
Sample records for conducting current generates
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Юрій Олексійович Кругляк
2015-07-01
Full Text Available General questions of electronic conductivity, current generation with the use of electrochemical potentials and Fermi functions, elastic resistor model, ballistic and diffusion transport, conductivity modes, n- and p-conductors and graphene, formulation of the generalized Ohm’s law, thermoelectric phenomena of Seebeck and Peltier, quality indicators and thermoelectric optimization, ballistic and diffusive phonon heat current are discussed in the frame of the «bottom – up» approach of modern nanoelectronics
-
Associating ground magnetometer observations with current or voltage generators
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hartinger, M. D.; Xu, Z.; Clauer, C. R.
2017-01-01
A circuit analogy for magnetosphere-ionosphere current systems has two extremes for driversof ionospheric currents: ionospheric elec tric fields/voltages constant while current/conductivity vary—the“voltage generator”—and current constant while electric field/conductivity vary—the “current generator.......”Statistical studies of ground magnetometer observations associated with dayside Transient High LatitudeCurrent Systems (THLCS) driven by similar mechanisms find contradictory results using this paradigm:some studies associate THLCS with voltage generators, others with current generators. We argue that mostof...... these two assumptions substantially alter expectations for magnetic perturbations associatedwith either a current or a voltage generator. Our results demonstrate that before interpreting groundmagnetometer observations of THLCS in the context of current/voltage generators, the location...
-
Threshold current for fireball generation
Dijkhuis, Geert C.
1982-05-01
Fireball generation from a high-intensity circuit breaker arc is interpreted here as a quantum-mechanical phenomenon caused by severe cooling of electrode material evaporating from contact surfaces. According to the proposed mechanism, quantum effects appear in the arc plasma when the radius of one magnetic flux quantum inside solid electrode material has shrunk to one London penetration length. A formula derived for the threshold discharge current preceding fireball generation is found compatible with data reported by Silberg. This formula predicts linear scaling of the threshold current with the circuit breaker's electrode radius and concentration of conduction electrons.
-
Tenke, Craig E.; Kayser, Jürgen
2012-01-01
The topographic ambiguity and reference-dependency that has plagued EEG/ERP research throughout its history are largely attributable to volume conduction, which may be concisely described by a vector form of Ohm’s Law. This biophysical relationship is common to popular algorithms that infer neuronal generators via inverse solutions. It may be further simplified as Poisson’s source equation, which identifies underlying current generators from estimates of the second spatial derivative of the field potential (Laplacian transformation). Intracranial current source density (CSD) studies have dissected the “cortical dipole” into intracortical sources and sinks, corresponding to physiologically-meaningful patterns of neuronal activity at a sublaminar resolution, much of which is locally cancelled (i.e., closed field). By virtue of the macroscopic scale of the scalp-recorded EEG, a surface Laplacian reflects the radial projections of these underlying currents, representing a unique, unambiguous measure of neuronal activity at scalp. Although the surface Laplacian requires minimal assumptions compared to complex, model-sensitive inverses, the resulting waveform topographies faithfully summarize and simplify essential constraints that must be placed on putative generators of a scalp potential topography, even if they arise from deep or partially-closed fields. CSD methods thereby provide a global empirical and biophysical context for generator localization, spanning scales from intracortical to scalp recordings. PMID:22796039
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bruma, C.; Cuperman, S.; Komoshvili, K.
1998-01-01
Several low aspect ratio (spherical) Tokamaks (ST's) are now in operation or under construction. These devices would permit cost-effective and attractive embodiment of future fusion reactors: they would provide high β, good confinement and steady state operation at modest field values. Now, a steady state reactor has to be sustained by non-inductively driven currents. Recently, the generation of non-inductive current drive by Alfven waves (AWCD) has been investigated theoretically within the framework of ideal (E p arallel=0) MHD and non-ideal, resistive (E p arallel≠0) MHD; however, in all these cases, the tokamak device consisted of a cylindrical plasma with simulated toroidal effects. Rather encouraging results have been obtained. In this work we further investigate AWCD in ST's as follows: (i) we use consistent equilibrium profiles with neoclassical conductivity corresponding to an ohmic START discharge; (ii) incorporate effects due to neoclassical conductivity in the elements of the resistive MHD dielectric tensor, in the solution of the full (E p arallel≠0) wave equation as well as in the calculation of AWCD; and (iii) carry out a systematic search for antenna parameters optimizing the AWCD. (author)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bruma, C.; Cuperman, S.; Komoshvili, K. [School of Physics and Astronomy, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv (Israel)
1998-08-01
Several low aspect ratio (spherical) Tokamaks (ST's) are now in operation or under construction. These devices would permit cost-effective and attractive embodiment of future fusion reactors: they would provide high {beta}, good confinement and steady state operation at modest field values. Now, a steady state reactor has to be sustained by non-inductively driven currents. Recently, the generation of non-inductive current drive by Alfven waves (AWCD) has been investigated theoretically within the framework of ideal (E{sub p}arallel=0) MHD and non-ideal, resistive (E{sub p}arallel{ne}0) MHD; however, in all these cases, the tokamak device consisted of a cylindrical plasma with simulated toroidal effects. Rather encouraging results have been obtained. In this work we further investigate AWCD in ST's as follows: (i) we use consistent equilibrium profiles with neoclassical conductivity corresponding to an ohmic START discharge; (ii) incorporate effects due to neoclassical conductivity in the elements of the resistive MHD dielectric tensor, in the solution of the full (E{sub p}arallel{ne}0) wave equation as well as in the calculation of AWCD; and (iii) carry out a systematic search for antenna parameters optimizing the AWCD. (author)
-
Laser diode with thermal conducting, current confining film
Hawrylo, Frank Z. (Inventor)
1980-01-01
A laser diode formed of a rectangular parallelopiped body of single crystalline semiconductor material includes regions of opposite conductivity type indium phosphide extending to opposite surfaces of the body. Within the body is a PN junction at which light can be generated. A stripe of a conductive material is on the surface of the body to which the P type region extends and forms an ohmic contact with the P type region. The stripe is spaced from the side surfaces of the body and extends to the end surfaces of the body. A film of germanium is on the portions of the surface of the P type region which is not covered by the conductive stripe. The germanium film serves to conduct heat from the body and forms a blocking junction with the P type region so as to confine the current through the body, across the light generating PN junction, away from the side surfaces of the body.
-
Williamson, P. R.; Banks, P. M.
1976-01-01
The objectives of the Tethered Balloon Current Generator experiment are to: (1) generate relatively large regions of thermalized, field-aligned currents, (2) produce controlled-amplitude Alfven waves, (3) study current-driven electrostatic plasma instabilities, and (4) generate substantial amounts of power or propulsion through the MHD interaction. A large balloon (a diameter of about 30 m) will be deployed with a conducting surface above the space shuttle at a distance of about 10 km. For a generally eastward directed orbit at an altitude near 400 km, the balloon, connected to the shuttle by a conducting wire, will be positive with respect to the shuttle, enabling it to collect electrons. At the same time, the shuttle will collect positive ions and, upon command, emit an electron beam to vary current flow in the system.
-
Superconducting current generators
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Genevey, P.
1970-01-01
After a brief summary of the principle of energy storage and liberation with superconducting coils,two current generators are described that create currents in the range 600 to 1400 A, used for two storage experiments of 25 kJ and 50 kJ respectively. The two current generators are: a) a flux pump and b) a superconducting transformer. Both could be developed into more powerful units. The study shows the advantage of the transformer over the flux pump in order to create large currents. The efficiencies of the two generators are 95 per cent and 40 to 60 per cent respectively. (author) [fr
-
Practical Application of Eddy Currents Generated by Wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dirba, I; Kleperis, J
2011-01-01
When a conductive material is subjected to time-varying magnetic fluxes, eddy (Foucault) currents are generated in it and magnetic field of opposite polarity as the applied one arises. Due to the internal resistance of the conductive material, the eddy currents will be dissipated into heat (Joule heating). Conventional domestic water heaters utilize gas burners or electric resistance heating elements to heat the water in the tank and substantial part of the energy to use for it is wasted. In this paper the origin of electromagnetic induction heat generated by wind turbine in special heat exchange camera connected to water boiler is discussed and material evaluation performed using mathematical modelling (comparing the 2D finite element model with analytical and numerical calculation results).
-
Practical Application of Eddy Currents Generated by Wind
Dirba, I.; Kleperis, J.
2011-06-01
When a conductive material is subjected to time-varying magnetic fluxes, eddy (Foucault) currents are generated in it and magnetic field of opposite polarity as the applied one arises. Due to the internal resistance of the conductive material, the eddy currents will be dissipated into heat (Joule heating). Conventional domestic water heaters utilize gas burners or electric resistance heating elements to heat the water in the tank and substantial part of the energy to use for it is wasted. In this paper the origin of electromagnetic induction heat generated by wind turbine in special heat exchange camera connected to water boiler is discussed and material evaluation performed using mathematical modelling (comparing the 2D finite element model with analytical and numerical calculation results).
-
Practical Application of Eddy Currents Generated by Wind
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Dirba, I; Kleperis, J, E-mail: imants.dirba@gmail.com [Institute of Solid State Physics of University of Latvia, 8 Kengaraga Street, Riga, LV-1063 (Latvia)
2011-06-23
When a conductive material is subjected to time-varying magnetic fluxes, eddy (Foucault) currents are generated in it and magnetic field of opposite polarity as the applied one arises. Due to the internal resistance of the conductive material, the eddy currents will be dissipated into heat (Joule heating). Conventional domestic water heaters utilize gas burners or electric resistance heating elements to heat the water in the tank and substantial part of the energy to use for it is wasted. In this paper the origin of electromagnetic induction heat generated by wind turbine in special heat exchange camera connected to water boiler is discussed and material evaluation performed using mathematical modelling (comparing the 2D finite element model with analytical and numerical calculation results).
-
Current distribution in conducting nanowire networks
Kumar, Ankush; Vidhyadhiraja, N. S.; Kulkarni, Giridhar U.
2017-07-01
Conducting nanowire networks find diverse applications in solar cells, touch-screens, transparent heaters, sensors, and various related transparent conducting electrode (TCE) devices. The performances of these devices depend on effective resistance, transmittance, and local current distribution in these networks. Although, there have been rigorous studies addressing resistance and transmittance in TCE, not much attention is paid on studying the distribution of current. Present work addresses this compelling issue of understanding current distribution in TCE networks using analytical as well as Monte-Carlo approaches. We quantified the current carrying backbone region against isolated and dangling regions as a function of wire density (ranging from percolation threshold to many multiples of threshold) and compared the wired connectivity with those obtained from template-based methods. Further, the current distribution in the obtained backbone is studied using Kirchhoff's law, which reveals that a significant fraction of the backbone (which is believed to be an active current component) may not be active for end-to-end current transport due to the formation of intervening circular loops. The study shows that conducting wire based networks possess hot spots (extremely high current carrying regions) which can be potential sources of failure. The fraction of these hot spots is found to decrease with increase in wire density, while they are completely absent in template based networks. Thus, the present work discusses unexplored issues related to current distribution in conducting networks, which are necessary to choose the optimum network for best TCE applications.
-
The influence of convective current generator on the global current
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. N. Morozov
2006-01-01
Full Text Available The mathematical generalization of classical model of the global circuit with taking into account the convective current generator, working in the planetary boundary layer was considered. Convective current generator may be interpreted as generator, in which the electromotive force is generated by processes, of the turbulent transport of electrical charge. It is shown that the average potential of ionosphere is defined not only by the thunderstorm current generators, working at the present moment, but by the convective current generator also. The influence of the convective processes in the boundary layer on the electrical parameters of the atmosphere is not only local, but has global character as well. The numerical estimations, made for the case of the convective-unstable boundary layer demonstrate that the increase of the average potential of ionosphere may be of the order of 10% to 40%.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Pain, H. J.; Fearn, D. G.; Distefano, E. [Imperial College. London (United Kingdom)
1966-10-15
(a) Electrode conduction processes have been investigated using a plasma produced in an electromagnetic shock tube operating with argon at 70 {mu}mHg pressure. Complete voltage-current characteristics were obtained by the variation of load and applied voltage. These indicated the existence of two conduction regimes with a complex transition region. In the first regime the current, controlled by ion mobility, rose linearly with voltage to saturate between 10 mA and 1 A depending on conditions. Electrode contamination was significant. The second regime involved large currents controlled by electron mobility and emission from the cathode. The current again increased linearly with voltage and reached 200 A. Observation of induced voltages in transverse magnetic fields and of plasma deceleration in non-uniform fields showed that in the electromagnetic shock tube the plasma was heated predominantly by the driver discharge. Its conductivity was calculated using properties measured by a Langmuir double probe. In both regimes the plasma conductivity was also found from the gradient of the voltage current characteristics using experimental electric field fringing factors and the experimental values were compared with theory. (b) Larger-scale experiments used a combustion-driven shock tube where argon plasma flow, magnetic field and induced current flow were mutually orthogonal. The supersonic flow velocity and thermodynamic parameters of the plasma were accurately known. The electrode channel consisted of a segmented system of 12 electrode pairs with an electrode insulator ratio ranging from 1 to 21, with electrode plus insulator length remaining constant, and with maximum Hall parameter values of unity. Different electrode load combinations (Faraday and Hall generators) have been studied in measuring the power generated and the flow of longitudinal currents between adjacent electrodes. A maximum power of 0,8 MW was obtained, the power output decreasing inversely with the
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pain, H.J.; Fearn, D.G.; Distefano, E.
1966-01-01
(a) Electrode conduction processes have been investigated using a plasma produced in an electromagnetic shock tube operating with argon at 70 μmHg pressure. Complete voltage-current characteristics were obtained by the variation of load and applied voltage. These indicated the existence of two conduction regimes with a complex transition region. In the first regime the current, controlled by ion mobility, rose linearly with voltage to saturate between 10 mA and 1 A depending on conditions. Electrode contamination was significant. The second regime involved large currents controlled by electron mobility and emission from the cathode. The current again increased linearly with voltage and reached 200 A. Observation of induced voltages in transverse magnetic fields and of plasma deceleration in non-uniform fields showed that in the electromagnetic shock tube the plasma was heated predominantly by the driver discharge. Its conductivity was calculated using properties measured by a Langmuir double probe. In both regimes the plasma conductivity was also found from the gradient of the voltage current characteristics using experimental electric field fringing factors and the experimental values were compared with theory. (b) Larger-scale experiments used a combustion-driven shock tube where argon plasma flow, magnetic field and induced current flow were mutually orthogonal. The supersonic flow velocity and thermodynamic parameters of the plasma were accurately known. The electrode channel consisted of a segmented system of 12 electrode pairs with an electrode insulator ratio ranging from 1 to 21, with electrode plus insulator length remaining constant, and with maximum Hall parameter values of unity. Different electrode load combinations (Faraday and Hall generators) have been studied in measuring the power generated and the flow of longitudinal currents between adjacent electrodes. A maximum power of 0,8 MW was obtained, the power output decreasing inversely with the
-
Modelling of the toroidal asymmetry of poloidal halo currents in conducting structures
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pomphrey, N.; Bialek, J.M.; Part, W.
1998-01-01
During plasma disruptions, substantial toroidal and poloidal eddy currents are generated in the vacuum vessel and other plasma facing conducting structures. Eddy currents that conduct charge through paths which close through the plasma periphery are called halo currents, and these can be of substantial magnitude. Of particular concern for tokamak design and operation is the observed toroidal asymmetry of the halo current distribution: such an asymmetric distribution leads to problematic non-uniform forces on the conducting structures. The premise is adopted that the source of toroidal asymmetry is the plasma deformation resulting from the non-linear external kink instability that develops during the current quench phase of a disruption. A simple model is presented of the kinked plasma that allows an analytic calculation of the dependence of the toroidal peaking factor (TPF) on the ratio of the halo current to the total toroidal plasma current, I h /I p . Expressions for the TPF as a function of I h /I p are derived for m/n=2/1 and m/n=1/1 helical instabilities. The expressions depend on a single parameter, which measures the amplitude of the saturated state of the kink instability. A comparison with disruption data from experiments shows good agreement. Numerical experiments that simulate non-linear external kinks provide guidance on the values expected for the saturated amplitude. It is proposed that a simple plasma halo model is adequate for assessing the engineering impact of asymmetric halo currents, since the force distribution on the conducting structures depends mainly on the 'resistive distribution' of the eddy currents. A brief description is given of an electromagnetics code that calculates the time development of eddy currents in conducting structures, and the code is applied to two halo current disruption scenarios. These are used to emphasize the importance of having an accurate eddy current calculation to correctly estimate the engineering impact of
-
High current transistor pulse generator
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nesterov, V.; Cassel, R.
1991-05-01
A solid state pulse generator capable of delivering high current trapezoidally shaped pulses into an inductive load has been developed at SLAC. Energy stored in the capacitor bank of the pulse generator is switched to the load through a pair of Darlington transistors. A combination of diodes and Darlington transistors is used to obtain trapezoidal or triangular shaped current pulses into an inductive load and to recover the remaining energy in the same capacitor bank without reversing capacitor voltage. The transistors work in the switch mode, and the power losses are low. The rack mounted pulse generators presently used at SLAC contain a 660 microfarad storage capacitor bank and can deliver 400 amps at 800 volts into inductive loads up to 3 mH. The pulse generators are used in several different power systems, including pulse to pulse bipolar power supplies and in application with current pulses distributed into different inductive loads. The current amplitude and discharge time are controlled by the central computer system through a specially developed multichannel controller. Several years of operation with the pulse generators have proven their consistent performance and reliability. 8 figs
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ma Qingyu; He Bin
2007-01-01
A theoretical study on the magnetoacoustic signal generation with magnetic induction and its applications to electrical conductivity reconstruction is conducted. An object with a concentric cylindrical geometry is located in a static magnetic field and a pulsed magnetic field. Driven by Lorentz force generated by the static magnetic field, the magnetically induced eddy current produces acoustic vibration and the propagated sound wave is received by a transducer around the object to reconstruct the corresponding electrical conductivity distribution of the object. A theory on the magnetoacoustic waveform generation for a circular symmetric model is provided as a forward problem. The explicit formulae and quantitative algorithm for the electrical conductivity reconstruction are then presented as an inverse problem. Computer simulations were conducted to test the proposed theory and assess the performance of the inverse algorithms for a multi-layer cylindrical model. The present simulation results confirm the validity of the proposed theory and suggest the feasibility of reconstructing electrical conductivity distribution based on the proposed theory on the magnetoacoustic signal generation with magnetic induction
-
Current amplification models of sensorineurall and conductive hearing loss
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ostojić Sanja
2012-01-01
Full Text Available The main function of a hearing aid is to improve auditory and language abilities of hearing impaired users. The amplification model has to be adapted according to age, degree and type of hearing loss. The goal of this paper is to analyze the current amplification models of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss which can provide a high quality of speech perception and sounds at any degree of hearing loss. The BAHA is a surgically implantable system for treatment of conductive hearing loss that works through direct bone conduction. BAHA is used to help people with chronic ear infections, congenital external auditory canal atresia and single sided deafness who cannot benefit from conventional hearing aids. The last generation of hearing aid for sensorineural hearing loss is cochlear implant. Bimodal amplification improves binaural hearing. Hearing aids alone do not make listening easier in all situations. The things that can interfere with listening are background noises, distance from a sound and reverberation or echo. The device used most often today is the Frequency Modulated (FM system.
-
Motionally-induced electromagnetic fields generated by idealized ocean currents
Tyler, R. H.; Mysak, L. A.
Using the induction equation, we investigate the generation of electromagnetic fields by the motional electromagnetic induction due to ocean currents. In this paper, solutions are presented for a linear induction equation for the magnetic flux density vector which contains prescribed time-independent ocean current and conductivity fields. Once the magnetic flux density is known, the electric field and electric current density are easily obtained by differentiation. Solutions are given for several examples of idealized flow which include: 1) Vertically and horizontally sheared plane-parallel flow with depth-dependent conductivity; 2) A simple Stommel circulation gyre; and 3) Symmetric gyres. The results indicate that typical ocean current features induce magnetic fields with magnitudes reaching 100's of nT within the water and about 1-10 outside of the water. For the case of a field of gyres, the ocean-induced magnetic fields decay away from the ocean on spatial scales set by the horizontal scale of the ocean feature. At the altitudes of magnetic field satellite surveys, ocean-induced magnetic fields may retain values of a few nT, which are strong enough to be detected. Thus it is concluded that satellite observations of the earth's main magnetic field and, in particular, the observed temporal variations, could be affected by the ocean circulation. Summary and discussion In Section 3, we found exact solutions to the induction equation for idealized flows. The results gave magnitudes of about tens to hundreds of nT for the magnetic fields bH, about 10-5 V/m for the electric fields E, and about 10-5 A/m2 for the electric current density J induced by the ocean currents. These figures are in general agreement with the calculations of Lilley et al. (1993). In Section 4.2 we obtained solutions for the magnetic field above the ocean surface for the case of a Stommel gyre and a field of symmetric gyres. It was found in the last case that ocean gyres with a total transport
-
Graphene Transparent Conductive Electrodes for Next- Generation Microshutter Arrays
Li, Mary; Sultana, Mahmooda; Hess, Larry
2012-01-01
Graphene is a single atomic layer of graphite. It is optically transparent and has high electron mobility, and thus has great potential to make transparent conductive electrodes. This invention contributes towards the development of graphene transparent conductive electrodes for next-generation microshutter arrays. The original design for the electrodes of the next generation of microshutters uses indium-tin-oxide (ITO) as the electrode material. ITO is widely used in NASA flight missions. The optical transparency of ITO is limited, and the material is brittle. Also, ITO has been getting more expensive in recent years. The objective of the invention is to develop a graphene transparent conductive electrode that will replace ITO. An exfoliation procedure was developed to make graphene out of graphite crystals. In addition, large areas of single-layer graphene were produced using low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD) with high optical transparency. A special graphene transport procedure was developed for transferring graphene from copper substrates to arbitrary substrates. The concept is to grow large-size graphene sheets using the LPCVD system through chemical reaction, transfer the graphene film to a substrate, dope graphene to reduce the sheet resistance, and pattern the film to the dimension of the electrodes in the microshutter array. Graphene transparent conductive electrodes are expected to have a transparency of 97.7%. This covers the electromagnetic spectrum from UV to IR. In comparison, ITO electrodes currently used in microshutter arrays have 85% transparency in mid-IR, and suffer from dramatic transparency drop at a wavelength of near-IR or shorter. Thus, graphene also has potential application as transparent conductive electrodes for Schottky photodiodes in the UV region.
-
Current generation by minority-species heating
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fisch, N.J.
1981-01-01
It is proposed that electric currents be generated from the preferential heating of ions travelling in one direction but with no net momentum injected into the system. This can be accomplished with, for example, travelling waves in a two-ion-species plasma. The current can be generated efficiently enough for the scheme to be of interest in maintaining steady-state toroidal currents in a reactor. (author)
-
Current generation by minority species heating
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fisch, N.J.
1980-07-01
It is proposed that electric currents be generated from the preferential heating of ions traveling in one direction but with no net momentum injected into the system. This can be accomplished with, for example, traveling waves in a two-ion-species plasma. The current can be generated efficiently enough for the scheme to be of interest in maintaining steady-state toroidal currents in a reactor
-
Reliability of eddy current examination of steam generator tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Birks, A.S.; Ferris, R.H.; Doctor, P.G.; Clark, R.A.; Spanner, G.E.
1985-04-01
A unique study of nondestructive examination reliability is underway at the Pacific Northwest Laboratory under US Nuclear Regulatory Commission sponsorship. Project participants include the Electric Power Research Institute and consortiums from France, Italy, and Japan. This study group has conducted a series of NDE examinations of tubes from a retired-from-service steam generator, using commercially available multifrequency eddy current equipment and ASME procedures. The examination results have been analyzed to identify factors contributing to variations in NDE inspection findings. The reliability of these examinations will then be validated by destructive analyses of the steam generator tubes. The program is expected to contribute to development of a model for steam generator inservice inspection sampling plans and inspection periods, as well as to improved regulatory guidelines for tube plugging
-
Influence of water conductivity on shock waves generated by underwater electrical wire explosion
Liu, Ben; Wang, Deguo; Guo, Yanbao
2018-01-01
The new application of electrical explosion of wire (EEW) used in petroleum industry is to enhance oil recovery (EOR). Because of the complex environment underground, the effect of underground water conductivity on EEW should be considered. This work describes the effect of water conductivities on discharge current, voltage and shock waves. It was found that the effect of water conductivity contains two parts. One is the shunt effect of saline water, which can be considered as a parallel load with the copper wire between the electrodes connected to the discharge circuit. The peak pressure of shock waves are gradually decrease with the increase of water conductivity. The other is the current loss through saline water directly to the ground ends without flowing through the electrodes. The shunt effect is the main factor affecting the wire discharge process. As the charging voltage increased, the energy loss caused by these two parts are all reduced. These indicate that increasing the charging voltage to a certain value will increase the energy efficiency to generate a more powerful shock waves in conductive water.
-
Nam, Joo-Youn
2010-01-15
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are operated with solutions containing various chemical species required for the growth of electrochemically active microorganisms including nutrients and vitamins, substrates, and chemical buffers. Many different buffers are used in laboratory media, but the effects of these buffers and their inherent electrolyte conductivities have not been examined relative to current generation in MFCs. We investigated the effect of several common buffers (phosphate, MES, HEPES, and PIPES) on power production in single chambered MFCs compared to a non-buffered control. At the same concentrations the buffers produced different solution conductivities which resulted in different ohmic resistances and power densities. Increasing the solution conductivities to the same values using NaCl produced comparable power densities for all buffers. Very large increases in conductivity resulted in a rapid voltage drop at high current densities. Our results suggest that solution conductivity at a specific pH for each buffer is more important in MFC studies than the buffer itself given relatively constant pH conditions. Based on our analysis of internal resistance and a set neutral pH, phosphate and PIPES are the most useful buffers of those examined here because pH was maintained close to the pKa of the buffer, maximizing the ability of the buffer to contribute to increase current generation at high power densities. © 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Nam, Joo-Youn; Kim, Hyun-Woo; Lim, Kyeong-Ho; Shin, Hang-Sik; Logan, Bruce E
2010-01-15
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are operated with solutions containing various chemical species required for the growth of electrochemically active microorganisms including nutrients and vitamins, substrates, and chemical buffers. Many different buffers are used in laboratory media, but the effects of these buffers and their inherent electrolyte conductivities have not been examined relative to current generation in MFCs. We investigated the effect of several common buffers (phosphate, MES, HEPES, and PIPES) on power production in single chambered MFCs compared to a non-buffered control. At the same concentrations the buffers produced different solution conductivities which resulted in different ohmic resistances and power densities. Increasing the solution conductivities to the same values using NaCl produced comparable power densities for all buffers. Very large increases in conductivity resulted in a rapid voltage drop at high current densities. Our results suggest that solution conductivity at a specific pH for each buffer is more important in MFC studies than the buffer itself given relatively constant pH conditions. Based on our analysis of internal resistance and a set neutral pH, phosphate and PIPES are the most useful buffers of those examined here because pH was maintained close to the pK(a) of the buffer, maximizing the ability of the buffer to contribute to increase current generation at high power densities. Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Semenov, V.D.; Furman, Eh.G.
1974-01-01
The paper describes a current pulse generator with an auxiliary network consisting of a choke and diode in series designed to enlarge the range of pulse frequency control. One output of the network is connected to an adjustable valve cathode and via antoher auxiliary condenser to the point where the cathode of the main key unit is joined to the start of the magnetizing coil. A second output is connected to the anode of another adjustable valve and via another auxiliary condenser to the point where the anode of the other main key unit is joined to the end of the magnetizing coil. The generator can be used to excite the electromagnets of charged particle accelerators or in devices designed to produce magnetic fields. (author)
-
Direct current hopping conductance along DNA chain
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
Ma Song-Shan; Xu Hui; Liu Xiao-Liang; Li Ming-Jun
2007-01-01
This paper proposes a model of direct current(DC) electron hopping transport in DNA,in which DNA is considered as a binary one-dimensional disordered system.To quantitatively study the DC conductivity in DNA,it numerically calculates the DC conductivity of DNA chains with difierent parameter values.The result shows that the DC conductivity of DNA chain increases with the increase of temperature.And the conductivity of DNA chain is depended on the probability P.which represents the degree of compositional disorder in a DNA sequence to some extent.For P<0.5,the conductivity of DNA chain decreases with the increase of P,while for P≥0.5,the conductivity increases with the increase of p.The DC conductivity in DNA chain also varies with the change of the electric field,it presents non-Ohm's law conductivity characteristics.
-
Regional absolute conductivity reconstruction using projected current density in MREIT
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sajib, Saurav Z K; Kim, Hyung Joong; Woo, Eung Je; Kwon, Oh In
2012-01-01
Magnetic resonance electrical impedance tomography (MREIT) is a non-invasive technique for imaging the internal conductivity distribution in tissue within an MRI scanner, utilizing the magnetic flux density, which is introduced when a current is injected into the tissue from external electrodes. This magnetic flux alters the MRI signal, so that appropriate reconstruction can provide a map of the additional z-component of the magnetic field (B z ) as well as the internal current density distribution that created it. To extract the internal electrical properties of the subject, including the conductivity and/or the current density distribution, MREIT techniques use the relationship between the external injection current and the z-component of the magnetic flux density B = (B x , B y , B z ). The tissue studied typically contains defective regions, regions with a low MRI signal and/or low MRI signal-to-noise-ratio, due to the low density of nuclear magnetic resonance spins, short T 2 or T* 2 relaxation times, as well as regions with very low electrical conductivity, through which very little current traverses. These defective regions provide noisy B z data, which can severely degrade the overall reconstructed conductivity distribution. Injecting two independent currents through surface electrodes, this paper proposes a new direct method to reconstruct a regional absolute isotropic conductivity distribution in a region of interest (ROI) while avoiding the defective regions. First, the proposed method reconstructs the contrast of conductivity using the transversal J-substitution algorithm, which blocks the propagation of severe accumulated noise from the defective region to the ROI. Second, the proposed method reconstructs the regional projected current density using the relationships between the internal current density, which stems from a current injection on the surface, and the measured B z data. Combining the contrast conductivity distribution in the entire imaging
-
Antiresonance induced spin-polarized current generation
Yin, Sun; Min, Wen-Jing; Gao, Kun; Xie, Shi-Jie; Liu, De-Sheng
2011-12-01
According to the one-dimensional antiresonance effect (Wang X R, Wang Y and Sun Z Z 2003 Phys. Rev. B 65 193402), we propose a possible spin-polarized current generation device. Our proposed model consists of one chain and an impurity coupling to the chain. The energy level of the impurity can be occupied by an electron with a specific spin, and the electron with such a spin is blocked because of the antiresonance effect. Based on this phenomenon our model can generate the spin-polarized current flowing through the chain due to different polarization rates. On the other hand, the device can also be used to measure the generated spin accumulation. Our model is feasible with today's technology.
-
Non-inductive electric current generation with the Alfven waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Assis, A.S. de.
1988-01-01
Non-inductive current generation by means of radio frequency waves is studied using one-dimensional (1D) quasilinear equations. The main results obtained in this thesis are the general expressions for the current generated, for the efficiency of current generation and for the critical power - the lowest power required for current saturation. (M.W.O.) [pt
-
Development of high current electron beam generator
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lee, Byeong Cheol; Lee, Jong Min; Kim, Sun Kook [and others
1997-05-01
A high-current electron beam generator has been developed. The energy and the average current of the electron beam are 2 MeV and 50 mA, respectively. The electron beam generator is composed of an electron gun, RF acceleration cavities, a 260-kW RF generator, electron beam optics components, and control system, etc. The electron beam generator will be used for the development of a millimeter-wave free-electron laser and a high average power infrared free-electron laser. The machine will also be used as a user facility in nuclear industry, environment industry, semiconductor industry, chemical industry, etc. (author). 15 tabs., 85 figs.
-
Development of high current electron beam generator
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lee, Byeong Cheol; Lee, Jong Min; Kim, Sun Kook
1997-05-01
A high-current electron beam generator has been developed. The energy and the average current of the electron beam are 2 MeV and 50 mA, respectively. The electron beam generator is composed of an electron gun, RF acceleration cavities, a 260-kW RF generator, electron beam optics components, and control system, etc. The electron beam generator will be used for the development of a millimeter-wave free-electron laser and a high average power infrared free-electron laser. The machine will also be used as a user facility in nuclear industry, environment industry, semiconductor industry, chemical industry, etc. (author). 15 tabs., 85 figs
-
Software Toolbox for Low-Frequency Conductivity and Current Density Imaging Using MRI.
Sajib, Saurav Z K; Katoch, Nitish; Kim, Hyung Joong; Kwon, Oh In; Woo, Eung Je
2017-11-01
Low-frequency conductivity and current density imaging using MRI includes magnetic resonance electrical impedance tomography (MREIT), diffusion tensor MREIT (DT-MREIT), conductivity tensor imaging (CTI), and magnetic resonance current density imaging (MRCDI). MRCDI and MREIT provide current density and isotropic conductivity images, respectively, using current-injection phase MRI techniques. DT-MREIT produces anisotropic conductivity tensor images by incorporating diffusion weighted MRI into MREIT. These current-injection techniques are finding clinical applications in diagnostic imaging and also in transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), deep brain stimulation (DBS), and electroporation where treatment currents can function as imaging currents. To avoid adverse effects of nerve and muscle stimulations due to injected currents, conductivity tensor imaging (CTI) utilizes B1 mapping and multi-b diffusion weighted MRI to produce low-frequency anisotropic conductivity tensor images without injecting current. This paper describes numerical implementations of several key mathematical functions for conductivity and current density image reconstructions in MRCDI, MREIT, DT-MREIT, and CTI. To facilitate experimental studies of clinical applications, we developed a software toolbox for these low-frequency conductivity and current density imaging methods. This MR-based conductivity imaging (MRCI) toolbox includes 11 toolbox functions which can be used in the MATLAB environment. The MRCI toolbox is available at http://iirc.khu.ac.kr/software.html . Its functions were tested by using several experimental datasets, which are provided together with the toolbox. Users of the toolbox can focus on experimental designs and interpretations of reconstructed images instead of developing their own image reconstruction softwares. We expect more toolbox functions to be added from future research outcomes. Low-frequency conductivity and current density imaging using MRI includes
-
Brushless power generating system having reduced conducted emissions in output power
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Walton, D.N.; Dolan, C.F.; Shah, M.J.
1991-01-01
This patent describes a brushless electrical power generating system. It comprises an exciter for producing alternating current from an exciter rotor; a rectifier mounted for rotation with the rotor for producing a rectified control current from the alternating current; a common mode inductor, coupled to the rectifier, for cancelling common mode noise components within the rectified control current; and a main generator, having a rotating field winding mounted on a main generator rotor excited by the control current and producing an alternating current power output from a stator
-
Direct Drive Generator for Renewable Power Conversion from Water Currents
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Segergren, Erik
2005-01-01
In this thesis permanent magnet direct drive generator for power conversion from water currents is studied. Water currents as a power source involves a number of constrains as well as possibilities, especially when direct drive and permanent magnets are considered. The high power fluxes and low current velocities of a water current, in combination with its natural variations, will affect the way the generator is operated and, flowingly, the appearance of the generator. The work in this thesis can, thus, be categorized into two general topics, generator technology and optimization. Under the first topic, fundamental generator technology is used to increase the efficiency of a water current generator. Under the latter topic, water current generators are optimized to a specific environment. The conclusion drawn from this work is that it is possible to design very low speed direct drive generators with good electromagnetic properties and wide efficiency peak
-
Eddy current inspection of steam generator tubing plugs
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cullen, W.K.
1990-01-01
In response to the issues raised regarding the integrity of nuclear steam generator tubing plugs manufactured from certain heats of Inconel 600, Westinghouse engineers have developed, qualified and implemented an eddy current inspection system for the in-place assessment of these plugs. The heart of the system is a robotic and effector which delivers an eddy current sensor through the reduced diameter of the plug expander and actuates the coil to physical contact with the expanded inside bore of the plug. Once deployed, the eddy current sensor is rotated along a helical path to produce a detailed scan of the plug surface above the final position of the expander. This testing produces an isometric display of degradation due to primary water stress corrosion cracking, on the inside surface of the plug. To date, successful inspections have been conducted at two nuclear units with two different robotic delivery systems. While designed specifically for mechanical plugs with a bottle bore cavity, the inspection system can also be used for expanded straight bore plugs. Details of the inspection system along with a discussion of qualification activities and actual field results are presented in this paper
-
Magnetic resonance electrical impedance tomography (MREIT): conductivity and current density imaging
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Seo, Jin Keun; Kwon, Ohin; Woo, Eung Je
2005-01-01
This paper reviews the latest impedance imaging technique called Magnetic Resonance Electrical Impedance Tomography (MREIT) providing information on electrical conductivity and current density distributions inside an electrically conducting domain such as the human body. The motivation for this research is explained by discussing conductivity changes related with physiological and pathological events, electromagnetic source imaging and electromagnetic stimulations. We briefly summarize the related technique of Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) that deals with cross-sectional image reconstructions of conductivity distributions from boundary measurements of current-voltage data. Noting that EIT suffers from the ill-posed nature of the corresponding inverse problem, we introduce MREIT as a new conductivity imaging modality providing images with better spatial resolution and accuracy. MREIT utilizes internal information on the induced magnetic field in addition to the boundary current-voltage measurements to produce three-dimensional images of conductivity and current density distributions. Mathematical theory, algorithms, and experimental methods of current MREIT research are described. With numerous potential applications in mind, future research directions in MREIT are proposed
-
Digital Signal Processing and Generation for a DC Current Transformer for Particle Accelerators
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zorzetti, Silvia [Fermi National Accelerator Lab. (FNAL), Batavia, IL (United States)
2013-01-01
The thesis topic, digital signal processing and generation for a DC current transformer, focuses on the most fundamental beam diagnostics in the field of particle accelerators, the measurement of the beam intensity, or beam current. The technology of a DC current transformer (DCCT) is well known, and used in many areas, including particle accelerator beam instrumentation, as non-invasive (shunt-free) method to monitor the DC current in a conducting wire, or in our case, the current of charged particles travelling inside an evacuated metal pipe. So far, custom and commercial DCCTs are entirely based on analog technologies and signal processing, which makes them inflexible, sensitive to component aging, and difficult to maintain and calibrate.
-
Electric conductivity and bootstrap current in tokamak
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mao Jianshan; Wang Maoquan
1996-12-01
A modified Ohm's law for the electric conductivity calculation is presented, where the modified ohmic current can be compensated by the bootstrap current. A comparison of TEXT tokamak experiment with the theories shows that the modified Ohm's law is a more close approximation to the tokamak experiments than the classical and neoclassical theories and can not lead to the absurd result of Z eff <1, and the extended neoclassical theory would be not necessary. (3 figs.)
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Holbøll, Joachim; Bambery, K. R.; Fleming, R. J.
2000-01-01
Electromagnetic theory predicts that a dielectric sample in which a steady DC current of density ε is flowing, and in which the ratio of permittivity ε to conductivity σ varies with position, will acquire a space charge density j·grad(ε/σ). A simple and convenient way to generate an ε/σ gradient...... in a homogeneous sample is to establish a temperature gradient across it. The resulting spatial variation in ε is usually small in polymeric insulators, but the variation in σ can be appreciable. Laser induced pressure pulse (LIPP) measurements were made on 1.5 mm thick plaques of ultra pure LDPE equipped...... with vacuum-evaporated aluminium electrodes. Temperature differences up to 27°C were maintained across the samples, which were subjected to DC fields up to 20 kV/mm. Current density was measured as a function of temperature and field. Negligible thermally generated space charge was observed. The charge...
-
On-electrode autonomous current generator for multi-frequency EIT
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jivet, I; Dragoi, B
2008-01-01
The paper presents an autonomous programmable current generator module for multi-frequency EIT systems. The module incorporates all stages from the sine wave generation with frequency and amplitude tuning, D/A converter and filter, a high output resistance voltage-to-current converter to the associated digital communication and control. The paper presents in depth the original digital quadrature signal generator and the output current generator with a high resistance. The other main blocks of the design use current practice specifications, since recent technological solutions proposed in the literature were found appropriate. The proposed signal generator circuit, characterized by a very low complexity, is analyzed in its capacity to produce multiple accurate signals up to 1 MHz in frequency. The precision output current source uses a modified current conveyor of type CCII with a high output resistance and low distortion. The output current frequency spectrum and linearity parameters obtained in the simulations are also described. The simulation results indicate a good linearity and high output resistance with an acceptable output voltage swing. The calculated performance parameters are validated with simulations, and future work for the prototype fabrication of the IC is outlined
-
Current pulse generator of an induction accelerator electromagnet
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Baginskij, B.A.; Makarevich, V.N.; Shtejn, M.M.
1987-01-01
Thyristor generator forming in betatron electromagnet coil sinusoidal and quasisinusoidal current unipolar pulses, the field being deforced at the beginning of acceleration cycle, and with the pulse flat top in the cycle end, is described. The current amplitude is controlled by pulse-phase method. The current pulse time shift permitted to decrease the loss rate in the accumulating capacitor. The generator is used in systems with 1-10 ms pulse duration, electromagnet magnetic field maximal energy - 45-450 J, the voltage amplitude in the coil 960-1500 V and amplitude of the current passing the coil 100-500 A, the repetition frequency being 50-200 Hz. In particular, the generator is used to supply betatrons designed for defectoscopy in nonstationary conditions, the accelerated electron energy being 4, 6, 8 and 15 MeV
-
Ion current rectification, limiting and overlimiting conductances in nanopores.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Liesbeth van Oeffelen
Full Text Available Previous reports on Poisson-Nernst-Planck (PNP simulations of solid-state nanopores have focused on steady state behaviour under simplified boundary conditions. These are Neumann boundary conditions for the voltage at the pore walls, and in some cases also Donnan equilibrium boundary conditions for concentrations and voltages at both entrances of the nanopore. In this paper, we report time-dependent and steady state PNP simulations under less restrictive boundary conditions, including Neumann boundary conditions applied throughout the membrane relatively far away from the nanopore. We simulated ion currents through cylindrical and conical nanopores with several surface charge configurations, studying the spatial and temporal dependence of the currents contributed by each ion species. This revealed that, due to slow co-diffusion of oppositely charged ions, steady state is generally not reached in simulations or in practice. Furthermore, it is shown that ion concentration polarization is responsible for the observed limiting conductances and ion current rectification in nanopores with asymmetric surface charges or shapes. Hence, after more than a decade of collective research attempting to understand the nature of ion current rectification in solid-state nanopores, a relatively intuitive model is retrieved. Moreover, we measured and simulated current-voltage characteristics of rectifying silicon nitride nanopores presenting overlimiting conductances. The similarity between measurement and simulation shows that overlimiting conductances can result from the increased conductance of the electric double-layer at the membrane surface at the depletion side due to voltage-induced polarization charges. The MATLAB source code of the simulation software is available via the website http://micr.vub.ac.be.
-
Megavolt nanosecond generator with semiconductor current breaker
Bushlyakov, A I; Rukin, S N; Slovikovskij, B G; Timoshenkov, S P
2002-01-01
The heavy-current nanosecond generator with the pulse capacity up to 1.6 GW and output voltage of 0.5-1 MW is described. The generator contains four capacity storages, one induction storage and six solid body commutators: one thyristor, four magnetic commutators and a semiconductor current breaker on the SOS-diodes. The results of studies on the energy change-over efficiency through a semiconductor breaker by various external resistance loads as well as the results of the thermal and frequency tests are presented. It is established that selection of the optimal cooling system provides for the generator continuous mode of operation with the pulse sequence frequency from 300 Hz up to 850 Hz
-
Spin-polarized current generated by magneto-electrical gating
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ma Minjie; Jalil, Mansoor Bin Abdul; Tan, Seng Ghee
2012-01-01
We theoretically study spin-polarized current through a single electron tunneling transistor (SETT), in which a quantum dot (QD) is coupled to non-magnetic source and drain electrodes via tunnel junctions, and gated by a ferromagnetic (FM) electrode. The I–V characteristics of the device are investigated for both spin and charge currents, based on the non-equilibrium Green's function formalism. The FM electrode generates a magnetic field, which causes a Zeeman spin-splitting of the energy levels in the QD. By tuning the size of the Zeeman splitting and the source–drain bias, a fully spin-polarized current is generated. Additionally, by modulating the electrical gate bias, one can effect a complete switch of the polarization of the tunneling current from spin-up to spin-down current, or vice versa. - Highlights: ► The spin polarized transport through a single electron tunneling transistor is systematically studied. ► The study is based on Keldysh non-equilibrium Green's function and equation of motion method. ► A fully spin polarized current is observed. ► We propose to reverse current polarization by the means of gate voltage modulation. ► This device can be used as a bi-polarization current generator.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Adi Kurniawan
2017-06-01
Full Text Available Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP is a method to protect metallic material such as ship hull from corrosion by using electric current. In this research, a prototype of thermoelectric generator is developed in order to supply the ICCP system. This thermoelectric generator is planned to utilize the exhaust gas from main engine of the ship. Method carried in this research is assembling the prototype of thermoelectric generator followed by conducted experiment to observe the potential energy of the prototype. After that, the required number of thermoelectric generator is calculated to supply the ICCP system to protect the ship from corrosion. The object in this research is live fish carrier “Wellboat” which has 396.08 m2 wetted area. The required voltage and current to protect the ship from corrosion for three years are 16.67 Volt and 2.66 Ampere. Based on the experiment, a prototype of thermoelectric generator can generate 0.34 Ampere and 4.43 Volt, causing the need of 8 series and 4 parallels connection. It can be concluded that the corrosion rate on the ship hull can be decelerated by using impressed current cathodic protection method without needing additional cost or fuel consumption to produce electric energy.
-
Insulin reduces neuronal excitability by turning on GABA(A channels that generate tonic current.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zhe Jin
Full Text Available Insulin signaling to the brain is important not only for metabolic homeostasis but also for higher brain functions such as cognition. GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid decreases neuronal excitability by activating GABA(A channels that generate phasic and tonic currents. The level of tonic inhibition in neurons varies. In the hippocampus, interneurons and dentate gyrus granule cells normally have significant tonic currents under basal conditions in contrast to the CA1 pyramidal neurons where it is minimal. Here we show in acute rat hippocampal slices that insulin (1 nM "turns on" new extrasynaptic GABA(A channels in CA1 pyramidal neurons resulting in decreased frequency of action potential firing. The channels are activated by more than million times lower GABA concentrations than synaptic channels, generate tonic currents and show outward rectification. The single-channel current amplitude is related to the GABA concentration resulting in a single-channel GABA affinity (EC(50 in intact CA1 neurons of 17 pM with the maximal current amplitude reached with 1 nM GABA. They are inhibited by GABA(A antagonists but have novel pharmacology as the benzodiazepine flumazenil and zolpidem are inverse agonists. The results show that tonic rather than synaptic conductances regulate basal neuronal excitability when significant tonic conductance is expressed and demonstrate an unexpected hormonal control of the inhibitory channel subtypes and excitability of hippocampal neurons. The insulin-induced new channels provide a specific target for rescuing cognition in health and disease.
-
Mechanical generation of spin current
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mamoru eMatsuo
2015-07-01
Full Text Available We focus the recent results on spin-current generation from mechanical motion such as rigid rotation and elastic deformations. Spin transport theory in accelerating frames is constructed by using the low energy expansion of the generally covariant Dirac equation. Related issues on spin-manipulation by mechanical rotation are also discussed.
-
Thermal conductivity measurement of HTS tapes and stacks for current lead applications
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Schwarz, Michael; Weiss, Klaus-Peter; Heller, Reinhard; Fietz, Walter H.
2009-01-01
The use of high-temperature-superconductors (HTS) within current leads offers a high potential to save cooling-power. The principle of HTS current leads is well established, e.g. for particle accelerators (LHC-CERN) but also on the commercial sector, which offer HTS current leads ready for use in small scale magnets and magnets systems. Future fusion machines currently under construction like ITER, W7-X or JT-60SA also will use HTS current leads. At the moment the standard material for HTS current leads is a Bi 2 Sr 2 Ca 2 Cu 3 O x (BSCCO)-AgAu composite tape. The common way to receive high current capacity current leads is to form stacks by sintering or soldering these tapes together. The solder changes the thermal conductivity of the stacks compared to the single tape in the temperature range from 4 K to 60 K. To estimate the heat flux from the warm environment to the cold application the measurement of the thermal conductivity of the soldered stack is mandatory. Therefore the thermal conductivity of stacks with different number of tapes is investigated. To measure the thermal conduction in the current flow direction, the axial heat flow method is used. Combining these results with FEM simulations gives the possibility to estimate the thermal conductivity normal to the flat tape plane. The resulting anisotropic thermal conductivity can be used to model the behaviour of the HTS tape under thermal disturbances more accurately.
-
High current high accuracy IGBT pulse generator
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nesterov, V.V.; Donaldson, A.R.
1995-05-01
A solid state pulse generator capable of delivering high current triangular or trapezoidal pulses into an inductive load has been developed at SLAC. Energy stored in a capacitor bank of the pulse generator is switched to the load through a pair of insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBT). The circuit can then recover the remaining energy and transfer it back to the capacitor bank without reversing the capacitor voltage. A third IGBT device is employed to control the initial charge to the capacitor bank, a command charging technique, and to compensate for pulse to pulse power losses. The rack mounted pulse generator contains a 525 μF capacitor bank. It can deliver 500 A at 900V into inductive loads up to 3 mH. The current amplitude and discharge time are controlled to 0.02% accuracy by a precision controller through the SLAC central computer system. This pulse generator drives a series pair of extraction dipoles
-
Superconducting current generators; Generateurs supraconducteurs de courant
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Genevey, P [Commissariat a l' Energie Atomique, Limeil-Brevannes (France). Centre d' Etudes
1970-07-01
After a brief summary of the principle of energy storage and liberation with superconducting coils,two current generators are described that create currents in the range 600 to 1400 A, used for two storage experiments of 25 kJ and 50 kJ respectively. The two current generators are: a) a flux pump and b) a superconducting transformer. Both could be developed into more powerful units. The study shows the advantage of the transformer over the flux pump in order to create large currents. The efficiencies of the two generators are 95 per cent and 40 to 60 per cent respectively. (author) [French] Apres un rappel succinct du principe de stockage d'energie dans un solenoide supraconducteur et de sa liberation, nous decrivons deux generateurs de courant qui nous ont permis d'obtenir les courants necessaires (600 a 1400 A) aux experiences de stockage d'energie envisagees (27 kJ et 50 kJ): 1) - une pompe a flux, 2) - un transformateur supraconducteur. Ces generateurs sont extrapolables. Cette etude montre que si nous voulons creer un courant intense, le transformateur grace a son rendement eleve (> 95 pour cent) est preferable actuellement aux pompes a flux dont le rendement est de 40 a 60 pour cent. (auteur)
-
Surface conductivity of Mercury provides current closure and may affect magnetospheric symmetry
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Janhunen
2004-04-01
Full Text Available We study what effect a possible surface conductivity of Mercury has on the closure of magnetospheric currents by making six runs with a quasi-neutral hybrid simulation. The runs are otherwise identical but use different synthetic conductivity models: run 1 has a fully conducting planet, run 2 has a poorly conducting planet ( m and runs 3-6 have one of the hemispheres either in the dawn-dusk or day-night directions, conducting well, the other one being conducting poorly. Although the surface conductivity is not known from observations, educated guesses easily give such conductivity values that magnetospheric currents may close partly within the planet, and as the conductivity depends heavily on the mineral composition of the surface, the possibility of significant horizontal variations cannot be easily excluded. The simulation results show that strong horizontal variations may produce modest magnetospheric asymmetries. Beyond the hybrid simulation, we also briefly discuss the possibility that in the nightside there may be a lack of surface electrons to carry downward current, which may act as a further source of surface-related magnetospheric asymmetry. Key words. Magnetospheric physics (planetary magnetospheres; current systems; solar wind-magnetosphere interactions.6
-
Current Trends in Sensors Based on Conducting Polymer Nanomaterials
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hyeonseok Yoon
2013-08-01
Full Text Available Conducting polymers represent an important class of functional organic materials for next-generation electronic and optical devices. Advances in nanotechnology allow for the fabrication of various conducting polymer nanomaterials through synthesis methods such as solid-phase template synthesis, molecular template synthesis, and template-free synthesis. Nanostructured conducting polymers featuring high surface area, small dimensions, and unique physical properties have been widely used to build various sensor devices. Many remarkable examples have been reported over the past decade. The enhanced sensitivity of conducting polymer nanomaterials toward various chemical/biological species and external stimuli has made them ideal candidates for incorporation into the design of sensors. However, the selectivity and stability still leave room for improvement.
-
Current Trends in Sensors Based on Conducting Polymer Nanomaterials
Yoon, Hyeonseok
2013-01-01
Conducting polymers represent an important class of functional organic materials for next-generation electronic and optical devices. Advances in nanotechnology allow for the fabrication of various conducting polymer nanomaterials through synthesis methods such as solid-phase template synthesis, molecular template synthesis, and template-free synthesis. Nanostructured conducting polymers featuring high surface area, small dimensions, and unique physical properties have been widely used to build various sensor devices. Many remarkable examples have been reported over the past decade. The enhanced sensitivity of conducting polymer nanomaterials toward various chemical/biological species and external stimuli has made them ideal candidates for incorporation into the design of sensors. However, the selectivity and stability still leave room for improvement. PMID:28348348
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Blomberg, L.G.; Marklund, G.T.
1988-02-01
The influence on the high-latitude ionospheric convection of conductivities associated with upward field-aligned currents is investigated. Potential patterns are calculated from a given distribution of field-aligned currents and a conductivity model. The resulting patterns are shown to be modified considerably by including a coupling term between the conductivity and the field-aligned current in the conductivity model. The clockwise rotation of the entire potential pattern is reduced when the conductivity enhancement coincides with the regions of upward field-aligned current. Also, the electric field within these regions turns out to be rather insensitive to change in the magnitude of the current. In regions of downward current or when the current-dependent conductivity is excluded there is on the other hand an almost linear relationship between current and electric field. Although the particles producing the conductivity enhancement may not be the same as those carrying the major part of the field-aligned current it is clear from observations that there is a positive correlation between upward current conductivity. Therefore, the simple relationship used in this study is believed to reflect rather well the principal features of the current-conductivity coupling, which is of im- portance to the modelling of ionospheric electrodynamics. (With 26 refs.) (authors)
-
Ionospheric control of the magnetosphere: conductance
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. J. Ridley
2004-01-01
Full Text Available It is well known that the ionosphere plays a role in determining the global state of the magnetosphere. The ionosphere allows magnetospheric currents to close, thereby allowing magnetospheric convection to occur. The amount of current which can be carried through the ionosphere is mainly determined by the ionospheric conductivity. This paper starts to quantify the nonlinear relationship between the ionospheric conductivity and the global state of the magnetosphere. It is found that the steady-state magnetosphere acts neither as a current nor as a voltage generator; a uniform Hall conductance can influence the potential pattern at low latitudes, but not at high latitude; the EUV generated conductance forces the currents to close in the sunlight, while the potential is large on the nightside; the solar generated Hall conductances cause a large asymmetry between the dawn and dusk potential, which effects the pressure distribution in the magnetosphere; a uniform polar cap potential removes some of this asymmetry; the potential difference between solar minimum and maximum is ∼11%; and the auroral precipitation can be related to the local field-aligned current through an exponential function. Key words. Ionosphere (ionosphere-magnetosphere interactions; modelling and forecasting; polar ionosphere
-
Sukhanov, D. Ya.; Zav'yalova, K. V.
2018-03-01
The paper represents induced currents in an electrically conductive object as a totality of elementary eddy currents. The proposed scanning method includes measurements of only one component of the secondary magnetic field. Reconstruction of the current distribution is performed by deconvolution with regularization. Numerical modeling supported by the field experiments show that this approach is of direct practical relevance.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Rodriguez, Pedro; Luna, Alvaro; Hermoso, Juan Ramon
2011-01-01
The operation of distributed power generation systems under grid fault conditions is a key issue for the massive integration of renewable energy systems. Several studies have been conducted to improve the response of such distributed generation systems under voltage dips. In spite of being less s...
-
Nonlinear spin current generation in noncentrosymmetric spin-orbit coupled systems
Hamamoto, Keita; Ezawa, Motohiko; Kim, Kun Woo; Morimoto, Takahiro; Nagaosa, Naoto
2017-06-01
Spin current plays a central role in spintronics. In particular, finding more efficient ways to generate spin current has been an important issue and has been studied actively. For example, representative methods of spin-current generation include spin-polarized current injections from ferromagnetic metals, the spin Hall effect, and the spin battery. Here, we theoretically propose a mechanism of spin-current generation based on nonlinear phenomena. By using Boltzmann transport theory, we show that a simple application of the electric field E induces spin current proportional to E2 in noncentrosymmetric spin-orbit coupled systems. We demonstrate that the nonlinear spin current of the proposed mechanism is supported in the surface state of three-dimensional topological insulators and two-dimensional semiconductors with the Rashba and/or Dresselhaus interaction. In the latter case, the angular dependence of the nonlinear spin current can be manipulated by the direction of the electric field and by the ratio of the Rashba and Dresselhaus interactions. We find that the magnitude of the spin current largely exceeds those in the previous methods for a reasonable magnitude of the electric field. Furthermore, we show that application of ac electric fields (e.g., terahertz light) leads to the rectifying effect of the spin current, where dc spin current is generated. These findings will pave a route to manipulate the spin current in noncentrosymmetric crystals.
-
Entropy generation by nanofluid with variable thermal conductivity ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
The entropy generation by nanofluid with variable thermal conductivity and viscosity of assisted convective flow across a riser pipe of a horizontal flat plate solar collector is investigated numerically. The water based nanofluid with copper nanoparticles is used as the working fluid inside the fluid passing riser pipe.
-
Current state and development trends of inspections of steam generator tubes by eddy currents method
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kubis, S.; Herman, M.
1988-01-01
The requirements are presented for steam generator tube testing and the factors are discussed affecting the accuracy of measurement by the eddy currents method. The individual types of the eddy currents method are described, such as the single-frequency method, the multi-frequency method and the pulse eddy currents method. The demands are summed up on manipulator systems whose design is adapted to the steam generator configuration conditions. (E.S.). 5 figs., 16 possu
-
Digital processing with single electrons for arbitrary waveform generation of current
Okazaki, Yuma; Nakamura, Shuji; Onomitsu, Koji; Kaneko, Nobu-Hisa
2018-03-01
We demonstrate arbitrary waveform generation of current using a GaAs-based single-electron pump. In our experiment, a digital processing algorithm known as delta-sigma modulation is incorporated into single-electron pumping to generate a density-modulated single-electron stream, by which we demonstrate the generation of arbitrary waveforms of current including sinusoidal, square, and triangular waves with a peak-to-peak amplitude of approximately 10 pA and an output bandwidth ranging from dc to close to 1 MHz. The developed current generator can be used as the precise and calculable current reference required for measurements of current noise in low-temperature experiments.
-
Electrodynamic forces and plasma conductivity inside the current sheet
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bogdanov, S.Yu.; Frank, A.G.; Markov, V.S.
1985-01-01
The process of accumulation and explosive release of magnetic energy was studied in a current sheet of plasma of a high-current linear discharge. The distribution of current density and of electrodynamic forces were measured and the time evolution of these quantities was determined. The evolution of the plasma conductivity was also obtained. The measured and calculated electrodynamic forces may explain the plasma acceleration up to the velocities about 3x10 4 m/s only near the sheet edges. (D.Gy.)
-
Ionospheric control of the magnetosphere: conductance
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. J. Ridley
2004-01-01
Full Text Available It is well known that the ionosphere plays a role in determining the global state of the magnetosphere. The ionosphere allows magnetospheric currents to close, thereby allowing magnetospheric convection to occur. The amount of current which can be carried through the ionosphere is mainly determined by the ionospheric conductivity. This paper starts to quantify the nonlinear relationship between the ionospheric conductivity and the global state of the magnetosphere. It is found that the steady-state magnetosphere acts neither as a current nor as a voltage generator; a uniform Hall conductance can influence the potential pattern at low latitudes, but not at high latitude; the EUV generated conductance forces the currents to close in the sunlight, while the potential is large on the nightside; the solar generated Hall conductances cause a large asymmetry between the dawn and dusk potential, which effects the pressure distribution in the magnetosphere; a uniform polar cap potential removes some of this asymmetry; the potential difference between solar minimum and maximum is ∼11%; and the auroral precipitation can be related to the local field-aligned current through an exponential function.
