inactive in circulation but exert their cytotoxicity upon binding to the target cancer cell. Earlier unsuccessful attempts to generate ADCs with therapeutic value have emphasized the important role each component plays in determining the efficacy and safety of the final ADC. Scientific advances in engineering antibodies for maximum efficacy as anticancer agents, identification of highly cytotoxic molecules, and generation of linkers with increased stability in circulation have all contributed to the development of the many ADCs that are currently in clinical trials. This review discusses parameters that guide the selection of the components of an ADC to increase its therapeutic window, provides a brief look at ADCs currently in clinical trials, and discusses future challenges in this field. Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier Inc.
-
Effect of TiO2 on conjugative transfer of RP4 plasmid
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Qian Di; Zhang Buchang; Yang Dong; Chen Zhaoli; Jin Min; Qiu Zhigang; Li Junwen
2013-01-01
Objective: To explore the effect and law of nano-titanium dioxide on the conjugative transfer of RP4 plasmid. Methods: Mating was conducted between Escherichia coli HB101 (RP4) and E. coli K12Rif in saline without stirring under certain conditions and the donor per recipient ratio was 1:1 constantly. The selective LB agar medium plates containing appropriate antibiotics were used to count the number of transconjugants and the conjugative transfer frequency. Results: Nano-titanium dioxide could promote the conjugative transfer of RP4. The nano-titanium dioxide concentration, bacterial concentration, mating temperature and mating time could affect the conjugative transfer of RP4. Conclusion: Nano-titanium dioxide can promote plasmid conjugal transfer in the liquid phase under certain conditions, which may pose a potential hazard to environmental and human health. (authors)
-
Lucarini, Simone; Fagioli, Laura; Campana, Raffaella; Cole, Hannah; Duranti, Andrea; Baffone, Wally; Vllasaliu, Driton; Casettari, Luca
2016-01-01
Sugar based surfactants conjugated with fatty acid chains are an emerging broad group of highly biocompatible and biodegradable compounds with established and potential future applications in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries. In this work, we investigated absorption enhancing and antimicrobial properties of disaccharide lactose, mono-esterified with unsaturated fatty acids through an enzymatic synthetic approach. After chemical and cytotoxicity characterizations, their permeab...
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Etrych, Tomáš; Tsukigawa, K.; Nakamura, H.; Chytil, Petr; Fang, J.; Ulbrich, Karel; Otagiri, M.; Maeda, H.
2017-01-01
Roč. 106, 30 August (2017), s. 10-19 ISSN 0928-0987 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GA15-02986S; GA MŠk(CZ) LQ1604; GA MŠk(CZ) ED1.1.00/02.0109 Grant - others:AV ČR,Japan Society for the Promotion of Science(CZ) JSPS-16-05 Program:Bilaterální spolupráce Institutional support: RVO:61389013 Keywords : pirarubicin * PHPMA conjugate * tandem-diblock PHPMA conjugate Subject RIV: FR - Pharmacology ; Medidal Chemistry OBOR OECD: Pharmacology and pharmacy Impact factor: 3.756, year: 2016
-
Baradat, Maryse; Jouanin, Isabelle; Dalleau, Sabine; Taché, Sylviane; Gieules, Mathilde; Debrauwer, Laurent; Canlet, Cécile; Huc, Laurence; Dupuy, Jacques; Pierre, Fabrice H F; Guéraud, Françoise
2011-11-21
Animal and epidemiological studies suggest that dietary heme iron would promote colorectal cancer. Oxidative properties of heme could lead to the formation of cytotoxic and genotoxic secondary lipid oxidation products, such as 4-hydroxy-2(E)-nonenal (HNE). This compound is more cytotoxic to mouse wild-type colon cells than to isogenic cells with a mutation on the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. The latter thus have a selective advantage, possibly leading to cancer promotion. This mutation is an early and frequent event in human colorectal cancer. To explain this difference, the HNE biotransformation capacities of the two cell types have been studied using radiolabeled and stable isotope-labeled HNE. Apc-mutated cells showed better biotransformation capacities than nonmutated cells did. Thiol compound conjugation capacities were higher for mutated cells, with an important advantage for the extracellular conjugation to cysteine. Both cells types were able to reduce HNE to 4-hydroxynonanal, a biotransformation pathway that has not been reported for other intestinal cells. Mutated cells showed higher capacities to oxidize 4-hydroxynonanal into 4-hydroxynonanoic acid. The mRNA expression of different enzymes involved in HNE metabolism such as aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1, 2 and 3A1, glutathione transferase A4-4, or cystine transporter xCT was upregulated in mutated cells compared with wild-type cells. In conclusion, this study suggests that Apc-mutated cells are more efficient than wild-type cells in metabolizing HNE into thiol conjugates and 4-hydroxynonanoic acid due to the higher expression of key biotransformation enzymes. These differential biotransformation capacities would explain the differences of susceptibility between normal and Apc-mutated cells regarding secondary lipid oxidation products.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of the antioxidative potential of minoxidil-polyamine conjugates.
Hadjipavlou-Litina, Dimitra; Magoulas, George E; Bariamis, Stavros E; Tsimali, Zinovia; Avgoustakis, Konstantinos; Kontogiorgis, Christos A; Athanassopoulos, Constantinos M; Papaioannou, Dionissios
2013-07-01
A series of conjugates (MNX-CO-PA) of minoxidil (MNX) with the polyamines (PAs) putrescine (PUT), spermidine (SPD) and spermine (SPM) as well as dopamine were produced through activation of MNX with N,N'-carbonyldiimidazole, followed by reaction with dopamine or selectively protected PAs and acid-mediated deprotection. These conjugates together with conjugates of the general type MNX-PA or PA-MNX-PA, readily produced using literature protocols, were tested as antioxidants. The most potent inhibitors of lipid peroxidation were the conjugates MNX-SPM (2, 94%), SPM-MNX-SPM (4, 94%) and MNX-N(4)-SPD (7, 91%) and MNX (91%). The most powerful lipoxygenase (LOX) inhibitors were MNX (IC50 = 20 μM) and the conjugates MNX-N(8)-SPD (9, IC50 = 22.1 μM), MNX-CO-dopamine (11, IC50 = 28 μM) and MNX-N(1)-SPD (8, IC50 = 30 μM). The most interesting conjugates 2, MNX-CO-PUT (5), 8 and 11 as well as MNX were generally found to exhibit weaker (22-36.5%) or no (conjugate 8) anti-inflammatory activity than indomethacin (47%) with the exception of MNX which showed almost equal potency (49%) to indomethacin. The cytocompatibility of conjugates and MNX at the highest concentration of 100 μM showed a survival percentage of 87-107%, with the exception of conjugates with SPM (compound 2) and MNX-CO-SPM (6), which showed considerable cytotoxicity (survival percentage 8-14%). Molecular docking studies were carried on conjugate 9 and the parent compound MNX and were found to be in accordance with our experimental biological results. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
-
Dirven, H.A.A.M.; Ommen, B. van; Bladeren, P.J. van
1994-01-01
Alkylating agents can be detoxified by conjugation with glutathione (GSH). One of the physiological significances of this lies in the observation that cancer cells resistant to the cytotoxic effects of alkylating agents have higher levels of GSH and high glutathione S-transferase (GST) activity.
-
Marcoux, Julien; Champion, Thierry; Colas, Olivier; Wagner-Rousset, Elsa; Corvaïa, Nathalie; Van Dorsselaer, Alain; Beck, Alain; Cianférani, Sarah
2015-08-01
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are biochemotherapeutics consisting of a cytotoxic chemical drug linked covalently to a monoclonal antibody. Two main classes of ADCs, namely cysteine and lysine conjugates, are currently available on the market or involved in clinical trials. The complex structure and heterogeneity of ADCs makes their biophysical characterization challenging. For cysteine conjugates, hydrophobic interaction chromatography is the gold standard technique for studying drug distribution, the naked antibody content, and the average drug to antibody ratio (DAR). For lysine ADC conjugates on the other hand, which are not amenable to hydrophobic interaction chromatography because of their higher heterogeneity, denaturing mass spectrometry (MS) and UV/Vis spectroscopy are the most powerful approaches. We report here the use of native MS and ion mobility (IM-MS) for the characterization of trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1, Kadcyla(®)). This lysine conjugate is currently being considered for the treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer, and combines the anti-HER2 antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin(®)), with the cytotoxic microtubule-inhibiting maytansine derivative, DM1. We show that native MS combined with high-resolution measurements and/or charge reduction is beneficial in terms of the accurate values it provides of the average DAR and the drug load profiles. The use of spectral deconvolution is discussed in detail. We report furthermore the use of native IM-MS to directly determine DAR distribution profiles and average DAR values, as well as a molecular modeling investigation of positional isomers in T-DM1. © 2015 The Protein Society.
-
Chemical profiling and cytotoxicity assay of bufadienolides in toad venom and toad skin.
Meng, Qiong; Yau, Lee-Fong; Lu, Jing-Guang; Wu, Zhen-Zhen; Zhang, Bao-Xian; Wang, Jing-Rong; Jiang, Zhi-Hong
2016-07-01
Toad venom and toad skin have been widely used for treating various cancers in China. Bufadienolides are regarded as the main anticancer components of toad venom, but the difference on composition and anticancer activities of bufadienolides between toad venom and toad skin remains unclear. Fractions enriched with free and conjugated bufadienolides were prepared from toad venom and toad skin. Bufadienolides in each fraction were comprehensively profiled by using a versatile UHPLC-TOF-MS method. Relative contents of major bufadienolides were determined by using three bufogenins and one bufotoxin as marker compounds with validated UHPLC-TOF-MS method. Furthermore, cytotoxicity of the fractions was examined by MTT assay. Two fractions, i.e., bufogenin and bufotoxin fractions (TV-F and TV-C) were isolated from toad venom, and one bufotoxin fraction (TS-C) was isolated from toad skin. Totally 56 bufadienolides in these three fractions were identified, and 29 were quantified or semi-quantified. Bufotoxins were identified in both toad venom and toad skin, whereas bufogenins exist only in toad venom. Bufalin-3-conjugated bufotoxins are major components in toad venom, whereas cinobufotalin and cinobufagin-3-conjugated bufotoxins are main bufotoxins in toad skin. MTT assay revealed potent cytotoxicity of all the fractions in an order of TV-F>TV-C>TS-C. Our study represents the most comprehensive investigation on the chemical profiles of toad venom and toad skin from both qualitative and quantitative aspects. Eight bufotoxins were identified in toad skin responsible for the cytotoxicity for the first time. Our research provides valuable chemical evidence for the appropriate processing method, quality control and rational exploration of toad skin and toad venom for the development of anticancer medicines. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Murgia, Sergio; Falchi, Angela Maria; Meli, Valeria; Schillén, Karin; Lippolis, Vito; Monduzzi, Maura; Rosa, Antonella; Schmidt, Judith; Talmon, Yeshayahu; Bizzarri, Ranieri; Caltagirone, Claudia
2015-05-01
We present here an innovative, fluorescent, monoolein-based cubosome dispersion. Rather than embedded within the monoolein palisade, the fluorescent imaging agent, namely dansyl, was conjugated to the terminal ethylene oxide moieties of the block copolymer Pluronic F108. We discuss the physicochemical and photophysical properties of this fluorescent Pluronic and of a cubosome formulation stabilized by a mixture of dansyl-conjugated and non-conjugated Pluronic, also including an anticancer drug (quercetin). Furthermore, we performed biocompatibility tests against HeLa cells to assess internalization and cytotoxicity features of this nanoparticles aqueous dispersion. Cryo-TEM, SAXS, and DLS analysis, proved the bicontinuous cubic inner nanostructure and the morphology of this fluorescent cubosome dispersion, while photophysical measurements and biocompatibility results basically validate their potential use for theranostic nanomedicine applications. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Lin, Cheng-Yi; Peng, Hsiu-Hui; Chen, Mei-Hsiu; Sun, Jui-Sheng; Chang, Chih-Ju; Liu, Tse-Ying; Chen, Ming-Hong
2016-05-01
The formation of fibrous tissue is part of the natural healing response following a laminectomy. Severe scar tissue adhesion, known as epidural fibrosis, is a common cause of failed back surgery syndrome. In this study, by combining the advantages of drug treatment with a physical barrier, an ibuprofen-conjugated crosslinkable polygalacturonic acid and hyaluronic acid hydrogel was developed for epidural fibrosis prevention. Conjugation was confirmed and measured by 1D(1)H NMR spectroscopy.In vitroanalysis showed that the ibuprofen-conjugated polygalacturonic acid-hyaluronic acid hydrogel showed low cytotoxicity. In addition, the conjugated ibuprofen decreased prostaglandin E2production of the lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells. Histological data inin vivostudies indicated that the scar tissue adhesion of laminectomized male adult rats was reduced by the application of our ibuprofen-conjugated polygalacturonic acid-hyaluronic acid hydrogel. Its use also reduced the population of giant cells and collagen deposition of scar tissue without inducing extensive cell recruitment. The results of this study therefore suggest that the local delivery of ibuprofenviaa polygalacturonic acid-hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel reduces the possibility of epidural fibrosis. © The Author(s) 2016.
-
Fang, Jun; Tsukigawa, Kenji; Liao, Long; Yin, Hongzhuan; Eguchi, Kanami; Maeda, Hiroshi
2016-01-01
Previous studies indicated the potential of zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP) as an antitumor agent targeting to the tumor survival factor heme oxygenase-1, and/or for photodynamic therapy (PDT). In this study, to achieve tumor-targeted delivery, styrene-maleic acid-copolymer conjugated ZnPP (SMA-ZnPP) was synthesized via amide bond, which showed good water solubility, having ZnPP loading of 15%. More importantly, it forms micelles in aqueous solution with a mean particle size of 111.6 nm, whereas it has an apparent Mw of 65 kDa. This micelle formation was not detracted by serum albumin, suggesting it is stable in circulation. Further SMA-ZnPP conjugate will behave as an albumin complex in blood with much larger size (235 kDa) by virtue of the albumin binding property of SMA. Consequently, SMA-ZnPP conjugate exhibited prolonged circulating retention and preferential tumor accumulation by taking advantage of enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. Clear tumor imaging was thus achieved by detecting the fluorescence of ZnPP. In addition, the cytotoxicity and PDT effect of SMA-ZnPP conjugate was confirmed in human cervical cancer HeLa cells. Light irradiation remarkably increased the cytotoxicity (IC50, from 33 to 5 μM). These findings may provide new options and knowledge for developing ZnPP based anticancer theranostic drugs.
-
Hyaluronan-conjugated liposomes encapsulating gemcitabine for breast cancer stem cells
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Han NK
2016-04-01
Full Text Available Na-Kyung Han,1,* Dae Hwan Shin,1,* Jung Seok Kim,1 Kwon Yeon Weon,2 Chang-Young Jang,1 Jin-Seok Kim1 1Research Center for Cell Fate Control (RCCFC and College of Pharmacy, Sookmyung Women’s University, Seoul, 2College of Pharmacy, Catholic University of Daegu, Gyeongbuk, Korea *These authors contributed equally to this work Abstract: Investigation of potential therapeutics for targeting breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs is important because these cells are regarded as culprit of breast cancer relapse. Accomplishing this kind of strategy requires a specific drug-delivery system using the distinct features of liposomes. Studies on targeted liposomal delivery systems have indicated the conjugation of hyaluronan (HA, a primary ligand for CD44 surface markers, as an appropriate method for targeting BCSCs. For this study, enriched BCSCs were obtained by culturing MCF-7 breast cancer cells in nonadherent conditions. The enriched BCSCs were challenged with HA-conjugated liposomes encapsulating gemcitabine (2, 2-difluoro-2-deoxycytidine, GEM. In vitro study showed that the HA-conjugated liposomes significantly enhanced the cytotoxicity, anti-migration, and anti-colony formation abilities of GEM through targeting of CD44 expressed on BCSCs. In pharmacokinetic study, area under the drug concentration vs time curve (AUC of the immunoliposomal GEM was 3.5 times higher than that of free GEM, indicating that the HA-conjugated liposomes enhanced the stability of GEM in the bloodstream and therefore prolonged its half-life time. The antitumor effect of the immunoliposomal GEM was 3.3 times higher than that of free GEM in a xenograft mouse model, probably reflecting the unique targeting of the CD44 receptor by HA and the increased cytotoxicity and stability through the liposomal formulation. Furthermore, marginal change in body weight demonstrated that the use of liposomes considerably reduced the systemic toxicity of GEM on normal healthy cells. Taken together
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Osnir S. Viana
2015-05-01
Full Text Available The application of fluorescent II-VI semiconductor quantum dots (QDs as active photosensitizers in photodymanic inactivation (PDI is still being evaluated. In the present study, we prepared 3 nm size CdTe QDs coated with mercaptosuccinic acid and conjugated them electrostatically with Zn(II meso-tetrakis (N-ethyl-2-pyridinium-2-yl porphyrin (ZnTE-2-PyP or ZnP, thus producing QDs-ZnP conjugates. We evaluated the capability of the systems, bare QDs and conjugates, to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS and applied them in photodynamic inactivation in cultures of Candida albicans by irradiating the QDs and testing the hypothesis of a possible combined contribution of the PDI action. Tests of in vitro cytotoxicity and phototoxicity in fibroblasts were also performed in the presence and absence of light irradiation. The overall results showed an efficient ROS production for all tested systems and a low cytotoxicity (cell viability >90% in the absence of radiation. Fibroblasts incubated with the QDs-ZnP and subjected to irradiation showed a higher cytotoxicity (cell viability <90% depending on QD concentration compared to the bare groups. The PDI effects of bare CdTe QD on Candida albicans demonstrated a lower reduction of the cell viability (~1 log10 compared to bare ZnP which showed a high microbicidal activity (~3 log10 when photoactivated. The QD-ZnP conjugates also showed reduced photodynamic activity against C. albicans compared to bare ZnP and we suggest that the conjugation with QDs prevents the transmembrane cellular uptake of the ZnP molecules, reducing their photoactivity.
-
Gold Nanoparticle Conjugation Enhances the Antiacanthamoebic Effects of Chlorhexidine
Aqeel, Yousuf; Siddiqui, Ruqaiyyah; Anwar, Ayaz; Shah, Muhammad Raza
2015-01-01
assays. In contrast, chlorhexidine alone, at a similar concentration, showed limited effects. Notably, neomycin alone or conjugated with nanoparticles did not show amoebicidal or amoebistatic effects. Pretreatment of A. castellanii with gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles reduced amoeba-mediated host cell cytotoxicity from 90% to 40% at 5 μM. In contrast, chlorhexidine alone, at similar concentrations, had no protective effects for the host cells. Similarly, amoebae treated with neomycin alone or neomycin-conjugated nanoparticles showed no protective effects. Overall, these findings suggest that gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles hold promise in the improved treatment of A. castellanii keratitis. PMID:26666949
-
Exploration of a Doxorubicin-Polymer Conjugate in Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticle Drug Delivery
Lough, Emily
Nanoparticle (NP) drug delivery is a major focus in the research community because of its potential to use existing drugs in safer and more effective ways. Chemotherapy encapsulation in NPs shields the drug from the rest of the body while it is within the NP, with less systemic exposure leading to fewer off-target effects of the drug. However, passive loading of drugs into NPs is a suboptimal method, often leading to burst release upon administration. This work explores the impact of incorporating the drug-polymer conjugate doxorubicin-poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid (Dox-PLGA) into a lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticle (LPN). The primary difference in using a drug-polymer conjugate for NP drug delivery is the drug's release kinetics. Dox-PLGA LPNs showed a more sustained and prolonged release profile over 28 days compared to LPNs with passively loaded, unconjugated doxorubicin. This sustained release translates to cytotoxicity; when systemic circulation was simulated using dialysis, Dox-PLGA LPNs retained their cytotoxicity at a higher level than the passively loaded LPNs. The in vivo implication of preserving cytotoxic potency through a slower release profile is that the majority of Dox delivered via Dox-PLGA LPNs will be kept within the LPN until it reaches the tumor. This will result in fewer systemic side effects and more effective treatments given the higher drug concentration at the tumor site. An intriguing clinical application of this drug delivery approach lies in using Dox-PLGA LPNs to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The incorporation of Dox-PLGA is hypothesized to have a protective effect on the BBB as its slow release profile will prevent drug from harming the BBB. Using induced pluripotent stem cells differentiated to human brain microvascular endothelial cells that comprise the BBB, the Dox-PLGA LPNs were shown to be less destructive to the BBB than their passively loaded counterparts. Dox-PLGA LPNs showed superior cytotoxicity against plated tumor
-
Lewinska, Anna; Adamczyk-Grochala, Jagoda; Kwasniewicz, Ewa; Deregowska, Anna; Wnuk, Maciej
2017-06-01
Plant-derived pentacyclic triterpenotids with multiple biological activities are considered as promising candidates for cancer therapy and prevention. However, their mechanisms of action are not fully understood. In the present study, we have analyzed the effects of low dose treatment (5-20 µM) of ursolic acid (UA) and betulinic acid (BA) on breast cancer cells of different receptor status, namely MCF-7 (ER + , PR +/- , HER2 - ), MDA-MB-231 (ER - , PR - , HER2 - ) and SK-BR-3 (ER - , PR - , HER2 + ). UA-mediated response was more potent than BA-mediated response. Triterpenotids (5-10 µM) caused G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, an increase in p21 levels and SA-beta-galactosidase staining that was accompanied by oxidative stress and DNA damage. UA (20 µM) also diminished AKT signaling that affected glycolysis as judged by decreased levels of HK2, PKM2, ATP and lactate. UA-induced energy stress activated AMPK that resulted in cytotoxic autophagy and apoptosis. UA-mediated elevation in nitric oxide levels and ATM activation may also account for AMPK activation-mediated cytotoxic response. Moreover, UA-promoted apoptosis was associated with decreased pERK1/2 signals and the depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential. Taken together, we have shown for the first time that UA at low micromolar range may promote its anticancer action by targeting glycolysis in phenotypically distinct breast cancer cells.
-
The Conjugative Relaxase TrwC Promotes Integration of Foreign DNA in the Human Genome.
González-Prieto, Coral; Gabriel, Richard; Dehio, Christoph; Schmidt, Manfred; Llosa, Matxalen
2017-06-15
Bacterial conjugation is a mechanism of horizontal DNA transfer. The relaxase TrwC of the conjugative plasmid R388 cleaves one strand of the transferred DNA at the oriT gene, covalently attaches to it, and leads the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) into the recipient cell. In addition, TrwC catalyzes site-specific integration of the transferred DNA into its target sequence present in the genome of the recipient bacterium. Here, we report the analysis of the efficiency and specificity of the integrase activity of TrwC in human cells, using the type IV secretion system of the human pathogen Bartonella henselae to introduce relaxase-DNA complexes. Compared to Mob relaxase from plasmid pBGR1, we found that TrwC mediated a 10-fold increase in the rate of plasmid DNA transfer to human cells and a 100-fold increase in the rate of chromosomal integration of the transferred DNA. We used linear amplification-mediated PCR and plasmid rescue to characterize the integration pattern in the human genome. DNA sequence analysis revealed mostly reconstituted oriT sequences, indicating that TrwC is active and recircularizes transferred DNA in human cells. One TrwC-mediated site-specific integration event was detected, proving that TrwC is capable of mediating site-specific integration in the human genome, albeit with very low efficiency compared to the rate of random integration. Our results suggest that TrwC may stabilize the plasmid DNA molecules in the nucleus of the human cell, probably by recircularization of the transferred DNA strand. This stabilization would increase the opportunities for integration of the DNA by the host machinery. IMPORTANCE Different biotechnological applications, including gene therapy strategies, require permanent modification of target cells. Long-term expression is achieved either by extrachromosomal persistence or by integration of the introduced DNA. Here, we studied the utility of conjugative relaxase TrwC, a bacterial protein with site
-
Gaowa, Arong; Horibe, Tomohisa; Kohno, Masayuki; Tabata, Yasuhiko; Harada, Hiroshi; Hiraoka, Masahiro; Kawakami, Koji
2015-05-01
To improve the anti-tumor activity of EGFR2R-lytic hybrid peptide, we prepared peptide-modified dextran conjugates with the disulfide bonds between thiolated carboxymethyl dextran (CMD-Cys) and cysteine-conjugated peptide (EGFR2R-lytic-Cys). In vitro release studies showed that the peptide was released from the CMD-s-s-peptide conjugate in a concentration-dependent manner in the presence of glutathione (GSH, 2μM-2mM). The CMD-s-s-peptide conjugate exhibited a similar cytotoxic activity with free peptide alone against human pancreatic cancer BxPC-3 cells in vitro. Furthermore, it was shown that the CMD-s-s-peptide conjugates were highly accumulated in tumor tissue in a mouse xenograft model using BxPC-3 cells, and the anti-tumor activity of the conjugate was more effective than that of the free peptide. In addition, the plasma concentrations of peptide were moderately increased and the elimination half-life of the peptide was prolonged after intravenous injection of CMD-s-s-peptide conjugates. These results demonstrated that the conjugate based on thiolated CMD polymer would be potentially useful carriers for the sustained release of the hybrid peptide in vivo. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Wang, Yuyuan; Wang, Yidan; Chen, Guojun; Li, Yitong; Xu, Wei; Gong, Shaoqin
2017-09-13
A quantum-dot (QD)-based micelle conjugated with an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) nanobody (Nb) and loaded with an anticancer drug, aminoflavone (AF), has been engineered for EGFR-overexpressing cancer theranostics. The near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence of the indium phosphate core/zinc sulfide shell QDs (InP/ZnS QDs) allowed for in vivo nanoparticle biodistribution studies. The anti-EGFR nanobody 7D12 conjugation improved the cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of the QD-based micelles in EGFR-overexpressing MDA-MB-468 triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. In comparison with the AF-encapsulated nontargeted (i.e., without Nb conjugation) micelles, the AF-encapsulated Nb-conjugated (i.e., targeted) micelles accumulated in tumors at higher concentrations, leading to more effective tumor regression in an orthotopic triple-negative breast cancer xenograft mouse model. Furthermore, there was no systemic toxicity observed with the treatments. Thus, this QD-based Nb-conjugated micelle may serve as an effective theranostic nanoplatform for EGFR-overexpressing cancers such as TNBCs.
-
Avaritt, Brittany R; Swaan, Peter W
2015-06-01
Internalization and intracellular trafficking of dendrimer-drug conjugates play an important role in achieving successful drug delivery. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the endocytosis mechanisms and subcellular localization of poly-l-lysine (PLL) dendrimers in Caco-2 cells. We also investigated the impact of fluorophore conjugation on cytotoxicity, uptake, and transepithelial transport. Oregon green 514 (OG) was conjugated to PLL G3 at either the dendrimer periphery or the core. Chemical inhibitors of clathrin-, caveolin-, cholesterol-, and dynamin-mediated endocytosis pathways and macropinocytosis were employed to establish internalization mechanisms, while colocalization with subcellular markers was used to determine dendrimer trafficking. Cell viability, internalization, and uptake were all influenced by the site of fluorophore conjugation. Uptake was found to be highly dependent on cholesterol- and dynamin-mediated endocytosis as well as macropinocytosis. Dendrimers were trafficked to endosomes and lysosomes, and subcellular localization was impacted by the fluorophore conjugation site. The results of this study indicate that PLL dendrimers exploit multiple pathways for cellular entry, and internalization and trafficking can be impacted by conjugation. Therefore, design of dendrimer-drug conjugates requires careful consideration to achieve successful drug delivery.
-
Chen, Yizhe; Youn, Pilju; Pysher, Theodore J; Scaife, Courtney L; Furgeson, Darin Y
2014-12-01
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) suffers high tumour recurrence rate after thermal ablation. Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) induced post-ablation is critical for tumour survival and progression. A combination therapy of thermal ablation and polymer conjugated Hsp90 chemotherapy was designed and evaluated for complete tumour eradication of HCC. A thermo-responsive, elastin-like polypeptide (ELP)-based tri-block biopolymer was developed and conjugated with a potent Hsp90 inhibitor, geldanamycin (GA). The anti-cancer efficacy of conjugates was evaluated in HCC cell cultures with and without hyperthermia (43 °C). The conjugates were also administered twice weekly in a murine HCC model as a single treatment or in combination with single electrocautery as the ablation method. ELP-GA conjugates displayed enhanced cytotoxicity in vitro and effective heat shock inhibition under hyperthermia. The conjugates alone significantly slowed the tumour growth without systemic toxicity. Four doses of thermo-responsive ELP-GA conjugates with concomitant simple electrocautery accomplished significant Hsp90 inhibition and sustained tumour suppression. Hsp90 inhibition plays a key role in preventing the recurrence of HCC, and the combination of ablation with targeted therapy holds great potential to improve prognosis and survival of HCC patients.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Catarina Oliveira Silva
Full Text Available The application of functionalized nanocarriers on photothermal therapy for cancer ablation has wide interest. The success of this application depends on the therapeutic efficiency and biocompatibility of the system, but also on the stability and biorecognition of the conjugated protein. This study aims at investigating the hypothesis that EGF functionalized polymer-coated gold nanoparticles promote EGF photostability and EGFR internalization, making these conjugated particles suitable for photothermal therapy. The conjugated gold nanoparticles (100-200 nm showed a plasmon absorption band located within the near-infrared range (650-900 nm, optimal for photothermal therapy applications. The effects of temperature, of polymer-coated gold nanoparticles and of UVB light (295nm on the fluorescence properties of EGF have been investigated with steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy. The fluorescence properties of EGF, including the formation of Trp and Tyr photoproducts, is modulated by temperature and by the intensity of the excitation light. The presence of polymeric-coated gold nanoparticles reduced or even avoided the formation of Trp and Tyr photoproducts when EGF is exposed to UVB light, protecting this way the structure and function of EGF. Cytotoxicity studies of conjugated nanoparticles carried out in normal-like human keratinocytes showed small, concentration dependent decreases in cell viability (0-25%. Moreover, conjugated nanoparticles could activate and induce the internalization of overexpressed Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in human lung carcinoma cells. In conclusion, the gold nanoparticles conjugated with Epidermal Growth Factor and coated with biopolymers developed in this work, show a potential application for near infrared photothermal therapy, which may efficiently destroy solid tumours, reducing the damage of the healthy tissue.
-
Silva, Catarina Oliveira; Petersen, Steffen B.; Reis, Catarina Pinto; Rijo, Patrícia; Molpeceres, Jesús; Fernandes, Ana Sofia; Gonçalves, Odete; Gomes, Andreia C.; Correia, Isabel; Vorum, Henrik; Neves-Petersen, Maria Teresa
2016-01-01
The application of functionalized nanocarriers on photothermal therapy for cancer ablation has wide interest. The success of this application depends on the therapeutic efficiency and biocompatibility of the system, but also on the stability and biorecognition of the conjugated protein. This study aims at investigating the hypothesis that EGF functionalized polymer-coated gold nanoparticles promote EGF photostability and EGFR internalization, making these conjugated particles suitable for photothermal therapy. The conjugated gold nanoparticles (100–200 nm) showed a plasmon absorption band located within the near-infrared range (650–900 nm), optimal for photothermal therapy applications. The effects of temperature, of polymer-coated gold nanoparticles and of UVB light (295nm) on the fluorescence properties of EGF have been investigated with steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy. The fluorescence properties of EGF, including the formation of Trp and Tyr photoproducts, is modulated by temperature and by the intensity of the excitation light. The presence of polymeric-coated gold nanoparticles reduced or even avoided the formation of Trp and Tyr photoproducts when EGF is exposed to UVB light, protecting this way the structure and function of EGF. Cytotoxicity studies of conjugated nanoparticles carried out in normal-like human keratinocytes showed small, concentration dependent decreases in cell viability (0–25%). Moreover, conjugated nanoparticles could activate and induce the internalization of overexpressed Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in human lung carcinoma cells. In conclusion, the gold nanoparticles conjugated with Epidermal Growth Factor and coated with biopolymers developed in this work, show a potential application for near infrared photothermal therapy, which may efficiently destroy solid tumours, reducing the damage of the healthy tissue. PMID:27788212
-
NGR-peptide-drug conjugates with dual targeting properties.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kata Nóra Enyedi
Full Text Available Peptides containing the asparagine-glycine-arginine (NGR motif are recognized by CD13/aminopeptidase N (APN receptor isoforms that are selectively overexpressed in tumor neovasculature. Spontaneous decomposition of NGR peptides can result in isoAsp derivatives, which are recognized by RGD-binding integrins that are essential for tumor metastasis. Peptides binding to CD13 and RGD-binding integrins provide tumor-homing, which can be exploited for dual targeted delivery of anticancer drugs. We synthesized small cyclic NGR peptide-daunomycin conjugates using NGR peptides of varying stability (c[KNGRE]-NH2, Ac-c[CNGRC]-NH2 and the thioether bond containing c[CH2-CO-NGRC]-NH2, c[CH2-CO-KNGRC]-NH2. The cytotoxic effect of the novel cyclic NGR peptide-Dau conjugates were examined in vitro on CD13 positive HT-1080 (human fibrosarcoma and CD13 negative HT-29 (human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines. Our results confirm the influence of structure on the antitumor activity and dual acting properties of the conjugates. Attachment of the drug through an enzyme-labile spacer to the C-terminus of cyclic NGR peptide resulted in higher antitumor activity on both CD13 positive and negative cells as compared to the branching versions.
-
Interconnection between thyroid hormone signalling pathways and parvovirus cytotoxic functions.
Vanacker, J M; Laudet, V; Adelmant, G; Stéhelin, D; Rommelaere, J
1993-01-01
Nonstructural (NS) proteins of autonomous parvoviruses can repress expression driven by heterologous promoters, an activity which thus far has not been separated from their cytotoxic effects. It is shown here that, in transient transfection assays, the NS-1 protein of the parvovirus minute virus of mice (MVMp) activates the promoter of the human c-erbA1 gene, encoding the thyroid hormone (T3) receptor alpha. The endogenous c-erbA1 promoter is also a target for induction upon MVMp infection. Moreover, T3 was found to up-modulate the level of cell sensitivity to parvovirus attack. These data suggest an interconnection between T3 signalling and NS cytotoxic pathways. Images PMID:8230488
-
Lv, Qingzhi; Yang, Jincheng; Zhang, Ruoshi; Yang, Zimeng; Yang, Zhengtao; Wang, Yongjun; Xu, Youjun; He, Zhonggui
2018-05-07
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most prevalent cancer among men in the United States and remains the second-leading cause of cancer mortality in men. Paclitaxel (PTX) is the first line chemotherapy for PCa treatment, but its therapeutic efficacy is greatly restricted by the nonspecific distribution in vivo. Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is overexpressed on the surface of most PCa cells, and its expression level increases with cancer aggressiveness, while being present at low levels in normal cells. The high expression level of PSMA in PCa cells offers an opportunity for target delivery of nonspecific cytotoxic drugs to PCa cells, thus improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing toxicity. PSMA has high affinity for DUPA, a glutamate urea ligand. Herein, a novel DUPA-PTX conjugate is developed using DUPA as the targeting ligand to deliver PTX specifically for treatment of PSMA expressing PCa. The targeting ligand DUPA enhances the transport capability and selectivity of PTX to tumor cells via PSMA mediated endocytosis. Besides, DUPA is conjugated with PTX via a disulfide bond, which facilitates the rapid and differential drug release in tumor cells. The DUPA-PTX conjugate exhibits potent cytotoxicity in PSMA expressing cell lines and induces a complete cessation of tumor growth with no obvious toxicity. Our findings give new insight into the PSMA-targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics and provide an opportunity for the development of novel active targeting drug delivery systems for PCa therapy.
-
Repenko, Tatjana; Kuehne, Alexander J. C.
2015-10-01
Fluorescent biomedical markers of today such as dye-infiltrated colloids, microgels and quantum dots suffer from fast bleaching, lack surface functionality (for targets or pharmaceutical agents) and potentially leach heavy metals in case of quantum dots (e.g. Cd). By contrast, conjugated polymer particles are non-cytotoxic, exhibit reduced bleaching, as the entire particle consists of fluorophore, they are hydrophobic and show high quantum yields. Consequently, conjugated polymer particles represent ideal materials for biological applications and imaging. However currently, conjugated polymer particles for biomedical imaging usually lack near-infrared (NIR) emission and are polydisperse. Fluorescent agents with emission in the NIR spectrum are interesting for biomedical applications due to their low photo-damage towards biological species and the ability of NIR radiation to penetrate deep into biological tissue.. I will present the development and synthesis of new conjugated polymers particles with fluorescence in the NIR spectral region for bio-imaging and clinical diagnosis. The particle synthesis proceeds in a one-step Pd or Ni-catalyzed dispersion polymerization of functional NIR emitters. The resulting monodisperse conjugated polymer particles are obtained as a dispersion in a non-hazardous solvent. Different sizes in the sub-micrometer range with a narrow size distribution can be produced. Furthermore biological recognition motifs can be easily attached to the conjugated polymers via thiol-yne click-chemistry providing specific tumor targeting without quenching of the fluorescence. References [1] Kuehne AJC, Gather MC, Sprakel J., Nature Commun. 2012, 3, 1088. [2] Repenko T, Fokong S, De Laporte L, Go D, Kiessling F, Lammers T, Kuehne AJC.,Chem Commun 2015, accepted.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jeong, Yunseong; Park, Jihye; Jin, Geunwoo; Park, Jongsang
2012-01-01
We successfully conjugated hydrophobic group, dexamethasone onto the surface of PAM-DET to synthesize PAM-DET-DX to form polyplexes with enhanced stability against ionic strength. We evaluated its stability by measuring the size of its polyplexes; the conjugated PAM-DET polyplex showed decreased growth compared to the PAM-DET polyplex in an environment with increased ionic strength, which implies that the conjugated PAM-DET has enhanced stability against increased ionic strength. Furthermore, conjugation of hydrophobic group caused a slight increase in the transfection efficiency without inducing toxicity. Of course, it isn't a neglectable factor that nuclear localization effect of DX can drive the advanced transfection efficiency of PAM-DET-DX polyplex. It means that the hydrophobic moieties which have some other positive properties in transfection are good candidates that can be introduced to non-viral polymeric gene delivery carrier. This strongly indicates that the introduction of hydrophobic moiety on PAM-DET is a good method to enhance polyplex stability against ionic strength without diminishing its advantageous properties, such as high transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Asha Jayakumar
2017-08-01
Full Text Available Intestinal tumorigenesis in the ApcMin/+ model is initiated by aberrant activation of Wnt pathway. Increased IL-4 expression in human colorectal cancer tissue and growth of colon cancer cell lines implied that IL-4–induced Stat6-mediated tumorigenic signaling likely contributes to intestinal tumor progression in ApcMin/+ mice. Stat6 also appears to promote expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs cells. MDSCs promote polyp formation in the ApcMin/+ model. Hence, Stat6 could have a broad role in coordinating both polyp cell proliferation and MDSC expansion. We found that IL-4–induced Stat6-mediated proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells is augmented by platelet-derived growth factor–BB, a tumor-promoting growth factor. To determine whether polyp progression in ApcMin/+ mice is dependent on Stat6 signaling, we disrupted Stat6 in this model. Total polyps in the small intestine were fewer in ApcMin/+ mice lacking Stat6. Furthermore, proliferation of polyp epithelial cells was reduced, indicating that Stat6 in part controlled polyp formation. Stat6 also promoted expansion of MDSCs in the spleen and lamina propria of ApcMin/+ mice, implying regulation of antitumor T-cell response. More CD8 cells and reduced PD-1 expression on CD4 cells correlated with reduced polyps. In addition, a strong CD8-mediated cytotoxic response led to killing of tumor cells in Stat6-deficient ApcMin/+ mice. Therefore, these findings show that Stat6 has an oncogenic role in intestinal tumorigenesis by promoting polyp cell proliferation and immunosuppressive mediators, and preventing an active cytotoxic process.
-
Jayakumar, Asha; Bothwell, Alfred L M
2017-08-01
Intestinal tumorigenesis in the ApcMin/+ model is initiated by aberrant activation of Wnt pathway. Increased IL-4 expression in human colorectal cancer tissue and growth of colon cancer cell lines implied that IL-4-induced Stat6-mediated tumorigenic signaling likely contributes to intestinal tumor progression in ApcMin/+ mice. Stat6 also appears to promote expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) cells. MDSCs promote polyp formation in the ApcMin/+ model. Hence, Stat6 could have a broad role in coordinating both polyp cell proliferation and MDSC expansion. We found that IL-4-induced Stat6-mediated proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells is augmented by platelet-derived growth factor-BB, a tumor-promoting growth factor. To determine whether polyp progression in ApcMin/+ mice is dependent on Stat6 signaling, we disrupted Stat6 in this model. Total polyps in the small intestine were fewer in ApcMin/+ mice lacking Stat6. Furthermore, proliferation of polyp epithelial cells was reduced, indicating that Stat6 in part controlled polyp formation. Stat6 also promoted expansion of MDSCs in the spleen and lamina propria of ApcMin/+ mice, implying regulation of antitumor T-cell response. More CD8 cells and reduced PD-1 expression on CD4 cells correlated with reduced polyps. In addition, a strong CD8-mediated cytotoxic response led to killing of tumor cells in Stat6-deficient ApcMin/+ mice. Therefore, these findings show that Stat6 has an oncogenic role in intestinal tumorigenesis by promoting polyp cell proliferation and immunosuppressive mediators, and preventing an active cytotoxic process. Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
A pH-responsive carboxymethyl dextran-based conjugate as a carrier of docetaxel for cancer therapy.
Han, Hwa Seung; Lee, Minchang; An, Jae Yoon; Son, Soyoung; Ko, Hyewon; Lee, Hansang; Chae, Yee Soo; Kang, Young Mo; Park, Jae Hyung
2016-05-01
Although docetaxel is available for the treatment of various cancers, its clinical applications are limited by its poor water solubility and toxicity to normal cells, resulting in severe adverse effects. In this study, we synthesized a polymeric conjugate with an acid-labile ester linkage, consisting of carboxymethyl dextran (CMD) and docetaxel (DTX), as a potential anticancer drug delivery system. The conjugate exhibited sustained release of DTX in physiological buffer (pH 7.4), whereas its release rate increased remarkably under mildly acidic conditions (pH < 6.5), mimicking the intracellular environment. Cytotoxicity tests conducted in vitro demonstrated that the conjugate exhibited much higher toxicity to cancer cells under mildly acidic conditions than at physiological buffer (pH 7.4). These results implied that the ester linkage in the conjugate allowed for selective release of biologically active DTX under mildly acidic conditions. The in vivo biodistribution of a Cy5.5-labeled conjugate was observed using the noninvasive optical imaging technique after its systemic administration into tumor-bearing mice. The conjugate was effectively accumulated into the tumor site, which may have been because of an enhanced permeability and retention effect. In addition, in vivo antitumor efficacy of the conjugate was significantly higher than that of free DTX. Overall, the CMD-based conjugate might have promising potential as a carrier of DTX for cancer therapy. © 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
-
Gautier, Violette|info:eu-repo/dai/nl/372660851; Boumeester, Anja J.; Lössl, Philip|info:eu-repo/dai/nl/371559693; Heck, Albert J R|info:eu-repo/dai/nl/105189332
2015-01-01
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are a novel class of biopharmaceuticals several of which are now being investigated in clinical studies. In ADCs, potent cytotoxic drugs are coupled via a linker to reactive residues in IgG monoclonal antibodies. Linkage to lysine residues in the IgGs, using
-
Levine, Paul M.; Lee, Eugine; Greenfield, Alex; Bonneau, Richard; Logan, Susan K.; Garabedian, Michael J.; Kirshenbaum, Kent
2013-01-01
Sustained treatment of prostate cancer with Androgen Receptor (AR) antagonists can evoke drug resistance, leading to castrate-resistant disease. Elevated activity of the AR is often associated with this highly aggressive disease state. Therefore, new therapeutic regimens that target and modulate AR activity could prove beneficial. We previously introduced a versatile chemical platform to generate competitive and non-competitive multivalent peptoid oligomer conjugates that modulate AR activity. In particular, we identified a linear and a cyclic divalent ethisterone conjugate that exhibit potent anti-proliferative properties in LNCaP-abl cells, a model of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Here, we characterize the mechanism of action of these compounds utilizing confocal microscopy, time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer, chromatin immunoprecipitation, flow cytometry, and microarray analysis. The linear conjugate competitively blocks AR action by inhibiting DNA binding. In addition, the linear conjugate does not promote AR nuclear localization or co-activator binding. In contrast, the cyclic conjugate promotes AR nuclear localization and induces cell-cycle arrest, despite its inability to compete against endogenous ligand for binding to AR in vitro. Genome-wide expression analysis reveals that gene transcripts are differentially affected by treatment with the linear or cyclic conjugate. Although the divalent ethisterone conjugates share extensive chemical similarities, we illustrate that they can antagonize the AR via distinct mechanisms of action, establishing new therapeutic strategies for potential applications in AR pharmacology. PMID:22871957
-
Intini, Francesco Paolo; Zajac, Juraj; Novohradsky, Vojtech; Saltarella, Teresa; Pacifico, Concetta; Brabec, Viktor; Natile, Giovanni; Kasparkova, Jana
2017-02-06
One concept how to improve anticancer effects of conventional metallodrugs consists in conjugation of these compounds with other biologically (antitumor) active agents, acting by a different mechanism. Here, we present synthesis, biological effects, and mechanisms of action of new Pt(II) derivatives containing one or two nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory diclofenac (DCF) ligands also known for their antitumor effects. The antiproliferative properties of these metallic conjugates show that these compounds are potent and cancer cell selective cytotoxic agents exhibiting activity in cisplatin resistant and the COX-2 positive tumor cell lines. One of these compounds, compound 3, in which DCF molecules are coordinated to Pt(II) through their carboxylic group, is more potent than parental conventional Pt(II) drug cisplatin, free DCF and the congeners of 3 in which DCF ligands are conjugated to Pt(II) via a diamine. The potency of 3 is due to several factors including enhanced internalization that correlates with enhanced DNA binding and cytotoxicity. Mechanistic studies show that 3 combines multiple effects. After its accumulation in cells, it releases Pt(II) drug capable of binding/damaging DNA and DCF ligands, which affect distribution of cells in individual phases of the cell cycle, inhibit glycolysis and lactate transport, collapse mitochondrial membrane potential, and suppress the cellular properties characteristic of metastatic progression.
-
Wu, Ling; Velander, Paul; Liu, Dongmin; Xu, Bin
2017-09-26
Oleuropein, a natural product derived from olive leaves, has reported anti-diabetic functions. However, detailed molecular mechanisms for how it affects β-cell functions remain poorly understood. Here, we present evidence that oleuropein promotes glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) in β-cells. The effect is dose-dependent and stimulates the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. We further demonstrated that oleuropein inhibits the cytotoxicity induced by amylin amyloids, a hallmark feature of type 2 diabetes. We demonstrated that these dual functions are structure-specific: we identified the 3-hydroxytyrosol moiety of oleuropein as the main functional entity responsible for amyloid inhibition, but the novel GSIS function requires the entire structure scaffold of the molecule.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Milczarek, Justyna; Pawlowska, Roza; Zurawinski, Remigiusz; Lukasik, Beata; Garner, Logan E.; Chworos, Arkadiusz
2017-05-01
Over the last few years, considerable efforts are taken, in order to find a molecular fluorescent probe fulfilling their applicability requirements. Due to a good optical properties and affinity to biological structures conjugated oligoelectrolytes (COEs) can be considered as a promising dyes for application in fluorescence-based bioimaging. In this work, we synthetized COEs with phenylenevinylene core (PV-COEs) and applied as fluorescent membranous-specific probes. Cytotoxicity effects of each COE were probed on cancerous and non-cancerous cell types and little to no toxicity effects were observed at the high range of concentrations. The intensity of cell fluorescence following the COE staining was determined by the photoluminescence analysis and fluorescence activated cell sorting method (FACS). Intercalation of tested COEs into mammalian cell membranes was revealed by fluorescent and confocal microscopy colocalization with commercial dyes specific for cellular structures including mitochondria, Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum. The phenylenevinylene conjugated oligoelectrolytes have been found to be suitable for fluorescent bioimaging of mammalian cells and membrane-rich organelles. Due to their water solubility coupled with spontaneous intercalation into cells, favorable photophysical features, ease of cell staining, low cytotoxicity and selectivity for membranous structures, PV-COEs can be applied as markers for fluorescence imaging of a variety of cell types.
-
Romain, Gabrielle; Senyukov, Vladimir; Rey-Villamizar, Nicolas; Merouane, Amine; Kelton, William; Liadi, Ivan; Mahendra, Ankit; Charab, Wissam; Georgiou, George; Roysam, Badrinath; Lee, Dean A.
2014-01-01
The efficacy of most therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting tumor antigens results primarily from their ability to elicit potent cytotoxicity through effector-mediated functions. We have engineered the fragment crystallizable (Fc) region of the immunoglobulin G (IgG) mAb, HuM195, targeting the leukemic antigen CD33, by introducing the triple mutation Ser293Asp/Ala330Leu/Ile332Glu (DLE), and developed Time-lapse Imaging Microscopy in Nanowell Grids to analyze antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity kinetics of thousands of individual natural killer (NK) cells and mAb-coated target cells. We demonstrate that the DLE-HuM195 antibody increases both the quality and the quantity of NK cell-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity by endowing more NK cells to participate in cytotoxicity via accrued CD16-mediated signaling and by increasing serial killing of target cells. NK cells encountering targets coated with DLE-HuM195 induce rapid target cell apoptosis by promoting simultaneous conjugates to multiple target cells and induce apoptosis in twice the number of target cells within the same period as the wild-type mAb. Enhanced target killing was also associated with increased frequency of NK cells undergoing apoptosis, but this effect was donor-dependent. Antibody-based therapies targeting tumor antigens will benefit from a better understanding of cell-mediated tumor elimination, and our work opens further opportunities for the therapeutic targeting of CD33 in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. PMID:25232058
-
Reduced cytotoxicity of insulin-immobilized CdS quantum dots using PEG as a spacer
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Choi Moon-Jeong
2011-01-01
Full Text Available Abstract Cytotoxicity is a severe problem for cadmium sulfide nanoparticles (CSNPs in biological systems. In this study, mercaptoacetic acid-coated CSNPs, typical semiconductor Q-dots, were synthesized in aqueous medium by the arrested precipitation method. Then, amino-terminated polyethylene glycol (PEG was conjugated to the surface of CSNPs (PCSNPs in order to introduce amino groups to the surface. Finally, insulin was immobilized on the surface of PCSNPs (ICSNPs to reduce cytotoxicity as well as to enhance cell compatibility. The presence of insulin on the surface of ICSNPs was confirmed by observing infrared absorptions of amide I and II. The mean diameter of ICSNPs as determined by dynamic light scattering was about 38 nm. Human fibroblasts were cultured in the absence and presence of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles to evaluate cytotoxicity and cell compatibility. The results showed that the cytotoxicity of insulin-immobilized cadmium sulfide nanoparticles was significantly suppressed by usage of PEG as a spacer. In addition, cell proliferation was highly facilitated by the addition of ICSNPs. The ICSNPs used in this study will be potentials to be used in bio-imaging applications.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kenji Yamamoto
2013-01-01
Full Text Available Silicon quantum dots (Si-QDs have great potential for biomedical applications, including their use as biological fluorescent markers and carriers for drug delivery systems. Biologically inert Si-QDs are less toxic than conventional cadmium-based QDs, and can modify the surface of the Si-QD with covalent bond. We synthesized water-soluble alminoprofen-conjugated Si-QDs (Ap-Si. Alminoprofen is a non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID used as an analgesic for rheumatism. Our results showed that the “silicon drug” is less toxic than the control Si-QD and the original drug. These phenomena indicate that the condensed surface integration of ligand/receptor-type drugs might reduce the adverse interaction between the cells and drug molecules. In addition, the medicinal effect of the Si-QDs (i.e., the inhibition of COX-2 enzyme was maintained compared to that of the original drug. The same drug effect is related to the integration ratio of original drugs, which might control the binding interaction between COX-2 and the silicon drug. We conclude that drug conjugation with biocompatible Si-QDs is a potential method for functional pharmaceutical drug development.
-
Antibody-Conjugated Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Manuel Arruebo
2009-01-01
Full Text Available Nanoscience and Nanotechnology have found their way into the fields of Biotechnology and Medicine. Nanoparticles by themselves offer specific physicochemical properties that they do not exhibit in bulk form, where materials show constant physical properties regardless of size. Antibodies are nanosize biological products that are part of the specific immune system. In addition to their own properties as pathogens or toxin neutralizers, as well as in the recruitment of immune elements (complement, improving phagocytosis, cytotoxicity antibody dependent by natural killer cells, etc., they could carry several elements (toxins, drugs, fluorochroms, or even nanoparticles, etc. and be used in several diagnostic procedures, or even in therapy to destroy a specific target. The conjugation of antibodies to nanoparticles can generate a product that combines the properties of both. For example, they can combine the small size of nanoparticles and their special thermal, imaging, drug carrier, or magnetic characteristics with the abilities of antibodies, such as specific and selective recognition. The hybrid product will show versatility and specificity. In this review, we analyse both antibodies and nanoparticles, focusing especially on the recent developments for antibody-conjugated nanoparticles, offering the researcher an overview of the different applications and possibilities of these hybrid carriers.
-
IGF-1 promotes the development and cytotoxic activity of human NK cells
Ni, Fang; Sun, Rui; Fu, Binqing; Wang, Fuyan; Guo, Chuang; Tian, Zhigang; Wei, Haiming
2013-01-01
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is a critical regulator of many physiological functions, ranging from longevity to immunity. However, little is known about the role of IGF-1 in natural killer cell development and function. Here, we identify an essential role for IGF-1 in the positive regulation of human natural killer cell development and cytotoxicity. Specifically, we show that human natural killer cells have the ability to produce IGF-1 and that differential endogenous IGF-1 expression leads to disparate cytotoxicity in human primary natural killer cells. Moreover, miR-483-3p is identified as a critical regulator of IGF-1 expression in natural killer cells. Overexpression of miR-483-3p has an effect similar to IGF-1 blockade and decreased natural killer cell cytotoxicity, whereas inhibition of miR-483-3p has the opposite effect, which is reversible with IGF-1 neutralizing antibody. These findings indicate that IGF-1 and miR-483-3p belong to a new class of natural killer cell functional modulators and strengthen the prominent role of IGF-1 in innate immunity. PMID:23403580
-
Ghadiri, Maryam; Vasheghani-Farahani, Ebrahim; Atyabi, Fatemeh; Kobarfard, Farzad; Mohamadyar-Toupkanlou, Farzaneh; Hosseinkhani, Hossein
2017-10-01
Application of many vital hydrophilic medicines have been restricted by blood-brain barrier (BBB) for treatment of brain diseases. In this study, a targeted drug delivery system based on dextran-spermine biopolymer was developed for drug transport across BBB. Drug loaded magnetic dextran-spermine nanoparticles (DS-NPs) were prepared via ionic gelation followed by transferrin (Tf) conjugation as targeting moiety. The characteristics of Tf conjugated nanoparticles (TDS-NPs) were analyzed by different methods and their cytotoxicity effects on U87MG cells were tested. The superparamagnetic characteristic of TDS-NPs was verified by vibration simple magnetometer. Capecitabine loaded TDS-NPs exhibited pH-sensitive release behavior with enhanced cytotoxicity against U87MG cells, compared to DS-NPs and free capecitabine. Prussian-blue staining and TEM-imaging showed the significant cellular uptake of TDS-NPs. Furthermore, a remarkable increase of Fe concentrations in brain was observed following their biodistribution and histological studies in vivo, after 1 and 7 days of post-injection. Enhanced drug transport across BBB and pH-triggered cellular uptake of TDS-NPs indicated that these theranostic nanocarriers are promising candidate for the brain malignance treatment. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. J Biomed Mater Res Part A: 105A: 2851-2864, 2017. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
-
Challenges and advances in the assessment of the disposition of antibody‐drug conjugates
Iyer, Suhasini
2015-01-01
Abstract Antibody‐drug conjugates (ADCs) are a rapidly growing therapeutic platform for the treatment of cancer. ADCs consist of a cytotoxic small molecule drug linked to an antibody to provide targeted delivery of the cytotoxic agent to the tumor. Understanding the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of ADCs is crucial in their design to optimize dose and regimen, to maximize efficacy and to minimize toxicity in patients. Significant progress has been made in recent years in this area, however, many fundamental questions still remain. This review discusses factors to consider while assessing the disposition of ADCs, and the unique challenges associated with these therapeutics. Current tools that are available and strategies to enable appropriate assessment are also discussed. © 2015 Genentech Inc. Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. PMID:25904406
-
Hosseinzadeh, Hosniyeh; Atyabi, Fatemeh; Varnamkhasti, Behrang Shiri; Hosseinzadeh, Reza; Ostad, Seyed Nasser; Ghahremani, Mohammad Hossein; Dinarvand, Rassoul
2017-06-30
Combination of chemotherapy and photothermal therapy has been proposed for better treatment of metastatic colon cancer. In this study SN38, a highly potent cytotoxic agent, was conjugated to negatively charged hyaluronic acid (HA), which was deposited on the surface of the positively charged gold nanoparticles via electrostatic interaction. The drug conjugation and its interaction with gold nanoparticles were verified by 1 H NMR and UV-vis spectroscopies, respectively. The prepared SN38-HA gold NPs are negatively charged spherical nanoparticles with an average size of 75±10nm. In vitro release study revealed that drug release in acidic conditions (pH 5.2) was faster than that in physiological pH. Red light emitting diode (LED, 630nm, 30mW) was used as a light source for photothermal experiments. The drug release in acidic conditions was increased up to 30% using red LED illumination (6min) in comparison with experiment carried out indark. The cytotoxicity study on MUC1 positive HT29, SW480 colon cancer cells and MUC1 negative CHO cells, showed higher toxicity of the nanoparticles on HT29 and SW480 cell lines compared to CHO cells. Confocal microscopy images along with flow cytometry analysis confirm the cytotoxicity results. The incubation time for reaching IC50 decreases from 48h to 24h by LED illumination after nanoparticle treatment. Migratory potential of the HT29 and SW480 cell lines was reduced by co-application of SN38-HA gold NPs and LED radiation. Also anti-proliferative study indicates that LED radiation has increased the cytotoxicity of the nanoparticles and this effect is remained up to 8days. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Yu, Qingsong; Zhang, Jiajing; Zhang, Guan; Gan, Zhihua
2015-04-01
Novel poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide) block copolymer (PEG-b-PHPMA) with well-defined composition was synthesized by RAFT polymerization. Folate and doxorubicin (DOX) were quantitatively introduced into the copolymer. The influences of folate content and pH value on folate receptor (FR) mediated cell endocytosis and pH-responsive DOX release were studied. It has been demonstrated that minimum folate content is needed for the enrichment of hydrophobic folate on the hydrophilic part of polymer conjugates. The cytotoxicity of targetable polymer drug conjugates was much higher than that of non-targetable ones and free DOX. It could be concluded that the folate plays a significant role in targeting and internalization of the conjugates against bladder cancer cells. © 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Peptide π-Electron Conjugates: Organic Electronics for Biology?
Ardoña, Herdeline Ann M; Tovar, John D
2015-12-16
Highly ordered arrays of π-conjugated molecules are often viewed as a prerequisite for effective charge-transporting materials. Studies involving these materials have traditionally focused on organic electronic devices, with more recent emphasis on biological systems. In order to facilitate the transition to biological environments, biomolecules that can promote hierarchical ordering and water solubility are often covalently appended to the π-electron unit. This review highlights recent work on π-conjugated systems bound to peptide moieties that exhibit self-assembly and aims to provide an overview on the development and emerging applications of peptide-based supramolecular π-electron systems.
-
A conjugate of an anti-midkine single-chain variable fragment to doxorubicin inhibits tumor growth
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zhao, Shuli [Immunology and Reproductive Biology Laboratory, Medical School & State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Nanjing University, Nanjing (China); Nanjing Affiliated First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing (China); Zhao, Guangfeng; Xie, Hao; Huang, Yahong [Immunology and Reproductive Biology Laboratory, Medical School & State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Nanjing University, Nanjing (China); Hou, Yayi [Immunology and Reproductive Biology Laboratory, Medical School & State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Nanjing University, Nanjing (China); Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, Nanjing University, Nanjing (China)
2012-01-27
Doxorubicin (DOX) was conjugated to a single-chain variable fragment (scFv) against human midkine (MK), and the conjugate (scFv-DOX) was used to target the chemotherapeutic agent to a mouse solid tumor model in which the tumor cells expressed high levels of human MK. The His-tagged recombinant scFv was expressed in bacteria, purified by metal affinity chromatography, and then conjugated to DOX using oxidative dextran (Dex) as a linker. The molecular formula of this immunoconjugate was scFv(Dex){sub 1.3}(DOX){sub 20}. In vitro apoptosis assays showed that the scFv-DOX conjugate was more cytotoxic against MK-transfected human adenocarcinoma cells (BGC823-MK) than untransfected cells (55.3 ± 2.4 vs 22.4 ± 3.8%) for three independent experiments. Nude mice bearing BGC823-MK solid tumors received scFv-DOX or equivalent doses of scFv + DOX for 2 weeks and tumor growth was more effectively inhibited by the scFv-DOX conjugate than by scFv + DOX (51.83% inhibition vs 40.81%). Histological analysis of the tumor tissues revealed that the highest levels of DOX accumulated in tumors from mice treated with scFv-DOX and this resulted in more extensive tumor cell death than in animals treated with the equivalent dose of scFv + DOX. These results show that the scFv-DOX conjugate effectively inhibited tumor growth in vivo and suggest that antigen-specific scFv may be competent drug-carriers.
-
A conjugate of an anti-midkine single-chain variable fragment to doxorubicin inhibits tumor growth
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zhao, Shuli; Zhao, Guangfeng; Xie, Hao; Huang, Yahong; Hou, Yayi
2012-01-01
Doxorubicin (DOX) was conjugated to a single-chain variable fragment (scFv) against human midkine (MK), and the conjugate (scFv-DOX) was used to target the chemotherapeutic agent to a mouse solid tumor model in which the tumor cells expressed high levels of human MK. The His-tagged recombinant scFv was expressed in bacteria, purified by metal affinity chromatography, and then conjugated to DOX using oxidative dextran (Dex) as a linker. The molecular formula of this immunoconjugate was scFv(Dex) 1.3 (DOX) 20 . In vitro apoptosis assays showed that the scFv-DOX conjugate was more cytotoxic against MK-transfected human adenocarcinoma cells (BGC823-MK) than untransfected cells (55.3 ± 2.4 vs 22.4 ± 3.8%) for three independent experiments. Nude mice bearing BGC823-MK solid tumors received scFv-DOX or equivalent doses of scFv + DOX for 2 weeks and tumor growth was more effectively inhibited by the scFv-DOX conjugate than by scFv + DOX (51.83% inhibition vs 40.81%). Histological analysis of the tumor tissues revealed that the highest levels of DOX accumulated in tumors from mice treated with scFv-DOX and this resulted in more extensive tumor cell death than in animals treated with the equivalent dose of scFv + DOX. These results show that the scFv-DOX conjugate effectively inhibited tumor growth in vivo and suggest that antigen-specific scFv may be competent drug-carriers
-
Peng, Zheng-Hong; Sima, Monika; Salama, Mohamed E; Kopečková, Pavla; Kopeček, Jindřich
2013-12-01
Combination of targeted delivery and controlled release is a powerful technique for cancer treatment. In this paper, we describe the design, synthesis, structure validation and biological properties of targeted and non-targeted N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA) copolymer-docetaxel conjugates. Docetaxel (DTX) was conjugated to HPMA copolymer via a tetrapeptide spacer (-GFLG-). 3-(1,3-dicarboxypropyl)-ureido]pentanedioic acid (DUPA) was used as the targeting moiety to actively deliver DTX for treatment of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) expressing prostate cancer. Short and long spacer DUPA monomers were prepared, and four HPMA copolymer--DTX conjugates (non-targeted, two targeted with short spacer of different molecular weight and targeted with long spacer) were prepared via Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT) copolymerization. Following confirmation of PSMA expression on C4-2 cell line, the DTX conjugates' in vitro cytotoxicity was tested against C4-2 tumor cells and their anticancer efficacies were assessed in nude mice bearing s.c. human prostate adenocarcinoma C4-2 xenografts. The in vivo results show that the spacer length between targeting moieties and HPMA copolymer backbone can significantly affect the treatment efficacy of DTX conjugates against C4-2 tumor bearing nu/nu mice. Moreover, histological analysis indicated that the DUPA-targeted DTX conjugate with longer spacer had no toxicity in major organs of treated mice.
