
Sample records for vlf emissions observed
-
On the observations of unique low latitude whistler-triggered VLF/ELF emissions
Altaf, M.; Singh, K. K.; Singh, A. K.; Lalmani
A detailed analysis of the VLF/ELF wave data obtained during a whistler campaign under All India Coordinated Program of Ionosphere Thermosphere Studies (AICPITS) at our low latitude Indian ground station Jammu (geomag. lat. = 22° 26‧ N, L = 1.17) has yielded two types of unusual and unique whistler-triggered VLF/ELF emissions. These include (1) whistler-triggered hook emissions and (2) whistler-triggered long enduring discrete chorus riser emissions in VLF/ELF frequency range during night time. Such types of whistler-triggered emissions have not been reported earlier from any of the ground observations at low latitudes. In the present study, the observed characteristics of these emissions are described and interpreted. Dispersion analysis of these emissions show that the whistlers as well as emissions have propagated along a higher geomagnetic field line path with L-values lying ∼L = 4, suggesting that these triggered emissions are to be regarded as mid-latitude emissions. These waves could have propagated along the geomagnetic field lines either in a ducted mode or in a pro-longitudinal (PL) mode. The measured intensity of the triggered emissions is almost equal to that of the source waves and does not vary throughout the period of observation on that day. It is speculated that these emissions may have been generated through a process of resonant interaction of the whistler waves with energetic electrons. Parameters related to this interaction are computed for different values of L and wave amplitude. The proposed mechanism explains some aspects of the dynamic spectra.
-
Numerical simulation of whistler-triggered VLF emissions observed in Antartica
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nunn, D. [Southhampton Univ., Southhampton (United Kingdom); Smith, A.J. [British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge (United Kingdom)
1996-03-01
The authors have extracted from VLF databases from British Antarctica Survey data taken at Halley and Faraday stations, examples of whistler-triggered emissions (WTE). The WTE are relatively narrow band emissions triggered by natural background whistlers undergoing nonlinear wave particle interactions generally in the equatorial regions. They occur with either rising or falling frequency relative to the triggering waves. Using a Vlasov type code the authors are able to simulate the types of emissions which are observed. 24 refs., 8 figs., 3 tabs.
-
Some unusual discrete VLF emissions observed at a low-latitude ground station at Agra
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. Singh
1997-08-01
Full Text Available A detailed analysis of the VLF emissions data obtained during occasional whistler campaigns at the low-latitude ground station Agra (geomagnetic latitude 17°1' N, L = 1.15 has yielded some unusual discrete VLF emissions of the rising type. These include (1 emissions occurring at time intervals increasing in ge ommetrical progression, (2 emissions occuring simulta neously in different frequency ranges and (3 emissions observed during daytime. In the present study, the observed characteristics of these emissions are described and interpreted. It is shown that the increasing time delay between different components of the emissions match closely with the propagation time delays between different hops of a whistler of dispersion 19 s1/2, the unusual occurrence of the emissions in two different frequency ranges approximately at the same time may possibly be linked with their generation at two different locations, and the occurrence of emissions during daytime may be due to propagation under the influence of equatorial anomaly.
-
World map of ELF/VLF emissions as observed by a low-orbiting satellite
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Parrot, M.
1990-01-01
Statistical studies were performed of the intensities of the ELF/VLF emissions observed by the low-orbiting satellite AUREOL-3. Data were obtained from filterbanks and the frequency range of observations extends from a few tens of Hz up to 15 kHz. The most important phenomena observed are ELF hiss and VLF hiss. Electric and magnetic components are used. Thus, representation of the waves intensities in geographical coordinates was made at different frequencies. The relative ability of natural waves (whistler, hiss) and man-made waves, such as powerful VLF transmitters or powerline harmonic radiations (PLHR), to precipitate particles in the slot region, is studied. Using geomagnetical representation, it is shown that ELF hiss is maximum between 06 and 20 Magnetic Local Time and in the invariant latitude range 50 0 -70 0 as usual, but geographic representation indicates that the waves are intensified at the longitudes of VLF transmitters and near the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). The SAA plays a dominant role in the localization of the strongest ELF hiss. Weakest intensities are observed to the east of the SAA. As to the VLF hiss, the maximum intensity is related to regions of enhanced thunderstorm activity, and may be influenced by powerline harmonic radiations (PLHR) over USA. Comparisons with past work, experimental as well as theoretical, are made
-
VLF emissions in the Venus foreshock - Comparison with terrestrial observations
Crawford, G. K.; Strangeway, R. J.; Russell, C. T.
1993-01-01
An examination is conducted of ELF/VLF emissions observed in the solar wind upstream of the Venus shock, for the 100 Hz-30 kHz range, using data from the Pioneer Venus Orbiter's electric field detector and magnetometer instruments. Detailed comparisons are made with terrestrial measurements for both the electron and ion foreshocks. The results obtained support the Crawford et al. (1990) identification of the Venus electron foreshock emissions as electron plasma oscillations, whose waves are generated in situ and act to isotropize the electron distributions.
-
Some unusual discrete VLF emissions observed at a low-latitude ground station at Agra
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. Singh
Full Text Available A detailed analysis of the VLF emissions data obtained during occasional whistler campaigns at the low-latitude ground station Agra (geomagnetic latitude 17°1' N, L = 1.15 has yielded some unusual discrete VLF emissions of the rising type. These include (1 emissions occurring at time intervals increasing in ge ommetrical progression, (2 emissions occuring simulta neously in different frequency ranges and (3 emissions observed during daytime. In the present study, the observed characteristics of these emissions are described and interpreted. It is shown that the increasing time delay between different components of the emissions match closely with the propagation time delays between different hops of a whistler of dispersion 19 s1/2, the unusual occurrence of the emissions in two different frequency ranges approximately at the same time may possibly be linked with their generation at two different locations, and the occurrence of emissions during daytime may be due to propagation under the influence of equatorial anomaly.
-
Auroral pulsations and accompanying VLF emissions
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. R. Tagirov
Full Text Available Results of simultaneous TV observations of pulsating auroral patches and ELF-VLF-emissions in the morning sector carried out in Sodankylä (Finland on February 15, 1991 are presented. Auroral pulsating activity was typical having pulsating patches with characteristic periods of about 7 s. Narrow-band hiss emissions and chorus elements at intervals of 0.3–0.4 s formed the main ELF-VLF activity in the frequency range 1.0–2.5 kHz at the same time. The analysis of auroral images with time resolution of 0.04 s allowed perfectly separate analysis of spatial and temporal variations in the auroral luminosity. Mutual correspondence between the behaviour of the luminous auroral patches and the appearance of ELF noise type hiss emissions and VLF chorus trains was found in two intervals chosen for analysis. While the hiss emissions were associated with the appearance of luminosity inside a limited area close to the zenith, the structured VLF emissions were accompanied by rapid motion of luminosity inside the area. The spatial dimension of the pulsating area was about 45–50 km and luminosity propagated inside it with velocity of about 10–12 kms. We discuss a new approach to explain the 5–15 s auroral pulsation based on the theory of flowing cyclotron maser and relaxation characteristics of ionosphere.
Key words. Magnetospheric physics (auroral phenomena; magnetosphere-ionosphere interactions · Space plasma physics (wave-particle interactions -
VLF emissions and whistlers observed during geomagnetic storms
Ondoh, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Nishizaki, R.; Nagayama, M.
1974-01-01
Whistler-triggered emissions and a narrowband hiss are described which were observed over Japan by ISIS 2 during the main phase of the geomagnetic storm of August 9, 1972. The characteristics of the narrowband hiss and increases in the whistler rate during the storm are discussed, and the ISIS-2 data are compared with data on whistler cutoffs and VLF noise breakups obtained by OGO 4 and Alouette I. Since the whistlers and narrowband hiss are usually observed inside and outside the plasmapause, it is thought that the plasmapause may have been located near the low-latitude end of the narrowband hiss during the main phase of the storm. It is suggested that the increases in the whistler rate may have been caused by the formation of whistler ducts in the disturbed plasmapause.
-
Quasi-periodic VLF emissions observed during daytime at a low ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
at a low latitude Indian ground station Jammu. K K Singh1, J .... Figure 4. Typical example of pulsing VLF hiss emission of longer period recorded during daytime at Jammu on 20 ..... Further,. Ward (1983) also paid attention to a certain simi-.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Belov, A. S.; Markov, G. A.; Ryabov, A. O.; Parrot, M.
2012-01-01
The characteristics of the plasma-wave disturbances stimulated in the near-Earth plasma by powerful VLF radiation from ground-based transmitters are investigated. Radio communication VLF transmitters of about 1 MW in power are shown to produce artificial plasma-wave channels (density ducts) in the near-Earth space that originate in the lower ionosphere above the disturbing emission source and extend through the entire ionosphere and magnetosphere of the Earth along the magnetic field lines. Measurements with the onboard equipment of the DEMETER satellite have revealed that under the action of emission from the NWC transmitter, which is one of the most powerful VLF radio transmitters, the generation of quasi-electrostatic (plasma) waves is observed on most of the satellite trajectory along the disturbed magnetic flux tube. This may probably be indicative of stimulated emission of a magnetospheric maser.
-
Combined VLF and VHF lightning observations of Hurricane Rita landfall
Henderson, B. G.; Suszcynsky, D. M.; Wiens, K. C.; Hamlin, T.; Jeffery, C. A.; Orville, R. E.
2009-12-01
Hurricane Rita displayed abundant lightning in its northern eyewall as it made landfall at 0740 UTC 24 Sep 2005 near the Texas/Louisiana border. For this work, we combined VHF and VLF lightning data from Hurricane Rita, along with radar observations from Gulf Coast WSR-88D stations, for the purpose of demonstrating the combined utility of these two spectral regions for hurricane lightning monitoring. Lightning is a direct consequence of the electrification and breakdown processes that take place during the convective stages of thunderstorm development. As Rita approached the Gulf coast, the VHF lightning emissions were distinctly periodic with a period of 1.5 to 2 hours, which is consistent with the rotational period of hurricanes. VLF lightning emissions, measured by LASA and NLDN, were present in some of these VHF bursts but not all of them. At landfall, there was a significant increase in lightning emissions, accompanied by a significant convective surge observed in radar. Furthermore, VLF and VHF lightning source heights clearly increase as a function of time. The evolution of the IC/CG ratio is consistent with that seen in thunderstorms, showing a dominance of IC activity during storm development, followed by an increase in CG activity at the storm’s peak. The periodic VHF lightning events are correlated with increases in convective growth (quantified by the volume of radar echo >40 dB) above 7 km altitude. VLF can discriminate between lightning types, and in the LASA data, Rita landfall lightning activity was dominated by Narrow Bi-polar Events (NBEs)—high-energy, high-altitude, compact intra-cloud discharges. The opportunity to locate NBE lightning sources in altitude may be particularly useful in quantifying the vertical extent (strength) of the convective development and in possibly deducing vertical charge distributions.
-
Frequency-time behavior of artificially stimulated vlf emissions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Stiles, G.S.; Helliwell, R.A.
1975-01-01
Artificially stimulated VLF emissions (ASE's) are emissions triggered in the magnetosphere by the whistler mode signals from VLF transmitters. These emissions may be separated into two classes, rising and falling, depending on whether the final value of df/dt is positive or negative. Several hundred ASE's triggered by three transmitters have been analyzed using the fast Fourier transform with a filter spacing of 25 Hz and an effective filter width of about 45 Hz. The study was limited to the initial frequency-time behavior of ASE's. Averages taken over many events reveal that both rising and falling tones show the same initial behavior. The emissions begin at the frequency of the triggering signal. Both tones initially rise in frequency, falling tones reversing slope at a point 25--300 Hz above the triggering signal. The slope of rising tones, particularly those triggered by NAA, often abruptly levels off in this same frequency range; as a result, a short (approximately 40 ms) plateau is formed that precedes the final rising phase. The initial frequency offset commonly observed in individual events appears to result from the frequent coincidence with this plateau of a peak in amplitude. Emissions stimulated by all three transmitters show essentially the same features; this finding indicates that their frequency behavior does not depend strongly on transmitter power. The process appears to be asymmetric in frequency; no evidence of initial growth below the triggering frequency has been found. (U.S.)
-
VLF Observation of Long Ionospheric Recovery Events
Cotts, B. R.; Inan, U. S.
2006-12-01
On the evening of 20 November 1992, three early/fast events were observed on the great circle path (GCP) from the NAU transmitter in Puerto Rico to Gander (GA), Newfoundland. These events were found to have significantly longer recovery times (up to 20 minutes) than any previously documented events. Typical early/fast events and Lightning-induced Electron Precipitation (LEP) events affect the D-region ionosphere near the night-time VLF-reflection height of ~85 km and exhibit recovery to pre-event levels of gigantic jets. In this context, preliminary results indicate that the lightning-associated VLF long recovery events appear to be more common in oceanic thunderstorms. In this paper, we present occurrence statistics and other measured properties of VLF long recovery events, observed on all-sea based and land based VLF great circle paths.
-
Disturbance phenomena in VLF standard radio wave observation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Muraoka, Yoshikazu
1977-01-01
Storm aftereffect, i.e. the phase disturbance after initiation of a magnetic storm has been revealed in the observation of VLF standard radio waves. In VLF long distance propagation at middle latitudes (L - 3), the phase disturbance for several days after the initiation of a magnetic storm is due to electron fall from the radiation belt. This has been confirmed by the comparison with electron flux detected by an artificial satellite. The correlations between VLF phase disturbance and magnetism activity or ionosphere absorption are described. The relation between winter anomaly and phase disturbance is also discussed. (Mori, K.)
-
New type of ensemble of quasi-periodic, long-lasting VLF emissions at the auroral zone
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Manninen
2012-12-01
Full Text Available A new type of the series of quasi-periodic (QP very low frequency (VLF emissions in frequency range of 1–5 kHz, and not associated with geomagnetic pulsations, has been discovered at auroral latitudes (L = 5.3 during the Finnish VLF campaign (held in December 2011. At least five unusually spectacular events, each with a duration of several hours, have been observed during the night under conditions of quiet geomagnetic activity (Kp = 0–1, although QPs usually occur during the daytime. Contrary to the QP emissions typically occurring during the day, the spectral structure of these QP events represented an extended, complicated sequence of repeated discrete rising VLF signals. Their duration was about 2–3 min each, with the repetition periods ranging from ~1 min to ~10 min. Two such nighttime non-typical events are reported in this paper. The fine structure of the separated QP elements may represent a mixture of the different frequency band signals, which seem to have independent origins. It was found that the periodic signals with lower frequency appear to trigger the strong dispersive upper frequency signals. The temporal dynamics of the spectral structure of the QPs studied were significantly controlled by some disturbances in the solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF. This finding is very important for future theoretical investigations because the generation mechanism of this new type of QP emissions is not yet understood.
-
Building and Testing a Portable VLF Receiver
McLaughlin, Robert; Krause, L.
2014-01-01
Unwanted emissions or signal noise is a major problem for VLF radio receivers. These can occur from man made sources such as power line hum, which can be prevalent for many harmonics after the fundamental 50 or 60 Hz AC source or from VLF radio transmissions such as LORAN, used for navigation and communications. Natural emissions can also be detrimental to the quality of recordings as some of the more interesting natural emissions such as whistlers or auroral chorus may be drowned out by the more common sferic emissions. VLF receivers must selectively filter out unwanted emissions and amplify the filtered signal to a record-able level without degrading the quality.
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Hayosh, Mykhaylo; Pasmanik, D. L.; Demekhov, A. G.; Santolík, Ondřej; Parrot, M.; Titova, E. E.
2013-01-01
Roč. 118, č. 7 (2013), s. 4523-4533 ISSN 2169-9380 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GAP209/11/2280; GA MŠk LH12231 Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : quasi-periodic ELF/VLF emission s in the magnetosphere * wave-particle interactions * demeter spacecraft measurements * whistler-mode waves Subject RIV: DG - Athmosphere Sciences, Meteorology Impact factor: 3.440, year: 2013 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jgra.50179/abstract
-
Spectral characteristics of VLF sferics associated with TGFs
Mezentsev, Andrew; Lehtinen, Nikolai; Ostgaard, Nikolai; Perez-Invernon, Javier; Cummer, Steven
2017-04-01
between the satellite measurements and radio recordings of TGFs. Distances from the analyzed TGF sources to the Duke VLF receiver range from 2000 to 4000 km. This involves the consideration of the propagation effects in the Earth-ionosphere wave guide (EIWG). The EIWG transfer function was calculated for each event using the full wave propagation method. Thus, the modeled energy spectrum of the TGF source current moment can be transformed into how it would look like for the Duke VLF receiver. Comparative analysis of the energy spectra of modeled TGF radio emission and associated VLF sferics for 20 events with WWLLN confirmed location and 15 events without WWLLN detection shows that 31 of these 35 events exhibit a good fit between the modeled and observed spectra, with only 4 exceptions, that look inconsistent with the proposed model. The second cutoff frequency fB with the number of avalanches Np define the shape of the observed energy spectrum of the sferic emitted by a TGF. Multiplicity of the TGF serves as another important discriminative factor that shows the consistency between the modeled and observed spectra. The results show that the number of avalanches Np should be relatively small, of the order of 30-300, to make the modeled TGF radio emission consistent with the observed VLF sferics. These small values of Np give an argument in favor of the leader model of the TGF production, and also might refer to streamers in the streamer zone of the leader tip, as candidates, producing initial seeding pulses that develop into RREAs, generating a TGF. [1]. Mezentsev, A., Østgaard, N., Gjesteland, T., Albrechtsen, K., Lehtinen, N., Marisaldi, M., Smith, D., and Cummer, S. (2016), Radio emissions from double RHESSI TGFs, J. Geophys. Res., 121, doi:10.1002/2016JD025111 [2]. Dwyer, J. R., and S. A. Cummer (2013), Radio emissions from terrestrial gamma ray flashes, J. Geophys. Res., 118, doi:10.1002/jgra.50188.
-
VLF imaging of the Venus foreshock
Crawford, G. K.; Strangeway, R. J.; Russell, C. T.
1993-01-01
VLF plasma wave measurements obtained from the Pioneer Venus Orbiter Electric Field Detector (OEFD) have been used to construct statistical images of the Venus foreshock. Our data set contains all upstream measurements from an entire Venus year (approximately 200 orbits). Since the foreshock VLF characteristics vary with Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF) orientation we restrict the study to IMF orientations near the nominal Parker spiral angle (25 to 45). Our results show a strong decrease in 30 kHz wave intensity with both foreshock depth and distance. There is also an asymmetry in the 30 kHz emissions from the upstream and downstream foreshocks. The ion foreshock is characterized by strong emissions in the 5.4 kHz OEFD channel which are positioned much deeper in the foreshock than expected from terrestrial observations. No activity is observed in the region where field aligned ion distributions are expected. ULF wave activity, while weaker than at Earth, shows similar behavior and may indicate the presence of similar ion distributions.
-
Observation of magntosphere and ionosphere through HF and VLF standard waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ogawa, Toru
1974-01-01
The observation of magnetosphere and ionosphere through HF and VLF standard waves is a part of the IMS research subject I on the structure and dynamics of the earth's plasmasphere. By receiving the HF and VLF standard waves with high accuracy, and through the changes of the phase and frequency, continuous observation is made concerning the lower plasmasphere at equator and middle/low latitudes and the upper layers in polar regions. In this way, the dynamic state at the time of disturbance such as magnetic storm can be explored. The following matters are described: features of standard-wave observation, purpose and observation plans, the exhcange of data with overseas countries and satellites, and the results of observation expected. (Mori, K.)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Rozhnoi
2008-10-01
Full Text Available In our earlier papers we have found the effect of VLF transmitter signal depression over epicenters of the large earthquakes from observation on the French DEMETER satellite that can be considered as new method of global diagnostics of seismic influence on the ionosphere. At present paper we investigate a possibility VLF signal-ionospheric turbulence interaction using additional characteristic of VLF signal-spectrum broadening. This characteristic is important for estimation of the interaction type: linear or nonlinear scattering. Our main results are the following:
– There are two zones of increased spectrum broadening, which are centered near magnetic latitudes Φ=±10° and Φ=±40°. Basing on the previous case study research and ground ionosonde registrations, probably it is evidence of nonlinear (active scattering of VLF signal on the ionospheric turbulence. However occurrence rate of spectrum broadening in the middle-latitude area is higher than in the near-equatorial zone (~15–20% in comparison with ~100% in former area that is probably coincides with the rate of ionospheric turbulence.
– From two years statistics of observation in the selected 3 low-latitude regions and 1 middle-latitude region inside reception area of VLF signal from NWC transmitter we find a correlation of spectrum broadening neither with ion-cyclotron noise (f=150–500 Hz, which possibly means poor representation of the turbulence by the noise due to its mixture with natural ELF emission (which correlates with whistler, nor with magnetic storm activity.
– We find rather evident correlation of ion-cyclotron frequency noise, VLF signal depression and weak correlation of spectrum broadening with seismicity in the middle-latitude region over Japan. But in the low-latitude regions we do not find such a correlation. Statistical decrease of VLF signal supports our previous case study results. However rather weak spectrum broadening -
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Foster, J.C.; Rosenberg, T.J.
1976-01-01
Correlated bursts of bremsstrahlung X rays and VLF emissions were recorded for approx.25 min at Siple Station, Antarctica, on January 2, 1971. The burst occurred quasi-periodically with spectral power predominantly in the period range 4--12 s. A typical VLF burst consisted of 3--5 rising elements of approx.0.1-s duration separated by approx.0.15 s and was confined to the frequency range 1.5--3.8 kHz. Evidence is presented to show that the bursts were triggered by the low-frequency tail of whistlers propagating from the northern hemisphere. The interpretation of the observations in terms of an equatorial cyclotron resonance interaction occurring at the outer edge of the plasmapause on the L=4.2 field line, offered initially by Rosenberg et al. (1971), is given further support by the more extensive analysis presented here of the electron energy-wave frequency relationship in the bursts and the propagation times for the resonant waves and electrons. It is inferred from the X ray data that the equatorial flux of trapped electrons was probably anisotropic and near the stable trapping limit at the time of this event. It is suggested that an important effect of the trigger signal is the increase of the anisotropy of the resonant electrons. Wave growth rates calculated in the random phase approximation for electron pitch angle distributions that might apply in this event can explain certain features of the VLF and precipitation data during and between the bursts
-
VLF Wave Properties During Geomagnetic Storms
Blancarte, J.; Artemyev, A.; Mozer, F.; Agapitov, O. V.
2017-12-01
Whistler-mode chorus is important for the global dynamics of the inner magnetosphere electron population due to its ability to scatter and accelerate electrons of a wide energy range in the outer radiation belt. The parameters of these VLF emissions change dynamically during geomagnetic storms. Presented is an analysis of four years of Van Allen probe data, utilizing electric and magnetic field in the VLF range focused on the dynamics of chorus wave properties during the enhancement of geomagnetic activity. It is found that VLF emissions respond to geomagnetic storms in more complicated ways than just by affecting the waves' amplitude growth or depletion. Oblique wave amplitudes grow together with parallel waves during periods of intermediate geomagnetic activity, while the occurrence rate of oblique waves decreases during larger geomagnetic storms.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
NaitAmor, S.; AlAbdoadaim, M. A.; Cohen, M. B.
2010-01-01
) were captured over the Mediterranean Sea by cameras at Pic du Midi (42.94°N, 0.14°E) and at Centre de Recherches Atmospheriques (CRA) in southwestern France (43.13°N, 0.37°E). The cameras observations are compared to collected VLF AWESOME data. We consider early VLF perturbations observed on 12-13, 17...
-
VLF Technique and Science in India
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chakravarty, S. C.
2010-01-01
Since IGY period (1957-58), natural and artificially produced Very Low Frequency (VLF) electromagnetic radiations are being recorded at large number of ground stations and on board satellites to study various wave-plasma interactive phenomena. The terrestrial propagation of these VLF radio waves are primarily enabled through the earth ionosphere wave guide (EIWG) system to long horizontal distances around the globe and ducted along the geomagnetic field lines into the conjugate hemisphere through the ionosphere-plasmasphere-magnetosphere routes. The time frequency spectra indicate presence of dispersion and various cut-off frequencies providing several types of received signals like whistlers, chorus, tweeks, hiss, hisslers etc., which can be heard on an earphone with distinguishing audio structures. While the VLF technique has been a very effective tool for studying middle and high latitude phenomena, the importance of various anomalous characteristics over the Indian low latitude stations provide potentially new challenges for their scientific interpretation and modelling. The ducted and non-ducted propagation, low latitude TRIMPI/TLE effects, D-region ionisation perturbations due to solar and stellar x- and γ ray emissions and detecting precursors of seismic activities are a few problems which will gain from low latitude studies. Since the conjugate points of Indian stations lie over the Indian oceanic region, the VLF propagation effects would be relatively noise free to observe rare and new phenomena requiring better SNR to detect such changes. The VLF signals emanating from the active seismic zones would require high sensitivity of the system and suitable network of transmitting and receiving stations. Results obtained on whistlers and related studies from a number of Indian stations covering geomagnetic latitude range between 13-24 deg. N are mentioned and reviewed in the background of theoretical understanding of the lightning return stroke signal elements
-
Observation of very low frequency emissions at Indian Antarctic ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
Recently, we have succeeded in recording VLF emissions at the Indian Antarctic station, Maitri (geom. lat. 62° S, geom. long. 57.23°E, =4.5) using a T-type antenna, pre/main amplifiers and digital audio tape recorder. VLF hiss in the frequency ranges 11–13 kHz and 13–14.5 kHz and some riser-type emissions in the ...
-
Electron and VLF travel time differences for wave-particle interactions at L=4: Pt. 2
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rash, J.P.S.; Scourfield, M.W.J.; Dougherty, M.K.
1984-01-01
The cyclotron resonance or gyroresonance interaction has been widely invoked as a generation mechanism for discrete VLF emissions and plasmaspheric hiss. This interaction involves electrons and VLF waves travelling in opposite directions along a geomagnetic field line. We examine, for an interaction region in the equatorial plane at L=4, the energy of the resonant electrons as a function of VLF wave frequency and ambient equatorial electron density. Then for two different spatial configurations of the interaction and two standard plasma distribution models we examine the difference in travel times to a ground-based observer in the Southern hemisphere for the electrons and waves taking part in the interaction. This difference in travel times is shown as a function of VLF wave frequency and equatorial electron density. The results, and their significance for observations of auroral electrons and VLF at Sanae, Antarctica, are discussed and compared with similar results for the Cerenkov interaction discussed in an earlier paper
-
A survey of ELF and VLF research on lightning-ionosphere interactions and causative discharges
Inan, U. S.; Cummer, S. A.; Marshall, R. A.
2010-06-01
Extremely low frequency (ELF) and very low frequency (VLF) observations have formed the cornerstone of measurement and interpretation of effects of lightning discharges on the overlying upper atmospheric regions, as well as near-Earth space. ELF (0.3-3 kHz) and VLF (3-30 kHz) wave energy released by lightning discharges is often the agent of modification of the lower ionospheric medium that results in the conductivity changes and the excitation of optical emissions that constitute transient luminous events (TLEs). In addition, the resultant ionospheric changes are best (and often uniquely) observable as perturbations of subionospherically propagating VLF signals. In fact, some of the earliest evidence for direct disturbances of the lower ionosphere in association with lightning discharges was obtained in the course of the study of such VLF perturbations. Measurements of the detailed ELF and VLF waveforms of parent lightning discharges that produce TLEs and terrestrial gamma ray flashes (TGFs) have also been very fruitful, often revealing properties of such discharges that maximize ionospheric effects, such as generation of intense electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) or removal of large quantities of charge. In this paper, we provide a review of the development of ELF and VLF measurements, both from a historical point of view and from the point of view of their relationship to optical and other observations of ionospheric effects of lightning discharges.
-
Basak, T.; Hobara, Y.
2015-12-01
A major part of the path of the annular solar eclipse of May 20, 2012 (magnitude 0.9439) was over southern Japan. The D-region ionospheric changes associated with that eclipse, led to several degree of observable perturbations of sub-ionospheric very low frequency (VLF) radio signal. The University of Electro-Communications (UEC) operates VLF observation network over Japan. The solar eclipse associated signal changes were recorded in several receiving stations (Rx) simultaneously for the VLF signals coming from NWC/19.8kHz, JJI/22.2kHz, JJY/40.0kHz, NLK/24.8kHz and other VLF transmitters (Tx). These temporal dependences of VLF signal perturbation have been analyzed and the spatio-temporal characteristics of respective sub-ionospheric perturbations has already been studied by earlier workers using 2D-Finite Difference Time Domain method of simulation. In this work, we determine the spatial scale, depth and temporal dependence of lower ionospheric perturbation in consistence with umbral and penumbral motion. We considered the 2-parameter D-region ionospheric model with exponential electron density profile. To model the solar obscuration effect over it, we assumed a generalized space-time dependent 2-dimensional elliptical Gaussian distribution for ionospheric parameters, such as, effective reflection height (h') and sharpness factor (β). The depth (△hmax, △βmax), center of shadow (lato(t), lono(t)) and spatial scale (σlat,lon) of that Gaussian distribution are used as model parameters. In the vicinity of the eclipse zone, we compute the VLF signal perturbations using Long Wave Propagation Capability (LWPC) code for several signal propagation paths. The propagation path characteristics, such as, ground and water conductivity and geomagnetic effect on ionosphere are considered from standard LWPC prescriptions. The model parameters are tuned to set an optimum agreement between our computation and observed positive and negative type of VLF perturbations. Thus
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tanaka, Y.; Hayakawa, M.; Lagoutte, D.; Lefeuvre, F.; Tajima, S.
1987-01-01
Electric and magnetic field wave data acquired on Aureol 3 satellite demonstrate the existence of a spectral broadening effect in which VLF transmitter signals from Alpha station (geographic coordinates, 50.5 degree N, 137 degree E) in USSR undergo a significant spectral broadening on electric fields as they propagate through the ionosphere up to the spacecraft in the altitude range of 500-2,000 km at middle latitudes (L ∼ 2). The spectral broadening phenomena may be divided into two types: (1) spectrally broadened components occurring without any association with ELF/VLF emissions under disturbed ionospheric conditions and (2) spectrally broadened components with predominant sideband structure in association with ELF emissions. Bicoherence computation results suggest a nonlinear mode coupling between the transmitter signal and ELF emission which produces sidebands that are quasi-electrostatic in nature. However, faint spectral broadened components in both types 1 and 2 may be connected with Doppler shift of quasi-electrostatic whistler mode waves with a broad spectrum of k near the resonance cone, due to scattering of the transmitter signals from ionospheric irregularities in the F region
-
Strangeway, R. J.; Crawford, G. K.
1995-01-01
Plasma waves observed in the VLF range upstream of planetary bow shocks not only modify the particle distributions, but also provide important information about the acceleration processes that occur at the bow shock. Electron plasma oscillations observed near the tangent field line in the electron foreshock are generated by electrons reflected at the bow shock through a process that has been referred to as Fast Fermi acceleration. Fast Fermi acceleration is the same as shock-drift acceleration, which is one of the mechanisms by which ions are energized at the shock. We have generated maps of the VLF emissions upstream of the Venus bow shock, using these maps to infer properties of the shock energization processes. We find that the plasma oscillations extend along the field line up to a distance that appears to be controlled by the shock scale size, implying that shock curvature restricsts the flux and energy of reflected electrons. We also find that the ion acoustic waves are observed in the ion foreshock, but at Venus these emissions are not detected near the ULF forshock boundary. Through analogy with terrestrial ion observations, this implies that the ion acoustic waves are not generated by ion beams, but are instead generated by diffuse ion distributions found deep within the ion foreshock. However, since the shock is much smaller at Venus, and there is no magnetosphere, we might expect ion distributions within the ion foreshock to be different than at the Earth. Mapping studies of the terrestrial foreshock similar to those carried out at Venus appear to be necessary to determine if the inferences drawn from Venus data are applicable to other foreshocks.
-
Effect of magnetic field-aligned currents on VLF emissions in the magnetosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kulkarni, V.H.
1988-01-01
The dispersion relation for the electromagnetic electron cyclotron waves in the presence of magnetic field-aligned currents has been obtained. The kinetic distribution of electrons for the main body of plasma with a temperature anisotropy and a loss cone distribution have been considered. In general, it has been seen that the current moving along the direction of resonant electrons reduce the growth rate. This effect has been analysed in the case of magnetospheric plasma to suggest possible correlations between the Birkeland currents and the emissions of very low frequency (VLF) electromagnetic waves. (author). 19 refs
-
Subionospheric VLF signatures and their association with sprites observed during EuroSprite 2003
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Mika, A.; Haldoupis, C.; Marshall, R.A.
2005-01-01
In this study, VLF observations during EuroSprite-2003 are analyzed in connection with many sprites observed above thunderstorms in central France. The sprites were detected with a sensitive camera from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi in the Pyrenees overlooking storms monitored by the French nat...
-
Similar Data Retrieval from Enormous Datasets on ELF/VLF Wave Spectrum Observed by Akebono
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y Kasahara
2010-02-01
Full Text Available As the total amount of data measured by scientific spacecraft is drastically increasing, it is necessary for researchers to develop new computation methods for efficient analysis of these enormous datasets. In the present study, we propose a new algorithm for similar data retrieval. We first discuss key descriptors that represent characteristics of the VLF/ELF waves observed by the Akebono spacecraft. Second, an algorithm for similar data retrieval is introduced. Finally, we demonstrate that the developed algorithm works well for the retrieval of the VLF spectrum with a small amount of CPU load.
-
ELF and VLF signatures of sprites registered onboard the low altitude satellite DEMETER
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Błęcki
2009-06-01
Full Text Available We report the observation of ELF and VLF signature of sprites recorded on the low altitude satellite DEMETER during thunderstorm activity. At an altitude of ~700 km, waves observed on the E-field spectrograms at mid-to-low latitudes during night time are mainly dominated by up-going 0+ whistlers. During the night of 20 July 2007 two sprites have been observed around 20:10:08 UT from the observatory located on the top of the mountain Śnieżka in Poland (50°44'09" N, 15°44'21" E, 1603 m and, ELF and VLF data have been recorded by the satellite at about 1200 km from the region of thunderstorm activity. During this event, the DEMETER instruments were switched in the burst mode and it was possible to register the wave forms. It is shown that the two sprites have been triggered by two intense +CG lightning strokes (100 kA occurring during the same millisecond but not at the same location. Despite the distance DEMETER has recorded at the same time intense and unusual ELF and VLF emissions. It is shown that the whistler wave propagates from the thunderstorm regions in the Earth-ionosphere guide and enters in the ionosphere below the satellite. They last several tens of milliseconds and the intensity of the ELF waveform is close to 1 mV/m. A particularly intense proton whistler is also associated with these emissions.
-
Magnetosphere VLF observation by satellite ISIS
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ondo, Tadanori; Nakamura, Yoshikatsu; Watanabe, Shigeaki; Murakami, Toshimitsu
1978-01-01
On the basis of the VLF (50 Hz -- 30 kHz) electric field data from the satellite ISIS, the following works carried out in The Radio Research Laboratories are described: deuteron whistler and whistler duct, detection of plasmapause by LHR hiss, and the origin of 5 kHz hiss at low/middle latitudes. The deuteron whistlers are observable distinctly only at low latitude because of gyro-frequency and the frequency resolution of spectral analyzers. Whistler echo occurs when a whistler moves back and forth through a duct along the line of magnetic force, so it is considered that the ISIS satellite crosses the duct. The variation in ion composition around plasmapause obtained through LHR hiss is explainable by the plasamapause position and the magnetic storm effect on the plasamapause. Concerning the narrow band hiss of 5 kHz +- 1.0 kHz frequently observed on the ground at low/middle latitudes, it may occur around plasmapause, propagate through the ionosphere and then to the ground in waveguide mode, or otherwise, it may occur above the ionosphere and then propagate directly to the ground penetrating through the ionosphere. (J.P.N.)
-
Whistler Triggered Upper Band Chorus Observed in Alaska
Hosseini, P.; Golkowski, M.
2017-12-01
VLF radiation from lightning discharges is one of several sources of energy injection into the inner magnetosphere from the Earth. Lightning discharges initially produce a broadband impulse or `sferic' but after propagation in the dispersive magnetosphere this waveform soon becomes quasi narrow band with the characteristic spectrographic form of the whistler. Most of the lightning induced VLF wave energy injected into the magnetosphere will be unducted with a k-vector which becomes increasingly oblique. Although unducted radiation is ubiquitous throughout the inner magnetosphere, it is generally of a low amplitude due to Landau damping and is not expected to produce strong nonlinear phenomena such as triggered emissions and chorus waves. However, VLF wave energy ducted or trapped in field-aligned plasma density enhancements can have relatively large amplitudes due to focusing and also linear cyclotron resonance growth. Therefore high amplitude ducted whistler waves can trigger a number of complex nonlinear phenomena. These include the triggering of VLF emissions and triggering of VLF hiss or chorus. Such phenomena are generally considered to result from nonlinear electron cyclotron phase trapping. Observation of such VLF emissions triggered by natural whistlers have been reported since the 1970s in Antarctica. We present observations of whistlers triggered upper band chorus emission from Alaska. Dispersion analyze of whistlers determine the L-shell range to be 4.5 clear frequency band gap between upper and lower band of the observed chorus emissions. The observations point to ducted chorus generation in the vicinity of the plasmapause boundary.
-
Sprites and Early ionospheric VLF perturbations
Haldoupis, Christos; Amvrosiadi, Nino; Cotts, Ben; van der Velde, Oscar; Chanrion, Olivier; Neubert, Torsten
2010-05-01
Past studies have shown a correlation between sprites and early VLF perturbations, but the reported correlation varies widely from ~ 50% to 100%. The present study resolves these large discrepancies by analyzing several case studies of sprite and narrowband VLF observations, in which multiple transmitter-receiver VLF links with great circle paths (GCPs) passing near a sprite-producing thunderstorm were available. In this setup, the multiple links act in a complementary way that makes the detection of early VLF perturbations much more probable compared to a single VLF link that can miss several of them, a fact that was overlooked in past studies. The evidence shows that sprites are accompanied by early VLF perturbations in a one-to-one correspondence. This implies that the sprite generation mechanism may cause also sub-ionospheric conductivity disturbances that produce early VLF events. However, the one-to-one "sprite to early" event relationship, if viewed conversely as "early to sprite", appears not to be always reciprocal. This is because the number of early events detected in some cases was considerably larger than the number of sprites. Since the great majority of the early events not accompanied by sprites was caused by positive cloud to ground (+CG) lightning discharges, it is possible that sprites or sprite halos were concurrently present in these events as well but were missed by the sprite-watch detection system. In order for this option to be resolved we need more studies using highly sensitive optical systems capable of detecting weaker sprites, sprite halos and elves.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Muraoka, Y; Murata, H; Sato, T [Hyogo Coll. Of Medicine (Japan). Dept. of Physics
1977-07-01
An attempt is made to investigate the quantitative relationship between VLF phase deviations in SPA (sudden phase anomalies) events and associated solar X-ray fluxes in the 1 to 8 A band during solar flares. The phase deviations (..delta..phi) of the 18.6 kHz VLF wave transmitted from NLK, USA are used in this analysis which were recorded at Nishinomiya, Japan during the period June 1974 to May 1975. The solar X-ray fluxes (F/sub 0/) in the 1 to 8 A band are estimated from fsub(min) variations using the empirical expression given by Sato (J.Geomag.Geoelectr.;27: 95(1975)), because no observed data were available on the 1 to 8 a X-ray fluxes during the period of the VLF observation. The result shows that the normalized phase variation, ..delta..phi/coschisub(min), where chisub(min) represents the minimum solar zenith angle on the VLF propagation path, increases with increasing logF/sub 0/. A theoretical explanation for this is presented assuming that enhanced ionizations produced in the lower ionosphere by a monochromatic solar X-ray emission are responsible for the VLF phase deviations. Also it is found that a threshold X-ray flux to produce a detectable SPA effect is approximately 1.5 x 10/sup -3/ cm/sup -2/ sec/sup -1/ in the 1 to 8 a band.
-
Terrestrial VLF transmitter injection into the magnetosphere
Cohen, M. B.; Inan, U. S.
2012-08-01
Very Low Frequency (VLF, 3-30 kHz) radio waves emitted from ground sources (transmitters and lightning) strongly impact the radiation belts, driving electron precipitation via whistler-electron gyroresonance, and contributing to the formation of the slot region. However, calculations of the global impacts of VLF waves are based on models of trans-ionospheric propagation to calculate the VLF energy reaching the magnetosphere. Limited comparisons of these models to individual satellite passes have found that the models may significantly (by >20 dB) overestimate amplitudes of ground based VLF transmitters in the magnetosphere. To form a much more complete empirical picture of VLF transmitter energy reaching the magnetosphere, we present observations of the radiation pattern from a number of ground-based VLF transmitters by averaging six years of data from the DEMETER satellite. We divide the slice at ˜700 km altitude above a transmitter into pixels and calculate the average field for all satellite passes through each pixel. There are enough data to see 25 km features in the radiation pattern, including the modal interference of the subionospheric signal mapped upwards. Using these data, we deduce the first empirical measure of the radiated power into the magnetosphere from these transmitters, for both daytime and nighttime, and at both the overhead and geomagnetically conjugate region. We find no detectable variation of signal intensity with geomagnetic conditions at low and mid latitudes (L ionospheric heating by one VLF transmitter which modifies the trans-ionospheric absorption of signals from other transmitters passing through the heated region.
-
Quantitative measurement of lightning-induced electron precipitation using VLF remote sensing
Peter, William Bolton
This dissertation examines the detection of lightning-induced energetic electron precipitation via subionospheric Very Low Frequency (VLF) remote sensing. The primary measurement tool used is a distributed set of VLF observing sites, the Holographic Array for Ionospheric/Lightning Research (HAIL), located along the eastern side of the Rocky Mountains in the Central United States. Measurements of the VLF signal perturbations indicate that 90% of the precipitation occurs over a region ˜8 degrees in latitudinal extent, with the peak of the precipitation poleward displaced ˜7 degrees from the causative discharge. A comparison of the VLF signal perturbations recorded on the HAIL array with a comprehensive model of LEP events allows for the quantitative measurement of electron precipitation and ionospheric density enhancement with unprecedented quantitative detail. The model consists of three major components: a test-particle model of gyroresonant whistler-induced electron precipitation; a Monte Carlo simulation of energy deposition into the ionosphere; and a model of VLF subionospheric signal propagation. For the two representative LEP events studied, the model calculates peak VLF amplitude and phase perturbations within a factor of three of those observed, well within the expected variability of radiation belt flux levels. The modeled precipitated energy flux (E>45 keV) peaks at ˜1 x 10-2 [ergs s-1 cm -2], resulting in a peak loss of ˜0.001% from a single flux tube at L˜2.2, consistent with previous satellite measurements of LEP events. Metrics quantifying the ionospheric density enhancement (N ILDE) and the electron precipitation (Gamma) are strongly correlated with the VLF signal perturbations calculated by the model. A conversion ratio Psi relates VLF signal amplitude perturbations (DeltaA) to the time-integrated precipitation (100-300 keV) along the VLF path (Psi=Gamma / DeltaA). The total precipitation (100-300 keV) induced by one of the representative LEP
-
Beating HF waves to generate VLF waves in the ionosphere
Kuo, Spencer; Snyder, Arnold; Kossey, Paul; Chang, Chia-Lie; Labenski, John
2012-03-01
Beat-wave generation of very low frequency (VLF) waves by two HF heaters in the ionosphere is formulated theoretically and demonstrated experimentally. The heater-induced differential thermal pressure force and ponderomotive force, which dominate separately in the D and F regions of the ionosphere, drive an electron current for the VLF emission. A comparison, applying appropriate ionospheric parameters shows that the ponderomotive force dominates in beat-wave generation of VLF waves. Three experiments, one in the nighttime in the absence of D and E layers and two in the daytime in the presence of D and E layers, were performed. X mode HF heaters of slightly different frequencies were transmitted at CW full power. VLF waves at 10 frequencies ranging from 3.5 to 21.5 kHz were generated. The frequency dependencies of the daytime and nighttime radiation intensities are quite similar, but the nighttime radiation is much stronger than the daytime one at the same radiation frequency. The intensity ratio is as large as 9 dB at 11.5 kHz. An experiment directly comparing VLF waves generated by the beat-wave approach and by the amplitude modulation (AM) approach was also conducted. The results rule out the likely contribution of the AM mechanism acting on the electrojet and indicate that beat-wave in the VLF range prefers to be generated in the F region of the ionosphere through the ponderomotive nonlinearity, consistent with the theory. In the nighttime experiment, the ionosphere was underdense to the HF heaters, suggesting a likely setting for effective beat-wave generation of VLF waves by the HF heaters.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Masashi Hayakawa
2013-01-01
Full Text Available By using network observation of subionospheric VLF (very low frequency/LF (low frequency signals in Japan and in Russia, we have found a significant ionospheric perturbation prior to the recent 2011 March 11 Japan earthquake (EQ which occurred at sea proximate to the Tohoku area on the main island (Honshu of Japan was an exceptionally huge plate-type EQ. A remarkable anomaly (with a decrease in the nighttime amplitude and also with enhancement in dispersion was detected on March 5 and 6 along the propagation path from the NLK (Seattle, USA transmitter to Chofu (together with Kochi and Kasugai. We also have observed the corresponding VLF anomaly during a prolonged period of March 1 - 6, with minima in the nighttime amplitude on March 3 and 4 along the path from JJI (Miyazaki, Kyushu to Kamchatka, Russia. This ionospheric perturbation has been discussed extensively with respect to its reliability. (1 How abnormal is this VLF/LF propagation anomaly? (2 What was the temporal evolution of terminator times? (3 Were there any solar-terrestrial effects (especially the effect from geomagnetic storms on the VLF/LF propagation anomaly? (4 The effect of any other EQs and foreshock activities on the VLF/LF anomaly? (5 Were there any correlations with other related phenomena? Finally, (6 are there any other examples of a VLF/LF propagation anomaly for oceanic EQs? We then compared the temporal properties of ionospheric perturbations for this EQ with those of a huge number of inland EQs and compared the corresponding spatial scale with the former result of the same oceanic 2004 Sumatra EQ with nearly the same magnitude. Finally, the generation mechanism of those seismo-ionospheric perturbations is briefly discussed.
-
A quantitative comparison of lightning-induced electron precipitation and VLF signal perturbations
Peter, W. B.; Inan, U. S.
2007-12-01
VLF signal perturbations recorded on the Holographic Array for Ionospheric/Lightning Research (HAIL) are quantitatively related to a comprehensive model of lightning-induced electron precipitation (LEP) events. The model consists of three major components: a test-particle model of gyroresonant whistler-induced electron precipitation, a Monte Carlo simulation of energy deposition into the ionosphere, and a model of VLF subionospheric signal propagation. For the two representative LEP events studied, the model calculates peak VLF amplitude perturbations within a factor of three of those observed, well within the expected variability of radiation belt flux levels. The phase response of the observed VLF signal to precipitation varied dramatically over the course of the two nights and this variability in phase response is not properly reproduced by the model. The model calculates a peak in the precipitation that is poleward displaced ~6° from the causative lightning flash, consistent with observations. The modeled precipitated energy flux (E > 45 keV) peaks at ~1 × 10-2 (ergs s-1 cm-2), resulting in a peak loss of ~0.001% from a single flux tube at L ~ 2.2, consistent with previous satellite measurements of LEP events. The precipitation calculated by the model is highly dependent on the near-loss-cone trapped radiation belt flux levels assumed, and hence our main objective is not to compare the model calculations and the VLF signal observations on an absolute basis but is rather to develop metrics with which we can characterize the VLF signal perturbations recorded on HAIL in terms of the associated precipitation flux. Metrics quantifying the ionospheric density enhancement (N ILDE) and the electron precipitation (Γ) along a VLF signal path are strongly correlated with the VLF signal perturbations calculated by the model. A conversion ratio Ψ, relating VLF signal amplitude perturbations (ΔA) to the time-integrated precipitation (100-300 keV) along the VLF path (�
-
VLF radio wave anomalies associated with the 2010 Ms 7.1 Yushu earthquake
Shen, Xuhui; Zhima, Zeren; Zhao, Shufan; Qian, Geng; Ye, Qing; Ruzhin, Yuri
2017-05-01
The VLF radio signals recorded both from the ground based VLF radio wave monitoring network and the DEMETER satellite are investigated during the 2010 Ms 7.1 Yushu earthquake. The ground-based observations show that the disturbance intensity of VLF wave's amplitude relative to the background gets an enhancement over 22% at 11.9 kHz, 27% at 12.6 kHz and 62% at 14.9 kHz VLF radio wave along the path from Novosibirsk - TH one day before the main shock, as compared to the maximum 20% observed during non-earthquake time. The space based observations indicate that there is a decrease of the signal to noise ratio (SNR) for the power spectral density data of 14.9 kHz VLF radio signal at electric field four days before the main shock, with disturbance intensity exceeding the background by over 5% as compared to the maximum 3% observed during non-earthquake time. The geoelectric field observations in the epicenter region also show that a sharp enhancement from ∼340 to 430 mV/km simultaneously appeared at two monitors 14 days before main shock. The comparative analysis from the ground and space based observations during the earthquake and non-earthquake time provides us convincible evidence that there exits seismic anomalies from the VLF radio wave propagation before the 2010 Ms 7.1 Yushu earthquake. The possible mechanism for VLF radio signal propagation anomaly during 2010 Yushu earthquake maybe related to the change of the geoelectric field nearby the earthquake zone.
-
Rocket experiment on spontaneously and artificially stimulated VLF plasma waves in the ionosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Matsumoto, H.; Miyatake, S.; Kimura, I.
1975-01-01
In situ active experiments on the nonlinear wave-wave and wave-particle interactions in the ionospheric plasma were performed by a Japanese sounding rocket K-9M-41. Both spontaneously and artificially stimulated plasma waves in the VLF range were observed. When a large amplitude electron plasma wave was transmitted from the rocket, parametrically excited ion acoustic waves were observed in addition to natural emissions such as whistlers, LHR emissions, and hisslike emissions. It was also found that 'risers' were triggered by the LHR emissions, which seem to be very similar to a phenomenon of the so-called ASE (artificially stimulated emissions). When a slow electron beam with energy lower than 3 eV was ejected from the rocket, a new type of periodic U-shaped discrete emission was observed which was excited through a wave-particle interaction. The frequency of these emissions is lower than the LHR frequency and decreases as the beam energy is increased. Spectrograms of the observed plasma are presented, and some are analyzed theoretically. (auth)
-
Characteristics of VLF/LF Sferics from Elve-producing Lightning Discharges
Blaes, P.; Zoghzoghy, F. G.; Marshall, R. A.
2013-12-01
Lightning return strokes radiate an electromagnetic pulse (EMP) which interacts with the D-region ionosphere; the largest EMPs produce new ionization, heating, and optical emissions known as elves. Elves are at least six times more common than sprites and other transient luminous events. Though the probability that a lightning return stroke will produce an elve is correlated with the return stroke peak current, many large peak current strokes do not produce visible elves. Apart from the lightning peak current, elve production may depend on the return stroke speed, lightning altitude, and ionospheric conditions. In this work we investigate the detailed structure of lightning that gives rise to elves by analyzing the characteristics of VLF/LF lightning sferics in conjunction with optical elve observations. Lightning sferics were observed using an array of six VLF/LF receivers (1 MHz sample-rate) in Oklahoma, and elves were observed using two high-speed photometers pointed over the Oklahoma region: one located at Langmuir Laboratory, NM and the other at McDonald Observatory, TX. Hundreds of elves with coincident LF sferics were observed during the summer months of 2013. We present data comparing the characteristics of elve-producing and non-elve producing lightning as measured by LF sferics. In addition, we compare these sferic and elve observations with FDTD simulations to determine key properties of elve-producing lightning.