Key words. Ionosphere (ionosphere-magnetosphere interactions; modelling and forecasting; polar ionosphere -
Current multiplier to improved generator-to-load coupling for pulse-power generators
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chuvatin, A.S.; Rudakov, L.I.; Weber, B.V.; Bayol, F.; Cadiergues, R.
2005-01-01
The circuit presented improves the coupling of existing and future pulsed power generators to physical loads. The efficiency of the proposed current multiplication scheme could theoretically exceed the values for a typical direct load-to-generator circuit. The scheme could be beneficial for use in actual applications and two examples of such applications are given [ru
-
The heat current density correlation function: sum rules and thermal conductivity
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Singh, Shaminder; Tankeshwar, K; Pathak, K N; Ranganathan, S
2006-01-01
Expressions for the second and fourth sum rules of the heat current density correlation function have been derived in an appropriate ensemble. The thermal conductivity of Lennard-Jones fluids has been calculated using these sum rules for the heat current density correlation function and the Gaussian form of the memory function. It is found that the results obtained for the thermal conductivity are in good agreement with the molecular dynamics simulation results over a wide range of densities and temperatures. Earlier results obtained using the energy current density correlation function are also discussed
-
The heat current density correlation function: sum rules and thermal conductivity
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Singh, Shaminder [Department of Physics, Panjab University, Chandigarh-160 014 (India); Tankeshwar, K [Department of Physics, Panjab University, Chandigarh-160 014 (India); Pathak, K N [Department of Physics, Panjab University, Chandigarh-160 014 (India); Ranganathan, S [Department of Physics, Royal Military College, Kingston, ON, K7K 7B4 (Canada)
2006-02-01
Expressions for the second and fourth sum rules of the heat current density correlation function have been derived in an appropriate ensemble. The thermal conductivity of Lennard-Jones fluids has been calculated using these sum rules for the heat current density correlation function and the Gaussian form of the memory function. It is found that the results obtained for the thermal conductivity are in good agreement with the molecular dynamics simulation results over a wide range of densities and temperatures. Earlier results obtained using the energy current density correlation function are also discussed.
-
Direct current hopping conductance in one-dimensional diagonal disordered systems
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
Ma Song-Shan; Xu Hui; Liu Xiao-Liang; Xiao Jian-Rong
2006-01-01
Based on a tight-binding disordered model describing a single electron band, we establish a direct current (dc) electronic hopping transport conductance model of one-dimensional diagonal disordered systems, and also derive a dc conductance formula. By calculating the dc conductivity, the relationships between electric field and conductivity and between temperature and conductivity are analysed, and the role played by the degree of disorder in electronic transport is studied. The results indicate the conductivity of systems decreasing with the increase of the degree of disorder, characteristics of negative differential dependence of resistance on temperature at low temperatures in diagonal disordered systems, and the conductivity of systems decreasing with the increase of electric field, featuring the non-Ohm's law conductivity.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ho, Cong Son; Tan, Seng Ghee; Jalil, Mansoor B. A.
2014-01-01
The generation of spin current and spin polarization in a two-dimensional electron gas structure is studied in the presence of Dresselhaus and Rashba spin-orbit couplings (SOC), the strength of the latter being modulated in time by an ac gate voltage. By means of the non-Abelian gauge field approach, we established the relation between the Lorentz spin force and the spin current in the SOC system, and showed that the longitudinal component of the spin force induces a transverse spin current. For a constant (time-invariant) Rashba system, we recover the universal spin Hall conductivity of e/(8π) , derived previously via the Berry phase and semi-classical methods. In the case of a time-dependent SOC system, the spin current is sustained even under strong impurity scattering. We evaluated the ac spin current generated by a time-modulated Rashba SOC in the absence of any dc electric field. The magnitude of the spin current reaches a maximum when the modulation frequency matches the Larmor frequency of the electrons
-
Current generation by monochromatic electromagnetic waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Belikov, V.S.; Kolesnichenko, Ya.I.; Plotnik, I.S.
1983-01-01
The generation of longitudinal currents in a magnetically confined plasma with travelling monochromatic electromagnetic waves of finite amplitude propagating at some angle to the external magnetic field is considered. By averaging over the particle cyclotron gyration period, the kinetic equation for the distribution function of electrons interacting with an electromagnetic wave is derived. This equation is solved for the case of low-frequency waves, on the assumption that the bounce period of electrons trapped by the wave field is small compared to the typical times of Coulomb collisions (in which case, the driving current is largest). From the solution obtained, analytic expressions for the driving current and the absorbed power, which are valid for a wide range of wave phase velocities, are found. The current drive method considered and the method using the wave packet are compared. (author)
-
Thermoelectric Generation Of Current - Theoretical And Experimental Analysis
Ruciński, Adam; Rusowicz, Artur
2017-12-01
This paper provides some information about thermoelectric technology. Some new materials with improved figures of merit are presented. These materials in Peltier modules make it possible to generate electric current thanks to a temperature difference. The paper indicates possible applications of thermoelectric modules as interesting tools for using various waste heat sources. Some zero-dimensional equations describing the conditions of electric power generation are given. Also, operating parameters of Peltier modules, such as voltage and electric current, are analyzed. The paper shows chosen characteristics of power generation parameters. Then, an experimental stand for ongoing research and experimental measurements are described. The authors consider the resistance of a receiver placed in the electric circuit with thermoelectric elements. Finally, both the analysis of experimental results and conclusions drawn from theoretical findings are presented. Voltage generation of about 1.5 to 2.5 V for the temperature difference from 65 to 85 K was observed when a bismuth telluride thermoelectric couple (traditionally used in cooling technology) was used.
-
Surface conductivity of Mercury provides current closure and may affect magnetospheric symmetry
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Janhunen
2004-04-01
Full Text Available We study what effect a possible surface conductivity of Mercury has on the closure of magnetospheric currents by making six runs with a quasi-neutral hybrid simulation. The runs are otherwise identical but use different synthetic conductivity models: run 1 has a fully conducting planet, run 2 has a poorly conducting planet (
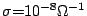 m
m and runs 3-6 have one of the hemispheres either in the dawn-dusk or day-night directions, conducting well, the other one being conducting poorly. Although the surface conductivity is not known from observations, educated guesses easily give such conductivity values that magnetospheric currents may close partly within the planet, and as the conductivity depends heavily on the mineral composition of the surface, the possibility of significant horizontal variations cannot be easily excluded. The simulation results show that strong horizontal variations may produce modest magnetospheric asymmetries. Beyond the hybrid simulation, we also briefly discuss the possibility that in the nightside there may be a lack of surface electrons to carry downward current, which may act as a further source of surface-related magnetospheric asymmetry.
and runs 3-6 have one of the hemispheres either in the dawn-dusk or day-night directions, conducting well, the other one being conducting poorly. Although the surface conductivity is not known from observations, educated guesses easily give such conductivity values that magnetospheric currents may close partly within the planet, and as the conductivity depends heavily on the mineral composition of the surface, the possibility of significant horizontal variations cannot be easily excluded. The simulation results show that strong horizontal variations may produce modest magnetospheric asymmetries. Beyond the hybrid simulation, we also briefly discuss the possibility that in the nightside there may be a lack of surface electrons to carry downward current, which may act as a further source of surface-related magnetospheric asymmetry.
Key words. Magnetospheric physics (planetary magnetospheres; current systems; solar wind-magnetosphere interactions.6 -
Shurupov, A. V.; Zavalova, V. E.; Kozlov, A. V.; Shurupov, M. A.; Povareshkin, M. N.; Kozlov, A. A.; Shurupova, N. P.
2018-01-01
Experimental models of microsecond duration powerful generators of current pulses on the basis of explosive magnetic generators and voltage impulse generator have been developed for the electromagnetic pulse effects on energy facilities to verify their stability. Exacerbation of voltage pulse carried out through the use of electro explosive current interrupter made of copper wires with diameters of 80 and 120 μm. Experimental results of these models investigation are represented. Voltage fronts about 100 ns and the electric field strength of 800 kV/m are registered.
-
Current generation by phased injection of pellets
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fisch, N.J.
1983-08-01
By phasing the injection of frozen pellets into a tokamak plasma, it is possible to generate current. The current occurs when the electron flux to individual members of an array of pellets is asymmetric with respect to the magnetic field. The utility of this method for tokamak reactors, however, is unclear; the current, even though free in a pellet-fueled reactor, may not be large enough to be worth the trouble. Uncertainty as to the utility of this method is, in part, due to uncertainty as to proper modeling of the one-pellet problem
-
Effect of nanoparticles generation method on ionic conductivity in Yttria stabilized zirconia
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Khare, J.; Joshi, M.P.; Kukreja, L.M.; Satapathy, S.
2013-01-01
Yttria stabilized zirconia nanoparticles were generated in pulsed and CW mode of laser operation using CO 2 laser based laser vaporization method. Impedance spectroscopic measurements were carried out in frequency range of 100 Hz - 1 MHz at various temperatures ranging from room temperature to 500 C. The deconvolution of grain and grain boundary contribution were obtained from impedance spectra by an equivalent circuit analysis. Grain and grain boundary ionic conductivity of pellet made from nanoparticles generated in pulsed mode was two orders of magnitude large in comparison to pellets made from nanoparticles generated in CW mode of laser operation. The difference in ionic conductivities of pellets made from nanoparticles generated in pulsed mode and CW mode were explained on the basis of defect associations in nanoparticles produced during nanoparticles generation. (author)
-
Internal current generation in respiration chambers
Saborowski, R.; Buchholz, F.
1998-06-01
A technical device generating a constant and directed current within a sealed respiration chamber is described. It does not involve any external pumps or tubing. This system is easy to handle, and improved the maintenance of rheotactic pelagic species like the Northern krill ( Meganyctiphanes norvegica, Crustacea) or small fishes ( Gasterosteus aculeatus) under experimental conditions.
-
Finfgeld-Connett, Deborah; Johnson, E Diane
2013-01-01
To report literature search strategies for the purpose of conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Qualitative systematic reviews lie on a continuum from knowledge-building and theory-generating to aggregating and summarizing. Different types of literature searches are needed to optimally support these dissimilar reviews. Articles published between 1989-Autumn 2011. These documents were identified using a hermeneutic approach and multiple literature search strategies. Redundancy is not the sole measure of validity when conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating systematic reviews. When conducting these types of reviews, literature searches should be consistent with the goal of fully explicating concepts and the interrelationships among them. To accomplish this objective, a 'berry picking' approach is recommended along with strategies for overcoming barriers to finding qualitative research reports. To enhance integrity of knowledge-building and theory-generating systematic reviews, reviewers are urged to make literature search processes as transparent as possible, despite their complexity. This includes fully explaining and rationalizing what databases were used and how they were searched. It also means describing how literature tracking was conducted and grey literature was searched. In the end, the decision to cease searching also needs to be fully explained and rationalized. Predetermined linear search strategies are unlikely to generate search results that are adequate for purposes of conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Instead, it is recommended that iterative search strategies take shape as reviews evolve. © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
-
Current status of NPP generation IV
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yohanes Dwi Anggoro; Dharu Dewi; Nurlaila; Arief Tris Yuliyanto
2013-01-01
Today development of nuclear technology has reached the stage of research and development of Generation IV nuclear power plants (advanced reactor systems) which is an innovative development from the previous generation of nuclear power plants. There are six types of power generation IV reactors, namely: Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR), Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR), Gas-cooled Fast Reactor (GFR), Lead-cooled Fast Reactor (LFR), Molten Salt Reactor (MSR), and Super Critical Water-cooled Reactor (SCWR). The purpose of this study is to know the development of Generation IV nuclear power plants that have been done by the thirteen countries that are members of the Gen IV International Forum (GIF). The method used is review study and refers to various studies related to the current status of research and development of generation IV nuclear power. The result of this study showed that the systems and technology on Generation IV nuclear power plants offer significant advances in sustainability, safety and reliability, economics, and proliferation resistance and physical protection. In addition, based on the research and development experience is estimated that: SFR can be used optimally in 2015, VHTR in 2020, while NPP types GFR, LFR, MSR, and SCWR in 2025. Utilization of NPP generation IV said to be optimal if fulfill the goal of NPP generation IV, such as: capable to generate energy sustainability and promote long-term availability of nuclear fuel, minimize nuclear waste and reduce the long term stewardship burden, has an advantage in the field of safety and reliability compared to the previous generation of NPP and VHTR technology have a good prospects in Indonesia. (author)
-
An Experimental Study on the Darrieus-Savonius Turbine for the Tidal Current Power Generation
Kyozuka, Yusaku
The Darrieus turbine is popular for tidal current power generation in Japan. It is simple in structure with straight wings rotating around a vertical axis, so that it has no directionality against the motion of tidal flow which changes its direction twice a day. However, there is one defect in the Darrieus turbine; its small starting torque. Once it stops, a Darrieus turbine is hard to re-start until a fairly fast current is exerted on it. To improve the starting torque of the Darrieus turbine used for tidal power generation, a hybrid turbine, composed of a Darrieus turbine and a Savonius rotor is proposed. Hydrodynamic characteristics of a semi-circular section used for the Savonius bucket were measured in a wind tunnel. The torque of a two bucket Savonius rotor was measured in a circulating water channel, where four different configurations of the bucket were compared. A combined Darrieus and Savonius turbine was tested in the circulating water channel, where the effect of the attaching angle between Darrieus wing and Savonius rotor was studied. Finally, power generation experiments using a 48 pole electric generator were conducted in a towing tank and the power coefficients were compared with the results of experiments obtained in the circulating water channel.
-
Current amplification models of sensorineurall and conductive hearing loss
Ostojić, Sanja; Mikić, Branka; Mirić, Danica
2012-01-01
The main function of a hearing aid is to improve auditory and language abilities of hearing impaired users. The amplification model has to be adapted according to age, degree and type of hearing loss. The goal of this paper is to analyze the current amplification models of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss which can provide a high quality of speech perception and sounds at any degree of hearing loss. The BAHA is a surgically implantable system for treatment of conductive hearing loss ...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Raj Senani
2014-06-01
Full Text Available It has been shown in two earlier papers published from this study that corresponding to a given single-operational trans-conductance amplifier (single-OTA-RC and dual-OTA-RC sinusoidal oscillators, there are three other structurally distinct equivalent forms having the same characteristic equation, one of which employs both grounded capacitors (GC. In this study, an earlier nullor-based theory of generating equivalent op-amp oscillator circuits, proposed by the first author, is extended to derive equivalent OTA-RC circuits which discloses the existence of an additional number of equivalent forms for the same given OTA-RC oscillators than those predicted by the quoted earlier works, and thereby considerably enlarging the set of equivalents of a given OTA-RC oscillator. Furthermore, the presented nullor-based theory of generating equivalent OTA-RC oscillators results in three additional interesting outcomes: (i the revelation that corresponding to any given OTA-RC oscillator there are two ‘both-GC’ oscillators (and not merely one, as derived in the quoted earlier works; (ii the availability of explicit current outputs in several of the derived equivalents and (iii the realisability explicit-current-output ‘quadrature oscillators’ in some of the generated equivalent oscillators. The workability of the generated equivalent OTA-RC oscillators has been verified by SPICE simulations, based on CMOS OTAs using 0.18 µm CMOS technology process parameters, and some sample results are given.
-
Study of non inductive current generation in a plasma
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rax, J.M.
1987-01-01
The problem of non-thermal bremsstrahlung during lower hybrid current drive is considered. The proposed method shows the role of the Compton effects at low frequencies and allows us to establish the link between the emitted power and the absorbed power at high frequency. The non-thermal emission is considered as a kinematical mode conversion between the absorbed radio-frequency mode and the emitted X ray photons. The fast electrons diagnostics and the ways to reach the wave structure are shown. Kinetic and electromagnetic problems concerning current generation are described. The plasma properties and diagnostics in the case of a non inductive current generation are discussed [fr
-
Study of runaway current generation following disruptions in KSTAR
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen, Z Y; Kim, W C; Yu, Y W; England, A C; Yoo, J W; Hahn, S H; Yoon, S W; Lee, K D; Oh, Y K; Kwak, J G; Kwon, M
2013-01-01
The high fraction of runaway current conversion following disruptions has an important effect on the first wall for next-generation tokamaks. Because of the potentially severe consequences of a large full current runaway beam on the first wall in an unmitigated disruption, runaway suppression is given a high priority. The behavior of runaway currents both in spontaneous disruptions and in D 2 massive gas injection (MGI) shutdown experiments is investigated in the KSTAR tokamak. The experiments in KSTAR show that the toroidal magnetic field threshold, B T >2 T, for runaway generation is not absolute. A high fraction of runaway current conversion following spontaneous disruptions is observed at a much lower toroidal magnetic field of B T = 1.3 T. A dedicated fast valve for high-pressure gas injection with 39.7 bar is developed for the study of disruptions. A study of runaway current parameters shows that the conversion efficiency of pre-disruptive plasma currents into runaway current can reach over 80% both in spontaneous disruptions and in D 2 MGI shutdown experiments in KSTAR. (paper)
-
The low-current low-temperature plasma generators
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dautov, G.Yu.
2000-01-01
In this article, the results of low-current gas-discharge plasma generator investigations carried out by a group of scientists from the Kazan' Aviation Institute are presented. When considered necessary, the results are compared with the data obtained by other authors. The basic configurations and theoretical calculation peculiarities of plasma generators are described. The electrical, thermal and energy characteristics of discharges in gas flows, as well as summarised empirical formulae and experimental data necessary for calculations and design of plasma devices are presented. (author)
-
Characteristics of alternating current hopping conductivity in DNA sequences
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
Ma Song-Shan; Xu Hui; Wang Huan-You; Guo Rui
2009-01-01
This paper presents a model to describe alternating current (AC) conductivity of DNA sequences,in which DNA is considered as a one-dimensional (1D) disordered system,and electrons transport via hopping between localized states.It finds that AC conductivity in DNA sequences increases as the frequency of the external electric field rises,and it takes the form of σac(ω)~ω2 ln2(1/ω).Also AC conductivity of DNA sequences increases with the increase of temperature,this phenomenon presents characteristics of weak temperature-dependence.Meanwhile,the AC conductivity in an off diagonally correlated case is much larger than that in the uncorrelated case of the Anderson limit in low temperatures,which indicates that the off-diagonal correlations in DNA sequences have a great effect on the AC conductivity,while at high temperature the off-diagonal correlations no longer play a vital role in electric transport. In addition,the proportion of nucleotide pairs p also plays an important role in AC electron transport of DNA sequences.For p<0.5,the conductivity of DNA sequence decreases with the increase of p,while for p > 0.5,the conductivity increases with the increase of p.
-
Generation of stationary current in a tokamak by electron cyclotron waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Parail, V.V.; Pereverzev, G.V.
1982-01-01
Analytical expression for stationary longitudinal current generated in plasma with electron-cyclotron (EC) waves has been derived on the basis of a kinetic equation for electrons with provision for electron-electron and electron- ion collisions. Comparative analysis of efficiency of current excitation with EC and low hybrid (LH) waves has been carried out. It is shown that under similar conditions (for the same introduced powers and the same intervals of interaction of LH waves and electrons) the current value generated with LH waves turns out to be functionally (Vsub(o)/Vsub(e))sup(2) times higher as compared with the current generated with EC waves (vsub(o)-initial velocity of electrons, Vsub(e)-√2Tsub(e)/m) [ru
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shamirzaev, S.Kh.; Dadamirzaev, M.G.; Gulyamov, G.; Gulyamov, A.G.
2009-01-01
Current generated in semiconductor diode that is in variable field is shown to define only by convection current, but the average value of displacement current is always zero and has not influence on current, outgoing from diode. This conclusion explains an origin of generated currents in different diode in electromagnetic field. The formula is found out allowing one to calculate the diode current with any nonlinear feature. (authors)
-
Bow Shock Generator Current Systems: MMS Observations of Possible Current Closure
Hamrin, M.; Gunell, H.; Lindkvist, J.; Lindqvist, P.-A.; Ergun, R. E.; Giles, B. L.
2018-01-01
We use data from the first two dayside seasons of the Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission to study current systems associated with quasi-perpendicular bow shocks of generator type. We have analyzed 154 MMS bow shock crossings near the equatorial plane. We compute the current density during the crossings and conclude that the component perpendicular to the shock normal (J⊥) is consistent with a pileup of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) inside the magnetosheath. For predominantly southward IMF, we observe a component Jn parallel (antiparallel) to the normal for GSM Y > 0 (MMS probing region. For IMF clock angles near 90∘, we find indications of the current system being tilted toward the north-south direction, obtaining a significant Jz component, and we suggest that the current closes off the equatorial plane at higher latitudes where the spacecraft are not probing. The observations are complicated for several reasons. For example, variations in the solar wind and the magnetospheric currents and loads affect the closure, and Jn is distributed over large regions, making it difficult to resolve inside the magnetosheath proper.
-
Alternating-current MHD conduction pump for ferrous metals
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nadezhnikov, N.M.; Krauya, V.M.; Yankop, E.K.
1979-01-01
Results are presented of theoretical and experimental studies pertaining to an ac MHD conduction pump with separate excitation and a C-core magnet structure. Its mathematical model is based on the following assumptions: (1) During complete braking the liquid metal in the channel is stationary; (2) there is no current leakage in the channel beyond the interelectrode region; (3) during operation the longitudinal axis of the pump is in a vertical position; (4) the current density in the electrodes at a distance infinitely far from the active channel segment is uniformly distributed; (5) there are no magnetic leakage fluxes in the model; and (6) the left-hand electrode in the model can be brought out in two different ways, variant I or variant II. 7 references
-
Characteristics of alternating current hopping conductivity in DNA sequences
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Song-Shan, Ma; Hui, Xu; Huan-You, Wang; Rui, Guo
2009-01-01
This paper presents a model to describe alternating current (AC) conductivity of DNA sequences, in which DNA is considered as a one-dimensional (1D) disordered system, and electrons transport via hopping between localized states. It finds that AC conductivity in DNA sequences increases as the frequency of the external electric field rises, and it takes the form of ø ac (ω) ∼ ω 2 ln 2 (1/ω). Also AC conductivity of DNA sequences increases with the increase of temperature, this phenomenon presents characteristics of weak temperature-dependence. Meanwhile, the AC conductivity in an off-diagonally correlated case is much larger than that in the uncorrelated case of the Anderson limit in low temperatures, which indicates that the off-diagonal correlations in DNA sequences have a great effect on the AC conductivity, while at high temperature the off-diagonal correlations no longer play a vital role in electric transport. In addition, the proportion of nucleotide pairs p also plays an important role in AC electron transport of DNA sequences. For p < 0.5, the conductivity of DNA sequence decreases with the increase of p, while for p ≥ 0.5, the conductivity increases with the increase of p. (cross-disciplinary physics and related areas of science and technology)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kapron, H.
1976-01-01
The investigations of pulsation in the MHD generators are described. The influence of termodynamic parameters pulsation on electric parameters of the MHD generator is presented using the method of little disturbances. The results of this investigation are formulas for momentary and average values of: electrical conductivity, the Hall parameter, current density and intensity of electrical field. Analitical investigations were verified by the experiments. (author)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Murugaiah, Anand [Momentive Performance Materials Quartz, Inc., Strongsville, OH (United States)
2016-12-30
The objective of this program is to generate novel LED package designs that would provide 30% improvement in lumen/$ output. This was to be achieved by improving thermal management in encapsulants/ phosphors to reduce their temperatures. Currently, the heat that is generated during down conversion of blue light to longer wavelengths by the phosphors dispersed in the encapsulant does not have optimum thermal pathways for dissipation due to poor thermal conductivity of the encapsulant material. Additionally, high temperature in the encapsulant during operation is one of the primary failure modes in LED luminaires resulting in much shorter than expected life. The thermal issues manifest in color instability (yellowing, browning), cracking and hot spots in the encapsulant leading to failures. This work explored boron nitride (hBN) as thermal fillers in encapsulants to improve thermal conductivity while minimally impacting optical properties. Various approaches to Boron Nitride (BN) were evaluated and over 380 samples were generated to down select appropriate BN morphologies. We developed a range or BN materials for enabling thermal properties while attempting to minimally impact to optical properties.
-
Thermoelectric Generation Of Current – Theoretical And Experimental Analysis
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ruciński Adam
2017-12-01
Full Text Available This paper provides some information about thermoelectric technology. Some new materials with improved figures of merit are presented. These materials in Peltier modules make it possible to generate electric current thanks to a temperature difference. The paper indicates possible applications of thermoelectric modules as interesting tools for using various waste heat sources. Some zero-dimensional equations describing the conditions of electric power generation are given. Also, operating parameters of Peltier modules, such as voltage and electric current, are analyzed. The paper shows chosen characteristics of power generation parameters. Then, an experimental stand for ongoing research and experimental measurements are described. The authors consider the resistance of a receiver placed in the electric circuit with thermoelectric elements. Finally, both the analysis of experimental results and conclusions drawn from theoretical findings are presented. Voltage generation of about 1.5 to 2.5 V for the temperature difference from 65 to 85 K was observed when a bismuth telluride thermoelectric couple (traditionally used in cooling technology was used.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shen, Y.; Lo, C. C. H.; Frishman, A. M.; Lee, C.; Nakagawa, N.
2007-01-01
This paper describes an eddy current model-based method for inverting near-surface conductivity deviation profiles of surface treated materials from swept-high frequency eddy current (SHFEC) data. This work forms part of our current research directed towards the development of an electromagnetic nondestructive technique for assessing residual stress of shot-peened superalloy components. The inversion procedure is based on the use of a parameterized function to describe the near-surface conductivity as a function of depth for a shot-peened surface, and the laterally uniform multi-layer theory of Cheng, Dodd and Deeds to calculate the resulting coil impedance deviations. The convergence of the inversion procedure has been tested against synthesized eddy current data. As a demonstration, the conductivity deviation profiles of a series of Inconel 718 specimens, shot peened at various Almen intensities, have been obtained by inversion. Several consistency tests were conducted to examine the reliability of the inverted conductivity profiles. The results show that conductivity deviation profiles can be reliably determined from SHFEC data within the accuracy of the current measurement system
-
Analysis of non-destructive current simulators of flux compression generators.
O'Connor, K A; Curry, R D
2014-06-01
Development and evaluation of power conditioning systems and high power microwave components often used with flux compression generators (FCGs) requires repeated testing and characterization. In an effort to minimize the cost and time required for testing with explosive generators, non-destructive simulators of an FCG's output current have been developed. Flux compression generators and simulators of FCGs are unique pulsed power sources in that the current waveform exhibits a quasi-exponential increasing rate at which the current rises. Accurately reproducing the quasi-exponential current waveform of a FCG can be important in designing electroexplosive opening switches and other power conditioning components that are dependent on the integral of current action and the rate of energy dissipation. Three versions of FCG simulators have been developed that include an inductive network with decreasing impedance in time. A primary difference between these simulators is the voltage source driving them. It is shown that a capacitor-inductor-capacitor network driving a constant or decreasing inductive load can produce the desired high-order derivatives of the load current to replicate a quasi-exponential waveform. The operation of the FCG simulators is reviewed and described mathematically for the first time to aid in the design of new simulators. Experimental and calculated results of two recent simulators are reported with recommendations for future designs.
-
Modeling, Simulation, and Experiment of Switched Reluctance Ocean Current Generator System
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hao Chen
2013-01-01
Full Text Available This paper presents nonlinear simulation model of switched reluctance (SR ocean current generator system on MATLAB/SIMULINK with describing the structure of generator system. The developed model is made up of main model, rotor position calculation module, controller module, gate module, power converter module, phase windings module, flux-linkage module, torque module, and power calculation module. The magnetization curves obtained by two-dimensional finite-element electromagnetic field calculation and the conjugated magnetic energy graphics obtained from the three-dimensional graphics of flux linkage are stored in the “Lookup Table” modules on MATLAB/SIMULINK. The hardware of the developed three-phase 12/8 structure SR ocean current generator system prototype with the experimental platform is presented. The simulation of the prototype is performed by the developed models, and the experiments have been carried out under the same condition with different output power, turn-off angle, and rotor speed. The simulated phase current waveforms agree well with the tested phase current waveforms experimentally. The simulated output voltage curves agree well with the tested output voltage curves experimentally. It is shown that the developed nonlinear simulation model of the three-phase 12/8 structure SR ocean current generator system is valid.
-
Small-Size High-Current Generators for X-Ray Backlighting
Chaikovsky, S. A.; Artyomov, A. P.; Zharova, N. V.; Zhigalin, A. S.; Lavrinovich, I. V.; Oreshkin, V. I.; Ratakhin, N. A.; Rousskikh, A. G.; Fedunin, A. V.; Fedushchak, V. F.; Erfort, A. A.
2017-12-01
The paper deals with the soft X-ray backlighting based on the X-pinch as a powerful tool for physical studies of fast processes. Proposed are the unique small-size pulsed power generators operating as a low-inductance capacitor bank. These pulse generators provide the X-pinch-based soft X-ray source (hν = 1-10 keV) of micron size at 2-3 ns pulse duration. The small size and weight of pulse generators allow them to be transported to any laboratory for conducting X-ray backlighting of test objects with micron space resolution and nanosecond exposure time. These generators also allow creating synchronized multi-frame radiographic complexes with frame delay variation in a broad range.
-
Current distribution and conductance quantization in the integer quantum Hall regime
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cresti, Alessandro; Farchioni, Riccardo; Grosso, Giuseppe; Parravicini, Giuseppe Pastori
2003-01-01
Charge transport of a two-dimensional electron gas in the presence of a magnetic field is studied by means of the Keldysh-Green function formalism and the tight-binding method. We evaluate the spatial distributions of persistent (equilibrium) and transport (nonequilibrium) currents, and give a vivid picture of their profiles. In the quantum Hall regime, we find exact conductance quantization both for persistent currents and for transport currents, even in the presence of impurity scattering centres and moderate disorder. (letter to the editor)
-
Current distribution and conductance quantization in the integer quantum Hall regime
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cresti, Alessandro [NEST-INFM and Dipartimento di Fisica ' E Fermi' , Universita di Pisa, via F Buonarroti 2, I-56127 Pisa (Italy); Farchioni, Riccardo [NEST-INFM and Dipartimento di Fisica ' E Fermi' , Universita di Pisa, via F Buonarroti 2, I-56127 Pisa (Italy); Grosso, Giuseppe [NEST-INFM and Dipartimento di Fisica ' E Fermi' , Universita di Pisa, via F Buonarroti 2, I-56127 Pisa (Italy); Parravicini, Giuseppe Pastori [NEST-INFM and Dipartimento di Fisica ' A Volta' , Universita di Pavia, via A Bassi 6, I-27100 Pavia (Italy)
2003-06-25
Charge transport of a two-dimensional electron gas in the presence of a magnetic field is studied by means of the Keldysh-Green function formalism and the tight-binding method. We evaluate the spatial distributions of persistent (equilibrium) and transport (nonequilibrium) currents, and give a vivid picture of their profiles. In the quantum Hall regime, we find exact conductance quantization both for persistent currents and for transport currents, even in the presence of impurity scattering centres and moderate disorder. (letter to the editor)
-
Escape of protists in predator-generated feeding currents
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Jakobsen, Hans Henrik
2002-01-01
The ciliate Strobilidium sp. and 2 flagellates, Chrysochromulina simplex and Gymnodinium sp., were exposed to predator-generated feeding currents, and their escape responses were quantified using 2- and 3-dimensional video techniques. All 3 studied organisms responded by escaping at a defined dis...
-
Evaluation of Current Controllers for Distributed Power Generation Systems
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Timbus, Adrian; Liserre, Marco; Teodorescu, Remus
2009-01-01
This paper discusses the evaluation of different current controllers employed for grid-connected distributed power generation systems having variable input power, such as wind turbines and photovoltaic systems. The focus is mainly set on linear controllers such as proportional-integral, proportio......This paper discusses the evaluation of different current controllers employed for grid-connected distributed power generation systems having variable input power, such as wind turbines and photovoltaic systems. The focus is mainly set on linear controllers such as proportional......-integral, proportional-resonant, and deadbeat (DB) controllers. Additionally, an improved DB controller robust against grid impedance variation is also presented. Since the paper discusses the implementation of these controllers for grid-connected applications, their evaluation is made in three operating conditions....... First, in steady-state conditions, the contribution of controllers to the total harmonic distortion of the grid current is pursued. Further on, the behavior of controllers in the case of transient conditions like input power variations and grid voltage faults is also examined. Experimental results...
-
Tethered by Self-Generated Flow: Mucus String Augmented Feeding Current Generation in Larval Oysters
Jiang, H.; Wheeler, J.; Anderson, E.
2016-02-01
Marine zooplankton live in a nutritionally dilute environment. To survive, they must process an enormous volume of water relative to their own body volume for food. To achieve this, many zooplankters including copepods, invertebrate larvae, and protists create a feeding current to concentrate and transport food items to their food gathering structures. To enhance the efficiency of the feeding current, these zooplankters often rely on certain "tethering" mechanisms to retard their translational motion for producing a strong feeding current. The tethering force may include excess weight due to gravity, force from attachment to solid surfaces, and drag experienced by strategically placed morphological structures. Larval oysters are known from previous studies to release mucus strings during feeding, presumably for supplying a tethering force to enhance their feeding-current efficiency. But the underlying mechanism is unclear. In this study, we used a high-speed microscale imaging system (HSMIS) to observe the behavior of freely swimming and feeding larval oysters. We also used HSMIS to measure larval imposed feeding currents via a micro-particle image velocimetry (µPIV) technique. HSMIS allows observations along a vertically oriented focal plane in a relatively large water vessel with unprecedented spatial and temporal resolutions. Our high-speed videos show that a feeding larval oyster continuously released a long mucus string into its feeding current that flows downward; the feeding current subsequently dragged the mucus string downward. Analysis of our µPIV data combined with a hydrodynamic model further suggests that the drag force experienced by the mucus string in the feeding current contributes significantly to the tethering force required to generate the feeding current. Thus, mucus strings in larval oysters act as "anchors" in larval self-generated flow to actively tether the feeding larvae.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
David M Fox
2017-06-01
Full Text Available Neuronal membrane potential resonance (MPR is associated with subthreshold and network oscillations. A number of voltage-gated ionic currents can contribute to the generation or amplification of MPR, but how the interaction of these currents with linear currents contributes to MPR is not well understood. We explored this in the pacemaker PD neurons of the crab pyloric network. The PD neuron MPR is sensitive to blockers of H- (IH and calcium-currents (ICa. We used the impedance profile of the biological PD neuron, measured in voltage clamp, to constrain parameter values of a conductance-based model using a genetic algorithm and obtained many optimal parameter combinations. Unlike most cases of MPR, in these optimal models, the values of resonant- (fres and phasonant- (fϕ = 0 frequencies were almost identical. Taking advantage of this fact, we linked the peak phase of ionic currents to their amplitude, in order to provide a mechanistic explanation the dependence of MPR on the ICa gating variable time constants. Additionally, we found that distinct pairwise correlations between ICa parameters contributed to the maintenance of fres and resonance power (QZ. Measurements of the PD neuron MPR at more hyperpolarized voltages resulted in a reduction of fres but no change in QZ. Constraining the optimal models using these data unmasked a positive correlation between the maximal conductances of IH and ICa. Thus, although IH is not necessary for MPR in this neuron type, it contributes indirectly by constraining the parameters of ICa.
-
Methodological Approaches in Conducting Overviews: Current State in HTA Agencies
Pieper, Dawid; Antoine, Sunya-Lee; Morfeld, Jana-Carina; Mathes, Tim; Eikermann, Michaela
2014-01-01
Objectives: Overviews search for reviews rather than for primary studies. They might have the potential to support decision making within a shorter time frame by reducing production time. We aimed to summarize available instructions for authors intending to conduct overviews as well as the currently applied methodology of overviews in…
-
Stator Current Harmonic Reduction in a Novel Half Quasi-Z-Source Wind Power Generation System
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Shoudao Huang
2016-09-01
Full Text Available The generator stator current gets distorted with unacceptable levels of total harmonic distortion (THD because impedance-source wind power generation systems use three-phase diode rectifiers. The stator current harmonics will cause increasing losses and torque ripple, which reduce the efficiency and stability of the system. This paper proposes a novel half quasi-Z-source inverter (H-qZSI for grid-connected wind power generation systems, which can reduce the generator stator current harmonics a great deal. When H-qZSI operates in the shoot-through zero state, the derivative of the generator stator current is only determined by the instantaneous value of the generator stator voltage, so the nonlinear relationship between generator stator current and stator voltage is improved compared with the traditional impedance-source inverter. Theoretically, it is indicated that the stator current harmonics can be reduced effectively by means of the proposed H-qZSI. Finally, simulation and experimental results are given to verify the theoretical analysis.
-
Secondary current properties generated by wind-induced water waves in experimental conditions
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Michio Sanjou
2014-06-01
Full Text Available Secondary currents such as the Langmuir circulation are of high interest in natural rivers and the ocean because they have striking impacts on scour, sedimentation, and mass transport. Basic characteristics have been well-studied in straight open-channel flows. However, little is known regarding secondary circulation induced by wind waves. The presented study describes the generation properties of wind waves observed in the laboratory tank. Wind-induced water waves are known to produce large scale circulations. The phenomenon is observed together with high-speed and low-speed streaks, convergence and divergence zones, respectively. Therefore, it is important to determine the hydrodynamic properties of secondary currents for wind-induced water waves within rivers and lakes. In this study, using two high-speed CMOS cameras, stereoscopic particle image velocimetry (PIV measurements were conducted in order to reveal the distribution of all three components of velocity vectors. The experiments allowed us to investigate the three-dimensional turbulent structure under water waves and the generation mechanism of large-scale circulations. Additionally, a third CMOS camera was used to measure the spanwise profile of thefree-surface elevation. The time-series of velocity components and the free-surface were obtained simultaneously. From our experiments, free-surface variations were found to influence the instantaneous velocity distributions of the cross-sectional plane. We also considered thegeneration process by the phase analysis related to gravity waves and compared the contribution of the apparent stress.
-
Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Gwiazda, R.; Paull, C. K.; Talling, P.; Parsons, D. R.; Maier, K. L.; Simmons, S.; Cartigny, M.
2017-12-01
During a large turbidity current event observed by seven moorings placed along Monterey Canyon, offshore central California, in the axial channel between 300 and 1900 meters water depth, a conductivity/temperature sensor placed 11 meters above canyon floor on the mooring at 1500 meters water depth recorded a rapid decrease of conductivity and increase of temperature during the passage of a large turbidity current. The conductivity decline is unlikely caused by fresh water input owing to lack of precipitation in the region prior to the event. We investigated the mechanisms of turbidity currents' high sediment concentration reducing the measured conductivity. By conducting a series of laboratory experiments with a range of different concentrations, grain size, and water temperature combinations, we quantified a relationship between reduced conductivity and the elevated sediment concentration. This relationship can be used for estimating the very high sediment concentrations in a turbidity current with a condition of assuming constant salinity of the ambient seawater. The empirical relationship was then applied to the in-situ time-series of temperature and conductivity measured during this turbidity current. The highest sediment concentration, in the head of the flow, reached nearly 400 g/L (volume concentration 17%). Such a high value, which has yet been reported in literature for an oceanic turbidity current, will have significant implications for the dynamics and deposits of such flows.
-
Conduction mechanism of leakage current due to the traps in ZrO2 thin film
Seo, Yohan; Lee, Sangyouk; An, Ilsin; Song, Chulgi; Jeong, Heejun
2009-11-01
In this work, a metal-oxide-semiconductor capacitor with zirconium oxide (ZrO2) gate dielectric was fabricated by an atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique and the leakage current characteristics under negative bias were studied. From the result of current-voltage curves there are two possible conduction mechanisms to explain the leakage current in the ZrO2 thin film. The dominant mechanism is the space charge limited conduction in the high-electric field region (1.5-5.0 MV cm-1) while the trap-assisted tunneling due to the existence of traps is prevailed in the low-electric field region (0.8-1.5 MV cm-1). Conduction caused by the trap-assisted tunneling is found from the experimental results of a weak temperature dependence of current, and the trap barrier height is obtained. The space charge limited conduction is evidenced, for different temperatures, by Child's law dependence of current density versus voltage. Child's law dependence can be explained by considering a single discrete trapping level and we can obtain the activation energy of 0.22 eV.
-
Shikin, A. M.; Voroshin, V. Yu; Rybkin, A. G.; Kokh, K. A.; Tereshchenko, O. E.; Ishida, Y.; Kimura, A.
2018-01-01
A new kind of 2D photovoltaic effect (PVE) with the generation of anomalously large surface photovoltage up to 210 meV in magnetically doped topological insulators (TIs) has been studied by the laser time-resolved pump-probe angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy. The PVE has maximal efficiency for TIs with high occupation of the upper Dirac cone (DC) states and the Dirac point located inside the fundamental energy gap. For TIs with low occupation of the upper DC states and the Dirac point located inside the valence band the generated surface photovoltage is significantly reduced. We have shown that the observed giant PVE is related to the laser-generated electron-hole asymmetry followed by accumulation of the photoexcited electrons at the surface. It is accompanied by the 2D relaxation process with the generation of zero-bias spin-polarized currents flowing along the topological surface states (TSSs) outside the laser beam spot. As a result, the spin-polarized current generates an effective in-plane magnetic field that is experimentally confirmed by the k II-shift of the DC relative to the bottom non-spin-polarized conduction band states. The realized 2D PVE can be considered as a source for the generation of zero-bias surface spin-polarized currents and the laser-induced local surface magnetization developed in such kind 2D TSS materials.
-
Policies for second generation biofuels: current status and future challenges
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Egger, Haakan; Greaker, Mads; Potter, Emily
2011-07-01
Current state-of-the-art knowledge concludes that green house gas (GHG) emissions must be controlled and reduced within the next 30-40 years. The transport sector contributes almost a fifth of the current global emissions, and its share is likely to increase in the future. The US and a number of European countries have therefore introduced various support schemes for research and development (RandD) of low emission fuels that can potentially replace the current fossil fuels. One such alternative is biofuels. The advantage of biofuels are that it is easy to introduce into the transport sector. On the other hand, recent research papers question whether the supply of feedstock is sufficient, and to what extent biofuels lead to GHG emission reductions. This report reviews the current status of second generation biofuels. Second generation biofuels are made from cellulose, which according to our survey of the literature, is in more abundant supply than the first generation biofuels feedstocks. Furthermore, it seems to have the potential to reduce GHG emissions from the transport sector without leading to devastating land use changes, which recent critique has held against first generation biofuels. Given that governments have decided to support RandD of low emission fuels, we ask the following questions: Should second generation biofuels receive RandD support to the same extent as other low emission fuels like hydrogen? How should support schemes for second generation biofuels be designed? Second generation biofuels can be divided according to the production process into thermo-chemical and bio-chemical. With respect to the thermo-chemical process the potential for cost reductions seems to be low. On the other hand, ethanol made from cellulose using the biochemical conversion process is far from a ripe technology. Expert reports point to several potential technological breakthroughs which may reduce costs substantially. Hence, cellulosic ethanol, should receive direct
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Kiyasatfar
2011-01-01
Full Text Available In the present study, simulation of steady state, incompressible and fully developed laminar flow has been conducted in a magneto hydrodynamic (MHD pump. The governing equations are solved numerically by finite-difference method. The effect of the magnetic flux density and current on the flow and temperature distributions in a MHD pump is investigated. The obtained results showed that controlling the flow and the temperature is possible through the controlling of the applied current and the magnetic flux. Furthermore, the effects of the magnetic flux density and current on entropy generation in MHD pump are considered. Our presented numerical results are in good agreement with the experimental data showed in literature.
-
Low-induction pulse current generator with a volume bus arrangement
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bocharov, Yu.N.; Krivosheev, S.I.; Lapin, N.G.; Shneerson, G.A.
1993-01-01
Pulse current generator (PC6) with 38 kj stored energy designed for up to 50 kV charging voltage used to obtain magnetic fields within megagauss range, is described. Space (volume) bus arrangement of its modules is used to reduce eigen inductance of PC6. Current is commutated by solid-body spark gaps. Under 3uH inductive load PC6 provides for formation of up to 2.25 MA current pulse with 3.3x10 12 A/s pulse rise time. Technique to determine low inductances as applied to PC6 elements is described. The described PC6 is used for experiments on generation of super-strong pulse magnetic fields in single-loop solenoid with volume occupied by magnetic field, 5-7 mm. Magnetic field with up to 350 T induction amplitude is obtained in these experiments
-
Microbial interspecies electron transfer via electric currents through conductive minerals
Kato, Souichiro; Hashimoto, Kazuhito; Watanabe, Kazuya
2012-01-01
In anaerobic biota, reducing equivalents (electrons) are transferred between different species of microbes [interspecies electron transfer (IET)], establishing the basis of cooperative behaviors and community functions. IET mechanisms described so far are based on diffusion of redox chemical species and/or direct contact in cell aggregates. Here, we show another possibility that IET also occurs via electric currents through natural conductive minerals. Our investigation revealed that electrically conductive magnetite nanoparticles facilitated IET from Geobacter sulfurreducens to Thiobacillus denitrificans, accomplishing acetate oxidation coupled to nitrate reduction. This two-species cooperative catabolism also occurred, albeit one order of magnitude slower, in the presence of Fe ions that worked as diffusive redox species. Semiconductive and insulating iron-oxide nanoparticles did not accelerate the cooperative catabolism. Our results suggest that microbes use conductive mineral particles as conduits of electrons, resulting in efficient IET and cooperative catabolism. Furthermore, such natural mineral conduits are considered to provide ecological advantages for users, because their investments in IET can be reduced. Given that conductive minerals are ubiquitously and abundantly present in nature, electric interactions between microbes and conductive minerals may contribute greatly to the coupling of biogeochemical reactions. PMID:22665802
-
Measuring electric conductivity in liquid metals by eddy current method
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zhuravlev, S.P.; Ostrovskij, O.I.; Grigoryan, V.A.
1982-01-01
Technique permitting to apply the method of vertiginous currents for investigation of electric conductivity of metal melts in the high temperature range is presented. Interferences affecting accuracy of measurements are specified and ways of their removing are pointed out. Scheme of measuring and design of the facility are described. Results of measuring electric resistance of liquid Fe, Co, Ni obtained for the first time by this method are presented. The data obtained agree with the results of measurements conducted by the method of the rotating magnetic field. Difference in absolute values of electric resistance in parallel experiments for each metal does not exceed 4%
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dolgachev, G.I.; Maslennikov, D.D.; Ushakov, A.G.
2006-01-01
Paper deals with a phenomenon of current breaking in a conducting plasma volume of plasma opening switchers with a nanosecond time of energy initiation and their application in high-power generators. One determined the conditions to ensure megavolt voltages under the erosion mode making use of external applied magnetic field to ensure magnetic insulation of gap of plasma opening switchers. One studied the peculiar features of application of plasma opening switchers under 5-6 MV voltages to ensure X-ray and gamma-radiation pulses [ru
-
Methods of high current magnetic field generator for transcranial magnetic stimulation application
Bouda, N. R.; Pritchard, J.; Weber, R. J.; Mina, M.
2015-05-01
This paper describes the design procedures and underlying concepts of a novel High Current Magnetic Field Generator (HCMFG) with adjustable pulse width for transcranial magnetic stimulation applications. This is achieved by utilizing two different switching devices, the MOSFET and insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT). Results indicate that currents as high as ±1200 A can be generated with inputs of +/-20 V. Special attention to tradeoffs between field generators utilizing IGBT circuits (HCMFG1) and MOSFET circuits (HCMFG2) was considered. The theory of operation, design, experimental results, and electronic setup are presented and analyzed.
-
Inverse anisotropic conductivity from internal current densities
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bal, Guillaume; Guo, Chenxi; Monard, François
2014-01-01
This paper concerns the reconstruction of a fully anisotropic conductivity tensor γ from internal current densities of the form J = γ∇u, where u solves a second-order elliptic equation ∇ · (γ∇u) = 0 on a bounded domain X with prescribed boundary conditions. A minimum number of n + 2 such functionals known on Y⊂X, where n is the spatial dimension, is sufficient to guarantee a unique and explicit reconstruction of γ locally on Y. Moreover, we show that γ is reconstructed with a loss of one derivative compared to errors in the measurement of J in the general case and no loss of derivatives in the special case where γ is scalar. We also describe linear combinations of mixed partial derivatives of γ that exhibit better stability properties and hence can be reconstructed with better resolution in practice. (paper)
-
Study of the generation and suppression of runaway currents in provoked disruptions in J-TEXT
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Chen, Z.Y., E-mail: zychen@mail.hust.edu.cn [State Key Laboratory of Advanced Electromagnetic Engineering and Technology, College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 (China); Chen, Z.P., E-mail: zpchen@mail.hust.edu.cn [State Key Laboratory of Advanced Electromagnetic Engineering and Technology, College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 (China); Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Fang, D.; Ba, W.G.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.J.; Ding, Y.H.; Zhuang, G. [State Key Laboratory of Advanced Electromagnetic Engineering and Technology, College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 (China)
2012-05-14
Runaway currents following disruptions have an important effect on the first wall for the next generation tokamak. The behaviors of runaway currents following intentional provoked disruptions have been investigated in the J-TEXT tokamak. It is found that the runaway current generation following provoked disruptions depends on both the toroidal magnetic field and the plasma current. The conversion efficiency of pre-disruptive plasma currents into runaway currents is in the ranges of 30% to 60% in J-TEXT. The runaway currents can be avoided by the intensive gas puffing of H{sub 2} due to the low multiplication factor in J-TEXT. -- Highlights: ► The regime of runaway generation in disruptions in J-TEXT has been established. ► The magnetic field threshold for runaway current generation in disruptions is 2.2 T. ► The conversion efficiency of runaway current is in the ranges of 30% to 60%. ► The runaway currents can be avoided by the intensive gas puffing of H{sub 2}.
-
Study of the generation and suppression of runaway currents in provoked disruptions in J-TEXT
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Fang, D.; Ba, W.G.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.J.; Ding, Y.H.; Zhuang, G.
2012-01-01
Runaway currents following disruptions have an important effect on the first wall for the next generation tokamak. The behaviors of runaway currents following intentional provoked disruptions have been investigated in the J-TEXT tokamak. It is found that the runaway current generation following provoked disruptions depends on both the toroidal magnetic field and the plasma current. The conversion efficiency of pre-disruptive plasma currents into runaway currents is in the ranges of 30% to 60% in J-TEXT. The runaway currents can be avoided by the intensive gas puffing of H 2 due to the low multiplication factor in J-TEXT. -- Highlights: ► The regime of runaway generation in disruptions in J-TEXT has been established. ► The magnetic field threshold for runaway current generation in disruptions is 2.2 T. ► The conversion efficiency of runaway current is in the ranges of 30% to 60%. ► The runaway currents can be avoided by the intensive gas puffing of H 2 .
-
RF current generation near the ion cyclotron frequency
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Watkins, J.G.
1982-01-01
An experiment has been conducted to measure unipolar currents driven by directional radio frequency waves in a cylindrical plasma mirror machine near the ion cyclotron frequency. The directional waves were launched using a four phase helical coupler which allowed the selection of both azimuthal mode number (m = +1) and direction of wave propagation. Plasma diagnostics include electron density measurements (4 mm microwave interferometer), electron temperature measurements (floating double probe), wave amplitude and coupling measurements (magnetic probes). RF power measurements (RF voltage and current probes) and RF driven plasma current measurements (Rogowski loops and current transformers). End electrodes provided a necessary external return path and an alternate method for measuring the current. Theoretical work includes an analytic approximation to the nonlinear problem of a particle in a traveling wave and computer simulations that extend this result. Nonlinear particle drifts other than trapping were found both with and without the presence of particle collisions
-
Chauhan, Munish; Vidya Shankar, Rohini; Ashok Kumar, Neeta; Kodibagkar, Vikram D; Sadleir, Rosalind
2018-01-01
Magnetic resonance electrical impedance tomography (MREIT) sequences typically use conventional spin or gradient echo-based acquisition methods for reconstruction of conductivity and current density maps. Use of MREIT in functional and electroporation studies requires higher temporal resolution and faster sequences. Here, single and multishot echo planar imaging (EPI) based MREIT sequences were evaluated to see whether high-quality MREIT phase data could be obtained for rapid reconstruction of current density, conductivity, and electric fields. A gel phantom with an insulating inclusion was used as a test object. Ghost artifact, geometric distortion, and MREIT correction algorithms were applied to the data. The EPI-MREIT-derived phase-projected current density and conductivity images were compared with simulations and spin-echo images as a function of EPI shot number. Good agreement among measures in simulated, spin echo, and EPI data was achieved. Current density errors were stable and below 9% as the shot number decreased from 64 to 2, but increased for single-shot images. Conductivity reconstruction relative contrast ratios were stable as the shot number decreased. The derived electric fields also agreed with the simulated data. The EPI methods can be combined successfully with MREIT reconstruction algorithms to achieve fast imaging of current density, conductivity, and electric field. Magn Reson Med 79:71-82, 2018. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
-
Evaluation of the eddy-current method of inspecting steam generator tubing
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Flora, J.H.; Brown, S.D.; Weeks, J.R.
1976-01-01
The objective of this project has been to evaluate the eddy-current method of inspecting steam generator tubing by conducting a series of laboratory experiments with conventional eddy-current equipment. The experiments have involved obtaining eddy-current measurements on samples of 7/8-inch OD Inconel-600 tubing provided by the Westinghouse Nuclear Energy Systems Division. A variety of machined defects and some chemically induced flaws, such as stress corrosion cracks were fabricated in the tubing. Statistical evaluation of the data was employed to estimate the error encountered in measuring corrosion defects of various depths. It appears that the eddy-current technique can provide a reasonable measure of defect depth under certain conditions. On the other hand, the evaluation indicates that it is difficult to determine the depth of certain types of flaws with reliability and precision. Furthermore, although some defects as shallow as 10 percent of the tube wall could be detected, it was not possible to detect other types of flaws that were less than 40 percent deep even when the tube supports were not near the defects. The difficulty in detecting small volume flaws is attributed to low signal-to-noise ratio. Noise is a result of unwanted signals from test variables, such as wobble and variations in tube properties. The error in measurement of certain types of larger defects is associatedin part with test variables and also with the effects that the geometry of the defect has on the eddy-current signal patterns. The distortions in signal patterns caused by gradual wastage type defects and the poor reproducibility of signal patterns obtained from notches that represent stress corrosion cracks are described. Some developments that will rectify these detection and depth measurement problems are discussed
-
A generative modeling approach to connectivity-Electrical conduction in vascular networks
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hald, Bjørn Olav
2016-01-01
The physiology of biological structures is inherently dynamic and emerges from the interaction and assembly of large collections of small entities. The extent of coupled entities complicates modeling and increases computational load. Here, microvascular networks are used to present a novel...... to synchronize vessel tone across the vast distances within a network. We hypothesize that electrical conduction capacity is delimited by the size of vascular structures and connectivity of the network. Generation and simulation of series of dynamical models of electrical spread within vascular networks...... of different size and composition showed that (1) Conduction is enhanced in models harboring long and thin endothelial cells that couple preferentially along the longitudinal axis. (2) Conduction across a branch point depends on endothelial connectivity between branches. (3) Low connectivity sub...
-
Computer simulation of airflow through a multi-generation tracheobronchial conducting airway
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Fan, B.; Cheng, Yung-Sung; Yeh, Hsu-Chi
1995-12-01
Knowledge of airflow patterns in the human lung is important for an analysis of lung diseases and drug delivery of aerosolized medicine for medical treatment. However, very little systematic information is available on the pattern of airflow in the lung and on how this pattern affects the deposition of toxicants in the lung, and the efficacy of aerosol drug therapy. Most previous studies have only considered the airflow through a single bifurcating airway. However, the flow in a network of more than one bifurcation is more complicated due to the effect of interrelated lung generations. Because of the variation of airway geometry and flow condition from generation to generation, a single bifurcating airway cannot be taken as a representative for the others in different generations. The flow in the network varies significantly with airway generations because of a redistribution of axial momentum by the secondary flow motions. The influence of the redistribution of flow is expected in every generation. Therefore, a systematic information of the airflow through a multi-generation tracheobronchial conducting airway is needed, and it becomes the purpose of this study. This study has provided information on airflow in a lung model which is necessary to the study of the deposition of toxicants and therapeutic aerosols.
-
Computer simulation of airflow through a multi-generation tracheobronchial conducting airway
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fan, B.; Cheng, Yung-Sung; Yeh, Hsu-Chi.
1995-01-01
Knowledge of airflow patterns in the human lung is important for an analysis of lung diseases and drug delivery of aerosolized medicine for medical treatment. However, very little systematic information is available on the pattern of airflow in the lung and on how this pattern affects the deposition of toxicants in the lung, and the efficacy of aerosol drug therapy. Most previous studies have only considered the airflow through a single bifurcating airway. However, the flow in a network of more than one bifurcation is more complicated due to the effect of interrelated lung generations. Because of the variation of airway geometry and flow condition from generation to generation, a single bifurcating airway cannot be taken as a representative for the others in different generations. The flow in the network varies significantly with airway generations because of a redistribution of axial momentum by the secondary flow motions. The influence of the redistribution of flow is expected in every generation. Therefore, a systematic information of the airflow through a multi-generation tracheobronchial conducting airway is needed, and it becomes the purpose of this study. This study has provided information on airflow in a lung model which is necessary to the study of the deposition of toxicants and therapeutic aerosols
-
Electron current generated in a toroidal plasma on injection of high-energy neutrals
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kolesnichenko, Ya.I.; Reznik, S.N.
1981-01-01
Problem of generation of electron current in toroidal plasma with a high-energy ion beam produced during neutral injection has been considered. The analysis was performed on the assumption that plasma is in the regime of rare collisions (banana regime) and ion beam velocity is considerably lower than thermal velocity of plasma ions. Formulae establishing the relation between beam current and electron current have been derived. It follows from them that toroidal affect considerably plasma current generated with the beam and under certain conditions result in changing this current direction in an area remoted from magne-- tic axis [ru
-
Modeling of the Direct Current Generator Including the Magnetic Saturation and Temperature Effects
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Alfonso J. Mercado-Samur
2013-11-01
Full Text Available In this paper the inclusion of temperature effect on the field resistance on the direct current generator model DC1A, which is valid to stability studies is proposed. First, the linear generator model is presented, after the effect of magnetic saturation and the change in the resistance value due to temperature produced by the field current are included. The comparison of experimental results and model simulations to validate the model is used. A direct current generator model which is a better representation of the generator is obtained. Visual comparison between simulations and experimental results shows the success of the proposed model, because it presents the lowest error of the compared models. The accuracy of the proposed model is observed via Modified Normalized Sum of Squared Errors index equal to 3.8979%.
-
Methods of high current magnetic field generator for transcranial magnetic stimulation application
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bouda, N. R.; Pritchard, J.; Weber, R. J.; Mina, M.
2015-01-01
This paper describes the design procedures and underlying concepts of a novel High Current Magnetic Field Generator (HCMFG) with adjustable pulse width for transcranial magnetic stimulation applications. This is achieved by utilizing two different switching devices, the MOSFET and insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT). Results indicate that currents as high as ±1200 A can be generated with inputs of +/−20 V. Special attention to tradeoffs between field generators utilizing IGBT circuits (HCMFG 1 ) and MOSFET circuits (HCMFG 2 ) was considered. The theory of operation, design, experimental results, and electronic setup are presented and analyzed
-
Methods of high current magnetic field generator for transcranial magnetic stimulation application
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bouda, N. R., E-mail: nybouda@iastate.edu; Pritchard, J.; Weber, R. J.; Mina, M. [Department of Electrical and Computer engineering, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa 50011 (United States)
2015-05-07
This paper describes the design procedures and underlying concepts of a novel High Current Magnetic Field Generator (HCMFG) with adjustable pulse width for transcranial magnetic stimulation applications. This is achieved by utilizing two different switching devices, the MOSFET and insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT). Results indicate that currents as high as ±1200 A can be generated with inputs of +/−20 V. Special attention to tradeoffs between field generators utilizing IGBT circuits (HCMFG{sub 1}) and MOSFET circuits (HCMFG{sub 2}) was considered. The theory of operation, design, experimental results, and electronic setup are presented and analyzed.