-
Erdoğar, Nazlı; Esendağlı, Güneş; Nielsen, Thorbjorn T; Şen, Murat; Öner, Levent; Bilensoy, Erem
2016-07-25
As nanomedicines are gaining momentum in the therapy of cancer, new biomaterials emerge as alternative platforms for the delivery of anticancer drugs with bioavailability problems. In this study, two novel amphiphilic cyclodextrins (FCD-1 and FCD-2) conjugated with folate group to enable active targeting to folate positive breast tumors were introduced. The objective of this study was to develop and characterize new folated-CD nanoparticles via 3(2) factorial design for optimal final parameters. Full physicochemical characterization studies were performed. Blank and paclitaxel loaded FCD-1 and FCD-2 nanoparticles remained within the range of 70-275nm and 125-185nm, respectively. Zeta potential values were neutral and -20mV for FCD-1 and FCD-2 nanoparticles, respectively. Drug release studies showed initial burst release followed by a longer sustained release. Blank nanoparticles had no cytotoxicity against L929 cells. T-47D and ZR-75-1 human breast cancer cells with different levels of folate receptor expression were used to assess anti-cancer efficacy. Through targeting the folate receptor, these nanoparticles were efficiently engulfed by the breast cancer cells. Additionally, breast cancer cells became more sensitive to cytotoxic and/or cytostatic effects of PCX delivered by FCD-1 and FCD-2. In conclusion, these novel folate-conjugated cyclodextrin nanoparticles can therefore be considered as promising alternative systems for safe and effective delivery of paclitaxel with a folate-dependent mechanism. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) for Personalized Treatment of Solid Tumors: A Review.
Lambert, John M; Morris, Charles Q
2017-05-01
Attaching a cytotoxic "payload" to an antibody to form an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) provides a mechanism for selective delivery of the cytotoxic agent to cancer cells via the specific binding of the antibody to cancer-selective cell surface molecules. The first ADC to receive marketing authorization was gemtuzumab ozogamicin, which comprises an anti-CD33 antibody conjugated to a highly potent DNA-targeting antibiotic, calicheamicin, approved in 2000 for treating acute myeloid leukemia. It was withdrawn from the US market in 2010 following an unsuccessful confirmatory trial. The development of two classes of highly potent microtubule-disrupting agents, maytansinoids and auristatins, as payloads for ADCs resulted in approval of brentuximab vedotin in 2011 for treating Hodgkin lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma, and approval of ado-trastuzumab emtansine in 2013 for treating HER2-positive breast cancer. Their success stimulated much research into the ADC approach, with >60 ADCs currently in clinical evaluation, mostly targeting solid tumors. Five ADCs have advanced into pivotal clinical trials for treating various solid tumors-platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, mesothelioma, triple-negative breast cancer, glioblastoma, and small cell lung cancer. The level of target expression is a key parameter in predicting the likelihood of patient benefit for all these ADCs, as well as for the approved compound, ado-trastuzumab emtansine. The development of a patient selection strategy linked to target expression on the tumor is thus critically important for identifying the population appropriate for receiving treatment.
-
Targeted Anticancer Immunotoxins and Cytotoxic Agents with Direct Killing Moieties
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Koji Kawakami
2006-01-01
Full Text Available Despite the progress of the bioinformatics approach to characterize cell-surface antigens and receptors on tumor cells, it remains difficult to generate novel cancer vaccines or neutralizing monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Among targeted cancer therapeutics, biologicals with targetable antibodies or ligands conjugated or fused to toxins or chemicals for direct cell-killing ability have been developed over the last 2 decades. These conjugated or fused chimeric proteins are termed immunotoxins or cytotoxic agents. Two agents, DAB389IL-2 (ONTAKTM targeting the interleukin-2 receptor and CD33-calicheamicin (Mylotarg®, have been approved by the FDA for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL and relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML, respectively. Such targetable agents, including RFB4(dsFv-PE38 (BL22, IL13-PE38QQR, and Tf-CRM107, are being tested in clinical trials. Several agents using unique technology such as a cleavable adapter or immunoliposomes with antibodies are also in the preclinical stage. This review summarizes the generation, mechanism, and development of these agents. In addition, possible future directions of this therapeutic approach are discussed.
-
Antibody-drug conjugates: Promising and efficient tools for targeted cancer therapy.
Nasiri, Hadi; Valedkarimi, Zahra; Aghebati-Maleki, Leili; Majidi, Jafar
2018-09-01
Over the recent decades, the use of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) has led to a paradigm shift in cancer chemotherapy. Antibody-based treatment of various human tumors has presented dramatic efficacy and is now one of the most promising strategies used for targeted therapy of patients with a variety of malignancies, including hematological cancers and solid tumors. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are able to selectively deliver cytotoxic drugs to tumor cells, which express specific antigens on their surface, and has been suggested as a novel category of agents for use in the development of anticancer targeted therapies. In contrast to conventional treatments that cause damage to healthy tissues, ADCs use mAbs to specifically attach to antigens on the surface of target cells and deliver their cytotoxic payloads. The therapeutic success of future ADCs depends on closely choosing the target antigen, increasing the potency of the cytotoxic cargo, improving the properties of the linker, and reducing drug resistance. If appropriate solutions are presented to address these issues, ADCs will play a more important role in the development of targeted therapeutics against cancer in the next years. We review the design of ADCs, and focus on how ADCs can be exploited to overcome multiple drug resistance (MDR). © 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
-
Jeong, Yunseong; Jin, Geun-Woo; Choi, Eunjung; Jung, Ji Hyuk; Park, Jong-Sang
2011-11-28
Polyplexes formed from cationic polymer/pDNA have been known to be vulnerable to external ionic strength. To improve polyplex stability against ionic strength, we attempted the chemical conjugation of the hydrophobic deoxycholate (DC) moiety to the polyamidoamine-diethylenetriamine (PAM-DET) dendrimer. Dynamic light scattering studies showed that the tolerance of the resulting PAM-DET-DC against ionic strength is higher than that of PAM-DET. In addition, we confirmed that the stability of polyplex has a strong relationship with the degree of conjugation of the DC moiety to the PAM-DET dendrimer and the charge ratio of PAM-DET-DC. Furthermore, the transfection efficiency of the PAM-DET-DC polyplex is higher than that of PAM-DET but its cytotoxicity remains the same. Therefore, the chemical conjugation of DC is a safe and effective method for increasing the stability of supramolecules formed from electrostatic interaction. Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Purification of SUMO conjugating enzymes and kinetic analysis of substrate conjugation
Yunus, Ali A.; Lima, Christopher D.
2009-01-01
SUMO conjugation to protein substrates requires the concerted action of a dedicated E2 ubiquitin conjugation enzyme (Ubc9) and associated E3 ligases. Although Ubc9 can directly recognize and modify substrate lysine residues that occur within a consensus site for SUMO modification, E3 ligases can redirect specificity and enhance conjugation rates during SUMO conjugation in vitro and in vivo. In this chapter, we will describe methods utilized to purify SUMO conjugating enzymes and model substrates which can be used for analysis of SUMO conjugation in vitro. We will also describe methods to extract kinetic parameters during E3-dependent or E3-independent substrate conjugation. PMID:19107417
-
Antimicrobial activity and cellular toxicity of nanoparticle-polymyxin B conjugates
Park, Soonhyang; Chibli, Hicham; Wong, Jody; Nadeau, Jay L.
2011-05-01
We investigate the antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity to mammalian cells of conjugates of the peptide antibiotic polymyxin B (PMB) to Au nanoparticles and CdTe quantum dots. Au nanoparticles fully covered with PMB are identical in antimicrobial activity to the free drug alone, whereas partially-conjugated Au particles show decreased effectiveness in proportion to the concentration of Au. CdTe-PMB conjugates are more toxic to Escherichia coli than PMB alone, resulting in a flattening of the steep PMB dose-response curve. The effect is most pronounced at low concentrations of PMB, with a greater effect on the concentration required to reduce growth by half (IC50) than on the concentration needed to inhibit all growth (minimum inhibitory concentration, MIC). The Gram positive organism Staphylococcus aureus is resistant to both PMB and CdTe, showing minimal increased sensitivity when the two are conjugated. Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation shows a significant reduction in photo-generated hydroxyl and superoxide radicals with CdTe-PMB as compared with bare CdTe. There is a corresponding reduction in toxicity of QD-PMB versus bare CdTe to mammalian cells, with nearly 100% survival in fibroblasts exposed to bactericidal concentrations of QD-PMB. The situation in bacteria is more complex: photoexcitation of the CdTe particles plays a small role in IC50 but has a significant effect on the MIC, suggesting that at least two different mechanisms are responsible for the antimicrobial action seen. These results show that it is possible to create antimicrobial agents using concentrations of CdTe quantum dots that do not harm mammalian cells.
-
Antimicrobial activity and cellular toxicity of nanoparticle-polymyxin B conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Park, Soonhyang; Chibli, Hicham; Wong, Jody; Nadeau, Jay L
2011-01-01
We investigate the antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity to mammalian cells of conjugates of the peptide antibiotic polymyxin B (PMB) to Au nanoparticles and CdTe quantum dots. Au nanoparticles fully covered with PMB are identical in antimicrobial activity to the free drug alone, whereas partially-conjugated Au particles show decreased effectiveness in proportion to the concentration of Au. CdTe-PMB conjugates are more toxic to Escherichia coli than PMB alone, resulting in a flattening of the steep PMB dose-response curve. The effect is most pronounced at low concentrations of PMB, with a greater effect on the concentration required to reduce growth by half (IC50) than on the concentration needed to inhibit all growth (minimum inhibitory concentration, MIC). The Gram positive organism Staphylococcus aureus is resistant to both PMB and CdTe, showing minimal increased sensitivity when the two are conjugated. Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation shows a significant reduction in photo-generated hydroxyl and superoxide radicals with CdTe-PMB as compared with bare CdTe. There is a corresponding reduction in toxicity of QD-PMB versus bare CdTe to mammalian cells, with nearly 100% survival in fibroblasts exposed to bactericidal concentrations of QD-PMB. The situation in bacteria is more complex: photoexcitation of the CdTe particles plays a small role in IC50 but has a significant effect on the MIC, suggesting that at least two different mechanisms are responsible for the antimicrobial action seen. These results show that it is possible to create antimicrobial agents using concentrations of CdTe quantum dots that do not harm mammalian cells.
-
Antimicrobial activity and cellular toxicity of nanoparticle-polymyxin B conjugates
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Park, Soonhyang; Chibli, Hicham; Wong, Jody; Nadeau, Jay L, E-mail: jay.nadeau@mcgill.ca [Department of Biomedical Engineering, McGill University, 3775 University Street, Montreal QC, H3A 2B4 (Canada)
2011-05-06
We investigate the antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity to mammalian cells of conjugates of the peptide antibiotic polymyxin B (PMB) to Au nanoparticles and CdTe quantum dots. Au nanoparticles fully covered with PMB are identical in antimicrobial activity to the free drug alone, whereas partially-conjugated Au particles show decreased effectiveness in proportion to the concentration of Au. CdTe-PMB conjugates are more toxic to Escherichia coli than PMB alone, resulting in a flattening of the steep PMB dose-response curve. The effect is most pronounced at low concentrations of PMB, with a greater effect on the concentration required to reduce growth by half (IC50) than on the concentration needed to inhibit all growth (minimum inhibitory concentration, MIC). The Gram positive organism Staphylococcus aureus is resistant to both PMB and CdTe, showing minimal increased sensitivity when the two are conjugated. Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation shows a significant reduction in photo-generated hydroxyl and superoxide radicals with CdTe-PMB as compared with bare CdTe. There is a corresponding reduction in toxicity of QD-PMB versus bare CdTe to mammalian cells, with nearly 100% survival in fibroblasts exposed to bactericidal concentrations of QD-PMB. The situation in bacteria is more complex: photoexcitation of the CdTe particles plays a small role in IC50 but has a significant effect on the MIC, suggesting that at least two different mechanisms are responsible for the antimicrobial action seen. These results show that it is possible to create antimicrobial agents using concentrations of CdTe quantum dots that do not harm mammalian cells.
-
Byun, Jong Hyuk; Jung, Il Hyo
2018-04-14
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs)are one of the most recently developed chemotherapeutics to treat some types of tumor cells. They consist of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), linkers, and potent cytotoxic drugs. Unlike common chemotherapies, ADCs combine selectively with a target at the surface of the tumor cell, and a potent cytotoxic drug (payload) effectively prevents microtubule polymerization. In this work, we construct an ADC model that considers both the target of antibodies and the receptor (tubulin) of the cytotoxic payloads. The model is simulated with brentuximab vedotin, one of ADCs, and used to investigate the pharmacokinetic (PK) characteristics of ADCs in vivo. It also predicts area under the curve (AUC) of ADCs and the payloads by identifying the half-life. The results show that dynamical behaviors fairly coincide with the observed data and half-life and capture AUC. Thus, the model can be used for estimating some parameters, fitting experimental observations, predicting AUC, and exploring various dynamical behaviors of the target and the receptor. Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Khan, Selina; Bijker, Martijn S; Weterings, Jimmy J; Tanke, Hans J; Adema, Gosse J; van Hall, Thorbald; Drijfhout, Jan W; Melief, Cornelis J M; Overkleeft, Hermen S; van der Marel, Gijsbert A; Filippov, Dmitri V; van der Burg, Sjoerd H; Ossendorp, Ferry
2007-07-20
Covalent conjugation of Toll-like receptor ligands (TLR-L) to synthetic antigenic peptides strongly improves antigen presentation in vitro and T lymphocyte priming in vivo. These molecularly well defined TLR-L-peptide conjugates, constitute an attractive vaccination modality, sharing the peptide antigen and a defined adjuvant in one single molecule. We have analyzed the intracellular trafficking and processing of two TLR-L conjugates in dendritic cells (DCs). Long synthetic peptides containing an ovalbumin cytotoxic T-cell epitope were chemically conjugated to two different TLR-Ls the TLR2 ligand, Pam(3)CysSK(4) (Pam) or the TLR9 ligand CpG. Rapid and enhanced uptake of both types of TLR-L-conjugated peptide occurred in DCs. Moreover, TLR-L conjugation greatly enhanced antigen presentation, a process that was dependent on endosomal acidification, proteasomal cleavage, and TAP translocation. The uptake of the CpG approximately conjugate was independent of endosomally-expressed TLR9 as reported previously. Unexpectedly, we found that Pam approximately conjugated peptides were likewise internalized independently of the expression of cell surface-expressed TLR2. Further characterization of the uptake mechanisms revealed that TLR2-L employed a different uptake route than TLR9-L. Inhibition of clathrin- or caveolin-dependent endocytosis greatly reduced uptake and antigen presentation of the Pam-conjugate. In contrast, internalization and antigen presentation of CpG approximately conjugates was independent of clathrin-coated pits but partly dependent on caveolae formation. Importantly, in contrast to the TLR-independent uptake of the conjugates, TLR expression and downstream TLR signaling was required for dendritic cell maturation and for priming of naïve CD8(+) T-cells. Together, our data show that targeting to two distinct TLRs requires distinct uptake mechanism but follows similar trafficking and intracellular processing pathways leading to optimal antigen
-
Interconnection between thyroid hormone signalling pathways and parvovirus cytotoxic functions.
Vanacker, J M; Laudet, V; Adelmant, G; Stéhelin, D; Rommelaere, J
1993-01-01
Nonstructural (NS) proteins of autonomous parvoviruses can repress expression driven by heterologous promoters, an activity which thus far has not been separated from their cytotoxic effects. It is shown here that, in transient transfection assays, the NS-1 protein of the parvovirus minute virus of mice (MVMp) activates the promoter of the human c-erbA1 gene, encoding the thyroid hormone (T3) receptor alpha. The endogenous c-erbA1 promoter is also a target for induction upon MVMp infection. M...
-
Jindal, A. B.; Wasnik, M. N.; Nair, Hema A.
2010-01-01
Modification of polymers by covalent attachment of thiol bearing pendant groups is reported to impart many beneficial properties to them. Hence in the present study, sodium alginate–cysteine conjugate was synthesized by carbodiimide mediated coupling under varying reaction conditions and the derivatives characterized for thiol content. The thiolated alginate species synthesized had bound thiol content ranging from 247.8±11.03–324.54±10.107 ΅mol/g of polymer depending on the reaction conditions. Matrix tablets based on sodium alginate-cysteine conjugate and native sodium alginate containing tramadol hydrochloride as a model drug were prepared and mucoadhesive strength and in vitro drug release from the tablets were compared. Tablets containing 75 mg sodium alginate-cysteine conjugate could sustain release of 10 mg of model drug for 3 h, whereas 90% of the drug was released within 1 h from corresponding tablets prepared using native sodium alginate. An approximately 2-fold increase in the minimal detachment force of the tablets from an artificial mucin film was observed for sodium alginate–cysteine conjugate as compared to native sodium alginate. In vitro cytotoxicity studies in L-929 mouse fibroblast cells studied using an MTT assay revealed that at low concentrations of polymer, sodium alginate–cysteine conjugate was less toxic to L-929 mouse fibroblast cell line when compared to native sodium alginate. Hence, thiolation is found to be a simple route to improving polymer performance. The combination of improved controlled drug release and mucoadhesive properties coupled with the low toxicity of these new excipients builds up immense scope for the use of thiolated polymers in mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. PMID:21969750
-
Considerations for the nonclinical safety evaluation of antibody drug conjugates for oncology.
Roberts, Stanley A; Andrews, Paul A; Blanset, Diann; Flagella, Kelly M; Gorovits, Boris; Lynch, Carmel M; Martin, Pauline L; Kramer-Stickland, Kimberly; Thibault, Stephane; Warner, Garvin
2013-12-01
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) include monoclonal antibodies that are linked to cytotoxic small molecules. A number of these agents are currently being developed as anti-cancer agents designed to improve the therapeutic index of the cytotoxin (i.e., cytotoxic small molecule or cytotoxic agent) by specifically delivering it to tumor cells. This paper presents primary considerations for the nonclinical safety evaluation of ADCs and includes strategies for the evaluation of the entire ADC or the various individual components (i.e., antibody, linker or the cytotoxin). Considerations are presented on how to design a nonclinical safety assessment program to identify the on- and off-target toxicities to enable first-in-human (FIH) studies. Specific discussions are also included that provide details as to the need and how to conduct the studies for evaluating ADCs in genetic toxicology, tissue cross-reactivity, safety pharmacology, carcinogenicity, developmental and reproductive toxicology, biotransformation, toxicokinetic monitoring, bioanalytical assays, immunogenicity testing, test article stability and the selection of the FIH dose. Given the complexity of these molecules and our evolving understanding of their properties, there is no single all-encompassing nonclinical strategy. Instead, each ADC should be evaluated on a case-by-case scientifically-based approach that is consistent with ICH and animal research guidelines. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Guidry, Erin N; Farand, Julie; Soheili, Arash; Parish, Craig A; Kevin, Nancy J; Pipik, Brenda; Calati, Kathleen B; Ikemoto, Nori; Waldman, Jacob H; Latham, Andrew H; Howell, Bonnie J; Leone, Anthony; Garbaccio, Robert M; Barrett, Stephanie E; Parmar, Rubina Giare; Truong, Quang T; Mao, Bing; Davies, Ian W; Colletti, Steven L; Sepp-Lorenzino, Laura
2014-02-19
Polymer based carriers that aid in endosomal escape have proven to be efficacious siRNA delivery agents in vitro and in vivo; however, most suffer from cytotoxicity due in part to a lack of selectivity for endosomal versus cell membrane lysis. For polymer based carriers to move beyond the laboratory and into the clinic, it is critical to find carriers that are not only efficacious, but also have margins that are clinically relevant. In this paper we report three distinct categories of polymer conjugates that improve the selectivity of endosomal membrane lysis by relying on the change in pH associated with endosomal trafficking, including incorporation of low pKa heterocycles, acid cleavable amino side chains, or carboxylic acid pH sensitive charge switches. Additionally, we determine the therapeutic index of our polymer conjugates in vivo and demonstrate that the incorporation of pH responsive elements dramatically expands the therapeutic index to 10-15, beyond that of the therapeutic index (less than 3), for polymer conjugates previously reported.
-
Women experiencing the intergenerationality of conjugal violence
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gilvânia Patrícia do Nascimento Paixão
2015-10-01
Full Text Available Objective: to analyze the family relationship, in childhood and adolescence, of women who experience conjugal violence.Method: qualitative study. Interviews were held with 19 women, who were experiencing conjugal violence, and who were resident in a community in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. The project was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (N. 42/2011.Results: the data was organized using the Discourse of the Collective Subject, identifying the summary central ideas: they witnessed violence between their parents; they suffered repercussions from the violence between their parents: they were angry about the mother's submission to her partner; and they reproduced the conjugal violence. The discourse showed that the women witnessed, in childhood and adolescence, violence between their parents, and were injured both physically and psychologically. As a result of the mother's submission, feelings of anger arose in the children. However, in the adult phase of their own lives, they noticed that their conjugal life resembled that of their parents, reproducing the violence.Conclusion: investment is necessary in strategies designed to break inter-generational violence, and the health professionals are important in this process, as it is a phenomenon with repercussions in health. Because they work in the Family Health Strategy, which focuses on the prevention of harm and illness, health promotion and interdepartmentality, the nurses are essential in the process of preventing and confronting this phenomenon.
-
Cytotoxic macrolides from a new species of the deep-water marine sponge Leiodermatium.
Sandler, Joel S; Colin, Patrick L; Kelly, Michelle; Fenical, William
2006-09-15
Chemical investigation of a new species of the deep-water marine sponge Leiodermatium, collected by manned submersible at a depth of 740 feet in Palau, resulted in the isolation of two cytotoxic macrolides, leiodolides A (1) and B (2). The leiodolides represent the first members of a new class of 19-membered ring macrolides, incorporating several unique functional groups including a conjugated oxazole ring, a bromine substituent, and an alpha-hydroxy-alpha-methyl carboxylic acid side-chain terminus. The structures of these new metabolites were established by spectroscopic analysis, chemical modification, and degradation. The relative and absolute stereochemistries at most chiral centers were assigned on detailed interpretation of spectroscopic data, coupled with chemical degradation and application of the modified Mosher ester method. Leiodolide A showed significant cytotoxicity (average GI(50) = 2.0 microM) in the National Cancer Institute's 60 cell line panel with enhanced activity against HL-60 leukemia and OVCAR-3 ovarian cancer cell lines.
-
Nateghian, Navid; Goodarzi, Navid; Amini, Mohsen; Atyabi, Fatemeh; Khorramizadeh, Mohammad Reza; Dinarvand, Rassoul
2016-01-01
Docetaxel (DTX) is a widely used chemotherapeutic agent with very low water solubility. Conjugation of DTX to human serum albumin (HSA) is an effective way to increase its water solubility. Attachment of folic acid (FA) or biotin as targeting moieties to DTX-HSA conjugates may lead to active targeting and specific uptake by cancer cells with overexpressed FA or biotin receptors. In this study, FA or biotin molecules were attached to DTX-HSA conjugates by two different methods. In one method, FA or biotin molecules were attached to remaining NH2 residues of HSA in DTX-HSA conjugate by covalent bonds. In the second method, HSA-FA or HSA-biotin conjugates were synthesized separately and then combined by DTX-HSA conjugate in proper ratio to prepare nanoparticles containing DTX-HSA plus HSA-FA or HSA-biotin. Cell viability of different nanoparticle was evaluated on MDA-MB-231 (folate receptor positive), A549 (folate receptor negative), and 4T1 (biotin receptor positive) and showed superior cytotoxicity compared with free docetaxel (Taxotere). In vivo studies of DTX-HSA-FA and DTX-HSA-biotin conjugates in BULB/c mice, tumorized by 4T1 cell line, showed the conjugates prepared in this study were more powerful in the reduction in tumor size and increasing the survival rate when compared to free docetaxel. © 2015 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
-
Zhang, Xi; Yao, Juan; Zhang, Lihong; Fang, Jianguo; Bian, Fengling
2014-03-15
Poly(ethylene glycol)-conjugated N-(2-hydroxy) propyl-3-trimethyl ammonium chitosan chloride (PHTAC) derivatives were prepared by incorporating PEG molecules onto quaternized chitosan backbone. The copolymers were characterized by FTIR, (1)H NMR and XRD. Agarose gel retardation assay indicated that PHTAC had good plasmid DNA (pDNA) binding capability and the particle sizes of PHTAC/pDNA complexes determined by DLS were about 200 nm. Cytotoxicity assays in HeLa and 293T cells showed that PHTAC had low cytotoxicity. In vitro luciferase assay showed that PHTAC with PEGylation degree of 9% (PHTAC-1) had good transfection efficiency about 5.3-fold higher than quaternized chitosan, which was comparable with PEI (25 kDa). These results suggest that PHTAC-1 is a promising candidate as an efficient nonviral gene vector. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Aptamer-conjugated DNA nano-ring as the carrier of drug molecules
Srivithya, Vellampatti; Roun, Heo; Sekhar Babu, Mitta; Hyung, Park Jae; Ha, Park Sung
2018-03-01
Due to its predictable self-assembly and structural stability, structural DNA nanotechnology is considered one of the main interdisciplinary subjects encompassing conventional nanotechnology and biotechnology. Here we have fabricated the mucin aptamer (MUC1)˗conjugated DNA nano˗ring intercalated with doxorubicin (DNRA˗DOX) as potential therapeutics for breast cancer. DNRA˗DOX exhibited significantly higher cytotoxicity to the MCF˗7 breast cancer cells than the controls, including DOX alone and the aptamer deficient DNA nano˗ring (DNR) with doxorubicin. Interactions between DOX and DNRA were studied using spectrophotometric measurements. Dose-dependent cytotoxicity was performed to prove that both DNR and DNRA were non-toxic to the cells. The drug release profile showed a controlled release of DOX at normal physiological pH 7.4, with approximately 61% released, but when exposed to lysosomal of pH 5.5, the corresponding 95% was released within 48 h. Owing to the presence of the aptamer, DNRA˗DOX was effectively taken up by the cancer cells, as confirmed by confocal microscopy, implying that it has potential for use in targeted drug delivery.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ma P
2015-03-01
located in the cytoplasm. The in vitro cytotoxicity of TMAB-conjugated PAMAM was lower than free PTX due to the slow release of PTX from the conjugate. In vivo targeting further demonstrated that TMAB-conjugated PAMAM accumulated in the BT474 tumor model more efficiently than non-conjugated PAMAM. Conclusion: TMAB can serve as an effective targeting agent, and the TMAB-conjugated PAMAM can be exploited as a potential targeted chemotherapeutic drug delivery system for tumors that overexpress HER2. Keywords: HER2, trastuzumab, PAMAM, active targeting, paclitaxel
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. Cavalli
2011-01-01
Full Text Available A new poly(amidoamine-cholesterol (PAA-cholesterol conjugate was synthesized, characterized and used to produce nanoparticles by the electrospraying technique. The electrospraying is a method of liquid atomization that consists in the dispersion of a solution into small charged droplets by an electric field. Tuning the electrospraying process parameters spherical PAA-chol nanoparticles formed. The PAA-cholesterol nanoparticles showed sizes lower than 500 nm and spherical shape. The drug incorporation capacity was investigated using tamoxifen, a lipophilic anticancer drug, as model drug. The incorporation of the tamoxifen did not affect the shape and sizes of nanoparticles showing a drug loading of 40%. Tamoxifen-loaded nanoparticles exhibited a higher dose-dependent cytotoxicity than free tamoxifen, while blank nanoparticles did not show any cytotoxic effect at the same concentrations. The electrospray technique might be proposed to produce tamoxifen-loaded PAA-chol nanoparticle in powder form without any excipient in a single step.
-
Sun, Minjie; Sun, Bin; Liu, Yun; Shen, Qun-Dong; Jiang, Shaojun
2016-01-01
Rapid growth in biological applications of nanomaterials brings about pressing needs for exploring nanomaterial-cell interactions. Cationic blue-emissive and anionic green-emissive conjugated polymers are applied as dual-color fluorescence probes to the surface of negatively charged magnetic nanoparticles through sequentially electrostatic adsorption. These conjugated polymers have large extinction coefficients and high fluorescence quantum yield (82% for PFN and 62% for ThPFS). Thereby, one can visualize trace amount (2.7 μg/mL) of fluorescence-labeled nanoparticles within cancer cells by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Fluorescence labeling by the conjugated polymers is also validated for quantitative determination of the internalized nanoparticles in each individual cell by flow cytometry analysis. Extensive overlap of blue and green fluorescence signals in the cytoplasm indicates that both conjugated polymer probes tightly bind to the surface of the nanoparticles during cellular internalization. The highly charged and fluorescence-labeled nanoparticles non-specifically bind to the cell membranes, followed by cellular uptake through endocytosis. The nanoparticles form aggregates inside endosomes, which yields a punctuated staining pattern. Cellular internalization of the nanoparticles is dependent on the dosage and time. Uptake efficiency can be enhanced three-fold by application of an external magnetic field. The nanoparticles are low cytotoxicity and suitable for simultaneously noninvasive fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging application. PMID:26931282
-
Aiba, Yuichiro; Honda, Yuta; Komiyama, Makoto
2015-03-02
Pseudo-complementary peptide nucleic acid (pcPNA), as one of the most widely used synthetic DNA analogues, invades double-stranded DNA according to Watson-Crick rules to form invasion complexes. This unique mode of DNA recognition induces structural changes at the invasion site and can be used for a range of applications. In this paper, pcPNA is conjugated with a nuclear localization signal (NLS) peptide, and its invading activity is notably promoted both thermodynamically and kinetically. Thus, the double-duplex invasion complex is formed promptly at low pcPNA concentrations under high salt conditions, where the invasion otherwise never occurs. Furthermore, NLS-modified pcPNA is successfully employed for site-selective DNA scission, and the targeted DNA is selectively cleaved under conditions that are not conducive for DNA cutters using unmodified pcPNAs. This strategy of pcPNA modification is expected to be advantageous and promising for a range of in vitro and in vivo applications. © 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Transport of S-cysteine conjugates in LL-PK1 cells and its role in toxicity
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Schaeffer, V.; Stevens, J.
1986-01-01
In order to study its role in S-cysteine conjugate toxicity, the transport of the nephrotoxic cysteine conjugate, S-1,2-dichlorovinyl-L-cysteine (L-DCVC), was investigated in the kidney cell line, LLC-PK1. When incubated with [ 35 S]-DCVC, accumulation of radioactivity within the cells was linear for at least 5 min with 92% of the 35 S present as unmetabolized L-DCVC. Kinetic analysis indicated two saturable uptake systems; Km = 6.8 μM and 1.6 mM; V/sub max/ = .048 and 1.4 nmol/min/mg protein. Both systems were Na + -independent and were inhibited by amino acid transport system L substrates but not substrates of systems A, ASC or organic anion transport. L-DCVC uptake at 5 μM and 500 μM was significantly greater in subconfluent cells than in confluent cultures by 5 and 2.8 fold, respectively. The presence of the non-toxic conjugates S-methyl-(SMC), S-ethyl-(SEC), S-benzyl-L- cysteine (SBC) and the D isomer of DCVC blocked the toxicity and inhibited the transport of L-DCVC in LLC-PK1 cells in the rank order of SBC > SEC congruent to D-DCVC > SMC. The metabolism of L-DCVC, previously shown to be required for cytotoxicity, was only slightly inhibited by these conjugates and did not correlate with their relative protection against toxicity. This study suggests that L-DCVC is transported into these cells by the system L transporter and that protection against toxicity by non-toxic S-cysteine conjugates is due to the inhibition of transport
-
Bai, Feng; Diao, Jiajing; Wang, Ying; Sun, Shixin; Zhang, Hongmei; Liu, Yunyun; Wang, Yanqing; Cao, Jian
2017-08-16
Curcumin is a dominating active component of Curcuma longa and has been studied widely because of its prominent biological activities. The extremely low aqueous solubility, stability, and bioavailability of curcumin limit its application in the field of medicine. In this study, we developed pectin-curcumin (PEC-CCM) conjugates that could self-assemble water-soluble nanomicelles in aqueous solution. The structure of PEC-CCM conjugates was characterized by ultraviolet-visible spectra, fluorescence spectra, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and 1 H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The thermal property of PEC-CCM conjugates was investigated by thermogravimetric analysis. It was found that PEC-CCM conjugates had formed nanomicelles in aqueous medium via self-assembly. These nanomicelles were observed as small spheres or ellipsoids and aggregated with a size range of 70-190 nm by transmission electron microscopy analysis. In a solution of nanomicelles, the stability of curcumin was improved, and its antioxidant property was preserved. The anticancer activity of PEC-CCM conjugates was quantified by the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] assay using a hepatic cancer cell line (HepG2), a breast cancer cell line (MCF-7), a cervical cancer cell line (HeLa), and a human normal kidney cell line (293A). It was found that the curcumin of PEC-CCM conjugates had a more significant inhibitory effect on cancer cells and was less cytotoxic to normal cells than free curcumin was. PEC-CCM conjugates have great potential for some food and pharmaceutical applications.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Woitok M
2017-07-01
Full Text Available Mira Woitok,1,2 Diana Klose,1 Stefano Di Fiore,1 Wolfgang Richter,3 Christoph Stein,1 Gerrit Gresch,1 Elena Grieger,1 Stefan Barth,1 Rainer Fischer,1,2 Katharina Kolberg,1,* Judith Niesen1,* 1Fraunhofer Institute for Molecular Biology and Applied Ecology (IME, Aachen, Germany; 2Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (Biology VII, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany; 3Tube Pharmaceuticals GmbH, Vienna, Austria *These authors contributed equally to this work Abstract: Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs can deliver toxins to specific targets such as tumor cells. They have shown promise in preclinical/clinical development but feature stoichiometrically undefined chemical linkages, and those based on full-size antibodies achieve only limited tumor penetration. SNAP-tag technology can overcome these challenges by conjugating benzylguanine-modified toxins to single-chain fragment variables (scFvs with 1:1 stoichiometry while preserving antigen binding. Two (human and mouse scFv-SNAP fusion proteins recognizing the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR were expressed in HEK 293T cells. The purified fusion proteins were conjugated to auristatin F (AURIF. Binding activity was confirmed by flow cytometry/immunohistochemistry, and cytotoxic activity was confirmed by cell viability/apoptosis and cell cycle arrest assays, and a novel microtubule dynamics disassembly assay was performed. Both ADCs bound specifically to their target cells in vitro and ex vivo, indicating that the binding activity of the scFv-SNAP fusions was unaffected by conjugation to AURIF. Cytotoxic assays confirmed that the ADCs induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at nanomolar concentrations and microtubule disassembly. The SNAP-tag technology provides a platform for the development of novel ADCs with defined conjugation sites and stoichiometry. We achieved the stable and efficient linkage of AURIF to human or murine scFvs using the SNAP-tag technology, offering a strategy to
-
Well-defined degradable brush polymer-drug conjugates for sustained delivery of Paclitaxel.
Yu, Yun; Chen, Chih-Kuang; Law, Wing-Cheung; Mok, Jorge; Zou, Jiong; Prasad, Paras N; Cheng, Chong
2013-03-04
To achieve a conjugated drug delivery system with high drug loading but minimal long-term side effects, a degradable brush polymer-drug conjugate (BPDC) was synthesized through azide-alkyne click reaction of acetylene-functionalized polylactide (PLA) with azide-functionalized paclitaxel (PTXL) and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). Well-controlled structures of the resulting BPDC and its precursors were verified by (1)H NMR and gel permeation chromatography (GPC) characterizations. With nearly quantitative click efficiency, drug loading amount of the BPDC reached 23.2 wt %. Both dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging indicated that the BPDC had a nanoscopic size around 10-30 nm. The significant hydrolytic degradability of the PLA backbone of the BPDC was confirmed by GPC analysis of its incubated solution. Drug release study showed that PTXL moieties can be released through the cleavage of the hydrolyzable conjugation linkage in pH 7.4 at 37 °C, with 50% release in about 22 h. As illustrated by cytotoxicity study, while the polymeric scaffold of the BPDC is nontoxic, the BPDC exhibited higher therapeutic efficacy toward MCF-7 cancer cells than free PTXL at 0.1 and 1 μg/mL. Using Nile red as encapsulated fluorescence probe, cell uptake study showed effective internalization of the BPDC into the cells.
-
Shinkai, Yasuhiro; Kashihara, Shinichi; Minematsu, Go; Fujii, Hirofumi; Naemura, Madoka; Kotake, Yojiro; Morita, Yasutaka; Ohnuki, Koichiro; Fokina, Alesya A; Stetsenko, Dmitry A; Filichev, Vyacheslav V; Fujii, Masayuki
2017-06-01
Herein we described the synthesis of siRNA-NES (nuclear export signal) peptide conjugates by solid phase fragment coupling and the application of them to silencing of bcr/abl chimeric gene in human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K562. Two types of siRNA-NES conjugates were prepared, and both sense strands at 5' ends were covalently linked to a NES peptide derived from TFIIIA and HIV-1 REV, respectively. Significant enhancement of silencing efficiency was observed for both of them. siRNA-TFIIIA NES conjugate suppressed the expression of BCR/ABL gene to 8.3% at 200 nM and 11.6% at 50 nM, and siRNA-HIV-1REV NES conjugate suppressed to 4.0% at 200 nM and 6.3% at 50 nM, whereas native siRNA suppressed to 36.3% at 200 nM and 30.2% at 50 nM. We could also show complex of siRNA-NES conjugate and designed amphiphilic peptide peptideβ7 could be taken up into cells with no cytotoxicity and showed excellent silencing efficiency. We believe that the complex siRNA-NES conjugate and peptideβ7 is a promising candidate for in vivo use and therapeutic applications.
-
Peng, Xia; Wang, Juan; Li, Xianyang; Lin, Lihui; Xie, Guogang; Cui, Zelin; Li, Jia; Wang, Yuping; Li, Li
2015-12-01
Mast cells and basophils are effector cells in the pathophysiology of allergic diseases. Targeted elimination of these cells may be a promising strategy for the treatment of allergic disorders. Our present study aims at targeted delivery of anti-FcεRIα Fab-conjugated celastrol-loaded micelles toward FcεRIα receptors expressed on mast cells and basophils to have enhanced anti-allergic effect. To achieve this aim, we prepared celastrol-loaded (PEO-block-PPO-block-PEO, Pluronic) polymeric nanomicelles using thin-film hydration method. The anti-FcεRIα Fab Fragment was then conjugated to carboxyl groups on drug-loaded micelles via EDC amidation reaction. The anti-FcεRIα Fab-conjugated celastrol-loaded micelles revealed uniform particle size (93.43 ± 12.93 nm) with high loading percentage (21.2 ± 1.5% w/w). The image of micelles showed oval and rod like. The anti-FcεRIα Fab-conjugated micelles demonstrated enhanced cellular uptake and cytotoxity toward target KU812 cells than non-conjugated micelles in vitro. Furthermore, diffusion of the drug into the cells allowed an efficient induction of cell apoptosis. In mouse model of allergic asthma, treatment with anti-FcεRIα Fab-conjugated micelles increased lung accumulation of micelles, and significantly reduced OVA-sIgE, histamine and Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, TNF-α) levels, eosinophils infiltration and mucus production. In addition, in mouse model of passive cutaneous anaphylaxis, anti-FcεRIα Fab-conjugated celastrol-loaded micelles treatment significantly decreased extravasated evan's in the ear. These results indicate that anti-FcεRIα Fab-conjugated celastrol-loaded micelles can target and selectively kill mast cells and basophils which express FcεRIα, and may be efficient reagents for the treatment of allergic disorders and mast cell related diseases.
-
Tian, Baomin; Wong, Wah Yau; Hegmann, Elda; Gaspar, Kim; Kumar, Praveen; Chao, Heman
2015-06-17
A novel immunoconjugate (L-DOS47) was developed and characterized as a therapeutic agent for tumors expressing CEACAM6. The single domain antibody AFAIKL2, which targets CEACAM6, was expressed in the Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) pT7-7 system. High purity urease (HPU) was extracted and purified from Jack bean meal. AFAIKL2 was activated using N-succinimidyl [4-iodoacetyl] aminobenzoate (SIAB) as the cross-linker and then conjugated to urease. The activation and conjugation reactions were controlled by altering pH. Under these conditions, the material ratio achieved conjugation ratios of 8-11 antibodies per urease molecule, the residual free urease content was practically negligible (95%) L-DOS47 conjugate was produced using only ultradiafiltration to remove unreacted antibody and hydrolyzed cross-linker. L-DOS47 was characterized by a panel of analytical techniques including SEC, IEC, Western blot, ELISA, and LC-MS(E) peptide mapping. As the antibody-urease conjugate ratio increased, a higher binding signal was observed. The specificity and cytotoxicity of L-DOS47 was confirmed by screening in four cell lines (BxPC-3, A549, MCF7, and CEACAM6-transfected H23). BxPC-3, a CEACAM6-expressing cell line was found to be most susceptible to L-DOS47. L-DOS47 is being investigated as a potential therapeutic agent in human phase I clinical studies for nonsmall cell lung cancer.
-
Derakhshi, Maryam; Ashkarran, Ali Akbar; Bahari, Ali; Bonakdar, Shahin
2018-07-01
Graphene-based nanomaterials contain unique physicochemical properties and have been widely investigated due to a variety of applications particularly in cancer therapy. Furthermore, Ag has been known for its extensive historical background for biomedical applications. Therefore, conjugation of shape-selective Ag nanostructures with graphene may provide new horizons for pharmaceutical applications such as cancer treatments. Here we report on the synthesis of Ag nanoparticles (NPs)/reduced graphene oxide (AgNPs/RGO) conjugate nanomaterials containing various shapes of AgNPs by a novel and simple synthesis route using the deformation of dimethylformamide (DMF) as the reducing and coupling agent. The cytotoxicity and anticancer properties of AgNPs, AgNPs/RGO conjugate nanomaterials, RGO and graphene oxide (GO) were probed against MDA-MB-231 cancer and MCF-10A normal human breast cells in vitro. The AgNPs/RGO nanocomposites exhibited a strong anticancer effect by penetration and apoptosis in cancer cells as well as the lowest influence on the viability of normal cells. It was found that cancer cell viability not only depends on the geometry of Ag nanostructures but also on the interaction between AgNPs and RGO nanoplatelets. It is suggested that AgNPs/RGO conjugate nanomaterials with various shapes of AgNPs is a promising therapeutic platform for cancer therapy.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Igor V. Alabugin
2011-06-01
Full Text Available Hybrid molecules combining photoactivated aryl acetylenes and a dicationic lysine moiety cause the most efficient double-strand (ds DNA cleavage known to date for a small molecule. In order to test the connection between the alkylating ability and the DNA-damaging properties of these compounds, we investigated the photoreactivity of three isomeric aryl–tetrafluoropyridinyl (TFP alkynes with amide substituents in different positions (o-, m-, and p- toward a model π-system. Reactions with 1,4-cyclohexadiene (1,4-CHD were used to probe the alkylating properties of the triplet excited states in these three isomers whilst Stern–Volmer quenching experiments were used to investigate the kinetics of photoinduced electron transfer (PET. The three analogous isomeric lysine conjugates cleaved DNA with different efficiencies (34, 15, and 0% of ds DNA cleavage for p-, m-, and o-substituted lysine conjugates, respectively consistent with the alkylating ability of the respective acetamides. The significant protecting effect of the hydroxyl radical and singlet oxygen scavengers to DNA cleavage was shown only with m-lysine conjugate. All three isomeric lysine conjugates inhibited human melanoma cell growth under photoactivation: The p-conjugate had the lowest CC50 (50% cell cytotoxicity value of 1.49 × 10−7 M.
-
Conjugation-promoted reaction of open-cage fullerene: A density functional theory study
Guo, Yong
2012-01-20
Density functional theory calculations are performed to study the addition mechanism of e-rich moieties such as triethyl phosphite to a carbonyl group on the rim of a fullerene orifice. Three possible reaction channels have been investigated. The obtained results show that the reaction of a carbonyl group on a fullerene orifice with triethyl phosphite most likely proceeds along the classical Abramov reaction; however, the classical product is not stable and is converted into the experimental product. An attack on a fullerene carbonyl carbon will trigger a rearrangement of the phosphate group to the carbonyl oxygen as the conversion transition state is stabilized by fullerene conjugation. This work provides a new insight on the reactivity of open-cage fullerenes, which may prove helpful in designing new switchable fullerene systems. Not that classical: The reaction of a carbonyl group on the fullerene orifice with triethyl phosphite most likely proceeds following the Abramov reaction to firstly form a classical product. However, this product is not stable and turns into an experimental product as the conversion transition state is stabilized by fullerene conjugation (see picture). Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Gasparro, F P; Knobler, R M; Yemul, S S; Bisaccia, E; Edelson, R L
1986-12-15
4'-Aminomethyl-4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen has been chemically conjugated to insulin using a carbodiimide derivative. The psoralen moiety retains its photochemical reactivity as evidenced by its ability to crosslink DNA after exposure to long wavelength ultraviolet light (UVA, 320-400 nm). This chimeric molecule has been used to selectively kill a population of lymphocytes whose expression of insulin receptors has been stimulated with phytohemagglutinin. Insulin carries the psoralen into the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis, where it is subsequently activated by exposure to UVA light. The UVA induced activity of AMT-insulin can be blocked by the presence of native insulin. The viability of unstimulated lymphocytes was not affected by AMT-insulin and UVA light. The hybrid insulin-psoralen molecule may be a prototype for a family of phototoxic drugs which can be selectively delivered to subsets of lymphocytes.
-
Efficient payload delivery by a bispecific antibody-drug conjugate targeting HER2 and CD63
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
de Goeij, Bart E.C.G.; Vink, Tom; Ten Napel, Hendrik
2016-01-01
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) are designed to be stable in circulation and to release potent cytotoxic drugs intracellularly following antigen-specific binding, uptake, and degradation in tumor cells. Efficient internalization and routing to lysosomes where proteolysis can take place is therefore......, for the first time, that intracellular trafficking of ADCs can be improved using a bsAb approach that targets the lysosomal membrane protein CD63 and provide a rationale for the development of novel bsADCs that combine tumor-specific targeting with targeting of rapidly internalizing antigens. © 2016 American...
-
Lu, Y P; Li, Z S; Rea, P A
1997-07-22
Because plants produce cytotoxic compounds to which they, themselves, are susceptible and are exposed to exogenous toxins (microbial products, allelochemicals, and agrochemicals), cell survival is contingent on mechanisms for detoxifying these agents. One detoxification mechanism is the glutathione S-transferase-catalyzed glutathionation of the toxin, or an activated derivative, and transport of the conjugate out of the cytosol. We show here that a transporter responsible for the removal of glutathione S-conjugates from the cytosol, a specific Mg2+-ATPase, is encoded by the AtMRP1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana. The sequence of AtMRP1 and the transport capabilities of membranes prepared from yeast cells transformed with plasmid-borne AtMRP1 demonstrate that this gene encodes an ATP-binding cassette transporter competent in the transport of glutathione S-conjugates of xenobiotics and endogenous substances, including herbicides and anthocyanins.
-
Lipid conjugated prodrugs for enzyme-triggered liposomal drug delivery to tumors
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Clausen, Mads Hartvig
2011-01-01
For some time we have been developing novel enzyme-triggered prodrugs for drug delivery targeting cancer. The liposomal prodrugs take advantage of the EPR effect to localize to tumors and of the local over-expression of secretory phospholipase A2 in tumors. Compared to conventional liposomal drug...... delivery systems, our prodrug-lipid conjugates have two main advantages: 1) the drugs are covalently linked to the lipids and thus leakage is circumvented and 2) the lipophilic bilayer of the formulated liposomes effectively shields the drugs from the aqueous environment in vivo. Consequently, the strategy...... targeting nuclear receptors and structural proteins. The presentation will highlight various strategies and recent progress towards improved systems, including chemical synthesis, enzyme activity and cytotoxicity....
-
Cheewatanakornkool, Kamonrak; Niratisai, Sathit; Dass, Crispin R; Sriamornsak, Pornsak
2018-07-10
The objective of this study was to investigate the in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo anticancer efficacy of redox-responsive microbeads containing thiolated pectin-doxorubicin (DOX) conjugate. Oral microbeads were coated with an enteric polymer to protect the drug from release in the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract and allow redox-triggered drug release in the colon. Morphology, particle size, drug content, and in vitro drug release behavior of the microbeads were characterized; in vitro cytotoxicity was tested on mouse colon carcinoma, human colorectal adenocarcinoma, and human bone osteosarcoma cell lines. In vivo anticancer efficacy of coated microbeads was examined in BALB/c mice with murine colon carcinoma. These coated microbeads significantly inhibited the growth of all cell lines. The in vivo study confirmed delivery of DOX to the colorectal tumor site, redox-responsiveness, and anticancer efficacy of coated microbeads. Coated microbeads also effectively inhibited primary tumor growth and suppressed tumor metastases without gross toxicity to the non-target tissue. No noticeable damage was found in mouse GI tissues, indicating lack of DOX toxicity. These novel coated microbeads containing thiolated pectin-DOX conjugate may be a promising vehicle for targeted clinical delivery of DOX to the colorectal cancer site by oral administration. Crown Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Taheri, Azade; Dinarvand, Rassoul; Atyabi, Fatemeh; Ahadi, Fatemeh; Nouri, Farank Salman; Ghahremani, Mohammad Hossein; Ostad, Seyed Nasser; Borougeni, Atefeh Taheri; Mansoori, Pooria
2011-01-01
Active targeting could increase the efficacy of anticancer drugs. Methotrexate-human serum albumin (MTX-HSA) conjugates, functionalized by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) as targeting moieties, with the aim of specifically targeting the cancer cells, were prepared. Owing to the high expression of LHRH receptors in many cancer cells as compared to normal cells, LHRH was used as the targeting ligand in this study. LHRH was conjugated to MTX-HSA nanoparticles via a cross-linker. Three types of LHRH targeted nanoparticles with a mean particle size between 120–138 nm were prepared. The cytotoxicity of LHRH targeted and non-targeted nanoparticles were determined on the LHRH positive and negative cell lines. The internalization of the targeted and non-targeted nanoparticles in LHRH receptor positive and negative cells was investigated using flow cytometry analysis and fluorescence microscopy. The cytotoxicity of the LHRH targeted nanoparticles on the LHRH receptor positive cells were significantly more than non-targeted nanoparticles. LHRH targeted nanoparticles were also internalized by LHRH receptor positive cells significantly more than non-targeted nanoparticles. There were no significant differences between the uptake of targeted and non-targeted nanoparticles to the LHRH receptor negative cells. The active targeting procedure using LHRH targeted MTX-HSA nanoparticles could increase the anti-tumoral activity of MTX. PMID:21845098
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Silva Junior, Eufranio N. da [Universidade Federal Fluminense (UFF), Niteroi , RJ (Brazil). Inst. de Quimica. Dept. de Quimica Organica; Moura, Maria Aline B. F. de [Universidade Federal de Alagoas (UFAL), Maceio, AL (Brazil). Inst. de Quimica e Biotecnologia; Pinto, Antonio V. [Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ), Rio de Janeiro, RJ (Brazil). Nucleo de Pesquisas de Produtos Naturais] (and others)
2009-07-01
The cytotoxicities of five nor-{beta}-lapachone-based 1,2,3-triazoles and the precursor azidonaphthoquinone were assayed against six neoplasic cancer cell lines: SF-295 (central nervous system), HCT-8 (colon), MDAMB-435 (melanoma), HL-60 (leukaemia), PC-3 (prostate) and B-16 (murine melanoma). IC{sub 50} values ranging from 0.43 to 9.48 {mu}M were obtained. 3-(4-(1-hydroxycyclohexyl)-{sup 1}H-1,2,3-triazol-1- yl)-2,2-dimethylnaphtho[1,2-b]furan-4,5-dione proved highly cytotoxic to MDAMB-435, with IC{sub 50} even lower than the one from doxorubicin (positive control). In an attempt to correlate physicochemical parameters (reduction potentials and calculated log P) with cytotoxic activity, electrochemical studies were conducted in acetate buffer, pH 4.5, using a vitreous carbon electrode and calculated log P values were obtained. Despite the absence of a structural conjugative interaction between the two systems (quinone and triazole), the heterocyclic group was found to influence the voltammetric behaviour, as indicated by anodic shifts in the reduction potentials. No correlation was found between Ep{sub Ic} and cytotoxicity. In contrast, a comparison of Ep{sub Ic} with previously reported trypanocidal activities reconfirmed the trend for higher activity coupled with better quinone electrophilicity (> Ep{sub Ic}). A leading term in the correlation of cytoxicity, despite the absence of a linear correlation, was the calculated log P: the lower the lipophilicity, the lower the cytoxicity (> IC{sub 50}). (author)
-
2012-01-01
antibody conjugation to HA The conjugation chemistry followed a method previously developed in our laboratory. Briefly, HA (12 mg) was modi - fied...Webster MW, McGill JB, Schwartz SL. Promotion and acceleration of diabetic ulcer healing by arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) peptide matrix. RGD...Study Group. Diabetes Care 1995; 18: 39–46. 32. Ho-Asjoe M, Chronnell CM, Frame JD, Leigh IM, Carver N. Immunohistochemical analysis of burn depth. J
-
Comparison of para-aminophenol cytotoxicity in rat renal epithelial cells and hepatocytes.
Li, Ying; Bentzley, Catherine M; Tarloff, Joan B
2005-04-01
Several chemicals, including para-aminophenol (PAP), produce kidney damage in the absence of hepatic damage. Selective nephrotoxicity may be related to the ability of the kidney to reabsorb filtered water, thereby raising the intraluminal concentration of toxicants and exposing tubular epithelial cells to higher concentrations than would be present in other tissues. The present experiments tested the hypothesis that hepatocytes and renal epithelial cells exposed to equivalent concentrations of PAP would be equally susceptible to toxicity. Hepatocytes and renal epithelial cells were prepared by collagenase digestion of tissues obtained from female Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicity was monitored using trypan blue exclusion, oxygen consumption and ATP content. We measured the rate of PAP clearance and formation of PAP-glutathione conjugate by HPLC. We found that renal epithelial cells accumulated trypan blue and showed declines in oxygen consumption and ATP content at significantly lower concentrations of PAP and at earlier time points than hepatocytes. The half-life of PAP in hepatocyte incubations was significantly shorter (0.71+/-0.07 h) than in renal epithelial cell incubations (1.33+/-0.23 h), suggesting that renal epithelial cells were exposed to PAP for longer time periods than hepatocytes. Renal epithelial cells formed significantly less glutathione conjugates of PAP (PAP-SG) than did hepatocytes, consistent with less efficient detoxification of reactive PAP intermediates by renal epithelial cells. Finally, hepatocytes contained significant more reduced glutathione (NPSH) than did renal epithelial cells, possibly explaining the enhanced formation of PAP-SG by this cell population. In conclusion, our data indicates that renal epithelial cells are intrinsically more susceptible to PAP cytotoxicity than are hepatocytes. This enhanced cytotoxicity may be due to longer exposure to PAP and/or reduced detoxification of reactive intermediates due to lower concentrations
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Elena De Gianni
2015-02-01
Full Text Available One important strategy to develop effective anticancer agents is based on natural products. Many active phytochemicals are in human clinical trials and have been used for a long time, alone and in association with conventional anticancer drugs, for the treatment of various types of cancers. A great number of in vitro, in vivo and clinical reports document the multi-target anticancer activities of isothiocyanates and of compounds characterized by a naphthalenetetracarboxylic diimide scaffold. In order to search for new anticancer agents with a better pharmaco-toxicological profile, we investigated hybrid compounds obtained by inserting isothiocyanate group(s on a naphthalenetetracarboxylic diimide scaffold. Moreover, since water-soluble fullerene derivatives can cross cell membranes thus favoring the delivery of anticancer therapeutics, we explored the cytostatic and cytotoxic activity of hybrid compounds conjugated with fullerene. We studied their cytostatic and cytotoxic effects on a human T-lymphoblastoid cell line by using different flow cytometric assays. In order to better understand their pharmaco-toxicological potential, we also analyzed their genotoxicity. Our global results show that the synthesized compounds reduced significantly the viability of leukemia cells. However, the conjugation with a non-toxic vector did not increase their anticancer potential. This opens an interesting research pattern for certain fullerene properties.
-
Pramod, P. S.; Shah, Ruchira; Jayakannan, Manickam
2015-04-01
The present work reports the development of pH and enzyme dual responsive polysaccharide vesicular nano-scaffolds for the administration of doxorubicin via physical loading and polymer-drug conjugation to breast cancer cells. Dextran was suitably modified with a renewable resource 3-pentadecyl phenol unit through imine and aliphatic ester chemical linkages that acted as pH and esterase enzyme stimuli, respectively. These dual responsive polysaccharide derivatives self-organized into 200 +/- 10 nm diameter nano-vesicles in water. The water soluble anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX.HCl) was encapsulated in the hydrophilic pocket to produce core-loaded polysaccharide vesicles whereas chemical conjugation produced DOX anchored at the hydrophobic layer of the dextran nano-vesicles. In vitro studies revealed that about 70-80% of the drug was retained under circulatory conditions at pH = 7.4 and 37 °C. At a low pH of 6.0 to 5.0 and in the presence of esterase; both imine and ester linkages were cleaved instantaneously to release 100% of the loaded drugs. Cytotoxicity assays on Wild Type Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (WTMEFs) confirmed the non-toxicity of the newly developed dextran derivatives at up to 500 μg mL-1 in PBS. MTT assays on fibroblast cells revealed that DOX.HCl loaded nano-vesicles exhibited better killing abilities than DOX conjugated polymer nano-vesicles. Both DOX loaded and DOX conjugated nano-vesicles were found to show significant killing in breast cancer cells (MCF 7). Confocal microscopy images confirmed the uptake of DOX loaded (or conjugated) nano-vesicles by cells compared to free DOX. Thus, the newly developed pH and enzyme dual responsive polysaccharide vesicular assemblies are potential drug vectors for the administration of DOX in both loaded and chemically conjugated forms for the efficient killing of breast cancer cells.The present work reports the development of pH and enzyme dual responsive polysaccharide vesicular nano-scaffolds for the
-
Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of TiO2/conjugated polymer complex nanoparticles
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
Shi Xiong Min; Fang Wang; Lei Feng; Yong Chun Tong; Zi Rong Yang
2008-01-01
A photocatalyst of nanometer TiO2/conjugated polymer complex was successfully synthesized and characterized by spectroscopic methods and photocatalytic experiments. The complex photocatalyst could be activated by absorbing both ultraviolet and visible light (λ=190-800nm). Methylene blue (MB) could be degraded more efficiently on the complex photocatalyst than on the TiO2 under natural light. The conjugated polymer played a promoting role in the photocatalytic degradation of MB. The calcination temperature had an important effect in degradation of dye and could be summarized as 260℃>300℃>340℃>220℃>180℃.
-
Lucarini, Simone; Fagioli, Laura; Campana, Raffaella; Cole, Hannah; Duranti, Andrea; Baffone, Wally; Vllasaliu, Driton; Casettari, Luca
2016-10-01
Sugar based surfactants conjugated with fatty acid chains are an emerging broad group of highly biocompatible and biodegradable compounds with established and potential future applications in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries. In this work, we investigated absorption enhancing and antimicrobial properties of disaccharide lactose, monoesterified with unsaturated fatty acids through an enzymatic synthetic approach. After chemical and cytotoxicity characterizations, their permeability enhancing activity was demonstrated using intestinal Caco-2 monolayers through transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and permeability studies. The synthesized compounds, namely lactose palmitoleate (URB1076) and lactose nervonate (URB1077), were shown to exhibit antimicrobial activity versus eight pathogenic species belonging to Gram-positive, Gram-negative microorganisms and fungi. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
The target invites a foe: antibody-drug conjugates in gynecologic oncology.
Campos, Maira P; Konecny, Gottfried E
2018-02-01
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) represent a promising new class of cancer therapeutics. Currently more than 60 ADCs are in clinical development, however, only very few trials focus on gynecologic malignancies. In this review, we summarize the most recent advances in ADC drug development with an emphasis on how this progress relates to patients diagnosed with gynecologic malignancies and breast cancer. The cytotoxic payloads of the majority of the ADCs that are currently in clinical trials for gynecologic malignancies or breast cancer are auristatins (MMAE, MMAF), maytansinoids (DM1, DM4), calicheamicin, pyrrolobenzodiazepines and SN-38. Both cleavable and noncleavable linkers are currently being investigated in clinical trials. A number of novel target antigens are currently being validated in ongoing clinical trials including folate receptor alpha, mesothelin, CA-125, NaPi2b, NOTCH3, protein tyrosine kinase-like 7, ephrin-A4, TROP2, CEACAM5, and LAMP1. For most ADCs currently in clinical development, dose-limiting toxicities appear to be unrelated to the targeted antigen but more tightly associated with the payload. Rational drug design involving optimization of the antibody, the linker and the conjugation chemistry is aimed at improving the therapeutic index of new ADCs. Antibody-drug conjugates can increase the efficacy and decrease the toxicity of their payloads in comparison with traditional cyctotoxic agents. A better and quicker translation of recent scientific advances in the field of ADCs into rational clinical trials for patients diagnosed with ovarian, endometrial or cervical cancer could create real improvements in tumor response, survival and quality of life for our patients.
-
de Lima, Ewelyne Miranda; Cazelli, Didley Sâmia Paiva; Pinto, Fernanda Endringer; Mazuco, Renata Alves; Kalil, Ieda Carneiro; Lenz, Dominik; Scherer, Rodrigo; de Andrade, Tadeu Uggere; Endringer, Denise Coutinho
2016-01-01
Protium heptaphyllum (Aubl.) March is popularly used as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent. This study aimed to evaluate the chemical composition of P. heptaphyllum essential oil, its cytotoxicity in a breast cancer cell line (MCF-7), antimicrobial activity, and its antimutagenicity in vivo. The chemical composition of the essential oil collected in three 3 years was determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The cytotoxicity was evaluated using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Annexin V conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate, caspase-3, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) assays were performed to evaluate apoptosis and inflammatory events. The antimutagenic activity at doses of 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg was determined using a micronucleus test in murine bone marrow. The essential oil showed a predominance of monoterpene compounds, being the terpinolene, p-cymene-8-ol, and p-cymene, present in the essential oil extracted in the 3 years. The essential oil showed a protection against cyclophosphamide-induced genotoxicity, and the cytotoxicity index polychromatic erythrocytes/normochromatic erythrocytes ratio in animals treated with oil at all doses (1.34 ± 0.33; 1.15 ± 0.1; 1.11 ± 0.13) did not differ from the negative control animal (1.31 ± 0.33), but from the cyclophosphamide group (0.61 ± 0.12). Cytotoxicity, at a concentration of 40.0 μg/mL, and antimicrobial activity were not observed for the essential oil (minimum inhibitory concentration ≥0.5 mg/mL). The essential oil did not change the levels of caspase-3 in the TNF-α level. The essential oil showed antimutagenic activity due to its chemical composition. Terpinolene, p-cymene-8-ol, and p-cymene are the main constituents of the essential oil of P. heptaphyllum collected within 3-yearsThe essential oil of P. heptaphyllum did not show antimicrobial activity (MIC >0.5 mg/mL) against E. coli, S. aureus, E. faecalis, and C. albicansThe essential oil
-
Asakura, Tadashi; Yokoyama, Masayuki; Shiraishi, Koichi; Aoki, Katsuhiko; Ohkawa, Kiyoshi
2018-03-01
CD147 (basigin/emmprin) is expressed on the surface of carcinoma cells. For studying the efficacy of CD147-targeting medicine on CD147-expressing cells, we studied the effect of anti-CD147-labeled polymeric micelles (CD147ab micelles) that encapsulated a conjugate of doxorubicin with glutathione (GSH-DXR), with specific accumulation and cytotoxicity against CD147-expressing A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells, Ishikawa human endometrial adenocarcinoma cells, and PC3 human prostate carcinoma cells. By treatment of each cell type with CD147ab micelles for 1 h, a specific accumulation of CD147ab micelles in CD147-expressing cells was observed. In addition, the cytotoxicity of GSH-DXR-encapsulated micelles against each cell type was measured by treatment of the micelles for 1 h. The cytotoxic effect of CD147ab micelles carrying GSH-DXR was 3- to 10-fold higher for these cells than that of micelles without GSH-DXR. These results suggest that GSH-DXR-encapsulated CD147ab micelles could serve as an effective drug delivery system to CD147-expressing carcinoma cells. Copyright© 2018, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
-
Intratumoral delivery of CpG-conjugated anti-MUC1 antibody enhances NK cell anti-tumor activity.