-
Excitation of VLF quasi-electrostatic oscillations in the ionospheric plasma
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. Lundin
Full Text Available A numerical solution of the dispersion equation for electromagnetic waves in a hot magnetized collisionless plasma has shown that, in a current-free ionospheric plasma, the distortion of the electron distribution function reproducing the downward flow of a thermal electron component and the compensating upward flow of the suprathermal electrons, which are responsible for the resulting heat flux, can destabilize quasi-electrostatic ion sound waves. The numerical analysis, performed with ion densities and electron temperature taken from the data recorded by the Interkosmos-24 (IK-24, Aktivny satellite, is compared with a VLF spectrum registered at the same time on board. This spectrum shows a wide frequency band emission below the local ion plasma frequency. The direction of the electron heat flux inherent to the assumed model of VLF emission generation is discussed
-
Excitation of VLF quasi-electrostatic oscillations in the ionospheric plasma
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. Lundin
1996-01-01
Full Text Available A numerical solution of the dispersion equation for electromagnetic waves in a hot magnetized collisionless plasma has shown that, in a current-free ionospheric plasma, the distortion of the electron distribution function reproducing the downward flow of a thermal electron component and the compensating upward flow of the suprathermal electrons, which are responsible for the resulting heat flux, can destabilize quasi-electrostatic ion sound waves. The numerical analysis, performed with ion densities and electron temperature taken from the data recorded by the Interkosmos-24 (IK-24, Aktivny satellite, is compared with a VLF spectrum registered at the same time on board. This spectrum shows a wide frequency band emission below the local ion plasma frequency. The direction of the electron heat flux inherent to the assumed model of VLF emission generation is discussed
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Manninen
2015-08-01
Full Text Available We investigate a non-typical very low frequency (VLF 1–4 kHz hiss representing a sequence of separated noise bursts with a strange "mushroom-like" shape in the frequency–time domain, each one lasting several minutes. These strange afternoon VLF emissions were recorded at Kannuslehto (KAN, ϕ = 67.74° N, λ = 26.27° E; L ∼ 5.5 in northern Finland during the late recovery phase of the small magnetic storm on 8 December 2013. The left-hand (LH polarized 2–3 kHz "mushroom caps" were clearly separated from the right-hand (RH polarized "mushroom stems" at the frequency of about 1.8–1.9 kHz, which could match the lower ionosphere waveguide cutoff (the first transverse resonance of the Earth–ionosphere cavity. We hypothesize that this VLF burst sequence could be a result of the modulation of the VLF hiss electron–cyclotron instability from the strong Pc5 geomagnetic pulsations observed simultaneously at ground-based stations as well as in the inner magnetosphere by the Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms mission probe (THEMIS-E; ThE. This assumption is confirmed by a similar modulation of the intensity of the energetic (1–10 keV electrons simultaneously observed by the same ThE spacecraft. In addition, the data of the European Incoherent Scatter Scientific Association (EISCAT radar at Tromsø show a similar quasi-periodicity in the ratio of the Hall-to-Pedersen conductance, which may be used as a proxy for the energetic particle precipitation enhancement. Our findings suggest that this strange mushroom-like shape of the considered VLF hiss could be a combined mutual effect of the magnetospheric ULF–VLF (ultra low frequency–very low frequency wave interaction and the ionosphere waveguide propagation.
-
Thunderstorm monitoring with VLF network and super dense meteorological observation system
Takahashi, Yukihiro; Sato, Mitsuteru
2015-04-01
It's not easy to understand the inside structure and developing process of thunderstorm only with existing meteorological instruments since its horizontal extent of the storm cell is sometimes smaller than an order of 10 km while one of the densest ground network in Japan, AMEDAS, consists of sites located every 17 km in average and the resolution of meteorological radar is 1-2 km in general. Even the X-band radar realizes the resolution of 250 m or larger. Here we suggest a thunderstorm monitoring system consisting of the network of VLF radio wave receivers and the super dense meteorological observation system with simple and low cost plate-type sensors that can be used for measurement both of raindrop and vertical electric field change caused by cloud-to-ground lightning discharge, adding to basic equipments for meteorological measurements. The plate-type sensor consists of two aluminum plates with a diameter of 10-20 cm. We carried out an observation campaign in summer of 2013 in the foothills of Mt. Yastugatake, Yamanashi and Nagano prefectures in Japan, installing 6 plate-type sensors at a distance of about 4 km. Horizontal location, height and charge amount of each lightning discharge are estimated successfully based on the information of electric field changes at several observing sites. Moreover, it was found that the thunderstorm has a very narrow structure smaller than 300 m that cannot be measured by any other ways, counting the positive and negative pulses caused by attachment of raindrop to the sensor plate, respectively. We plan to construct a new super dense observation network in the north Kanto region, Japan, where the lightning activity is most prominent in summer Japan and surrounded by our VLF systems developed for detecting sferics from lightning discharge, distributing more than several tens of sensors at every 4 km or shorter, such as an order of 100 m at minimum. This kind of new type network will reveal the unknown fine structures of
-
More evidence for a one-to-one correlation between Sprites and Early VLF perturbations
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Haldoupis, C.; Amvrosiadi, N.; Cotts, B. R. T.
2010-01-01
Past studies have shown a correlation between sprites and early VLF perturbations, but the reported correlation varies widely from ∼50% to 100%. The present study resolves these large discrepancies by analyzing several case studies of sprite and narrowband VLF observations, in which multiple...... VLF events. However, the one‐to‐one visible sprite to early VLF event correspondence, if viewed conversely, appears not to be always reciprocal. This is because the number of early events detected in some case studies was considerably larger than the number of visible sprites. Since the great majority...
-
Bell, T. F.
1984-01-01
A theory is presented of the nonlinear gyroresonance interaction that takes place in the magnetosphere between energetic electrons and coherent VLF waves propagating in the whistler mode at an arbitrary angle psi with respect to the earth's magnetic field B-sub-0. Particularly examined is the phase trapping (PT) mechanism believed to be responsible for the generation of VLF emissions. It is concluded that near the magnetic equatorial plane gradients of psi may play a very important part in the PT process for nonducted waves. Predictions of a higher threshold value for PT for nonducted waves generally agree with experimental data concerning VLF emission triggering by nonducted waves.
-
Intensity fluctuations of mid-latitude background VLF-noises and the interplanetary magnetic field
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gorshkov, Yu.N.; Klejmenova, N.G.
1986-01-01
Influence of interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) sector structure polarity and also variations of solar wind velocity and density on the intensity of mid-latitude VLF background noises are studied. For analysis continuous observations of VLF radiations in Magadan Observatory (phi=53.7 deg, L=2.7) from November, 1972 to June, 1973 were used. It is shown that IMF sector sign has no sufficient effect on the level of mid-latitude VLF background noises at the frequences f < 4-5 kHz. In magnetoperturbed periods when IMF Bsub(z)-component was directed to the South and the Earth was in the region of high-speed plasma flux, in mid-latitudes abatement of intensity of VLF background noises was seen
-
Massive Statistics of VLF-Induced Ionospheric Disturbances
Pailoor, N.; Cohen, M.; Golkowski, M.
2017-12-01
The impact of lightning of the D-region of the ionosphere has been measured by Very Low Frequency (VLF) remote sensing, and can be seen through the observance of Early-Fast events. Previous research has indicated that several factors control the behavior and occurrence of these events, including the transmitter-receiver geometry, as well as the peak current and polarity of the strike. Unfortunately, since each event is unique due to the wide variety of impacting factors, it is difficult to make broad inferences about the interactions between the lightning and ionosphere. By investigating a large database of lightning-induced disturbances over a span of several years and over a continental-scale region, we seek to quantify the relationship between geometry, lightning parameters, and the apparent disturbance of the ionosphere as measured with VLF transmitters. We began with a set of 860,000 cases where an intense lightning stroke above 150 kA occurred within 300 km of a transmiter-receiver path. To then detect ionospheric disturbances from the large volume of VLF data and lightning incidents, we applied a number of classification methods to the actual VLF amplitude data, and find that the most accurate is a convolutional neural network, which yielded a detection efficiency of 95-98%, and a false positive rate less than 25%. Using this model, we were able to assemble a database of more than 97,000 events, with each event stored with its corresponding time, date, receiver, transmitter, and lightning parameters. Estimates for the peak and slope of each disruption were also calculated. From this data, we were able to chart the relationships between geometry and lightning parameters (peak current and polarity) towards the occurrence probability, perturbation intensity, and recovery time, of the VLF perturbation. The results of this analysis are presented here.
-
Chand, Atishnal Elvin; Kumar, Sushil
2017-08-01
Very low frequency (VLF) signals from navigational transmitters propagate through the Earth-ionosphere waveguide formed by the Earth and the lower conducting ionosphere and show the pronounced minima during solar terminator transition between transmitter and receiver. Pronounced amplitude minima observed on 19.8 kHz (NWC transmitter) and 24.8 kHz (NLK transmitter) signals recorded at Suva (18.149°S, 178.446°E), Fiji, during 2013-2014, have been used to estimate the VLF modal interference distance (DMS) and nighttime D region VLF reflection height (hN). The NWC transmitter signal propagates mostly in west-east direction, and the NLK transmitter follows a transequatorial path propagating significantly in the east-west direction. The values of DMS calculated using midpath terminator speed are 2103 ± 172 km and 2507 ± 373 km for these paths having west-east and east-west components of VLF subionospheric propagation, respectively, which agree with previously published results and within 10% with theoretical values. We have also compared the DMS estimated using a terminator time method with that calculated using terminator speed for a particular day and found both the values to be consistent. The hN values were found to be maximum during winter of Southern Hemisphere for NWC signal and winter of Northern Hemisphere for NLK signal VLF propagation paths to Suva. The hN also shows significant day-to-day and seasonal variabilities with a maximum of about 10 km and 23 km for NWC and NLK signal propagation paths, respectively, which could be due to the atmospheric gravity waves associated with solar terminator transition, as well as meteorological factors such as strong lightnings.
-
Haldoupis, Christos; Cohen, Morris; Arnone, Enrico; Cotts, Benjamin; Dietrich, Stefano
2013-08-01
Subionospheric VLF recordings are investigated in relation with intense cloud-to-ground (CG) lightning data. Lightning impacts the lower ionosphere via heating and ionization changes which produce VLF signal perturbations known as early VLF events. Typically, early events recover in about 100 s, but a small subclass does not recover for many minutes, known as long-recovery early events (LORE). In this study, we identify LORE as a distinct category of early VLF events, whose signature may occur either on its own or alongside the short-lived typical early VLF event. Since LORE onsets coincide with powerful lightning strokes of either polarity (±), we infer that they are due to long-lasting ionization changes in the uppermost D region ionosphere caused by electromagnetic pulses emitted by strong ± CG lightning peak currents of typically > 250 kA, which are also known to generate elves. The LORE perturbations are detected when the discharge is located within ~250 km from the great circle path of a VLF transmitter-receiver link. The probability of occurrence increases with stroke intensity and approaches unity for discharges with peak currents ≥ ~300 kA. LOREs are nighttime phenomena that occur preferentially, at least in the present regional data set, during winter when strong ± CG discharges are more frequent and intense. The evidence suggests LORE as a distinct signature representing the VLF fingerprint of elves, a fact which, although was predicted by theory, it escaped identification in the long-going VLF research of lightning effects in the lower ionosphere.
-
More evidence for a one-to-one correlation between Sprites and Early VLF perturbations
Haldoupis, C.; Amvrosiadi, N.; Cotts, B. R. T.; van der Velde, O. A.; Chanrion, O.; Neubert, T.
2010-07-01
Past studies have shown a correlation between sprites and early VLF perturbations, but the reported correlation varies widely from ˜50% to 100%. The present study resolves these large discrepancies by analyzing several case studies of sprite and narrowband VLF observations, in which multiple transmitter-receiver VLF pairs with great circle paths (GCPs) passing near a sprite-producing thunderstorm were available. In this setup, the multiple paths act in a complementary way that makes the detection of early VLF perturbations much more probable compared to a single VLF path that can miss several of them, a fact that was overlooked in past studies. The evidence shows that visible sprite occurrences are accompanied by early VLF perturbations in a one-to-one correspondence. This implies that the sprite generation mechanism may cause also sub-ionospheric conductivity disturbances that produce early VLF events. However, the one-to-one visible sprite to early VLF event correspondence, if viewed conversely, appears not to be always reciprocal. This is because the number of early events detected in some case studies was considerably larger than the number of visible sprites. Since the great majority of the early events not accompanied by visible sprites appeared to be caused by positive cloud to ground (+CG) lightning discharges, it is possible that sprites or sprite halos were concurrently present in these events as well but were missed by the sprite-watch camera detection system. In order for this option to be resolved we need more studies using highly sensitive optical systems capable of detecting weaker sprites, sprite halos and elves.
-
Oike, Yuta; Kasahara, Yoshiya; Goto, Yoshitaka
2014-09-01
We statistically analyzed lightning whistlers detected from the analog waveform data below 15 kHz observed by the VLF instruments onboard Akebono. We examined the large amount of data obtained at Uchinoura Space Center in Japan for 22 years from 1989 to 2010. The lightning whistlers were mainly observed inside the L shell region below 2. Seasonal dependence of the occurrence frequency of lightning whistlers has two peaks around July to August and December to January. As lightning is most active in summer, in general, these two peaks correspond to summer in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, respectively. Diurnal variation of the occurrence frequency showed that lightning whistlers begin to increase in the early evening and remain at a high-occurrence level through the night with a peak around 21 in magnetic local time (MLT). This peak shifts toward nightside compared with lightning activity, which begins to rise around noon and peaks in the late afternoon. This trend is supposed to be caused by attenuation of VLF wave in the ionosphere in the daytime. Comparison study with the ground-based observation revealed consistent results, except that the peak of the ground-based observation appeared after midnight while our measurements obtained by Akebono was around 21 in MLT. This difference is explained qualitatively in terms that lightning whistlers measured at the ground station passed through the ionosphere twice above both source region and the ground station. These facts provide an important clue to evaluate quantitatively the absorption effect of lightning whistler in the ionosphere.
-
Rocket observations of the precipitation of electrons by ground VLF transmitters
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Arnoldy, R.L.; Kintner, P.M.
1989-01-01
Below an altitude of 400 km or less over the NASA Wallops Island range, stably trapped particles do not exist because of the South Atlantic Anomaly. In an experiment to measure scattered electrons at these altitudes (NASA flight 36:013), electron detectors clearly measured two monoenergetic electron peaks above the low background. The two monoernergetic peaks are attributed to the resonant interaction of electrons with VLF waves from Navy ground transmitters at Cutler, Maine, and Annapolis, Maryland. The transmitter signals were measured with electric and magnetic receivers aboard the rocket, and their propagation through the ionosphere and correlation with the precipitated electrons are discussed. In addition, energetic ions were also measured to be in the bounce loss cone during this rocket flight. Because of increased geomagnetic activity, it apears that the ring current extended inward to at least the L=2.5 magnetic shell and enhanced convection eroded the plasmasphere. The inward movement or compression of the plasmapause is consistent with a steep gradient in the equatorial cold plasma density and a localized equatorial interaction region needed to account for the monoenergetic elecrtron precipitation. The role of the geomagnetic activity in ''priming'' the trapped electron population for cyclotron resonance with VLF waves such that there is continuous scattering into the bounce loss cone remains uncertain. copyright American Geophysical Union 1989
-
Verification of Bwo Model of Vlf Chorus Generation Using Magion 5 Data
Titova, E. E.; Kozelov, B. V.; Jiricek, F.; Smilauer, J.; Demekhov, A. G.; Trakhtengerts, V. Yu.
We present a detailed study of chorus emissions in the magnetosphere detected on- board the Magion 5, when the satellite was at low magnetic latitudes. We determine the frequency sweep rate and the periods of electromagnetic VLF chorus emissions. These results are considered within the concept of the backward wave oscillator (BWO) regime of chorus generation. Comparison of the frequency sweep rate of chorus el- ements shows: (i) There is a correlation between the frequency sweep rates and the chorus amplitudes. The frequency sweep rate increases with chorus amplitude in ac- cord with expectations from the BWO model. (ii) The chorus growth rate, estimated from the frequency sweep rate, is in accord with that inferred from the BWO gener- ation mechanism. (iii) The BWO regime of chorus generation ensures the observed decrease in the frequency sweep rate of the chorus elements with increasing L shell. We also discuss the relationship between the observed periods of chorus elements with the predictions following from the BWO model of chorus generation.
-
Comparisons of Measurements and Modeling of Solar Eclipse Effects on VLF Transmissions
Eccles, J. V.; Rice, D. D.; Sojka, J. J.; Marshall, R. A.; Drob, D. P.; Decena, J. C.
2017-12-01
The solar eclipse of 2017 August 21 provides an excellent opportunity to examine Very Low Frequency (VLF) radio signal propagation through the path of the solar eclipse between Navy VLF transmitters and several VLF receivers. The VLF transmitters available for this study radio signal propagation study are NLK in Jim Creek, Washington (24.8 kHz, 192 kW, 48.20N, 121.90W), NML in LaMour, North Dakota (25.2 kHz, 500 kW 46.37N, 93.34W), and NAA in Cutler, Maine (24.0 kHz, 1000 kW, 44.65N, 67.29W). These VLF transmitters provide propagation paths to three VLF receivers at Utah State University (41.75N, 111.76W), Bear Lake Observatory (41.95N, 111.39W), Salt Lake City (40.76N, 111.89W) and one receiver in Boulder, Colorado (40.02N, 105.27W). The solar eclipse shadow will cross all propagations paths during the day and will modify the D region electron density within the solar shadow. The week prior to the solar eclipse will be used to generate a diurnal baseline of VLF single strength for each transmitter-receiver pair. These will be compared to the day of the solar eclipse to identify VLF propagation differences through the solar eclipse shawdow. Additionally, the electron density effects of the week prior and of the solar eclipse day will be modeled using the Data-Driven D Region (DDDR) model [Eccles et al., 2005] with a detailed eclipse solar flux mask. The Long-Wave Propagation Code and the HASEL RF ray-tracing code will be used to generate VLF signal strength for each measured propagation path through the days prior and the solar eclipse day. Model-measurement comparisons will be presented and the D region electron density effects of the solar eclipse will be examined. The DDDR is a time-dependent D region model, which makes it very suitable for the solar eclipse effects on the electron density for the altitude range of 36 to 130 km. Eccles J. V., R. D. Hunsucker, D. Rice, J. J. Sojka (2005), Space weather effects on midlatitude HF propagation paths: Observations and
-
Investigations of equatorial ionosphere nighttime mode conversion at VLF
Hildebrand, Verne
1993-05-01
VLF Radiowave propagation provides one of the few viable tools for exploring the properties of the lower D-region ionosphere. Conversely, VLF communications coverage analysis and prediction is directly dependent on the quality of models for the D-region ionosphere. The VLF Omega navigation signals are an excellent and under-utilized resource for conducting D-region research in direct support of VLF communications. Stations are well placed for investigating polar, mid latitude, and equatorial phenomena. Much can be learned by fully utilizing the very stable signals radiated at five frequencies, available from each of the eight transmitters, and taking full advantage of modal structure. While the Omega signals, 10.2 to 13.6 kHz, are well below the VLF communications band, we contend that much of the knowledge gained on D-region characteristics can be directly applied at the higher frequencies. The opportunity offered by Omega needs to be exploited. With the Global Positioning System (GPS) coming onboard as the prime means for global navigation, pressure is mounting to phase out Omega. In this paper we describe how we are using Omega along with computer codes of full wave VLF propagation, provided to us by the U.S. Naval Ocean Systems Center (NOSC), for ionosphere research and by example illustrate the potential for other investigations.
-
The Radio And Very Low Frequency (VLF) Electromagnetic ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
The Radio And Very Low Frequency (VLF) Electromagnetic Response Of A Layered Earth Media With Variable Dielectric Permittivity. ... A radio frequency of 125 KHz and a very low frequency (VLF) of 20 KHz were used in the computations and the field parameters studied over a dimensionless induction number, B. The ...
-
Study of the effect of solar flares on VLF signals during D-layer preparation or disappearance time
Ray, Suman; Chakrabarti, Sandip Kumar; Palit, Sourav
2016-07-01
"Very Low Frequency" (VLF) is one of the bands of the Radio waves having frequency 3-30 KHz, which propagates through the Earth-ionosphere wave-guide. In relation to propagation of radio waves through ionosphere, low mass and high mobility cause electrons to play a vital role. Electrons are not distributed uniformly in the ionosphere and depending on this factor, ionosphere has different layers namely D, E and F. Different ionospheric layers generally exist during day and night time. During day-time when the main source of the ionization of the ionosphere is Sun, the lower most layer of ionosphere is D-layer. But during the night-time when Sun is absent and cosmic ray is the main source of the ionization of the ionosphere, this D-layer disappears and E-layer becomes the lower most region of the ionosphere. Normally, patterns of VLF signal depend on regular solar flux variations. However, during solar flares extra energetic particles are released from Sun, which makes the changes in the ionization of the ionosphere and these changes can perturb VLF signal amplitude. Usually if a solar flare occurs during any time of day, it only affects the amplitude and phase of the VLF signals. But in the present work, we found the if the flare occurs during D-layer preparation / disappearance time, then it will not only affect to amplitude and phase of the VLF signals but also to terminator times of VLF signals. We have observed that the sun set terminator time of the VLF signals shifted towards night time due to the effect of a M-class solar flare which occurred during the D-layer disappearance time. The shift is so high that it crossed 5σ level. We are now trying to a make model using the ion-chemistry and LWPC code to explain this observed effect.
-
D-region Ionospheric Imaging Using VLF/LF Broadband Sferics, Forward Modeling, and Tomography
McCormick, J.; Cohen, M.
2017-12-01
The D-region of the ionosphere (60-90 km altitude) is highly variable on timescales from fractions of a second to many hours, and on spatial scales from 10 km to many hundreds of km. VLF and LF (3-30kHz, 30-300kHz) radio waves are guided to global distances by reflecting off of the ground and the D-region, making the Earth-ionosphere waveguide (EIWG). Therefore, information about the current state of the ionosphere is encoded in received VLF/LF radio waves since they act like probes of the D-region. The return stroke of lightning is an impulsive event that radiates powerful broadband radio emissions in VLF/LF bands known as `radio atmospherics' or `sferics'. Lightning flashes occur about 40-50 times per second throughout the Earth. An average of 2000 lightning storms occur each day with a mean duration of 30 minutes creating a broad spatial and temporal distribution of lightning VLF/LF sources. With careful processing, we can recover high fidelity measurements of amplitude and phase of both the radial and azimuthal magnetic field sferic components. By comparison to a theoretical EIWG propagation model such as the Long Wave Propagation Capability (LWPC) developed by the US Navy, with a standard forward modeling approach, we can infer information about the current state of the D-region. Typically, the ionosphere is parametrized to reduce the dimensionality of the problem which usually results in an electron density vs altitude profile. For large distances (Greater than 1000 km), these results can be interpreted as path-averaged information. In contrast to studies using navy transmitters to study the D-region, the full spectral information allows for more complete information and less ambiguous inferred ionospheric parameters. With the spatial breadth of lightning sources taken together with a broadly distributed VLF/LF receiver network, a dense set of measurements are acquired in a tomographic sense. Using the wealth of linear algebra and imaging techniques it is
-
Determining the VLF/ULF source height using phase measurements
Ryabov, A.; Kotik, D. S.
2012-12-01
Generation of ULF/VLF waves in the ionosphere using powerful RF facilities has been studied for the last 40 years, both theoretically and experimentally. During this time, it was proposed several mechanisms for explaining the experimental results: modulation of ionospheric currents based on thermal nonlinearity, ponderomotive mechanisms for generation both VLF and ULF signals, cubic nonlinearity, etc. According mentioned above mechanisms the VLF/ULF signal source could be located in the lower or upper ionosphere. The group velocity of signal propagation in the ionosphere is significantly smaller than speed of light. As a result the appreciable time delay of the received signals will occur at the earth surface. This time delay could be determine by measuring the phase difference between received and reference signals, which are GPS synchronized. The experiment on determining the time delay of ULF signal propagation from the ionospheric source was carried out at SURA facility in 2012 and the results are presented in this paper. The comparison with numerical simulation of the time delay using the adjusted IRI model and ionosonde data shows well agreement with the experimental observations. The work was supported by RFBR grant 11-02-00419-a and RF Ministry of education and science by state contract 16.518.11.7066.
-
Stimulated growth of coherent VLF waves in the magnetosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Stiles, G.S.; Helliwell, R.A.
1977-01-01
The amplitude behavior of several hundred VLF whistler mode pulse signals and of their associated artificially stimulated emissions (ASE's) was analyzed with digital signal processing techniques. A survey of the results indicates that the pulse signals characteristically show exponential growth with time that is highly repeatable over short periods. However, the growth rate varies widely from time to time, covering a range of 25 to 250 dB/s. During the exponential growth phase of the pulse there is no observable change in frequency. Emissions may begin when growth stops or when the input pulse terminates, whichever occurs first. Low growth rates and falling emissions characterize the beginning and ending of extended periods of emission activity. Rising emissions are prominent at the height of activity. ASE's triggered by station NAA (14.7 kHz, 1 MW radiated) begin when the transmitted Morse dash terminates (dash length, 150 ms). Some ASE's triggered by pulses from Siple Station, Antarctica (1.6 to 7 kHz, < or = to 1 kW), and Omega, New York (10.2 kHz, 100 W), show similar behavior; others, however, begin prior to the termination of the triggering pulse when the pulse length exceeds 200 ms. Growth and frequency change of the ASE tend to be independent of one another. For transmitted pulses of sufficient duration the amplitude saturates prior to termination. Signal amplitudes may reach 30 dB or more above the initial level. During growth the measured bandwidth of the signal remains near the minimum possible (approximately 27 Hz) with the given analysis resolution (approximately 30 ms, approximately 50 Hz). By comparison with mathematical models it is shown that the observed signals have the maximum possible coherence for the measured values of growth rate and duration. These observations are in qualitative agreement with a model that attributes signal growth and ASE's to an interaction between coherent waves and counterstreaming gyroresonant electrons
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Němec, František; Santolík, Ondřej; Parrot, M.; Rodger, C. J.
2010-01-01
Roč. 115, - (2010), A08315/1-A08315/10 ISSN 0148-0227 R&D Projects: GA ČR GA205/09/1253; GA ČR GAP205/10/2279; GA MŠk ME09107 Institutional research plan: CEZ:AV0Z30420517 Keywords : lightning activity * VLF electromagnetic waves * DEMETER satellite Subject RIV: BL - Plasma and Gas Discharge Physics Impact factor: 3.303, year: 2010
-
Moldovan, I. A.; Moldovan, A. S.; Biagi, P. F.; Ionescu, C.; Schwingenschuh, K.; Boudjada, M. Y.
2012-04-01
files to synchronize the user-side data with the receiver's data. Missing zipped files are also automatically downloaded. The application appends daily files into monthly and anual files and performs 3D colour-coded maps with graphic representations of VLF and LF signals' intensities versus the minute-of-the-day and the day-of-the-month, facilitating a near real-time observation of VLF and LF electromagnetic waves' propagation. This type of representation, highlights the modification of the terminator time versus the length of the solar-day, improves the user's capability to detect possible propagation anomalies due to ionosphere conditions and allows a quick visual inspection of unexpected behaviors of transmission channels at different frequencies and paths. A very special result, was observed on the recordings made on the propagation path to Iceland (NRK, 37.5kHz). Recordings are made once a minute, for a period of 303 days. Icelandic channel propagation anomalies present in the range of 40-90 days are considered to be precursory phenomena associated with Eyjafjallajokull - Iceland, volcanic eruption occurred in April-May 2010.
-
Trapped electron losses by interactions with coherent VLF waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Walt, M.; Inan, U.S.; Voss, H.D.
1996-01-01
VLF whistler waves from lightning enter the magnetosphere and cause the precipitation of energetic trapped electrons by pitch angle scattering. These events, known as Lightning-induced Electron Precipitation (LEP) have been detected by satellite and rocket instruments and by perturbations of VLF waves traveling in the earth-ionosphere waveguide. Detailed comparison of precipitating electron energy spectra and time dependence are in general agreement with calculations of trapped electron interactions with ducted whistler waves. In particular the temporal structure of the precipitation and the dynamic energy spectra of the electrons confirm this interpretation of the phenomena. There are discrepancies between observed and measured electron flux intensities and pitch angle distributions, but these quantities are sensitive to unknown wave intensities and trapped particle fluxes near the loss cone angle. The overall effect of lightning generated VLF waves on the lifetime of trapped electrons is still uncertain. The flux of electrons deflected into the bounce loss cone by a discrete whistler wave has been measured in a few cases. However, the area of the precipitation region is not known, and thus the total number of electrons lost in an LEP event can only be estimated. While the LEP events are dramatic, more important effects on trapped electrons may arise from the small but numerous deflections which increase the pitch angle diffusion rate of the electron population. copyright 1996 American Institute of Physics
-
Trapped electron losses by interactions with coherent VLF waves
Walt, M.; Inan, U. S.; Voss, H. D.
1996-07-01
VLF whistler waves from lightning enter the magnetosphere and cause the precipitation of energetic trapped electrons by pitch angle scattering. These events, known as Lightning-induced Electron Precipitation (LEP) have been detected by satellite and rocket instruments and by perturbations of VLF waves traveling in the earth-ionosphere waveguide. Detailed comparison of precipitating electron energy spectra and time dependence are in general agreement with calculations of trapped electron interactions with ducted whistler waves. In particular the temporal structure of the precipitation and the dynamic energy spectra of the electrons confirm this interpretation of the phenomena. There are discrepancies between observed and measured electron flux intensities and pitch angle distributions, but these quantities are sensitive to unknown wave intensities and trapped particle fluxes near the loss cone angle. The overall effect of lightning generated VLF waves on the lifetime of trapped electrons is still uncertain. The flux of electrons deflected into the bounce loss cone by a discrete whistler wave has been measured in a few cases. However, the area of the precipitation region is not known, and thus the total number of electrons lost in an LEP event can only be estimated. While the LEP events are dramatic, more important effects on trapped electrons may arise from the small but numerous deflections which increase the pitch angle diffusion rate of the electron population.
-
VLF/LF Radio Sounding of Ionospheric Perturbations Associated with Earthquakes
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Masashi Hayakawa
2007-07-01
Full Text Available It is recently recognized that the ionosphere is very sensitive to seismic effects,and the detection of ionospheric perturbations associated with earthquakes, seems to bevery promising for short-term earthquake prediction. We have proposed a possible use ofVLF/LF (very low frequency (3-30 kHz /low frequency (30-300 kHz radio sounding ofthe seismo-ionospheric perturbations. A brief history of the use of subionospheric VLF/LFpropagation for the short-term earthquake prediction is given, followed by a significantfinding of ionospheric perturbation for the Kobe earthquake in 1995. After showingprevious VLF/LF results, we present the latest VLF/LF findings; One is the statisticalcorrelation of the ionospheric perturbation with earthquakes and the second is a case studyfor the Sumatra earthquake in December, 2004, indicating the spatical scale and dynamicsof ionospheric perturbation for this earthquake.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Larsen, T.R.; Potemra, T.A.; Imhof, W.L.; Reagan, J.B.
1977-01-01
Enhanced fluxes of electrons precipitating over middle latitudes (L approx. 3--4) were detected by the polar-orbiting satellite 1971-089A following a period of magnetic activity starting on December 16, 1971. The electron fluxes measured in 256 differential channels between 130 and 2800 keV have been coordinated with phase observations of VLF radio waves propagating in the earth-ionosphere waveguide. The VLF paths in question, NLK (near Seattle, Washington) and GBR (at Rugby, England) to APL (near Washington, D. C.), cover approx. =120 0 in longitude and range from L approx. 2.5 to L approx. 4.0 in invariant latitude. These paths showed marked daytime and nighttime phase advances from 1650 UT on December 17 (in excess of 10 μs during maximum disturbance). The phase values did not return to prestorm levels before December 22--23. The unusual presence of these daytime VLF disturbances is offered as evidence for the widespread precipitation at low L shell vales of nearly relativistic electrons (E/sub e/> approx.200 keV) which would be required to penetrate below approx.70-km altitude to affect the daytime VLF transmissions. Wave guide mode calculations using D region electron density profiles deduced from the satellite particle data predict phase advances which agree reasonably well with the observed values. It is concluded that the observed long-lived VLF phase disturbances can be explained by excess D region ionization caused by energetic electrons precipitating from the earth's radiation belt following their injection deep into the magnetosphere during the magnetic storm
-
Propagation properties of quasiperiodic VLF emissions observed by the DEMETER spacecraft
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Hayosh, Mykhaylo; Němec, F.; Santolík, Ondřej; Parrot, M.
2016-01-01
Roč. 43, č. 3 (2016), s. 1007-1014 ISSN 0094-8276 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GAP209/11/2280; GA ČR(CZ) GA14-31899S; GA MŠk(CZ) LH15304 Grant - others:AV ČR(CZ) AP1401 Program:Akademická prémie - Praemium Academiae Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : quasiperiodic emissions * wave propagation in ionosphere * DEMETER spacecraft Subject RIV: BL - Plasma and Gas Discharge Physics Impact factor: 4.253, year: 2016 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2015GL067373/pdf
-
Lightning and radar observations of hurricane Rita landfall
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Henderson, Bradley G [Los Alamos National Laboratory; Suszcynsky, David M [Los Alamos National Laboratory; Hamlin, Timothy E [Los Alamos National Laboratory; Jeffery, C A [Los Alamos National Laboratory; Wiens, Kyle C [TEXAS TECH U.; Orville, R E [TEXAS A& M
2009-01-01
Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) owns and operates an array of Very-Low Frequency (VLF) sensors that measure the Radio-Frequency (RF) waveforms emitted by Cloud-to-Ground (CG) and InCloud (IC) lightning. This array, the Los Alamos Sferic Array (LASA), has approximately 15 sensors concentrated in the Great Plains and Florida, which detect electric field changes in a bandwidth from 200 Hz to 500 kHz (Smith et al., 2002). Recently, LANL has begun development of a new dual-band RF sensor array that includes the Very-High Frequency (VHF) band as well as the VLF. Whereas VLF lightning emissions can be used to deduce physical parameters such as lightning type and peak current, VHF emissions can be used to perform precise 3d mapping of individual radiation sources, which can number in the thousands for a typical CG flash. These new dual-band sensors will be used to monitor lightning activity in hurricanes in an effort to better predict intensification cycles. Although the new LANL dual-band array is not yet operational, we have begun initial work utilizing both VLF and VHF lightning data to monitor hurricane evolution. In this paper, we present the temporal evolution of Rita's landfall using VLF and VHF lightning data, and also WSR-88D radar. At landfall, Rita's northern eyewall experienced strong updrafts and significant lightning activity that appear to mark a transition between oceanic hurricane dynamics and continental thunderstorm dynamics. In section 2, we give a brief overview of Hurricane Rita, including its development as a hurricane and its lightning history. In the following section, we present WSR-88D data of Rita's landfall, including reflectivity images and temporal variation. In section 4, we present both VHF and VLF lightning data, overplotted on radar reflectivity images. Finally, we discuss our observations, including a comparison to previous studies and a brief conclusion.
-
Long recovery VLF perturbations associated with lightning discharges
Salut, M. M.; Abdullah, M.; Graf, K. L.; Cohen, M. B.; Cotts, B. R. T.; Kumar, Sushil
2012-08-01
Long D-region ionospheric recovery perturbations are a recently discovered and poorly understood subcategory of early VLF events, distinguished by exceptionally long ionospheric recovery times of up to 20 min (compared to more typical ˜1 min recovery times). Characteristics and occurrence rates of long ionospheric recovery events on the NWC transmitter signal recorded at Malaysia are presented. 48 long recovery events were observed. The location of the causative lightning discharge for each event is determined from GLD360 and WWLLN data, and each discharge is categorized as being over land or sea. Results provide strong evidence that long recovery events are attributed predominately to lightning discharges occurring over the sea, despite the fact that lightning activity in the region is more prevalent over land. Of the 48 long recovery events, 42 were attributed to lightning activity over water. Analysis of the causative lightning of long recovery events in comparison to all early VLF events reveals that these long recovery events are detectable for lighting discharges at larger distances from the signal path, indicating a different scattering pattern for long recovery events.
-
Simulation of VLF chorus emissions in the magnetosphere and comparison with THEMIS spacecraft data
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Demekhov, A. G.; Taubenschuss, Ulrich; Santolík, Ondřej
2017-01-01
Roč. 122, č. 1 (2017), s. 166-184 ISSN 2169-9380 R&D Projects: GA MŠk(CZ) LH15304 Grant - others:AV ČR(CZ) AP1401 Program:Akademická prémie - Praemium Academiae Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : VLF chorus * THEMIS data * numerical simulations Subject RIV: BL - Plasma and Gas Discharge Physics OBOR OECD: Fluids and plasma physics (including surface physics) Impact factor: 2.733, year: 2016 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2016JA023057/full
-
Airborne VLF survey of Izu-Oshima volcano
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Murakami, Yutaka; Yukutake, Takeshi
1988-05-17
Resistivity distribution in underground indicates anomaly in some cases due to volcanic activity, airborne VLF survey of Izu-Oshima volcano in whole area was carried out by measurement of the anomalous vertical magnetic field. The flight direction was determined with reference to both of the transmitter direction of the VLF waves and the running direction of the geologic formation. The flight altitude and the flight lines spacing were 100 m and 200 m respectively. Typical profiles of four lines of measurement were investigated. The resistivity anomalies were indicated corresponding to the position of known geologic fissure line, the lip of the caldera, the line of the craters and side volcanos. Several anomalous trends were detected by the contour drawing of the Fraser filter output. The detected results were as follow: new volcanos with the resistivity anomaly, the resistivity anomalies spread to the north-northwest from Goshinka jaya, the anomalies due to flowed lava, the anomalies by encroached water from the caldera wall, the effects from side volcanoes and so on. The resistivity anomalies by airborne VLF survey correspond to the known volcanic activities, and they are useful for elucidation of the underground volcanism. (6 figs, 4 refs)
-
A generation mechanism for chorus emission
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. Y. Trakhtengerts
1999-01-01
Full Text Available A chorus generation mechanism is discussed, which is based on interrelation of ELF/VLF noise-like and discrete emissions under the cyclotron wave-particle interactions. A natural ELF/VLF noise radiation is excited by the cyclotron instability mechanism in ducts with enhanced cold plasma density or at the plasmapause. This process is accompanied by a step-like deformation of the energetic electron distribution function in the velocity space, which is situated at the boundary between resonant and nonresonant particles. The step leads to the strong phase correlation of interacting particles and waves and to a new backward wave oscillator (BWO regime of wave generation, when an absolute cyclotron instability arises at the central cross section of the geomagnetic trap, in the form of a succession of discrete signals with growing frequency inside each element. The dynamical spectrum of a separate element is formed similar to triggered ELF/VLF emission, when the strong wavelet starts from the equatorial plane. The comparison is given of the model developed using some satellite and ground-based data. In particular, the appearance of separate groups of chorus signals with a duration 2-10 s can be connected with the preliminary stage of the step formation. BWO regime gives a succession period smaller than the bounce period of energetic electrons between the magnetic mirrors and can explain the observed intervals between chorus elements.Key words. Magnetospheric physics (Energetic particles · trapped. Space plasma physics (wave-particle interactions; waves and instabilities
-
VLF wave injections from the ground
Helliwell, R. A.
1983-01-01
Experiments on wave-particle interactions using VLF whistler-mode waves injected into the magnetosphere from Antartica are described. The injected signals are single-frequency coherent waves whose amplitudes and frequencies may be changed slowly with time, or else two or more coherent wave trains transmitted simultaneously to determine the nature of the response to multifrequency excitation. The waves may be amplified 30 dB or more and may trigger intense emissions having bandwidths that vary from a few to several hundred Hertz. In most cases significant growth and triggering occur only when the driving signal is essentially monochromatic (bandwidth 10 Hz). If two frequencies are transmitted simultaneously the signal at the lower frequency tends to be suppressed by 20 dB or more. These results are interpreted in terms of a feedback interaction between the waves and counter-streaming cyclotron resonant electrons in a region several hundred wavelengths long, centered on the magnetic equator.
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Martinez‐Calderon, C.; Shiokawa, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Keika, K.; Ozaki, M.; Schofield, I.; Connors, M.; Kletzing, C.; Hanzelka, Miroslav; Santolík, Ondřej; Kurth, W. S.
2016-01-01
Roč. 121, č. 6 (2016), s. 5384-5393 ISSN 2169-9380 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GA14-31899S Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : QP * conjugate event * VLF/ELF * propagation * time delay * ray tracing Subject RIV: BL - Plasma and Gas Discharge Physics Impact factor: 2.733, year: 2016 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2015JA022264/full
-
Nonlinear Scattering of VLF Waves in the Radiation Belts
Crabtree, Chris; Rudakov, Leonid; Ganguli, Guru; Mithaiwala, Manish
2014-10-01
Electromagnetic VLF waves, such as whistler mode waves, control the lifetime of trapped electrons in the radiation belts by pitch-angle scattering. Since the pitch-angle scattering rate is a strong function of the wave properties, a solid understanding of VLF wave sources and propagation in the magnetosphere is critical to accurately calculate electron lifetimes. Nonlinear scattering (Nonlinear Landau Damping) is a mechanism that can strongly alter VLF wave propagation [Ganguli et al. 2010], primarily by altering the direction of propagation, and has not been accounted for in previous models of radiation belt dynamics. Laboratory results have confirmed the dramatic change in propagation direction when the pump wave has sufficient amplitude to exceed the nonlinear threshold [Tejero et al. 2014]. Recent results show that the threshold for nonlinear scattering can often be met by naturally occurring VLF waves in the magnetosphere, with wave magnetic fields of the order of 50-100 pT inside the plasmapause. Nonlinear scattering can then dramatically alter the macroscopic dynamics of waves in the radiation belts leading to the formation of a long-lasting wave-cavity [Crabtree et al. 2012] and, when amplification is present, a multi-pass amplifier [Ganguli et al. 2012]. By considering these effects, the lifetimes of electrons can be dramatically reduced. This work is supported by the Naval Research Laboratory base program.
-
Rocket investigations of electron precipitation and VLF waves in the Antarctic upper atmosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sheldon, W.R.; Benbrook, J.R.; Bering, E.A.
1988-01-01
The results of two Antarctic rocket campaigns, primarily initiated to investigate electron precipitation stimulated by signals from the Siple-Station ground-based VLF transmitter, are presented. While the primary objective of the campaigns was not achieved, the Siple VLF transmitter facilitated a study of the wave environment in the ionosphere. Standing wave patterns in the ionosphere were observed for the first time by detectors flown aboard the Nike-Tomahawk rockets; the same detectors monitored a continuous signal from the transmitter through the neutral atmosphere and into the ionosphere, providing unique data for comparison with theoretical studies of wave propagation. The measurements of penetrating electron precipitation were interpreted in terms of a model of energetic electron precipitation from the trapped radiational belts. 52 references
-
The VLF Wave and Particle Precipitation Mapper (VPM) Cubesat Payload Suite
Inan, U.; Linscott, I.; Marshall, R. A.; Lauben, D.; Starks, M. J.; Doolittle, J. H.
2012-12-01
The VLF Wave and Particle Precipitation Mapper (VPM) payload is under development at Stanford University for a Cubesat mission that is planned to fly in low-earth-orbit in 2015. The VPM payload suite includes a 2-meter electric-field dipole antenna; a single-axis magnetic search coil; and a two-channel relativistic electron detector, measuring both trapped and loss-cone electrons. VPM will measure waves and relativistic electrons with the following primary goals: i) develop an improved climatology of plasmaspheric hiss in the L-shell range 1 < L < 3 at all local times; ii) detect VLF waves launched by space-based VLF transmitters, as well as energetic electrons scattered by those in-situ injected waves; iii) develop an improved climatology of lightning-generated whistlers and lightning-induced electron precipitation; iv)measure waves and electron precipitation produced by ground-based VLF transmitters; and v) validate propagation and wave-particle interaction models. In this paper we outline these science objectives of the VPM payload instrument suite, and describe the payload instruments and data products that will meet these science goals.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Pier Francesco Biagi
2012-04-01
Full Text Available
Signals from very low frequency (VLF/ low frequency (LF transmitters recorded on the ground station at Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky and on board the French DEMETER satellite were analyzed for the Simushir earthquake (M 8.3; November 15, 2006. The period of analysis was from October 1, 2006, to January 31, 2007. The ground and satellite data were processed by a method based on the difference between the real signal at night-time and the model signal. The model for the ground observations was the monthly averaged signal amplitudes and phases, as calculated for the quiet days of every month. For the satellite data, a two-dimensional model of the signal distribution over the selected area was constructed. Preseismic effects were found several days before the earthquake, in both the ground and satellite observations.
-
A generation mechanism for chorus emission
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. Y. Trakhtengerts
Full Text Available A chorus generation mechanism is discussed, which is based on interrelation of ELF/VLF noise-like and discrete emissions under the cyclotron wave-particle interactions. A natural ELF/VLF noise radiation is excited by the cyclotron instability mechanism in ducts with enhanced cold plasma density or at the plasmapause. This process is accompanied by a step-like deformation of the energetic electron distribution function in the velocity space, which is situated at the boundary between resonant and nonresonant particles. The step leads to the strong phase correlation of interacting particles and waves and to a new backward wave oscillator (BWO regime of wave generation, when an absolute cyclotron instability arises at the central cross section of the geomagnetic trap, in the form of a succession of discrete signals with growing frequency inside each element. The dynamical spectrum of a separate element is formed similar to triggered ELF/VLF emission, when the strong wavelet starts from the equatorial plane. The comparison is given of the model developed using some satellite and ground-based data. In particular, the appearance of separate groups of chorus signals with a duration 2-10 s can be connected with the preliminary stage of the step formation. BWO regime gives a succession period smaller than the bounce period of energetic electrons between the magnetic mirrors and can explain the observed intervals between chorus elements.
Key words. Magnetospheric physics (Energetic particles · trapped. Space plasma physics (wave-particle interactions; waves and instabilities -
Hiss emissions during quiet and disturbed periods
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
sound. VLF hiss activity observed at ground stations spread in latitude and ... The intensity and dynamic spectrum of VLF hiss can be explained by ... have shown experimentally that amplification of background noise to the level of observed.
-
VLF wave generation by beating of two HF waves in the ionosphere
Kuo, Spencer; Snyder, Arnold; Kossey, Paul; Chang, Chia-Lie; Labenski, John
2011-05-01
Theory of a beat-wave mechanism for very low frequency (VLF) wave generation in the ionosphere is presented. The VLF current is produced by beating two high power HF waves of slightly different frequencies through the nonlinearity and inhomogeneity of the ionospheric plasma. Theory also shows that the density irregularities can enhance the beat-wave generation. An experiment was conducted by transmitting two high power HF waves of 3.2 MHz and 3.2 MHz + f, where f = 5, 8, 13, and 2.02 kHz, from the HAARP transmitter. In the experiment, the ionosphere was underdense to the O-mode heater, i.e., the heater frequency f0 > foF2, and overdense or slightly underdense to the X-mode heater, i.e., f0 < fxF2 or f0 ≥ fxF2. The radiation intensity increased with the VLF wave frequency, was much stronger with the X-mode heaters, and was not sensitive to the electrojet. The strongest VLF radiation of 13 kHz was generated when the reflection layer of the X-mode heater was just slightly below the foF2 layer and the spread of the O-mode sounding echoes had the largest enhancement, suggesting an optimal setting for beat-wave generation of VLF waves by the HF heaters.
-
DEMETER observations of manmade waves that propagate in the ionosphere
Parrot, Michel
2018-01-01
This paper is a review of manmade waves observed by the ionospheric satellite DEMETER. It concerns waves emitted by the ground-based VLF and ELF transmitters, by broadcasting stations, by the power line harmonic radiation, by industrial noise, and by active experiments. Examples are shown including, for the first time, the record of a wave coming from an ELF transmitter. These waves propagate upwards in the magnetosphere and they can be observed in the magnetically conjugated region of emission. Depending on their frequencies, they perturb the ionosphere and the particles in the radiation belts, and additional emissions are triggered. xml:lang="fr"
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Арнольд Наумович Флейшман
2017-10-01
Conclusion. The results of sex differences of the new VLF100 and VLF50 indicators and their interconnection with LF and HF were essential to the study of autonomic provision in the body, characterizing central mechanisms of regulation.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Inan, U.S.; Shafer, D.C.; Yip, W.Y.; Orville, R.E.
1988-01-01
A 12-hour sequence of perturbations of subionospheric VLF signals observed in association with lightning provided preliminary evidence that the ionospheric regions perturbed in these events may be confined to within ∼ 150 km of the lightning discharges, and that intracloud flashes as well as cloud-to-ground lightning may be important in producing the perturbations. High-resolution analysis of event signatures indicated the presence of two different classes of events. For one set of events, observed during the most active central 6 hours of the observations period, a ∼ 0.6-s delay between the causative lightning and VLF event onset and a ∼ 1-s onset duration was observed, consistent with previously suggested models of the gyroresonant whistler-paritcle interaction that leads to particle precipitation and perturbation of the Earth-ionosphere waveguide. However, another set of events, observed during the first 2 hours of the observation period, exhibited a very different temporal signature, characterized by a much smaller (<50 ms) delay and sometimes also very short (< 50 ms) rise times. Such events are possibly related to previously reported cases of similarly early/fast events and may involve a more direct coupling between the lightning discharge and the lower ionosphere
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Greenberg, E.; Price, C.; Yair, Y.
2009-01-01
) discharges had peak current intensities between +8 and +130 kA whereas their charge moment changes (CMC) ranged from 500 to 3500 C km. Furthermore, the peak current reported by the Météorage lightning network are well correlated with the amplitudes of the VLF bursts, while showing poor correlation......%) an ELF transient was not associated with sprite occurrence, suggesting that long continuing current of tens of ms may not always be a necessary condition for sprite production, a finding which influences the estimation of the global sprite rate based on Schumann resonance (SR) measurements....
-
Estimating Parameters for the Earth-Ionosphere Waveguide Using VLF Narrowband Transmitters
Gross, N. C.; Cohen, M.
2017-12-01
Estimating the D-region (60 to 90 km altitude) ionospheric electron density profile has always been a challenge. The D-region's altitude is too high for aircraft and balloons to reach but is too low for satellites to orbit at. Sounding rocket measurements have been a useful tool for directly measuring the ionosphere, however, these types of measurements are infrequent and costly. A more sustainable type of measurement, for characterizing the D-region, is remote sensing with very low frequency (VLF) waves. Both the lower ionosphere and Earth's ground strongly reflect VLF waves. These two spherical reflectors form what is known as the Earth-ionosphere waveguide. As VLF waves propagate within the waveguide, they interact with the D-region ionosphere, causing amplitude and phase changes that are polarization dependent. These changes can be monitored with a spatially distributed array of receivers and D-region properties can be inferred from these measurements. Researchers have previously used VLF remote sensing techniques, from either narrowband transmitters or sferics, to estimate the density profile, but these estimations are typically during a short time frame and over a narrow propagation region. We report on an effort to improve the understanding of VLF wave propagation by estimating the commonly known h' and beta two parameter exponential electron density profile. Measurements from multiple narrowband transmitters at multiple receivers are taken, concurrently, and input into an algorithm. The cornerstone of the algorithm is an artificial neural network (ANN), where input values are the received narrowband amplitude and phase and the outputs are the estimated h' and beta parameters. Training data for the ANN is generated using the Navy's Long-Wavelength Propagation Capability (LWPC) model. Emphasis is placed on profiling the daytime ionosphere, which has a more stable and predictable profile than the nighttime. Daytime ionospheric disturbances, from high solar
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Píša, David; Němec, F.; Santolík, Ondřej; Parrot, M.; Rycroft, M.
2013-01-01
Roč. 118, č. 8 (2013), s. 5286-5295 ISSN 2169-9380 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GAP209/11/2280; GA ČR GA205/09/1253 Grant - others:European Community Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013),(XE) 262005; AV ČR(CZ) M100431206. Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : DEMETER * VLF waves * preseismic activity * Earth-ionosphere waveguide Subject RIV: DG - Athmosphere Sciences, Meteorology Impact factor: 3.440, year: 2013 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jgra.50469/abstract
-
LEP Events, TLE's, and Q-bursts observed from the Antarctic
Moore, R. C.; Kim, D.; Flint, Q. A.
2017-12-01
ELF/VLF measurements at Palmer Station, McMurdo Station, and South Pole Station, Antarctica are used to detect lightning-generated ELF/VLF radio atmospherics from around the globe and to remote sense ionospheric disturbances in the Southern hemisphere. The Antarctic ELF/VLF receivers complement a Northern hemisphere ELF/VLF monitoring array. In this paper, we present our latest observational results, including a full statistical analysis of conjugate observations of lightning-induced electron precipitation and radio atmospherics associated specifically with the transient luminous events known as gigantic jets and sprites.
-
Unexpected very low frequency (VLF) radio events recorded by the ionospheric satellite DEMETER
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Parrot, M.; Berthelier, J. J.; Blecki, J.; Brochot, J. Y.; Hobara, Y.; Lagoutte, D.; Lebreton, J. P.; Němec, F.; Onishi, T.; Pincon, J. L.; Píša, David; Santolík, Ondřej; Sauvaud, J. A.; Slominska, E.