-
Conduction mechanism of leakage current due to the traps in ZrO2 thin film
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Seo, Yohan; Lee, Sangyouk; An, Ilsin; Jeong, Heejun; Song, Chulgi
2009-01-01
In this work, a metal-oxide-semiconductor capacitor with zirconium oxide (ZrO 2 ) gate dielectric was fabricated by an atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique and the leakage current characteristics under negative bias were studied. From the result of current–voltage curves there are two possible conduction mechanisms to explain the leakage current in the ZrO 2 thin film. The dominant mechanism is the space charge limited conduction in the high-electric field region (1.5–5.0 MV cm −1 ) while the trap-assisted tunneling due to the existence of traps is prevailed in the low-electric field region (0.8–1.5 MV cm −1 ). Conduction caused by the trap-assisted tunneling is found from the experimental results of a weak temperature dependence of current, and the trap barrier height is obtained. The space charge limited conduction is evidenced, for different temperatures, by Child's law dependence of current density versus voltage. Child's law dependence can be explained by considering a single discrete trapping level and we can obtain the activation energy of 0.22 eV
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Clark, R.
1989-01-01
The increasing sophistication of eddy current signal interpretation in steam generator tubing has improved capabilities, but has also made the process of analysis more complex and time consuming. Westinghouse has developed an intelligent computerised tool - the IEDA (Intelligent Eddy Current Data Analysis) system, to lighten the load on analysts. Since 1985, 44 plants have been inspected with IEDA, representing over 400,000 tubes. The system has provided a repeatability and a consistency not achieved by human operators. (U.K.)
-
Mapping return currents in laser-generated Z-pinch plasmas using proton deflectometry
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Manuel, M. J.-E.; Sinenian, N.; Seguin, F. H.; Li, C. K.; Frenje, J. A.; Rinderknecht, H. G.; Casey, D. T.; Zylstra, A. B.; Petrasso, R. D.; Beg, F. N.
2012-01-01
Dynamic return currents and electromagnetic field structure in laser-generated Z-pinch plasmas have been measured using proton deflectometry. Experiments were modeled to accurately interpret deflections observed in proton radiographs. Current flow is shown to begin on axis and migrate outwards with the expanding coronal plasma. Magnetic field strengths of ∼1 T are generated by currents that increase from ∼2 kA to ∼7 kA over the course of the laser pulse. Proton deflectometry has been demonstrated to be a practical alternative to other magnetic field diagnostics for these types of plasmas.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Blomberg, L.G.; Marklund, G.T.
1988-03-01
A numerical model for the calculation of ionospheric convection patterns from given distributions of field-aligned current and ionospheric conductivity is described. The model includes a coupling between the conductivity and the field-aligned current, so that the conductivity peaks in regions of upward current, as usually observed by measurements. The model is very flexible in that the input distributions, the field-aligned current and the conductivity, have been parameterized in a convenient way. From the primary model output, namely the ionospheric electrostatic potential (or convection) in the corotating frame, a number of other quantities can be computed. These include: the potential in a Sun-fixed frame, the distribution of ionospheric (horizontal) current, and the Joule heating in the ionosphere. This model has been used together with input data inferred from satellite measurements to calculate the high-latitude potential distribution prevailing during a particular event. The model potential variation along the satellite orbit was found to be in excellent agreement with the measured electric field. The model has also been used to study some fundamental properties of the electrodynamics of the high-latitude ionosphere. The results of these different applications of the model have been published separately. (With 23 refs.) (authors)
-
SSWL and BWL: finite element models of compressed magnetic field current generators
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tucker, T.J.; Leeman, J.E.
1976-01-01
Documentation is presented for two new computer codes modeling the behavior of compressed magnetic field current generators. Code output results for the typical generator configurations are presented and compared to experimental results. (auth)
-
Experimental observation of current generation by asymmetrical heating of ions in a tokamak plasma
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gahl, J.; Ishihara, O.; Wong, K.L.; Kristiansen, M.; Hagler, M.
1986-01-01
The first experimental observation of current generation by asymmetrical heating of ions is reported. Ions were asymmetrically heated by a unidirectional fast Alfven wave launched by a slow wave antenna inside a tokamak. Current generation was detected by measuring the asymmetry of the toroidal plasma current with probes at the top and bottom of the toroidal plasma column
-
RMS Current of a Photovoltaic Generator in Grid-Connected PV Systems: Definition and Application
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. J. Pérez
2008-01-01
Full Text Available This paper includes a definition of a new and original concept in the photovoltaic field, RMS current of a photovoltaic generator for grid-connected systems. The RMS current is very useful for calculating energy losses in cables used in a PV generator. As well, a current factor has been defined in order to simplify RMS current calculation. This factor provides an immediate (quick and easy calculation method for the RMS current that does not depend on the case particular conditions (orientation, location, etc.. RMS current and current factor values have been calculated for different locations and modules.
-
Meson exchange current (MEC) models in neutrino interaction generators
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Katori, Teppei
2015-01-01
Understanding of the so-called 2 particle-2 hole (2p-2h) effect is an urgent program in neutrino interaction physics for current and future oscillation experiments. Such processes are believed to be responsible for the event excesses observed by recent neutrino experiments. The 2p-2h effect is dominated by the meson exchange current (MEC), and is accompanied by a 2-nucleon emission from the primary vertex, instead of a single nucleon emission from the charged-current quasi-elastic (CCQE) interaction. Current and future high resolution experiments can potentially nail down this effect. For this reason, there are world wide efforts to model and implement this process in neutrino interaction simulations. In these proceedings, I would like to describe how this channel is modeled in neutrino interaction generators
-
Submerged electricity generation plane with marine current-driven motors
Dehlsen, James G.P.; Dehlsen, James B.; Fleming, Alexander
2014-07-01
An underwater apparatus for generating electric power from ocean currents and deep water tides. A submersible platform including two or more power pods, each having a rotor with fixed-pitch blades, with drivetrains housed in pressure vessels that are connected by a transverse structure providing buoyancy, which can be a wing depressor, hydrofoil, truss, or faired tube. The platform is connected to anchors on the seafloor by forward mooring lines and a vertical mooring line that restricts the depth of the device in the water column. The platform operates using passive, rather than active, depth control. The wing depressor, along with rotor drag loads, ensures the platform seeks the desired operational current velocity. The rotors are directly coupled to a hydraulic pump that drives at least one constant-speed hydraulic-motor generator set and enables hydraulic braking. A fluidic bearing decouples non-torque rotor loads to the main shaft driving the hydraulic pumps.
-
Chiral current generation in QED by longitudinal photons
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Acosta Avalo, J.L., E-mail: jlacosta@instec.cu [Instituto Superior de Tecnologías y Ciencias Aplicadas (INSTEC), Ave Salvador Allende, No. 1110, Vedado, La Habana 10400 (Cuba); Pérez Rojas, H., E-mail: hugo@icimaf.cu [Instituto de Cibernética, Matemática y Física (ICIMAF), Calle E esq 15, No. 309, Vedado, La Habana 10400 (Cuba)
2016-08-15
We report the generation of a pseudovector electric current having imbalanced chirality in an electron–positron strongly magnetized gas in QED. It propagates along the external applied magnetic field B as a chiral magnetic effect in QED. It is triggered by a perturbative electric field parallel to B, associated to a pseudovector longitudinal mode propagating along B. An electromagnetic chemical potential was introduced, but our results remain valid even when it vanishes. A nonzero fermion mass was assumed, which is usually considered vanishing in the literature. In the quantum field theory formalism at finite temperature and density, an anomaly relation for the axial current was found for a medium of massive fermions. It bears some analogy to the Adler–Bell–Jackiw anomaly. From the expression for the chiral current in terms of the photon self-energy tensor in a medium, it is obtained that electrons and positrons scattered by longitudinal photons (inside the light cone) contribute to the chiral current, as well as the to pair creation due to longitudinal photons (out of light cone). In the static limit, an electric pseudovector current is obtained in the lowest Landau level.
-
Chiral current generation in QED by longitudinal photons
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J.L. Acosta Avalo
2016-08-01
Full Text Available We report the generation of a pseudovector electric current having imbalanced chirality in an electron–positron strongly magnetized gas in QED. It propagates along the external applied magnetic field B as a chiral magnetic effect in QED. It is triggered by a perturbative electric field parallel to B, associated to a pseudovector longitudinal mode propagating along B. An electromagnetic chemical potential was introduced, but our results remain valid even when it vanishes. A nonzero fermion mass was assumed, which is usually considered vanishing in the literature. In the quantum field theory formalism at finite temperature and density, an anomaly relation for the axial current was found for a medium of massive fermions. It bears some analogy to the Adler–Bell–Jackiw anomaly. From the expression for the chiral current in terms of the photon self-energy tensor in a medium, it is obtained that electrons and positrons scattered by longitudinal photons (inside the light cone contribute to the chiral current, as well as the to pair creation due to longitudinal photons (out of light cone. In the static limit, an electric pseudovector current is obtained in the lowest Landau level.
-
Bulk electron spin polarization generated by the spin Hall current
Korenev, V. L.
2005-01-01
It is shown that the spin Hall current generates a non-equilibrium spin polarization in the interior of crystals with reduced symmetry in a way that is drastically different from the previously well-known equilibrium polarization during the spin relaxation process. The steady state spin polarization value does not depend on the strength of spin-orbit interaction offering possibility to generate relatively high spin polarization even in the case of weak spin-orbit coupling.
-
Bulk electron spin polarization generated by the spin Hall current
Korenev, V. L.
2006-07-01
It is shown that the spin Hall current generates a nonequilibrium spin polarization in the interior of crystals with reduced symmetry in a way that is drastically different from the previously well-known “equilibrium” polarization during the spin relaxation process. The steady state spin polarization value does not depend on the strength of spin-orbit interaction offering possibility to generate relatively high spin polarization even in the case of weak spin-orbit coupling.
-
High-temperature current conduction through three kinds of Schottky diodes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fei, Li; Xiao-Ling, Zhang; Yi, Duan; Xue-Song, Xie; Chang-Zhi, Lü
2009-01-01
Fundamentals of the Schottky contacts and the high-temperature current conduction through three kinds of Schottky diodes are studied. N-Si Schottky diodes, GaN Schottky diodes and AlGaN/GaN Schottky diodes are investigated by I–V–T measurements ranging from 300 to 523 K. For these Schottky diodes, a rise in temperature is accompanied with an increase in barrier height and a reduction in ideality factor. Mechanisms are suggested, including thermionic emission, field emission, trap-assisted tunnelling and so on. The most remarkable finding in the present paper is that these three kinds of Schottky diodes are revealed to have different behaviours of high-temperature reverse currents. For the n-Si Schottky diode, a rise in temperature is accompanied by an increase in reverse current. The reverse current of the GaN Schottky diode decreases first and then increases with rising temperature. The AlGaN/GaN Schottky diode has a trend opposite to that of the GaN Schottky diode, and the dominant mechanisms are the effects of the piezoelectric polarization field and variation of two-dimensional electron gas charge density. (condensed matter: electronic structure, electrical, magnetic, and optical properties)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cheng, Weiying; Komura, Ichiro
2008-01-01
A transient eddy current measurement method is presented to determine the thickness and conductivity of a conductive plate. The conductive plate is induced by an air-cored coil, the magnetic flux density along the axial is measured and the various signals corresponding to plates with different thickness and conductivity are calculated using a 3D transient eddy current simulator. Characteristic features are obtained from the transient response. A similarity-based modeling method is utilized in this study to estimate the thickness and conductivity of the conductive plate. (author)
-
Wang, Rubing; Qian, Yuting; Li, Weiwei; Zhu, Shoupu; Liu, Fengkui; Guo, Yufen; Chen, Mingliang; Li, Qi; Liu, Liwei
2018-01-01
Graphene has been widely used in the active material, conductive agent, binder or current collector for supercapacitors, due to its large specific surface area, high conductivity, and electron mobility. However, works simultaneously employing graphene as conductive agent and current collector were rarely reported. Here, we report improved activated carbon (AC) electrodes (AC@G@NiF/G) simultaneously combining chemical vapor deposition (CVD) graphene-modified nickel foams (NiF/Gs) current collectors and high quality few-layer graphene conductive additive instead of carbon black (CB). The synergistic effect of NiF/Gs and graphene additive makes the performances of AC@G@NiF/G electrodes superior to those of electrodes with CB or with nickel foam current collectors. The performances of AC@G@NiF/G electrodes show that for the few-layer graphene addition exists an optimum value around 5 wt %, rather than a larger addition of graphene, works out better. A symmetric supercapacitor assembled by AC@G@NiF/G electrodes exhibits excellent cycling stability. We attribute improved performances to graphene-enhanced conductivity of electrode materials and NiF/Gs with 3D graphene conductive network and lower oxidation, largely improving the electrical contact between active materials and current collectors. PMID:29762528
-
Wang, Rubing; Qian, Yuting; Li, Weiwei; Zhu, Shoupu; Liu, Fengkui; Guo, Yufen; Chen, Mingliang; Li, Qi; Liu, Liwei
2018-05-15
Graphene has been widely used in the active material, conductive agent, binder or current collector for supercapacitors, due to its large specific surface area, high conductivity, and electron mobility. However, works simultaneously employing graphene as conductive agent and current collector were rarely reported. Here, we report improved activated carbon (AC) electrodes (AC@G@NiF/G) simultaneously combining chemical vapor deposition (CVD) graphene-modified nickel foams (NiF/Gs) current collectors and high quality few-layer graphene conductive additive instead of carbon black (CB). The synergistic effect of NiF/Gs and graphene additive makes the performances of AC@G@NiF/G electrodes superior to those of electrodes with CB or with nickel foam current collectors. The performances of AC@G@NiF/G electrodes show that for the few-layer graphene addition exists an optimum value around 5 wt %, rather than a larger addition of graphene, works out better. A symmetric supercapacitor assembled by AC@G@NiF/G electrodes exhibits excellent cycling stability. We attribute improved performances to graphene-enhanced conductivity of electrode materials and NiF/Gs with 3D graphene conductive network and lower oxidation, largely improving the electrical contact between active materials and current collectors.
-
Watt, D.A.
1956-07-01
A current transfer system is described for transferring current between a rotating member and a co-axial stationary member. The particular area of application for the invention is in connection with homopolar generators where a low voltage and high current are generated. The current tramsfer system of the invention comprises a rotor member and a co-axial stator member wherein one of the members is shaped to provide a circumferential surface concave in section and the other member is shaped to have a peripheral portion in close proximity to the surface, whereby a liquid metal can be stably supported between the two members when they are moving relative to one another to establish an electrical conducting path between the members.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cefalas, A.C., E-mail: ccefalas@eie.gr [National Hellenic Research Foundation, Theoretical and Physical Chemistry Institute, 48 Vassileos Constantinou Avenue, Athens 11635 (Greece); Kollia, Z.; Spyropoulos-Antonakakis, N.; Gavriil, V. [National Hellenic Research Foundation, Theoretical and Physical Chemistry Institute, 48 Vassileos Constantinou Avenue, Athens 11635 (Greece); Christofilos, D.; Kourouklis, G. [Physics Division, School of Technology, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki 54124 (Greece); Semashko, V.V.; Pavlov, V. [Kazan Federal University, Institute of Physics, 18 Kremljovskaja str., Kazan 420008 (Russian Federation); Sarantopoulou, E. [National Hellenic Research Foundation, Theoretical and Physical Chemistry Institute, 48 Vassileos Constantinou Avenue, Athens 11635 (Greece); Kazan Federal University, Institute of Physics, 18 Kremljovskaja str., Kazan 420008 (Russian Federation)
2017-02-28
Highlights: • The work links the surface morphology of amorphous semiconductors with both their electric-thermal properties and current stability at the nanoscale (<1 μm). • Measured high correlation value between surface morphological spatial gradient and conductive electron energy spatial gradient or thermal gradient. • Unidirectional current stability is associated with asymmetric nanodomains along nanosize conductive paths. • Bidirectional current stability is inherent with either long conductive paths or nanosize conductive paths along symmetric nanodomains. • Conclusion: Surface design improves current stability across nanoelectonic junctions. - Abstract: A link between the morphological characteristics and the electric properties of amorphous layers is established by means of atomic, conductive, electrostatic force and thermal scanning microscopy. Using amorphous Ta{sub 2}O{sub 5} (a-Ta{sub 2}O{sub 5}) semiconductive layer, it is found that surface profile gradients (morphological gradient), are highly correlated to both the electron energy gradient of trapped electrons in interactive Coulombic sites and the thermal gradient along conductive paths and thus thermal and electric properties are correlated with surface morphology at the nanoscale. Furthermore, morphological and electron energy gradients along opposite conductive paths of electrons intrinsically impose a current stability anisotropy. For either long conductive paths (L > 1 μm) or along symmetric nanodomains, current stability for both positive and negative currents i is demonstrated. On the contrary, for short conductive paths along non-symmetric nanodomains, the set of independent variables (L, i) is spanned by two current stability/intability loci. One locus specifies a stable state for negative currents, while the other locus also describes a stable state for positive currents.
-
Bruserud, Kjersti; Haver, Sverre; Myrhaug, Dag
2018-04-01
Measured current speed data show that episodes of wind-generated inertial oscillations dominate the current conditions in parts of the northern North Sea. In order to acquire current data of sufficient duration for robust estimation of joint metocean design conditions, such as wind, waves, and currents, a simple model for episodes of wind-generated inertial oscillations is adapted for the northern North Sea. The model is validated with and compared against measured current data at one location in the northern North Sea and found to reproduce the measured maximum current speed in each episode with considerable accuracy. The comparison is further improved when a small general background current is added to the simulated maximum current speeds. Extreme values of measured and simulated current speed are estimated and found to compare well. To assess the robustness of the model and the sensitivity of current conditions from location to location, the validated model is applied at three other locations in the northern North Sea. In general, the simulated maximum current speeds are smaller than the measured, suggesting that wind-generated inertial oscillations are not as prominent at these locations and that other current conditions may be governing. Further analysis of the simulated current speed and joint distribution of wind, waves, and currents for design of offshore structures will be presented in a separate paper.
-
High performance current generator with one-picoampere resolution
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Grillo, L.; Manfredi, P.F.; Marchesini, R.
1975-01-01
A high-performance current generator for the picoampere region is presented. Although it was primarily developed as a part of an automatic test system to calibrate charge integrators for accelerating machines. It can suit a wide range of applications. It consists basically of a positive feedback loop of controlled gain which includes a varactor bridge operational amplifier. The essential features of the instrument are a 1 pA resolution and a 10 15 Ω output impedance. The output is guarded and floating between - 120 V and + 120 V, and the voltage across the external loads is measured without affecting the delivered current by a digital panel meter on the front panel. The unit can therefore operate as a high-accuracy dc impedance meter. (Auth.)
-
Slurry steam generator program and baseline eddy current examination
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Clark, R.A.; Doctor, P.G.
1985-01-01
The Steam Generator Group Project was initiated in January 1982 with formation of consortium including NRC, EPRI, Japanese, French, and Italian participants. The project utilizes a retired-from-service nuclear steam generator established in a specially designed facility which houses the unit in its normal vertical operating position. The most important objectives deal with validation of nondestructive examination (NDE) techniques used to characterize steam generators during service. This research generator offers the first opportunity to characterize a statistically significant number of service-induced defects nondestructively followed by destructive metallographic confirmation. The project seeks to establish the reliability of defect detection and the accuracy of sizing defects via current state-of-the-art NDE. Other service degraded tubes will be burst tested to establish remaining service integrity. The integrity information and NDE reliability results will serve as inputs to establish a model for steam generator in-service inspections, and provide a data base for evaluation of tube plugging criteria. In addition to NDE validation goals, the project will use the service degraded generator as a specimen for demonstration/proof testing of repair and maintenance techniques, including chemical cleaning/decontamination technologies. In addition to the efforts associated with NDE, a multitude of other project tasks have continued through 1984, and results are presented
-
Surry steam generator program and baseline eddy current examination
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Clark, R.A.; Doctor, P.G.
1985-01-01
The Steam Generator Group Project was initiated in January 1982 with formation of consortium including NRC, EPRI, Japanese, French, and Italian participants. The project utilizes a retired-from-service nuclear steam generator established in a specially designed facility which houses the unit in its normal vertical operating position. The most important objectives deal with validation of nondestructive examination (NDE) techniques used to characterize steam generators during service. This research generator offers the first opportunity to characterize a statistically significant number of service-induced defects nondestructively followed by destructive metallographic confirmation. The project seeks to establish the reliability of defect detection and the accuracy of sizing defects via current state-of-the-art NDE. Other service degraded tubes will be burst tested to establish remaining service integrity. The integrity information and NDE reliability results will serve as inputs to establish a model for steam generator in-service inspections, and provide a data base for evaluation of tube plugging criteria. In addition to NDE validation goals, the project will use the service degraded generator as a specimen for demonstration/proof testing of repair and maintenance techniques, including chemical cleaning/decontamination technologies. In addition to the efforts associated with NDE, a multitude of other project tasks have continued through 1984, and results are presented
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Aziz, A.; Bouaziz, M.N.
2011-01-01
Highlights: → Analytical solutions for a rectangular fin with temperature dependent heat generation and thermal conductivity. → Graphs give temperature distributions and fin efficiency. → Comparison of analytical and numerical solutions. → Method of least squares used for the analytical solutions. - Abstract: Approximate but highly accurate solutions for the temperature distribution, fin efficiency, and optimum fin parameter for a constant area longitudinal fin with temperature dependent internal heat generation and thermal conductivity are derived analytically. The method of least squares recently used by the authors is applied to treat the two nonlinearities, one associated with the temperature dependent internal heat generation and the other due to temperature dependent thermal conductivity. The solution is built from the classical solution for a fin with uniform internal heat generation and constant thermal conductivity. The results are presented graphically and compared with the direct numerical solutions. The analytical solutions retain their accuracy (within 1% of the numerical solution) even when there is a 60% increase in thermal conductivity and internal heat generation at the base temperature from their corresponding values at the sink temperature. The present solution is simple (involves hyperbolic functions only) compared with the fairly complex approximate solutions based on the homotopy perturbation method, variational iteration method, and the double series regular perturbation method and offers high accuracy. The simple analytical expressions for the temperature distribution, the fin efficiency and the optimum fin parameter are convenient for use by engineers dealing with the design and analysis of heat generating fins operating with a large temperature difference between the base and the environment.
-
Design of flexible polyphenylene proton-conducting membrane for next-generation fuel cells.
Miyake, Junpei; Taki, Ryunosuke; Mochizuki, Takashi; Shimizu, Ryo; Akiyama, Ryo; Uchida, Makoto; Miyatake, Kenji
2017-10-01
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are promising devices for clean power generation in automotive, stationary, and portable applications. Perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) ionomers (for example, Nafion) have been the benchmark PEMs; however, several problems, including high gas permeability, low thermal stability, high production cost, and environmental incompatibility, limit the widespread dissemination of PEMFCs. It is believed that fluorine-free PEMs can potentially address all of these issues; however, none of these membranes have simultaneously met the criteria for both high performance (for example, proton conductivity) and durability (for example, mechanical and chemical stability). We present a polyphenylene-based PEM (SPP-QP) that fulfills the required properties for fuel cell applications. The newly designed PEM exhibits very high proton conductivity, excellent membrane flexibility, low gas permeability, and extremely high stability, with negligible degradation even under accelerated degradation conditions, which has never been achieved with existing fluorine-free PEMs. The polyphenylene PEM also exhibits reasonably high fuel cell performance, with excellent durability under practical conditions. This new PEM extends the limits of existing fluorine-free proton-conductive materials and will help to realize the next generation of PEMFCs via cost reduction as well as the performance improvement compared to the present PFSA-based PEMFC systems.
-
Exploiting current-generation graphics hardware for synthetic-scene generation
Tanner, Michael A.; Keen, Wayne A.
2010-04-01
Increasing seeker frame rate and pixel count, as well as the demand for higher levels of scene fidelity, have driven scene generation software for hardware-in-the-loop (HWIL) and software-in-the-loop (SWIL) testing to higher levels of parallelization. Because modern PC graphics cards provide multiple computational cores (240 shader cores for a current NVIDIA Corporation GeForce and Quadro cards), implementation of phenomenology codes on graphics processing units (GPUs) offers significant potential for simultaneous enhancement of simulation frame rate and fidelity. To take advantage of this potential requires algorithm implementation that is structured to minimize data transfers between the central processing unit (CPU) and the GPU. In this paper, preliminary methodologies developed at the Kinetic Hardware In-The-Loop Simulator (KHILS) will be presented. Included in this paper will be various language tradeoffs between conventional shader programming, Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA) and Open Computing Language (OpenCL), including performance trades and possible pathways for future tool development.
-
Experimental measurements of the eddy current signal due to a flawed, conducting half space
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Long, S.A.; Toomsawasdi, S.; Zaman, A.J.M.
1984-01-01
This chapter reports on an experimental investigation in which the change in impedance of a practical multi-turn eddy current coil near a conducting half space is measured as a function of the conductivity and the lift-off distance. The results are compared in a qualitative fashion with the analytical results for a single-turn coil. Measurements are also made of the change in impedance due to a small void in the conducting half space as a function of both its depth and radial position. The results indicate that, at least in a qualitative fashion, the precisely derived analytical solutions adequately predict the general behavior of the change in complex impedance of an eddy current coil above a conducting ground plane as a function of lift-off distance. It is determined that the effect of a sub-surface void on the change in inductance of the test coil correlates well with theoretical calculations
-
Koshti, Ajay M.
2018-03-01
Like other NDE methods, eddy current surface crack detectability is determined using probability of detection (POD) demonstration. The POD demonstration involves eddy current testing of surface crack specimens with known crack sizes. Reliably detectable flaw size, denoted by, a90/95 is determined by statistical analysis of POD test data. The surface crack specimens shall be made from a similar material with electrical conductivity close to the part conductivity. A calibration standard with electro-discharged machined (EDM) notches is typically used in eddy current testing for surface crack detection. The calibration standard conductivity shall be within +/- 15% of the part conductivity. This condition is also applicable to the POD demonstration crack set. Here, a case is considered, where conductivity of the crack specimens available for POD testing differs by more than 15% from that of the part to be inspected. Therefore, a direct POD demonstration of reliably detectable flaw size is not applicable. Additional testing is necessary to use the demonstrated POD test data. An approach to estimate the reliably detectable flaw size in eddy current testing for part made from material A using POD crack specimens made from material B with different conductivity is provided. The approach uses additional test data obtained on EDM notch specimens made from materials A and B. EDM notch test data from the two materials is used to create a transfer function between the demonstrated a90/95 size on crack specimens made of material B and the estimated a90/95 size for part made of material A. Two methods are given. For method A, a90/95 crack size for material B is given and POD data is available. Objective of method A is to determine a90/95 crack size for material A using the same relative decision threshold that was used for material B. For method B, target crack size a90/95 for material A is known. Objective is to determine decision threshold for inspecting material A.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Gabet, A; Taieb, J
1950-07-01
An instrument consisting of two electronic tubes, a triode and a pentode, connected in series, serves as a stabilizer of the current that charges a working model of a van de Graaff generator. The current is maintained at a level corresponding to an auxiliary variable voltage. The triode maintains that voltage, while the pentode regulates the current. Another application of the circuit, viz., the stabilizing of the generator voltage, will be described elsewhere. (author)
-
Velocity spread of REB generated by high current diode
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Vrba, P.
1994-05-01
A theoretical analysis and numerical simulations of the Relativistic Electron Beam (REB) generation in a high current diode immersed in an external magnetic field were performed. The calculations confirmed the generated beam to be homogeneous and monoenergetic in a broad central region. In the case of a cylindrical diode the mixing of electron trajectories was only observed in a narrow peripheral beam region. The angle between particle trajectories and the external longitudinal magnetic field varies chaotically form 0 to -25 deg. This phenomenon suppresses the excitation of the two-stream instability excited by REB in a plasma column. (author) 2 tabs., 12 figs., 7 refs
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Blomberg, L.G.; Marklund, G.T.
1991-08-01
A numerical model for the calculation of ionospheric convection patterns from given distributions of field-aligned current and ionospheric conductivity is described. The model includes a coupling between the conductivity and the field-aligned current, so that the conductivity peaks in regions of upward current, as is usually observed by measurements. The model is very flexible in that the input distributions, the field-aligned current and the conductivity, have been parametrized in a convenient way. From the primary model output, namely the ionospheric electrostatic potential (or convection) in the corotating frame, a number of other quantities can be computed. These include; the potential in the inertial frame (the transformation takes into account the non-alignment of the Earths magnetic and geographic axes), the potential in the magnetospheric equatorial plane (projected using either a dipole magnetic field model or the Tsyganenko-Usmanov model, and the assumption of either vanishing parallel electric field or a proportionality between parallel potential and upward field-aligned current), the distribution of ionospheric (horizontal) current, and the Joule heating in the ionosphere. This model has been used together with a new snapshot technique to calculate the high-latitude potential distribution prevailing during a particular event by combining information from global auroral images and local measurements of fields and particles. The model potential variation along the satellite orbit was found to be in excellent agreement with that calculated from the measured electric field. The model has also been used to study some fundamental properties of the electrodynamics of the high-latitude ionosphere. The results of these different applications of the model have been published separately. (au) (39 refs.)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Senve, Vinay; Narasimham, G.S.V.L.
2011-01-01
Highlights: → Transport processes in isothermal hexagonal sheath with 19 heat generating rods is studied. → Correlation is given to predict the maximum temperature considering all transport processes. → Effective thermal conductivity of rod bundle can be obtained using max temperature. → Data on the critical Rayleigh numbers for p/d ratios of 1.1-2.0 is presented. → Radiative heat transfer contributes to heat dissipation of 38-65% of total heat. - Abstract: A numerical study of conjugate natural convection and surface radiation in a horizontal hexagonal sheath housing 19 solid heat generating rods with cladding and argon as the fill gas, is performed. The natural convection in the sheath is driven by the volumetric heat generation in the solid rods. The problem is solved using the FLUENT CFD code. A correlation is obtained to predict the maximum temperature in the rod bundle for different pitch-to-diameter ratios and heat generating rates. The effective thermal conductivity is related to the heat generation rate, maximum temperature and the sheath temperature. Results are presented for the dimensionless maximum temperature, Rayleigh number and the contribution of radiation with changing emissivity, total wattage and the pitch-to-diameter ratio. In the simulation of a larger system that contains a rod bundle, the effective thermal conductivity facilitates simplified modelling of the rod bundle by treating it as a solid of effective thermal conductivity. The parametric studies revealed that the contribution of radiation can be 38-65% of the total heat generation, for the parameter ranges chosen. Data for critical Rayleigh number above which natural convection comes into effect is also presented.
-
Hyperthermia generated by Foucault currents for oncological treatments with COMSOL
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Romero C, R. L.; Cordova F, T.; Basurto I, G.; Guzman C, R.; Castro L, J.
2017-10-01
The hyperthermia generated by variable magnetic fields is a promising power method for oncological therapy, because apoptosis is induced in tumor cells at temperatures between 42 and 45 degrees Celsius. It is known that an alternating magnetic field on the FeO 4 magnetite particles produces heat through three paths: is generated by parasitic currents, lost in hysteresis cycles and losses by magnetization relaxation; taking advantage of the energy losses through the joule effect and the transformation into heat, a simulation is shown in COMSOL about the temporal distribution of temperature in transformed biological systems, to have an estimate of the properties and behavior of the temperature gradient when magnetic hyperthermia is generated in human transformed tissue. (Author)
-
Current-voltage characteristics of individual conducting polymer nanotubes and nanowires
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
Long Yun-ze; Yin Zhi-Hua; Li Meng-Meng; Gu Chang-Zhi; Duvail Jean-Luc; Jin Ai-zi; Wan Mei-xiang
2009-01-01
We report the current-voltage (Ⅰ-Ⅴ) characteristics of individual polypyrrole nanotubes and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) nanowires in a temperature range from 300 K to 2 K. Considering the complex structures of such quasi-one-dimensional systems with an array of ordered conductive regions separated by disordered barriers, we use the extended fluctuation-induced tunneling (FIT) and thermal excitation model (Kaiser expression) to fit the temperature and electric-field dependent Ⅰ-Ⅴ curves. It is found that the Ⅰ-Ⅴ data measured at higher temperatures or higher voltages can be well fitted by the Kaiser expression. However, the low-temperature data around the zero bias clearly deviate from those obtained from this model. The deviation (or zero-bias conductance suppression)could be possibly ascribed to the occurrence of the Coulomb-gap in the density of states near the Femi level and/or the enhancement of electron-electron interaction resulting from nanosize effects, which have been revealed in the previous studies on low-temperature electronic transport in conducting polymer films, pellets and nanostructures. In addition,similar Ⅰ-Ⅴ characteristics and deviation are also observed in an isolated K0.27MnO2 nanowire.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Iniguez, J; Raposo, V; Flores, A G; Zazo, M; Hernandez-Lopez, A
2005-01-01
We report a study on magnetic levitation by induced ac currents in non-magnetic conductors at low frequencies. Our discussion, based on Faraday's induction law, allows us to distinguish the two components of the current responsible for levitation and heating, respectively. The experimental evaluation of the levitation force in a copper ring revealed the accuracy of our analysis, clearly illustrating its asymptotic behaviour versus frequency, and validating it for the qualitative analysis of magnetic levitation and heating in conductors of different shapes such as tubes and discs, composed of collections of conductive loops. The analysis of the results allows precise values of its electrical conductivity to be found. With the help of a simulation technique, this work also reveals the progressive deformation undergone by magnetic induction lines due to magnetic screening when frequency increases
-
Feasibility of Imaging Tissue Electrical Conductivity by Switching Field Gradients with MRI.
Gibbs, Eric; Liu, Chunlei
2015-12-01
Tissue conductivity is a biophysical marker of tissue structure and physiology. Present methods of measuring tissue conductivity are limited. Electrical impedance tomography, and magnetic resonance electrical impedance tomography rely on passing external current through the object being imaged, which prevents its use in most human imaging. Recently, the RF field used for MR excitation has been used to non-invasively measure tissue conductivity. This technique is promising, but conductivity at higher frequencies is less sensitive to tissue structure. Measuring tissue conductivity non-invasively at low frequencies remains elusive. It has been proposed that eddy currents generated during the rise and decay of gradient pulses could act as a current source to map low-frequency conductivity. This work centers on a gradient echo pulse sequence that uses large gradients prior to excitation to create eddy currents. The electric and magnetic fields during a gradient pulse are simulated by a finite-difference time-domain simulation. The sequence is also tested with a phantom and an animal MRI scanner equipped with gradients of high gradient strengths and slew rate. The simulation demonstrates that eddy currents in materials with conductivity similar to biological tissue decay with a half-life on the order of nanoseconds and any eddy currents generated prior to excitation decay completely before influencing the RF signal. Gradient-induced eddy currents can influence phase accumulation after excitation but the effect is too small to image. The animal scanner images show no measurable phase accumulation. Measuring low-frequency conductivity by gradient-induced eddy currents is presently unfeasible.
-
Printing of highly conductive solution by alternating current electrohydrodynamic direct-write
Jiang, Jiaxin; Zheng, Gaofeng; Wang, Xiang; Zheng, Jianyi; Liu, Juan; Liu, Yifang; Li, Wenwang; Guo, Shumin
2018-03-01
Electrohydrodynamic Direct-Write (EDW) is a novel technology for the printing of micro/nano structures. In this paper, Alternating Current (AC) electrical field was introduced to improve the ejection stability of jet with highly conductive solution. By alternating the electrical field, the polarity of free charges on the surface of jet was changed and the average density of charge, as well as the repulsive force, was reduced to stabilize the jet. When the frequency of AC electrical field increased, the EDW process became more stable and the shape of deposited droplets became more regular. The diameter of printed droplets decreased and the deposition frequency increased with the increase of voltage frequency. The phenomenon of corona discharge was overcome effectively as well. To further evaluate the performance of AC EDW for highly conductive solution, more NaCl was added to the solution and the conductivity was increased to 2810μs/cm. With such high conductivity, the problem of serious corona discharge could still be prevented by AC EDW, and the diameter of printed droplets decreased significantly. This work provides an effective way to accelerate industrial applications of EDW.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Catarelli, Samantha Raisa; Lonsdale, Daniel [Uniscan Instruments Ltd., Macclesfield (United Kingdom); Cheng, Lei [Energy Storage and Distribution Resources Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA (United States); Materials Sciences and Engineering Department, University of California Berkeley, Berkeley, CA (United States); Syzdek, Jaroslaw [Bio-Logic USA LLC, Knoxville, TN (United States); Doeff, Marca, E-mail: mmdoeff@lbl.gov [Energy Storage and Distribution Resources Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA (United States)
2016-03-31
Intermittent contact alternating current scanning electrochemical microscopy (ic-ac-SECM) has been used to determine the electrochemical response to an ac signal of several types of materials. A conductive gold foil and insulating Teflon sheet were first used to demonstrate that the intermittent contact function allows the topography and conductivity to be mapped simultaneously and independently in a single experiment. Then, a dense pellet of an electronically insulating but Li ion conducting garnet phase, Al-substituted Li{sub 7}La{sub 3}Zr{sub 2}O{sub 12} (LLZO), was characterized using the same technique. The polycrystalline pellet was prepared by classical ceramic sintering techniques and was comprised of large (~150 μm) grains. Critical information regarding the contributions of grain and grain boundary resistances to the total conductivity of the garnet phase was lacking due to ambiguities in the impedance data. In contrast, the use of the ic-ac-SECM technique allowed spatially resolved information regarding local conductivities to be measured directly. Impedance mapping of the pellet showed that the grain boundary resistance, while generally higher than that of grains, varied considerably, revealing the complex nature of the LLZO sample.
-
Current Status and Future Outlook of Nuclear Power Generation in Japan
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Suzuki, Yasuro; Yoshii, Ryosuke
2007-07-01
For Japan, a country poor in natural resources, in light of the tough energy situation in recent times, a National Energy Strategy with energy security at its core was established in May 2006. The key point of the Strategy is nuclear power generation, and the aim is to ensure that nuclear power generation continues to account for 30 to 40 percent or more of total electricity generated even after 2030. The first step to achieving this goal is to make maximum use of existing plants (55 plants, 49580MWe), and the aim is to achieve a 60-year service life by making improvements to plant operation and maintenance, such as extending current monitoring and maintenance of plant condition, and the implementation of plant aging management. In Japan, plant construction has been continuous since the 1970s. The current new plant construction plan (13 plants, 17230MWe) is to be achieved with a concerted, cohesive national effort. In addition, in order to complete the nuclear fuel cycle, a reprocessing plant is being constructed strictly for peaceful use, and construction of a site for disposing of high-level radioactive waste is also proceeding. Development of the next generation light water reactors and fast breeder reactor cycle is also underway. (auth)
-
U(1) current from the AdS/CFT: diffusion, conductivity and causality
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bu, Yanyan [Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva 84105 (Israel); Lublinsky, Michael [Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva 84105 (Israel); Physics Department, University of Connecticut, 2152 Hillside Road, Storrs, CT 06269-3046 (United States); Sharon, Amir [Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva 84105 (Israel)
2016-04-21
For a holographically defined finite temperature theory, we derive an off-shell constitutive relation for a global U(1) current driven by a weak external non-dynamical electromagnetic field. The constitutive relation involves an all order gradient expansion resummed into three momenta-dependent transport coefficient functions: diffusion, electric conductivity, and “magnetic” conductivity. These transport functions are first computed analytically in the hydrodynamic limit, up to third order in the derivative expansion, and then numerically for generic values of momenta. We also compute a diffusion memory function, which, as a result of all order gradient resummation, is found to be causal.
-
U(1) current from the AdS/CFT: diffusion, conductivity and causality
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bu, Yanyan; Lublinsky, Michael; Sharon, Amir
2016-01-01
For a holographically defined finite temperature theory, we derive an off-shell constitutive relation for a global U(1) current driven by a weak external non-dynamical electromagnetic field. The constitutive relation involves an all order gradient expansion resummed into three momenta-dependent transport coefficient functions: diffusion, electric conductivity, and “magnetic” conductivity. These transport functions are first computed analytically in the hydrodynamic limit, up to third order in the derivative expansion, and then numerically for generic values of momenta. We also compute a diffusion memory function, which, as a result of all order gradient resummation, is found to be causal.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cuperman, S.; Bruma, C.; Komoshvili, K
2003-05-12
The generation in low aspect ratio tokamaks (LARTs) of ponderomotive forces and non-inductive current drive by the resonant fast wave-plasma interaction with mode conversion to kinetic Alfven waves (KAWs) and subsequent deposition, mainly by resonant electron Landau damping, is considered. The calculations follow the rigorous solution of the full wave equations upon using a dielectric tensor operator consisting of (i) a parallel conductivity including both kinetic effects (collisionless Landau damping on passing electrons) and collisional damping on both trapped electrons and passing electrons+ions and (ii) perpendicular components provided by the resistive two-fluid model equations. The fast waves are launched by an antenna located on the low field side and extending {+-}45 deg. about the equatorial plane. A parametric investigation of the structure and importance of the various components of the ponderomotive forces and current drive generated in START-like plasmas is carried out and their suitability for supplementing the required non-rf toroidal equilibrium current is demonstrated.
-
Remote sub-wavelength focusing of ultrasonically activated Lorentz current
Rekhi, Angad S.; Arbabian, Amin
2017-04-01
We propose the use of a combination of ultrasonic and magnetic fields in conductive media for the creation of RF electrical current via the Lorentz force, in order to achieve current generation with extreme sub-wavelength resolution at large depth. We demonstrate the modeling, generation, and measurement of Lorentz current in a conductive solution and show that this current can be localized at a distance of 13 cm from the ultrasonic source to a region about three orders of magnitude smaller than the corresponding wavelength of electromagnetic waves at the same operation frequency. Our results exhibit greater depth, tighter localization, and closer agreement with prediction than previous work on the measurement of Lorentz current in a solution of homogeneous conductivity. The proposed method of RF current excitation overcomes the trade-off between focusing and propagation that is fundamental in the use of RF electromagnetic excitation alone and has the potential to improve localization and depth of operation for RF current-based biomedical applications.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Musumeci
2013-10-01
Full Text Available The evolution of picosecond modulations of the longitudinal profile of an electron beam generated in an rf photoinjector is analyzed and optimized with the goal of obtaining high peak current electron bunch trains at very high frequencies (≥THz. Taking advantage of nonlinear longitudinal space charge forces, it is found that more than 500 A peak current 1 THz bunch trains can be generated using a standard 1.6 cell SLAC/UCLA/BNL rf gun. Postacceleration is used to freeze the longitudinal phase space dynamics after one half plasma oscillation. Applications range from tunable narrow bandwidth THz radiation generation to drivers for high frequency high gradient accelerators.
-
Current generation by unidirectional lower hybrid waves in the ACT-1 toroidal device
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wong, K.L.; Horton, R.; Ono, M.
1980-05-01
An unambiguious experimental observation of current generation by unidirectional lower hybrid waves in a toroidal plasma is reported. Up to 10 amperes of current was driven by 500 watts of rf power at 160 MHz
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shulishova, O.I.; Zyrin, A.V.; Ismalgaliev, R.K.; Izmajlov, Sh.Z.; Kovylyaev, V.V.; Shevchuk, N.V.; Shcherbak, I.A.
1990-01-01
The electron-probe microanalysis permits investigating the interaction on the boundary of current-conducting and glass-binding phases in cermet films without noble metals on the base of ruthenium oxide. The performed studies along with experiments on model microsections subject to annealing in different media have shown the differences in the process of formation of structure and properties of cermet resistive elements as well as a significance of the oxidation process of current-conducting phase in formation of high working characteristics of cermet resistors on the base of hexaborides of the rare-earth elements
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Abdusalam, Mohamed; Karimi, Shahram; Saadate, Shahrokh [Groupe de Recherche en Electrotechnique et Electronique de Nancy (GREEN), CNRS UMR 7037 (France); Poure, Philippe [Laboratoire d' Instrumentation Electronique de Nancy (LIEN), EA 3440, Universite Henri Poincare - Nancy Universite, B.P. 239, 54506 Vandoeuvre les Nancy Cedex (France)
2009-05-15
In this paper, a new reference current computation method suitable for shunt active power filter control under distorted voltage conditions is proposed. The active power filter control is based on the use of self-tuning filters (STF) for the reference current generation and on a modulated hysteresis current controller. This active filter is intended for harmonic compensation of a diode rectifier feeding a RL load under distorted voltage conditions. The study of the active filter control is divided in two parts. The first one deals with the harmonic isolator which generates the harmonic reference currents and is experimentally implemented in a DS1104 card of a DSPACE prototyping system. The second part focuses on the generation of the switching pattern of the inverter by using a modulated hysteresis current controller, implemented in an analogue card. The use of STF instead of classical extraction filters allows extracting directly the voltage and current fundamental components in the {alpha}-{beta} axis without phase locked loop (PLL). The performances are good even under distorted voltage conditions. First, the effectiveness of the new proposed method is mathematically studied and verified by computer simulation. Then, experimental results are presented using a DSPACE system associated with the analogue current controller for a real shunt active power filter. (author)
-
Application of an eddy current technique to steam generator U-bend characterization. Final report
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cramer, W.E.; de la Pintiere, L.; Narita, S.; Bergander, M.J.
1982-04-01
Eddy current nondestructive testing techniques are used widely throughout the utility industry for the early detection of tube damage in critical power plant components such as steam generators. In this project, the application of an eddy current technique for the characterization of U-bend transitions in the first row tubing in Westinghouse 51 Series Steam Generators has been investigated. A method has been developed for detection of the opposite transition in the U-bend and for defining its severity. Investigation included two different types of U-bend transitions. Using the developed eddy current method for U-bend characterization, on-site inspection was performed on all tubes in the first row in four 51 Series steam generators in Power Plant Unit No. 2 and in one 51 Series steam generator in Power Plant Unit No. 1. The advantages and limitations of the developed method as well as the recommendations for further investigations are included
-
Field generated within the SSC magnets due to persistant currents in the superconductor
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Green, M.A.
1984-01-01
This report presents the results of a number of computer studies of the magnetic fields generated by persistent circulating currents in the superconductor of superconducting dipoles. These magnetic fields are referred to as residual fields throughout this report. Since the field generated by persistent currents have a hysteric behavior, they are analagous to the residual filed found in iron bound conventional solenoids. The residual field calculations presented in this report were done using the LBL SCMAG4 computer code. This code has not been well tested against measured data, but a comparison with measured CBA data given in this report suggests that good agreement is possible. The residual fields generated by persistent superconducting currents are rich in higher multipoles. This is of concern to the accelerator designer for SSC. This report shows the effect of various superconductor parameters and coil parameters on the magnitude and structure of the residual fields. The effect of the magnet charging history on residual fields is aldo discussed. 14 references
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Iniguez, J; Raposo, V; Flores, A G; Zazo, M; Hernandez-Lopez, A [Departamento de Fisica Aplicada, Universidad de Salamanca, E-37071, Salamanca (Spain)
2005-11-01
We report a study on magnetic levitation by induced ac currents in non-magnetic conductors at low frequencies. Our discussion, based on Faraday's induction law, allows us to distinguish the two components of the current responsible for levitation and heating, respectively. The experimental evaluation of the levitation force in a copper ring revealed the accuracy of our analysis, clearly illustrating its asymptotic behaviour versus frequency, and validating it for the qualitative analysis of magnetic levitation and heating in conductors of different shapes such as tubes and discs, composed of collections of conductive loops. The analysis of the results allows precise values of its electrical conductivity to be found. With the help of a simulation technique, this work also reveals the progressive deformation undergone by magnetic induction lines due to magnetic screening when frequency increases.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Egorov, Alexander; Kucheryavskiy, Sergey V.; Polyakov, Viktor
2017-01-01
The effect of eddy currents is widely used for diagnostics of conductive materials. It allows to create very simple and inexpensive systems for non-destructive measurements. However, the results of the measurements depend on many factors, including first of all, a conductivity of material...
-
Variable speed wind turbine generator system with current controlled voltage source inverter
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Muyeen, S.M.; Al-Durra, Ahmed; Tamura, J.
2011-01-01
highlights: → Current controlled voltage source inverter scheme for wind power application. → Low voltage ride through of wind farm. → Variable speed wind turbine driven permanent magnet synchronous generator-operation and control. -- Abstract: The present popular trend of wind power generation is to use variable speed wind turbine (VSWT) driving a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), wound field synchronous generator (WFSG) or permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG). Among them, stability analyses of DFIG type of VSWT have already been reported in many literatures. However, transient stability and low voltage ride through (LVRT) characteristics analyses for synchronous generator type of VSWT is not sufficient enough. This paper focuses on detailed LVRT characteristic analysis of variable speed wind turbine driving a PMSG (VSWT-PMSG) with current controlled voltage source inverter (CC-VSI). Modeling and suitable control strategies for overall system are developed to augment the low voltage ride through capability of variable speed wind generator, considering recent wind farm grid code. Both symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults are analyzed as network disturbances in this paper. The permanent fault due to unsuccessful reclosing of circuit breakers is taken into consideration, which is a salient feature of this study. Moreover, the dynamic characteristic is analyzed using real wind speed data measured in Hokkaido Island, Japan. The proposed control scheme is simulated by using the standard power system simulation package PSCAD/EMTDC and results are verified by comparing that of voltage controlled voltage source inverter scheme available in power system literature.
-
Variable speed wind turbine generator system with current controlled voltage source inverter
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Muyeen, S.M., E-mail: muyeen0809@yahoo.co [Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Petroleum Institute, P.O. Box 2533, Abu Dhabi (United Arab Emirates); Al-Durra, Ahmed [Dept. of Electrical Engineering, The Petroleum Institute, P.O. Box 2533, Abu Dhabi (United Arab Emirates); Tamura, J. [Dept. of EEE, Kitami Institute of Technology, 165 Koen-cho, Kitami 090-8507 (Japan)
2011-07-15
highlights: {yields} Current controlled voltage source inverter scheme for wind power application. {yields} Low voltage ride through of wind farm. {yields} Variable speed wind turbine driven permanent magnet synchronous generator-operation and control. -- Abstract: The present popular trend of wind power generation is to use variable speed wind turbine (VSWT) driving a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), wound field synchronous generator (WFSG) or permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG). Among them, stability analyses of DFIG type of VSWT have already been reported in many literatures. However, transient stability and low voltage ride through (LVRT) characteristics analyses for synchronous generator type of VSWT is not sufficient enough. This paper focuses on detailed LVRT characteristic analysis of variable speed wind turbine driving a PMSG (VSWT-PMSG) with current controlled voltage source inverter (CC-VSI). Modeling and suitable control strategies for overall system are developed to augment the low voltage ride through capability of variable speed wind generator, considering recent wind farm grid code. Both symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults are analyzed as network disturbances in this paper. The permanent fault due to unsuccessful reclosing of circuit breakers is taken into consideration, which is a salient feature of this study. Moreover, the dynamic characteristic is analyzed using real wind speed data measured in Hokkaido Island, Japan. The proposed control scheme is simulated by using the standard power system simulation package PSCAD/EMTDC and results are verified by comparing that of voltage controlled voltage source inverter scheme available in power system literature.
-
Yaroshchuk, Andriy; Luxbacher, Thomas
2010-07-06
It is shown that in tangential electrokinetic measurements with porous films the porous structure makes contribution not only to the cell electric conductance (as demonstrated previously) but also to the observed streaming current. Both of these contributions give rise to dependences of streaming-potential and streaming-current coefficients on the channel height. However, due to the combined contribution of two phenomena, the dependence of streaming-potential coefficient on the channel height may be rather complicated and not allow for simple extrapolation. At the same time, the dependences of streaming-current coefficient and cell electric conductance on the channel height turn out linear and can be easily extrapolated to zero channel heights. This enables one to determine separately the contributions of external surface of porous film and of its porous structure to the streaming current and of the channel and porous structure to the cell electric conductance. This procedure is illustrated by the measurements of tangential electrokinetic phenomena and electric conductance with Millipore mixed-cellulose membrane filters of various average pore sizes (from 0.025 to 5 mum) in the so-called adjustable-gap cell of SurPASS electrokinetic instrument (Anton Paar GmbH). The design of this cell allows for easy and quasi-continuous variation of channel height as well as accurate determination of cell electric conductance, streaming-current coefficient, and channel height (from the cell hydraulic permeability). The quality of linear fits of experimental data has been found to be very good, and thus, the extrapolation procedures were quite reliable and accurate. Zeta-potentials could be determined of both external film and internal pore surfaces. It is demonstrated that the porous structures make considerable contributions to both streaming-current coefficient and cell electric conductance especially in the case of filters with larger pores. It is also found that, rather
-
Evaluation and field validation of Eddy-Current array probes for steam generator tube inspection
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dodd, C.V.; Pate, J.R.
1996-07-01
The objective of the Improved Eddy-Current ISI for Steam Generator Tubing program is to upgrade and validate eddy-current inspections, including probes, instrumentation, and data processing techniques for inservice inspection of new, used, and repaired steam generator tubes; to improve defect detection, classification, and characterization as affected by diameter and thickness variations, denting, probe wobble, tube sheet, tube supports, copper and sludge deposits, even when defect types and other variables occur in combination; to transfer this advanced technology to NRC's mobile NDE laboratory and staff. This report describes the design of specialized high-speed 16-coil eddy-current array probes. Both pancake and reflection coils are considered. Test results from inspections using the probes in working steam generators are given. Computer programs developed for probe calculations are also supplied
-
Fundamental Issues in Manufacturing Photovoltaic Modules Beyond the Current Generation of Materials
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. F. Alapatt
2012-01-01
Full Text Available Many methods to improve the solar cell’s efficiency beyond current generation of bulk and thin film of photovoltaic (PV devices have been reported during the last five decades. Concepts such as multiple exciton generations (MEG, carrier multiplication (CM, hot carrier extraction, and intermediate band solar cells have fundamental flaws, and there is no experimental evidence of fabricating practical higher efficiency solar cells based on the proposed concepts. To take advantages of quantum features of nanostructures for higher performance PV devices, self-assembly-based bottom-up processing techniques are not suitable for manufacturing due to inherent problems of variability, defects, reliability, and yield. For processing nanostructures, new techniques need to be invented with the features of critical dimensional control, structural homogeneity, and lower cost of ownership as compared to the processing tools used in current generations of bulk and thin-film solar cells.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Velikhov, E.P.; Golubev, V.S.; Dykhne, A.M.
1976-01-01
The paper assesses the position in 1975 of theoretical and experimental work on the physics of a magnetohydrodynamic generator with non-equilibrium plasma conductivity. This research started at the beginning of the 1960s; as work on the properties of thermally non-equilibrium plasma in magnetic fields and also in MHD generator ducts progressed, a number of phenomena were discovered and investigated that had either been unknown in plasma physics or had remained uninvestigated until that time: ionization instability and ionization turbulence of plasma in a magnetic field, acoustic instability of a plasma with anisotropic conductivity, the non-equilibrium ionization wave and the energy balance of a non-equilibrium plasma. At the same time, it was discovered what physical requirements an MHD generator with non-equilibrium conductivity must satisfy to achieve high efficiency in converting the thermal or kinetic energy of the gas flow into electric energy. The experiments on MHD power generation with thermally non-equilibrium plasma carried out up to 1975 indicated that it should be possible to achieve conversion efficiencies of up to 20-30%. (author)
-
Sekido, Kota; Kitaori, Noriyuki
2008-12-01
A small-sized generator of ozonated water was developed using an electro-conductive diamond. We studied the optimum conditions for producing ozonated water. As a result, we developed a small-sized generator of ozonated water driven by a dry-cell for use in the average household. This generator was easily able to produce ozonated water with an ozone concentration (over 4 mg/L) sufficient for disinfection. In addition, we verified the high disinfecting performance of the water produced in an actual hospital.
-
Spike train generation and current-to-frequency conversion in silicon diodes
Coon, D. D.; Perera, A. G. U.
1989-01-01
A device physics model is developed to analyze spontaneous neuron-like spike train generation in current driven silicon p(+)-n-n(+) devices in cryogenic environments. The model is shown to explain the very high dynamic range (0 to the 7th) current-to-frequency conversion and experimental features of the spike train frequency as a function of input current. The devices are interesting components for implementation of parallel asynchronous processing adjacent to cryogenically cooled focal planes because of their extremely low current and power requirements, their electronic simplicity, and their pulse coding capability, and could be used to form the hardware basis for neural networks which employ biologically plausible means of information coding.
-
System of ionospheric currents excited by a magnetospheric generator in the boundary layer
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Denisenko, V.V.; Zamaj, S.S.; Kitaev, A.V.; Matveenkov, I.T.; Pivovarov, V.G.
1992-01-01
A model of ionospheric electric fields and currents in the vicinity of the daytime cusp is proposed; the fields and currents occur due to diffusion mechanism of electric field generation at the boundary of Earth's magnetosphere. The results of calculating electric fields and currents are presented for various values of magnetic field components in the solar wind
-
Simple engineering design for complex thermoelectric generators based on reduced current approach
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Wijesooriyage, Waruna Dissanayaka; Rezaniakolaei, Alireza; Rosendahl, Lasse
2015-01-01
Thermoelectric generators (TEGs) are niche candidate for the field of energy management as electrical generator devices. Generally, comprehensive and accurate design techniques for TEGs (thermoelectric generators), such as reduced current approach (RCA), are complex and time consuming processes....... This study develops a simple, comprehensive and accurate TEG designing technique based on RCA. The proposed method can predict the most efficient TEG architecture with more than 97% accuracy comparing to the RCA over wide range of possible temperature and zT for present TEG applications. Moreover...
-
Current forgings and their properties for steam generator of nuclear plant
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tsukada, Hisashi; Suzuki, Komei; Kusuhashi, Mikio; Sato, Ikuo
1997-01-01
Current steel forgings for steam generator (SG) of PWR plant are reviewed in the aspect of design and material improvement. The following three items are introduced. The use of integral type steel forgings for the fabrication of steam generator enhances the structural integrity and makes easier fabrication and inspection including in-service inspection. The following examples of current integral type forgings developed by the Japan Steel Works, Ltd. (JSW) are introduced: (1) primary head integrated with nozzles, manways and supports; (2) steam drum head integrated with nozzle and handhole; (3) conical shell integrated with cylindrical sections and handholes. In order to decrease the weight of steam generator, the high strength materials such as SA508, Cl.3a steel have been adopted in some cases. The properties of this steel are introduced and the chemistry and heat treatment condition are discussed. As one of the methods to minimize the macro- and micro-segregations, the use of vacuum carbon deoxidation (VCD), i.e. deoxidization of steel by gaseous CO reaction, with addition of Al for grain refining was investigated. The properties of SA508, Cl.3 steels with Low Si content are compared with those of conventional one
-
Current forgings and their properties for steam generator of nuclear plant
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tsukada, Hisashi; Suzuki, Komei; Kusuhashi, Mikio; Sato, Ikuo [Japan Steel Works Ltd., Muroran (Japan)
1997-12-31
Current steel forgings for steam generator (SG) of PWR plant are reviewed in the aspect of design and material improvement. The following three items are introduced. The use of integral type steel forgings for the fabrication of steam generator enhances the structural integrity and makes easier fabrication and inspection including in-service inspection. The following examples of current integral type forgings developed by the Japan Steel Works, Ltd. (JSW) are introduced: (1) primary head integrated with nozzles, manways and supports; (2) steam drum head integrated with nozzle and handhole; (3) conical shell integrated with cylindrical sections and handholes. In order to decrease the weight of steam generator, the high strength materials such as SA508, Cl.3a steel have been adopted in some cases. The properties of this steel are introduced and the chemistry and heat treatment condition are discussed. As one of the methods to minimize the macro- and micro-segregations, the use of vacuum carbon deoxidation (VCD), i.e. deoxidization of steel by gaseous CO reaction, with addition of Al for grain refining was investigated. The properties of SA508, Cl.3 steels with Low Si content are compared with those of conventional one.