Schettini, Jorge; Kidiyoor, Amritha; Besmer, Dahlia M; Tinder, Teresa L; Roy, Lopamudra Das; Lustgarten, Joseph; Gendler, Sandra J; Mukherjee, Pinku
2012-11-01
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against tumor-associated antigens are useful anticancer agents. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) is one of the major mechanisms responsible for initiating natural killer cell (NK)-mediated killing of tumors. However, the regulation of ADCC via NK cells is poorly understood. We have investigated the cytolytic activity of NK cells against pancreatic cancer cells that were coated with an antibody directed against the human tumor antigen, Mucin-1 designated HMFG-2, either alone or conjugated to CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG ODN). Conjugated antibodies were tested for their ability to elicit ADCC in vitro and in vivo against pancreatic cancer cells. NK cells cultured in the presence of immobilized CpG ODN, HMFG-2 Ab, or CpG ODN-conjugated HMFG-2 Ab were able to up-regulate perforin similarly. Interestingly, a significant higher ADCC was observed when CpG ODN-conjugated HMFG-2-coated tumor cells were co-cultured with NK cells compared to unconjugated HMFG-2 Ab or CpG ODN alone. Moreover, MyD88-deficient NK cells can perform ADCC in vitro. Furthermore, intratumoral injections of CpG ODN-conjugated HMFG-2 induced a significant reduction in tumor burden in vivo in an established model of pancreatic tumor in nude mice compared to CpG ODN or the HMFG-2 alone. Depletion of macrophages or NK cells before treatment confirmed that both cells were required for the anti-tumor response in vivo. Results also suggest that CpG ODN and HMFG-2 Ab could be sensed by NK cells on the mAb-coated tumor cells triggering enhanced ADCC in vitro and in vivo.
-
Cui, Lina
2012-09-26
New conjugation chemistry for polysaccharides, exemplified by dextran, was developed to enable the attachment of therapeutic or other functional moieties to the polysaccharide through cleavable acetal linkages. The acid-lability of the acetal groups allows the release of therapeutics under acidic conditions, such as that of the endocytic compartments of cells, regenerating the original free polysaccharide in the end. The physical and chemical behavior of these acetal groups can be adjusted by modifying their stereoelectronic and steric properties, thereby providing materials with tunable degradation and release rates. We have applied this conjugation chemistry in the development of water-soluble siRNA carriers, namely acetal-linked amino-dextrans, with various amine structures attached through either slow- or fast-degrading acetal linker. The carriers with the best combination of amine moieties and structural composition of acetals showed high in vitro transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity in the delivery of siRNA. © 2012 American Chemical Society.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hadley, S.W.; Wilbur, D.S.
1990-01-01
The preparations and conjugations of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorophenyl 5-[125I/131I]iodo-4-pentenoate (7a) and 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorophenyl 3,3-dimethyl-5-[125I/131I]iodo-4-pentenoate (7b) to monoclonal antibodies are reported. Reagents 7a and 7b were prepared in high radiochemical yield by iododestannylation of their corresponding 5-tri-n-butylstannyl precursors. Radioiodinated antibody conjugates were prepared by reaction of 7a or 7b with the protein at basic pH. Evaluation of these conjugates by several in vitro procedures demonstrated that the radiolabel was attached to the antibody in a stable manner and that the conjugates maintained immunoreactivity. Comparative dual-isotope biodistribution studies of a monoclonal antibody Fab fragment conjugate of 7a and 7b with the same Fab fragment labeled with N-succinimidyl p-[131I]iodobenzoate (PIB, p-iodobenzoate, 2) or directly radioiodinated have been carried out in tumor-bearing nude mice. Coinjection of the Fab conjugate of 7a with the Fab conjugate of 2 demonstrated that the biodistributions were similar in most organs, except the neck tissue (thyroid-containing) and the stomach, which contained substantially increased levels of the 7a label. Coinjection of the Fab conjugate of 7a with the Fab fragment radioiodinated by using the chloramine-T method demonstrated that the biodistributions were remarkably similar, suggesting roughly equivalent in vivo deiodination of these labeled antibody fragments. Coinjection of the Fab conjugate of 7a with the Fab conjugate of 7b indicated that there was ∼ a 2-fold reduction in the amount of in vivo deiodination of the 7b conjugate as compared to the 7a conjugate
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jian YS
2017-03-01
Full Text Available You-Sin Jian,1 Ching-Wen Chen,1 Chih-An Lin,2 Hsiu-Ping Yu,1 Hua-Yang Lin,3 Ming-Yuan Liao,1 Shu-Huan Wu,1 Yan-Fu Lin,1 Ping-Shan Lai1,2,4,5 1Department of Chemistry, 2PhD Program in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, 3Preclinical Development Research Department, Holy Stone Healthcare Co., Ltd., Taipei, 4Research Center for Sustainable Energy and Nanotechnology, 5Rong Hsing Research Center for Translational Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan Abstract: Carrier-mediated drug delivery systems are promising therapeutics for targeted delivery and improved efficacy and safety of potent cytotoxic drugs. Nimesulide is a multifactorial cyclooxygenase 2 nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug with analgesic, antipyretic and potent anticancer properties; however, the low solubility of nimesulide limits its applications. Drugs conjugated with hyaluronic acid (HA are innovative carrier-mediated drug delivery systems characterized by CD44-mediated endocytosis of HA and intracellular drug release. In this study, hydrophobic nimesulide was conjugated to HA of two different molecular weights (360 kDa as HA with high molecular weight [HAH] and 43kDa as HA with low molecular weight [HAL] to improve its tumor-targeting ability and hydrophilicity. Our results showed that hydrogenated nimesulide (N-[4-amino-2-phenoxyphenyl]methanesulfonamide was successfully conjugated with both HA types by carbodiimide coupling and the degree of substitution of nimesulide was 1%, which was characterized by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance 400 MHz and total correlation spectroscopy. Both Alexa Fluor® 647 labeled HAH and HAL could selectively accumulate in CD44-overexpressing HT-29 colorectal tumor area in vivo, as observed by in vivo imaging system. In the in vitro cytotoxic test, HA–nimesulide conjugate displayed >46% cell killing ability at a nimesulide concentration of 400 µM in HT-29 cells, whereas
-
Yang, Conglian; Wu, Tingting; Qin, Yuting; Qi, Yan; Sun, Yu; Kong, Miao; Jiang, Xue; Qin, Xianya; Shen, Yaqi; Zhang, Zhiping
2018-01-01
Doxorubicin (DOX) is an effective chemotherapeutic agent but severe side effects limit its clinical application. Nanoformulations can reduce the toxicity while still have various limitations, such as complexity, low drug loading capability and excipient related concerns. An amphiphilic conjugate, doxorubicin-dichloroacetate, was synthesized and the corresponding nanoparticles were prepared. The in vitro cytotoxicity and intracellular uptake, in vivo imaging, antitumor effects and systemic toxicities of nanoparticles were carried out to evaluate the therapeutic efficiency of tumor. Doxorubicin-dichloroacetate conjugate can self-assemble into nanoparticles with small amount of DSPE-PEG 2000 , leading to high drug loading (71.8%, w/w) and diminished excipient associated concerns. The nanoparticles exhibited invisible systemic toxicity and high maximum tolerated dose of 75 mg DOX equiv./kg, which was 15-fold higher than that of free DOX. It also showed good tumor targeting capability and enhanced antitumor efficacy in murine melanoma model. This work provides a promising strategy to simplify the drug preparation process, increase drug loading content, reduce systemic toxicity as well as enhance antitumor efficiency.
-
Boro, Robin C; Singh, K Vikas; Suri, C Raman
2009-01-01
The generation of specific and sensitive antibodies against small molecules is greatly dependent upon the characteristics of the hapten-protein conjugates. In this study, we report a new fluorescence-based method for the characterization of hapten-protein conjugates. The method is based on an effect promoted by hapten-protein conjugation density upon the fluorescence intensity of the intrinsic tryptophan chromophore molecules of the protein. The proposed methodology is applied to quantify the hapten-protein conjugation density for two different chlorophenoxyacetic acid pesticides, 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and 2,4-dichlorophenoxybutyric acid (2,4-DB), coupled to carrier protein. Highly sensitive anti-2,4-D and anti-2,4-DB antibodies were obtained using these well-characterized hapten-protein conjugates. The generated antibodies were used in an immunoassay format demonstrating inhibitory concentration (IC50) values equal to 30 and 7 ng/mL for 2,4-D and 2,4-DB, respectively. Linearity was observed in the concentration range between 0.1-500 nglmL with LODs around 4 and 3 ng/mL for 2,4-D and 2,4-DB, respectively, in standard water samples. The proposed method was successfully applied for the determination of the extent of hapten-protein conjugation to produce specific antibodies for immunoassay development against pesticides.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nair, Baiju G.; Fukuda, Takahiro; Mizuki, Toru; Hanajiri, Tatsuro; Maekawa, Toru
2012-01-01
Highlights: ► We study the intracellular localisation of TAT-SPIONs using 3-D electron tomography. ► 3-D images of TAT-SPIONs in a cell are clearly shown. ► Release of TAT-SPIONs from endocytic vesicles into the cytoplasm is clearly shown. -- Abstract: Internalisation of nanoparticles conjugated with cell penetrating peptides is a promising approach to various drug delivery applications. Cell penetrating peptides such as transactivating transcriptional activator (TAT) peptides derived from HIV-1 proteins are effective intracellular delivery vectors for a wide range of nanoparticles and pharmaceutical agents thanks to their amicable ability to enter cells and minimum cytotoxicity. Although different mechanisms of intracellular uptake and localisation have been proposed for TAT conjugated nanoparticles, it is necessary to visualise the particles on a 3-D plane in order to investigate the actual intracellular uptake and localisation. Here, we study the intracellular localisation and trafficking of TAT peptide conjugated superparamagnetic ion oxide nanoparticles (TAT-SPIONs) using 3-D electron tomography. 3-D tomograms clearly show the location of TAT-SPIONs in a cell and their slow release from the endocytic vesicles into the cytoplasm. The present methodology may well be utilised for further investigations of the behaviours of nanoparticles in cells and eventually for the development of nano drug delivery systems.
-
Short-chain analogs of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone containing cytotoxic moieties.
Janáky, T; Juhász, A; Rékási, Z; Serfözö, P; Pinski, J; Bokser, L; Srkalovic, G; Milovanovic, S; Redding, T W; Halmos, G
1992-11-01
Five hexapeptide and heptapeptide analogs of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH) were synthesized for use as carriers for cytotoxic compounds. These short analogs were expected to enhance target selectivity of the antineoplastic agents linked to them. Native LH-RH-(3-9) and LH-RH-(4-9) containing D-lysine and D-ornithine at position 6 were amidated with ethylamine and acylated on the N terminus. The receptor-binding affinity of one hexapeptide carrier AJ-41 (Ac-Ser-Tyr-D-Lys-Leu-Arg-Pro-NH-Et) to human breast cancer cell membranes was similar to that of [D-Trp6]LH-RH. Alkylating nitrogen mustards (melphalan, Ac-melphalan), anthraquinone derivatives including anticancer antibiotic doxorubicin, antimetabolite (methotrexate), and cisplatin-like platinum complex were linked to these peptides through their omega-amino group at position 6. The hybrid molecules showed no LH-RH agonistic activity in vitro and in vivo but had nontypical antagonistic effects on pituitary cells in vitro at the doses tested. These analogs showed a wide range of receptor-binding affinities to rat pituitaries and cell membranes of human breast cancer and rat Dunning prostate cancer. Several of these conjugates exerted some cytotoxic effects on MCF-7 breast cancer cell line.
-
Amino Acid Conjugated Anthraquinones from the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO sof101.
Luo, Minghe; Cui, Zhaomeng; Huang, Hongbo; Song, Xianqin; Sun, Aijun; Dang, Yongjun; Lu, Laichun; Ju, Jianhua
2017-05-26
Emodacidamides A-H (1-8), natural products featuring anthraquinone-amino acid conjugates, have been isolated from a marine-derived fungus, Penicillium sp. SCSIO sof101, together with known anthraquinones 9 and 10. The planar structures of 1-8 were elucidated using a combination of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. The absolute configurations of the amino acid residues were confirmed using Marfey's method and chiral-phase HPLC analyses. Additionally, isolates were evaluated for possible immunomodulatory and cytotoxic activities. Emodacidamides A (1), C (3), D (4), and E (5) inhibited interleukin-2 secretion from Jurkat cells with IC 50 values of 4.1, 5.1, 12, and 5.4 μM, respectively.
-
Jadhav, Swati B; Singhal, Rekha S
2013-10-15
Two enzymes, α-amylase and glucoamylase have been individually and co-conjugated to pectin by covalent binding. Both the enzyme systems showed better thermal and pH stability over the free enzyme system with the complete retention of original activities. Mixture of individually conjugated enzymes showed lower inactivation rate constant with longer half life than the co-conjugated enzyme system. Individually conjugated enzymes showed an increase of 56.48 kJ/mole and 38.22 kJ/mole in activation energy for denaturation than the free enzymes and co-conjugated enzymes, respectively. Km as well as Vmax of individually and co-conjugated enzymes was found to be higher than the free enzymes. SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis confirmed the formation of conjugate and co-conjugate as evident by increased molecular weight. Both the enzyme systems were used for starch hydrolysis where individually conjugated enzymes showed highest release of glucose at 60 °C and pH 5.0 as compared to free and co-conjugated enzyme. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Emami, Jaber; Rezazadeh, Mahboubeh; Sadeghi, Hojjat; Khadivar, Khashayar
2017-05-01
The treatment of brain cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology. The purpose of this study was to develop transferrin-conjugated nanostructured lipid carriers (Tf-NLCs) for brain delivery of paclitaxel (PTX). PTX-loaded NLCs (PTX-NLCs) were prepared using solvent evaporation method and the impact of various formulation variables were assessed using Box-Behnken design. Optimized PTX-NLC was coupled with transferrin as targeting ligand and in vitro cytotoxicity of it was investigated against U-87 brain cancer cell line. As a result, 14.1 mg of cholesterol, 18.5 mg of triolein, and 0.5% poloxamer were used to prepare the optimal formulation. Mean particle size (PS), zeta potential (ZP), entrapment efficiency (EE), drug loading (DL), mean release time (MRT) of adopted formulation were confirmed to be 205.4 ± 11 nm, 25.7 ± 6.22 mV, 91.8 ± 0.5%, 5.38 ± 0.03% and 29.3 h, respectively. Following conjugation of optimized PTX-NLCs with transferrin, coupling efficiency was 21.3 mg transferrin per mmol of stearylamine; PS and MRT were increased while ZP, EE and DL decreased non-significantly. Tf-PTX-NLCs showed higher cytotoxic activity compared to non-targeted NLCs and free drug. These results indicated that the Tf-PTX-NLCs could potentially be exploited as a delivery system in brain cancer cells.
-
Safe handling of cytotoxic compounds in a biopharmaceutical environment.
Hensgen, Miriam I; Stump, Bernhard
2013-01-01
Handling cytotoxic drugs such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) in a biopharmaceutical environment represents a challenge based on the potency of the compounds. These derivatives are dangerous to humans if they accidentally get in contact with the skin, are inhaled, or are ingested, either as pure compounds in their solid state or as a solution dissolved in a co-solvent. Any contamination of people involved in the manufacturing process has to be avoided. On the other hand, biopharmaceuticals need to be protected simultaneously against any contamination from the manufacturing personnel. Therefore, a tailor-made work environment is mandatory in order to manufacture ADCs. This asks for appropriate technical equipment to keep potential hazardous substances contained. In addition, clearly defined working procedures based on risk assessments as well as proper training for all personnel involved in the manufacturing process are needed to safely handle these highly potent pharmaceuticals.
-
Conjugated linolenic acids (CLnA, super CLA – natural sources and biological activity
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Agnieszka Białek
2014-11-01
Full Text Available Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA have a wide range of biological activity. Among them conjugated fatty acids are of great interest. Conjugated linoleic acids (CLA, which exert a multidirectional health-benefiting influence, and conjugated linolenic acids (CLnA, super CLA are examples of this group of fatty acids. CLnA are a group of positional and geometric isomers of octadecatrienoic acid (C18:3, which possess double bonds at positions 9, 11, 13 or 8, 10, 12 of their chain. Some vegetable oils are rich sources of CLnA, e.g. bitter melon oil (from Momordica charantia seeds and pomegranate oil (from Punica granatum seeds. The aim of this paper was to present information concerning natural sources and health-promoting activities of conjugated linolenic acids.The presented data reveal that conjugated linolenic acids may be very useful in prevention and treatment of many diseases, especially diabetes, arteriosclerosis , obesity and cancers (mammary, prostate and colon cancer. Among many potential mechanisms of their action, the fact that some CLnA are converted by oxidoreductases into CLA is very important. It seems to be very reasonable to conduct research concerning the possibility of CLnA use in prevention of many diseases.
-
IGF-1 promotes the development and cytotoxic activity of human NK cells
Ni, Fang; Sun, Rui; Fu, Binqing; Wang, Fuyan; Guo, Chuang; Tian, Zhigang; Wei, Haiming
2013-01-01
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is a critical regulator of many physiological functions, ranging from longevity to immunity. However, little is known about the role of IGF-1 in natural killer cell development and function. Here, we identify an essential role for IGF-1 in the positive regulation of human natural killer cell development and cytotoxicity. Specifically, we show that human natural killer cells have the ability to produce IGF-1 and that differential endogenous IGF-1 expression...
-
Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity of mPEG-SH modified gold nanorods
Didychuk, Candice L.; Ephrat, Pinhas; Belton, Michelle; Carson, Jeffrey J. L.
2008-02-01
Plasmon-resonant gold nanorods show great potential as an agent for contrast-enhanced biomedical imaging or for phototherapeutics. This is primarily due to the high molar extinction coefficient at the absorption maximum and the dependence of the wavelength of the absorption maximum on the aspect ratio, which is tunable in the near-infrared (NIR) during synthesis. Although gold nanorods can be produced in high-yield through the seed-mediated growth technique, the presence of residual cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), a stabilizing surfactant required for nanorod growth, interferes with cell function and causes cytotoxicity. To overcome this potential obstacle to in vivo use, we synthesized gold nanorods and conjugated them to a methoxy (polyethylene glycol)-thiol (mPEG (5000)-SH). This approach yielded mPEG-SH modified gold nanorods with optical and morphometric properties that were similar to raw (CTAB) nanorods. Both the CTAB and mPEG-SH nanorods were tested for cytotoxicity against the HL-60 human leukemia cell line by trypan blue exclusion, and the mPEG-SH modified gold nanorods were also tested against a rat insulinoma (RIN-38) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCCVII) cell line. Cells incubated for 24 h with the mPEG-SH modified nanorods had little change in cell viability compared to cells incubated with vehicle alone. This was in contrast to cytotoxicity of CTAB nanorods on HL-60 cells. These results suggest that mPEG-SH modified gold nanorods are better suited for cell loading protocols and injection into animals and facilitate their use for imaging and phototherapeutic purposes.
-
Enhanced A3 adenosine receptor selectivity of multivalent nucleoside-dendrimer conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Shainberg Asher
2008-10-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background An approach to use multivalent dendrimer carriers for delivery of nucleoside signaling molecules to their cell surface G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs was recently introduced. Results A known adenosine receptor (AR agonist was conjugated to polyamidoamine (PAMAM dendrimer carriers for delivery of the intact covalent conjugate to on the cell surface. Depending on the linking moiety, multivalent conjugates of the N6-chain elongated functionalized congener ADAC (N6-[4-[[[4-[[[(2-aminoethylamino]carbonyl]methyl]anilino]carbonyl]methyl]phenyl]-adenosine achieved unanticipated high selectivity in binding to the cytoprotective human A3 AR, a class A GPCR. The key to this selectivity of > 100-fold in both radioreceptor binding (Ki app = 2.4 nM and functional assays (EC50 = 1.6 nM in inhibition of adenylate cyclase was maintaining a free amino group (secondary in an amide-linked chain. Attachment of neutral amide-linked chains or thiourea-containing chains preserved the moderate affinity and efficacy at the A1 AR subtype, but there was no selectivity for the A3 AR. Since residual amino groups on dendrimers are associated with cytotoxicity, the unreacted terminal positions of this A3 AR-selective G2.5 dendrimer were present as carboxylate groups, which had the further benefit of increasing water-solubility. The A3 AR selective G2.5 dendrimer was also visualized binding the membrane of cells expressing the A3 receptor but did not bind cells that did not express the receptor. Conclusion This is the first example showing that it is feasible to modulate and even enhance the pharmacological profile of a ligand of a GPCR based on conjugation to a nanocarrier and the precise structure of the linking group, which was designed to interact with distal extracellular regions of the 7 transmembrane-spanning receptor. This ligand tool can now be used in pharmacological models of tissue rescue from ischemia and to probe the existence of A3 AR
-
Requirement for Vibrio cholerae integration host factor in conjugative DNA transfer.
McLeod, Sarah M; Burrus, Vincent; Waldor, Matthew K
2006-08-01
The requirement for host factors in the transmission of integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) has not been extensively explored. Here we tested whether integration host factor (IHF) or Fis, two host-encoded nucleoid proteins, are required for transfer of SXT, a Vibrio cholerae-derived ICE that can be transmitted to many gram-negative species. Fis did not influence the transfer of SXT to or from V. cholerae. In contrast, IHF proved to be required for V. cholerae to act as an SXT donor. In the absence of IHF, V. cholerae displayed a modest defect for serving as an SXT recipient. Surprisingly, SXT integration into or excision from the V. cholerae chromosome, which requires an SXT-encoded integrase related to lambda integrase, did not require IHF. Therefore, the defect in SXT transmission in the V. cholerae IHF mutant is probably not related to IHF's ability to promote DNA recombination. The V. cholerae IHF mutant was also highly impaired as a donor of RP4, a broad-host-range conjugative plasmid. Thus, the V. cholerae IHF mutant appears to have a general defect in conjugation. Escherichia coli IHF mutants were not impaired as donors or recipients of SXT or RP4, indicating that IHF is a V. cholerae-specific conjugation factor.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Xiao-Na Pan
Full Text Available Nowadays, drug resistance still represents a major obstacle to successful acute myeloid leukemia (AML treatment and the underlying mechanism is not fully elucidated. Here, we found that high expression of c-Myc was one of the cytogenetic characteristics in the drug-resistant leukemic cells. c-Myc over-expression in leukemic cells induced resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs, enhanced colony formation capacity and inhibited cell differentiation induced by all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA. Meanwhile, inhibition of c-Myc by shRNA or specific c-Myc inhibitor 10058-F4 rescued the sensitivity to cytotoxic drugs, restrained the colony formation ability and promoted differentiation. RT-PCR and western blotting analysis showed that down-regulation of C/EBPβ contributed to the poor differentiation state of leukemic cells induced by c-Myc over-expression. Importantly, over-expression of C/EBPβ could reverse c-Myc induced drug resistance. In primary AML cells, the c-Myc expression was negatively correlated with C/EBPβ. 10058-F4, displayed anti-proliferative activity and increased cellular differentiation with up-regulation of C/EBPβ in primary AML cells. Thus, our study indicated that c-Myc could be a novel target to overcome drug resistance, providing a new approach in AML therapy.
-
The mechanism of the photoluminescence changes in bio-conjugated CdSe/ZnS quantum dots
Borkovska, L.; Korsunska, N.; Stara, T.; Kolomys, O.; Strelchuk, V.; Rachkov, O.; Kryshtab, T.
2013-09-01
The change of the photoluminescence (PL) and optical characteristics in non-conjugated and conjugated with S6K2 antibody CdSe/ZnS core/shell quantum dots (QDs) during storage in air has been studied by the conventional PL, micro-PL and micro-Raman techniques. The QDs dried on a crystalline Si substrate were kept in the darkness and under illumination. In the PL spectra, the storage resulted in a blue shift of PL peak position, in the increasing of the full width at a half maximum (FWHM) of the PL band and in the decreasing of the PL intensity. In the Raman spectra, the shift of the CdSe LO peak position to the low frequency region and the increasing of its FWHM were observed. The transformations in the PL and optical characteristics correlate with each other and are found to be the largest in bio-conjugated QDs stored under illumination. The increase of the light intensity accelerated the changes occurred during storage. An oxidation of the QD core, which decreases the QD size, is supposed to be responsible for observed transformations. The bio-conjugation is assumed to promote QD oxidation that results in different PL peak position in stored non-conjugated and bio-conjugated QDs. The mechanism of the effect is discussed.
-
TNP-specific Lyt-2+ cytolytic T cell clones preferentially respond to TNP-conjugated epidermal cells
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shimada, S.; Katz, S.I.
1985-01-01
A most effective method for the induction of hapten-specific allergic contact sensitivity (CS) is via epicutaneous application of the hapten. Another effective method is by the administration of haptenated epidermal cells (EC) subcutaneously. The latter method induces more intense and longer lasting CS than does the subcutaneous administration of haptenated spleen cells (SC). Thus, there may be something unique about EC which, when haptenated, allows them to generate effector cells more effectively than do SC. The authors therefore, attempted to generate T cell clones that were both hapten- and epidermal-specific. Four days after painting mice with 7% trinitrochlorobenzene, draining lymph node cells were obtained and T cells were purified. These cells were co-cultured with trinitrophenylated (TNP) Langerhans cell-enriched EC. After 4 days, cells were harvested and rested on non-TNP-conjugated EC. The cells were restimulated and rested three times, and were then cloned by limiting dilution with added interleukin 2, which was then continually added. Proliferation of T cells was assessed by [ 3 H]-thymidine incorporation. Cytotoxicity assays utilized TNP-conjugated concanavalin A SC blasts or EC as targets. Clones A-2 and E-4 are Thy-1+, Lyt-2+, and L3T4-, and TNP-specific. In contrast to noncloned TNP-specific T cells, the clones proliferate preferentially in response to TNP-EC rather than TNP-SC. Also in contrast to noncloned T cells, the clones were preferentially cytotoxic for TNP-EC; compared to TNP-SC, there was an eight- to 32-fold increase in killing when TNP-EC were used as targets. Clones A-2 and E-4 therefore exhibit hapten and epidermal specificity
-
Kano, Taichi; Sugimoto, Hisashi; Maruyama, Hiroki; Maruoka, Keiji
2015-07-13
A simple axially chiral amine catalyst promoted the regio-, diastereo-, and enantioselective conjugate addition of aldehydes to β-tosyl enones, which serve as ynone surrogates. The adducts were readily converted by treatment with L-selectride into less accessible enones with a γ stereogenic center. Such compounds cannot be prepared through the amine-catalyzed conjugate addition of aldehydes to ynones. The obtained enones underwent further conjugate addition of diorganozinc compounds in the presence of a copper catalyst. © 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
van Lith, Sanne A M; van Duijnhoven, Sander M J; Navis, Anna C; Leenders, William P J; Dolk, Edward; Wennink, Jos W H; van Nostrum, Cornelus F; van Hest, Jan C M
2017-02-15
Conjugation of llama single domain antibody fragments (Variable Heavy chain domains of Heavy chain antibodies, VHHs) to diagnostic or therapeutic nanoparticles, peptides, proteins, or drugs offers many opportunities for optimized targeted cancer treatment. Currently, mostly nonspecific conjugation strategies or genetic fusions are used that may compromise VHH functionality. In this paper we present a versatile modular approach for bioorthogonal VHH modification and conjugation. First, sortase A mediated transPEGylation is used for introduction of a chemical click moiety. The resulting clickable VHHs are then used for conjugation to other groups employing the Cu + -independent strain-promoted alkyne-azide cycloadition (SPAAC) reaction. Using this approach, tail-to-tail bispecific VHHs and VHH-targeted nanoparticles are generated without affecting VHH functionality. Furthermore, this approach allows the bioconjugation of multiple moieties to VHHs for simple and convenient production of VHH-based theranostics.
-
Receptor-targeted aptamer-siRNA conjugate-directed transcriptional regulation of HIV-1
Zhou, Jiehua; Lazar, Daniel; Li, Haitang; Xia, Xin; Satheesan, Sangeetha; Charlins, Paige; O'Mealy, Denis; Akkina, Ramesh; Saayman, Sheena; Weinberg, Marc S.; Rossi, John J.; Morris, Kevin V.
2018-01-01
Gene-based therapies represent a promising therapeutic paradigm for the treatment of HIV-1, as they have the potential to maintain sustained viral inhibition with reduced treatment interventions. Such an option may represent a long-term treatment alternative to highly active antiretroviral therapy. Methods: We previously described a therapeutic approach, referred to as transcriptional gene silencing (TGS), whereby small noncoding RNAs directly inhibit the transcriptional activity of HIV-1 by targeting sites within the viral promoter, specifically the 5' long terminal repeat (LTR). TGS differs from traditional RNA interference (RNAi) in that it is characterized by concomitant silent-state epigenetic marks on histones and DNA. To deliver TGS-inducing RNAs, we developed functional RNA conjugates based on the previously reported dual function of the gp120 (A-1) aptamer conjugated to 27-mer Dicer-substrate anti-HIV-1 siRNA (dsiRNA), LTR-362. Results: We demonstrate here that high levels of processed guide RNAs localize to the nucleus in infected T lymphoblastoid CEM cell line and primary human CD4+ T-cells. Treatment of the aptamer-siRNA conjugates induced TGS with an ~10-fold suppression of viral p24 levels as measured at day 12 post infection. To explore the silencing efficacy of aptamer-siRNA conjugates in vivo, HIV-1-infected humanized NOD/SCID/IL2 rγnull mice (hu-NSG) were treated with the aptamer-siRNA conjugates. Systemic delivery of the A-1-stick-LTR-362 27-mer siRNA conjugates suppressed HIV-1 infection and protected CD4+ T cell levels in viremia hu-NSG mice. Principle conclusions: Collectively these data suggest that the gp120 aptamer-dsiRNA conjugate design is suitable for systemic delivery of small RNAs that can be used to suppress HIV-1. PMID:29556342
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Le, Thi Thuy Duong; Pham, Thu Hong; Ngo, Thi Hong Giang; Le, Quang Huan; Nguyen, Trong Nghia; Hoang, Thi My Nhung
2016-01-01
Three-dimensional culture cells (spheroids) are one of the multicellular culture models that can be applied to anticancer chemotherapeutic development. Multicellular spheroids more closely mimic in vivo tumor-like patterns of physiologic environment and morphology. In previous research, we designed docetaxel-loaded pegylated poly(D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles conjugated with anti-HER2 single chain antibodies (scFv–Doc–PLGA–PEG) and evaluated them in 2D cell culture. In this study, we continuously evaluate the cellular uptake and cytotoxic effect of scFv–Doc–PLGA–PEG on a 3D tumor spheroid model of BT474 (HER2-overexpressing) and HCT116 (HER2-underexpressing) cancer cells. The results showed that the nanoparticle formulation conjugated with scFv had a significant internalization effect on the spheroids of HER2-overexpressing cancer cells as compared to the spheroids of HER2-underexpressing cancer cells. Therefore, cytotoxic effects of targeted nanoparticles decreased the size and increased necrotic score of HER2-overexpressing tumor spheroids. Thus, these scFv–Doc–PLGA–PEG nanoparticles have potential for active targeting for HER2-overexpressing cancer therapy. In addition, BT474 and HCT116 spheroids can be used as a tumor model for evaluation of targeting therapies. (paper)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Phumyen A
2014-11-01
Full Text Available Achara Phumyen,1–3 Siriporn Jantasorn,1 Amonrat Jumnainsong,1 Chanvit Leelayuwat1–4 1The Centre for Research and Development of Medical Diagnostic Laboratories (CMDL, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, 2The Liver Fluke and Cholangiocarcinoma Research Center, Faculty of Medicine, 3Research Cluster: Specific Health Problem of Grater Maekong Subregion (SHeP-GMS, 4Department of Clinical Immunology and Transfusion Sciences, Faculty of Associated Medical Sciences, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand Background: Cancer therapy by systemic administration of anticancer drugs, besides the effectiveness shown on cancer cells, demonstrated the side effects and cytotoxicity on normal cells. The targeted drug-carrying nanoparticles may decrease the required drug concentration at the site and the distribution of drugs to normal tissues. Overexpression of major histocompatibility complex class I chain–related A (MICA in cancer is useful as a targeted molecule for the delivery of doxorubicin to MICA-expressing cell lines. Methods: The application of 1-ethyl-3-[3-dimethylaminopropyl] carbodiimide (EDC chemistry was employed to conjugate the major coat protein of bacteriophages carrying anti-MICA and doxorubicin in a mildly acid condition. Doxorubicin (Dox on phages was determined by double fluorescence of phage particles stained by M13-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC and drug autofluorescence by flow cytometry. The ability of anti-MICA on phages to bind MICA after doxorubicin conjugation was evaluated by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. One cervical cancer and four cholangiocarcinoma cell lines expressing MICA were used as models to evaluate targeting activity by cell cytotoxicity test. Results: Flow cytometry and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay demonstrated that most of the phages (82% could be conjugated with doxorubicin, and the Dox-carrying phage-displaying anti-MICA (Dox-phage remained the binding activity against MICA
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae triggers a cytotoxic effect on airway epithelial cells
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Llobet-Brossa Enrique
2009-08-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background Klebsiella pneumoniae is a capsulated Gram negative bacterial pathogen and a frequent cause of nosocomial infections. Despite its clinical relevance, little is known about the features of the interaction between K. pneumoniae and lung epithelial cells on a cellular level, neither about the role of capsule polysaccharide, one of its best characterised virulence factors, in this interaction. Results The interaction between Klebsiella pneumoniae and cultured airway epithelial cells was analysed. K. pneumoniae infection triggered cytotoxicity, evident by cell rounding and detachment from the substrate. This effect required the presence of live bacteria and of capsule polysaccharide, since it was observed with isolates expressing different amounts of capsule and/or different serotypes but not with non-capsulated bacteria. Cytotoxicity was analysed by lactate dehydrogenase and formazan measurements, ethidium bromide uptake and analysis of DNA integrity, obtaining consistent and complementary results. Moreover, cytotoxicity of non-capsulated strains was restored by addition of purified capsule during infection. While a non-capsulated strain was avirulent in a mouse infection model, capsulated K. pneumoniae isolates displayed different degrees of virulence. Conclusion Our observations allocate a novel role to K. pneumoniae capsule in promotion of cytotoxicity. Although this effect is likely to be associated with virulence, strains expressing different capsule levels were not equally virulent. This fact suggests the existence of other bacterial requirements for virulence, together with capsule polysaccharide.
-
Herter, Sylvia; Birk, Martina C; Klein, Christian; Gerdes, Christian; Umana, Pablo; Bacac, Marina
2014-03-01
Therapeutic Abs possess several clinically relevant mechanisms of action including perturbation of tumor cell signaling, activation of complement-dependent cytotoxicity, Ab-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), Ab-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), and induction of adaptive immunity. In view of the important role of phagocytic lineage cells in the mechanism of action of therapeutic Abs, we analyzed FcγR receptor-dependent effector functions of monocytes and macrophages triggered by glycoengineered (GE) Abs (having enhanced FcγRIIIa [CD16a] binding affinity) versus their wild-type (WT) counterparts under different experimental conditions. We first defined the precise FcγR repertoire on classical and nonclassical intermediate monocytes--M1 and M2c macrophage populations. We further show that WT and GE Abs display comparable binding and induce similar effector functions (ADCC and ADCP) in the absence of nonspecific, endogenous IgGs. However, in the presence of these IgGs (i.e., in a situation that more closely mimics physiologic conditions), GE Abs display significantly superior binding and promote stronger monocyte and macrophage activity. These data show that in addition to enhancing CD16a-dependent NK cell cytotoxicity, glycoengineering also enhances monocyte and macrophage phagocytic and cytotoxic activities through enhanced binding to CD16a under conditions that more closely resemble the physiologic setting.
-
Bacteriophytochromes control conjugation in Agrobacterium fabrum.
Bai, Yingnan; Rottwinkel, Gregor; Feng, Juan; Liu, Yiyao; Lamparter, Tilman
2016-08-01
Bacterial conjugation, the transfer of single stranded plasmid DNA from donor to recipient cell, is mediated through the type IV secretion system. We performed conjugation assays using a transmissible artificial plasmid as reporter. With this assay, conjugation in Agrobacterium fabrum was modulated by the phytochromes Agp1 and Agp2, photoreceptors that are most sensitive in the red region of visible light. In conjugation studies with wild-type donor cells carrying a pBIN-GUSINT plasmid as reporter that lacked the Ti (tumor inducing) plasmid, no conjugation was observed. When either agp1(-) or agp2(-) knockout donor strains were used, plasmid DNA was delivered to the recipient, indicating that both phytochromes suppress conjugation in the wild type donor. In the recipient strains, the loss of Agp1 or Agp2 led to diminished conjugation. When wild type cells with Ti plasmid and pBIN-GUS reporter plasmid were used as donor, a high rate of conjugation was observed. The DNA transfer was down regulated by red or far-red light by a factor of 3.5. With agp1(-) or agp2(-) knockout donor cells, conjugation in the dark was about 10 times lower than with the wild type donor, and with the double knockout donor no conjugation was observed. These results imply that the phytochrome system has evolved to inhibit conjugation in the light. The decrease of conjugation under different temperature correlated with the decrease of phytochrome autophosphorylation. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Rhodium(I)-Complexes Catalyzed 1,4-Conjugate Addition of Arylzinc Chlorides to N-Boc-4-pyridone.
Guo, Fenghai; McGilvary, Matthew A; Jeffries, Malcolm C; Graves, Briana N; Graham, Shekinah A; Wu, Yuelin
2017-05-01
Rhodium(I)-complexes catalyzed the 1,4-conjugate addition of arylzinc chlorides to N -Boc-4-pyridone in the presence of chlorotrimethylsilane (TMSCl). A combination of [RhCl(C₂H₄)₂]₂ and BINAP was determined to be the most effective catalyst to promote the 1,4-conjugate addition reactions of arylzinc chlorides to N -Boc-4-pyridone. A broad scope of arylzinc reagents with both electron-withdrawing and electron-donating substituents on the aromatic ring successfully underwent 1,4-conjugate addition to N -Boc-4-pyridone to afford versatile 1,4-adducts 2-substituted-2,3-dihydropyridones in good to excellent yields (up to 91%) and excellent ee (up to 96%) when ( S )-BINAP was used as chiral ligand.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nair, Baiju G.; Fukuda, Takahiro; Mizuki, Toru; Hanajiri, Tatsuro [Bio-Nano Electronics Research Centre, Toyo University, Saitama 350-8585 (Japan); Maekawa, Toru, E-mail: maekawa@toyo.jp [Bio-Nano Electronics Research Centre, Toyo University, Saitama 350-8585 (Japan)
2012-05-18
Highlights: Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer We study the intracellular localisation of TAT-SPIONs using 3-D electron tomography. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer 3-D images of TAT-SPIONs in a cell are clearly shown. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Release of TAT-SPIONs from endocytic vesicles into the cytoplasm is clearly shown. -- Abstract: Internalisation of nanoparticles conjugated with cell penetrating peptides is a promising approach to various drug delivery applications. Cell penetrating peptides such as transactivating transcriptional activator (TAT) peptides derived from HIV-1 proteins are effective intracellular delivery vectors for a wide range of nanoparticles and pharmaceutical agents thanks to their amicable ability to enter cells and minimum cytotoxicity. Although different mechanisms of intracellular uptake and localisation have been proposed for TAT conjugated nanoparticles, it is necessary to visualise the particles on a 3-D plane in order to investigate the actual intracellular uptake and localisation. Here, we study the intracellular localisation and trafficking of TAT peptide conjugated superparamagnetic ion oxide nanoparticles (TAT-SPIONs) using 3-D electron tomography. 3-D tomograms clearly show the location of TAT-SPIONs in a cell and their slow release from the endocytic vesicles into the cytoplasm. The present methodology may well be utilised for further investigations of the behaviours of nanoparticles in cells and eventually for the development of nano drug delivery systems.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Poon, Kirsten Achilles, E-mail: achilles.kirsten@gene.com [Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, CA (United States); Flagella, Kelly; Beyer, Joseph [Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, CA (United States); Tibbitts, Jay [UCB, Brussels (Belgium); Kaur, Surinder; Saad, Ola; Yi, Joo-Hee; Girish, Sandhya; Dybdal, Noel; Reynolds, Theresa [Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, CA (United States)
2013-12-01
Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) is the first antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) approved for patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastatic breast cancer. The therapeutic premise of ADCs is based on the hypothesis that targeted delivery of potent cytotoxic drugs to tumors will provide better tolerability and efficacy compared with non-targeted delivery, where poor tolerability can limit efficacious doses. Here, we present results from preclinical studies characterizing the toxicity profile of T-DM1, including limited assessment of unconjugated DM1. T-DM1 binds primate ErbB2 and human HER2 but not the rodent homolog c-neu. Therefore, antigen-dependent and non-antigen-dependent toxicity was evaluated in monkeys and rats, respectively, in both single- and repeat-dose studies; toxicity of DM1 was assessed in rats only. T-DM1 was well tolerated at doses up to 40 mg/kg (∼ 4400 μg DM1/m{sup 2}) and 30 mg/kg (∼ 6000 μg DM1/m{sup 2}) in rats and monkeys, respectively. In contrast, DM1 was only tolerated up to 0.2 mg/kg (1600 μg DM1/m{sup 2}). This suggests that at least two-fold higher doses of the cytotoxic agent are tolerated in T-DM1, supporting the premise of ADCs to improve the therapeutic index. In addition, T-DM1 and DM1 safety profiles were similar and consistent with the mechanism of action of DM1 (i.e., microtubule disruption). Findings included hepatic, bone marrow/hematologic (primarily platelet), lymphoid organ, and neuronal toxicities, and increased numbers of cells of epithelial and phagocytic origin in metaphase arrest. These adverse effects did not worsen with chronic dosing in monkeys and are consistent with those reported in T-DM1-treated patients to date. - Highlights: • T-DM1 was well tolerated in preclinical studies in rats and cynomolgus monkeys. • T-DM1 is associated with bone marrow/hematologic, hepatic, and neuronal toxicities. • T-DM1 toxicities are related to DM1 mechanisms of action and pharmacologic
-
Piras, Anna Maria; Zambito, Ylenia; Burgalassi, Susi; Monti, Daniela; Tampucci, Silvia; Terreni, Eleonora; Fabiano, Angela; Balzano, Federica; Uccello-Barretta, Gloria; Chetoni, Patrizia
2018-03-30
The ocular bioavailability of lipophilic drugs, such as dexamethasone, depends on both drug water solubility and mucoadhesion/permeation. Cyclodextrins and chitosan are frequently employed to either improve drug solubility or prolong drug contact onto mucosae, respectively. Although the covalent conjugation of cyclodextrin and chitosan brings to mucoadhesive drug complexes, their water solubility is restricted to acidic pHs. This paper describes a straightforward grafting of methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MCD) on quaternary ammonium chitosan (QA-Ch60), mediated by hexamethylene diisocyanate. The resulting product is a water-soluble chitosan derivative, having a 10-atom long spacer between the quaternized chitosan and the cyclodextrin. The derivative is capable of complexing the model drug dexamethasone and stable complexes were also observed for the lyophilized products. Furthermore, the conjugate preserves the mucoadhesive properties typical of quaternized chitosan and its safety as solubilizing excipient for ophthalmic applications was preliminary assessed by in vitro cytotoxicity evaluations. Taken as a whole, the observed features appear promising for future processing of the developed product into 3D solid forms, such as controlled drug delivery systems, films or drug eluting medical devices.
-
Polymers for Protein Conjugation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gianfranco Pasut
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Polyethylene glycol (PEG at the moment is considered the leading polymer for protein conjugation in view of its unique properties, as well as to its low toxicity in humans, qualities which have been confirmed by its extensive use in clinical practice. Other polymers that are safe, biodegradable and custom-designed have, nevertheless, also been investigated as potential candidates for protein conjugation. This review will focus on natural polymers and synthetic linear polymers that have been used for protein delivery and the results associated with their use. Genetic fusion approaches for the preparation of protein-polypeptide conjugates will be also reviewed and compared with the best known chemical conjugation ones.
-
Dubey, Ravindra Dhar; Klippstein, Rebecca; Wang, Julie Tzu-Wen; Hodgins, Naomi; Mei, Kuo-Ching; Sosabowski, Jane; Hider, Robert C.; Abbate, Vincenzo; Gupta, Prem N.; Al-Jamal, Khuloud T.
2017-01-01
Hyaluronic acid, a natural CD44 receptor ligand, has attracted attention in the past years as a macromolecular delivery of anticancer agents to cancer. At the same time, the clinical applications of Gemcitabine (Gem) have been hindered by its short biological half-life, high dose and development of drug resistance. This work reports the synthesis of a hyaluronic acid (HA) conjugate for nuclear imaging, and in vivo Gem delivery to CD44-expressing solid tumors in mice. HA was individually conjugated, via amide coupling, to Gem (HA-Gem), 4'-(aminomethyl)fluorescein hydrochloride (HA-4'-AMF) or tris(hydroxypyridinone) amine (HA-THP) for cancer therapy, in vitro tracking or single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) imaging, respectively. Gem conjugation to HA was directly confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR), gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and UV-visible spectrometry, or indirectly by a nucleoside transporter inhibition study. Gem conjugation to HA improved its plasma stability, reduced blood hemolysis and resulted in delayed cytotoxicity in vitro. Uptake inhibition studies in colon CT26 and pancreatic PANC-1 cells, by flow cytometry, revealed that uptake of fluorescent HA conjugate is CD44 receptor and macropinocytosis-dependent. Gamma scintigraphy and SPECT/CT imaging confirmed the relatively prolonged blood circulation profile and uptake in CT26 (1.5 % ID/gm) and PANC-1 (1 % ID/gm) subcutaneous tumors at 24 h after intravenous injection in mice. Four injections of HA-Gem at ~15 mg/kg, over a 28-day period, resulted in significant delay in CT26 tumor growth and prolonged mice survival compared to the free drug. This study reports for the first time dual nuclear imaging and drug delivery (Gem) of HA conjugates to solid tumors in mice. The conjugates show great potential in targeting, imaging and killing of CD44-over expressing cells in vivo. This work is likely to open new avenues for the application of HA
-
Metabolism of tert-butylhydroquinone to S-substituted conjugates in the male fischer 344 rat
Peters, M.M.C.G.; Lau, S.S.; Dulik, D.; Murphy, D.; Ommen, B. van; Bladeren, P.J. van; Monks, T.J.
1996-01-01
tert-Butyl-4-hydroxyanisole (BHA) and its demethylated analog, tert- butyl-hydroquinone (TBHQ), are antioxidants used in food. Both BHA and TBHQ have been shown to promote kidney and bladder carcinogenesis in the rat. We have previously demonstrated that glutathione (GSH) conjugates of a variety of
-
Ahmad Khanbeigi, Raha; Abelha, Thais Fedatto; Woods, Arcadia; Rastoin, Olivia; Harvey, Richard D; Jones, Marie-Christine; Forbes, Ben; Green, Mark A; Collins, Helen; Dailey, Lea Ann
2015-03-09
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles are being developed for a variety of diagnostic and theranostic applications. The conjugated polymer, F8BT, a polyfluorene derivative, was used as a model system to examine the biological behavior of conjugated polymer nanoparticle formulations stabilized with ionic (sodium dodecyl sulfate; F8BT-SDS; ∼207 nm; -31 mV) and nonionic (pegylated 12-hydroxystearate; F8BT-PEG; ∼175 nm; -5 mV) surfactants, and compared with polystyrene nanoparticles of a similar size (PS200; ∼217 nm; -40 mV). F8BT nanoparticles were as hydrophobic as PS200 (hydrophobic interaction chromatography index value: 0.96) and showed evidence of protein corona formation after incubation with serum-containing medium; however, unlike polystyrene, F8BT nanoparticles did not enrich specific proteins onto the nanoparticle surface. J774A.1 macrophage cells internalized approximately ∼20% and ∼60% of the F8BT-SDS and PS200 delivered dose (calculated by the ISDD model) in serum-supplemented and serum-free conditions, respectively, while cell association of F8BT-PEG was minimal (<5% of the delivered dose). F8BT-PEG, however, was more cytotoxic (IC50 4.5 μg cm(-2)) than F8BT-SDS or PS200. The study results highlight that F8BT surface chemistry influences the composition of the protein corona, while the properties of the conjugated polymer nanoparticle surfactant stabilizer used determine particle internalization and biocompatibility profile.
-
Swain, Shasank S; Paidesetty, Sudhir K; Padhy, Rabindra N
2017-03-01
. aureus) and -10.19 (conjugate-2 against S. pneumoniae. Conjugates-2 and -5 were the most effective antibacterials based on Lipinski rule of five with lethal doses 3471 and 3500mg/kg, respectively and toxicity class levels. Conjugate-2 and conjugate-5 were more effective than individual monoterpenes and SMZ, against pathogenic bacteria. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro antibacterial study with acute toxicity testing for Wister rat model of the conjugate-5 could land at success in the recorded computational trial and it could be promoted for synthesis in the control of MDR bacteria. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Cole, Stephanie J; Yoon, Alexander J; Faull, Kym F; Diener, Andrew C
2014-08-01
Three pathogenic forms, or formae speciales (f. spp.), of Fusarium oxysporum infect the roots of Arabidopsis thaliana below ground, instigating symptoms of wilt disease in leaves above ground. In previous reports, Arabidopsis mutants that are deficient in the biosynthesis of abscisic acid or salicylic acid or insensitive to ethylene or jasmonates exhibited either more or less wilt disease, than the wild-type, implicating the involvement of hormones in the normal host response to F. oxysporum. Our analysis of hormone-related mutants finds no evidence that endogenous hormones contribute to infection in roots. Mutants that are deficient in abscisic acid and insensitive to ethylene show no less infection than the wild-type, although they exhibit less disease. Whether a mutant that is insensitive to jasmonates affects infection depends on which forma specialis (f. sp.) is infecting the roots. Insensitivity to jasmonates suppresses infection by F. oxysporum f. sp. conglutinans and F. oxysporum f. sp. matthioli, which produce isoleucine- and leucine-conjugated jasmonate (JA-Ile/Leu), respectively, in culture filtrates, whereas insensitivity to jasmonates has no effect on infection by F. oxysporum f. sp. raphani, which produces no detectable JA-Ile/Leu. Furthermore, insensitivity to jasmonates has no effect on wilt disease of tomato, and the tomato pathogen F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici produces no detectable jasmonates. Thus, some, but not all, F. oxysporum pathogens appear to utilize jasmonates as effectors, promoting infection in roots and/or the development of symptoms in shoots. Only when the infection of roots is promoted by jasmonates is wilt disease enhanced in a mutant deficient in salicylic acid biosynthesis. © 2014 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Viswanathan, Kaliyaperumal; Rathish, P.; Gopinath, V.P.; Janice, R.; Dhinakar Raj, G.
2014-01-01
In this report, the hybrid calcium phosphate (CaP) nanoparticles were synthesized and functionalized with Newcastle disease virus (NDV). These nanoparticles were synthesized by a combination of co-precipitation and polymerization process and functionalized with amino propyl triethoxy silane before coupling to NDV. The 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay of chicken spleen cells incubated with these nanoparticles indicated that, these particles did not exert any significant cytotoxicity. The effects of hybrid CaP nanoparticles on cell cycle were assayed using a flow cytometer. The results demonstrated that the cell viability and proliferation capacity of spleen cells were not affected by hybrid CaP nanoparticles compared with their control cells. The hybrid CaP nanoparticles were characterized by scanning/transmission electron microscopy (SEM/TEM); Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction patterns (XRD), Raman spectroscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). These methods revealed that NDV was successfully conjugated on nanoparticles. The ability of the hybrid CaP nanoparticles to induce different cytokine mRNAs in the spleen cells of 18-day old embryonated chicken eggs (ECEs) was studied by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). NDV conjugated particles induced a high expression of Th1 cytokines such as interferon (IFN)-α, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α of and Th2 cytokines, interleukin (IL) 6 and IL-10. Uncoupled NDV induced only Th1 cytokines, IFN-α, INF-γ and TNF-α. The hybrid particles alone did not induce any cytokines. This confirmed that nanoparticle coupling could induce differential cytokine profiles and hence can be used as an alternate strategy to direct favorable immune responses in animals or chickens using appropriate vaccination carrier. - Highlights: • NDV conjugated hybrid CaP NP induced differential cytokine profiles in embryonated chicken eggs. �
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Viswanathan, Kaliyaperumal [Translational Research Platform for Veterinary Biologicals (TRPVB), Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Chennai 600 051, Tamil Nadu (India); Rathish, P.; Gopinath, V.P.; Janice, R. [Department of Animal Biotechnology, Madras Veterinary College, Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Chennai 600 007 (India); Dhinakar Raj, G., E-mail: dhinakarrajg@tanuvas.org.in [Department of Animal Biotechnology, Madras Veterinary College, Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Chennai 600 007 (India); Translational Research Platform for Veterinary Biologicals (TRPVB), Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Chennai 600 051, Tamil Nadu (India)
2014-12-01
In this report, the hybrid calcium phosphate (CaP) nanoparticles were synthesized and functionalized with Newcastle disease virus (NDV). These nanoparticles were synthesized by a combination of co-precipitation and polymerization process and functionalized with amino propyl triethoxy silane before coupling to NDV. The 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay of chicken spleen cells incubated with these nanoparticles indicated that, these particles did not exert any significant cytotoxicity. The effects of hybrid CaP nanoparticles on cell cycle were assayed using a flow cytometer. The results demonstrated that the cell viability and proliferation capacity of spleen cells were not affected by hybrid CaP nanoparticles compared with their control cells. The hybrid CaP nanoparticles were characterized by scanning/transmission electron microscopy (SEM/TEM); Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction patterns (XRD), Raman spectroscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). These methods revealed that NDV was successfully conjugated on nanoparticles. The ability of the hybrid CaP nanoparticles to induce different cytokine mRNAs in the spleen cells of 18-day old embryonated chicken eggs (ECEs) was studied by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). NDV conjugated particles induced a high expression of Th1 cytokines such as interferon (IFN)-α, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α of and Th2 cytokines, interleukin (IL) 6 and IL-10. Uncoupled NDV induced only Th1 cytokines, IFN-α, INF-γ and TNF-α. The hybrid particles alone did not induce any cytokines. This confirmed that nanoparticle coupling could induce differential cytokine profiles and hence can be used as an alternate strategy to direct favorable immune responses in animals or chickens using appropriate vaccination carrier. - Highlights: • NDV conjugated hybrid CaP NP induced differential cytokine profiles in embryonated chicken eggs. �
-
Cetuximab-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles for cancer imaging and therapy
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tseng SH
2015-05-01
Full Text Available Shih-Heng Tseng,1,2 Min-Yuan Chou,2 I-Ming Chu1 1Department of Chemical Engineering, National Tsing Hua University, 2Biomedical Technology and Device Research Laboratories, Industrial Technology Research Institute, Hsinchu, Taiwan Abstract: We have developed a theranostic nanoparticle, ie, cet-PEG-dexSPIONs, by conjugation of the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR monoclonal antibody, cetuximab, to dextran-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs via periodate oxidation. Approximately 31 antibody molecules were conjugated to each nanoparticle. Cet-PEG-dexSPIONs specifically bind to EGFR-expressing tumor cells and enhance image contrast on magnetic resonance imaging. Cet-PEG-dexSPION-treated A431 cells showed significant inhibition of epidermal growth factor-induced EGFR phosphorylation and enhancement of EGFR internalization and degradation. In addition, a significant increase in apoptosis was detected in EGFR-overexpressing cell lines, A431 and 32D/EGFR, after 24 hours of incubation at 37°C with cet-PEG-dexSPIONs compared with cetuximab alone. The antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of cetuximab was observed in cet-PEG-dexSPIONs. The results demonstrated that cet-PEG-dexSPIONs retained the therapeutic effect of cetuximab in addition to having the ability to target and image EGFR-expressing tumors. Cet-PEG-dexSPIONs represent a promising targeted magnetic probe for early detection and treatment of EGFR-expressing tumor cells. Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor, cetuximab, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle, magnetic resonance imaging, sodium periodate, polyethylene glycol
-
A single-layer peptide nanofiber for enhancing the cytotoxicity of trastuzumab (anti-HER)
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Malik, Ruchi; Wagh, Anil; Qian, Steven; Law, Benedict, E-mail: Shek.law@ndsu.edu [College of Pharmacy, Nursing, and Allied Sciences, North Dakota State University, Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences (United States)
2013-06-15
A multivalent system is often employed to enhance the effectiveness of a targeted therapy. In the present study, we report a single-layer peptide nanofiber (NFP) as a multivalent targeting platform to improve the cytotoxicity of trastuzumab (anti-HER), a monoclonal antibody targeting the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) in approximately 20 % of breast cancer patients. The trastuzumab-conjugated nanofiber (anti-HER/NFP) was 100 Multiplication-Sign 4 nm in size and was assembled from multiple peptide units (mPEG-BK(FITC)SGASNRA-kldlkldlkldl-CONH{sub 2}). The optimized preparation was attached with approximately 10 antibodies at the surface. Because of an increase in the multivalency, anti-HER/NFP was able to truncate more cell surface HER-2 and, thus, showed an enhanced cytotoxicity toward HER-2 positive SKBr-3 human breast cancer as compared to the free anti-HER. Western blot analysis and fluorescence microscopic studies confirmed that there was a significant downregulation of the HER-2 level and also inhibition of the cell survival cell signaling pathways including the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Our data suggested that NFP can be useful as a multivalent platform for immunotherapy, especially in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents in the future.
-
Asada, Ryoko; Kageyama, Katsuhiro; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Kimura, Masatugu; Saitoh, Yasukazu; Miwa, Nobuhiko
2012-05-01
In this study, using human tongue squamous carcinoma cells (HSC-4) carcinostatic activity was compared for diverse L-ascorbic acid (Asc) derivatives, including the 'straight-C(16)-chain types', 6-O-palmitoyl-Asc (A6-P) and Asc-2-phosphate-6-O-palmitate sodium salt (APPS), as well as the 'branched-C(16)-chain types', Asc-2-phosphate-6-O-(2'-hexyl)decanoate (APHD), an isomer of APPS, and Asc-2,3,5,6-O-tetra-(2'-hexyl)decanoate (VCIP). The order of magnitude of the carcinostatic effects at 37°C was: APPS>A6-P = APHD>VCIP and at 42°C was APPS = A6-P>APHD>VCIP. Therefore, the two straight-C(16)-chain derivatives, APPS and A6-P, had a greater effect compared to the two branched-C(16)-chain Asc derivatives, which are considered to have more difficulty with 'orientation along cell-membrane-glycerolipid direction'. APPS-treated HCS-4 cells were observed for a decrease in cell number, cell shrinkage, pycnosis indicative of apoptosis and cell deformation. The order of cytotoxicity for the normal human dermal fibroblasts (OUMS-36) at 37°C was: A6-P (50% inhibitory concentration: 150-300 μM)>APHD (450-600 μM)>Asc = APPS (800-1000 μM). Accordingly, APHD was more cytotoxic than APPS, since the straight-C(16)-chain type, which was eliminated after the enzymatic esterolysis of APPS, is metabolized via the 'fatty acid β-oxidation cycle' more efficiently in normal cells. Thus, APPS had a greater advantage over APHD, A6-P and VCIP in terms of carcinostatic effects at 37°C, carcinostasis promotion at 42°C and a decrease of cytotoxicity to normal cells. This observation suggests a marked potential for aliphatic chain-moiety structures as anticancer agents, due to their cancer-selective carcinostasis and combined efficacy with hyperthermia, without causing side effects.
-
Voltan, Rebecca; Rimondi, Erika; Melloni, Elisabetta; Rigolin, Gian Matteo; Casciano, Fabio; Arcidiacono, Maria Vittoria; Celeghini, Claudio; Cuneo, Antonio; Zauli, Giorgio; Secchiero, Paola
2016-10-25
The aim of this study was to investigate the anti-leukemic activity of the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor Ibrutinib in combination with the small molecule MDM-2 inhibitor Nutlin-3 in preclinical models. The potential efficacy of the Ibrutinib/Nutlin-3 combination was evaluated in vitro in a panel of B leukemic cell lines (EHEB, JVM-2, JVM-3, MEC-1, MEC-2) and in primary B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) patient samples, by assessing cell viability, cell cycle profile, apoptosis and intracellular pathway modulations. Validation of the combination therapy was assessed in a B leukemic xenograft mouse model. Ibrutinib exhibited variable anti-leukemic activity in vitro and the combination with Nutlin-3 synergistically enhanced the induction of apoptosis independently from the p53 status. Indeed, the Ibrutinib/Nutlin-3 combination was effective in promoting cytotoxicity also in primary B-CLL samples carrying 17p13 deletion and/or TP53 mutations, already in therapy with Ibrutinib. Molecular analyses performed on both B-leukemic cell lines as well as on primary B-CLL samples, while confirming the switch-off of the MAPK and PI3K pro-survival pathways by Ibrutinib, indicated that the synergism of action with Nutlin-3 was independent by p53 pathway and was accompanied by the activation of the DNA damage cascade signaling through the phosphorylation of the histone protein H2A.X. This observation was confirmed also in the JVM-2 B leukemic xenograft mouse model. Taken together, our data emphasize that the Ibrutinib/Nutlin-3 combination merits to be further evaluated as a therapeutic option for B-CLL.
-
Tang, Yang; Zhang, Siqi; Chang, Yajing; Fan, Dacheng; Agostini, Ariane De; Zhang, Lijuan; Jiang, Tao
2018-04-12
Most β-d-xylosides with hydrophobic aglycones are nontoxic primers for glycosaminoglycan assembly in animal cells. However, when Ebselen was conjugated to d-xylose, d-glucose, d-galactose, and d-lactose (8A-D), only Ebselen β-d-xyloside (8A) showed significant cytotoxicity in human cancer cells. The following facts indicated that the aglycone Ebselen and β-d-xyloside primed glycosaminoglycans co-contributed to the observed cytotoxicity: 1. Ebselen induced S phase cell cycle arrest, whereas 8A induced G2/M cell cycle arrest; 2. 8A augmented early and late phase cancer cell apoptosis significantly compared to that of Ebselen and 8B-D; 3. Both 8A and phenyl-β-d-xyloside primed glycosaminoglycans with similar disaccharide compositions in CHO-pgsA745 cells; 4. Glycosaminoglycans could be detected inside of cells only when treated with 8A, indicating Ebselen contributed to the unique property of intracellular localization of the primed glycosaminoglycans. Thus, 8A represents a lead compound for the development of novel antitumor strategy by targeting glycosaminoglycans.
-
Fisher, Robert A
1983-01-01
This book appears at a time of intense activity in optical phase conjugation. We chose not to await the maturation of the field, but instead to provide this material in time to be useful in its development. We have tried very hard to elucidate and interrelate the various nonlinear phenomena which can be used for optical phase conjugation.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Niescioruk, Anna; Nieciecka, Dorota; Puszko, Anna K.; Królikowska, Agata [University of Warsaw, Faculty of Chemistry (Poland); Kosson, Piotr [Polish Academy of Sciences, Department of Neuropeptides, Mossakowski Medical Research Centre (Poland); Perret, Gerard Y. [Université Paris 13, Sorbonne Paris Cité (France); Krysinski, Pawel; Misicka, Aleksandra, E-mail: misicka@chem.uw.edu.pl [University of Warsaw, Faculty of Chemistry (Poland)
2017-05-15
Superparamagnetic iron oxide-based nanoparticles (SPIONs) are promising carriers as targeted drug delivery vehicles, because they can be guided to their target with the help of an external magnetic field. Functionalization of nanoparticles’ surface with molecules, which bind with high affinity to receptors on target tissue significantly facilitates delivery of coated nanoparticles to their targeted site. Here, we demonstrate conjugation of an antiangiogenic and antitumor peptide ATWLPPR (A7R) to SPIONs modified with sebacic acid (SPIONs-SA). Successful conjugation was confirmed by various analytical techniques (FTIR, SERS, SEM-EDS, TEM, TGA). Cell cytotoxicity studies, against two cell lines (HUVEC and MDA-MB-231) indicated that SPIONs modified with A7R reduced HUVEC cell viability at concentrations higher than 0.01 mg Fe/mL, in comparison to cells that were exposed to either the nanoparticles modified with sebacic acid or A7R peptide solely, what might be partially caused by a process of internalization.