2015-01-01
Roč. 36, č. 3 (2015), s. 483-511 ISSN 0169-3298 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GA14-31899S; GA MŠk LH12231 Grant - others:Rada Programu interní podpory projektů mezinárodní spolupráce AV ČR(CZ) M100421206; Rada Programu interní podpory projektů mezinárodní spolupráce AV ČR(CZ) M100421206 Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : ionosphere * natural and man-made VLF radio emissions * anomalies Subject RIV: BL - Plasma and Gas Discharge Physics Impact factor: 3.622, year: 2015 http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10712-015-9315-5
-
Sub-ionospheric VLF signal anomaly due to geomagnetic storms: a statistical study
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
K. Tatsuta
2015-11-01
Full Text Available We investigate quantitatively the effect of geomagnetic storms on the sub-ionospheric VLF/LF (Very Low Frequency/Low Frequency propagations for different latitudes based on 2-year nighttime data from Japanese VLF/LF observation network. Three statistical parameters such as average signal amplitude, variability of the signal amplitude, and nighttime fluctuation were calculated daily for 2 years for 16–21 independent VLF/LF transmitter–receiver propagation paths consisting of three transmitters and seven receiving stations. These propagation paths are suitable to simultaneously study high-latitude, low-mid-latitude and mid-latitude D/E-region ionospheric properties. We found that these three statistical parameters indicate significant anomalies exceeding at least 2 times of their standard deviation from the mean value during the geomagnetic storm time period in the high-latitude paths with an occurrence rate of anomaly between 40 and 50 % presumably due to the auroral energetic electron precipitation. The mid-latitude and low-mid-latitude paths have a smaller influence from the geomagnetic activity because of a lower occurrence rate of anomalies even during the geomagnetically active time period (from 20 to 30 %. The anomalies except geomagnetic storm periods may be caused by atmospheric and/or lithospheric origins. The statistical occurrence rates of ionospheric anomalies for different latitudinal paths during geomagnetic storm and non-storm time periods are basic and important information not only to identify the space weather effects toward the lower ionosphere depending on the latitudes but also to separate various external physical causes of lower ionospheric disturbances.
-
Plasma waves observed by sounding rockets
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kimura, I.
1977-01-01
Observations of plasma wave phenomena have been conducted with several rockets launched at Kagoshima Space Center, Kyushu, Japan, and at Showa Base, Antarctica. This report presents some results of the observations in anticipation of having valuable comments from other plasma physicists, especially from those who are concerned with laboratory plasma. In the K-9M-41 rocket experiment, VLF plasma waves were observed. In this experiment, the electron beam of several tens of uA was emitted from a hot cathode when a positive dc bias changing from 0 to 10V at 1V interval each second was applied to a receiving dipole antenna. The discrete emissions with 'U' shaped frequency spectrum were observed for the dc bias over 3 volts. The U emissions appeared twice per spin period of the rocket. Similar rocket experiment was performed at Showa Base using a loop and dipole antenna and without hot cathode. Emissions were observed with varying conditions. At present, the authors postulate that such emissions may be produced just in the vicinity of a rocket due to a kind of wake effect. (Aoki, K.)
-
Anomalies in vlf propagation and possible interpretations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shubova, R.S.; Knyazeva, N.A.; Sopel'nikov, M.D.
1985-01-01
This study considers cases of anomalous increase in the amplitude of a vlf signal on the Rugby-Khar'kov path. It is shown that such increases may be caused by change in the ratio of normal wave amplitudes, due to a decrease in electron concentration at the lower boundary of the ionosphere
-
Electric and VLF-MT survey of Tegatayama tunnel; Tegatayama tunnel no denki tansa oyobi VLF tansa
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nishitani, T [Akita University, Akita (Japan). Mining College
1997-05-27
To survey the structure at the depth between 20 and 30 m, field tests were conducted by means of vertical electric and VFL-MT (magnetotelluric) survey. Tegatayama tunnel has a total length of 276 m, width of 7.5 m, and height of 4.7 m, and the depth from the surface is about 28 m near the top of mountain. Near the tunnel, the thickness of surface soil is about 60 cm, which consists of clay soil including soft mudstone gravel. It was found that terrace deposit is distributed up to the depth of 8 m, and that mudstone is distributed below the depth of 8 m. Weighted four-electrode method was adopted for the vertical electrical survey. Measurements were conducted at the immediately above the tunnel, 10 m apart from the center of tunnel in the right and left, and 20 m apart from the center in the east. For the VLF-MT method, component of frequency 22.2 kHz was used. As a result of the tests, it was difficult to illustrate the existence of tunnel from the vertical electrical survey only at one point. Feature of the tunnel could be well illustrated by means of the VLF-MT method. 3 refs., 9 figs.
-
Variations of the VLF/LF signals during seismic activity in Japan in November 2016
Rozhnoi, Alexander; Solovieva, Maria; Levin, Boris; Chebrov, Danila; Hayakawa, Masashi; Fedun, Viktor
2017-04-01
The measurements of the very low and low frequency (VLF/LF) signals at the Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky and Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk stations were used for the analysis in connection with two underwater earthquakes which occurred near Japan in November 2016. The first earthquake with M=6.1 (depth 42 km) happened on 11 November. The second earthquake was recorded on 21 November with M=6.9 (depth 11 km) and had series of aftershocks with M up to 5.6 (USGS/NEIC). The significant negative nighttime amplitude anomalies were found for two sub-ionospheric paths: NWC-Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky and JJY-Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk during about a week in case of the first earthquake. The anomalies of signal in the path JJY-Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky were observed during 4-5 days before the second earthquake and during 3 days after it. Taking into account the possible influence of other factors which can produce perturbations in VLF/LF signals (geomagnetic storm, proton burst and the relativistic electron fluxes, as well as atmospheric parameters), also using control paths, we may conclude that observed anomalies very likely were caused by impending earthquakes.
-
A Semi-Automatic, Remote-Controlled Video Observation System for Transient Luminous Events
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Allin, Thomas Højgaard; Neubert, Torsten; Laursen, Steen
2003-01-01
In support for global ELF/VLF observations, HF measurements in France, and conjugate photometry/VLF observations in South Africa, we developed and operated a semi-automatic, remotely controlled video system for the observation of middle-atmospheric transient luminous events (TLEs). Installed...
-
Modification of the ionosphere by VLF wave-induced electron precipitation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Doolittle, J.H.
1982-01-01
Very low frequency (VLF) waves propagating in the whistler mode in the magnetosphere are known to cause precipitation of energetic electrons at middle latitudes. The interactions between the waves and electrons trapped in the magnetic field are believed to occur through cyclotron resonance. As a monochromatic wave propagates along a field line, the condition for resonance can be satisfied by electrons of a minimum energy at the equator and higher energies at increasing latitudes. Resonant interactions occurring in a field aligned region extending several thousand kilometers on both sides of the equator can therefore result in a precipitation flux with a wide range of energies. Electrons which are scattered into the loss cone will collide with the constituents of the ionosphere, causing additional ionization optical emissions, x-rays and heating. A computational technique is introduced which allows the temporal shape of pulse of precipitation to be modeled. A realistic energy distribution is used to weigh the contribution to the total precipitation energy flux resulting from resonant interactions in each segment of the duct. Wave growth along the path is found to affect the shape of the pulse. In its simplest application, the model sets limits on the time window in which a precipitation event can occur. The model arrival times are shown to agree with experimental correlations of VLF waves and effects of precipitation occurring on three occasions, thus supporting the assumption, that the precipitation results from cyclotron resonant scattering. Various techniques that have been employed for detecting wave-induced precipitation are compared. A quantitative analysis of the use of an HF radar for this purpose is introduced, based on the changes in the phase and group paths of the radar signals that are reflected from the perturbed ionosphere
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Palit
2013-09-01
Full Text Available X-ray photons emitted during solar flares cause ionization in the lower ionosphere (~60 to 100 km in excess of what is expected to occur due to a quiet sun. Very low frequency (VLF radio wave signals reflected from the D-region of the ionosphere are affected by this excess ionization. In this paper, we reproduce the deviation in VLF signal strength during solar flares by numerical modeling. We use GEANT4 Monte Carlo simulation code to compute the rate of ionization due to a M-class flare and a X-class flare. The output of the simulation is then used in a simplified ionospheric chemistry model to calculate the time variation of electron density at different altitudes in the D-region of the ionosphere. The resulting electron density variation profile is then self-consistently used in the LWPC code to obtain the time variation of the change in VLF signal. We did the modeling of the VLF signal along the NWC (Australia to IERC/ICSP (India propagation path and compared the results with observations. The agreement is found to be very satisfactory.
-
Dudkin, Denys; Pilipenko, Vyacheslav; Dudkin, Fedir; Pronenko, Vira; Klimov, Stanislav
2015-04-01
The overhead power lines are the sources of intense wideband electromagnetic (EM) emission, especially in ELF-VLF range, because of significant length (up to a few thousand kilometers) and strong 50/60 Hz currents with noticeable distortion. The radiation efficiency of the power line emission (PLE) increases with the harmonic order, so they are well observed by ground-based EM sensors. However their observations by low orbiting satellites (LEO) are very rare, particularly at basic harmonic 50/60 Hz, because of the ionospheric plasma opacity in ELF band. The Schumann resonance (SR) is the narrow-band EM noise that occurs due to the global thunderstorm activity in the Earth-ionosphere cavity. The first five eigenmodes of the SR are 7.8, 14.3, 20.8, 27.3 and 33.8 Hz and, thus, SR harmonics are also strongly absorbed by the Earth ionosphere. The published numerical simulations show that the penetration depth of such an ELF emission into the Earth's ionosphere is limited to 50-70 km for electric field and 120-240 km for magnetic field. From this follows, that PLE and SR can hardly ever be detected by LEO satellites, i.e. above the F-layer of ionosphere. In spite of this fact, these emissions were recently observed with use of the electric field antennas placed on the satellites C/NOFS (USA) and Chibis-M (Russia). Microsatellite Chibis-M was launched on January 24, 2012, at 23:18:30 UTC from the cargo ship "Progress M-13M" to circular orbit with altitude ~500 km and inclination ~52° . Chibis-M mass is about 40 kg where one third is a scientific instrumentation. The dimensions of the microsatellite case are 0.26x0.26x0.54 m with the outside mounted solar panels, service and scientific instrumentation. The main scientific objective of Chibis-M is the theoretical model verification for the atmospheric gamma-ray bursts. It requires the study of the accompanying EM processes such as the plasma waves produced by the lightning discharges in the VLF band. Chibis-M decayed on 15
-
Observed Barium Emission Rates
Stenbaek-Nielsen, H. C.; Wescott, E. M.; Hallinan, T. J.
1993-01-01
The barium releases from the CRRES satellite have provided an opportunity for verifying theoretically calculated barium ion and neutral emission rates. Spectra of the five Caribbean releases in the summer of 1991 were taken with a spectrograph on board a U.S. Air Force jet aircraft. Because the line of sight release densities are not known, only relative rates could be obtained. The observed relative rates agree well with the theoretically calculated rates and, together with other observations, confirm the earlier detailed theoretical emission rates. The calculated emission rates can thus with good accuracy be used with photometric observations. It has been postulated that charge exchange between neutral barium and oxygen ions represents a significant source for ionization. If so. it should be associated with emissions at 4957.15 A and 5013.00 A, but these emissions were not detected.
-
Excitation of the Magnetospheric Cavity by Space-Based ELF/VLF Transmitters
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Bell, Timothy F; Inan, Umran; Kulkarni, P
2004-01-01
During the period of performance Stanford University: 1. Developed an analytical model describing the distribution of current along a dipole antenna radiating ELF/VLF waves in the magnetospheric cavity...
-
Wulandari, Asri; Asti Anggari, Ega; Dwiasih, Novi; Suyanto, Imam
2018-03-01
Very Low Frequency (VLF) measurement has been done at Pagerkandang Volcanic, Dieng Volcanic Complex (DVC) to examine the possible existence of conductive zones that related with geothermal manifestation. VLF – EM survey used tilt mode with T-VLF BRGM Iris Instrument operated with two frequencies, they are 22200 Hz from Japan (JJI) and 19800 Hz from Australia (NWC). There are five lines with distance between lines is 50 m, and distance between measure points is 20 m. The parameters measured from VLF method are tilt angle (%) and elliptisity (%). Data processed by tilt angle value with fraser and Karous – Hjelt filter used WinVLF program. Karous – Hjelt filter resulted current density contour to estimate lateral location from conductive and resistive zones. The conductive zone is interpreted as the area which have high current density value. This area located at eastern dan western of Pagerkandang Volcanic. The conductive zone related to geothermal manifestation as like as fumarol that appeared because presenced of normal fault. Whereas the resistive zone is interpreted as the area which have low current density value. This area spread almost in the middle of the Pagerkandang Volcanic. The resistive zone was caused by the high weathering in claystone.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kikuchi, T.; Evans, D.S.
1983-01-01
The phase anomalies associated with substorms are observed on VLF signals propagating on transauroral paths (transmitters at OMEGA-ALDRA (13.6 kHz), GBR (16.0 kHz), and OMEGA--NORTH DAKOTA (13.6 kHz)) which were continually received at Inubo, Japan, during the events on November 13, 1979. Detailed comparisons are made between these phase anomalies and geomagnetic bays, and quantitative relations are obtained with precipitating energetic electrons (E>30, E>100, and E>300 keV) detected on board the TIROS-N and NOAA 6 satellites. It is concluded that two types of VLF phase anomalies exist which, in turn, are associated with two phases in the history of energetic electron precipitation into the atmosphere. The first type of phase anomaly is associated with direct injection of energetic electrons into the outer magnetosphere and atmosphere which, in turn, is completely correlated in time with development of the auroral electrojet current system. The second type arises from energetic electrons which subsequently precipitate from a trapped electron population and has a delayed onset and prolonged duration. An excellent quantitative correlation is obtained between the logarithm of the electron flux and the magnitude of the phase anomaly on the OMEGA-ALDRA signal. From the local time characteristics of this quantitative relation it is deduced that the electrons with E>300 keV are the main source of D region ionization responsible for the VLF phase anomaly
-
Characteristics of severe thunderstorms studied with the aid of VLF ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
oped well calibrated GPS locked software VLF receiver, located at the ... last only a few hours, there is a need to develop .... ally under the joint influence of the South–West .... Meteorological Applications of Lightning Data, San Diego,. CA, Am.
-
Moldovan, Iren Adelina; Emilian Toader, Victorin; Nenovski, Petko; Biagi, Pier Francesco; Maggipinto, Tommaso; Septimiu Moldovan, Adrian; Ionescu, Constantin
2013-04-01
In 2009, INFREP, a network of VLF (20-60 kHz) and LF (150-300 kHz) radio receivers, was put into operation in Europe having as principal goal, the study of disturbances produced by the earthquakes on the propagation properties of these signals. On May 22nd, 2012 an earthquake with Mw=567 occurred in Bulgaria, near Sofia, inside the "sensitive" area of the INFREP VLF/LF electromagnetic network. The data collected on different frequencies, during April-May 2012 were studied using different methods of analysis: daily correlation methods, spectral approaches and terminator time techniques, in order to find out possible connections between the seismic activity and the subionospheric propagation properties of radio waves. The studies were performed with the help of a specially designed LabVIEW application, which accesses the VLF/LF receiver through internet. This program opens the receiver's web-page and automatically retrieves the list of data files to synchronize the user-side data with the receiver's data. Missing zipped files are also automatically downloaded. The application performs primary, statistical correlation and spectral analysis, appends daily files into monthly and annual files and performs 3D colour-coded maps with graphic representations of VLF and LF signals' intensities versus the minute-of-the-day and the day-of-the-month, facilitating a near real-time observation of VLF and LF electromagnetic waves' propagation. Another feature of the software is the correlation of the daily recorded files for the studied frequencies by overlaying the 24 hours radio activity and taking into account the sunrise and sunset. Data are individually processed (spectral power, correlations, differentiation, filtered using bandpass, lowpass, highpass). JTFA spectrograms (Cone-Shaped Distribution CSD, Gabor, Wavelet, short-time Fourier transform STFT, Wigner-Ville Distribution WVD, Choi-Williams Distribution CWD) are used, too.
-
Plasma waves produced by an ion beam: observations by the VLF experiment on Porcupine
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jones, D.
1980-01-01
Results are presented from the VLF electric field experiments flown on Porcupine flights F3 and F4, which also had ejectable xenon ion sources. The xenon ion beam was found to produce plasma instabilities whose frequencies could be linked to the local proton gyrofrequency fsub(cH + ). The main energy in the instabilities lies at approximately 3kHz for events when the Xe + source is close to the rocket, and at approximately 7kHz when the source is farther away. Theory predicts that these frequencies should be the lower-hybrid-resonance and this implies that Xe + is the dominant ion in the first case and that it is the ambient plasma that dominates later. There is no discernable antenna spin-modulation during the Xe events which indicates that the wave k-vectors are not unidirectional. A theory is cited based on the 'setting up' of the proton cyclotron harmonic waves by the Xe + or O + cyclotron harmonic waves. The second Xe + event on both flights exhibited an, as yet, unexplained harmonic structure related to fsub(cH + )/2. (Auth.)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Eager, G.S. Jr.; Fryszczyn, B.; Katz, C.; ElBadaly, H.A.; Jean, A.R.
1992-01-01
This paper reports that according to the experience of some power utilities, the application of industry recommended high voltage d.c. field tests on 5-35 kV extruded dielectric cables, containing water trees, sometimes causes further deterioration of the insulation. Tests conducted on laboratory aged 15 kV ethylene propylene rubber (EP) and 15 and 28 kV crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) insulated cables indicate that d.c. proof tests in accordance with AEIC specifications an IEEE test guides without flashover do not appear to cause further deterioration. Depending on the degree of cable aging and the level of test voltage, when flashovers take place, damage may be inflicted to XLPE cables. No damage was observed on aged EP cable, at the same test levels. Because of the aforementioned power utility experience, some users have requested an alternate field proof test. Tests conducted on new XLPE and EP cables indicate that damage to the insulation structure can be detected using VLF (0.1 Hz) voltage at approximately one-third the d.c. voltage level. Field tests conducted on severely tree deteriorated 15 kV polyethylene (PE) cable using AEIC recommended d.c. voltage level of about five times operating voltage level caused cable failure; VLF voltage levels up to two times operating voltage did not. VLF voltage appears to be a suitable alternate to d.c. voltage for field proof testing
-
Cataldi, Daniele; Cataldi, Gabriele; Straser, Valentino
2017-04-01
On August 24, 2016 at 01:36:32 UTC a destructive earthquake hit Central Italy with a magnitude of M6.2. The authors of this study have recorded some electromagnetic signals that have preceded this strong earthquake. These signals were recorded through two electromagnetic monitoring stations realized by Gabriele Cataldi and Daniele Cataldi, located near the town of Albano Laziale (Rome, Italy) and near the city of Lariano (Rome, Italy) and can monitor the radio spectrum 24h7 between 0.001 Hz and 96 kHz (SELF-LF band). The electromagnetic monitoring allowed to identify two interesting types of electromagnetic anomalies: the first electromagnetic anomaly was recorded on August 18, 2016 between 02:47 UTC and 06:21 UTC, in the VLF band prevalently between 18kHz and 26kHz; the second electromagnetic anomaly was registered between 08:00 UTC on August 23, 2016 and 05:00 UTC on August 24, 2016, prevalently between 0.01 and 0.7Hz: the most intense signals were recorded at 08:50 UTC on August 23, 2016 and approximately 1 hour before the strong earthquake. The Earth's electromagnetic background monitoring in the SELF-VLF band (0HzM6+ earthquakes that occur on a global scale are always preceded by an increase of the solar wind proton density near Earth, the solar and geomagnetic activity monitoring is a seismic prediction method that has proven reliable for understanding when we can expect a recovery of the M6+ global seismic activity and could be used internationally as an indicator of seismic risk in the countries where there are potentially destructive earthquakes and tsunamis.
-
VLF Cutler: September 1997 Four-Panel Tests; RADHAZ and Field Strength Measurement
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Hansen, P
1998-01-01
The objective of the four panel tests was to provide VLF Cutler with the capability of performing the special painting project and normal maintenance on the bow tie area towers of an inactive array...
-
VLF and X-ray Instruments for Stratospheric Balloons: ABOVE2 and EPEx
Cully, C. M.; Galts, D.; Patrick, M.; Duffin, C.; Jang, A. C.; Pitzel, J.; Trumpour, T.; McCarthy, M.; Milling, D. K.
2017-12-01
The ABOVE2 (2016) and EPEx (2018) stratospheric balloon missions are designed to study energetic electrons precipitating from the radiation belts into the atmosphere. The payloads include instruments that measure Very Low Frequency (VLF) magnetic and electric fields, and bremsstrahlung X-rays. The ABOVE2 VLF instrument is an FPGA-based design with >200 kHz sampling rates, sub-microsecond timing accuracy and onboard spectral processing, designed in a Cubesat-friendly format. The EPEx X-ray instrument is a hard X-ray imaging system, also in a Cubesat-friendly format, incorporating a commercially-available Cadmium-Zinc-Telluride module. The imager is sufficiently lightweight that we can launch it on-demand with low-volume latex balloons. I will discuss the design and performance of both instruments, and present data from the ABOVE2 flights.
-
Observation of an ionospheric disturbance caused by a gamma-ray burst
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fishman, G.J.; Inan, U.S.
1988-01-01
We report a first observation of an ionospheric disturbance from a gamma-ray burst. The burst, GB830801, occurred at 22:14:18 UT on 1 August 1983 and was one of the strongest ever observed. The total fluence was 2 x 10 -3 erg cm -2 , most of which occurred in the first 4 s of the burst. Simultaneously, a change was observed in the amplitude of a very-low-frequency (VLF) radio signal from a transmitter in Rugby, England, monitored at Palmer Station, Antarctica, indicative of an ionospheric disturbance. Weaker disturbances were also recorded at the same receiving site on signals from VLF stations in Annapolis, Maryland and Lualualei, Hawaii. The times of the burst and the disturbances are coincident within the 10-s resolution of the VLF recording system. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fedyakina, N.I.; Khorosheva, O.V.
1989-01-01
Dependence between the development of geomagnetic storm and VLF noise storm is studied. Two conditions should be met for the development of noise storm in VLF-hiss (f ≅ 0.5-10 kHz): a) threshold intensity of electron fluxes with E e > 40 keV in plasma layers; b) the presence of substorms resulting to widening of electron belt and its collision with cold plasma of plasmasphere. The noise storm at the fixed longitude begins about midnight independently of the phase of magnetic storm; Noise storm duration is connected with geomagnetic storm intensity by direct linear relationship
-
Grard, Rejean; Berthelin, Stephanie; Beghin, Christian; Hamelin, Michel; Berthelier, Jean-Jacques; Lopez-Moreno, Jose J.; Simoes, Fernando
2011-01-01
Morente et al. have recently revisited the VLF electric field measurements made with the Permittivity, Wave and Altimetry (PWA) instrument during the descent of the Huygens Probe through the atmosphere of Titan. They assert that they have identified several harmonics of the transverse resonance mode of the surface?]ionosphere cavity, which would prove the existence of an electrical activity in the atmosphere of the largest satellite of Saturn. We refute this finding on the basis that it results from an artifact due to an improper analysis of the data set. [2] The investigators of the Permittivity, Wave and Altimetry (PWA) experiment on the Huygens Probe have reported the extremely low frequency (ELF) and very low frequency (VLF) electric signals recorded during the descent through the atmosphere of Titan. The PWA data are archived in the Planetary Science Archive (PSA) of ESA, and an extensive description of the instrument is at the disposal of the scientific community. Morente and his coworkers have revisited this data set and reported the results of their investigations in two papers. In a first paper, they claim that they have detected in the ELF range (0.100 Hz) several harmonics of a global resonance allegedly generated by lightning activity in the spherical cavity guide formed by the surface of Titan and the inner boundary of the ionosphere, a phenomenon similar to the Schumann resonance observed at EartH In the second paper dedicated to the VLF electric signal recorded by PWA, in the range 0.10 kHz, they argue that they can also bring out the transverse resonance and its harmonics, a more local phenomenon that develops around the excitation source and whose frequency is controlled by the separation between Titan?fs surface and the inner ionospheric boundary. [3] The PWA investigators have analyzed the narrowband ELF signal at about 36 Hz effectively observed during the entire descent. They have not endorsed, however, the alternative approach of Morente et al
-
Nonlinear VLF Wave Physics in the Radiation Belts
Crabtree, C. E.; Tejero, E. M.; Ganguli, G.; Mithaiwala, M.; Rudakov, L.; Hospodarsky, G. B.; Kletzing, C.
2014-12-01
Electromagnetic VLF waves, such as whistler mode waves, both control the lifetime of trapped electrons in the radiation belts by pitch-angle scattering and are responsible for the energization of electrons during storms. Traditional approaches to understanding the influence of waves on trapped electrons have assumed that the wave characteristics (frequency spectrum, wave-normal angle distribution, etc.) were both stationary in time and amplitude independent from event to event. In situ data from modern satellite missions, such as the Van Allen probes, are showing that this assumption may not be justified. In addition, recent theoretical results [Crabtree et al. 2012] show that the threshold for nonlinear wave scattering can often be met by naturally occurring VLF waves in the magnetosphere, with wave magnetic fields of the order of 50-100 pT inside the plasmapause. Nonlinear wave scattering (Nonlinear Landau Damping) is an amplitude dependent mechanism that can strongly alter VLF wave propagation [Ganguli et al. 2010], primarily by altering the direction of propagation. Laboratory results have confirmed the dramatic change in propagation direction when the pump wave has sufficient amplitude to exceed the nonlinear threshold [Tejero et al. 2014]. Nonlinear scattering can alter the macroscopic dynamics of waves in the radiation belts leading to the formation of a long-lasting wave-cavity [Crabtree et al. 2012] and, when amplification is present, a multi-pass amplifier [Ganguli et al., 2012]. Such nonlinear wave effects can dramatically reduce electron lifetimes. Nonlinear wave dynamics such as these occur when there are more than one wave present, such a condition necessarily violates the assumption of traditional wave-normal analysis [Santolik et al., 2003] which rely on the plane wave assumption. To investigate nonlinear wave dynamics using modern in situ data we apply the maximum entropy method [Skilling and Bryan, 1984] to solve for the wave distribution function
-
Investigation of the receivability of VLF standard time and frequency ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
This study is on the receivability of some standard time and frequency signals in the VLF range in Zaria, Nigeria. Signal field strengths of various stations were estimated, and a suitable radio receiving system was set up to receive them. Using the assembled receiver, some of the transmissions, including the Omega W/L at ...
-
INSPIRE: Interactive NASA Space Physics Ionosphere Radio Experiment
Franzen, K. A.; Garcia, L. N.; Webb, P. A.; Green, J. L.
2007-12-01
The INSPIRE Project is a non-profit scientific and educational corporation whose objective is to bring the excitement of observing very low frequency (VLF) natural radio waves to high school students. Underlying this objective is the conviction that science and technology are the underpinnings of our modern society, and that only with an understanding of these disciplines can people make correct decisions in their lives. Since 1989, the INSPIRE Project has provided specially designed radio receiver kits to over 2,500 students and other groups to make observations of signals in the VLF frequency range. These kits provide an innovative and unique opportunity for students to actively gather data that can be used in a basic research project. Natural VLF emissions that can be studied with the INSPIRE receiver kits include sferics, tweeks, whistlers, and chorus, which originate from phenomena such as lightning. These emissions can either come from the local atmospheric environment within a few tens of kilometers of the receiver or from outer space thousands of kilometers from the Earth. VLF emissions are at such low frequencies that they can be received, amplified and turned into sound that we can hear, with each emission producing in a distinctive sound. In 2006 INSPIRE was re-branded and its mission has expanded to developing new partnerships with multiple science projects. Links to magnetospheric physics, astronomy, and meteorology are being identified. This presentation will introduce the INSPIRE project, display the INSPIRE receiver kits, show examples of the types of VLF emissions that can be collected and provide information on scholarship programs being offered.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. Höller
2009-10-01
Full Text Available This paper describes lightning characteristics as obtained in four sets of lightning measurements during recent field campaigns in different parts of the world from mid-latitudes to the tropics by the novel VLF/LF (very low frequency/low frequency lightning detection network (LINET. The paper gives a general overview on the approach, and a synopsis of the statistical results for the observation periods as a whole and for one special day in each region. The focus is on the characteristics of lightning which can specifically be observed by this system like intra-cloud and cloud-to-ground stroke statistics, vertical distributions of intra-cloud strokes or peak current distributions. Some conclusions regarding lightning produced NOx are also presented as this was one of the aims of the tropical field campaigns TROCCINOX (Tropical Convection, Cirrus and Nitrogen Oxides Experiment and TroCCiBras (Tropical Convection and Cirrus Experiment Brazil in Brazil during January/February 2005, SCOUT-O3 (Stratospheric-Climate Links with Emphasis on the Upper Troposphere and Lower Stratosphere and TWP-ICE (Tropical Warm Pool-International Cloud Experiment during November/December 2005 and January/February 2006, respectively, in the Darwin area in N-Australia, and of AMMA (African Monsoon Multidisciplinary Analyses in W-Africa during June–November 2006.
Regional and temporal characteristics of lightning are found to be dependent on orographic effects (e.g. S-Germany, Brazil, Benin, land-sea breeze circulations (N-Australia and especially the evolution of the monsoons (Benin, N-Australia. Large intra-seasonal variability in lightning occurrence was found for the Australian monsoon between the strong convection during build-up and break phases and the weak active monsoon phase with only minor lightning activity. Total daily lightning stroke rates can be of comparable intensity in all regions with the heaviest events found in Germany and N -
Kawano, T.; Tatsuta, K.; Hobara, Y.
2015-12-01
Continuous monitoring of signal amplitudes of worldwide VLF transmitters is a powerful tool to study the lower ionospheric condition. Although, lower ionospheric perturbations prior to some of the major earthquakes have been reported for years, their occurrence and coupling mechanism between the ground and overlaying ionosphere prior to the earthquakes are not clear yet. In this paper, we carried out a statistical analysis based on the nighttime averaged signal amplitude data from the UEC's VLF/LF transmitter observation network. Two hundred forty three earthquakes were occurred within the 5th Fresnel zone of transmitter-receiver paths around Japan during the time period of 2007 to 2012. These earthquakes were characterized into three different groups based on the Centroid-Moment-Tensor (CMT) solution such as reverse fault type, normal fault type and stress slip type. The ionospheric anomaly was identified by a large change in the VLF/LF amplitude during nighttime. As a result, we found the ionospheric perturbations associated with both ground and sea earthquakes. Remarkably, the reverse fault type earthquakes have the highest occurrence rate of ionospheric perturbation among the three types both for sea (41%) and ground events (61%). The occurrence rates for normal type fault are 35% and 56% for sea and ground earthquakes respectively and the same for stress slip type are 39% and 20% for sea and ground earthquakes respectively. In both cases the occurrence rates are smaller than the reverse fault type. The clear difference of occurrence rate of the ionospheric perturbations may indicate that the coupling efficiency of seismic activity into the overlaying ionosphere is controlled by the pressure in the earth's crust. This gives us further physical insight of Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere (LAI) coupling processes.
-
Zablocki, C.J.
1978-01-01
The very low-frequency (VLF) induction method has found exceptional utility in studying various volcanic processes of Kilauea volcano, Hawaii because: (1) significant anomalies result exclusively from ionically conductive magma or still-hot intrusions (> 800??C) and the attendant electrolytically conductive hot groundwater; (2) basalt flows forming the bulk of Kilauea have very high resistivities at shallow depths that result in low geologic noise levels and relatively deep depths of investigation (???100 m); and (3) the azimuths to two of the usable transmitters (NLK and NPM) are aligned favorably with most of the principal geologic features. Measurements of the tilt angle and ellipticity of the polarization ellipse of the magnetic field, using a simple, hand-held receiver, have been used to: (1) delineate the lateral extent of shallow, partially solidified lava lakes, active lava tubes, and recent intrusive dikes; (2) obtain an indication of the attitude of some recent dikes; (3) show that many eruptive fissures cool faster than their intrusive counterparts; (4) show that some fumarolic areas are underlain by shallow, highly altered, and conductive zones; and (5) provide control information for interpreting data obtained with other electrical techniques. Complementary measurements of scalar apparent resistivity and surface impedance phase, using a new attachment for the VLF receiver, have substantially increased the utility of VLF studies in Kilauea. They provide better lateral resolution of conductors and reduce the ambiguity in interpretation. Notwithstanding recent advances in theoretical modeling techniques, the excellent quality of some of the data warrants extension of interpretive techniques, particularly for quantitatively characterizing the configuration and conductivity of small-dimension bodies. These VLF induction methods should have wide application to studies of active volcanic regions in other parts of the world and could provide some insights into
-
Quasi-static electric fields, turbulence and VLF waves in the ionosphere and magnetosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Temerin, M.A.
1978-01-01
Two rocket payloads launched from Greenland in December 1974 and January 1975 into the dayside auroral oval measured large scale electric fields. Sunward convection in regions of polar cusp type particle precipitation argues for the existence of a turbulent entry region at the magnetopause. Smaller scale changes in the electric field and energetic electron precipitation require field-aligned currents predominately at the boundaries of auroral arcs. Measurements of electric fields parallel to the magnetic field place upper limits to the parallel electric field. An analysis of the effect of zero-frequency electric field turbulence on the output of an electric field double probe detector is applied to data from two satellites, OVI-17 and S3-3. It is found that the electric field of high latitude low frequency turbulence is polarized perpendicular to the magnetic field and that the frequency is measured by the satellites is due to the Doppler shift of near zero frequency turbulence both in the ionosphere and magnetosphere. In addition, rocket measurements of low frequency turbulence in the dayside auroral oval reveal characteristics similar to those of the large electric field regions recently seen on S3-3 indicating that the turbulence from those regions extends into the ionosphere. VLF waves were also observed during the two rocket flights into the dayside auroral oval. The correlation of the VLF hiss intensity with the fluxes of precipitating electrons above 500 eV on a short spatial and time scale is often poor, even when a positive slope exists in the electron phase space density. The frequency of the lower hybrid waves were used to measure the ratio of NO + and O 2 + to O + . Electrostatic waves were observed during a barium release
-
Electron beam injection during active experiments. I - Electromagnetic wave emissions
Winglee, R. M.; Kellogg, P. J.
1990-01-01
The wave emissions produced in Echo 7 experiment by active injections of electron beams were investigated to determine the properties of the electromagnetic and electrostatic fields for both the field-aligned and cross-field injection in such experiments and to evaluate the sources of free energy and relative efficiencies for the generation of the VLF and HF emissions. It is shown that, for typical beam energies in active experiments, electromagnetic effects do not substantially change the bulk properties of the beam, spacecraft charging, and plasma particle acceleration. Through simulations, beam-generated whistlers; fundamental z-mode and harmonic x-mode radiation; and electrostatic electron-cyclotron, upper-hybrid, Langmuir, and lower-hybrid waves were identified. The characteristics of the observed wave spectra were found to be sensitive to both the ratio of the electron plasma frequency to the cyclotron frequency and the angle of injection relative to the magnetic field.
-
Daytime tropical D region parameters from short path VLF phase and amplitude
Thomson, Neil R.
2010-09-01
Observed phases and amplitudes of VLF radio signals, propagating on a short (˜300-km) path, are used to find improved parameters for the lowest edge of the (D region of the) Earth's ionosphere. The phases, relative to GPS 1-s pulses, and the amplitudes were measured both near (˜100 km from) the transmitter, where the direct ground wave is very dominant, and at distances of ˜300 km near where the ionospherically reflected waves form a (modal) minimum with the (direct) ground wave. The signals came from the 19.8 kHz, 1 MW transmitter, NWC, on the North West Cape of Australia, propagating ˜300 km ENE, mainly over the sea, to the vicinity of Karratha/Dampier on the N.W. coast of Australia. The bottom edge of the mid-day tropical/equatorial ionosphere was thus found to be well-modeled by H‧ = 70.5 ± 0.5 km and β = 0.47 ± 0.03 km-1 where H‧ and β are the traditional height and sharpness parameters as used by Wait and by the U.S. Navy in their Earth-ionosphere VLF radio waveguide programs. U.S. Navy modal waveguide code calculations are also compared with those from the wave hop code of Berry and Herman (1971). At least for the vertical electric fields on the path studied here, the resulting phase and amplitude differences (between the ˜100-km and ˜300-km sites) agree very well after just a small adjustment of ˜0.2 km in H‧ between the two codes. Such short paths also allow more localization than the usual long paths; here this localization is to low latitudes.
-
Schmitter, E. D.
2013-04-01
Remote sensing of the ionosphere bottom using long wave radio signal propagation is a still going strong and inexpensive method for continuous monitoring purposes. We present a propagation model describing the time development of solar flare effects. Based on monitored amplitude and phase data from VLF/LF transmitters gained at a mid-latitude site during the currently increasing solar cycle no. 24 a parameterized electron density profile is calculated as a function of time and fed into propagation calculations using the LWPC (Long Wave Propagation Capability). The model allows to include lower ionosphere recombination and attachment coefficients, as well as to identify the relevant forcing X-ray wavelength band, and is intended to be a small step forward to a better understanding of the solar-lower ionosphere interaction mechanisms within a consistent framework.
-
Sotnikov, V.; Kim, T.; Caplinger, J.; Main, D.; Mishin, E.; Gershenzon, N.; Genoni, T.; Paraschiv, I.; Rose, D.
2018-04-01
The concept of a parametric antenna in ionospheric plasma is analyzed. Such antennas are capable of exciting electromagnetic radiation fields, specifically the creation of whistler waves generated at the very low frequency (VLF) range, which are also capable of propagating large distances away from the source region. The mechanism of whistler wave generation is considered a parametric interaction of quasi-electrostatic whistler waves (also known as low oblique resonance (LOR) oscillations) excited by a conventional loop antenna. The interaction of LOR waves with quasi-neutral density perturbations in the near field of an antenna gives rise to electromagnetic whistler waves on combination frequencies. It is shown in this work that the amplitude of these waves can considerably exceed the amplitude of whistler waves directly excited by a loop. Additionally, particle-in-cell simulations, which demonstrate the excitation and spatial structure of VLF waves excited by a loop antenna, are presented. Possible applications including the wave-particle interactions to mitigate performance anomalies of low Earth orbit satellites, active space experiments, communication via VLF waves, and modification experiments in the ionosphere will be discussed.
-
Radial plasma drifts deduced from VLF whistler mode signals - A modelling study
Poulter, E. M.; Andrews, M. K.; Bailey, G. J.; Moffett, R. J.
1984-05-01
VLF whistler mode signals have previously been used to infer radial plasma drifts in the equatorial plane of the plasmasphere and the field-aligned ionosphere-protonosphere coupling fluxes. Physical models of the plasmasphere consisting of O(+) adn H(+) ions along dipole magnetic field lines, and including radial E x B drifts, are applied to a mid-latitude flux tube appropriate to whistler mode signals received at Wellington, New Zealand, from the fixed frequency VLF transmitter NLK (18.6 kHz) in Seattle, U.S.A. These models are first shown to provide a good representation of the recorded Doppler shift and group delay data. They are then used to simulate the process of deducing the drifts and fluxes from the recorded data. Provided the initial whistler mode duct latitude and the ionospheric contributions are known, the drifts at the equatorial plane can be estimated to about + or - 20 m/s (approximately 10-15 percent), and the two hemisphere ionosphere-protonosphere coupling fluxes to about + or - 10 to the 12th/sq m-sec (approximately 40 percent).
-
Conjugate Ground-Spacecraft Observations of VLF Chorus Elements
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Demekhov, A. G.; Manninen, J.; Santolík, Ondřej; Titova, E. E.
2017-01-01
Roč. 44, č. 23 (2017), s. 11735-11744 ISSN 0094-8276 Grant - others:AV ČR(CZ) AP1401 Program:Akademická prémie - Praemium Academiae Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : VAN ALLEN PROBES * WHISTLER-MODE WAVES * MAGNETOSPHERIC CHORUS * PROPAGATION * EMISSIONS * BAND * FREQUENCY * AMPLITUDE * MASER * GUIDE Subject RIV: BL - Plasma and Gas Discharge Physics OBOR OECD: Fluids and plasma physics (including surface physics) Impact factor: 4.253, year: 2016 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2017GL076139/epdf
-
Optical observations geomagnetically conjugate to sprite-producing lightning discharges
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. A. Marshall
2005-09-01
Full Text Available Theoretical studies have predicted that large positive cloud-to-ground discharges can trigger a runaway avalanche process of relativistic electrons, forming a geomagnetically trapped electron beam. The beam may undergo pitch angle and energy scattering during its traverse of the Earth's magnetosphere, with a small percentage of electrons remaining in the loss cone and precipitating in the magnetically conjugate atmosphere. In particular, N2 1P and N2+1N optical emissions are expected to be observable. In July and August 2003, an attempt was made to detect these optical emissions, called "conjugate sprites", in correlation with sprite observations in Europe near . Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam. Keywords. Ionosphere (Ionsophere-magnetosphere interactions; Ionospheric disturbances; Instruments and techniques
-
ELF-VLF communications through-the-Earth
Buettner, H. M.; Burke, G. J.; Didwall, E. M.; Holladay, G.; Lytle, R. J.
1985-06-01
We use computer models and experiments to explore the feasibility of communication between points underground and on the Earth's surface. Emphasis is placed on ELF-VLF electromagnetic propagation through the Earth; nominally, we investigated propagation in the 200 Hz-30 kHz frequency range. The computer modeling included calculations of the fields of a point electric or magnetic source in a homogeneous half space or a stratified Earth. Initial results for an insulated antenna of finite length are also considered. The experiments involved through-the-Earth transmissions at two locations in Pennsylvania, both of which had large formations of limestone. Initial results indicate that information rates as high as kbits/s may be possible for subsurface depths of 300 m or less. Accuracy of these estimates depends on the electromagnetic propagation constants of the rock, the noise characteristics, and modulation scheme. Although a nuisance for evaluating through-the-Earth propagation, the existence of subsurface metal conductors can improve the transmission character of the site.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gonzalez, W.D.; Pinto Junior, O.; Dutra, S.L.G.; Takahashi, H.
1988-01-01
A summary of the proposal for measurements of VLF wave-particle interactions, expected to occur at the South Atlantic magnetic anomaly, to be carried out on board a Brazilian geophysical satellite, will be presented. The expected domain of such interactions refers to electromagnetic VLF waves and to energetic-relativistic inner belt electrons, pitch angle diffusing into the atmosphere via cyclotron resonances. The detectors involve a tri-axial search coil magnetometer and a surface barrier silicon telescope. A modified and preliminary version of this proposed experiment will be carried out on board long duration balloon flights, well before the beginning of the intended satellite measurements. For the ballon flights the particle detector will be replaced by an x-ray detector, which can also monitor parameters related to the electron precipitation. (author) [pt
-
Kotik, D. S.; Raybov, A. V.; Ermakova, E. N.
2012-12-01
During the last three years the comprehensive study of ionospheric generation of the artificial signals in ULF/VLF band was carried out at SURA facility. This research was stimulated by successive HAARP experiments on detection the low frequency signals genreated due the action of the ponderomotive forces. Two experimental campaigns under different ionospheric, geomagnetic and facility operation mode conditions was undertaken every year from 2010 to 2012. Here we are summarizing the main features of the artificial ULF/VLF signals observed in vicinity the SURA site. The signals in the 2-20 Hz band were observed in the small area around the facility with the radius approximately 15 km. It was not signal detection at the 30 km distance. The maximum of the amplitude was detected in the nearest receiving point about 3 km away from the transmitting array. The amplitude increased about 3 times when the beam was inclined on16 degrees to the south so the footprint of the geomagnetic field line comes close to the point of observation. The ULF signals increased slightly when the SURA operating frequency overlaps the critical foF2 frequency. As a rule the daytime signals are smaller then nighttime one. No any correlation was observed with geomagnetic disturbances. The time delay of the ionospheric ULF signals measured by phase method was estimated as 300-400 ms. Polarization of the ULF signals has a pronounced elliptical character. Sometimes it was linear. The part of measurements in June 2012 was coincide with magnetic storm (June 16-18, Kp=6). It was observed broadening of the signal line at frequencies of 11 and 17 Hz up to 0.2 Hz at the recovery stage of the storm at June 18 (see the figure). This fact can be interpreted as the result of the signal interaction with the radiation belt protons appeared over there during the storm time. In 2012 campaigns it was firstly observed at SURA signals on frequencies of several kilohertz at nightime which could not be explained by
-
Optical observations geomagnetically conjugate to sprite-producing lightning discharges
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. A. Marshall
2005-09-01
Full Text Available Theoretical studies have predicted that large positive cloud-to-ground discharges can trigger a runaway avalanche process of relativistic electrons, forming a geomagnetically trapped electron beam. The beam may undergo pitch angle and energy scattering during its traverse of the Earth's magnetosphere, with a small percentage of electrons remaining in the loss cone and precipitating in the magnetically conjugate atmosphere. In particular, N2 1P and N2+1N optical emissions are expected to be observable. In July and August 2003, an attempt was made to detect these optical emissions, called "conjugate sprites", in correlation with sprite observations in Europe near
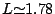 . Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam.
. Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam.
Keywords. Ionosphere (Ionsophere-magnetosphere interactions; Ionospheric disturbances; Instruments and techniques -
Photometric evidence of electron precipitation induced by first hop whistlers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Doolittle, J.H.; Carpenter, D.L.
1983-01-01
Electron precipitation events induced by discrete VLF whistler mode waves have previously been detected by photometers at Siple Station, Antarctica. This paper presents the first observations of ionospheric optical emissions correlated with VLF waves at the conjugate location, near Roberval, Quebec. Since most whistlers recorded at Siple or Roberval originate in the north, Roberval affords a clear perspective on the direct precipitation induced during the first pass of the wave as it propagates southward. For such a wave the direct precipitation and that induced in the ''mirrored mode'' by the returning two-hop wave should differ in arrival time by roughly twice the wave propagation time between hemispheres, while at Siple the effects of the direct and mirrored modes may overlap in time. A well defined series of observations of structured lambda4278 optical emissions was observed on August 30, 1979 in the aftermath of an intense magnetic storm. The optical emissions were found to lead the arrival time of the two-hop waves by about 0.7 s instead of lagging the local waves by about 1--2 s as had been previously observed for whistler driven events at Siple. The observed arrival time relationships are consistent with the predictions of a cyclotron resonance interaction model, and thus support previous observations of x-rays at Roberval. The importance of the first pass of the wave is further emphasized by an approximate proportionality between the amplitude of the VLF waves recorded at Siple and the intensity of the optical emission bursts at Roberval. Although structured optical emissions correlated with wave bursts can clearly be detected at Roberval, relatively large magnetospheric particle fluxes may be required to produce such events
-
Wave-particle interaction phenomena observed by antarctic rockets
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kimura, I.; Hirasawa, T.
1979-01-01
Rocket measurements of wave and particles activities made at Syowa Station in Antarctica during IMS period are reviewed. Nine rockets were used for such observations, out of which 6 rockets were launched in the auroral sky. In the VLF frequency range, 0 - 10 KHz, wideband spectra of wave electric and magnetic fields, Poynting flux and the direction of propagation vector were measured for chorus, ELF and VLF hiss, and for electrostatic noises. In the MF and HF range, the dynamic frequency spectra of 0.1 - 10 MHz were measured. The relationship of these wave phenomena with energetic particle activities measured by the same rockets are discussed. (author)
-
A tiered observational system for anthropogenic methane emissions
Duren, R. M.; Miller, C. E.; Hulley, G. C.; Hook, S. J.; Sander, S. P.
2014-12-01
Improved understanding of anthropogenic methane emissions is required for closing the global carbon budget and addressing priority challenges in climate policy. Several decades of top-down and bottom-up studies show that anthropogenic methane emissions are systematically underestimated in key regions and economic sectors. These uncertainties have been compounded by the dramatic rise of disruptive technologies (e.g., the transformation in the US energy system due to unconventional gas and oil production). Methane flux estimates derived from inverse analyses and aircraft-based mass balance approaches underscore the disagreement in nationally and regionally reported methane emissions as well as the possibility of a long-tail distribution in fugitive emissions spanning the US natural gas supply chain; i.e. a small number of super-emitters may be responsible for most of the observed anomalies. Other studies highlight the challenges of sectoral and spatial attribution of fugitive emissions - including the relative contributions of dairies vs oil and gas production or disentangling the contributions of natural gas transmission, distribution, and consumption or landfill emissions in complex urban environments. Limited observational data remains a foundational barrier to resolving these challenges. We present a tiered observing system strategy for persistent, high-frequency monitoring over large areas to provide remote detection, geolocation and quantification of significant anthropogenic methane emissions across cities, states, basins and continents. We describe how this would both improve confidence in methane emission estimates and expedite resolution of fugitive emissions and leaks. We summarize recent prototype field campaigns that employ multiple vantage points and measurement techniques (including NASA's CARVE and HyTES aircraft and PanFTS instrument on Mt Wilson). We share preliminary results of this tiered observational approach including examples of individual
-
Cluster observations and simulations of He+ EMIC triggered emissions
Grison, B.; Shoji, M.; Santolik, O.; Omura, Y.
2012-12-01
EMIC triggered emissions have been reported in the inner magnetosphere at the edge of the plasmapause nightside [Pickett et al., 2010]. The generation mechanism proposed by Omura et al. [2010] is very similar to the one of the whistler chorus emissions and simulation results agree with observations and theory [Shoji et Omura, 2011]. The main characteristics of these emissions generated in the magnetic equatorial plane region are a frequency with time dispersion and a high level of coherence. The start frequency of previously mentioned observations is above half of the proton gyrofrequency. It means that the emissions are generated on the proton branch. On the He+ branch, generation of triggered emissions, in the same region, requests more energetic protons and the triggering process starts below the He+ gyrofrequency. It makes their identification in Cluster data rather difficult. Recent simulation results confirm the possibility of EMIC triggered emission on the He+ branch. In the present contribution we propose to compare a Cluster event to simulation results in order to investigate the possibility to identify observations to a He+ triggered emission. The impact of the observed waves on particle precipitation is also investigated.
-
Zarif, Fardous; Slater, Lee; Mabrouk, Mohamed; Youssef, Ahmed; Al-Temamy, Ayman; Mousa, Salah; Farag, Karam; Robinson, Judy
2018-01-01
Understanding and developing groundwater resources in arid regions such as El Salloum basin, along the northwestern coast of Egypt, remains a challenging issue. One-dimensional (1D) electrical sounding (ES), two-dimensional (2D) electrical resistivity imaging (ERI), and very low frequency electromagnetic (VLF-EM) measurements were used to investigate the hydrogeological framework of El Salloum basin with the aim of determining the potential for extraction of potable water. 1D resistivity sounding models were used to delineate geoelectric sections and water-bearing layers. 2D ERI highlighted decreases in resistivity with depth, attributed to clay-rich limestone combined with seawater intrusion towards the coast. A depth of investigation (DOI) index was used to constrain the information content of the images at depths up to 100 m. The VLF-EM survey identified likely faults/fractured zones across the study area. A combined analysis of the datasets of the 1D ES, 2D ERI, and VLF-EM methods identified potential zones of groundwater, the extent of seawater intrusion, and major hydrogeological structures (fracture zones) in El Salloum basin. The equivalent geologic layers suggest that the main aquifer in the basin is the fractured chalky limestone middle Miocene) south of the coastal plain of the study area. Sites likely to provide significant volumes of potable water were identified based on relatively high resistivity and thickness of laterally extensive layers. The most promising locations for drilling productive wells are in the south and southeastern parts of the region, where the potential for potable groundwater increases substantially.
-
Observational Trends of Cometary X-ray Emission
Lisse, C. M.
2001-05-01
The unexpected discovery of x-ray emission from Comet Hyakutake in March 1996 (Lisse et al. 1996) has produced a number of questions about the physical mechanism producing the radiation. The original detection and subsequent observations (Dennerl et al. 1997, Mumma et al. 1997, Krasnopolsky et al. 1998, Owens et al. 1998, Lisse et al. 1999, Lisse et a. 2001, Dennerl et al. 2001) have shown that the very soft (best fit thermal bremsstrahlung model kT = 0.23 keV) emission is due to an interaction between the solar wind and the comet's atmosphere. Using the results from the more than 15 comets detected to date in x-rays, we report on the latest results on cometary x-ray emission. Our emphasis will be on understanding the physical mechanism producing the emission, and using this to determine the nature of the cometary coma and solar wind flux. As-observed morphologies, spectra, and light curves will be discussed. We also report on the status of current cometary observations using the new powerful x-ray observatories Chandra and XMM. This work has been graciously supported by grants from the NASA Planetary Astronomy and Astrophysical Data Programs.
-
Accurate Modeling of Ionospheric Electromagnetic Fields Generated by a Low Altitude VLF Transmitter
2009-03-31
AFRL-RV-HA-TR-2009-1055 Accurate Modeling of Ionospheric Electromagnetic Fields Generated by a Low Altitude VLF Transmitter ...m (or even 500 m) at mid to high latitudes . At low latitudes , the FDTD model exhibits variations that make it difficult to determine a reliable...Scientific, Final 3. DATES COVERED (From - To) 02-08-2006 – 31-12-2008 4. TITLE AND SUBTITLE Accurate Modeling of Ionospheric Electromagnetic Fields
-
Denton, J. J.; Denton, M. H.; Kavanagh, A. J.; Harron, H.; Ulich, T.; Denton, J. S.
2012-01-01
We report on a school-university collaboration to involve students in the deployment, testing, and operation of a very low frequency (VLF) radio receiver as part of an international network of such experiments. A background to the collaboration is presented, along with a summary of planning and development, and the ultimate deployment of the…
-
Fast Emission Estimates in China Constrained by Satellite Observations (Invited)
Mijling, B.; van der A, R.