-
Study of noninductive current generation in a plasma
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rax, J.M.
1987-01-01
Three aspects of noninductive current generation are treated: (1) The kinetic problem, i.e., coupling between current-carrying energetic electrons on the one hand, and the electromagnetic wave and thermal particles on the other. (2). The electromagnetic problem, i.e., calculation of the wave structure produced by the antennas. (3) The study of nonthermal radiation and electrical responses. Green's functions are used to solve the kinetic problem. The electron distribution function is calculated. For the electromagnetic problem of wave structure at different wave numbers, the Green's function of the Maxwell equations in an inhomogeneous, anisotropic medium which is spatially and temporally scattered was calculated. Perturbation of propagation by diffusion and conversion was studied. The calculation of nonthermal radiation and of transfer of electromagnetic wave energy into magnetic energy is derived from the two preceding problems. A method to produce fusion power quasi-continuously using two inductively and thermally coupled tokamaks is proposed [fr
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Bejtkovský Jiří
2016-12-01
Full Text Available The corporations using the varied workforce can supply a greater variety of solutions to problems in service, sourcing, and allocation of their resources. The current labor market mentions four generations that are living and working today: the Baby boomers generation, the Generation X, the Generation Y and the Generation Z. The differences between generations can affect the way corporations recruit and develop teams, deal with change, motivate, stimulate and manage employees, and boost productivity, competitiveness and service effectiveness. A corporation’s success and competitiveness depend on its ability to embrace diversity and realize the competitive advantages and benefits. The aim of this paper is to present the current generation of employees (the employees of Baby Boomers Generation, Generation X, Generation Y and Generation Z in the labor market by secondary research and then to introduce the results of primary research that was implemented in selected corporations in the Czech Republic. The contribution presents a view of some of the results of quantitative and qualitative research conducted in selected corporations in the Czech Republic. These researches were conducted in 2015 on a sample of 3,364 respondents, and the results were analyzed. Two research hypotheses and one research question have been formulated. The verification or rejection of null research hypothesis was done through the statistical method of the Pearson’s Chi-square test. It was found that perception of the choice of superior from a particular generation does depend on the age of employees in selected corporations. It was also determined that there are statistically significant dependences between the preference for eterogeneous or homogeneous cooperation and the age of employees in selected corporations.
-
Drag and lift forces between a rotating conductive sphere and a cylindrical magnet
Nurge, Mark A.; Youngquist, Robert C.; Starr, Stanley O.
2018-06-01
Modeling the interaction between a non-uniform magnetic field and a rotating conductive object provides insight into the drag force, which is used in applications such as eddy current braking and linear induction motors, as well as the transition to a repulsive force, which is the basis for magnetic levitation systems. Here, we study the interaction between a non-uniform field generated by a cylindrical magnet and a rotating conductive sphere. Each eddy current in the sphere generates a magnetic field which in turn generates another eddy current, eventually feeding back on itself. A two-step mathematical process is developed to find a closed-form solution in terms of only three eddy currents. However, the complete solution requires decomposition of the magnetic field into a summation of spherical harmonics, making it more suitable for a graduate-level electromagnetism lecture or lab. Finally, the forces associated with these currents are calculated and then verified experimentally.
-
Drag and Lift Forces Between a Rotating Conductive Sphere and a Cylindrical Magnet
Nurge, Mark A.; Youngquist, Robert C.
2017-01-01
Modeling the interaction between a non-uniform magnetic field and a rotating conductive object allows study of the drag force which is used in applications such as eddy current braking and linear induction motors as well as the transition to a repulsive force that is the basis for magnetic levitation systems. Here, we study the interaction between a non-uniform field generated by a cylindrical magnet and a rotating conductive sphere. Each eddy current in the sphere generates a magnetic field which in turn generates another eddy current, eventually feeding back on itself. A two step mathematics process is developed to find a closed form solution in terms of only two eddy currents. However, the complete solution requires decomposition of the magnetic field into a summation of spherical harmonics, making it more suitable for a graduate level electromagnetism lecture or lab. Finally, the forces associated with these currents are calculated and then verified experimentally.
-
Devi, Sushila; Brogi, B. B.; Ahluwalia, P. K.; Chand, S.
2018-06-01
Electronic transport through asymmetric parallel coupled quantum dot system hybridized between normal leads has been investigated theoretically in the Coulomb blockade regime by using Non-Equilibrium Green Function formalism. A new decoupling scheme proposed by Rabani and his co-workers has been adopted to close the chain of higher order Green's functions appearing in the equations of motion. For resonant tunneling case; the calculations of current and differential conductance have been presented during transition of coupled quantum dot system from series to symmetric parallel configuration. It has been found that during this transition, increase in current and differential conductance of the system occurs. Furthermore, clear signatures of negative differential conductance and negative current appear in series case, both of which disappear when topology of system is tuned to asymmetric parallel configuration.
-
Surry steam generator - examination and evaluation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Clark, R.A.; Doctor, P.G.; Ferris, R.H.
1985-10-01
This report summarizes research conducted during the fourth year of the five year Steam Generator Group Project. During this period the project conducted numerous nondestructive examination (NDE) round robin inspections of the original Surry 2A steam generator. They included data acquisition/analysis and analysis-only round robins using multifrequency bobbin coil eddy current tests. In addition, the generator was nondestructively examined by alternate or advanced techniques including ultrasonics, optical fiber, profilometry and special eddy current instrumentation. The round robin interpretation data were compared. To validate the NDE results and for tube integrity testing, a selection of tubing samples, determined to be representative of the generator, was designated for removal. Initial sample removals from the generator included three sections of tube sheet, two sections of support plate and encompassed tubes, and a number of straight and U-bend tubing sections. Metallographic examination of these sections was initiated. Details of significant results are presented in the following paper. 13 figs
-
Surry steam generator - examination and evaluation
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Clark, R A; Doctor, P G; Ferris, R H
1987-01-01
This report summarizes research conducted during the fourth year of the five year Steam Generator Group Project. During this period the project conducted numerous nondestructive examination (NDE) round robin inspections of the original Surry 2A steam generator. They included data acquisition/analysis and analysis-only round robins using multifrequency bobbin coil eddy current tests. In addition, the generator was nondestructively examined by alternate or advanced techniques including ultrasonics, optical fiber, profilometry and special eddy current instrumentation. The round robin interpretation data were compared. To validate the NDE results and for tube integrity testing, a selection of tubing samples, determined to be representative of the generator, was designated for removal. Initial sample removals from the generator included three sections of tube sheet, two sections of support plate and encompassed tubes, and a number of straight and U-bend tubing sections. Metallographic examination of these sections was initiated. Details of significant results are presented in the following paper.
-
Kim, Yong-Jung
2015-06-23
We show the well-posedness of the conductivity image reconstruction problem with a single set of interior electrical current data and boundary conductivity data. Isotropic conductivity is considered in two space dimensions. Uniqueness for similar conductivity reconstruction problems has been known for several cases. However, the existence and the stability are obtained in this paper for the first time. The main tool of the proof is the method of characteristics of a related curl equation.
-
Kim, Yong-Jung; Lee, Min-Gi
2015-01-01
We show the well-posedness of the conductivity image reconstruction problem with a single set of interior electrical current data and boundary conductivity data. Isotropic conductivity is considered in two space dimensions. Uniqueness for similar conductivity reconstruction problems has been known for several cases. However, the existence and the stability are obtained in this paper for the first time. The main tool of the proof is the method of characteristics of a related curl equation.
-
Prediction of burnout of a conduction-cooled BSCCO current lead
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Seol, S.Y.; Cha, Y.S.; Niemann, R.C.; Hull, J.R.
1996-01-01
A one-dimensional heat conduction model is employed to predict burnout of a Bi 2 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8 current lead. The upper end of the lead is assumed to be at 77 K and the lower end is at 4 K. The results show that burnout always occurs at the warmer end of the lead. The lead reaches its burnout temperature in two distinct stage. Initially, the temperature rises slowly when part of the lead is in flux-flow state. As the local temperature reaches the critical temperature, it begins to increase sharply. Burnout time depends strongly on flux-flow resistivity
-
Application of numerical analysis techniques to eddy current testing for steam generator tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Morimoto, Kazuo; Satake, Koji; Araki, Yasui; Morimura, Koichi; Tanaka, Michio; Shimizu, Naoya; Iwahashi, Yoichi
1994-01-01
This paper describes the application of numerical analysis to eddy current testing (ECT) for steam generator tubes. A symmetrical and three-dimensional sinusoidal steady state eddy current analysis code was developed. This code is formulated by future element method-boundary element method coupling techniques, in order not to regenerate the mesh data in the tube domain at every movement of the probe. The calculations were carried out under various conditions including those for various probe types, defect orientations and so on. Compared with the experimental data, it was shown that it is feasible to apply this code to actual use. Furthermore, we have developed a total eddy current analysis system which consists of an ECT calculation code, an automatic mesh generator for analysis, a database and display software for calculated results. ((orig.))
-
Nikam, Pravin N.; Deshpande, Vineeta D.
2016-05-01
Polymer nanocomposites based on metal oxide (ceramic) nanoparticles are a new class of materials with unique properties and designed for various applications such as electronic device packaging, insulation, fabrication and automotive industries. Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET)/alumina (Al2O3) nanocomposites with filler content between 1 wt% and 5 wt% were prepared by melt compounding method using co-rotating twin screw extruder and characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and precision LCR meter techniques. The results revealed that proper uniform dispersion at lower content up to 2 wt% of nano-alumina observed by using TEM. Aggregation of nanoparticles was observed at higher content of alumina examined by using SEM and TEM. The frequency dependences of the alternating current (AC) conductivity (σAC) of PET/alumina nanocomposites on the filler content and DC bias were investigated in the frequency range of 20Hz - 1MHz. The results showed that the AC and direct current (DC) conductivity increases with increasing DC bias and nano-alumina content upto 3 wt%. It follows the Jonscher's universal power law of solids. It revealed that σAC of PET/alumina nanocomposites can be well characterized by the DC conductivity (σDC), critical frequency (ωc), critical exponent of the power law (s). Roll of DC bias potential led to an increase of DC conductivity (σDC) due to the creation of additional conducting paths with the polymer nanocomposites and percolation behavior achieved through co-continuous morphology.
-
Design of Jet lower hybrid current drive generator and operation of high power test bed
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dobbing, J.A.; Bosia, G.; Brandon, M.; Gammelin, M.; Gormezano, C.; Jacquinot, J.; Jessop, G.; Lennholm, M.; Pain, M.; Sibley, A.
1989-01-01
The JET Lower Hybrid Current Drive (LHCD) generator consists of 24 klystrons each rated for 650 KW operating at 3.7 GHz, giving a nominal generator power of 15.6 MW for 10 seconds or 12 MW for 20 seconds. This power will be transmitted through 24 waveguides to a phased array launcher on one of the main ports of the JET machine. In addition, two klystrons are currently being operated on a high power test bed to establish reliable operation of the generators components and test high power microwave components prior to their installation
-
Improved eddy-current inspection for steam generator tubing
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dodd, C.V.; Pate, J.R.; Allen, J.D. Jr.
1989-01-01
Computer programs have been written to allow the analysis of different types of eddy-current probes and their performance under different steam generator test conditions. The probe types include the differential bobbin probe, the absolute bobbin probe, the pancake probe and the reflection probe. The generator test conditions include tube supports, copper deposits, magnetite deposits, denting, wastage, pitting, cracking and IGA. These studies are based mostly on computed values, with the limited number of test specimens available used to verify the computed results. The instrument readings were computed for a complete matrix of the different test conditions, and then the test conditions determined as a function of the readings by a least-squares technique. A comparison was made of the errors in fit and instrument drift for the different probe types. The computations of the change in instrument reading due to the defects have led to an ''inversion'' technique in which the defect properties can be computed from the instrument readings. This has been done both experimentally and analytically for each of these probe types. 3 refs., 13 figs., 1 tab
-
Model and performance of current sensor observers for a doubly fed induction generator
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Li, Hui; Yang, Chao; Hu, Yaogang
2014-01-01
. A stator and rotor current observer model, which is based on the state-space models of doubly fed induction generators, is then derived by using the stator and rotor voltage signals as inputs. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed current observer, its dynamic performance is simulated using...
-
Im, Chang-Hwan; Park, Ji-Hye; Shim, Miseon; Chang, Won Hyuk; Kim, Yun-Hee
2012-04-01
In this study, local electric field distributions generated by transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) with an extracephalic reference electrode were evaluated to address extracephalic tDCS safety issues. To this aim, we generated a numerical model of an adult male human upper body and applied the 3D finite element method to electric current conduction analysis. In our simulations, the active electrode was placed over the left primary motor cortex (M1) and the reference electrode was placed at six different locations: over the right temporal lobe, on the right supraorbital region, on the right deltoid, on the left deltoid, under the chin, and on the right buccinator muscle. The maximum current density and electric field intensity values in the brainstem generated by the extracephalic reference electrodes were comparable to, or even less than, those generated by the cephalic reference electrodes. These results suggest that extracephalic reference electrodes do not lead to unwanted modulation of the brainstem cardio-respiratory and autonomic centers, as indicated by recent experimental studies. The volume energy density was concentrated at the neck area by the use of deltoid reference electrodes, but was still smaller than that around the active electrode locations. In addition, the distributions of elicited cortical electric fields demonstrated that the use of extracephalic reference electrodes might allow for the robust prediction of cortical modulations with little dependence on the reference electrode locations.
-
Current practices in generation of small molecule new leads.
Goodnow, R A
2001-01-01
The current drug discovery processes in many pharmaceutical companies require large and growing collections of high quality lead structures for use in high throughput screening assays. Collections of small molecules with diverse structures and "drug-like" properties have, in the past, been acquired by several means: by archive of previous internal lead optimization efforts, by purchase from compound vendors, and by union of separate collections following company mergers. More recently, many drug discovery companies have established dedicated efforts to effect synthesis by internal and/or outsourcing efforts of targeted compound libraries for new lead generation. Although high throughput/combinatorial chemistry is an important component in the process of new lead generation, the selection of library designs for synthesis and the subsequent design of library members has evolved to a new level of challenge and importance. The potential benefits of screening multiple small molecule compound library designs against multiple biological targets offers substantial opportunity to discover new lead structures. Subsequent optimization of such compounds is often accelerated because of the structure-activity relationship (SAR) information encoded in these lead generation libraries. Lead optimization is often facilitated due to the ready applicability of high-throughput chemistry (HTC) methods for follow-up synthesis. Some of the strategies, trends, and critical issues central to the success of lead generation processes are discussed below. Copyright 2002 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
-
A TRMM/GPM retrieval of the total mean generator current for the global electric circuit
Peterson, Michael; Deierling, Wiebke; Liu, Chuntao; Mach, Douglas; Kalb, Christina
2017-09-01
A specialized satellite version of the passive microwave electric field retrieval algorithm (Peterson et al., 2015) is applied to observations from the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) and Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) satellites to estimate the generator current for the Global Electric Circuit (GEC) and compute its temporal variability. By integrating retrieved Wilson currents from electrified clouds across the globe, we estimate a total mean current of between 1.4 kA (assuming the 7% fraction of electrified clouds producing downward currents measured by the ER-2 is representative) to 1.6 kA (assuming all electrified clouds contribute to the GEC). These current estimates come from all types of convective weather without preference, including Electrified Shower Clouds (ESCs). The diurnal distribution of the retrieved generator current is in excellent agreement with the Carnegie curve (RMS difference: 1.7%). The temporal variability of the total mean generator current ranges from 110% on semi-annual timescales (29% on an annual timescale) to 7.5% on decadal timescales with notable responses to the Madden-Julian Oscillation and El Nino Southern Oscillation. The geographical distribution of current includes significant contributions from oceanic regions in addition to the land-based tropical chimneys. The relative importance of the Americas and Asia chimneys compared to Africa is consistent with the best modern ground-based observations and further highlights the importance of ESCs for the GEC.
-
Unbundling in Current Broadband and Next-Generation Ultra-Broadband Access Networks
Gaudino, Roberto; Giuliano, Romeo; Mazzenga, Franco; Valcarenghi, Luca; Vatalaro, Francesco
2014-05-01
This article overviews the methods that are currently under investigation for implementing multi-operator open-access/shared-access techniques in next-generation access ultra-broadband architectures, starting from the traditional "unbundling-of-the-local-loop" techniques implemented in legacy twisted-pair digital subscriber line access networks. A straightforward replication of these copper-based unbundling-of-the-local-loop techniques is usually not feasible on next-generation access networks, including fiber-to-the-home point-to-multipoint passive optical networks. To investigate this issue, the article first gives a concise description of traditional copper-based unbundling-of-the-local-loop solutions, then focalizes on both next-generation access hybrid fiber-copper digital subscriber line fiber-to-the-cabinet scenarios and on fiber to the home by accounting for the mix of regulatory and technological reasons driving the next-generation access migration path, focusing mostly on the European situation.
-
Application possibility of the direct current conduction method for nondestructive crack measurement
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Riedl, R.
1982-01-01
An important value to determine the danger of cracks is the determination of crack depths. The crack depth can be determined quite accurate by means of the direct current conduction method, if one holds onto certain rules. Often complicated experimental set-ups are applied. However, portable commercial devices can be obtained that can be used for partial fluxation, that yield good results. By means of two examples: crack conduction samples in which the built-up of a constant-cracking is persued up to a certain depth, as well as the persuasion of an continuing crack in a bearing cylinder, shall be demonstrated that is very well possible to record accurate profiles with commercial devices and to avoid expensive measurement devices. (orig.) [de
-
Thyristor current-pulse generator for betatron electromagnet with independent low-voltage supply
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Baginskii, B.A.; Makarevich, V.N.; Shtein, M.M.
1989-01-01
A thyristor generator is described that produces unipolar current pulses in the winding of a betatron electromagnet. The voltage on the electro-magnet is increased and the shape of the current pulses is improved by use of an intermediate inductive storage device. The current pulses have a duration of 11 msec, an amplitude of 190 A, and a repetition frequency of 50 Hz. The maximum magnetic-field energy is 450 J, the voltage on the electromagnet winding is 1.5 kV, and the supply voltage is 27 V
-
Multifrequency eddy current testing of helical tubes of steam generators
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pigeon, M.; David, B.
1983-06-01
In the event of a water-sodium reaction in a steam-generator of a fast breeder reactor, it is necessary to test the tubes close to the leak to evaluate the damage. In SUPERPHENIX, the tubes are about 100m long and are coiled on a dead body. This report describes the equipment and the technic to test such tubes with multifrequency eddy current technics [fr
-
Mini Solar and Sea Current Power Generation System
Almenhali, Abdulrahman; Alshamsi, Hatem; Aljunaibi, Yaser; Almussabi, Dheyab; Alshehhi, Ahmed; Hilal, Hassan Bu
2017-07-01
The power demand in United Arab Emirates is increased so that there is a consistent power cut in our region. This is because of high power consumption by factories and also due to less availability of conventional energy resources. Electricity is most needed facility for the human being. All the conventional energy resources are depleting day by day. So we have to shift from conventional to non-conventional energy resources. In this the combination of two energy resources is takes place i.e. wind and solar energy. This process reviles the sustainable energy resources without damaging the nature. We can give uninterrupted power by using hybrid energy system. Basically this system involves the integration of two energy system that will give continuous power. Solar panels are used for converting solar energy and wind turbines are used for converting wind energy into electricity. This electrical power can utilize for various purpose. Generation of electricity will be takes place at affordable cost. This paper deals with the generation of electricity by using two sources combine which leads to generate electricity with affordable cost without damaging the nature balance. The purpose of this project was to design a portable and low cost power system that combines both sea current electric turbine and solar electric technologies. This system will be designed in efforts to develop a power solution for remote locations or use it as another source of green power.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nishi, Shohei; Taguchi, Dai; Manaka, Takaaki; Iwamoto, Mitsumasa, E-mail: iwamoto@pe.titech.ac.jp [Department of Physical Electronics, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 2-12-1 S3-33, O-okayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 152-8552 (Japan)
2015-06-28
By using electric-field-induced optical second-harmonic generation measurement coupled with the conventional current-voltage (I-V) measurement, we studied the carrier transport of organic double-layer diodes with a Au/pentacene/fluorine polymer (FP)/indium zinc oxide (IZO) structure. The rectifying I-V characteristics were converted into the I-E characteristics of the FP and pentacene layers. Results suggest a model in which Schottky-type electron injection from the IZO electrode to the FP layer governs the forward electrical conduction (V > 0), where the space charge electric field produced in the FP layer by accumulated holes at the pentacene/FP interface makes a significant contribution. On the other hand, Schottky-type injection by accumulated interface electrons from the pentacene layer to the FP layer governs the backward electrical conduction (V < 0). The electroluminescence generated from the pentacene layer in the region V > 0 verifies the electron transport across the FP layer, and supports the above suggested model.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nishi, Shohei; Taguchi, Dai; Manaka, Takaaki; Iwamoto, Mitsumasa
2015-01-01
By using electric-field-induced optical second-harmonic generation measurement coupled with the conventional current-voltage (I-V) measurement, we studied the carrier transport of organic double-layer diodes with a Au/pentacene/fluorine polymer (FP)/indium zinc oxide (IZO) structure. The rectifying I-V characteristics were converted into the I-E characteristics of the FP and pentacene layers. Results suggest a model in which Schottky-type electron injection from the IZO electrode to the FP layer governs the forward electrical conduction (V > 0), where the space charge electric field produced in the FP layer by accumulated holes at the pentacene/FP interface makes a significant contribution. On the other hand, Schottky-type injection by accumulated interface electrons from the pentacene layer to the FP layer governs the backward electrical conduction (V < 0). The electroluminescence generated from the pentacene layer in the region V > 0 verifies the electron transport across the FP layer, and supports the above suggested model
-
Ghasemi, Kasra; Siavashi, Majid
2017-11-01
MHD natural convection of Cu-water nanofluid in a square porous enclosure is investigated using a parallel LBM code, considering temperature dependence of viscosity and viscous dissipation. Effects of nanofluid concentration (φ = 0 - 0.12), Rayleigh (Ra =103 -106), Hartmann (Ha = 0-20) and porous-fluid thermal conductivity ratio (K∗ = 1-70) on heat transfer and entropy generation are investigated. It is shown that K∗ is a very important parameter, and porous media with low K∗ numbers can confine convection effects, but by increasing K∗ both conduction and convection effects can substantially improve. Also, magnetic field always has negative impact on Nu, however this impact can be controlled by φ and K∗. A magnetic instability has also observed in Ra = 104, and Nu exhibits a sinusoidal variation with Ha. It is proved that, depending on K∗, Ra and Ha values, use of nanofluid with porous media to enhance heat transfer can be either beneficial or detrimental. Also, for given K∗, Ra and Ha numbers an optimal φ exists to improve heat transfer. Finally, entropy generation study performed and results state that in low and high Ra values the thermal and frictional entropy generation are respectively dominant, while for moderate Ra they have the same order of magnitude.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nikam, Pravin N., E-mail: pravinya26@gmail.com; Deshpande, Vineeta D., E-mail: drdeshpandevd@gmail.com [Department of Physics, Institute of Chemical Technology, Matunga, Mumbai-400019, Maharashtra (India)
2016-05-06
Polymer nanocomposites based on metal oxide (ceramic) nanoparticles are a new class of materials with unique properties and designed for various applications such as electronic device packaging, insulation, fabrication and automotive industries. Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET)/alumina (Al{sub 2}O{sub 3}) nanocomposites with filler content between 1 wt% and 5 wt% were prepared by melt compounding method using co-rotating twin screw extruder and characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and precision LCR meter techniques. The results revealed that proper uniform dispersion at lower content up to 2 wt% of nano-alumina observed by using TEM. Aggregation of nanoparticles was observed at higher content of alumina examined by using SEM and TEM. The frequency dependences of the alternating current (AC) conductivity (σ{sub AC}) of PET/alumina nanocomposites on the filler content and DC bias were investigated in the frequency range of 20Hz - 1MHz. The results showed that the AC and direct current (DC) conductivity increases with increasing DC bias and nano-alumina content upto 3 wt%. It follows the Jonscher’s universal power law of solids. It revealed that σ{sub AC} of PET/alumina nanocomposites can be well characterized by the DC conductivity (σ{sub DC}), critical frequency (ω{sub c}), critical exponent of the power law (s). Roll of DC bias potential led to an increase of DC conductivity (σ{sub DC}) due to the creation of additional conducting paths with the polymer nanocomposites and percolation behavior achieved through co-continuous morphology.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nikam, Pravin N.; Deshpande, Vineeta D.
2016-01-01
Polymer nanocomposites based on metal oxide (ceramic) nanoparticles are a new class of materials with unique properties and designed for various applications such as electronic device packaging, insulation, fabrication and automotive industries. Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET)/alumina (Al_2O_3) nanocomposites with filler content between 1 wt% and 5 wt% were prepared by melt compounding method using co-rotating twin screw extruder and characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and precision LCR meter techniques. The results revealed that proper uniform dispersion at lower content up to 2 wt% of nano-alumina observed by using TEM. Aggregation of nanoparticles was observed at higher content of alumina examined by using SEM and TEM. The frequency dependences of the alternating current (AC) conductivity (σ_A_C) of PET/alumina nanocomposites on the filler content and DC bias were investigated in the frequency range of 20Hz - 1MHz. The results showed that the AC and direct current (DC) conductivity increases with increasing DC bias and nano-alumina content upto 3 wt%. It follows the Jonscher’s universal power law of solids. It revealed that σ_A_C of PET/alumina nanocomposites can be well characterized by the DC conductivity (σ_D_C), critical frequency (ω_c), critical exponent of the power law (s). Roll of DC bias potential led to an increase of DC conductivity (σ_D_C) due to the creation of additional conducting paths with the polymer nanocomposites and percolation behavior achieved through co-continuous morphology.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Bo Dong
2015-01-01
Full Text Available During geomagnetic disturbances, the telluric currents which are driven by the induced electric fields will flow in conductive Earth. An approach to model the Earth conductivity structures with lateral conductivity changes for calculating geoelectric fields is presented in this paper. Numerical results, which are obtained by the Finite Element Method (FEM with a planar grid in two-dimensional modelling and a solid grid in three-dimensional modelling, are compared, and the flow of induced telluric currents in different conductivity regions is demonstrated. Then a three-dimensional conductivity structure is modelled and the induced currents in different depths and the geoelectric field at the Earth’s surface are shown. The geovoltages by integrating the geoelectric field along specific paths can be obtained, which are very important regarding calculations of geomagnetically induced currents (GIC in ground-based technical networks, such as power systems.
-
Current Status on the Development of a Double Wall Tube Steam Generator
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nam, Ho Yun; Choi, Byoung Hae; Kim, Jong Man; Kim, Byung Ho
2007-12-15
A fast reactor, which uses sodium as a coolant, has a lot of merits as a next generation nuclear reactor. However, the possibility of a sodium-water reaction occurrence hinders the commercialization of this reactor. As one way to improve the reliability of a steam generator, a double-wall tube steam generator is being developed in GEN-4 program. In this report, the current state of the technical developments for a double-wall tube steam generator are reviewed and a future plan for the development of a double-wall tube steam generator is established. The current focuses of this research are an improvement of the heat transfer capability for a double-wall tube and the development of a proper leak detection method for the failure of a double-wall tube during a reactor operation. The ideal goal is an on-line leak detection of a double wall tube to prevent the sodium-water reaction. However, such a method is not developed as yet. An alternative method is being used to improve the reliability of a steam generator by performing a non-destructive test of a double wall tube during the refueling period of a reactor. In this method a straight double wall tube is employed to perform this test easily, but has a difficulty regarding an absorption of a thermal expansion of the used materials. If an on-line leak detection method is developed, the demerits of a straight double-wall tube are avoided by using a helical type double-wall tube, and the probability of a sodium-water reaction can be reduced to a level less than the design-based accident.
-
Eddy-current tests on operational evaluation of steam generator tubes in nuclear power plants
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lopez, Luiz Antonio Negro Martin; Ting, Daniel Kao Sun
2000-01-01
This paper presents a worldwide research on the technical and economical impacts due to failure in tube bundles of nuclear power plant steam generators. An Eddy current non destructive test using Foucault currents for the inspection and failure detection on the tubes, and also the main type of defects. The paper also presents the signals generated by a Zetec MIZ-40 test equipment. This paper also presents a brief description of an automatic system for data analysis which is under development by using a fuzzy logic and artificial intelligence
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lepine, B.A.; Van Langen, J.; Obrutsky, L.
2006-01-01
This paper presents an overview of the x-probe MB 350 eddy current inspection array probe, for detection of open OD axial crack-like flaws in Monel 400 tubes at Pickering Nuclear Generating Station. This report contains a selection of inspection results from the field inspections performed with this probe during the 2003 and 2004 period at Pickering Nuclear Generating Station A and B. During the 2003 in-service eddy current inspection results of Pickering Nuclear Generating Station A (PNGS-A) Unit 2, a 13 mm (0.5 inch) long axial indication was detected by the CTR1 bobbin and CTR2-C4 array probes in Tube R25-C52 of Steam Generator (SG) 11 in the hot leg sludge pile region. An experimental magnetic bias X-probe, specially designed by Zetec for inspection of Monel 400 tubing, was deployed and the indication was characterized as a potential out diameter (OD) axially oriented crack. Post-inspection tube pulling and destructive examination confirmed the presence of an Environmentally Assisted Crack (EAC), approximately 80% deep and 13mm long. Due to the significance of this discovery, Ontario Power Generation (OPG) requested AECL to initiate a program for qualification of the X-probe MB 350 for the detection of OD axial cracks in medium to high magnetic permeability μ r Monel 400 PNGS-A and B steam generator tubing at different locations. The X-probe MB 350 subsequently has been deployed as a primary inspection probe for crack detection for PNGS steam generators. (author)
-
Non-Gaussian conductivity fluctuations in semiconductors
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Melkonyan, S.V.
2010-01-01
A theoretical study is presented on the statistical properties of conductivity fluctuations caused by concentration and mobility fluctuations of the current carriers. It is established that mobility fluctuations result from random deviations in the thermal equilibrium distribution of the carriers. It is shown that mobility fluctuations have generation-recombination and shot components which do not satisfy the requirements of the central limit theorem, in contrast to the current carrier's concentration fluctuation and intraband component of the mobility fluctuation. It is shown that in general the mobility fluctuation consist of thermal (or intraband) Gaussian and non-thermal (or generation-recombination, shot, etc.) non-Gaussian components. The analyses of theoretical results and experimental data from literature show that the statistical properties of mobility fluctuation and of 1/f-noise fully coincide. The deviation from Gaussian statistics of the mobility or 1/f fluctuations goes hand in hand with the magnitude of non-thermal noise (generation-recombination, shot, burst, pulse noises, etc.).
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Lin, Li; Jensen, Flemming; Herstrøm, Berit
Transparent conductive aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO) layer was deposited on GaN-based near-ultraviolet (NUV) light emitting epitaxial wafers as current spreading layer by a sputtering process. Efforts were made to improve the electrical properties of AZO in order to produce ohmic contact....
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Takeuchi, Esther [Stony Brook Univ., NY (United States)
2016-11-30
Our results for this program “Electrochemically smart bimetallic materials featuring Group 11 metals: in-situ conductive matrix generation and its impact on battery capacity, power and reversibility” have been highly successful: 1) we demonstrated material structures which generated in-situ conductive networks through electrochemical activation with increases in conductivity up to 10,000 fold, 2) we pioneered in situ analytical methodology to map the cathodes at several stages of discharge through the use of Energy Dispersive X-ray Diffraction (EDXRD) to elucidate the kinetic dependence of the conductive network formation, and 3) we successfully designed synthetic methodology for direct control of material properties including crystallite size and surface area which showed significant impact on electrochemical behavior.
-
Roll type conducting polymer legs for rigid-flexible thermoelectric generator
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Teahoon Park
2017-07-01
Full Text Available A roll-type conducting polymer film was explored as a flexible organic p-type thermoelectric leg using poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (PEDOT doped with tosylate. The PEDOT films were prepared through solution casting polymerization and rolled up for a roll-type leg. Due to the high flexibility, the roll-type PEDOT leg enabled easy contact to both top and bottom electrodes. Simulation on the dynamic heat transfer and convective cooling for a vertically roosted rod- and roll-type PEDOT leg showed that the temperature difference (ΔT between the hot and cold sides of the leg was much higher in the roll than that of the rod. The PEDOT legs were integrated with n-type Bi2Te3 blocks, to give a 36-couple rigid-flexible thermoelectric generator (RF-TEG. The maximum output voltage from the 36-couple RF-TEG under a ΔT of 7.9 K was determined as 36.7 mV along with a high output power of 115 nW. A wearable RF-TEG was prepared upon the combination of the 36-couple RF-TEG with an arm warmer, to afford an output voltage of 10.6 mV, which was generated constantly and steadily from human wrist heat.
-
Generation of stable mixed-compact-toroid rings by inducing plasma currents in strong E rings
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jayakumar, R.; Taggart, D.P.; Parker, M.R.; Fleischmann, H.H.
1989-01-01
In the RECE-Christa device, hybrid-type compact toroid rings are generated by inducing large toroidal plasma currents I rho in strong electron rings using a thin induction coil positioned along the ring axis. Starting from field-reversal values δ ο = 50 - 120 percent of the original pure fast-electron ring, the induced plasma current I rho raises δ to a maximum value of up to 240 percent with I rho contributing more than 50 percent of the total ring current. Quite interestingly, the generated hybrid compact toroid configurations appear gross-stable during the full I rho pulse length (half-amplitude width about 100 μs)
-
On the evaluation of currents in a tokamak plasma during combined Ohmic and RF current drive
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Eckhartt, D.
1986-09-01
By taking into account the rf-generated enhancement of the plasma electric conductivity (as formulated by Fisch in the limit of weak dc electric fields) a relation is derived between the ratio of rf to Ohmically driven currents and other plasma parameters to be measured before and after the rf onset under the condition of constant net plasma current. (author)
-
Self-consistent model for the radial current generation during fishbone activity
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lutsenko, V.V.; Marchenko, V.S.
2002-01-01
Line broadened quasilinear burst model, originally developed for the bump-on-tail instability [H. L. Berk et al., Nucl. Fusion 35, 1661 (1995)], is extended to the problem of sheared flow generation by the fishbone burst. It is supposed that the radial current of the resonant fast ions can be sufficient to create the transport barrier
-
Li, Yi; Yin, Kang-Sheng; Zhang, Mei-Yun; Cheng, Long; Lu, Ke; Long, Shi-Bing; Zhou, Yaxiong; Wang, Zhuorui; Xue, Kan-Hao; Liu, Ming; Miao, Xiang-Shui
2017-11-01
Memristors are attracting considerable interest for their prospective applications in nonvolatile memory, neuromorphic computing, and in-memory computing. However, the nature of resistance switching is still under debate, and current fluctuation in memristors is one of the critical concerns for stable performance. In this work, random telegraph noise (RTN) as the indication of current instabilities in distinct resistance states of the Pt/Ti/HfO2/W memristor is thoroughly investigated. Standard two-level digital-like RTN, multilevel current instabilities with non-correlation/correlation defects, and irreversible current transitions are observed and analyzed. The dependence of RTN on the resistance and read bias reveals that the current fluctuation depends strongly on the morphology and evolution of the conductive filament composed of oxygen vacancies. Our results link the current fluctuation behaviors to the evolution of the conductive filament and will guide continuous optimization of memristive devices.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Vich, Catalina; Berg, Rune W.; Guillamon, Antoni
2017-01-01
Subthreshold fluctuations in neuronal membrane potential traces contain nonlinear components, and employing nonlinear models might improve the statistical inference. We propose a new strategy to estimate synaptic conductances, which has been tested using in silico data and applied to in vivo...... recordings. The model is constructed to capture the nonlinearities caused by subthreshold activated currents, and the estimation procedure can discern between excitatory and inhibitory conductances using only one membrane potential trace. More precisely, we perform second order approximations of biophysical...... models to capture the subthreshold nonlinearities, resulting in quadratic integrate-and-fire models, and apply approximate maximum likelihood estimation where we only suppose that conductances are stationary in a 50–100 ms time window. The results show an improvement compared to existent procedures...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Thatcher, G.; Ferguson, B.G.; Winstanley, J.P.
1984-01-01
An induced current heating probe is of thimble form and has an outer conducting sheath and a water flooded flux-generating unit formed from a stack of ferrite rings coaxially disposed in the sheath. The energising coil is made of solid wire which connects at one end with a coaxial water current tube and at the other end with the sheath. The stack of ferrite rings may include non-magnetic insulating rings which help to shape the flux. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sakurai, Keiichi; Okuda, Takayoshi; Tanaka, Yuji.
1977-01-01
The effect of finite conductivity on the stability of a tokamak plasma column with noncircular cross section without conducting shell was investigated by considering the current filaments model. The study is made for the plasma with rectangular cross section, and in this case, the position control of plasma column is a serious problem. The equation of motion of the plasma column is described for the vertical force applied to the column. The calculation of stability was made for the cases with cross sections of circular, rectangular and D type shapes. The plasma column was considered as an assembly of a lot of circular conductors, and this method can be applied to the plasma column with proper distribution of conductivity. As the results of calculation, it can be said that the electromotive force produced by the column moving in the magnetic field generates surface current on the plasma column, and in case of the finite conductivity of plasma, this current attenuates with time, and the distribution of the current soaks into the plasma column. Consequently, the recovery force acting on the plasma column is reduced, but contributes to the vertical stabilization for several hundreds μsec. (Kato, T.)
-
Spin-current emission governed by nonlinear spin dynamics.
Tashiro, Takaharu; Matsuura, Saki; Nomura, Akiyo; Watanabe, Shun; Kang, Keehoon; Sirringhaus, Henning; Ando, Kazuya
2015-10-16
Coupling between conduction electrons and localized magnetization is responsible for a variety of phenomena in spintronic devices. This coupling enables to generate spin currents from dynamical magnetization. Due to the nonlinearity of magnetization dynamics, the spin-current emission through the dynamical spin-exchange coupling offers a route for nonlinear generation of spin currents. Here, we demonstrate spin-current emission governed by nonlinear magnetization dynamics in a metal/magnetic insulator bilayer. The spin-current emission from the magnetic insulator is probed by the inverse spin Hall effect, which demonstrates nontrivial temperature and excitation power dependences of the voltage generation. The experimental results reveal that nonlinear magnetization dynamics and enhanced spin-current emission due to magnon scatterings are triggered by decreasing temperature. This result illustrates the crucial role of the nonlinear magnon interactions in the spin-current emission driven by dynamical magnetization, or nonequilibrium magnons, from magnetic insulators.
-
Nayak, Rabindra S; Shafiuddin, Bareera; Pasha, Azam; Vinay, K; Narayan, Anjali; Shetty, Smitha V
2015-07-01
Technological advances in wire selection and bracket design have led to improved treatment efficiency and allowed longer time intervals between appliance adjustments. The wires remain in the mouth for a longer duration and are subjected to electrochemical reactions, mechanical forces of mastication and generalized wear. These cause different types of corrosion. This study was done to compare the galvanic currents generated between different combinations of brackets and archwires commonly used in orthodontic practices. The materials used for the study included different commercially available orthodontic archwires and brackets. The galvanic current generated by individual materials and different combinations of these materials was tested and compared. The orthodontic archwires used were 0.019″ × 0.025″ heat-activated nickel-titanium (3M Unitek), 0.019″ × 0.025″ beta-titanium (3M Unitek) and 0.019″ × 0.025″ stainless steel (3M Unitek). The orthodontic brackets used were 0.022″ MBT laser-cut (Victory Series, 3M Unitek) and metal-injection molded (Leone Company) maxillary central incisor brackets respectively. The ligature wire used for ligation was 0.009″ stainless steel ligature (HP Company). The galvanic current for individual archwires, brackets, and the different bracket-archwire-ligature combinations was measured by using a Potentiostat machine. The data were generated using the Linear Sweep Voltammetry and OriginPro 8.5 Graphing and Data Analysis Softwares. The study was conducted in two phases. Phase I comprised of five groups for open circuit potential (OCP) and galvanic current (I), whereas Phase II comprised of six groups for galvanic current alone. Mean, standard deviation and range were computed for the OCP and galvanic current (I) values obtained. Results were subjected to statistical analysis through ANOVA. In Phase I, higher mean OCP was recorded in stainless steel archwire, followed by beta-titanium archwire, heat-activated nickel
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rath, Pravat Kumar; Dash, G.C.; Patra, Ajit Kumar
2010-01-01
Effect of Hall current on the unsteady free convection flow of an electrically conducting incompressible viscous fluid past an exponentially accelerated vertical porous flat plate with internal heat absorption/generation in the presence of foreign gases (such as H 2 , CO 2 , H 2 O, NH 3 ) and chemical reaction has been investigated. An uniform magnetic field transverse to the plate has been applied. The effects of the Hall current m, the hydromagnetic parameter Mt, the chemical reaction parameter K c the Grashof number for heat transfer G r , the Grashof number for mass transfer G c , the Schmidt number S c , the Prandtl number P r and the transpiration parameter α are discussed in detail. (author)
-
Current generation by alpha particles interacting with lower hybrid waves in TOKAMAKS
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Belikov, V.S.; Kolesnichenko, Ya.I.; Lisak, M.; Anderson, D.
1990-01-01
The problem of the influence of fusion generated alpha particles on lower-hybrid-wave current drive is examined. Analysis is based on a new equation for the LH-wave-fast ion interaction which is derived by taking into consideration the non-zero value of the longitudinal wave number. The steady-state velocity distribution function for high energy alpha particles is found. The alpha current driven by LH-waves as well as the RF-power absorbed by alpha particle are calculated. (authors)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Torabi, Mohsen; Zhang, Kaili
2015-01-01
Highlights: • First and second laws of thermodynamics have been investigated in a composite wall. • Convective–radiative heat transfer is assumed on both surfaces. • Optimum interface location is calculated to minimize the total entropy generation rate. • Thermal conductivities ratio has great effects on the temperature and entropy generation. - Abstract: Composite geometries have numerous applications in industry and scientific researches. This work investigates the temperature distribution, and local and total entropy generation rates within two-layer composite walls using conjugate convection and radiation boundary conditions. Thermal conductivities of the materials of walls are assumed temperature-dependent. Temperature-dependent internal heat generations are also incorporated into the modeling. The differential transformation method (DTM) is used as an analytical technique to tackle the highly nonlinear system of ordinary differential equations. Thereafter, the local and total entropy generation rates are calculated using the DTM formulated temperature distribution. An exact analytical solution, for the temperature-independent model without radiation effect, is also derived. The correctness and accuracy of the DTM solution are checked against the exact solution. After verification, effects of thermophysical parameters such as location of the interface, convection–conduction parameters, radiation–conduction parameters, and internal heat generations, on the temperature distribution, and both local and total entropy generation rates are examined. To deliver the minimum total entropy generation rate, optimum values for some parameters are also found. Since composite walls are widely used in many fields, the abovementioned investigation is a beneficial tool for many engineering industries and scientific fields to minimize the entropy generation, which is the exergy destruction, of the system
-
Reconstitution of Biological Molecular generators of electric current. Bacteriorhodopsin.
Drachev, L A; Frolov, V N; Kaulen, A D; Liberman, E A; Ostroumov, S A; Plakunova, V G; Semenov, A Y; Skulachev, V P
1976-11-25
1. Photoinduced generation of electric current by bacteriorhodopsin, incorporated into the planar phospholipid membrane, has been directly measured with conventional electrometer techniques. 2. Two methods for bacteriorhodopsin incorporation have been developed: (a) formation of planar membrane from a mixture of decane solution of phospholipids and of the fraction of violet fragments of the Halobacterium halobium membrane (bacteriorhodopsin sheets), and (b) adhesion of bacteriorhodopsin-containing reconstituted spherical membranes (proteoliposomes) to the planar membrane in the presence of Ca2+ or some other cations. In both cases, illumination was found to induce electric current generation directed across the planar membrane, an effect which was measured by macroelectrodes immersed into electrolyte solutions on both sides of the membrane. 3. The maximal values of the transmembrane electric potential were of about 150 mV at a current of about 10(-11) A. The electromotive force measured by means of counterbalancing the photoeffect by an external battery, was found to reach the value of 300 mV. 4. The action spectrum of the photoeffect coincides with the bacteriorhodopsin absorption spectrum (maximum about 570 nm). 5. Both components of the electrochemical potential of H+ ions (electric potential and delta pH) across the planar membrane affect the bacteriorhodopsin photoelectric response in a fashion which could be expected if bacteriorhodopsin were a light-dependent electrogenic proton pump. 6. La3+ ions were shown to inhibit operation of those bacteriorhodopsin which pump out H+ ions from the La3+-containing compartment. 7. The photoeffect, mediated by proteoliposomes associated with thick planar membrane, is decreased by gramicidin A at concentrations which do not influence the planar membrane resistance in the light. On the contrary, a protonophorous uncoupler, trichlorocarbonylcyanidephenylhydrazone, decreases the photoeffect only if it is added at a
-
Electricity generation in the world and Ukraine: Current status and future developments
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Alexander Zvorykin
2017-11-01
Full Text Available Electricity generation is the key factor for advances in industry, agriculture, technology and the level of living. Also, strong power industry with diverse energy sources is very important for country independence. In general, electricity can be generated from: 1 non-renewable energy sources such as coal, natural gas, oil, and nuclear; and 2 renewable energy sources such as hydro, biomass, wind, geothermal, solar, and wave power. However, the major energy sources for electricity generation in the world are: 1 thermal power – primarily using coal (~40% and secondarily natural gas (~23%; 2 “large” hydro power plants (~17% and 3 nuclear power from various reactor designs (~11%. The rest of the energy sources for electricity generation is from using oil (~4% and renewable sources such as biomass, wind, geothermal and solar (~5%, which have just visible impact in selected countries. In addition, energy sources, such as wind and solar, and some others, like tidal and wave-power, are intermittent from depending on Mother Nature. And cannot be used alone for industrial electricity generation. Nuclear power in Ukraine is the most important source of electricity generation in the country. Currently, Ukrainian Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs generate about 45.5% of the total electricity followed with coal generation ‒ 38%, gas generation 9.6% and the rest is based on renewable sources, mainly on hydro power plants – 5.9%. Nuclear-power industry is based on four NPPs (15 Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs including the largest one in Europe ‒ Zaporizhzhya NPP with about 6,000 MWel gross installed capacity. Two of these 15 reactors have been built and put into operation in 70-s, ten in 80-s, one in 90-s and just two in 2004. Therefore, based on an analysis of the world power reactors in terms of their maximum years of operation (currently, the oldest reactors are ~45-year old several projections have been made for future of the nuclear-power industry
-
The current waste generation and management trends in South Africa: A Review
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Nkosi, N
2013-04-01
Full Text Available This paper, a continuation and expansion of the work of Muzenda et al, 2012 [1] looks at the current waste generation and management trends in South Africa. The waste tyre problem in South Africa is also briefly discussed. Solid waste management...
-
Eddy Current Loss Modeling for Design of PM Generators for Wind Turbines
Jassal, A.
2014-01-01
This thesis deals with analysis, calculation and validation of eddy current loss models for Permanent Magnet (PM) direct drive generators for wind turbines. The modelling approach is a mixed use of analytical and Finite Element (FE) methods. The models are validated experimentally and design
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Koliner, J. J.; Boguski, J., E-mail: boguski@wisc.edu; Anderson, J. K.; Chapman, B. E.; Den Hartog, D. J.; Duff, J. R.; Goetz, J. A.; McGarry, M.; Morton, L. A.; Parke, E. [Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin 53706 (United States); Cianciosa, M. R. [Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 37831 (United States); Hanson, J. D. [Department of Physics, Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama 36849 (United States); Brower, D. L.; Ding, W. X. [Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90095 (United States)
2016-03-15
In order to characterize the Madison Symmetric Torus (MST) reversed-field pinch (RFP) plasmas that bifurcate to a helical equilibrium, the V3FIT equilibrium reconstruction code was modified to include a conducting boundary. RFP plasmas become helical at a high plasma current, which induces large eddy currents in MST's thick aluminum shell. The V3FIT conducting boundary accounts for the contribution from these eddy currents to external magnetic diagnostic coil signals. This implementation of V3FIT was benchmarked against MSTFit, a 2D Grad-Shafranov solver, for axisymmetric plasmas. The two codes both fit B{sub θ} measurement loops around the plasma minor diameter with qualitative agreement between each other and the measured field. Fits in the 3D case converge well, with q-profile and plasma shape agreement between two distinct toroidal locking phases. Greater than 60% of the measured n = 5 component of B{sub θ} at r = a is due to eddy currents in the shell, as calculated by the conducting boundary model.
-
Hamachi, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Tohei, T.; Imanishi, M.; Imade, M.; Mori, Y.; Sakai, A.
2018-04-01
The mechanisms associated with electrical conduction through individual threading dislocations (TDs) in a Na-flux GaN crystal grown with a multipoint-seed-GaN technique were investigated by conductive atomic force microscopy (C-AFM). To focus on individual TDs, dislocation-related etch pits (DREPs) were formed on the Na-flux GaN surface by wet chemical etching, after which microscopic Pt electrodes were locally fabricated on the DREPs to form conformal contacts to the Na-flux GaN crystal, using electron beam assisted deposition. The C-AFM data clearly demonstrate that the leakage current flows through the individual TD sites. It is also evident that the leakage current and the electrical conduction mechanism vary significantly based on the area within the Na-flux GaN crystal where the TDs are formed. These regions include the c-growth sector (cGS) in which the GaN grows in the [0001 ] direction on top of the point-seed with a c-plane growth front, the facet-growth sector (FGS) in which the GaN grows with {10 1 ¯ 1 } facets on the side of the cGS, the boundary region between the cGS and FGS (BR), and the coalescence boundary region between FGSs (CBR). The local current-voltage (I-V) characteristics of the specimen demonstrate space charge limited current conduction and conduction related to band-like trap states associated with TDs in the FGS, BR, and CBR. A detailed analysis of the I-V data indicates that the electrical conduction through TDs in the cGS may proceed via the Poole-Frenkel emission mechanism.
-
Performance demonstration requirements for eddy current steam generator tube inspection
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kurtz, R.J.; Heasler, P.G.; Anderson, C.M.
1992-10-01
This paper describes the methodology used for developing performance demonstration tests for steam generator tube eddy current (ET) inspection systems. The methodology is based on statistical design principles. Implementation of a performance demonstration test based on these design principles will help to ensure that field inspection systems have a high probability of detecting and correctly sizing tube degradation. The technical basis for the ET system performance thresholds is presented. Probability of detection and flaw sizing tests are described
-
Detection and study of photo-generated spin currents in nonmagnetic semiconductor materials
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Miah, M. Idrish; Kityk, I.V.; Gray, E. MacA.
2007-01-01
The longitudinal current in Si-doped gallium arsenide was spin-polarized using circularly polarized light. The spin current was detected by the extraordinary Hall effect. An enhancement of Hall conductivity with increasing moderately Si-doping was found, indicating that the introduction of dopants increases the electronic spin polarization. This finding may provide an opportunity for controlling and manipulating nonmagnetic semiconductors via electron spin for operating device applications. Band energy calculations using pseudopotentials confirm the influence of Si content and electron-phonon interaction on the behaviour of the spin current and hence on the spin-dependent Hall voltage
-
Detection and study of photo-generated spin currents in nonmagnetic semiconductor materials
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Miah, M. Idrish [Nanoscale Science and Technology Centre, Griffith University, Nathan, Brisbane, QLD 4111 (Australia); Department of Physics, University of Chittagong, Chittagong 4331 (Bangladesh)], E-mail: m.miah@griffith.edu.au; Kityk, I.V. [Institute of Physics, J. Dlugosz University Czestochowa, PL-42201 Czestochowa (Poland); Gray, E. MacA. [Nanoscale Science and Technology Centre, Griffith University, Nathan, Brisbane, QLD 4111 (Australia)
2007-10-15
The longitudinal current in Si-doped gallium arsenide was spin-polarized using circularly polarized light. The spin current was detected by the extraordinary Hall effect. An enhancement of Hall conductivity with increasing moderately Si-doping was found, indicating that the introduction of dopants increases the electronic spin polarization. This finding may provide an opportunity for controlling and manipulating nonmagnetic semiconductors via electron spin for operating device applications. Band energy calculations using pseudopotentials confirm the influence of Si content and electron-phonon interaction on the behaviour of the spin current and hence on the spin-dependent Hall voltage.
-
On the generation of steady currents in a plasma cylinder using RF waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hugrass, W.N.
1980-10-01
The generation of a steady current in a resistive plasma cylinder by means of a travelling wave magnetic field has been studied using the resistive MHD equations. The nonlinear initial-boundary value problem has been solved using a semi-Lagrangian two dimensional algorithm. The numerical code has been used to simulate the Synchromak experiment of Nagoya University. Hollow d.c. current profiles, similar to the experimental data, have been obtained. A simple analytical argument, of a more general nature, shows that classical resistive diffusion cannot lead to a more uniform current distribution
-
2015-01-01
The cercal system of crickets detects low-frequency air currents produced by approaching predators and self-generated air currents during singing, which may provide sensory feedback to the singing motor network. We analyzed the effect of cercal stimulation on singing motor pattern generation to reveal the response of a singing interneuron to predator-like signals and to elucidate the possible role of self-generated air currents during singing. In fictive singing males, we recorded an interneuron of the singing network while applying air currents to the cerci; additionally, we analyzed the effect of abolishing the cercal system in freely singing males. In fictively singing crickets, the effect of short air stimuli is either to terminate prematurely or to lengthen the interchirp interval, depending on their phase in the chirp cycle. Within our stimulation paradigm, air stimuli of different velocities and durations always elicited an inhibitory postsynaptic potential in the singing interneuron. Current injection in the singing interneuron elicited singing motor activity, even during the air current-evoked inhibitory input from the cercal pathway. The disruptive effects of air stimuli on the fictive singing pattern and the inhibitory response of the singing interneuron point toward the cercal system being involved in initiating avoidance responses in singing crickets, according to the established role of cerci in a predator escape pathway. After abolishing the activity of the cercal system, the timing of natural singing activity was not significantly altered. Our study provides no evidence that self-generated cercal sensory activity has a feedback function for singing motor pattern generation. PMID:26334014
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Catalina Vich
2017-07-01
Full Text Available Subthreshold fluctuations in neuronal membrane potential traces contain nonlinear components, and employing nonlinear models might improve the statistical inference. We propose a new strategy to estimate synaptic conductances, which has been tested using in silico data and applied to in vivo recordings. The model is constructed to capture the nonlinearities caused by subthreshold activated currents, and the estimation procedure can discern between excitatory and inhibitory conductances using only one membrane potential trace. More precisely, we perform second order approximations of biophysical models to capture the subthreshold nonlinearities, resulting in quadratic integrate-and-fire models, and apply approximate maximum likelihood estimation where we only suppose that conductances are stationary in a 50–100 ms time window. The results show an improvement compared to existent procedures for the models tested here.
-
König, S.; Suriyah, M. R.; Leibfried, T.
2017-08-01
A lumped-parameter model for vanadium redox flow batteries, which use metallic current collectors, is extended into a one-dimensional model using the plug flow reactor principle. Thus, the commonly used simplification of a perfectly mixed cell is no longer required. The resistances of the cell components are derived in the in-plane and through-plane directions. The copper current collector is the only component with a significant in-plane conductance, which allows for a simplified electrical network. The division of a full-scale flow cell into 10 layers in the direction of fluid flow represents a reasonable compromise between computational effort and accuracy. Due to the variations in the state of charge and thus the open circuit voltage of the electrolyte, the currents in the individual layers vary considerably. Hence, there are situations, in which the first layer, directly at the electrolyte input, carries a multiple of the last layer's current. The conventional model overestimates the cell performance. In the worst-case scenario, the more accurate 20-layer model yields a discharge capacity 9.4% smaller than that computed with the conventional model. The conductive current collector effectively eliminates the high over-potentials in the last layers of the plug flow reactor models that have been reported previously.
-
Testing and analysis of tube voltage and tube current in the radiation generator for mammography
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jung, Hong Ryang; Hong, Dong Hee; Han, Beom Hui
2014-01-01
Breast shooting performance management and quality control of the generator is applied to the amount of current IEC(International Electrotechnical Commission) 60601-2-45 tube voltage and tube current are based on standards that were proposed in the analysis of the test results were as follows. Tube voltage according to the value of the standard deviation by year of manufacture from 2001 to 2010 as a 42-3.15 showed the most significant, according to the year of manufacture by tube amperage value of the standard deviation to 6.38 in the pre-2000 showed the most significant , manufactured after 2011 the standard deviation of the devices, the PAE(Percent Average Error) was relatively low. This latest generation device was manufactured in the breast of the tube voltage and tube diagnosed shooting the correct amount of current to maintain the performance that can be seen. The results of this study as the basis for radiography diagnosed breast caused by using the device's performance and maintain quality control, so the current Food and Drug Administration 'about the safety of diagnostic radiation generator rule' specified in the test cycle during three years of self-inspection radiation on a radiation generating device ensure safety and performance of the device using a coherent X-ray(constancy) by two ultimately able to keep the radiation dose to the public to reduce the expected effect is expected
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
I. J. Uwanta
2014-01-01
Full Text Available This study investigates the unsteady natural convection and mass transfer flow of viscous reactive, heat generating/absorbing fluid in a vertical channel formed by two infinite parallel porous plates having temperature dependent thermal conductivity. The motion of the fluid is induced due to natural convection caused by the reactive property as well as the heat generating/absorbing nature of the fluid. The solutions for unsteady state temperature, concentration, and velocity fields are obtained using semi-implicit finite difference schemes. Perturbation techniques are used to get steady state expressions of velocity, concentration, temperature, skin friction, Nusselt number, and Sherwood number. The effects of various flow parameters such as suction/injection (γ, heat source/sinks (S, Soret number (Sr, variable thermal conductivity δ, Frank-Kamenetskii parameter λ, Prandtl number (Pr, and nondimensional time t on the dynamics are analyzed. The skin friction, heat transfer coefficients, and Sherwood number are graphically presented for a range of values of the said parameters.
-
Early stages of wind wave and drift current generation under non-stationary wind conditions.