-
Li, Dandan; Chen, Xin; Wang, Hong; Liu, Jie; Zheng, Meiling; Fu, Yang; Yu, Yuan; Zhi, Jinfang
2017-12-01
In this study, a multicomponent nanodiamonds (NDs)-based targeting drug delivery system, cetuximab-NDs-cisplatin bioconjugate, combining both specific targeting and enhanced therapeutic efficacy capabilities, is developed and characterized. The specific targeting ability of cetuximab-NDs-cisplatin system on human liver hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells is evaluated through epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) blocking experiments, since EGFR is over-expressed on HepG2 cell membrane. Besides, cytotoxic evaluation confirms that cetuximab-NDs-cisplatin system could significantly inhibit the growth of HepG2 cells, and the therapeutic activity of this system is proven to be better than that of both nonspecific NDs-cisplatin conjugate and specific EGF-NDs-cisplatin conjugate. Furthermore, a 3-dimensional (3D) Raman imaging technique is utilized to visualize the targeting efficacy and enhanced internalization of cetuximab-NDs-cisplatin system in HepG2 cells, using the NDs existing in the bioconjugate as Raman probes, based on the characteristic Raman signal of NDs at 1332 cm -1 . These advantageous properties of cetuximab-NDs-cisplatin system propose a prospective imaging and treatment tool for further diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. © 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Neeson, Paul J; Hsu, Andy K; Chen, Yin R; Halse, Heloise M; Loh, Joanna; Cordy, Reece; Fielding, Kate; Davis, Joanne; Noske, Josh; Davenport, Alex J; Lindqvist-Gigg, Camilla A; Humphreys, Robin; Tai, Tsin; Prince, H Miles; Trapani, Joseph A; Smyth, Mark J; Ritchie, David S
2015-09-01
There is increasing evidence that some cancer therapies can promote tumor immunogenicity to boost the endogenous antitumor immune response. In this study, we used the novel combination of agonistic anti-TRAIL-R1 antibody (mapatumumab, Mapa) with low dose bortezomib (LDB) for this purpose. The combination induced profound myeloma cell apoptosis, greatly enhanced the uptake of myeloma cell apoptotic bodies by dendritic cell (DC) and induced anti-myeloma cytotoxicity by both CD8 + T cells and NK cells. Cytotoxic lymphocyte expansion was detected within 24 h of commencing therapy and was maximized when myeloma-pulsed DC were co-treated with low dose bortezomib and mapatumumab (LDB+Mapa) in the presence of NK cells. This study shows that Mapa has two distinct but connected modes of action against multiple myeloma (MM). First, when combined with LDB, Mapa produced powerful myeloma cell apoptosis; secondly, it promoted DC priming and an NK cell-mediated expansion of anti-myeloma cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL). Overall, this study indicates that Mapa can be used to drive potent anti-MM immune responses.
-
Molecular design of sequence specific DNA alkylating agents.
Minoshima, Masafumi; Bando, Toshikazu; Shinohara, Ken-ichi; Sugiyama, Hiroshi
2009-01-01
Sequence-specific DNA alkylating agents have great interest for novel approach to cancer chemotherapy. We designed the conjugates between pyrrole (Py)-imidazole (Im) polyamides and DNA alkylating chlorambucil moiety possessing at different positions. The sequence-specific DNA alkylation by conjugates was investigated by using high-resolution denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). The results showed that polyamide chlorambucil conjugates alkylate DNA at flanking adenines in recognition sequences of Py-Im polyamides, however, the reactivities and alkylation sites were influenced by the positions of conjugation. In addition, we synthesized conjugate between Py-Im polyamide and another alkylating agent, 1-(chloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-1,2-dihydro-3H-benz[e]indole (seco-CBI). DNA alkylation reactivies by both alkylating polyamides were almost comparable. In contrast, cytotoxicities against cell lines differed greatly. These comparative studies would promote development of appropriate sequence-specific DNA alkylating polyamides against specific cancer cells.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
William I. O’Malley
2016-02-01
Full Text Available A new bifunctional macrocyclic chelator featuring a conjugatable alkynyl-naphthalimide fluorophore pendant group has been prepared and its Gd(III complex coupled to a cell-penetrating lipidated azido-Tat peptide derivative using Cu(I-catalysed “click” chemistry. The resulting fluorescent conjugate is able to enter CAL-33 tongue squamous carcinoma cells, as revealed by confocal microscopy, producing a very modest anti-proliferative effect (IC50 = 93 µM. Due to the photo-reactivity of the naphthalimide moiety, however, the conjugate’s cytotoxicity is significantly enhanced (IC50 = 16 µM upon brief low-power UV-A irradiation.
-
Amphotericin B-conjugated polypeptide hydrogels as a novel innovative strategy for fungal infections
Shu, Chang; Li, Tengfei; Yang, Wen; Li, Duo; Ji, Shunli; Ding, Li
2018-03-01
The present work is focused on the design and development of novel amphotericin B (AmB)-conjugated biocompatible and biodegradable polypeptide hydrogels to improve the antifungal activity. Using three kinds of promoting self-assembly groups (2-naphthalene acetic acid (Nap), naproxen (Npx) and dexamethasone (Dex)) and polypeptide sequence (Phe-Phe-Asp-Lys-Tyr, FFDKY), we successfully synthesized the Nap-FFDK(AmB)Y gels, Npx-FFDK(AmB)Y gels and Dex-FFDK(AmB)Y gels. The AmB-conjugated hydrogelators are highly soluble in different aqueous solutions. The cryo-transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy micrographs of hydrogels afford nanofibres with a width of 20-50 nm. Powder X-ray diffraction analyses demonstrate that the crystalline structures of the AmB and Dex are changed into amorphous structures after the formation of hydrogels. Circular dichroism spectra of the solution of blank carriers and the corresponding drug deliveries further help elucidate the molecular arrangement in gel phase, indicating the existence of turn features. The in vitro drug releases suggest that the AmB-conjugated hydrogels are suitable as drug-controlled release vehicles for hydrophobic drugs. The antifungal effect of AmB-conjugated hydrogels significantly exhibits the antifungal activity against Candida albicans. The results of the present study indicated that the AmB-conjugated hydrogels are suitable carriers for poorly water soluble drugs and for enhancement of therapeutic efficacy of antifungal drugs.
-
Guarnieri, Daniela; Biondi, Marco; Yu, Hui; Belli, Valentina; Falanga, Andrea P; Cantisani, Marco; Galdiero, Stefania; Netti, Paolo A
2015-03-01
A major issue in chemotherapy is the lack of specificity of many antitumor drugs, which cause severe side effects and an impaired therapeutic response. Here we report on the design and characterization of model tumor activated prodrug-conjugated polystyrene (PS) nanoparticles (TAP-NPs) for the release of doxorubicin (Dox) triggered by matrix metalloprotease-2 (MMP2) enzyme, which is overexpressed in the extracellular matrix of tumors. In particular, TAP-NPs were produced by attaching Dox to poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) through two MMP2-cleavable enzymes. The resulting adduct was then tethered to PS NPs. Results showed that Dox release was actually triggered by MMP2 cleavage and was dependent on enzyme concentration, with a plateau around 20 nM. Furthermore, significant cell cytotoxicity was observed towards three cell lines only in the presence of MMP2, but not in cells without enzyme pre-treatment, even after NP internalization by cells. These findings indicate the potential of TAP-NPs as suitable nanocarriers for an on demand, tumor--specific delivery of antitumor drugs after the response to an endogenous stimulus. Further advancements will focus on the translation of this production technology to biodegradable systems for the safe transport of cytotoxic drug to tumor tissues. © 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
-
Qualidade conjugal: mapeando conceitos
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Clarisse Mosmann
2006-12-01
Full Text Available Apesar da ampla utilização do conceito de qualidade conjugal, identifica-se falta de clareza conceitual acerca das variáveis que o compõem. Esse artigo apresenta revisão da literatura na área com o objetivo de mapear o conceito de qualidade conjugal. Foram analisadas sete principais teorias sobre o tema: Troca Social, Comportamental, Apego, Teoria da Crise, Interacionismo Simbólico. Pelos postulados propostos nas diferentes teorias, podem-se identificar três grupos de variáveis fundamentais na definição da qualidade conjugal: recursos pessoais dos cônjuges, contexto de inserção do casal e processos adaptativos. Neste sentido, a qualidade conjugal é resultado do processo dinâmico e interativo do casal, razão deste caráter multidimensional.
-
Kumar, Neeraj; George, Blassan Plackal Adimuriyil; Abrahamse, Heidi; Parashar, Vyom; Ngila, Jane Catherine
2017-02-01
Nanotechnology provides an emerging potent alternate mode of cancer therapy. Nanomaterials dispersion or solubility is of particular concern in utilising their full potential applications in biomedical fields. PEGylation of nanomaterials is considered to provide products with stealth properties, and physiological environment with no obvious adverse effects. The purpose of this work was to develop a sustainable one-step method for fabrication of hierarchical microspheres of PEGylated MoS2 nanosheets using a stoichiometric ratio of Mo(VI) and thiourea. This study further investigated the cytotoxicity of the PEGylated MoS2 nanosheets towards lung (A549) and breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines by analysing morphological changes and performing dose-dependent cell proliferation, and cytotoxicity analysis using adenosine 5‧-triphosphate (ATP), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay. For comparison, MoO3 nanorods were synthesised by simple chemical route and their cytotoxicity towards lung (A549) and breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines were checked. The findings suggested that PEGylated MoS2 nanosheets have excellent cytotoxicity towards breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines, and MoO3 have better cytotoxicity towards lung (A549) cancer cell lines. This work envisages an accessible foundation for engineering sophisticated biomolecule-MoS2 nanosheets conjugation due to the defect-rich biocompatible surface, to achieve great versatility, additional functions, and further advances in the biomedical field.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cai, Demin; Li, Hongji; Zhou, Bo; Han, Liqiang; Zhang, Xiaomei; Yang, Guoyu; Yang, Guoqing
2012-01-01
Highlights: ► Conjugated linoleic acid supplementation suppresses perilipin1 in epididymal fat. ► Conjugated linoleic acid inhibits promoter activity of perilipin1 in 3T3-L1 cells. ► Conjugated linoleic acids elevate basal but blunt hormone-stimulated lipolysis. -- Abstract: Perilipin1, a coat protein of lipid droplet, plays a key role in adipocyte lipolysis and fat formation of adipose tissues. However, it is not clear how the expression of perilipin1 is affected in the decreased white adipose tissues (WAT) of mice treated with dietary supplement of conjugated linoleic acids (CLA). Here we obtained lipodystrophic mice by dietary administration of CLA which exhibited reduced epididymal (EPI) WAT, aberrant adipocytes and decreased expression of leptin in this tissue. We found both transcription and translation of perilipin1 was suppressed significantly in EPI WAT of CLA-treated mice compared to that of control mice. The gene expression of negative regulator tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and the positive regulator Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ (PPARγ) of perilipin1 was up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively. In cultured 3T3-L1 cells the promoter activity of perilipin1 was dramatically inhibited in the presence of CLA. Using ex vivo experiment we found that the basal lipolysis was elevated but the hormone-stimulated lipolysis blunted in adipose explants of CLA-treated mice compared to that of control mice, suggesting that the reduction of perilipin1 in white adipose tissues may at least in part contribute to CLA-mediated alternation of lipolysis of WAT.
-
Mind Bomb Regulates Cell Death during TNF Signaling by Suppressing RIPK1’s Cytotoxic Potential
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Rebecca Feltham
2018-04-01
Full Text Available Summary: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF is an inflammatory cytokine that can signal cell survival or cell death. The mechanisms that switch between these distinct outcomes remain poorly defined. Here, we show that the E3 ubiquitin ligase Mind Bomb-2 (MIB2 regulates TNF-induced cell death by inactivating RIPK1 via inhibitory ubiquitylation. Although depletion of MIB2 has little effect on NF-κB activation, it sensitizes cells to RIPK1- and caspase-8-dependent cell death. We find that MIB2 represses the cytotoxic potential of RIPK1 by ubiquitylating lysine residues in the C-terminal portion of RIPK1. Our data suggest that ubiquitin conjugation of RIPK1 interferes with RIPK1 oligomerization and RIPK1-FADD association. Disruption of MIB2-mediated ubiquitylation, either by mutation of MIB2’s E3 activity or RIPK1’s ubiquitin-acceptor lysines, sensitizes cells to RIPK1-mediated cell death. Together, our findings demonstrate that Mind Bomb E3 ubiquitin ligases can function as additional checkpoint of cytokine-induced cell death, selectively protecting cells from the cytotoxic effects of TNF. : Feltham et al. show that MIB2 directly ubiquitylates RIPK1 upon TNF stimulation, suppressing the cytotoxic potential of RIPK1 and acting as a checkpoint within the TNF signaling pathway. Keywords: MIB2, RIPK1, TNF, cell death, caspase-8, IAPs, ubiquitin
-
Bacalocostantis, Irene; Mane, Viraj P; Kang, Michael S; Goodley, Addison S; Muro, Silvia; Kofinas, Peter
2012-05-14
Polymers have attracted much attention as potential gene delivery vectors due to their chemical and structural versatility. However, several challenges associated with polymeric carriers, including low transfection efficiencies, insufficient cargo release, and high cytotoxicity levels have prevented clinical implementation. Strong electrostatic interactions between polymeric carriers and DNA cargo can prohibit complete cargo release within the cell. As a result, cargo DNA never reaches the cell's nucleus where gene expression takes place. In addition, highly charged cationic polymers have been correlated with high cytotoxicity levels, making them unsuitable carriers in vivo. Using poly(allylamine) (PAA) as a model, we investigated how pH-sensitive disulfide cross-linked polymer networks can improve the delivery potential of cationic polymer carriers. To accomplish this, we conjugated thiol-terminated pendant chains onto the primary amines of PAA using 2-iminothiolane, developing three new polymer vectors with 5, 13, or 20% thiol modification. Unmodified PAA and thiol-conjugated polymers were tested for their ability to bind and release plasmid DNA, their capacity to protect genetic cargo from enzymatic degradation, and their potential for endolysosomal escape. Our results demonstrate that polymer-plasmid complexes (polyplexes) formed by the 13% thiolated polymer demonstrate the greatest delivery potential. At high N/P ratios, all thiolated polymers (but not unmodified counterparts) were able to resist decomplexation in the presence of heparin, a negatively charged polysaccharide used to mimic in vivo polyplex-protein interactions. Further, all thiolated polymers exhibited higher buffering capacities than unmodified PAA and, therefore, have a greater potential for endolysosomal escape. However, 5 and 20% thiolated polymers exhibited poor DNA binding-release kinetics, making them unsuitable carriers for gene delivery. The 13% thiolated polymers, on the other hand
-
Cross-Conjugated n-Dopable Aromatic Polyketone
Voortman, Thomas P.; Bartesaghi, Davide; Koster, L. Jan Anton; Chiechi, Ryan C.
2015-01-01
This paper describes the synthesis and characterization of a high molecular weight cross-conjugated polyketone synthesized via scalable Friedel Crafts chemistry. Cross-conjugated polyketones are precursors to conjugated polyions; they become orders of magnitude more conductive after a two-electron
-
Structure-cytotoxicity relationships for dietary flavonoids
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Breinholt, V.; Dragsted, L.O.
1998-01-01
The cytotoxicity of a large series of dietary flavonoids was tested in a non-tumorigenic mouse and two human cancer cell lines, using the neutral red dye exclusion assay. All compounds tested exhibited a concentration-dependent cytotoxic action in the employed cell lines. The relative cytotoxicity...... of the flavonoids, however, Tvas found to vary greatly among the different cell Lines. With a few exceptions, the investigated flavonoids were more cytotoxic to the human cancer cell lines, than the mouse cell line. The differences in cytotoxicity were accounted for in part by differences in cellular uptake...... and metabolic capacity among the different cell types. In 3T3 cells fairly consistent structure-cytotoxicity relationships were found. The most cytotoxic structures tested in 3T3 cells were flavonoids with adjacent 3',4' hydroxy groups on the B-ring, such as luteolin, quercetin, myricetin, fisetin, eriodictyol...
-
Laminin-111-derived peptide conjugated fibrin hydrogel restores salivary gland function.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kihoon Nam
Full Text Available Hyposalivation reduces the patient quality of life, as saliva is important for maintaining oral health. Current treatments for hyposalivation are limited to medications such as the muscarinic receptor agonists, pilocarpine and cevimeline. However, these therapies only provide temporary relief. Therefore, alternative therapies are essential to restore salivary gland function. An option is to use bioengineered scaffolds to promote functional salivary gland regeneration. Previous studies demonstrated that the laminin-111 protein is critical for intact salivary gland cell cluster formation and organization. However, laminin-111 protein as a whole is not suitable for clinical applications as some protein domains may contribute to unwanted side effects such as degradation, tumorigenesis and immune responses. Conversely, the use of synthetic laminin-111 peptides makes it possible to minimize the immune reactivity or pathogen transfer. In addition, it is relatively simple and inexpensive as compared to animal-derived proteins. Therefore, the goal of this study was to demonstrate whether a 20 day treatment with laminin-111-derived peptide conjugated fibrin hydrogel promotes tissue regeneration in submandibular glands of a wound healing mouse model. In this study, laminin-111-derived peptide conjugated fibrin hydrogel significantly accelerated formation of salivary gland tissue. The regenerated gland tissues displayed not only structural but also functional restoration.
-
Aldose reductase regulates acrolein-induced cytotoxicity in human small airway epithelial cells.
Yadav, Umesh C S; Ramana, K V; Srivastava, Satish K
2013-12-01
Aldose reductase (AR), a glucose-metabolizing enzyme, reduces lipid aldehydes and their glutathione conjugates with more than 1000-fold efficiency (Km aldehydes 5-30 µM) relative to glucose. Acrolein, a major endogenous lipid peroxidation product as well as a component of environmental pollutants and cigarette smoke, is known to be involved in various pathologies including atherosclerosis, airway inflammation, COPD, and age-related disorders, but the mechanism of acrolein-induced cytotoxicity is not clearly understood. We have investigated the role of AR in acrolein-induced cytotoxicity in primary human small airway epithelial cells (SAECs). Exposure of SAECs to varying concentrations of acrolein caused cell death in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. AR inhibition by fidarestat prevented the low-dose (5-10 µM) but not the high-dose (>10 µM) acrolein-induced SAEC death. AR inhibition protected SAECs from low-dose (5 µM) acrolein-induced cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Inhibition of acrolein-induced apoptosis by fidarestat was confirmed by decreased condensation of nuclear chromatin, DNA fragmentation, comet tail moment, and annexin V fluorescence. Further, fidarestat inhibited acrolein-induced translocation of the proapoptotic proteins Bax and Bad from the cytosol to the mitochondria and that of Bcl2 and BclXL from the mitochondria to the cytosol. Acrolein-induced cytochrome c release from mitochondria was also prevented by AR inhibition. The mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), such as extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2, stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, and p38MAPK, and c-Jun were transiently activated in airway epithelial cells by acrolein in a concentration- and time-dependent fashion, which was significantly prevented by AR inhibition. These results suggest that AR inhibitors could prevent acrolein-induced cytotoxicity in the lung epithelial cells. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights
-
Aldose reductase regulates acrolein-induced cytotoxicity in human small airway epithelial cells
Yadav, Umesh CS; Ramana, KV; Srivastava, SK
2013-01-01
Aldose reductase (AR), a glucose metabolizing enzyme, reduces lipid aldehydes and their glutathione conjugates with more than 1000-fold efficiency (Km aldehydes 5-30μM) than glucose. Acrolein, a major endogenous lipid peroxidation product as well as component of environmental pollutant and cigarette smoke, is known to be involved in various pathologies including atherosclerosis, airway inflammation, COPD, and age-related disorders but the mechanism of acrolein-induced cytotoxicity is not clearly understood. We have investigated the role of AR in acrolein-induced cytotoxicity in primary human small airway epithelial cells SAECs. Exposure of SAECs to varying concentrations of acrolein caused cell-death in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. AR inhibition by fidarestat prevented the low (5 to 10 μM) but not high (>10 μM) concentrations of acrolein-induced SAECs cell death. AR inhibition protected SAECs from low dose (5 μM) acrolein-induced cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Inhibition of acrolein-induced apoptosis by fidarestat was confirmed by decreased condensation of nuclear chromatin, DNA fragmentation, comet tail-moment, and annexin-V fluorescence. Further, fidarestat inhibited acrolein-induced translocation of pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bad from cytosol to the mitochondria, and that of Bcl2 and BclXL from mitochondria to cytosol. Acrolein-induced cytochrome c release from mitochondria was also prevented by AR inhibition. The mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) such as extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2), stress-activated protein kinases/c-jun NH2-terminal kinases (SAPK/JNK) and p38MAPK, and c-jun were transiently activated in airway epithelial cells by acrolein in a concentration and time-dependent fashion, which were significantly prevented by AR inhibition. These results suggest that AR inhibitors could prevent acrolein-induced cytotoxicity in the lung epithelial cells. PMID:23770200
-
Li, Yi; Gu, Christine; Gruenhagen, Jason; Zhang, Kelly; Yehl, Peter; Chetwyn, Nik P; Medley, Colin D
2015-05-08
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are complex therapeutic agents combining the specific targeting properties of antibodies and highly potent cytotoxic small molecule drugs to selectively eliminate tumor cells while limiting the toxicity to normal healthy tissues. One unique critical quality attribute of ADCs is the content of unconjugated small molecule drug present from either incomplete conjugation or degradation of the ADC. In this work, size exclusion chromatography (SEC) was coupled with reversed-phase (RP) HPLC in an online 2-dimensional chromatography format for identification and quantitation of unconjugated small molecule drugs and related small molecule impurities in ADC samples directly without sample preparation. The SEC method in the 1st dimension not only separated the small molecule impurities from the intact ADC, but also provided information about the size variants (monomer, dimer, aggregates, etc.) of the ADC. The small molecule peak from the SEC was trapped and sent to a RP-HPLC in the 2nd dimension to further separate and quantify the different small molecule impurities present in the ADC sample. This SEC-RP 2D-LC method demonstrated excellent precision (%RSDmolecule degradation products and aggregation of the conjugate were observed in the stability samples and the degradation pathways of the ADC were investigated. This 2D-LC method offers a powerful tool for ADC characterization and provides valuable information for conjugation and formulation development. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Parab, Harshala J; Huang, Jing-Hong; Liu, Ru-Shi; Lai, Tsung-Ching; Jan, Yi-Hua; Wang, Jui-Ling; Hsiao, Michael; Chen, Chung-Hsuan; Hwu, Yeu-Kuang; Tsai, Din Ping; Chuang, Shih-Yi; Pang, Jong-Hwei S
2011-01-01
The feasibility of using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for biomedical applications has led to considerable interest in the development of novel synthetic protocols and surface modification strategies for AuNPs to produce biocompatible molecular probes. This investigation is, to our knowledge, the first to elucidate the synthesis and characterization of sodium hexametaphosphate (HMP)-stabilized gold nanoparticles (Au-HMP) in an aqueous medium. The role of HMP, a food additive, as a polymeric stabilizing and protecting agent for AuNPs is elucidated. The surface modification of Au-HMP nanoparticles was carried out using polyethylene glycol and transferrin to produce molecular probes for possible clinical applications. In vitro cell viability studies performed using as-synthesized Au-HMP nanoparticles and their surface-modified counterparts reveal the biocompatibility of the nanoparticles. The transferrin-conjugated nanoparticles have significantly higher cellular uptake in J5 cells (liver cancer cells) than control cells (oral mucosa fibroblast cells), as determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. This study demonstrates the possibility of using an inexpensive and non-toxic food additive, HMP, as a stabilizer in the large-scale generation of biocompatible and monodispersed AuNPs, which may have future diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Parab, Harshala J; Huang, Jing-Hong; Liu, Ru-Shi [Department of Chemistry, National Taiwan University, Taipei 106, Taiwan (China); Lai, Tsung-Ching; Jan, Yi-Hua; Wang, Jui-Ling; Hsiao, Michael; Chen, Chung-Hsuan [Genomics Research Center, Academia Sinica, Taipei 115, Taiwan (China); Hwu, Yeu-Kuang [Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica, Taipei 115, Taiwan (China); Tsai, Din Ping [Department of Physics, National Taiwan University, Taipei 106, Taiwan (China); Chuang, Shih-Yi; Pang, Jong-Hwei S, E-mail: rsliu@ntu.edu.tw, E-mail: mhsiao@gate.sinica.edu.tw [Graduate Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, Chang Gung University, Tao-Yuan, Taiwan (China)
2011-09-30
The feasibility of using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for biomedical applications has led to considerable interest in the development of novel synthetic protocols and surface modification strategies for AuNPs to produce biocompatible molecular probes. This investigation is, to our knowledge, the first to elucidate the synthesis and characterization of sodium hexametaphosphate (HMP)-stabilized gold nanoparticles (Au-HMP) in an aqueous medium. The role of HMP, a food additive, as a polymeric stabilizing and protecting agent for AuNPs is elucidated. The surface modification of Au-HMP nanoparticles was carried out using polyethylene glycol and transferrin to produce molecular probes for possible clinical applications. In vitro cell viability studies performed using as-synthesized Au-HMP nanoparticles and their surface-modified counterparts reveal the biocompatibility of the nanoparticles. The transferrin-conjugated nanoparticles have significantly higher cellular uptake in J5 cells (liver cancer cells) than control cells (oral mucosa fibroblast cells), as determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. This study demonstrates the possibility of using an inexpensive and non-toxic food additive, HMP, as a stabilizer in the large-scale generation of biocompatible and monodispersed AuNPs, which may have future diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
-
Evaluation of antitumor effects of folate-conjugated methyl-β-cyclodextrin in melanoma.
Motoyama, Keiichi; Onodera, Risako; Tanaka, Nao; Kameyama, Kazuhisa; Higashi, Taishi; Kariya, Ryusho; Okada, Seiji; Arima, Hidetoshi
2015-01-01
Melanoma is a life-threatening disorder and its incidence is increasing gradually. Despite the numerous treatment approaches, conventional systemic chemotherapy has not reduced the mortality rate among melanoma patients, probably due to the induction of toxicity to normal tissues. Recently, we have developed folate-conjugated methyl-β-cyclodextrin (FA-M-β-CyD) and clarified its potential as a new antitumor agent involved in autophagic cell death. However, it remains uncertain whether FA-M-β-CyD exerts anticancer effects against melanomas. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the effects of FA-M-β-CyD on the folate receptor-α (FR-α)-expressing melanoma cell-selective cytotoxic effect. FA-M-β-CyD showed cytotoxic effects in Ihara cells, a human melanoma cell line expressing FR-α. In sharp contrast to methyl-β-cyclodextrin, FA-M-β-CyD entered Ihara cells [FR-α(+)] through FR-α-mediated endocytosis. Additionally, FA-M-β-CyD elicited the formation of autophagosomes in Ihara cells. Notably, FA-M-β-CyD suppressed melanoma growth in BALB/c nude recombinase-activating gene-2 (Rag-2)/Janus kinase 3 (Jak3) double deficient mice bearing Ihara cells. Therefore, these results suggest that FA-M-β-CyD could be utilized as a potent anticancer agent for melanoma chemotherapy by regulating autophagy.
-
Waghela, Bhargav N.; Sharma, Anupama; Dhumale, Suhashini; Pandey, Shashibahl M.; Pathak, Chandramani
2015-01-01
Curcumin, an ingredient of turmeric, exhibits a variety of biological activities such as anti-inflammatory, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-proliferative, anti-oxidant, anti-cancer and anti-metastatic. It is a highly pleiotropic molecule that inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Despite its imperative biological activities, chemical instability, photo-instability and poor bioavailability limits its utilization as an effective therapeutic agent. Therefore, enhancing the bioavailability of curcumin may improve its therapeutic index for clinical setting. In the present study, we have conjugated curcumin with a biodegradable polymer Poly (D, L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) and evaluated its apoptotic potential in human colon carcinoma cells (HCT 116). The results show that curcumin-PLGA conjugate efficiently inhibits cell proliferation and cell survival in human colon carcinoma cells as compared to native curcumin. Additionally, curcumin conjugated with PLGA shows improved cellular uptake and exhibits controlled release at physiological pH as compared to native curcumin. The curcumin-PLGA conjugate efficiently activates the cascade of caspases and promotes intrinsic apoptotic signaling. Thus, the results suggest that conjugation potentiates the sustainability, anti-proliferative and apoptotic activity of curcumin. This approach could be a promising strategy to improve the therapeutic index of cancer therapy. PMID:25692854
-
Block-conjugate-gradient method
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McCarthy, J.F.
1989-01-01
It is shown that by using the block-conjugate-gradient method several, say s, columns of the inverse Kogut-Susskind fermion matrix can be found simultaneously, in less time than it would take to run the standard conjugate-gradient algorithm s times. The method improves in efficiency relative to the standard conjugate-gradient algorithm as the fermion mass is decreased and as the value of the coupling is pushed to its limit before the finite-size effects become important. Thus it is potentially useful for measuring propagators in large lattice-gauge-theory calculations of the particle spectrum
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wenjie Jian
2018-03-01
Full Text Available The pulsed electric fields (PEF treatment is a novel method for obtaining glycated proteins by way of a Maillard reaction between proteins and polysaccharides but its effect on the preparation of protein–monosaccharide conjugate has not been explored. This study aimed to prepare bovine serum albumin (BSA–glucose and BSA–mannose conjugates using PEF in pH 10.0 at an intensity of 10 or 20 kV/cm, frequency of 1 kHz, pulse width of 20 μs and 73.5 pulses. The conjugates were evaluated for physicochemical properties. The results indicated that PEF not only promoted Maillard reaction between BSA and glucose or mannose but also alleviated the undesirable browning. PEF treatment favored the increased surface hydrophobicity and emulsifying activity in BSA but reduced surface hydrophobicity and foaming stability and improved foaming capacity in BSA–glucose and BSA–mannose conjugates. These findings provided useful considerations in the application of PEF treatment as a potential method to prepare BSA–monosaccharide conjugates by Maillard reaction.
-
Horiyama, Shizuyo; Kunitomo, Masaru; Yoshikawa, Noriko; Nakamura, Kazuki
2016-01-01
Cigarette smoke contains many harmful chemicals that contribute to the pathogenesis of smoking-related diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer, and cardiovascular disease. Many studies have been done to identify cytotoxic chemicals in cigarette smoke and elucidate the onset of the above-mentioned diseases caused by smoking. However, definitive mechanisms for cigarette smoke toxicity remain unknown. As candidates for cytotoxic chemicals, we have recently found methyl vinyl ketone (MVK) and acetic anhydride in nicotine/tar-free cigarette smoke extract (CSE) using L-tyrosine (Tyr), an amino acid with highly reactive hydroxyl group. The presence of MVK and acetic anhydride in CSE was confirmed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS). We also found new reaction products formed in B16-BL6 mouse melanoma (B16-BL6) cells treated with CSE using LC/MS. These were identified as glutathione (GSH) conjugates of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, MVK, crotonaldehyde (CA), and acrolein (ACR), by the mass value and product ion spectra of these new products. ACR and MVK are type-2 alkenes, which are well known as electron acceptors and form Michael-type adducts to nucleophilic side chain of amino acids on peptides. These α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds may have a key role in CSE-induced cell death.
-
Low cytotoxicity fluorescent PAMAM dendrimer as gene carriers for monitoring the delivery of siRNA
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Guan, Lingmei [Sichuan University, State Key Laboratory of Bio-resources and Eco-environment, The Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences (China); Huang, Saipeng [Chinese Academy of Sciences, State Key Laboratory for Structural Chemistry of Unstable and Stable Species, Center for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry (China); Chen, Zhao [Xi’an Jiaotong University, School of Science (China); Li, Yanchao [Chinese Academy of Sciences, State Key Laboratory for Structural Chemistry of Unstable and Stable Species, Center for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry (China); Liu, Ke [Sichuan University, State Key Laboratory of Bio-resources and Eco-environment, The Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences (China); Liu, Yang, E-mail: yliu@iccas.ac.cn; Du, Libo, E-mail: dulibo@iccas.ac.cn [Chinese Academy of Sciences, State Key Laboratory for Structural Chemistry of Unstable and Stable Species, Center for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry (China)
2015-09-15
Visual detection of gene vectors has attracted a great deal of attention due to the application of these vectors in monitoring and evaluating the effect of gene carriers in living cells. A non-viral vector, the fluorescent PAMAM dendrimer (F-PAMAM), was synthesized through conjugation of PAMAM dendrimers and fluorescein. In vitro and ex vivo experiments show that F-PAMAM exhibits superphotostability, low cytotoxicity and facilitates endocytosis by A549 cells. The vector has a high siRNA binding affinity and it increases the efficiency of cy5-siRNA delivery in A549 cells, in comparison with a cy5-siRNA monomer. Our results provide a new method for simultaneously monitoring the delivery of siRNA and its non-viral carriers in living cells.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wang, Hua-Jie; Yu, Xue-Hong; Wang, Cai-Feng; Cao, Ying
2013-01-01
Series of self-assembled and mono-dispersed bovine serum albumin (BSA)-conjugated ZnS/CuS nano-composites with different Zn/Cu ratios had been successfully synthesized by a combination method of the biomimetic synthesis and ion-exchange strategy under the gentle conditions. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy observation, Fourier transform infrared spectra and zeta potential analysis demonstrated that BSA-conjugated ZnS/CuS nano-composites with well dispersity had the hierarchical structure and BSA was a key factor to control the morphology and surface electro-negativity of final products. The real-time monitoring by atomic absorption spectroscopy and powder X-ray diffraction revealed that the Zn/Cu ratio of nano-composites could be controlled by adjusting the ion-exchange time. In addition, the metabolic and morphological assays indicated that the metabolic proliferation and spread of rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells could be inhibited by nano-composites, with the high anti-cancer activity at a low concentration (4 ppm). What were more important, Zn and Cu in nano-composites exhibited a positive cooperativity at inhibiting cancer cell functions. The microscope observation and biochemical marker analysis clearly revealed that the nano-composites-included lipid peroxidation and disintegration of membrane led to the death of PC12 cells. Summarily, the present study substantiated the potential of BSA-conjugated ZnS/CuS nano-composites as anti-cancer drug
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Wang, Hua-Jie, E-mail: wanghuajie972001@163.com; Yu, Xue-Hong; Wang, Cai-Feng; Cao, Ying, E-mail: caoying1130@sina.com [Henan Normal University, Key Laboratory of Green Chemical Media and Reactions, Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering (China)
2013-11-15
Series of self-assembled and mono-dispersed bovine serum albumin (BSA)-conjugated ZnS/CuS nano-composites with different Zn/Cu ratios had been successfully synthesized by a combination method of the biomimetic synthesis and ion-exchange strategy under the gentle conditions. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy observation, Fourier transform infrared spectra and zeta potential analysis demonstrated that BSA-conjugated ZnS/CuS nano-composites with well dispersity had the hierarchical structure and BSA was a key factor to control the morphology and surface electro-negativity of final products. The real-time monitoring by atomic absorption spectroscopy and powder X-ray diffraction revealed that the Zn/Cu ratio of nano-composites could be controlled by adjusting the ion-exchange time. In addition, the metabolic and morphological assays indicated that the metabolic proliferation and spread of rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells could be inhibited by nano-composites, with the high anti-cancer activity at a low concentration (4 ppm). What were more important, Zn and Cu in nano-composites exhibited a positive cooperativity at inhibiting cancer cell functions. The microscope observation and biochemical marker analysis clearly revealed that the nano-composites-included lipid peroxidation and disintegration of membrane led to the death of PC12 cells. Summarily, the present study substantiated the potential of BSA-conjugated ZnS/CuS nano-composites as anti-cancer drug.
-
Protein carriers of conjugate vaccines
Pichichero, Michael E
2013-01-01
The immunogenicity of polysaccharides as human vaccines was enhanced by coupling to protein carriers. Conjugation transformed the T cell-independent polysaccharide vaccines of the past to T cell-dependent antigenic vaccines that were much more immunogenic and launched a renaissance in vaccinology. This review discusses the conjugate vaccines for prevention of infections caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Specifically, the characteristics of the proteins used in the construction of the vaccines including CRM, tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane complex, and Hemophilus influenzae protein D are discussed. The studies that established differences among and key features of conjugate vaccines including immunologic memory induction, reduction of nasopharyngeal colonization and herd immunity, and antibody avidity and avidity maturation are presented. Studies of dose, schedule, response to boosters, of single protein carriers with single and multiple polysaccharides, of multiple protein carriers with multiple polysaccharides and conjugate vaccines administered concurrently with other vaccines are discussed along with undesirable consequences of conjugate vaccines. The clear benefits of conjugate vaccines in improving the protective responses of the immature immune systems of young infants and the senescent immune systems of the elderly have been made clear and opened the way to development of additional vaccines using this technology for future vaccine products. PMID:23955057
-
Conjugated polymer zwitterions and solar cells comprising conjugated polymer zwitterions
Emrick, Todd; Russell, Thomas; Page, Zachariah; Liu, Yao
2018-06-05
A conjugated polymer zwitterion includes repeating units having structure (I), (II), or a combination thereof ##STR00001## wherein Ar is independently at each occurrence a divalent substituted or unsubstituted C3-30 arylene or heteroarylene group; L is independently at each occurrence a divalent C1-16 alkylene group, C6-30arylene or heteroarylene group, or alkylene oxide group; and R1 is independently at each occurrence a zwitterion. A polymer solar cell including the conjugated polymer zwitterion is also disclosed.
-
Shahin, Mostafa; Lavasanifar, Afsaneh
2010-04-15
Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PEO-b-PCL) copolymers bearing paclitaxel (PTX) side groups on PCL (PEO-b-P(CL-PTX) were synthesized and assembled to particles of 123 nm average diameter. At 20% (w/w) PTX to polymer conjugation, PEO-b-P(CL-PTX) demonstrated only 5.0 and 6.7% PTX release after 72 h incubation at pH 7.4 and 5.0, respectively, but revealed signs of chain cleavage at pH 5.0. The cytotoxicity of PEO-b-P(CL-PTX) against MDA-MB-435 cancer cells increased as incubation time was raised from 72 to 96 h (IC(50) of 680 and 475 ng/mL, respectively), but it was still significantly lower than the cytotoxicity of free PTX (IC(50) of 3.5 ng/mL at 72 h). In further studies, micelles of PEO-b-PCL and those bearing benzyl or PTX on PCL were used for physical encapsulation of PTX, where maximum level of loading was achieved by PEO-b-P(CL-PTX) (2.22%, w/w). The release of PTX from this carrier was rapid; however. The in vitro cytotoxicity of physically loaded PTX was independent of carrier and similar to that of free PTX. This was attributed to the low concentration of polymers which fell below their critical micellar concentration in the cytotoxicity study. The results point to the potential of chemically tailored PEO-b-PCL for optimum PTX solubilization and delivery. Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Research study of conjugate materials; Conjugate material no chosa kenkyu
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
1998-03-01
The paper reported an introductory research on possibilities of new glass `conjugate materials.` The report took up the structure and synthetic process of conjugate materials to be researched/developed, classified them according to structural elements on molecular, nanometer and cluster levels, and introduced the structures and functions. Further, as glasses with new functions to be proposed, the paper introduced transparent and high-strength glass used for houses and vehicles, light modulation glass which realizes energy saving and optical data processing, and environmentally functional glass which realizes environmental cleaning or high performance biosensor. An initial survey was also conducted on rights of intellectual property to be taken notice of in Japan and abroad in the present situation. Reports were summed up and introduced of Osaka National Research Institute, Electrotechnical Laboratory, and National Industrial Research Institute of Nagoya which are all carrying out leading studies of conjugate materials. 235 refs., 135 figs., 6 tabs.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Chen Z
2016-08-01
Full Text Available Zhanfei Chen,1,* Fen Lian,1,* Xiaoqian Wang,1 Yanling Chen,1,2 Nanhong Tang1,2 1Fujian Institute of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, 2Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Gastrointestinal Cancer, Research Center for Molecular Medicine, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, People’s Republic of China *These authors contributed equally to this work Abstract: The polyamidoamine (PAMAM dendrimer, a type of macromolecule material, has been used in spheroidal cell culture and drug delivery in recent years. However, PAMAM is not involved in the study of hepatic cell-spheroid culture or its biological activity, particularly in detoxification function. Here, we constructed a PAMAM-dendrimer conjugate decorated by an integrin ligand: arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (RGD peptide. Our studies demonstrate that RGD–polyethylene glycol (PEG–PAMAM conjugates can promote singly floating hepatic cells to aggregate together in a sphere-like growth with a weak reactive oxygen species. Moreover, RGD-PEG-PAMAM conjugates can activate the AKT–MAPK pathway in hepatic cells to promote cell proliferation and improve basic function and ammonia metabolism. Together, our data support the hepatocyte sphere treated by RGD-PEG-PAMAM conjugates as a potential source of hepatic cells for a biological artificial liver system. Keywords: dendrimer, arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (RGD, liver cell, spheroid culture, ammonia metabolism
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Xu H
2012-09-01
Full Text Available Hao Xu, Chen Liu, Jiansheng Mei, Cuiping Yao, Sijia Wang, Jing Wang, Zheng Li, Zhenxi ZhangKey Laboratory of Biomedical Information Engineering of Education Ministry, Institute of Biomedical Analytical Technology and Instrumentation, School of Life Science and Technology, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, Shannxi, People’s Republic of ChinaPurpose: As a precursor of the potent photosensitizer protoporphyrin IX (PpIX, 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA, was conjugated onto cationic gold nanoparticles (GNPs to improve the efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT.Methods: Cationic GNPs reduced by branched polyethyleneimine and 5-ALA were conjugated onto the cationic GNPs by creating an electrostatic interaction at physiological pH. The efficacy of ALA-GNP conjugates in PDT was investigated under irradiation with a mercury lamp (central wavelength of 395 nm and three types of light-emitting diode arrays (central wavelengths of 399, 502, and 621 nm, respectively. The impacts of GNPs on PDT were then analyzed by measuring the intracellular PpIX levels in K562 cells and the singlet oxygen yield of PpIX under irradiation.Results: The 2 mM ALA-GNP conjugates showed greater cytotoxicity against K562 cells than ALA alone. Light-emitting diode (505 nm irradiation of the conjugates caused a level of K562 cell destruction similar to that with irradiation by a mercury lamp, although it had no adverse effects on drug-free control cells. These results may be attributed to the singlet oxygen yield of PpIX, which can be enhanced by GNPs.Conclusion: Under irradiation with a suitable light source, ALA-GNP conjugates can effectively destroy K562 cells. The technique offers a new strategy of PDT.Keywords: nonradiative energy transfer, photodamage, protoporphyrin IX, selective destruction, singlet oxygen sensor green reagent, surface plasmon resonance
-
Feng, Lan; Wu, Huali; Ma, Ping; Mumper, Russell J; Benhabbour, S Rahima
2011-01-01
THREE DOCETAXEL (DX) LIPID CONJUGATES: 2'-lauroyl-docetaxel (C12-DX), 2'-stearoyl-docetaxel (C18-DX), and 2'-behenoyl-docetaxel (C22-DX) were synthesized to enhance drug loading, entrapment, and retention in liquid oil-filled lipid nanoparticles (NPs). The three conjugates showed ten-fold higher solubility in the liquid oil phase Miglyol 808 than DX. To further increase the drug entrapment efficiency in NPs, orthogonal design was performed. The optimized formulation was composed of Miglyol 808, Brij 78, and Vitamin E tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate (TPGS). The conjugates were successfully entrapped in the reduced-surfactant NPs with entrapment efficiencies of about 50%-60% as measured by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) at a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. All three conjugates showed 45% initial burst release in 100% mouse plasma. Whereas C12-DX showed another 40% release over the next 8 hours, C18-DX and C22-DX in NPs showed no additional release after the initial burst of drug. All conjugates showed significantly lower cytotoxicity than DX in human DU-145 prostate cancer cells. The half maximal inhibitory concentration values (IC(50)) of free conjugates and conjugate NPs were comparable except for C22-DX, which was nontoxic in the tested concentration range and showed only vehicle toxicity when entrapped in NPs. In vivo, the total area under the curve (AUC(0-∞)) values of all DX conjugate NPs were significantly greater than that of Taxotere, demonstrating prolonged retention of drug in the blood. The AUC(0-∞) value of DX in Taxotere was 8.3-fold, 358.0-fold, and 454.5-fold lower than that of NP-formulated C12-DX, C18-DX, and C22-DX, respectively. The results of these studies strongly support the idea that the physical/chemical properties of DX conjugates may be fine-tuned to influence the affinity and retention of DX in oil-filled lipid NPs, which leads to very different pharmacokinetic profiles and blood exposure of an otherwise potent chemo
-
Moral, Mario E G; Siahaan, Teruna J
2017-01-01
Overexpressed cell-surface receptors are hallmarks of many disease states and are often used as markers for targeting diseased cells over healthy counterparts. Cell adhesion peptides, which are often derived from interacting regions of these receptor-ligand proteins, mimic surfaces of intact proteins and, thus, have been studied as targeting agents for various payloads to certain cell targets for cancers and autoimmune diseases. Because many cytotoxic agents in the free form are often harmful to healthy cells, the use of cell adhesion peptides in targeting their delivery to diseased cells has been studied to potentially reduce required effective doses and associated harmful side-effects. In this review, multiple cell adhesion peptides from extracellular matrix and ICAM proteins were used to selectively direct drug payloads, signal-inhibitor peptides, and diagnostic molecules, to diseased cells over normal counterparts. RGD constructs have been used to improve the selectivity and efficacy of diagnostic and drug-peptide conjugates against cancer cells. From this precedent, novel conjugates of antigenic and cell adhesion peptides, called Bifunctional Peptide Inhibitors (BPIs), have been designed to selectively regulate immune cells and suppress harmful inflammatory responses in autoimmune diseases. Similar peptide conjugations with imaging agents have delivered promising diagnostic methods in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. BPIs have also been shown to generate immune tolerance and suppress autoimmune diseases in animal models of type-1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. Collectively, these studies show the potential of cell adhesion peptides in improving the delivery of drugs and diagnostic agents to diseased cells in clinical settings. Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
-
Yi, Jiang; Lam, Tina I; Yokoyama, Wallace; Cheng, Luisa W; Zhong, Fang
2014-09-03
Undesirable aggregation of nanoparticles stabilized by proteins may occur at the protein's isoelectric point when the particle has zero net charge. Stability against aggregation of nanoparticles may be improved by reacting free amino groups with reducing sugars by the Maillard reaction. β-Lactoglobulin (BLG)-dextran conjugates were characterized by SDS-PAGE and CD. Nanoparticles (60-70 nm diameter) of β-carotene (BC) encapsulated by BLG or BLG-dextran were prepared by the homogenization-evaporation method. Both BLG and BLG-dextran nanoparticles appeared to be spherically shaped and uniformly dispersed by TEM. The stability and release of BC from the nanoparticles under simulated gastrointestinal conditions were evaluated. Dextran conjugation prevented the flocculation or aggregation of BLG-dextran particles at pH ∼4-5 compared to very large sized aggregates of BLG nanoparticles. The released contents of BC from BLG and BLG-dextran nanoparticles under acidic gastric conditions were 6.2 ± 0.9 and 5.4 ± 0.3%, respectively. The release of BC from BLG-dextran nanoparticles by trypsin digestion was 51.8 ± 4.3% of total encapsulated BC, and that from BLG nanoparticles was 60.9 ± 2.9%. Neither BLG-BC nanoparticles nor the Maillard-reacted BLG-dextran conjugates were cytotoxic to Caco-2 cells, even at 10 mg/mL. The apparent permeability coefficient (Papp) of Caco-2 cells to BC was improved by nanoencapsulation, compared to free BC suspension. The results indicate that BC-encapsulated β-lactoglobulin-dextran-conjugated nanoparticles are more stable to aggregation under gastric pH conditions with good release and permeability properties.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cai, Demin [College of Animal Sciences and Veterinary Medicine, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, People' s Republic of China (China); Li, Hongji [Key Laboratory of Animal Biochemistry and Nutrition, Ministry of Agriculture, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, People' s Republic of China (China); Zhou, Bo [College of Animal Sciences and Veterinary Medicine, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, People' s Republic of China (China); Han, Liqiang [Key Laboratory of Animal Biochemistry and Nutrition, Ministry of Agriculture, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, People' s Republic of China (China); Zhang, Xiaomei [College of Animal Sciences and Veterinary Medicine, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, People' s Republic of China (China); Yang, Guoyu, E-mail: haubiochem@163.com [Key Laboratory of Animal Biochemistry and Nutrition, Ministry of Agriculture, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, People' s Republic of China (China); Yang, Guoqing, E-mail: gqyang@yeah.net [College of Animal Sciences and Veterinary Medicine, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, People' s Republic of China (China)
2012-06-15
Highlights: Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Conjugated linoleic acid supplementation suppresses perilipin1 in epididymal fat. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Conjugated linoleic acid inhibits promoter activity of perilipin1 in 3T3-L1 cells. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Conjugated linoleic acids elevate basal but blunt hormone-stimulated lipolysis. -- Abstract: Perilipin1, a coat protein of lipid droplet, plays a key role in adipocyte lipolysis and fat formation of adipose tissues. However, it is not clear how the expression of perilipin1 is affected in the decreased white adipose tissues (WAT) of mice treated with dietary supplement of conjugated linoleic acids (CLA). Here we obtained lipodystrophic mice by dietary administration of CLA which exhibited reduced epididymal (EPI) WAT, aberrant adipocytes and decreased expression of leptin in this tissue. We found both transcription and translation of perilipin1 was suppressed significantly in EPI WAT of CLA-treated mice compared to that of control mice. The gene expression of negative regulator tumor necrosis factor {alpha} (TNF{alpha}) and the positive regulator Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-{gamma} (PPAR{gamma}) of perilipin1 was up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively. In cultured 3T3-L1 cells the promoter activity of perilipin1 was dramatically inhibited in the presence of CLA. Using ex vivo experiment we found that the basal lipolysis was elevated but the hormone-stimulated lipolysis blunted in adipose explants of CLA-treated mice compared to that of control mice, suggesting that the reduction of perilipin1 in white adipose tissues may at least in part contribute to CLA-mediated alternation of lipolysis of WAT.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Schmøkel, Julie; Voldum, Anders; Tsakiridou, Georgia
2017-01-01
-linked aptamer to that of aptamer alone was found using an anticoagulant activity assay measuring temporal levels of activated partial thrombin. Covalent albumin-aptamer conjugation, however, substantially compromized binding to hFcRn, to 10% affinity of that of non-conjugated WT, determined by biolayer......-life, predominately facilitated by engagement with the cellular recycling neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), and ligand transport properties of albumin promote it as an attractive candidate to improve the pharmacokinetic profile of aptamers. This study investigates the effect of Cys34 site-selective covalent attachment...... of a factor IXa anticoagulant aptamer on aptamer functionality and human FcRn (hFcRn) engagement using recombinant human albumin (rHA) of either a wild type (WT) or an engineered human FcRn high binding variant (HB). Albumin-aptamer conjugates, connected covalently through a heterobifunctional succinimidyl 4...
-
Self-Adjuvanting Glycopeptide Conjugate Vaccine against Disseminated Candidiasis
Xin, Hong; Cartmell, Jonathan; Bailey, Justin J.; Dziadek, Sebastian; Bundle, David R.; Cutler, Jim E.
2012-01-01
Our research on pathogenesis of disseminated candidiasis led to the discovery that antibodies specific for Candida albicans cell surface β-1, 2–mannotriose [β-(Man)3] protect mice. A 14 mer peptide Fba, which derived from the N-terminal portion of the C. albicans cytosolic/cell surface protein fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, was used as the glycan carrier and resulted in a novel synthetic glycopeptide vaccine β-(Man)3-Fba. By a dendritic cell-based immunization approach, this conjugate induced protective antibody responses against both the glycan and peptide parts of the vaccine. In this report, we modified the β-(Man)3-Fba conjugate by coupling it to tetanus toxoid (TT) in order to improve immunogenicity and allow for use of an adjuvant suitable for human use. By new immunization procedures entirely compatible with human use, the modified β-(Man)3-Fba-TT was administered either alone or as a mixture made with alum or monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL) adjuvants and given to mice by a subcutaneous (s.c.) route. Mice vaccinated with or, surprisingly, without adjuvant responded well by making robust antibody responses. The immunized groups showed a high degree of protection against a lethal challenge with C. albicans as evidenced by increased survival times and reduced kidney fungal burden as compared to control groups that received only adjuvant or DPBS buffer prior to challenge. To confirm that induced antibodies were protective, sera from mice immunized against the β-(Man)3-Fba-TT conjugate transferred protection against disseminated candidiasis to naïve mice, whereas C. albicans-absorbed immune sera did not. Similar antibody responses and protection induced by the β-(Man)3-Fba-TT vaccine was observed in inbred BALB/c and outbred Swiss Webster mice. We conclude that addition of TT to the glycopeptide conjugate results in a self-adjuvanting vaccine that promotes robust antibody responses without the need for additional adjuvant, which is novel and represents a
-
Misonidazole-glutathione conjugates in CHO cells
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Varghese, A.J.; Whitmore, G.F.
1984-01-01
Misonidazole, after reduction to the hydroxylamine derivative, reacts with glutathione (GSH) under physiological conditions. The reaction product has been identified as a mixture of two isomeric conjugates. When water soluble extracts of CHO cells exposed to misonidazole under hypoxic conditions are subjected to HPLC analysis, misonidazole derivatives, having the same chromatographic properties as the GSH-MISO conjugates, were detected. When CHO cells were incubated with misonidazole in the presence of added GSH, a substantial increase in the amount of the conjugate was detected. When extracts of CHO cells exposed to misonidazole under hypoxia were subsequently exposed to GSH, an increased formation of the conjugate was observed. A rearrangement product of the hydroxylamine derivative of misonidazole is postulated as the reactive intermediate responsible for the formation of the conjugate
-
Modelling conjugation with stochastic differential equations
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Philipsen, Kirsten Riber; Christiansen, Lasse Engbo; Hasman, Henrik
2010-01-01
Enterococcus faecium strains in a rich exhaustible media. The model contains a new expression for a substrate dependent conjugation rate. A maximum likelihood based method is used to estimate the model parameters. Different models including different noise structure for the system and observations are compared......Conjugation is an important mechanism involved in the transfer of resistance between bacteria. In this article a stochastic differential equation based model consisting of a continuous time state equation and a discrete time measurement equation is introduced to model growth and conjugation of two...... using a likelihood-ratio test and Akaike's information criterion. Experiments indicating conjugation on the agar plates selecting for transconjugants motivates the introduction of an extended model, for which conjugation on the agar plate is described in the measurement equation. This model is compared...
-
In vitro cytotoxicity of chemical preservatives on human fibroblast cells
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Daniel Gonsales Spindola
2018-05-01
Full Text Available ABSTRACT Preservatives are widely used substances that are commonly added to various cosmetic and pharmaceutical products to prevent or inhibit microbial growth. In this study, we compared the in vitro cytotoxicity of different types of currently used preservatives, including methylparaben, imidazolidinyl urea (IMU, and sodium benzoate, using the human newborn fibroblast cell line CCD1072Sk. Of the tested preservatives, only IMU induced a reduction in cell viability, as shown using the MTT assay and propidium iodide staining (IMU>methylparaben>sodium benzoate. IMU was shown to promote homeostatic alterations potentially related to the initiation of programed cell death, such as decreased mitochondrial membrane potential and caspase-3 activation, in the treated cells. Methylparaben and sodium benzoate were shown to have a very low cytotoxic activity. Taken together, our results suggest that IMU induces programed cell death in human fibroblasts by a canonical intrinsic pathway via mitochondrial perturbation and subsequent release of proapoptotic factors.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Liu Y
2015-04-01
Full Text Available Ying Liu,1,* Man He,1,* Mengmeng Niu,1 Yiqing Zhao,1 Yuanzhang Zhu,1 Zhenhua Li,2 Nianping Feng1 1Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China; 2Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA *These authors contributed equally to this work Abstract: Rapid drug release at the specific site of action is still a challenge for antitumor therapy. Development of stimuli-responsive hybrid nanocarriers provides a promising strategy to enhance therapeutic effects by combining the unique features of each component. The present study explored the use of drug–gold nanoparticle conjugates incorporated into liposomes to enhance antitumor efficiency. A model drug, vincristine sulfate, was physically conjugated with gold nanoparticles and verified by UV-visible and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and differential scanning calorimetry. The conjugates were incorporated into liposomes by film dispersion to yield nanoparticles (113.4 nm with light-responsive release properties, as shown by in vitro release studies. Intracellular uptake and distribution was studied in HeLa cells using transmission electron microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy. This demonstrated liposome internalization and localization in endosomal–lysosomal vesicles. Fluorescence intensity increased in cells exposed to UV light, indicating that this stimulated intracellular drug release; this finding was confirmed by quantitative analyses using flow cytometry. Antitumor efficacy was evaluated in HeLa cells, both in culture and in implants in vivo in nude mice. HeLa cell viability assays showed that light exposure enhanced liposome cytotoxicity and induction of apoptosis. Furthermore, treatment with the prepared liposomes coupled with UV light exposure produced greater antitumor effects in nude mice and reduced side effects, as compared with free vincristine sulfate
-
Poly(2-oxazoline)-Antibiotic Conjugates with Penicillins.
Schmidt, Martin; Bast, Livia K; Lanfer, Franziska; Richter, Lena; Hennes, Elisabeth; Seymen, Rana; Krumm, Christian; Tiller, Joerg C
2017-09-20
The conjugation of antibiotics with polymers is rarely done, but it might be a promising alternative to low-molecular-weight derivatization. The two penicillins penicillin G (PenG) and penicillin V (PenV) were attached to the end groups of different water-soluble poly(2-oxazoline)s (POx) via their carboxylic acid function. This ester group was shown to be more stable against hydrolysis than the β-lactam ring of the penicillins. The conjugates are still antimicrobially active and up to 20 times more stable against penicillinase catalyzed hydrolysis. The antibiotic activity of the conjugates against Staphylococcus aureus in the presence of penicillinase is up to 350 times higher compared with the free antibiotics. Conjugates with a second antimicrobial function, a dodecyltrimethylammonium group (DDA-X), at the starting end of the PenG and PenV POx conjugates are more antimicrobially active than the conjugates without DDA-X and show high activity in the presence of penicillinase. For example, the conjugates DDA-X-PEtOx-PenG and DDA-X-PEtOx-PenV are 200 to 350 times more active against S. aureus in the presence of penicillinase and almost as effective as the penicillinase stable cloxacollin (Clox) under these conditions. These conjugates show even greater activity compared to cloxacollin without this enzyme present. Further, both conjugates kill Escherichia coli more effectively than PenG and Clox.
-
Mechanisms Underlying Cytotoxicity Induced by Engineered Nanomaterials: A Review of In Vitro Studies
Nogueira, Daniele R.; Mitjans, Montserrat; Rolim, Clarice M. B.; Vinardell, M. Pilar
2014-01-01
Engineered nanomaterials are emerging functional materials with technologically interesting properties and a wide range of promising applications, such as drug delivery devices, medical imaging and diagnostics, and various other industrial products. However, concerns have been expressed about the risks of such materials and whether they can cause adverse effects. Studies of the potential hazards of nanomaterials have been widely performed using cell models and a range of in vitro approaches. In the present review, we provide a comprehensive and critical literature overview on current in vitro toxicity test methods that have been applied to determine the mechanisms underlying the cytotoxic effects induced by the nanostructures. The small size, surface charge, hydrophobicity and high adsorption capacity of nanomaterial allow for specific interactions within cell membrane and subcellular organelles, which in turn could lead to cytotoxicity through a range of different mechanisms. Finally, aggregating the given information on the relationships of nanomaterial cytotoxic responses with an understanding of its structure and physicochemical properties may promote the design of biologically safe nanostructures. PMID:28344232
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Melanie B. Berkmen
2014-08-01
Full Text Available Students are engaged and improve their critical thinking skills in laboratory courses when they have the opportunity to design and conduct inquiry-based experiments that generate novel results. A discovery-driven project for a microbiology, genetics, or multidisciplinary research laboratory course was developed to familiarize students with the scientific method. In this multi-lab module, students determine whether their chosen stress conditions induce conjugation and/or cell death of the model BSL-1 Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Through consultation of the primary literature, students identify conditions or chemicals that can elicit DNA damage, the SOS response, and/or cellular stress. In groups, students discuss their selected conditions, develop their hypotheses and experimental plans, and formulate their positive and negative controls. Students then subject the B. subtilis donor cells to the stress conditions, mix donors with recipients to allow mating, and plate serial dilutions of the mixtures on selective plates to measure how the treatments affect conjugation frequency and donor cell viability. Finally, students analyze and discuss their collective data in light of their controls. The goals of this module are to encourage students to be actively involved in the scientific process while contributing to our understanding of the conditions that stimulate horizontal gene transfer in bacteria.
-
Torabi, Raheleh; Ghourchian, Hedayatollah; Amanlou, Massoud; Pasalar, Parvin
2017-06-01
Inhibition of the binding of retinol to its carrier, retinol binding protein 4, is a new strategy for treating type 2 diabetes; for this purpose, we have provided an aptamer-functionalized multishell calcium phosphate nanoparticle. First, calcium phosphate nanoparticles were synthesized and conjugated to the aptamer. The cytotoxicity of nanoparticles releases the process of aptamer from nanoparticles and their inhibition function of binding retinol to retinol binding protein 4. After synthesizing and characterizing the multishell calcium phosphate nanoparticles and observing the noncytotoxicity of conjugate, the optimum time (48 hours) and the pH (7.4) for releasing the aptamer from the nanoparticles was determined. The half-maximum inhibitory concentration (IC 50 ) value for inhibition of retinol binding to retinol binding protein 4 was 210 femtomolar (fmol). The results revealed that the aptamer could prevent connection between retinol and retinol binding protein 4 at a very low IC 50 value (210 fmol) compared to other reported inhibitors. It seems that this aptamer could be used as an efficient candidate not only for decreasing the insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes, but also for inhibiting the other retinol binding protein 4-related diseases. Copyright © 2017 Diabetes Canada. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Choi SY
2015-07-01
Full Text Available Seon Young Choi,1 Min Seok Song,1 Pan Dong Ryu,1 Anh Thu Ngoc Lam,2 Sang-Woo Joo,2 So Yeong Lee1 1Laboratory of Veterinary Pharmacology, Research Institute for Veterinary Science, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, 2Department of Chemistry, Soongsil University, Seoul, South Korea Abstract: Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs are attractive materials for use in biomedicine due to their physical properties. Increasing evidence suggests that several nanoparticles induce the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts and adipocytes. In this study, we hypothesized that chitosan-conjugated AuNPs promote the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. For the evaluation of osteogenic differentiation, alizarin red staining, an alamarBlue® assay, and a quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis were performed. In order to examine specific signaling pathways, immunofluorescence and a western blotting assay were performed. Our results demonstrate that chitosan-conjugated AuNPs increase the deposition of calcium content and the expression of marker genes related to osteogenic differentiation in human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells at nontoxic concentrations. These results indicate that chitosan-conjugated AuNPs promote osteogenesis through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Therefore, chitosan-conjugated AuNPs can be used as a reagent for promoting bone formation. Keywords: chitosan-conjugated gold nanoparticle, mineralization, nonphosphorylated beta-catenin
-
Approximate error conjugation gradient minimization methods
Kallman, Jeffrey S
2013-05-21
In one embodiment, a method includes selecting a subset of rays from a set of all rays to use in an error calculation for a constrained conjugate gradient minimization problem, calculating an approximate error using the subset of rays, and calculating a minimum in a conjugate gradient direction based on the approximate error. In another embodiment, a system includes a processor for executing logic, logic for selecting a subset of rays from a set of all rays to use in an error calculation for a constrained conjugate gradient minimization problem, logic for calculating an approximate error using the subset of rays, and logic for calculating a minimum in a conjugate gradient direction based on the approximate error. In other embodiments, computer program products, methods, and systems are described capable of using approximate error in constrained conjugate gradient minimization problems.