2013-12-01
Emission inventories of air pollutants are crucial information for policy makers and form important input data for air quality models. Unfortunately, bottom-up emission inventories, compiled from large quantities of statistical data, are easily outdated for an emerging economy such as China, where rapid economic growth changes emissions accordingly. Alternatively, top-down emission estimates from satellite observations of air constituents have important advantages of being spatial consistent, having high temporal resolution, and enabling emission updates shortly after the satellite data become available. Constraining emissions from concentration measurements is, however, computationally challenging. Within the GlobEmission project of the European Space Agency (ESA) a new algorithm has been developed, specifically designed for fast daily emission estimates of short-lived atmospheric species on a mesoscopic scale (0.25 × 0.25 degree) from satellite observations of column concentrations. The algorithm needs only one forward model run from a chemical transport model to calculate the sensitivity of concentration to emission, using trajectory analysis to account for transport away from the source. By using a Kalman filter in the inverse step, optimal use of the a priori knowledge and the newly observed data is made. We apply the algorithm for NOx emission estimates in East China, using the CHIMERE model together with tropospheric NO2 column retrievals of the OMI and GOME-2 satellite instruments. The observations are used to construct a monthly emission time series, which reveal important emission trends such as the emission reduction measures during the Beijing Olympic Games, and the impact and recovery from the global economic crisis. The algorithm is also able to detect emerging sources (e.g. new power plants) and improve emission information for areas where proxy data are not or badly known (e.g. shipping emissions). The new emission estimates result in a better
-
The effect of earth tides as observed in seismo-electromagnetic precursory signals
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Hayakawa
2009-10-01
Full Text Available Studies on the effect of earth tides in triggering earthquakes (EQs had a great progress in recent years, which has provided convincing evidence of earth tides in EQ triggering. On the other hand, there have been accumulated a lot of evidences on the presence of seismogenic electromagnetic effects (such as ULF electromagnetic emissions from the lithosphere, ionospheric perturbations as detected by subionospheric VLF/LF propagation, etc.. Since the initial agent of these seismogenic electromagnetic effects is obviously due to some mechanical action around the EQ focal zone, the tidal effect as seen in EQ sequence should appear also in seismo-electromagnetic phenomena. Based on this expectation we have studied the tidal effect in different seismogenic phenomena, and have found that lithospheric ULF emissions exhibit a clear maximum-minimum-maximum pattern synchronized with the lunar phase of the EQ during several months before the EQ. As for VLF/LF propagation anomaly representing the lower ionospheric perturbation, we have found the tidal modulation very similar to ULF emissions, but less clear, and also there are some differences from the ULF case (such as occasional shift with respect to the lunar phase and/or the presence of higher frequency modulation, etc.. These findings are indicative that those electromagnetic phenomena reported to be in possible association with an EQ are really related with any preparatory phase of an EQ. This kind of study would be a bridge between the seismology and our seismo-electromagnetic study.
-
Phanikumar, D. V.; Kwak, Y.-S.; Patra, A. K.; Maurya, A. K.; Singh, Rajesh; Park, S.-M.
2014-09-01
In this paper, we analyze VLF signals received at Busan to study the the D-region changes linked with the solar eclipse event of 22 July 2009 for very short (∼390 km) transmitter-receiver great circle path (TRGCP) during local noon time 00:36-03:13 UT (09:36-12:13 KST). The eclipse crossed south of Busan with a maximum obscuration of ∼84%. Observations clearly show a reduction of ∼6.2 dB in the VLF signal strength at the time of maximum solar obscuration (84% at 01:53 UT) as compared to those observed on the control days. Estimated values of change in Wait ionospheric parameters: reflection height (h‧) in km and inverse scale height parameter (β) in km-1 from Long Wave Propagation Capability (LWPC) model during the maximum eclipse phase as compared to unperturbed ionosphere are 7 km and 0.055 km-1, respectively. Moreover, the D-region electron density estimated from model computation shows 95% depletion in electron density at the height of ∼71 km. The reflection height is found to increase by ∼7 km in the D-region during the eclipse as compared to those on the control days, implying a depletion in the Lyman-α flux by a factor of ∼7. The present observations are discussed in the light of current understanding on the solar eclipse induced D-region dynamics.
-
OBSERVATION OF CORRELATED OPTICAL AND GAMMA EMISSIONS FROM GRB 081126
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Klotz, A.; Boer, M.; Gendre, B.; Atteia, J. L.; Coward, D. M.; Imerito, A. C.
2009-01-01
We present an analysis of time-resolved optical emissions observed from the gamma-ray burst GRB 081126 during the prompt phase. The analysis employed time-resolved photometry using optical data obtained by the TAROT telescope, using BAT data from the Swift spacecraft, and time-resolved spectroscopy at high energies from the GBM instrument onboard the Fermi spacecraft. The optical emission of GRB 081126 is found to be compatible with the second gamma emission pulse shifted by a positive time lag of 8.4 ± 3.9 s. This is the first well-resolved observation of a time lag between optical and gamma emissions during a gamma-ray burst. Our observations could potentially provide new constraints on the fireball model for gamma-ray burst early emissions. Furthermore, observations of time lags between optical and gamma ray photons provides an exciting opportunity to constrain quantum gravity theories.
-
Macotela, Edith L.; Raulin, Jean-Pierre; Manninen, Jyrki; Correia, Emília; Turunen, Tauno; Magalhães, Antonio
2017-12-01
The daytime lower ionosphere behaves as a solar X-ray flare detector, which can be monitored using very low frequency (VLF) radio waves that propagate inside the Earth-ionosphere waveguide. In this paper, we infer the lower ionosphere sensitivity variation over a complete solar cycle by using the minimum X-ray fluence (FXmin) necessary to produce a disturbance of the quiescent ionospheric conductivity. FXmin is the photon energy flux integrated over the time interval from the start of a solar X-ray flare to the beginning of the ionospheric disturbance recorded as amplitude deviation of the VLF signal. FXmin is computed for ionospheric disturbances that occurred in the time interval of December-January from 2007 to 2016 (solar cycle 24). The computation of FXmin uses the X-ray flux in the wavelength band below 0.2 nm and the amplitude of VLF signals transmitted from France (HWU), Turkey (TBB), and U.S. (NAA), which were recorded in Brazil, Finland, and Peru. The main result of this study is that the long-term variation of FXmin is correlated with the level of solar activity, having FXmin values in the range (1 - 12) × 10-7 J/m2. Our result suggests that FXmin is anticorrelated with the lower ionosphere sensitivity, confirming that the long-term variation of the ionospheric sensitivity is anticorrelated with the level of solar activity. This result is important to identify the minimum X-ray fluence that an external source of ionization must overcome in order to produce a measurable ionospheric disturbance during daytime.
-
Egret observations of the extragalactic gamma-ray emission
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Sreekumar, P.; Bertsch, D.L.; Dingus, B.L.
1998-01-01
The all-sky survey in high-energy gamma rays (E > 30 MeV) carried out by EGRET aboard the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory provides a unique opportunity to examine in detail the diffuse gamma-ray emission. The observed diffuse emission has a Galactic component arising from cosmic-ray interactions wi...
-
Fast emission estimates in China and South Africa constrained by satellite observations
Mijling, Bas; van der A, Ronald
2013-04-01
Emission inventories of air pollutants are crucial information for policy makers and form important input data for air quality models. Unfortunately, bottom-up emission inventories, compiled from large quantities of statistical data, are easily outdated for emerging economies such as China and South Africa, where rapid economic growth change emissions accordingly. Alternatively, top-down emission estimates from satellite observations of air constituents have important advantages of being spatial consistent, having high temporal resolution, and enabling emission updates shortly after the satellite data become available. However, constraining emissions from observations of concentrations is computationally challenging. Within the GlobEmission project (part of the Data User Element programme of ESA) a new algorithm has been developed, specifically designed for fast daily emission estimates of short-lived atmospheric species on a mesoscopic scale (0.25 × 0.25 degree) from satellite observations of column concentrations. The algorithm needs only one forward model run from a chemical transport model to calculate the sensitivity of concentration to emission, using trajectory analysis to account for transport away from the source. By using a Kalman filter in the inverse step, optimal use of the a priori knowledge and the newly observed data is made. We apply the algorithm for NOx emission estimates in East China and South Africa, using the CHIMERE chemical transport model together with tropospheric NO2 column retrievals of the OMI and GOME-2 satellite instruments. The observations are used to construct a monthly emission time series, which reveal important emission trends such as the emission reduction measures during the Beijing Olympic Games, and the impact and recovery from the global economic crisis. The algorithm is also able to detect emerging sources (e.g. new power plants) and improve emission information for areas where proxy data are not or badly known (e
-
Journal of Earth System Science | Indian Academy of Sciences
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
pp 209-216. Quasi-periodic VLF emissions observed during daytime at a low latitude Indian ground station Jammu · K K Singh J Singh R P Patel A K Singh R P Singh Rejesh Singh P A Ganai · More Details Abstract Fulltext PDF. This paper reports quasi-periodic pulsing hiss emissions recorded during daytime in the ...
-
Observations of EMIC Triggered Emissions off the Magnetic Equatorial Plane
Grison, B.; Breuillard, H.; Santolik, O.; Cornilleau-Wehrlin, N.
2016-12-01
On 19/08/2005 Cluster spacecraft had their perigee close to the dayside of the Earth magnetic equatorial plane, at about 14 hours Magnetic Local Time. The spacecraft crossed the equator from the southern hemisphere toward the northern hemisphere. In the Southern hemisphere, at about -23° magnetic latitude (MLAT) and at distance of 5.25 Earth Radii from Earth, Cluster 3 observes an EMIC triggered emission between the He+ and the proton local gyrofrequencies. The magnetic waveform (STAFF instrument data) is transformed into the Fourier space for a study based on single value decomposition (SVD) analysis. The emission lasts about 30s. The emission frequency rises from 1Hz up to 1.9Hz. The emission polarization is left-hand, its coherence value is high and the propagation angle is field aligned (lower than 30º). The Poynting flux orientation could not be established. Based on previous study results, these properties are indicative of an observation in vicinity of the source region of the triggered emission. From our knowledge this is the first time that EMIC triggered emission are observed off the magnetic equator. In order to identify the source region we study two possibilities: a source region at higher latitudes than the observations (and particles orbiting in "Shabansky" orbits) and a source region close to the magnetic equatorial plane, as reported in previous studies. We propose to identify the source region from ray tracing analysis and to compare the observed propagation angle in several frequency ranges to the ray tracing results.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Hayakawa
2011-02-01
Full Text Available Ionospheric perturbations in possible association with the 2010 Haiti earthquake occurred on 12 January 2010 (with a magnitude of 7.0 and depth of 10 km are investigated on the basis of subionospheric propagation data from the NAA transmitter on the east coast of the USA to a VLF receiving station in Peru. The local nighttime VLF amplitude data are extensively investigated during the period from the beginning of October 2009 to the end of March 2010, in which the trend (nighttime average amplitude, dispersion and nighttime fluctuation are analysed. It is found that a clear precursory ionosphere perturbation is detected just around New Years day of 2010, about 12 days before the main shock, which is characterised by the simultaneous decrease in the trend and the increases in dispersion and nighttime fluctuation. An additional finding might be the presence of the effect of the Earth's tide one and two months before the main shock, which can only be seen for a huge EQ.
-
Observations of Anomalous Microwave Emission from HII Regions
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Clive Dickinson
2013-01-01
free-free emission from UCHII regions may be also be significant in some cases. The AME emissivity, defined as the ratio of the AME brightness to the 100 μm brightness, is comparable to the value observed in high-latitude diffuse cirrus in some regions, but is significantly lower in others. However, this value is dependent on the dust temperature. More data, both at high frequencies (>~5 GHz and high resolution (~1′ or better is required to disentangle the emission processes in such complex regions.
-
The impact of PMSE and NLC particles on VLF propagation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
D. Nunn
2004-04-01
Full Text Available PMSE or Polar Mesosphere Summer Echoes are a well-known phenomenon in the summer northern polar regions, in which anomalous VHF/UHF radar echoes are returned from heights ~85km. Noctilucent clouds and electron density biteouts are two phenomena that sometimes occur together with PMSE. Electron density biteouts are electron density depletion layers of up to 90%, which may be several kms thick. Using the NOSC Modefndr code based on Wait's modal theory for subionospheric propagation, we calculate the shifts in received VLF amplitude and phase that occur as a result of electron density biteouts. The code assumes a homogeneous background ionosphere and a homogeneous biteout layer along the Great Circle Path (GCP corridor, for transmitter receiver path lengths in the range of 500–6000km.
For profiles during the 10h about midnight and under quiet geomagnetic conditions, where the electron density at 85km would normally be less than 500el/cc, it was found that received signal perturbations were significant, of the order of 1–4dB and 5–40° of phase. Perturbation amplitudes increase roughly as the square root of frequency. At short range perturbations are rather erratic, but more consistent at large ranges, readily interpretable in terms of the shifts in excitation factor, attenuation factor and v/c ratios for Wait's modes. Under these conditions such shifts should be detectable by a well constituted experiment involving multiple paths and multiple frequencies in the north polar region in summer. It is anticipated that VLF propagation could be a valuable diagnostic for biteout/PMSE when electron density at 85km is under 500el/cc, under which circumstances PMSE are not directly detectable by VHF/UHF radars.
Key words. Electromagnetism (wave propagation – Ionosphere (polar ionosphere – Radioscience (ionospheric propagation -
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Meloni, A.; Di Mauro, D.; Mele, G.; Palangio, P. [Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Rome (Italy); Ernst, T.; Teisseyre, R. [Institute of Geophysics, Warszawa (Poland)
2001-04-01
Magnetotelluric data were collected at Collemeluccio (41.72{sup 0}N, 14.37{sup 0}E) in Central Italy from summer 1991 to spring 1998. Analyzed by means of tensor decomposition on the geoelectric potential and robust estimation on the geomagnetic field, this set of data allowed the investigation of the electromagnetic induction, is presented here in its time evolution and compared to local and regional seismic activity. Tecto magnetic field observations from absolute magnetic field level in Central Italy were also made on data simultaneously recorded at four magnetometer stations, using L'Aquila Geomagnetic Observatory as a reference for differentiation. Recent results gathered from a system of two VLF search coil wide-band antennas, installed in the L'Aquila Observatory, are also discussed in relation to local seismic activity.
-
First Observation of Lion Roar Emission in Saturn's Magnetosheath
Píša, D.; Sulaiman, A. H.; Santolík, O.; Hospodarsky, G. B.; Kurth, W. S.; Gurnett, D. A.
2018-01-01
We present an observation of intense emissions in Saturn's magnetosheath as detected by the Cassini spacecraft. The emissions are observed in the dawn sector (magnetic local time ˜06:45) of the magnetosheath over a time period of 11 h before the spacecraft crossed the bow shock and entered the unshocked solar wind. They are found to be narrow-banded with a peak frequency of about 0.16 fce, where fce is the local electron gyrofrequency. Using plane wave propagation analysis, we show that the waves are right hand circularly polarized in the spacecraft frame and propagate at small wave normal angles (lion roars" have been reported by numerous missions in the terrestrial magnetosheath. Here we show the first evidence such emission outside the terrestrial environment. Our observations suggest that lion roars are a solar-system-wide phenomenon and capable of existing in a broad range of parameter space. This also includes 1 order of magnitude difference in frequencies. We anticipate our result to provide new insight into such emissions in a new parameter regime characterized by a higher plasma beta (owing to the substantially higher Mach number bow shock) compared to Earth.
-
SCIAMACHY formaldehyde observations: constraint for isoprene emission estimates over Europe?
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. Dufour
2009-03-01
Full Text Available Formaldehyde (HCHO is an important intermediate compound in the degradation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs in the troposphere. Sources of HCHO are largely dominated by its secondary production from VOC oxidation, methane and isoprene being the main precursors in unpolluted areas. As a result of the moderate lifetime of HCHO, its spatial distribution is determined by reactive hydrocarbon emissions. We focus here on Europe and investigate the influence of the different emissions on HCHO tropospheric columns with the CHIMERE chemical transport model in order to interpret the comparisons between SCIAMACHY and simulated HCHO columns. Europe was never specifically studied before for these purposes using satellite observations. The bias between measurements and model is less than 20% on average. The differences are discussed according to the errors on the model and the observations and remaining discrepancies are attributed to a misrepresentation of biogenic emissions. This study requires the characterisation of: (1 the model errors and performances concerning formaldehyde. The errors on the HCHO columns, mainly related to chemistry and mixed emission types, are evaluated to 2×1015 molecule/cm2 and the model performances evaluated using surface measurements are satisfactory (~13%; (2 the observation errors that define the needs in spatial and temporal averaging for meaningful comparisons. Using SCIAMACHY observations as constraint for biogenic isoprene emissions in an inverse modelling scheme reduces their uncertainties by about a factor of two in region of intense emissions. The retrieved correction factors for the isoprene emissions range from a factor of 0.15 (North Africa to a factor of 2 (Poland, the United Kingdom depending on the regions.
-
Henne, Stephan; Leuenberger, Markus; Steinbacher, Martin; Eugster, Werner; Meinhardt, Frank; Bergamaschi, Peter; Emmenegger, Lukas; Brunner, Dominik
2017-04-01
Similar to other Western European countries, agricultural sources dominate the methane (CH4) emission budget in Switzerland. 'Bottom-up' estimates of these emissions are still connected with relatively large uncertainties due to considerable variability and uncertainties in observed emission factors for the underlying processes (e.g., enteric fermentation, manure management). Here, we present a regional-scale (˜300 x 200 km2) atmospheric inversion study of CH4 emissions in Switzerland making use of the recently established CarboCount-CH network of four stations on the Swiss Plateau as well as the neighbouring mountain-top sites Jungfraujoch and Schauinsland (Germany). Continuous observations from all CarboCount-CH sites are available since 2013. We use a high-resolution (7 x 7 km2) Lagrangian particle dispersion model (FLEXPART-COSMO) in connection with two different inversion systems (Bayesian and extended Kalman filter) to estimate spatially and temporally resolved CH4 emissions for the Swiss domain in the period 2013 to 2016. An extensive set of sensitivity inversions is used to assess the overall uncertainty of our inverse approach. In general we find good agreement of the total Swiss CH4 emissions between our 'top-down' estimate and the national 'bottom-up' reporting. In addition, a robust emission seasonality, with reduced winter time values, can be seen in all years. No significant trend or year-to-year variability was observed for the analysed four-year period, again in agreement with a very small downward trend in the national 'bottom-up' reporting. Special attention is given to the influence of boundary conditions as taken from different global scale model simulations (TM5, FLEXPART) and remote observations. We find that uncertainties in the boundary conditions can induce large offsets in the national total emissions. However, spatial emission patterns are less sensitive to the choice of boundary condition. Furthermore and in order to demonstrate the
-
Observations of gamma-ray emission in solar flares
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Forrest, D.J.; Chupp, E.L.; Suri, A.N.; Reppin, C.
1973-01-01
This paper reviews the observations of gamma-ray emission made from the OSO-7 satellite in connection with two solar flares in early August 1972. The details of the measurements and a preliminary interpretation of some of the observed features are given. (U.S.)
-
Mizuno, Taeko; Tamakoshi, Koji; Tanabe, Keiko
2017-08-01
To assess the longitudinal change in autonomic nervous system (ANS) activity during pregnancy and the association between anxiety during pregnancy and ANS activity. Pregnant Japanese women with a singleton fetus and normal pregnancy were recruited (n=65). ANS activity and anxiety were measured using a self-rating questionnaire at approximately 20, 30, and 36weeks of gestation. Very low (VLF) and high (HF) frequency bands of heart rate variability spectrums were used. Anxiety was assessed using the Japanese version of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. A score of 45 or more on trait-anxiety and the other represent the trait-anxiety group and the non- trait-anxiety group, respectively. The state-anxiety group and the non-state-anxiety group were defined in the same manner. Longitudinal observation of individual pregnant women indicated the significant increasing trend (p=0.002) of VLF power and the significant decreasing trend (p<0.001) of HF power during 20 to 36 gestation weeks. Compared with the non-trait-anxiety group, the trait-anxiety group had significantly lower VLF values at 20 gestational weeks (p=0.033) and had significantly lower HF values at 30 and 36 gestational weeks (p=0.015 and p=0.044, respectively). The increasing rate of VLF from 20 to 36 gestational weeks was higher among the trait-anxiety group. The same associations were observed between the state-anxiety and non-state-anxiety groups at 20 gestational weeks. Anxiety during pregnancy decreased heart rate variability. Anxiety in second trimester pregnancy promoted a subsequent increase in sympathetic activity. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
O. Molchanov
2006-01-01
Full Text Available The analysis of the VLF signals radiated by ground transmitters and received on board of the French DEMETER satellite, reveals a drop of the signals (scattering spot connected with the occurrence of large earthquakes. The extension of the "scattering spots" zone is large enough (1000–5000 km and, probably, it increases with the magnitude of the "relative" earthquake. A possible model to explain the phenomenology, based on the acoustic gravity waves and the ionosphere turbulence, is proposed. The method of diagnostics applied to this study has the advantage to be a global one due to the world wide location of the powerful VLF transmitters and of the satellite reception. However, a specific disadvantage exists because the method requires rather a long time period of analysis due to the large longitudinal displacements among the successive satellite orbits. At the moment, at least, one month seems to be necessary.
-
Observed decrease in atmospheric mercury explained by global decline in anthropogenic emissions
Yanxu Zhang,; Daniel J. Jacob,; Hannah M. Horowitz,; Long Chen,; Helen M. Amos,; Krabbenhoft, David P.; Franz Slemr,; Vincent L. St. Louis,; Elsie M. Sunderland,
2015-01-01
Observations of elemental mercury (Hg0) at sites in North America and Europe show large decreases (∼1–2% y−1) from 1990 to present. Observations in background northern hemisphere air, including Mauna Loa Observatory (Hawaii) and CARIBIC (Civil Aircraft for the Regular Investigation of the atmosphere Based on an Instrument Container) aircraft flights, show weaker decreases (inventories indicating flat or increasing emissions over that period. However, the inventories have three major flaws: (i) they do not account for the decline in atmospheric release of Hg from commercial products; (ii) they are biased in their estimate of artisanal and small-scale gold mining emissions; and (iii) they do not properly account for the change in Hg0/HgII speciation of emissions from coal-fired utilities after implementation of emission controls targeted at SO2 and NOx. We construct an improved global emission inventory for the period 1990 to 2010 accounting for the above factors and find a 20% decrease in total Hg emissions and a 30% decrease in anthropogenic Hg0 emissions, with much larger decreases in North America and Europe offsetting the effect of increasing emissions in Asia. Implementation of our inventory in a global 3D atmospheric Hg simulation [GEOS-Chem (Goddard Earth Observing System-Chemistry)] coupled to land and ocean reservoirs reproduces the observed large-scale trends in atmospheric Hg0 concentrations and in HgII wet deposition. The large trends observed in North America and Europe reflect the phase-out of Hg from commercial products as well as the cobenefit from SO2 and NOx emission controls on coal-fired utilities.
-
Galactic water vapor emission: further observations of variability.
Knowles, S H; Mayer, C H; Sullivan, W T; Cheung, A C
1969-10-10
Recent observations of the 1.35-centimeter line emission of water vapor from galactic sources show short-term variability in the spectra of several sources. Two additional sources, Cygnus 1 and NGC 6334N, have been observed, and the spectra of W49 and VY Canis Majoris were measured over a wider range of radial velocity.
-
First observation of lion roar-like emissions in Saturn's magnetosheath
Pisa, David; Sulaiman, Ali H.; Santolik, Ondrej; Hospodarsky, George B.; Kurth, William S.; Gurnett, Donald A.
2017-04-01
Electromagnetic whistler mode waves known as "lion roars" have been reported by many missions inside the terrestrial magnetosheath. We show the observation of similar intense emissions in Saturn's magnetosheath as detected by the Cassini spacecraft. The emissions were observed inside the dawn sector (MLT˜0730) of the magnetosheath over a time period of nine hours before the satellite crossed the bow shock and entered the solar wind. The emissions were narrow-banded with a typical frequency of about 15 Hz well below the local electron cyclotron frequency (fce ˜100 Hz). Using the minimum variance analysis method, we show that the waves are right hand circularly polarized and propagate at small wave normal angles with respect to the ambient magnetic field. Here, for the first time, we report the evidence of lion roar-like emissions in Saturn's magnetosheath which represents a new and unique parameter regime.
-
Maritime NOx Emissions Over Chinese Seas Derived From Satellite Observations
Ding, J.; van der A, R. J.; Mijling, B.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Levelt, P. F.
2018-02-01
By applying an inversion algorithm to NOx satellite observations from Ozone Monitoring Instrument, monthly NOx emissions for a 10 year period (2007 to 2016) over Chinese seas are presented for the first time. No effective regulations on NOx emissions have been implemented for ships in China, which is reflected in the trend analysis of maritime emissions. The maritime emissions display a continuous increase rate of about 20% per year until 2012 and slow down to 3% after that. The seasonal cycle of shipping emissions has regional variations, but all regions show lower emissions during winter. Simulations by an atmospheric chemistry transport model show a notable influence of maritime emissions on air pollution over coastal areas, especially in summer. The satellite-derived spatial distribution and the magnitude of maritime emissions over Chinese seas are in good agreement with bottom-up studies based on the Automatic Identification System of ships.
-
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
Northern Central Indian Ridge and their geodynamic implications. 659 ... during winter over a tropical inland station –. Kharagpur .... potential water harvesting sites in the Kali Water- shed, Mahi .... late organic carbon (POC) in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. 1 ... Quasi-periodic VLF emissions observed during daytime at a ...
-
Agarwal VK see Balaji C 331 Ahmad Ishfaq Mir see Kessarkar ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
tures during winter over a tropical inland station –. Kharagpur (22. ... dient between Indian landmass and neighbouring oceans and .... potential water harvesting sites in the Kali Water- shed, Mahi ... Quasi-periodic VLF emissions observed during daytime at a ... late organic carbon (POC) in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. 1.
-
Updated SO2 emission estimates over China using OMI/Aura observations
Elissavet Koukouli, Maria; Theys, Nicolas; Ding, Jieying; Zyrichidou, Irene; Mijling, Bas; Balis, Dimitrios; van der A, Ronald Johannes
2018-03-01
The main aim of this paper is to update existing sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission inventories over China using modern inversion techniques, state-of-the-art chemistry transport modelling (CTM) and satellite observations of SO2. Within the framework of the EU Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) MarcoPolo (Monitoring and Assessment of Regional air quality in China using space Observations) project, a new SO2 emission inventory over China was calculated using the CHIMERE v2013b CTM simulations, 10 years of Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI)/Aura total SO2 columns and the pre-existing Multi-resolution Emission Inventory for China (MEIC v1.2). It is shown that including satellite observations in the calculations increases the current bottom-up MEIC inventory emissions for the entire domain studied (15-55° N, 102-132° E) from 26.30 to 32.60 Tg annum-1, with positive updates which are stronger in winter ( ˜ 36 % increase). New source areas were identified in the southwest (25-35° N, 100-110° E) as well as in the northeast (40-50° N, 120-130° E) of the domain studied as high SO2 levels were observed by OMI, resulting in increased emissions in the a posteriori inventory that do not appear in the original MEIC v1.2 dataset. Comparisons with the independent Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research, EDGAR v4.3.1, show a satisfying agreement since the EDGAR 2010 bottom-up database provides 33.30 Tg annum-1 of SO2 emissions. When studying the entire OMI/Aura time period (2005 to 2015), it was shown that the SO2 emissions remain nearly constant before the year 2010, with a drift of -0.51 ± 0.38 Tg annum-1, and show a statistically significant decline after the year 2010 of -1.64 ± 0.37 Tg annum-1 for the entire domain. Similar findings were obtained when focusing on the greater Beijing area (30-40° N, 110-120° E) with pre-2010 drifts of -0.17 ± 0.14 and post-2010 drifts of -0.47 ± 0.12 Tg annum-1. The new SO2 emission inventory is publicly available and forms
-
Modeled and observed ozone sensitivity to mobile-source emissions in Mexico City
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Zavala
2009-01-01
Full Text Available The emission characteristics of mobile sources in the Mexico City Metropolitan Area (MCMA have changed significantly over the past few decades in response to emission control policies, advancements in vehicle technologies and improvements in fuel quality, among others. Along with these changes, concurrent non-linear changes in photochemical levels and criteria pollutants have been observed, providing a unique opportunity to understand the effects of perturbations of mobile emission levels on the photochemistry in the region using observational and modeling approaches. The observed historical trends of ozone (O3, carbon monoxide (CO and nitrogen oxides (NOx suggest that ozone production in the MCMA has changed from a low to a high VOC-sensitive regime over a period of 20 years. Comparison of the historical emission trends of CO, NOx and hydrocarbons derived from mobile-source emission studies in the MCMA from 1991 to 2006 with the trends of the concentrations of CO, NOx, and the CO/NOx ratio during peak traffic hours also indicates that fuel-based fleet average emission factors have significantly decreased for CO and VOCs during this period whereas NOx emission factors do not show any strong trend, effectively reducing the ambient VOC/NOx ratio.
This study presents the results of model analyses on the sensitivity of the observed ozone levels to the estimated historical changes in its precursors. The model sensitivity analyses used a well-validated base case simulation of a high pollution episode in the MCMA with the mathematical Decoupled Direct Method (DDM and the standard Brute Force Method (BFM in the 3-D CAMx chemical transport model. The model reproduces adequately the observed historical trends and current photochemical levels. Comparison of the BFM and the DDM sensitivity techniques indicates that the model yields ozone values that increase linearly with -
Whistler Observations on DEMETER Compared with Full Electromagnetic Wave Simulations
Compston, A. J.; Cohen, M.; Lehtinen, N. G.; Inan, U.; Linscott, I.; Said, R.; Parrot, M.
2014-12-01
Terrestrial Very Low Frequency (VLF) electromagnetic radiation, which strongly impacts the Van Allen radiation belt electron dynamics, is injected across the ionosphere into the Earth's plasmasphere from two primary sources: man-made VLF transmitters and lightning discharges. Numerical models of trans-ionospheric propagation of such waves remain unvalidated, and early models may have overestimated the absorption, hindering a comprehensive understanding of the global impact of VLF waves in the loss of radiation belt electrons. In an attempt to remedy the problem of a lack of accurate trans-ionospheric propagation models, we have used a full electromagnetic wave method (FWM) numerical code to simulate the propagation of lightning-generated whistlers into the magnetosphere and compared the results with whistlers observed on the DEMETER satellite and paired with lightning stroke data from the National Lightning Detection Network (NLDN). We have identified over 20,000 whistlers occuring in 14 different passes of DEMETER over the central United States during the summer of 2009, and 14,000 of those occured within the 2000 km x 2000 km simulation grid we used. As shown in the attached figure, which shows a histogram of the ratio of the simulated whistler energy to the measured whistler energy for the 14,000 whistlers we compared, the simulation tends to slightly underestimate the total whistler energy injected by about 5 dB. However, the simulation underestimates the DEMETER measurements more as one gets further from the source lightning stroke, so since the signal to noise ratio of more distant whistlers will be smaller, possibly additive noise in the DEMETER measurements (which of course is not accounted for in the model) may explain some of the observed discrepancy.
-
Vogel, F. R.; Chan, E.; Huang, L.; Levin, I.; Worthy, D.
2013-12-01
Urban areas are said to be responsible for approximately 75% of anthropogenic Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) emissions while comprising only two percent of the land area [1]. This limited spatial expansion should facilitate a monitoring of anthropogenic GHGs from atmospheric observations. As major sources of emissions, cities also have a huge potential to drive emissions reductions. To effectively manage emissions, cities must however, first measure and report these publicly [2]. Modelling studies and measurements of CO2 from fossil fuel burning (FFCO2) in densely populated areas does, however, pose several challenges: Besides continuous in-situ observations, i.e. finding an adequate atmospheric transport model, a sufficiently fine-grained FFCO2 emission model and the proper background reference observations to distinguish the large-scale from the local/urban contributions to the observed FFCO2 concentration offsets ( ΔFFCO2) are required. Pilot studies which include the data from two 'sister sites*' in the vicinity of Toronto, Canada helped to derive flux estimates for Non-CO2 GHGs [3] and improve our understanding of urban FFCO2 emissions. Our 13CO2 observations reveal that the contribution of natural gas burning (mostly due to domestic heating) account for 80%×7% of FFCO2 emissions in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) during winter. Our 14CO2 observations in the GTA, furthermore, show that the local offset of CO2 (ΔCO2) between our two sister sites can be largely attributed to urban FFCO2 emissions. The seasonal cycle of the observed ΔFFCO2 in Toronto, combined with high-resolution atmospheric modeling, helps to independently assess the contribution from different emission sectors (transportation, primary energy and industry, domestic heating) as predicted by a dedicated city-scale emission inventory, which deviates from a UNFCCC-based inventory. [1] D. Dodman. 2009. Blaming cities for climate change? An analysis of urban greenhouse gas emissions inventories
-
Systematic errors in VLF direction-finding of whistler ducts
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Strangeways, H.J.; Rycroft, M.J.
1980-01-01
In the previous paper it was shown that the systematic error in the azimuthal bearing due to multipath propagation and incident wave polarisation (when this also constitutes an error) was given by only three different forms for all VLF direction-finders currently used to investigate the position of whistler ducts. In this paper the magnitude of this error is investigated for different ionospheric and ground parameters for these three different systematic error types. By incorporating an ionosphere for which the refractive index is given by the full Appleton-Hartree formula, the variation of the systematic error with ionospheric electron density and latitude and direction of propagation is investigated in addition to the variation with wave frequency, ground conductivity and dielectric constant and distance of propagation. The systematic bearing error is also investigated for the three methods when the azimuthal bearing is averaged over a 2 kHz bandwidth. This is found to lead to a significantly smaller bearing error which, for the crossed-loops goniometer, approximates the bearing error calculated when phase-dependent terms in the receiver response are ignored. (author)
-
Updated SO2 emission estimates over China using OMI/Aura observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. E. Koukouli
2018-03-01
Full Text Available The main aim of this paper is to update existing sulfur dioxide (SO2 emission inventories over China using modern inversion techniques, state-of-the-art chemistry transport modelling (CTM and satellite observations of SO2. Within the framework of the EU Seventh Framework Programme (FP7 MarcoPolo (Monitoring and Assessment of Regional air quality in China using space Observations project, a new SO2 emission inventory over China was calculated using the CHIMERE v2013b CTM simulations, 10 years of Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI/Aura total SO2 columns and the pre-existing Multi-resolution Emission Inventory for China (MEIC v1.2. It is shown that including satellite observations in the calculations increases the current bottom-up MEIC inventory emissions for the entire domain studied (15–55° N, 102–132° E from 26.30 to 32.60 Tg annum−1, with positive updates which are stronger in winter ( ∼ 36 % increase. New source areas were identified in the southwest (25–35° N, 100–110° E as well as in the northeast (40–50° N, 120–130° E of the domain studied as high SO2 levels were observed by OMI, resulting in increased emissions in the a posteriori inventory that do not appear in the original MEIC v1.2 dataset. Comparisons with the independent Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research, EDGAR v4.3.1, show a satisfying agreement since the EDGAR 2010 bottom-up database provides 33.30 Tg annum−1 of SO2 emissions. When studying the entire OMI/Aura time period (2005 to 2015, it was shown that the SO2 emissions remain nearly constant before the year 2010, with a drift of −0.51 ± 0.38 Tg annum−1, and show a statistically significant decline after the year 2010 of −1.64 ± 0.37 Tg annum−1 for the entire domain. Similar findings were obtained when focusing on the greater Beijing area (30–40° N, 110–120° E with pre-2010 drifts of −0.17 ± 0.14 and post-2010
-
Anomalies in VLF radio signals prior the Abruzzo earthquake (M=6.3) on 6 April 2009
Rozhnoi, A.; Solovieva, M.; Molchanov, O.; Schwingenschuh, K.; Boudjada, M.; Biagi, P. F.; Maggipinto, T.; Castellana, L.; Ermini, A.; Hayakawa, M.
2009-01-01
The VLF/LF radio signals method for studying preseimic activity is applied to the Abruzzo earthquake (M=6.3, 6 April 2009). The data collected by three receivers located in Moscow (Russia), Graz (Austria) and Bari (Italy) at about 3000 km, 1000 km and 500 km from the epicenter were used. The signals received from the Sardinia (20.27 kHz) and the Sicily (45.9 kHz) transmitters, both located in Italy, were compared with those received from the Iceland (37.5 kHz), the Great Bri...
-
Ground and space observations of medium frequency auroral radio emissions
Broughton, Matthew C.
The auroral zone is a rich source of natural radio emissions that can be observed in space and at ground-level. By studying these waves, scientists can gain insight into the plasma processes that generate them and use the near-Earth space environment as a large-scale plasma physics laboratory. This thesis uses both ground-level and in situ observations to study two kinds of natural radio emissions. First, we report observations of a new kind of auroral radio emission. The waves have frequencies ranging from 1.3-2.2 MHz, bandwidths ranging from 90-272 kHz, and durations ranging from 16-355 s. Spectral analysis of the waveform data has revealed that the emission has a complex combination of at least three kinds of fine structures. For model auroral electron distributions, calculations indicate that Langmuir waves could be excited at frequencies consistent with observations. The remainder of the thesis discusses auroral medium frequency (MF) burst, an impulsive, broadband natural radio emission observed at ground-level within a few minutes of local substorm onset. LaBelle [2011] proposed that MF burst originates as Langmuir/Z-mode waves on the topside of the ionosphere that subsequently mode convert to L-mode waves and propagate to ground-level. Using continuous waveform measurements and combined observations with the Sondrestrom Incoherent Scatter Radar, we have performed two tests of this mechanism. The results of these tests are consistent with the mechanism described in LaBelle [2011]. A survey of 8,624 half-orbits of the DEMETER spacecraft has revealed 68 observations of bursty MF waves. We have compared the wave properties of these waves to those of MF burst and have found that although it is uncertain, the balance of the evidence suggests that the bursty MF waves observed with DEMETER are the same phenomenon as the ground-level MF burst. Finally, we have used numerical simulations to model both the fine structure of MF burst and to estimate the attenuation the
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Breneman, A. W.; Crew, A.; Sample, J.; Klumpar, D.; Johnson, A.; Agapitov, O.; Shumko, M.; Turner, D. L.; Santolík, Ondřej; Wygant, J. R.; Cattell, C. A.; Thaller, S. A.; Blake, B.; Spence, H.; Kletzing, C. A.
2017-01-01
Roč. 44, č. 22 (2017), s. 11265-11272 ISSN 0094-8276 R&D Projects: GA ČR GA17-07027S Grant - others:AV ČR(CZ) AP1401 Program:Akademická prémie - Praemium Academiae Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : VLF-CHORUS * RADIATION BELT * ZONE ELECTRONS * SOURCE REGION * AURORAL-ZONE * GEM STORMS * PRECIPITATION * ASSOCIATION * RESOLUTION * EMISSIONS Subject RIV: BL - Plasma and Gas Discharge Physics OBOR OECD: Fluids and plasma physics (including surface physics) Impact factor: 4.253, year: 2016 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2017GL075001/epdf
-
Understanding NOx emission trends in China based on OMI observations
Wang, Y.; Ga, D.; Smeltzer, C. D.; Yi, R.; Liu, Z.
2012-12-01
We analyze OMI observations of NO2 columns over China from 2005 to 2010. Simulations using a regional 3-D chemical transport model (REAM) are used to derive the top-down anthropogenic NOx emissions. The Kendall method is then applied to derive the emission trend. The emission trend is affected by the economic slowdown in 2009. After removing the effect of one year abnormal data, the overall emission trend is 4.35±1.42% per year, which is slower than the linear-regression trend of 5.8-10.8% per year reported for previous years. We find large regional, seasonal, and urban-rural variations in emission trend. The annual emission trends of Northeast China, Central China Plain, Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta are 44.98±1.39%, 5.24±1.63%, 3.31±1.02% and -4.02±1.87%, respectively. The annual emission trends of four megacities, Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen are 0.7±0.27%, -0.75±0.31%, -4.08±1.21% and -6.22±2.85%,, considerably lower than the regional averages. These results appear to suggest that a number of factors, including migration of high-emission industries, vehicle emission regulations, emission control measures of thermal power plants, increased hydro-power usage, have reduced or reversed the increasing trend of NOx emissions in more economically developed megacities and southern coastal regions.
-
Sasmal, Sudipta; Basak, Tamal; Chakraborty, Suman; Palit, Sourav; Chakrabarti, Sandip K.
2017-07-01
Characteristics of very low frequency (VLF) signal depends on solar illumination across the propagation path. For a long path, solar zenith angle varies widely over the path and this has a significant influence on the propagation characteristics. To study the effect, Indian Centre for Space Physics participated in the 27th and 35th Scientific Expedition to Antarctica. VLF signals transmitted from the transmitters, namely, VTX (18.2 kHz), Vijayanarayanam, India, and NWC (19.8 kHz), North West Cape, Australia, were recorded simultaneously at Indian permanent stations Maitri and Bharati having respective geographic coordinates 70.75°S, 11.67°E, and 69.4°S, 76.17°E. A very stable diurnal variation of the signal has been obtained from both the stations. We reproduced the signal variations of VLF signal using solar zenith angle model coupled with long wavelength propagation capability (LWPC) code. We divided the whole path into several segments and computed the solar zenith angle (χ) profile. We assumed a linear relationship between the Wait's exponential model parameters effective reflection height (h'), steepness parameter (β), and solar zenith angle. The h' and β values were later used in the LWPC code to obtain the VLF signal amplitude at a particular time. The same procedure was repeated to obtain the whole day signal. Nature of the whole day signal variation from the theoretical modeling is also found to match with our observation to some extent.
-
Correlation of Solar X-ray Flux and SID Modified VLF Signal Strength
2015-03-26
Motivation ...……………………………………………………………………1-1 Background …………………………………………………………………….1-1 Research Objectives ……………………………………………………………1-3 II...SOLAR X-RAY FLUX AND SID MODIFIED VLF SIGNAL STRENGTH I. Introduction 1.1 Motivation The ionosphere greatly influences long wave radio...accomplished by a research group from Cambridge in the late 1940s. The group recorded the 16 kHz signal of the transmitter in Rugby , England, with the call
-
Preliminary results from the MEMO multicomponent measurements of waves on-board INTERBALL 2
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. Lefeuvre
Full Text Available The MEMO (MEsure Multicomposante des Ondes experiment is a part of the INTERBALL 2 wave consortium. It is connected to a total of six electric and nine magnetic independent sensors. It provides waveforms associated with the measurement of two to five components in three frequency bands: ELF (5–1000 Hz, VLF (1–20 kHz, LF (20–250 kHz. Preliminary analyses of low and high resolution data are presented. The emphasis is put on the estimation of the propagation characteristics of the observed waves.VLF hiss emissions are shown to be mainly whistler mode emissions, but other modes are present. An accurate estimation of the local plasma frequency is proposed when the low L = 0 cutoff frequency is identified. AKR emissions observed just above source regions are studied. R-X and L-O modes are found: the first at the lowest frequencies and the second at the highest. Both propagate with wave normal directions weakly oblique or quasi-parallel to the Earth's magnetic field direction. Propagation characteristics are also determined for a (non-drifting fine structure of AKR. There is no fundamental difference with structurless events. Nightside and dayside bursts of ELF electromagnetic emissions are presented. It is not clear whether the two emissions belong to the "lion roar" emissions or not.
Key words. Magnetospheric physics (auroral phenomena; plasma waves and instabilities; instruments and techniques -
Preliminary results from the MEMO multicomponent measurements of waves on-board INTERBALL 2
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. Lefeuvre
1998-09-01
Full Text Available The MEMO (MEsure Multicomposante des Ondes experiment is a part of the INTERBALL 2 wave consortium. It is connected to a total of six electric and nine magnetic independent sensors. It provides waveforms associated with the measurement of two to five components in three frequency bands: ELF (5–1000 Hz, VLF (1–20 kHz, LF (20–250 kHz. Preliminary analyses of low and high resolution data are presented. The emphasis is put on the estimation of the propagation characteristics of the observed waves.VLF hiss emissions are shown to be mainly whistler mode emissions, but other modes are present. An accurate estimation of the local plasma frequency is proposed when the low L = 0 cutoff frequency is identified. AKR emissions observed just above source regions are studied. R-X and L-O modes are found: the first at the lowest frequencies and the second at the highest. Both propagate with wave normal directions weakly oblique or quasi-parallel to the Earth's magnetic field direction. Propagation characteristics are also determined for a (non-drifting fine structure of AKR. There is no fundamental difference with structurless events. Nightside and dayside bursts of ELF electromagnetic emissions are presented. It is not clear whether the two emissions belong to the "lion roar" emissions or not.Key words. Magnetospheric physics (auroral phenomena; plasma waves and instabilities; instruments and techniques
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. S. Chang
2014-05-01
Full Text Available Modulated high-frequency (HF heating of the ionosphere provides a feasible means of artificially generating extremely low-frequency (ELF/very low-frequency (VLF whistler waves, which can leak into the inner magnetosphere and contribute to resonant interactions with high-energy electrons in the plasmasphere. By ray tracing the magnetospheric propagation of ELF/VLF emissions artificially generated at low-invariant latitudes, we evaluate the relativistic electron resonant energies along the ray paths and show that propagating artificial ELF/VLF waves can resonate with electrons from ~ 100 keV to ~ 10 MeV. We further implement test particle simulations to investigate the effects of resonant scattering of energetic electrons due to triggered monotonic/single-frequency ELF/VLF waves. The results indicate that within the period of a resonance timescale, changes in electron pitch angle and kinetic energy are stochastic, and the overall effect is cumulative, that is, the changes averaged over all test electrons increase monotonically with time. The localized rates of wave-induced pitch-angle scattering and momentum diffusion in the plasmasphere are analyzed in detail for artificially generated ELF/VLF whistlers with an observable in situ amplitude of ~ 10 pT. While the local momentum diffusion of relativistic electrons is small, with a rate of −7 s−1, the local pitch-angle scattering can be intense near the loss cone with a rate of ~ 10−4 s−1. Our investigation further supports the feasibility of artificial triggering of ELF/VLF whistler waves for removal of high-energy electrons at lower L shells within the plasmasphere. Moreover, our test particle simulation results show quantitatively good agreement with quasi-linear diffusion coefficients, confirming the applicability of both methods to evaluate the resonant diffusion effect of artificial generated ELF/VLF whistlers.
-
Observations of EUV and X-ray Emission from Comets
Lisse, C.
The unexpected discovery of x-ray emission from Comet Hyakutake in March 1996 (Lisse et al. 1996) produced a number of questions about the physical mechanism producing the radiation. The original detection and subsequent observations have shown that the very soft (best fit thermal bremsstrahlung model kT0.2 keV) emission is due to an interaction between the solar wind and the comet's atmosphere. Using the results from the more than 15 comets detected to date in x-rays, I report here on the latest results on cometary x-ray emission, including new results from Chandra, and show that charge exchange between highly ionized minor ions in the solar wind and neutral gases in the cometary coma is the most likely operative mechanism. I then use this result to study a number of problems of astrophysical interest: the nature of the cometary coma, other possible sources of x-ray emission in the solar system, the structure of the solar wind in the heliosphere, and the source of the local x-ray background.
-
Biogenic nonmethane hydrocarbon emissions estimated from tethered balloon observations
Davis, K. J.; Lenschow, D. H.; Zimmerman, P. R.
1994-01-01
A new technique for estimating surface fluxes of trace gases, the mixed-layer gradient technique, is used to calculate isoprene and terpene emissions from forests. The technique is applied to tethered balloon measurements made over the Amazon forest and a pine-oak forest in Alabama at altitudes up to 300 m. The observations were made during the dry season Amazon Boundary Layer Experiment (ABLE 2A) and the Rural Oxidants in the Southern Environment 1990 experiment (ROSE I). Results from large eddy simulations of scalar transport in the clear convective boundary layer are used to infer fluxes from the balloon profiles. Profiles from the Amazon give a mean daytime emission of 3630 +/- 1400 micrograms isoprene sq m/h, where the uncertainty represents the standard deviation of the mean of eight flux estimates. Twenty profiles from Alabama give emissions of 4470 +/- 3300 micrograms isoprene sq m/h, 1740 +/- 1060 micrograms alpha-pinene sq m/h, and 790 +/- 560 micrograms beta-pinene sq m/h, respectively. These results are in agreement with emissions derived from chemical budgets. The emissions may be overestimated because of uncertainty about how to incorporate the effects of the canopy on the mixed-layer gradients. The large variability in these emission estimates is probably due to the relatively short sampling times of the balloon profiles, though spatially heterogeneous emissions may also play a role. Fluxes derived using this technique are representative of an upwind footprint of several kilometers and are independent of hydrocarbon oxidation rate and mean advection.
-
Coherent emission mechanisms in astrophysical plasmas
Melrose, D. B.
2017-12-01
radio emission from extensive air showers in the Earth's atmosphere is reviewed briefly. The difference in theoretical approach from astrophysical theories is pointed out and discussed. Fine structures in DAM and in pulsar radio emission are discussed, and it is suggested that trapping in a large-amplitude wave, as in a model for discrete VLF emission, provides a plausible explanation. A possible direct measure of coherence is pointed out.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
DeFries, Ruth; Achard, Frederic; Brown, Sandra; Herold, Martin; Murdiyarso, Daniel; Schlamadinger, Bernhard; Souza, Carlos de
2007-01-01
In response to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) process investigating the technical issues surrounding the ability to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from deforestation in developing countries, this paper reviews technical capabilities for monitoring deforestation and estimating emissions. Implementation of policies to reduce emissions from deforestation require effective deforestation monitoring systems that are reproducible, provide consistent results, meet standards for mapping accuracy, and can be implemented at the national level. Remotely sensed data supported by ground observations are key to effective monitoring. Capacity in developing countries for deforestation monitoring is well-advanced in a few countries and is a feasible goal in most others. Data sources exist to determine base periods in the 1990s as historical reference points. Forest degradation (e.g. from high impact logging and fragmentation) also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions but it is more technically challenging to measure than deforestation. Data on carbon stocks, which are needed to estimate emissions, cannot currently be observed directly over large areas with remote sensing. Guidelines for carbon accounting from deforestation exist and are available in approved Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports and can be applied at national scales in the absence of forest inventory or other data. Key constraints for implementing programs to monitor greenhouse gas emissions from deforestation are international commitment of resources to increase capacity, coordination of observations to ensure pan-tropical coverage, access to free or low-cost data, and standard and consensual protocols for data interpretation and analysis
-
Observations of the 10-micron natural laser emission from the mesospheres of Mars and Venus
Espenak, F.; Deming, D.; Jennings, D.; Kostiuk, T.; Mumma, M.; Zipoy, D.
1983-01-01
Observations of the total flux and center to limb dependence of the nonthermal emission occurring in the cores of the 9.4 and 10.4 micrometers CO2 bands on Mars are compared to a theoretical model based on this mechanism. The model successfully reproduces the observed center to limb dependence of this emission, to within the limits imposed by the spatial resolution of the observations of Mars and Venus. The observed flux from Mars agrees closely with the prediction of the model; the flux observed from Venus is 74 percent of the flux predicted by the model. This emission is used to obtain the kinetic temperatures of the Martian and Venusian mesospheres. For Mars near 70 km altitude, a rotational temperature analysis using five lines gives T = 135 + or - 20 K. The frequency width of the emission is also analyzed to derive a temperature of 126 + or - 6 K. In the case of the Venusian mesosphere near 109 km, the frequency width of the emission gives T = 204 + or - 10 K.
-
Observations of the 10 micrometer natural laser emission from the mesospheres of Mars and Venus
Deming, D.; Espenak, F.; Jennings, D.; Kostiuk, T.; Mumma, M. J.
1983-01-01
Observations of the total flux and center to limb dependence of the nonthermal emission occurring in the cores of the 9.4 and 10.4 micrometers CO2 bands on Mars are compared to a theoretical model based on this mechanism. The model successfully reproduces the observed center to limb dependence of this emission, to within the limits imposed by the spatial resolution of the observations of Mars and Venus. The observed flux from Mars agrees closely with the prediction of the model; the flux observed from Venus is 74% of the flux predicted by the model. This emission is used to obtain the kinetic temperatures of the Martian and Venusian mesospheres. For Mars near 70 km altitude, a rotational temperature analysis using five lines gives T = 135 + or - 20 K. The frequency width of the emission is also analyzed to derive a temperature of 126 + or - 6 K. In the case of the Venusian mesosphere near 109 km, the frequency width of the emission gives T = 204 + or - 10 K.
-
Observations of the 10 micrometer natural laser emission from the mesospheres of Mars and Venus
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Deming, D.; Espenak, F.; Jennings, D.; Kostiuk, T.; Mumma, M.J.