Robles-Diaz, Lucia; Ocampo-Torres, Francisco J.; Branger, Hubert
2016-04-01
Generation and amplification mechanisms of ocean waves are well understood under constant wind speed or limited fetch conditions. Under these situations, the momentum and energy transfers from air to water are also quite well known. However during the wind field evolution over the ocean, we may observe sometime high wind acceleration/deceleration situations (e.g. Mexican Tehuano or Mediterranean Mistral wind systems). The evolution of wave systems under these conditions is not well understood. The purpose of these laboratory experiments is to better understand the early stages of water-waves and surface-drift currents under non-stationary wind conditions and to determine the balance between transfers creating waves and surface currents during non-equilibrium situations. The experiments were conducted in the Institut Pythéas wind-wave facility in Marseille-France. The wave tank is 40 m long, 2.7 m wide and 1 m deep. The air section is 50 m long, 3 m wide and 1.8 m height. We used 11 different resistive wave-gauges located along the tank. The momentum fluxes in the air column were estimated from single and X hot-film anemometer measurements. The sampling frequency for wind velocity and surface displacement measurements was 256 Hz. Water-current measurements were performed with a profiling velocimeter. This device measures the first 3.5 cm of the water column with a frequency rate of 100Hz. During the experiments, the wind intensity was abruptly modified with a constant acceleration and deceleration over time. We observed that wind drag coefficient values for accelerated wind periods are lower than the ones reported in previous studies for constant wind speed (Large and Pond 1981; Ocampo-Torres et al. 2010; Smith 1980; Yelland and Taylor 1996). This is probably because the turbulent boundary layer is not completely developed during the increasing-wind sequence. As it was reported in some theoretical studies (Miles 1957; Phillips 1957; Kahma and Donelan 1988), we
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Pankaj Chowdhury
2017-05-01
Full Text Available Today, global warming and green energy are important topics of discussion for every intellectual gathering all over the world. The only sustainable solution to these problems is the use of solar energy and storing it as hydrogen fuel. Photocatalytic and photo-electrochemical water splitting and sacrificial hydrogen generation show a promise for future energy generation from renewable water and sunlight. This article mainly reviews the current research progress on photocatalytic and photo-electrochemical systems focusing on dye-sensitized overall water splitting and sacrificial hydrogen generation. An overview of significant parameters including dyes, sacrificial agents, modified photocatalysts and co-catalysts are provided. Also, the significance of statistical analysis as an effective tool for a systematic investigation of the effects of different factors and their interactions are explained. Finally, different photocatalytic reactor configurations that are currently in use for water splitting application in laboratory and large scale are discussed.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Iváncsy, T; Kiss, I; Tamus, Z Á; Szücs, L
2015-01-01
The lightning current generates time-varying magnetic field near the down-conductor and the down-conductors are mounted on the wall of the buildings where residential places might be situated. It is well known that the rapidly changing magnetic fields can generate dangerous eddy currents in the human body.The higher duration and gradient of the magnetic field can cause potentially life threatening cardiac stimulation. The coupling mechanism between the electromagnetic field and the human body is based on a well-known physical phenomena (e.g. Faradays law of induction). However, the calculation of the induced current is very complicated because the shape of the organs is complex and the determination of the material properties of living tissues is difficult, as well. Our previous study revealed that the cardiac stimulation is independent of the rising time of the lightning current and only the peak of the current counts.In this study, the authors introduce an improved model of the interaction of electromagnetic fields of lighting current near down-conductor and human body. Our previous models are based on the quasi stationer field calculations, the new improved model is a transient model. This is because the magnetic field around the down-conductor and in the human body can be determined more precisely, therefore the dangerous currents in the body can be estimated. (paper)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cho, Tae Won; Sohn, Dong-Seong; Kim, Yeon Soo
2015-01-01
This paper describes the effects of particle sphericity, interfacial thermal resistance, stereography, and heat generation on the thermal conductivity of U–Mo/Al dispersion fuel. The ABAQUS finite element method (FEM) tool was used to calculate the effective thermal conductivity of U–Mo/Al dispersion fuel by implementing fuel particles. For U–Mo/Al, the particle sphericity effect was insignificant. However, if the effect of the interfacial thermal resistance between the fuel particles and Al matrix was considered, the thermal conductivity of U–Mo/Al was increased as the particle size increases. To examine the effect of stereography, we compared the two-dimensional modeling and three-dimensional modeling. The results showed that the two-dimensional modeling predicted lower than the three-dimensional modeling. We also examined the effect of the presence of heat sources in the fuel particles and found a decrease in thermal conductivity of U–Mo/Al from that of the typical homogeneous heat generation modeling. (author)
-
Cho, Shin Hyo; Park, Su-Moon
2006-12-28
Electrical properties of contacts formed between conducting polymers and noble metal nanoparticles have been examined using current-sensing atomic force microscopy (CS-AFM). Contacts formed between electrochemically prepared pi-conjugated polymer films such as polypyrrole (PPy), poly(3-methylthiophene) (P3MeT), as well as poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) and noble metal nanoparticles including platinum (Pt), gold (Au), and silver (Ag) have been examined. The Pt nanoparticles were electrochemically deposited on a pre-coated PPy film surface by reducing a platinum precursor (PtCl62-) at a constant potential. Both current and scanning electron microscopic images of the film showed the presence of Pt islands. The Au and Ag nanoparticles were dispersed on the P3MeT and PEDOT film surfaces simply by dipping the polymer films into colloid solutions containing Au or Ag particles for specified periods (5 to approximately 10 min). The deposition of Au or Ag particles resulted from either their physical adsorption or chemical bonding between particles and the polymer surface depending on the polymer. When compared with PPy, P3MeT and PEDOT showed a stronger binding to Au or Ag nanoparticles when dipped in their colloidal solutions for the same period. This indicates that Au and Ag particles are predominantly linked with the sulfur atoms via chemical bonding. Of the two, PEDOT was more conductive at the sites where the particles are connected to the polymer. It appears that PEDOT has better aligned sulfur atoms on the surface and is strongly bonded to Au and Ag nanoparticles due to their strong affinity to gold and silver. The current-voltage curves obtained at the metal islands demonstrate that the contacts between these metal islands and polymers are ohmic.
-
Method for conducting nonlinear electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
Adler, Stuart B.; Wilson, Jamie R.; Huff, Shawn L.; Schwartz, Daniel T.
2015-06-02
A method for conducting nonlinear electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The method includes quantifying the nonlinear response of an electrochemical system by measuring higher-order current or voltage harmonics generated by moderate-amplitude sinusoidal current or voltage perturbations. The method involves acquisition of the response signal followed by time apodization and fast Fourier transformation of the data into the frequency domain, where the magnitude and phase of each harmonic signal can be readily quantified. The method can be implemented on a computer as a software program.
-
Exponential current pulse generation for efficient very high-impedance multisite stimulation.
Ethier, S; Sawan, M
2011-02-01
We describe in this paper an intracortical current-pulse generator for high-impedance microstimulation. This dual-chip system features a stimuli generator and a high-voltage electrode driver. The stimuli generator produces flexible rising exponential pulses in addition to standard rectangular stimuli. This novel stimulation waveform is expected to provide superior energy efficiency for action potential triggering while releasing less toxic reduced ions in the cortical tissues. The proposed fully integrated electrode driver is used as the output stage where high-voltage supplies are generated on-chip to significantly increase the voltage compliance for stimulation through high-impedance electrode-tissue interfaces. The stimuli generator has been implemented in 0.18-μm CMOS technology while a 0.8-μm CMOS/DMOS process has been used to integrate the high-voltage output stage. Experimental results show that the rectangular pulses cover a range of 1.6 to 167.2 μA with a DNL and an INL of 0.098 and 0.163 least-significant bit, respectively. The maximal dynamic range of the generated exponential reaches 34.36 dB at full scale within an error of ± 0.5 dB while all of its parameters (amplitude, duration, and time constant) are independently programmable over wide ranges. This chip consumes a maximum of 88.3 μ W in the exponential mode. High-voltage supplies of 8.95 and -8.46 V are generated by the output stage, boosting the voltage swing up to 13.6 V for a load as high as 100 kΩ.
-
Electric fields and field-aligned current generation in the magnetosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Alexeev, I.I.; Belenkaya, E.S.; Kalegaev, V.V.; Lyutov, Yu.G.
1993-01-01
The authors present a calculation of the electric potential, field-aligned currents, and plasma convection caused by the penetration of the solar wind electric field into the magnetosphere. Ohm's law and the continuity equation of ionospheric currents are used. It is shown that the large-scale convection system is reversed in the plasma sheet flanks. In this region the plasma flow is antisunward earthward of the neutral line and sunward tailward of it. The interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) B z dependences on the dimension of the magnetopause open-quotes windowsclose quotes which are intersected by open field lines, on the potential drop across the polar cap, and on the distance to the neutral line are determined. Because of the IMF effect and the effect of seasonal or daily variations of the geomagnetic field which violate its symmetry relative to the equatorial plane, there may arise a potential drop along field lines which causes field-aligned currents. The values and directions of these currents, the field-aligned potential drop, and a self-consistent solution for the potential at the ionosphere level for high field-aligned conductivity have been determined. 41 refs., 7 figs
-
Voltage-Controlled Square/Triangular Wave Generator with Current Conveyors and Switching Diodes
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Martin Janecek
2012-12-01
Full Text Available A novel relaxation oscillator based on integrating the diode-switched currents and Schmitt trigger is presented. It is derived from a known circuit with operational amplifiers where these active elements were replaced by current conveyors. The circuit employs only grounded resistances and capacitance and is suitable for high frequency square and triangular signal generation. Its frequency can be linearly and accurately controlled by voltage that is applied to a high-impedance input. Computer simulation with a model of a manufactured conveyor prototype verifies theoretic assumptions.
-
EMAT Evaluation of Thin Conductive Sheets
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ivo Cap
2006-01-01
Full Text Available At present a non-destructive testing of conducting materials becomes very important one in connection with monitoring and control of strategic technical facilities, e.g. nuclear power plants. There are more methods of material testing and evaluation and every of them has its advantages and disadvantages. Recently the electromagnetic methods are in increasing interest. There are many ways of conducting material testing. One of them often used utilises investigation of eddy currents induced in the surface layer by means of a proper coil. The arrangement is very simple and inexpensive but it offers only local information on cracks and other inhomogeneities in the thin surface layer. On the other hand there exist a method based on an electromagnetic – acoustic transducer (EMAT, which is able to generate and detect acoustic wave in a conducting body in a contact-less way. The present paper deals with a survey of EMATs for investigation of thin metalliclayers by means of Lamb waves. The new design of generation coil is presented.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Sun, Guotao; Thygesen, Anders; Meyer, Anne S.
2016-01-01
Implementation of microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for electricity production requires effective current generation from waste products via robust cathode reduction. Three cathode types using dissolved oxygen cathodes (DOCs), ferricyanide cathodes (FeCs) and air cathodes (AiCs) were therefore assessed...... to be the most sustainable option since it does not require ferricyanide. The data offer a new add-on option to the straw biorefinery by using bioethanol effluent for microbial electricity production....... using bioethanol effluent, containing 20.5 g/L xylose, 1.8 g/L arabinose and 2.5 g/L propionic acid. In each set-up the anode and cathode had an electrode surface area of 88 cm(2), which was used for calculation of the current density. Electricity generation was evaluated by quantifying current...
-
Population dynamics and current-generation mechanisms in cassette-electrode microbial fuel cells
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Watanabe, Kazuya [ERATO/JST, Tokyo (Japan). Hashimoto Light Energy Conversion Project; Tokyo Univ. (Japan). Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology; Tokyo Univ. of Pharmacy and Life Sciences (Japan). School of Life Sciences; Miyahara, Morio [ERATO/JST, Tokyo (Japan). Hashimoto Light Energy Conversion Project; Shimoyama, Takefumi [Tokyo Univ. (Japan). Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology; Hashimoto, Kazuhito [ERATO/JST, Tokyo (Japan). Hashimoto Light Energy Conversion Project; Tokyo Univ. (Japan). Dept. of Applied Chemistry
2011-12-15
Cassette-electrode microbial fuel cells (CE-MFCs) have been demonstrated useful to treat biomass wastes and recover electric energy from them. In order to reveal electricity-generation mechanisms in CE-MFCs, the present study operated a bench-scale reactor (1 l in capacity; approximately 1,000 cm{sup 2} in anode and cathode areas) for treating a high-strength model organic wastewater (comprised of starch, peptone, and fish extract). Approximately 1 month was needed for the bench reactor to attain a stable performance, after which volumetric maximum power densities persisted between 120 and 150 mW/l throughout the experiment (for over 2 months). Temporal increases in the external resistance were found to induce subsequent increases in power outputs. After electric output became stable, electrolyte and anode were sampled from the reactor for evaluating their current-generation abilities; it was estimated that most of current (over 80%) was generated by microbes in the electrolyte. Cyclic voltammetry of an electrolyte supernatant detected several electron shuttles with different standard redox potentials at high concentrations (equivalent to or more than 100 {mu}M 5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone). Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and quantitative real-time PCR of 16S ribosomal RNA gene fragments showed that bacteria related to the genus Dysgonomonas occurred abundantly in association with the increases in power outputs. These results suggest that mediated electron transfer was the main mechanism for electricity generation in CE-MFC, where high-concentration electron shuttles and Dysgonomonas bacteria played important roles. (orig.)
-
Skill, Judgement and Conduct for the First Generation of Neurosurgeons, 1900-1930.
Gavrus, Delia
2015-07-01
Historical contingency complicates a reading of skill as a self-explanatory and always positive attribute. By focusing on the attempts of the first generation of neurosurgeons to build a community and fashion a collective neurosurgical self, this article highlights the extent to which the relationship between surgical skill and professional judgement is reflected in broader concerns that shape the landscape of medicine at a given time. Some early twentieth-century surgeons expressed concern about the spectacularisation of surgery and the skilful but problematic work of 'brilliant operators'. The neurosurgeons' policies of inclusion and exclusion show that in the process of fashioning a neurosurgical persona, this first generation sanctioned specific norms of conduct underwritten by similar moral imperatives, such as self-control. These norms governed the doctors' work both in the operating room and on the public stage (in their engagement with the press). The meetings of the first neurosurgical society staged a critical encounter between the host neurosurgeon and the members who watched him perform surgery. These technical performances in the operating theatre, followed by discussions, were designed to encourage particular norms, to negotiate surgical knowledge, and to demonstrate the skills and character of the neurosurgeon. The performances acted as a technology of the self that aligned the operator to a community and helped that community refine its norms of surgical conduct. The awkward surgeon with inferior technical ability was preferable to the brilliant but vain operator who lacked the capacity to judge when he should not deploy his spectacular skills.
-
Blakeslee, Richard J.; Mach, Douglas M.; Bateman, Monte J.; Bailey, Jeffrey C.
2011-01-01
We present total conduction (Wilson) currents for more than 1000 high-altitude aircraft overflights of electrified clouds acquired over nearly two decades. The overflights include a wide geographical sample of storms over land and ocean, with and without lightning, and with positive (i.e., upward-directed) and negative current. Peak electric field, with lightning transients removed, ranged from -1.0 kV/m to 16. kV/m, with mean (median) of 0.9 kV/m (0.29 kV/m). Total conductivity at flight altitude ranged from 0.6 pS/m to 3.6 pS/m, with mean and median of 2.2 pS/m. Peak current densities ranged from -2.0 nA m(exp -2) to 33.0 nA m(exp -2) with mean (median) of 1.9 nA m(exp -2) (0.6 nA m(exp -2)). Total upward current flow from storms in our dataset ranged from -1.3 to 9.4 A. The mean current for storms with lightning is 1.7 A over ocean and 1.0 A over land. The mean current for electrified shower clouds (i.e. electrified storms without lightning) is 0.41 A for ocean and 0.13 A for land. About 78% (43%) of the land (ocean) storms have detectable lightning. Land storms have 2.8 times the mean flash rate as ocean storms (2.2 versus 0.8 flashes min-1, respectively). Approximately 7% of the overflights had negative current. The mean and median currents for positive (negative) polarity storms are 1.0 and 0.35 A (-0.30 and -0.26 A). We found no regional or latitudinal-based patterns in our storm currents, nor support for simple scaling laws between cloud top height and lightning flash rate.
-
Control of the current density profile with lower hybrid current drive on PBX-M
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bell, R.E.; Bernabei, S.; Chu, T.K.; Gettelfinger, G.; Greenough, N.; Hatcher, R.; Ignat, D.; Jardin, S.; Kaita, R.; Kaye, S.; Kozub, T.; Kugel, H.; LeBlanc, B.; Okabayashi, M.; Paul, S.; Sauthoff, N.; Sesnic, S.; Sun, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Tighe, W.; Valeo, E.; von Goeler, S.; Jones, S.; Kesner, J.; Luckhardt, S.; Paoletti, F.; Levinton, F.; Timini, F.
1993-07-01
Lower hybrid current drive (LHCD) is being explored as a means to control the current density profile on PBX-M with the goal of raising the central safety factor q(O) to values of 1.5-2 to facilitate access to a full-volume second stable regime. Initial experiments have been conducted with up to 400 kW of 4.6 GHz LH power in circular and indented plasmas with modest parameters. A tangential-viewing two-dimensional hard x-ray imaging diagnostic has been used to observe the bremsstrahlung emission from the suprathermal electrons generated during LHCD. Hollow hard x-ray images have indicated off-axis localization of the driven current. A serious obstacle to the control of the current density profile with LHCD is the concomitant generation of MHD activity, which can seriously degrade the confinement of suprathermal electrons. By combining neutral beam injection with LHCD, an MHD-free condition has been obtained where q(O) is raised above 1
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Breinbjerg, Olav
1992-01-01
An approach for including higher order edge diffraction in the equivalent edge current (EEC) method is proposed. This approach, which applies to monostatic as well as bistatic radar configurations with perfectly conducting polygonal plates, involves three distinct sets of EECs. All of these sets...
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Guo, Yougui; Zeng, Ping; Li, Lijuan
2011-01-01
Adaptive hysteresis band current control(AHB CC) is used to control the three-phase grid currents by means of grid side converter in wind power generation system in this paper. AHB has reached the good purpose with PLL (Lock phase loop). First the mathematical models of each part are given......, transformer and grid, and control parts, etc. The simulation results have verified that the control strategy is feasible to fit for control of gird currents, active power, reactive power and DC-link voltage in wind power generation system....
-
High temperature superconductor current leads
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zeimetz, B.; Liu, H.K.; Dou, S.X.
1996-01-01
Full text: The use of superconductors in high electrical current applications (magnets, transformers, generators etc.) usually requires cooling with liquid Helium, which is very expensive. The superconductor itself produces no heat, and the design of Helium dewars is very advanced. Therefore most of the heat loss, i.e. Helium consumption, comes from the current lead which connects the superconductor with its power source at room temperature. The current lead usually consists of a pair of thick copper wires. The discovery of the High Temperature Superconductors makes it possible to replace a part of the copper with superconducting material. This drastically reduces the heat losses because a) the superconductor generates no resistive heat and b) it is a very poor thermal conductor compared with the copper. In this work silver-sheathed superconducting tapes are used as current lead components. The work comprises both the production of the tapes and the overall design of the leads, in order to a) maximize the current capacity ('critical current') of the superconductor, b) minimize the thermal conductivity of the silver clad, and c) optimize the cooling conditions
-
Polymeric salt bridges for conducting electric current in microfluidic devices
Shepodd, Timothy J [Livermore, CA; Tichenor, Mark S [San Diego, CA; Artau, Alexander [Humacao, PR
2009-11-17
A "cast-in-place" monolithic microporous polymer salt bridge for conducting electrical current in microfluidic devices, and methods for manufacture thereof is disclosed. Polymeric salt bridges are formed in place in capillaries or microchannels. Formulations are prepared with monomer, suitable cross-linkers, solvent, and a thermal or radiation responsive initiator. The formulation is placed in a desired location and then suitable radiation such as UV light is used to polymerize the salt bridge within a desired structural location. Embodiments are provided wherein the polymeric salt bridges have sufficient porosity to allow ionic migration without bulk flow of solvents therethrough. The salt bridges form barriers that seal against fluid pressures in excess of 5000 pounds per square inch. The salt bridges can be formulated for carriage of suitable amperage at a desired voltage, and thus microfluidic devices using such salt bridges can be specifically constructed to meet selected analytical requirements.
-
Four-point probe measurements of a direct current potential drop on layered conductive cylinders
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lu, Yi; Bowler, John R
2012-01-01
We have determined the steady state electric field due to direct current flowing via point contacts at the cylindrical surface of a uniformly layered conductive rod of finite length. The solution allows one to use four-point probe potential drop measurements to estimate the conductivity or thickness of the layer assuming that the other parameters are known. The electrical potential in the rod has a zero radial derivative at its surface except at the injection and extractions points. This means that the required solution can be expressed in terms of a Green’s function satisfying a Neumann boundary condition. Four-point measurements have been made to demonstrate the validity of theoretical results. (paper)
-
Four-point probe measurements of a direct current potential drop on layered conductive cylinders
Lu, Yi; Bowler, John R.
2012-11-01
We have determined the steady state electric field due to direct current flowing via point contacts at the cylindrical surface of a uniformly layered conductive rod of finite length. The solution allows one to use four-point probe potential drop measurements to estimate the conductivity or thickness of the layer assuming that the other parameters are known. The electrical potential in the rod has a zero radial derivative at its surface except at the injection and extractions points. This means that the required solution can be expressed in terms of a Green’s function satisfying a Neumann boundary condition. Four-point measurements have been made to demonstrate the validity of theoretical results.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Miwa, T.
1991-01-01
Electric power demand aspects and current status of nuclear power generation in Japan are outlined. Although the future plan for nuclear power generation has not been determined yet the Japanese nuclear research centers and institutes are investigating and developing some projects on the next generation of light water reactors and other types of reactors. The paper describes these main activities
-
Chhatbar, Pratik Y; Kautz, Steven A; Takacs, Istvan; Rowland, Nathan C; Revuelta, Gonzalo J; George, Mark S; Bikson, Marom; Feng, Wuwei
2018-03-13
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a promising brain modulation technique for several disease conditions. With this technique, some portion of the current penetrates through the scalp to the cortex and modulates cortical excitability, but a recent human cadaver study questions the amount. This insufficient intracerebral penetration of currents may partially explain the inconsistent and mixed results in tDCS studies to date. Experimental validation of a transcranial alternating current stimulation-generated electric field (EF) in vivo has been performed on the cortical (using electrocorticography, ECoG, electrodes), subcortical (using stereo electroencephalography, SEEG, electrodes) and deeper thalamic/subthalamic levels (using DBS electrodes). However, tDCS-generated EF measurements have never been attempted. We aimed to demonstrate that tDCS generates biologically relevant EF as deep as the subthalamic level in vivo. Patients with movement disorders who have implanted deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrodes serve as a natural experimental model for thalamic/subthalamic recordings of tDCS-generated EF. We measured voltage changes from DBS electrodes and body resistance from tDCS electrodes in three subjects while applying direct current to the scalp at 2 mA and 4 mA over two tDCS montages. Voltage changes at the level of deep nuclei changed proportionally with the level of applied current and varied with different tDCS montages. Our findings suggest that scalp-applied tDCS generates biologically relevant EF. Incorporation of these experimental results may improve finite element analysis (FEA)-based models. Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Physical Mechanisms Responsible for Electrical Conduction in Pt/GaN Schottky Diodes
H. MAZARI; K. AMEUR; N. BENSEDDIK; Z. BENAMARA; R. KHELIFI; M. MOSTEFAOUI; N. ZOUGAGH; N. BENYAHYA; R. BECHAREF; G. BASSOU; B. GRUZZA; J. M. BLUET; C. BRU-CHEVALLIER
2014-01-01
The current-voltage (I-V) characteristics of Pt/(n.u.d)-GaN and Pt/Si-doped-GaN diodes Schottky are investigated. Based on these measurements, physical mechanisms responsible for electrical conduction have been suggested. The contribution of thermionic-emission current and various other current transport mechanisms were assumed when evaluating the Schottky barrier height. Thus the generation-recombination, tunneling and leakage currents caused by inhomogeneities and defects at metal-semicondu...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sullivan, S.P.; Cecco, V.S.; Carter, J.R.; Spanner, M.; McElvanney, M.; Krause, T.W.; Tkaczyk, R.
2000-01-01
Licensing requirements for eddy current inspections for nuclear steam generators and heat exchangers are becoming increasingly stringent. The traditional industry-standard method of comparing inspection signals with flaw signals from simple in-line calibration standards is proving to be inadequate. A more complete understanding of eddy current and magnetic field interactions with flaws and other anomalies is required for the industry to generate consistently reliable inspections. Computer modeling is a valuable tool in improving the reliability of eddy current signal analysis. Results from computer modeling are helping inspectors to properly discriminate between real flaw signals and false calls, and improving reliability in flaw sizing. This presentation will discuss complementary eddy current computer modeling techniques such as the Finite Element Method (FEM), Volume Integral Method (VIM), Layer Approximation and other analytic methods. Each of these methods have advantages and limitations. An extension of the Layer Approximation to model eddy current probe responses to ferromagnetic materials will also be presented. Finally examples will be discussed demonstrating how some significant eddy current signal analysis problems have been resolved using appropriate electromagnetic computer modeling tools
-
Variable speed DFIG wind energy system for power generation and harmonic current mitigation
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Gaillard, A.; Saadate, S. [Groupe de Recherche en Electrotechnique et Electronique de Nancy, Nancy Universite - Universite Henri Poincare Nancy 1, BP239, 54506 Vandoeuvre les Nancy Cedex (France); Poure, P. [Laboratoire d' Instrumentation Electronique de Nancy, Nancy Universite - Universite Henri Poincare Nancy 1, BP239, 54506 Vandoeuvre les Nancy Cedex (France); Machmoum, M. [IREENA, 37 Boulevard de l' Universite, BP 406, 44602 Saint-Nazaire Cedex (France)
2009-06-15
This paper presents a novel approach for simultaneous power generation and harmonic current mitigation using variable speed WECS with DFIG. A new control strategy is proposed to upgrade the DFIG control to achieve simultaneously a green active and reactive power source with active filtering capability. To ensure high filtering performance, we studied an improved harmonic isolator in the time-domain, based on a new high selectivity filter developed in our laboratory. We examined two solutions for harmonic current mitigation: first, by compensating the whole harmonic component of the grid currents or second, by selective isolation of the predominant harmonic currents to ensure active filtering of the 5th and 7th harmonics. Simulation results for a 3 MW WECS with DFIG confirm the effectiveness and the performance of the two proposed approaches. (author)
-
Thermal spin current generation and spin transport in Pt/magnetic-insulator/Py heterostructures
Chen, Ching-Tzu; Safranski, Christopher; Krivorotov, Ilya; Sun, Jonathan
Magnetic insulators can transmit spin current via magnon propagation while blocking charge current. Furthermore, under Joule heating, magnon flow as a result of the spin Seeback effect can generate additional spin current. Incorporating magnetic insulators in a spin-orbit torque magnetoresistive memory device can potentially yield high switching efficiencies. Here we report the DC magneto-transport studies of these two effects in Pt/magnetic-insulator/Py heterostructures, using ferrimagnetic CoFexOy (CFO) and antiferromagnet NiO as the model magnetic insulators. We observe the presence and absence of the inverse spin-Hall signals from the thermal spin current in Pt/CFO/Py and Pt/NiO/Py structures. These results are consistent with our spin-torque FMR linewidths in comparison. We will also report investigations into the magnetic field-angle dependence of these observations.
-
Induced mitochondrial membrane potential for modeling solitonic conduction of electrotonic signals.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R R Poznanski
Full Text Available A cable model that includes polarization-induced capacitive current is derived for modeling the solitonic conduction of electrotonic potentials in neuronal branchlets with microstructure containing endoplasmic membranes. A solution of the nonlinear cable equation modified for fissured intracellular medium with a source term representing charge 'soakage' is used to show how intracellular capacitive effects of bound electrical charges within mitochondrial membranes can influence electrotonic signals expressed as solitary waves. The elastic collision resulting from a head-on collision of two solitary waves results in localized and non-dispersing electrical solitons created by the nonlinearity of the source term. It has been shown that solitons in neurons with mitochondrial membrane and quasi-electrostatic interactions of charges held by the microstructure (i.e., charge 'soakage' have a slower velocity of propagation compared with solitons in neurons with microstructure, but without endoplasmic membranes. When the equilibrium potential is a small deviation from rest, the nonohmic conductance acts as a leaky channel and the solitons are small compared when the equilibrium potential is large and the outer mitochondrial membrane acts as an amplifier, boosting the amplitude of the endogenously generated solitons. These findings demonstrate a functional role of quasi-electrostatic interactions of bound electrical charges held by microstructure for sustaining solitons with robust self-regulation in their amplitude through changes in the mitochondrial membrane equilibrium potential. The implication of our results indicate that a phenomenological description of ionic current can be successfully modeled with displacement current in Maxwell's equations as a conduction process involving quasi-electrostatic interactions without the inclusion of diffusive current. This is the first study in which solitonic conduction of electrotonic potentials are generated by
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Oyoshi, K.; Nigo, S.; Inoue, J.; Sakai, O.; Kitazawa, H.; Kido, G.
2010-01-01
Anodic porous alumina (APA) films have a honeycomb cell structure of pores and a voltage-induced bi-stable switching effect. We have applied conducting atomic force microscopy (CAFM) as a method to form and to disrupt current paths in the APA films. A bi-polar switching operation was confirmed. We have firstly observed terminals of current paths as spots or areas typically on the center of the triangle formed by three pores. In addition, though a part of the current path showed repetitive switching, most of them were not observed again at the same position after one cycle of switching operations in the present experiments. This suggests that a part of alumina structure and/or composition along the current paths is modified during the switching operations.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Oyoshi, K., E-mail: oyoshi.keiji@nims.go.jp [National Institute for Materials Science, 1-2-1 Sengen, Tsukuba 305-0047 (Japan); Nigo, S.; Inoue, J.; Sakai, O.; Kitazawa, H.; Kido, G. [National Institute for Materials Science, 1-2-1 Sengen, Tsukuba 305-0047 (Japan)
2010-11-15
Anodic porous alumina (APA) films have a honeycomb cell structure of pores and a voltage-induced bi-stable switching effect. We have applied conducting atomic force microscopy (CAFM) as a method to form and to disrupt current paths in the APA films. A bi-polar switching operation was confirmed. We have firstly observed terminals of current paths as spots or areas typically on the center of the triangle formed by three pores. In addition, though a part of the current path showed repetitive switching, most of them were not observed again at the same position after one cycle of switching operations in the present experiments. This suggests that a part of alumina structure and/or composition along the current paths is modified during the switching operations.
-
Magnetohydraulic flow through a packed bed of electrically conducting spheres
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sanders, T.L.
1985-01-01
The flow of an electrically conducting fluid through a packed bed of electrically conducting spheres in the presence of a strong magnetic field constitutes a very complex flow situation due to the constant turning of the fluid in and out of magnetic field lines. The interaction of the orthogonal components of the velocity and magnetic field will induce electric fields that are orthogonal to both and the electric fields in turn can cause currents that interact with the magnetic field to generate forces against the direction of flow. The strengths of these generated forces depend primarily upon the closure paths taken by the induced currents which, in turn, depend upon the relative ratio of the electrical resistance of the solid spheres to that of the fluid. Both experimental and analytical analyses of the slow flow of a eutectic mixture of sodium and potassium (NaK) through packed cylinders containing stainless steel spheres in the presence of a strong transverse magnetic field were completed. A theory of magnetohydraulic flow is developed by analogy with the development of hydraulic radius theories of flow through porous media. An exact regional analysis is successfully applied to an infinite bed of electrically conducting spheres with a conducting or non-conducting constraining wall on one side. The equations derived are solved for many different combinations of flowrate, magnetic field strength, porosity, and electrical resistance ratio
-
Model-Based Prediction of Pulsed Eddy Current Testing Signals from Stratified Conductive Structures
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zhang, Jian Hai; Song, Sung Jin; Kim, Woong Ji; Kim, Hak Joon; Chung, Jong Duk
2011-01-01
Excitation and propagation of electromagnetic field of a cylindrical coil above an arbitrary number of conductive plates for pulsed eddy current testing(PECT) are very complex problems due to their complicated physical properties. In this paper, analytical modeling of PECT is established by Fourier series based on truncated region eigenfunction expansion(TREE) method for a single air-cored coil above stratified conductive structures(SCS) to investigate their integrity. From the presented expression of PECT, the coil impedance due to SCS is calculated based on analytical approach using the generalized reflection coefficient in series form. Then the multilayered structures manufactured by non-ferromagnetic (STS301L) and ferromagnetic materials (SS400) are investigated by the developed PECT model. Good prediction of analytical model of PECT not only contributes to the development of an efficient solver but also can be applied to optimize the conditions of experimental setup in PECT
-
Validating eddy current array probes for inspecting steam generator tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sullivan, S.P.; Cecco, V.S.; Obrutsky, L.S.
1997-01-01
A CANDU nuclear reactor was shut down for over one year because steam generator (SG) tubes had failed with outer diameter stress-corrosion cracking (ODSCC) in the U-bend section. Novel, single-pass eddy current transmit-receive probes, denoted as C3, were successful in detecting all significant cracks so that the cracked tubes could be plugged and the unit restarted. Significant numbers of tubes with SCC were removed from a SG in order to validate the results of the new probe. Results from metallurgical examinations were used to obtain probability-of-detection (POD) and sizing accuracy plots to quantify the performance of this new inspection technique. Though effective, the above approach of relying on tubes removed from a reactor is expensive, in terms of both economic and radiation-exposure costs. This led to a search for more affordable methods to validate inspection techniques and procedures. Methods are presented for calculating POD curves based on signal-to-noise studies using field data. Results of eddy current scans of tubes with laboratory-induced ODSCC are presented with associated POD curves. These studies appear promising in predicting realistic POD curves for new inspection technologies. They are being used to qualify an improved eddy current array probe in preparation for field use. (author)
-
Z a Fast Pulsed Power Generator for Ultra-High Magnetic Field Generation
Spielman, R. B.; Stygar, W. A.; Struve, K. W.; Asay, J. R.; Hall, C. A.; Bernard, M. A.; Bailey, J. E.; McDaniel, D. H.
2004-11-01
Advances in fast, pulsed-power technologies have resulted in the development of very high current drivers that have current rise times ~100 ns. The largest such pulsed power driver today is the new Z accelerator located at Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Z can deliver more than 20 MA with a time-to-peak of 105 ns to low inductance (~1 nH) loads. Such large drivers are capable of directly generating magnetic fields approaching 3 kT in small, 1 cm3 volumes. In addition to direct field generation, Z can be used to compress an applied, axial seed field with a plasma. Flux compression schemes are not new and are, in fact, the basis of all explosive flux-compression generators, but we propose the use of plasma armatures rather than solid, conducting armatures. We present experimental results from the Z accelerator in which magnetic fields of ~2 kT are generated and measured with several diagnostics. Issues such as energy loss in solid conductors and dynamic response of current-carrying conductors to very large magnetic fields are reviewed in context with Z experiments. We describe planned flux-compression experiments that are expected to create the highest-magnitude uniform-field volumes yet attained in the laboratory.
-
Signal Characteristics of Eddy Current Test for Intergranular Attack of Steam Generator Tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Choi, Myung Sik; Lee, Deok Hyun; Han, Jung Ho; Hur, Do Haeng; Cho, Se Gon; Yim, Chang Jae
2002-01-01
Because intergranular attack (IGA), one of the localized corrosion forms occurring on steam generator tubes, can not be fabricated by an electric discharge machining method, there are few data for the eddy current test (ECT) characteristics of IGA. In this paper, the characteristics of eddy current signals are evaluated using nonexpanded tubes with IGA defects formed in 0.1 M sodium tetrathionate solution at 40 .deg. C. The detectability and sizing accuracy of IGA were discussed in terms of the coil type and frequency of the ECT probes
-
Generation IV nuclear reactors: Current status and future prospects
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Locatelli, Giorgio; Mancini, Mauro; Todeschini, Nicola
2013-01-01
Generation IV nuclear power plants (GEN IV NPPs) are supposed to become, in many countries, an important source of base load power in the middle–long term (2030–2050). Nowadays there are many designs of these NPPs but for political, strategic and economic reasons only few of them will be deployed. International literature proposes many papers and reports dealing with GEN IV NPPs, but there is an evident difference in the types and structures of the information and a general unbiased overview is missing. This paper fills the gap, presenting the state-of-the-art for GEN IV NPPs technologies (VHTR, SFR, SCWR, GFR, LFR and MSR) providing a comprehensive literature review of the different designs, discussing the major R and D challenges and comparing them with other advanced technologies available for the middle- and long-term energy market. The result of this research shows that the possible applications for GEN IV technologies are wider than current NPPs. The economics of some GEN IV NPPs is similar to actual NPPs but the “carbon cost” for fossil-fired power plants would increase the relative valuation. However, GEN IV NPPs still require substantial R and D effort, preventing short-term commercial adoption. - Highlights: • Generation IV reactors are the middle–long term technology for nuclear energy. • This paper provides an overview and a taxonomy for the designs under consideration. • R and D efforts are in the material, heat exchangers, power conversion unit and fuel. • The life cycle costs are competitive with other innovative technologies. • The hydrogen economy will foster the development of Generation IV reactors
-
Steam generator degradation: Current mitigation strategies for controlling corrosion
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Millett, P.
1997-01-01
Steam Generator degradation has caused substantial losses of power generation, resulted in large repair and maintenance costs, and contributed to significant personnel radiation exposures in Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs) operating throughout the world. EPRI has just published the revised Steam Generator Reference Book, which reviews all of the major forms of SG degradation. This paper discusses the types of SG degradation that have been experienced with emphasis on the mitigation strategies that have been developed and implemented in the field. SG degradation is presented from a world wide perspective as all countries operating PWRs have been effected to one degree or another. The paper is written from a US. perspective where the utility industry is currently undergoing tremendous change as a result of deregulation of the electricity marketplace. Competitive pressures are causing utilities to strive to reduce Operations and Maintenance (O ampersand M) and capital costs. SG corrosion is a major contributor to the O ampersand M costs of PWR plants, and therefore US utilities are evaluating and implementing the most cost effective solutions to their corrosion problems. Mitigation strategies developed over the past few years reflect a trend towards plant specific solutions to SG corrosion problems. Since SG degradation is in most cases an economic problem and not a safety problem, utilities can focus their mitigation strategies on their unique financial situation. Accordingly, the focus of R ampersand D has shifted from the development of more expensive, prescriptive solutions (e.g. reduced impurity limits) to corrosion problems to providing the utilities with a number of cost effective mitigation options (e.g. molar ratio control, boric acid treatment)
-
Pereverzev, Andrey; Sewell, Tommy
2018-03-01
Lattice heat-current time correlation functions for insulators and semiconductors obtained using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations exhibit features of both pure exponential decay and oscillatory-exponential decay. For some materials the oscillatory terms contribute significantly to the lattice heat conductivity calculated from the correlation functions. However, the origin of the oscillatory terms is not well understood, and their contribution to the heat conductivity is accounted for by fitting them to empirical functions. Here, a translationally invariant expression for the heat current in terms of creation and annihilation operators is derived. By using this full phonon-picture definition of the heat current and applying the relaxation-time approximation we explain, at least in part, the origin of the oscillatory terms in the lattice heat-current correlation function. We discuss the relationship between the crystal Hamiltonian and the magnitude of the oscillatory terms. A solvable one-dimensional model is used to illustrate the potential importance of terms that are omitted in the commonly used phonon-picture expression for the heat current. While the derivations are fully quantum mechanical, classical-limit expressions are provided that enable direct contact with classical quantities obtainable from MD.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Birguel, Oezlem; Eyueboglu, B Murat; Ider, Y Ziya
2003-01-01
Conventional injected-current electrical impedance tomography (EIT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques can be combined to reconstruct high resolution true conductivity images. The magnetic flux density distribution generated by the internal current density distribution is extracted from MR phase images. This information is used to form a fine detailed conductivity image using an Ohm's law based update equation. The reconstructed conductivity image is assumed to differ from the true image by a scale factor. EIT surface potential measurements are then used to scale the reconstructed image in order to find the true conductivity values. This process is iterated until a stopping criterion is met. Several simulations are carried out for opposite and cosine current injection patterns to select the best current injection pattern for a 2D thorax model. The contrast resolution and accuracy of the proposed algorithm are also studied. In all simulation studies, realistic noise models for voltage and magnetic flux density measurements are used. It is shown that, in contrast to the conventional EIT techniques, the proposed method has the capability of reconstructing conductivity images with uniform and high spatial resolution. The spatial resolution is limited by the larger element size of the finite element mesh and twice the magnetic resonance image pixel size
-
Removing Eddy-current probe wobble noise from steam generator tubes testing using wavelet transform
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lopez, Luiz Antonio Negro Martin; Ting, Daniel Kao Sun; Upadhyaya, Belle R.
2005-01-01
One of the most import nondestructive evaluation (NDE) applied to steam generator tubes inspection is the electromagnetic Eddy-Current testing (ECT). The signals generated in this NDE, in general, contain many noises which make difficult the interpretation and analysis of ECT signals. One of the noises present in the signals is the probe wobble noise, which is caused by the existing slack between the probe and the tube. In this work, Wavelet Transform (WT) is used in the probe wobble de-noising. WT is a relatively recent mathematical tool, which allows local analysis of non stationary signals such as ECT signals. This is a great advantage of WT when compared with other analysis tools such as Fourier Transform. However, using WT involves wavelets and coefficients selection as well as choosing the number of decomposition level needed. This work presents a probe wobble de-noising method when used in conjunction with the traditional ECT evaluation. Comparative results using several WT applied do Eddy-Current signals are presented in a reliable way, in other words, without loss of inherent defect information. A stainless steel tube, with 2 artificial defects generated by electro-erosion, was inspected by a ZETEC MIZ-17ET ECT equipment. The signals were de-noised through several different WT and the results are presented. The method offer good results and is a promising method because allows for the removal of Eddy-Current signals probe wobble effect without loss of essential signal information. (author)
-
Automation of inspection methods for eddy current testing of steam generator tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Meurgey, P.; Baumaire, A.
1990-01-01
Inspection of all the tubes of a steam generator when the reactor is stopped is required for some of these exchangers affected by stress corrosion cracking. Characterization of each crack, in each tube is made possible by the development of software for processing the signals from an eddy current probe. The ESTELLE software allows a rapid increase of tested tubes, more than 80,000 in 1989 [fr
-
Skill, Judgement and Conduct for the First Generation of Neurosurgeons, 1900–1930
Gavrus, Delia
2015-01-01
Historical contingency complicates a reading of skill as a self-explanatory and always positive attribute. By focusing on the attempts of the first generation of neurosurgeons to build a community and fashion a collective neurosurgical self, this article highlights the extent to which the relationship between surgical skill and professional judgement is reflected in broader concerns that shape the landscape of medicine at a given time. Some early twentieth-century surgeons expressed concern about the spectacularisation of surgery and the skilful but problematic work of ‘brilliant operators’. The neurosurgeons’ policies of inclusion and exclusion show that in the process of fashioning a neurosurgical persona, this first generation sanctioned specific norms of conduct underwritten by similar moral imperatives, such as self-control. These norms governed the doctors’ work both in the operating room and on the public stage (in their engagement with the press). The meetings of the first neurosurgical society staged a critical encounter between the host neurosurgeon and the members who watched him perform surgery. These technical performances in the operating theatre, followed by discussions, were designed to encourage particular norms, to negotiate surgical knowledge, and to demonstrate the skills and character of the neurosurgeon. The performances acted as a technology of the self that aligned the operator to a community and helped that community refine its norms of surgical conduct. The awkward surgeon with inferior technical ability was preferable to the brilliant but vain operator who lacked the capacity to judge when he should not deploy his spectacular skills. PMID:26090734
-
First demonstration of HF-driven ionospheric currents
Papadopoulos, K.; Chang, C.-L.; Labenski, J.; Wallace, T.
2011-10-01
The first experimental demonstration of HF driven currents in the ionosphere at low ELF/ULF frequencies without relying in the presence of electrojets is presented. The effect was predicted by theoretical/computational means in a recent letter and given the name Ionospheric Current Drive (ICD). The effect relies on modulated F-region HF heating to generate Magneto-Sonic (MS) waves that drive Hall currents when they reach the E-region. The Hall currents inject ELF waves into the Earth-Ionosphere waveguide and helicon and Shear Alfven (SA) waves in the magnetosphere. The proof-of-concept experiments were conducted using the HAARP heater in Alaska under the BRIOCHE program. Waves between 0.1-70 Hz were measured at both near and far sites. The letter discusses the differences between ICD generated waves and those relying on modulation of electrojets.
-
Neutron generator for BNCT based on high current ECR ion source with gyrotron plasma heating.
Skalyga, V; Izotov, I; Golubev, S; Razin, S; Sidorov, A; Maslennikova, A; Volovecky, A; Kalvas, T; Koivisto, H; Tarvainen, O
2015-12-01
BNCT development nowadays is constrained by a progress in neutron sources design. Creation of a cheap and compact intense neutron source would significantly simplify trial treatments avoiding use of expensive and complicated nuclear reactors and accelerators. D-D or D-T neutron generator is one of alternative types of such sources for. A so-called high current quasi-gasdynamic ECR ion source with plasma heating by millimeter wave gyrotron radiation is suggested to be used in a scheme of D-D neutron generator in the present work. Ion source of that type was developed in the Institute of Applied Physics of Russian Academy of Sciences (Nizhny Novgorod, Russia). It can produce deuteron ion beams with current density up to 700-800 mA/cm(2). Generation of the neutron flux with density at the level of 7-8·10(10) s(-1) cm(-2) at the target surface could be obtained in case of TiD2 target bombardment with deuteron beam accelerated to 100 keV. Estimations show that it is enough for formation of epithermal neutron flux with density higher than 10(9) s(-1) cm(-2) suitable for BNCT. Important advantage of described approach is absence of Tritium in the scheme. First experiments performed in pulsed regime with 300 mA, 45 kV deuteron beam directed to D2O target demonstrated 10(9) s(-1) neutron flux. This value corresponds to theoretical estimations and proofs prospects of neutron generator development based on high current quasi-gasdynamic ECR ion source. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Self-organization process of a magnetohydrodynamic plasma in the presence of thermal conduction
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zhu, Shao-ping; Horiuchi, Ritoku; Sato, Tetsuya; Watanabe, K.; Hayashi, T.; Todo, Y.; Watanabe, T.H.; Kageyama, A.; Takamaru, H.
1995-12-01
A self-organization process of a magnetohydrodynamic(MHD) plasma with a finite thermal conductivity is investigated by means of a three-dimensional MHD simulation. With no thermal conduction an MHD system self-organizes to a non-Taylor's state in which the electric current perpendicular to the magnetic field remains comparable to the parallel electric current. In the presence of thermal conductivity the perpendicular component of electric current and the nonuniformity of thermal pressure generated by driven reconnection tend to be smoothened. Thus, the self-organized state approaches to a force-free minimum energy state under the influence of thermal conduction. Detailed energy conversion processes are also studied to find that the rapid decay of magnetic energy during the self-organization process is caused not only through the ohmic heating, but also through the work done by the j x B force. (author)
-
Schmidt, Christian; Wagner, Sven; Burger, Martin; van Rienen, Ursula; Wolters, Carsten H.
2015-08-01
Objective. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique to modify neural excitability. Using multi-array tDCS, we investigate the influence of inter-individually varying head tissue conductivity profiles on optimal electrode configurations for an auditory cortex stimulation. Approach. In order to quantify the uncertainty of the optimal electrode configurations, multi-variate generalized polynomial chaos expansions of the model solutions are used based on uncertain conductivity profiles of the compartments skin, skull, gray matter, and white matter. Stochastic measures, probability density functions, and sensitivity of the quantities of interest are investigated for each electrode and the current density at the target with the resulting stimulation protocols visualized on the head surface. Main results. We demonstrate that the optimized stimulation protocols are only comprised of a few active electrodes, with tolerable deviations in the stimulation amplitude of the anode. However, large deviations in the order of the uncertainty in the conductivity profiles could be noted in the stimulation protocol of the compensating cathodes. Regarding these main stimulation electrodes, the stimulation protocol was most sensitive to uncertainty in skull conductivity. Finally, the probability that the current density amplitude in the auditory cortex target region is supra-threshold was below 50%. Significance. The results suggest that an uncertain conductivity profile in computational models of tDCS can have a substantial influence on the prediction of optimal stimulation protocols for stimulation of the auditory cortex. The investigations carried out in this study present a possibility to predict the probability of providing a therapeutic effect with an optimized electrode system for future auditory clinical and experimental procedures of tDCS applications.
-
Physical Mechanisms Responsible for Electrical Conduction in Pt/GaN Schottky Diodes
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. MAZARI
2014-05-01
Full Text Available The current-voltage (I-V characteristics of Pt/(n.u.d-GaN and Pt/Si-doped-GaN diodes Schottky are investigated. Based on these measurements, physical mechanisms responsible for electrical conduction have been suggested. The contribution of thermionic-emission current and various other current transport mechanisms were assumed when evaluating the Schottky barrier height. Thus the generation-recombination, tunneling and leakage currents caused by inhomogeneities and defects at metal-semiconductor interface were taken into account.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tomków Łukasz
2017-12-01
Full Text Available Superconducting magnets in the SIS100 particle accelerator require the supply of liquid helium and electric current. Both are transported with by-pass lines designed at Wrocław University of Technology. Bus-bars used to transfer an electric current between the sections of the accelerator will be encased in a steel shell. Eddy currents are expected to appear in the shell during fast-ramp operation of magnets. Heat generation, which should be limited in any cryogenic system, will appear in the shell. In this work the amount of heat generated is assessed depending on the geometry of an assembly of the bus-bars and the shell. Numerical and analytical calculations are described. It was found that heat generation in the shell is relatively small when compared to other sources present in the accelerator and its value strongly depends on the geometry of the shell. The distribution of eddy currents and generated heat for different geometrical options are presented. Based on the results of the calculations the optimal design is proposed.
-
Nonlinear Hydroelastic Waves Generated due to a Floating Elastic Plate in a Current
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ping Wang
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Effects of underlying uniform current on the nonlinear hydroelastic waves generated due to an infinite floating plate are studied analytically, under the hypotheses that the fluid is homogeneous, incompressible, and inviscid. For the case of irrotational motion, the Laplace equation is the governing equation, with the boundary conditions expressing a balance among the hydrodynamics, the uniform current, and elastic force. It is found that the convergent series solutions, obtained by the homotopy analysis method (HAM, consist of the nonlinear hydroelastic wave profile and the velocity potential. The impacts of important physical parameters are discussed in detail. With the increment of the following current intensity, we find that the amplitudes of the hydroelastic waves decrease very slightly, while the opposing current produces the opposite effect on the hydroelastic waves. Furthermore, the amplitudes of waves increase very obviously for higher opposing current speed but reduce very slightly for higher following current speed. A larger amplitude of the incident wave increases the hydroelastic wave deflections for both opposing and following current, while for Young’s modulus of the plate there is the opposite effect.
-
Electrohydrodynamic simulation of electrically controlled droplet generation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ouedraogo, Yun; Gjonaj, Erion; Weiland, Thomas; Gersem, Herbert De; Steinhausen, Christoph; Lamanna, Grazia; Weigand, Bernhard
2017-01-01
Highlights: • We develop a full electrohydrodynamic simulation approach which allows for the accurate modeling of droplet dynamics under the influence of transient electric fields. The model takes into account conductive, capacitive as well as convective electrical currents in the fluid. • Simulation results are shown for an electrically driven droplet generator using highly conductive acetone droplets and low conductivity pentane droplets, respectively. Excellent agreement with measurement is found. • We investigate the operation characteristic of the droplet generator by computing droplet sizes and detachment times with respect to the applied voltage. • The droplet charging effect is demonstrated for pentane droplets as well as for acetone droplets under long voltage pulses. We show that due to the very different relaxation times, the charging behavior of the two liquids is very different. • We demonstrate that due to this behavior, also the detachment mechanisms for acetone and pentane droplets are different. For low conductivity (pentane) droplets, droplet detachment is only possible after the electric fields are switched off. This is because the effective electric polarization force points upwards, thus, inhibiting the detachment of the droplet from the capillary tip. - Abstract: An electrohydrodynamic model for the simulation of droplet formation, detachment and motion in an electrically driven droplet generator is introduced. The numerical approach is based on the coupled solution of the multiphase flow problem with the charge continuity equation. For the latter, a modified convection-conduction model is applied, taking into account conductive, capacitive as well as convective electrical currents in the fluid. This allows for a proper description of charge relaxation phenomena in the moving fluid. In particular, the charge received by the droplet after detachment is an important parameter influencing the droplet dynamics in the test chamber
-
Scale Thickness Measurement of Steam Generator Tubing Using Eddy Current Signal of Bobbin Coil
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kim, Chang Soo; Um, Ki Soo; Kim, Jae Dong
2012-01-01
Steam generator is one of the major components of nuclear power plant and steam generator tubes are the pressure boundary between primary and secondary side, which makes them critical for nuclear safety. As the operating time of nuclear power plant increases, not only damage mechanisms but also scaled deposits on steam generator tubes are known to be problematic causing tube support flow hole blockage and heat fouling. The ability to assess the extent and location of scaled deposits on tubes became essential for management and maintenance of steam generator and eddy current bobbin data can be utilized to measure thickness of scale on tubes. In this paper, tube reference standards with various thickness of scaled deposit has been set up to provide information about the overall deposit condition of steam generator tubes, providing essential tool for steam generator management and maintenance to predict and prevent future damages. Also, methodology to automatically measure scale thickness on tubes has been developed and applied to field data to estimate overall scale amount.
-
Progress and plans for the EnCurrent power generation system
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bear, C. [New Energy Corp. Inc., Calgary, AB (Canada)
2008-07-01
This presentation discussed a new vertical axis hydro turbine designed by New Energy Corporation. The EnCurrent turbine design was based on the Darrieus wind turbine, and suited for use in rivers, irrigation canals, industrial outflows, and tidal current applications. The turbine has a flexible deployment configuration with a variable aspect ratio. Designs for the turbine were initiated in fresh water applications, and the size of the equipment was increased to include tidal applications and large river arrays after the technology was proven. A study has demonstrated that use of the turbines in Canada's canal systems would result in significant annual power generation revenues. The use of smaller turbine systems can provide indirect sales to owners through local resellers, while larger systems can provide power or additional revenues for utilities, large cooperatives, and project developers. Case studies of small turbine installations were provided, as well as case studies of turbines used by larger commercial plants. The presentation also discussed several large projects recently undertaken by the company, including the $6.5 million Canoe pass installation. tabs., figs.
-
EddyOne automated analysis of PWR/WWER steam generator tubes eddy current data
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nadinic, B.; Vanjak, Z.
2004-01-01
INETEC Institute for Nuclear Technology developed software package called Eddy One which has option of automated analysis of bobbin coil eddy current data. During its development and on site use, many valuable lessons were learned which are described in this article. In accordance with previous, the following topics are covered: General requirements for automated analysis of bobbin coil eddy current data; Main approaches to automated analysis; Multi rule algorithms for data screening; Landmark detection algorithms as prerequisite for automated analysis (threshold algorithms and algorithms based on neural network principles); Field experience with Eddy One software; Development directions (use of artificial intelligence with self learning abilities for indication detection and sizing); Automated analysis software qualification; Conclusions. Special emphasis is given on results obtained on different types of steam generators, condensers and heat exchangers. Such results are then compared with results obtained by other automated software vendors giving clear advantage to INETEC approach. It has to be pointed out that INETEC field experience was collected also on WWER steam generators what is for now unique experience.(author)
-
RF generated currents in a magnetized plasma using a slow wave structure
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Poole, B.R.; Cheo, B.R.; Kuo, S.P.; Tang, M.G.
1983-01-01
The generation of a dc current in a plasma by using RF waves is of importance for the operation of steadystate toroidal devices. An experimental investigation in the use of unidirectional, low frequency RF waves to drive currents has been made. Instead of using a natural plasma wave a slow wave guiding structure is used along the entire length of the plasma. When the RF wave is injected an increase in ionization and T/sub e/, and hence the background current is observed. However, the change depends on wave direction: The +k/sub z/ excitation yields a much larger electron current compared with the -k/sub z/ excitation indicating a net wave driven current. The measured modification in electron density and T/sub e/ is independent of wave direction. The current with a standing wave excitation generally falls at the average of the travelling wave (+ or - k/sub z/) driven currents. The net wave driven current is proportional to the feed power at approx. = 10 mA/kW. No saturation of the current is observed with feed powers up to 1 kW. Since the exciting structure is only 1 wavelength long, its k/sub z/ spectrum is relatively broad and hence no sharp resonances are observed as various plasma parameters and B/sub O/ are changed. There is no measurable difference between the power absorbed by the load resistors and the input power to the slow wave structure. Thus the current is driven by the wave field exclamation E exclamation 2 rather than the power absorbed in the plasma. The theoretical background and the physical mechanism is presented
-
Current and future trends in global landfill gas generation and emissions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Meadows, M.; Franklin, C.; Campbell, D.
1996-01-01
This paper assesses the magnitude and distribution of current and future methane generation and emissions from landfill on a world-wide basis. It also estimates the current and future global potential for energy recovery from landfill methane. The mass of methane emitted from land disposal of wastes in any country depends on the waste management strategy of that country. In turn, the waste management strategy of a country depends on its population size, relative proportion living in rural or urban regions and the economic development of the country. We estimate by 2010 there will be a large increase in global methane emissions from solid wastes disposed on land. This increase will be largely from developing regions of the world. The main factor driving this increase is a population shift from rural to urban areas, particularly in regions of highest population, i.e. China and India. This will lead to a greater concentration of waste generation, in turn leading to increased disposal of wastes in deeper sites. In addition increased industrialisation and improved standard of living in regions of high population, will increase the mass of waste disposed of per person and the degradable carbon content of the waste, i.e. the waste will become more like waste from developed countries. In contrast, methane emissions from waste disposed on land in developed countries is likely to decrease by 2010, mainly as result of increased collection and combustion of landfill methane. (Author)
-
Lignite mining and electricity generation in Poland: The current state and future prospects
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Widera, Marek; Kasztelewicz, Zbigniew; Ptak, Miranda
2016-01-01
This opinion paper presents the current state and future scenarios of Polish lignite mining. For many years, over 1/3 of domestic electricity, that is about 53–55 TWh, has been generated by lignite-fired power plants. Currently, with 63–66 million tons of extraction, Poland is the fourth lignite producer worldwide and the second in the European Union. There are three possible scenarios for the development of lignite mining in Poland by 2050. Unfortunately, despite the huge lignite resources, amounting to more than 23.5 billion tons, and great potential of the mining industry, the future of Polish lignite mining does not look optimistic from the economic point of view. This is associated with social and environmental problems, including the European Union's climate and energy policy. However, this may change in the event of a global economic crisis and unstable geopolitical conditions. Therefore, a new energy doctrine for Poland at least by 2050 is urgently needed. - Highlights: •Poland is one of the leaders in lignite production in the European Union. •Energy policy in Poland assumes a key role of lignite in energy mix. •Almost one-third of Polish electricity is currently generated from lignite. •For Polish lignite mining exist pessimistic, realistic and optimistic scenarios. •Extraction of lignite in Poland will gradually decrease in the coming decades.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ohkubo, K.; Toi, K.; Kawahata, K.
1984-10-01
Suprathermal electrons which carry a seed current are generated by non-resonant parametric decay instability during initial phase of lower hybrid current startup in the JIPP T-IIU tokamak. From the numerical analysis, it is found that parametrically excited lower hybrid waves at lower side band can bridge the spectral gap between the thermal velocity and the low velocity end in the pump power spectrum. (author)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Sulpizio, Roberto; Dellino, Pierfrancesco; Mele, Daniela; La Volpe, Luigi [CIRISIVU, c/o Dipartimento Geomineralogico, via Orabona 4, 70125, Bari (Italy)], E-mail: r.sulpizio@geomin.uniba.it
2008-10-01
Pyroclastic density currents (PDCs) are among the most amazing, complex and dangerous volcanic phenomena. They are moving mixtures of particles and gas that flow across the ground, and originate in different ways and from various sources, during explosive eruptions or gravity-driven collapse of domes. We present results from experimental work to investigate the generation of large-scale, multiphase, gravity-driven currents. The experiments described here are particularly devoted to understanding the inception and development of PDCs under impulsive injection conditions by means of the fast application of a finite stress to a finite mass of pyroclastic particles via expansion of compressed gas. We find that, in summary, PDC generation from collapse of pressure-adjusted or overpressurised pyroclastic jets critically depends on behaviour of injection into the atmosphere, which controls the collapsing mechanisms and then the physical parameters of the initiating current.
-
Bhadra, Narendra; Foldes, Emily; Vrabec, Tina; Kilgore, Kevin; Bhadra, Niloy
2018-02-01
Objective. Application of kilohertz frequency alternating current (KHFAC) waveforms can result in nerve conduction block that is induced in less than a second. Conduction recovers within seconds when KHFAC is applied for about 5-10 min. This study investigated the effect of repeated and prolonged application of KHFAC on rat sciatic nerve with bipolar platinum electrodes. Approach. Varying durations of KHFAC at signal amplitudes for conduction block with intervals of no stimulus were studied. Nerve conduction was monitored by recording peak Gastrocnemius muscle force utilizing stimulation electrodes proximal (PS) and distal (DS) to a blocking electrode. The PS signal traveled through the block zone on the nerve, while the DS went directly to the motor end-plate junction. The PS/DS force ratio provided a measure of conduction patency of the nerve in the block zone. Main results. Conduction recovery times were found to be significantly affected by the cumulative duration of KHFAC application. Peak stimulated muscle force returned to pre-block levels immediately after cessation of KHFAC delivery when it was applied for less than about 15 min. They fell significantly but recovered to near pre-block levels for cumulative stimulus of 50 ± 20 min, for the tested On/Off times and frequencies. Conduction recovered in two phases, an initial fast one (60-80% recovery), followed by a slower phase. No permanent conduction block was seen at the end of the observation period during any experiment. Significance. This carry-over block effect may be exploited to provide continuous conduction block in peripheral nerves without continuous application of KHFAC.