-
Oxidative Mechanisms of Monocyte-Mediated Cytotoxicity
Weiss, Stephen J.; Lobuglio, Albert F.; Kessler, Howard B.
1980-01-01
Human monocytes stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate were able to rapidly destroy autologous erythrocyte targets. Monocyte-mediated cytotoxicity was related to phorbol myristate acetate concentration and monocyte number. Purified preparations of lymphocytes were incapable of mediating erythrocyte lysis in this system. The ability of phorbol myristate acetate-stimulated monocytes to lyse erythrocyte targets was markedly impaired by catalase or superoxide dismutase but not by heat-inactivated enzymes or albumin. Despite a simultaneous requirement for superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide in the cytotoxic event, a variety of hydroxyl radical and singlet oxygen scavengers did not effect cytolysis. However, tryptophan significantly inhibited cytotoxicity. The myeloperoxidase inhibitor cyanide enhanced erythrocyte destruction, whereas azide reduced it modestly. The inability of cyanide to reduce cytotoxicity coupled with the protective effect of superoxide dismutase suggests that cytotoxicity is independent of the classic myeloperoxidase system. We conclude that monocytes, stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate, generate superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide, which together play an integral role in this cytotoxic mechanism.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kumar, Neeraj; George, Blassan Plackal Adimuriyil; Abrahamse, Heidi; Parashar, Vyom; Ngila, Jane Catherine
2017-01-01
Highlights: • Microspheres of PEGylated MoS 2 nanosheets were synthesised by hydrothermal route. • PEGylated MoS 2 have shown good cytotoxicity towards breast cancer (MCF-7) cells. • For comparison, h-MoO 3 nanorods were prepared by simple chemical route. • h-MoO 3 have exhibited excellent cytotoxicity towards lung (A549) cancer cells. - Abstract: Nanotechnology provides an emerging potent alternate mode of cancer therapy. Nanomaterials dispersion or solubility is of particular concern in utilising their full potential applications in biomedical fields. PEGylation of nanomaterials is considered to provide products with stealth properties, and physiological environment with no obvious adverse effects. The purpose of this work was to develop a sustainable one-step method for fabrication of hierarchical microspheres of PEGylated MoS 2 nanosheets using a stoichiometric ratio of Mo(VI) and thiourea. This study further investigated the cytotoxicity of the PEGylated MoS 2 nanosheets towards lung (A549) and breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines by analysing morphological changes and performing dose-dependent cell proliferation, and cytotoxicity analysis using adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay. For comparison, MoO 3 nanorods were synthesised by simple chemical route and their cytotoxicity towards lung (A549) and breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines were checked. The findings suggested that PEGylated MoS 2 nanosheets have excellent cytotoxicity towards breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines, and MoO 3 have better cytotoxicity towards lung (A549) cancer cell lines. This work envisages an accessible foundation for engineering sophisticated biomolecule–MoS 2 nanosheets conjugation due to the defect-rich biocompatible surface, to achieve great versatility, additional functions, and further advances in the biomedical field.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Abdullah O. Ba-Salem
2015-04-01
Full Text Available Two new DTPA-bis(amide based ligands conjugated with the arylpiperazinyl moiety were synthesized and subsequently transformed into their corresponding Gd(III complexes 1 and 2 of the type [Gd(LH2O]·nH2O. The relaxivity (R1 of these complexes was measured, which turned out to be comparable with that of Omniscan®, a commercially available MRI contrast agent. The cytotoxicity studies of these complexes indicated that they are non-toxic, which reveals their potential and physiological suitability as MRI contrast agents. All the synthesized ligands and complexes were characterized with the aid of analytical and spectroscopic methods, including elemental analysis, 1H-NMR, FT-IR, XPS and fast atom bombardment (FAB mass spectrometry.
-
Calcium Contributes to the Cytotoxic Interaction Between Diclofenac and Cytokines.
Maiuri, Ashley R; Breier, Anna B; Turkus, Jonathan D; Ganey, Patricia E; Roth, Robert A
2016-02-01
Diclofenac (DCLF) is a widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is associated with idiosyncratic, drug-induced liver injury (IDILI) in humans. The mechanisms of DCLF-induced liver injury are unknown; however, patients with certain inflammatory diseases have an increased risk of developing IDILI, which raises the possibility that immune mediators play a role in the pathogenesis. DCLF synergizes with the cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) and interferon-gamma (IFN) to cause hepatocellular apoptosis in vitro by a mechanism that involves activation of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response pathway and of the mitogen-activated protein kinases, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). DCLF also causes an increase in intracellular calcium (Ca(++)) in hepatocytes, but the role of this in the cytotoxic synergy between DCLF and cytokines is unknown. We tested the hypothesis that Ca(++) contributes to DCLF/cytokine-induced cytotoxic synergy. Treatment of HepG2 cells with DCLF led to an increase in intracellular Ca(++) at 6 and 12 h, and this response was augmented in the presence of TNF and IFN at 12 h. The intracellular Ca(++) chelator BAPTA/AM reduced cytotoxicity and caspase-3 activation caused by DCLF/cytokine cotreatment. BAPTA/AM also significantly reduced DCLF-induced activation of the ER stress sensor, protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase (PERK), as well as activation of JNK and ERK. Treatment of cells with an inositol trisphosphate receptor antagonist almost completely eliminated DCLF/cytokine-induced cytotoxicity and decreased DCLF-induced activation of PERK, JNK, and ERK. These findings indicate that Ca(++) contributes to DCLF/cytokine-induced cytotoxic synergy by promoting activation of the ER stress-response pathway and JNK and ERK. © The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
-
Chen, Tao; Su, Dian; Gruenhagen, Jason; Gu, Christine; Li, Yi; Yehl, Peter; Chetwyn, Nik P; Medley, Colin D
2016-01-05
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) offer new therapeutic options for advanced cancer patients through precision killing with fewer side effects. The stability and efficacy of ADCs are closely related, emphasizing the urgency and importance of gaining a comprehensive understanding of ADC stability. In this work, a chemical de-conjugation approach was developed to investigate the in-situ stability of the small molecule drug while it is conjugated to the antibody. This method involves chemical-mediated release of the small molecule drug from the ADC and subsequent characterization of the released small molecule drug by HPLC. The feasibility of this technique was demonstrated utilizing a model ADC containing a disulfide linker that is sensitive to the reducing environment within cancer cells. Five reducing agents were screened for use in de-conjugation; tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine (TCEP) was selected for further optimization due to its high efficiency and clean impurity profile. The optimized de-conjugation assay was shown to have excellent specificity and precision. More importantly, it was shown to be stability indicating, enabling the identification and quantification of the small molecule drug and its degradation products under different formulation pHs and storage temperatures. In summary, the chemical de-conjugation strategy demonstrated here offers a powerful tool to assess the in-situ stability of small molecule drugs on ADCs and the resulting information will shed light on ADC formulation/process development and storage condition selection. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Cytotoxicity of Portland cement with different radiopacifying agents: a cell death study.
Gomes Cornélio, Ana Lívia; Salles, Loise Pedrosa; Campos da Paz, Mariana; Cirelli, Joni Augusto; Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Juliane Maria; Tanomaru Filho, Mário
2011-02-01
The aim of this study was to investigate the cytotoxicity of white Portland cement (PC) alone or associated with bismuth oxide (PCBi), zirconium oxide (PCZir), and calcium tungstate (PCCa) in 2 cell lineages. Murine periodontal ligament cells (mPDL) and rat osteosarcoma cells (ROS 17/2.8) were exposed for 24 hours to specific concentrations of fresh PC and PC associations with radiopacifiers. Zinc oxide-eugenol cement and hydrogen peroxide treatment were applied as cytotoxic positive controls. Cell viability after incubation with the cements was assessed by mitochondrial dehydrogenase enzymatic assay. Cell morphology was microscopically analyzed by cresyl violet staining, and the mechanism of cell death was determined by acridine orange/ethidium bromide methodology. All data were analyzed statistically by analysis of variance and Tukey post hoc test (P cement elutes. PC alone was not cytotoxic, even at 100 mg/mL. Microscopic images showed that none of the PC formulations caused damage to any cell lines. Statistical analysis of apoptosis/necrosis data demonstrated that PC and PC plus radiopacifying agents promoted significant necrosis cell death only at 100 mg/mL. The mPDL cells were more sensitive than ROS17/2.8. The results showed that PC associated with bismuth oxide, zirconium oxide, or calcium tungstate is not cytotoxic to mPDL or ROS17/2.8. Zirconium oxide and calcium tungstate might be good alternatives as radiopacifying agents. Copyright © 2011 American Association of Endodontists. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Conjugation-promoted reaction of open-cage fullerene: a density functional theory study.
Guo, Yong; Yan, Jingjing; Khashab, Niveen M
2012-02-01
Density functional theory calculations are performed to study the addition mechanism of e-rich moieties such as triethyl phosphite to a carbonyl group on the rim of a fullerene orifice. Three possible reaction channels have been investigated. The obtained results show that the reaction of a carbonyl group on a fullerene orifice with triethyl phosphite most likely proceeds along the classical Abramov reaction; however, the classical product is not stable and is converted into the experimental product. An attack on a fullerene carbonyl carbon will trigger a rearrangement of the phosphate group to the carbonyl oxygen as the conversion transition state is stabilized by fullerene conjugation. This work provides a new insight on the reactivity of open-cage fullerenes, which may prove helpful in designing new switchable fullerene systems. Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Photoluminescence in conjugated polymers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Furst, J.E.; Laugesen, R.; Dastoor, P.; McNeill, C.
2002-01-01
Full text: Conjugated polymers combine the electronic and optical properties of semiconductors with the processability of polymers. They contain a sequence of alternate single and double carbon bonds so that the overlap of unhybridised p z orbitals creates a delocalised ρ system which gives semiconducting properties with p-bonding (valence) and p* -antibonding (conduction) bands. Photoluminesence (PL) in conjugated polymers results from the radiative decay of singlet excitons confined to a single chain. The present work is the first in a series of studies in our laboratory that will characterize the optical properties of conjugated polymers. The experiment involves the illumination of thin films of conjugated polymer with UV light (I=360 nm) and observing the subsequent fluorescence using a custom-built, fluorescence spectrometer. Photoluminesence spectra provide basic information about the structure of the polymer film. A typical spectrum is shown in the accompanying figure. The position of the first peak is related to the polymer chain length and resolved multiple vibronic peaks are an indication of film structure and morphology. We will also present results related to the optical degradation of these materials when exposed to air and UV light
-
Bio-Conjugates for Nanoscale Applications
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Villadsen, Klaus
Bio-conjugates for Nanoscale Applications is the title of this thesis, which covers three different projects in chemical bio-conjugation research, namely synthesis and applications of: Lipidated fluorescent peptides, carbohydrate oxime-azide linkers and N-aryl O-R2 oxyamine derivatives. Lipidated...
-
Khan, Selina; Weterings, Jimmy J; Britten, Cedrik M; de Jong, Ana R; Graafland, Dirk; Melief, Cornelis J M; van der Burg, Sjoerd H; van der Marel, Gijs; Overkleeft, Hermen S; Filippov, Dmitri V; Ossendorp, Ferry
2009-03-01
Covalent conjugation of synthetic Toll-like receptor ligands (TLR-L) to synthetic antigenic peptides provides well-defined constructs that have significantly improved capacity to induce efficient priming of CD8(+) T lymphocytes in vivo. We have recently explored the cellular mechanisms underlying the efficient induction of a CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocyte response by such synthetic model vaccines [Khan, S., Bijker, M.S., Weterings, J.J., Tanke, H.J., Adema, G.J., van, H.T., Drijfhout, J.W., Melief, C.J., Overkleeft, H.S., van der Marel, G.A., Filippov, D.V., van der Burg, S.H., Ossendorp, F., 2007. Distinct uptake mechanisms but similar intracellular processing of two different toll-like receptor ligand-peptide conjugates in dendritic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 21145-21159.]. In the current study we have investigated the behaviour of two diastereomers of the TLR-2 ligand Pam(3)CSK(4) (Pam) derivatives, namely the R- and S-epimers at C-2 of the glycerol moiety. Other studies have shown that the Pam(3)Cys based lipopeptides of R-configuration (Pam(R)) in the glycerol moiety enhanced macrophage and B-cell activation compared to those with S-configuration (Pam(S)). Here we report that Pam(R)-conjugates lead to better activation of dendritic cells than the Pam(S)-conjugates as judged by higher IL-12 secretion, upregulation of relevant markers for dendritic cell maturation. In contrast both epimers were internalized equally efficient in a clathrin-dependent manner indicating no qualitative difference in the uptake of the two stereoisomeric Pam-conjugates. We conclude that the enhanced DC activation is due to enhanced TLR-2 triggering by the Pam(R)-conjugate in contrast to the Pam(S)-conjugate. Importantly, induction of specific CD8(+) T-cells was significantly higher in mice injected with the Pam(R)-conjugates compared to mice injected with the Pam(S)-conjugate. In summary we show that the favourable effects of the Pam(R)-configuration of TLR-2 ligand can be attributed to
-
Lima, Igo T.; Risko, Chad; Aziz, Saadullah Gary; Da Silva Filho, Demé trio A Da Silva; Bredas, Jean-Luc
2014-01-01
Donor-acceptor π-conjugated copolymers are of interest for a wide range of electronic applications, including field-effect transistors and solar cells. Here, we present a density functional theory (DFT) study of the impact of varying the conjugation pathway on the geometric, electronic, and optical properties of donor-acceptor systems. We consider both linear ("in series"), traditional conjugation among the donor-acceptor moieties versus structures where the acceptor units are appended orthogonally to the linear, donor-only conjugated backbone. Long-range-corrected hybrid functionals are used in the investigation with the values of the tuned long-range separation parameters providing an estimate of the extent of conjugation as a function of the oligomer architecture. Considerable differences in the electronic and optical properties are determined as a function of the nature of the conjugation pathway, features that should be taken into account in the design of donor-acceptor copolymers.
-
Investigational Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Treatment of B-lineage Malignancies.
Herrera, Alex F; Molina, Arturo
2018-05-10
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are tripartite molecules consisting of a monoclonal antibody, a covalent linker, and a cytotoxic payload. ADC development has aimed to target the specificity inherent in antigen-antibody interactions to deliver potent cytotoxins preferentially to tumor cells and maximize antitumor activity and simultaneously minimize off-target toxicity. The earliest ADCs provided disappointing results in the clinic; however, the lessons learned regarding the need for human or humanized antibodies, more stable linkers, and greater potency payloads led to improved ADCs. Three ADCs, gemtuzumab ozogamicin, brentuximab vedotin (BV), and inotuzumab ozogamicin, have been approved for hematologic malignancies. Site-specific conjugation methods have now resulted in a new generation of more uniform, molecularly defined ADCs. These are expected to display improved in vivo properties and have recently entered the clinic. We reviewed investigational ADCs currently in clinical testing for the treatment of B-cell lineage malignancies, including leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma. The rationales for antigen targeting, data reported to date, current trial status, and preclinical results for several newer ADCs expected to enter first-in-human studies are presented. Owing to the large number of ongoing and reported BV clinical studies, only the studies of BV for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and those combining BV with checkpoint inhibitors in B-lineage malignancies have been reviewed. With > 40 ongoing clinical trials and 7 investigational ADCs already having advanced to phase II studies, the role of ADCs in the armamentarium for the treatment of B-lineage malignancies continues to be elucidated. Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Vaithilingam, Vijayaganapathy; Steinkjer, Bjørg; Ryan, Liv; Larsson, Rolf; Tuch, Bernard Edward; Oberholzer, Jose; Rokstad, Anne Mari
2017-09-15
Host reactivity to biocompatible immunoisolation devices is a major challenge for cellular therapies, and a human screening model would be of great value. We designed new types of surface modified barium alginate microspheres, and evaluated their inflammatory properties using human whole blood, and the intraperitoneal response after three weeks in Wistar rats. Microspheres were modified using proprietary polyallylamine (PAV) and coupled with macromolecular heparin conjugates (Corline Heparin Conjugate, CHC). The PAV-CHC strategy resulted in uniform and stable coatings with increased anti-clot activity and low cytotoxicity. In human whole blood, PAV coating at high dose (100 µg/ml) induced elevated complement, leukocyte CD11b and inflammatory mediators, and in Wistar rats increased fibrotic overgrowth. Coating of high dose PAV with CHC significantly reduced these responses. Low dose PAV (10 µg/ml) ± CHC and unmodified alginate microbeads showed low responses. That the human whole blood inflammatory reactions paralleled the host response shows a link between inflammatory potential and initial fibrotic response. CHC possessed anti-inflammatory activity, but failed to improve overall biocompatibility. We conclude that the human whole blood assay is an efficient first-phase screening model for inflammation, and a guiding tool in development of new generation microspheres for cell encapsulation therapy.
-
Ree, J.H.; Jeganathan, K.B.; Malureanu, L.; Deursen, J.M.A. van
2010-01-01
The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) E3 ubiquitin ligase functions with the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UbcH10 in the orderly progression through mitosis by marking key mitotic regulators for destruction by the 26-S proteasome. UbcH10 is overexpressed in many human cancer types and
-
Sedlacek, Ondrej; Monnery, Bryn D; Mattova, Jana; Kucka, Jan; Panek, Jiri; Janouskova, Olga; Hocherl, Anita; Verbraeken, Bart; Vergaelen, Maarten; Zadinova, Marie; Hoogenboom, Richard; Hruby, Martin
2017-11-01
We designed and synthesized a new delivery system for the anticancer drug doxorubicin based on a biocompatible hydrophilic poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEtOx) carrier with linear architecture and narrow molar mass distribution. The drug is connected to the polymer backbone via an acid-sensitive hydrazone linker, which allows its triggered release in the tumor. The in vitro studies demonstrate successful cellular uptake of conjugates followed by release of the cytostatic cargo. In vivo experiments in EL4 lymphoma bearing mice revealed prolonged blood circulation, increased tumor accumulation and enhanced antitumor efficacy of the PEtOx conjugate having higher molecular weight (40 kDa) compared to the lower molecular weight (20 kDa) polymer. Finally, the in vitro and in vivo anti-cancer properties of the prepared PEtOx conjugates were critically compared with those of the analogous system based on the well-established PHPMA carrier. Despite the relatively slower intracellular uptake of PEtOx conjugates, resulting also in their lower cytotoxicity, there are no substantial differences in in vivo biodistribution and anti-cancer efficacy of both classes of polymer-Dox conjugates. Considering the synthetic advantages of poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline)s, the presented study demonstrates their potential as a versatile alternative to well-known PEO- or PHPMA-based materials for construction of drug delivery systems. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Organometallic B12-DNA conjugate
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hunger, Miriam; Mutti, Elena; Rieder, Alexander
2014-01-01
Design, synthesis, and structural characterization of a B12-octadecanucleotide are presented herein, a new organometallic B12-DNA conjugate. In such covalent conjugates, the natural B12 moiety may be a versatile vector for controlled in vivo delivery of oligonucleotides to cellular targets in hum...
-
The Conjugate Acid-Base Chart.
Treptow, Richard S.
1986-01-01
Discusses the difficulties that beginning chemistry students have in understanding acid-base chemistry. Describes the use of conjugate acid-base charts in helping students visualize the conjugate relationship. Addresses chart construction, metal ions, buffers and pH titrations, and the organic functional groups and nonaqueous solvents. (TW)
-
REVIEW ARTICLE Conjugated Hyperbilirubinaemia in Early Infancy ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
REVIEW ARTICLE Conjugated Hyperbilirubinaemia in Early Infancy. AOK Johnson. Abstract. Conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia exists when the conjugated serum bilirubin level is more than 2 mg/dl or more than 20 per cent of the total serum bilirubin. It is always pathological in early infancy. The causes are many and diverse ...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ponizovskiy MR
2015-04-01
Full Text Available “Prolonged medical starvation” as the method of cancer therapy was borrowed from folk healers Omelchenko A and Breuss R. Author was convinced in efficiency of this method of cancer treatment via examination of cured patients and on own experience. The mechanism of this method of cancer therapy operates via Warburg effect targeting that promotes efficient cancer treatment with small cytotoxic drugs. Just it was described the mechanism of Warburg effect as well as mechanism transmutation of mitochondrial function in cancer metabolism which are exhibited in connection with operation of described method cancer therapy. There were described the biochemical and biophysical mechanisms of formations resistance to some cytotoxic drugs and recurrence cancer disease after disease remission which occur sometimes as result of treatment with great dosage of cytotoxic drugs. Also it was described the benefits of use the method “Prolonged medical starvation” with decreased dosage of cytotoxic drugs for cancer treatment. The significance of this work that it was substantiated the mechanism operation of combination “Prolonged medical starvation” with small dosages cytotoxic drugs of cancer treatment, which mechanism leads to prevention recurrence cancer disease and resistance to anticancer drugs in comparison with intensive anticancer chemotherapy with great dosages of cytotoxic drugs in cancer therapy. Also the offered concepts of cancer therapy mechanism gave possibility to explain mechanisms of some results of experiments eliminating the doubts of the authors these experiments.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kumar, Neeraj [Department of Applied Chemistry, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein 2028, South Africa, (South Africa); George, Blassan Plackal Adimuriyil; Abrahamse, Heidi [Laser Research Centre, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein 2028 (South Africa); Parashar, Vyom, E-mail: vyomparashar@gmail.com [Department of Applied Chemistry, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein 2028, South Africa, (South Africa); Ngila, Jane Catherine, E-mail: jcngila@uj.ac.za [Department of Applied Chemistry, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein 2028, South Africa, (South Africa)
2017-02-28
Highlights: • Microspheres of PEGylated MoS{sub 2} nanosheets were synthesised by hydrothermal route. • PEGylated MoS{sub 2} have shown good cytotoxicity towards breast cancer (MCF-7) cells. • For comparison, h-MoO{sub 3} nanorods were prepared by simple chemical route. • h-MoO{sub 3} have exhibited excellent cytotoxicity towards lung (A549) cancer cells. - Abstract: Nanotechnology provides an emerging potent alternate mode of cancer therapy. Nanomaterials dispersion or solubility is of particular concern in utilising their full potential applications in biomedical fields. PEGylation of nanomaterials is considered to provide products with stealth properties, and physiological environment with no obvious adverse effects. The purpose of this work was to develop a sustainable one-step method for fabrication of hierarchical microspheres of PEGylated MoS{sub 2} nanosheets using a stoichiometric ratio of Mo(VI) and thiourea. This study further investigated the cytotoxicity of the PEGylated MoS{sub 2} nanosheets towards lung (A549) and breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines by analysing morphological changes and performing dose-dependent cell proliferation, and cytotoxicity analysis using adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay. For comparison, MoO{sub 3} nanorods were synthesised by simple chemical route and their cytotoxicity towards lung (A549) and breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines were checked. The findings suggested that PEGylated MoS{sub 2} nanosheets have excellent cytotoxicity towards breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines, and MoO{sub 3} have better cytotoxicity towards lung (A549) cancer cell lines. This work envisages an accessible foundation for engineering sophisticated biomolecule–MoS{sub 2} nanosheets conjugation due to the defect-rich biocompatible surface, to achieve great versatility, additional functions, and further advances in the biomedical field.
-
Kiss, János; Papp, Péter Pál; Szabó, Mónika; Farkas, Tibor; Murányi, Gábor; Szakállas, Erik; Olasz, Ferenc
2015-10-15
The genomic island SGI1 and its variants, the important vehicles of multi-resistance in Salmonella strains, are integrative elements mobilized exclusively by the conjugative IncA/C plasmids. Integration and excision of the island are carried out by the SGI1-encoded site-specific recombinase Int and the recombination directionality factor Xis. Chromosomal integration ensures the stable maintenance and vertical transmission of SGI1, while excision is the initial step of horizontal transfer, followed by conjugation and integration into the recipient. We report here that SGI1 not only exploits the conjugal apparatus of the IncA/C plasmids but also utilizes the regulatory mechanisms of the conjugation system for the exact timing and activation of excision to ensure efficient horizontal transfer. This study demonstrates that the FlhDC-family activator AcaCD, which regulates the conjugation machinery of the IncA/C plasmids, serves as a signal of helper entry through binding to SGI1 xis promoter and activating SGI1 excision. Promoters of int and xis genes have been identified and the binding site of the activator has been located by footprinting and deletion analyses. We prove that expression of xis is activator-dependent while int is constitutively expressed, and this regulatory mechanism is presumably responsible for the efficient transfer and stable maintenance of SGI1. © The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
-
Application of optical phase conjugation to plasma diagnostics (invited)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jahoda, F.C.; Anderson, B.T.; Forman, P.R.; Weber, P.G.
1985-01-01
Several possibilities for plasma diagnostics provided by optical phase conjugation and, in particular, self-pumped phase conjugation in barium titanate (BaTiO 3 ) are discussed. These include placing a plasma within a dye laser cavity equipped with a phase conjugate mirror for intracavity absorption measurements, time differential refractometry with high spatial resolution, and simplified real-time holographic interferometry. The principles of phase conjugation with particular reference to photorefractive media and the special advantages of self-pumped phase conjugation are reviewed prior to the discussion of the applications. Distinctions are made in the applications between those for which photorefractive conjugators are essential and those for which they only offer experimental simplification relative to other types of phase conjugators
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mehran Nikan
2016-01-01
Full Text Available The use of siRNA-based therapies for the treatment of neurodegenerative disease requires efficient, nontoxic distribution to the affected brain parenchyma, notably the striatum and cortex. Here, we describe the synthesis and activity of a fully chemically modified siRNA that is directly conjugated to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, the most abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid in the mammalian brain. DHA conjugation enables enhanced siRNA retention throughout both the ipsilateral striatum and cortex following a single, intrastriatal injection (ranging from 6–60 μg. Within these tissues, DHA conjugation promotes internalization by both neurons and astrocytes. We demonstrate efficient and specific silencing of Huntingtin mRNA expression in both the ipsilateral striatum (up to 73% and cortex (up to 51% after 1 week. Moreover, following a bilateral intrastriatal injection (60 μg, we achieve up to 80% silencing of a secondary target, Cyclophilin B, at both the mRNA and protein level. Importantly, DHA-hsiRNAs do not induce neural cell death or measurable innate immune activation following administration of concentrations over 20 times above the efficacious dose. Thus, DHA conjugation is a novel strategy for improving siRNA activity in mouse brain, with potential to act as a new therapeutic platform for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders.
-
McNerny, Daniel Q.; Leroueil, Pascale R.; Baker, James R.
2010-01-01
Dendrimer conjugates for pharmaceutical development are capable of enhancing the local delivery of cytotoxic drugs. The ability to conjugate different targeting ligands to the dendrimer allows for the cytotoxic drug to be focused at the intended target cell while minimizing collateral damage in normal cells. Dendrimers offer several advantages over other polymer conjugates by creating a better defined, more monodisperse therapeutic scaffold. Toxicity from the dendrimer, targeted and nonspecif...
-
Li, Yi; Gu, Christine; Gruenhagen, Jason; Yehl, Peter; Chetwyn, Nik P; Medley, Colin D
2016-01-01
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are complex therapeutic agents that use the specific targeting properties of antibodies and the highly potent cytotoxicity of small molecule drugs to selectively eliminate tumor cells while limiting the toxicity to normal healthy tissues. Two critical quality attributes of ADCs are the purity and stability of the active small molecule drug linked to the ADC, but these are difficult to assess once the drug is conjugated to the antibody. In this study, we report a enzyme deconjugation approach to cleave small molecule drugs from ADCs, which allows the drugs to be subsequently characterized by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. The model ADC we used in this study utilizes a valine-citrulline linker that is designed to be sensitive to endoproteases after internalization by tumor cells. We screened several proteases to determine the most effective enzyme. Among the 3 cysteine proteases evaluated, papain had the best efficiency in cleaving the small molecule drug from the model ADC. The deconjugation conditions were further optimized to achieve complete cleavage of the small molecule drug. This papain deconjugation approach demonstrated excellent specificity and precision. The purity and stability of the active drug on an ADC drug product was evaluated and the major degradation products of the active drug were identified. The papain deconjugation method was also applied to several other ADCs, with the results suggesting it could be applied generally to ADCs containing a valine-citrulline linker. Our results indicate that the papain deconjugation method is a powerful tool for characterizing the active small molecule drug conjugated to an ADC, and may be useful in ensuring the product quality, efficacy and the safety of ADCs.
-
Cysteine Cathepsins as Regulators of the Cytotoxicity of NK and T Cells
Perišić Nanut, Milica; Sabotič, Jerica; Jewett, Anahid; Kos, Janko
2014-01-01
Cysteine cathepsins are lysosomal peptidases involved at different levels in the processes of the innate and adaptive immune responses. Some, such as cathepsins B, L, and H are expressed constitutively in most immune cells. In cells of innate immunity they play a role in cell adhesion and phagocytosis. Other cysteine cathepsins are expressed more specifically. Cathepsin X promotes dendritic cell maturation, adhesion of macrophages, and migration of T cells. Cathepsin S is implicated in major histocompatibility complex class II antigen presentation, whereas cathepsin C, expressed in cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells, is involved in processing pro-granzymes into proteolytically active forms, which trigger cell death in their target cells. The activity of cysteine cathepsins is controlled by endogenous cystatins, cysteine protease inhibitors. Of these, cystatin F is the only cystatin that is localized in endosomal/lysosomal vesicles. After proteolytic removal of its N-terminal peptide, cystatin F becomes a potent inhibitor of cathepsin C with the potential to regulate pro-granzyme processing and cell cytotoxicity. This review is focused on the role of cysteine cathepsins and their inhibitors in the molecular mechanisms leading to the cytotoxic activity of T lymphocytes and NK cells in order to address new possibilities for regulation of their function in pathological processes. PMID:25520721
-
Cetuximab Enhanced the Cytotoxic Activity of Immune Cells during Treatment of Colorectal Cancer
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lin Wang
2017-11-01
Full Text Available Background/Aims: Cetuximab is a chimeric IgG1 monoclonal antibody which targets the extracellular domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. This antibody is widely used for colorectal cancer (CRC treatment but its influence on the immune system is incompletely understood. Methods: The immune influence of cetuximab therapy in CRC patients was investigated by analyzing peripheral blood mononuclear cells using flow cytometry. We undertook in vitro cytotoxicity and cytokine-profile assays to ascertain the immunomodulatory effect of cetuximab treatment. Results: The number of CD3+ T, CD8+ T, and natural killer (NK cells was increased significantly and T-regulatory cells reduced gradually after cetuximab treatment. Percentage of CD4+ T, natural killer T (NKT-like, invariant NKT, and dendritic cells was similar between baseline patients and cetuximab patients. Expression of CD137 on NK and CD8+ T cells was increased significantly after 4 weeks of cetuximab therapy. In vitro cetuximab treatment markedly increased expression of CD137 and CD107a on NK and CD8+ T cells. Cetuximab treatment promoted the cytotoxic activity of NK and CD8+ T cells against tumor cells. Conclusion: Cetuximab treatment promotes activation of the immune response but alleviates immunosuppression: this might be the underlying anti-CRC effect of cetuximab.
-
Molecular cytotoxic mechanisms of anticancer hydroxychalcones.
Sabzevari, Omid; Galati, Giuseppe; Moridani, Majid Y; Siraki, Arno; O'Brien, Peter J
2004-06-30
Chalcones are being considered as anticancer agents as they are natural compounds that are particularly cytotoxic towards K562 leukemia or melanoma cells. In this study, we have investigated phloretin, isoliquiritigenin, and 10 other hydroxylated chalcones for their cytotoxic mechanisms towards isolated rat hepatocytes. All hydroxychalcones partly depleted hepatocyte GSH and oxidized GSH to GSSG. These chalcones also caused a collapse of mitochondrial membrane potential and increased oxygen uptake. Furthermore, glycolytic or citric acid cycle substrates prevented cytotoxicity and mitochondrial membrane potential collapse. The highest pKa chalcones were the most effective at collapsing the mitochondrial membrane potential which suggests that the cytotoxic activity of hydroxychalcones are likely because of their ability to uncouple mitochondria.
-
Sadjadpour, Susan; Safarian, Shahrokh; Zargar, Seyed Jalal; Sheibani, Nader
2016-01-01
In photodynamic therapy (PDT) of cancer both the light and the photosensitizing agent are normally harmless, but in combination they could result in selective tumor killing. Zinc oxide nanoparticles were synthesized and coated with the amino acid cysteine to provide an adequate arm for conjugation with porphyrin photosensitizers (meso-tetra (4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin [MTCP] and CuMTCP). Porphyrin-conjugated nanoparticles were characterized by TEM, FTIR, and UV-vis, and fluorescence spectrophotometry. The 3-[4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was used to measure cell viability in the presence or absence of porphyrin conjugates following UV and X-ray irradiation. The uptake of the porphyrin-conjugated ZnO nanoparticles by cells was detected using fluorescence microscopy. Our results indicated that the survival of T-47D cells was significantly compromised in the presence of ZnO-MTCP-conjugated nanostructures with UV light exposure. Exhibition of cytotoxic activity of ZnO-MTCP for human prostate cancer (Du145) cells occurred at a higher concentration, indicating the more resistant nature of these tumor cells. ZnO-CuMTCP showed milder cytotoxic effects in human breast cancer (T-47D) and no cytotoxic effects in Du145 with UV light exposure, consistent with its lower cytotoxic potency as well as cellular uptake. Surprisingly, none of the ZnO-porphyrin conjugates exhibited cytotoxic effects with X-ray irradiation, whereas ZnO alone exerted cytotoxicity. Thus, ZnO and ZnO-porphyrin nanoparticles with UV or X-ray irradiation may provide a suitable treatment option for various cancers. © 2015 International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
-
Targeted Delivery and Sustained Antitumor Activity of Triptolide through Glucose Conjugation.
He, Qing-Li; Minn, Il; Wang, Qiaoling; Xu, Peng; Head, Sarah A; Datan, Emmanuel; Yu, Biao; Pomper, Martin G; Liu, Jun O
2016-09-19
Triptolide, a key ingredient from the traditional Chinese medicinal plant thunder god vine, which has been used to treat inflammation and autoimmune diseases for centuries, has been shown to be an irreversible inhibitor of the XPB subunit of the transcription factor TFIIH and initiation of RNA polymerase II mediated transcription. The clinical development of triptolide over the past two decades has been limited by its toxicity and low water solubility. Herein, we report the development of a glucose conjugate of triptolide, named glutriptolide, which was intended to target tumor cells overexpressing glucose transporters selectively. Glutriptolide did not inhibit XPB activity in vitro but demonstrated significantly higher cytotoxicity against tumor cells over normal cells with greater water solubility than triptolide. Furthermore, it exhibited remarkable tumor control in vivo, which is likely due to sustained stepwise release of active triptolide within cancer cells. These findings indicate that glutriptolide may serve as a promising lead for developing a new mechanistic class of anticancer drugs. © 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Antibody drug conjugates and bystander killing: is antigen-dependent internalisation required?
Staudacher, Alexander H; Brown, Michael P
2017-12-05
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) employ the exquisite specificity of tumour-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAb) for the targeted delivery of highly potent cytotoxic drugs to the tumour site. The chemistry of the linker, which connects the drug to the mAb, determines how and when the drug is released from the mAb. This, as well as the chemistry of the drug, can dictate whether the drug can diffuse into surrounding cells, resulting in 'bystander killing'. Initially, any bystander killing mechanism of action of an ADC was understood to involve an essential sequence of steps beginning with surface antigen targeting, internalisation, intracellular linker cleavage, drug release, and diffusion of drug away from the targeted cell. However, recent studies indicate that, depending on the linker and drug combination, this mechanism may not be essential and ADCs can be cleaved extracellularly or via other mechanisms. In this minireview, we will examine the role of bystander killing by ADCs and explore the emerging evidence of how this can occur independently of internalisation.
-
Campos, Jaqueline Ferreira; dos Santos, Uilson Pereira; Macorini, Luis Fernando Benitez; de Melo, Adriana Mary Mestriner Felipe; Balestieri, José Benedito Perrella; Paredes-Gamero, Edgar Julian; Cardoso, Claudia Andrea Lima; de Picoli Souza, Kely; dos Santos, Edson Lucas
2014-03-01
Propolis from stingless bees is well known for its biologic properties; however, few studies have demonstrated these effects. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the chemical composition and antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of propolis from the stingless bee Melipona orbignyi, found in Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. The chemical composition of the ethanol extract of propolis (EEP) indicated the presence of aromatic acids, phenolic compounds, alcohols, terpenes and sugars. The EEP was active against the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus and the fungus Candida albicans. The EEP showed antioxidant activity by scavenging free radicals and inhibiting hemolysis and lipid peroxidation in human erythrocytes incubated with an oxidizing agent. Additionally, EEP promoted cytotoxic activity and primarily necrotic death in K562 erythroleukemia cells. Taken together, these results indicate that propolis from M. orbignyi has therapeutic potential for the treatment and/or prevention of diseases related to microorganism activity, oxidative stress and tumor cell proliferation. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Masunaga, Shin-ichiro; Nagasawa, Hideko; Gotoh, Keiko
2006-01-01
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of 5 new 10 B-compounds (TX-2091, TX-2095, TX-2097, TX-2100, and TX-2110) as 10 B-carriers in boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). They were conjugates that had been synthesized from a hypoxia-specific cytotoxic bioreductive agent, quinoxaline oxide TX-402, and a clinically used 10 B-carrier, sodium borocaptate- 10 B (BSH). The 5 new compounds were hybrid compounds that have both a hypoxic cytotoxin unit and a thermal neutron-sensitizing unit, BSH. These new compounds and BSH were administered intraperitoneally to SCC VII tumor-bearing mice. Then, the 10 B concentrations in the tumors and normal tissues were measured by γ-ray spectrometry. Subsequently, SCC VII tumor-bearing mice were continuously given 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU) to label all proliferating (P) cells in the tumors, then treated with TX-2100, which was chosen based on the results of the above-mentioned biodistribution analyses, or BSH in the same manner as in the biodistribution studies. Right after irradiation, during which intratumor 10 B concentrations were kept at levels similar to each other, the tumors were excised, minced, and trypsinized. The tumor cell suspensions thus obtained were incubated with cytochalasin-B (a cytokinesis blocker), and the micronucleus (MN) frequency in cells without BrdU labeling [=quiescent (Q) cells] was determined using immunofluorescence staining for BrdU. Meanwhile, the MN frequency in the total (P+Q) tumor cell population was determined from the tumors that were not pretreated with BrdU. Clonogenic cell survival was also determined in mice given no BrdU. 10 B biodistribution analyses in tumors, brain, skin, muscles, blood, and liver indicated that TX-2100 has the most favorable characteristics for concentrating a sufficient amount of 10 B in tumors and maintaining a high enough 10 B concentration during irradiation. In addition, TX-2100 had a significantly stronger radio-sensitizing effect with
-
Enoch, Israel V. M. V.; Ramasamy, Sivaraj; Mohiyuddin, Shanid; Gopinath, Packirisamy; Manoharan, R.
2018-05-01
Magnetic nanoparticles are envisaged to overcome the impediments in the methods of targeted drug delivery and hence cure cancer effectively. We report herein, manganese ferrite nanoparticles, coated with β-cyclodextrin-modified polyethylene glycol as a carrier for the drug, camptothecin. The particles are of the size of 100 nm and they show superparamagnetic behaviour. The saturation magnetization does not get diminished on polymer coverage of the nanoparticles. The β-cyclodextrin-polyethylene glycol conjugates are characterized using NMR and mass spectrometric techniques. By coating the magnetic nanoparticles with the cyclodextrin-tethered polymer, the drug-loading capacity is enhanced and the observed release of the drug is slow and sustained. The cell viability of HEK293 and HCT15 cells is evaluated and the cytotoxicity is enhanced when the drug is loaded in the polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticles. The noncovalent-binding based and enhanced drug loading on the nanoparticles and the sustained release make the nanocarrier a promising agent for carrying the payload to the target.
-
Zhang, Wen; Tan, Davin; Lee, Richmond; Tong, Guanghu; Chen, Wenchao; Qi, Baojian; Huang, Kuo-Wei; Tan, Choonhong; Jiang, Zhiyong
2012-01-01
The strength of the weak: An L-tert-leucine-derived amine-thiourea catalyst (see scheme, green box) promotes the asymmetric vinylogous conjugate addition reaction between γ-aryl- and alkyl-substituted butenolides with the butenamides and enoates shown. Computational studies show the preference for the observed stereochemistry is a result of favourable weak non-bonding interactions, which stabilize the transition state. Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Zhang, Wen
2012-09-05
The strength of the weak: An L-tert-leucine-derived amine-thiourea catalyst (see scheme, green box) promotes the asymmetric vinylogous conjugate addition reaction between γ-aryl- and alkyl-substituted butenolides with the butenamides and enoates shown. Computational studies show the preference for the observed stereochemistry is a result of favourable weak non-bonding interactions, which stabilize the transition state. Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Liu, Zhenning; Sun, Mingli; Wang, Yu; Zhang, Lichun; Zhao, Hang; Zhao, Min
2018-02-01
Oxidative stress and inflammation are involved in paraquat-induced cytotoxicity. Silymarin can exert a potent antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effect in various pathophysiological processes. The aim of this current study is to explore the protective effect and potential mechanism of silymarin in paraquat-induced macrophage injury. Cells were pretreated with different doses of silymarin for 3h before exposure to paraquat. At 24h after exposure to paraquat, the paraquat-induced cytotoxicity to macrophage was measured via the MTT assay and LDH release. The levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species, GSH-Px, SOD, and lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde were measured to evaluate the oxidative effect of paraquat. NLRP3 inflammasome and cytokines secretion in macrophage exposed to paraquat at 24h were measured via immunofluorescence microscopy, western blot or Elisa. Our results revealed that paraquat could dramatically cause cytotoxicity and reactive oxygen species generation, enhance TXNIP expression, and induce NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cytokines secretion. The pretreatment with silymarin could remarkably reduce the cytotoxicity, promote the expression of Trx and antioxidant enzymes, and suppress the TXNIP and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. In conclusion, silymarin attenuated paraquat-induced cytotoxicity in macrophage by inhibiting oxidative stress, NLRP3 inflammasome activation, cytokines secretion and apoptosis. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Tao, Ran; Wang, Chengzhang; Zhang, Changwei; Li, WenJun; Zhou, Hao; Chen, Hongxia; Ye, Jianzhong
2018-07-01
The structure and bioactivity of Ginkgo biloba leaves polyprenol (GBP) are similar to that of dolichol which widely exists in human and mammalian organs. GBP possesses potential pharmacological activities against cancer. This study involved oil-in-water type nanoemulsion (NE) loading GBP was prepared by dissolving polyprenol in nanoemulsion of sodium tripolyphosphate (TPP)/TiO 2 solution, Triton X-100, and 1-octanol by inversed-phase emulsification (EIP) and ultrasonic emulsification (UE) method. Folic acid (FA)-coupled chitosan (CS) nanoparticles (NPs), GBP-FA-CS-NPs and GBP-TiO 2 -FA-CS-NPs, were fabricated by ionic cross-linking of positively charged FA-CS conjugates and negatively charged nanoemulsion with TPP/TiO 2 . And characterizations of them were investigated by TEM, SEM, FTIR, particle size, and zeta potential. The cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of GBP-TiO 2 -FA-CS-NP treatment were higher than GBP-NE, GBP-FA-CS-NPs, TiO 2 -NE, GBP-TiO 2 -NE, TiO 2 -FA-CS-NPs, and GBP-TiO 2 -FA-CS-NP treatment at the same tested concentrations in HepG2 cells. GBP-TiO 2 -FA-CS-NPs at low TiO 2 concentration (from 1 to 2.5 μg/ml) showed good inhibition capacity on HepG2 cells and low cytotoxic and genotoxic effects on HL-7702 cells. The possible mechanism of cytotoxicity on GBP-TiO 2 -FA-CS-NPs against HepG2 cells is by preventing excessive intracellular Ca 2+ into extracellular spaces via inhibiting Ca 2+ -ATPase and Ca 2+ /Mg 2+ -ATPase.
-
Wu, Hao; Radomkit, Suttipol; O’Brien, Jeannette M.; Hoveyda, Amir H.
2012-01-01
The first broadly applicable metal-free enantioselective method for boron conjugate addition (BCA) to α,β-unsaturated carbonyls is presented. The C–B bond forming reactions are promoted in the presence of 2.5–7.5 mol % of a readily accessible C1-symmetric chiral imidazolinium salt, which is converted, in situ, to the catalytically active diastereo- and enantiomerically pure N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) by the common organic base 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (dbu). In addition to the commercially available bis(pinacolato)diboron [B2(pin)2], and in contrast to reactions with the less sterically demanding achiral NHCs, the presence of MeOH is required for high efficiency. Acyclic and cyclic α,β-unsaturated ketones, as well as acyclic esters, Weinreb amides and aldehydes can serve as suitable substrates; the desired β-boryl carbonyls are isolated in up to 94% yield and >98:2 enantiomer ratio (er). Transformations are often carried out at ambient temperature. In certain cases, such as when the relatively less reactive unsaturated amides are used, elevated temperatures are required (50–66 °C); nonetheless, reactions remain highly enantioselective. The utility of the NHC-catalyzed method is demonstrated through comparison with the alternative Cu-catalyzed protocols; in cases involving a polyfunctional substrate, unique profiles in chemoselectivity are exhibited by the metal-free approach (e.g., conjugate addition vs reaction with an alkyne, allene or aldehyde). PMID:22559866
-
CONJUGATED BLOCK-COPOLYMERS FOR ELECTROLUMINESCENT DIODES
Hilberer, A; Gill, R.E; Herrema, J.K; Malliaras, G.G; Wildeman, J.; Hadziioannou, G
In this article we review results obtained in our laboratory on the design and study of new light-emitting polymers. We are interested in the synthesis and characterisation of block copolymers with regularly alternating conjugated and non conjugated sequences. The blocks giving rise to luminescence
-
Tetrafullerene conjugates for all-organic photovoltaics
Fernández, G.; Sánchez, L.; Veldman, D.; Wienk, M.M.; Atienza, C.M.; Guldi, D.M.; Janssen, R.A.J.; Martin, N.
2008-01-01
The synthesis of two new tetrafullerene nanoconjugates in which four C60 units are covalently connected through different -conjugated oligomers (oligo(p-phenylene ethynylene) and oligo(p-phenylene vinylene)) is described. The photovoltaic (PV) response of these C60-based conjugates was evaluated by
-
Cytotoxic glucosphingolipid from Celtis Africana.
Perveen, Shagufta; Al-Taweel, Areej Mohammad; Fawzy, Ghada Ahmed; El-Shafae, Azza Muhammed; Khan, Afsar; Proksch, Peter
2015-05-01
Literature survey proved the use of the powdered sun-dried bark and roots of Celtis africana for the treatment of cancer in South Africa. The aim of this study was to do further isolation work on the ethyl acetate fraction and to investigate the cytotoxic activities of the various fractions and isolated compound. Cytotoxicity of petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, n-butanol fractions and compound 1 were tested on mouse lymphoma cell line L5178Y using the microculture tetrazolium assay. One new glucosphingolipid 1 was isolated from the aerial parts of C. africana. The structure of the new compound was determined by extensive analysis by one-dimensional and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. The ethyl acetate fraction and compound 1 showed strong cytotoxic activity with an EC50 value of 8.3 μg/mL and 7.8 μg/mL, respectively, compared with Kahalalide F positive control (6.3 μg/mL). This is the first report of the occurrence of a cytotoxic glucosphingolipid in family Ulmaceae.
-
Weber, T E; Schinckel, A P; Houseknecht, K L; Richert, B T
2001-10-01
An experiment was conducted to determine the efficacy of dietary conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) as a growth promotant in weanling swine. Weanling pigs (n = 192; 7.6 kg and 29 d of age) were randomly assigned to four treatments that were arranged as a 2 x 2 factorial. Concentrations of dietary CLA (0 or 0.6%) and antibiotics (+/-) constituted the main effect variables. Dietary CLA treatments consisted of a 1% addition of an oil containing 60% CLA isomers or 1% soybean oil, and dietary antibiotic treatments were antibiotics or no antibiotics. The experimental diets were fed for 9 wk in four phases (1, wk 1; 2, wk 2 and 3; 3, wk 4 through 6; and 4, wk 7 through 9), after which all pigs were fed identical medicated diets for the duration of the finishing phase. Live weights were recorded at wk 17 postweaning and at marketing to determine any residual effects of dietary treatments on finisher ADG and days to market. Medicated diets fed during phases 1 and 2 contained 55 mg carbadox/kg; during phase 3 contained 299 mg tilmicosin/kg; and during phase 4 contained 110 mg tylosin and 110 mg sulfamethazine/kg. Pigs fed medicated diets had higher overall ADG than pigs fed unmedicated diets for wk 0 through 9 (P pigs fed medicated diets than for pigs fed unmedicated diets during phase 1 (P residual effects of nursery CLA or antibiotics on finisher ADG and days to market. Blood samples collected from a subset of pigs (n = 72) at the completion of phases 2, 3, and 4 were assayed for serum IGF-I and antibody concentrations to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. There was a tendency for pigs fed medicated diets to have greater IGF-I concentrations than pigs fed unmedicated diets at the completion of phase 4 (P Pigs fed CLA had greater antibody titers (P pigs fed diets without CLA. These results indicate that feeding 0.6% dietary CLA did not enhance growth performance in weanling swine and that the use of dietary antibiotics can
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Noaman, E.
2008-01-01
Cancer cells possess nitric oxide syntheses (NOS) which metabolize L-Arginine (L-Arg) for producing nitric oxide (NO) The present study investigates the relations between NO and ionizing radiation in the Ehrlich ascites carcinoma (EAC) cell line. NOS activity was stimulated by exposure of cells to L-Arg just after irradiation. L-Arg (5 m M) supply led to an increase in ionizing radiation induced cytotoxicity (% of viability 18± 3 %) whereas, neither L-Arg itself nor ionizing irradiation caused cell death at the doses used in this study. Also, cells were treated either with L-Thio citrulline (L-Thio), an irreversible inhibitor of NOS or with exogenous superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. L-Thio and SOD prevented L-Arg mediated deleterious effects on Irradiated cells, whereas catalase was ineffective. Intracellular antioxidant enzyme activity was also determined. Ionizing radiation + L-Arg stress altered the activity of catalase (66 % decrease) and glutathione peroxidase (83 % decrease). Our findings demonstrated that L-Arg induces increase the radiation-mediated deleterious effects in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells cytotoxicity and that the ratio NO/ O 2 plays a key role in these processes. NO could participate the deleterious effect of irradiation, in conjugation with others reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced during the oxidation of intracellular components by ionizing radiation (dose 6 Gy)
-
Novel Aflatoxin Derivatives and Protein Conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Reinhard Niessner
2007-03-01
Full Text Available Aflatoxins, a group of structurally related mycotoxins, are well known for their toxic and carcinogenic effects in humans and animals. Aflatoxin derivatives and protein conjugates are needed for diverse analytical applications. This work describes a reliable and fast synthesis of novel aflatoxin derivatives, purification by preparative HPLC and characterisation by ESI-MS and one- and two-dimensional NMR. Novel aflatoxin bovine serum albumin conjugates were prepared and characterised by UV absorption and MALDI-MS. These aflatoxin protein conjugates are potentially interesting as immunogens for the generation of aflatoxin selective antibodies with novel specificities.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wei Chen
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Ethyl carbamate (EC is a food and environmental toxicant and is a cause of concern for human exposure. Several studies indicated that EC-induced toxicity was associated with oxidative stress. Mulberry fruits are reported to have a wide range of bioactive compounds and pharmacological activities. The present study was therefore aimed to investigate the protective property of mulberry fruit extract (MFE on EC-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress. Chemical composition analysis showed that total phenolic content and total flavonoid content in MFE were 502.43 ± 5.10 and 219.12 ± 4.45 mg QE/100 g FW. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside and cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside were the major anthocyanins in MFE. In vitro antioxidant studies (DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays jointly exhibited the potent antioxidant capacity of MFE. Further study indicated that MFE protected human liver HepG2 cells from EC-induced cytotoxicity by scavenging overproduced cellular ROS. EC treatment promoted intracellular glutathione (GSH depletion and caused mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP collapse, as well as mitochondrial membrane lipid peroxidation, whereas MFE pretreatment significantly inhibited GSH depletion and restored the mitochondrial membrane function. Overall, our study suggested that polyphenolic-rich MFE could afford a potent protection against EC-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress.
-
Structure Property Relationships in Organic Conjugated Systems
O'Neill, Luke
2008-01-01
A series of pi(п) conjugated oligomers containing 1 to 6 monomer units were studied by absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopies. The results are discussed and examined with regard to the variation of the optical properties with the increase of effective conjugation length. It was found that there was a linear relationship between the positioning of the absorption and photoluminescence maxima plotted against inverse conjugation length. The relationships are in good agreement with the si...
-
Sources and Bioactive Properties of Conjugated Dietary Fatty Acids.
Hennessy, Alan A; Ross, Paul R; Fitzgerald, Gerald F; Stanton, Catherine
2016-04-01
The group of conjugated fatty acids known as conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) isomers have been extensively studied with regard to their bioactive potential in treating some of the most prominent human health malignancies. However, CLA isomers are not the only group of potentially bioactive conjugated fatty acids currently undergoing study. In this regard, isomers of conjugated α-linolenic acid, conjugated nonadecadienoic acid and conjugated eicosapentaenoic acid, to name but a few, have undergone experimental assessment. These studies have indicated many of these conjugated fatty acid isomers commonly possess anti-carcinogenic, anti-adipogenic, anti-inflammatory and immune modulating properties, a number of which will be discussed in this review. The mechanisms through which these bioactivities are mediated have not yet been fully elucidated. However, existing evidence indicates that these fatty acids may play a role in modulating the expression of several oncogenes, cell cycle regulators, and genes associated with energy metabolism. Despite such bioactive potential, interest in these conjugated fatty acids has remained low relative to the CLA isomers. This may be partly attributed to the relatively recent emergence of these fatty acids as bioactives, but also due to a lack of awareness regarding sources from which they can be produced. In this review, we will also highlight the common sources of these conjugated fatty acids, including plants, algae, microbes and chemosynthesis.
-
Preparation and immunological properties of procaine-protein conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Liakopoulou, A.
1981-01-01
Procaine was conjugated to BSA and rat and rabbit Gf using the carbodiimide method and 14 C-procaine as tracer. The composition of the conjugates could be varied depending on the time of incubation and the concentration of procaine in the reaction mixtures. Procaine-BSA conjugates were soluble in water or saline. However, procaine conjugates to rat or rabbit Gf were not readily soluble in saline. These conjugates were good for immunization purposes, but it was cumbersome to work with them when clear solutions were needed, as in the immunochemical procedures used in this study. The immunological properties of the conjugates were studied in rats and rabbits. Rats responded with production of IgGa and precipitating antibodies to the procaine group, but IgE antibodies to the immunogen could not be detected. Furthermore, precipitating antibodies towards the procaine group were raised in rabbits. When BSA was the protein carrier, antibodies to the carrier molecule were also detected in both rats and rabbits. The conjugates of procaine to rat or rabbit Gf did not elicit antibody response to the carrier molecule when used in the homologous species. Hapten inhibition studies suggested that, in the rabbit, antibodies were also produced with specificity directed towards the molecular configuration of the hapten-carrier bond. (author)
-
IRDye78 Conjugates for Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Atif Zaheer
2002-10-01
Full Text Available The detection of human malignancies by near-infrared (NIR fluorescence will require the conjugation of cancer-specific ligands to NIR fluorophores that have optimal photoproperties and pharmacokinetics. IRDye78, a tetra-sulfonated heptamethine indocyanine NIR fluorophore, meets most of the criteria for an in vivo imaging agent, and is available as an N-hydroxysuccinimide ester for conjugation to low-molecular-weight ligands. However, IRDye78 has a high charge-to-mass ratio, complicating purification of conjugates. It also has a potentially labile linkage between fluorophore and ligand. We have developed an ion-pairing purification strategy for IRDye78 that can be performed with a standard C18 column under neutral conditions, thus preserving the stability of fluorophore, ligand, and conjugate. By employing parallel evaporative light scatter and absorbance detectors, all reactants and products are identified, and conjugate purity is maximized. We describe reversible and irreversible conversions of IRDye78 that can occur during sample purification, and describe methods for preserving conjugate stability. Using seven ligands, spanning several classes of small molecules and peptides (neutral, charged, and/or hydrophobic, we illustrate the robustness of these methods, and confirm that IRDye78 conjugates so purified retain bioactivity and permit NIR fluorescence imaging of specific targets.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Feng L
2011-10-01
Full Text Available Lan Feng1, Huali Wu2, Ping Ma1, Russell J Mumper1,3, S Rahima Benhabbour11Division of Molecular Pharmaceutics, Center for Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery, UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy, 2Division of Pharmacotherapy and Experimental Therapeutics, UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy, 3UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, NC, USAAbstract: Three docetaxel (DX lipid conjugates: 2’-lauroyl-docetaxel (C12-DX, 2’-stearoyl-docetaxel (C18-DX, and 2’-behenoyl-docetaxel (C22-DX were synthesized to enhance drug loading, entrapment, and retention in liquid oil-filled lipid nanoparticles (NPs. The three conjugates showed ten-fold higher solubility in the liquid oil phase Miglyol 808 than DX. To further increase the drug entrapment efficiency in NPs, orthogonal design was performed. The optimized formulation was composed of Miglyol 808, Brij 78, and Vitamin E tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate (TPGS. The conjugates were successfully entrapped in the reduced-surfactant NPs with entrapment efficiencies of about 50%–60% as measured by gel permeation chromatography (GPC at a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. All three conjugates showed 45% initial burst release in 100% mouse plasma. Whereas C12-DX showed another 40% release over the next 8 hours, C18-DX and C22-DX in NPs showed no additional release after the initial burst of drug. All conjugates showed significantly lower cytotoxicity than DX in human DU-145 prostate cancer cells. The half maximal inhibitory concentration values (IC50 of free conjugates and conjugate NPs were comparable except for C22-DX, which was nontoxic in the tested concentration range and showed only vehicle toxicity when entrapped in NPs. In vivo, the total area under the curve (AUC0-∞ values of all DX conjugate NPs were significantly greater than that of Taxotere, demonstrating prolonged retention of drug in the blood. The AUC0-∞ value of DX in Taxotere was 8.3-fold, 358
-
Potential genotoxic and cytotoxicity of emamectin benzoate in human normal liver cells.
Zhang, Zhijie; Zhao, Xinyu; Qin, Xiaosong
2017-10-10
Pesticide residue inducing cancer-related health problems draw people more attention recently. Emamectin benzoate (EMB) has been widely used in agriculture around the world based on its specificity targets. Although potential risk and the molecular mechanism of EMB toxicity to human liver has not been well-characterized. Unlike well-reported toxicity upon central nervous system, potential genotoxic and cytotoxicity of EMB in human liver cell was ignored and very limited. In this study, we identify genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of EMB to human normal liver cells (QSG7701 cell line) in vitro . We demonstrate that EMB inhibited the viability of QSG7701 cells and induced the DNA damage. Established assays of cytotoxicity were performed to characterize the mechanism of EMB toxicity on QSG7701 cells. Typical chromatin condensation and DNA fragmentation indicated the apoptosis of QSG7701 cells induced by EMB. And the intracellular biochemical results demonstrated that EMB-enhanced apoptosis of QSG7701 cells concurrent with generated ROS, a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, the cytochrome-c release, up regulate the Bax/Bcl-2 and the activation of caspase-9/-3. Our results of EMB induces the death of QSG7701 cells maybe via mitochondrial-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathways would contribute to promote the awareness of EMB as an extensive used pesticide to human being effects and reveal the underlying mechanisms of potential genotoxic.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Masahisa Hemmi
2017-11-01
Full Text Available Few current vaccines can establish antigen (Ag-specific immune responses in both mucosal and systemic compartments. Therefore, development of vaccines providing defense against diverse infectious agents in both compartments is of high priority in global health. Intramuscular vaccination of an adenovirus vector (Adv has been shown to induce Ag-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs in both systemic and gut-mucosal compartments. We previously found that type I interferon (IFN signaling is required for induction of gut-mucosal, but not systemic, CTLs following vaccination; however, the molecular mechanism involving type I IFN signaling remains unknown. Here, we found that T helper 17 (Th17-polarizing cytokine expression was down-regulated in the inguinal lymph nodes (iLNs of Ifnar2−/− mice, resulting in the reduction of Ag-specific Th17 cells in the iLNs and gut mucosa of the mice. We also found that prior transfer of Th17 cells reversed the decrease in the number of Ag-specific gut-mucosal CTLs in Ifnar2−/− mice following Adv vaccination. Additionally, prior transfer of Th17 cells into wild-type mice enhanced the induction of Ag-specific CTLs in the gut mucosa, but not in systemic compartments, suggesting a gut mucosa-specific mechanism where Th17 cells regulate the magnitude of vaccine-elicited Ag-specific CTL responses. These data suggest that Th17 cells translate systemic type I IFN signaling into a gut-mucosal CTL response following vaccination, which could promote the development of promising Adv vaccines capable of establishing both systemic and gut-mucosal protective immunity.
-
Kung Sutherland, May S; Walter, Roland B; Jeffrey, Scott C; Burke, Patrick J; Yu, Changpu; Kostner, Heather; Stone, Ivan; Ryan, Maureen C; Sussman, Django; Lyon, Robert P; Zeng, Weiping; Harrington, Kimberly H; Klussman, Kerry; Westendorf, Lori; Meyer, David; Bernstein, Irwin D; Senter, Peter D; Benjamin, Dennis R; Drachman, Jonathan G; McEarchern, Julie A
2013-08-22
Outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remain unsatisfactory, and novel treatments are urgently needed. One strategy explores antibodies and their drug conjugates, particularly those targeting CD33. Emerging data with gemtuzumab ozogamicin (GO) demonstrate target validity and activity in some patients with AML, but efficacy is limited by heterogeneous drug conjugation, linker instability, and a high incidence of multidrug resistance. We describe here the development of SGN-CD33A, a humanized anti-CD33 antibody with engineered cysteines conjugated to a highly potent, synthetic DNA cross-linking pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer via a protease-cleavable linker. The use of engineered cysteine residues at the sites of drug linker attachment results in a drug loading of approximately 2 pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimers per antibody. In preclinical testing, SGN-CD33A is more potent than GO against a panel of AML cell lines and primary AML cells in vitro and in xenotransplantation studies in mice. Unlike GO, antileukemic activity is observed with SGN-CD33A in AML models with the multidrug-resistant phenotype. Mechanistic studies indicate that the cytotoxic effects of SGN-CD33A involve DNA damage with ensuing cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death. Together, these data suggest that SGN-CD33A has CD33-directed antitumor activity and support clinical testing of this novel therapeutic in patients with AML.
-
Preconditioning the modified conjugate gradient method ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
In this paper, the convergence analysis of the conventional conjugate Gradient method was reviewed. And the convergence analysis of the modified conjugate Gradient method was analysed with our extension on preconditioning the algorithm. Convergence of the algorithm is a function of the condition number of M-1A.
-
Kreutz, M.; Giquel, B.; Hu, Q.; Abuknesha, R.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; Nestle, F.O.; Diebold, S.S.
2012-01-01
Antibody-antigen conjugates, which promote antigen-presentation by dendritic cells (DC) by means of targeted delivery of antigen to particular DC subsets, represent a powerful vaccination approach. To ensure immunity rather than tolerance induction the co-administration of a suitable adjuvant is
-
Cytotoxic Effects of Bangladeshi Medicinal Plant Extracts
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Shaikh J. Uddin
2011-01-01
Full Text Available To investigate the cytotoxic effect of some Bangladeshi medicinal plant extracts, 16 Bangladeshi medicinal plants were successively extracted with n-hexane, dichloromethane, methanol and water. The methanolic and aqueous extracts were screened for cytotoxic activity against healthy mouse fibroblasts (NIH3T3 and three human cancer-cell lines (gastric: AGS; colon: HT-29; and breast: MDA-MB-435S using the MTT assay. Two methanolic extracts (Hygrophila auriculata and Hibiscus tiliaceous and one aqueous extract (Limnophila indica showed no toxicity against healthy mouse fibroblasts, but selective cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells (IC50 1.1–1.6 mg mL−1. Seven methanolic extracts from L. indica, Clerodendron inerme, Cynometra ramiflora, Xylocarpus moluccensis, Argemone mexicana, Ammannia baccifera and Acrostichum aureum and four aqueous extracts from Hygrophila auriculata, Bruguiera gymnorrhiza, X. moluccensis and Aegiceras corniculatum showed low toxicity (IC50 > 2.5 mg mL−1 against mouse fibroblasts but selective cytotoxicity (IC50 0.2–2.3 mg mL−1 against different cancer cell lines. The methanolic extract of Blumea lacera showed the highest cytotoxicity (IC50 0.01–0.08 mg mL−1 against all tested cell lines among all extracts tested in this study. For some of the plants their traditional use as anticancer treatments correlates with the cytotoxic results, whereas for others so far unknown cytotoxic activities were identified.