1983-06-01
Observations of the total flux and center to limb dependence of the nonthermal emission occurring in the cores of the 9.4 and 10.4 micrometers CO2 bands on Mars are compared to a theoretical model based on this mechanism. The model successfully reproduces the observed center to limb dependence of this emission, to within the limits imposed by the spatial resolution of the observations of Mars and Venus. The observed flux from Mars agrees closely with the prediction of the model the flux observed from Venus is 74% of the flux predicted by the model. This emission is used to obtain the kinetic temperatures of the Martian and Venusian mesospheres. For Mars near 70 km altitude, a rotational temperature analysis using five lines gives T 135 + or - 20 K. The frequency width of the emission is also analyzed to derive a temperature of 126 + or - 6 K. In the case of the Venusian mesosphere near 109 km, the frequency width of the emission gives T 204 + or - 10 K
-
Chandra Observations of Extended X-Ray Emission in ARP 220
McDowell, J. C.; Clements, D. L.; Lamb, S. A.; Shaked, S.; Hearn, N. C.; Colina, L.; Mundell, C.; Borne, K.; Baker, A. C.; Arribas, S.
2003-01-01
We resolve the extended X-ray emission from the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy Arp 220. Extended, faint, edge-brightened, soft X-ray lobes outside the optical galaxy are observed to a distance of 1CL 15 kpc on each side of the nuclear region. Bright plumes inside the optical isophotes coincide with the optical line emission and extend 1 1 kpc from end to end across the nucleus. The data for the plumes cannot be fitted by a single-temperature plasma and display a range of temperatures from 0.2 to 1 keV. The plumes emerge from bright, diffuse circumnuclear emission in the inner 3 kpc centered on the Ha peak, which is displaced from the radio nuclei. There is a close morphological correspondence between the Ha and soft X-ray emission on all spatial scales. We interpret the plumes as a starburst-driven superwind and discuss two interpretations of the emission from the lobes in the context of simulations of the merger dynamics of Arp 220.
-
Dalsøren, Stig B.; Myhre, Gunnar; Hodnebrog, Øivind; Myhre, Cathrine Lund; Stohl, Andreas; Pisso, Ignacio; Schwietzke, Stefan; Höglund-Isaksson, Lena; Helmig, Detlev; Reimann, Stefan; Sauvage, Stéphane; Schmidbauer, Norbert; Read, Katie A.; Carpenter, Lucy J.; Lewis, Alastair C.; Punjabi, Shalini; Wallasch, Markus
2018-03-01
Ethane and propane are the most abundant non-methane hydrocarbons in the atmosphere. However, their emissions, atmospheric distribution, and trends in their atmospheric concentrations are insufficiently understood. Atmospheric model simulations using standard community emission inventories do not reproduce available measurements in the Northern Hemisphere. Here, we show that observations of pre-industrial and present-day ethane and propane can be reproduced in simulations with a detailed atmospheric chemistry transport model, provided that natural geologic emissions are taken into account and anthropogenic fossil fuel emissions are assumed to be two to three times higher than is indicated in current inventories. Accounting for these enhanced ethane and propane emissions results in simulated surface ozone concentrations that are 5-13% higher than previously assumed in some polluted regions in Asia. The improved correspondence with observed ethane and propane in model simulations with greater emissions suggests that the level of fossil (geologic + fossil fuel) methane emissions in current inventories may need re-evaluation.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Watanabe, Kyoko; Shimizu, Toshifumi; Masuda, Satoshi; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi; Ohno, Masanori
2013-01-01
White-light emissions were observed from an X1.7 class solar flare on 2012 January 27, using three continuum bands (red, green, and blue) of the Solar Optical Telescope on board the Hinode satellite. This event occurred near the solar limb, and so differences in the locations of the various emissions are consistent with differences in heights above the photosphere of the various emission sources. Under this interpretation, our observations are consistent with the white-light emissions occurring at the lowest levels of where the Ca II H emission occurs. Moreover, the centers of the source regions of the red, green, and blue wavelengths of the white-light emissions are significantly displaced from each other, suggesting that those respective emissions are emanating from progressively lower heights in the solar atmosphere. The temperature distribution was also calculated from the white-light data, and we found the lower-layer emission to have a higher temperature. This indicates that high-energy particles penetrated down to near the photosphere, and deposited heat into the ambient lower layers of the atmosphere
-
Cometary X-ray Emission: the View After the First Chandra Observations
Lisse, C. M.
2002-01-01
The unexpected discovery of x-ray emission from Comet Hyakutake in March 1996 (Lisse et al. 1996) has produced a number of questions about the physical mechanism producing the radiation. The original detection and subsequent observations (Dennerl et al. 1997, Mumma et al. 1997, Krasnopolsky et al. 1998, Owens et al. 1998, Lisse et al. 1999) have shown that the very soft (best fit thermal bremsstrahlung model kT ~ 0.2 keV) emission is due to an interaction between the solar wind and the comet's atmosphere. Using the results from the 15 comets detected to date in x-rays, we report on the latest results on cometary x-ray emission, including new results from Chandra and XMM. As-observed morphologies, spectra, and light curves will be discussed. Our emphasis will be on understanding the physical mechanism producing the emission, and using this to determine the nature of the cometary coma, the structure of the solar wind in the heliosphere, and the source of the local soft x-ray background. This work has been graciously supported by grants from the NASA Planetary Astronomy and Astrophysical Data Programs.
-
AMI OBSERVATIONS OF THE ANOMALOUS MICROWAVE EMISSION IN THE PERSEUS MOLECULAR CLOUD
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tibbs, C. T.; Scaife, A. M. M.; Dickinson, C.; Davies, R. D.; Davis, R. J.; Watson, R. A.; Paladini, R.; Grainge, K. J. B.
2013-01-01
We present observations of the known anomalous microwave emission region, G159.6–18.5, in the Perseus molecular cloud at 16 GHz performed with the Arcminute Microkelvin Imager Small Array. These are the highest angular resolution observations of G159.6–18.5 at microwave wavelengths. By combining these microwave data with infrared observations between 5.8 and 160 μm from the Spitzer Space Telescope, we investigate the existence of a microwave-infrared correlation on angular scales of ∼2'. We find that the overall correlation appears to increase toward shorter infrared wavelengths, which is consistent with the microwave emission being produced by electric dipole radiation from small, spinning dust grains. We also find that the microwave-infrared correlation peaks at 24 μm (6.7σ), suggesting that the microwave emission is originating from a population of stochastically heated small interstellar dust grains rather than polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
-
Thermal field emission observation of single-crystal LaB6
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nagata, H.; Harada, K.; Shimizu, R.
1990-01-01
TFE (thermal field emission) properties of LaB 6 left-angle 100 right-angle and left-angle 310 right-angle single crystals were investigated by emission pattern observation. It was found that field evaporation with the tip temperature held at ∼1500 degree C is very useful to get a clean pattern of fourfold symmetry. Each of four bright spots in the clean pattern was presumed to correspond to left-angle 310 right-angle emission. It is proposed, as the most appropriate operating condition, to use the left-angle 310 right-angle LaB 6 tip at a temperature ∼1000 degree C in vacuum of 10 -9 Torr region, promising a new TF emitter of high brightness and stability for practical use
-
Soft x-ray emission from gamma-ray bursts observed with ginga
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yoshida, Atsumasa; Murakami, Toshio; Itoh, Masayuki
1989-01-01
The soft X-ray emission of gamma-ray bursts below 10 keV provides information about size, location, and emission mechanism. The Gamma-ray Burst Detector (GBD) on board Ginga, which consists of a proportional counter and a scintillation detector, covers an energy range down to 1.5 keV with 63 cm 2 effective area. In several of the observed gamma-ray bursts, the intensity of the soft X-ray emission showed a longer decay time of 50 to 100s after the higher energy gamma-ray emission had ended. Although we cannot rule out other models, such as bremsstrahlung and thermal cyclotron types, due to poor statistics, the soft X-ray spectra are consistent with a blackbody of 1 to 2 keV in the late phase of the gamma-ray bursts. This enables us to estimate the size of the blackbody responsible for the X-ray emission. (author)
-
Dark matter line emission constraints from NuSTAR observations of the Bullet Cluster
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Riemer-Sørensen, S.; Wik, D.; Madejski, G.
2015-01-01
Some dark matter candidates, e.g., sterile neutrinos, provide observable signatures in the form of mono-energetic line emission. We present the first search for dark matter line emission in the range in a pointed observation of the Bullet Cluster with NuSTAR. We do not detect any significant line...... emission and instead we derive upper limits (95% CL) on the flux, and interpret these constraints in the context of sterile neutrinos and more generic dark matter candidates. NuSTAR does not have the sensitivity to constrain the recently claimed line detection at , but improves on the constraints...... for energies of 10–25 keV....
-
CO2 non-LTE limb emissions in Mars' atmosphere as observed by OMEGA/Mars Express
Piccialli, A.; López-Valverde, M. A.; Määttänen, A.; González-Galindo, F.; Audouard, J.; Altieri, F.; Forget, F.; Drossart, P.; Gondet, B.; Bibring, J. P.
2016-06-01
We report on daytime limb observations of Mars upper atmosphere acquired by the OMEGA instrument on board the European spacecraft Mars Express. The strong emission observed at 4.3 μm is interpreted as due to CO2 fluorescence of solar radiation and is detected at a tangent altitude in between 60 and 110 km. The main value of OMEGA observations is that they provide simultaneously spectral information and good spatial sampling of the CO2 emission. In this study we analyzed 98 dayside limb observations spanning over more than 3 Martian years, with a very good latitudinal and longitudinal coverage. Thanks to the precise altitude sounding capabilities of OMEGA, we extracted vertical profiles of the non-local thermodynamic equilibrium (non-LTE) emission at each wavelength and we studied their dependence on several geophysical parameters, such as the solar illumination and the tangent altitude. The dependence of the non-LTE emission on solar zenith angle and altitude follows a similar behavior to that predicted by the non-LTE model. According to our non-LTE model, the tangent altitude of the peak of the CO2 emission varies with the thermal structure, but the pressure level where the peak of the emission is found remains constant at ˜0.03 ± 0.01 Pa, . This non-LTE model prediction has been corroborated by comparing SPICAM and OMEGA observations. We have shown that the seasonal variations of the altitude of constant pressure levels in SPICAM stellar occultation retrievals correlate well with the variations of the OMEGA peak emission altitudes, although the exact pressure level cannot be defined with the spectroscopy for the investigation of the characteristics of the atmosphere of Venus (SPICAM) nighttime data. Thus, observed changes in the altitude of the peak emission provide us information on the altitude of the 0.03 Pa pressure level. Since the pressure at a given altitude is dictated by the thermal structure below, the tangent altitude of the peak emission represents
-
Barkley, Z.; Davis, K.; Lauvaux, T.; Miles, N.; Richardson, S.; Martins, D. K.; Deng, A.; Cao, Y.; Sweeney, C.; Karion, A.; Smith, M. L.; Kort, E. A.; Schwietzke, S.
2015-12-01
Leaks in natural gas infrastructure release methane (CH4), a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. The estimated fugitive emission rate associated with the production phase varies greatly between studies, hindering our understanding of the natural gas energy efficiency. This study presents a new application of inverse methodology for estimating regional fugitive emission rates from natural gas production. Methane observations across the Marcellus region in northeastern Pennsylvania were obtained during a three week flight campaign in May 2015 performed by a team from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Global Monitoring Division and the University of Michigan. In addition to these data, CH4 observations were obtained from automobile campaigns during various periods from 2013-2015. An inventory of CH4 emissions was then created for various sources in Pennsylvania, including coalmines, enteric fermentation, industry, waste management, and unconventional and conventional wells. As a first-guess emission rate for natural gas activity, a leakage rate equal to 2% of the natural gas production was emitted at the locations of unconventional wells across PA. These emission rates were coupled to the Weather Research and Forecasting model with the chemistry module (WRF-Chem) and atmospheric CH4 concentration fields at 1km resolution were generated. Projected atmospheric enhancements from WRF-Chem were compared to observations, and the emission rate from unconventional wells was adjusted to minimize errors between observations and simulation. We show that the modeled CH4 plume structures match observed plumes downwind of unconventional wells, providing confidence in the methodology. In all cases, the fugitive emission rate was found to be lower than our first guess. In this initial emission configuration, each well has been assigned the same fugitive emission rate, which can potentially impair our ability to match the observed spatial variability
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. Holzinger
2005-01-01
Full Text Available Vertical gradients of mixing ratios of volatile organic compounds have been measured in a Ponderosa pine forest in Central California (38.90° N, 120.63° W, 1315m. These measurements reveal large quantities of previously unreported oxidation products of short lived biogenic precursors. The emission of biogenic precursors must be in the range of 13-66µmol m-2h-1 to produce the observed oxidation products. That is 6-30 times the emissions of total monoterpenes observed above the forest canopy on a molar basis. These reactive precursors constitute a large fraction of biogenic emissions at this site, and are not included in current emission inventories. When oxidized by ozone they should efficiently produce secondary aerosol and hydroxyl radicals.
-
Mid-latitude Narrowband Stimulated Electromagnetic Emissions (NSEE): New Observations and Modeling
Nossa, E.; Mahmoudian, A.; Isham, B.; Bernhardt, P. A.; Briczinski, S. J., Jr.
2017-12-01
High power electromagnetic waves (EM) transmitted from the ground interact with the local plasma in the ionosphere and can produce Stimulated Electromagnetic Emissions (SEE) through the parametric decay instability (PDI). The classical SEE features known as wideband SEE (WSEE) with frequency offset of 1 kHz up to 100 kHz have been observed and studied in detail in the 1980s and 1990s. A new era of ionospheric remote sensing techniques was begun after the recent update of the HF transmitter at the HAARP. Sideband emissions of unprecedented strength have been reported during recent campaigns at HAARP, reaching up to 10 dB relative to the reflected pump wave which are by far the strongest spectral features of secondary radiation that have been reported. These emissions known as narrowband SEE (NSEE) are shifted by only up to a few tens of Hertz from radio-waves transmitted at several megahertz. One of these new NSEE features are emission lines within 100 Hz of the pump frequency and are produced through magnetized stimulated Brillouin scatter (MSBS) process. Stimulated Brillouin Scatter (SBS) is a strong SEE mode involving a direct parametric decay of the pump wave into an electrostatic wave (ES) and a secondary EM wave that sometimes could be stronger than the HF pump. SBS has been studied in laboratory plasma experiments by the interaction of high power lasers with plasmas. The SBS instability in magnetized ionospheric plasma was observed for the first time at HAARP in 2010. Our recent work at HAARP has shown that MSBS emission lines can be used to asses electron temperature in the heated region, ion mass spectrometry, determine minor ion species and their densities in the ionosphere, study the physics associated with electron acceleration and artificial airglow. Here, we present new observations of narrowband SEE (NSEE) features at the new mid-latitude heating facility at Arecibo. This includes the direct mode conversion of pump wave through MSBS process. Collected
-
Study of Seismic Activity Using Geophysical and Radio Physical Equipment for Observation
Kvavadze, N.; Tsereteli, N. S.
2015-12-01
One of the most dangerous and destructive natural hazards are earthquakes, which is confirmed by recent earthquakes such as Nepal 2015, Japan and Turkey 2011. Because of this, study of seismic activity is important. Studying any process, it is necessary to use different methods of observation, which allows us to increase accuracy of obtained data. Seismic activity is a complex problem and its study needs different types of observation methods. Two main problems of seismic activity study are: reliable instrumental observations and earthquake short-term predictions. In case of seismic risks it is necessary to have reliable accelerometer data. One of the most promising field in earthquake short-term prediction is very low frequency (VLF) electromagnetic wave propagation in ionosphere observation. To study Seismic activity of Caucasus region, was created observation complex using Accelerometer, Velocimeter and VLF electromagnetic waves received from communication stations (located in different area of the world) reflected from low ionosphere. System is created and operates at Tbilisi State University Ionosphere Observatory, near Tbilisi in Tabakhmela 42.41'70 N, 44.80'92 E, Georgia. Data obtained is sent to a local server located at M. Nodia Institute of Geophysics, TSU, for storage and processing. Diagram for complex is presented. Also data analysis methods were created and preliminary processing was done. In this paper we present some of the results: Earthquake data from ionosphere observations as well as local earthquakes recorded with accelerometer and velocimeter. Complex is first in 6 that will be placed around Georgia this year. We plan on widening network every year.
-
A Pilot Study to Evaluate California's Fossil Fuel CO2 Emissions Using Atmospheric Observations
Graven, H. D.; Fischer, M. L.; Lueker, T.; Guilderson, T.; Brophy, K. J.; Keeling, R. F.; Arnold, T.; Bambha, R.; Callahan, W.; Campbell, J. E.; Cui, X.; Frankenberg, C.; Hsu, Y.; Iraci, L. T.; Jeong, S.; Kim, J.; LaFranchi, B. W.; Lehman, S.; Manning, A.; Michelsen, H. A.; Miller, J. B.; Newman, S.; Paplawsky, B.; Parazoo, N.; Sloop, C.; Walker, S.; Whelan, M.; Wunch, D.
2016-12-01
Atmospheric CO2 concentration is influenced by human activities and by natural exchanges. Studies of CO2 fluxes using atmospheric CO2 measurements typically focus on natural exchanges and assume that CO2 emissions by fossil fuel combustion and cement production are well-known from inventory estimates. However, atmospheric observation-based or "top-down" studies could potentially provide independent methods for evaluating fossil fuel CO2 emissions, in support of policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. Observation-based estimates of fossil fuel-derived CO2 may also improve estimates of biospheric CO2 exchange, which could help to characterize carbon storage and climate change mitigation by terrestrial ecosystems. We have been developing a top-down framework for estimating fossil fuel CO2 emissions in California that uses atmospheric observations and modeling. California is implementing the "Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006" to reduce total greenhouse gas emissions to 1990 levels by 2020, and it has a diverse array of ecosystems that may serve as CO2 sources or sinks. We performed three month-long field campaigns in different seasons in 2014-15 to collect flask samples from a state-wide network of 10 towers. Using measurements of radiocarbon in CO2, we estimate the fossil fuel-derived CO2 present in the flask samples, relative to marine background air observed at coastal sites. Radiocarbon (14C) is not present in fossil fuel-derived CO2 because of radioactive decay over millions of years, so fossil fuel emissions cause a measurable decrease in the 14C/C ratio in atmospheric CO2. We compare the observations of fossil fuel-derived CO2 to simulations based on atmospheric modeling and published fossil fuel flux estimates, and adjust the fossil fuel flux estimates in a statistical inversion that takes account of several uncertainties. We will present the results of the top-down technique to estimate fossil fuel emissions for our field
-
Application of High Resolution Air-Borne Remote Sensing Observations for Monitoring NOx Emissions
Souri, A.; Choi, Y.; Pan, S.; Curci, G.; Janz, S. J.; Kowalewski, M. G.; Liu, J.; Herman, J. R.; Weinheimer, A. J.
2017-12-01
Nitrogen oxides (NOx=NO+NO2) are one of the air pollutants, responsible for the formation of tropospheric ozone, acid rain and particulate nitrate. The anthropogenic NOx emissions are commonly estimated based on bottom-up inventories which are complicated by many potential sources of error. One way to improve the emission inventories is to use relevant observations to constrain them. Fortunately, Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is one of the most successful detected species from remote sensing. Although many studies have shown the capability of using space-borne remote sensing observations for monitoring emissions, the insufficient sample number and footprint of current measurements have introduced a burden to constrain emissions at fine scales. Promisingly, there are several air-borne sensors collected for NASA's campaigns providing high spatial resolution of NO2 columns. Here, we use the well-characterized NO2 columns from the Airborne Compact Atmospheric Mapper (ACAM) onboard NASA's B200 aircraft into a 1×1 km regional model to constrain anthropogenic NOx emissions in the Houston-Galveston-Brazoria area. Firstly, in order to incorporate the data, we convert the NO2 slant column densities to vertical ones using a joint of a radiative transfer model and the 1x1 km regional model constrained by P3-B aircraft measurements. After conducting an inverse modeling method using the Kalman filter, we find the ACAM observations are resourceful at mitigating the overprediction of model in reproducing NO2 on regular days. Moreover, the ACAM provides a unique opportunity to detect an anomaly in emissions leading to strong air quality degradation that is lacking in previous works. Our study provides convincing evidence that future geostationary satellites with high spatial and temporal resolutions will give us insights into uncertainties associated with the emissions at regional scales.
-
Diffuse radio emission in the Coma cluster and Abell 1367: observations at 430 and 1400 MHz
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hanisch, R.J.
1980-01-01
Two rich clusters of galaxies, Abell 1656 (the Coma cluster) and Abell 1367, have been mapped at both 430 and 1400 MHz with the 305-m telescope at Arecibo. The contribution to the observed radio emission due to known discrete sources has been calculated by convolving interferometrically determined source lists with observed Arecibo beam patterns, and maps of the diffuse radio emission alone have been constructed. Both clusters contain regions of diffuse radio emission, although the source in Coma is larger and much more luminous than the source in Abell 1367. The linear extent of the diffuse emission and its dependence on frequency have been used to study particle propagation rates and modes of diffusion in the intracluster medium. The possible correlations between the diffuse radio emission and x-ray emission in these clusters have been investigated, and it has been found that the observed x-ray luminosities can be accounted for if the intracluster gas is heated through Coulomb interactions with the relativistic electrons responsible for the diffuse radio emission
-
Orton, G. S.; Momary, T.; Tabataba-Vakili, F.; Janssen, M. A.; Hansen, C. J.; Bolton, S. J.; Li, C.; Adriani, A.; Mura, A.; Grassi, D.; Fletcher, L. N.; Brown, S. T.; Fujiyoshi, T.; Greathouse, T. K.; Kasaba, Y.; Sato, T. M.; Stephens, A.; Donnelly, P.; Eichstädt, G.; Rogers, J.
2017-12-01
Ground-breaking measurements of thermal emission at very long wavelengths have been made by the Juno mission's Microwave Radiometer (MWR). We examine the relationship between these and other thermal emission measurements by the Jupiter Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) at 5 µm and ground-based supporting observations in the thermal infrared that cover the 5-25 µm range. The relevant ground-based observations of thermal emission are constituted from imaging and scanning spectroscopy obtained at the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF), the Gemini North Telescope, the Subaru Telescope and the Very Large Telescope. A comparison of these results clarifies the physical properties responsible for the observed emissions, i.e. variability of the temperature field, the cloud field or the distribution of gaseous ammonia. Cross-references to the visible cloud field from Juno's JunoCam experiment and Earth-based images are also useful. This work continues an initial comparison by Orton et al. (2017, GRL 44, doi: 10.1002/2017GL073019) between MWR and JIRAM results, together with ancillary 5-µm IRTF imaging and with JunoCam and ground-based visible imaging. These showed a general agreement between MWR and JIRAM results for the 5-bar NH3 abundance in specific regions of low cloud opacity but only a partial correlation between MWR and 5-µm radiances emerging from the 0.5-5 bar levels of the atmosphere in general. Similar to the latter, there appears to be an inconsistent correlation between MWR channels sensitive to 0.5-10 bars and shorter-wavelength radiances in the "tails" of 5-µm hot spots , which may be the result of the greater sensitivity of the latter to particulate opacity that could depend on the evolution history of the particular features sampled. Of great importance is the interpretation of MWR radiances in terms of the variability of temperature vs. NH3 abundances in the 0.5-5 bar pressure range. This is particularly important to understand MWR results in
-
Inclusive observables and hard gluon emission in neutrino deep inelastic scattering
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bouchiat, C.; Meyer, P.; Mezard, M.
1980-01-01
We derive the predictions of perturbative QCD together with non-perturbative corrections for a set of inclusive observables connected with the angular distribution of light-cone energy in deep inelastic neutrino scattering. Our particular choice of observables has been made in order to meet important physical requirements besides the necessary condition of infrared regularity. Our inclusive observables receive their dominant contribution from the quark fragmentation region. The non-perturbative contribution is calculable in a rather model-independent way and stays at an acceptable level in realistic experimental conditions. The QCD perturbative contribution, which takes the simple form of a convolution product, exhibits a strongly decreasing behaviour as a function of the Bjorken scaling variable x, superimposed on a constant background associated with the non-perturbative terms, allowing a rather clean separation of the two effects. The perturbative term being dominated by the process of hard-gluon emission, an experimental investigation of the observables discussed here may be a good way to detect the effect of gluon emission in deep inelastic neutrino scattering. (orig.)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. P. Burrows
2012-09-01
Full Text Available Measurements of the OH Meinel emissions in the terrestrial nightglow are one of the standard ground-based techniques to retrieve upper mesospheric temperatures. It is often assumed that the emission peak altitudes are not strongly dependent on the vibrational level, although this assumption is not based on convincing experimental evidence. In this study we use Envisat/SCIAMACHY (Scanning Imaging Absorption spectroMeter for Atmospheric CHartographY observations in the near-IR spectral range to retrieve vertical volume emission rate profiles of the OH(3-1, OH(6-2 and OH(8-3 Meinel bands in order to investigate whether systematic differences in emission peak altitudes can be observed between the different OH Meinel bands. The results indicate that the emission peak altitudes are different for the different vibrational levels, with bands originating from higher vibrational levels having higher emission peak altitudes. It is shown that this finding is consistent with the majority of the previously published results. The SCIAMACHY observations yield differences in emission peak altitudes of up to about 4 km between the OH(3-1 and the OH(8-3 band. The observations are complemented by model simulations of the fractional population of the different vibrational levels and of the vibrational level dependence of the emission peak altitude. The model simulations reproduce the observed vibrational level dependence of the emission peak altitude well – both qualitatively and quantitatively – if quenching by atomic oxygen as well as multi-quantum collisional relaxation by O2 is considered. If a linear relationship between emission peak altitude and vibrational level is assumed, then a peak altitude difference of roughly 0.5 km per vibrational level is inferred from both the SCIAMACHY observations and the model simulations.
-
Simulations of Galactic polarized synchrotron emission for Epoch of Reionization observations
Spinelli, M.; Bernardi, G.; Santos, M. G.
2018-06-01
The detection of the redshifted cosmological 21 cm line signal requires the removal of the Galactic and extragalactic foreground emission, which is orders of magnitude brighter anywhere in the sky. Foreground cleaning methods currently used are efficient in removing spectrally smooth components. However, they struggle in the presence of not spectrally smooth contamination that is, therefore, potentially the most dangerous one. An example of this is the polarized synchrotron emission, which is Faraday rotated by the interstellar medium and leaks into total intensity due to instrumental imperfections. In this work we present new full-sky simulations of this polarized synchrotron emission in the 50 - 200 MHz range, obtained from the observed properties of diffuse polarized emission at low frequencies. The simulated polarized maps are made publicly available, aiming to provide more realistic templates to simulate the effect of instrumental leakage and the effectiveness of foreground separation techniques.
-
Pickett, J. S.; Grison, B.; Omura, Y.; Engebretson, M. J.; Dandouras, I.; Masson, A.; Adrian, M. L.; Santolík, O.; Décréau, P. M. E.; Cornilleau-Wehrlin, N.; Constantinescu, D.
2010-05-01
The Cluster spacecraft were favorably positioned on the nightside near the equatorial plasmapause of Earth at L ˜ 4.3 on 30 March 2002 to observe electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EMIC) rising tone emissions in association with Pc1 waves at 1.5 Hz. The EMIC rising tone emissions were found to be left-hand, circularly polarized, dispersive, and propagating away from the equator. Their burstiness and dispersion of ˜30s/Hz rising out of the 1.5 Hz Pc1 waves are consistent with their identification as EMIC triggered chorus emissions, the first to be reported through in situ observations near the plasmapause. Along with the expected H+ ring current ions seen at higher energies (>300 eV), lower energy ions (300 eV and less) were observed during the most intense EMIC triggered emission events. Nonlinear wave-particle interactions via cyclotron resonance between the ˜2-10 keV H+ ions with temperature anisotropy and the linearly-amplified Pc1 waves are suggested as a possible generation mechanism for the EMIC triggered emissions.
-
Spectral and interferometric observation of four emission nebulas
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lozinskaya, T.A.; Klement'eva, A.Yu.; Zhukov, G.V.; Shenavrin, V.I.
1975-01-01
Results of spectrophotometric and interferometric observations of four emission nebulae are presented; electron temperature Te and electron density Ne are estimated; mean beam velocities and parameters of the internal motion in the nebylae are determined. The following objects have been investigated: 1) a bright compact nebulae of unknown nature 2.5 in size which is identified with the non-thermal radiosource G6.4-0.5 in the region W28; 2) nebulae RCW171 5' in size which is identified with the radiosource G23.1+0.6; 3) the nebulae Simeiz 34/Sharpless 261/d 1950 =6sup(h)05sup(m), sigma 1950 =+15 deg 49'; its diameter is approximately 30 an extensive complex of bright emission fibres in the nebulae Swan, which are partially projected into a possible remainder of the outburst of a supernova W63; L 1950 =20sup(h)17sup(m); S 1950 =45 deg 30' its diameter is approximately 1 deg 5
-
Modeling the Observed Microwave Emission from Shallow Multi-Layer Tundra Snow Using DMRT-ML
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Nastaran Saberi
2017-12-01
Full Text Available The observed brightness temperatures (Tb at 37 GHz from typical moderate density dry snow in mid-latitudes decreases with increasing snow water equivalent (SWE due to volume scattering of the ground emissions by the overlying snow. At a certain point, however, as SWE increases, the emission from the snowpack offsets the scattering of the sub-nivean emission. In tundra snow, the Tb slope reversal occurs at shallower snow thicknesses. While it has been postulated that the inflection point in the seasonal time series of observed Tb V 37 GHz of tundra snow is controlled by the formation of a thick wind slab layer, the simulation of this effect has yet to be confirmed. Therefore, the Dense Media Radiative Transfer Theory for Multi Layered (DMRT-ML snowpack is used to predict the passive microwave response from airborne observations over shallow, dense, slab-layered tundra snow. Airborne radiometer observations coordinated with ground-based in situ snow measurements were acquired in the Canadian high Arctic near Eureka, NT, in April 2011. The DMRT-ML was parameterized with the in situ snow measurements using a two-layer snowpack and run in two configurations: a depth hoar and a wind slab dominated pack. With these two configurations, the calibrated DMRT-ML successfully predicted the Tb V 37 GHz response (R correlation of 0.83 when compared with the observed airborne Tb footprints containing snow pits measurements. Using this calibrated model, the DMRT-ML was applied to the whole study region. At the satellite observation scale, observations from the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-Earth Observing System (AMSR-E over the study area reflected seasonal differences between Tb V 37 GHz and Tb V 19 GHz that supports the hypothesis of the development of an early season volume scattering depth hoar layer, followed by the growth of the late season emission-dominated wind slab layer. This research highlights the necessity to consider the two
-
The Pioneer 9 electric field experiment. III - Radial gradients and storm observations.
Scarf, F. L.; Green, I. M.; Burgess, J. S.
1973-01-01
We present a detailed analysis of the Pioneer 9 VLF electric field observations for 20 selected storm periods covering a heliocentric range extending from 0.754 AU to 0.99 AU. Although data from only two low frequency channels are available, the results of the present study tend to confirm the preliminary speculation by Scarf and Siscoe (1971) that the turbulent E-field spectrum in the disturbed solar wind has a significant radial gradient.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
K. C. Wells
2012-07-01
Full Text Available Methanol retrievals from nadir-viewing space-based sensors offer powerful new information for quantifying methanol emissions on a global scale. Here we apply an ensemble of aircraft observations over North America to evaluate new methanol measurements from the Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer (TES on the Aura satellite, and combine the TES data with observations from the Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer (IASI on the MetOp-A satellite to investigate the seasonality of methanol emissions from northern midlatitude ecosystems. Using the GEOS-Chem chemical transport model as an intercomparison platform, we find that the TES retrieval performs well when the degrees of freedom for signal (DOFS are above 0.5, in which case the model:TES regressions are generally consistent with the model:aircraft comparisons. Including retrievals with DOFS below 0.5 degrades the comparisons, as these are excessively influenced by the a priori. The comparisons suggest DOFS >0.5 as a minimum threshold for interpreting retrievals of trace gases with a weak tropospheric signal. We analyze one full year of satellite observations and find that GEOS-Chem, driven with MEGANv2.1 biogenic emissions, underestimates observed methanol concentrations throughout the midlatitudes in springtime, with the timing of the seasonal peak in model emissions 1–2 months too late. We attribute this discrepancy to an underestimate of emissions from new leaves in MEGAN, and apply the satellite data to better quantify the seasonal change in methanol emissions for midlatitude ecosystems. The derived parameters (relative emission factors of 11.0, 0.26, 0.12 and 3.0 for new, growing, mature, and old leaves, respectively, plus a leaf area index activity factor of 0.5 for expanding canopies with leaf area index <1.2 provide a more realistic simulation of seasonal methanol concentrations in midlatitudes on the basis of both the IASI and TES measurements.
-
IUE observations of circumstellar emission from the late-type variable R AQR (M6 + pec)
Hobbs, R. W.; Michalitsianos, A. G.; Kafatos, M.
1981-01-01
The IUE observations of R Aqr (M7 + pec) obtained in low dispersion are discussed with particular reference to circumstellar emission. Strong permitted, semiforbidden, and forbidden emission lines are seen, superimposed on a bright ultraviolet continuum. It is deduced that the strong emission line spectrum that involves C III, C IV, Si III, (0 II) and (0 III) probably arises from a dense compact nebula the size of which is comparable to the orbital radius of the binary system of which R Aqr is the primary star. The low excitation emission lines of Fe II, Mg II, 0 I, and Si II probably a white dwarf, comparable to or somewhat brighter than the Sun, since such a star can produce enough ionizing photons to excite the continuum and emission line spectrum and yet be sufficiently faint as to escape detection by direct observation. The UV continuum is attributed to Balmer recombination from the dense nebula and not to blackbody emission from the hot companion.
-
Dust emission mechanisms in the central Sahara: new insights from remote field observations
Allen, C.; Washington, R.; Engelstaedter, S.
2013-12-01
North Africa is the world's largest source of mineral aerosol (dust). The Fennec Project, an international consortium led by the University of Oxford, is the first project to systematically instrument the remote central Sahara Desert. These observations have, among others, provided new insights into the atmospheric mechanisms of dust emission. Bordj Badji Mokhtar, in south-west Algeria, is within kilometres of the centre of the global mean summer dust maximum. The site, operated by Fennec partners ONM Algerie, has been heavily instrumented since summer 2011. During the Intensive Observation Period (IOP) in June 2011, four main emission mechanisms were observed and documented: cold pool outflows, low level jets (LLJs), monsoon surges and dry convective plumes. Establishing the relative importance of dust emission mechanisms has been a long-standing research goal. A detailed partitioning exercise of dust events during the IOP shows that 45% of the dust over BBM was generated by local emission in cold pool outflows, 14% by LLJs and only 2% by dry convective plumes. 27% of the dust was advected to the site rather than locally emitted and 12% of the dust was residual or ';background' dust. The work shows the primacy of cold pool outflows for dust emission in the region and also the important contribution of dust advection. In accordance with long-held ideas, the cube of wind speed is strongly correlated with dust emission. Surprisingly however, particles in long-range advection (>500km) were found to be larger than locally emitted dust. Although a clear LLJ wind structure is evident in the mean diurnal cycle during the IOP (12m/s peak winds at 935hPa between 04-05h), LLJs are only responsible for a relatively small amount of dust emission. There is significant daily variability in LLJ strength; the strongest winds are produced by a relatively small number of events. The position and strength of the Saharan Heat Low is strongly associated with the development (or
-
Why is observable radio recombination line emission from galactic HII regions always close to LTE
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shaver, P.A.
1980-01-01
There is no evidence for significant deviations from LTE in single-dish observations of radio recombination line emission from galactic HII regions. This is in agreement with the known properties of HII regions, particularly their density variations and limited range of excitation parameters; the optimum configuration for strong observable non-LTE effects, low electron density and high emission measure, simply does not exist in galactic HII regions, and the observed lines are emitted under near-LTE conditions. Models of the Orion Nebulae and NGC 6604 are presented which fit all available data and show only weak stimulated emission. It is concluded that reliable electron temperatures can indeed be obtained from straightforward analysis of appropriate radio recombination lines. (orig.)
-
Bhardwaj, Anil; Elsner, Ronald F.; Gladstone, G. Randall; Cravens, Thomas E.; Waiate J. Hunter, Jr.; Branduardi-Raymont, Graziella; Ford, Peter
2004-01-01
Chandra observed X-rays from Jupiter during 24-26 February 2003 for about 40 hours with the ACIS-S and HRC-I instruments. The analysis of Jovian low-latitude "disk" Xray emissions are presented and compared with the high-latitude "auroral" emissions. We report the first Chandra ACIS-S measured X-ray spectrum (0.3-2 keV) of Jupiter's low-latitude disk The disk X-ray emission is harder and extends to higher energies than the auroral spectrum. The temporal variation in the Jovian disk X-rays is on an average consistent with those in the solar X-rays observed by GOES, and TIMED/SSE. Contrary to the auroral X-rays, the disk emissions are uniformly distributed over Jupiter; no indication of longitudinal dependence or correlation with surface magneh field strength is visible. Also, unlike the approx. 40 +/- 20 min periodic oscillations seen in the auroral X-ray emissions, the disk emissions do not show any periodic oscillations. The disk spectrum seems to be consistent with resonant and fluorescent scattering of solar X-rays by the Jovian upper atmosphere. Jupiter's disk is found to be about 50% dimmer in soft X-rays in February 2003 compared that in December 2000, which is consistent with the decrease in solar activity. No evidence of lightning-induced X-rays is seen in the Chandra X-ray data. The Jovian disk spectra observed with Chandra-ACIS is stronger than that observed with XMM-Newton two months later during April 28-29, 2003. The XMM-Newton Xray image of Jupiter shows evidence of limb darkening on the anti-sunward side as seen from Earth, as well as an asymmetry with respect to the subsolar point: suggesting a solar driven process.
-
FERMI OBSERVATIONS OF HIGH-ENERGY GAMMA-RAY EMISSION FROM GRB 090217A
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Bechtol, K.; Berenji, B.; Blandford, R. D.; Borgland, A. W.; Bouvier, A.; Baldini, L.; Bellazzini, R.; Bregeon, J.; Brez, A.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Baring, M. G.; Bastieri, D.; Bhat, P. N.; Briggs, M. S.; Bissaldi, E.; Bonamente, E.; Brigida, M.
2010-01-01
The Fermi observatory is advancing our knowledge of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) through pioneering observations at high energies, covering more than seven decades in energy with the two on-board detectors, the Large Area Telescope (LAT) and the Gamma-ray Burst Monitor (GBM). Here, we report on the observation of the long GRB 090217A which triggered the GBM and has been detected by the LAT with a significance greater than 9σ. We present the GBM and LAT observations and on-ground analyses, including the time-resolved spectra and the study of the temporal profile from 8 keV up to ∼1 GeV. All spectra are well reproduced by a Band model. We compare these observations to the first two LAT-detected, long bursts GRB 080825C and GRB 080916C. These bursts were found to have time-dependent spectra and exhibited a delayed onset of the high-energy emission, which are not observed in the case of GRB 090217A. We discuss some theoretical implications for the high-energy emission of GRBs.
-
Chasing Lightning: Sferics, Tweeks and Whistlers
Webb, P. A.; Franzen, K.; Garcia, L.; Schou, P.; Rous, P.
2008-12-01
We all know what lightning looks like during a thunderstorm, but the visible flash we see is only part of the story. This is because lightning also generates light with other frequencies that we cannot perceive with our eyes, but which are just as real as visible light. Unlike the visible light from lightning, these other frequencies can carry the lightning's energy hundreds or thousands of miles across the surface of the Earth in the form of special signals called "tweeks" and "sferics". Some of these emissions can even travel tens of thousands of miles out into space before returning to the Earth as "whistlers". The INSPIRE Project, Inc is a non-profit scientific and educational corporation whose beginning mission was to bring the excitement of observing these very low frequency (VLF) natural radio waves emissions from lightning to high school students. Since 1989, INSPIRE has provided specially designed radio receiver kits to over 2,600 participants around the world to make observations of signals in the VLF frequency range. Many of these participants are using the VLF data they collect in very creative projects that include fiction, music and art exhibitions. During the Fall 2008 semester, the first INSPIRE based university-level course was taught at University of Maryland Baltimore County (UMBC) as part of its First-Year Seminar (FYS) series. The FYS classes are limited to 20 first-year students per class and are designed to create an active-learning environment that encourages student participation and discussion that might not otherwise occur in larger first-year classes. This presentation will cover the experiences gained from using the INSPIRE kits as the basis of a university course. This will include the lecture material that covers the basic physics of lightning, thunderstorms and the Earth's atmosphere, as well as the electronics required to understand the basic workings of the VLF kit. It will also cover the students assembly of the kit in an
-
Theory and observation of electromagnetic ion cyclotron triggered emissions in the magnetosphere
Omura, Yoshiharu; Pickett, Jolene; Grison, Benjamin; Santolik, Ondrej; Dandouras, Iannis; Engebretson, Mark; Décréau, Pierrette M. E.; Masson, Arnaud
2010-07-01
We develop a nonlinear wave growth theory of electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EMIC) triggered emissions observed in the inner magnetosphere. We first derive the basic wave equations from Maxwell's equations and the momentum equations for the electrons and ions. We then obtain equations that describe the nonlinear dynamics of resonant protons interacting with an EMIC wave. The frequency sweep rate of the wave plays an important role in forming the resonant current that controls the wave growth. Assuming an optimum condition for the maximum growth rate as an absolute instability at the magnetic equator and a self-sustaining growth condition for the wave propagating from the magnetic equator, we obtain a set of ordinary differential equations that describe the nonlinear evolution of a rising tone emission generated at the magnetic equator. Using the physical parameters inferred from the wave, particle, and magnetic field data measured by the Cluster spacecraft, we determine the dispersion relation for the EMIC waves. Integrating the differential equations numerically, we obtain a solution for the time variation of the amplitude and frequency of a rising tone emission at the equator. Assuming saturation of the wave amplitude, as is found in the observations, we find good agreement between the numerical solutions and the wave spectrum of the EMIC triggered emissions.
-
On the conditions for nonlinear growth in magnetospheric chorus and triggered emissions
Gołkowski, Mark; Gibby, Andrew R.
2017-09-01
The nonlinear whistler mode instability associated with magnetospheric chorus and VLF triggered emissions continues to be poorly understood. Following up on formulations of other authors, an analytical exploration of the stability of the phenomenon from a new vantage point is given. This exploration derives an additional requirement on the anisotropy of the energetic electron distribution relative to the linear treatment of the instability, and shows that the nonlinear instability is most favorable to increasing growth rate when electrons become initially trapped in the wave potential of a constant frequency wave. These results imply that the initiation of the nonlinear instability at the equator requires a positive frequency sweep rate, while the initiation of the instability by a constant frequency triggering wave must occur at a location downstream of the geomagnetic equator.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hoffman, Ian M. [St. Paul' s School, Concord, NH 03301 (United States); Seojin Kim, Stella, E-mail: ihoffman@sps.edu [Current address: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA 02139 (United States)
2011-12-15
We present new maser emission from {sup 14}NH{sub 3} (9,6) in NGC 7538. Our observations include the known spectral features near v{sub LSR} = -60 km s{sup -1} and -57 km s{sup -1} and several more features extending to -46 km s{sup -1}. In three epochs of observation spanning two months we do not detect any variability in the ammonia masers, in contrast to the >10-fold variability observed in other {sup 14}NH{sub 3} (9,6) masers in the Galaxy over comparable timescales. We also present observations of water masers in all three epochs for which emission is observed over the velocity range -105 km s{sup -1} < v{sub LSR} < -4 km s{sup -1}, including the highest velocity water emission yet observed from NGC 7538. Of the remarkable number of maser species in IRS 1, H{sub 2}O and, now, {sup 14}NH{sub 3} are the only masers known to exhibit emission outside of the velocity range -62 km s{sup -1} < v{sub LSR} < -51 km s{sup -1}. However, we find no significant intensity or velocity correlations between the water emission and ammonia emission. We also present a non-detection in the most sensitive search to date toward any source for emission from the CC{sup 32}S and CC{sup 34}S molecules, indicating an age greater than Almost-Equal-To 10{sup 4} yr for IRS 1-3. We discuss these findings in the context of embedded stellar cores and recent models of the region.
-
Sun, Kang
As the third most abundant nitrogen species in the atmosphere, ammonia (NH3) is a key component of the global nitrogen cycle. Since the industrial revolution, humans have more than doubled the emissions of NH3 to the atmosphere by industrial nitrogen fixation, revolutionizing agricultural practices, and burning fossil fuels. NH3 is a major precursor to fine particulate matter (PM2.5), which has adverse impacts on air quality and human health. The direct and indirect aerosol radiative forcings currently constitute the largest uncertainties for future climate change predictions. Gas and particle phase NH3 eventually deposits back to the Earth's surface as reactive nitrogen, leading to the exceedance of ecosystem critical loads and perturbation of ecosystem productivity. Large uncertainties still remain in estimating the magnitude and spatiotemporal patterns of NH3 emissions from all sources and over a range of scales. These uncertainties in emissions also propagate to the deposition of reactive nitrogen. To improve our understanding of NH3 emissions, observational constraints are needed from local to global scales. The first part of this thesis is to provide quality-controlled, reliable NH3 measurements in the field using an open-path, quantum cascade laser-based NH3 sensor. As the second and third part of my research, NH3 emissions were quantified from a cattle feedlot using eddy covariance (EC) flux measurements, and the similarities between NH3 turbulent fluxes and those of other scalars (temperature, water vapor, and CO2) were investigated. The fourth part involves applying a mobile laboratory equipped with the open-path NH3 sensor and other important chemical/meteorological measurements to quantify fleet-integrated NH3 emissions from on-road vehicles. In the fifth part, the on-road measurements were extended to multiple major urban areas in both the US and China in the context of five observation campaigns. The results significantly improved current urban NH3
-
THE IMPORTANCE OF NEBULAR CONTINUUM AND LINE EMISSION IN OBSERVATIONS OF YOUNG MASSIVE STAR CLUSTERS
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Reines, Amy E.; Nidever, David L.; Whelan, David G.; Johnson, Kelsey E.
2010-01-01
In this spectroscopic study of infant massive star clusters, we find that continuum emission from ionized gas rivals the stellar luminosity at optical wavelengths. In addition, we find that nebular line emission is significant in many commonly used broadband Hubble Space Telescope (HST) filters including the F814W I-band, the F555W V-band, and the F435W B-band. Two young massive clusters (YMCs) in the nearby starburst galaxy NGC 4449 were targeted for follow-up spectroscopic observations after Reines et al. discovered an F814W I-band excess in their photometric study of radio-detected clusters in the galaxy. The spectra were obtained with the Dual Imaging Spectrograph (DIS) on the 3.5 m Apache Point Observatory (APO) telescope and have a spectral range of ∼3800-9800 A. We supplement these data with HST and Sloan Digital Sky Survey photometry of the clusters. By comparing our data to the Starburst99 and GALEV evolutionary synthesis models, we find that nebular continuum emission competes with the stellar light in our observations and that the relative contribution from the nebular continuum is largest in the U- and I-bands, where the Balmer (3646 A) and Paschen jumps (8207 A) are located. The spectra also exhibit strong line emission including the [S III] λλ9069, 9532 lines in the HST F814W I-band. We find that the combination of nebular continuum and line emission can account for the F814W I-band excess previously found by Reines et al. In an effort to provide a benchmark for estimating the impact of ionized gas emission on photometric observations of young massive stellar populations, we compute the relative contributions of the stellar continuum, nebular continuum, and emission lines to the total observed flux of a 3 Myr old cluster through various HST filter/instrument combinations, including filters in the Wide Field Camera 3. We urge caution when comparing observations of YMCs to evolutionary synthesis models since nebular continuum and line emission can
-
Modelling of X-ray emission supernova remnants observed by the European satellite XMM-Newton
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cassam-Chenai, G.
2004-01-01
This thesis deals with the X-ray emission of supernova remnants (SNRs) observed by the European satellite XMM-Newton. In SNRs, the matter heated to millions of degrees shines brightly in X-rays. This emission depends on the hydrodynamical evolution of the SNR, on the chemical composition of the ejected matter and on the ambient medium. Moreover, the blast-wave is considered to be the prime site of the production and the acceleration of cosmic-rays in our Galaxy. XMM-Newton is one of the first to allow the investigation of these different aspects thanks to its spatially-resolved spectroscopy and its very good sensitivity. l first studied Kepler's SNR (SN 1604) whose X-ray emission is dominated by the ejecta. Its observation has allowed to obtain information on the nucleosynthesis products, on their spatial distribution and on the temperature structure in the shocked ejecta. This gives strong constraints on the physics of the explosion and on the progenitor's type. l have shown also that the X-ray emission at the shock is likely to be non-thermal. Then, l studied the SNR G347.3-0.5 whose X-ray emission is entirely due to the synchrotron radiation of relativistic (TeV) electrons accelerated at the shock. From five pointing, l made a full mapping of the X-ray emission characteristics (brightness, absorption and spectral index) at small scale. Combined to radio observations, these results have indicated a clear interaction between the SNR and molecular clouds located at 1 kpc and not at 6 kpc as previously estimated. Lastly, in the framework of a self-similar hydrodynamical model coupled with non-linear particle acceleration, l have obtained the synchrotron emission profile in SNRs, including the adiabatic and radiative losses of the accelerated electrons. (author) [fr
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
W. Li
2017-11-01
Full Text Available The use of dynamic global vegetation models (DGVMs to estimate CO2 emissions from land-use and land-cover change (LULCC offers a new window to account for spatial and temporal details of emissions and for ecosystem processes affected by LULCC. One drawback of LULCC emissions from DGVMs, however, is lack of observation constraint. Here, we propose a new method of using satellite- and inventory-based biomass observations to constrain historical cumulative LULCC emissions (ELUCc from an ensemble of nine DGVMs based on emerging relationships between simulated vegetation biomass and ELUCc. This method is applicable on the global and regional scale. The original DGVM estimates of ELUCc range from 94 to 273 PgC during 1901–2012. After constraining by current biomass observations, we derive a best estimate of 155 ± 50 PgC (1σ Gaussian error. The constrained LULCC emissions are higher than prior DGVM values in tropical regions but significantly lower in North America. Our emergent constraint approach independently verifies the median model estimate by biomass observations, giving support to the use of this estimate in carbon budget assessments. The uncertainty in the constrained ELUCc is still relatively large because of the uncertainty in the biomass observations, and thus reduced uncertainty in addition to increased accuracy in biomass observations in the future will help improve the constraint. This constraint method can also be applied to evaluate the impact of land-based mitigation activities.
-
Anthropogenic emissions and space-borne observations of carbon monoxide over South Asia
Ul-Haq, Zia; Tariq, Salman; Ali, Muhammad
2016-11-01
The focus of this study is to understand anthropogenic emissions, spatiotemporal variability and trends of carbon monoxide (CO) over South Asia by using datasets from MACCity (Monitoring Atmospheric Composition and Climate, MACC and megaCITY - Zoom for the Environment, CityZEN), REAS (Regional Emission inventory in Asia), AIRS (Atmospheric Infrared Sounder) and SCIAMACHY (SCanning Imaging Absorption spectroMeter for Atmospheric CartograpHY). MACCity anthropogenic emissions show an overall increase of 16.5% during 2000-2010. Elevated levels of MACCity CO are found in Indo-Gangetic Basin (IGB), eastern mining region of India, Bangladesh and large urban areas. Some of the major contributors of these emissions have been identified as agricultural waste burning, land transport, industrial production, and energy generation and distribution. An area averaged mean value of AIRS CO at 600 hPa is found to be 114 ± 2 ppbv (slope -0.48 ± 0.2 ppbv yr-1, y-intercept 117 ± 1 ppbv and r = 0.68) with a minor declining trend at -0.41 ± 0.18% yr-1 over the region during 2003-2015. A strong seasonality in AIRS CO concentration is observed with spring season peak in March 129 ± 1.9 ppbv, whereas low values have been observed in summer monsoon with sturdy dip in July 99.6 ± 1.94 ppbv. AIRS CO and SCIAMACHY CO Total Column (CO TC) over the study region show spatial patterns similar to MACCity and REAS emissions. An analysis of SCIAMACHY CO TC tendencies has been performed which indicates minor rising trends over some parts of the region. Background CO, Recent Emissions (RE), and spatial anomalies in RE over high anthropogenic activity zones of Indus Basin, Ganges Basin and Eastern Region were analyzed using AIRS and SCIAMACHY CO data.
-
Observations of the Polarisation of the Anomalous Microwave Emission: A Review
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. A. Rubiño-Martín
2012-01-01
Full Text Available The observational status of the polarisation of the anomalous microwave emission (AME is reviewed, both for individual compact Galactic regions as well as for the large-scale Galactic emission. There are six Galactic regions with existing polarisation constraints in the relevant range of 10–40 GHz: four dust clouds (Perseus, ρ Ophiuchi, LDN1622, and Pleiades and two HII regions (LPH96 and the Helix nebula. These constraints are discussed in detail and are complemented by deriving upper limits on the polarisation of the AME for those objects without published WMAP constraints. For the case of large-scale emission, two recent works, based on WMAP data, are reviewed. Currently, the best constraints on the fractional polarisation of the AME, at frequencies near the peak of the emission (i.e., 20–30 GHz, are at the level of ~1% (95.4% confidence level. Finally, we compare these constraints with the predictions of some theoretical AME models and discuss the possible impact of polarised AME on future primordial B-mode experiments.