-
Shih, Josephine H; Eberhart, Nicole K
2008-08-01
Stress generation is a process in which individuals contribute to stressful life events. While research has supported an association between current depression and stress generation, it has been noted that individuals with prior depression tend to contribute to stressors even when they are no longer experiencing a depressive episode. The aim of the study is to elucidate the pathways through which prior major depression predicts interpersonal stress generation in women. Specifically, we examined current subsyndromal depressive symptoms and problematic interpersonal behaviours as potential mediators. Fifty-one college women were followed prospectively for 6 weeks. Participants were interviewed to assess current and past depression as well as stressful life events they experienced over the 6-week period. The findings suggest that prior major depression continues to have an impact even after the episode has ended, as the disorder continues to contribute to stress generation through residual depressive symptoms.
-
Simulation of current generation in a 3-D plasma model
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tsung, F.S.; Dawson, J.M.
1996-01-01
Two wires carrying current in the same direction will attract each other, and two wires carrying current in the opposite direction will repel each other. Now, consider a test charge in a plasma. If the test charge carries current parallel to the plasma, then it will be pulled toward the plasma core, and if the test charge carries current anti-parallel to the plasma, then it will be pushed to the edge. The electromagnetic coupling between the plasma and a test charge (i.e., the A parallel circ v parallel term in the test charge's Hamiltonian) breaks the symmetry in the parallel direction, and gives rise to a diffusion coefficient which is dependent on the particle's parallel velocity. This is the basis for the open-quotes preferential lossclose quotes mechanism described in the work by Nunan et al. In our previous 2+1/2 D work, in both cylindrical and toroidal geometries, showed that if the plasma column is centrally fueled, then an initial current increases steadily. The results in straight, cylindrical plasmas showed that self generated parallel current arises without trapped particle or neoclassical diffusion, as assumed by the bootstrap theory. It suggests that the fundamental mechanism seems to be the conservation of particles canonical momenta in the direction of the ignorable coordinate. We have extended the simulation to 3D to verify the model put forth. A scalable 3D EM-PIC code, with a localized field-solver, has been implemented to run on a large class of parallel computers. On the 512-node SP2 at Cornell Theory Center, we have benchmarked the 2+1/2 D calculations using 32 grids in the previously ignored direction, and a 100-fold increase in the number of particles. Our preliminary results show good agreements between the 2+1/2 D and the 3D calculations. We will present our 3D results at the meeting
-
2014-09-30
alongshore winds favoring upwelling circulation. As for the other EBUS (e.g., Humboldt, Benguela, and Canary Currents ), equatorward winds drive...Eddy Effects in the General Circulation, Spanning Mean Currents , Mesoscale Eddies, and Topographic Generation, Including Submesoscale Nests...environments OBJECTIVES The central scientific questions are how the eddies control the persistent currents by their eddy-induced momentum and buoyancy fluxes
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Fulmek, Paul; Nicolics, Johann [Institute of Sensor & Actuator Systems, Vienna University of Technology, Gusshausstraße 27-29, A-1040 Vienna (Austria); Nemitz, Wolfgang; Schweitzer, Susanne; Sommer, Christian; Hartmann, Paul [Institute of Surface Technologies and Photonics, Joanneum Research Forschungsges mbH, Franz-Pichler Straße 30, A-8160 Weiz (Austria); Schrank, Franz [Tridonic Jennersdorf GmbH, Technologiepark 10, A-8380 Jennersdorf (Austria); Wenzl, Franz P., E-mail: Franz-Peter.Wenzl@joanneum.at [Institute of Sensor & Actuator Systems, Vienna University of Technology, Gusshausstraße 27-29, A-1040 Vienna (Austria)
2016-01-15
For a systematic approach to improve the reliability and the white light quality of phosphor converted light-emitting diodes (LEDs) it is imperative to gain a better understanding of the individual parameters that affect color temperature constancy and maintenance. By means of a combined optical and thermal simulation procedure, in this contribution we give a comprehensive discussion on the impact of different thermal conductivities of the color conversion elements (CCE) of phosphor converted LEDs on their respective thermal load for different current driving schemes. In particular we show that, while for the thermal load of CCEs with low thermal conductivities also effects due to the non-linearity between the blue radiant flux and the current have to be considered, these effects are largely diminished in case of CCEs with higher thermal conductivities. - Highlights: • We discuss the thermal load of phosphor based LEDs for different current driving. • We report on the time scales for the thermal load of phosphor based LEDs. • We report on the impact of the non-linearity of the radiant flux on the thermal load. • We discuss the impact of the thermal conductivity on the thermal load.
-
Optical approach to thermopower and conductivity measurements in thin-film semiconductors
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dersch, H.; Amer, N.M.
1984-01-01
An optical beam deflection technique is applied to measure the Joule and Peltier heat generated by electric currents through thin-film semiconductors. The method yields a spatially resolved conductivity profile and allows the determination of Peltier coefficients. Results obtained on doped hydrogenated amorphous silicon films are presented
-
Strategies for the Use of Tidal Stream Currents for Power Generation
Orhan, Kadir; Mayerle, Roberto
2015-04-01
Indonesia is one of the priority countries in Southeast Asia for the development of ocean renewable energy facilities and The National Energy Council intends to increase the role of ocean energy significantly in the energy mix for 2010-2050. To this end, the joint German-Indonesian project "Ocean Renewable Energy ORE-12" aims at the identification of marine environments in the Indonesian Archipelago, which are suitable for the efficient generation of electric power by converter facilities. This study, within the ORE-12 project, is focused on the tidal stream currents on the straits between the Indian Ocean and Flores Sea to estimate the energy potentials and to develop strategies for producing renewable energy. FLOW module of Delft3D has been used to run hydrodynamic models for site assessment and design development. In site assessment phase, 2D models have been operated for a-month long periods and with a resolution of 500 m. Later on, in design development phase, detailed 3D models have been developed and operated for three-month long periods and with a resolution of 50 m. Bathymetric data for models have been obtained from the GEBCO_08 Grid and wind data from the Global Forecast System of NOAA's National Climatic Data Center. To set the boundary conditions of models, tidal forcing with 11 harmonic constituents was supplied from TPXO Indian Ocean Atlas (1/12° regional model) and data from HYCOM+NCODA Global 1/12° Analysis have been used to determine salinity and temperature on open boundaries. After the field survey is complete, water level time-series supplied from a tidal gauge located in the domain of interest (8° 20΄ 9.7" S, 122° 54΄ 51.9" E) have been used to verify the models and then energy potentials of the straits have been estimated. As a next step, correspondence between model outputs and measurements taken by the radar system of TerraSAR-X satellite (DLR) will be analysed. Also for the assessment of environmental impacts caused by tidal stream
-
Generation of Low-Energy High-Current Electron Beams in Plasma-Anode Electron Guns
Ozur, G. E.; Proskurovsky, D. I.
2018-01-01
This paper is a review of studies on the generation of low-energy high-current electron beams in electron guns with a plasma anode and an explosive-emission cathode. The problems related to the initiation of explosive electron emission under plasma and the formation and transport of high-current electron beams in plasma-filled systems are discussed consecutively. Considerable attention is given to the nonstationary effects that occur in the space charge layers of plasma. Emphasis is also placed on the problem of providing a uniform energy density distribution over the beam cross section, which is of critical importance in using electron beams of this type for surface treatment of materials. Examples of facilities based on low-energy high-current electron beam sources are presented and their applications in materials science and practice are discussed.
-
Current redistribution and generation of kinetic energy in the stagnated Z pinch.
Ivanov, V V; Anderson, A A; Papp, D; Astanovitskiy, A L; Talbot, B R; Chittenden, J P; Niasse, N
2013-07-01
The structure of magnetic fields was investigated in stagnated wire-array Z pinches using a Faraday rotation diagnostic at the wavelength of 266 nm. The distribution of current in the pinch and trailing material was reconstructed. A significant part of current can switch from the main pinch to the trailing plasma preheated by x-ray radiation of the pinch. Secondary implosions of trailing plasma generate kinetic energy and provide enhanced heating and radiation of plasma at stagnation. Hot spots in wire-array Z pinches also provide enhanced radiation of the Z pinch. A collapse of a single hot spot radiates 1%-3% of x-ray energy of the Z pinch with a total contribution of hot spots of 10%-30%.
-
Naggar H. Saad; Ahmed A. El-Sattar; Mohamed I. Marei
2016-01-01
The main challenges of wind energy conversion systems (WECS) are to maximize the energy capture from the wind and injecting reactive power during the fault. This paper presents a current controlled matrix converter to interface Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generators (PMSG) based WECS with the grid. To achieve fast dynamic response with reduced current ripples, a hysteresis current control is utilized. The proposed control system decouples the active and reactive components of the PMSG curren...
-
Multifrequency eddy-current system for inspection of steam generator turbine
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Davis, T.J.
1980-11-01
The objectives of this program were to: determine the maximum advantage of the multifrequency eddy current method for nuclear steam generator tubing inspection; simplify system operating procedures and enhance presentation of mutifrequency data; and evaluate multifrequency methods for inspecting recently encountered types of anomalies such as circumferential cracks, inside diameter flaws, and flaws in dented regions. New test methods developed under the program have resulted in a dramatic improvement over earlier multifrequency work. The methods rely on judicious selection of test frequencies and the simultaneous use of differential and absolute multiparameter inspection. Flaws may be sized and profiled with increased accuracy over that of the single-frequency method, and improved rejection of indications from unwanted parameters such as support plates and probe wobble has been obtained. The ability to detect and size support cracks in both corroded and non-corroded supports has been demonstrated on a laboratory basis. A field-usable test system employing four test frequencies was developed under the program and has been evaluated in the EPRI steam generator mockup. Some of the new technology used in this system has been commercialized into the new Zetec MIZ-12 multifrequency system
-
Evaluation of Semi-Automatic Metadata Generation Tools: A Survey of the Current State of the Art
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jung-ran Park
2015-09-01
Full Text Available Assessment of the current landscape of semi-automatic metadata generation tools is particularly important considering the rapid development of digital repositories and the recent explosion of big data. Utilization of (semiautomatic metadata generation is critical in addressing these environmental changes and may be unavoidable in the future considering the costly and complex operation of manual metadata creation. To address such needs, this study examines the range of semi-automatic metadata generation tools (n=39 while providing an analysis of their techniques, features, and functions. The study focuses on open-source tools that can be readily utilized in libraries and other memory institutions. The challenges and current barriers to implementation of these tools were identified. The greatest area of difficulty lies in the fact that the piecemeal development of most semi-automatic generation tools only addresses part of the issue of semi-automatic metadata generation, providing solutions to one or a few metadata elements but not the full range elements. This indicates that significant local efforts will be required to integrate the various tools into a coherent set of a working whole. Suggestions toward such efforts are presented for future developments that may assist information professionals with incorporation of semi-automatic tools within their daily workflows.
-
Blakeslee, Richard J.; Mach, Douglas M.; Bateman, Monte J.; Bailey, Jeffrey C.
2011-01-01
We determined total conduction currents and flash rates for around 900 high-altitude aircraft overflights of electrified clouds over 17 years. The overflights include a wide geographical sample of storms over land and ocean, with and without lightning, and with positive (i.e., upward-directed) and negative current. Peak electric field, with lightning transients removed, ranged from -1.0 kV m(sup -1) to 16. kV m(sup -1), with mean (median) of 0.9 kV m(sup -1) (0.29 kV m(sup -1)). Total conductivity at flight altitude ranged from 0.6 pS m(sup -1) to 3.6 pS m(sup -1), with mean and median of 2.2 pS m(sup -1). Peak current densities ranged from -2.0 nA m(sup -2) to 33.0 nA m(sup -2) with mean (median) of 1.9 nA m(sup -2) (0.6 nA m(sup -2)). Total upward current flow from storms in our dataset ranged from -1.3 to 9.4 A. The mean current for storms with lightning is 1.6 A over ocean and 1.0 A over land. The mean current for electrified shower clouds (i.e. electrified storms without lightning) is 0.39 A for ocean and 0.13 A for land. About 78% (43%) of the land (ocean) storms have detectable lightning. Land storms have 2.8 times the mean flash rate as ocean storms (2.2 versus 0.8 flashes min(sup -1), respectively). Approximately 7% of the overflights had negative current. The mean and median currents for positive (negative) polarity storms are 1.0 and 0.35 A (-0.30 and -0.26 A). We found no regional or latitudinal-based patterns in our storm currents, nor support for simple scaling laws between cloud top height and lightning flash rate.
-
Phase modulation mode of scanning ion conductance microscopy
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Li, Peng; Zhang, Changlin [State Key Laboratory of Robotics, Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016 (China); University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049 (China); Liu, Lianqing, E-mail: lqliu@sia.cn, E-mail: gli@engr.pitt.edu; Wang, Yuechao; Yang, Yang [State Key Laboratory of Robotics, Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016 (China); Li, Guangyong, E-mail: lqliu@sia.cn, E-mail: gli@engr.pitt.edu [Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15261 (United States)
2014-08-04
This Letter reports a phase modulation (PM) mode of scanning ion conductance microscopy. In this mode, an AC current is directly generated by an AC voltage between the electrodes. The portion of the AC current in phase with the AC voltage, which is the current through the resistance path, is modulated by the tip-sample distance. It can be used as the input of feedback control to drive the scanner in Z direction. The PM mode, taking the advantages of both DC mode and traditional AC mode, is less prone to electronic noise and DC drift but maintains high scanning speed. The effectiveness of the PM mode has been proven by experiments.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nagasaki, Y., E-mail: nagasaki@rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp [Research Institute of Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011 (Japan); Nakamura, T. [Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, Kyotodaigakukatsura, Nishikyo, Kyoto 615-8530 (Japan); Funaki, I. [Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 252-5210 (Japan); Ashida, Y.; Yamakawa, H. [Research Institute of Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011 (Japan)
2013-09-15
Highlights: • We model current transport and thermal performances of conduction-cooled HTS coil. • We investigate the effect of the longitudinal inhomogeneity of the HTS tape. • The analysis can precisely estimate performances of the conduction-cooled coil. • The longitudinal inhomogeneity of the HTS tape deteriorates coil performances. • Quench currents of the HTS coil are not consistent with the critical currents. -- Abstract: This paper investigated the quantitative current transport performance and thermal behaviour of a high temperature superconducting (HTS) coil, and the effect of the critical current inhomogeneity along the longitudinal direction of HTS tapes on the coil performances. We fabricated a double-pancake coil using a Bi-2223/Ag tape with a length of 200 m as a scale-down model for a magnetic sail spacecraft. We measured the current transport property and temperature rises during current applications of the HTS coil in a conduction-cooled system, and analytically reproduced the results on the basis of the percolation depinning model and three-dimensional heat balance equation. The percolation depinning model can describe the electric field versus current density of HTS tapes as a function of temperature and magnetic field vector, and we also introduced the longitudinal distribution of the local critical current of the HTS tape into this model. As a result, we can estimate the critical currents of the HTS coil within 10% error for a wide range of the operational temperatures from 45 to 80 K, and temperature rises on the coil during current applications. These results showed that our analysis and conduction-cooled system were successfully realized. The analysis also suggested that the critical current inhomogeneity along the length of the HTS tape deteriorated the current transport performance and thermal stability of the HTS coil. The present study contributes to the characterization of HTS coils and design of a coil system for the
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nagasaki, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Funaki, I.; Ashida, Y.; Yamakawa, H.
2013-01-01
Highlights: • We model current transport and thermal performances of conduction-cooled HTS coil. • We investigate the effect of the longitudinal inhomogeneity of the HTS tape. • The analysis can precisely estimate performances of the conduction-cooled coil. • The longitudinal inhomogeneity of the HTS tape deteriorates coil performances. • Quench currents of the HTS coil are not consistent with the critical currents. -- Abstract: This paper investigated the quantitative current transport performance and thermal behaviour of a high temperature superconducting (HTS) coil, and the effect of the critical current inhomogeneity along the longitudinal direction of HTS tapes on the coil performances. We fabricated a double-pancake coil using a Bi-2223/Ag tape with a length of 200 m as a scale-down model for a magnetic sail spacecraft. We measured the current transport property and temperature rises during current applications of the HTS coil in a conduction-cooled system, and analytically reproduced the results on the basis of the percolation depinning model and three-dimensional heat balance equation. The percolation depinning model can describe the electric field versus current density of HTS tapes as a function of temperature and magnetic field vector, and we also introduced the longitudinal distribution of the local critical current of the HTS tape into this model. As a result, we can estimate the critical currents of the HTS coil within 10% error for a wide range of the operational temperatures from 45 to 80 K, and temperature rises on the coil during current applications. These results showed that our analysis and conduction-cooled system were successfully realized. The analysis also suggested that the critical current inhomogeneity along the length of the HTS tape deteriorated the current transport performance and thermal stability of the HTS coil. The present study contributes to the characterization of HTS coils and design of a coil system for the
-
True random bit generators based on current time series of contact glow discharge electrolysis
Rojas, Andrea Espinel; Allagui, Anis; Elwakil, Ahmed S.; Alawadhi, Hussain
2018-05-01
Random bit generators (RBGs) in today's digital information and communication systems employ a high rate physical entropy sources such as electronic, photonic, or thermal time series signals. However, the proper functioning of such physical systems is bound by specific constrains that make them in some cases weak and susceptible to external attacks. In this study, we show that the electrical current time series of contact glow discharge electrolysis, which is a dc voltage-powered micro-plasma in liquids, can be used for generating random bit sequences in a wide range of high dc voltages. The current signal is quantized into a binary stream by first using a simple moving average function which makes the distribution centered around zero, and then applying logical operations which enables the binarized data to pass all tests in industry-standard randomness test suite by the National Institute of Standard Technology. Furthermore, the robustness of this RBG against power supply attacks has been examined and verified.
-
Search for the fourth generation charge -1/3 quark via flavor changing neutral currents
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Greenlee, H.B.
1996-08-01
There is some likelihood that a light ( t ) fourth generation charge -1/3 quark (b') would decay predominantly via loop induced flavor changing neutral currents. The charged current decay of b' to charm wuld be highly Cabibbo suppressed due to the fact that it changes the generation number by two. The D0 experiment has searched for b' pair production where one or both b' quarks decays via b' → b + γ, giving signatures photon + three jets and photon + two jets. We do not see a significant excess of such events over background. In both modes, we set an upper limit on the cross section times branching ratio that is sufficient to rule out a standard sequential b' decaying predominantly via FCNC in the mass range m Z /2 b' Z + m b . For b' masses larger than this, the dominant FCNC decay mode is expected to be b' → b + Z. 10 refs., 10 figs., 10 tabs
-
Search for a fourth generation charge -1/3 quark via flavor changing neutral currents
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
1996-07-01
There is some likelihood that a light ( t ) fourth generation charge -1/3 quark (b') would decay predominantly via loop induced flavor changing neutral currents. The charged current decay of b' to charm would be highly Cabibbo suppressed due to the fact that it changes the generation number by two. The D0 experiment has searched for b' pair production where one or both b' quarks decays via b' → b+γ, giving signatures photon + three jets and two photons + two jets. WE don not see a significant excess of such events over background. In both modes, we set an upper limit on the cross section times branching ratio that is sufficient to rule out a standard sequential b' decaying predominantly via FCNC in the mass range m Z /2 b' Z + m b . For b' masses larger than this, the dominant FCNC decay mode is expected to be b' → b + Z. 14 refs., 13 figs., 5 tabs
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lyubutin, S.K.; Rukin, S.N.; Slovikovskij, B.G.
2000-01-01
Compact generator with a semiconductor current interrupter (SOS-diode), forming on the resistive load pulses with the amplitude up to 300 kV, duration from 30 up to 50 ns and the pulse sequence frequency 300 Hz by long operation and up to 2 kHz in the 30-second packet, is described. The generator contains a thyristor charge unit, magnetic compressor and inductive storage with a semiconductor current interrupter on the SOS-diode basis. The generator mean output capacity by the pulse maximum sequence frequency and 250 kV voltage equals 16 kw. The generator dimensions are 0.85 x 0.65 x 0.42 m, its mass equals approximately 115 kg [ru
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Latyshev, A. V., E-mail: avlatyshev@mail.ru; Yushkanov, A. A. [Moscow State Regional University (Russian Federation)
2015-09-15
A distribution function for collisionless plasma is derived from the Vlasov kinetic equation in the quadratic approximation with respect to the electromagnetic field. Formulas for calculation of the electric current at an arbitrary temperature (arbitrary degree of degeneration of the electron gas) are deduced. The case of small wavenumbers is considered. It is shown that nonlinearity leads to the generation of an electric current directed along the wave vector. This longitudinal current is orthogonal to the classical transverse current, well known in the linear theory. A distribution function for collisionless quantum plasma is derived from the kinetic equation with the Wigner integral in the quadratic approximation with respect to the vector potential. Formulas for calculation of the electric current at an arbitrary temperature are deduced. The case of small wavenumbers is considered. It is shown that, at small values of the wavenumber, the value of the longitudinal current for quantum plasma coincides with that for classical plasma. The dimensionless currents in quantum and classical plasmas are compared graphically.
-
Ocean Current Power Generator. Final Report
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
O' Sullivan, G. A.
2002-07-26
The Ocean Power Generator is both technically and economically suitable for deployment in the Gulf Stream from the US Navy facility in Dania, Florida. Yet to be completed is the calibration test in the Chesapeake Bay with the prototype dual hydroturbine Underwater Electric Kite. For the production units a revised design includes two ballast tanks mounted as pontoons to provide buoyancy and depth control. The power rating of the Ocean Power Generator has been doubled to 200 kW ready for insertion into the utility grid. The projected cost for a 10 MW installation is $3.38 per watt, a cost that is consistent with wind power pricing when it was in its deployment infancy, and a cost that is far better than photovoltaics after 25 years of research and development. The Gulf Stream flows 24 hours per day, and water flow is both environmentally and ecologically perfect as a renewable energy source. No real estate purchases are necessary, and you cannot see, hear, smell, or touch an Ocean Power Generator.
-
Jin, Nan Ge; Koh, Sang Don; Sanders, Kenton M
2009-10-01
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) discharge unitary potentials in gastrointestinal muscles that constitute the basis for pacemaker activity. Caffeine has been used to block unitary potentials, but the ionic conductance responsible for unitary potentials is controversial. We investigated currents in cultured ICC from murine jejunum that may underlie unitary potentials and studied the effects of caffeine. Networks of ICC generated slow wave events under current clamp, and these events were blocked by caffeine in a concentration-dependent manner. Single ICC generated spontaneous transient inward currents (STICs) under voltage clamp at -60 mV and noisy voltage fluctuations in current clamp. STICs were unaffected when the equilibrium potential for Cl- (ECl) was set to -60 mV (excluding Cl- currents) and reversed at 0 mV, demonstrating that a nonselective cationic conductance, and not a Cl- conductance, is responsible for STICs in ICC. Caffeine inhibited STICs in a concentration-dependent manner. Reduced intracellular Ca2+ and calmidazolium (CMZ; 1 microM) activated persistent inward, nonselective cation currents in ICC. Currents activated by CMZ and by dialysis of cells with 10 mM BAPTA were also inhibited by caffeine. Excised inside-out patches contained channels that exhibited spontaneous openings, and resulting currents reversed at 0 mV. Channel openings were increased by reducing Ca2+ concentration from 10(-6) M to 10(-8) M. CMZ (1 microM) also increased openings of nonselective cation channels. Spontaneous currents and channels activated by CMZ were inhibited by caffeine (5 mM). The findings demonstrate that the Ca2+-inhibited nonselective cation channels that generate STICs in ICC are blocked directly by caffeine. STICs are responsible for unitary potentials in intact muscles, and the block of these events by caffeine is consistent with the idea that a nonselective cation conductance underlies unitary potentials in ICC.
-
Experimental analysis of current conduction through thermally ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
Electrical properties of SiO2 grown on the Si-face of the epitaxial 4H-SiC ... Thermal oxide reliability is one of the most critical concerns in the realization of ... material for high temperature, high power, high frequency, and nonvolatile .... conduction mechanism in MOSiC system with varying oxide thicknesses has been.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lei Chen
2016-09-01
Full Text Available Concerning the development of a micro-grid integrated with multiple intermittent renewable energy resources, one of the main issues is related to the improvement of its robustness against short-circuit faults. In a sense, the superconducting fault current limiter (SFCL can be regarded as a feasible approach to enhance the transient performance of a micro-grid under fault conditions. In this paper, the fault transient analysis of a micro-grid, including distributed generation, energy storage and power loads, is conducted, and regarding the application of one or more flux-coupling-type SFCLs in the micro-grid, an integrated technical evaluation method considering current-limiting performance, bus voltage stability and device cost is proposed. In order to assess the performance of the SFCLs and verify the effectiveness of the evaluation method, different fault cases of a 10-kV micro-grid with photovoltaic (PV, wind generator and energy storage are simulated in the MATLAB software. The results show that, the efficient use of the SFCLs for the micro-grid can contribute to reducing the fault current, improving the voltage sags and suppressing the frequency fluctuations. Moreover, there will be a compromise design to fully take advantage of the SFCL parameters, and thus, the transient performance of the micro-grid can be guaranteed.
-
Generation of intense transient magnetic fields
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Benjamin, R.F.
1983-01-01
In a laser system, the return current of a laser generated plasma is conducted near a target to subject that target to a magnetic field. The target may be either a small non-fusion object for testing under the magnetic field or a laser-fusion pellet. In the laser-fusion embodiment, the laser-fusion pellet is irradiated during the return current flow and the intense transient magnetic field is used to control the hot electrons thereof to hinder them from striking and heating the core of the irradiated laser-fusion pellet. An emitter, e.g. a microballoon of glass, metal or plastics, is subjected to a laser pulse to generate the plasma from which the return current flows into a wire cage or a coil and then to earth. (author)
-
On the generation of steady currents in a plasma cylinder using m=0 radio-frequency waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hugrass, W.N.
1981-01-01
The generation of a steady current in a resistive plasma cylinder by means of a travelling-wave magnetic field has been studied by using the resistive MHD equations. The non-linear initial-boundary value problem has been solved numerically. Hollow DC current profiles, similar to the experimental data obtained by other workers, have been found. A simple analytical argument, of a more general nature, shows that classical resistive diffusion cannot lead to a more uniform current distribution. (author)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gębura Andrzej
2016-08-01
Full Text Available The study deals with the issue how to apply two different types of current generators at the same time, namely a three-phase AC generator and a DC generator of commutator type. What is more interesting, the two generators would be able to collaborate both during the phase of electromechanical sampling and the phase of electronic sampling. It will enable structural improvement of sensitivity and resolution parameters and shall open new opportunities to investigate new types if mechanical phenomena (that have not been already tracked by means of the FAM-C and FDM-A methods, such as torsion of torque transmission shafts.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Thydén, Karl Tor Sune; Barfod, Rasmus; Liu, Yi-Lin
2006-01-01
The degradation of electrical conductivity in porous nickel-yttria stabilized zirconia composite cermets in a H2/H2O atmosphere under high temperature treatments has been investigated. The parameters varied were: temperature, water partial pressure, and electrical current load. The microstructure...... fraction of percolated Ni was measured. Temperature proved to have the largest effect on the degradation. Samples tested at 1000°C, in contrast to 750°C, showed a severe decrease of conductivity and growth of Ni particles. Higher water partial pressure accelerated Ni particle growth at both temperatures......, but the loss of percolation and conductivity at 1000°C was less severe under high water partial pressure. A possible explanation for this behavior is discussed....
-
Automated WWER steam generator eddy current testing and plugging control system
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gorecan, I.; Gortan, K.; Grzalja, I.
2004-01-01
The structural architecture of the system contains three main components which are described as follows: Manipulator Guidance System; Eddy Current Testing System; Plugging System. The manipulator system has the task to position the end-effectors to the desired tube position. When the final position is reached, the Eddy Current testing system performs data acquisition. In case defects are found, the plugging system performs tube plug installment. Each system is composed of 3 layers. The first layer is the hardware layer consisting of motors driving the effectors along with sensors needed to obtain the positioning data, pusher motors used to push the test probes into tubes of the WWER steam generator, and plugging hardware tool. The second layer is the control box performing basic monitoring and control routines as an interconnection between first and third layer. The highest layer is the control software, running on the PC, which is used as a human-machine-interface.(author)
-
Liu, Gao
2017-07-11
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a composition of matter comprising a silicon (Si) nanoparticle coated with a conductive polymer. Another embodiment discloses a method for preparing a composition of matter comprising a plurality of silicon (Si) nanoparticles coated with a conductive polymer comprising providing Si nanoparticles, providing a conductive polymer, preparing a Si nanoparticle, conductive polymer, and solvent slurry, spraying the slurry into a liquid medium that is a non-solvent of the conductive polymer, and precipitating the silicon (Si) nanoparticles coated with the conductive polymer. Another embodiment discloses an anode comprising a current collector, and a composition of matter comprising a silicon (Si) nanoparticle coated with a conductive polymer.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Antoni, Bernard; Nazet, Christian.
1975-07-01
A generator of electrical energy in which magnetic field compression is achieved by a solid explosive is described. The magnetic flux losses have been calculated for generators of various configurations by the skin depth concept. Calculations take the Joule heating of conductors into account. In helical generators the magnetic flux losses are higher than those calculated by considering diffusion only. Additional losses approximately as important as diffusion losses have already been observed elsewhere on similar devices. Detailed calculations of the motion of the explosively driven inner conductor show that losses come from the jumps encountered by sliding contact moving along the helix. The jumps are caused by little geometrical defects and the consequence on losses is strongly dependent on current intensity. The jumps decrease when the pitch of helix increases. The jumps are detrimental to the efficient use of the explosive energy. With helical generators only 5% of the energy is transferred into magnetic energy [fr
-
A review on the current status and production technology for 188W-188Re generator system
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kuznetsov, R. A.; Han, H. S.; Cho, W. K.; Park, U. J.; Kim, Y. M.
1998-11-01
The current status of 188 W- 188 Re generator production technology were reviewed in PART 1. Main interests were given to the aspects of 188 W reactor production, irradiated targets reprocessing and generator loading technologies, such as alumina type and gel type generators. In order to develop the more convenient and advanced 188 W- 188 Re generator, further studies must be carried out to get the precise evaluation of production and burn-up cross section of 188 W, the more easily realizable generator loading procedure, and also to optimize the column and generator design to compensate the deterioration of generator performance because of parent radionuclide decay. By irradiation of 186 W enriched sample, 188 W- 188 Re generator production experiments were performed to evaluate the possibility of 188 W- 188 Re generator production using HANARO, and PART 2 describes about the experiments. The experimental results shows the possibility of practical 188 W- 188 Re generator production using of low-specific activity 188 W produced in HANARO. (author). 79 refs., 4 tabs., 26 figs
-
Ionizing radiation induced conductivity in Mylar (PET) and Kapton (Polyimide)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gregorio Filho, R.
1986-01-01
The extensive results of measurements of the prompt and delayed radiation-induced conductivity of samples of PET and Kapton are presented. Experimental parameters, such as the effective energy of the radiation, the exposure rate, the total dose, the value of the applied electric field, the nature of the electrodes, and the ambiental conditions were changed within wide limits. We also report measurement of thermally stimulated currents for non-irradiated and for irradiated samples which allowed us to investigate the trap-structure of the materials. Measurements of photo-Compton currents with different electrode materials and sample thicknesses gave information about the relation between the nature of the electrodes and the amplitudes of the currents. Based on the generalized rate theory of radiation-induced conduction we developed a theoretical model which includes the effect of the applied electric field on the carrier generation yield (geminate recombination, Onsager effect). Comparison of experimental and theoretical curves allowed us to determine the values of the main conduction parameters, such as carrier mobility, recombination coefficient, trap densities, for the materials under investigation. (Author) [pt
-
High thermal conductivity materials for thermal management applications
Broido, David A.; Reinecke, Thomas L.; Lindsay, Lucas R.
2018-05-29
High thermal conductivity materials and methods of their use for thermal management applications are provided. In some embodiments, a device comprises a heat generating unit (304) and a thermally conductive unit (306, 308, 310) in thermal communication with the heat generating unit (304) for conducting heat generated by the heat generating unit (304) away from the heat generating unit (304), the thermally conductive unit (306, 308, 310) comprising a thermally conductive compound, alloy or composite thereof. The thermally conductive compound may include Boron Arsenide, Boron Antimonide, Germanium Carbide and Beryllium Selenide.
-
Quasi-equilibrium channel model of an constant current arc
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gerasimov Alexander V.
2003-01-01
Full Text Available The rather simple method of calculation of electronic and gas temperature in the channel of arc of plasma generator is offered. This method is based on self-consistent two-temperature channel model of an electric arc. The method proposed enables to obtain radial allocation of gas and electronic temperatures in a non-conducting zone of an constant current arc, for prescribed parameters of discharge (current intensity and power of the discharge, with enough good precision. The results obtained can be used in model and engineering calculations to estimate gas and electronic temperatures in the channel of an arc plasma generator.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Babykin, V.M.; Chikin, R.V.; Dolgachev, G.I.; Golovanov, Yu.P.; Kovalev, Yu.I.; Ushakov, A.G.; Zakatov, L.P.
1993-01-01
This paper is a follow up to previously published work on microsecond plasma current interrupting switches (PCIS), which has been conducted in the I.V. Kurchatov Inst. Here the authors present some information on the practical implementation of such devices, and provide an overview of new research facilities
-
DC Link Current Estimation in Wind-Double Feed Induction Generator Power Conditioning System
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
MARIAN GAICEANU
2010-12-01
Full Text Available In this paper the implementation of the DC link current estimator in power conditioning system of the variable speed wind turbine is shown. The wind turbine is connected to double feed induction generator (DFIG. The variable electrical energy parameters delivered by DFIG are fitted with the electrical grid parameters through back-to-back power converter. The bidirectional AC-AC power converter covers a wide speed range from subsynchronous to supersynchronous speeds. The modern control of back-to-back power converter involves power balance concept, therefore its load power should be known in any instant. By using the power balance control, the DC link voltage variation at the load changes can be reduced. In this paper the load power is estimated from the dc link, indirectly, through a second order DC link current estimator. The load current estimator is based on the DC link voltage and on the dc link input current of the rotor side converter. This method presents certain advantages instead of using measured method, which requires a low pass filter: no time delay, the feedforward current component has no ripple, no additional hardware, and more fast control response. Through the numerical simulation the performances of the proposed DC link output current estimator scheme are demonstrated.
-
Automation of eddy current system for in-service inspection of turbine and generator bores
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Viertl, J.R.M.
1988-01-01
The most commonly applied inspection method for ferromagnetic turbine and generator rotor bores is the magnetic particle test technique. This method is subjective, depends on the test operator's skill and diligence in identifying test indications, and suffers from poor repeatability, especially for small indications. Automation would improve repeatability. However, magnetic particle tests are not easily automated, because the data are in the form of sketches, photographs, and written and oral descriptions of the indications. Eddy current inspection has obvious potential to replace magnetic particle methods in this application. Eddy current tests can be readily automated, as the data are in the form of voltages that can be recorded, digitized, and manipulated by a computer. The current project continues the investigation of the correlation between eddy current and magnetic particle inspection. Two systems have been combined to acquire eddy current data automatically. This combination of systems consists of the Nortec-25L Eddyscope (to provide the analog eddy current signals) and the General Electric DATAQ (TM) System (to perform the automatic data acquisition). The automation of the system is discussed
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sylvain Druart
2014-01-01
Full Text Available We present a methodology and a circuit to extract liquid resistance and capacitance simultaneously from the same output signal using interdigitated sensing electrodes. The principle consists in the generation of a current square wave and its application to the sensor to create a triangular output voltage which contains both the conductivity and permittivity parameters in a single periodic segment. This concept extends the Triangular Waveform Voltage (TWV signal generation technique and is implemented by a system which consists in a closed-loop current-controlled oscillator and only requires DC power to operate. The system interface is portable and only a small number of electrical components are used to generate the expected signal. Conductivities of saline NaCl and KCl solutions, being first calibrated by commercial equipment, are characterized by a system prototype. The results show excellent linearity and prove the repeatability of the measurements. Experiments on water-glycerol mixtures validate the proposed sensing approach to measure the permittivity and the conductivity simultaneously. We discussed and identified the sources of measurement errors as circuit parasitic capacitances, switching clock feedthrough, charge injection, bandwidth, and control-current quality.
-
Optimize of Deuteron Current of 150 keV, 1 mA Neutron Generator
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sri Sulamdari; Djasiman
2003-01-01
It has been characterized a 150 keV/1 mA Neutron Generator. It has been used some local components, except accelerator tube and vacuum system. To produce neutron, it has been used a deuterium gas bombarded into tritium target through reaction 3 H(d,n) 4 He. For preliminary experiment, we used the air as an ion source. The beam current of deuteron as a function of process parameters are presented in this paper. It's found that the optimum beam current of deuteron was 1000 μA, and this conditions was achieved at accelerations voltage 30 kV, extraction voltage 5 kV, guide voltage -11 kV and vacuum 10 -6 mbar. (author)
-
Observation of Self-Generated Flows in Tokamak Plasmas with Lower-Hybrid-Driven Current
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ince-Cushman, A.; Rice, J. E.; Reinke, M.; Greenwald, M.; Wallace, G.; Parker, R.; Fiore, C.; Hughes, J. W.; Bonoli, P.; Shiraiwa, S.; Hubbard, A.; Wolfe, S.; Hutchinson, I. H.; Marmar, E.; Bitter, M.; Wilson, J.; Hill, K.
2009-01-01
In Alcator C-Mod discharges lower hybrid waves have been shown to induce a countercurrent change in toroidal rotation of up to 60 km/s in the central region of the plasma (r/a∼<0.4). This modification of the toroidal rotation profile develops on a time scale comparable to the current redistribution time (∼100 ms) but longer than the energy and momentum confinement times (∼20 ms). A comparison of the co- and countercurrent injected waves indicates that current drive (as opposed to heating) is responsible for the rotation profile modifications. Furthermore, the changes in central rotation velocity induced by lower hybrid current drive (LHCD) are well correlated with changes in normalized internal inductance. The application of LHCD has been shown to generate sheared rotation profiles and a negative increment in the radial electric field profile consistent with a fast electron pinch
-
Evaluation of the inner wall axial cracks of steam generator tubes by eddy current test
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hur, Do Haeng; Choi, Myung Sik; Lee, Doek Hyun; Han, Jung Ho
2001-01-01
For the enhancement of ECT reliability on the primary water stress corrosion cracks of nuclear steam generator tubes, it is important to comprehend the signal characteristics on crack morphology and to select an appropriate probe type. In this paper, the sizing accuracy and the detectability for the inner wall axial cracks of tubes were quantitatively evaluated using the electric discharge machined notches and the corrosion cracks which were developed on the operating steam generator tubes. The difference of eddy current signal characteristics between pancake and axial coil were also investigated. The results obtained from this study provide a useful information for more precise evaluation on the inner wall axial cracks of steam generator tubes.
-
Improvement of thermal conductivity of ceramic matrix composites for 4. generation nuclear reactors
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cabrero, J.
2009-11-01
This study deals with thermal conductivity improvement of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composites materials to be used as cladding material in 4. generation nuclear reactor. The purpose of the study is to develop a composite for which both the temperature and irradiation effect is less pronounced on thermal conductivity of material than for SiC. This material will be used as matrix in CMC with SiC fibers. Some TiC-SiC composites with different SiC volume contents were prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS). The sintering process enables to fabricate specimens very fast, with a very fine microstructure and without any sintering aids. Neutron irradiation has been simulated using heavy ions, at room temperature and at 500 C. Evolution of the thermal properties of irradiated materials is measured using modulated photothermal IR radiometry experiment and was related to structural evolution as function of dose and temperature. It appears that such approach is reliable to evaluate TiC potentiality as matrix in CMC. Finally, CMC with TiC matrix and SiC fibers were fabricated and both mechanical and thermal properties were measured and compare to SiCf/SiC CMC. (author)
-
Yilmazel, Yasemin D.
2017-10-02
Few microorganisms have been examined for current generation under thermophilic (40–65 °C) or hyperthermophilic temperatures (≥ 80 °C) in microbial electrochemical systems. Two iron-reducing archaea from the family Archaeoglobaceae, Ferroglobus placidus and Geoglobus ahangari, showed electro-active behavior leading to current generation at hyperthermophilic temperatures in single-chamber microbial electrolysis cells (MECs). A current density (j) of 0.68 ± 0.11 A/m2 was attained in F. placidus MECs at 85 °C, and 0.57 ± 0.10 A/m2 in G. ahangari MECs at 80 °C, with an applied voltage of 0.7 V. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) showed that both strains produced a sigmoidal catalytic wave, with a mid-point potential of − 0.39 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) for F. placidus and − 0.37 V for G. ahangari. The comparison of CVs using spent medium and turnover CVs, coupled with the detection of peaks at the same potentials in both turnover and non-turnover conditions, suggested that mediators were not used for electron transfer and that both archaea produced current through direct contact with the electrode. These two archaeal species, and other hyperthermophilic exoelectrogens, have the potential to broaden the applications of microbial electrochemical technologies for producing biofuels and other bioelectrochemical products under extreme environmental conditions.
-
Yilmazel, Yasemin D.; Zhu, Xiuping; Kim, Kyoung-Yeol; Holmes, Dawn E.; Logan, Bruce E.
2017-01-01
Few microorganisms have been examined for current generation under thermophilic (40–65 °C) or hyperthermophilic temperatures (≥ 80 °C) in microbial electrochemical systems. Two iron-reducing archaea from the family Archaeoglobaceae, Ferroglobus placidus and Geoglobus ahangari, showed electro-active behavior leading to current generation at hyperthermophilic temperatures in single-chamber microbial electrolysis cells (MECs). A current density (j) of 0.68 ± 0.11 A/m2 was attained in F. placidus MECs at 85 °C, and 0.57 ± 0.10 A/m2 in G. ahangari MECs at 80 °C, with an applied voltage of 0.7 V. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) showed that both strains produced a sigmoidal catalytic wave, with a mid-point potential of − 0.39 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) for F. placidus and − 0.37 V for G. ahangari. The comparison of CVs using spent medium and turnover CVs, coupled with the detection of peaks at the same potentials in both turnover and non-turnover conditions, suggested that mediators were not used for electron transfer and that both archaea produced current through direct contact with the electrode. These two archaeal species, and other hyperthermophilic exoelectrogens, have the potential to broaden the applications of microbial electrochemical technologies for producing biofuels and other bioelectrochemical products under extreme environmental conditions.
-
Method of imaging the electrical conductivity distribution of a subsurface
Johnson, Timothy C.
2017-09-26
A method of imaging electrical conductivity distribution of a subsurface containing metallic structures with known locations and dimensions is disclosed. Current is injected into the subsurface to measure electrical potentials using multiple sets of electrodes, thus generating electrical resistivity tomography measurements. A numeric code is applied to simulate the measured potentials in the presence of the metallic structures. An inversion code is applied that utilizes the electrical resistivity tomography measurements and the simulated measured potentials to image the subsurface electrical conductivity distribution and remove effects of the subsurface metallic structures with known locations and dimensions.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Soleymani, S.; Ranjbar, A.M.; Mirabedini, H.
2001-01-01
One method for on-line fault diagnosis in synchronous generator is stator current harmonics analysis. Then artificial neural network is considered in this paper in order to evaluate stator current harmonics in different loads. Training set of artificial neural network is made ready by generator modeling, finite element method and state space model. Many points from generator capability curve are used in order to complete this set. Artificial neural network which is used in this paper is a percept ron network with a single hidden layer, Eight hidden neurons and back propagation algorithm. Results are indicated that the trained artificial neural network can identify stator current harmonics for arbitrary load from the capability curve. The error is less than 10% in comparison with values obtained directly from the CFE-SS algorithm. The rating parameters of modeled generator are 43950 (kV A), 11(KV), 3000 (rpm), 50 (H Z), (P F=0.8)
-
Design of a high-current low-energy beam transport line for an intense D-T/D-D neutron generator
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lu, Xiaolong; Wang, Junrun; Zhang, Yu; Li, Jianyi; Xia, Li; Zhang, Jie; Ding, Yanyan; Jiang, Bing; Huang, Zhiwu; Ma, Zhanwen; Wei, Zheng; Qian, Xiangping; Xu, Dapeng; Lan, Changlin; Yao, Zeen
2016-01-01
An intense D-T/D-D neutron generator is currently being developed at the Lanzhou University. The Cockcroft–Walton accelerator, as a part of the neutron generator, will be used to accelerate and transport the high-current low-energy beam from the duoplasmatron ion source to the rotating target. The design of a high-current low-energy beam transport (LEBT) line and the dynamics simulations of the mixed beam were carried out using the TRACK code. The results illustrate that the designed beam line facilitates smooth transportation of a deuteron beam of 40 mA, and the number of undesired ions can be reduced effectively using two apertures.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Benner, J.
1985-10-01
The computer code ERATO is used for the calculation of eddy-currents in three-dimensional conductive structures and their secondary magnetic field. ERATO is a revised version of the code FEDIFF, developed at IPP Garching. For the calculation the Finite-Element-Network (FEN) method is used, where the structure is simulated by an equivalent electric network. In the ERATO-code, the calculation of the finite-element discretization, the eddy-current analysis, and the final evaluation of the results are done in separate programs. So the eddy-current analysis as the central step is perfectly independent of a special geometry. For the finite-element discretization there are two so called preprocessors, which treat a torus-segment and a rectangular, flat plate. For the final evaluation postprocessors are used, by which the current-distributions can be printed and plotted. In the report, the theoretical foundation of the FEN-Method is discussed, the structure and the application of the programs (preprocessors, analysis-program, postprocessors, supporting programs) are shown, and two examples for calculations are presented. (orig.) [de
-
Evaluation of Eddy Current Signals from the Inner Wall Axial Cracks of Steam Generator Tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Choi, Myung Sik; Hur, Do Haeng; Lee, Doek Hyun; Han, Jung Ho; Park, Jung Am
2001-01-01
For the enhancement of ECT reliability on the primary water stress corrosion cracks of nuclear steam generator tubes, of which the occurrence is on the increase, it is important to comprehend the signal characteristics on crack morphology and to select an appropriate probe type. In this paper, the sizing accuracy and the detectability for the inner wall axial cracks of tubes were quantitatively evaluated using the following specimens: the electric discharge machined notches and the corrosion cracks which were developed on the operating steam generator tubes. The difference of eddy current signal characteristics between pancake and axial coil were also Investigated. The results obtained from this study provide a useful information for more precise evaluation on the inner wall axial tracks oi steam generator tubes
-
Measurement by eddy currents of tube-antivibratory bar gap steam generators of PWR power plants
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Savin, E.; Bieth, M.; Floze, J.C.
1990-01-01
In steam generators tubes are maintained by AVB to limit vibrations amplitude induced by secondary fluid flow. After some years wear sometimes occurs. For gap measurement between tubes and AVB Framatome developed a method based on eddy current and using a probe rotating inside the tube [fr
-
System and method for generating steady state confining current for a toroidal plasma fusion reactor
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bers, A.
1981-01-01
A system for generating steady state confining current for a toroidal plasma fusion reactor providing steady-state generation of the thermonuclear power. A dense, hot toroidal plasma is initially prepared with a confining magnetic field with toroidal and poloidal components. Continuous wave rf energy is injected into said plasma to estalish a spectrum of traveling waves in the plasma, where the traveling waves have momentum components substantially either all parallel, or all anti-parallel to the confining magnetic field. The injected rf energy is phased to couple to said traveling waves with both a phase velocity component and a wave momentum component in the direction of the plasma traveling wave components. The injected rf energy has a predetermined spectrum selected so that said traveling waves couple to plasma electrons having velocities in a predetermined range delta . The velocities in the range are substantially greater than the thermal electron velocity of the plasma. In addition, the range is sufficiently broad to produce a raised plateau having width delta in the plasma electron velocity distribution so that the plateau electrons provide steady-state current to generate a poloidal magnetic field component sufficient for confining the plasma. In steady state operation of the fusion reactor, the fusion power density in the plasma exceeds the power dissipated inthe plasma
-
Shear flow generation and transport barrier formation on rational surface current sheets in tokamaks
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wang Xiaogang; Xiao Chijie; Wang Jiaqi
2009-01-01
Full text: A thin current sheet with a magnetic field component in the same direction can form the electrical field perpendicularly pointing to the sheet, therefore an ExB flow with a strong shear across the current sheet. An electrical potential well is also found on the rational surface of RFP as well as the neutral sheet of the magnetotail with the E-field pointing to the rational (neutral) surface. Theoretically, a current singularity is found to be formed on the rational surface in ideal MHD. It is then very likely that the sheet current on the rational surfaces will generate the electrical potential well in its vicinity so the electrical field pointing to the sheet. It results in an ExB flow with a strong shear in the immediate neighborhood of the rational surface. It may be the cause of the transport barrier often seen near the low (m, n) rational surfaces with MHD signals. (author)
-
Electronic constant current and current pulse signal generator for nuclear instrumentation testing
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brown, R.A.
1994-01-01
Circuitry is described for testing the ability of an intermediate range nuclear instrument to detect and measure a constant current and a periodic current pulse. The invention simulates the resistance and capacitance of the signal connection of a nuclear instrument ion chamber detector and interconnecting cable. An LED flasher/oscillator illuminates an LED at a periodic rate established by a timing capacitor and circuitry internal to the flasher/oscillator. When the LED is on, a periodic current pulse is applied to the instrument. When the LED is off, a constant current is applied. An inductor opposes battery current flow when the LED is on. 1 figures
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lim, Yun Seng; Koh, Siong Lee [Department of Physical Science, Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Tunku Abdul Rahman University (Malaysia)
2010-05-15
Malaysia is heavily dependent on fossil fuel for electricity generation. With the rapidly diminishing of its fuel reserve and the increasingly negative effects of fossil fuels to the environment, the government has begun to utilise bio-fuel and solar radiation for electricity generation. However, the potential of harnessing other renewable sources, particular ocean energy, in Malaysia has not been fully realised. Therefore, studies were carried out to identify the potential of harnessing ocean energy for electricity generation. The Princeton Ocean Model was used to create a three-dimensional numerical ocean model for Malaysia which was calibrated against measurement by a means of adjoint data assimilation approach. A set of reliable tidal speed and tidal elevation data was therefore generated to determine the types of tides available in Malaysia, the potential areas of installing marine current turbines (MCTs), the total amount of electricity to be generated by MCT, the economical viability and the environmental benefits of using MCT in Malaysia. This paper presents the findings on the studies, encompassing the technical, economical and environmental aspects of installing MCT in Malaysia. The results are critical to policy makers and the potential investors on tidal energy in Malaysia for decision making. It may also help the neighboring countries to realize the possible potential of their ocean energy for electricity generation. (author)
-
Current status of production and supply of molybdenum-99 and 99Mo/99mTc generators in Indonesia
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mutalib, A.
2003-01-01
Production of high-specific activity molybdenum-99 and 99 Mo/ 99m Tc Generators in Indonesia commenced when a new production facility supported by the presence of a 30 MW multipurpose reactor (RSG-GAS) was established in Serpong in 1990. This report describes the current production and supply of molybdenum-99m devoted mainly to fulfill the domestic demands in supplying 99 Mo/ 99m Tc Generators. Recent development on the use of LEU (Low Enriched Uranium) targets for replacing current HEU (High Enriched Uranium) targets in the production of 99 Mo will be reviewed briefly. (author)
-
Grönlund, Leila; Hölttä, Teemu; Mäkelä, Annikki
2016-08-01
Shoot size and other shoot properties more or less follow the availability of light, but there is also evidence that the topological position in a tree crown has an influence on shoot development. Whether the hydraulic properties of new shoots are more regulated by the light or the position affects the shoot acclimation to changing light conditions and thereby to changing evaporative demand. We investigated the leaf-area-specific conductivity (and its components sapwood-specific conductivity and Huber value) of the current-year shoots of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) in relation to light environment and topological position in three different tree classes. The light environment was quantified in terms of simulated transpiration and the topological position was quantified by parent branch age. Sample shoot measurements included length, basal and tip diameter, hydraulic conductivity of the shoot, tracheid area and density, and specific leaf area. In our results, the leaf-area-specific conductivity of new shoots declined with parent branch age and increased with simulated transpiration rate of the shoot. The relation to transpiration demand seemed more decisive, since it gave higher R(2) values than branch age and explained the differences between the tree classes. The trend of leaf-area-specific conductivity with simulated transpiration was closely related to Huber value, whereas the trend of leaf-area-specific conductivity with parent branch age was related to a similar trend in sapwood-specific conductivity. © The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Li, Xuebao, E-mail: lxb08357x@ncepu.edu.cn; Cui, Xiang, E-mail: x.cui@ncepu.edu.cn; Ma, Wenzuo; Bian, Xingming; Wang, Donglai [State Key Laboratory of Alternate Electrical Power System with Renewable Energy Sources, North China Electric Power University, Beijing 102206 (China); Lu, Tiebing, E-mail: tiebinglu@ncepu.edu.cn [Beijing Key Laboratory of High Voltage and EMC, North China Electric Power University, Beijing 102206 (China); Hiziroglu, Huseyin [Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Kettering University, Flint, Michigan 48504 (United States)
2016-03-15
The corona-generated audible noise (AN) has become one of decisive factors in the design of high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission lines. The AN from transmission lines can be attributed to sound pressure pulses which are generated by the multiple corona sources formed on the conductor, i.e., transmission lines. In this paper, a detailed time-domain characteristics of the sound pressure pulses, which are generated by the DC corona discharges formed over the surfaces of a stranded conductors, are investigated systematically in a laboratory settings using a corona cage structure. The amplitude of sound pressure pulse and its time intervals are extracted by observing a direct correlation between corona current pulses and corona-generated sound pressure pulses. Based on the statistical characteristics, a stochastic model is presented for simulating the sound pressure pulses due to DC corona discharges occurring on conductors. The proposed stochastic model is validated by comparing the calculated and measured A-weighted sound pressure level (SPL). The proposed model is then used to analyze the influence of the pulse amplitudes and pulse rate on the SPL. Furthermore, a mathematical relationship is found between the SPL and conductor diameter, electric field, and radial distance.
-
Li, Xuebao; Cui, Xiang; Lu, Tiebing; Ma, Wenzuo; Bian, Xingming; Wang, Donglai; Hiziroglu, Huseyin
2016-03-01
The corona-generated audible noise (AN) has become one of decisive factors in the design of high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission lines. The AN from transmission lines can be attributed to sound pressure pulses which are generated by the multiple corona sources formed on the conductor, i.e., transmission lines. In this paper, a detailed time-domain characteristics of the sound pressure pulses, which are generated by the DC corona discharges formed over the surfaces of a stranded conductors, are investigated systematically in a laboratory settings using a corona cage structure. The amplitude of sound pressure pulse and its time intervals are extracted by observing a direct correlation between corona current pulses and corona-generated sound pressure pulses. Based on the statistical characteristics, a stochastic model is presented for simulating the sound pressure pulses due to DC corona discharges occurring on conductors. The proposed stochastic model is validated by comparing the calculated and measured A-weighted sound pressure level (SPL). The proposed model is then used to analyze the influence of the pulse amplitudes and pulse rate on the SPL. Furthermore, a mathematical relationship is found between the SPL and conductor diameter, electric field, and radial distance.
-
Gas Generation Testing of Spherical Resorcinol-Formaldehyde (sRF) Resin
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Colburn, Heather A. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Bryan, Samuel A. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Camaioni, Donald M. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Mahoney, Lenna A. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Adami, Susan R. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States)
2018-01-19
This report describes gas generation testing of the spherical resorcinol-formaldehyde (sRF) resin that was conducted to support the technology maturation of the LAWPS facility. The current safety basis for the LAWPS facility is based primarily on two studies that had limited or inconclusive data sets. The two studies indicated a 40% increase in hydrogen generation rate of water (as predicted by the Hu model) with sRF resin over water alone. However, the previous studies did not test the range of conditions (process fluids and temperatures) that are expected in the LAWPS facility. Additionally, the previous studies did not obtain replicate test results or comparable liquid-only control samples. All of the testing described in this report, conducted with water, 0.45M nitric acid, and waste simulants with and without sRF resin, returned hydrogen generation rates that are within the current safety basis for the facility of 1.4 times the Hu model output for water.
-
Amarillo, Yimy; Tissone, Angela I; Mato, Germán; Nadal, Marcela S
2018-06-01
Slow repetitive burst firing by hyperpolarized thalamocortical (TC) neurons correlates with global slow rhythms (rectifier potassium current I Kir induces repetitive burst firing at slow and delta frequency bands. We demonstrate this in mouse TC neurons in brain slices by manipulating the Kir maximum conductance with dynamic clamp. We also performed a thorough theoretical analysis that explains how the unique properties of I Kir enable this current to induce slow periodic bursting in TC neurons. We describe a new ionic mechanism based on the voltage- and time-dependent interaction of I Kir and hyperpolarization-activated cationic current I h that endows TC neurons with the ability to oscillate spontaneously at very low frequencies, even below 0.5 Hz. Bifurcation analysis of conductance-based models of increasing complexity demonstrates that I Kir induces bistability of the membrane potential at the same time that it induces sustained oscillations in combination with I h and increases the robustness of low threshold-activated calcium current I T -mediated oscillations. NEW & NOTEWORTHY The strong inwardly rectifying potassium current I Kir of thalamocortical neurons displays a region of negative slope conductance in the current-voltage relationship that generates potassium currents activated by hyperpolarization. Bifurcation analysis shows that I Kir induces bistability of the membrane potential; generates sustained subthreshold oscillations by interacting with the hyperpolarization-activated cationic current I h ; and increases the robustness of oscillations mediated by the low threshold-activated calcium current I T . Upregulation of I Kir in thalamocortical neurons induces repetitive burst firing at slow and delta frequency bands (<4 Hz).
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. Huang
2015-01-01
Full Text Available We report on measurements and analysis of a field-emitted electron current in the very-high-frequency (VHF gun, a room temperature rf gun operating at high field and continuous wave (CW mode at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL. The VHF gun is the core of the Advanced Photo-injector Experiment (APEX at LBNL, geared toward the development of an injector for driving the next generation of high average power x-ray free electron lasers. High accelerating fields at the cathode are necessary for the high-brightness performance of an electron gun. When coupled with CW operation, such fields can generate a significant amount of field-emitted electrons that can be transported downstream the accelerator forming the so-called “dark current.” Elevated levels of a dark current can cause radiation damage, increase the heat load in the downstream cryogenic systems, and ultimately limit the overall performance and reliability of the facility. We performed systematic measurements that allowed us to characterize the field emission from the VHF gun, determine the location of the main emitters, and define an effective strategy to reduce and control the level of dark current at APEX. Furthermore, the energy spectra of isolated sources have been measured. A simple model for energy data analysis was developed that allows one to extract information on the emitter from a single energy distribution measurement.
-
Potency of Thermoelectric Generator for Hybrid Vehicle
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Nandy Putra
2010-10-01
Full Text Available Thermoelectric Generator (TEG has been known as electricity generation for many years. If the temperature difference occurred between two difference semi conductor materials, the current will flow in the material and produced difference voltage. This principle is known as Seebeck effect that is the opposite of Peltier effect Thermoelectric Cooling (TEC. This research was conducted to test the potential of electric source from twelve peltier modules. Then, these thermoelectric generators were applied in hybrid car by using waste heat from the combustion engine. The experiment has been conducted with variations of peltier module arrangements (series and parallels and heater as heat source for the thermoelectric generator, with variations of heater voltage input (110V and 220V applied. The experimental result showed that twelve of peltier modules arranged in series and heater voltage of 220V generated power output of 8.11 Watts with average temperature difference of 42.82°C. This result shows that TEG has a bright prospect as alternative electric source.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Buck, J.; Underhill, P.R.; Mokros, S.G.; Morelli, J.; Krause, T.W.; Babbar, V.K.; Lepine, B.