-
Lee, Hwankyu; Larson, Ronald G
2009-10-08
We performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of one or two copies of polyethylene glycol of molecular weight 550 (PEG550) and 5000 (PEG5000) daltons, conjugated to generation 3 (G3) to 5 (G5) polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers with explicit water using a coarse-grained model. We found the radii of gyration of these dendrimer-PEG molecules to be close to those measured in experiments by Hedden and Bauer (Hedden , R. C. ; Bauer , B. J. Macromolecules 2003 , 36 , 1829.). Densely grafted PEG ligands (>50% of the dendrimer surface) extend like brushes, with layer thickness in agreement with theory for starlike polymers. Two dendrimer-PEG complexes in the box drift away from each other, indicating that no aggregation is induced by either short or long PEG chains, conflicting with a recent view that the cytotoxicity of some PEGylated particles might be due to particle aggregation for long PEG lengths.
-
Bis-polymer lipid-peptide conjugates and nanoparticles thereof
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Xu, Ting; Dong, He; Shu, Jessica; Dube, Nikhil
2018-04-24
The present invention provides bis-polymer lipid-peptide conjugates containing a hydrophobic block and headgroup containing a helical peptide and two polymer blocks. The conjugates can self-assemble to form helix bundle subunits, which in turn assemble to provide micellar nanocarriers for drug cargos and other agents. Particles containing the conjugates and methods for forming the particles are also disclosed.
-
Cytotoxic constituents of ethyl acetate fraction from Dianthus superbus.
Ding, Chengli; Zhang, Wu; Li, Jie; Lei, Jiachuan; Yu, Jianqing
2013-01-01
The ethyl acetate fraction (EE-DS) from Dianthus superbus was found to possess the cytotoxic activity against cancer cells in previous study. To investigate cytotoxic constituents, the bioassay-guided isolation of compounds from EE-DS was performed. Two dianthramides (1 and 2), three flavonoids (3-5), two coumarins (6 and 7) and three other compounds (8-10) were obtained. Structures of isolated compounds were identified by spectroscopic analysis. Cytotoxicity of the compounds against HepG2 cells was evaluated. Compound 1 showed the strongest cytotoxicity, compounds 10, 4, 3 and 5 had moderate cytotoxicity.
-
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles, methods of using, and methods of making
Habuchi, Satoshi; Piwonski, Hubert Marek; Michinobu, Tsuyoshi
2017-01-01
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide for conjugated polymer nanoparticle, method of making conjugated polymer nanoparticles, method of using conjugated polymer nanoparticle, polymers, and the like.
-
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles, methods of using, and methods of making
Habuchi, Satoshi
2017-03-16
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide for conjugated polymer nanoparticle, method of making conjugated polymer nanoparticles, method of using conjugated polymer nanoparticle, polymers, and the like.
-
Do Dental X-Rays Induce Genotoxicity and Cytotoxicity in Oral Mucosa Cells? A Critical Review.
Angelieri, Fernanda; Yujra, Veronica Quispe; Oshima, Celina Tizuko Fujiyama; Ribeiro, Daniel Araki
2017-10-01
Dental X-rays are widely used in clinical practice, since the technique is an important approach for diagnosing diseases in dental and periodontal tissues. However, it is widely known that radiation is capable of causing damage to cellular systems, such as genotoxicity or cytotoxicity. Thus, the aim of this review was to present a critical analysis regarding the studies published on genotoxicity and cytotoxicity induced by dental X-rays in oral mucosa cells. Such studies have revealed that some oral cell types are more sensitive than others following exposure to dental X-rays. Certainly, this review will contribute to a better understanding of this matter as well as to highlighting perspectives for further studies. Ultimately, such data will promote better safety for both patients and dental professionals. Copyright© 2017, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
-
Quantitative structure-cytotoxicity relationship of phenylpropanoid amides.
Shimada, Chiyako; Uesawa, Yoshihiro; Ishihara, Mariko; Kagaya, Hajime; Kanamoto, Taisei; Terakubo, Shigemi; Nakashima, Hideki; Takao, Koichi; Saito, Takayuki; Sugita, Yoshiaki; Sakagami, Hiroshi
2014-07-01
A total of 12 phenylpropanoid amides were subjected to quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) analysis, based on their cytotoxicity, tumor selectivity and anti-HIV activity, in order to investigate on their biological activities. Cytotoxicity against four human oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell lines and three human oral normal cells was determined by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) method. Tumor selectivity was evaluated by the ratio of the mean CC50 (50% cytotoxic concentration) against normal oral cells to that against OSCC cell lines. Anti-HIV activity was evaluated by the ratio of CC50 to EC50 (50% cytoprotective concentration from HIV infection). Physicochemical, structural, and quantum-chemical parameters were calculated based on the conformations optimized by the LowModeMD method followed by density functional theory (DFT) method. Twelve phenylpropanoid amides showed moderate cytotoxicity against both normal and OSCC cell lines. N-Caffeoyl derivatives coupled with vanillylamine and tyramine exhibited relatively higher tumor selectivity. Cytotoxicity against normal cells was correlated with descriptors related to electrostatic interaction such as polar surface area and chemical hardness, whereas cytotoxicity against tumor cells correlated with free energy, surface area and ellipticity. The tumor-selective cytotoxicity correlated with molecular size (surface area) and electrostatic interaction (the maximum electrostatic potential). The molecular size, shape and ability for electrostatic interaction are useful parameters for estimating the tumor selectivity of phenylpropanoid amides. Copyright© 2014 International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. John G. Delinassios), All rights reserved.
-
Nonlinear conjugate gradient methods in micromagnetics
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Fischbacher
2017-04-01
Full Text Available Conjugate gradient methods for energy minimization in micromagnetics are compared. The comparison of analytic results with numerical simulation shows that standard conjugate gradient method may fail to produce correct results. A method that restricts the step length in the line search is introduced, in order to avoid this problem. When the step length in the line search is controlled, conjugate gradient techniques are a fast and reliable way to compute the hysteresis properties of permanent magnets. The method is applied to investigate demagnetizing effects in NdFe12 based permanent magnets. The reduction of the coercive field by demagnetizing effects is μ0ΔH = 1.4 T at 450 K.
-
Usta, M.; Wortelboer, H.M.; Vervoort, J.J.M.; Boersma, M.G.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Bladeren, van P.J.; Cnubben, N.H.P.
2007-01-01
Curcumin, an alpha,beta-unsaturated carbonyl compound, reacts with glutathione, leading to the formation of two monoglutathionyl curcumin conjugates. In the present study, the structures of both glutathione conjugates of curcumin were identified by LC-MS and one- and two-dimensional H-1 NMR
-
Buri, Marcus V; Torquato, Heron F Vieira; Barros, Carlos Castilho; Ide, Jaime S; Miranda, Antonio; Paredes-Gamero, Edgar J
2017-07-01
Several reports described different modes of cell death triggered by antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) due to direct effects on membrane disruption, and more recently by apoptosis and necrosis-like patterns. Cytotoxic curves of four β-hairpin AMPs (gomesin, protegrin, tachyplesin, and polyphemusin) were obtained from several human leukemic lineages and normal monocytes and Two cell lines were then selected based on their cytotoxic sensitivity. One was sensitive to AMPs (K562) and the other resistant (KG-1) and their effect compared between these lineages. Thus, these lineages were chosen to further investigate biological features related with their cytotoxicities to AMPs. Stimulation with AMPs produced cell death, with activation of caspase-3, in K562 lineage. Increase on the fluidity of plasmatic membrane by reducing cholesterol potentiated cytotoxicity of AMPs in both lineages. Quantification of internal and external gomesin binding to the cellular membrane of both K562 and KG-1 cells showed that more peptide is accumulated inside of K562 cells. Additionally, evaluation of multi-drug resistant pumps activity showed that KG-1 has more activity than K562 lineage. A comparison of intrinsic gene patterns showed great differences between K562 and KG-1, but stimulation with gomesin promoted few changes in gene expression patterns. Differences in internalization process through the plasma membrane, multidrug resistance pumps activity, and gene expression pattern are important features to AMPs regulated cell death. J. Cell. Biochem. 118: 1764-1773, 2017. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
-
Selective Covalent Conjugation of Phosphorothioate DNA Oligonucleotides with Streptavidin
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Christof M. Niemeyer
2011-08-01
Full Text Available Protein-DNA conjugates have found numerous applications in the field of diagnostics and nanobiotechnology, however, their intrinsic susceptibility to DNA degradation by nucleases represents a major obstacle for many applications. We here report the selective covalent conjugation of the protein streptavidin (STV with phosphorothioate oligonucleotides (psDNA containing a terminal alkylthiolgroup as the chemically addressable linking unit, using a heterobifunctional NHS-/maleimide crosslinker. The psDNA-STV conjugates were synthesized in about 10% isolated yields. We demonstrate that the terminal alkylthiol group selectively reacts with the maleimide while the backbone sulfur atoms are not engaged in chemical conjugation. The novel psDNA-STV conjugates retain their binding capabilities for both biotinylated macromolecules and the complementary nucleic acid. Moreover, the psDNA-STV conjugate retained its binding capacity for complementary oligomers even after a nuclease digestion step, which effectively degrades deoxyribonucleotide oligomers and thus the binding capability of regular DNA-STV conjugates. The psDNA-STV therefore hold particular promise for applications e.g. in proteome research and novel biosensing devices, where interfering endogenous nucleic acids need to be removed from analytes by nuclease digestion.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, K.T.; Spanggaard, H.; Krebs, Frederik C
2004-01-01
. Electroluminescent devices of the homopolymer itself and of the zinc-porphyrin containing polymer were prepared and the nature of the electroluminescence was characterized. The homopolymer segments were found to optically pump the emission of the zinc-porphyrin dye moities. The homopolymer exhibits blue......Zinc-porphyrin dye molecules were incorporated into the backbone of a conjugated polymer material by a method, which allowed for the incorporation of only one zinc-porphyrin dye molecule into the backbone of each conjugated polymer molecule. The electronic properties of the homopolymer were...
-
Lipid-peptide-polymer conjugates and nanoparticles thereof
Xu, Ting; Dong, He; Shu, Jessica
2015-06-02
The present invention provides a conjugate having a peptide with from about 10 to about 100 amino acids, wherein the peptide adopts a helical structure. The conjugate also includes a first polymer covalently linked to the peptide, and a hydrophobic moiety covalently linked to the N-terminus of the peptide, wherein the hydrophobic moiety comprises a second polymer or a lipid moiety. The present invention also provides helix bundles form by self-assembling the conjugates, and particles formed by self-assembling the helix bundles. Methods of preparing the helix bundles and particles are also provided.
-
Novel β-cyclodextrin-eosin conjugates.
Benkovics, Gábor; Afonso, Damien; Darcsi, András; Béni, Szabolcs; Conoci, Sabrina; Fenyvesi, Éva; Szente, Lajos; Malanga, Milo; Sortino, Salvatore
2017-01-01
Eosin B (EoB) and eosin Y (EoY), two xanthene dye derivatives with photosensitizing ability were prepared in high purity through an improved synthetic route. The dyes were grafted to a 6-monoamino-β-cyclodextrin scaffold under mild reaction conditions through a stable amide linkage using the coupling agent 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium chloride. The molecular conjugates, well soluble in aqueous medium, were extensively characterized by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Preliminary spectroscopic investigations showed that the β-cyclodextrin-EoY conjugate retains both the fluorescence properties and the capability to photogenerate singlet oxygen of the unbound chromophore. In contrast, the corresponding β-cyclodextrin-EoB conjugate did not show either relevant emission or photosensitizing activity probably due to aggregation in aqueous medium, which precludes any response to light excitation.
-
Novel β-cyclodextrin–eosin conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gábor Benkovics
2017-03-01
Full Text Available Eosin B (EoB and eosin Y (EoY, two xanthene dye derivatives with photosensitizing ability were prepared in high purity through an improved synthetic route. The dyes were grafted to a 6-monoamino-β-cyclodextrin scaffold under mild reaction conditions through a stable amide linkage using the coupling agent 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl-4-methylmorpholinium chloride. The molecular conjugates, well soluble in aqueous medium, were extensively characterized by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Preliminary spectroscopic investigations showed that the β-cyclodextrin–EoY conjugate retains both the fluorescence properties and the capability to photogenerate singlet oxygen of the unbound chromophore. In contrast, the corresponding β-cyclodextrin–EoB conjugate did not show either relevant emission or photosensitizing activity probably due to aggregation in aqueous medium, which precludes any response to light excitation.
-
Chang, Chih-Jung; Chen, Yi-Yuan M; Lu, Chia-Chen; Lin, Chuan-Sheng; Martel, Jan; Tsai, Sheng-Hui; Ko, Yun-Fei; Huang, Tsung-Teng; Ojcius, David M; Young, John D; Lai, Hsin-Chih
2014-04-01
Ganoderma lucidum (G. lucidum) is a medicinal mushroom long used in Asia as a folk remedy to promote health and longevity. Recent studies indicate that G. lucidum activates NK cells, but the molecular mechanism underlying this effect has not been studied so far. To address this question, we prepared a water extract of G. lucidum and examined its effect on NK cells. We observed that G. lucidum treatment increases NK cell cytotoxicity by stimulating secretion of perforin and granulysin. The mechanism of activation involves an increased expression of NKG2D and natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCRs), as well as increased phosphorylation of intracellular MAPKs. Our results indicate that G. lucidum induces NK cell cytotoxicity against various cancer cell lines by activating NKG2D/NCR receptors and MAPK signaling pathways, which together culminate in exocytosis of perforin and granulysin. These observations provide a cellular and molecular mechanism to account for the reported anticancer effects of G. lucidum extracts in humans.
-
Folate-conjugated boron nitride nanospheres for targeted delivery of anticancer drug
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Feng S
2016-09-01
Full Text Available Shini Feng,1 Huijie Zhang,1 Ting Yan,1 Dandi Huang,1 Chunyi Zhi,2 Hideki Nakanishi,1 Xiao-Dong Gao1 1Key Laboratory of Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biotechnology, Ministry of Education, School of Biotechnology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, People’s Republic of China Abstract: With its unique physical and chemical properties and structural similarity to carbon, boron nitride (BN has attracted considerable attention and found many applications. Biomedical applications of BN have recently started to emerge, raising great hopes in drug and gene delivery. Here, we developed a targeted anticancer drug delivery system based on folate-conjugated BN nanospheres (BNNS with receptor-mediated targeting. Folic acid (FA was successfully grafted onto BNNS via esterification reaction. In vitro cytotoxicity assay showed that BNNS-FA complexes were non-toxic to HeLa cells up to a concentration of 100 µg/mL. Then, doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX, a commonly used anticancer drug, was loaded onto BNNS-FA complexes. BNNS-FA/DOX complexes were stable at pH 7.4 but effectively released DOX at pH 5.0, which exhibited a pH sensitive and sustained release pattern. BNNS-FA/DOX complexes could be recognized and specifically internalized by HeLa cells via FA receptor-mediated endocytosis. BNNS-FA/DOX complexes exhibited greater cytotoxicity to HeLa cells than free DOX and BNNS/DOX complexes due to the increased cellular uptake of DOX mediated by the FA receptor. Therefore, BNNS-FA complexes had strong potential for targeted cancer therapy. Keywords: boron nitride nanospheres, folic acid, doxorubicin, targeted delivery, cancer therapy
-
Photodynamic tissue adhesion with chlorin(e6) protein conjugates.
Khadem, J; Veloso, A A; Tolentino, F; Hasan, T; Hamblin, M R
1999-12-01
To test the hypothesis that a photodynamic laser-activated tissue solder would perform better in sealing scleral incisions when the photosensitizer was covalently linked to the protein than when it was noncovalently mixed. Conjugates and mixtures were prepared between the photosensitizer chlorin(e6) and various proteins (albumin, fibrinogen, and gelatin) in different ratios and used to weld penetrating scleral incisions made in human cadaveric eyes. A blue-green (488-514 nm) argon laser activated the adhesive, and the strength of the closure was measured by increasing the intraocular pressure until the wound showed leakage. Both covalent conjugates and noncovalent mixtures showed a light dose-dependent increase in leaking pressure. A preparation of albumin chlorin(e6) conjugate with additional albumin added (2.5 protein to chlorin(e6) molar ratio) showed significantly higher weld strength than other protein conjugates and mixtures. This is the first report of dye-protein conjugates as tissue solders. These conjugates may have applications in ophthalmology.
-
Usta, M.; Wortelboer, H.M.; Vervoort, J.; Boersma, M.G.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Bladeren, P.J. van; Cnubben, N.H.P.
2007-01-01
Curcumin, an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound, reacts with glutathione, leading to the formation of two monoglutathionyl curcumin conjugates. In the present study, the structures of both glutathione conjugates of curcumin were identified by LC-MS and one- and two-dimensional 1H NMR analysis, and
-
DENDRIMER CONJUGATES FOR SELECTIVE OF PROTEIN AGGREGATES
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
2004-01-01
Dendrimer conjugates are presented, which are formed between a dendrimer and a protein solubilising substance. Such dendrimer conjugates are effective in the treatment of protein aggregate-related diseases (e.g. prion-related diseases). The protein solubilising substance and the dendrimer together...
-
Boulenouar, Selma; Michelet, Xavier; Duquette, Danielle; Alvarez, David; Hogan, Andrew E; Dold, Christina; O'Connor, Donal; Stutte, Suzanne; Tavakkoli, Ali; Winters, Desmond; Exley, Mark A; O'Shea, Donal; Brenner, Michael B; von Andrian, Ulrich; Lynch, Lydia
2017-02-21
Adipose tissue has a dynamic immune system that adapts to changes in diet and maintains homeostatic tissue remodeling. Adipose type 1 innate lymphoid cells (AT1-ILCs) promote pro-inflammatory macrophages in obesity, but little is known about their functions at steady state. Here we found that human and murine adipose tissue harbor heterogeneous populations of AT1-ILCs. Experiments using parabiotic mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD) showed differential trafficking of AT1-ILCs, particularly in response to short- and long-term HFD and diet restriction. At steady state, AT1-ILCs displayed cytotoxic activity toward adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs). Depletion of AT1-ILCs and perforin deficiency resulted in alterations in the ratio of inflammatory to anti-inflammatory ATMs, and adoptive transfer of AT1-ILCs exacerbated metabolic disorder. Diet-induced obesity impaired AT1-ILC killing ability. Our findings reveal a role for AT1-ILCs in regulating ATM homeostasis through cytotoxicity and suggest that this function is relevant in both homeostasis and metabolic disease. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jacob Thomas
Full Text Available Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs are agents of horizontal gene transfer and have major roles in evolution and acquisition of new traits, including antibiotic resistances. ICEs are found integrated in a host chromosome and can excise and transfer to recipient bacteria via conjugation. Conjugation involves nicking of the ICE origin of transfer (oriT by the ICE-encoded relaxase and transfer of the nicked single strand of ICE DNA. For ICEBs1 of Bacillus subtilis, nicking of oriT by the ICEBs1 relaxase NicK also initiates rolling circle replication. This autonomous replication of ICEBs1 is critical for stability of the excised element in growing cells. We found a conserved and previously uncharacterized ICE gene that is required for conjugation and replication of ICEBs1. Our results indicate that this gene, helP (formerly ydcP, encodes a helicase processivity factor that enables the host-encoded helicase PcrA to unwind the double-stranded ICEBs1 DNA. HelP was required for both conjugation and replication of ICEBs1, and HelP and NicK were the only ICEBs1 proteins needed for replication from ICEBs1 oriT. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we measured association of HelP, NicK, PcrA, and the host-encoded single-strand DNA binding protein Ssb with ICEBs1. We found that NicK was required for association of HelP and PcrA with ICEBs1 DNA. HelP was required for association of PcrA and Ssb with ICEBs1 regions distal, but not proximal, to oriT, indicating that PcrA needs HelP to progress beyond nicked oriT and unwind ICEBs1. In vitro, HelP directly stimulated the helicase activity of the PcrA homologue UvrD. Our findings demonstrate that HelP is a helicase processivity factor needed for efficient unwinding of ICEBs1 for conjugation and replication. Homologues of HelP and PcrA-type helicases are encoded on many known and putative ICEs. We propose that these factors are essential for ICE conjugation, replication, and genetic stability.
-
... version Home Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerve Disorders Cranial Nerve Disorders Conjugate Gaze Palsies Horizontal gaze palsy Vertical ... Version. DOCTORS: Click here for the Professional Version Cranial Nerve Disorders Overview of the Cranial Nerves Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia ...
-
Synthesis of Mikto-Arm Star Peptide Conjugates.
Koo, Jin Mo; Su, Hao; Lin, Yi-An; Cui, Honggang
2018-01-01
Mikto-arm star peptide conjugates are an emerging class of self-assembling peptide-based structural units that contain three or more auxiliary segments of different chemical compositions and/or functionalities. This group of molecules exhibit interesting self-assembly behavior in solution due to their chemically asymmetric topology. Here we describe the detailed procedure for synthesis of an ABC Mikto-arm star peptide conjugate in which two immiscible entities (a saturated hydrocarbon and a hydrophobic and lipophobic fluorocarbon) are conjugated onto a short β-sheet forming peptide sequence, GNNQQNY, derived from the Sup35 prion, through a lysine junction. Automated and manual Fmoc-solid phase synthesis techniques are used to synthesize the Mikto-arm star peptide conjugates, followed by HPLC purification. We envision that this set of protocols can afford a versatile platform to synthesize a new class of peptidic building units for diverse applications.
-
Fullerene-biomolecule conjugates and their biomedicinal applications.
Yang, Xinlin; Ebrahimi, Ali; Li, Jie; Cui, Quanjun
2014-01-01
Fullerenes are among the strongest antioxidants and are characterized as "radical sponges." The research on biomedicinal applications of fullerenes has achieved significant progress since the landmark publication by Friedman et al in 1993. Fullerene-biomolecule conjugates have become an important area of research during the past 2 decades. By a thorough literature search, we attempt to update the information about the synthesis of different types of fullerene-biomolecule conjugates, including fullerene-containing amino acids and peptides, oligonucleotides, sugars, and esters. Moreover, we also discuss in this review recently reported data on the biological and pharmaceutical utilities of these compounds and some other fullerene derivatives of biomedical importance. While within the fullerene-biomolecule conjugates, in which fullerene may act as both an antioxidant and a carrier, specific targeting biomolecules conjugated to fullerene will undoubtedly strengthen the delivery of functional fullerenes to sites of clinical interest.
-
Analytical characterization of polymer-drug conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rizzo, V.; Gigli, M.; Pinciroli, V.
1998-01-01
A few polymeric conjugates of antitumor drugs have been recently developed in view of possible therapeutic advantages: solubilization of sparingly soluble drugs in water, improvement of therapeutic index, organ targeting through a second chemical species bound to the same polymeric chain. In this article it's described the analytical approach used in the characterization of the conjugates for chemical identity, purity and strength of the contained active ingredient. The techniques are: high field NMR and size exclusion chromatography with non-aqueous mobile phase for identity; selective hydrolysis and HPLC for strength and purity. A complete and reliable picture is thus obtained both for qualitative and for quantitative aspects. This is an important step forward in the direction of further development and marketing of polymer-drug conjugates [it
-
Conjugate gradient algorithms using multiple recursions
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Barth, T.; Manteuffel, T.
1996-12-31
Much is already known about when a conjugate gradient method can be implemented with short recursions for the direction vectors. The work done in 1984 by Faber and Manteuffel gave necessary and sufficient conditions on the iteration matrix A, in order for a conjugate gradient method to be implemented with a single recursion of a certain form. However, this form does not take into account all possible recursions. This became evident when Jagels and Reichel used an algorithm of Gragg for unitary matrices to demonstrate that the class of matrices for which a practical conjugate gradient algorithm exists can be extended to include unitary and shifted unitary matrices. The implementation uses short double recursions for the direction vectors. This motivates the study of multiple recursion algorithms.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Borg, D C; Schaich, K M
1984-01-01
A comprehensive reaction schema for oxidative cytotoxicity is presented, integrating known chemical mechanisms of oxygen radical reactions and observed pathophysiology. The key features of the schema are the coupling of (1) redox cycling of autoxidizable substrates to form the equilibrium pair of superoxide anion (O/sub 2//sup -/)/and its conjugate acid, perhydroxyl radical (HO/sub 2/.); (2) hydrogen peroxide (H/sub 2/O/sub 2/) generation via O/sub 2//sup -/ dimutation; (3) catalytic redox cycling of metals reducing H/sub 2/O/sub 2/ to reactive hydroxyl radicals (OH.); (4) direct reaction of OH. with target molecules, including critical cell macromolecules and polyunsaturated lipids in membranes; (5) transfer of oxidative potential from initial to distant sites via H/sub 2/O/sub 2/ and O/sub 2/-/HO/sub 2/ diffusion, lipid free radical chain peroxidations in membranes, and migration of non-radical lipid oxidation products; and (6) cytotoxic damage at those distant sites mediated by reaction of lipid radical species and other lipid oxidation products with critical target molecules (proteins, DNA, etc.). Although there is a broad consensus of agreement within the cognizant research community concerning many aspects of this schema, there exists considerable controversy and/or misconception about several important issues. Critical analyses of four presently controversial points are presented.
-
Four-wave mixing and phase conjugation in plasmas
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Federici, J.F.
1989-01-01
Nonlinear optical effects such as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering, Stimulated Raman Scattering, self-focusing, wave-mixing, parametric mixing, etc., have a long history in plasma physics. Recently, four-wave mixing in plasmas and its applications to phase conjugation has been extensively studied. Although four-wave mixing (FWM), using various nonlinear mediums, has many practical applications in the visible regime, no successful attempt has been made to study or demonstrate FWM for wavelengths longer than 10μm. Plasmas as phase conjugate mirrors have received considerable attention since they become more efficient at longer wavelengths (far-infrared to microwave). The purpose of this thesis is to study various fundamental issues which concern the suitability of plasmas for four-wave mixing and phase conjugation. The major contributions of this thesis are the identification and study of thermal and ionization nonlinearities as potential four-wave mixing and phase conjugation mechanisms and the study of the affect of density inhomogeneities on the FWM process. Using a fluid description for the plasma, this thesis demonstrates that collisional heating generates a thermal force which substantially enhances the phase conjugate reflectivity. The prospect of using a novel ionization nonlinearity in weakly ionized plasmas for wave-mixing and phase conjugation is discussed. The ionization nonlinearity arises from localized heating of the plasma by the beat-wave. Wherever, the local temperature is increased, a plasma density grating is produced due to increased electron-impact ionization. Numerical estimates of the phase conjugate reflectivity indicate reflectivities in the range of 10 -4 -10 -3 are possible in a weakly ionized steady-state gas discharge plasma
-
The antioxidant properties, cytotoxicity and monoamine oxidase ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
ajl yemi
2011-11-28
Nov 28, 2011 ... and the nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) assay. The cytotoxicity ... The antioxidant activity and cytotoxic effect of the extracts increased with increase ... supplements are concoctions of plants and/or plant .... In vitro antioxidant assay.
-
Cytotoxic, mutagenicity, and genotoxicity effects of guanylhydrazone derivatives.
Pinhatti, Valéria Rodrigues; da Silva, Juliana; Martins, Tales Leandro Costa; Moura, Dinara Jaqueline; Rosa, Renato Moreira; Villela, Izabel; Stopiglia, Cheila Denise Ottonelli; da Silva Santos, Selma; Scroferneker, Maria Lúcia; Machado, Carlos Renato; Saffi, Jenifer; Henriques, João Antonio Pêgas
2016-08-01
Several studies have reported that guanylhydrazones display a variety of desirable biological properties, such as antihypertensive, antibacterial, and antimalarial behaviour. They furthermore promote anti-pneumocystosis and anti-trypanosomiasis, exhibit antitumor activity, and show significant cytotoxicity against cancer cell lines. In this work, we have evaluated the cytotoxicity, mutagenicity, and genotoxicity of two guanylhydrazones derivatives, (E)-2-[(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl) methylene] hydrazine carboxymidamide hydrochloride (2,3-DMeB) and (E)-2-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl) methylene] hydrazine carboxymidamide hydrochloride (3,4-DMeB), in different biological models. Both 2,3-DMeB and 3,4-DMeB induce weak cytotoxic and mutagenic effects in bacteria and yeast. The genotoxicity of these compounds was determined in a fibroblast cell line (V79) using alkaline comet assay, as well as a modified comet assay with bacterial enzymes formamidopyrimidine DNA-glycosylase (FPG) and endonuclease III (EndoIII). Both guanylhydrazone derivatives induced DNA damage. Treatment of V79 cells with EndoIII and FPG proteins demonstrated a significant effect of 2,3-DMeB and 3,4-DMeB with respect to oxidized bases. In addition, the derivatives induced a significant increase in the frequency of micronucleated cells at high doses. The antifungal and anti-trypanosomal properties of these guanylhydrazone derivatives were also evaluated, and the obtained results suggest that 2,3-DMeB is more effective than 3,4-DMeB. The biological activity of 2,3-DMeB and 3,4-DMeB may thus be related, at least in part, to their oxidative potential, as well as to their ability to interact with DNA. Considering the previously reported in vitro antitumor activity of guanylhydrazone derivatives in combination with the lack of acute toxicity and the fact that DNA damage is only observed at high doses should render both compounds good candidates for in vivo studies on antitumor activity. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B
-
Hu, Shun; Yu, Weili; Hu, Chunyang; Wei, Dong; Shen, Lijuan; Hu, Tao; Yi, Youjin
2017-11-01
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is a serious fatal pathogen that causes tuberculosis (TB). Effective vaccination is urgently needed to deal with the serious threat from TB. Mtb-secreted protein antigens are important virulence determinants of Mtb with poor immunogenicity. Adjuvants and antigen delivery systems are thus highly desired to improve the immunogenicity of protein antigens. Inulin is a biocompatible polysaccharide (PS) adjuvant that can stimulate a strong cellular and humoral immunity. Bacterial capsular PS and haptens have been conjugated with cross-reacting material 197 (CRM 197 ) to improve their immunogenicity. CFP10 and TB10.4 were two Mtb-secreted immunodominant protein antigens. A CFP10-TB10.4 fusion protein (CT) was used as the antigen for covalent conjugation with the CRM 197 -inulin conjugate (CRM-inu). The resultant conjugate (CT-CRM-inu) elicited high CT-specific IgG titers, stimulated splenocyte proliferation and provoked the secretion of Th1-type and Th2-type cytokines. Conjugation with CRM-inu significantly prolonged the systemic circulation of CT and exposure to the immune system. Moreover, CT-CRM-inu showed no apparent toxicity to cardiac, hepatic and renal functions. Thus, conjugation of CT with CRM-inu provided an effective strategy for development of protein-based vaccines against Mtb infection. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
New hybrid conjugate gradient methods with the generalized Wolfe line search.
Xu, Xiao; Kong, Fan-Yu
2016-01-01
The conjugate gradient method was an efficient technique for solving the unconstrained optimization problem. In this paper, we made a linear combination with parameters β k of the DY method and the HS method, and putted forward the hybrid method of DY and HS. We also proposed the hybrid of FR and PRP by the same mean. Additionally, to present the two hybrid methods, we promoted the Wolfe line search respectively to compute the step size α k of the two hybrid methods. With the new Wolfe line search, the two hybrid methods had descent property and global convergence property of the two hybrid methods that can also be proved.
-
O:2-CRM(197) conjugates against Salmonella Paratyphi A.
Micoli, Francesca; Rondini, Simona; Gavini, Massimiliano; Lanzilao, Luisa; Medaglini, Donata; Saul, Allan; Martin, Laura B
2012-01-01
Enteric fevers remain a common and serious disease, affecting mainly children and adolescents in developing countries. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi was believed to cause most enteric fever episodes, but several recent reports have shown an increasing incidence of S. Paratyphi A, encouraging the development of a bivalent vaccine to protect against both serovars, especially considering that at present there is no vaccine against S. Paratyphi A. The O-specific polysaccharide (O:2) of S. Paratyphi A is a protective antigen and clinical data have previously demonstrated the potential of using O:2 conjugate vaccines. Here we describe a new conjugation chemistry to link O:2 and the carrier protein CRM(197), using the terminus 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO), thus leaving the O:2 chain unmodified. The new conjugates were tested in mice and compared with other O:2-antigen conjugates, synthesized adopting previously described methods that use CRM(197) as carrier protein. The newly developed conjugation chemistry yielded immunogenic conjugates with strong serum bactericidal activity against S. Paratyphi A.
-
O:2-CRM(197 conjugates against Salmonella Paratyphi A.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Francesca Micoli
Full Text Available Enteric fevers remain a common and serious disease, affecting mainly children and adolescents in developing countries. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi was believed to cause most enteric fever episodes, but several recent reports have shown an increasing incidence of S. Paratyphi A, encouraging the development of a bivalent vaccine to protect against both serovars, especially considering that at present there is no vaccine against S. Paratyphi A. The O-specific polysaccharide (O:2 of S. Paratyphi A is a protective antigen and clinical data have previously demonstrated the potential of using O:2 conjugate vaccines. Here we describe a new conjugation chemistry to link O:2 and the carrier protein CRM(197, using the terminus 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO, thus leaving the O:2 chain unmodified. The new conjugates were tested in mice and compared with other O:2-antigen conjugates, synthesized adopting previously described methods that use CRM(197 as carrier protein. The newly developed conjugation chemistry yielded immunogenic conjugates with strong serum bactericidal activity against S. Paratyphi A.
-
Integrated circuits based on conjugated polymer monolayer.
Li, Mengmeng; Mangalore, Deepthi Kamath; Zhao, Jingbo; Carpenter, Joshua H; Yan, Hongping; Ade, Harald; Yan, He; Müllen, Klaus; Blom, Paul W M; Pisula, Wojciech; de Leeuw, Dago M; Asadi, Kamal
2018-01-31
It is still a great challenge to fabricate conjugated polymer monolayer field-effect transistors (PoM-FETs) due to intricate crystallization and film formation of conjugated polymers. Here we demonstrate PoM-FETs based on a single monolayer of a conjugated polymer. The resulting PoM-FETs are highly reproducible and exhibit charge carrier mobilities reaching 3 cm 2 V -1 s -1 . The high performance is attributed to the strong interactions of the polymer chains present already in solution leading to pronounced edge-on packing and well-defined microstructure in the monolayer. The high reproducibility enables the integration of discrete unipolar PoM-FETs into inverters and ring oscillators. Real logic functionality has been demonstrated by constructing a 15-bit code generator in which hundreds of self-assembled PoM-FETs are addressed simultaneously. Our results provide the state-of-the-art example of integrated circuits based on a conjugated polymer monolayer, opening prospective pathways for bottom-up organic electronics.
-
A cytotoxic serine proteinase isolated from mouse submandibular gland.
Shimamura, T; Nagumo, N; Ikigai, H; Murakami, K; Okubo, S; Toda, M; Ohnishi, R; Tomita, M
1989-08-01
We have isolated a novel cytotoxic factor from the submandibular glands of male BALB/c mice by Sephadex G-50 gel filtration chromatography and reverse-phase HPLC. The cytotoxic factor is a serine proteinase, which belongs to the mouse glandular kallikrein (mGK) family, with an Mr of approximately 27,000. The purified serine proteinase showed cytotoxic activity against mouse thymocytes in a dose-dependent manner, and a serine proteinase inhibitor, diisopropyl fluorophosphate, blocked its cytotoxic activity.
-
METHOD OF CONJUGATED CIRCULAR ARCS TRACING
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
N. Ageyev Vladimir
2017-01-01
Full Text Available The geometric properties of conjugated circular arcs connecting two points on the plane with set directions of tan- gent vectors are studied in the work. It is shown that pairs of conjugated circular arcs with the same conditions in frontier points create one-parameter set of smooth curves tightly filling all the plane. One of the basic properties of this set is the fact that all coupling points of circular arcs are on the circular curve going through the initially given points. The circle radius depends on the direction of tangent vectors. Any point of the circle curve, named auxiliary in this work, determines a pair of conjugated arcs with given boundary conditions. One more condition of the auxiliary circle curve is that it divides the plane into two parts. The arcs going from the initial point are out of the circle limited by this circle curve and the arcs coming to the final point are inside it. These properties are the basis for the method of conjugated circular arcs tracing pro- posed in this article. The algorithm is rather simple and allows to fulfill all the needed plottings using only the divider and ruler. Two concrete examples are considered. The first one is related to the problem of tracing of a pair of conjugated arcs with the minimal curve jump when going through the coupling point. The second one demonstrates the possibility of trac- ing of the smooth curve going through any three points on the plane under condition that in the initial and final points the directions of tangent vectors are given. The proposed methods of conjugated circular arcs tracing can be applied in solving of a wide variety of problems connected with the tracing of cam contours, for example pattern curves in textile industry or in computer-aided-design systems when programming of looms with numeric control.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hansen, Paul Robert
2015-01-01
To produce antibodies against synthetic peptides it is necessary to couple them to a protein carrier. This chapter provides a nonspecialist overview of peptide-carrier conjugation. Furthermore, a protocol for coupling cysteine-containing peptides to bovine serum albumin is outlined....
-
Tutton, P J; Barkla, D H
1978-01-01
The cytotoxicity of 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine (5,6-DHT), 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine (5,7-DHT), bromolysergic acid diethylamide (BOL), methysergide, and cyproheptadine, and also of 5,6-DHT together with either BOL, methysergide, or cyproheptadine in dimethylhydrazine-induced (DMH) carcinomata of rat colon was evaluated by estimating the percentage of necrotic cells in histological sections of tissues taken 15 h after injection of each of the drugs. In addition, the influence of methysergide and cyproheptadine on the tumour cell mitotic rate was estimated by means of a stathmokinetic technique. Both 5,6-DHT and 5,7-DHT were cytotoxic at each dose tested and for each of these agents the percentage of necrotic cells was directly correlated with the dose of drug used. BOL was not found to be cytotoxic to the colonic carcinomata, whereas both methysergide and cyproheptadine did cause detectable tumour cell necrosis. Methysergide was also found to accelerate tumour cell proliferation, whereas cyproheptadine did not. BOL competitively inhibited the cytotoxicity of 5,6-DHT and neither methysergide nor cyproheptadine potentiated the effect of 5,6 DHT.
-
Class, Kinship Density, and Conjugal Role Segregation.
Hill, Malcolm D.
1988-01-01
Studied conjugal role segregation in 150 married women from intact families in working-class community. Found that, although involvement in dense kinship networks was associated with conjugal role segregation, respondents' attitudes toward marital roles and phase of family cycle when young children were present were more powerful predictors of…
-
Solar multi-conjugate adaptive optics performance improvement
Zhang, Zhicheng; Zhang, Xiaofang; Song, Jie
2015-08-01
In order to overcome the effect of the atmospheric anisoplanatism, Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics (MCAO), which was developed based on turbulence correction by means of several deformable mirrors (DMs) conjugated to different altitude and by which the limit of a small corrected FOV that is achievable with AO is overcome and a wider FOV is able to be corrected, has been widely used to widen the field-of-view (FOV) of a solar telescope. With the assistance of the multi-threaded Adaptive Optics Simulator (MAOS), we can make a 3D reconstruction of the distorted wavefront. The correction is applied by one or more DMs. This technique benefits from information about atmospheric turbulence at different layers, which can be used to reconstruct the wavefront extremely well. In MAOS, the sensors are either simulated as idealized wavefront gradient sensors, tip-tilt sensors based on the best Zernike fit, or a WFS using physical optics and incorporating user specified pixel characteristics and a matched filter pixel processing algorithm. Only considering the atmospheric anisoplanatism, we focus on how the performance of a solar MCAO system is related to the numbers of DMs and their conjugate heights. We theoretically quantify the performance of the tomographic solar MCAO system. The results indicate that the tomographic AO system can improve the average Strehl ratio of a solar telescope by only employing one or two DMs conjugated to the optimum altitude. And the S.R. has a significant increase when more deformable mirrors are used. Furthermore, we discuss the effects of DM conjugate altitude on the correction achievable by the MCAO system, and present the optimum DM conjugate altitudes.
-
Abrin immunotoxin: targeted cytotoxicity and intracellular trafficking pathway.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sudarshan Gadadhar
Full Text Available BACKGROUND: Immunotherapy is fast emerging as one of the leading modes of treatment of cancer, in combination with chemotherapy and radiation. Use of immunotoxins, proteins bearing a cell-surface receptor-specific antibody conjugated to a toxin, enhances the efficacy of cancer treatment. The toxin Abrin, isolated from the Abrus precatorius plant, is a type II ribosome inactivating protein, has a catalytic efficiency higher than any other toxin belonging to this class of proteins but has not been exploited much for use in targeted therapy. METHODS: Protein synthesis assay using (3[H] L-leucine incorporation; construction and purification of immunotoxin; study of cell death using flow cytometry; confocal scanning microscopy and sub-cellular fractionation with immunoblot analysis of localization of proteins. RESULTS: We used the recombinant A chain of abrin to conjugate to antibodies raised against the human gonadotropin releasing hormone receptor. The conjugate inhibited protein synthesis and also induced cell death specifically in cells expressing the receptor. The conjugate exhibited differences in the kinetics of inhibition of protein synthesis, in comparison to abrin, and this was attributed to differences in internalization and trafficking of the conjugate within the cells. Moreover, observations of sequestration of the A chain into the nucleus of cells treated with abrin but not in cells treated with the conjugate reveal a novel pathway for the movement of the conjugate in the cells. CONCLUSIONS: This is one of the first reports on nuclear localization of abrin, a type II RIP. The immunotoxin mAb F1G4-rABRa-A, generated in our laboratory, inhibits protein synthesis specifically on cells expressing the gonadotropin releasing hormone receptor and the pathway of internalization of the protein is distinct from that seen for abrin.
-
Tissue Specific Promoters in Colorectal Cancer
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. R. Rama
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Colorectal carcinoma is the third most prevalent cancer in the world. In the most advanced stages, the use of chemotherapy induces a poor response and is usually accompanied by other tissue damage. Significant progress based on suicide gene therapy has demonstrated that it may potentiate the classical cytotoxic effects in colorectal cancer. The inconvenience still rests with the targeting and the specificity efficiency. The main target of gene therapy is to achieve an effective vehicle to hand over therapeutic genes safely into specific cells. One possibility is the use of tumor-specific promoters overexpressed in cancers. They could induce a specific expression of therapeutic genes in a given tumor, increasing their localized activity. Several promoters have been assayed into direct suicide genes to cancer cells. This review discusses the current status of specific tumor-promoters and their great potential in colorectal carcinoma treatment.
-
Site-Selective Conjugation of Native Proteins with DNA
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Trads, Julie Brender; Tørring, Thomas; Gothelf, Kurt Vesterager
2017-01-01
Conjugation of DNA to proteins is increasingly used in academia and industry to provide proteins with tags for identification or handles for hybridization to other DNA strands. Assay technologies such as immuno-PCR and proximity ligation and the imaging technology DNA-PAINT require DNA-protein....... The introduction of a bioorthogonal handle at a specific position of a protein by recombinant techniques provides an excellent approach to site-specific conjugation, but for many laboratories and for applications where several proteins are to be labeled, the expression of recombinant proteins may be cumbersome...... conjugates. In DNA nanotechnology, the DNA handle is exploited to precisely position proteins by self-assembly. For these applications, site-selective conjugation is almost always desired because fully functional proteins are required to maintain the specificity of antibodies and the activity of enzymes...
-
Conjugated Polymers for Flexible Energy Harvesting and Storage.
Zhang, Zhitao; Liao, Meng; Lou, Huiqing; Hu, Yajie; Sun, Xuemei; Peng, Huisheng
2018-03-01
Since the discovery of conjugated polymers in the 1970s, they have attracted considerable interest in light of their advantages of having a tunable bandgap, high electroactivity, high flexibility, and good processability compared to inorganic conducting materials. The above combined advantages make them promising for effective energy harvesting and storage, which have been widely studied in recent decades. Herein, the key advancements in the use of conjugated polymers for flexible energy harvesting and storage are reviewed. The synthesis, structure, and properties of conjugated polymers are first summarized. Then, their applications in flexible polymer solar cells, thermoelectric generators, supercapacitors, and lithium-ion batteries are described. The remaining challenges are then discussed to highlight the future direction in the development of conjugated polymers. © 2018 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Lipke, Elisabeth; Michalik, Peter
2012-11-01
Sperm conjugation, where two or more sperm are physically united, is a rare but widespread pheno-menon across the animal kingdom. One group well known for its different types of sperm conjugation are spiders. Particularly, haplogyne spiders show a high diversity of sperm traits. Besides individual cleistospermia, primary (synspermia) and secondary (coenospermia, "spermatophore") sperm conjugation occurs. However, the evolution of sperm conjugates and sperm is not understood in this group. Here, we look at how sperm are transferred in Caponiidae (Haplogynae) in pursuit of additional information about the evolution of sperm transfer forms in spiders. Additionally, we investigated the male reproductive system and spermatozoa using light- and transmission electron-microscopy and provide a 3D reconstruction of individual as of well as conjugated spermatozoa. Mature spermatozoa are characterized by an extremely elongated, helical nucleus resulting in the longest spider sperm known to date. At the end of spermiogenesis, synspermia are formed by complete fusion of four spermatids. Thus, synspermia might have evolved early within ecribellate Haplogynae. The fused sperm cells are surrounded by a prominent vesicular area. The function of the vesicular area remains still unknown but might be correlated with the capacitation process inside the female. Further phylogenetic and functional implications of the spermatozoa and sperm conjugation are discussed. Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Design and biological activity of β-sheet breaker peptide conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rocha, Sandra; Cardoso, Isabel; Boerner, Hans; Pereira, Maria Carmo; Saraiva, Maria Joao; Coelho, Manuel
2009-01-01
The sequence LPFFD (iAβ 5 ) prevents amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) fibrillogenesis and neurotoxicity, hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD), as previously demonstrated. In this study iAβ 5 was covalently linked to poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and the activity of conjugates was assessed and compared to the activity of the peptide alone by in vitro studies. The conjugates were characterized by MALDI-TOF. Competition binding assays established that conjugates retained the ability to bind Aβ with similar strength as iAβ 5 . Transmission electron microscopy analysis showed that iAβ 5 conjugates inhibited amyloid fibril formation, which is in agreement with binding properties observed for the conjugates towards Aβ. The conjugates were also able to prevent amyloid-induced cell death, as evaluated by activation of caspase 3. These results demonstrated that the biological activity of iAβ 5 is not affected by the pegylation process.
-
Poulin-Laprade, Dominic; Carraro, Nicolas; Burrus, Vincent
2015-01-01
Nowadays, healthcare systems are challenged by a major worldwide drug resistance crisis caused by the massive and rapid dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and associated emergence of multidrug resistant pathogenic bacteria, in both clinical and environmental settings. Conjugation is the main driving force of gene transfer among microorganisms. This mechanism of horizontal gene transfer mediates the translocation of large DNA fragments between two bacterial cells in direct contact. Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) of the SXT/R391 family (SRIs) and IncA/C conjugative plasmids (ACPs) are responsible for the dissemination of a broad spectrum of antibiotic resistance genes among diverse species of Enterobacteriaceae and Vibrionaceae. The biology, diversity, prevalence and distribution of these two families of conjugative elements have been the subject of extensive studies for the past 15 years. Recently, the transcriptional regulators that govern their dissemination through the expression of ICE- or plasmid-encoded transfer genes have been described. Unrelated repressors control the activation of conjugation by preventing the expression of two related master activator complexes in both types of elements, i.e., SetCD in SXT/R391 ICEs and AcaCD in IncA/C plasmids. Finally, in addition to activating ICE- or plasmid-borne genes, these master activators have been shown to specifically activate phylogenetically unrelated mobilizable genomic islands (MGIs) that also disseminate antibiotic resistance genes and other adaptive traits among a plethora of pathogens such as Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella enterica.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Dominic ePoulin-Laprade
2015-08-01
Full Text Available Nowadays, healthcare systems are challenged by a major worldwide drug resistance crisis caused by the massive and rapid dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and associated emergence of multidrug resistant pathogenic bacteria, in both clinical and environmental settings. Conjugation is the main driving force of gene transfer among microorganisms. This mechanism of horizontal gene transfer mediates the translocation of large DNA fragments between two bacterial cells in direct contact. Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs of the SXT/R391 family (SRIs and IncA/C conjugative plasmids (ACPs are responsible for the dissemination of a broad spectrum of antibiotic resistance genes among diverse species of Enterobacteriaceae and Vibrionaceae. The biology, diversity, prevalence and distribution of these two families of conjugative elements have been the subject of extensive studies for the past 15 years. Recently, the transcriptional regulators that govern their dissemination through the expression of ICE- or plasmid-encoded transfer genes have been described. Unrelated repressors control the activation of conjugation by preventing the expression of two related master activator complexes in both types of elements, i.e. SetCD in SXT/R391 ICEs and AcaCD in IncA/C plasmids. Finally, in addition to activating ICE- or plasmid-borne genes, these master activators have been shown to specifically activate phylogenetically unrelated mobilizable genomic islands (MGIs that also disseminate antibiotic resistance genes and other adaptive traits among a plethora of pathogens such as Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella enterica.
-
Yen, Hui-Ju; Young, Yen-An; Tsai, Tsung-Neng; Cheng, Kuang-Ming; Chen, Xin-An; Chen, Ying-Chuan; Chen, Cheng-Cheung; Young, Jenn-Jong; Hong, Po-da
2018-03-01
In this study, we synthesized various quaternary chitosan derivatives and used them to stabilize gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). These chitosan derivatives comprised N-(2-hydroxy)propyl-3-trimethylammonium chitosan chloride (HTCC), folate-HTCC, galactosyl-HTCC, and their fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated derivatives. Various positively surface-charged AuNPs were prepared under alkaline conditions using glucose as a reducing agent in the presence of the HTCC derivatives (HTCCs). The effects of the concentration of NaOH, glucose, and HTCCs on the particles size, zeta potential, and stability were studied in detail. Cell cycle assays verify that none of the HTCCs or HTCCs-AuNPs was cytotoxic to human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Flow cytometry analysis showed that the folate HTCC-AuNPs were internalized in Caco-2, HepG2, and HeLa cancer cells to a significantly greater extent than AuNPs without folate. But, galactosyl HTCC-AuNPs only showed high cell uptake by HepG2 cells. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Interleukin-2 activation of cytotoxic cells in postmastectomy seroma.
Gercel-Taylor, C; Hoffman, J P; Taylor, D D; Owens, K J; Eisenberg, B L
1996-02-15
Lymphocytes were isolated from breast seroma fluids and used to study the mechanism of activation of cytotoxic lymphocytes and possible role of immunological potentiation following surgery in breast cancer patients. Single or serial samples were obtained from patients who had undergone mastectomy or lumpectomy with axillary node dissection. Lymphocytes were activated with rIL-2 (interleukin-2) and their cytotoxic activity was studied against Daudi and K562 cells and against a breast tumor line (SKBr-3). All of the patients (21/21) responded to IL-2 stimulation by significant activation of cytotoxic activity. The unstimulated cytotoxic activity of these cells against NK targets was low with less than 10% specific release in cytotoxicity assays. In simultaneous experiments, autologous seroma fluid was included during activation of lymphocytes to study possible regulatory molecules that may be present. In 17/21 patients, the presence of their seroma fluid, during the activation period, enhanced or did not effect the cytotoxic potential of their lymphocytes; inhibition was observed when seroma fluids from 4/21 patients were included. Analysis of the cytotoxic population derived from combined IL-2 and seroma treatments indicates the presence of cells with increased expression of CD56, and CD2, as well as in some cases CD16 expression. Cytotoxic lymphocytes derived from IL-2 and seroma treatments appeared to be more effective killers. Modulation of CD2 expression with seroma alone appeared to result in the generation of this highly cytotoxic population. This study demonstrates the role of CD2 expression in the effectiveness of LAK cell killing and also potential benefit of an immunotherapeutic approach to the postoperative treatment of carcinoma of the breast.
-
Idarubicin induces mTOR-dependent cytotoxic autophagy in leukemic cells
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ristic, Biljana; Bosnjak, Mihajlo; Arsikin, Katarina; Mircic, Aleksandar; Suzin-Zivkovic, Violeta; Bogdanovic, Andrija; Perovic, Vladimir; Martinovic, Tamara; Kravic-Stevovic, Tamara; Bumbasirevic, Vladimir; Trajkovic, Vladimir; Harhaji-Trajkovic, Ljubica
2014-01-01
We investigated if the antileukemic drug idarubicin induces autophagy, a process of programmed cellular self-digestion, in leukemic cell lines and primary leukemic cells. Transmission electron microscopy and acridine orange staining demonstrated the presence of autophagic vesicles and intracellular acidification, respectively, in idarubicin-treated REH leukemic cell line. Idarubicin increased punctuation/aggregation of microtubule-associated light chain 3B (LC3B), enhanced the conversion of LC3B-I to autophagosome-associated LC3B-II in the presence of proteolysis inhibitors, and promoted the degradation of the selective autophagic target p62, thus indicating the increase in autophagic flux. Idarubicin inhibited the phosphorylation of the main autophagy repressor mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and its downstream target p70S6 kinase. The treatment with the mTOR activator leucine prevented idarubicin-mediated autophagy induction. Idarubicin-induced mTOR repression was associated with the activation of the mTOR inhibitor AMP-activated protein kinase and down-regulation of the mTOR activator Akt. The suppression of autophagy by pharmacological inhibitors or LC3B and beclin-1 genetic knockdown rescued REH cells from idarubicin-mediated oxidative stress, mitochondrial depolarization, caspase activation and apoptotic DNA fragmentation. Idarubicin also caused mTOR inhibition and cytotoxic autophagy in K562 leukemic cell line and leukocytes from chronic myeloid leukemia patients, but not healthy controls. By demonstrating mTOR-dependent cytotoxic autophagy in idarubicin-treated leukemic cells, our results warrant caution when considering combining idarubicin with autophagy inhibitors in leukemia therapy. - Highlights: • Idarubicin induces autophagy in leukemic cell lines and primary leukemic cells. • Idarubicin induces autophagy by inhibiting mTOR in leukemic cells. • mTOR suppression by idarubicin is associated with AMPK activation and Akt blockade. �
-
Idarubicin induces mTOR-dependent cytotoxic autophagy in leukemic cells
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ristic, Biljana [Institute of Microbiology and Immunology, School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Dr. Subotica 1, 11000 Belgrade (Serbia); Bosnjak, Mihajlo [Institute of Histology and Embryology, School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Belgrade (Serbia); Arsikin, Katarina [Institute of Microbiology and Immunology, School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Dr. Subotica 1, 11000 Belgrade (Serbia); Mircic, Aleksandar; Suzin-Zivkovic, Violeta [Institute of Histology and Embryology, School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Belgrade (Serbia); Bogdanovic, Andrija [Clinic for Hematology, Clinical Centre of Serbia, School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Belgrade (Serbia); Perovic, Vladimir [Institute of Microbiology and Immunology, School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Dr. Subotica 1, 11000 Belgrade (Serbia); Martinovic, Tamara; Kravic-Stevovic, Tamara; Bumbasirevic, Vladimir [Institute of Histology and Embryology, School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Belgrade (Serbia); Trajkovic, Vladimir, E-mail: vtrajkovic@med.bg.ac.rs [Institute of Microbiology and Immunology, School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Dr. Subotica 1, 11000 Belgrade (Serbia); Harhaji-Trajkovic, Ljubica, E-mail: buajk@yahoo.com [Institute for Biological Research, University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Despot Stefan Blvd. 142, 11000 Belgrade (Serbia)
2014-08-01
We investigated if the antileukemic drug idarubicin induces autophagy, a process of programmed cellular self-digestion, in leukemic cell lines and primary leukemic cells. Transmission electron microscopy and acridine orange staining demonstrated the presence of autophagic vesicles and intracellular acidification, respectively, in idarubicin-treated REH leukemic cell line. Idarubicin increased punctuation/aggregation of microtubule-associated light chain 3B (LC3B), enhanced the conversion of LC3B-I to autophagosome-associated LC3B-II in the presence of proteolysis inhibitors, and promoted the degradation of the selective autophagic target p62, thus indicating the increase in autophagic flux. Idarubicin inhibited the phosphorylation of the main autophagy repressor mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and its downstream target p70S6 kinase. The treatment with the mTOR activator leucine prevented idarubicin-mediated autophagy induction. Idarubicin-induced mTOR repression was associated with the activation of the mTOR inhibitor AMP-activated protein kinase and down-regulation of the mTOR activator Akt. The suppression of autophagy by pharmacological inhibitors or LC3B and beclin-1 genetic knockdown rescued REH cells from idarubicin-mediated oxidative stress, mitochondrial depolarization, caspase activation and apoptotic DNA fragmentation. Idarubicin also caused mTOR inhibition and cytotoxic autophagy in K562 leukemic cell line and leukocytes from chronic myeloid leukemia patients, but not healthy controls. By demonstrating mTOR-dependent cytotoxic autophagy in idarubicin-treated leukemic cells, our results warrant caution when considering combining idarubicin with autophagy inhibitors in leukemia therapy. - Highlights: • Idarubicin induces autophagy in leukemic cell lines and primary leukemic cells. • Idarubicin induces autophagy by inhibiting mTOR in leukemic cells. • mTOR suppression by idarubicin is associated with AMPK activation and Akt blockade. �
-
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
Davood; Mahdian; Milad; Iranshahy; Abolfazl; Shakeri; Azar; Hoseini; Hoda; Yavari; Melika; Nazemi; Mehrdad; Iranshahi
2015-01-01
Objective: To screen the cytotoxic effects of some marine sponges extracts on HeLa and PC12 cells.Methods: Five marine sponges including Ircinia echinata(I. echinata), Dysidea avara,Axinella sinoxea, Haliclona tubifera and Haliclona violacea were collected from the Persian Gulf(Hengam Island). The cytotoxic effect of these sponges was evaluated by using MTT assay. The metabolic high performance liquid chromatography fingerprint of I. echinata was also carried out at two wavelengths(254 and 280 nm).Results: Among the sponges tested in this study, the extracts of I. echinata and Dysidea avara possessed the cytotoxic effect on HeLa and PC12 cells. The obtained fractions from high performance liquid chromatography were evaluated for their cytotoxic properties against the cell lines. The isolated fractions did not show significant cytotoxic properties.Conclusions: I. echinata could be considered as a potential extract for chemotherapy.Further investigation is needed to determine the accuracy of mechanism.
-
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
Davood Mahdian; Milad Iranshahy; Abolfazl Shakeri; Azar Hoseini; Hoda Yavari; Melika Nazemi; Mehrdad Iranshahi
2015-01-01
Objective:To screen the cytotoxic effects of some marine sponges extracts on HeLa and PC12 cells. Methods: Five marine sponges including Ircinia echinata (I. echinata), Dysidea avara, Axinella sinoxea, Haliclona tubifera and Haliclona violacea were collected from the Persian Gulf (Hengam Island). The cytotoxic effect of these sponges was evaluated by using MTT assay. The metabolic high performance liquid chromatography fingerprint of I. echinata was also carried out at two wavelengths (254 and 280 nm). Results:Among the sponges tested in this study, the extracts of I. echinata and Dysidea avara possessed the cytotoxic effect on HeLa and PC12 cells. The obtained fractions from high performance liquid chromatography were evaluated for their cytotoxic properties against the cell lines. The isolated fractions did not show significant cytotoxic properties. Conclusions:I. echinata could be considered as a potential extract for chemotherapy. Further investigation is needed to determine the accuracy of mechanism.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Niu, Xiao-Fang; Liu, Bao-Qin; Du, Zhen-Xian; Gao, Yan-Yan; Li, Chao; Li, Ning; Guan, Yifu; Wang, Hua-Qin
2011-01-01
It was reported recently that resveratrol could sensitize a number of cancer cells to the antitumoral effects of some conventional chemotherapy drugs. The current study was designed to investigate whether resveratrol could sensitize leukemic cells to proteasome inhibitors. Leukemic cells were treated with MG132 alone or in combination with resveratrol. Cell viability was investigated using MTT assay, and induction of apoptosis and cell cycle distribution was measured using flow cytometry. Western blot and real-time RT-PCR were used to investigate the expression of FOXO1 and p27 Kip1 . CHIP was performed to investigate the binding of FOXO1 to the p27 Kip1 promoter. Resveratrol strongly reduced cytotoxic activities of proteasome inhibitors against leukemic cells. MG132 in combination with resveratrol caused cell cycle blockade at G1/S transition via p27 Kip1 accumulation. Knockdown of p27 Kip1 using siRNA dramatically attenuated the protective effects of resveratrol on cytotoxic actions of proteasome inhibitors against leukemic cells. Resveratrol induced FOXO1 expression at the transcriptional level, while MG132 increased nuclear distribution of FOXO1. MG132 in combination with resveratrol caused synergistic induction of p27 Kip1 through increased recruitment of FOXO1 on the p27 Kip1 promoter. Resveratrol may have the potential to negate the cytotoxic effects of proteasome inhibitors via regulation of FOXO1 transcriptional activity and accumulation of p27 Kip1
-
Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of gold nanoparticle conjugates with cefotaxime
Titanova, Elena O.; Burygin, Gennady L.
2016-04-01
Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have attracted significant interest as a novel platform for various applications to nanobiotechnology and biomedicine. The conjugates of GNPs with antibiotics and antibodies were also used for selective photothermal killing of protozoa and bacteria. Also the conjugates of some antibiotics with GNPs decreased the number of bacterial growing cells. In this work was made the procedure optimization for conjugation of cefotaxime (a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic) with GNPs (15 nm) and we examined the antimicrobial properties of this conjugate to bacteria culture of E. coli K-12. Addition of cefotaxime solution to colloidal gold does not change their color and extinction spectrum. For physiologically active concentration of cefotaxime (3 μg/mL), it was shown that the optimum pH for the conjugation was more than 9.5. A partial aggregation of the GNPs in saline medium was observed at pH 6.5-7.5. The optimum concentration of K2CO3 for conjugation cefotaxime with GNPs-15 was 5 mM. The optimum concentration of cefotaxime was at 0.36 μg/mL. We found the inhibition of the growth of E. coli K12 upon application cefotaxime-GNP conjugates.
-
Highly fluorescent CdTe quantum dots with reduced cytotoxicity-A Robust biomarker
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jandi Kim
2015-03-01
Full Text Available l-Cysteine (Cys capped CdTe quantum dots (CdTe@Cys QDs were successfully synthesized in an aqueous medium. The synthesized CdTe@Cys samples were analyzed using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR spectroscopy, fluorescence (FL spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM, confocal microscopy and subsequently subjected to the antibacterial test. Systematic investigations were carried out for the determination of optimal conditions namely the ratios of Cd:Te, CdTe:Cys, pH value and the chemical stability of CdTe@Cys. Moreover, the reactivation of FL intensity in the CdTe@Cys sample was done easily by the addendum of Cys. The introduction of additional cysteine to the CdTe@Cys QDs sample showed an enhancement in terms of the FL intensity and stability along with the reduced antibacterial activity. This was further confirmed through Thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT assays. Both the result of the bio-stability tests namely the antibacterial test and MTT assay displayed similarities between the externally added Cys and cytotoxicity of the bacteria and human HeLa cancer cell lines. Confocal microscopic images were captured for the CdTe@Cys conjugated Escherichia coli.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hozumi Kentaro
2016-11-01
Full Text Available Mimicking the biological function of the extracellular matrix is an approach to developing cell adhesive biomaterials. The RGD peptide, derived from fibronectin (Fn, mainly binds to integrin αvβ3 and has been widely used as a cell adhesive peptide on various biomaterials. However, cell adhesion to Fn is thought to be mediated by several integrin subtypes and syndecans. In this study, we synthesized an RGD-containing peptide (FIB1 and four integrin α4β1-binding-related motif-containing peptides (LDV, IDAPS, KLDAPT, and PRARI and constructed peptide-chitosan matrices. The FIB1-chitosan matrix promoted human dermal fibroblast (HDF attachment, and the C-terminal elongated PRARI (ePRARI-C-conjugated chitosan matrix significantly promoted HDF attachment through integrin α4β1 and syndecan binding. Next, we constructed a mixed ePRARI-C- and FIB1-chitosan matrix to develop a Fn mimetic biomaterial. The mixed ePRARI-C/FIB1-chitosan matrix promoted significantly better cell attachment and neurite outgrowth compared to those of either ePRARI-C- or FIB1-chitosan matrices. HDF adhesion to the ePRARI-C/FIB1-chitosan matrix was mediated by integrin, α4β1, α5β1, and αvβ3, similar to HDF adhesion to Fn. These data suggest that an ePRARI-C/FIB1-chitosan matrix can be used as a tool to analyze the multiple functions of Fn and can serve as a Fn-mimetic biomaterial.