-
Gamma-Ray Emission in Dissipative Pulsar Magnetospheres: from Theory to Fermi Observations
Kalapotharakos, Konstantinos; Harding, Alice K.; Kazanas, Demosthenes
2014-01-01
We compute the patterns of gamma-ray emission due to curvature radiation in dissipative pulsar magnetospheres. Our ultimate goal is to construct macrophysical models that are able to reproduce the observed gamma-ray light curve phenomenology recently published in the Second Fermi Pulsar Catalog. We apply specific forms of Ohm's law on the open field lines using a broad range for the macroscopic conductivity values that result in solutions ranging, from near-vacuum to near-force-free. Using these solutions, we generate model gamma-ray light curves by calculating realistic trajectories and Lorentz factors of radiating particles under the influence of both the accelerating electric fields and curvature radiation reaction. We further constrain our models using the observed dependence of the phase lags between the radio and gamma-ray emission on the gamma-ray peak separation. We perform a statistical comparison of our model radio-lag versus peak-separation diagram and the one obtained for the Fermi standard pulsars. We find that for models of uniform conductivity over the entire open magnetic field line region, agreement with observations favors higher values of this parameter. We find, however, significant improvement in fitting the data with models that employ a hybrid form of conductivity, specifically, infinite conductivity interior to the light cylinder and high but finite conductivity on the outside. In these models the gamma-ray emission is produced in regions near the equatorial current sheet but modulated by the local physical properties. These models have radio lags near the observed values and statistically best reproduce the observed light curve phenomenology. Additionally, they also produce GeV photon cut-off energies.
-
Yamashita, Kozo; Takahashi, Yukihiro; Ohya, Hiroyo; Tsuchiya, Fuminori; Sato, Mitsuteru; Matsumoto, Jun
2013-04-01
Data of lightning discharge has been focused on as an effective way for monitoring and nowcasting of thunderstorm activity which causes extreme weather. Spatial distribution of lightning discharge has been used as a proxy of the presence or absence of deep convection. Latest observation shows that there is extremely huge lightning whose scale is more than hundreds times bigger than that of averaged event. This result indicates that lightning observation should be carried out to estimate not only existence but also scale for quantitative evaluation of atmospheric convection. In this study, lightning observation network in the Maritime Continent is introduced. This network is consisted of the sensors which make possible to measure electromagnetic wave radiated from lightning discharges. Observation frequency is 0.1 - 40 kHz for the measurement of magnetic field and 1 - 40 kHz for that of electric field. Sampling frequency is 100 kHz. Waveform of electromagnetic wave is recorded by personal computer. We have already constructed observation stations at Tainan in Taiwan (23.1N, 121.1E), Saraburi in Thailand (14.5N, 101.0E), and Pontianak in Indonesia (0.0N, 109.4E). Furthermore, we plan to install the monitoring system at Los Banos in Philippines (14.18, 121.25E) and Hanoi in Viet Nam. Data obtained by multipoint observation is synchronized by GPS receiver installed at each station. By using data obtained by this network, location and scale of lightning discharge can be estimated. Location of lightning is determined based on time of arrival method. Accuracy of geolocation could be less than 10km. Furthermore, charge moment is evaluated as a scale of each lightning discharge. It is calculated from electromagnetic waveform in ELF range (3-30 kHz). At the presentation, we will show the initial result about geolocation for source of electromagnetic wave and derivation of charge moment value based on the measurement of ELF and VLF sferics.
-
Stavrakou, Trissevgeni; Müller, Jean-François; Bauwens, Maite; De Smedt, Isabelle; Van Roozendael, Michel
2017-04-01
Biogenic hydrocarbon emissions (BVOC) respond to temperature, photosynthetically active radiation, leaf area index, as well as to factors like leaf age, soil moisture, and ambient CO2 concentrations. Isoprene is the principal contributor to BVOC emissions and accounts for about half of the estimated total emissions on the global scale, whereas monoterpenes are also significant over boreal ecosystems. Due to their large emissions, their major role in the tropospheric ozone formation and contribution to secondary organic aerosols, BVOCs are highly relevant to both air quality and climate. Their oxidation in the atmosphere leads to the formation of formaldehyde (HCHO) at high yields. Satellite observations of HCHO abundances can therefore inform us on the spatial and temporal variability of the underlying sources and on their emission trends. The main objective of this study is to investigate the interannual variability and trends of observed HCHO columns during the growing season, when BVOC emissions are dominant, and interpret them in terms of BVOC emission flux variability. To this aim, we use the MEGAN-MOHYCAN model driven by the ECMWF ERA-interim meteorology to calculate bottom-up BVOC fluxes on the global scale (Müller et al. 2008, Stavrakou et al. 2014) over 2003-2015, and satellite HCHO observations from SCIAMACHY (2003-2011) and OMI (2005-2015) instruments (De Smedt et al. 2008, 2015). We focus on mid- and high-latitude regions of the Northern Hemisphere in summertime, as well as tropical regions taking care to exclude biomass burning events which also lead to HCHO column enhancements. We find generally a very strong temporal correlation (>0.7) between the simulated BVOC emissions and the observed HCHO columns over temperate and boreal ecosystems. Positive BVOC emission trends associated to warming climate are found in almost all regions and are well corroborated by the observations. Furthermore, using OMI HCHO observations over 2005-2015 as constraints in
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lau, Jason; Hung, W.T.; Cheung, C.S.
2012-01-01
In this study on-road gaseous emissions of vehicles are investigated using remote sensing measurements collected over three different periods. The results show that a high percentage of gaseous pollutants were emitted from a small percentage of vehicles. Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) vehicles generally have higher gaseous emissions compared to other vehicles, particularly among higher-emitting vehicles. Vehicles with high vehicle specific power (VSP) tend to have lower CO and HC emissions while petrol and LPG vehicles tend to have higher NO emissions when engine load is high. It can be observed that gaseous emission factors of petrol and LPG vehicles increase greatly within 2 years of being introduced to the vehicle fleet, suggesting that engine and catalyst performance deteriorate rapidly. It can be observed that LPG vehicles have higher levels of gaseous emissions than petrol vehicles, suggesting that proper maintenance of LPG vehicles is essential in reducing gaseous emissions from vehicles. - Highlights: ► Emissions collected in 3 different periods to examine changes in emission over time. ► LPG vehicles generally emit more gaseous pollutants compared to other vehicles. ► Large increase in emissions from modern petrol/LPG vehicles after 2 years' operation. ► CO and NO emissions of modern diesel vehicles are similar to those of older vehicles. - Remote sensing measurements show large increases in gaseous emissions from vehicles in Hong Kong after 2 years of operation, indicating that engine and catalyst performance deteriorate rapidly.
-
Shusterman, A.; Kim, J.; Lieschke, K.; Newman, C.; Cohen, R. C.
2017-12-01
Global momentum is building for drastic, regulated reductions in greenhouse gas emissions over the coming decade. With this increasing regulation comes a clear need for increasingly sophisticated monitoring, reporting, and verification (MRV) strategies capable of enforcing and optimizing emissions-related policy, particularly as it applies to urban areas. Remote sensing and/or activity-based emission inventories can offer MRV insights for entire sectors or regions, but are not yet sophisticated enough to resolve unexpected trends in specific emitters. Urban surface monitors can offer the desired proximity to individual greenhouse gas sources, but due to the densely-packed nature of typical urban landscapes, surface observations are rarely representative of a single source. Most previous efforts to decompose these complex signals into their contributing emission processes have involved inverse atmospheric modeling techniques, which are computationally intensive and believed to depend heavily on poorly understood a priori estimates of error covariance. Here we present a number of transparent, low-computation approaches for extracting source-specific emissions estimates from signals with a variety of nearfield influences. Using observations from the first several years of the BErkeley Atmospheric CO2 Observation Network (BEACO2N), we demonstrate how to exploit strategic pairings of monitoring "nodes," anomalous wind conditions, and well-understood temporal variations to hone in on specific CO2 sources of interest. When evaluated against conventional, activity-based bottom-up emission inventories, these strategies are seen to generate quantitatively rigorous emission estimates. With continued application as the BEACO2N data set grows in time and space, these approaches offer a promising avenue for optimizing greenhouse gas mitigation strategies into the future.
-
ELF-VLF communications through the Earth Project report for calendar year 1984, revision 1
Buettner, H. M.; Burker, G. J.; Didwall, E. M.; Holladay, G.; Lytle, R. J.
1985-08-01
We use computer models and experiments to explore the feasibility of communication between points underground and on the Earth's surface. Emphasis is placed on ELF-VLF electromagnetic propagation through the Earth; nominally, we investigated propagation in the 200 Hz-30 kHz frequency range. The computer modeling included calculations of the fields of a point electric or magnetic source in a homogeneous half space or a stratified earth. Initial results for an insulated antenna of finite length are also considered. The experiments involved through-the-Earth transmissions at two locations in Pennsylvania, both of which had large formations of limestone. Initial results indicate that information rates as high as kbits/s may be possible for subsurface depths of 300 m or less. Accuracy of these estimates depends on the electromagnetic propagation constant of the rock, the noise characteristics, and the modulation scheme. Although a nuisance for evaluating through-the-Earth propagation, the existence of subsurface metal conductors can improve the transmission character of the site.
-
ELF-VLF Communications through the Earth Project report for calendar year 1984. Revision 1
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Buettner, H.M.; Burke, G.J.; Didwall, E.M.; Holladay, G.; Lytle, R.J.
1985-08-01
We use computer models and experiments to explore the feasibility of communication between points underground and on the Earth's surface. Emphasis is placed on ELF-VLF electromagnetic propagation through the Earth; nominally, we investigated propagation in the 200 Hz-30 kHz frequency range. The computer modeling included calculations of the fields of a point electric or magnetic source in a homogeneous half space or a stratified earth. Initial results for an insulated antenna of finite length are also considered. The experiments involved through-the-earth transmissions at two locations in Pennsylvania, both of which had large formations of limestone. Initial results indicate that information rates as high as kbits/s may be possible for subsurface depths of 300 m or less. Accuracy of these estimates depends on the electromagnetic propagation constant of the rock, the noise characteristics, and the modulation scheme. Although a nuisance for evaluating through-the-Earth propagation, the existence of subsurface metal conductors can improve the transmission character of the site.
-
Observation of vibronic emission spectrum of jet-cooled 3,5-difluorobenzyl radical.
Lee, Seung Woon; Yoon, Young Wook; Lee, Sang Kuk
2010-09-02
We applied the technique of corona-excited supersonic expansion using a pinhole-type glass nozzle to observe the vibronic emission spectrum of jet-cooled benzyl-type radicals from the corona discharge of precursor 3,5-difluorotoluene seeded in a large amount of inert helium carrier gas. The vibronically well-resolved emission spectrum was recorded with a long-path monochromator in the visible region. After subtracting the vibronic bands originating from isomeric difluorobenzyl radicals from the observed spectrum, we identified for the first time the bands belonging to the 3,5-difluorobenzyl radical, from which the electronic energy and vibrational mode frequencies of the 3,5-difluorobenzyl radical were accurately determined in the ground electronic state by comparison with those of the precursor and with those from an ab initio calculation.
-
Observed effects of soil organic matter content on the microwave emissivity of soils
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
O'Neill, P.E.; Jackson, T.J.
1990-01-01
In order to determine the significance of organic matter content on the microwave emissivity of soils when estimating soil moisture, a series of field experiments were conducted in which 1.4 GHz microwave emissivity data were collected over test plots of sandy loam soil with different organic matter levels (1.8%, 4.0%, and 6.1%) for a range of soil moisture values. Analyses of the observed data showed only minor variation in microwave emissivity due to a change in organic matter content at a given moisture level for soils with similar texture and structure. Predictions of microwave emissivity made using a dielectric model for aggregated soils exhibited the same trends and type of response as the measured data when adjusted values for the input parameters were utilized
-
Atmospheric Signatures and Effects of Space-based Relativistic Electron Beam Injection
Marshall, R. A.; Sanchez, E. R.; Kero, A.; Turunen, E. S.; Marsh, D. R.
2017-12-01
Future relativistic electron beam injection experiments have the potential to provide groundbreaking insights into the physics of wave-particle interactions and beam-neutral interactions, relevant to space physics and to fundamental plasma physics. However, these experiments are only useful if their signatures can be detected. In this work, we use a physics-based forward modeling framework to investigate the observable signatures of a relativistic beam interacting with the upper atmosphere. The modeling framework is based around the Electron Precipitation Monte Carlo (EPMC) model, used to simulate electron precipitation in the upper atmosphere. That model is coupled to physics-based models of i) optical emission production; ii) bremsstrahlung photon production and propagation; iii) D-region ion chemistry; and iv) VLF wave propagation in the Earth-ionosphere waveguide. Using these modeling tools, we predict the optical, X-ray, chemical, radar, and VLF signatures of a realistic beam injection, based on recent space-based accelerator designs. In particular, we inject a beam pulse of 10 mA for a duration of 500 μs at an energy of 1 MeV, providing a total pulse energy of 5 J. We further investigate variations in these parameters, in particular the total energy and the electron energy. Our modeling shows that for this 5 J pulse injection at 1 MeV electron energy, the optical signal is easily detectable from the ground in common emission bands, but the X-ray signal is likely too weak to be seen from either balloons or LEO orbiting spacecraft. We further predict the optical signal-to-noise ratio that would be expected in different optical systems. Chemical signatures such as changes to NOx and HOx concentrations are too short-lived to be detectable; however our modeling provides a valuable estimate of the total chemical response. Electron density perturbations should be easily measurable from ground-based high-power radars and via VLF subionospheric remote sensing
-
MODELING ATMOSPHERIC EMISSION FOR CMB GROUND-BASED OBSERVATIONS
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Errard, J.; Borrill, J. [Space Sciences Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 (United States); Ade, P. A. R. [School of Physics and Astronomy, Cardiff University, Cardiff CF10 3XQ (United Kingdom); Akiba, Y.; Chinone, Y. [High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK), Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0801 (Japan); Arnold, K.; Atlas, M.; Barron, D.; Elleflot, T. [Department of Physics, University of California, San Diego, CA 92093-0424 (United States); Baccigalupi, C.; Fabbian, G. [International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA), Trieste I-34014 (Italy); Boettger, D. [Department of Astronomy, Pontifica Universidad Catolica de Chile (Chile); Chapman, S. [Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, B3H 4R2 (Canada); Cukierman, A. [Department of Physics, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 (United States); Delabrouille, J. [AstroParticule et Cosmologie, Univ Paris Diderot, CNRS/IN2P3, CEA/Irfu, Obs de Paris, Sorbonne Paris Cité (France); Dobbs, M.; Gilbert, A. [Physics Department, McGill University, Montreal, QC H3A 0G4 (Canada); Ducout, A.; Feeney, S. [Department of Physics, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom); Feng, C. [Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Irvine (United States); and others
2015-08-10
Atmosphere is one of the most important noise sources for ground-based cosmic microwave background (CMB) experiments. By increasing optical loading on the detectors, it amplifies their effective noise, while its fluctuations introduce spatial and temporal correlations between detected signals. We present a physically motivated 3D-model of the atmosphere total intensity emission in the millimeter and sub-millimeter wavelengths. We derive a new analytical estimate for the correlation between detectors time-ordered data as a function of the instrument and survey design, as well as several atmospheric parameters such as wind, relative humidity, temperature and turbulence characteristics. Using an original numerical computation, we examine the effect of each physical parameter on the correlations in the time series of a given experiment. We then use a parametric-likelihood approach to validate the modeling and estimate atmosphere parameters from the polarbear-i project first season data set. We derive a new 1.0% upper limit on the linear polarization fraction of atmospheric emission. We also compare our results to previous studies and weather station measurements. The proposed model can be used for realistic simulations of future ground-based CMB observations.
-
Imprints of cosmic rays in multifrequency observations of the interstellar emission
Orlando, E.
2018-04-01
Ever since the discovery of cosmic rays (CRs), significant advancements have been made in modelling their propagation in the Galaxy and in the Heliosphere. However, propagation models suffer from degeneracy of many parameters. To complicate the picture, the precision of recent data have started challenging existing models. To tackle these issues, we use available multifrequency observations of the interstellar emission from radio to gamma rays, together with direct CR measurements, to study local interstellar spectra (LIS) and propagation models. As a result, the electron LIS is characterized without any assumption on solar modulation, and favourite propagation models are put forwards. More precisely, our analysis leads to the following main conclusions: (1) the electron injection spectrum needs at least a break below a few GeV; (2) even though consistent with direct CR measurements, propagation models producing a LIS with large all-electron density from a few hundreds of MeV to a few GeV are disfavoured by both radio and gamma-ray observations; (3) the usual assumption that direct CR measurements, after accounting for solar modulation, are representative of the proton LIS in our ˜1 kpc region is challenged by the observed local gamma-ray H I emissivity. We provide the resulting proton LIS, all-electron LIS, and propagation parameters based on synchrotron, gamma-ray, and direct CR data. A plain diffusion model and a tentative diffusive-reacceleration model are put forwards. The various models are investigated in the inner-Galaxy region in X-rays and gamma rays. Predictions of the interstellar emission for future gamma-ray instruments (e-ASTROGAM and AMEGO) are derived.
-
Validation of the Swiss methane emission inventory by atmospheric observations and inverse modelling
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Henne
2016-03-01
Full Text Available Atmospheric inverse modelling has the potential to provide observation-based estimates of greenhouse gas emissions at the country scale, thereby allowing for an independent validation of national emission inventories. Here, we present a regional-scale inverse modelling study to quantify the emissions of methane (CH4 from Switzerland, making use of the newly established CarboCount-CH measurement network and a high-resolution Lagrangian transport model. In our reference inversion, prior emissions were taken from the "bottom-up" Swiss Greenhouse Gas Inventory (SGHGI as published by the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment in 2014 for the year 2012. Overall we estimate national CH4 emissions to be 196 ± 18 Gg yr−1 for the year 2013 (1σ uncertainty. This result is in close agreement with the recently revised SGHGI estimate of 206 ± 33 Gg yr−1 as reported in 2015 for the year 2012. Results from sensitivity inversions using alternative prior emissions, uncertainty covariance settings, large-scale background mole fractions, two different inverse algorithms (Bayesian and extended Kalman filter, and two different transport models confirm the robustness and independent character of our estimate. According to the latest SGHGI estimate the main CH4 source categories in Switzerland are agriculture (78 %, waste handling (15 % and natural gas distribution and combustion (6 %. The spatial distribution and seasonal variability of our posterior emissions suggest an overestimation of agricultural CH4 emissions by 10 to 20 % in the most recent SGHGI, which is likely due to an overestimation of emissions from manure handling. Urban areas do not appear as emission hotspots in our posterior results, suggesting that leakages from natural gas distribution are only a minor source of CH4 in Switzerland. This is consistent with rather low emissions of 8.4 Gg yr−1 reported by the SGHGI but inconsistent with the much higher value of 32 Gg yr−1 implied by the
-
Quantifying global fossil-fuel CO2 emissions: from OCO-2 to optimal observing designs
Ye, X.; Lauvaux, T.; Kort, E. A.; Oda, T.; Feng, S.; Lin, J. C.; Yang, E. G.; Wu, D.; Kuze, A.; Suto, H.; Eldering, A.
2017-12-01
Cities house more than half of the world's population and are responsible for more than 70% of the world anthropogenic CO2 emissions. Therefore, quantifications of emissions from major cities, which are only less than a hundred intense emitting spots across the globe, should allow us to monitor changes in global fossil-fuel CO2 emissions, in an independent, objective way. Satellite platforms provide favorable temporal and spatial coverage to collect urban CO2 data to quantify the anthropogenic contributions to the global carbon budget. We present here the optimal observation design for future NASA's OCO-2 and Japanese GOSAT missions, based on real-data (i.e. OCO-2) experiments and Observing System Simulation Experiments (OSSE's) to address different error components in the urban CO2 budget calculation. We identify the major sources of emission uncertainties for various types of cities with different ecosystems and geographical features, such as urban plumes over flat terrains, accumulated enhancements within basins, and complex weather regimes in coastal areas. Atmospheric transport errors were characterized under various meteorological conditions using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model at 1-km spatial resolution, coupled to the Open-source Data Inventory for Anthropogenic CO2 (ODIAC) emissions. We propose and discuss the optimized urban sampling strategies to address some difficulties from the seasonality in cloud cover and emissions, vegetation density in and around cities, and address the daytime sampling bias using prescribed diurnal cycles. These factors are combined in pseudo data experiments in which we evaluate the relative impact of uncertainties on inverse estimates of CO2 emissions for cities across latitudinal and climatological zones. We propose here several sampling strategies to minimize the uncertainties in target mode for tracking urban fossil-fuel CO2 emissions over the globe for future satellite missions, such as OCO-3 and future
-
Wei Li; Philippe Ciais; Shushi Peng; Chao Yue; Yilong Wang; Martin Thurner; Sassan S. Saatchi; Almut Arneth; Valerio Avitabile; Nuno Carvalhais; Anna B. Harper; Etsushi Kato; Charles Koven; Yi Y. Liu; Julia E. M. S. Nabel; Yude Pan; Julia Pongratz; Benjamin Poulter; Thomas A. M. Pugh; Maurizio Santoro; Stephen Sitch; Benjamin D. Stocker; Nicolas Viovy; Andy Wiltshire; Rasoul Yousefpour; Sönke Zaehle
2017-01-01
The use of dynamic global vegetation models (DGVMs) to estimate CO2 emissions from land-use and land-cover change (LULCC) offers a new window to account for spatial and temporal details of emissions and for ecosystem processes affected by LULCC. One drawback of LULCC emissions from DGVMs, however, is lack of observation constraint. Here, we...
-
Solar-terrestrial disturbances of June-September 1982, 4
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ondoh, Tadanori; Nakamura, Yoshikatsu; Watanabe, Shigeaki
1986-01-01
Wide-band VLF hisses similar to the auroral hiss, choruses and a hook-type emission were observed at mid-latitudes during the daytime of four geomagnetic storms in July and September 1982 by ISIS satellites at Kashima Station, Radio Research Laboratories (RRL), Japan. The occurrences of the high-latitude-type VLF emissions in mid-latitudes are clearly caused by geomagnetic storm effects. During the main phase of geomagnetic storm on July 14, 1982, auroral-type hisses occurred at frequencies above 4 kHz at invariant latitudes above 43 deg which were below the observed latitude, 47 deg of whistler echo trains. The auroral type hiss observed at mid-latitudes seems to be generated by the Cherenkov radiations from precipitating electrons with energy above a few keV. The precipitating electrons may result from an interaction of the ring current particles with the plasmaspheric cold plasma. The occurrence of choruses at mid-latitudes during the geomagnetic storm of September 22 seems to represent inward movements of the outer-radiation-zone electrons due to an enhanced westward electric field in the magnetosphere during the geomagnetic storm. Another storm effect observed is that the upper limit frequency, lower limit frequency and bandwidth of ELF hiss became smaller at lower latitudes. This effect seems to be caused by the ionic compositions of the topside ionosphere and the conditions of the outer plasmasphere, where the ELF hiss is generated, during geomagnetic storms. (author)
-
Fontaine, Alain; Sauvage, Bastien; Pétetin, Hervé; Auby, Antoine; Boulanger, Damien; Thouret, Valerie
2016-04-01
Since 1994, the IAGOS program (In-Service Aircraft for a Global Observing System http://www.iagos.org) and its predecessor MOZAIC has produced in-situ measurements of the atmospheric composition during more than 46000 commercial aircraft flights. In order to help analyzing these observations and further understanding the processes driving their evolution, we developed a modelling tool SOFT-IO quantifying their source/receptor link. We improved the methodology used by Stohl et al. (2003), based on the FLEXPART plume dispersion model, to simulate the contributions of anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions from the ECCAD database (http://eccad.aeris-data.fr) to the measured carbon monoxide mixing ratio along each IAGOS flight. Thanks to automated processes, contributions are simulated for the last 20 days before observation, separating individual contributions from the different source regions. The main goal is to supply add-value products to the IAGOS database showing pollutants geographical origin and emission type. Using this information, it may be possible to link trends in the atmospheric composition to changes in the transport pathways and to the evolution of emissions. This tool could be used for statistical validation as well as for inter-comparisons of emission inventories using large amounts of data, as Lagrangian models are able to bring the global scale emissions down to a smaller scale, where they can be directly compared to the in-situ observations from the IAGOS database.
-
Estimation of Methane Emissions in the Los Angeles Basin using CLARS-FTS Observations
Sander, S.; Zeng, Z. C.; Pongetti, T.; Duren, R. M.; Shia, R. L.; Yung, Y. L.; He, L.; Gurney, K. R.
2017-12-01
The Los Angeles Basin (LA Basin), covering almost 10,743 square miles, is home to over 16.8 million people - about half the population of the state of California. It is also the second most populated urban area in the United States and one of the major source of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. Using FTIR observations from the California Laboratory for Atmospheric Remote Sensing (CLARS) located on Mount Wilson at an altitude of 1673m, we measure the reflected near infrared sunlight from 33 surface targets in the Los Angeles megacity including the direct solar beam which gives the free tropospheric background. We then retrieve the excess slant column abundances of important trace gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) in the LA basin. Using atmospheric tracer - tracer correlations for CH4 and CO2 to eliminate the effect of aerosol scattering in the retrieval, we infer methane emissions based on the ratio of XCH4 excess to XCO2 excess. Significant variability is observed in the spatial distributions of excess CH4. Methane emissions in the LA basin show consistent peaks in late summer and winter during the period from Sep 2011 to the present. The strong correlation between natural gas usage data and derived CLARS methane emissions (r2 = 0.5) implies that natural gas leakage during transmission and/or consumption accounts for a significant fraction of the inferred seasonal variability of methane emissions in the LA basin. We will report updated annual trends in CH4 emissions from 2011 to the present. Copyright 2017. All rights reserved.
-
Lindenmaier, Rodica; Dubey, Manvendra K.; Henderson, Bradley G.; Butterfield, Zachary T.; Herman, Jay R.; Rahn, Thom; Lee, Sang-Hyun
2014-01-01
There is a pressing need to verify air pollutant and greenhouse gas emissions from anthropogenic fossil energy sources to enforce current and future regulations. We demonstrate the feasibility of using simultaneous remote sensing observations of column abundances of CO2, CO, and NO2 to inform and verify emission inventories. We report, to our knowledge, the first ever simultaneous column enhancements in CO2 (3–10 ppm) and NO2 (1–3 Dobson Units), and evidence of δ13CO2 depletion in an urban region with two large coal-fired power plants with distinct scrubbing technologies that have resulted in ∆NOx/∆CO2 emission ratios that differ by a factor of two. Ground-based total atmospheric column trace gas abundances change synchronously and correlate well with simultaneous in situ point measurements during plume interceptions. Emission ratios of ∆NOx/∆CO2 and ∆SO2/∆CO2 derived from in situ atmospheric observations agree with those reported by in-stack monitors. Forward simulations using in-stack emissions agree with remote column CO2 and NO2 plume observations after fine scale adjustments. Both observed and simulated column ∆NO2/∆CO2 ratios indicate that a large fraction (70–75%) of the region is polluted. We demonstrate that the column emission ratios of ∆NO2/∆CO2 can resolve changes from day-to-day variation in sources with distinct emission factors (clean and dirty power plants, urban, and fires). We apportion these sources by using NO2, SO2, and CO as signatures. Our high-frequency remote sensing observations of CO2 and coemitted pollutants offer promise for the verification of power plant emission factors and abatement technologies from ground and space. PMID:24843169
-
On radiation emission from a microbunched beam with wavefront tilt and its experimental observation
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Geloni, Gianluca [European XFEL GmbH, Hamburg (Germany); Kocharyan, Vitali; Saldin, Evgeni [Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (DESY), Hamburg (Germany)
2017-06-15
In this paper we compare experimental observations and theory of radiation emission from a microbunched beam with microbunching wavefront tilt with respect to the direction of motion. The theory refers to the work of T. Tanaka, H. Kitamura, and T. Shintake (2004), which predicts, in this case, exponential suppression of coherent radiation along the kicked direction. The observations refer to a recent experiment performed at the LCLS, where a microbunched beam was kicked by a bend and sent to a radiator undulator. The experiment resulted in the emission of strong coherent radiation that had its maximum along the kicked direction of motion, when the undulator parameter was detuned to a value larger than the nominal one. We first analyze the theory in detail, and we confirm the correctness of its derivation according to the conventional theory of radiation emission from charged particles. Subsequently, we look for possible peculiarities in the experiment, which may not be modeled by the theory. We show that only spurious effects are not accounted for. We conclude that the experiment defies explanation in terms of the conventional theory of radiation emission.
-
On radiation emission from a microbunched beam with wavefront tilt and its experimental observation
Geloni, Gianluca; Kocharyan, Vitali; Saldin, Evgeni
2018-03-01
In this paper we compare experimental observations and theory of radiation emission from a microbunched beam with microbunching wavefront tilt with respect to the direction of motion. The theory refers to the work Tanaka et al. (2004) , which predicts, in this case, exponential suppression of coherent radiation along the kicked direction. The observations refer to a recent experiment performed at the LCLS (Nuhn et al., 2015; Lutman etal., 2016), where a microbunched beam was kicked by a bend and sent to a radiator undulator. The experiment resulted in the emission of strong coherent radiation that had its maximum along the kicked direction of motion, when the undulator parameter was detuned to a value larger than the nominal one. We first analyze the theory in detail, and we confirm the correctness of its derivation according to the conventional theory of radiation emission from charged particles. Subsequently, we look for possible peculiarities in the experiment, which may not be modeled by the theory. We show that only spurious effects are not accounted for. We conclude that the experiment defies explanation in terms of the conventional theory of radiation emission.
-
On waves below the local proton gyrofrequency in auroral acceleration regions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gustafsson, G.; Andre, M.; Matson, L.; Koskinen, H.
1990-01-01
The Viking wave electric field and density fluctuation measurements together with simultaneous particle observations are used to study waves at frequencies below the local proton gyrofrequency. Such waves were observed during about 20% of nightside auroral field line crossings by Viking at altitudes between 2,000 and 10,000 km. The observations are different from earlier spacecraft observations of similar waves in such a way that the center frequency in about one out of four of the observed events was below the gyrofrequency of singly charged helium, which has not been reported previously. The waves were well correlated with precipitating electrons of energies of a few keV and with VLF auroral hiss. Detailed investigations of simultaneously observed wave emissions, particles, and total densities strongly suggest that secondary peaks at keV energies in the distributions of downgoing electrons can cause the emissions
-
Kurata, G.; Lalitaporn, P.
2012-12-01
Since the economic growth of the countries in Southeast Asia is significantly rapid, the emission of air pollutant from the anthropogenic activity, such as industry, power generation and transportation is rapidly increasing. Moreover, biomass burning due to unsuitable agricultural management, deforestation and expansion of farmland are discharging large amount of pollutants, such as Carbon monoxide, volatile organic compound and particulate matter. Especially, the particulate matter from biomass burning causes the serious haze pollution in surrounding area in Southeast Asia. Furthermore, the biomass fuel used for cooking at residential sector discharges harmful pollutants including a particulate matter, and causes the adverse health impact to people on indoor and outdoor. In this study, we evaluated the spatial distribution and the seasonal variation of emission inventory for Southeast Asia region by comparing with satellite observation data in order to improve the accuracy of the impact assessment of air pollution by regional atmospheric chemistry transport model (WRF and CMAQ). As an emission inventory data, we used our original regional emission inventory for Southeast Asia region developed from detail transportation and industry data sets as well as a several existing emission inventories. As satellite observation data, the vertical column density of NO2, Particulate matter and Carbon monoxide obtained by various satellite, such as GOME, GOME2, SCIAMACY, OMI and so on. As a result of comparisons between satellite observation and emission inventories from 1996 to 2011, in the case of anthropogenic emission, seasonal variation was comparatively well in agreement with the seasonal variation of satellite data. However, the uncertainty of the seasonal variation was large on several large cities. In the case of emission from biomass burning, the seasonal variation was clear, but inter-annual variation was also large due to large scale climate condition.
-
Observations of interstellar H2O emission at 183 Gigahertz
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Waters, J.W.; Gustincic, J.J.; Kakar, R.K.; Kuiper, T.B.H.; Roscoe, H.K.; Swanson, P.N.; Rodriguez Kuiper, E.N.; Kerr, A.R.; Thaddeus, P.
1980-01-01
Line emission at 183 GHz by the 3 13 --2 20 rotational transition of water vapor has been detected from the Orion Nebula with the NASA Kuiper Airborne Observatory 91 cm telescope. The peak antenna temperature of the line is 15 K, its LSR velocity is 8 km s -1 , and its width is 15 km s -1 . The velocity profile has characteristics similar to those for CO:a narrow (approx.4 km s -1 ) ''spike'' centered at 9.5 km s -1 and a broad ''plateau'' with flaring wings centered at approx.8 km s -1 . Our 7'.5 antenna beam did not resolve the source. The 183 GHz H 2 O plateau emission appears enhanced above that expected for thermal excitation if it originates from the no greater than 1' region characteristic of plateau emission from all other observed molecules. The spike emission is consistent with an optically thick source of the approximated size of the well-known molecular ridge in Orion having the H 2 O in thermal equilibrium at Tapprox. =50 K. If this is the case, then the H 2 O column density giving rise to the spike is N/sub H/2/sub O/> or =3 x 10 17 cm -2 . An excitation calculation implies N/sub H/2/sub O/approx. =10 18 cm -2 for a source the size of the molecular ridge. These results imply that H 2 O is one of the more abundant species in the Orion Molecualr Cloud.H 2 O emission at 183 GHz was not detected in Sgr A, Sgr B2, W3, W43, W49, W51, DR 21, NGC 1333, NGC 7027, GL 2591, or the rho Oph cloud; it may have been detected in M17
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Qiu Jiong; Longcope, Dana W.; Liu Wenjuan [Department of Physics, Montana State University, Bozeman, MT 59717-3840 (United States); Sturrock, Zoe [Department of Applied Mathematics, University of St. Andrews (United Kingdom); Klimchuk, James A. [NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 (United States)
2013-09-01
A solar flare is composed of impulsive energy release events by magnetic reconnection, which forms and heats flare loops. Recent studies have revealed a two-phase evolution pattern of UV 1600 A emission at the feet of these loops: a rapid pulse lasting for a few seconds to a few minutes, followed by a gradual decay on timescales of a few tens of minutes. Multiple band EUV observations by the Atmosphere Imaging Assembly further reveal very similar signatures. These two phases represent different but related signatures of an impulsive energy release in the corona. The rapid pulse is an immediate response of the lower atmosphere to an intense thermal conduction flux resulting from the sudden heating of the corona to high temperatures (we rule out energetic particles due to a lack of significant hard X-ray emission). The gradual phase is associated with the cooling of hot plasma that has been evaporated into the corona. The observed footpoint emission is again powered by thermal conduction (and enthalpy), but now during a period when approximate steady-state conditions are established in the loop. UV and EUV light curves of individual pixels may therefore be separated into contributions from two distinct physical mechanisms to shed light on the nature of energy transport in a flare. We demonstrate this technique using coordinated, spatially resolved observations of UV and EUV emissions from the footpoints of a C3.2 thermal flare.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hollmann, E M; Doerner, R P; Nishijima, D; Pigarov, A Yu
2017-01-01
Growth of nanostructured fuzz on a tungsten target in a helium plasma is found to cause a significant (∼3×) reduction in ion impact secondary electron emission in a linear plasma device. The ion impact secondary electron emission is separated from the electron impact secondary electron emission by varying the target bias voltage and fitting to expected contributions from electron impact, both thermal and non-thermal; with the non-thermal electron contribution being modeled using Monte-Carlo simulations. The observed (∼3×) reduction is similar in magnitude to the (∼2×) reduction observed in previous work for the effect of tungsten fuzz formation on secondary electron emission due to electron impact. It is hypothesized that the observed reduction results from re-absorption of secondary electrons in the tungsten fuzz. (paper)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zheng, W. [Department of Physics, University of Michigan, 450 Church Street, Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (United States); Shen, R. F. [Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario M5S 3H4 (Canada); Sakamoto, T. [Center for Research and Exploration in Space Science and Technology (CRESST), NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 (United States); Beardmore, A. P. [Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, Leicester LE1 7RH (United Kingdom); De Pasquale, M. [Mullard Space Science Laboratory, University College London, Holmbury Road, Holmbury St. Mary, Dorking RH5 6NT (United Kingdom); Wu, X. F.; Zhang, B. [Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Nevada Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV 89154 (United States); Gorosabel, J. [Instituto de Astrofisica de Andalucia (IAA-CSIC), 18008 Granada (Spain); Urata, Y. [Institute of Astronomy, National Central University, Chung-Li 32054, Taiwan (China); Sugita, S. [EcoTopia Science Institute, Nagoya University, Furo-cho, chikusa, Nagoya 464-8603 (Japan); Pozanenko, A. [Space Research Institute (IKI), 84/32 Profsoyuznaya St., Moscow 117997 (Russian Federation); Nissinen, M. [Taurus Hill Observatory, Haerkaemaeentie 88, 79480 Kangaslampi (Finland); Sahu, D. K. [CREST, Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Koramangala, Bangalore 560034 (India); Im, M. [Center for the Exploration of the Origin of the Universe, Department of Physics and Astronomy, FPRD, Seoul National University, Shillim-dong, San 56-1, Kwanak-gu, Seoul (Korea, Republic of); Ukwatta, T. N. [Department of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824 (United States); Andreev, M. [Terskol Branch of Institute of Astronomy of RAS, Kabardino-Balkaria Republic 361605 (Russian Federation); Klunko, E., E-mail: zwk@umich.edu, E-mail: rfshen@astro.utoronto.ca, E-mail: zhang@physics.unlv.edu [Institute of Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Lermontov St., 126a, Irkutsk 664033 (Russian Federation); and others
2012-06-01
We present a comprehensive analysis of a bright, long-duration (T{sub 90} {approx} 257 s) GRB 110205A at redshift z = 2.22. The optical prompt emission was detected by Swift/UVOT, ROTSE-IIIb, and BOOTES telescopes when the gamma-ray burst (GRB) was still radiating in the {gamma}-ray band, with optical light curve showing correlation with {gamma}-ray data. Nearly 200 s of observations were obtained simultaneously from optical, X-ray, to {gamma}-ray (1 eV to 5 MeV), which makes it one of the exceptional cases to study the broadband spectral energy distribution during the prompt emission phase. In particular, we clearly identify, for the first time, an interesting two-break energy spectrum, roughly consistent with the standard synchrotron emission model in the fast cooling regime. Shortly after prompt emission ({approx}1100 s), a bright (R = 14.0) optical emission hump with very steep rise ({alpha} {approx} 5.5) was observed, which we interpret as the reverse shock (RS) emission. It is the first time that the rising phase of an RS component has been closely observed. The full optical and X-ray afterglow light curves can be interpreted within the standard reverse shock (RS) + forward shock (FS) model. In general, the high-quality prompt and afterglow data allow us to apply the standard fireball model to extract valuable information, including the radiation mechanism (synchrotron), radius of prompt emission (R{sub GRB} {approx} 3 Multiplication-Sign 10{sup 13} cm), initial Lorentz factor of the outflow ({Gamma}{sub 0} {approx} 250), the composition of the ejecta (mildly magnetized), the collimation angle, and the total energy budget.
-
Identification and classification of very low frequency waves on a coral reef flat
Gawehn, Matthijs; van Dongeran, Ap; van Rooijen, Arnold; Storlazzi, Curt; Cheriton, Olivia; Reniers, Ad
2016-01-01
Very low frequency (VLF, 0.001–0.005 Hz) waves are important drivers of flooding of low-lying coral reef-islands. In particular, VLF wave resonance is known to drive large wave runup and subsequent overwash. Using a 5 month data set of water levels and waves collected along a cross-reef transect on Roi-Namur Island in the Republic of the Marshall Islands, the observed VLF motions were categorized into four different classes: (1) resonant, (2) (nonresonant) standing, (3) progressive-growing, and (4) progressive-dissipative waves. Each VLF class is set by the reef flat water depth and, in the case of resonance, the incident-band offshore wave period. Using an improved method to identify VLF wave resonance, we find that VLF wave resonance caused prolonged (∼0.5–6.0 h), large-amplitude water surface oscillations at the inner reef flat ranging in wave height from 0.14 to 0.83 m. It was induced by relatively long-period, grouped, incident-band waves, and occurred under both storm and nonstorm conditions. Moreover, observed resonant VLF waves had nonlinear, bore-like wave shapes, which likely have a larger impact on the shoreline than regular, sinusoidal waveforms. As an alternative technique to the commonly used Fast Fourier Transformation, we propose the Hilbert-Huang Transformation that is more computationally expensive but can capture the wave shape more accurately. This research demonstrates that understanding VLF waves on reef flats is important for evaluating coastal flooding hazards.
-
Identification and classification of very low frequency waves on a coral reef flat
Gawehn, Matthijs; van Dongeren, Ap; van Rooijen, Arnold; Storlazzi, Curt D.; Cheriton, Olivia M.; Reniers, Ad
2016-10-01
Very low frequency (VLF, 0.001-0.005 Hz) waves are important drivers of flooding of low-lying coral reef-islands. In particular, VLF wave resonance is known to drive large wave runup and subsequent overwash. Using a 5 month data set of water levels and waves collected along a cross-reef transect on Roi-Namur Island in the Republic of the Marshall Islands, the observed VLF motions were categorized into four different classes: (1) resonant, (2) (nonresonant) standing, (3) progressive-growing, and (4) progressive-dissipative waves. Each VLF class is set by the reef flat water depth and, in the case of resonance, the incident-band offshore wave period. Using an improved method to identify VLF wave resonance, we find that VLF wave resonance caused prolonged (˜0.5-6.0 h), large-amplitude water surface oscillations at the inner reef flat ranging in wave height from 0.14 to 0.83 m. It was induced by relatively long-period, grouped, incident-band waves, and occurred under both storm and nonstorm conditions. Moreover, observed resonant VLF waves had nonlinear, bore-like wave shapes, which likely have a larger impact on the shoreline than regular, sinusoidal waveforms. As an alternative technique to the commonly used Fast Fourier Transformation, we propose the Hilbert-Huang Transformation that is more computationally expensive but can capture the wave shape more accurately. This research demonstrates that understanding VLF waves on reef flats is important for evaluating coastal flooding hazards.
-
Dayalu, A.; Munger, J. W.; Wang, Y.; Wofsy, S.; Zhao, Y.; Nielsen, C. P.; Nehrkorn, T.; McElroy, M. B.; Chang, R.
2017-12-01
China has pledged to peak carbon emissions by 2030, but there continues to be significant uncertainty in estimates of its anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. In this study, we evaluate the performance of three anthropogenic CO2 inventories, two global and one regional, using five years of continuous hourly observations from a site in Northern China. We model five years of continuous hourly observations (2005 to 2009) using the Stochastic Time-Inverted Lagrangian Transport Model (STILT) run in backward time mode driven by high resolution meteorology from the Weather Research and Forecasting Model version 3.6.1 (WRF) with vegetation fluxes prescribed by a simple biosphere model. We calculate regional enhancements to advected background CO2 derived from NOAA CarbonTracker on seasonal and annual bases and use observations to optimize emissions inventories within the site's influence region at these timescales. Finally, we use annual enhancements to examine carbon intensity of provinces in and adjacent to Northern China as CO2 per unit of the region's GDP to evaluate the effects of local and global economic events on CO2 emissions. With the exception of peak growing season where discrepancies are confounded by errors in the vegetation model, we find the regional inventory agrees significantly better with observations than the global inventories at all timescales. Here we use a single measurement site; significant improvements in inventory optimizations can be achieved with a network of measurements stations. This study highlights the importance of China-specific data over global averages in emissions evaluation and demonstrates the value of top-down studies in independently evaluating inventory performance. We demonstrate the framework's ability to resolve differences of at least 20% among inventories, establishing a benchmark for ongoing efforts to decrease uncertainty in China's reported CO2 emissions estimates.
-
Moldovan, Iren-Adelina; Oikonomou, Christina; Haralambous, Haris; Nastase, Eduard; Emilian Toader, Victorin; Biagi, Pier Francesco; Colella, Roberto; Toma-Danila, Dragos
2017-04-01
Ionospheric TEC (Total Electron Content) variations and Low Frequency (LF) signal amplitude data prior to five moderate earthquakes (Mw≥5) occurred in Romania, in Vrancea crustal and subcrustal seismic zones, during the last decade were analyzed using observations from the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and the European INFREP (International Network for Frontier Research on Earthquake Precursors) networks respectively, aiming to detect potential ionospheric anomalies related to these events and describe their characteristics. For this, spectral analysis on TEC data and terminator time method on VLF/LF data were applied. It was found that TEC perturbations appeared few days (1-7) up to few hours before the events lasting around 2-3 hours, with periods 20 and 3-5 minutes which could be associated with the impending earthquakes. In addition, in all three events the sunrise terminator times were delayed approximately 20-40 min few days prior and during the earthquake day. Acknowledgments This work was partially supported by the Partnership in Priority Areas Program - PNII, under MEN-UEFISCDI, DARING Project no. 69/2014 and the Nucleu Program - PN 16-35, Project no. 03 01
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dingle, B.; Carpenter, D.L.
1981-01-01
A new type of wave-induced electron precipitation event has been identified. During observations at conjugate stations Siple, Antarctica, and Roberval, Canada (L-4.2), VLF noise bursts were found to be associated on a one-to-one basis with amplitude perturbations of subionispheric radio propagation. The amplitude perturbations are attributed to patches of enhanced ionization that extended below approx.80 km in the nighttime ionosphere and that were produced by precipitating electron bursts. Similar amplitude perturbations seen previously were correlated with whistlers that propagated within the plasmasphere. For the new events the driving waves were structured collections of rising elements that propagated just beyond the plasmapause at roughly 5-min intervals over a several-hour period. These noise bursts were of relatively long duration (approx.10 s) and strong intensity (inferred to be >30 pT at the equator). Triggering of the noise bursts appears to have been mostly by whistlers but changed in character with time. Some later bursts had narrowband precursors at constant frequencies possibly locked to power line harmonic radiation. The burst initiation characteristics suggest the existence of a variable threshold for rapid temporal growth in the magnetosphere controlled by the trapped electron dynamics. The temporal signatures of the amplitude perturbations show that precipitation was maintained over multiple bounces of the trapped magnetospheric electrons. In some cases these signatures include a new undershoot effect during the recovery phase lasting 2--5 min. This effect may have been related to cutoff of background drizzle precipitation. Precipitation effects were observed on both long (approx.10 Mm) and short (approx.1/2 Mm) subionospheric paths and were monitored simultaneously at the conjugate stations. Similarities in the perturbation signatures on long and short paths suggest that the form of the signatures was governed by ionospheric changes
-
Motor vehicle nanoparticle emissions: Numerical simulations and comparisons with recent observations
Yu, F.
2002-05-01
Epidemiological studies have linked urban fine particles (FPs, diameter standards on the mass concentration of ambient FPs. Recently it has been pointed out that it is not sufficient to study only the mass of FPs. The main concern is that, while nanoparticles (NPs, diameter control measures to reduce FP mass emissions may paradoxically increase the number emissions of NPs. Future standards might be imposed on NP emissions and NP emissions from gasoline engines might also become a concern. Effective and least costly means of NP emission reduction must be based on a firm physical understanding of the formation mechanisms of NPs in the exhaust of motor vehicles. Measurements of NPs in motor engine exhaust have been made both in the laboratory and in the atmosphere under various conditions. In this study, we investigate the key processes and parameters controlling formation and evolution of NPs in vehicle exhaust through model simulations and comparisons with field measurements. The detailed aerosol dynamics are simulated with an advanced multi-type, multi-component, size-resolved microphysics model. The classical binary homogeneous nucleation of H2SO4-H2O fails to explain the observed NP properties. We find that chemiions generated in engine combustor may play an important role in the formation of NPs in vehicle exhaust. The predicted NP properties based on our ion-mediated nucleation of H2SO4-H2O consistently explain the measurements in terms of total NP concentrations, and their sensitivity to fuel sulfur contents, on-road vehicle speeds, soot concentrations, and dilution conditions. Our study indicates that total number of NPs formed is very sensitive to chemiion concentrations, and we propose a potentially effective technique to control vehicle NP emissions by imposing an electrical field (voltage < ~ 100 volts) on a section of the tailpipe to remove small ions.
-
Machavariani, Kakhaber; Khazaradze, Giorgi; Turazashvili, Ioseb; Kachakhidze, Nino; Kachakhidze, Manana; Gogoberidze, Vitali
2016-04-01
The world's scientific literature recently published many very important and interesting works of VLF / LF electromagnetic emissions, which is observed in the process of earthquake preparation. This works reliable earthquake prediction in terms of trends. Because, Georgia is located in Trans Asian earthquake zone, VLF / LF electromagnetic emissions network are essential. In this regard, it was possible to take first steps. It is true that our university has Shota Rustaveli National Science Foundation № DI / 21 / 9-140 / 13 grant, which included the installation of a receiver in Georgia, but failed due to lack of funds to buy this device. However, European friends helped us (Prof. Dr. PF Biagi and Prof. Dr. Aydın BÜYÜKSARAÇ) and made possible the installation of a receiver. Turkish scientists expedition in Georgia was organized in August 2015. They brought with them VLF / LF electromagnetic emissions receiver and together with Georgian scientists install near Tbilisi. The station was named GEO-TUR. It should be noted that Georgia was involved in the work of the European network. It is possible to completely control the earthquake in Georgia in terms of electromagnetic radiation. This enables scientists to obtain the relevant information not only on the territory of our country, but also on seismically active European countries as well. In order to maintain and develop our country in this new direction, it is necessary to keep independent group of scientists who will learn electromagnetic radiation ahead of an earthquake in Georgia. At this stage, we need to remedy this shortcoming, it is necessary and appropriate specialists to Georgia to engage in a joint international research. The work is carried out in the frame of grant (DI/21/9-140/13 „Pilot project of before earthquake detected Very Low Frequency/Low Frequency electromagnetic emission network installation in Georgia") by financial support of Shota Rustaveli National Science Foundation.
-
Effects of LatticeQCD EoS and Continuous Emission on Some Observables
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hama, Y.; Andrade, R.; Grassi, F.; Socolowski, O.; Kodama, T.; Tavares, B.; Padula, S. S.
2006-01-01
Effects of lattice-QCD-inspired equations of state and continuous emission on some observables are discussed, by solving a 3D hydrodynamics. The particle multiplicity as well ν 2 are found to increase in the mid-rapidity. We also discuss the effects of the initial-condition fluctuations
-
Turner, Alexander J.; Jacob, Daniel J.; Benmergui, Joshua; Brandman, Jeremy; White, Laurent; Randles, Cynthia A.
2018-06-01
Anthropogenic methane emissions originate from a large number of fine-scale and often transient point sources. Satellite observations of atmospheric methane columns are an attractive approach for monitoring these emissions but have limitations from instrument precision, pixel resolution, and measurement frequency. Dense observations will soon be available in both low-Earth and geostationary orbits, but the extent to which they can provide fine-scale information on methane sources has yet to be explored. Here we present an observation system simulation experiment (OSSE) to assess the capabilities of different satellite observing system configurations. We conduct a 1-week WRF-STILT simulation to generate methane column footprints at 1.3 × 1.3 km2 spatial resolution and hourly temporal resolution over a 290 × 235 km2 domain in the Barnett Shale, a major oil and gas field in Texas with a large number of point sources. We sub-sample these footprints to match the observing characteristics of the recently launched TROPOMI instrument (7 × 7 km2 pixels, 11 ppb precision, daily frequency), the planned GeoCARB instrument (2.7 × 3.0 km2 pixels, 4 ppb precision, nominal twice-daily frequency), and other proposed observing configurations. The information content of the various observing systems is evaluated using the Fisher information matrix and its eigenvalues. We find that a week of TROPOMI observations should provide information on temporally invariant emissions at ˜ 30 km spatial resolution. GeoCARB should provide information available on temporally invariant emissions ˜ 2-7 km spatial resolution depending on sampling frequency (hourly to daily). Improvements to the instrument precision yield greater increases in information content than improved sampling frequency. A precision better than 6 ppb is critical for GeoCARB to achieve fine resolution of emissions. Transient emissions would be missed with either TROPOMI or GeoCARB. An aspirational high
-
NuSTAR observations of the bullet cluster: constraints on inverse compton emission
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Wik, Daniel R.; Hornstrup, Allan; Molendi, S.