2015-01-01
Nuclear steam generator (SG) support structure degradation and fouling can result in damage to SG tubes and loss of SG efficiency. Conventional eddy current technology is extensively used to detect cracks, frets at supports and other flaws, but has limited capabilities in the presence of multiple degradation modes or fouling. Pulsed eddy current (PEC) combined with principal components analysis (PCA) and multiple linear regression models was examined for the inspection of support structure degradation and SG tube off-centering with the goal of extending results to include additional degradation modes. (author)
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Li, Hui; Yang, Chao; Hu, Yaogang
2014-01-01
Fault-tolerant control of current sensors is studied in this paper to improve the reliability of a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG). A fault-tolerant control system of current sensors is presented for the DFIG, which consists of a new current observer and an improved current sensor fault...... detection algorithm, and fault-tolerant control system are investigated by simulation. The results indicate that the outputs of the observer and the sensor are highly coherent. The fault detection algorithm can efficiently detect both soft and hard faults in current sensors, and the fault-tolerant control...
-
Circulating persistent current and induced magnetic field in a fractal network
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Saha, Srilekha [Condensed Matter Physics Division, Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics, Sector-I, Block-AF, Bidhannagar, Kolkata 700 064 (India); Maiti, Santanu K., E-mail: santanu.maiti@isical.ac.in [Physics and Applied Mathematics Unit, Indian Statistical Institute, 203 Barrackpore Trunk Road, Kolkata 700 108 (India); Karmakar, S.N. [Condensed Matter Physics Division, Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics, Sector-I, Block-AF, Bidhannagar, Kolkata 700 064 (India)
2016-04-29
We present the overall conductance as well as the circulating currents in individual loops of a Sierpinski gasket (SPG) as we apply bias voltage via the side attached electrodes. SPG being a self-similar structure, its manifestation on loop currents and magnetic fields is examined in various generations of this fractal and it has been observed that for a given configuration of the electrodes, the physical quantities exhibit certain regularity as we go from one generation to another. Also a notable feature is the introduction of anisotropy in hopping causes an increase in magnitude of overall transport current. These features are a subject of interest in this article. - Highlights: • Voltage driven circular current is analyzed in a fractal network. • Current induced magnetic field is strong enough to flip a spin. • Anisotropy in hopping enhances overall transport current.
-
Performance demonstration tests for eddy current inspection of steam generator tubing
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kurtz, R.J.; Heasler, P.G.; Anderson, C.M.
1996-05-01
This report describes the methodology and results for development of performance demonstration tests for eddy current (ET) inspection of steam generator tubes. Statistical test design principles were used to develop the performance demonstration tests. Thresholds on ET system inspection performance were selected to ensure that field inspection systems would have a high probability of detecting and and correctly sizing tube degradation. The technical basis for the ET system performance thresholds is presented in detail. Statistical test design calculations for probability of detection and flaw sizing tests are described. A recommended performance demonstration test based on the design calculations is presented. A computer program for grading the probability of detection portion of the performance demonstration test is given
-
Performance demonstration tests for eddy current inspection of steam generator tubing
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kurtz, R.J.; Heasler, P.G.; Anderson, C.M.
1996-05-01
This report describes the methodology and results for development of performance demonstration tests for eddy current (ET) inspection of steam generator tubes. Statistical test design principles were used to develop the performance demonstration tests. Thresholds on ET system inspection performance were selected to ensure that field inspection systems would have a high probability of detecting and and correctly sizing tube degradation. The technical basis for the ET system performance thresholds is presented in detail. Statistical test design calculations for probability of detection and flaw sizing tests are described. A recommended performance demonstration test based on the design calculations is presented. A computer program for grading the probability of detection portion of the performance demonstration test is given.
-
The influence of increased membrane conductance on response properties of spinal motoneurons
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Grigonis, Ramunas; Guzulaitis, Robertas; Buisas, Rokas
2016-01-01
During functional spinal neural network activity motoneurons receive massive synaptic excitation and inhibition, and their membrane conductance increases considerably – they are switched to a high-conductance state. High-conductance states can substantially alter response properties of motoneurons....... In the present study we investigated how an increase in membrane conductance affects spike frequency adaptation, the gain (i.e., the slope of the frequency-current relationship) and the threshold for action potential generation. We used intracellular recordings from adult turtle motoneurons in spinal cord slices....... Membrane conductance was increased pharmacologically by extracellular application of the GABAA receptor agonist muscimol. Our findings suggest that an increase in membrane conductance of about 40–50% increases the magnitude of spike frequency adaptation, but does not change the threshold for action...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shin, R.H.; Jo, W.; Kim, D.W.; Yun, Jae Ho; Ahn, S.
2011-01-01
Electrical transport properties on polycrystalline Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 (CIGS) (Ga/(In+Ga) ∼35%) thin films were examined by conductive atomic force microscopy. The CIGS thin films with a (112) preferential or random texture were deposited on Mo-coated glass substrates. Triangular pyramidal grain growths were observed in the CIGS thin films preferentially textured to the (112) planes. Current maps of the CIGS surface were acquired with a zero or non-zero external voltage bias. The contrast of the images on the grain boundaries and intragrains displayed the conduction path in the materials. Local current-voltage measurements were performed to evaluate the charge conduction properties of the CIGS thin films. (orig.)
-
Alvarez, J.; Boutchich, M.; Kleider, J. P.; Teraji, T.; Koide, Y.
2014-09-01
The origin of the high leakage current measured in several vertical-type diamond Schottky devices is conjointly investigated by conducting probe atomic force microscopy and confocal micro-Raman/photoluminescence imaging analysis. Local areas characterized by a strong decrease of the local resistance (5-6 orders of magnitude drop) with respect to their close surrounding have been identified in several different regions of the sample surface. The same local areas, also referenced as electrical hot-spots, reveal a slightly constrained diamond lattice and three dominant Raman bands in the low-wavenumber region (590, 914 and 1040 cm-1). These latter bands are usually assigned to the vibrational modes involving boron impurities and its possible complexes that can electrically act as traps for charge carriers. Local current-voltage measurements performed at the hot-spots point out a trap-filled-limited current as the main conduction mechanism favouring the leakage current in the Schottky devices.
-
Effects of Birkeland current limitation on high-latitude convection patterns
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Marklund, G.T.; Raadu, M.A.; Lindqvist, P.-A.
1984-12-01
It is shown how the high-latitude convection pattern may be mo- dified by substorm-enhanced polarization electric fields. These are generated whenever the flow of those Birkeland currents which are associated with ionospheric conductivity gradients is limited. Such Birkeland currents are fed mainly by the enhanced Pedersen current in the evening and morning sectors of the auro- ral oval and by the enhanced Hall current around local midnight. As the current limitation increases, the ionospheric potential, represented here by a symmetric two-cell pattern, will rotate clockwise and deform, just as the associated Birkeland current distribution. The resulting patterns are shown to agree well with observations. A pronounced westward intrusion of the equi- potential contours occurs in the auroral oval, and may be asso- ciated with the Westward Travelling Surge. This feature does not however require any assumed longitudinal conductivity gradi- ents. Rather it falls out naturally when the limitation of the enhanced Pedersen current is taken into account. (Author)
-
Pulse generator circuit triggerable by nuclear radiation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fredrickson, P.B.
1980-01-01
A pulse generator circuit triggerable by a pulse of nuclear radiation is described. The pulse generator circuit includes a pair of transistors arranged, together with other electrical components, in the topology of a standard monostable multivibrator circuit. The circuit differs most significantly from a standard monostable multivibrator circuit in that the circuit is adapted to be triggered by a pulse of nuclear radiation rather than electrically and the transistors have substantially different sensitivities to radiation, due to different physical and electrical characteristics and parameters. One of the transistors is employed principally as a radiation detector and is in a normally non-conducting state and the other transistor is normally in a conducting state. When the circuit is exposed to a pulse of nuclear radiation, currents are induced in the collector-base junctions of both transistors but, due to the different radiation sensitivities of the transistors, the current induced in the collector-base junction of the radiation-detecting transistor is substantially greater than that induced in the collector-base junction of the other transistor. The pulse of radiation causes the radiation-detecting transistor to operate in its conducting state, causing the other transistor to operate in its non-conducting state. As the radiation-detecting transistor operates in its conducting state, an output signal is produced at an output terminal connected to the radiation-detecting transistor indicating the presence of a predetermined intensity of nuclear radiation
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Wang, Xiongfei; Blaabjerg, Frede; Chen, Zhe
2012-01-01
Harmonic current filtering and resonance damping have become important concerns on the control of an islanded microgrids. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a control method of inverter-interfaced Distributed Generation (DG) units, which can autonomously share harmonic currents and ...
-
System and method for generating steady state confining current for a toroidal plasma fusion reactor
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fisch, N.J.
1981-01-01
A system for generating steady state confining current for a toroidal plasma fusion reactor providing steady-state generation of the thermonuclear power. A dense, hot toroidal plasma is initially prepared with a confining magnetic field with toroidal and poloidal components. Continuous wave rf energy is injected into said plasma to establish a spectrum of traveling waves in the plasma, where the traveling waves have momentum components substantially either all parallel, or all anti-parallel to the confining magnetic field. The injected rf energy is phased to couple to said traveling waves with both a phase velocity component and a wave momentum component in the direction of the plasma traveling wave components. The injected rf energy has a predetermined spectrum selected so that said traveling waves couple to plasma electrons having velocities in a predetermined range delta . The velocities in the range are substantially greater than the thermal electron velocity of the plasma. In addition, the range is sufficiently broad to produce a raised plateau having width delta in the plasma electron velocity distribution so that the plateau electrons provide steady-state current to generate a poloidal magnetic field component sufficient for confining the plasma. In steady state operation of the fusion reactor, the fusion power density in the plasma exceeds the power dissipated in the plasma
-
Current status of the UCSF second-generation PACS
Huang, H. K.; Arenson, Ronald L.; Wong, Albert W. K.; Bazzill, Todd M.; Lou, Shyhliang A.; Andriole, Katherine P.; Wang, Jun; Zhang, Jianguo; Wong, Stephen T. C.
1996-05-01
This paper describes the current status of the second generation PACS at UCSF commenced in October 1992. The UCSF PACS is designed in-house as a hospital-integrated PACS based on an open architecture concept using industrial standards including UNIX operating system, C programming language, X-Window user interface, TCP/IP communication protocol, DICOM 3.0 image standard and HL7 health data format. Other manufacturer's PACS components which conform with these standards can be easily integrated into the system. Relevant data from HIS and RIS is automatically incorporated into the PACS using HL7 data format and TCP/IP communication protocol. The UCSF system also takes advantage of state-of-the-art communication, storage, and software technologies in ATM, multiple storage media, automatic programming, multilevel processes for a better cost-performance system. The primary PACS network is the 155 Mbits/sec OC3 ATM with the Ethernet as the back-up. The UCSF PACS also connects Mt. Zion Hospital and San Francisco VA Medical Center in the San Francisco Bay area via an ATM wide area network with a T1 line as the back-up. Currently, five MR and five CT scanners from multiple sites, two computed radiography systems, two film digitizers, one US PACS module, the hospital HIS and the department RIS have been connected to the PACS network. The image data is managed by a mirrored database (Sybase). The PACS controller, with its 1.3 terabyte optical disk library, acquires 2.5 gigabytes digital data daily. Four 2K, five, 1,600-line multiple monitor display workstations are on line in neuroradiology, pediatric radiology and intensive care units for clinical use. In addition, the PACS supports over 100 Macintosh users in the department and selected hospital sites for both images and textual retrieval through a client/server mechanism. We are also developing a computation and visualization node in the PACS network for advancing radiology research.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Naggar H. Saad
2016-05-01
Full Text Available The main challenges of wind energy conversion systems (WECS are to maximize the energy capture from the wind and injecting reactive power during the fault. This paper presents a current controlled matrix converter to interface Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generators (PMSG based WECS with the grid. To achieve fast dynamic response with reduced current ripples, a hysteresis current control is utilized. The proposed control system decouples the active and reactive components of the PMSG current to extract the maximum power from the wind at a given wind velocity and to inject reactive power to the grid. Reactive power injection during the fault satisfying the grid-codes requirement. The proposed WECS has been modeled and simulated using PSCAD/EMTDC software package.
-
Electrochemical supercapacitors from conducting polyaniline-graphene platforms.
Ashok Kumar, Nanjundan; Baek, Jong-Beom
2014-06-18
Energy storage devices such as electrochemical supercapacitors, with high power and energy densities are required to address the colossal energy requirements against the backdrop of global warming and the looming energy crisis. Nanocarbon, particularly two-dimensional graphene and graphene-based conducting polymer composites are promising electrode materials for such energy storage devices. Owing to their environmental stability, the low cost of polymers with high electroactivity and pseudocapacitance, such composite hybrids are expected to have wide implications in next generation clean and efficient energy systems. In this feature article, an overview of current research and important advances over the past four years on the development of conducting polyaniline (PANI)-graphene based composite electrodes for electrochemical supercapacitors are highlighted. Particular emphasis is made on the design, fabrication and assembly of nanostructured electrode architectures comprising PANI and graphene along with metal oxides/hydroxides and carbon nanotubes. Comments on the challenges and perspectives towards rational design and synthesis of graphene-based conducting polymer composites for energy storage are discussed.
-
Current status of research and development of 99Mo/99mTc generator in Korea
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Park, U.J.; Lee, J.S.; Son, K.J.; Nam, S.S.; Kwak, S.I.; Han, H.S.
2006-01-01
To supply 99m Tc in stable and economical manner in Korea, a chromatographic generator has been under development at KAERI since late 1980's. The chromatographic type of technetium generator is preferred in hospital because it is more convenient and less time-restricted for applications. Hence, the demand of 99m Tc in medical applications is keep increasing. In Korea, there are more than 200 gamma cameras including SPECT in hospitals. For these applications, approximately 100 units/week of 99m Tc generators of which annual cost reached 3 million US dollars were required in 2002. Hence, the development of 99m Tc generators and technology of fission 99 Mo processing were started while installing the generator loading facility (GLF) at KAERI. This facility is currently on a trial run for the commercial production of 99m Tc generators and expected to produce more than 200 generators per week in 2004. For the fission 99 Mo production, an annulus U foil target was considered as the LEU target. The designed LEU target is being used for target manufacturing test and accident analysis. The develop gel type 99m Tc generators by using a poly zirconium complex (PZC) and alumina column, KAERI has cooperated with a Japanese company since late 1990's. In 2003, experimental studies for molybdate adsorption capacity and elution characteristics of the PZC samples from three different batches produced by Kaken Co. were carried out. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ogino, T.
1986-01-01
A global computer simulation of the interaction of the solar wind with the earth's magnetosphere was executed by using a three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic model. As a result, we were able to reproduce quasi-steady-state magnetospheric configurations and a Birkeland field-aligned current system which depend on the polarity of the z component of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF). Twin convection cells and a dawn to dusk electric potential of 30--100 kV appeared at the equator in the magnetosphere. Four types of field-aligned currents were observed. Region 1 and 2 field-aligned currents generated for all IMF conditions were 0.6--1.0 x 10 6 A and 0.15--0.61 x 10 6 A, respectively, in the total current. Region 1 currents at high latitudes are generated from the field-aligned vorticity at the flanks through a viscous interaction and are strengthened by a twisting of open magnetic field lines in the tail region for southward IMF. On the other hand, the low-latitude region 2 currents probably are generated mainly from the inner pressure gradient of the plasma sheet. The region 1 current obtained from the simulation was in good agreement with an estimate from our theoretical analysis of the localized Alfven mode. The other two types of field-aligned currents are the dayside magnetopause currents in the dayside cusp region, which increase for northward IMF, and the dayside cusp currents for southward IMF. The cusp currents are associated with a twisting of open magnetic field lines in the magnetopause region
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lahreche, A.; Beggah, Y.; Corkish, R.
2011-01-01
The effect of electron range on electron beam induced current (EBIC) is demonstrated and the problem of the choice of the optimal electron ranges to use with simple uniform and point generation function models is resolved by proposing a method to extract an electron range-energy relationship (ERER). The results show that the use of these extracted electron ranges remove the previous disagreement between the EBIC curves computed with simple forms of generation model and those based on a more realistic generation model. The impact of these extracted electron ranges on the extraction of diffusion length, surface recombination velocity and EBIC contrast of defects is discussed. It is also demonstrated that, for the case of uniform generation, the computed EBIC current is independent of the assumed shape of the generation volume. -- Highlights: → Effect of electron ranges on modeling electron beam induced current is shown. → A method to extract an electron range for simple form of generation is proposed. → For uniform generation the EBIC current is independent of the choice of it shape. → Uses of the extracted electron ranges remove some existing literature ambiguity.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lee, Deok Hyun; Choi, Myung Sik; Hur, Do Haeng; Kim, Kyung Mo; Han, Jung Ho
2008-01-01
An eddy current inspection has been applied for a pre-service and in-service examination of a steam generator in nuclear power plants. The experience from the inspection of steam generators showed that many plants had an excessive number of tubes with eddy current noise signals over several hundreds, which originated from manufacturing anomalies. The plants in U.S suffered significant downstream inspection costs, history reviews, and diagnostic testing because some signals resembled flaws and others masked a flaw. These lessens learned resulted in issuing the guidelines for steam generator tubing specifications and repair, in order to reduce the number of anomalous signals in the tubes and also to provide the requirement of a signal to noise ratio by applying a field type examination with bobbin coil eddy current probes at a manufacturing process. Besides the noise signals of a bobbin coil eddy current probe from manufacturing anomalies, the excessive background noise of the rotating coil eddy current probe signal is frequently observed from a tube and it negatively affects the detection and sizing estimate of a defect. Since the inspection intervals are being extended up to 60 months for the more recent steam generator of corrosion resistant alloy 690TT tubing, the detection of an earlier crack and an accurate sizing are becoming more important in the activity of a non-destructive examination. In this study, the cause of an eddy current signal noise of a rotating coil probe from a steam generator tube was examined and its influence on the detectability of a crack was analyzed
-
Abhirup Lahiri
2011-01-01
This paper reports two new circuit topologies using second-generation current conveyors (CCIIs) for realizing variable frequency sinusoidal oscillators with minimum passive components. The proposed topologies in this paper provide new realizations of resistance-controlled and capacitor-controlled variable frequency oscillators (VFOs) using only four passive components. The first topology employs three CCIIs, while the second topology employs two CCIIs. The second topology provides an advantag...
-
Considerations on heat deposition by eddy currents in the cold structure of INTOR/NET
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bloemer, B.; Farfaletti-Casali, F.
1983-01-01
In a tokamak like INTOR/NET large eddy currents can be induced in all conductive parts of the reactor mainly by the time-varying poloidal fields. In order to minimize the refrigeration power the heat load generated by eddy currents has to be kept as small as possibly especially in the large toroidal- and poloidal-field coil support structures, which are conductive and at temperatures of less than 4.2 K. A method is described identifying the parts of the structure wherein most of the heat generated by eddy currents is dissipated. By dividing a given configuration into reasonable segments of appointed geometry eddy current losses can easily be calculated. Compared to sophisticated computer programs this procedure is simple but of sufficient accuracy for a lot of applications and it delivers prompt results. The method is applied to the TF coil support structure of a specific design of INTOR/NET. As the results show that the heat load is intolerably high a modified design is proposed. (author)
-
Radevici, Ivan; Tiira, Jonna; Sadi, Toufik; Oksanen, Jani
2018-05-01
Current crowding close to electrical contacts is a common challenge in all optoelectronic devices containing thin current spreading layers (CSLs). We analyze the effects of current spreading on the operation of the so-called double diode structure (DDS), consisting of a light emitting diode (LED) and a photodiode (PD) fabricated within the same epitaxial growth process, and providing an attractive platform for studying electroluminescent (EL) cooling under high bias conditions. We show that current spreading in the common n-type layer between the LED and the PD can be dramatically improved by the strong optical coupling between the diodes, as the coupling enables a photo-generated current through the PD. This reduces the current in the DDS CSL and enables the study of EL cooling using structures that are not limited by the conventional light extraction challenges encountered in normal LEDs. The current spreading in the structures is studied using optical imaging techniques, electrical measurements, simulations, as well as simple equivalent circuit models developed for this purpose. The improved current spreading leads further to a mutual dependence with the coupling efficiency, which is expected to facilitate the process of optimizing the DDS. We also report a new improved value of 63% for the DDS coupling quantum efficiency.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sun Li-Jie; He Dong-Kai; Xu Xiao-Qiu; Zhong Ze; Wu Xiao-Peng; Lin Bi-Xia; Fu Zhu-Xi
2010-01-01
We experimentally find that the ZnO thin films deposited by dc-magnetron sputtering have different conduction types after annealing at high temperature in different ambient. Hall measurements show that ZnO films annealed at 1100°C in N 2 and in O 2 ambient become n-type and p-type, respectively. This is due to the generation of different intrinsic defects by annealing in different ambient. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and photolumi-nescence measurements indicate that zinc interstitial becomes a main defects after annealing at 1100°C in N 2 ambient, and these defects play an important role for n-type conductivity of ZnO. While the ZnO films annealed at 1100°C in O 2 ambient, the oxygen antisite contributes ZnO films to p-type. (condensed matter: structure, mechanical and thermal properties)
-
Frick, Paul J.; Nigg, Joel T.
2015-01-01
This review evaluates the diagnostic criteria for three of the most common disorders for which children and adolescents are referred for mental health treatment: attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and conduct disorder (CD). Although research supports the validity and clinical utility of these disorders, several issues are highlighted that could enhance the current diagnostic criteria. For ADHD, defining the core features of the disorder and its fit with other disorders, enhancing the validity of the criteria through the lifespan, considering alternative ways to form subtypes of the disorder, and modifying the age-of-onset criterion are discussed relative to the current diagnostic criteria. For ODD, eliminating the exclusionary criteria of CD, recognizing important symptom domains within the disorder, and using the cross-situational pervasiveness of the disorder as an index of severity are highlighted as important issues for improving classification. Finally, for CD, enhancing the current subtypes related to age of onset and integrating callous-unemotional traits into the diagnostic criteria are identified as key issues for improving classification. PMID:22035245
-
Frick, Paul J; Nigg, Joel T
2012-01-01
This review evaluates the diagnostic criteria for three of the most common disorders for which children and adolescents are referred for mental health treatment: attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and conduct disorder (CD). Although research supports the validity and clinical utility of these disorders, several issues are highlighted that could enhance the current diagnostic criteria. For ADHD, defining the core features of the disorder and its fit with other disorders, enhancing the validity of the criteria through the lifespan, considering alternative ways to form subtypes of the disorder, and modifying the age-of-onset criterion are discussed relative to the current diagnostic criteria. For ODD, eliminating the exclusionary criteria of CD, recognizing important symptom domains within the disorder, and using the cross-situational pervasiveness of the disorder as an index of severity are highlighted as important issues for improving classification. Finally, for CD, enhancing the current subtypes related to age of onset and integrating callous-unemotional traits into the diagnostic criteria are identified as key issues for improving classification.
-
Turbidity current flow over an erodible obstacle and phases of sediment wave generation
Strauss, Moshe; Glinsky, Michael E.
2012-06-01
We study the flow of particle-laden turbidity currents down a slope and over an obstacle. A high-resolution 2-D computer simulation model is used, based on the Navier-Stokes equations. It includes poly-disperse particle grain sizes in the current and substrate. Particular attention is paid to the erosion and deposition of the substrate particles, including application of an active layer model. Multiple flows are modeled from a lock release that can show the development of sediment waves (SW). These are stream-wise waves that are triggered by the increasing slope on the downstream side of the obstacle. The initial obstacle is completely erased by the resuspension after a few flows leading to self consistent and self generated SW that are weakly dependant on the initial obstacle. The growth of these waves is directly related to the turbidity current being self sustaining, that is, the net erosion is more than the net deposition. Four system parameters are found to influence the SW growth: (1) slope, (2) current lock height, (3) grain lock concentration, and (4) particle diameters. Three phases are discovered for the system: (1) "no SW," (2) "SW buildup," and (3) "SW growth". The second phase consists of a soliton-like SW structure with a preserved shape. The phase diagram of the system is defined by isolating regions divided by critical slope angles as functions of current lock height, grain lock concentration, and particle diameters.
-
High frequency conductivity of hot electrons in carbon nanotubes
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Amekpewu, M., E-mail: mamek219@gmail.com [Department of Applied Physics, University for Development Studies, Navrongo (Ghana); Mensah, S.Y. [Department of Physics, College of Agriculture and Natural Sciences, U.C.C. (Ghana); Musah, R. [Department of Applied Physics, University for Development Studies, Navrongo (Ghana); Mensah, N.G. [Department of Mathematics, College of Agriculture and Natural Sciences, U.C.C. (Ghana); Abukari, S.S.; Dompreh, K.A. [Department of Physics, College of Agriculture and Natural Sciences, U.C.C. (Ghana)
2016-05-01
High frequency conductivity of hot electrons in undoped single walled achiral Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) under the influence of ac–dc driven fields was considered. We investigated semi-classically Boltzmann's transport equation with and without the presence of the hot electrons’ source by deriving the current densities in CNTs. Plots of the normalized current density versus frequency of ac-field revealed an increase in both the minimum and maximum peaks of normalized current density at lower frequencies as a result of a strong injection of hot electrons. The applied ac-field plays a twofold role of suppressing the space-charge instability in CNTs and simultaneously pumping an energy for lower frequency generation and amplification of THz radiations. These have enormous promising applications in very different areas of science and technology.
-
An integrated automatic system for the eddy-current testing of the steam generator tubes
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Woo, Hee Gon; Choi, Seong Su [Korea Electric Power Corp. (KEPCO), Taejon (Korea, Republic of). Research Center
1995-12-31
This research project was focused on automation of steam generator tubes inspection for nuclear power plants. ECT (Eddy Current Testing) inspection process in nuclear power plants is classified into 3 subprocesses such as signal acquisition process, signal evaluation process, and inspection planning and data management process. Having been automated individually, these processes were effectively integrated into an automatic inspection system, which was implemented in HP workstation with expert system developed (author). 25 refs., 80 figs.
-
An integrated automatic system for the eddy-current testing of the steam generator tubes
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Woo, Hee Gon; Choi, Seong Su [Korea Electric Power Corp. (KEPCO), Taejon (Korea, Republic of). Research Center
1996-12-31
This research project was focused on automation of steam generator tubes inspection for nuclear power plants. ECT (Eddy Current Testing) inspection process in nuclear power plants is classified into 3 subprocesses such as signal acquisition process, signal evaluation process, and inspection planning and data management process. Having been automated individually, these processes were effectively integrated into an automatic inspection system, which was implemented in HP workstation with expert system developed (author). 25 refs., 80 figs.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mitchard, D.; Clark, D.; Carr, D.; Haddad, A.
2016-01-01
A technique was developed for the comparison of observed emission spectra from lightning current arcs generated through self-breakdown in air and the use of two types of initiation wire, aluminum bronze and nichrome, against previously published spectra of natural lightning events. A spectrograph system was used in which the wavelength of light emitted by the lightning arc was analyzed to derive elemental interactions. A lightning impulse of up to 100 kA was applied to a two hemispherical tungsten electrode configuration which allowed the effect of the lightning current and lightning arc length to be investigated. A natural lightning reference spectrum was reconstructed from literature, and generated lightning spectra were obtained from self-breakdown across a 14.0 mm air gap and triggered along initiation wires of length up to 72.4 mm. A comparison of the spectra showed that the generated lightning arc induced via self-breakdown produced a very similar spectrum to that of natural lightning, with the addition of only a few lines from the tungsten electrodes. A comparison of the results from the aluminum bronze initiation wire showed several more lines, whereas results from the nichrome initiation wire differed greatly across large parts of the spectrum. This work highlights the potential use for spectrographic techniques in the study of lightning interactions with surrounding media and materials, and in natural phenomena such as recently observed ball lightning.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Shin, R.H.; Jo, W. [Ewha Womans University, Department of Physics, Seoul (Korea, Republic of); Kim, D.W. [Ewha Womans University, Department of Physics, Seoul (Korea, Republic of); Ewha Womans University, Department of Chemistry and Nanosciences, Seoul (Korea, Republic of); Yun, Jae Ho; Ahn, S. [Korea Institute of Energy Research, Daejeon (Korea, Republic of)
2011-09-15
Electrical transport properties on polycrystalline Cu(In,Ga)Se{sub 2} (CIGS) (Ga/(In+Ga) {approx}35%) thin films were examined by conductive atomic force microscopy. The CIGS thin films with a (112) preferential or random texture were deposited on Mo-coated glass substrates. Triangular pyramidal grain growths were observed in the CIGS thin films preferentially textured to the (112) planes. Current maps of the CIGS surface were acquired with a zero or non-zero external voltage bias. The contrast of the images on the grain boundaries and intragrains displayed the conduction path in the materials. Local current-voltage measurements were performed to evaluate the charge conduction properties of the CIGS thin films. (orig.)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wulf-Dieter C. Krenz
2015-10-01
Full Text Available Experimental and computational studies demonstrate that different sets of intrinsic and synaptic conductances can give rise to equivalent activity patterns. This is because the balance of conductances, not their absolute values, defines a given activity feature. Activity-dependent feedback mechanisms maintain neuronal conductance correlations and their corresponding activity features. This study demonstrates that tonic nM concentrations of monoamines enable slow, activity-dependent processes that can maintain a correlation between the transient potassium current (IA and the hyperpolarization activated current (Ih over the long-term (i.e., regulatory change persists for hours after removal of modulator. Tonic 5nM DA acted through an RNA interference silencing complex (RISC- and RNA polymerase II-dependent mechanism to maintain a long-term positive correlation between IA and Ih in the lateral pyloric neuron (LP but not in the pyloric dilator neuron (PD. In contrast, tonic 5nM 5HT maintained a RISC-dependent positive correlation between IA and Ih in PD but not LP over the long-term. Tonic 5nM OCT maintained a long-term negative correlation between IA and Ih in PD but not LP; however, it was only revealed when RISC was inhibited. This study also demonstrated that monoaminergic tone can also preserve activity features over the long-term: The timing of LP activity, LP duty cycle and LP spike number per burst were maintained by tonic 5nM DA. The data suggest that low-level monoaminergic tone acts through multiple slow processes to permit cell-specific, activity-dependent regulation of ionic conductances to maintain conductance correlations and their corresponding activity features over the long-term.
-
Pacemaker neuron and network oscillations depend on a neuromodulator-regulated linear current
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Shunbing Zhao
2010-05-01
Full Text Available Linear leak currents have been implicated in the regulation of neuronal excitability, generation of neuronal and network oscillations, and network state transitions. Yet, few studies have directly tested the dependence of network oscillations on leak currents or explored the role of leak currents on network activity. In the oscillatory pyloric network of decapod crustaceans neuromodulatory inputs are necessary for pacemaker activity. A large subset of neuromodulators is known to activate a single voltage-gated inward current IMI, which has been shown to regulate the rhythmic activity of the network and its pacemaker neurons. Using the dynamic clamp technique, we show that the crucial component of IMI for the generation of oscillatory activity is only a close-to-linear portion of the current-voltage relationship. The nature of this conductance is such that the presence or the absence of neuromodulators effectively regulates the amount of leak current and the input resistance in the pacemaker neurons. When deprived of neuromodulatory inputs, pyloric oscillations are disrupted; yet, a linear reduction of the total conductance in a single neuron within the pacemaker group recovers not only the pacemaker activity in that neuron, but also leads to a recovery of oscillations in the entire pyloric network. The recovered activity produces proper frequency and phasing that is similar to that induced by neuromodulators. These results show that the passive properties of pacemaker neurons can significantly affect their capacity to generate and regulate the oscillatory activity of an entire network, and that this feature is exploited by neuromodulatory inputs.
-
Shikanov, A. E.; Vovchenko, E. D.; Kozlovskii, K. I.; Rashchikov, V. I.; Shatokhin, V. L.
2018-04-01
A model for acceleration of deuterons and generation of neutrons in a compact laser-plasma diode with electron isolation using magnetic field generated by a hollow cylindrical permanent magnet is presented. Experimental and computer-simulated neutron yields are compared for the diode structure under study. An accelerating neutron tube with a relatively high neutron generation efficiency can be constructed using suppression of electron conduction with the aid of a magnet placed in the vacuum volume.
-
An automated eddy current in-service inspection system for nuclear steam generator tubing
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wells, N.S.
1981-06-01
A prototype steam generator in-service inspection system incorporating remotely-controlled instrumentation linked by a digital transmission line to an instrument and control trailer outside the reactor containment has been designed and manufactured and is presently undergoing field tests. The (Monel 400) steam generator tubes are scanned two at a time using absolute eddy current probes controlled by two remotely-operated probe drives at a scanning speed of 0.5 m/s. The probes are positioned on the tubesheet by a light-weight (1.5 kg) microprocessor-operated tubesheet walker mechanism. Digitized control and data signals are transmitted up to 300 m to the control trailer. There the control and analysis computers extract the relevant signal information and present it in condensed form as labelled graphics on CRT consoles for on-line visual assessment. Hard copy output is also provided for each tube scanned (one per minute). Condensed data is archived on magnetic tapes for additional off-line analysis and comparisons with other inspections
-
Analysis of switching surges generated by current interruption in an energy-storage coil
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chowdhuri, P.
1981-01-01
The paper presents an analysis of the transient voltages which are generated when the current in a large magnetic energy storage coil is interrupted by a dc vacuum circuit breaker. The effect of the various parameters in the circuit on the transient voltage is discussed. The self inductance of the dump resistor must be minimized to control the generated transient. Contrary to general belief, a capacitor across the coil is not an effective surge suppressor. In fact, the capacitor may excite oscillations of higher magnitude. However, a capacitor, in addition to a surge suppressor, may be used to modify the frequency components of the transient voltage so that these frequency components are not coincident with the natural frequencies of the coil. Otherwise, resonant oscillations inside the coil may attain damaging magnitudes. The capacitor would also reduce the steepness of the wavefront of the transient across the coil, thus reducing the nonlinear voltage distribution inside the coil
-
Fluid simulation of the conduction phase of the plasma erosion opening switch
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Grossmann, J.M.; Mosher, D.; Ottinger, P.F.
1987-01-01
The conduction phase of the plasma erosion openings switch (PEOS) is studied using a 1 1/2-D electromagnetic two-fluid code. The focus of this work is on understanding how two effects, a current-limiting model of electron emission, and the magnetic insulation of electrons at the cathode, determine current conduction in the plasma. Simulations are performed in the parameter regimes of the Gamble I, POP, and PBFA II pulsed power generators, and previous low-density, short-rise time simulations of the PEOS. Fluid code results are compared to a 1-D analytic theory and to the Gamble I and POP experiments. Good agreement between theory and simulation, but mixed agreement between simulation and experiment is found. Experimental Β-field measurements on POP show weaker j x Β compression than the simulation. Current penetration and plasma current channels qualitatively similar to experimental observation are found in the Gamble I regime. However, magnetic insulation of electrons emitted from the cathode bunches the electron flow into narrower current channels than observed experimentally. In several cases, the presence of an electron-scattering or energy-loss mechanism near the cathode must be invoked to overcome magnetic insulation and widen the current channels
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Endo, Takashi; Kamimura, Takeo; Nishihara, Masatoshi; Araki, Yasuo; Fukui, Shigetaka.
1982-05-01
Eddy current flaw detection techniques are applied to the in-service inspection (ISI) of steam generator tubes in pressurized water reactors (PWR) plant. To improve the reliability and operating efficiency of the plants, efforts are being made to develop eddy current testing methods of various kinds. Multi-frequency eddy current testing method, one of new method, has recently been applied to actual heat exchanger tubes, contributing to the improvement of the detectability and signal evaluation of the ISI. The outline of multi-frequency eddy current testing method and its effects on the improvement of flaw detecting and signal evaluation accuracy are described. (author)
-
Takamoto, M.
2018-05-01
In this paper, the temporal evolution of three-dimensional relativistic current sheets in Poynting-dominated plasma is studied for the first time. Over the past few decades, a lot of efforts have been conducted on studying the evolution of current sheets in two-dimensional space, and concluded that sufficiently long current sheets always evolve into the so-called plasmoid chain, which provides a fast reconnection rate independent of its resistivity. However, it is suspected that plasmoid chain can exist only in the case of two-dimensional approximation, and would show transition to turbulence in three-dimensional space. We performed three-dimensional numerical simulation of relativistic current sheet using resistive relativistic magnetohydrodynamic approximation. The results showed that the three-dimensional current sheets evolve not into plasmoid chain but turbulence. The resulting reconnection rate is 0.004, which is much smaller than that of plasmoid chain. The energy conversion from magnetic field to kinetic energy of turbulence is just 0.01 per cent, which is much smaller than typical non-relativistic cases. Using the energy principle, we also showed that the plasmoid is always unstable for a displacement in the opposite direction to its acceleration, probably interchange-type instability, and this always results in seeds of turbulence behind the plasmoids. Finally, the temperature distribution along the sheet is discussed, and it is found that the sheet is less active than plasmoid chain. Our finding can be applied for many high-energy astrophysical phenomena, and can provide a basic model of the general current sheet in Poynting-dominated plasma.
-
Rare-earth hafnium oxide materials for magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) generator application
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Marchant, D. D; Bates, J. L.
1979-01-01
Several ceramic materials based on rare-earth hafnium oxides have been identified as potential high-temperature electrodes and low-temperature current leadouts for open cycle coal-fired MHD generator channels. The electrode-current leadouts combination must operate at temperatures between 400 and 2000K with an electrical conductivity greater than 10/sup -2/ ohm/sup -1/ cm/sup -1/. The electrodes will be exposed to flowing (linear flow rates up to 100 m/s) potassium seeded coal combustion gases (plasma core temperatures between 2400 to 3200/sup 0/K) and coal slag. During operation the electrodes must conduct direct electric current at densities near 1.5 amp/cm/sup 2/. Consequently, the electrodes must be resistant to electrochemical decompositions and interactions with both the coal slag and potassium salts (e.g., K/sub 2/SO/sub 4/, K/sub 2/CO/sub 3/). The current leadout materials are placed between the hot electrodes and the water-cooled copper structural members and must have electrical conductivities greater than 10/sup -2/ ohm/sup -1/ cm/sup -1/ between 1400 and 400/sup 0/K. The current leadouts must be thermally and electrochemically compatible with the electrode, copper, and potassium salts. Ideally, the electrodes and current leadouts should exhibit minimal ionic conductivity. The fabrication, electrical conductivity, and electrochemical corrosion of rare-earth hafnium oxide materials are discussed. (WHK)
-
GABA-independent GABAA Receptor Openings Maintain Tonic Currents
Wlodarczyk, Agnieszka I.; Sylantyev, Sergiy; Herd, Murray B.; Kersanté, Flavie; Lambert, Jeremy J.; Rusakov, Dmitri A.; Linthorst, Astrid C.E.; Semyanov, Alexey; Belelli, Delia; Pavlov, Ivan; Walker, Matthew C.
2013-01-01
Activation of GABAA receptors (GABAARs) produces two forms of inhibition: ‘phasic’ inhibition generated by the rapid, transient activation of synaptic GABAARs by presynaptic GABA release, and tonic inhibition generated by the persistent activation of peri- or extrasynaptic GABAARs which can detect extracellular GABA. Such tonic GABAAR-mediated currents are particularly evident in dentate granule cells in which they play a major role in regulating cell excitability. Here we show that in rat dentate granule cells in ex-vivo hippocampal slices, tonic currents are predominantly generated by GABA-independent GABAA receptor openings. This tonic GABAAR conductance is resistant to the competitive GABAAR antagonist SR95531, which at high concentrations acts as a partial agonist, but can be blocked by an open channel blocker picrotoxin. When slices are perfused with 200 nM GABA, a concentration that is comparable to cerebrospinal fluid concentrations but is twice that measured by us in the hippocampus in vivo using zero-net-flux microdialysis, negligible GABA is detected by dentate granule cells. Spontaneously opening GABAARs, therefore, maintain dentate granule cell tonic currents in the face of low extracellular GABA concentrations. PMID:23447601
-
Jain, Vishal; Visani, Anand; Srinivasan, R; Agarwal, Vivek
2018-03-01
This paper presents a new power supply architecture for generating a uniform dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma in air medium at atmospheric pressure. It is quite a challenge to generate atmospheric pressure uniform glow discharge plasma, especially in air. This is because air plasma needs very high voltage for initiation of discharge. If the high voltage is used along with high current density, it leads to the formation of streamers, which is undesirable for most applications like textile treatment, etc. Researchers have tried to generate high-density plasma using a RF source, nanosecond pulsed DC source, and medium frequency AC source. However, these solutions suffer from low current discharge and low efficiency due to the addition of an external resistor to control the discharge current. Moreover, they are relatively costly and bulky. This paper presents a new power supply configuration which is very compact and generates high average density (∼0.28 W/cm 2 ) uniform glow DBD plasma in air at atmospheric pressure. The efficiency is also higher as no external resistor is required to control the discharge current. An inherent feature of this topology is that it can drive higher current oscillations (∼50 A peak and 2-3 MHz frequency) into the plasma that damp out due to the plasma dissipation only. A newly proposed model has been used with experimental validation in this paper. Simulations and experimental validation of the proposed topology are included. Also, the application of the generated plasma for polymer film treatment is demonstrated.
-
Edge Plasma Boundary Layer Generated By Kink Modes in Tokamaks
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zakharov, L.E.
2010-01-01
This paper describes the structure of the electric current generated by external kink modes at the plasma edge using the ideally conducting plasma model. It is found that the edge current layer is created by both wall touching and free boundary kink modes. Near marginal stability, the total edge current has a universal expression as a result of partial compensation of the (delta)-functional surface current by the bulk current at the edge. The resolution of an apparent paradox with the pressure balance across the plasma boundary in the presence of the surface currents is provided.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Alvarez, J; Boutchich, M; Kleider, J P; Teraji, T; Koide, Y
2014-01-01
The origin of the high leakage current measured in several vertical-type diamond Schottky devices is conjointly investigated by conducting probe atomic force microscopy and confocal micro-Raman/photoluminescence imaging analysis. Local areas characterized by a strong decrease of the local resistance (5–6 orders of magnitude drop) with respect to their close surrounding have been identified in several different regions of the sample surface. The same local areas, also referenced as electrical hot-spots, reveal a slightly constrained diamond lattice and three dominant Raman bands in the low-wavenumber region (590, 914 and 1040 cm −1 ). These latter bands are usually assigned to the vibrational modes involving boron impurities and its possible complexes that can electrically act as traps for charge carriers. Local current–voltage measurements performed at the hot-spots point out a trap-filled-limited current as the main conduction mechanism favouring the leakage current in the Schottky devices. (paper)
-
Control of the electrode metal transfer by means of the welding current pulse generator
Knyaz'kov, A.; Pustovykh, O.; Verevkin, A.; Terekhin, V.; Shachek, A.; Knyaz'kov, S.; Tyasto, A.
2016-04-01
The paper presents a generator of welding current pulses to transfer an electrode metal into the molten pool. A homogeneous artificial line is used to produce near rectangular pulses. The homogeneous artificial line provides the minimum heat input with in the pulse to transfer the electrode metal, and it significantly decreases the impact of disturbances affecting this transfer. The pulse frequency does not exceed 300 Hz, and the duration is 0.6 ÷ 0.9 ms.
-
Space-charge-limited currents in electron-irradiated dielectrics
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nunes de Oliveira, L.; Gross, B.
1975-01-01
This paper develops the theory of steady-state currents generated in a dielectric placed between positively or negatively biased electrodes and irradiated with a partially penetrating electron beam. The dielectric is divided into an irradiated region (IR), which extends from the electrode of incidence to the extrapolated range of the beam, and a nonirradiated region (NIR). In the IR the primary beam generates an electron-hole plasma. Its end plane acts as a virtual electrode embedded in the dielectric. Currents are space-charge limited in the NIR and Ohmic in the IR which is characterized by a uniform radiation-induced conductivity. Depending on the polarity of the electrode bias, electrons or holes are drawn from the IR into the NIR. The theory correctly predicts an apparent threshold effect for the inset of steady-state currents: the current amplitudes remain small as long as the electron range is smaller than half the sample thickness, and increase strongly only afterwards. Calculated current curves for different beam energies are in satisfactory agreement with experimental results. The role of the electron beam as a virtual electrode is discussed
-
Thermal analysis of the conduction cooling system for HTS SMES system of 600 kJ class
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hong, Yong Ju; Yeom, Han Kil; Park, Seong Je; Kim, Hyo Bong; Koh, Deuk Yong
2007-01-01
SMES systems need cryogenic cooling systems. Conduction cooling system has more effective, compact structure than cryogen. In general, 2 stage GM cryocoolers are used for conduction cooling of HTS SMES system. 1st stages of cryocoolers are used for the cooling of current leads and radiation shields, and 2nd stages of cryocoolers for HTS coil. For the effective conduction cooling of the HTS SMES system, the temperature difference between the cryocooler and HTS coil should be minimized. In this paper, a cryogenic conduction cooling system for HTS SMES is analyzed to evaluate the performance of the cooling system. The analysis is carried out for the steady state with the heat generation of the HTS coil and effects of the thermal contact resistance. The results show the effects of the heat generation and thermal contact resistance on the temperature distribution
-
RF generator interlock by plasma grid bias current - An alternate to Hα interlock
Bandyopadhyay, M.; Gahlaut, A.; Yadav, R. K.; Pandya, K.; Tyagi, H.; Vupugalla, M.; Bhuyan, M.; Bhagora, J.; Chakraborty, A.
2017-08-01
ROBIN is inductively coupled plasma (ICP) based negative hydrogen ion source, operated with a 100kW, 1MHz Tetrode based RF generator (RFG). Inductive plasma ignition by the RFG in ROBIN is associated with electron seeding by a hot filament and a gas puff. RFG is triggered by the control system to deliver power just at the peak pressure of the gas puff. Once plasma is ignited due to proper impedance matching, a bright light, dominated by Hα (˜656nm wavelength) radiation is available inside RF driver which is used as a feedback signal to the RFG to continue its operation. If impedance matching is not correct, plasma is not produced due to lack of power coupling and bright light is not available. During such condition, reflected RF power may damage the RFG. Therefore, to protect the RFG, it needs to be switched off automatically within 200ms by the control system in such cases. This plasma light based RFG interlock is adopted from BATMAN ion source. However, in case of vacuum immersed RF ion source in reactor grade NBI system, such plasma light based interlock may not be feasible due to lack of adequate optical fiber interfaces. In reactor grade NBI system, neutron and gamma radiations have impact on materials which may lead to frequent maintenance and machine down time. The present demonstration of RFG interlock by Bias Current (BC) in ROBIN testbed gives an alternate option in this regard. In ROBIN, a bias plate (BP) is placed in the plasma chamber near the plasma grid (PG). BP is electrically connected to the plasma chamber wall of the ion source and PG is isolated from the wall. A high current ˜85 A direct current (DC) power supply of voltage in the range of 0 - 33V is connected between the PG and the BP in such a way that PG can be biased positively with respect to the BP or plasma chamber. This arrangement is actually made to absorb electrons and correspondingly reduce co-extracted electron current during beam extraction. However, in case of normal plasma
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lois, Alejandro E.
2001-01-01
During service at high temperature or in aggressive media, metallic structures and components may suffer different types of changes or degradation. As an example, phase transformations may occur, second phases may precipitate, and in consequence the mechanical and chemical properties of the material may change. Their behavior will therefore differ from that considered for the design of the component. The knowledge of the amount of a precipitated second phase in a component should be an important tool in the hands of the maintenance engineer. And it would be very important to obtain this knowledge nondestructively and reliably. The objective of this project is to evaluate by eddy currents the amount of the hydrogen incorporated during service in structural zirconium base materials. For this purpose, a series of Zircaloy-4 specimens with oxide layers of different thickness and different concentration of hydrogen obtained by controlled autoclave treatments were used. These specimens were tested with eddy current equipment. The information produced by an eddy current test is the superposition of many variables, e.g.: thickness of oxide layers, conductance, thickness of specimen, etc. In order to sort out this information, an analytical model of the impedance plane was programmed in a PC, with which this information was processed, permitting, in this way, to evaluate the conductivity of materials, taking into account the effect of oxide layers thickness. A linear relationship between the conductivity and the hydrogen content in the range of hydrogen concentrations of technological interest was observed. Therefore, the calculated electrical conductivity may be transformed to the amount of hydrogen content, using a suitable calibration curve. This process will allow for the nondestructive assessment of the amount of hydrogen in reactor components, such as pressure and calandria tubes, a knowledge which will enable the experts to predict the degree of fragility of those
-
Runway logic: "Y" Generation Y prefer fashion brand over country-of-origin
Nathalia C. Tjandra; Maktoba Omar; Robert L. Williams, Jr.; John Ensor
2013-01-01
With approximately 1.38 billion, Generation Y are currently in the job market or about to enter the job market, they are increasingly taking over the spending power of the previous generation, the Baby Boomers. The purpose of this qualitative study was to explore the impact country-of-origin information on the perception of Generation Y towards international fashion brands. This study was conducted in the context of fashion products, one of the key interests of the Generation Y, and covered a...
-
Conductivity-limiting bipolar thermal conductivity in semiconductors
Wang, Shanyu; Yang, Jiong; Toll, Trevor; Yang, Jihui; Zhang, Wenqing; Tang, Xinfeng
2015-01-01
Intriguing experimental results raised the question about the fundamental mechanisms governing the electron-hole coupling induced bipolar thermal conduction in semiconductors. Our combined theoretical analysis and experimental measurements show that in semiconductors bipolar thermal transport is in general a “conductivity-limiting” phenomenon, and it is thus controlled by the carrier mobility ratio and by the minority carrier partial electrical conductivity for the intrinsic and extrinsic cases, respectively. Our numerical method quantifies the role of electronic band structure and carrier scattering mechanisms. We have successfully demonstrated bipolar thermal conductivity reduction in doped semiconductors via electronic band structure modulation and/or preferential minority carrier scatterings. We expect this study to be beneficial to the current interests in optimizing thermoelectric properties of narrow gap semiconductors. PMID:25970560
-
Piot, P; Behrens, C; Gerth, C; Dohlus, M; Lemery, F; Mihalcea, D; Stoltz, P; Vogt, M
2012-01-20
We report on the successful experimental generation of electron bunches with ramped current profiles. The technique relies on impressing nonlinear correlations in the longitudinal phase space using a superconducing radio frequency linear accelerator operating at two frequencies and a current-enhancing dispersive section. The produced ~700-MeV bunches have peak currents of the order of a kilo-Ampère. Data taken for various accelerator settings demonstrate the versatility of the method and, in particular, its ability to produce current profiles that have a quasilinear dependency on the longitudinal (temporal) coordinate. The measured bunch parameters are shown, via numerical simulations, to produce gigavolt-per-meter peak accelerating electric fields with transformer ratios larger than 2 in dielectric-lined waveguides. © 2012 American Physical Society
-
Self-triggering superconducting fault current limiter
Yuan, Xing [Albany, NY; Tekletsadik, Kasegn [Rexford, NY
2008-10-21
A modular and scaleable Matrix Fault Current Limiter (MFCL) that functions as a "variable impedance" device in an electric power network, using components made of superconducting and non-superconducting electrically conductive materials. The matrix fault current limiter comprises a fault current limiter module that includes a superconductor which is electrically coupled in parallel with a trigger coil, wherein the trigger coil is magnetically coupled to the superconductor. The current surge doing a fault within the electrical power network will cause the superconductor to transition to its resistive state and also generate a uniform magnetic field in the trigger coil and simultaneously limit the voltage developed across the superconductor. This results in fast and uniform quenching of the superconductors, significantly reduces the burnout risk associated with non-uniformity often existing within the volume of superconductor materials. The fault current limiter modules may be electrically coupled together to form various "n" (rows).times."m" (columns) matrix configurations.
-
Current status of waste power generation in Japan and its impact on carbon dioxide reduction
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Takaoka, Masaki; Takeda, Nobuo; Yamagata, Naruo; Masuda, Takahiro
2010-01-01
In this research, we discuss current status of waste power generation (WPG) in Japan and various scenarios about the indirect reduction of carbon dioxide by WPG. The numbers of WPG facilities are 291 domestically as of 2006. Power generation capacity achieves 1584 MW and power generation amount is 7179 G Wh/ year. When we consider to reduce the used electricity for operation and office by WPG and emission coefficient of electricity for operation and office is to be 0.555 kg-CO 2 / kWh in default value, then carbon dioxide reduction amount is calculated to 3.9 million tons, which is equivalent to 26.7 % of 14.6 million tons of carbon dioxide emitted by municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) in 2005. Using various existing technological options, it finds that the efficiency of power generation will achieve more than 20 % in MSWI with the power generation efficiency of 20% as a feasible assumption, the total power generation amount and the carbon dioxide reduction amount will become 16540 G Wh/ year and 9.18 million tons, respectively. So, it is equivalent to 62.7% of carbon dioxide emitted by MSWI. Also, the ratio of additional reduction amount of carbon dioxide by WPG to total additional reduction amount in Japan during the first commitment period is 26.3%, which suggests that the promotion of WPG in MSWI is one of effective options for prevention of global warming. (author)
-
A review on the current status and production technology for {sup 188}W-{sup 188}Re generator system
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kuznetsov, R. A.; Han, H. S.; Cho, W. K.; Park, U. J.; Kim, Y. M
1998-11-01
The current status of {sup 188}W-{sup 188}Re generator production technology were reviewed in PART 1. Main interests were given to the aspects of {sup 188}W reactor production, irradiated targets reprocessing and generator loading technologies, such as alumina type and gel type generators. In order to develop the more convenient and advanced {sup 188}W-{sup 188}Re generator, further studies must be carried out to get the precise evaluation of production and burn-up cross section of {sup 188}W, the more easily realizable generator loading procedure, and also to optimize the column and generator design to compensate the deterioration of generator performance because of parent radionuclide decay. By irradiation of {sup 186}W enriched sample, {sup 188}W-{sup 188}Re generator production experiments were performed to evaluate the possibility of {sup 188}W-{sup 188}Re generator production using HANARO, and PART 2 describes about the experiments. The experimental results shows the possibility of practical {sup 188}W-{sup 188}Re generator production using of low-specific activity {sup 188}W produced in HANARO. (author). 79 refs., 4 tabs., 26 figs.
-
Electrical and thermal characteristics of Bi2212/Ag HTS coils for conduction-cooled SMES
Hayakawa, N.; Noguchi, S.; Kurupakorn, C.; Kojima, H.; Endo, F.; Hirano, N.; Nagaya, S.; Okubo, H.
2006-06-01
In this paper, we investigated the electrical and thermal performance of conduction-cooled Bi2212/Ag HTS coils with 4K-GM cryocooler system. First, we measured the critical current Ic for different ambient temperatures T0 at 4.2 K - 40 K. Experimental results revealed that Ic increased with the decrease in T0 and was saturated at T0 account of temperature dependence of specific heat and thermal conductivity of the materials. We also measured the temperature rise of Bi2212/Ag HTS coil for different continuous current levels at T0 = 4.8 K. Experimental results revealed the criterion of thermal runaway, which was discussed in terms of heat generation and propagation in the test coil.
-
Intense relativistic electron beam generation from KALI-5000 pulse accelerator
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Roy, A.; Mondal, J.; Mitra, S.; Durga Praveen Kumar, D.; Sharma, Archana; Nagesh, K.V.; Chakravarthy, D.P.
2006-01-01
Intense Relativistic Electron Beam (IREB) with parameters 420 keV, 22 kA, 100 ns has been generated from indigenously developed pulse power system KALI- 5000. High current electron beam is generated from explosive field emission graphite cathodes. Studies have been conducted by changing the diameter of graphite cathode and also the anode cathode gap. In order to avoid prepulse effect it was concluded that anode cathode (AK) gap should be kept larger than estimated by the Child Langmuir relation. Beam voltage has been measured by a copper sulphate voltage divider, beam current by a self integrating Rogowski coil and B-dot probe. Electron beam diode Impedance and Perveance were obtained from the experimentally measured beam voltage and current. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yamamoto, Shunji; Ishii, Shozo; Kawamoto, Shigeshi; Hayashi, Izumi
1981-01-01
Experimental study on the dynamic stabilization of MHD instability with a pinch plasma generator was done, and the results were compared with the theoretical works. The previous results of theoretical analysis showed that a conducting shell worked effectively for the dynamic stabilization of MHD instability. The present experiment was carried out with a linear plasma generator which consisted of a discharge tube, a coil and a conducting shell. The macroscopic behavior of plasma was observed with an image converter camera, and the phenomena due to the instability was measured by a magnetic probe. A sine-cosine coil was employed for the observation of the growth of instability. The following results were obtained. When the frequency of RF current for dynamic stabilization was larger than the growth rate of instability, the experimental results were in agreement with the theoretical ones. The effect of a conducting shell was clearly seen. For the helical instability of short wave length, the dynamic stabilization was easily obtained even without a conducting shell. The self-reversal phenomena due to the helical instability of short wave length was suppressed by the RF current along the axis of a discharge tube. (Kato, T.)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Calhoun, R K; Holler, F J [Kentucky Univ., Lexington, KY (United States). Dept. of Chemistry; Geiger, jr, R F; Nieman, T A [Illinois Univ., Urbana, IL (United States). Dept. of Chemistry; Caserta, K J [Procter and Gamble Co., Cincinnati, OH (United States)
1991-11-05
An instrument for measuring solution conductance using the bipolar pulse technique is described. The instrument is capable of measuring conductances in the range of 5x10{sup -9}-10{Omega}{sup -1} with 1% accuracy or better in as little as 32 {mu}s. Accuracy of 0.001-0.01% is achievable over the range 1x10{sup -6}-1{Omega}{sup -1}. Circuitry and software are described that allow the instrument to adjust automatically the pulse height, pulse duration, excitation mode (current or voltage pulse) and data acquisition mode (sampled or integrated) to acquire data of optimum accuracy and precision. The urease-catalyzed decomposition of urea is used to illustrate the versality of the instrument, and other applications are cited. (author). 60 refs.; 7 figs.; 2 tabs.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Georgel, B.; Zorgati, R.
1992-01-01
Improving speed and quality of Eddy Current non-destructive testing of steam generator tubes leads to automation of all process that contribute to diagnosis. This paper describes how signal processing, pattern recognition and artificial and artificial intelligence are used to build a software package that is able to automatically provide an efficient diagnosis. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Georgel, B.; Zorgati, R.
1994-01-01
Improving speed and quality of Eddy Current non-destructive testing of steam generator tubes leads to automatize all processes that contribute to diagnosis. This paper describes how we use signal processing, pattern recognition and artificial intelligence to build a software package that is able to automatically provide an efficient diagnosis. (authors). 2 figs., 5 refs
-
Samanta, Piyas
2017-09-01
We present a detailed investigation on temperature-dependent current conduction through thin tunnel oxides grown on degenerately doped n-type silicon (n+-Si) under positive bias ( VG ) on heavily doped n-type polycrystalline silicon (n+-polySi) gate in metal-oxide-semiconductor devices. The leakage current measured between 298 and 573 K and at oxide fields ranging from 6 to 10 MV/cm is primarily attributed to Poole-Frenkel (PF) emission of trapped electrons from the neutral electron traps located in the silicon dioxide (SiO2) band gap in addition to Fowler-Nordheim (FN) tunneling of electrons from n+-Si acting as the drain node in FLOating gate Tunnel OXide Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory devices. Process-induced neutral electron traps are located at 0.18 eV and 0.9 eV below the SiO2 conduction band. Throughout the temperature range studied here, PF emission current IPF dominates FN electron tunneling current IFN at oxide electric fields Eox between 6 and 10 MV/cm. A physics based new analytical formula has been developed for FN tunneling of electrons from the accumulation layer of degenerate semiconductors at a wide range of temperatures incorporating the image force barrier rounding effect. FN tunneling has been formulated in the framework of Wentzel-Kramers-Brilloiun taking into account the correction factor due to abrupt variation of the energy barrier at the cathode/oxide interface. The effect of interfacial and near-interfacial trapped-oxide charges on FN tunneling has also been investigated in detail at positive VG . The mechanism of leakage current conduction through SiO2 films plays a crucial role in simulation of time-dependent dielectric breakdown of the memory devices and to precisely predict the normal operating field or applied floating gate (FG) voltage for lifetime projection of the devices. In addition, we present theoretical results showing the effect of drain doping concentration on the FG leakage current.