-
Conjugated Polymer Solar Cells
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Paraschuk, Dmitry Y
2006-01-01
This report results from a contract tasking Moscow State University as follows: Conjugated polymers are promising materials for many photonics applications, in particular, for photovoltaic and solar cell devices...
-
Characteristics of medication errors with parenteral cytotoxic drugs
Fyhr, A; Akselsson, R
2012-01-01
Errors involving cytotoxic drugs have the potential of being fatal and should therefore be prevented. The objective of this article is to identify the characteristics of medication errors involving parenteral cytotoxic drugs in Sweden. A total of 60 cases reported to the national error reporting systems from 1996 to 2008 were reviewed. Classification was made to identify cytotoxic drugs involved, type of error, where the error occurred, error detection mechanism, and consequences for the pati...
-
Cytotoxicity and intracellular dissolution of nickel nanowires
Perez, Jose E.
2015-12-22
The assessment of cytotoxicity of nanostructures is a fundamental step for their development as biomedical tools. As widely used nanostructures, nickel nanowires (Ni NWs) seem promising candidates for such applications. In this work, Ni NWs were synthesized and then characterized using vibrating sample magnetometry, energy dispersive X-Ray analysis and electron microscopy. After exposure to the NWs, cytotoxicity was evaluated in terms of cell viability, cell membrane damage and induced apoptosis/necrosis on the model human cell line HCT 116. The influence of NW to cell ratio (10:1 to 1000:1) and exposure times up to 72 hours was analyzed for Ni NWs of 5.4 µm in length, as well as for Ni ions. The results show that cytotoxicity markedly increases past 24 hours of incubation. Cellular uptake of NWs takes place through the phagocytosis pathway, with a fraction of the dose of NWs dissolved inside the cells. Cell death results from a combination of apoptosis and necrosis, where the latter is the outcome of the secondary necrosis pathway. The cytotoxicity of Ni ions and Ni NWs dissolution studies suggest a synergistic toxicity between NW aspect ratio and dissolved Ni, with the cytotoxic effects markedly increasing after 24 hours of incubation.
-
Cytotoxicity and intracellular dissolution of nickel nanowires.
Perez, Jose E; Contreras, Maria F; Vilanova, Enrique; Felix, Laura P; Margineanu, Michael B; Luongo, Giovanni; Porter, Alexandra E; Dunlop, Iain E; Ravasi, Timothy; Kosel, Jürgen
2016-09-01
The assessment of cytotoxicity of nanostructures is a fundamental step for their development as biomedical tools. As widely used nanostructures, nickel nanowires (Ni NWs) seem promising candidates for such applications. In this work, Ni NWs were synthesized and then characterized using vibrating sample magnetometry, energy dispersive X-Ray analysis, and electron microscopy. After exposure to the NWs, cytotoxicity was evaluated in terms of cell viability, cell membrane damage, and induced apoptosis/necrosis on the model human cell line HCT 116. The influence of NW to cell ratio (10:1 to 1000:1) and exposure times up to 72 hours was analyzed for Ni NWs of 5.4 μm in length, as well as for Ni ions. The results show that cytotoxicity markedly increases past 24 hours of incubation. Cellular uptake of NWs takes place through the phagocytosis pathway, with a fraction of the dose of NWs dissolved inside the cells. Cell death results from a combination of apoptosis and necrosis, where the latter is the outcome of the secondary necrosis pathway. The cytotoxicity of Ni ions and Ni NWs dissolution studies suggest a synergistic toxicity between NW aspect ratio and dissolved Ni, with the cytotoxic effects markedly increasing after 24 hours of incubation.
-
Cytotoxicity and intracellular dissolution of nickel nanowires
Perez, Jose E.; Contreras, Maria F.; Vidal, Enrique Vilanova; Felix Servin, Laura P.; Margineanu, Michael B.; Luongo, Giovanni; Porter, Alexandra E.; Dunlop, Iain E.; Ravasi, Timothy; Kosel, Jü rgen
2015-01-01
The assessment of cytotoxicity of nanostructures is a fundamental step for their development as biomedical tools. As widely used nanostructures, nickel nanowires (Ni NWs) seem promising candidates for such applications. In this work, Ni NWs were synthesized and then characterized using vibrating sample magnetometry, energy dispersive X-Ray analysis and electron microscopy. After exposure to the NWs, cytotoxicity was evaluated in terms of cell viability, cell membrane damage and induced apoptosis/necrosis on the model human cell line HCT 116. The influence of NW to cell ratio (10:1 to 1000:1) and exposure times up to 72 hours was analyzed for Ni NWs of 5.4 µm in length, as well as for Ni ions. The results show that cytotoxicity markedly increases past 24 hours of incubation. Cellular uptake of NWs takes place through the phagocytosis pathway, with a fraction of the dose of NWs dissolved inside the cells. Cell death results from a combination of apoptosis and necrosis, where the latter is the outcome of the secondary necrosis pathway. The cytotoxicity of Ni ions and Ni NWs dissolution studies suggest a synergistic toxicity between NW aspect ratio and dissolved Ni, with the cytotoxic effects markedly increasing after 24 hours of incubation.
-
Soluble polymer conjugates for drug delivery.
Minko, Tamara
2005-01-01
The use of water-soluble polymeric conjugates as drug carriers offers several possible advantages. These advantages include: (1) improved drug pharmacokinetics; (2) decreased toxicity to healthy organs; (3) possible facilitation of accumulation and preferential uptake by targeted cells; (4) programmed profile of drug release. In this review, we will consider the main types of useful polymeric conjugates and their role and effectiveness as carriers in drug delivery systems.: © 2005 Elsevier Ltd . All rights reserved.
-
Diffeomorphisms Holder conjugate to Anosov diffeomorphisms
Gogolev, Andrey
2008-01-01
We show by means of a counterexample that a $C^{1+Lip}$ diffeomorphism Holder conjugate to an Anosov diffeomorphism is not necessarily Anosov. The counterexample can bear higher smoothness up to $C^3$. Also we include a result from the 2006 Ph.D. thesis of T. Fisher: a $C^{1+Lip}$ diffeomorphism Holder conjugate to an Anosov diffeomorphism is Anosov itself provided that Holder exponents of the conjugacy and its inverse are sufficiently large.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Bian X
2016-05-01
Full Text Available Xinyu Bian,* Puyuan Wu,* Huizi Sha, Hanqing Qian, Qing Wang, Lei Cheng, Yang Yang, Mi Yang, Baorui LiuComprehensive Cancer Center of Drum-Tower Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Clinical Cancer Institute of Nanjing University, Nanjing, People’s Republic of China*These authors contributed equally to this workAbstract: In this study, we report a novel kind of targeting with paclitaxel (PTX-loaded silk fibroin nanoparticles conjugated with iRGD–EGFR nanobody recombinant protein (anti-EGFR-iRGD. The new nanoparticles (called A-PTX-SF-NPs were prepared using the carbodiimide-mediated coupling procedure and their characteristics were evaluated. The cellular cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of A-PTX-SF-NPs were also investigated. The results in vivo suggested that NPs conjugated with the recombinant protein exhibited more targeting and anti-neoplastic property in cells with high EGFR expression. In the in vivo antitumor efficacy assay, the A-PTX-SF-NPs group showed slower tumor growth and smaller tumor volumes than PTX-SF-NPs in a HeLa xenograft mouse model. A real-time near-infrared fluorescence imaging study showed that A-PTX-SF-NPs could target the tumor more effectively. These results suggest that the anticancer activity and tumor targeting of A-PTX-SF-NPs were superior to those of PTX-SF-NPs and may have the potential to be used for targeted delivery for tumor therapies. Keywords: EGFR, nanobody, iRGD, recombinant protein, targeting drug carriers, antitumor efficiency
-
Conjugate Problems in Convective Heat Transfer: Review
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Abram Dorfman
2009-01-01
Full Text Available A review of conjugate convective heat transfer problems solved during the early and current time of development of this modern approach is presented. The discussion is based on analytical solutions of selected typical relatively simple conjugate problems including steady-state and transient processes, thermal material treatment, and heat and mass transfer in drying. This brief survey is accompanied by the list of almost two hundred publications considering application of different more and less complex analytical and numerical conjugate models for simulating technology processes and industrial devices from aerospace systems to food production. The references are combined in the groups of works studying similar problems so that each of the groups corresponds to one of selected analytical solutions considered in detail. Such structure of review gives the reader the understanding of early and current situation in conjugate convective heat transfer modeling and makes possible to use the information presented as an introduction to this area on the one hand, and to find more complicated publications of interest on the other hand.
-
Improvement of Emulsifying Properties of Wheat Gluten Hydrolysate λ-Carrageenan Conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jin-Shui Wang
2006-01-01
Full Text Available Gluten hydrolysate was prepared through limited enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat gluten resulting from the byproducts of wheat starch. The enzyme applied in the present study was Protamex. Response surface methodology was used to investigate the effects of pH, gluten hydrolysate (GHPλ-carrageenan (C ratio and reaction time on emulsifying properties of the GHP-C conjugate. The regression model for emulsion activity index (EAI was significant at p=0.001, while reaction time had a significant effect on EAI of the conjugate with regression coefficient of 4.25. The interactions of pH and GHP/ C ratio, and GHP/C ratio and reaction time significantly affected the EAI of the conjugate. Both the emulsifying property and nitrogen solubility index (NSI of GHP-C conjugate prepared under the optimal conditions increased more remarkably, compared to the control. The denaturation temperature of GHP-C conjugate obviously increased compared to wheat gluten. The addition of GHP-C conjugate had different effects on dough characteristics. Moreover, this conjugate can delay the increase in the bread crumb firmness during storage. It demonstrated that this conjugate couldimprove the dough characteristics and had anti-staling properties of bread.
-
Cytotoxic activity of four Mexican medicinal plants.
Vega-Avila, Elisa; Espejo-Serna, Adolfo; Alarcón-Aguilar, Francisco; Velasco-Lezama, Rodolfo
2009-01-01
Ibervillea sonorae Greene, Cucurbita ficifolia Bouché, Tagetes lucida Cav and Justicia spicigera Scheltdd are Mexican native plants used in the treatment of different illnesses. The ethanolic extract of J. spicigera and T. lucida as well as aqueous extracts from I. sonorae, C. ficifolia, T. lucida and J. spicigera were investigated using sulforhodamine B assay. These extracts were assessed using two cell line: T47D (Human Breast cancer) and HeLa (Human cervix cancer). Colchicine was used as the positive control. Data are presented as the dose that inhibited 50% control growth (ED50). All of the assessed extracts were cytotoxic (ED50 < 20 microg/ml) against T47D cell line, meanwhile only the aqueous extract from T. lucida and the ethanolic extract from J. spicigera were cytotoxic to HeLa cell line. Ethanolic extract from J. spicigera presented the best cytotoxic effect. The cytotoxic activity of J. spicigera correlated with one of the popular uses, the treatment of cancer.
-
Effect of radiotherapy on lymphocyte cytotoxicity in vitro
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Wasserman, J; Melen, B [Central Microbiological Laboratory, Stockholm County Council (Sweden); Blomgren, H; Glas, U; Perlmann, P
1975-11-01
The cytotoxic functions of highly purified blood lymphocytes from patients with breast cancer were studied before and after radiotherapy. Addition of PHA or of rabbit antibodies to target cells (chicken erythrocytes) were chosen as two means of inducing lymphocyte cytotoxicity in vitro. The proportion of T and non-T lymphocytes was determined by means of E and EAC rosette tests. The antibody-induced cytotoxicity of lymphocytes decreased following radiotherapy while that mediated by PHA remained unchanged. There was some reduction in the percentage of EAC rosette-forming cells. These results, as well as earlier observations, suggest that the decrease in the peripheral blood of the proportion of lymphocytes with receptors for activated complement is responsible for changes in the antibody-mediated lymphocyte cytotoxicity.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Matern, S.; Gerok, W.
1977-01-01
Specific radioimmunoassays for separate determinations of serum unconjugated cholic, conjugated cholic and conjugated deoxycholic acids have been developed. Prior to the radioimmunoassay, extraction of serum bile acids was performed with Amberlite XAD-2. Unconjugated cholic acid was separated from glyco- and taurocholic acids by thin-layer chromatography. At 50% displacement of bound labeled glyco[ 3 H]cholic acid using antiserum obtained after immunization with cholic acid-bovine serum albumin-conjugate the cross-reactivity of taurocholic acid was 100%, cholic acid 80%, glycochenodeoxycholic acid 10%, chenodeoxycholic acid 7%, conjugated deoxycholic acid 3%, and conjugated lithocholic acid 3 H]cholic acid was linear on a logit-log plot from 5 to 80 pmol of unlabeled glycocholic acid. Fasting serum conjugated cholic acid in healthy subjects was 0.68 +- 0.34 μmol/l. Unconjugated cholic acid was determined by a solid phase radioimmunoassay using the cholic acid antibody chemically bound to Sepharose. The displacement curve of [ 3 H]cholic acid in the solid phase radioimmunoassay was linear on a logit-log plot from 5 to 200 pmol of unlabeled cholic acid. The coefficient of variation between samples was 5%. Fasting serum conjugated deoxycholic acid concentrations in 10 healthy subjects ranged from 0.18 to 0.92 μmol/l determined by a radioimmunoassay using antiserum obtained after immunization with deoxycholic acid-bovine serum albumin-conjugate. The clinical application of these bile acid radioimmunoassays is shown by an 'oral cholate tolerance test' as a sensitive indicator of liver function and by an 'oral cholyglycine tolerance test' as a useful test for bile acid absorption. (orig.) [de
-
Vogel, Curtis R; Yang, Qiang
2006-08-21
We present two different implementations of the Fourier domain preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm (FD-PCG) to efficiently solve the large structured linear systems that arise in optimal volume turbulence estimation, or tomography, for multi-conjugate adaptive optics (MCAO). We describe how to deal with several critical technical issues, including the cone coordinate transformation problem and sensor subaperture grid spacing. We also extend the FD-PCG approach to handle the deformable mirror fitting problem for MCAO.
-
Preparation and biodistribution study of 99Tcm labelled dextran conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yang Chunhui; Li Hongyu; Liang Jixin; Lu Jia; Luo Hongyi; Zheng Deqiang; Sun Guiquan
2012-01-01
99 Tc m Mannosylated dextran conjugates were prepared through [ 99 Tc m (CO) 3 ] + precursor synthesized by carbonyl Isolink kit. The labelled conjugates were injected sub-dermally into the rear foots of the mice, and the patent blue solution was injected at the same site 10 min before sacrifice. The mice were killed at 1 h and 4 h postinjection, and the samples of different tissues including SLN, 2LN, injection site, liver, spleen, blood were dissected and counted. The uptake in terms was calculated. The results of biodistribution demonstrated that the SLN uptakes of radiopharmaceutical (without mannose in the molecules) were rather low and in vivo excretion of these conjugates were comparatively faster, and the uptake of injection site was also low; on the other hand, the SLN uptakes of radio pharmaceutical (with mannose in their molecules) were much higher than those of their corresponding dextran conjugates without mannose, but the retention in the injection site of these conjugates increased too. The results indicated that the affinity of mannosyl-dextran conjugates to the receptors on the surface of macrophages in the lymph node. In addition, the different relative molecular mass of dextran conjugates also cause different biodistribution results, the major one had higher SLN uptake, the difference was significant (P 99 Tc m (CO) 3 ] + labelled mannosylated dextran conjugates showed promising properties as SLN imaging agent and worth further investigation. (authors)
-
Target-mediated drug disposition model and its approximations for antibody-drug conjugates.
Gibiansky, Leonid; Gibiansky, Ekaterina
2014-02-01
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is a complex structure composed of an antibody linked to several molecules of a biologically active cytotoxic drug. The number of ADC compounds in clinical development now exceeds 30, with two of them already on the market. However, there is no rigorous mechanistic model that describes pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of these compounds. PK modeling of ADCs is even more complicated than that of other biologics as the model should describe distribution, binding, and elimination of antibodies with different toxin load, and also the deconjugation process and PK of the released toxin. This work extends the target-mediated drug disposition (TMDD) model to describe ADCs, derives the rapid binding (quasi-equilibrium), quasi-steady-state, and Michaelis-Menten approximations of the TMDD model as applied to ADCs, derives the TMDD model and its approximations for ADCs with load-independent properties, and discusses further simplifications of the system under various assumptions. The developed models are shown to describe data simulated from the available clinical population PK models of trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1), one of the two currently approved ADCs. Identifiability of model parameters is also discussed and illustrated on the simulated T-DM1 examples.
-
Tsend-Ayush, Altansukh; Zhu, Xiumei; Ding, Yu; Yao, Jianxu; Yin, Lifang; Zhou, Jianping; Yao, Jing
2017-05-01
Many effective anti-cancer drugs have limited use in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) therapy due to the drug resistance mechanisms in liver cells. In recent years, tumor-targeted drug delivery and the inhibition of drug-resistance-related mechanisms has become an integrated strategy for effectively combating chemo-resistant cancer. Herein, lactobionic acid-conjugated d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS-LA conjugate) has been developed as a potential asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR)-targeted nanocarrier and an efficient inhibitor of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) to enhance etoposide (ETO) efficacy against HCC. The main properties of ETO-loaded TPGS-LA nanoparticles (NPs) were tested through in vitro and in vivo studies after being prepared using the nanoprecipitation method and characterized by dynamic light scattering (DLS). According to the results, smaller (˜141.43 nm), positively charged ETO-loaded TPGS-LA NPs were more suitable for providing efficient delivery to hepatoma cells by avoiding the clearance mechanisms. It was found that ETO-loaded TPGS-LA NPs were noticeably able to enhance the cytotoxicity of ETO in HepG2 cells. Besides this, markedly higher internalization by the ASGPR-overexpressed HepG2 cells and efficient accumulation at the tumor site in vivo were revealed in the TPGS-LA NP group. More importantly, animal studies confirmed that ETO-loaded TPGS-LA NPs achieved the highest therapeutic efficacy against HCC. Interestingly, ETO-loaded TPGS-LA NPs also exhibited a great inhibitory effect on P-gp compared to the ETO-loaded TPGS NPs. These results suggest that TPGS-LA NPs could be used as a potential ETO delivery system against HCC.
-
Phytochemical and Cytotoxic Investigations of Alpinia mutica Rhizomes
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kae Shin Sim
2011-01-01
Full Text Available The methanol and fractionated extracts (hexane, ethyl acetate and water of Alpinia mutica (Zingiberaceae rhizomes were investigated for their cytotoxic effect against six human carcinoma cell lines, namely KB, MCF7, A549, Caski, HCT116, HT29 and non-human fibroblast cell line (MRC 5 using an in vitro cytotoxicity assay. The ethyl acetate extract possessed high inhibitory effect against KB, MCF7 and Caski cells (IC50 values of 9.4, 19.7 and 19.8 µg/mL, respectively. Flavokawin B (1, 5,6-dehydrokawain (2, pinostrobin chalcone (3 and alpinetin (4, isolated from the active ethyl acetate extract were also evaluated for their cytotoxic activity. Of these, pinostrobin chalcone (3 and alpinetin (4 were isolated from this plant for the first time. Pinostrobin chalcone (3 displayed very remarkable cytotoxic activity against the tested human cancer cells, such as KB, MCF7 and Caski cells (IC50 values of 6.2, 7.3 and 7.7 µg/mL, respectively. This is the first report of the cytotoxic activity of Alpinia mutica.
-
Tung, Bui Thanh; Hai, Nguyen Thanh; Son, Phan Ke
2016-01-01
Curcumin has been shown to possess strong cytotoxic effect against various cancer cell lines. However, curcumin has not applied as a drug for treatment of cancer yet due to low solubility in water and low bioavailability. The aims of this study were to prepare a new polyethylene glycol (PEG) conjugated curcumin and to evaluate its antitumor activity in vitro. PEG-CUR was prepared by the reaction between curcumin and PEG. PEG-CUR which was characterized by SEM, TEM, FTIR, DSC and 1H NMR analysis. The physicochemical parameters of PEG-CUR such as zeta potential, size distribution, solubility and percentage of curcumin were also investigated. Our results showed that the percentage of curcumin in PEG-CUR was 13.26 ± 1.25 %. PEG-CUR has nanosize values of 96.3 nm and the zeta potential values of - 48.4 mV. The PEG-CUR showed significantly increasing curcumin's solubility in water and another medium such as in 0,1 N HCl, phosphate buffer pH 4.5 and pH 6.8 solution and n-octanol. Our data also have shown cytotoxicity effect of PEG-CUR was much greater than curcumin-free in two different HepG2 and HCT116 cancer cell lines. It could be concluded from our results that the PEG-CUR may be a potential candidate for cancer treatment. Further studies are needed to evaluate the antitumor efficacy of PEG-CUR in vivo.
-
Conjugated linoleic acid as a potential protective factor in prevention of breast cancer
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Agnieszka Białek
2013-01-01
Full Text Available Cancers are the second leading cause of deaths in Poland, among both women and men. Breast cancer is the malignancy most frequently diagnosed in women. In 2008 mammary cancer was diagnosed in up to 14 500 patients. It is also the second most common cause of cancer deaths among women in our country. Although the etiology of most cases of this disease is not known, risk factors include a variety of nutritional factors. The amount of fat consumed in the diet and the quantity and quality of fatty acids are especially crucial. Among fatty acids to which great importance in modification of cancer risk is attributed are conjugated linoleic acid. Conjugated linoleic acids (CLA are a group of positional and geometric isomers of linoleic acid, with a conjugated double bond system in the carbon chain. The main natural source of them is milk and dairy products and meat of different species of ruminants, in which cis-9, trans-11 octadecadienoic acid (rumenic acid occurs in the largest quantities, constituting over 90�0of the total pool of CLA. Another important isomer is trans-10, cis-12 octadecadienoic acid, which occurs with rumenic acid in dietary supplements, usually in the ratio 1:1. Surveys conducted show their possible health promoting effects in obesity, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis, diabetes, insulin resistance, inflammation, and various types of cancer, especially breast cancer.
-
Functional properties of nisin–carbohydrate conjugates formed by radiation induced Maillard reaction
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Muppalla, Shobita R.; Sonavale, Rahul; Chawla, Surinder P.; Sharma, Arun
2012-01-01
Nisin–carbohydrate conjugates were prepared by irradiating nisin either with glucose or dextran. Increase in browning and formation of intermediate products was observed with a concomitant decrease in free amino and reducing sugar groups indicating occurrence of the Maillard reaction catalyzed by irradiation. Nisin–carbohydrate conjugates showed a broad spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fluorescence) as well as Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus). Results of antioxidant assays, including that of DPPH radical-scavenging activity and reducing power, showed that the nisin–dextran conjugates possessed better antioxidant potential than nisin–glucose conjugate. These results suggested that it was possible to enhance the functional properties of nisin by preparing radiation induced conjugates suitable for application in food industry. - Highlights: ► Nisin–carbohydrate conjugates were prepared using radiation induced Maillard reaction. ► Conjugation of nisin with dextran/glucose resulted in improvement of antibacterial spectrum. ► Conjugates of nisin with dextran/glucose had significant radical scavenging activity.
-
Peptide-Conjugated Quantum Dots Act as the Target Marker for Human Pancreatic Carcinoma Cells
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Shuang-ling Li
2016-03-01
Full Text Available Background/Aims: In the present study, we describe a novel and straightforward approach to produce a cyclic- arginine-glycine-aspartic (RGD-peptide-conjugated quantum dot (QD probe as an ideal target tumor biomarker. Due to its specific structure, the probe can be used for targeted imaging of pancreatic carcinoma cells. Methods: Pancreatic carcinoma cells were routinely cultured and marked with QD-RGD probe. The QD-RGD probe on the fluorescence-labeled cancer cell was observed by fluorescence microscopy and laser confocal microscopy. Cancer cell viability was detected by MTT assay after culturing with QD-RGD probe. Results: Fluorescence microscopy and laser confocal microscopy displayed that 10nmol/L QD-RGD probe was able to effectively mark pancreatic carcinoma cells. In comparison with organic dyes and fluorescent proteins, the quantum dot-RGD probe had unique optical and electronic properties. Conclusion: QD-RGD probe has a low cytotoxicity with an excellent optical property and biocompatibility. These findings support further evaluation of QD-RGD probes for the early detection of pancreatic cancer.
-
Kim, G G; Donnenberg, V S; Donnenberg, A D; Gooding, W; Whiteside, T L
2007-08-31
Natural killer (NK) cell-or T cell-mediated cytotoxicity traditionally is measured in 4-16 h (51)Cr-release assays (CRA). A new four-color flow cytometry-based cytotoxicity assay (FCC) was developed to simultaneously measure NK cell cytotoxicity and NK cell phenotype (CD3(-)CD16(+)CD56(+)). Target cells, K562 or Daudi, were labeled with Cell Tracker Orange (CTO) prior to the addition of effector cells. Following co-incubation, 7 amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD) was added to measure death of target cells. The phenotype of effectors, viability of targets, the formation of tumor-effector cell conjugates and absolute numbers of all cells were measured based on light scatter (FSC/SSC), double discrimination of the fluorescence peak integral and height, and fluorescence intensity. Kinetic studies (0.5 and 1 to 4 h) at different effector to target (E:T) cell ratios (50, 25, 12, and 6) confirmed that the 3 h incubation was optimal. The FCC assay is more sensitive than the CRA, has a coefficient of variation (CV) 8-13% and reliably measures NK cell-or lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell-mediated killing of target cells in normal controls and subjects with cancer. The FCC assay can be used to study a range of phenotypic attributes, in addition to lytic activity of various subsets of effector cells, without radioactive tracers and thus, it is relatively inexpensive. The FCC assay has a potential for providing information about molecular interactions underlying target cell lysis and thus becoming a major tool for studies of disease pathogenesis as well as development of novel immune therapies.
-
Shariat, Sheida; Badiee, Ali; Jalali, Seyed Amir; Mansourian, Mercedeh; Yazdani, Mona; Mortazavi, Seyed Alireza; Jaafari, Mahmoud Reza
2014-12-01
Vaccines containing synthetic peptides derived from tumor-associated antigens (TAA) can elicit potent cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) response if they are formulated in an optimal vaccine delivery system. The aim of this study was to develop a simple and effective lipid-based vaccine delivery system using P5 HER2/neu-derived peptide conjugated to Maleimide-PEG2000-DSPE. The conjugated lipid was then incorporated into liposomes composed of DMPC:DMPG:Chol:DOPE containing Monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL) (Lip-DOPE-P5-MPL). Different liposome formulations were prepared and characterized for their physicochemical properties. To evaluate anti-tumoral efficacy, BALB/c mice were immunized subcutaneously 3 times in two-week intervals and the generated immune response was studied. The results demonstrated that Lip-DOPE-P5-MPL induced a significantly higher IFN-γ production by CD8+ T cells intracellularly which represents higher CTL response in comparison with other control formulations. CTL response induced by this formulation caused the lowest tumor size and the longest survival time in a mice model of TUBO tumor. The encouraging results achieved by Lip-DOPE-P5-MPL formulation could make it a promising candidate in developing effective vaccines against Her2 positive breast cancers. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ryo Miyazaki
Full Text Available Conjugative transfer of the integrative and conjugative element ICEclc in the bacterium Pseudomonas knackmussii is the consequence of a bistable decision taken in some 3% of cells in a population during stationary phase. Here we study the possible control exerted by the stationary phase sigma factor RpoS on the bistability decision. The gene for RpoS in P. knackmussii B13 was characterized, and a loss-of-function mutant was produced and complemented. We found that, in absence of RpoS, ICEclc transfer rates and activation of two key ICEclc promoters (P(int and P(inR decrease significantly in cells during stationary phase. Microarray and gene reporter analysis indicated that the most direct effect of RpoS is on P(inR, whereas one of the gene products from the P(inR-controlled operon (InrR transmits activation to P(int and other ICEclc core genes. Addition of a second rpoS copy under control of its native promoter resulted in an increase of the proportion of cells expressing the P(int and P(inR promoters to 18%. Strains in which rpoS was replaced by an rpoS-mcherry fusion showed high mCherry fluorescence of individual cells that had activated P(int and P(inR, whereas a double-copy rpoS-mcherry-containing strain displayed twice as much mCherry fluorescence. This suggested that high RpoS levels are a prerequisite for an individual cell to activate P(inR and thus ICEclc transfer. Double promoter-reporter fusions confirmed that expression of P(inR is dominated by extrinsic noise, such as being the result of cellular variability in RpoS. In contrast, expression from P(int is dominated by intrinsic noise, indicating it is specific to the ICEclc transmission cascade. Our results demonstrate how stochastic noise levels of global transcription factors can be transduced to a precise signaling cascade in a subpopulation of cells leading to ICE activation.
-
Cross-conjugation and quantum interference: a general correlation?
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Valkenier, Hennie; Guedon, Constant M.; Markussen, Troels
2014-01-01
We discuss the relationship between the pi-conjugation pattern, molecular length, and charge transport properties of molecular wires, both from an experimental and a theoretical viewpoint. Specifically, we focus on the role of quantum interference in the conductance properties of cross-conjugated...
-
Noya, Yoichi; Seki, Koh-Ichi; Asano, Hiroshi; Mai, Yosuke; Horinouchi, Takahiro; Higashi, Tsunehito; Terada, Koji; Hatate, Chizuru; Hoshi, Akimasa; Nepal, Prabha; Horiguchi, Mika; Kuge, Yuji; Miwa, Soichi
2013-12-06
Smoking is a major risk factor for atherosclerotic vascular diseases, but the mechanism for its genesis is unknown. We have recently shown that the gas phase of cigarette smoke (nicotine- and tar-free cigarette smoke extract; CSE) likely to reach the systemic circulation contains stable substances which cause cytotoxicity like plasma membrane damage and cell death in cultured cells, and also that the plasma membrane damage is caused through sequential activation of protein kinase C (PKC) and NADPH oxidase (NOX) and the resulting generation of reactive oxygen species (PKC/NOX-dependent mechanism), whereas cell death is caused through PKC/NOX-dependent and -independent mechanisms. To identify these stable substances, the CSE was prepared by passing the main-stream smoke of 10 cigarettes through a Cambridge glass fiber filter, trapping of the smoke in a vessel cooled at -80°C, and subsequent dissolution in 10ml of water. The CSE was fractionated into nine fractions using reversed-phase HPLC, and each fraction was screened for cytotoxicity in cultured cells, using propidium iodide uptake assay for cell membrane damage and MTS [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium] reduction assay for cell viability. The cytotoxicity was positive in two of the nine fractions (Fr2 and Fr5). After extraction of the active fractions into dichloromethane, GC/MS analysis identified 2-cyclopenten-1-one (CPO) in Fr5 but none in Fr2. After derivatization of the active fractions with O-(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzyl) hydroxylamine hydrochloride, GC/MS analysis identified acrolein, acetone and propionaldehyde in Fr2, and methyl vinyl ketone (MVK) in Fr5. After 4-h incubation, authentic acrolein and MVK induced concentration-dependent cytotoxicity with EC50 values of 75.9±8.2 and 47.0±8.0μM (mean±SEM; n=3), respectively, whereas acetone, propionaldehyde and CPO were without effect. However, after 24-h incubation, CPO induced concentration
-
das Neves, José; Michiels, Johan; Ariën, Kevin K; Vanham, Guido; Amiji, Mansoor; Bahia, Maria Fernanda; Sarmento, Bruno
2012-06-01
To assess the intracellular delivery, antiretroviral activity and cytotoxicity of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) nanoparticles containing the antiretroviral drug dapivirine. Dapivirine-loaded nanoparticles with different surface properties were produced using three surface modifiers: poloxamer 338 NF (PEO), sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) and cetyl trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). The ability of nanoparticles to promote intracellular drug delivery was assessed in different cell types relevant for vaginal HIV transmission/microbicide development. Also, antiretroviral activity of nanoparticles was determined in different cell models, as well as their cytotoxicity. Dapivirine-loaded nanoparticles were readily taken up by different cells, with particular kinetics depending on the cell type and nanoparticles, resulting in enhanced intracellular drug delivery in phagocytic cells. Different nanoparticles showed similar or improved antiviral activity compared to free drug. There was a correlation between increased antiviral activity and increased intracellular drug delivery, particularly when cell models were submitted to a single initial short-course treatment. PEO-PCL and SLS-PCL nanoparticles consistently showed higher selectivity index values than free drug, contrasting with high cytotoxicity of CTAB-PCL. These results provide evidence on the potential of PCL nanoparticles to affect in vitro toxicity and activity of dapivirine, depending on surface engineering. Thus, this formulation approach may be a promising strategy for the development of next generation microbicides.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Baran, Erkan T., E-mail: erkantur@metu.edu.tr; Tuzlakoglu, Kadriye, E-mail: kadriye@dep.uminho.pt; Mano, Joao F., E-mail: jmano@dep.uminho.pt; Reis, Rui L., E-mail: rgreis@dep.uminho.pt
2012-08-01
The objective of this study was to investigate the influence of silk fibroin and oxidized starch conjugation on the enzymatic degradation behavior and the cytocompatability of chitosan based biomaterials. The tensile stress of conjugate membranes, which was at 50 Megapascal (MPa) for the lowest fibroin and starch composition (10 weight percent (wt.%)), was decreased significantly with the increased content of fibroin and starch. The weight loss of conjugates in {alpha}-amylase was more notable when the starch concentration was the highest at 30 wt.%. The conjugates were resistant to the degradation by protease and lysozyme except for the conjugates with the lowest starch concentration. After 10 days of cell culture, the proliferation of osteoblast-like cells (SaOS-2) was stimulated significantly by higher fibroin compositions and the DNA synthesis on the conjugate with the highest fibroin (30 wt.%) was about two times more compared to the native chitosan. The light microscopy and the image analysis results showed that the cell area and the lengths were decreased significantly with higher fibroin/chitosan ratio. The study proved that the conjugation of fibroin and starch with the chitosan based biomaterials by the use of non-toxic reductive alkylation crosslinking significantly improved the cytocompatibility and modulated the biodegradation, respectively. - Highlights: Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Silk fibroin, starch and chitosan conjugates were prepared by reductive alkylation. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer The enzymatic biodegradation and the cytocompatibility of conjugates were tested. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer The conjugate with 30% starch composition was degraded by {alpha}-amylase significantly. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Higher starch composition in conjugates prevented protease and lysozyme degradation. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Fibroin incorporation effectively increased the cell proliferation of conjugates.
-
Recent Advances in Conjugated Polymers for Light Emitting Devices
AlSalhi, Mohamad Saleh; Alam, Javed; Dass, Lawrence Arockiasamy; Raja, Mohan
2011-01-01
A recent advance in the field of light emitting polymers has been the discovery of electroluminescent conjugated polymers, that is, kind of fluorescent polymers that emit light when excited by the flow of an electric current. These new generation fluorescent materials may now challenge the domination by inorganic semiconductor materials of the commercial market in light-emitting devices such as light-emitting diodes (LED) and polymer laser devices. This review provides information on unique properties of conjugated polymers and how they have been optimized to generate these properties. The review is organized in three sections focusing on the major advances in light emitting materials, recent literature survey and understanding the desirable properties as well as modern solid state lighting and displays. Recently, developed conjugated polymers are also functioning as roll-up displays for computers and mobile phones, flexible solar panels for power portable equipment as well as organic light emitting diodes in displays, in which television screens, luminous traffic, information signs, and light-emitting wallpaper in homes are also expected to broaden the use of conjugated polymers as light emitting polymers. The purpose of this review paper is to examine conjugated polymers in light emitting diodes (LEDs) in addition to organic solid state laser. Furthermore, since conjugated polymers have been approved as light-emitting organic materials similar to inorganic semiconductors, it is clear to motivate these organic light-emitting devices (OLEDs) and organic lasers for modern lighting in terms of energy saving ability. In addition, future aspects of conjugated polymers in LEDs were also highlighted in this review. PMID:21673938
-
Cytotoxicity of fluorographene
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Teo, W. Z.; Sofer, Z.; Šembera, Filip; Janoušek, Zbyněk; Pumera, M.
2015-01-01
Roč. 5, č. 129 (2015), s. 107158-107165 ISSN 2046-2069 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GA15-09001S Institutional support: RVO:61388963 Keywords : fluorinated graphene * viability assays * cytotoxicity Subject RIV: CC - Organic Chemistry Impact factor: 3.289, year: 2015
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jiayang Li
2013-05-01
Full Text Available Here we report supramolecular hydrogelators made of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID and small peptides. The covalent linkage of Phe–Phe and NSAIDs results in conjugates that self-assemble in water to form molecular nanofibers as the matrices of hydrogels. When the NSAID is naproxen (1, the resultant hydrogelator 1a forms a hydrogel at a critical concentration (cgc of 0.2 wt % at pH 7.0. Hydrogelator 1a, also acting as a general motif, enables enzymatic hydrogelation in which the precursor turns into a hydrogelator upon hydrolysis catalyzed by a phosphatase at physiological conditions. The conjugates of Phe–Phe with other NSAIDs, such as (R-flurbiprofen (2, racemic flurbiprofen (3, and racemic ibuprofen (4, are able to form molecular hydrogels, except in the case of aspirin (5. After the conjugation with the small peptides, NSAIDs exhibit improved selectivity to their targets. In addition, the peptides made of D-amino acids help preserve the activities of NSAIDs. Besides demonstrating that common NSAIDs are excellent candidates to promote aromatic–aromatic interaction in water to form hydrogels, this work contributes to the development of functional molecules that have dual or multiple roles and ultimately may lead to new molecular hydrogels of therapeutic agents for topical use.
-
Some aspects of geomagnetically conjugate phenomena
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rycroft, M.J.
1987-12-01
Both charged particles and waves convey information about the thermosphere, ionosphere and magnetosphere from the Northern to the Southern Hemisphere and vice versa, along geomagnetic flux tubes.The interhemispheric travel time of electrons or ions, being dependent upon L-value , pitch angle and energy (which may lie between less than or equal to 1 eV and greater than or equal to 1 MeV) may be many hours, ranging down to less than or equal to 1 s. However, the one-hop propagation time for magnetohydrodynamic or whistler mode waves generally lies between 10/sup 2/s and 1 s. Such times, therefore, give the time scales of transient phenomena that are geomagnetically conjugate and of changes in steady-state plasma processes occurring in geomagnetically conjugate regions. Contrasting examples are presented of conjugate physical phenomena, obtained using satellite, rocket, aircraft and ground-based observations; the latter capitalise upon the rather rare disposition of land - rather than ocean - at each end of a geophysically interesting flux tube. Particular attention is paid to the interactions between whistler mode waves and energetic electrons. Geomagnetic, radio, optical and plasma observations, taken together with model computations, provide a wealth of knowledge on conjugate phenomena and their dependence on conditions in the solar wind, substorms, L-value, etc... Finally, some suggestions are made for future lines of research.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yin, Nina; Han, Yongming; Xu, Hanlin; Gao, Yisen; Yi, Tao; Yao, Jiale; Dong, Li; Cheng, Dejun; Chen, Zebin
2016-01-01
Type 1 diabetes was a life-long disease that affected numerous people around the world. Insulin therapy has its limitations that may involve hyperglycemia and heavy burden of patient by repeated dose. Islet transplantation emerged as a promising approach to reach periodical reverse of diabetes, however, transplanted islets suffer from foreign body reaction and lack of nutrition and oxygen supply, especially in the blood-vessel-shortage subcutaneous site which was preferred by patient and surgeon. In this study, we designed and synthesized a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) conjugated alginate material to encapsulate the transplanted islets via 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide/N-hydroxysuccinimide (EDC/NHS) reaction, and successful conjugation was confirmed by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance H1 spectrum. The best VEGF concentration (100 ng/ml) was determined by the combined studies of the mechanical property and endothelial cell growth assay. In vivo study, conjugated VEGF on alginate exhibited sustained promoting angiogenesis property after subcutaneous transplantation by histology study and islets encapsulated in this material achieved long term therapeutic effect (up to 50 days) in the diabetic mice model. In conclusion, this study establishes a simple biomaterial strategy for islet transplantation to enhance islet survival and function, which could be a feasible therapeutic alternative for type 1 diabetes. - Highlights: • We synthesized VEGF-conjugated alginate material to encapsulate the transplanted islets. • The biomaterials improve islet engraftment and function due to angiogenesis. • The biomaterials could be a strong support for cell therapy with islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Yin, Nina; Han, Yongming [Department of Anatomy, Basic Medical College, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, Hubei (China); Xu, Hanlin [Pharmacy Faculty, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, Hubei (China); Gao, Yisen; Yi, Tao [Acupuncture and Moxibustion College, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, Hubei (China); Yao, Jiale; Dong, Li; Cheng, Dejun [Basic Medical College, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, Hubei (China); Chen, Zebin, E-mail: chenzebin-hbtcm@outlook.com [Acupuncture and Moxibustion College, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine/Hubei Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center of Preventive Treatment by Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Wuhan, Hubei (China)
2016-02-01
Type 1 diabetes was a life-long disease that affected numerous people around the world. Insulin therapy has its limitations that may involve hyperglycemia and heavy burden of patient by repeated dose. Islet transplantation emerged as a promising approach to reach periodical reverse of diabetes, however, transplanted islets suffer from foreign body reaction and lack of nutrition and oxygen supply, especially in the blood-vessel-shortage subcutaneous site which was preferred by patient and surgeon. In this study, we designed and synthesized a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) conjugated alginate material to encapsulate the transplanted islets via 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide/N-hydroxysuccinimide (EDC/NHS) reaction, and successful conjugation was confirmed by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance H1 spectrum. The best VEGF concentration (100 ng/ml) was determined by the combined studies of the mechanical property and endothelial cell growth assay. In vivo study, conjugated VEGF on alginate exhibited sustained promoting angiogenesis property after subcutaneous transplantation by histology study and islets encapsulated in this material achieved long term therapeutic effect (up to 50 days) in the diabetic mice model. In conclusion, this study establishes a simple biomaterial strategy for islet transplantation to enhance islet survival and function, which could be a feasible therapeutic alternative for type 1 diabetes. - Highlights: • We synthesized VEGF-conjugated alginate material to encapsulate the transplanted islets. • The biomaterials improve islet engraftment and function due to angiogenesis. • The biomaterials could be a strong support for cell therapy with islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes.
-
The future of cytotoxic therapy: selective cytotoxicity based on biology is the key
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bono, Johann S de; Tolcher, Anthony W; Rowinsky, Eric K
2003-01-01
Although mortality from breast cancer is decreasing, 15% or more of all patients ultimately develop incurable metastatic disease. It is hoped that new classes of target-based cytotoxic therapeutics will significantly improve the outcome for these patients. Many of these novel agents have displayed cytotoxic activity in preclinical and clinical evaluations, with little toxicity. Such preferential cytotoxicity against malignant tissues will remain tantamount to the Holy Grail in oncologic therapeutics because this portends improved patient tolerance and overall quality of life, and the capacity to deliver combination therapy. Combinations of such rationally designed target-based therapies are likely to be increasingly important in treating patients with breast carcinoma. The anticancer efficacy of these agents will, however, remain dependent on the involvement of the targets of these agents in the biology of the individual patient's disease. Results of DNA microarray analyses have raised high hopes that the analyses of RNA expression levels can successfully predict patient prognosis, and indicate that the ability to rapidly 'fingerprint' the oncogenic profile of a patient's tumor is now possible. It is hoped that these studies will support the identification of the molecules driving a tumor's growth, and the selection of the appropriate combination of targeted agents in the near future
-
Anticancer activity of drug conjugates in head and neck cancer cells.
Majumdar, Debatosh; Rahman, Mohammad Aminur; Chen, Zhuo Georgia; Shin, Dong M
2016-06-01
Sexually transmitted oral cancer/head and neck cancer is increasing rapidly. Human papilloma virus (HPV) is playing a role in the pathogenesis of a subset of squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck (SCCHN). Paclitaxel is a widely used anticancer drug for breast, ovarian, testicular, cervical, non-small cell lung, head and neck cancer. However, it is water insoluble and orally inactive. We report the synthesis of water soluble nanosize conjugates of paclitaxel, branched PEG, and EGFR-targeting peptide by employing native chemical ligation. We performed a native chemical ligation between the N-hydroxy succinimide (NHS) ester of paclitaxel succinate and cysteine at pH 6.5 to give the cysteine-conjugated paclitaxel derivative. The thiol functionality of cysteine was activated and subsequently conjugated to multiarm thiol-PEG to obtain the paclitaxel branched PEG conjugate. Finally, we conjugated an EGFR-targeting peptide to obtain conjugates of paclitaxel, branched PEG, and EGFR-targeting peptide. These conjugates show anticancer activity against squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck cells (SCCHN, Tu212).
-
Small angle scattering from protein/sugar conjugates
Jackson, Andrew; White, John
2006-11-01
The Maillard reaction between free amine groups on proteins and sugars is well known. We have examined the effect of the reaction of the casein group of milk proteins with sugars on their nanoscale structure and aggregation. The small angle neutron scattering from beta casein and sodium caseinate and their sugar conjugates have been studied as a function of solution concentration. At high conjugate concentration (greater than ca. 5 mg/ml) the addition of sugar reduces supra-micellar aggregation of the protein whilst at lower concentration, where the protein is expected to be deaggregated already, little effect is seen. Guinier analysis of the scattering data show a radius of gyration of around 75 A˚ for beta casein in solution and around 80 A˚ for the sucrose conjugate.
-
Assessment of okadaic acid effects on cytotoxicity, DNA damage and DNA repair in human cells.
Valdiglesias, Vanessa; Méndez, Josefina; Pásaro, Eduardo; Cemeli, Eduardo; Anderson, Diana; Laffon, Blanca
2010-07-07
Okadaic acid (OA) is a phycotoxin produced by several types of dinoflagellates causing diarrheic shellfish poisoning (DSP) in humans. Symptoms induced by DSP toxins are mainly gastrointestinal, but the intoxication does not appear to be fatal. Despite this, this toxin presents a potential threat to human health even at concentrations too low to induce acute toxicity, since previous animal studies have shown that OA has very potent tumour promoting activity. However, its concrete action mechanism has not been described yet and the results reported with regard to OA cytotoxicity and genotoxicity are often contradictory. In the present study, the genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of OA on three different types of human cells (peripheral blood leukocytes, HepG2 hepatoma cells, and SHSY5Y neuroblastoma cells) were evaluated. Cells were treated with a range of OA concentrations in the presence and absence of S9 fraction, and MTT test and Comet assay were performed in order to evaluate cytotoxicity and genotoxicity, respectively. The possible effects of OA on DNA repair were also studied by means of the DNA repair competence assay, using bleomycin as DNA damage inductor. Treatment with OA in absence of S9 fraction induced not statistically significant decrease in cell viability and significant increase in DNA damage in all cell types at the highest concentrations investigated. However, only SHSY5Y cells showed OA induced genotoxic and cytotoxic effects in presence of S9 fraction. Furthermore, we found that OA can induce modulations in DNA repair processes when exposure was performed prior to BLM treatment, in co-exposure, or during the subsequent DNA repair process. Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Quantum dot-polymer conjugates for stable luminescent displays.
Ghimire, Sushant; Sivadas, Anjaly; Yuyama, Ken-Ichi; Takano, Yuta; Francis, Raju; Biju, Vasudevanpillai
2018-05-23
The broad absorption of light in the UV-Vis-NIR region and the size-based tunable photoluminescence color of semiconductor quantum dots make these tiny crystals one of the most attractive antennae in solar cells and phosphors in electrooptical devices. One of the primary requirements for such real-world applications of quantum dots is their stable and uniform distribution in optically transparent matrices. In this work, we prepare transparent thin films of polymer-quantum dot conjugates, where CdSe/ZnS quantum dots are uniformly distributed at high densities in a chitosan-polystyrene copolymer (CS-g-PS) matrix. Here, quantum dots in an aqueous solution are conjugated to the copolymer by a phase transfer reaction. With the stable conjugation of quantum dots to the copolymer, we prevent undesired phase separation between the two and aggregation of quantum dots. Furthermore, the conjugate allows us to prepare transparent thin films in which quantum dots are uniformly distributed at high densities. The CS-g-PS copolymer helps us in not only preserving the photoluminescence properties of quantum dots in the film but also rendering excellent photostability to quantum dots at the ensemble and single particle levels, making the conjugate a promising material for photoluminescence-based devices.
-
Free and conjugated dopamine in human ventricular fluid
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sharpless, N.S.; Thal, L.J.; Wolfson, L.I.; Tabaddor, K.; Tyce, G.M.; Waltz, J.M.
1981-01-01
Free dopamine and an acid hydrolyzable conjugate of dopamine were measured in human ventricular fluid specimens with a radioenzymatic assay and by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection. Only trace amounts of free norepinephrine and dopamine were detected in ventricular fluid from patients with movement disorders. When the ventricular fluid was hydrolyzed by heating in HClO 4 or by lyophilization in dilute HClO 4 , however, a substantial amount of free dopamine was released. Values for free plus conjugated dopamine in ventricular fluid from patients who had never taken L-DOPA ranged from 139 to 340 pg/ml when determined by HPLC and from 223 to 428 pg/ml when measured radioenzymatically. The correlation coefficient for values obtained by the two methods in the same sample of CSF was 0.94 (P<0.001). Patients who had been treated with L-DOPA had higher levels of conjugated dopamine in their ventricular CSF which correlated inversely with the time between the last dose of L-DOPA and withdrawal of the ventricular fluid. Additionally, one patient with acute cerebral trauma had elevated levels of free norepinephrine and both free and conjugated dopamine in his ventricular fluid. Conjugation may be an important inactivation pathway for released dopamine in man. (Auth.)
-
Antibody-radioisotope conjugates for tumor localization and treatment
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Larson, S.M.; Carrasquillo, J.A.
1985-01-01
In principle, anti-tumor antibodies can be used to carry radioactivity to tumors for in-vivo diagnosis and treatment of cancer. First, for diagnostic purposes, an antibody that targets a specific antigen (for example, the p97 antigen of human melanoma tumor), is labeled with a tracer amount of radioactivity. When this antibody-radioisotope conjugate is injected into the blood stream, the antibody carries the radioactivity throughout the body and in time, percolates through all the tissues of the body. Because the tumor has specific antigens to which the antibody can bind, the antibody conjugate progressively accumulates in the tumor. Using conventional nuclear medicine imaging equipment, the body of the patient is scanned for radioactivity content, and a map of the distribution of the radioactivity is displayed on photographic film. The tumor shows up as a dense area of radio-activity. These same antibody-radioisotope conjugates may be used for therapy of tumors, except that in this case large amounts of radioactivity are loaded on the antibody. After localization of the conjugate there is sufficient radiation deposited in the tumor of radiotherapy. The success of this approach in the clinic is determined in large measure by the concentration gradient that can be achieved between tissue antibody conjugate in tumor versus normal tissue
-
Conjugal conflict and violence: a review and theoretical paradigm.
Smilkstein, G; Aspy, C B; Quiggins, P A
1994-02-01
Conjugal violence has been described as having multiple etiologies. The variables are so numerous that intervention and research protocols are difficult to effect. This paper proposes a paradigm that establishes conjugal conflict and violence as separate entities. According to the paradigm, conjugal conflict is viewed as "an inevitable part of human association," whereas conjugal violence is determined to be a learned behavioral tactic that is employed as a coping strategy when an individual's conflict threshold potential is exceeded. Evidence will be offered that violence is learned from family of origin and from observing what is common or accepted practice in the community. Use of this paradigm would give primacy to community education programs that advance the concept of conflict resolution through rational discourse.
-
Hsiao, Shih-Chia; Francis, Matthew B.; Bertozzi, Carolyn; Mathies, Richard; Chandra, Ravi; Douglas, Erik; Twite, Amy; Toriello, Nicholas; Onoe, Hiroaki
2016-05-03
The present invention provides conjugates of DNA and cells by linking the DNA to a native functional group on the cell surface. The cells can be without cell walls or can have cell walls. The modified cells can be linked to a substrate surface and used in assay or bioreactors.
-
Hsiao, Shih-Chia; Francis, Matthew B.; Bertozzi, Carolyn; Mathies, Richard; Chandra, Ravi; Douglas, Erik; Twite, Amy; Toriello, Nicholas; Onoe, Hiroaki
2018-05-15
The present invention provides conjugates of DNA and cells by linking the DNA to a native functional group on the cell surface. The cells can be without cell walls or can have cell walls. The modified cells can be linked to a substrate surface and used in assay or bioreactors.
-
Jung, Jung-Il; Park, Kyeong-Yong; Lee, Yura; Park, Mira; Kim, Jiyeon
2018-03-15
Vitamin C-linker-conjugated Ala-His-Lys tripeptide (Vit C-AHK) is a derivative of Vitamin C-conjugated tripeptides, which were originally developed as a component of a product for collagen synthesis enhancement or human dermal fibroblast growth. Here, we investigated the effect of Vit C-AHK on bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2-induced osteoblast differentiation in a cell culture model. Vit C-AHK enhanced proliferation of C2C12 cells and induction of BMP-2-induced alkaline phosphatase, a typical marker of osteoblast differentiation. Vit C-AHK also stimulated the phosphorylation and translocation of Smad1/5/8 to the nucleus and phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) including ERK1/2 and p38. In addition, Vit C-AHK enhanced the BMP-2-induced mRNA expression of osteoblast differentiation-related genes such as ALP, BMP-2, Osteocalcin, and Runx2. Our results suggest that Vit C-AHK exerts an enhancing effect on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation through activation of Smad1/5/8 and MAPK ERK1/2 and p38 signaling and without significant cytotoxicity. These results provide important data for the development of peptide-based bone-regenerative agents and treatment of bone-related disorders. Copyright © 2018 International Society of Differentiation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Structure and function of nanoparticle-protein conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Aubin-Tam, M-E; Hamad-Schifferli, K
2008-01-01
Conjugation of proteins to nanoparticles has numerous applications in sensing, imaging, delivery, catalysis, therapy and control of protein structure and activity. Therefore, characterizing the nanoparticle-protein interface is of great importance. A variety of covalent and non-covalent linking chemistries have been reported for nanoparticle attachment. Site-specific labeling is desirable in order to control the protein orientation on the nanoparticle, which is crucial in many applications such as fluorescence resonance energy transfer. We evaluate methods for successful site-specific attachment. Typically, a specific protein residue is linked directly to the nanoparticle core or to the ligand. As conjugation often affects the protein structure and function, techniques to probe structure and activity are assessed. We also examine how molecular dynamics simulations of conjugates would complete those experimental techniques in order to provide atomistic details on the effect of nanoparticle attachment. Characterization studies of nanoparticle-protein complexes show that the structure and function are influenced by the chemistry of the nanoparticle ligand, the nanoparticle size, the nanoparticle material, the stoichiometry of the conjugates, the labeling site on the protein and the nature of the linkage (covalent versus non-covalent)
-
Fullerene–biomolecule conjugates and their biomedicinal applications
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yang X
2013-12-01
Full Text Available Xinlin Yang,1 Ali Ebrahimi,1 Jie Li,1,2 Quanjun Cui11Orthopaedic Research Laboratory, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA, USA; 2School of Materials Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, People's Republic of ChinaAbstract: Fullerenes are among the strongest antioxidants and are characterized as "radical sponges." The research on biomedicinal applications of fullerenes has achieved significant progress since the landmark publication by Friedman et al in 1993. Fullerene–biomolecule conjugates have become an important area of research during the past 2 decades. By a thorough literature search, we attempt to update the information about the synthesis of different types of fullerene–biomolecule conjugates, including fullerene-containing amino acids and peptides, oligonucleotides, sugars, and esters. Moreover, we also discuss in this review recently reported data on the biological and pharmaceutical utilities of these compounds and some other fullerene derivatives of biomedical importance. While within the fullerene–biomolecule conjugates, in which fullerene may act as both an antioxidant and a carrier, specific targeting biomolecules conjugated to fullerene will undoubtedly strengthen the delivery of functional fullerenes to sites of clinical interest.Keywords: fullerene, amino acid, peptide, oligonucleotide, sugar, ester
-
The Synthesis of Substituted Piperazine-cholesterol Conjugates for ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
A small library of cholesterol-piperazine conjugates were synthesized by the reaction of cholesteryl chloroformate with a set of substituted piperazines in dichloromethane at room temperature. The conjugates, all obtained in good to excellent yields, were synthesized to be key components of nucleic acid transfection ...
-
Phenolics, Antiradical Assay and Cytotoxicity of Processed Mango ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
Phenolics, Antiradical Assay and Cytotoxicity of Processed Mango ( Mangifera indica ) and Bush Mango ( Irvingia gabonensis ) Kernels. ... Nigerian Food Journal ... Phenolic constituents (total phenols, flavonoids, tannins, and anthocyanins), comparative antiradical potency and cytotoxicity of processed mango (Mangifera ...
-
Elgawish, Mohamed Saleh; Shimomai, Chikako; Kishikawa, Naoya; Ohyama, Kaname; Wada, Mitsuhiro; Kuroda, Naotaka
2013-09-16
Menadione (2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone, MQ), a component of multivitamin drugs with antihemorrhagic, antineoplastic, and antimalarial activity, is frequently used to investigate quinone-induced cytotoxicity. The formation of MQ conjugates with glutathione (GSH) by Michael addition and subsequent biotransformation to yield N-acetyl-l-cysteine conjugates is believed to be an important detoxification process. However, the resulting conjugates, 2-methyl-3-(glutathione-S-yl)-1,4-naphthoquinone (MQ-GS) and 2-methyl-3-(N-acetyl-l-cysteine-S-yl)-1,4-naphthoquinone (MQ-NAC), retain the ability to redox cycle and to arylate cellular nucleophiles. Although the nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity of MQ-thiol conjugates have been reported in vitro, methods for their determination in vivo have yet to be published. Herein, a highly sensitive, simple, and selective HPLC-chemiluminescence (HPLC-CL) coupled method is reported, allowing for the first time the simultaneous determination of MQ, MQ-GS, and MQ-NAC in rat plasma after MQ administration. Our method exploits the unique redox characteristics of MQ, MQ-GS, and MQ-NAC to react with dithiothreitol (DTT) to liberate reactive oxygen species (ROS) which are detected by a CL assay using luminol as a CL probe. To verify the proposed mechanism, MQ-GS and MQ-NAC were synthetically prepared. Specimen preparation involved solid-phase extraction on an Oasis HLB cartridge followed by isocratic elution on an ODS column. No interference from endogenous substances was detected. Linearity was observed in the range of 5-120 nM for MQ-GS and MQ-NAC and 10-240 nM for MQ, with detection limits (S/N of 3) of 1.4, 0.8, and 128 fmol for MQ-GS, MQ-NAC, and MQ, respectively. The application of our method reported here is the first to extensively study the stability and reversibility of thiol-quinones.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Xie Y
2016-07-01
Full Text Available Yuexia Xie,1,2,* Dejun Liu,3,* Chenlei Cai,1,* Xiaojing Chen,1 Yan Zhou,1 Liangliang Wu,1 Yongwei Sun,3 Huili Dai,1,2 Xianming Kong,1,2 Peifeng Liu1,2 1Central Laboratory, 2State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes, Shanghai Cancer Institute, 3Department of Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China *These authors contributed equally to this work Abstract: The application of Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs has made great progress in the diagnosis of disease and in the drug delivery system for cancer therapy, but the relative mechanisms of potential toxicity induced by Fe3O4 have not kept pace with its development in the application, which has hampered its further clinical application. In this article, we used two kinds of human hepatoma cell lines, SK-Hep-1 and Hep3B, to investigate the cytotoxic effects and the involved mechanisms of small Fe3O4 NPs with different diameters (6 nm, 9 nm, and 14 nm. Results showed that the size of NPs effectively influences the cytotoxicity of hepatoma cells: 6 nm Fe3O4 NPs exhibited negligible cytotoxicity and 9 nm Fe3O4 NPs affected cytotoxicity via cellular mitochondrial dysfunction and by inducing necrosis mediated through the mitochondria-dependent intracellular reactive oxygen species generation. Meanwhile, 14 nm Fe3O4 NPs induced cytotoxicity by impairing the integrity of plasma membrane and promoting massive lactate dehydrogenase leakage. These results explain the detailed mechanism of different diameters of small Fe3O4 NPs-induced cytotoxicity. We anticipate that this study will provide different insights into the cytotoxicity mechanism of Fe3O4 NPs, so as to make them safer to use in clinical application. Keywords: hepatoma cells, nanoparticles, cytotoxicity, mechanism, oxidative stress
-
Nanostructured conjugated polymers in chemical sensors: synthesis, properties and applications.
Correa, D S; Medeiros, E S; Oliveira, J E; Paterno, L G; Mattoso, Luiz C
2014-09-01
Conjugated polymers are organic materials endowed with a π-electron conjugation along the polymer backbone that present appealing electrical and optical properties for technological applications. By using conjugated polymeric materials in the nanoscale, such properties can be further enhanced. In addition, the use of nanostructured materials makes possible miniaturize devices at the micro/nano scale. The applications of conjugated nanostructured polymers include sensors, actuators, flexible displays, discrete electronic devices, and smart fabric, to name a few. In particular, the use of conjugated polymers in chemical and biological sensors is made feasible owning to their sensitivity to the physicochemical conditions of its surrounding environment, such as chemical composition, pH, dielectric constant, humidity or even temperature. Subtle changes in these conditions bring about variations on the electrical (resistivity and capacitance), optical (absorptivity, luminescence, etc.), and mechanical properties of the conjugated polymer, which can be precisely measured by different experimental methods and ultimately associated with a specific analyte and its concentration. The present review article highlights the main features of conjugated polymers that make them suitable for chemical sensors. An especial emphasis is given to nanostructured sensors systems, which present high sensitivity and selectivity, and find application in beverage and food quality control, pharmaceutical industries, medical diagnosis, environmental monitoring, and homeland security, and other applications as discussed throughout this review.
-
Intense correlation between brain infarction and protein-conjugated acrolein.
Saiki, Ryotaro; Nishimura, Kazuhiro; Ishii, Itsuko; Omura, Tomohiro; Okuyama, Shigeru; Kashiwagi, Keiko; Igarashi, Kazuei
2009-10-01
We recently found that increases in plasma levels of protein-conjugated acrolein and polyamine oxidases, enzymes that produce acrolein, are good markers for stroke. The aim of this study was to determine whether the level of protein-conjugated acrolein is increased and levels of spermine and spermidine, the substrates of acrolein production, are decreased at the locus of infarction. A unilateral infarction was induced in mouse brain by photoinduction after injection of Rose Bengal. The volume of the infarction was analyzed using the public domain National Institutes of Health image program. The level of protein-conjugated acrolein at the locus of infarction and in plasma was measured by Western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively. The levels of polyamines at the locus of infarction and in plasma were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. The level of protein-conjugated acrolein was greatly increased, and levels of spermine and spermidine were decreased at the locus of infarction at 24 hours after the induction of stroke. The size of infarction was significantly decreased by N-acetylcysteine, a scavenger of acrolein. It was also found that the increases in the protein-conjugated acrolein, polyamines, and polyamine oxidases in plasma were observed after the induction of stroke. The results indicate that the induction of infarction is well correlated with the increase in protein-conjugated acrolein at the locus of infarction and in plasma.