2014-01-01
and have degree-scale fields of view, their backgrounds are both high and difficult to characterize. The associated uncertainties result in lower sensitivity to IC emission and a greater chance of false detection. In this work, we present 266 ks NuSTAR observations of the Bullet cluster, which is detected......-but not perfectly-described as an isothermal plasma with kT = 14.2 ± 0.2 keV. To slightly improve the fit, a second temperature component is added, which appears to account for lower temperature emission from the cool core, pushing the primary component to kT ~ 15.3 keV. We see no convincing need to invoke an IC...
-
Observations and numerical studies of gamma-ray emission in colliding-wind binaries
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Reitberger, K.
2014-01-01
Massive stars in binary systems have long been regarded as potential sources of high-energy gamma rays. The emission is thought to arise in the region where the stellar winds collide, thereby producing accelerated particles which subsequently emit gamma rays.This scenario is supported by observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope presented in this thesis. To address the underlying emission mechanisms in a quantitative way, numerical simulations that incorporate hydrodynamics, the acceleration of charged particles as well as the subsequent gamma-ray emission were found to be needed.This thesis presents the analysis of a high-energy gamma-ray source and its identification with the particle-accelerating colliding-wind binary system Eta Carinae. In order to go beyond the present understanding of such objects, this work provides detailed description of a new 3D-hydrodynamical model, which incorporates the line-driven acceleration of the winds, gravity, orbital motion and the radiative cooling of the shocked plasma, as well as the diffusive shock acceleration of charged particles in the wind collision region. In a subsequent step we simulate and study the resulting gamma-ray emission via relativistic bremsstrahlung, anisotropic inverse Compton radiation and neutral pion decay. (author) [de
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Bauwens
2016-08-01
Full Text Available As formaldehyde (HCHO is a high-yield product in the oxidation of most volatile organic compounds (VOCs emitted by fires, vegetation, and anthropogenic activities, satellite observations of HCHO are well-suited to inform us on the spatial and temporal variability of the underlying VOC sources. The long record of space-based HCHO column observations from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI is used to infer emission flux estimates from pyrogenic and biogenic volatile organic compounds (VOCs on the global scale over 2005–2013. This is realized through the method of source inverse modeling, which consists in the optimization of emissions in a chemistry-transport model (CTM in order to minimize the discrepancy between the observed and modeled HCHO columns. The top–down fluxes are derived in the global CTM IMAGESv2 by an iterative minimization algorithm based on the full adjoint of IMAGESv2, starting from a priori emission estimates provided by the newly released GFED4s (Global Fire Emission Database, version 4s inventory for fires, and by the MEGAN-MOHYCAN inventory for isoprene emissions. The top–down fluxes are compared to two independent inventories for fire (GFAS and FINNv1.5 and isoprene emissions (MEGAN-MACC and GUESS-ES. The inversion indicates a moderate decrease (ca. 20 % in the average annual global fire and isoprene emissions, from 2028 Tg C in the a priori to 1653 Tg C for burned biomass, and from 343 to 272 Tg for isoprene fluxes. Those estimates are acknowledged to depend on the accuracy of formaldehyde data, as well as on the assumed fire emission factors and the oxidation mechanisms leading to HCHO production. Strongly decreased top–down fire fluxes (30–50 % are inferred in the peak fire season in Africa and during years with strong a priori fluxes associated with forest fires in Amazonia (in 2005, 2007, and 2010, bushfires in Australia (in 2006 and 2011, and peat burning in Indonesia (in 2006 and 2009, whereas
-
Aura OMI observations of changes in SO2 and NO2 emissions at local, regional and global scales
Krotkov, N. A.; McLinden, C. A.; Li, C.; Lamsal, L. N.; Celarier, E. A.; Marchenko, S. V.; Swartz, W.; Bucsela, E. J.; Joiner, J.; Duncan, B. N.; Boersma, K. F.; Veefkind, P.; Levelt, P.; Fioletov, V.; Dickerson, R. R.; He, H.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D. G.
2015-12-01
Space-based pollution monitoring from current and planned satellite UV-Vis spectrometers play an increasingly important role in studies of tropospheric chemistry and also air quality applications to help mitigate anthropogenic and natural impacts on sensitive ecosystems, and human health. We present long-term changes in tropospheric SO2 and NO2 over some of the most polluted industrialized regions of the world observed by the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) onboard NASA's Aura satellite. Using OMI data, we identified about 400 SO2 "hot spots" and estimated emissions from them. In many regions emissions and their ambient pollution levels have decreased significantly, such as over eastern US, Europe and China. OMI observed about 50% reduction in SO2 and NO2 pollution over the North China plain in 2012-2014 that can be attributed to both government efforts to restrain emissions from the power and industrial sectors and the economic slowdown. While much smaller, India's SO2 and NO2 emissions from coal power plants and smelters are growing at a fast pace, increasing by about 200% and 50% from 2005 to 2014. Over Europe and the US OMI-observed trends agree well with those from available in situ measurements of surface concentrations, deposition and emissions data. However, for some regions (e.g., Mexico, Middle East) the emission inventories may be incomplete and OMI can provide emission estimates for missing sources, such as SO2 sources observed over the Persian Gulf. It is essential to continue long-term overlapping satellite data records of air quality with increased spatial and temporal resolution to resolve point pollution sources using oversampling technique. We discuss how Aura OMI pollution measurements and emission estimates will be continued with the US JPSS and European Sentinel series for the next 20 years and further enhanced by the addition of three geostationary UV-VIS instruments.
-
Hard X-ray Emission from Galaxy Clusters Observed with INTEGRAL and Prospects for Simbol-X
Eckert, D.; Paltani, S.; Courvoisier, T. J.-L.
2009-05-01
Some galaxy clusters are known to contain a large population of relativistic electrons, which produce radio emission through synchrotron radiation. Therefore, it is expected that inverse-Compton scattering of the relativistic electrons with the CMB produce non-thermal emission which should be observable in the hard X-ray domain. Here we focus on the recent results by INTEGRAL, which shed a new light on the non-thermal emission thanks to its angular resolution and sensitivity in the hard X-ray range. We also present the exciting prospects in this field for Simbol-X, which will allow us to detect the non-thermal emission in a number of clusters and map the magnetic field throughout the intra-cluster medium.
-
The large scale infrared emission in the galactic plane - observations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Okuda, H.
1981-01-01
Infrared radiation is deeply involved in a variety of matters and processes in the galaxy. Near infrared radiation is predominantly emitted by late type stars which include the major part of the mass in the Galaxy and hence govern its dynamics. Short wavelength radiation (UV and visible) emitted from early type stars is easily absorbed by dust around the stars themselves or by interstellar dust, and reemitted in middle or far infrared regions. A variety of emission lines, fine structure lines of neutral and ionized heavy elements, as well as many molecular lines are also clustered in the middle and far infrared regions. Since their line intensities are generally very weak, and, moreover, spectroscopic observations demand relatively difficult techniques in their detection, the surveys so far done have been limited mostly to continuum emission. This article compiles them and discusses briefly their implications to the structure of the Galaxy in its inner region. (Auth.)
-
Ring, Allison M.; Canty, Timothy P.; Anderson, Daniel C.; Vinciguerra, Timothy P.; He, Hao; Goldberg, Daniel L.; Ehrman, Sheryl H.; Dickerson, Russell R.; Salawitch, Ross J.
2018-01-01
We investigate the representation of emissions from the largest (Class 3) commercial marine vessels (c3 Marine) within the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model. In present emissions inventories developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), c3 Marine emissions are divided into off-shore and near-shore files. Off-shore c3 Marine emissions are vertically distributed within the atmospheric column, reflecting stack-height and plume rise. Near-shore c3 Marine emissions, located close to the US shoreline, are erroneously assumed to occur only at the surface. We adjust the near-shore c3 Marine emissions inventory by vertically distributing these emissions to be consistent with the off-shore c3 Marine inventory. Additionally, we remove near-shore c3 Marine emissions that overlap with off-shore c3 Marine emissions within the EPA files. The CMAQ model generally overestimates surface ozone (O3) compared to Air Quality System (AQS) site observations, with the largest discrepancies occurring near coastal waterways. We compare modeled O3 from two CMAQ simulations for June, July, and August (JJA) 2011 to surface O3 observations from AQS sites to examine the efficacy of the c3 Marine emissions improvements. Model results at AQS sites show average maximum 8-hr surface O3 decreases up to ∼6.5 ppb along the Chesapeake Bay, and increases ∼3-4 ppb around Long Island Sound, when the adjusted c3 Marine emissions are used. Along with the c3 Marine emissions adjustments, we reduce on-road mobile NOX emissions by 50%, motivated by work from Anderson et al. 2014, and reduce the lifetime of the alkyl nitrate species group from ∼10 days to ∼1 day based on work by Canty et al. 2015, to develop the ;c3 Science; model scenario. Simulations with these adjustments further improve model representation of the atmosphere. We calculate the ratio of column formaldehyde (HCHO) and tropospheric column nitrogen dioxide (NO2) using observations from the Ozone
-
Smith, Mackenzie L; Kort, Eric A; Karion, Anna; Sweeney, Colm; Herndon, Scott C; Yacovitch, Tara I
2015-07-07
We present high time resolution airborne ethane (C2H6) and methane (CH4) measurements made in March and October 2013 as part of the Barnett Coordinated Campaign over the Barnett Shale formation in Texas. Ethane fluxes are quantified using a downwind flight strategy, a first demonstration of this approach for C2H6. Additionally, ethane-to-methane emissions ratios (C2H6:CH4) of point sources were observationally determined from simultaneous airborne C2H6 and CH4 measurements during a survey flight over the source region. Distinct C2H6:CH4 × 100% molar ratios of 0.0%, 1.8%, and 9.6%, indicative of microbial, low-C2H6 fossil, and high-C2H6 fossil sources, respectively, emerged in observations over the emissions source region of the Barnett Shale. Ethane-to-methane correlations were used in conjunction with C2H6 and CH4 fluxes to quantify the fraction of CH4 emissions derived from fossil and microbial sources. On the basis of two analyses, we find 71-85% of the observed methane emissions quantified in the Barnett Shale are derived from fossil sources. The average ethane flux observed from the studied region of the Barnett Shale was 6.6 ± 0.2 × 10(3) kg hr(-1) and consistent across six days in spring and fall of 2013.
-
Whistler-triggered chorus emissions observed during daytime at low latitude ground station Jammu
Pratap Patel, Ravindra; Singh, K. K.; Singh, A. K.; Singh, R. P.
In this paper, we present whistler-triggered chorus emission recorded during daytime at low latitude ground station Jammu (geomag. Lat. = 22 degree 26 minute N; L = 1.17) during the period from 1996 to 2003. After analysis of the eight years collected data, we found out 29 events, which are definitely identified as chorus emission triggered by whistlers. During the observation period the magnetic activity is high. Analysis shows that the whistlers have propagated along the geomagnetic field line having L-values lying between L = 1.9 and 4.4. These waves could have propagated along the geomagnetic field lines either in ducted mode or pro-longitudinal mode. The measured relative intensity of the triggered emission and whistler wave is approximately the same and also varies from one event to another. It is proposed that these waves are generated through a process of wave-particle interaction and wave-wave interactions. Related parameters of this interaction are computed for different L-value and wave amplitude. With the help of dynamic spectra of these emissions, the proposed mechanisms are explained.
-
Koutroumpa, Dimitra; Smith, Randall K.; Edgar, Richard J.; Kuntz, Kip D.; Plucinsky, Paul P.; Snowden, Steven L.
2010-01-01
We present the first analysis of an XMM-Newton observation of the nearby molecular cloud MBM 12. We find that in the direction of MBM 12 the total O VII (0.57 keV) triplet emission is 1.8(+0.5/-0.6) photons/sq cm/s/sr (or Line Units - LU) while for the O VIII (0.65 keV) line emission we find a 3(sigma) upper limit of by Solar Wind Charge-eXchange (SWCX) which we compare to the XMM-Newton observations. This comparison provides new constraints on the relative heliospheric and Local Bubble contributions to the local diffuse X-ray background. The heliospheric SWCX model predicts 0.82 LU for O VII, which accounts for approx. 46+/-15% of the observed value, and 0.33 LU for the O VIII line emission consistent with the XMM-Newton observed value. We discuss our results in combination with previous observations of the MBM 12 with CHANDRA and Suzaku.
-
Observation of heavy cluster emission from radioactive 230U nuclei
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pan Qiangyan; Yuan Shuanggui; Yang Weifan; Li Zongwei; Ma Taotao; Guo Junsheng; Liu Mingyi; Liu Hongye; Xu Shuwei; Gan Zaiguo; Kong Dengming; Qiao Jimin; Luo Zihua; Zhang Mutian; Wang Shuhong
1999-01-01
230 Pa was produced with the reaction 232 Th (p, 3n) 230 Pa in the irradiation powder targets of ThO 2 with 35 MeV proton beam. Sources of 230 Pa→ 230 U + β - were prepared by radiochemical method. Using solid-state track registration detectors, two events of 230 U decay with heavy cluster emission have been observed. The preliminary branching ratio to α-decay comes out to be B = λ Ne /λ α = (1.3 ± 0.8) x 10 -14
-
Galactic neutral hydrogen emission-absorption observations from Arecibo
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dickey, J.M.; Salpeter, E.E.; Terzian, Y.
1978-01-01
We have observed the interstellar medium in the directions of 27 extragalactic sources at high and intermediate galactic latitudes (vertical-barb/sup ii/vertical-bar>5 0 ) at 21 cm wavelength with the upgraded Arecibo telescope (HPBW=3'.2, gainapprox.6 K Jy -1 ). The small beam greatly reduces the uncertainty in the derived on-source emission profile and increases confidence that it corresponds to the same material as the absorption spectrum. Each region has been observed for approximately 2 hours to tetect optical depths as low as 10 -2 in most cases. The data allow the derivation of optical depths, harmonic mean spin temperatures, and column densities for the neutral hydrogen as a function of velocity in the range -200 -1 (LSR) with resolution as fine as 0.25 km s -1 . Spin temperatures as high as 1000 K are evident with a significant fraction of the neutral hydrogen still hotter. The cooler material is distributed over all temperatures from 30 K to at least 800 K. At latitudes below vertical-barb/sup ii/vertical-bar 0 values for the harmonic mean temperature T/sub spin/ in the range 100 K to 300 K are most common.We have detected 66 separate absorption features, tentatively associated with neutral hydrogen clouds, with central temperatures ranging from 30 to 500 K. These features conform well to the relationship T/sub spin/=45(1-e/sup -tau/)/sup -0.5/ (K), over a broad range of values of the optical depth. The velocity distribution of these clouds shows a significant negative-velocity ''tail'' at high and intermediate latitudes. The mean square velocity of the clouds seems to depend on optical depth: v/sub rms/ is greater (approx.11 km s -1 ) for the optically thin clouds (tau -1 ). High-negative-velocity emission (v -1 ) has been detected in six directions; in two of these corresponding absorption features are evident, indicating cool neutral material
-
Sato, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Kubota, H.; Hamada, J. I.; Momota, E.; Marciano, J. J.
2017-12-01
Lightning activity represents the thunderstorm activity, that is, the precipitation and/or updraft intensity and area. Thunderstorm activity is also an important parameter in terms of the energy inputs from the ocean to the atmosphere inside tropical cyclone, which is one of severe weather events. Recent studies suggest that it is possible to predict the maximum wind velocity and minimum pressure near the center of the tropical cyclone by one or two days before if we monitor the lightning activities in the tropical cyclone. Many countries in the western Pacific region suffer from the attack of tropical cyclone (typhoon) and have a strong demand to predict the intensity development of typhoons. Thus, we started developing a new lightning observation system and installing the observation system at Guam, Palau, and Manila in the Philippines from this summer. The lightning observation system consists of a VLF sensor detecting lightning-excited electromagnetic waves in the frequency range of 1-5 kHz, an automatic data-processing unit, solar panels, and batteries. Lightning-excited pulse signals detected by the VLF sensor are automatically analyzed by the data-processing unit, and only the extracted information of the trigger time and pulse amplitude is transmitted to a data server via the 3G data communications. In addition, we are now developing an upgraded lightning and weather observation system, which will be installed at 50 automated weather stations in Metro Manila and 10 radar sites in the Philippines under the 5-year project (SATREPS) scheme. At the presentation, we will show the initial results derived from the lightning observation system in detail and will show the detailed future plan of the SATREPS project.
-
Source location of chorus emissions observed by Cluster
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Parrot
Full Text Available One of the objectives of the Cluster mission is to study sources of various electromagnetic waves using the four satellites. This paper describes the methods we have applied to data recorded from the STAFF spectrum analyser. This instrument provides the cross spectral matrix of three magnetic and two electric field components. This spectral matrix is analysed to determine, for each satellite, the direction of the wave normal relative to the Earth’s magnetic field as a function of frequency and of time. Due to the Cluster orbit, chorus emissions are often observed close to perigee, and the data analysis determines the direction of these waves. Three events observed during different levels of magnetic activity are reported. It is shown that the component of the Poynting vector parallel to the magnetic field changes its sense when the satellites cross the magnetic equator, which indicates that the chorus waves propagate away from the equator. Detailed analysis indicates that the source is located in close vicinity of the plane of the geomagnetic equator.
Key words. Magnetospheric physics (plasma waves and instabilities; storms and substorms; Space plasma physics (waves and instabilities -
Observed decrease in atmospheric mercury explained by global decline in anthropogenic emissions
Yanxu Zhang,; Daniel J. Jacob,; Hannah M. Horowitz,; Long Chen,; Helen M. Amos,; Krabbenhoft, David P.; Franz Slemr,; Vincent L. St. Louis,; Elsie M. Sunderland,
2015-01-01
Observations of elemental mercury (Hg0) at sites in North America and Europe show large decreases (∼1–2% y−1) from 1990 to present. Observations in background northern hemisphere air, including Mauna Loa Observatory (Hawaii) and CARIBIC (Civil Aircraft for the Regular Investigation of the atmosphere Based on an Instrument Container) aircraft flights, show weaker decreases (Asia. Implementation of our inventory in a global 3D atmospheric Hg simulation [GEOS-Chem (Goddard Earth Observing System-Chemistry)] coupled to land and ocean reservoirs reproduces the observed large-scale trends in atmospheric Hg0 concentrations and in HgII wet deposition. The large trends observed in North America and Europe reflect the phase-out of Hg from commercial products as well as the cobenefit from SO2 and NOx emission controls on coal-fired utilities.
-
Image isocon observations of emission lines in the spectrum of lambda Cephei
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hutchings, J.B.; Sanyal, A.
1976-01-01
Line profiles of the lambda lambda 4640, 4686 emission lines were observed in the spectrum of lambda Cep, with high time resolution, and high signal-to-noise ratio. Profile changes above the 1 percent level can occur within hours. Possible periodicities in profile changes suggest a connection with rapid stellar rotation. The lambda 4686 profile is consistent with a rotating nonspherical envelope
-
Lynch, K. A.; Arnoldy, R. L.; Kintner, P. M.; Schuck, P.; Bonnell, J. W.; Coffey, V.
In this paper we present a review of sounding rocket observations of the ion acceleration seen in nightside auroral zone lower hybrid solitary structures. Observations from Topaz3, Amicist, and Phaze2 are presented on various spatial scales, including the two-point measurements of the Amicist mission. From this collection of observations we will demonstrate the following characteristics of transverse acceleration of ions (TAI) in lower hybrid solitary structures (LHSS). The ion acceleration process is narrowly confined to 90° pitch angle, in spatially confined regions of up to a few hundred meters across B. The acceleration process does not affect the thermal core of the ambient distribution and does not directly create a measurable effect on the ambient ion population outside the LHSS themselves. This precludes observation with these data of any nonlinear feedback between the ion acceleration and the existence or evolution of the density irregularities on which these LHSS events grow. Within the LHSS region the acceleration process creates a high-energy tail beginning at a few times the thermal ion speed. The ion acceleration events are closely associated with localized wave events. Accelerated ions bursts are also seen without a concurrent observation of a localized wave event, for two possible reasons. In some cases, the pitch angles of the accelerated tail ions are elevated above perpendicular; that is, the acceleration occurred below the observer and the mirror force has begun to act upon the distribution, moving it upward from the source. In other cases, the accelerated ion structure is spatially larger than the wave event structure, and the observation catches only the ion event. The occurrence rate of these ion acceleration events is related to the ambient environment in two ways: its altitude dependence can be modeled with the parameter B2/ne, and it is highest in regions of intense VLF activity. The cumulative ion outflow from these LHSS TAI is
-
XMM-Newton Observations of NGC 253: Resolving the Emission Components in the Disk and Nuclear Area
Pietsch, W.; Borozdin, K. N.; Branduardi-Raymont, G.; Cappi, M.; Ehle, M.; Ferrando, P.; Freyberg, M. J.; Kahn, S. M.; Ponman, T. J.; Ptak, A.
2000-01-01
We describe the first XMM-Newton observations of the starburst galaxy NGC 253. As known from previous X-ray observations, NGC 253 shows a mixture of extended (disk and halo) and point-source emission. The high XMM-Newton throughput allows for the first time a detailed investigation of the spatial, spectral and variability properties of these components simultaneously. We detect a bright X-ray transient approx. 70 sec SSW of the nucleus and show the spectrum and light curve of the brightest point source (approx. 30 sec S of the nucleus, most likely a black-hole X-ray binary, BHXRB). The unprecedented combination of RGS and EPIC also sheds new light on the emission of the complex nuclear region, the X-ray plume and the disk diffuse emission. In particular, EPIC images reveal that the limb-brightening of the plume is mostly seen in higher ionization emission lines, while in the lower ionization lines, and below 0.5 keV, the plume is more homo- geneously structured, pointing to new interpretations as to the make up of the starburst-driven outflow. Assuming that type IIa supernova remnants (SNRs) are mostly responsible for the E greater than 4 keV emission, the detection with EPIC of the 6.7 keV line allows us to estimate a supernova rate within the nuclear starburst of 0.2 /yr.
-
EGRET observations of diffuse gamma-ray emission in taurus and perseus
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Digel, Seth W.; Grenier, Isabelle A.
2001-01-01
We present an analysis of the interstellar gamma-ray emission observed toward the extensive molecular cloud complexes in Taurus and Perseus by the Energetic Gamma-Ray Experiment Telescope (EGRET). The region's large size (more than 300 square degrees) and location below the plane in the anticenter are advantageous for straightforward interpretation of the interstellar emission. The complex of clouds in Taurus has a distance of ∼140 pc and is near the center of the Gould Belt. The complex in Perseus, adjacent to Taurus on the sky, is near the rim of the Belt at a distance of ∼300 pc. The findings for the cosmic-ray density and the molecular mass-calibrating ratio N(H 2 )/W CO in Taurus and Perseus are compared with results for other nearby cloud complexes resolved by EGRET. The local clouds that now have been studied in gamma rays can be used to trace the distribution of high-energy cosmic rays within 1 kpc of the sun
-
Observational study of generation conditions of substorm-associated low-frequency AKR emissions
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Olsson
2004-11-01
Full Text Available It has lately been shown that low-frequency bursts of auroral kilometric radiation (AKR are nearly exclusively associated with substorm expansion phases. Here we study low-frequency AKR using Polar PWI and Interball POLRAD instruments to constrain its possible generation mechanisms. We find that there are more low-frequency AKR emission events during wintertime and equinoxes than during summertime. The dot-AKR emission radial distance range coincides well with the region where the deepest density cavities are seen statistically during Kp>2. We suggest that the dot-AKR emissions originate in the deepest density cavities during substorm onsets. The mechanism for generating dot-AKR is possibly strong Alfvén waves entering the cavity from the magnetosphere and changing their character to more inertial, which causes the Alfvén wave associated parallel electric field to increase. This field may locally accelerate electrons inside the cavity enough to produce low-frequency AKR emission. We use Interball IESP low-frequency wave data to verify that in about half of the cases the dot-AKR is accompanied by low-frequency wave activity containing a magnetic component, i.e. probably inertial Alfvén waves. Because of the observational geometry, this result is consistent with the idea that inertial Alfvén waves might always be present in the source region when dot-AKR is generated. The paper illustrates once more the importance of radio emissions as a powerful remote diagnostic tool of auroral processes, which is not only relevant for the Earth's magnetosphere but may be relevant in the future in studying extrasolar planets.
-
MULTIWAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF RADIO-QUIET QUASARS WITH WEAK EMISSION LINES
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Plotkin, Richard M.; Anderson, Scott F.; MacLeod, Chelsea L.; Brandt, W. N.; Schneider, Donald P.; Diamond-Stanic, Aleksandar M.; Fan Xiaohui; Shemmer, Ohad
2010-01-01
We present radio and X-ray observations, as well as optical light curves, for a subset of 26 BL Lac candidates from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) lacking strong radio emission and with z < 2.2. Half of these 26 objects are shown to be stars, galaxies, or absorbed quasars. We conclude that the other 13 objects are active galactic nuclei (AGNs) with abnormally weak emission features; 10 of those 13 are definitively radio quiet, and, for those with available optical light curves, their level of optical flux variability is consistent with radio-quiet quasars. We cannot exclude the possibility that some of these 13 AGNs lie on the extremely radio-faint tail of the BL Lac distribution, but our study generally supports the notion that all BL Lac objects are radio-loud. These radio-quiet AGNs appear to have intrinsically weak or absent broad emission line regions (BELRs), and, based on their X-ray properties, we argue that some are low-redshift analogs to weak line quasars (WLQs). SDSS BL Lac searches are so far the only systematic surveys of the SDSS database capable of recovering such exotic low-redshift WLQs. There are 71 more z < 2.2 radio-quiet BL Lac candidates already identified in the SDSS, but not considered here, and many of those might be best unified with WLQs as well. Future studies combining low- and high-redshift WLQ samples will yield new insight on our understanding of the structure and formation of AGN BELRs.
-
Jaegle, Lyatt; Steinberger, Linda; Martin, Randall V.; Chance, Kelly
2005-01-01
This document contains the following abstract for the paper "Global partitioning of NOx sources using satellite observations: Relative roles of fossil fuel combustion, biomass burning and soil emissions." Satellite observations have been used to provide important new information about emissions of nitrogen oxides. Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are significant in atmospheric chemistry, having a role in ozone air pollution, acid deposition and climate change. We know that human activities have led to a three- to six-fold increase in NOx emissions since pre-industrial times, and that there are three main surface sources of NOx: fuel combustion, large-scale fires, and microbial soil processes. How each of these sources contributes to the total NOx emissions is subject to some doubt, however. The problem is that current NOx emission inventories rely on bottom-up approaches, compiling large quantities of statistical information from diverse sources such as fuel and land use, agricultural data, and estimates of burned areas. This results in inherently large uncertainties. To overcome this, Lyatt Jaegle and colleagues from the University of Washington, USA, used new satellite observations from the Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment (GOME) instrument. As the spatial and seasonal distribution of each of the sources of NOx can be clearly mapped from space, the team could provide independent topdown constraints on the individual strengths of NOx sources, and thus help resolve discrepancies in existing inventories. Jaegle's analysis of the satellite observations, presented at the recent Faraday Discussion on "Atmospheric Chemistry", shows that fuel combustion dominates emissions at northern mid-latitudes, while fires are a significant source in the Tropics. Additionally, she discovered a larger than expected role for soil emissions, especially over agricultural regions with heavy fertilizer use. Additional information is included in the original extended abstract.
-
Observations of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts: Prompt Emission and Afterglow
Berger, Edo
2011-09-01
The study of short gamma-ray bursts has been revolutionized by the discovery of afterglows and host galaxies. In this talk I will review observations of the prompt emission, afterglows, and host galaxies, primarily as they pertain to the nature of the progenitor systems. The bulk of the evidence points to the merger of compact objects (NS-NS or NS-BH) making short GRBs the prime candidate for gravitational wave detections with the next generation detectors. This work is partially supported by funds from NASA (through the Swift and Chandra GO programs) and the NSF through an AAG grant.
-
Ogasawara, K.; Dayeh, M. A.; Fuselier, S. A.; Goldstein, J.; McComas, D. J.; Valek, P. W.
2017-12-01
We report daylong continuous observations of bright terrestrial energetic neutral atom (ENA) emissions in the energy of 0.5-6.0 keV by Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX). The unique vantage point of IBEX, 48 Earth radii (Re) from the dawn/dusk side, made an unprecedented long duration monitoring of ENAs possible from almost stable locations. This type of observation is difficult with the other ENA imager satellites since they are orbiting closer to the Earth in shorter periods. The studied energy range is unique due to the coverage of the transition from the solar wind plasma to the magnetospheric particles with a single sensor. In addition, the Coulomb decay becomes important for the protons with energy less than 1 keV. In order to minimize contamination from the sub-solar magnetosphere or the cusp emissions, we focused on two events when the auroral electrojet (AE) index exceeded 300 nT in this study. We will also show the ENA images from Two Wide-Angle Imaging Neutral-Atom Spectrometers (TWINS) in support of the IBEX observations. We found a significant correlation between the observed ENA profile and the AE indices, whose correlation coefficients were maximized at >0.75 for >1.4 keV energy. There are systematic differences between two events in terms of AU, AL, and Asy-H correlations: One event has the stronger AU correlation than AL and the Asy-H correlation, suggesting partial ring current contribution. The other has the stronger AL correlation than AU without Asy-H correlation, which suggests substorm related ENA emissions. On the contrary, we could not find a meaningful correlation with Sym-H for these two events. The other important finding is the decay time of these ENA emissions. The observed e-folding decay time, 2 to 4 hours for most of the energy bands, was a little shorter than the conventional ring-current decay time (typically >6 hours) expected from the charge exchange and the field-line curvature effect, suggesting the stronger effect of the
-
PULSED VERY HIGH ENERGY γ-RAY EMISSION CONSTRAINTS FOR PSR B1951+32 FROM STACEE OBSERVATIONS
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zweerink, J.; Ball, J.; Carson, J. E.; Jarvis, A.; Ong, R. A.; Kildea, J.; Hanna, D. S.; Lindner, T.; Mueller, C.; Ragan, K.; Covault, C. E.; Driscoll, D. D.; Fortin, P.; Mukherjee, R.; Gingrich, D. M.; Williams, D. A.
2009-01-01
The Solar Tower Atmospheric Cherenkov Effect Experiment (STACEE) is a ground-based telescope that uses the wave-front-sampling technique to detect very high energy (VHE) gamma rays. STACEE's sensitivity in the energy range near 100 GeV permits useful observations of pulsars with the potential to discriminate between various proposed mechanisms for pulsed gamma-ray emission. Based on the 11.3 hr of data taken during the 2005 and 2006 observing seasons, we derive an upper limit on the pulsed gamma-ray emission from PSR B1951+32 of -11 photons cm -2 s -1 above an energy threshold of 117 GeV.
-
Observations of the 12.3 micron Mg I emission line during a major solar flare
Deming, Drake; Jennings, Donald E.; Osherovich, Vladimir; Wiedemann, Gunter; Hewagama, Tilak
1990-01-01
The extremely Zeeman-sensitive 12.32 micron Mg I solar emission line was observed during a 3B/X5.7 solar flare on October 24, 1989. When compared to postflare values, Mg I emission-line intensity in the penumbral flare ribbon was 20 percent greater at the peak of the flare in soft X-rays, and the 12 micron continuum intensity was 7 percent greater. The flare also excited the emission line in the umbra where it is normally absent. The umbral flare emission exhibits a Zeeman splitting 200 G less than the adjacent penumbra, suggesting that it is excited at higher altitude. The absolute penumbral magnetic field strength did not change by more than 100 G between the flare peak and postflare period. However, a change in the inclination of the field lines, probably related to the formation and development of the flare loop system, was seen.
-
Exosat observations of 4U 1705-44 - Type I bursts and persistent emission
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Langmeier, A.; Sztajno, M.; Hasinger, G.; Truemper, J.; Gottwald, M.; EXOSAT Observatory, Noordwijk, Netherlands)
1987-01-01
During four Exosat observations, the bright galactic X-ray source 4U 1705-44 exhibited persistent emission variations from 1.3 to 10.7 x 10 to the -9th ergs/sq cm per sec in the 1-20 keV band. Type I X-ray bursts have been detected from this source whose properties correlate with source intensity. The burst shape changed with increasing intensity from a slow burst profile with a decay time of 100 sec to a feast profile with a decay time of 25 sec. The spectrum during maximum was best-fitted by a two-component model involving a blackbody together with a Boltzmann-Wien law, and an additional iron K emission line. 28 references
-
Temporal feature of X-ray laser plasma observed from 3ω0/2, 2ω0 harmonic emission
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Li Wenhong; Mei Qiyong; Zhao Xuewei; Chen Yuting; Chunyu Shutai
1995-01-01
Temporal feature of X-ray laser plasma density was observed from 3ω 0 /2, 2ω 0 harmonic emission in the experiments. The temporal feature of 3ω 0 /2 harmonic emission of the germanium film is much different from that of the slab germanium target. The production of x-ray laser is closely related to 3ω 0 /2 harmonic emission in the slab germanium targets
-
Observation of hard X-rays line emission from Her X-1
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Polcaro, V.F.; Bazzano, A.; la Padula, C.; Ubertini, P.; Vialetto, G.; Manchanda, R.K.; Damle, S.V.
1982-04-01
We present the results of a hard X-ray measurement of the binary source Her X-1, carried out with a balloon borne X-ray telescope consisting of two Multiwire Proportional Counters, having 900 cm/sup 2/ sensitive area each and spectral resolution of 15% and 24% FWHM respectively at 60 keV. The source was observed during the 'Mid-on' state. Our data confirm the previously reported high energy emission line overimposed on the low energy thermal spectrum.
-
Borbon, A.; Gilman, J. B.; Kuster, W. C.; McKeen, S. A.; Holloway, J. S.; Gros, V.; Gaimoz, C.; Beekmann, M.; De Gouw, J. A.
2011-12-01
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) affect urban air quality and regional climate change by contributing to ozone formation and the build-up of Secondary Organic Aerosols (SOA). Quantification of VOC emissions is a first critical step to predict VOC environmental impacts and to design effective abatement strategies. Indeed, the quality of ozone and SOA forecasts strongly depends on an accurate knowledge of the primary VOC emissions. However, commonly used bottom-up approaches are highly uncertain due to source multiplicity (combustion processes, storage and distribution of fossil fuels, solvent use, etc.) because of numerous controlling factors (driving conditions, fuel type, temperature, radiation, etc.), and their great variability in time and space. Field observations of VOC and other trace gases can provide valuable top-down constraints to evaluate VOC emission inventories at urban scales. In addition, the implementation of emission reduction measures raises the question of the increasing importance of VOC sources other than traffic. Here, we will evaluate VOC emissions of two mid-latitude megacities in the Northern Hemisphere: the Greater Paris area (Europe) and Los Angeles (USA). In 2009 and 2010, three intensive field campaigns took place in Paris and Los Angeles in the framework of the MEGAPOLI (EU FP7) and CalNex-2010 projects, respectively. Very detailed measurements of aerosol composition and properties, and their gaseous VOC precursors were carried out at ground-based sites (urban center and suburban) and on various mobile platforms. This contribution uses a comprehensive suite of VOC measurements collected by GC-MS/FID techniques at ground-based sites in both cities by a source-receptor methodology. First, emission ratios were estimated from the observations (uncertainty of ± 20%) and compared regarding regional characteristics and European vs. Californian control policies. Then, determined emission ratios were used to assess the accuracy of up
-
Programme of Indian Centre for Space Physics using Very Low Frequency Radio Waves
Chakrabarti, Sandip Kumar; Sasmal, Sudipta; Pal, Sujay; Kanta Maji, Surya; Ray, Suman
Indian Centre for Space Physics conducted two major VLF campaigns all over Indian Sub-continent to study the propagation effects of VLF radio waves. It made multi-receiver observations during solar eclipse. ICSP not only recorded multitudes of solar flares, it also reproduced VLF observation from ab initio calculation. ICSP extended its study to the field of earthquake predictions using signal anomalies and using case by case studies as well as statistical analysis, showed that anomalies are real and more studies are required to understand them. Using earth as a gigantic detector, it detected ionospheric perturbations due to soft gamma-ray repeaters and gamma-ray bursts.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Michael E. Contadakis
2012-04-01
Full Text Available
In 2008, a radio receiver that works in very low frequency (VLF; 20-60 kHz and LF (150-300 kHz bands was developed by an Italian factory. The receiver can monitor 10 frequencies distributed in these bands, with the measurement for each of them of the electric field intensity. Since 2009, to date, six of these radio receivers have been installed throughout Europe to establish a ‘European VLF/LF Network’. At present, two of these are into operation in Italy, and the remaining four are located in Greece, Turkey, Portugal and Romania. For the present study, the LF radio data collected over about two years were analysed. At first, the day-time data and the night-time data were separated for each radio signal. Taking into account that the LF signals are characterized by ground-wave and sky-wave propagation modes, the day-time data are related to the ground wave and the night-time data to the sky wave. In this framework, the effects of solar activity and storm activity were defined in the different trends. Then, the earthquakes with M ≥5.0 that occurred over the same period were selected, as those located in a 300-km radius around each receiver/transmitter and within the 5th Fresnel zone related to each transmitter-receiver path. Where possible, the wavelet analysis was applied on the time series of the radio signal intensity, and some anomalies related to previous earthquakes were revealed. Except for some doubt in one case, success appears to have been obtained in all of the cases related to the 300 km circles in for the ground waves and the sky waves. For the Fresnel cases, success in two cases and one failure were seen in analysing the sky waves. The failure occurred in August/September, and might be related to the disturbed conditions of the ionosphere in summer.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yau, A.W.; Whalen, B.A.; Harris, F.R.; Gattinger, R.L.; Pongratz, M.B.; Bernhardt, P.A.
1985-01-01
In an ionospheric depletion experiment where chemically reactive vapors such as H 2 O and CO 2 are injected into the O + dominant F region to accelerate the plasma recombination rate and to reduce the plasma density, the ion composition in the depleted region is modified, and photometric emissions are produced. We compare in situ ion composition, density, and photometric measurements from two ionospheric depletion experiments with predictions from chemical modeling. The two injections, Waterhole I and III, were part of an auroral perturbation experiment and occurred in different ambient conditions. In both injections a core region of greater than fivefold plasma depletion was observed over roughly-equal5-km diameter within seconds of the injection, surrounded by an outer region of less drastic and slower depletion. In Waterhole I the plasma density was depleted tenfold over a 30-km diamter region after 2 min. The ambient O + density was drastically reduced, and the molecular O + 2 abundance was enhanced fivehold in the depletion region. OH airglow emission associated with the depletion was observed with a peak emission intensity of roughly-equal1 kR. In Waterhole III the ambient density was a decade lower, and the plasma depletion was less drastic, being twofold over 30 km after 2 min. The airglow emissions were also much less intense and below measurement sensitivity (30 R for the OH 306.4-nm emission; 50 R for the 630.0-nm emission)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Da Liu
2015-11-01
Full Text Available Satellite observations can be used to detect the changes of CO2 concentration at global and regional scales. With the column-averaged CO2 dry-air mole fraction (Xco2 data derived from satellite observations, the issue is how to extract and assess these changes, which are related to anthropogenic emissions and biosphere absorptions. We propose a k-means cluster analysis to extract the temporally changing features of Xco2 in the Central-Eastern Asia using the data from 2009 to 2013 obtained by Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite (GOSAT, and assess the effects of anthropogenic emissions and biosphere absorptions on CO2 changes combining with the data of emission and vegetation net primary production (NPP. As a result, 14 clusters, which are 14 types of Xco2 seasonal changing patterns, are obtained in the study area by using the optimal clustering parameters. These clusters are generally in agreement with the spatial pattern of underlying anthropogenic emissions and vegetation absorptions. According to correlation analysis with emission and NPP, these 14 clusters are divided into three groups: strong emission, strong absorption, and a tendency of balancing between emission and absorption. The proposed clustering approach in this study provides us with a potential way to better understand how the seasonal changes of CO2 concentration depend on underlying anthropogenic emissions and vegetation absorptions.
-
Constraints on Eurasian ship NOx emissions using OMI NO2 observations and GEOS-Chem
Vinken, Geert C. M.; Boersma, Folkert; van Donkelaar, Aaron; Zhang, Lin
2013-04-01
Ships emit large quantities of nitrogen oxides (NOx = NO + NO2), important precursors for ozone (O3) and particulate matter formation. Ships burn low-grade marine heavy fuel due to the limited regulations that exist for the maritime sector in international waters. Previous studies showed that global ship NOx emission inventories amount to 3.0-10.4 Tg N per year (15-30% of total NOx emissions), with most emissions close to land and affecting air quality in densely populated coastal regions. Bottom-up inventories depend on the extrapolation of a relatively small number of measurements that are often unable to capture annual emission changes and can suffer from large uncertainties. Satellites provide long-term, high-resolution retrievals that can be used to improve emission estimates. In this study we provide top-down constraints on ship NOx emissions in major European ship routes, using observed NO2 columns from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) and NO2 columns simulated with the nested (0.5°×0.67°) version of the GEOS-Chem chemistry transport model. We use a plume-in-grid treatment of ship NOx emissions to account for in-plume chemistry in our model. We ensure consistency between the retrievals and model simulations by using the high-resolution GEOS-Chem NO2 profiles as a priori. We find evidence that ship emissions in the Mediterranean Sea are geographically misplaced by up to 150 km and biased high by a factor of 4 as compared to the most recent (EMEP) ship emission inventory. Better agreement is found over the shipping lane between Spain and the English Channel. We extend our approach and also provide constraints for major ship routes in the Red Sea and Indian Ocean. Using the full benefit of the long-term retrieval record of OMI, we present a new Eurasian ship emission inventory for the years 2005 to 2010, based on the EMEP and AMVER-ICOADS inventories, and top-down constraints from the satellite retrievals. Our work shows that satellite retrievals can
-
Panfilov, A. A.
2014-06-01
The paper presents the results of laboratory experiments on electromagnetic emissions excitation (the electric component of electromagnetic fields) by rock samples due to different forms of mechanical stress applications. It was shown that samples generate electric impulses with different spectra when the impact action, gradual loading or dynamic friction is applied. It was ascertained that level and spectral compositions of signals, generated by rock samples, change with an increasing number of hits. It was found that strong electromagnetic signals, generated while rock samples were fracturing, were accompanied by repetitive weak but perceptible variations in the electric field intensity in short frequency ranges.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Chu, B [Key Laboratory of the Excited States Process, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 16-Dong NanHu Road, Economic Development Area, Changchun, 130033 (China); Li, W L [Key Laboratory of the Excited States Process, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 16-Dong NanHu Road, Economic Development Area, Changchun, 130033 (China); Hong, Z R [Key Laboratory of the Excited States Process, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 16-Dong NanHu Road, Economic Development Area, Changchun, 130033 (China); Zang, F X [Key Laboratory of the Excited States Process, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 16-Dong NanHu Road, Economic Development Area, Changchun, 130033 (China); Wei, H Z [Key Laboratory of the Excited States Process, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 16-Dong NanHu Road, Economic Development Area, Changchun, 130033 (China); Wang, D Y [Key Laboratory of the Excited States Process, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 16-Dong NanHu Road, Economic Development Area, Changchun, 130033 (China); Li, M T [Key Laboratory of the Excited States Process, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 16-Dong NanHu Road, Economic Development Area, Changchun, 130033 (China); Lee, C S [Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong (China); Lee, S T [Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong (China)
2006-11-07
Samarium (dibenzoylmethanato){sub 3} bathophenanthroline (Sm(DBM){sub 3} bath) was employed as an emitting and electron transport layer in organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs), and narrow electroluminescent (EL) emissions of a Sm{sup 3+} ion were observed in the visible and near infrared (NIR) region, differing from those of the same devices with Eu{sup 3+}- or Tb{sup 3+}-complex EL devices with the same structure. The EL emissions of the Sm{sup 3+}-devices originate from transitions from {sup 4}G{sub 5/2} to the lower respective levels of Sm{sup 3+} ions. A maximum luminance of 490 cd m{sup -2} at 15 V and an EL efficiency of 0.6% at 0.17 mA cm{sup -2} were obtained in the visible region, and the improved efficiency should be attributed to introducing a transitional layer between the N,N'-diphenyl-N,N'-bis(3-methylphenyl)-1,1'-diphenyl-4,4'-diamine (TPD) film and the Sm(DBM){sub 3} bath film and the avoidance of interfacial exciplex emission in devices. Sharp emissions of Sm{sup 3+} ions in the NIR region were also observed under a lower threshold value less than 4.5 V.
-
Fluorescent H{sub 2} Emission Lines from the Reflection Nebula NGC 7023 Observed with IGRINS
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Le, Huynh Anh N.; Pak, Soojong; Lee, Hye-In [School of Space Research, Kyung Hee University, 1732 Deogyeong-daero, Giheung-gu, Yongin-si, Gyeonggi-do 17104 (Korea, Republic of); Kaplan, Kyle; Mace, Gregory; Pavel, Michael; Jaffe, Daniel T. [Department of Astronomy, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 78712 (United States); Lee, Sungho; Jeong, Ueejeong; Chun, Moo-Young; Yuk, In-Soo; Hwang, Narae; Kim, Kang-Min; Park, Chan; Oh, Jae Sok; Yu, Young Sam; Park, Byeong-Gon; Minh, Young Chol [Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute, Daejeon 34055 (Korea, Republic of); Oh, Heeyoung [Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul National University, 1 Gwanak-ro, Gwanak-gu, Seoul 08826 (Korea, Republic of); Pyo, Tae-Soo, E-mail: huynhanh7@khu.ac.kr, E-mail: soojong@khu.ac.kr [Subaru Telescope, National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS), 650 North Aohoku Place, Hilo, HI 96720 (United States)
2017-05-20
We have analyzed the temperature, velocity, and density of H{sub 2} gas in NGC 7023 with a high-resolution near-infrared spectrum of the northwestern filament of the reflection nebula. By observing NGC 7023 in the H and K bands at R ≃ 45,000 with the Immersion GRating INfrared Spectrograph, we detected 68 H{sub 2} emission lines within the 1″ × 15″ slit. The diagnostic ratio of 2-1 S(1)/1-0 S(1) is 0.41−0.56. In addition, the estimated ortho-to-para ratio (OPR) is 1.63−1.82, indicating that the H{sub 2} emission transitions in the observed region arise mostly from gas excited by UV fluorescence. Gradients in the temperature, velocity, and OPR within the observed area imply motion of the photodissociation region (PDR) relative to the molecular cloud. In addition, we derive the column density of H{sub 2} from the observed emission lines and compare these results with PDR models in the literature covering a range of densities and incident UV field intensities. The notable difference between PDR model predictions and the observed data, in high rotational J levels of ν = 1, is that the predicted formation temperature for newly formed H{sub 2} should be lower than that of the model predictions. To investigate the density distribution, we combine pixels in 1″ × 1″ areas and derive the density distribution at the 0.002 pc scale. The derived gradient of density suggests that NGC 7023 has a clumpy structure, including a high clump density of ∼10{sup 5} cm{sup −3} with a size smaller than ∼5 × 10{sup −3} pc embedded in lower-density regions of 10{sup 3}–10{sup 4} cm{sup −3}.
-
Mars atmosphere studies with the SPICAM IR emission phase function observations
Trokhimovskiy, Alexander; Fedorova, Anna; Montmessin, Franck; Korablev, Oleg; Bertaux, Jean-Loup
Emission Phase Function (EPF) observations is a powerful tool for characterization of atmosphere and surface. EPF sequence provides the extensive coverage of scattering angles above the targeted surface location which allow to separate the surface and aerosol scattering, study a vertical distribution of minor species and aerosol properties. SPICAM IR instrument on Mars Express mission provides continuous atmospheric observations in near IR (1-1.7 mu) in nadir and limb starting from 2004. For the first years of SPICAM operation only a very limited number of EPFs was performed. But from the mid 2013 (Ls=225, MY31) SPICAM EPF observations become rather regular. Based on the multiple-scattering radiative transfer model SHDOM, we analyze equivalent depths of carbon dioxide (1,43 mu) and water vapour (1,38 mu) absorption bands and their dependence on airmass during observation sequence to get aerosol optical depths and properties. The derived seasonal dust opacities from near IR can be used to retrieve the size distribution from comparison with simultaneous results of other instruments in different spectral ranges. Moreover, the EPF observations of water vapour band allow to access poorly known H2O vertical distribution for different season and locations.
-
Observable Emission Features of Black Hole GRMHD Jets on Event Horizon Scales
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Pu, Hung-Yi [Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, 31 Caroline Street North, Waterloo, ON, N2L 2Y5 (Canada); Wu, Kinwah [Mullard Space Science Laboratory, University College London, Holmbury St. Mary, Dorking, Surrey, RH5 6NT (United Kingdom); Younsi, Ziri; Mizuno, Yosuke [Institut für Theoretische Physik, Max-von-Laue-Straße 1, D-60438 Frankfurt am Main (Germany); Asada, Keiichi; Nakamura, Masanori, E-mail: hpu@perimeterinstitute.ca, E-mail: asada@asiaa.sinica.edu.tw, E-mail: nakamura@asiaa.sinica.edu.tw, E-mail: kinwah.wu@ucl.ac.uk, E-mail: younsi@th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de, E-mail: mizuno@th.physik.uni-frankfurt.de [Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, 11F of Astronomy-Mathematics Building, AS/NTU No. 1, Taipei 10617, Taiwan (China)
2017-08-20
The general-relativistic magnetohydrodynamical (GRMHD) formulation for black hole-powered jets naturally gives rise to a stagnation surface, where inflows and outflows along magnetic field lines that thread the black hole event horizon originate. We derive a conservative formulation for the transport of energetic electrons, which are initially injected at the stagnation surface and subsequently transported along flow streamlines. With this formulation the energy spectra evolution of the electrons along the flow in the presence of radiative and adiabatic cooling is determined. For flows regulated by synchrotron radiative losses and adiabatic cooling, the effective radio emission region is found to be finite, and geometrically it is more extended along the jet central axis. Moreover, the emission from regions adjacent to the stagnation surface is expected to be the most luminous as this is where the freshly injected energetic electrons are concentrated. An observable stagnation surface is thus a strong prediction of the GRMHD jet model with the prescribed non-thermal electron injection. Future millimeter/submillimeter (mm/sub-mm) very-long-baseline interferometric observations of supermassive black hole candidates, such as the one at the center of M87, can verify this GRMHD jet model and its associated non-thermal electron injection mechanism.
-
Analysis and Modeling of Jovian Radio Emissions Observed by Galileo
Menietti, J. D.
2003-01-01
Our studies of Jovian radio emission have resulted in the publication of five papers in refereed journals, with three additional papers in progress. The topics of these papers include the study of narrow-band kilometric radio emission; the apparent control of radio emission by Callisto; quasi-periodic radio emission; hectometric attenuation lanes and their relationship to Io volcanic activity; and modeling of HOM attenuation lanes using ray tracing. A further study of the control of radio emission by Jovian satellites is currently in progress. Abstracts of each of these papers are contained in the Appendix. A list of the publication titles are also included.
-
Simonenkov, Denis V.; Raputa, Vladimir F.; Yaroslavtseva, Tatyana V.; Belan, Boris D.; Antokhina, Olga Yu.
2017-11-01
Models for estimating the regional transport of active and passive impurities based on the data of route observations in the vicinity of point and area sources are proposed. Approbation of models on the data of airborne probing of atmospheric pollution in the Norilsk industrial region was carried out. In the range of distances of 60-100 km from the source of emissions, the active gas-to-particle conversion was analyzed on the basis of the observed data.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. V. Martin
2008-09-01
Full Text Available An inverse modeling method was developed and tested for identifying possible biases in emission inventories using satellite observations. The relationships between emission inputs and modeled ambient concentrations were estimated using sensitivities calculated with the decoupled direct method in three dimensions (DDM-3D implemented within the framework of the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ regional model. As a case study to test the approach, the method was applied to regional ground-level NOx emissions in the southeastern United States as constrained by observations of NO2 column densities derived from the Scanning Imaging Absorption Spectrometer for Atmospheric Chartography (SCIAMACHY satellite instrument. A controlled "pseudodata" scenario with a known solution was used to establish that the methodology can achieve the correct solution, and the approach was then applied to a summer 2004 period where the satellite data are available. The results indicate that emissions biases differ in urban and rural areas of the southeast. The method suggested slight downward (less than 10% adjustment to urban emissions, while rural region results were found to be highly sensitive to NOx processes in the upper troposphere. As such, the bias in the rural areas is likely not solely due to biases in the ground-level emissions. It was found that CMAQ was unable to predict the significant level of NO2 in the upper troposphere that was observed during the NASA Intercontinental Chemical Transport Experiment (INTEX measurement campaign. The best correlation between satellite observations and modeled NO2 column densities, as well as comparison to ground-level observations of NO2, was obtained by performing the inverse while accounting for the significant presence of NO2 in the upper troposphere not captured by the regional model.
-
Radio-emission of pre-main sequence stars of the Rho Ophiuchi cloud: observations and interpretation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Andre, P.