-
Lv, Hui; Yu, Yonglin; Shu, Tan; Huang, Dexiu; Jiang, Shan; Barry, Liam P
2010-03-29
Photonic ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses are generated by direct current modulation of a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) section of an SOA-integrated sampled grating distributed Bragg reflector (SGDBR) laser. Modulation responses of the SOA section of the laser are first simulated with a microwave equivalent circuit model. Simulated results show a resonance behavior indicating the possibility to generate UWB signals with complex shapes in the time domain. The UWB pulse generation is then experimentally demonstrated for different selected wavelength channels with an SOA-integrated SGDBR laser.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Machado, L.V.R.; Moraes, E.T.; Correa, R.R.
2011-01-01
The NTC has been used as a temperature sensor, protection of electrical equipment, hospital instruments and automotive industry, thereby justifying its study. This pottery was processed, by a Spex mill by varying the concentration of Al_2O_3 in the oxides calcined at 1100 ° C to form the desired phases, then compressed to 120 MPa in a mold of 10mm"2 in size and 3mm thick and sintered at 1200 ° C and 1300 ° C, thermogravimetric analysis and DSC justified these temperatures. The XRD was used as powder for phase identification and FEG present in the pastilles to check the influence of microstructure on electrical property. A DC characterization was presented in an indirect way, by measuring the voltage through a constant current source, which eliminates the effect of the positive feedback generated by Joule effect. The electrical conductance is determined by Ohm's law. Samples with higher content of Al_2O_3 showed lower electrical conductivity. (author)
-
Lewis, Nathan S.; Spurgeon, Joshua M.
2016-10-25
The solar fuels generator includes an ionically conductive separator between a gaseous first phase and a second phase. A photoanode uses one or more components of the first phase to generate cations during operation of the solar fuels generator. A cation conduit is positioned provides a pathway along which the cations travel from the photoanode to the separator. The separator conducts the cations. A second solid cation conduit conducts the cations from the separator to a photocathode.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Driga, M.D.; Bird, W.L.; Tolk, K.M.; Weldon, W.F.; Rylander, H.G.; Woodson, H.H.
1977-01-01
Asymmetries in the applied magnetic field due to manufacturing tolerances and rotor-stator misalignments can cause significant forces and moments in a homopolar generator. Parasitic eddy-currents in the rotor, brushes and bearings are also important effects of such asymmetries. The finite element method is used to calculate the magnetic flux distributions in the TEXT homopolar generators. The axial magnetic thrust force and the magnetic tilt moment acting on the rotor are calculated. Eddy-current torques opposing rotor motion are determined using the theory for eddy-current brakes. The results have been used in the design of the TEXT homopolar generator which have been proposed to provide the energy store and conversion for the toroidal field and ohmic heating coils of the new Texas Experimental Tokamak
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lopez, Luiz Antonio Negro Martin
2002-01-01
Nuclear power plants steam generators around the world have presented early damage history in their tubes, caused either by design errors or by inappropriate operation, which besides reducing the availability and the safety of the nuclear power plants it also generates heavy economical burden. To monitor the steam generators operational condition, the Eddy Current testing of their tubes is the non destructive method used to detect, localize, classify and to size the defects. The inspection is performed by inserting probes with coils in the tubes generating a signal correlated to the defect. These signals produced by the probe electric circuit are composed by the resistance and the inductive components which can be combined to produce a Lissajous figure in the complex plane. However, Eddy-Current signals contain noise which induce subjectivity inducing to errors in the inspector diagnosis. It is not uncommon to have different diagnosis from two inspectors about the same signal. The present work has the objective of supplying a methodology to analyze the signals which could help the inspector in the difficult task of interpreting the Eddy Current signals. It is proposed a method to remove the noise based on Wavelets Transforms. It is also proposed a normalization in the signal phase angle measurements. Furthermore, two additional characteristics are also studied, namely: the signal amplitudes and the widths of the Lissajous petals. The use of a Fuzzy Logic based inference engine is also developed and its use is demonstrated to be viable. The defects studied in this work are those which produces volumetric changes in the material. In order to test the proposed methodology, several artificial defects were produced in tubes using different types of materials like: brass, 316L stainless steel and Inconel 600 to produce a experimental data base. An Eddy-Current inspection equipment, the MIZ-17ET was used. Around 1000 time series signals of defects were acquired through
-
Karlsson, Maths
2015-01-07
This article is concerned with the use of quasielastic neutron scattering as a technique for investigation of the dynamical properties of proton conducting oxides. Currently, the main interest in these materials comes from their promise as electrolytes in future electrochemical devices and particularly through their use as electrolytes in next-generation, intermediate-temperature, fuel cells. However, the realization of such devices depends critically on the development of new, more highly proton conducting oxides. Such a development depends on increasing the current understanding of proton conduction in oxides and for this purpose quasielastic neutron scattering is an important mean. The aim of this article is to introduce the non-specialist reader to the basic principles of quasielastic neutron scattering, its advantages and disadvantages, to summarize the work that has been done on proton conducting oxides using this technique, as well as to discuss future opportunities within this field of research.
-
Wu, Xing; Li, Kun; Raghavan, Nagarajan; Bosman, Michel; Wang, Qing-Xiao; Cha, Dong Kyu; Zhang, Xixiang; Pey, Kin-Leong
2011-01-01
Resistive switching in transition metal oxides could form the basis for next-generation non-volatile memory (NVM). It has been reported that the current in the high-conductivity state of several technologically relevant oxide materials flows through
-
Steam generator waterlancing at DNGS
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Seppala, D.; Malaugh, J.
1995-01-01
Darlington Nuclear Generating Station (DNGS) is a four 900 MW Unit nuclear station forming part of the Ontario Hydro East System. There are four identical steam generators(SGs) per reactor unit. The Darlington SGs are vertical heat exchangers with an inverted U-tube bundle in a cylindrical shell. The DNGS Nuclear Plant Life Assurance Group , a department of DNGS Engineering Services have taken a Proactive Approach to ensure long term SG integrity. Instead of waiting until the tubesheets are covered by a substantial and established hard deposit; DNGS plan to clean each steam generator's tubesheet, first half lattice tube support assembly and bottom of the thermal plate every four years. The ten year business plan provides for cleaning and inspection to be conducted on all four SGs in each unit during maintenance outages (currently scheduled for every four years)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Abhirup Lahiri
2011-01-01
Full Text Available This paper reports two new circuit topologies using second-generation current conveyors (CCIIs for realizing variable frequency sinusoidal oscillators with minimum passive components. The proposed topologies in this paper provide new realizations of resistance-controlled and capacitor-controlled variable frequency oscillators (VFOs using only four passive components. The first topology employs three CCIIs, while the second topology employs two CCIIs. The second topology provides an advantageous feature of frequency tuning through two grounded elements. Application of the proposed circuits as a wide-frequency range digitally controlled sinusoid generator is exhibited wherein the digital frequency control has been enabled by replacing both the capacitors by two identical variable binary capacitor banks tunable by means of the same binary code. SPICE simulations of the CMOS implementation of the oscillators using 0.35 μm TSMC CMOS technology parameters and bipolar implementation of the oscillators using process parameters for NR200N-2X (NPN and PR200N-2X (PNP of bipolar arrays ALA400-CBIC-R have validated their workability. One of the oscillators (with CMOS implementation is exemplified as a digitally controlled sinusoid generator with frequency generation from 25 kHz to 6.36 MHz, achieved by switching capacitors and with power consumption of 7 mW in the entire operating frequency range.
-
New eddy current testing system in steam generator tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nagata, Yasuyuki; Shimone, Junri; Maeda, Kotaro; Harada, Yutaka; Murakami, Ryuji
2003-01-01
Eddy Current Testing (ECT) technique is applied to PWR Steam Generator (SG) tubes during refueling outage inspection. Bobbin type probe is generally used for the inspection, but it cannot provide sufficient detectability for very tight cracks. NEL, R/D Tech (Canada) and AECL (Canada) jointly developed new ECT probe. The probe is transmit and receive type array probe. It has axial defect detection mode and circumferential defect detection mode. Its inspection speed is as fast as conventional bobbin probe, and detectability performance is same or better than performance of rotating pancake coil (RPC) probe, which is used for detailed inspection. As a tester of the new probe, we have developed new ECT tester TC7700. It is able to transmit composite wave from the 4 independent oscillators (simultaneous excitation system) compared with the conventional inspection system. As regarding for field inspection system, we have integrated Zetec (USA) probe positioner, probe pusher and R/D Tech TC7700. We are also developing new analysis software. The software has automated data screening function, which can deal with large amount of data compared with conventional bobbin probe. We plan to perform a large-scale field trial using the probe and new system in near future. (author)
-
Current and next-generation bleutongue vaccines
Feenstra, Femke; Rijn, van P.A.
2017-01-01
Bluetongue virus (BTV) causes the hemorrhagic disease bluetongue (BT) in ruminants. The best way to control outbreaks is vaccination. Currently, conventionally modified-live and inactivated vaccines are commercially available, which have been successfully used to control BT, but nonetheless have
-
Darroy, Jean Michel
1993-01-01
Current trends in the spacecraft mission operations area (spacecraft & mission complexity, project duration, required flexibility are requiring a breakthrough for what concerns philosophy, organization, and support tools. A major evolution is related to space operations 'informationalization', i.e adding to existing operations support & data processing systems a new generation of tools based on advanced information technologies (object-oriented programming, artificial intelligence, data bases, hypertext) that automate, at least partially, operations tasks that used be performed manually (mission & project planning/scheduling, operations procedures elaboration & execution, data analysis & failure diagnosis). All the major facets of this 'informationalization' are addressed at MATRA MARCONI SPACE, operational applications were fielded and generic products are becoming available. These various applications have generated a significant feedback from the users (at ESA, CNES, ARIANESPACE, MATRA MARCONI SPACE), which is now allowing us to precisely measure how the deployment of this new generation of tools, that we called OPSWARE, can 'reengineer' current spacecraft mission operations philosophy, how it can make space operations faster, better, and cheaper. This paper can be considered as an update of the keynote address 'Knowledge-Based Systems for Spacecraft Control' presented during the first 'Ground Data Systems for Spacecraft Control' conference in Darmstadt, June 1990, with a special emphasis on these last two years users feedback.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yehia, Ashraf; Mizuno, Akira
2013-01-01
An analytical study was made in this paper for calculating the ozone generation by negative dc corona discharges. The corona discharges were formed in a coaxial wire-cylinder reactor. The reactor was fed by dry air flowing with constant rates at atmospheric pressure and room temperature, and stressed by a negative dc voltage. The current-voltage characteristics of the negative dc corona discharges formed inside the reactor were measured in parallel with concentration of the generated ozone under different operating conditions. An empirical equation was derived from the experimental results for calculating the ozone concentration generated inside the reactor. The results, that have been recalculated by using the derived equation, have agreed with the experimental results over the whole range of the investigated parameters, except in the saturation range for the ozone concentration. Therefore, the derived equation represents a suitable criterion for expecting the ozone concentration generated by negative dc corona discharges in dry air fed coaxial wire-cylinder reactors under any operating conditions in range of the investigated parameters.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Volkov, N.V.; Petrakovskij, G.A.; Sablina, K.A.
1999-01-01
The experimental results of the study on the effect of the low frequency transport current on the conductivity in UHF-range of the La 0.7 Pb 0.3 MnO 3 monocrystals are presented. In absence of the external magnetic field the UHF-conductivity response signal on the current impact has the form of the relaxation process. The peak of the amplitude resonance growth is observed in the external magnetic field in the response spectrum. The resonance response is of nonlinear character. The temperature and field dependences of the UHF-response basic parameters are in direct correlation with the magnetoresistance behaviour. The results obtained are analyzed within the frames of the oscillatory approximation. The mechanism of the phases electron separation is proposed as the possible mechanism of the current impact [ru
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Milinski, N.; Milinski, E.
2002-01-01
Amorphous conductors such as liquid metals and alloys are subject to dc conductivity σ calculation here. Principal aim is to explore the impact on σ of the constitutive equation α * = 1, formulated and developed in the preceding papers. The nearly free electrons (NFE) model has been applied. Alkali metals are assumed to fit this model well, and sodium the best. Consequently, the results on these metals have been assumed reliable and relevant for conclusions making. The conclusion we made is: instead of the Fermi radius k f proper for the statistical ensemble in state of thermodynamics equilibrium, a new k ' f number is needed to be introduced into the linear response formula when calculating σ and α * . This k ' f is the length of the corresponding axis of ellipsoid proper for describing the statistical ensemble in the state with dc current. In the traditional interpretation of the linear response formula (Kubo formula) this conversion has been overlooked. Parameters of the mentioned ellipsoids are determined in this paper for a number of liquid metals of valency numbers 1,2,3,4, in addition to a selection of some binary and ternary conducting alloys. It is up to experimental measurements to decide how real this concept of restructuring the statistical ensemble is. (Authors)
-
Adeyemi, Oladipupo; Alvarez-Laviada, Anita; Schultz, Francisca; Ibrahim, Effendi; Trauner, Michael; Williamson, Catherine; Glukhov, Alexey V.
2017-01-01
Background Increased maternal serum bile acid concentrations in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) are associated with fetal cardiac arrhythmias. Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) has been shown to demonstrate anti-arrhythmic properties via preventing ICP-associated cardiac conduction slowing and development of reentrant arrhythmias, although the cellular mechanism is still being elucidated. Methods High-resolution fluorescent optical mapping of electrical activity and electrocardiogram measurements were used to characterize effects of UDCA on one-day-old neonatal and adult female Langendorff-perfused rat hearts. ICP was modelled by perfusion of taurocholic acid (TC, 400μM). Whole-cell calcium currents were recorded from neonatal rat and human fetal cardiomyocytes. Results TC significantly prolonged the PR interval by 11.0±3.5% (P<0.05) and slowed ventricular conduction velocity (CV) by 38.9±5.1% (P<0.05) exclusively in neonatal and not in maternal hearts. A similar CV decline was observed with the selective T-type calcium current (ICa,T) blocker mibefradil 1μM (23.0±6.2%, P<0.05), but not with the L-type calcium current (ICa,L) blocker nifedipine 1μM (6.9±6.6%, NS). The sodium channel blocker lidocaine (30μM) reduced CV by 60.4±4.5% (P<0.05). UDCA co-treatment was protective against CV slowing induced by TC and mibefradil, but not against lidocaine. UDCA prevented the TC-induced reduction in the ICa,T density in both isolated human fetal (−10.2±1.5 versus −5.5±0.9 pA/pF, P<0.05) and neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (−22.3±1.1 versus −9.6±0.8 pA/pF, P<0.0001), whereas UDCA had limited efficacy on the ICa,L. Conclusion Our findings demonstrate that ICa,T plays a significant role in ICP-associated fetal cardiac conduction slowing and arrhythmogenesis, and is an important component of the fetus-specific anti-arrhythmic activity of UDCA. PMID:28934223
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Oladipupo Adeyemi
Full Text Available Increased maternal serum bile acid concentrations in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP are associated with fetal cardiac arrhythmias. Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA has been shown to demonstrate anti-arrhythmic properties via preventing ICP-associated cardiac conduction slowing and development of reentrant arrhythmias, although the cellular mechanism is still being elucidated.High-resolution fluorescent optical mapping of electrical activity and electrocardiogram measurements were used to characterize effects of UDCA on one-day-old neonatal and adult female Langendorff-perfused rat hearts. ICP was modelled by perfusion of taurocholic acid (TC, 400μM. Whole-cell calcium currents were recorded from neonatal rat and human fetal cardiomyocytes.TC significantly prolonged the PR interval by 11.0±3.5% (P<0.05 and slowed ventricular conduction velocity (CV by 38.9±5.1% (P<0.05 exclusively in neonatal and not in maternal hearts. A similar CV decline was observed with the selective T-type calcium current (ICa,T blocker mibefradil 1μM (23.0±6.2%, P<0.05, but not with the L-type calcium current (ICa,L blocker nifedipine 1μM (6.9±6.6%, NS. The sodium channel blocker lidocaine (30μM reduced CV by 60.4±4.5% (P<0.05. UDCA co-treatment was protective against CV slowing induced by TC and mibefradil, but not against lidocaine. UDCA prevented the TC-induced reduction in the ICa,T density in both isolated human fetal (-10.2±1.5 versus -5.5±0.9 pA/pF, P<0.05 and neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (-22.3±1.1 versus -9.6±0.8 pA/pF, P<0.0001, whereas UDCA had limited efficacy on the ICa,L.Our findings demonstrate that ICa,T plays a significant role in ICP-associated fetal cardiac conduction slowing and arrhythmogenesis, and is an important component of the fetus-specific anti-arrhythmic activity of UDCA.
-
A linear current injection generator for the generation of electrons in a nuclear reactor
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kar, Moutushi; Thakur, Satish Kumar; Agiwal, Mamta; Sholapurwala, Zarir H.
2011-01-01
While, operating a nuclear reactor it is absolutely necessary for generating a chain reaction or fission. A chain reaction can be initiated by bombardment of a heavy nucleus with fast moving particles. One of the common methods used for generating a fast moving particle is injecting a very high voltage into a particle accelerator and accelerating high energy particle beams using machine like cyclotron, synchrotron, linear accelerators i.e. linac and similar equipment. These equipment generated and run by several high voltage applications like simple high voltage DC systems and supplies or pulsed electron systems. (author)
-
A Study of Frequency Mixing Approaches for Eddy Current Testing of Steam Generator Tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jung, Hee Jun; Song, Sung Jin; Kim, Chang Hwan; Kim, Dae Kwang
2009-01-01
The multifrequency eddy current testing(ECT) have been proposed various frequency mixing algorithms. In this study, we compare these approaches to frequency mixing of ECT signals from steam generator tubes; time-domain optimization, discrete cosine transform-domain optimization. Specifically, in this study, two different frequency mixing algorithms, a time-domain optimization method and a discrete cosine transform(DCT) optimization method, are investigated using the experimental signals captured from the ASME standard tube. The DCT domain optimization method is computationally fast but produces larger amount of residue.
-
Rotstein, Horacio G
2017-08-01
Subthreshold (membrane potential) resonance and phasonance (preferred amplitude and zero-phase responses to oscillatory inputs) in single neurons arise from the interaction between positive and negative feedback effects provided by relatively fast amplifying currents and slower resonant currents. In 2D neuronal systems, amplifying currents are required to be slave to voltage (instantaneously fast) for these phenomena to occur. In higher dimensional systems, additional currents operating at various effective time scales may modulate and annihilate existing resonances and generate antiresonance (minimum amplitude response) and antiphasonance (zero-phase response with phase monotonic properties opposite to phasonance). We use mathematical modeling, numerical simulations and dynamical systems tools to investigate the mechanisms underlying these phenomena in 3D linear models, which are obtained as the linearization of biophysical (conductance-based) models. We characterize the parameter regimes for which the system exhibits the various types of behavior mentioned above in the rather general case in which the underlying 2D system exhibits resonance. We consider two cases: (i) the interplay of two resonant gating variables, and (ii) the interplay of one resonant and one amplifying gating variables. Increasing levels of an amplifying current cause (i) a response amplification if the amplifying current is faster than the resonant current, (ii) resonance and phasonance attenuation and annihilation if the amplifying and resonant currents have identical dynamics, and (iii) antiresonance and antiphasonance if the amplifying current is slower than the resonant current. We investigate the underlying mechanisms by extending the envelope-plane diagram approach developed in previous work (for 2D systems) to three dimensions to include the additional gating variable, and constructing the corresponding envelope curves in these envelope-space diagrams. We find that antiresonance and
-
Eddy current technology for heat exchanger and steam generator tube inspection
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Obrutsky, L.; Lepine, B.; Lu, J.; Cassidy, R.; Carter, J. [Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River, Ontario (Canada)
2004-07-01
A variety of degradation modes can affect the integrity of both heat exchanger (HX) and balance of plant tubing, resulting in expensive repairs, tube plugging or replacement of tube bundles. One key component for ensuring tube integrity is inspection and monitoring for detection and characterization of the degradation. In-service inspection of HX and balance of plant tubing is usually carried out using eddy current (EC) bobbin coils, which are adequate for the detection of volumetric degradations. However, detection and quantification of additional modes of degradation such as pitting, intergranular attack (IGA), axial cracking and circumferential cracking require specialized probes. The need for timely, reliable detection and characterization of these modes of degradation is especially critical in Nuclear Generating Stations. Transmit-receive single-pass array probes, developed by AECL, offer high defect detectability in conjunction with fast and reliable inspection capabilities. They have strong directional properties, permitting probe optimization for circumferential or axial crack detection. Compared to impedance probes, they offer improved performance in the presence of variable lift-off. This EC technology can help resolve critical detection issues at susceptible areas, such as the rolled-joint transitions at the tubesheet, U-bends and tube-support intersections. This paper provides an overview of the operating principles and the capabilities of advanced ET inspection technology available for HX tube inspection. Examples of recent application of this technology in Nuclear Generating Stations (NGSs) are discussed. (author)
-
Eddy current technology for heat exchanger and steam generator tube inspection
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Obrutsky, L.; Lepine, B.; Lu, J.; Cassidy, R.; Carter, J.
2004-01-01
A variety of degradation modes can affect the integrity of both heat exchanger (HX) and balance of plant tubing, resulting in expensive repairs, tube plugging or replacement of tube bundles. One key component for ensuring tube integrity is inspection and monitoring for detection and characterization of the degradation. In-service inspection of HX and balance of plant tubing is usually carried out using eddy current (EC) bobbin coils, which are adequate for the detection of volumetric degradations. However, detection and quantification of additional modes of degradation such as pitting, intergranular attack (IGA), axial cracking and circumferential cracking require specialized probes. The need for timely, reliable detection and characterization of these modes of degradation is especially critical in Nuclear Generating Stations. Transmit-receive single-pass array probes, developed by AECL, offer high defect detectability in conjunction with fast and reliable inspection capabilities. They have strong directional properties, permitting probe optimization for circumferential or axial crack detection. Compared to impedance probes, they offer improved performance in the presence of variable lift-off. This EC technology can help resolve critical detection issues at susceptible areas, such as the rolled-joint transitions at the tubesheet, U-bends and tube-support intersections. This paper provides an overview of the operating principles and the capabilities of advanced ET inspection technology available for HX tube inspection. Examples of recent application of this technology in Nuclear Generating Stations (NGSs) are discussed. (author)
-
Alfven Wave Reflection Model of Field-Aligned Currents at Mercury
Lyatsky, Wladislaw; Khazanov, George V.; Slavin, James
2010-01-01
An Alfven Wave Reflection (AWR) model is proposed that provides closure for strong field-aligned currents (FACs) driven by the magnetopause reconnection in the magnetospheres of planets having no significant ionospheric and surface electrical conductance. The model is based on properties of the Alfven waves, generated at high altitudes and reflected from the low-conductivity surface of the planet. When magnetospheric convection is very slow, the incident and reflected Alfven waves propagate along approximately the same path. In this case, the net field-aligned currents will be small. However, as the convection speed increases. the reflected wave is displaced relatively to the incident wave so that the incident and reflected waves no longer compensate each other. In this case, the net field-aligned current may be large despite the lack of significant ionospheric and surface conductivity. Our estimate shows that for typical solar wind conditions at Mercury, the magnitude of Region 1-type FACs in Mercury's magnetosphere may reach hundreds of kilo-Amperes. This AWR model of field-aligned currents may provide a solution to the long-standing problem of the closure of FACs in the Mercury's magnetosphere. c2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Stefano eCavallari
2014-03-01
Full Text Available Models of networks of Leaky Integrate-and-Fire neurons (LIF are a widely used tool for theoretical investigations of brain function. These models have been used both with current- and conductance-based synapses. However, the differences in the dynamics expressed by these two approaches have been so far mainly studied at the single neuron level. To investigate how these synaptic models affect network activity, we compared the single-neuron and neural population dynamics of conductance-based networks (COBN and current-based networks (CUBN of LIF neurons. These networks were endowed with sparse excitatory and inhibitory recurrent connections, and were tested in conditions including both low- and high-conductance states. We developed a novel procedure to obtain comparable networks by properly tuning the synaptic parameters not shared by the models. The so defined comparable networks displayed an excellent and robust match of first order statistics (average single neuron firing rates and average frequency spectrum of network activity. However, these comparable networks showed profound differences in the second order statistics of neural population interactions and in the modulation of these properties by external inputs. The correlation between inhibitory and excitatory synaptic currents and the cross-neuron correlation between synaptic inputs, membrane potentials and spike trains were stronger and more stimulus-sensitive in the COBN. Because of these properties, the spike train correlation carried more information about the strength of the input in the COBN, although the firing rates were equally informative in both network models. Moreover, COBN showed stronger neuronal population synchronization in the gamma band, and their spectral information about the network input was higher and spread over a broader range of frequencies. These results suggest that second order properties of network dynamics depend strongly on the choice of synaptic model.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen Hai-Feng; Guo Li-Xin; Zheng Pu-Yang; Dong Zhao; Zhang Qian
2015-01-01
Drain-modulated generation current I DMG induced by interface traps in an n-type metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (nMOSFET) is investigated. The formation of I DMG ascribes to the change of the Si surface potential φ s . This change makes the channel suffer transformation from the inversion state, depletion I state to depletion II state. The simulation result agrees with the experiment in the inversion and depletion I states. In the depletion II state, the theoretical curve goes into saturation, while the experimental curve drops quickly as V D increases. The reason for this unconformity is that the drain-to-gate voltage V DG lessens φ s around the drain corner and controls the falling edge of the I DMG curve. The experiments of gate-modulated generation and recombination currents are also applied to verify the reasonability of the mechanism. Based on this mechanism, a theoretical model of the I DMG falling edge is set up in which I DMG has an exponential attenuation relation with V DG . Finally, the critical fitting coefficient t of the experimental curves is extracted. It is found that t = 80 mV = 3kT/q. This result fully shows the accuracy of the above mechanism. (paper)
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Wang, L.; Lee, D. J.; Lee, W. J.
2008-01-01
wind turbines andWells turbines to respectively capture wind energy and wave energy from marine wind and oceanwave. In addition to wind-turbine generators(WTGs) andwave-energy turbine generators (WETGs) employed in the studied system, diesel-engine generators (DEGs) and an aqua electrolyzer (AE......This paper presents both time-domain and frequency-domain simulated results of a novel marine hybrid renewable-energy power generation/energy storage system (PG/ESS) feeding isolated loads through an high-voltage direct current (HVDC) link. The studied marine PG subsystems comprise both offshore......) absorbing a part of generated energy from WTGs and WETGs to generate available hydrogen for fuel cells (FCs) are also included in the PG subsystems. The ES subsystems consist of a flywheel energy storage system(FESS) and a compressed air energy storage (CAES) system to balance the required energy...
-
Structural and electrical properties of conducting diamond nanowires.
Sankaran, Kamatchi Jothiramalingam; Lin, Yen-Fu; Jian, Wen-Bin; Chen, Huang-Chin; Panda, Kalpataru; Sundaravel, Balakrishnan; Dong, Chung-Li; Tai, Nyan-Hwa; Lin, I-Nan
2013-02-01
Conducting diamond nanowires (DNWs) films have been synthesized by N₂-based microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. The incorporation of nitrogen into DNWs films is examined by C 1s X-ray photoemission spectroscopy and morphology of DNWs is discerned using field-emission scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The electron diffraction pattern, the visible-Raman spectroscopy, and the near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy display the coexistence of sp³ diamond and sp² graphitic phases in DNWs films. In addition, the microstructure investigation, carried out by high-resolution TEM with Fourier transformed pattern, indicates diamond grains and graphitic grain boundaries on surface of DNWs. The same result is confirmed by scanning tunneling microscopy and scanning tunneling spectroscopy (STS). Furthermore, the STS spectra of current-voltage curves discover a high tunneling current at the position near the graphitic grain boundaries. These highly conducting regimes of grain boundaries form effective electron paths and its transport mechanism is explained by the three-dimensional (3D) Mott's variable range hopping in a wide temperature from 300 to 20 K. Interestingly, this specific feature of high conducting grain boundaries of DNWs demonstrates a high efficiency in field emission and pave a way to the next generation of high-definition flat panel displays or plasma devices.
-
High-temperature superconducting fault-current limiter - optimisation of superconducting elements
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
2004-01-01
This report summarises the findings of a study initiated to continue the work of a DTI-LINK Collaborative Research Programme 'Enhancing the Properties of Bulk High Temperature Superconductors and their Potential Application as Fault Current Limiters (FCL). Details are given of computer modelling of the quenching process involving the transition from superconducting to normal conducting states undergone by the material when large currents are present. The design of compound elements, and a multi-element model are described along with FCL design covering distribution bus-coupler, embedded generator connection, larger generator connection, hazardous area safety, and interconnection to fault-prone network. The evaluation of thermal loss, test equipment and schedule, the optimised element, installed cost data, and the UK market are considered
-
Disposal and handling of nuclear steam generator chemical cleaning wastes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Larrick, A.P.; Schneidmiller, D.
1978-01-01
A large number of pressurized water nuclear reactor electrical generating plants have experienced a corrosion-related problem with their steam generators known as denting. Denting is a mechanical deformation of the steam generator tubes that occurs at the tube support plates. Corrosion of the tube support plates occurs within the annuli through which the tubes pass and the resulting corrosion oxides, which are larger in volume than the original metal, compress and deform the tubes. In some cases, the induced stresses have been severe enough to cause tube and/or support cracking. The problem was so severe at the Turkey Point and Surrey plants that the tubing is being replaced. For less severe cases, chemical cleaning of the oxides, and other materials which deposit in the annuli from the water, is being considered. A Department of Energy-sponsored program was conducted by Consolidated Edison Co. of New York which identified several suitable cleaning solvents and led to in-plant chemical cleaning pilot demonstrations in the Indian Point Unit 1 steam generators. Current programs to improve the technology are being conducted by the Electric Power Research Institute, and the three PWR NSSS vendors with the assistance of numerous consultants, vendors, and laboratories. These programs are expected to result in more effective, less corrosive solvents. However, after a chemical cleaning is conducted, a large problem still remains- that of disposing of the spent wastes. The paper summarizes some of the methods currently available for handling and disposal of the wastes
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tsukamoto, O.; Utsunomiya, A.
2007-01-01
We propose an HTS bulk bearing flywheel energy system (FWES) with rotor shaft stabilization system using feed-back control of the armature currents of the motor-generator. In the proposed system the rotor shift has a pivot bearing at one end of the shaft and an HTS bulk bearing (SMB) at the other end. The fluctuation of the rotor shaft with SMB is damped by feed-back control of the armature currents of the motor-generator sensing the position of the rotor shaft. The method has merits that the fluctuations are damped without active control magnet bearings and extra devices which may deteriorate the energy storage efficiency and need additional costs. The principle of the method was demonstrated by an experiment using a model permanent magnet motor
-
Tsukamoto, O.; Utsunomiya, A.
2007-10-01
We propose an HTS bulk bearing flywheel energy system (FWES) with rotor shaft stabilization system using feed-back control of the armature currents of the motor-generator. In the proposed system the rotor shift has a pivot bearing at one end of the shaft and an HTS bulk bearing (SMB) at the other end. The fluctuation of the rotor shaft with SMB is damped by feed-back control of the armature currents of the motor-generator sensing the position of the rotor shaft. The method has merits that the fluctuations are damped without active control magnet bearings and extra devices which may deteriorate the energy storage efficiency and need additional costs. The principle of the method was demonstrated by an experiment using a model permanent magnet motor.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Andrade, Maria Celia Ramos; Ludwig, Gerson Otto [Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE), Sao Jose dos Campos, SP (Brazil). Lab. Associado de Plasma]. E-mail: mcr@plasma.inpe.br
2004-07-01
Different bootstrap current formulations are implemented in a self-consistent equilibrium calculation obtained from a direct variational technique in fixed boundary tokamak plasmas. The total plasma current profile is supposed to have contributions of the diamagnetic, Pfirsch-Schlueter, and the neoclassical Ohmic and bootstrap currents. The Ohmic component is calculated in terms of the neoclassical conductivity, compared here among different expressions, and the loop voltage determined consistently in order to give the prescribed value of the total plasma current. A comparison among several bootstrap current models for different viscosity coefficient calculations and distinct forms for the Coulomb collision operator is performed for a variety of plasma parameters of the small aspect ratio tokamak ETE (Experimento Tokamak Esferico) at the Associated Plasma Laboratory of INPE, in Brazil. We have performed this comparison for the ETE tokamak so that the differences among all the models reported here, mainly regarding plasma collisionality, can be better illustrated. The dependence of the bootstrap current ratio upon some plasma parameters in the frame of the self-consistent calculation is also analysed. We emphasize in this paper what we call the Hirshman-Sigmar/Shaing model, valid for all collisionality regimes and aspect ratios, and a fitted formulation proposed by Sauter, which has the same range of validity but is faster to compute than the previous one. The advantages or possible limitations of all these different formulations for the bootstrap current estimate are analysed throughout this work. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wu, You-Lin; Liao, Chun-Wei; Ling, Jing-Jenn
2014-01-01
The electrical characterization of HfO 2 /ITO/Invar resistive switching memory structure was studied using conductive atomic force microscopy (AFM) with a semiconductor parameter analyzer, Agilent 4156C. The metal alloy Invar was used as the metal substrate to ensure good ohmic contact with the substrate holder of the AFM. A conductive Pt/Ir AFM tip was placed in direct contact with the HfO 2 surface, such that it acted as the top electrode. Nanoscale current-voltage (I-V) characteristics of the HfO 2 /ITO/Invar structure were measured by applying a ramp voltage through the conductive AFM tip at various current compliances and ramp voltage sweep rates. It was found that the resistance of the low resistance state (RLRS) decreased with increasing current compliance value, but resistance of high resistance state (RHRS) barely changed. However, both the RHRS and RLRS decreased as the voltage sweep rate increased. The reasons for this dependency on current compliance and voltage sweep rate are discussed.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Bak-Jensen, Birgitte; Kawady, T.A.; Abdel-Rahman, Mansour Hassan
2010-01-01
is investigated. Simulation test cases using MATLAB-Simulink are implemented on a 365-MW wind farm in AL-Zaafarana, Egypt. The simulation results show the influence of the FRT capability on the protective relaying coordination in wind farms, showing that the FRT may work in situations where is were expected......Fault Ride-Through (FRT) capabilities set up according to the grid codes may affect the performance of related protective elements during fault periods. Therefore, in this paper the coordination between the FRT capability and over-current protection of DFIG Wind Generators in MV networks...... not to work, and then disabling the over-current protection, which should have worked in this situation....
-
Hortelano, V.; Weidlich, H.; Semtsiv, M. P.; Masselink, W. T.; Ramsteiner, M.; Jahn, U.; Biermann, K.; Takagaki, Y.
2018-04-01
Nanometer-sized channels are fabricated in (In,Ga)As-InP heterostructures using Ar ion milling. The ion milling causes spontaneous creation of nanowires, and moreover, electrical conduction of the surface as carriers is generated by sputtering-induced defects. We demonstrate a method to restore electrical isolation in the etched area that is compatible with the presence of the nanochannels. We remove the heavily damaged surface layer using a diluted HCl solution and subsequently recover the crystalline order in the moderately damaged part by annealing. We optimize the HCl concentration to make the removal stop on its own before reaching the conduction channel part. The lateral depletion in the channels is shown to be almost absent.
-
Technical Note: Influence of Compton currents on profile measurements in small-volume ion chambers
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tanny, Sean; Sperling, Nicholas; Parsai, E. Ishmael, E-mail: e.parsai@utoledo.edu [Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Toledo Medical Center, 1325 Conference Drive, Toledo, Ohio 43614 (United States); Holmes, Shannon [Standard Imaging, 3120 Deming Way, Middleton, Wisconsin 53562 (United States)
2015-10-15
Purpose: This work is to evaluate the effects of Compton current generation in three small-volume ionization chambers on measured beam characteristics for electron fields. Methods: Beam scans were performed using Exradin A16, A26, and PTW 31014 microchambers. Scans with varying chamber components shielded were performed. Static point measurements, output factors, and cable only irradiations were performed to determine the contribution of Compton currents to various components of the chamber. Monte Carlo simulations were performed to evaluate why one microchamber showed a significant reduction in Compton current generation. Results: Beam profiles demonstrated significant distortion for two of the three chambers when scanned parallel to the chamber axis, produced by electron deposition within the wire. Measurements of ionization produced within the cable identified Compton current generation as the cause of these distortions. The size of the central collecting wire was found to have the greatest influence on the magnitude of Compton current generation. Conclusions: Microchambers can demonstrate significant (>5%) deviations from properties as measured with larger volume chambers (0.125 cm{sup 3} and above). These deviations can be substantially reduced by averaging measurements conducted at opposite polarities.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bakhtiari, S.; Elmer, T.W.
2009-01-01
Computer-aided data analysis tools can help improve the efficiency and reliability of flaw sizing based on nondestructive examination data. They can further help produce more consistent results, which is important for both in-service inspection applications and for engineering assessments associated with steam generator tube integrity. Results of recent investigations at Argonne on the development of various algorithms for sizing of flaws in steam generator tubes based on eddy current rotating probe data are presented. The research was carried out as part of the activities under the International Steam Generator Tube Integrity Program (ISG-TIP) sponsored by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. A computer-aided data analysis tool has been developed for off-line processing of eddy current inspection data. The main objectives of the work have been to a) allow all data processing stages to be performed under the same user interface, b) simplify modification and testing of signal processing and data analysis scripts, and c) allow independent evaluation of viable flaw sizing algorithms. The focus of most recent studies at Argonne has been on the processing of data acquired with the +Point probe, which is one of the more widely used eddy current rotating probes for steam generator tube examinations in the U.S. The probe employs a directional surface riding differential coil, which helps reduce the influence of tubing artifacts and in turn helps improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Various algorithms developed under the MATLAB environment for the conversion, segmentation, calibration, and analysis of data have been consolidated within a single user interface. Data acquired with a number of standard eddy current test equipment are automatically recognized and converted to a standard format for further processing. Because of its modular structure, the graphical user interface allows user-developed routines to be easily incorporated, modified, and tested independent of the
-
Design Concept of Array ECT Sensor for Steam Generator Tubing Inspection
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cho, Chan Hee; Lee, Tae Hun; Yoo, Hyun Ju [Korea Hydro and Nuclear Power Co. Ltd. CRI, Daejeon (Korea, Republic of)
2015-05-15
The eddy current testing, which is one of the nondestructive examination methods, is widely used for the inspection of heat exchangers including steam generator tubing in the nuclear power plant. It uses electromagnetic induction to detect flaws in conductive materials. Two types of eddy current probes are conventionally used for the inspection of steam generator tubing according to the main purpose. One is the bobbin probe technology and the other is the rotating probe. During the inspection, they have restrictions for the flaw detection or the inspection speed. An array probe can be alternative to the bobbin and rotating probes. The design concept of array coils with high sensitivity is described in this paper. It is expected that the eddy current testing using this type of array sensors may provide high detectability and resolution for flaws in steam generator tubing. Eddy current technology has some barriers for the inspection of steam generator tubing in the nuclear power plant. Bobbin probes offer poor circumferential crack detection and rotating probes are time and money consuming due to the mechanical rotation. Array probe inspection technique can replace bobbin and rotating probe techniques due to its sensitivity for flaw detection and inspection speed. In general, circular-shaped coils are considered in an array eddy current probe.
-
Influence of sodium deposits in steam generator tubes on remote field eddy current signals
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Thirunavukkarasu, S. [EMSI Section, NDE Division, Metallurgy and Materials Group, Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research, Kalpakkam 603 102, Tamil Nadu (India); Rao, B.P.C. [EMSI Section, NDE Division, Metallurgy and Materials Group, Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research, Kalpakkam 603 102, Tamil Nadu (India)], E-mail: bpcrao@igcar.gov.in; Vaidyanathan, S.; Jayakumar, T.; Raj, Baldev [EMSI Section, NDE Division, Metallurgy and Materials Group, Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research, Kalpakkam 603 102, Tamil Nadu (India)
2008-04-15
The presence of sodium deposits in defective regions of steam generator (SG) tubes of fast-breeder reactors is expected to influence the remote field eddy current (RFEC) signals. By exposing five SG tubes having uniform wall loss grooves to a sodium environment in a specially designed test vessel, changes in the shape of RFEC signals were observed and it was possible to approximate the volume of sodium deposited in defects. An invariant signal parameter was determined for quantitative characterization of defects despite the presence of sodium in the defects.
-
Voltage-current characteristics of multiterminal HVDC-VSC for offshore wind farms
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Gomis-Bellmunt, Oriol [Centre d' Innovacio Tecnologica en Convertidors Estatics i Accionaments (CITCEA-UPC), Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya UPC, Av. Diagonal, 647, Pl. 2., 08028 Barcelona (Spain); IREC Catalonia Institute for Energy Research, Barcelona (Spain); Liang, Jun; Ekanayake, Janaka; Jenkins, Nicholas [School of Engineering, Cardiff University, Queen' s Buildings, The Parade, Cardiff CF24 3AA, Wales (United Kingdom)
2011-02-15
Voltage-current characteristics and equilibrium points for the DC voltages of multiterminal HVDC systems using voltage source converters are discussed. The wind farm rectifiers and grid connected inverters are analyzed through their operating modes, governing equations and graphical characteristics. Using the converter equations and the HVDC grid conductance matrix the equilibrium voltages and currents are found. Case studies are presented considering wind power generation, loss of a converter and voltage sags in the AC grid. (author)
-
Artigao, Estefania; Honrubia-Escribano, Andres; Gomez-Lazaro, Emilio
2017-11-01
Operation and maintenance (O&M) of wind turbines is recently becoming the spotlight in the wind energy sector. While wind turbine power capacities continue to increase and new offshore developments are being installed, O&M costs keep raising. With the objective of reducing such costs, the new trends are moving from corrective and preventive maintenance toward predictive actions. In this scenario, condition monitoring (CM) has been identified as the key to achieve this goal. The induction generator of a wind turbine is a major contributor to failure rates and downtime where doubly-fed induction generators (DFIG) are the dominant technology employed in variable speed wind turbines. The current work presents the analysis of an in-service DFIG. A one-year measurement campaign has been used to perform the study. Several signal processing techniques have been applied and the optimal method for CM has been identified. A diagnosis has been reached, the DFIG under study shows potential gearbox damage.
-
Generation of pure spin currents via spin Seebeck effect in self-biased hexagonal ferrite thin films
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Li, Peng; Ellsworth, David; Chang, Houchen; Janantha, Praveen; Richardson, Daniel; Phillips, Preston; Vijayasarathy, Tarah; Wu, Mingzhong, E-mail: mwu@lamar.colostate.edu [Department of Physics, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 80523 (United States); Shah, Faisal [Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, Indiana 46556 (United States)
2014-12-15
Light-induced generation of pure spin currents in a Pt(2.5 nm)/BaFe{sub 12}O{sub 19}(1.2 μm)/sapphire(0.5 mm) structure is reported. The BaFe{sub 12}O{sub 19} film had strong in-plane uniaxial anisotropy and was therefore self-biased. Upon exposure to light, a temperature difference (ΔT) was established across the BaFe{sub 12}O{sub 19} thickness that gave rise to a pure spin current in the Pt via the spin Seebeck effect. Via the inverse spin Hall effect, the spin current produced an electric voltage across one of the Pt lateral dimensions. The voltage varied with time in the same manner as ΔT and flipped its sign when the magnetization in BaFe{sub 12}O{sub 19} was reversed.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rao, Simha Sandeep; Zhao, Huijuan; Liu, Ming; Peng, Fei; Zhang, Bo
2016-01-01
We adopt a finite element numerical modeling approach to investigate the electromagnetic coupling effect of two parallel electric conductors with tunable electric conductivity σ and magnetic permeability μ . For two parallel conductors C and S ( μ C ⋅ σ C ≤ μ S ⋅ σ S ), we find that the shape of current density profile of conductor S is dependent on the product of μ C ⋅ σ C , while the magnitude is determined by the AC current frequency f . On the other hand, the frequency f affects not only the shape but also the magnitude of the current density profile of conductor C. We further adopt a coplanar model to investigate the signal sensitivity of alternating current potential drop (ACPD) measurement for both surface crack and inner crack detection. We find that with modified coating materials (lower electric conductivity and higher magnetic permeability, compared with the substrate material properties), the crack detection signal sensitivity can be greatly enhanced for both the cracks within the coating and at the coating/substrate interface, where cracks are most commonly encountered in real situations. (paper)
-
Remote field eddy current testing for steam generator inspection of fast reactor
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kobayashi, Noriyasu, E-mail: noriyasu.kobayashi@toshiba.co.jp [Power and Industrial Systems Research and Development Center, Toshiba Corporation, 8, Shinsugita-cho, Isogo-ku, Yokohama 235-8523 (Japan); Ueno, Souichi; Nagai, Satoshi; Ochiai, Makoto [Power and Industrial Systems Research and Development Center, Toshiba Corporation, 8, Shinsugita-cho, Isogo-ku, Yokohama 235-8523 (Japan); Jimbo, Noboru [Isogo Nuclear Engineering Center, Toshiba Corporation, 8, Shinsugita-cho, Isogo-ku, Yokohama 235-8523 (Japan)
2011-12-15
Highlights: Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer We confirmed defect detection performances of remote field eddy current testing. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer It is difficult to inspect outer surface of double wall tube steam generator. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer We used coils with flux guide made of iron-nickel alloy for high sensitivity. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Output voltage of detector coil increased more than 100 times. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer We were able to detect small hole defect of 1mm in diameter on outer surface. - Abstract: We confirmed the defect detection performances of the remote field eddy current testing (RFECT) in order to inspect the helical-coil-type double wall tube steam generator (DWTSG) with the wire mesh layer for the new small fast reactor 4S (Super-Safe, Small and Simple). As the high sensitivity techniques, we tried to increase the direct magnetic field intensity in the vicinity of the inner wall of the tube and decrease the direct magnetic field around the central axis of the tube using the exciter coil with the flux guide made of the iron-nickel alloy. We adopted the horizontal type multiple detector coils with the flux guides arrayed circumferentially to enhance the sensitivity of the radial component. According to the experimental results, the output voltage of the detector coil in the region of indirect magnetic field increased more than 100 times by the application of the exciter and detector coils with the flux guides. Finally, we were able to detect the small hole defect of 1 mm in diameter and 20% of the outer tube thickness in depth over the wire mesh layer by the adoption of the exciter coil and horizontal type multiple detector coils with the flux guides. We also confirmed that the RFECT probe is useful for detecting thinning defects. These experimental results indicated that there is the possibility that we can inspect the double wall tube with the wire mesh layer using the RFECT.
-
The intense neutron generator INGE-1 at the Technical University of Dresden
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bittner, M.; Meisner, A.; Paffrath, E.; Schwiers, H.; Seeliger, D.
1989-01-01
The INGE-1 neutron generator developed for intergal 14 MeV neutron experiments is described. The accelerator produces steady d + ion beam in the current range of 1-10 mA with 120-240 keV energies at the target position. The beam is produced with a combined duoplasmatron focalization system on high voltage. A 30 keV beam is accelerated on final energy by a two-gap acceleration tube. The estimations conducted show that the generator maximum strength can reach up to 2x10 12 s -1 at 10 mA beam current and 220 keV energy. 4 refs
-
Eddy current testing of steam generator tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Neumaier, P.
1981-01-01
A rotating probe is described for improving the inspection of tubes and end plate in steam generators. The method allows a representation of the whole defect, consequently the observer is able to determine directly the type of defect, signal processing in-line or off-line is possible [fr
-
Effect of dose on radiation-induced conductivity in polymers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tyutnev, A.P.; Saenko, V.S.; Pozhidaev, E.D.; Ikhsanov, R.Sh.
2007-01-01
Numerical simulation of radiation-induced conductivity in polymers upon long-term irradiation on the basis of the generalized Rose-Fowler-Vaisberg model, which allows for both dipolar carrier transport and generation of radiation traps during irradiation, was performed. The unusual properties of radiation-induced conductivity, such as the appearance of a maximum on current transients, the absence of a steady state, and a substantial difference between these curves for the first and subsequent irradiation, are rationalized in terms of the formation of free radicals, the major feature of radiolysis in the chemical aspect. This interpretation does not require the involvement of degradation or crosslinking processes, unlike other interpretations that appear in the literature. With the use of low-density polyethylene as an example, it was shown that radiation-induced conductivity both upon pulse and continuous irradiation can satisfactorily be described with the unified set of parameters of the generalized Rose-Fowler-Vaisberg model [ru
-
Steam generator tube integrity program: Phase II, Final report
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kurtz, R.J.; Bickford, R.L.; Clark, R.A.; Morris, C.J.; Simonen, F.A.; Wheeler, K.R.
1988-08-01
The Steam Generator Tube Integrity Program (SGTIP) was a three phase program conducted for the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) by Pacific Northwest Laboratory (PNL). The first phase involved burst and collapse testing of typical steam generator tubing with machined defects. The second phase of the SGTIP continued the integrity testing work of Phase I, but tube specimens were degraded by chemical means rather than machining methods. The third phase of the program used a removed-from-service steam generator as a test bed for investigating the reliability and effectiveness of in-service nondestructive eddy-current inspection methods and as a source of service degraded tubes for validating the Phase I and Phase II data on tube integrity. This report describes the results of Phase II of the SGTIP. The object of this effort included burst and collapse testing of chemically defected pressurized water reactor (PWR) steam generator tubing to validate empirical equations of remaining tube integrity developed during Phase I. Three types of defect geometries were investigated: stress corrosion cracking (SCC), uniform thinning and elliptical wastage. In addition, a review of the publicly available leak rate data for steam generator tubes with axial and circumferential SCC and a comparison with an analytical leak rate model is presented. Lastly, nondestructive eddy-current (EC) measurements to determine accuracy of defect depth sizing using conventional and alternate standards is described. To supplement the laboratory EC data and obtain an estimate of EC capability to detect and size SCC, a mini-round robin test utilizing several firms that routinely perform in-service inspections was conducted.
-
Steam generator tube integrity program: Phase II, Final report
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kurtz, R.J.; Bickford, R.L.; Clark, R.A.; Morris, C.J.; Simonen, F.A.; Wheeler, K.R.
1988-08-01
The Steam Generator Tube Integrity Program (SGTIP) was a three phase program conducted for the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) by Pacific Northwest Laboratory (PNL). The first phase involved burst and collapse testing of typical steam generator tubing with machined defects. The second phase of the SGTIP continued the integrity testing work of Phase I, but tube specimens were degraded by chemical means rather than machining methods. The third phase of the program used a removed-from-service steam generator as a test bed for investigating the reliability and effectiveness of in-service nondestructive eddy-current inspection methods and as a source of service degraded tubes for validating the Phase I and Phase II data on tube integrity. This report describes the results of Phase II of the SGTIP. The object of this effort included burst and collapse testing of chemically defected pressurized water reactor (PWR) steam generator tubing to validate empirical equations of remaining tube integrity developed during Phase I. Three types of defect geometries were investigated: stress corrosion cracking (SCC), uniform thinning and elliptical wastage. In addition, a review of the publicly available leak rate data for steam generator tubes with axial and circumferential SCC and a comparison with an analytical leak rate model is presented. Lastly, nondestructive eddy-current (EC) measurements to determine accuracy of defect depth sizing using conventional and alternate standards is described. To supplement the laboratory EC data and obtain an estimate of EC capability to detect and size SCC, a mini-round robin test utilizing several firms that routinely perform in-service inspections was conducted
-
Gunawan, R.; Sugiarti, E.; Isnaeni; Purawiardi, R. I.; Widodo, H.; Muslimin, A. N.; Yuliasari; Ronaldus, C. E.; Prastomo, N.; Hastuty, S.
2018-03-01
The optical, electrical and structural characteristics of InGaN-based blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) were investigated to identify the degradation of LED before and after current injection. The sample was injected by high current of 200 A/cm2 for 5 and 20 minutes. It was observed that injection of current shifts light intensity and wavelength characteristics that indicated defect generation. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) characterization was carried out in order to clarify the structure degradation caused by defect in active layer which consisted of 14 quantum well with thickness of about 5 nm and confined with barrier layer with thickness of about 12 nm. TEM results showed pre-existing defect in LED before injection with high current. Furthermore, discontinue and edge defect was found in dark spot region of LED after injection with high current.
-
Qualification Practices in Nuclear Industry: Steam Generator Eddy Current Probe Qualification
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Vavrous, M.; Gracin, R.
2010-01-01
Through history of nuclear power plant operation, a large number of nuclear power plant forced outages related to tube failures occurred. It resulted with large amount of repair and outage costs, what initiated implementation of regulated practice of periodical tube examination and tube condition monitoring. Purpose of examinations is to detect existing or potential tube degradations that could affect tube integrity and therefore result in forced outages and unwanted costs related to emergency repair activities and loss of ability for electrical power production. With increased examination activities, additional information about steam generator tube condition became available and additional methods for ensuring tube integrity became available. As the number of examination solutions increased, need for validation and assessment of examination methods occurred. For that purpose, a large number of standards and guidelines with its requirements were implemented in nuclear industry regulatory requirements to ensure that adequately validated examinations are applied. With this purpose, qualification requirements for inspection activities were implemented with other requirements. With progress of technology, progress was also achieved in examination methods and more advanced examination methods and advanced inspection systems were developed. This advancement is accompanied by advancement in regulatory requirements regarding inspection and monitoring of tube integrity and condition. Ultimate goal of implementation of qualification processes and its requirements in all aspects of nuclear industry is to achieve minimal rate of forced outages, which would ensure maximum electrical power production capabilities and maximum optimization of operational costs while maintaining safe operation in accordance with environmental policies. This article will focus on qualification of steam generator eddy current bobbin probe.(author).
-
Evaluation of the eddy-current method for the inspection of steam generator tubing: denting
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brown, S.D.; Flora, J.H.
1977-01-01
Continued evaluation of existing eddy-current in-service inspection (ISI) methods for steam generator tubing has emphasized the effects of denting. Denting is a circumferential deformation of the tube in the support region as a result of the formation of a magnetite, Fe 3 O 4 , corrosion product on the carbon steel tube support plate in the crevice between the support plate and the tube wall. The effects of denting on eddy current inspection are twofold: (1) The detection and measurement of defects in the dented region is hampered by the distortion of the eddy-current response signals caused by the dents and (2) large dents may prevent the passage of high fill factor probes forcing the inspection teams to use a smaller probe in undented regions. Unless appropriate measures are taken, less reliable detection of defects and estimation of their depth can result. The report presents an experimental evaluation of existing eddy-current ISI methods when used to inspect dented regions. Tubes were mechanically dented to simulate various degrees of service induced denting. These tubes were then inserted in carbon steel tube support plates and the crevice region between the support plate and tube was subsequently packed with powdered magnetite. Diametral dent sizes considered during this program varied between 1 and 10 mils. Eddy-current signal patterns and strip chart recordings were obtained using a variety of test parameters, such as frequency, phase rotation and coil configuration, on tube samples containing various degrees of denting and with several types of defects in the dented system
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Shaw, Joseph E.; Perumal, Ajay; Bradley, Donal D. C.; Stavrinou, Paul N.; Anthopoulos, Thomas D., E-mail: t.anthopoulos@ic.ac.uk [Department of Physics and Centre for Plastic Electronics, Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom)
2016-05-21
We use conductive atomic force microscopy (CAFM) to study the origin of long-range conductivity in model transparent conductive electrodes composed of networks of reduced graphene oxide (rGO{sub X}) and silver nanowires (AgNWs), with nanoscale spatial resolution. Pristine networks of rGO{sub X} (1–3 monolayers-thick) and AgNWs exhibit sheet resistances of ∼100–1000 kΩ/□ and 100–900 Ω/□, respectively. When the materials are deposited sequentially to form bilayer rGO{sub X}/AgNW electrodes and thermally annealed at 200 °C, the sheet resistance reduces by up to 36% as compared to pristine AgNW networks. CAFM was used to analyze the current spreading in both systems in order to identify the nanoscale phenomena responsible for this effect. For rGO{sub X} networks, the low intra-flake conductivity and the inter-flake contact resistance is found to dominate the macroscopic sheet resistance, while for AgNW networks the latter is determined by the density of the inter-AgNW junctions and their associated resistance. In the case of the bilayer rGO{sub X}/AgNWs' networks, rGO{sub X} flakes are found to form conductive “bridges” between AgNWs. We show that these additional nanoscopic electrical connections are responsible for the enhanced macroscopic conductivity of the bilayer rGO{sub X}/AgNW electrodes. Finally, the critical role of thermal annealing on the formation of these nanoscopic connections is discussed.
-
Influence of short-term solar disturbances on the fair weather conduction current
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Elhalel Gal
2014-01-01
Full Text Available The fair weather atmospheric electrical current (Jz couples the ionosphere to the lower atmosphere and thus provides a route by which changes in solar activity can modify processes in the lower troposphere. This paper examines the temporal variations and spectral characteristics of continuous measurements of Jz conducted at the Wise Observatory in Mitzpe-Ramon, Israel (30°35′ N, 34°45′ E, during two large CMEs, and during periods of increased solar wind density. Evidence is presented for the effects of geomagnetic storms and sub-storms on low latitude Jz during two coronal mass ejections (CMEs, on 24–25th October 2011 and 7–8th March 2012, when the variability in Jz increased by an order of magnitude compared to normal fair weather conditions. The dynamic spectrum of the increased Jz fluctuations exhibit peaks in the Pc5 frequency range. Similar low frequency characteristics occur during periods of enhanced solar wind proton density. During the October 2011 event, the periods of increased fluctuations in Jz lasted for 7 h and coincided with fluctuations of the inter-planetary magnetic field (IMF detected by the ACE satellite. We suggest downward mapping of ionospheric electric fields as a possible mechanism for the increased fluctuations.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Anitha Karthikeyan
2018-03-01
Full Text Available In this paper we derived the fractional order model of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator (PMSG from its integer model. The PMSG was employing a shaft sensor for the speed sensing and control. But this sensor would increase the hardware complexity as well as the cost of the system. Hence we have developed a Fractional order Nonlinear adaptive control method for speed and current tracking of the PMSG. The objective of an adaptive controller is to first define a virtual control state and force it to become a stabilizing function in accordance with a corresponding error dynamics. In order to study the Lyapunov exponents of the fractional order controller, we proposed a new method which would remove the complexity of finding the sign of the Lyapunov first derivative. The Fractional order control scheme is implemented in LabVIEW for simulation results. The simulation results indicated that the estimated rotor position and speed correspond to their actual values well. Keywords: Chaos suppression, Fractional order systems, Permanent magnet synchronous generator, Speed and current control, Lyapunov stability
-
A new high current laboratory and pulsed homopolar generator power supply at the University of Texas
Floyd, J. E.; Aanstoos, T. A.
1984-03-01
The University of Texas at Austin is constructing a facility for research in pulse power technology for the Center for Electromechanics at the Balcones Research Center. The facility, designed to support high-current experiments, will be powered by six homopolar generators, each rated at 10 MJ and arranged to allow matching the requirements of resistive and inductive loads at various voltage and current combinations. Topics covered include the high bay, the power supply configuration and parameters, the speed and field control, and the magnetic circuit. Also considered are the removable air-cooled brushes, the water-cooled field coils, the hydraulic motor sizing and direct coupling, the low-impedance removable field coils, and the hydrostatic bearing design.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Witalis, E.A.
1965-12-01
Rigorous derivations are given of the basic equations and methods available for the analysis of transverse MHD flow when Hall currents are not suppressed. The gas flow is taken to be incompressible and viscous with uniform tensor conductivity and arbitrary magnetic Reynold's number. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the flow and has variable strength. Analytical solutions can be obtained either in terms of the induced magnetic field or from two types of electric potential. The relevant set of suitable simplifications, restrictive conditions and boundary value considerations for each method is given
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Witalis, E A
1965-12-15
Rigorous derivations are given of the basic equations and methods available for the analysis of transverse MHD flow when Hall currents are not suppressed. The gas flow is taken to be incompressible and viscous with uniform tensor conductivity and arbitrary magnetic Reynold's number. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the flow and has variable strength. Analytical solutions can be obtained either in terms of the induced magnetic field or from two types of electric potential. The relevant set of suitable simplifications, restrictive conditions and boundary value considerations for each method is given.