-
Lee, Jonghwan; Choi, Kyung-Ju; Moon, Sung Ung; Kim, Soonhag
2016-01-01
Recently, microRNA (miRNA or miR) has emerged as a new cancer biomarker because of its high expression level in various cancer types and its role in the control of tumor suppressor genes. In cancer studies, molecular imaging and treatment based on target cancer markers have been combined to facilitate simultaneous cancer diagnosis and therapy. In this study, for combined therapy with diagnosis of cancer, we developed a doxorubicin-conjugated miR-221 molecular beacon (miR-221 DOXO MB) in a single platform composed of three different nucleotides: miR-221 binding sequence, black hole quencher 1 (BHQ1), and doxorubicin binding site. Imaging of endogenous miR-221 was achieved by specific hybridization between miR-221 and the miR-221 binding site in miR-221 DOXO MB. The presence of miR-221 triggered detachment of the quencher oligo and subsequent activation of a fluorescent signal of miR-221 DOXO MB. Simultaneous cancer therapy in C6 astrocytoma cells and nude mice was achieved by inhibition of miRNA-221 function that downregulates tumor suppressor genes. The detection of miR-221 expression and inhibition of miR-221 function by miR-221 DOXO MB provide the feasibility as a cancer theragnostic probe. Furthermore, a cytotoxic effect was induced by unloading of doxorubicin intercalated into miR-221 DOXO MB inside cells. Loss of miR-221 function and cytotoxicity induced by the miR-221 DOXO MB provides combined therapeutic efficacy against cancers. This method could be used as a new theragnostic probe with enhanced therapy to detect and inhibit many cancer-related miRNAs. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Yu, Hai-Yue; Ma, Dan-Dan; Wu, Bu-Ling
2017-05-20
To evaluate the cytotoxicity of gelatin/alginate hydrogel scaffolds prepared by 3D bioprinting in human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) and compare the cell adhesion and proliferation of the cells seeded in the biomaterial using two different methods. HDPCs isolated by tissue block culture and enzyme digestion were cultured and passaged. Gelatin/alginate hydrogel scaffolds were printed using a bioplotter, and the cytotoxicity of the aqueous extracts of the scaffold material was tested in the third passage of HDPCs using cell counting kit-8. Scanning electron microscopy and trypan blue were used to assess the adhesion and proliferation of the cells seeded in the scaffold material at a low or high concentration. The aqueous extract of the scaffolds at different concentrations showed no obvious cytotoxicity and promoted the proliferation of HDPCs. The scaffolds had a good biocompatibility and HDPCs seeded in the scaffold showed good cell growth. Cell seeding at a high concentration in the scaffold better promoted the adhesion of HDPCs and resulted in a greater cell number on the scaffold surface compared with low-concentration cell seeding after a 5-day culture (Palginate hydrogel scaffolds prepared by 3D bioprinting has a good biocompatibility and promotes the proliferation of HDPCs, and can be used as a scaffold material for tooth regeneration. Cell seeding at a high concentration can better promote cell adhesion to the scaffold material.
-
Novel bioadhesive polymers as intra-articular agents: Chondroitin sulfate-cysteine conjugates.
Suchaoin, Wongsakorn; Bonengel, Sonja; Griessinger, Julia Anita; Pereira de Sousa, Irene; Hussain, Shah; Huck, Christian W; Bernkop-Schnürch, Andreas
2016-04-01
The aim of this study was to generate and characterize a chondroitin sulfate-cysteine conjugate (CS-cys) as a novel bioadhesive agent for intra-articular use. Mucoadhesive properties of synthesized CS-cys were investigated by rheological measurement of polymer-mucus mixture and rotating cylinder method, while bioadhesive features of CS-cys on porcine articular cartilage were evaluated via tensile studies. Thiolation was achieved by attachment of l-cysteine to CS via amide bond formation mediated by carbodiimide as a coupling reagent. The conjugate exhibited 421.17±35.14 μmol free thiol groups per gram polymer. The reduced CS-cys displayed 675.09±39.67 μmol free thiol groups per gram polymer after disulfide bonds reduction using tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride. The increase in dynamic viscosity of thiolated CS due to oxidative disulfide bond formation was demonstrated using capillary viscometer. The combination of CS-cys and mucus led to 4.57-fold increase in dynamic viscosity in comparison with mucus control. Furthermore, adhesion time to porcine mucosa of CS-cys-based test disk was enhanced by 2.48-fold compared to unmodified CS as measured by rotating cylinder method suggesting the interaction between thiomers and mucus gel layer via disulfide bonds formation. Tensile studies of thiolated CS on porcine articular cartilage showed 5.37- and 1.76-fold increase in the total work of adhesion and the maximum detachment force, respectively, in comparison with unmodified CS indicating bioadhesive features of CS-cys. Cytotoxicity of CS-cys was assessed in Caco-2 cells and rat primary articular chondrocytes using MTT and LDH release assay, thereby showing the safety of CS-cys at a concentration of 0.25% (w/v) in Caco-2 cells. Furthermore, 0.1% of CS-cys was found non-toxic to rat primary articular chondrocytes. According to these results, CS-cys provides improved bioadhesive properties that might be useful as an intra-articular agent for treatment of
-
Optical observations geomagnetically conjugate to sprite-producing lightning discharges
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. A. Marshall
2005-09-01
Full Text Available Theoretical studies have predicted that large positive cloud-to-ground discharges can trigger a runaway avalanche process of relativistic electrons, forming a geomagnetically trapped electron beam. The beam may undergo pitch angle and energy scattering during its traverse of the Earth's magnetosphere, with a small percentage of electrons remaining in the loss cone and precipitating in the magnetically conjugate atmosphere. In particular, N2 1P and N2+1N optical emissions are expected to be observable. In July and August 2003, an attempt was made to detect these optical emissions, called "conjugate sprites", in correlation with sprite observations in Europe near . Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam. Keywords. Ionosphere (Ionsophere-magnetosphere interactions; Ionospheric disturbances; Instruments and techniques
-
Minimizing inner product data dependencies in conjugate gradient iteration
Vanrosendale, J.
1983-01-01
The amount of concurrency available in conjugate gradient iteration is limited by the summations required in the inner product computations. The inner product of two vectors of length N requires time c log(N), if N or more processors are available. This paper describes an algebraic restructuring of the conjugate gradient algorithm which minimizes data dependencies due to inner product calculations. After an initial start up, the new algorithm can perform a conjugate gradient iteration in time c*log(log(N)).
-
Covalently bound conjugates of albumin and heparin: Synthesis, fractionation and characterization
Hennink, Wim E.; Feijen, Jan; Ebert, Charles D.; Kim, Sung Wan
1983-01-01
Covalently bound conjugates of human serum albumin and heparin were prepared as compounds which could improve the blood-compatibility of polymer surfaces either by preadsorption or by covalent coupling of the conjugates onto blood contacting surfaces. The conjugates (10–16 weight % of heparin) were
-
Small angle scattering from protein/sugar conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jackson, Andrew; White, John
2006-01-01
The Maillard reaction between free amine groups on proteins and sugars is well known. We have examined the effect of the reaction of the casein group of milk proteins with sugars on their nanoscale structure and aggregation. The small angle neutron scattering from beta casein and sodium caseinate and their sugar conjugates have been studied as a function of solution concentration. At high conjugate concentration (greater than ca. 5mg/ml) the addition of sugar reduces supra-micellar aggregation of the protein whilst at lower concentration, where the protein is expected to be deaggregated already, little effect is seen. Guinier analysis of the scattering data show a radius of gyration of around 75A-bar for beta casein in solution and around 80A-bar for the sucrose conjugate
-
Small angle scattering from protein/sugar conjugates
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jackson, Andrew [Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200 (Australia)]. E-mail: ajj@nist.gov; White, John [Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200 (Australia)
2006-11-15
The Maillard reaction between free amine groups on proteins and sugars is well known. We have examined the effect of the reaction of the casein group of milk proteins with sugars on their nanoscale structure and aggregation. The small angle neutron scattering from beta casein and sodium caseinate and their sugar conjugates have been studied as a function of solution concentration. At high conjugate concentration (greater than ca. 5mg/ml) the addition of sugar reduces supra-micellar aggregation of the protein whilst at lower concentration, where the protein is expected to be deaggregated already, little effect is seen. Guinier analysis of the scattering data show a radius of gyration of around 75A-bar for beta casein in solution and around 80A-bar for the sucrose conjugate.
-
Deciphering conjugative plasmid permissiveness in wastewater microbiomes
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Jacquiod, Samuel Jehan Auguste; Brejnrod, Asker Daniel; Milani, Stefan Morberg
2017-01-01
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are designed to robustly treat polluted water. They are characterized by ceaseless flows of organic, chemical and microbial matter, followed by treatment steps before environmental release. WWTPs are hotspots of horizontal gene transfer between bacteria via...... still remains largely uncharted. Furthermore, current in vitro methods used to assess conjugation in complex microbiomes do not include in situ behaviours of recipient cells, resulting in partial understanding of transfers. We investigated the in vitro conjugation capacities of WWTP microbiomes from...... inlet sewage and outlet treated water using the broad-host range IncP-1 conjugative plasmid, pKJK5. A thorough molecular approach coupling metagenomes to 16S rRNA DNA/cDNA amplicon sequencing was established to characterize microbiomes using the ecological concept of functional response groups. A broad...
-
Anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities of five Veronica species.
Harput, U Sebnem; Saracoglu, Iclal; Inoue, Makoto; Ogihara, Yukio
2002-04-01
Biological activities of five Veronica species (Scrophulariaceae), V. cymbalaria, V. hederifolia, V. pectinata var. glandulosa, V. persica and V. polita were studied for their anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities. Their methanol extracts showed both the inhibitory activity of nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages and cytotoxic activity against KB epidermoid carcinoma and B16 melanoma. When the methanol extracts were fractionated between water and chloroform, water fractions significantly inhibited NO production without any cytotoxicity, while chloroform fractions showed cytotoxicity dose-dependently. When the radical scavenging activity was determined using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH), water fractions of the five Veronica species scavenged free radicals effectively, suggesting that the inhibitory effect of this species on NO production was due to their radical scavenging activity. On the other hand, chloroform fractions of Veronica species except for V. cymbalaria showed similar cytotoxic activity against KB and B16 melanoma cells.
-
A fluorescence-based rapid screening assay for cytotoxic compounds
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Montoya, Jessica; Varela-Ramirez, Armando; Estrada, Abril; Martinez, Luis E.; Garza, Kristine; Aguilera, Renato J.
2004-01-01
A simple fluorescence-based assay was developed for the rapid screening of potential cytotoxic compounds generated by combinatorial chemistry. The assay is based on detection of nuclear green fluorescent protein (GFP) staining of a human cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) carrying an integrated histone H2B-GFP fusion gene. Addition of a cytotoxic compound to the HeLa-GFP cells results in the eventual degradation of DNA and loss of the GFP nuclear fluorescence. Using this assay, we screened 11 distinct quinone derivatives and found that several of these compounds were cytotoxic. These compounds are structurally related to plumbagin an apoptosis-inducing naphthoquinone isolated from Black Walnut. In order to determine the mechanism by which cell death was induced, we performed additional experiments with the most cytotoxic quinones. These compounds were found to induce morphological changes (blebbing and nuclear condensation) consistent with induction of apoptosis. Additional tests revealed that the cytotoxic compounds induce both necrotic and apoptotic modes of death
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Elnaz Shaabani
2017-04-01
Full Text Available Objective(s: Biological applications of gold nanoparticles have limitations because of the toxic chemicals used in their synthesis. Curcumin can be used as reducing as well as capping agent in synthesis of GNPs to eliminate the cytotoxicity. Conjugation of curcumin to gold also helps in increasing its solubility and bioavailability. Materials and Methods: Here we report synthesis of gold nanoparticles coated with citrate and curcumin and of two different sizes via chemical routes. UV-Vis absorbance spectroscopy, Dynamic Light Scattering and Transmission Electron Microscopy were applied to study the average particle size, size stability of the samples and zeta potential. Fourier transform infrared, Raman Spectroscopy and Fluorescence Spectroscopy were applied for detection of curcumin on the surface of GNPs. The antioxidant activity was evaluated using DPPH assay and Cytotoxicity was evaluated by MTT assay.Results: Particles were synthesized of 6 and 16 nm size. The average particle size was found to be 21.7 ± 5.7 by TEM. The zeta potential on the surface of Cur-GNPs was negative and larger than 25 mV which is a sign of their high stability. The stability of these particles (with different coatings but with similar sizes at different time intervals (up to 3 months and also in different media like cell culture medium, different buffers, glucose and at different pH conditions have been investigated thoroughly. Appearance of functional groups assigned to curcumin in FTIR and SERS spectra are sign of presence of curcumin in the sample. The quenching of the fluorescence in the presence of GNPs reveals the clear indication of the capping and binding of curcumin with GNPs. Cur-GNP1 (16 nm were found to exhibit highest antioxidant activity than other gold nanoparticles. Cytotoxicity evaluation using MTT assay on L929 cell line proved curcumin coated gold nanoparticles were non-toxic up to 40 ppm.Conclusion: The results revealed that larger curcumin
-
Cheewatanakornkool, Kamonrak; Niratisai, Sathit; Manchun, Somkamol; Dass, Crispin R; Sriamornsak, Pornsak
2017-10-15
In this paper, pectin was cross-linked by a coupling reaction with either thioglycolic acid or cystamine dihydrochloride to form thiolated pectins. The thiolated pectins were then coupled with doxorubicin (DOX) derivative to obtain thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates by two different methods, disulfide bond formation and disulfide bond exchange. The disulfide bond exchange method provided a simple, fast, and efficient approach for synthesis of thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates, compared to the disulfide bond formation. Characteristics, physicochemical properties, and morphology of thiolated pectins and thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates were determined. DOX content in thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates using low methoxy pectin was found to be higher than that using high methoxy pectin. The in vitro anticancer activity of thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates was significantly higher than that of free DOX, in mouse colon carcinoma and human bone osteosarcoma cells, but insignificantly different from that of free DOX, in human prostate cancer cells. Due to their promising anticancer activity in mouse colon carcinoma cells, the thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates might be suitable for building drug platform for colorectal cancer-targeted delivery of DOX. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Less is More: A Comparison of Antibody-Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates of Different Ratios.
Byzova, Nadezhda A; Safenkova, Irina V; Slutskaya, Elvira S; Zherdev, Anatoly V; Dzantiev, Boris B
2017-11-15
This comprehensive study is related to gold nanoparticles (GNPs) conjugated with antibodies. The goal of the study is to determine the minimal concentration of antibodies for conjugate synthesis when the conjugates have high antigen-capturing activity. Two systems were studied: gold nanoparticles conjugated with monoclonal antibodies (mAb-GNP) specific to Helicobacter pylori and gold nanoparticles conjugated with polyclonal antibodies (pAb-GNP) specific to mouse immunoglobulins. Several conjugates were synthesized with different GNP-to-antibody molar ratios (from 1:1 to 1:245) through nondirectional and noncovalent immobilization on a surface of GNPs with a diameter of 25.3 ± 4.6 nm. The maximal antigen-capturing activities and equilibrium constants of the conjugates correlate with the formation of a constant hydrodynamic radius of the conjugates for mAb-GNP (GNP to antibody molar ratio 1:58) and with the stabilizing concentration by flocculation curves for pAb-GNP (GNP to antibody molar ratio 1:116). The application of the conjugates to the lateral flow immunoassay shows that the antibody concentrations used for the conjugation can be reduced (below the stabilizing concentration) without losing activity for the mAb-GNP conjugates. The findings highlight that the optimal concentration of antibodies immobilized on the surface of GNPs is not always equal to the stabilizing concentration determined by the flocculation curve.
-
Cui, Zhisong; Luan, Xiao; Jiang, Huichao; Li, Qian; Xu, Guangfei; Sun, Chengjun; Zheng, Li; Song, Yizhi; Davison, Paul A; Huang, Wei E
2018-06-01
A toxicity biosensor Acinetobacter baylyi Tox2 was constructed with the host strain A. baylyi ADP1 harboring a new and medium-copy-number plasmid pWH1274_lux, and was applied to detect the cytotoxicity of heavy metal contaminated seawater. The gene cassette luxCDABE was controlled by constitutively expressed promoter P tet on pWH1274_lux and the bioluminescence intensity of the biosensor reduces in proportional to the concentrations of toxic compounds. A. baylyi Tox2 exhibits tolerance to salinity, hence it is applicable to seawater samples. A. baylyi Tox2 and Mugilogobius chulae were exposed to different concentrations of heavy metals (Hg 2+ , Zn 2+ , Cu 2+ , and Cd 2+ ) in artificial seawater for performance comparison and Pearson correlation analysis showed a significant correlation (p heavy metal contaminated seawater. Furthermore, A. baylyi Tox2 was used to evaluate cytotoxicity of field-collected seawater samples. The results indicate that there was a significant correlation between the luminescence inhibition ratio (IR) of A. baylyi Tox2 and heavy metal concentrations detected by ICP-MS in the samples. Two seawater samples, which contained a high concentration of total heavy metals, exhibited stronger cytotoxicity than the samples containing low concentrations of heavy metals. In conclusion, A. baylyi Tox2 can be used as an alternative tool to aquatic animals for the evaluation of the cytotoxicity of heavy metal contamination in the marine environment. Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Conjugation vs hyperconjugation in molecular structure of acrolein
Shishkina, Svitlana V.; Slabko, Anzhelika I.; Shishkin, Oleg V.
2013-01-01
Analysis of geometric parameters of butadiene and acrolein reveals the contradiction between the Csp2-Csp2 bond length in acrolein and classical concept of conjugation degree in the polarized molecules. In this Letter the reasons of this contradiction have been investigated. It is concluded that the Csp2-Csp2 bond length in acrolein is determined by influence of the bonding for it π-π conjugation and antibonding n → σ∗ hyperconjugation between the oxygen lone pair and the antibonding orbital of the single bond. It was shown also this bond length depends on the difference in energy of conjugative and hyperconjugative interactions.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Eliza Hawrylik
2018-05-01
Full Text Available The aim of the study was to evaluate the usefulness of Escherichia coli K-12 RFM 443 recA::lux for cytotoxicity and genotoxicity monitoring of metoprolol in the environment. Metoprolol is one of the most popular cardiac drug which belongs to the group of β–blockers. The drug was applied at concentrations ranging from 0.01 µg/cm3 to 100 µg/cm3. The conducted studies are preliminary studies aimed at validation of the recA::lux gene construct in the direction of determining its sensitivity to metoprolol. The drug concentrations were selected experimentally to obtain a positive luminescence response. Obtained data indicated the influence of metoprolol on lux gene expression and recA promoter activity based on the use of laboratory samples using PBS buffer. Results indicate a potential possibility of using a bacterial biosensor Escherichia coli K - 12 RFM 443 with recA::lux gene fusion in cytotoxicity and genotoxicity monitoring of the cardiac drugs residue in the environment.
-
Enhanced photodynamic efficacy of zinc phthalocyanine by conjugating to heptalysine.
Li, Linsen; Luo, Zhipu; Chen, Zhuo; Chen, Jincan; Zhou, Shanyong; Xu, Peng; Hu, Ping; Wang, Jundong; Chen, Naisheng; Huang, Jinling; Huang, Mingdong
2012-11-21
Zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc) is a promising photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy, but faces some challenges: ZnPc is insoluble in water and thus requires either special formulation of ZnPc by, e.g., liposome or Cremophor EL, or chemical modification of Pc ring to enhance its bioavailability and photodynamic efficacy. Here, we conjugated monosubstituted ZnPc-COOH with a series of oligolysine moieties with different numbers of lysine residues (ZnPc-(Lys)(n) (n = 1, 3, 5, 7, 9) to improve the water solubility of the ZnPc conjugates. We measured the photosensitizing efficacies and the cellular uptakes of this series of conjugates on a normal and a cancerous cell line. In addition, we developed a sensitive in situ method to distinguish the difference in photodynamic efficacy among conjugates. Our results showed that ZnPc-(Lys)(7) has the highest photodynamic efficacy compared to the other conjugates investigated.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Sun, Qingwen [Shanghai Chest Hospital, Shanghai 200433 (China); State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433 (China); Jiang, Songmin [State Key Laboratory of Genetic Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433 (China); Han, Baohui [Shanghai Chest Hospital, Shanghai 200433 (China); Sun, Tongwen [Wuhan Junyu Innovation Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Wuhan 430079 (China); Li, Zhengnan; Zhao, Lina; Gao, Qiang [College of Biotechnology, Tianjin University of Science and Technology, Tianjin 300457 (China); Sun, Jialin, E-mail: jialin_sun@126.com [Wuhan Junyu Innovation Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Wuhan 430079 (China)
2012-11-02
Highlights: Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer We construct and purify a fusion protein VEGF-SEA. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer VEGF-SEA strongly repressed the growth of murine solid sarcoma 180 (S180) tumors. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer T cells driven by VEGF-SEA were accumulated around tumor cells bearing VEGFR by mice image model. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer VEGF-SEA can serve as a tumor targeting agent and sequester CTLs into the tumor site. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer The induced CTLs could release the cytokines, perforins and granzyme B to kill the tumor cells. -- Abstract: T cells are major lymphocytes in the blood and passengers across the tumor vasculature. If these T cells are retained in the tumor site, a therapeutic potential will be gained by turning them into tumor-reactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). A fusion protein composed of human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) with a D227A mutation strongly repressed the growth of murine solid sarcoma 180 (S180) tumors (control versus VEGF-SEA treated with 15 {mu}g, mean tumor weight: 1.128 g versus 0.252 g, difference = 0.876 g). CD4{sup +} and CD8{sup +} T cells driven by VEGF-SEA were accumulated around VEGFR expressing tumor cells and the induced CTLs could release the tumoricidal cytokines, such as interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Meanwhile, intratumoral CTLs secreted cytolytic pore-forming perforin and granzyme B proteins around tumor cells, leading to the death of tumor cells. The labeled fusion proteins were gradually targeted to the tumor site in an imaging mice model. These results show that VEGF-SEA can serve as a tumor targeting agent and sequester active infiltrating CTLs into the tumor site to kill tumor cells, and could therefore be a potential therapeutical drug for a variety of cancers.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sun, Qingwen; Jiang, Songmin; Han, Baohui; Sun, Tongwen; Li, Zhengnan; Zhao, Lina; Gao, Qiang; Sun, Jialin
2012-01-01
Highlights: ► We construct and purify a fusion protein VEGF–SEA. ► VEGF–SEA strongly repressed the growth of murine solid sarcoma 180 (S180) tumors. ► T cells driven by VEGF–SEA were accumulated around tumor cells bearing VEGFR by mice image model. ► VEGF–SEA can serve as a tumor targeting agent and sequester CTLs into the tumor site. ► The induced CTLs could release the cytokines, perforins and granzyme B to kill the tumor cells. -- Abstract: T cells are major lymphocytes in the blood and passengers across the tumor vasculature. If these T cells are retained in the tumor site, a therapeutic potential will be gained by turning them into tumor-reactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). A fusion protein composed of human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) with a D227A mutation strongly repressed the growth of murine solid sarcoma 180 (S180) tumors (control versus VEGF–SEA treated with 15 μg, mean tumor weight: 1.128 g versus 0.252 g, difference = 0.876 g). CD4 + and CD8 + T cells driven by VEGF–SEA were accumulated around VEGFR expressing tumor cells and the induced CTLs could release the tumoricidal cytokines, such as interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Meanwhile, intratumoral CTLs secreted cytolytic pore-forming perforin and granzyme B proteins around tumor cells, leading to the death of tumor cells. The labeled fusion proteins were gradually targeted to the tumor site in an imaging mice model. These results show that VEGF–SEA can serve as a tumor targeting agent and sequester active infiltrating CTLs into the tumor site to kill tumor cells, and could therefore be a potential therapeutical drug for a variety of cancers.
-
Application of the conjugate-gradient method to ground-water models
Manteuffel, T.A.; Grove, D.B.; Konikow, Leonard F.
1984-01-01
The conjugate-gradient method can solve efficiently and accurately finite-difference approximations to the ground-water flow equation. An aquifer-simulation model using the conjugate-gradient method was applied to a problem of ground-water flow in an alluvial aquifer at the Rocky Mountain Arsenal, Denver, Colorado. For this application, the accuracy and efficiency of the conjugate-gradient method compared favorably with other available methods for steady-state flow. However, its efficiency relative to other available methods depends on the nature of the specific problem. The main advantage of the conjugate-gradient method is that it does not require the use of iteration parameters, thereby eliminating this partly subjective procedure. (USGS)
-
Cytotoxic effect of betulinic acid and betulinic acid acetate isolated ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
Cytotoxic effect of betulinic acid and betulinic acid acetate isolated from Melaleuca cajuput on human myeloid leukemia (HL-60) cell line. ... The cytotoxic effect of betulinic acid (BA), isolated from Melaleuca cajuput a Malaysian plant and its four synthetic derivatives were tested for their cytotoxicity in various cell line or ...
-
Nonlinear propagation of phase-conjugate focused sound beams in water
Brysev, A. P.; Krutyansky, L. M.; Preobrazhensky, V. L.; Pyl'nov, Yu. V.; Cunningham, K. B.; Hamilton, M. F.
2000-07-01
Nonlinear propagation of phase-conjugate, focused, ultrasound beams is studied. Measurements are presented of harmonic amplitudes along the axis and in the focal plane of the conjugate beam, and of the waveform and spectrum at the focus. A maximum peak pressure of 3.9 MPa was recorded in the conjugate beam. The measurements are compared with simulations based on the KZK equation, and satisfactory agreement is obtained.
-
Repenko, Tatjana; Rix, Anne; Ludwanowski, Simon; Go, Dennis; Kiessling, Fabian; Lederle, Wiltrud; Kuehne, Alexander J C
2017-09-07
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles exhibit strong fluorescence and have been applied for biological fluorescence imaging in cell culture and in small animals. However, conjugated polymer particles are hydrophobic and often chemically inert materials with diameters ranging from below 50 nm to several microns. As such, conjugated polymer nanoparticles cannot be excreted through the renal system. This drawback has prevented their application for clinical bio-medical imaging. Here, we present fully conjugated polymer nanoparticles based on imidazole units. These nanoparticles can be bio-degraded by activated macrophages. Reactive oxygen species induce scission of the conjugated polymer backbone at the imidazole unit, leading to complete decomposition of the particles into soluble low molecular weight fragments. Furthermore, the nanoparticles can be surface functionalized for directed targeting. The approach opens a wide range of opportunities for conjugated polymer particles in the fields of medical imaging, drug-delivery, and theranostics.Conjugated polymer nanoparticles have been applied for biological fluorescence imaging in cell culture and in small animals, but cannot readily be excreted through the renal system. Here the authors show fully conjugated polymer nanoparticles based on imidazole units that can be bio-degraded by activated macrophages.
-
Liu, Ang; Kozhich, Alexander; Passmore, David; Gu, Huidong; Wong, Richard; Zambito, Frank; Rangan, Vangipuram S; Myler, Heather; Aubry, Anne-Françoise; Arnold, Mark E; Wang, Jian
2015-10-01
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are complex molecules composed of two pharmacologically distinct components, the cytotoxic payload and the antibody. The measurement of the payload molecules that are attached to the antibody in vivo is important for the evaluation of the safety and efficacy of ADCs, and can also provide distinct information compared to the antibody-related analytes. However, analyzing the antibody-conjugated payload is challenging and in some cases may not be feasible. The in vivo change in drug antibody ratio (DAR), due to deconjugation, biotransformation or other clearance phenomena, generates unique and additional challenges for ADC analysis in biological samples. Here, we report a novel hybrid approach with immuno-capture of the ADC, payload cleavage by specific enzyme, and LC-MS/MS of the cleaved payload to quantitatively measure the concentration of payload molecules still attached to the antibody via linker in plasma. The ADC reference material used for the calibration curve is not likely to be identical to the ADC measured in study samples due to the change in DAR distribution over the PK time course. The assay clearly demonstrated that there was no bias in the measurement of antibody-conjugated payload for ADC with varying DAR, which thus allowed accurate quantification even when the DAR distribution dynamically changes in vivo. This hybrid assay was fully validated based on a combination of requirements for both chromatographic and ligand binding methods, and was successfully applied to support a GLP safety study in monkeys. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Cytotoxicity of the coagulant Moringa oleifera lectin (cMoL) to B16-F10 melanoma cells.
de Andrade Luz, Luciana; Rossato, Franco Aparecido; Costa, Rute Alves Pereira E; Napoleão, Thiago Henrique; Paiva, Patrícia Maria Guedes; Coelho, Luana Cassandra Breitenbach Barroso
2017-10-01
Moringa oleifera seeds are used in alternative medicine to treat inflammation, tumors and bacterial and protozoan infections, for example. The seeds contain lectins, which are carbohydrate-binding proteins with several biological properties including cytotoxicity to cancer cells. In this work, we examined the cytotoxicity of the coagulant M. oleifera lectin (cMoL) on B16-F10 murine melanoma cells. cMoL cytotoxic effects were evaluated through trypan blue assay and flow cytometry analysis. Mitochondrial superoxide levels and activation of caspases 3, 8 and 9 were measured. cMoL (1.5-16μM) reduced viability and caused cell death of B16-F10 cells with an IC 50 of 9.72μM. Flow cytometry analysis indicated induction of necrosis and suggested the presence of cells in late apoptosis. Specificity for tumor cells was observed since death of normal human fibroblasts (GN) was not higher than 20% in treatments with cMoL from 1.5 to 16μM. Microscopy images revealed rounded shape and reduction of volume in B16-F10 cells treated with cMoL. cMoL increased mitochondrial ROS production and promoted caspases 3, 8 and 9 activation in B16-F10 cells, indicating the activation of apoptosis-related pathway. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that cMoL is cytotoxic to B16-F10 cells, which stimulates more investigation on the anticancer potential of this lectin. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Optical observations geomagnetically conjugate to sprite-producing lightning discharges
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. A. Marshall
2005-09-01
Full Text Available Theoretical studies have predicted that large positive cloud-to-ground discharges can trigger a runaway avalanche process of relativistic electrons, forming a geomagnetically trapped electron beam. The beam may undergo pitch angle and energy scattering during its traverse of the Earth's magnetosphere, with a small percentage of electrons remaining in the loss cone and precipitating in the magnetically conjugate atmosphere. In particular, N2 1P and N2+1N optical emissions are expected to be observable. In July and August 2003, an attempt was made to detect these optical emissions, called "conjugate sprites", in correlation with sprite observations in Europe near
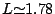 . Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam.
. Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam.
Keywords. Ionosphere (Ionsophere-magnetosphere interactions; Ionospheric disturbances; Instruments and techniques -
Cytotoxic activity of plants from East Azarbaijan province, Iran
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Irani
2017-11-01
Full Text Available Background and objectives: Due to the high cancer mortality rates and side effects of different types of cancer treatments, discovering effective treatments without or with fewer side effects is the main purpose of many researchers all around the world. Plants play an important role in the discovery of new drugs. Iran owns rich and varied vegetation but the majority of these plants have not yet undergone chemical, pharmacological and toxicological studies. In the present study, some species from East Azarbaijan province of Iran were evaluated for cytotoxicity effects. Methods: Total methanol extract of 29 plants from 18 families were screened for their cytotoxic activities. The inhibition of cell growth for these extracts was evaluated against MCF-7, A-549, Hep-G2, HT-29 and MDBK cell lines. Their 50% inhibitions of growth (IC50 were determined by MTT assay. Moreover, cytotoxic evaluation of different fractions (ether de petrol, chloroform and methanol of the most potent species was performed. Results: Total extracts and fractions of Bryonia aspera, Centaurea salicifolia, Cuscuta chinensis, Ecbalium elaterium, Gypsophila ruscifolia, Ononis spinosa exhibited potent cytotoxic activity against one or more of the cell lines. Three of the mentioned total extracts presented cytotoxicity effects exclusively against HT-29 cells. Also three fractions (one ether de petrol and two chloroform fractions demonstrated selective cytotoxicity effects against MCF-7cells. Conclusion: It was concluded that these 6 potent species were proper candidates for identification and isolation of active ingredients with cytotoxic effects and further studies about these species are recommended.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pan, Jie; Jiang, Lijun; Chan, Chi-Fai; Tsoi, Tik-Hung; Shiu, Kwok-Keung; Kwong, Daniel W.J.; Wong, Wing-Tak; Wong, Wai-Kwok; Wong, Ka-Leung
2017-01-01
Porphyrins are good photodynamic therapy (PDT) agents due to its flexibility for modifications to achieve tumor localization and photo-cytotoxicity against cancer. Yet they are not perfect. In a Ru(polypyridyl)-porphyrin system, the Ru(polypyridyl) moiety improves the water solubility and cell permeability. Consider the similar excited state energies between Ru(polypyridyl) and porphyrin moieties; a small perturbation (e.g. Zn(II) metalation) would lead to a marked change in the energy migration process. In this work, we have synthesized a series of porphyrins conjugated with Ru(polypyridyl) complexes using different linkers and investigated their photophysical properties, which included singlet oxygen quantum yield and their in vitro biological properties, resulting from linker variation and porphyrin modification by Zn(II) metalation. - Graphical abstract: Four amphiphilic ruthenium(II)-porphyrin complexes were prepared that display energy transfer conversion with zinc coordination, lysosome specific target, low dark toxicity and efficient photodynamic therapy.
-
Aptamer-miRNA-212 Conjugate Sensitizes NSCLC Cells to TRAIL
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Margherita Iaboni
2016-01-01
Full Text Available TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL is a promising antitumor agent for its remarkable ability to selectively induce apoptosis in cancer cells, without affecting the viability of healthy bystander cells. The TRAIL tumor suppressor pathway is deregulated in many human malignancies including lung cancer. In human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC cells, sensitization to TRAIL therapy can be restored by increasing the expression levels of the tumor suppressor microRNA-212 (miR-212 leading to inhibition of the anti-apoptotic protein PED/PEA-15 implicated in treatment resistance. In this study, we exploited a previously described RNA aptamer inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase receptor Axl (GL21.T expressed on lung cancer cells, as a means to deliver miR-212 into human NSCLC cells expressing Axl. We demonstrate efficient delivery of miR-212 following conjugation of the miR to GL21.T (GL21.T-miR212 chimera. We show that the chimera downregulates PED and restores TRAIL-mediate cytotoxicity in cancer cells. Importantly, treatment of Axl+ lung cancer cells with the chimera resulted in (i an increase in caspase activation and (ii a reduction of cell viability in combination with TRAIL therapy. In conclusion, we demonstrate that the GL21.T-miR212 chimera can be employed as an adjuvant to TRAIL therapy for the treatment of lung cancer.
-
Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Activities of Acacia nilotica Lam ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
Erah
that had maximum bactericidal activity against all the tested isolates, but showed < 30 % host cell cytotoxicity. Conclusion: The lysate of Acacia nilotica ... cytotoxic effects on human cells. EXPERIMENTAL. Plant material. Acacia nilotica Lam .... a detergent that permeabilizes eukaryotic cells and results in HBMEC damage.
-
Identification of SlpB, a Cytotoxic Protease from Serratia marcescens.
Shanks, Robert M Q; Stella, Nicholas A; Hunt, Kristin M; Brothers, Kimberly M; Zhang, Liang; Thibodeau, Patrick H
2015-07-01
The Gram-negative bacterium and opportunistic pathogen Serratia marcescens causes ocular infections in healthy individuals. Secreted protease activity was characterized from 44 ocular clinical isolates, and a higher frequency of protease-positive strains was observed among keratitis isolates than among conjunctivitis isolates. A positive correlation between protease activity and cytotoxicity to human corneal epithelial cells in vitro was determined. Deletion of prtS in clinical keratitis isolate K904 reduced, but did not eliminate, cytotoxicity and secreted protease production. This indicated that PrtS is necessary for full cytotoxicity to ocular cells and implied the existence of another secreted protease(s) and cytotoxic factors. Bioinformatic analysis of the S. marcescens Db11 genome revealed three additional open reading frames predicted to code for serralysin-like proteases noted here as slpB, slpC, and slpD. Induced expression of prtS and slpB, but not slpC and slpD, in strain PIC3611 rendered the strain cytotoxic to a lung carcinoma cell line; however, only prtS induction was sufficient for cytotoxicity to a corneal cell line. Strain K904 with deletion of both prtS and slpB genes was defective in secreted protease activity and cytotoxicity to human cell lines. PAGE analysis suggests that SlpB is produced at lower levels than PrtS. Purified SlpB demonstrated calcium-dependent and AprI-inhibited protease activity and cytotoxicity to airway and ocular cell lines in vitro. Lastly, genetic analysis indicated that the type I secretion system gene, lipD, is required for SlpB secretion. These genetic data introduce SlpB as a new cytotoxic protease from S. marcescens. Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Møller, Thea S B; Liu, Gang; Boysen, Anders
2017-01-01
research suggests that the effect of antibiotic treatment on plasmid conjugation frequencies, and hence the spread of resistance plasmids, may have been overestimated. We addressed the question by quantifying transfer proteins and conjugation frequencies of a blaCTX-M-1 encoding IncI1 resistance plasmid....... The frequency of plasmid conjugation, measured in an antibiotic free environment, increased significantly when the donor was pre-grown in broth containing CTX compared to growth without this drug, regardless of whether blaCTX-M-1 was located on the plasmid or in trans on the chromosome. The results shows...
-
125I Radioimmunoassay of serum ursodeoxycholyl conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hill, A.; Ross, P.E.; Bouchier, I.A.D.
1983-01-01
A radioimmunoassay for serum ursodeoxycholic conjugates using an iodine-125 ligand has been developed. The bile acid was present in normal fasting serum (0.19 +- SD 0.19 μmol/l, n=24) and 2-hour post-prandial serum (0.8 +- SD 0.8 μmol/l, n=16). Gallstone patients undergoing oral ursodeoxycholic acid therapy had significantly higher post-prandial serum levels (21.5 +- SD 14.0 μmol/l, n=15) by radioimmunoassay. Gas liquid chromatography analysis indicated that in normal serum ursodeoxycholic acid was totally conjugated, whereas sera from gallstone patients contained a proportion as the free bile acid (10.2 +- SD 8.1 μmol/l, n=15). Following an oral dose of ursodeoxycholic acid, both unconjugated and conjugated forms of the bile acid appeared in the serum of healthy individuals. (Auth.)
-
Scintillation Reduction using Conjugate-Plane Imaging (Abstract)
Vander Haagen, G. A.
2017-12-01
(Abstract only) All observatories are plagued by atmospheric turbulence exhibited as star scintillation or "twinkle" whether a high altitude adaptive optics research or a 30-cm amateur telescope. It is well known that these disturbances are caused by wind and temperature-driven refractive gradients in the atmosphere and limit the ultimate photometric resolution of land-based facilities. One approach identified by Fuchs (1998) for scintillation noise reduction was to create a conjugate image space at the telescope and focus on the dominant conjugate turbulent layer within that space. When focused on the turbulent layer little or no scintillation exists. This technique is described whereby noise reductions of 6 to 11/1 have been experienced with mathematical and optical bench simulations. Discussed is a proof-of-principle conjugate optical train design for an 80-mm, f7 telescope.
-
Shabani, Ronak; Ashjari, Mohsen; Ashtari, Khadijeh; Izadyar, Fariborz; Behnam, Babak; Khoei, Samideh; Asghari-Jafarabadi, Mohamad; Koruji, Morteza
2018-01-01
Some male survivors of childhood cancer are suffering from azoospermia. In addition, spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs) are necessary for the improvement of spermatogenesis subsequent to exposure to cytotoxic agents such as cisplatin. The aim of this study was to evaluate the anticancer activity of cisplatin-loaded folic acid-conjugated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles (NPs) on mouse malignant cell line (EL4) and SSCs in vitro. SSCs were co-cultured with mouse malignant cell line (EL4) cells and divided into four culture groups: 1) control (cells were co-cultured in the culture medium), 2) co-cultured cells were treated with cisplatin (10 μg/mL), 3) co-cultured cells were treated with cisplatin-loaded folic acid-conjugated PLGA NPs, and 4) co-cultures were treated with folic acid-conjugated PLGA for 48 hours. The NPs were prepared, characterized, and targeted with folate. In vitro release characteristics, loading efficiency, and scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy images were studied. Cancer cells were assayed after treatment using flow cytometry and TUNEL assay. The co-cultures of SSCs and EL4 cells were injected into seminiferous tubules of the testes after treating with cis-diaminedichloroplatinum/PLGA NPs. The mean diameter of PLGA NPs ranged between 150 and 250 nm. The number of TUNEL-positive cells increased, and the expression of Bax and caspase-3 were upregulated in EL4 cells in Group 4 compared with Group 2. There was no pathological tumor in testes after transplantation with treated co-cultured cells. The PLGA NPs appeared to act as a promising carrier for cisplatin administration, which was consistent with a higher activation of apoptosis than free drug.
-
Cytotoxic triterpenoid saponins from Clematis tangutica.
Zhao, Min; Da-Wa, Zhuo-Ma; Guo, Da-Le; Fang, Dong-Mei; Chen, Xiao-Zhen; Xu, Hong-Xi; Gu, Yu-Cheng; Xia, Bing; Chen, Lei; Ding, Li-Sheng; Zhou, Yan
2016-10-01
Eight previously undescribed oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins, clematangoticosides A-H, together with eight known saponins, were isolated from the whole plants of Clematis tangutica (Maxim.) Korsh. Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analysis, in combination with chemical methods (acid hydrolysis and mild alkaline hydrolysis). Clematangoticosides D-G were found to be unusual 23, 28-bidesmosidic glycosides. The cytotoxic activities of all of the isolated saponins were evaluated against the four human cancer cell lines SGC-7901, HepG2, HL-60 and U251MG. Clematoside S, sapindoside B, kalopanax saponin A, and koelreuteria saponin A exhibited cytotoxicity against all of the test cancer cell lines with IC50 values in the range of 1.88-27.20 μM, while clematangoticoside D and F showed selective cytotoxicity against SGC-7901 with IC50 values of 24.22 and 21.35 μM, respectively. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Synthesis and characterization of nido-carborane-cobalamin conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hogenkamp, Harry P.C.; Collins, Douglas A.; Live, David; Benson, Linda M.; Naylor, Stephen
2000-01-01
Three vitamin B 12 (cyanocobalamin) conjugates bearing one nido-carborane molecule or two nido-carborane molecules linked to the propionamide side chains via a four carbon linker have been synthesized. Reaction of o-carboranoylchloride with 1,4-diaminobutane in pyridine produced nido-carboranoyl(4-amidobutyl)amine, which was linked to the b- and d-monocarboxylic acids and the b,d-dicarboxylic acid of cyanocobalamin. Mass spectrometry analysis as well as 11 B nuclear magnetic resonance demonstrated that during the reaction of o-carboranonylchloride with diaminobutane one of the boron atoms was eliminated. In vitro biological activity of the cyanocobalamin-nido-carborane conjugates was assessed by the unsaturated vitamin B 12 binding capacity assay. When compared with 57 Co cyanocobalamin, the biological activity of cyanocobalamin-b-nido-carborane, cyanocobalamin-d-nido-carborane, and cyanocobalamin-b-d-bis-nido-carborane conjugates were 92.93%, 35.75%, and 37.02%, respectively. These findings suggest that the 10 B cobalamin conjugates might be useful agents in treating malignant tumors via neutron capture therapy
-
Schmøkel, Julie; Voldum, Anders; Tsakiridou, Georgia; Kuhlmann, Matthias; Cameron, Jason; Sørensen, Esben S.; Wengel, Jesper; Howard, Kenneth A.
2017-05-01
Aptamers are an attractive molecular medicine that offers high target specificity. Nucleic acid-based aptamers, however, are prone to nuclease degradation and rapid renal excretion that require blood circulatory half-life extension enabling technologies. The long circulatory half-life, predominately facilitated by engagement with the cellular recycling neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), and ligand transport properties of albumin promote it as an attractive candidate to improve the pharmacokinetic profile of aptamers. This study investigates the effect of Cys34 site-selective covalent attachment of a factor IXa anticoagulant aptamer on aptamer functionality and human FcRn (hFcRn) engagement using recombinant human albumin (rHA) of either a wild type (WT) or an engineered human FcRn high binding variant (HB). Albumin-aptamer conjugates, connected covalently through a heterobifunctional succinimidyl 4-(N-maleimidomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylate linker, were successfully prepared and purified by high performance liquid chromatography as confirmed by gel electrophoresis band-shift analysis and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight. Minimal reduction (∼25%) in activity of WT-linked aptamer to that of aptamer alone was found using an anticoagulant activity assay measuring temporal levels of activated partial thrombin. Covalent albumin-aptamer conjugation, however, substantially compromized binding to hFcRn, to 10% affinity of that of non-conjugated WT, determined by biolayer interferometry. Binding could be rescued by aptamer conjugation to recombinant albumin engineered for higher FcRn affinity (HB) that exhibited an 8-fold affinity compared to WT alone. This work describes a novel albumin-based aptamer delivery system whose hFcRn binding can be increased using a HB engineered albumin.
-
Structure Property Relationships in Organic Conjugated Systems
O'Neill, Luke; Lynch, Patrick; McNamara, Mary
2005-01-01
A series of π conjugated oligomers were studied by absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopy. A linear relationship between the positioning of the absorption and photoluminescence maxima plotted against inverse conjugation length is observed. The relationships are in good agreement with the simple particle in a box method, one of the earliest descriptions of the properties of one-dimensional organic molecules. In addition to the electronic transition energies, it was observed that the Sto...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hsieh DS
2012-03-01
Full Text Available Dar-Shih Hsieh1,2, Hsiu-Chin Lu5, Cheng-Cheung Chen1,3, Chang-Jer Wu1,*, Ming-Kung Yeh4,* 1Department of Food Science, National Taiwan Ocean University, Keelung, Taiwan; 2Division of Urology, 3Department of Pathology, Tri-Service General Hospital, 4Institute of Preventive Medicine, National Defence Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan; 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan*These authors contributed equally to this workAbstract: Nanogold particles are commonly used in nanomedicine. We generated physical nanogold (pNG conjugated with different ratios of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG and evaluated its physicochemical properties, antioxidant activity, and cytotoxicity in vitro as well as anticancer activity in vivo. Results showed that the EGCG-pNG conjugates were successfully prepared at ratios between 23:1 and 23:5, with the percentage of EGCG content increasing with the EGCG:pNG ratio from 23:1 (2.0% ± 0.02% to 23:5 (28% ± 0.3%. EGCG-pNG particles at ratios of 23:1 and 23:5 demonstrated significantly decreased size from 500 to 20 nm and decreasing zeta potentials of 21 mV to –22 mV, respectively. At a ratio of 23:2.5, the EGCG-pNG particles (27% EGCG, 50 nm in size, zeta potential of –8 mV showed longer EGCG activity half-life (110 days vs 5 hours, controlled release (2 hours vs 30 minutes, and higher antioxidant activity (four times, as well as inhibition of tumor cell growth, than controls. The present study indicated that EGCG-pNG possesses promising therapeutic potential, based on its strong free-radical scavenging and anticancer activities.Keywords: EGCG, nanoparticles, antioxidant, antitumor activity, nanogold
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Fazel Anvari-Yazdi, Abbas [Department of Biomedical Engineering, Materials and Biomaterials Research Center (MBMRC), Tehran, IR (Iran, Islamic Republic of); Tahermanesh, Kobra, E-mail: tahermanesh.k@iums.ac.ir [Endometriosis and Gynecologic Disorders Research Center, Department of Ob. & Gyn., Rasoul-e Akram Hospital, Iran University of Medical Sciences (IUMS), Tehran, IR (Iran, Islamic Republic of); Hadavi, Seyed Mohammad Mehdi [Materials and Energy Research Center (MERC), Karaj, IR (Iran, Islamic Republic of); Talaei-Khozani, Tahereh [Tissue Engineering Lab, Anatomy Department, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (SUMS), Shiraz, IR (Iran, Islamic Republic of); Razmkhah, Mahboobeh [Shiraz Institute for Cancer Research, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (SUMS), Shiraz, IR (Iran, Islamic Republic of); Abed, Seyedeh Mehr [School of Medicine, Yasuj University of Medical Sciences (YUMS), Yasuj, IR (Iran, Islamic Republic of); Mohtasebi, Maryam Sadat [Shiraz Institute for Cancer Research, School of Medicine, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (SUMS), Shiraz, IR (Iran, Islamic Republic of)
2016-12-01
Magnesium (Mg)-based alloys have been extensively considered as biodegradable implant materials for orthopedic surgery. Mg and its alloys are metallic biomaterials that can degrade in the body and promote new bone formation. In this study, the corrosion behavior and cytotoxicity of Mg-Zn-Ca alloys are evaluated with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs). Mg-2Zn and Mg-2Zn-xCa (x = 1, 2 and 3 wt.%) alloys were designated. Mg alloys were analyzed with scanning electron microscopy and potentiodynamic polarization. To understand the in-vitro biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of Mg-2Zn and Mg-2Zn-xCa alloys, ASCs were cultured for 24 and 72 h in contact with 10%, 50% and 100% extraction of all alloys prepared in DMEM. Cell cytotoxicity and viability of ASCs were examined by MTT assay. Alloying elements including Zn and Ca improved the corrosion resistance of alloys were compared with pure Mg. The cytotoxicity results showed that all alloys had no significant adverse effects on cell viability in 24 h. After 72 h, cell viability and proliferation increased in the cells exposed to pure Mg and Mg-2Zn-1Ca extracts. The release of Mg, Zn and Ca ions in culture media had no toxic impacts on ASCs viability and proliferation. Mg-2Zn-1Ca alloy can be suggested as a good candidate to be used in biomedical applications. - Highlights: • Short and long term corrosion behavior of Mg-Zn-Ca alloys studied • Viability and toxicity of Adipose-derived Stem cells studied with Mg-Zn-Ca alloys • Understanding the morphology of cultured adipose stem cells on Mg alloys • Stem cells on Mg-Zn-Ca alloys could proliferate and expand.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fazel Anvari-Yazdi, Abbas; Tahermanesh, Kobra; Hadavi, Seyed Mohammad Mehdi; Talaei-Khozani, Tahereh; Razmkhah, Mahboobeh; Abed, Seyedeh Mehr; Mohtasebi, Maryam Sadat
2016-01-01
Magnesium (Mg)-based alloys have been extensively considered as biodegradable implant materials for orthopedic surgery. Mg and its alloys are metallic biomaterials that can degrade in the body and promote new bone formation. In this study, the corrosion behavior and cytotoxicity of Mg-Zn-Ca alloys are evaluated with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs). Mg-2Zn and Mg-2Zn-xCa (x = 1, 2 and 3 wt.%) alloys were designated. Mg alloys were analyzed with scanning electron microscopy and potentiodynamic polarization. To understand the in-vitro biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of Mg-2Zn and Mg-2Zn-xCa alloys, ASCs were cultured for 24 and 72 h in contact with 10%, 50% and 100% extraction of all alloys prepared in DMEM. Cell cytotoxicity and viability of ASCs were examined by MTT assay. Alloying elements including Zn and Ca improved the corrosion resistance of alloys were compared with pure Mg. The cytotoxicity results showed that all alloys had no significant adverse effects on cell viability in 24 h. After 72 h, cell viability and proliferation increased in the cells exposed to pure Mg and Mg-2Zn-1Ca extracts. The release of Mg, Zn and Ca ions in culture media had no toxic impacts on ASCs viability and proliferation. Mg-2Zn-1Ca alloy can be suggested as a good candidate to be used in biomedical applications. - Highlights: • Short and long term corrosion behavior of Mg-Zn-Ca alloys studied • Viability and toxicity of Adipose-derived Stem cells studied with Mg-Zn-Ca alloys • Understanding the morphology of cultured adipose stem cells on Mg alloys • Stem cells on Mg-Zn-Ca alloys could proliferate and expand
-
Protein carriers of conjugate vaccines: characteristics, development, and clinical trials.
Pichichero, Michael E
2013-12-01
The immunogenicity of polysaccharides as human vaccines was enhanced by coupling to protein carriers. Conjugation transformed the T cell-independent polysaccharide vaccines of the past to T cell-dependent antigenic vaccines that were much more immunogenic and launched a renaissance in vaccinology. This review discusses the conjugate vaccines for prevention of infections caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Specifically, the characteristics of the proteins used in the construction of the vaccines including CRM, tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane complex, and Hemophilus influenzae protein D are discussed. The studies that established differences among and key features of conjugate vaccines including immunologic memory induction, reduction of nasopharyngeal colonization and herd immunity, and antibody avidity and avidity maturation are presented. Studies of dose, schedule, response to boosters, of single protein carriers with single and multiple polysaccharides, of multiple protein carriers with multiple polysaccharides and conjugate vaccines administered concurrently with other vaccines are discussed along with undesirable consequences of conjugate vaccines. The clear benefits of conjugate vaccines in improving the protective responses of the immature immune systems of young infants and the senescent immune systems of the elderly have been made clear and opened the way to development of additional vaccines using this technology for future vaccine products.
-
Identification and Actions of a Novel Third Maresin Conjugate in Tissue Regeneration: MCTR3.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jesmond Dalli
Full Text Available Maresin conjugates in tissue regeneration (MCTR are a new family of evolutionarily conserved chemical signals that orchestrate host responses to promote tissue regeneration and resolution of infections. Herein, we identified the novel MCTR3 and established rank order potencies and matched the stereochemistries of MCTR1, MCTR2 and MCTR3 using material prepared by total organic synthesis and mediators isolated from both mouse and human systems. MCTR3 was produced from endogenous substrate by E. coli activated human macrophages and identified in sepsis patients. Each of the three synthetic MCTR dose-dependently (1-100 nM accelerated tissue regeneration in planaria by 0.6-0.9 days. When administered at the onset or peak of inflammation, each of the MCTR promoted resolution of E. coli infections in mice. They increased bacterial phagocytosis by exudate leukocytes (~15-50%, limited neutrophil infiltration (~20-50%, promoted efferocytosis (~30% and reduced eicosanoids. MCTR1 and MCTR2 upregulated human neutrophil and macrophage phagocytic responses where MCTR3 also proved to possess potent actions. These results establish the complete stereochemistry and rank order potencies for MCTR1, MCTR2 and MCTR3 that provide novel resolution moduli in regulating host responses to clear infections and promote tissue regeneration.
-
Qi, Lei; Lv, Xiujuan; Zhang, Tongwei; Jia, Peina; Yan, Ruiying; Li, Shuli; Zou, Ruitao; Xue, Yuhua; Dai, Liming
2016-06-01
A variety of nanomaterials have been developed for ocular diseases. The ability of these nanomaterials to pass through the blood-ocular barrier and their biocompatibility are essential characteristics that must be considered. Bacterial magnetosomes (BMs) are a type of biogenic magnetic nanomaterials synthesized by magnetotactic bacteria. Due to their unique biomolecular membrane shell and narrow size distribution of approximately 30 nm, BMs can pass through the blood-brain barrier. The similarity of the blood-ocular barrier to the blood-brain barrier suggests that BMs have great potential as treatments for ocular diseases. In this work, BMs were isolated from magnetotactic bacteria and evaluated in various cytotoxicity and genotoxicity studies in human retinal pigment epithelium (ARPE-19) cells. The BMs entered ARPE-19 cells by endocytosis after a 6-h incubation and displayed much lower cytotoxicity than chemically synthesized magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs). MNPs exhibited significantly higher genotoxicity than BMs and promoted the expression of Bax (the programmed cell death acceleration protein) and the induction of greater cell necrosis. In BM-treated cells, apoptosis tended to be suppressed via increased expression of the Bcl-2 protein. In conclusion, BMs display excellent biocompatibility and potential for use in the treatment of ocular diseases.
-
Demonstration of conjugated dopamine in monkey CSF by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Elchisak, M A; Powers, K H; Ebert, M H
1982-09-01
A method for measuring unconjugated and conjugated dopamine in body tissues and fluids is described. Conjugated dopamine was hydrolyzed in acid to unconjugated dopamine, separated from the sample matrix by alumina chromatography, and assayed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Conjugated dopamine was detected in greater concentrations than unconjugated dopamine in CSF taken from lateral ventricle or thecal sac of the Rhesus monkey. Haloperidol administration did not increase the levels of conjugated dopamine in lumbar CSF.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Marzena Matejczyk
2014-12-01
Full Text Available Escherichia coli K-12 GFP-based bacterial biosensors allowed the detection of cytotoxic and genotoxic effect of anticancer drug– cyclophosphamide and antidiabetic drug – metformin in PBS buffer and surface water. Experimental data indicated that recA::gfpmut2 genetic system was sensitive to drugs and drugs mixture applied in experiment. RecA promoter was a good bioindicator in cytotoxic and genotoxic effect screening of cyclophosphamide, metformin and the mixture of the both drugs in PBS buffer and surface water. The results indicated that E. coli K-12 recA::gfp mut2 strain could be potentially useful for first-step screening of cytotoxic and genotoxic effect of anticancer and antidiabetic pharmacist residues in water. Next steps in research will include more experimental analysis to validate recA::gfpmut2 genetic system in E. coli K-12 on different anticancer drugs.
-
Social behaviour and decision making in bacterial conjugation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Günther eKoraimann
2014-04-01
Full Text Available Bacteria frequently acquire novel genes by HGT (horizontal gene transfer. HGT through the process of bacterial conjugation is highly efficient and depends on the presence of conjugative plasmids (CPs or integrated conjugative elements (ICEs that provide the necessary genes for DNA transmission. This review focuses on recent advancements in our understanding of ssDNA transfer systems and regulatory networks ensuring timely and spatially controlled DNA transfer (tra gene expression. As will become obvious by comparing different systems, by default, tra genes are shut off in cells in which conjugative elements are present. Only when conditions are optimal, donor cells – through epigenetic alleviation of negatively acting roadblocks and direct stimulation of DNA transfer genes – become transfer competent. These transfer competent cells have developmentally transformed into specialized cells capable of secreting ssDNA via a T4S (type IV secretion complex directly into recipient cells. Intriguingly, even under optimal conditions, only a fraction of the population undergoes this transition, a finding that indicates specialization and cooperative, social behavior. Thereby, at the population level, the metabolic burden and other negative consequences of tra gene expression are greatly reduced without compromising the ability to horizontally transfer genes to novel bacterial hosts. This undoubtedly intelligent strategy may explain why conjugative elements – CPs and ICEs – have been successfully kept in and evolved with bacteria to constitute a major driving force of bacterial evolution.
-
Factors contributing to the immunogenicity of meningococcal conjugate vaccines
Bröker, Michael; Berti, Francesco; Costantino, Paolo
2016-01-01
ABSTRACT Various glycoprotein conjugate vaccines have been developed for the prevention of invasive meningococcal disease, having significant advantages over pure polysaccharide vaccines. One of the most important features of the conjugate vaccines is the induction of a T-cell dependent immune response, which enables both the induction of immune memory and a booster response after repeated immunization. The nature of the carrier protein to which the polysaccharides are chemically linked, is often regarded as the main component of the vaccine in determining its immunogenicity. However, other factors can have a significant impact on the vaccine's profile. In this review, we explore the physico-chemical properties of meningococcal conjugate vaccines, which can significantly contribute to the vaccine's immunogenicity. We demonstrate that the carrier is not the sole determining factor of the vaccine's profile, but, moreover, that the conjugate vaccine's immunogenicity is the result of multiple physico-chemical structures and characteristics. PMID:26934310
-
Tummala, Shashank; Gowthamarajan, K; Satish Kumar, M N; Praveen, T K; Yamjala, Karthik; Tripuraneni, Naga Srinivas; Prakash, Ashwati
2016-12-01
Conventional chemotherapy majorly lacks clinical application attributed to its inspecificity, adverse effects and inability to penetrate into tumor cells. Hence, the aim of the study was to prepare oxaliplatin solid lipid nanoparticles (OP-SLN) by microemulsion method optimizing it by Box-Behnken design and then covalently conjugated to TRAIL (CD-253) monoclonal antibody (TR-OP-SLN) for targeting colorectal cancer cells. The optimized OP-SLN3 has shown an appreciable particle size (121 ± 1.22 nm), entrapment efficiency (78 ± 0.09%) and drug loading (32 ± 1.01%). Fluorescence study and the Bradford assay further confirmed the binding of the protein. A 1.5-fold increase in cytotoxicity of immuno-nanoparticles (4.9 μM) was observed.
-
Zhang, Shao-Hui; Miao, Dong-Yue; Tan, Li; Liu, Ai-Lin; Lu, Wen-Qing
2016-01-01
The implications of disinfection by-products (DBPs) present in drinking water are of public health concern because of their potential mutagenic, carcinogenic and other toxic effects on humans. In this study, we selected 13 main DBPs found in drinking water to quantitatively analyse their cytotoxicity and genotoxicity using a microplate-based cytotoxicity assay and a developed SOS/umu assay in Salmonella typhimurium TA1535/pSK1002. With the developed SOS/umu test, eight DBPs: 3-chloro-4-(dichloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-2[5H]-fura3-chloro-4-(dichloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-2-[5H]-furanone (MX), dibromoacetonitrile (DBN), iodoacetic acid (IA), bromochloroacetonitrile (BCN), bromoacetic acid (BA), trichloroacetonitrile (TCN), dibromoacetic acid (DBA) and dichloroacetic acid (DCA) were significantly genotoxic to S. typhimurium. Three DBPs: chloroacetic acid (CA), trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and dichloroacetonitrile (DCN) were weakly genotoxic, whereas the remaining DBPs: chloroacetonitrile (CN) and chloral hydrate (CH) were negative. The rank order in decreasing genotoxicity was as follows: MX > DBN > IA > BCN > BA > TCN > DBA > DCA > CA, TCA, DCN > CN, CH. MX was approximately 370 000 times more genotoxic than DCA. In the microplate-based cytotoxicity assay, cytotoxic potencies of the 13 DBPs were compared and ranked in decreasing order as follows: MX > IA > DBN > BCN > BA > TCN > DCN > CA > DCA > DBA > CN > TCA > CH. MX was approximately 19 200 times more cytotoxic than CH. A statistically significant correlation was found between cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of the 13 DBPs in S. typhimurium. Results suggest that microplate-based cytotoxicity assay and the developed SOS/umu assay are feasible tools for analysing the cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of DBPs, particularly for comparing their toxic intensities quantitatively. © The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the UK Environmental Mutagen Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e
-
Efficient conjugate gradient algorithms for computation of the manipulator forward dynamics
Fijany, Amir; Scheid, Robert E.
1989-01-01
The applicability of conjugate gradient algorithms for computation of the manipulator forward dynamics is investigated. The redundancies in the previously proposed conjugate gradient algorithm are analyzed. A new version is developed which, by avoiding these redundancies, achieves a significantly greater efficiency. A preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm is also presented. A diagonal matrix whose elements are the diagonal elements of the inertia matrix is proposed as the preconditioner. In order to increase the computational efficiency, an algorithm is developed which exploits the synergism between the computation of the diagonal elements of the inertia matrix and that required by the conjugate gradient algorithm.
-
Functional Hybrid Biomaterials based on Peptide-Polymer Conjugates for Nanomedicine
Shu, Jessica Yo
The focus of this dissertation is the design, synthesis and characterization of hybrid functional biomaterials based on peptide-polymer conjugates for nanomedicine. Generating synthetic materials with properties comparable to or superior than those found in nature has been a "holy grail" for the materials community. Man-made materials are still rather simplistic when compared to the chemical and structural complexity of a cell. Peptide-polymer conjugates have the potential to combine the advantages of the biological and synthetic worlds---that is they can combine the precise chemical structure and diverse functionality of biomolecules with the stability and processibility of synthetic polymers. As a new family of soft matter, they may lead to materials with novel properties that have yet to be realized with either of the components alone. In order for peptide-polymer conjugates to reach their full potential as useful materials, the structure and function of the peptide should be maintained upon polymer conjugation. The success in achieving desirable, functional assemblies relies on fundamentally understanding the interactions between each building block and delicately balancing and manipulating these interactions to achieve targeted assemblies without interfering with designed structures and functionalities. Such fundamental studies of peptide-polymer interactions were investigated as the nature of the polymer (hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic) and the site of its conjugation (end-conjugation vs. side-conjugation) were varied. The fundamental knowledge gained was then applied to the design of amphiphiles that self-assemble to form stable functional micelles. The micelles exhibited exceptional monodispersity and long-term stability, which is atypical of self-assembled systems. Thus such micelles based on amphiphilic peptide-polymer conjugates may meet many current demands in nanomedicine, in particular for drug delivery of hydrophobic anti-cancer therapeutics. Lastly