1987-11-01
Observations of the radio continuum emission of a young star population have been made at VLA on the whole molecular cloud Rho Ophiuchi, one of the closest site of star formation. A dozen of stellar sources have been detected. Radio emission of some identified objects seems to have a magnetic nature and be produced by gyrosynchrotron mechanism. In particular, one of the sources shows a radio radiation circularly polarized; two other stars have a radiation strongly variable probably due to magnetic eruptions more important than those detected in X radiation. More generally, radio observations select probably a specific population of young stars characterized by magnetic field presence extended on several stellar radii and by absence of dense circumstellar environment. Spatial distribution of these objects suggest, they are younger than most of the pre-main sequence stars [fr
-
Silva, B. Marta; Zaroubi, Saleem; Kooistra, Robin; Cooray, Asantha
2018-04-01
The H α line emission is an important probe for a number of fundamental quantities in galaxies, including their number density, star formation rate (SFR), and overall gas content. A new generation of low-resolution intensity mapping (IM) probes, e.g. SPHEREx and CDIM, will observe galaxies in H α emission over a large fraction of the sky from the local Universe till a redshift of z ˜ 6 - 10, respectively. This will also be the target line for observations by the high-resolution Euclid and WFIRST instruments in the z ˜ 0.7-2 redshift range. In this paper, we estimate the intensity and power spectra of the H α line in the z ˜ 0-5 redshift range using observed line luminosity functions (LFs), when possible, and simulations, otherwise. We estimate the significance of our predictions by accounting for the modelling uncertainties (e.g. SFR, extinction, etc.) and observational contamination. We find that IM surveys can make a statistical detection of the full H α emission between z ˜ 0.8 and 5. Moreover, we find that the high-frequency resolution and the sensitivity of the planned CDIM surveys allow for the separation of H α emission from several interloping lines. We explore ways to use the combination of these line intensities to probe galaxy properties. As expected, our study indicates that galaxy surveys will only detect bright galaxies that contribute up to a few per cent of the overall H α intensity. However, these surveys will provide important constraints on the high end of the H α LF and put strong constraints on the active galactic nucleus LF.
-
What would dense atmospheric observation networks bring to the quantification of city CO2 emissions?
Wu, Lin; Broquet, Grégoire; Ciais, Philippe; Bellassen, Valentin; Vogel, Felix; Chevallier, Frédéric; Xueref-Remy, Irène; Wang, Yilong
2016-06-01
Cities currently covering only a very small portion ( directly release to the atmosphere about 44 % of global energy-related CO2, but they are associated with 71-76 % of CO2 emissions from global final energy use. Although many cities have set voluntary climate plans, their CO2 emissions are not evaluated by the monitoring, reporting, and verification (MRV) procedures that play a key role for market- or policy-based mitigation actions. Here we analyze the potential of a monitoring tool that could support the development of such procedures at the city scale. It is based on an atmospheric inversion method that exploits inventory data and continuous atmospheric CO2 concentration measurements from a network of stations within and around cities to estimate city CO2 emissions. This monitoring tool is configured for the quantification of the total and sectoral CO2 emissions in the Paris metropolitan area (˜ 12 million inhabitants and 11.4 TgC emitted in 2010) during the month of January 2011. Its performances are evaluated in terms of uncertainty reduction based on observing system simulation experiments (OSSEs). They are analyzed as a function of the number of sampling sites (measuring at 25 m a.g.l.) and as a function of the network design. The instruments presently used to measure CO2 concentrations at research stations are expensive (typically ˜ EUR 50 k per sensor), which has limited the few current pilot city networks to around 10 sites. Larger theoretical networks are studied here to assess the potential benefit of hypothetical operational lower-cost sensors. The setup of our inversion system is based on a number of diagnostics and assumptions from previous city-scale inversion experiences with real data. We find that, given our assumptions underlying the configuration of the OSSEs, with 10 stations only the uncertainty for the total city CO2 emission during 1 month is significantly reduced by the inversion by ˜ 42 %. It can be further reduced by extending the
-
A Climatology of Dust-Emission Events over North Africa Based on 27 Years of Surface Observations
Cowie, S.; Knippertz, P.; Schepanski, K.
2012-04-01
The huge quantity of mineral dust emitted annually from North Africa makes this area crucial to the global dust cycle. Once in the atmosphere, dust aerosols have a significant impact on the global radiation budget, clouds, the carbon cycle and can even act as a fertilizer to rain forests in South America. Current model estimates of dust production from North Africa are uncertain. At the heart of this problem is insufficient understanding of key dust emitting processes such as haboobs (cold pools generated through evaporation of convective precipitation), low-level jets (LLJs), and dry convection (dust devils and dust plumes). Scarce observations in this region, in particular in the Sahara, make model evaluation difficult. This work uses long-term surface observations from the MIDAS data set (~120 stations in the arid part of North Africa) to explore the diurnal, seasonal, decadal and geographical variations in dust emission events and their associated wind thresholds. The threshold values are determined from probability density functions of observed 10-minute anemomenter wind speeds. Emission events are defined using the present weather codes (WW) of SYNOP reports. These codes represent events of smaller intensity such as "Dust or sand raised by wind" to severe dust storms. During the 27-year study period (1984-2011) stations are required to have a minimum of 1000 dust observations to be included in the analysis. Dust emission frequency (DEF) is calculated for different time intervals (e.g. monthly, 3-hourly) taking into account the different number of measurements available at each station. North of 25°N a maximum during March-May is evident and relatively consistent over the whole North African region. Wind-speed thresholds for dust emission north of 25°N are higher than south of 25°N in the Sahel, where station-to-station variability is larger, and enhanced DEF activity during February-March is observed. The variability in this region is closely linked to the
-
Hughes, Eric J.; Krotkov, Nickolay; da Silva, Arlindo; Colarco, Peter
2015-01-01
Simulation of volcanic emissions in climate models requires information that describes the eruption of the emissions into the atmosphere. While the total amount of gases and aerosols released from a volcanic eruption can be readily estimated from satellite observations, information about the source parameters, like injection altitude, eruption time and duration, is often not directly known. The AeroCOM volcanic emissions inventory provides estimates of eruption source parameters and has been used to initialize volcanic emissions in reanalysis projects, like MERRA. The AeroCOM volcanic emission inventory provides an eruptions daily SO2 flux and plume top altitude, yet an eruption can be very short lived, lasting only a few hours, and emit clouds at multiple altitudes. Case studies comparing the satellite observed dispersal of volcanic SO2 clouds to simulations in MERRA have shown mixed results. Some cases show good agreement with observations Okmok (2008), while for other eruptions the observed initial SO2 mass is half of that in the simulations, Sierra Negra (2005). In other cases, the initial SO2 amount agrees with the observations but shows very different dispersal rates, Soufriere Hills (2006). In the aviation hazards community, deriving accurate source terms is crucial for monitoring and short-term forecasting (24-h) of volcanic clouds. Back trajectory methods have been developed which use satellite observations and transport models to estimate the injection altitude, eruption time, and eruption duration of observed volcanic clouds. These methods can provide eruption timing estimates on a 2-hour temporal resolution and estimate the altitude and depth of a volcanic cloud. To better understand the differences between MERRA simulations and volcanic SO2 observations, back trajectory methods are used to estimate the source term parameters for a few volcanic eruptions and compared to their corresponding entry in the AeroCOM volcanic emission inventory. The nature of
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. Osterman
2009-06-01
Full Text Available The impact of surface emissions on the zonal structure of tropical tropospheric ozone and carbon monoxide is investigated for November 2004 using satellite observations, in-situ measurements, and chemical transport models in conjunction with inverse-estimated surface emissions.Vertical ozone profiles from the Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer (TES and ozone sonde measurements from the Southern Hemisphere Additional Ozonesondes (SHADOZ network show elevated concentrations of ozone over Indonesia and Australia (60–70 ppb in the lower troposphere against the backdrop of the well-known zonal "wave-one" pattern with ozone concentrations of (70–80 ppb centered over the Atlantic . Observational evidence from TES CO vertical profiles and Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI NO2 columns point to regional surface emissions as an important contributor to the elevated ozone over Indonesia. This contribution is investigated with the GEOS-Chem chemistry and transport model using surface emission estimates derived from an optimal inverse model, which was constrained by TES and Measurements Of Pollution In The Troposphere (MOPITT CO profiles (Jones et al., 2009. These a posteriori estimates, which were over a factor of 2 greater than climatological emissions, reduced differences between GEOS-Chem and TES ozone observations by 30–40% over Indonesia. The response of the free tropospheric chemical state to the changes in these emissions is investigated for ozone, CO, NOx, and PAN. Model simulations indicate that ozone over Indonesian/Australian is sensitive to regional changes in surface emissions of NOx but relatively insensitive to lightning NOx. Over sub-equatorial Africa and South America, free tropospheric NOx was reduced in response to increased surface emissions potentially muting ozone production.
-
Stavrakou, T.; Muller, J. F.; Bauwens, M.; De Smedt, I.; Lerot, C.; Van Roozendael, M.
2015-12-01
Crop residue burning is an important contributor to global biomass burning. In the North China Plain, one of the largest and densely populated world plains, post-harvest crop burning is a common agricultural management practice, allowing for land clearing from residual straw and preparation for the subsequent crop cultivation. The most extensive crop fires occur in the North China Plain in June after the winter wheat comes to maturity, and have been blamed for spikes in air pollution leading to serious health problems. Estimating harvest season burning emissions is therefore of primary importance to assess air quality and define best policies for its improvement in this sensitive region. Bottom-up approaches, either based on crop production and emission factors, or on satellite burned area and fire radiative power products, have been adopted so far, however, these methods crucially depend, among other assumptions, on the satellite skill to detect small fires, and could lead to underestimation of the actual emissions. The flux inversion of atmospheric observations is an alternative, independent approach for inferring the emissions from crop fires. Satellite column observations of formaldehyde (HCHO) exhibit a strong peak over the North China Plain in June, resulting from enhanced pyrogenic emissions of a large suite of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), precursors of HCHO. We use vertical columns of formaldehyde retrieved from the OMI instrument between 2005 and 2012 as constraints in an adjoint inversion scheme built on IMAGESv2 CTM, and perform the optimization of biogenic, pyrogenic, and anthropogenic emission parameters at the model resolution. We investigate the interannual variability of the top-down source, quantify its importance for the atmospheric composition on the regional scale, and explore its uncertainties. The OMI-based crop burning source is compared with the corresponding anthropogenic flux in the North China Plain, and is evaluated against HCHO
-
Polarisation observations of VY Canis Majoris H2O 532-441 620.701 GHz maser emission with HIFI
Harwit, M.; Houde, M.; Sonnentrucker, P.; Boogert, A. C. A.; Cernicharo, J.; De Beck, E.; Decin, L.; Henkel, C.; Higgins, R. D.; Jellema, W.; Kraus, A.; McCoey, C.; Melnick, G. J.; Menten, K. M.; Risacher, C.; Teyssier, D.; Vaillancourt, J. E.; Alcolea, J.; Bujarrabal, V.; Dominik, C.; Justtanont, K.; de Koter, A.; Marston, A. P.; Olofsson, H.; Planesas, P.; Schmidt, M.; Schöier, F. L.; Szczerba, R.; Waters, L. B. F. M.
2010-10-01
Context. Water vapour maser emission from evolved oxygen-rich stars remains poorly understood. Additional observations, including polarisation studies and simultaneous observation of different maser transitions may ultimately lead to greater insight. Aims: We have aimed to elucidate the nature and structure of the VY CMa water vapour masers in part by observationally testing a theoretical prediction of the relative strengths of the 620.701 GHz and the 22.235 GHz maser components of ortho H2O. Methods: In its high-resolution mode (HRS) the Herschel Heterodyne Instrument for the Far Infrared (HIFI) offers a frequency resolution of 0.125 MHz, corresponding to a line-of-sight velocity of 0.06 km s-1, which we employed to obtain the strength and linear polarisation of maser spikes in the spectrum of VY CMa at 620.701 GHz. Simultaneous ground based observations of the 22.235 GHz maser with the Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie 100-m telescope at Effelsberg, provided a ratio of 620.701 GHz to 22.235 GHz emission. Results: We report the first astronomical detection to date of H2O maser emission at 620.701 GHz. In VY CMa both the 620.701 and the 22.235 GHz polarisation are weak. At 620.701 GHz the maser peaks are superposed on what appears to be a broad emission component, jointly ejected from the star. We observed the 620.701 GHz emission at two epochs 21 days apart, both to measure the potential direction of linearly polarised maser components and to obtain a measure of the longevity of these components. Although we do not detect significant polarisation levels in the core of the line, they rise up to approximately 6% in its wings. Herschel is an ESA space observatory with science instruments provided by European-led Principal Investigator consortia and with important participation from NASA.Appendix (page 5) is only available in electronic form at http://www.aanda.org
-
King, Ronold W. P.; Sandler, Sheldon S.
1996-09-01
Formulas for the transverse components of the electric and magnetic fields of the traveling-wave currents of three different types of three-wire, three-phase high-voltage power lines and of a typical VLF transmitter are given. From them, exposure situations for the human body are chosen which permit the analytical determination of the total current induced in that body. With this, the fraction of the total axial current, the axial current density, and the axial electric field in each organ of the body are obtained at any desired cross section. The dimensions and conductivity of these organs must be known. The electric field so obtained is the average macroscopic field in which the cells in each organ are immersed when the whole body is exposed to a known incident field. It corresponds in vivo to the electric field used in vitro to expose cells in tissues.
-
Thermal and Nonthermal Emissions of a Composite Flare Derived from NoRH and SDO Observations
Lee, Jeongwoo; White, Stephen M.; Jing, Ju; Liu, Chang; Masuda, Satoshi; Chae, Jongchul
2017-12-01
Differential emission measure (DEM) derived from the extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lines of the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on board the Solar Dynamic Observatory is used in the analysis of a solar flare observed by the Nobeyama Radioheliograph (NoRH). The target was a composite event consisting of an impulsive flare, SOL2015-06-21T01:42 (GOES class M2.0), and a gradual flare, SOL2015-06-21T02:36 (M2.6), for which separation of thermal plasma heating from nonthermal particle acceleration was of major interest. We have calculated the thermal free-free intensity maps with the AIA-derived DEM and compared them against the observed NoRH maps to attribute the difference to the nonthermal component. In this way, we were able to locate three distinct sources: the major source with thermal and nonthermal components mixed, a nonthermal source devoid of thermal particles, and a thermal source lacking microwave emission. Both the first and the second nonthermal sources produced impulsively rising 17 GHz intensities and moved away from the local magnetic polarization inversion lines in correlation with the flare radiation. In contrast, the thermal sources stay in fixed locations and show temporal variations of the temperature and emission measure uncorrelated with the flare radiation. We interpret these distinct properties as indicating that nonthermal sources are powered by magnetic reconnection and thermal sources passively receive energy from the nonthermal donor. The finding of these distinct properties between thermal and nonthermal sources demonstrates the microwave and EUV emission measure combined diagnostics.
-
Pal, S.; Hobara, Y.; Chakrabarti, S. K.; Schnoor, P. W.
2017-07-01
This paper presents effects of the major sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) event of 2009 on the subionospheric very low frequency/low frequency (VLF/LF) radio signals propagating in the Earth-ionosphere waveguide. Signal amplitudes from four transmitters received by VLF/LF radio networks of Germany and Japan corresponding to the major SSW event are investigated for possible anomalies and atmospheric influence on the high- to middle-latitude ionosphere. Significant anomalous increase or decrease of nighttime and daytime amplitudes of VLF/LF signals by ˜3-5 dB during the SSW event have been found for all propagation paths associated with stratospheric temperature rise at 10 hPa level. Increase or decrease in VLF/LF amplitudes during daytime and nighttime is actually due to the modification of the lower ionospheric boundary conditions in terms of electron density and electron-neutral collision frequency profiles and associated modal interference effects between the different propagating waveguide modes during the SSW period. TIMED/SABER mission data are also used to investigate the upper mesospheric conditions over the VLF/LF propagation path during the same time period. We observe a decrease in neutral temperature and an increase in pressure at the height of 75-80 km around the peak time of the event. VLF/LF anomalies are correlated and in phase with the stratospheric temperature and mesospheric pressure variation, while minimum of mesospheric cooling shows a 2-3 day delay with maximum VLF/LF anomalies. Simulations of VLF/LF diurnal variation are performed using the well-known Long Wave Propagating Capability (LWPC) code within the Earth-ionosphere waveguide to explain the VLF/LF anomalies qualitatively.
-
Foster, C. S.; Crosman, E. T.; Holland, L.; Mallia, D. V.; Fasoli, B.; Bares, R.; Horel, J.; Lin, J. C.
2017-12-01
Large CH4 leak rates have been observed in the Uintah Basin of eastern Utah, an area with over 10,000 active and producing natural gas and oil wells. In this paper, we model CH4 concentrations at four sites in the Uintah Basin and compare the simulated results to in situ observations at these sites during two spring time periods in 2015 and 2016. These sites include a baseline location (Fruitland), two sites near oil wells (Roosevelt and Castlepeak), and a site near natural gas wells (Horsepool). To interpret these measurements and relate observed CH4 variations to emissions, we carried out atmospheric simulations using the Stochastic Time-Inverted Lagrangian Transport model driven by meteorological fields simulated by the Weather Research and Forecasting and High Resolution Rapid Refresh models. These simulations were combined with two different emission inventories: (1) aircraft-derived basin-wide emissions allocated spatially using oil and gas well locations, from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and (2) a bottom-up inventory for the entire U.S., from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). At both Horsepool and Castlepeak, the diurnal cycle of modeled CH4 concentrations was captured using NOAA emission estimates but was underestimated using the EPA inventory. These findings corroborate emission estimates from the NOAA inventory, based on daytime mass balance estimates, and provide additional support for a suggested leak rate from the Uintah Basin that is higher than most other regions with natural gas and oil development.
-
Fermi observations of high-energy gamma-ray emission from GRB 080916C.
Abdo, A A; Ackermann, M; Arimoto, M; Asano, K; Atwood, W B; Axelsson, M; Baldini, L; Ballet, J; Band, D L; Barbiellini, G; Baring, M G; Bastieri, D; Battelino, M; Baughman, B M; Bechtol, K; Bellardi, F; Bellazzini, R; Berenji, B; Bhat, P N; Bissaldi, E; Blandford, R D; Bloom, E D; Bogaert, G; Bogart, J R; Bonamente, E; Bonnell, J; Borgland, A W; Bouvier, A; Bregeon, J; Brez, A; Briggs, M S; Brigida, M; Bruel, P; Burnett, T H; Burrows, D; Busetto, G; Caliandro, G A; Cameron, R A; Caraveo, P A; Casandjian, J M; Ceccanti, M; Cecchi, C; Celotti, A; Charles, E; Chekhtman, A; Cheung, C C; Chiang, J; Ciprini, S; Claus, R; Cohen-Tanugi, J; Cominsky, L R; Connaughton, V; Conrad, J; Costamante, L; Cutini, S; Deklotz, M; Dermer, C D; de Angelis, A; de Palma, F; Digel, S W; Dingus, B L; do Couto E Silva, E; Drell, P S; Dubois, R; Dumora, D; Edmonds, Y; Evans, P A; Fabiani, D; Farnier, C; Favuzzi, C; Finke, J; Fishman, G; Focke, W B; Frailis, M; Fukazawa, Y; Funk, S; Fusco, P; Gargano, F; Gasparrini, D; Gehrels, N; Germani, S; Giebels, B; Giglietto, N; Giommi, P; Giordano, F; Glanzman, T; Godfrey, G; Goldstein, A; Granot, J; Greiner, J; Grenier, I A; Grondin, M-H; Grove, J E; Guillemot, L; Guiriec, S; Haller, G; Hanabata, Y; Harding, A K; Hayashida, M; Hays, E; Hernando Morat, J A; Hoover, A; Hughes, R E; Jóhannesson, G; Johnson, A S; Johnson, R P; Johnson, T J; Johnson, W N; Kamae, T; Katagiri, H; Kataoka, J; Kavelaars, A; Kawai, N; Kelly, H; Kennea, J; Kerr, M; Kippen, R M; Knödlseder, J; Kocevski, D; Kocian, M L; Komin, N; Kouveliotou, C; Kuehn, F; Kuss, M; Lande, J; Landriu, D; Larsson, S; Latronico, L; Lavalley, C; Lee, B; Lee, S-H; Lemoine-Goumard, M; Lichti, G G; Longo, F; Loparco, F; Lott, B; Lovellette, M N; Lubrano, P; Madejski, G M; Makeev, A; Marangelli, B; Mazziotta, M N; McBreen, S; McEnery, J E; McGlynn, S; Meegan, C; Mészáros, P; Meurer, C; Michelson, P F; Minuti, M; Mirizzi, N; Mitthumsiri, W; Mizuno, T; Moiseev, A A; Monte, C; Monzani, M E; Moretti, E; Morselli, A; Moskalenko, I V; Murgia, S; Nakamori, T; Nelson, D; Nolan, P L; Norris, J P; Nuss, E; Ohno, M; Ohsugi, T; Okumura, A; Omodei, N; Orlando, E; Ormes, J F; Ozaki, M; Paciesas, W S; Paneque, D; Panetta, J H; Parent, D; Pelassa, V; Pepe, M; Perri, M; Pesce-Rollins, M; Petrosian, V; Pinchera, M; Piron, F; Porter, T A; Preece, R; Rainò, S; Ramirez-Ruiz, E; Rando, R; Rapposelli, E; Razzano, M; Razzaque, S; Rea, N; Reimer, A; Reimer, O; Reposeur, T; Reyes, L C; Ritz, S; Rochester, L S; Rodriguez, A Y; Roth, M; Ryde, F; Sadrozinski, H F-W; Sanchez, D; Sander, A; Saz Parkinson, P M; Scargle, J D; Schalk, T L; Segal, K N; Sgrò, C; Shimokawabe, T; Siskind, E J; Smith, D A; Smith, P D; Spandre, G; Spinelli, P; Stamatikos, M; Starck, J-L; Stecker, F W; Steinle, H; Stephens, T E; Strickman, M S; Suson, D J; Tagliaferri, G; Tajima, H; Takahashi, H; Takahashi, T; Tanaka, T; Tenze, A; Thayer, J B; Thayer, J G; Thompson, D J; Tibaldo, L; Torres, D F; Tosti, G; Tramacere, A; Turri, M; Tuvi, S; Usher, T L; van der Horst, A J; Vigiani, L; Vilchez, N; Vitale, V; von Kienlin, A; Waite, A P; Williams, D A; Wilson-Hodge, C; Winer, B L; Wood, K S; Wu, X F; Yamazaki, R; Ylinen, T; Ziegler, M
2009-03-27
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are highly energetic explosions signaling the death of massive stars in distant galaxies. The Gamma-ray Burst Monitor and Large Area Telescope onboard the Fermi Observatory together record GRBs over a broad energy range spanning about 7 decades of gammaray energy. In September 2008, Fermi observed the exceptionally luminous GRB 080916C, with the largest apparent energy release yet measured. The high-energy gamma rays are observed to start later and persist longer than the lower energy photons. A simple spectral form fits the entire GRB spectrum, providing strong constraints on emission models. The known distance of the burst enables placing lower limits on the bulk Lorentz factor of the outflow and on the quantum gravity mass.
-
Fermi Observations of high-energy gamma-ray emissions from GRB 080916C
Abdo, A A; Arimoto, M; Asano, K; Atwood, W B; Axelsson, M; Baldini, L; Ballet, J; Band, D L; Barbiellini, Guido; Baring, Matthew G; Bastieri, Denis; Battelino, M; Baughman, B M; Bechtol, K; Bellardi, F; Bellazzini, R; Berenji, B; Bhat, P N; Bissaldi, E; Blandford, R D; Bloom, Elliott D; Bogaert, G; Bogart, J R; Bonamente, E; Bonnell, J; Borgland, A W; Bouvier, A; Bregeon, J; Brez, A; Briggs, M S; Brigida, M; Bruel, P; Burnett, Thompson H; Burrows, David N; Busetto, Giovanni; Caliandro, G A; Cameron, R A; Caraveo, P A; Casandjian, J M; Ceccanti, M; Cecchi, C; Celotti, Annalisa; Charles, E; Chekhtman, A; Cheung, C.C.Teddy; Chiang, J; Ciprini, S; Claus, R; Cohen-Tanugi, Johann; Cominsky, Lynn R; Connaughton, V; Conrad, J; Costamante, L; Cutini, S; DeKlotz, M; Dermer, C D; De Angelis, Alessandro; de Palma, F; Digel, S W; Dingus, B L; do Couto e Silva, Eduardo; Drell, P S; Dubois, R; Dumora, D; Edmonds, Y; Evans, P A; Fabiani, D; Farnier, C; Favuzzi, C; Finke, Justin D; Fishman, G; Focke, W B; Frailis, M; Fukazawa, Y; Funk, S; Fusco, P; Gargano, F; Gasparrini, D; Gehrels, N; Germani, S; Giebels, B; Giglietto, N; Giommi, P; Giordano, F; Glanzman, Thomas Lynn; Godfrey, Gary L; Goldstein, A; Granot, J; Greiner, J; Grenier, I A; Grondin, M H; Grove, J.Eric; Guillemot, L; Guiriec, S; Haller, G; Hanabata, Y; Harding, Alice K; Hayashida, M; Hays, Elizabeth A; Hernando Morata, J A; Hoover, A; Hughes, R E; Johannesson, G; Johnson, A S; Johnson, R P; Johnson, T J; Johnson, W N; Kamae, Tsuneyoshi; Katagiri, H; Kataoka, J; Kavelaars, A; Kawai, N; Kelly, H; Kennea, J; Kerr, M; Kippen, R M; Knodlseder, J; Kocevski, D; Kocian, M L; Komin, N; Kouveliotou, C; Kuehn, Frederick Gabriel Ivar; Kuss, Michael; Lande, J; Landriu, D; Larsson, S; Latronico, L; Lavalley, C; Lee, B; Lee, S H; Lemoine-Goumard, M; Lichti, G G; Longo, F; Loparco, F; Lott, B; Lovellette, M N; Lubrano, Pasquale; Madejski, G M; Makeev, A; Marangelli, B; Mazziotta, M N; McBreen, Sheila; McEnery, J E; McGlynn, S; Meegan, C; Miszaros, P; Meurer, C; Michelson, P F; Minuti, M; Mirizzi, N; Mitthumsiri, W; Mizuno, T; Moiseev, A A; Monte, C; Monzani, M E; Moretti, E; Morselli, A; Moskalenko, Igor Vladimirovich; Murgia, Simona; Nakamori, T; Nelson, D; Nolan, P L; Norris, J P; Nuss, E; Ohno, M; Ohsugi, Takashi; Okumura, Akira; Omodei, N; Orlando, E; Ormes, J F; Ozaki, M; Paciesas, W S; Paneque, D; Panetta, J H; Parent, D; Pelassa, V; Pepe, M; Perri, M; Pesce-Rollins, M; Petrosian, Vahe; Pinchera, M; Piron, F; Porter, Troy A; Preece, R; Rainr, S; Ramirez-Ruiz, E; Rando, R; Rapposelli, E; Razzano, M; Razzaque, Soebur; Rea, N; Reimer, A; Reimer, O; Reposeur, Thierry; Reyes, Luis C; Ritz, S; Rochester, L S; Rodriguez, A Y; Roth, M; Ryde, F; Sadrozinski, H F W; Sanchez, D; Sander, A; Parkinson, P.M.Saz; Scargle, J D; Schalk, T L; Segal, K N; Sgro, C; Shimokawabe, T; Siskind, E J; Smith, D A; Smith, P D; Spandre, G; Spinelli, P; Stamatikos, M; Starck, Jean-Luc; Stecker, Floyd William; Steinle, H; Stephens, T E; Strickman, M S; Suson, Daniel J; Tagliaferri, G.; Tajima, Hiroyasu; Takahashi, H; Takahashi, T; Tanaka, T; Tenze, A; Thayer, J B; Thayer, J G; Thompson, D J; Tibaldo, L; Torres, Diego F; Tosti, G; Tramacere, A; Turri, M; Tuvi, S; Usher, T L; van der Horst, A J; Vigiani, L; Vilchez, N; Vitale, V; von Kienlin, A; Waite, A P; Williams, D A; Wilson-Hodge, C; Winer, B L; Wood, K S; Wu, X F; Yamazaki, R; Ylinen, T; Ziegler, M
2009-01-01
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are highly energetic explosions signaling the death of massive stars in distant galaxies. The Gamma-ray Burst Monitor and Large Area Telescope onboard the Fermi Observatory together record GRBs over a broad energy range spanning about 7 decades of gammaray energy. In September 2008, Fermi observed the exceptionally luminous GRB 080916C, with the largest apparent energy release yet measured. The high-energy gamma rays are observed to start later and persist longer than the lower energy photons. A simple spectral form fits the entire GRB spectrum, providing strong constraints on emission models. The known distance of the burst enables placing lower limits on the bulk Lorentz factor of the outflow and on the quantum gravity mass.
-
Lin, Jintai; Nielsen, Chris P; Zhao, Yu; Lei, Yu; Liu, Yang; McElroy, Michael B
2010-10-15
The Chinese government has moved aggressively since 2005 to reduce emissions of a number of pollutants including primary particulate matter (PM) and sulfur dioxide (SO(2)), efforts inadvertently aided since late 2008 by economic recession. Satellite observations of aerosol optical depth (AOD) and column nitrogen dioxide (NO(2)) provide independent indicators of emission trends, clearly reflecting the sharp onset of the recession in the fall of 2008 and rebound of the economy in the latter half of 2009. Comparison of AOD with ground-based observations of PM over a longer period indicate that emission-control policies have not been successful in reducing concentrations of aerosol pollutants at smaller size range over industrialized regions of China. The lack of success is attributed to the increasing importance of anthropogenic secondary aerosols formed from precursor species including nitrogen oxides (NO(x)), non-methane volatile organic compounds (NMVOC), and ammonia (NH(3)).
-
Emmons, L. K.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Park, M.; Kaser, L.; Apel, E. C.; Guenther, A. B.
2014-12-01
Numerous measurements of compounds produced by biogenic and fire emissions were made during several recent field campaigns in the southeast United States, providing a unique data set for emissions and chemical model evaluation. The NCAR Community Atmosphere Model with Chemistry (CAM-chem) is coupled to the Community Land Model (CLM), which includes the biogenic emissions model MEGAN-v2.1, allowing for online calculation of emissions from vegetation for 150 compounds. Simulations of CAM-chem for summers 2012 and 2013 are evaluated with the aircraft and ground-based observations from DC3, NOMADSS and SEAC4RS. Comparison of directly emitted biogenic species, such as isoprene, terpenes, methanol and acetone, are used to evaluate the MEGAN emissions. Evaluation of oxidation products, including methyl vinyl ketone (MVK), methacrolein, formaldehyde, and other oxygenated VOCs are used to test the model chemistry mechanism. In addition, several biomass burning inventories are used in the model, including FINN, QFED, and FLAMBE, and are compared for their impact on atmospheric composition and ozone production, and evaluated with the aircraft observations.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. Liu
2016-04-01
Full Text Available We present a new method to quantify NOx emissions and corresponding atmospheric lifetimes from OMI NO2 observations together with ECMWF wind fields without further model input for sources located in a polluted background. NO2 patterns under calm wind conditions are used as proxy for the spatial patterns of NOx emissions, and the effective atmospheric NOx lifetime is determined from the change of spatial patterns measured at larger wind speeds. Emissions are subsequently derived from the NO2 mass above the background, integrated around the source of interest. Lifetimes and emissions are estimated for 17 power plants and 53 cities located in non-mountainous regions across China and the USA. The derived lifetimes for the ozone season (May–September are 3.8 ± 1.0 h (mean ± standard deviation with a range of 1.8 to 7.5 h. The derived NOx emissions show generally good agreement with bottom-up inventories for power plants and cities. Regional inventory shows better agreement with top-down estimates for Chinese cities compared to global inventory, most likely due to different downscaling approaches adopted in the two inventories.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kimura, Iwane
1977-01-01
Wave-particle interaction was observed, using three rockets, S-210 JA-20, -21 and S-310 JA-2, launched from the South Pole into aurora. Electron density and temperature were measured with these rockets. Simultaneous observations of waves were also made from a satellite (ISIS-II) and at two ground bases (Showa base and Mizuho base). Observed data are presented in this paper. These include electron density and temperature in relation to altitude; variation of electron (60 - 80 keV) count rate with altitude; VLF spectra measured by the PWL of S-210 JA-20 and -21 rockets and the corresponding VLF spectra at the ground bases; low-energy (<10 keV) electron flux measured by S-310 JA-2 rocket; and VLF spectrum measured with S-310 JA-2 rocket. Scheduled measurements for the next project are also briefly described. (Aoki, K.)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Platov, Yu.V.; Vanyarkha, N.Ya.; Vanyarkha, E.S.
1989-01-01
Shape of brightness vertical profile for the ionospheric emission layers, observed near the night horizon from space vehicles, depends essentially on structure of luminescence regions. Brightness profiles, obtained from photometry of the first emission layer photons at ∼ 100 km heights, are compared with calculated ones for model distribution of the excited atom concentration to determine typical dimensions of heterogeneities. Luminescence region in the used model was represented by symmetric spot with concentration exponentially decreasing in horizontal direction and with vertical distribution of concentration characterized by rather abrupt maximum at ∼ 10 km height
-
Lu, Zifeng; Streets, David D.; de Foy, Benjamin; Krotkov, Nickolay A.
2014-01-01
Due to the rapid growth of electricity demand and the absence of regulations, sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions from coal-fired power plants in India have increased notably in the past decade. In this study, we present the first interannual comparison of SO2 emissions and the satellite SO2 observations from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) for Indian coal-fired power plants during the OMI era of 2005-2012. A detailed unit-based inventory is developed for the Indian coal-fired power sector, and results show that its SO2 emissions increased dramatically by 71 percent during 2005-2012. Using the oversampling technique, yearly high-resolution OMI maps for the whole domain of India are created, and they reveal a continuous increase in SO2 columns over India. Power plant regions with annual SO2 emissions greater than 50 Gg year-1 produce statistically significant OMI signals, and a high correlation (R equals 0.93) is found between SO2 emissions and OMI-observed SO2 burdens. Contrary to the decreasing trend of national mean SO2 concentrations reported by the Indian Government, both the total OMI-observed SO2 and average SO2 concentrations in coal-fired power plant regions increased by greater than 60 percent during 2005-2012, implying the air quality monitoring network needs to be optimized to reflect the true SO2 situation in India.
-
Cluster observations of reflected EMIC-triggered emission
Grison, B.; Darrouzet, F.; Santolík, O.; Cornilleau-Wehrlin, N.; Masson, A.
2016-05-01
On 19 March 2001, the Cluster fleet recorded an electromagnetic rising tone on the nightside of the plasmasphere. The emission was found to propagate toward the Earth and toward the magnetic equator at a group velocity of about 200 km/s. The Poynting vector is mainly oblique to the background magnetic field and directed toward the Earth. The propagation angle θk,B0 becomes more oblique with increasing magnetic latitude. Inside each rising tone θk,B0 is more field aligned for higher frequencies. Comparing our results to previous ray tracing analysis we conclude that this emission is a triggered electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EMIC) wave generated at the nightside plasmapause. We detect the wave just after its reflection in the plasmasphere. The reflection makes the tone slope shallower. This process can contribute to the formation of pearl pulsations.
-
High-Resolution Spectroscopic Observations of Potassium Emissions in the Lunar Exosphere
Robertson, Sarena D.; Oliversen, Ronald J.; Mierkiewicz, Edwin J.; Kuruppuaratchi, Dona Chathuni P.; Derr, Nicholas James; Gallant, Margaret A.; McFarland, Christina G.; Sarantos, Menelaos
2018-01-01
We investigate lunar exospheric potassium D1 emissions (7698.9646 Å) using high-resolution (R = 180,000 or 1.7 km/s) spectroscopy with our dual-etalon Fabry-Perot instrument to measure line widths and radial velocities. The Field of View (FOV) is 2 arcmins (~224 km at the mean lunar distance of 384,400 km) positioned tangent to the sunlit limb. The FOV placements are at cardinal directions from a variety of reference craters. All observations are collected at the National Solar Observatory McMath-Pierce Telescope in Kitt Peak, Arizona. The data are from several observations from 2014 through 2017 at various times of the year. Results are produced via a newly created automated data reduction using Python. Python was chosen as an open-source alternative to the previously used IDL and MATLAB scripts to decrease the cost of software licenses and maintenance. The potassium spectral line profiles provide a direct method to track exospheric effective temperatures and velocities. By monitoring the state of the potassium emissions over different lunar phases, solar activity, and the influx of meteor streams, we can constrain physical processes of sources and sinks at the lunar surface. Mechanisms that create the exosphere include photon-stimulated desorption, thermal evaporation, meteoroid impact vaporization, and ion sputtering via solar wind. In contrast, the exosphere is diminished due to the low lunar escape velocity, solar radiation pressure, and neutral gas being ionized and swept away by the interplanetary and terrestrial magnetic field. Preliminary analysis of 2017 data (January through June, excluding February) indicates an average potassium temperature of 1140 K but varying over the range of 550 K to 2000 K. Preliminary results from 2014 data depict a similar range of temperatures to that of 2017. Further analysis is expected for additional data from 2014 to later observations in 2017 that were not included in the initial set of models.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brosius, Jeffrey W.; Daw, Adrian N.; Rabin, D. M.
2014-01-01
We present spatially resolved EUV spectroscopic measurements of pervasive, faint Fe XIX 592.2 Å line emission in an active region observed during the 2013 April 23 flight of the Extreme Ultraviolet Normal Incidence Spectrograph (EUNIS-13) sounding rocket instrument. With cooled detectors, high sensitivity, and high spectral resolution, EUNIS-13 resolves the lines of Fe XIX at 592.2 Å (formed at temperature T ≈ 8.9 MK) and Fe XII at 592.6 Å (T ≈ 1.6 MK). The Fe XIX line emission, observed over an area in excess of 4920 arcsec 2 (2.58 × 10 9 km 2 , more than 60% of the active region), provides strong evidence for the nanoflare heating model of the solar corona. No GOES events occurred in the region less than 2 hr before the rocket flight, but a microflare was observed north and east of the region with RHESSI and EUNIS during the flight. The absence of significant upward velocities anywhere in the region, particularly the microflare, indicates that the pervasive Fe XIX emission is not propelled outward from the microflare site, but is most likely attributed to localized heating (not necessarily due to reconnection) consistent with the nanoflare heating model of the solar corona. Assuming ionization equilibrium we estimate Fe XIX/Fe XII emission measure ratios of ∼0.076 just outside the AR core and ∼0.59 in the core.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Brosius, Jeffrey W. [Catholic University of America at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Solar Physics Laboratory, Code 671, Greenbelt, MD 20771 (United States); Daw, Adrian N. [NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Solar Physics Laboratory, Code 671, Greenbelt, MD 20771 (United States); Rabin, D. M., E-mail: Jeffrey.W.Brosius@nasa.gov [NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Heliophysics Science Division, Code 670, Greenbelt, MD 20771 (United States)
2014-08-01
We present spatially resolved EUV spectroscopic measurements of pervasive, faint Fe XIX 592.2 Å line emission in an active region observed during the 2013 April 23 flight of the Extreme Ultraviolet Normal Incidence Spectrograph (EUNIS-13) sounding rocket instrument. With cooled detectors, high sensitivity, and high spectral resolution, EUNIS-13 resolves the lines of Fe XIX at 592.2 Å (formed at temperature T ≈ 8.9 MK) and Fe XII at 592.6 Å (T ≈ 1.6 MK). The Fe XIX line emission, observed over an area in excess of 4920 arcsec{sup 2} (2.58 × 10{sup 9} km{sup 2}, more than 60% of the active region), provides strong evidence for the nanoflare heating model of the solar corona. No GOES events occurred in the region less than 2 hr before the rocket flight, but a microflare was observed north and east of the region with RHESSI and EUNIS during the flight. The absence of significant upward velocities anywhere in the region, particularly the microflare, indicates that the pervasive Fe XIX emission is not propelled outward from the microflare site, but is most likely attributed to localized heating (not necessarily due to reconnection) consistent with the nanoflare heating model of the solar corona. Assuming ionization equilibrium we estimate Fe XIX/Fe XII emission measure ratios of ∼0.076 just outside the AR core and ∼0.59 in the core.
-
Ojha, Roopesh
2012-01-01
The gamma-ray satellite Fermi and the ground based TeV facilities MAGIC, VERITAS and HESS have ushered in a new era in the observation of high-energy emission from active galaxies. The energy budgets of these objects have a major contribution from gamma-rays and it is simply not possible to understand their physics without high-energy observations. Though the exact mechanisms for high-energy production in galaxies remains an open question, gamma-rays typically result from interactions between high-energy particles. Via different interactions these same particles can produce radio emission. Thus the non-thermal nature of gamma-ray emission practically guarantees that high-energy emitters are also radio loud. Aside from their obvious role as a component of multiwavelength analysis, radio observations provide two crucial elements essential to understanding the source structure and physical processes of high-energy emitters: very high timing resolution and very high spatial resolution. A brief overview of the unique role played by radio observations in unraveling the mysteries of the high energy Universe as presented here.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pietsch, W.; Reppin, C.; Truemper, J.; Voges, W.; Kendziorra, E.; Staubert, R.; Tuebingen Univ.
1978-01-01
During a balloon observation from Palestine, Texas, the authors detected for the first time the 1.24 sec pulsation of Hercules X-1 in the hard X-ray range up to 70 keV and discovered strong line emission in its spectrum at 58 keV. They estimated a line flux of 3x10 -3 photons cm -2 sec -1 and a line width of less than 12 keV. The phenomenon is interpreted as electron cyclotron emission at the basic frequency emitted by the hot polar plasma of the rotating neutron star. The line measured leads to a magnetic field strength of 5.3x10 12 gauss. In further observations during a balloon campaign in Sept./Oct. 1977 the authors confirmed the existence of the line emission and for the first time found pulsed X-ray emission above 15 keV during the 'short on' - and 'off'-state of the Her X-1 35 day cycle. The pulse to interpulse ratio seems to vary with the 35 day phase
-
Observing and modelling F-region ionospheric dynamics using the OII 7320A emission
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Carr, S.S.
1992-01-01
Limb-scan observations of Doppler line profiles from the (OII) lambda 7320A emission at F-Region altitudes, made with the Fabry-Perot interferometer (FPI) on the Dynamics Explorer-2 (DE-2) spacecraft, were analyzed to provide measurements of the meridional component of the ion convection velocity along the instrument line-of-sight. The DE-2 results presented demonstrate the first spaceborne use of the remote-sensing Doppler technique for measurements of ionospheric convection. The FPI meridional ion drift measurements were compared with nearly simultaneous in situ ion drift measurements from the Retarding Potential Analyzer (RPA) on DE-2. Once allowance is made for the temporal lag between the in situ and remote measurements, the results from the two techniques are found to be in good agreement, within specified experimental errors, giving confidence in the FPI measurements. The spaceborne interferometric technique has future utility for 2-dimensional imaging of polar ionospheric convection. Results from a simulated space-based observing platform, based on the DE-2 technique and an extension of a 7320A aeronomical model, are presented to demonstrate that a large fraction of the entire polar ionospheric convection pattern can be monitored from space during approximately 16-minute polar passes of a suitably-instrumented satellite. In the simulation, the polar-orbiting satellite's FPI system views the 7320A emission at various tangent point altitudes at +/- 45 deg and +/- 135 deg to the satellite velocity vector. By adjusting the horizon scan angle, several swaths of vectors at different horizontal spacing from the satellite can be recovered. Doppler line profiles from the (OII) 7320A emission at F-Region altitudes, made with the FPI at Sondre Stromfjord, Greenland, were analyzed to provide ion drift vectors and temperatures
-
Wang, Yilong; Broquet, Grégoire; Ciais, Philippe; Chevallier, Frédéric; Vogel, Felix; Wu, Lin; Yin, Yi; Wang, Rong; Tao, Shu
2018-03-01
Combining measurements of atmospheric CO2 and its radiocarbon (14CO2) fraction and transport modeling in atmospheric inversions offers a way to derive improved estimates of CO2 emitted from fossil fuel (FFCO2). In this study, we solve for the monthly FFCO2 emission budgets at regional scale (i.e., the size of a medium-sized country in Europe) and investigate the performance of different observation networks and sampling strategies across Europe. The inversion system is built on the LMDZv4 global transport model at 3.75° × 2.5° resolution. We conduct Observing System Simulation Experiments (OSSEs) and use two types of diagnostics to assess the potential of the observation and inverse modeling frameworks. The first one relies on the theoretical computation of the uncertainty in the estimate of emissions from the inversion, known as posterior uncertainty, and on the uncertainty reduction compared to the uncertainty in the inventories of these emissions, which are used as a prior knowledge by the inversion (called prior uncertainty). The second one is based on comparisons of prior and posterior estimates of the emission to synthetic true emissions when these true emissions are used beforehand to generate the synthetic fossil fuel CO2 mixing ratio measurements that are assimilated in the inversion. With 17 stations currently measuring 14CO2 across Europe using 2-week integrated sampling, the uncertainty reduction for monthly FFCO2 emissions in a country where the network is rather dense like Germany, is larger than 30 %. With the 43 14CO2 measurement stations planned in Europe, the uncertainty reduction for monthly FFCO2 emissions is increased for the UK, France, Italy, eastern Europe and the Balkans, depending on the configuration of prior uncertainty. Further increasing the number of stations or the sampling frequency improves the uncertainty reduction (up to 40 to 70 %) in high emitting regions, but the performance of the inversion remains limited over low
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. Wang
2018-03-01
Full Text Available Combining measurements of atmospheric CO2 and its radiocarbon (14CO2 fraction and transport modeling in atmospheric inversions offers a way to derive improved estimates of CO2 emitted from fossil fuel (FFCO2. In this study, we solve for the monthly FFCO2 emission budgets at regional scale (i.e., the size of a medium-sized country in Europe and investigate the performance of different observation networks and sampling strategies across Europe. The inversion system is built on the LMDZv4 global transport model at 3.75° × 2.5° resolution. We conduct Observing System Simulation Experiments (OSSEs and use two types of diagnostics to assess the potential of the observation and inverse modeling frameworks. The first one relies on the theoretical computation of the uncertainty in the estimate of emissions from the inversion, known as posterior uncertainty, and on the uncertainty reduction compared to the uncertainty in the inventories of these emissions, which are used as a prior knowledge by the inversion (called prior uncertainty. The second one is based on comparisons of prior and posterior estimates of the emission to synthetic true emissions when these true emissions are used beforehand to generate the synthetic fossil fuel CO2 mixing ratio measurements that are assimilated in the inversion. With 17 stations currently measuring 14CO2 across Europe using 2-week integrated sampling, the uncertainty reduction for monthly FFCO2 emissions in a country where the network is rather dense like Germany, is larger than 30 %. With the 43 14CO2 measurement stations planned in Europe, the uncertainty reduction for monthly FFCO2 emissions is increased for the UK, France, Italy, eastern Europe and the Balkans, depending on the configuration of prior uncertainty. Further increasing the number of stations or the sampling frequency improves the uncertainty reduction (up to 40 to 70 % in high emitting regions, but the performance of the inversion
-
observations of hot molecular gas emission from embedded low-mass protostars
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Visser, R.; Kristensen, L. E.; Bruderer, S.
2012-01-01
Aims. Young stars interact vigorously with their surroundings, as evident from the highly rotationally excited CO (up to Eu/k = 4000 K) and H2O emission (up to 600 K) detected by the Herschel Space Observatory in embedded low-mass protostars. Our aim is to construct a model that reproduces...... the observations quantitatively, to investigate the origin of the emission, and to use the lines as probes of the various heating mechanisms. Methods. The model consists of a spherical envelope with a power-law density structure and a bipolar outflow cavity. Three heating mechanisms are considered: passive heating...... such as luminosity and envelope mass. Results. The bulk of the gas in the envelope, heated by the protostellar luminosity, accounts for 3–10% of the CO luminosity summed over all rotational lines up to J = 40–39; it is best probed by low-J CO isotopologue lines such as C18O 2–1 and 3–2. The UV-heated gas and the C...
-
Marbach, T.; Beirle, S.; Khokhar, F.; Platt, U.
2005-12-01
We present case studies for combined HCHO, NO2, and SO2 satellite observations, derived from GOME measurements. Launched on the ERS-2 satellite in April 1995, GOME has already performed continuous operations over 8 years providing global observations of the different trace gases. In this way, satellite observations provide unique opportunities for the identifications of trace gas sources. The satellite HCHO observations provide information concerning the localization of biomass burning (intense source of HCHO). The principal biomass burning areas can be observed in the Amazon basin region and in central Africa Weaker HCHO sources (south east of the United States, northern part of the Amazon basin, and over the African tropical forest), not correlated with biomass burning, could be due to biogenic isoprene emissions. The HCHO data can be compared with NO2 and SO2 results to identify more precisely the tropospheric sources (biomass burning events, human activities, additional sources like volcanic emissions). Biomass burning are important tropospheric sources for both HCHO and NO2. Nevertheless HCHO reflects more precisely the biomass burning as it appears in all biomass burning events. NO2 correlate with HCHO over Africa (grassland fires) but not over Indonesia (forest fires). In south America, an augmentation of the NO2 concentrations can be observed with the fire shift from the forest to grassland vegetation. So there seems to be a dependence between the NO2 emissions during biomass burning and the vegetation type. Other high HCHO, SO2, and NO2 emissions can be correlated with climatic events like the El Nino in 1997, which induced dry conditions in Indonesia causing many forest fires.
-
LOW-FREQUENCY OBSERVATIONS OF TRANSIENT QUASI-PERIODIC RADIO EMISSION FROM THE SOLAR ATMOSPHERE
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Sasikumar Raja, K.; Ramesh, R., E-mail: sasikumar@iiap.res.in [Indian Institute of Astrophysics, II Block, Koramangala, Bangalore 560 034 (India)
2013-09-20
We report low-frequency observations of quasi-periodic, circularly polarized, harmonic type III radio bursts whose associated sunspot active regions were located close to the solar limb. The measured periodicity of the bursts at 80 MHz was ≈5.2 s, and their average degree of circular polarization (dcp) was ≈0.12. We calculated the associated magnetic field B (1) using the empirical relationship between the dcp and B for the harmonic type III emission, and (2) from the observed quasi-periodicity of the bursts. Both the methods result in B ≈ 4.2 G at the location of the 80 MHz plasma level (radial distance r ≈ 1.3 R{sub ☉}) in the active region corona.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Christopher Martin, D.; Chang, Daphne; Matuszewski, Matt; Morrissey, Patrick; Rahman, Shahin; Moore, Anna; Steidel, Charles C.; Matsuda, Yuichi
2014-01-01
The intergalactic medium (IGM) is the dominant reservoir of baryons, delineates the large-scale structure of the universe at low to moderate overdensities, and provides gas from which galaxies form and evolve. Simulations of a cold-dark-matter- (CDM-) dominated universe predict that the IGM is distributed in a cosmic web of filaments and that galaxies should form along and at the intersections of these filaments. While observations of QSO absorption lines and the large-scale distribution of galaxies have confirmed the CDM paradigm, the cosmic web of IGM has never been confirmed by direct imaging. Here we report our observation of the Lyα blob 2 (LAB2) in SSA22 with the Cosmic Web Imager (CWI). This is an integral field spectrograph optimized for low surface brightness, extended emission. With 22 hr of total on- and off-source exposure, CWI has revealed that LAB2 has extended Lyα emission that is organized into azimuthal zones consistent with filaments. We perform numerous tests with simulations and the data to secure the robustness of this result, which relies on data with modest signal-to-noise ratios. We have developed a smoothing algorithm that permits visualization of data cube slices along image or spectral image planes. With both raw and smoothed data cubes we demonstrate that the filaments are kinematically associated with LAB2 and display double-peaked profiles characteristic of optically thick Lyα emission. The flux is 10-20 times brighter than expected for the average emission from the IGM but is consistent with boosted fluorescence from a buried QSO or gravitation cooling radiation. Using simple emission models, we infer a baryon mass in the filaments of at least 1-4 × 10 11 M ☉ , and the dark halo mass is at least 2 × 10 12 M ☉ . The spatial-kinematic morphology is more consistent with inflow from the cosmic web than outflow from LAB2, although an outflow feature maybe present at one azimuth. LAB2 and the surrounding gas have significant and
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Christopher Martin, D.; Chang, Daphne; Matuszewski, Matt; Morrissey, Patrick; Rahman, Shahin [Cahill Center for Astrophysics, California Institute of Technology, 1216 East California Boulevard, Mail Code 278-17, Pasadena, CA 91125 (United States); Moore, Anna [Caltech Optical Observatories, Cahill Center for Astrophysics, California Institute of Technology, 1216 East California Boulevard, Mail Code 11-17, Pasadena, CA 91125 (United States); Steidel, Charles C.; Matsuda, Yuichi, E-mail: cmartin@srl.caltech.edu [Cahill Center for Astrophysics, California Institute of Technology, 1216 East California Boulevard, Mail Code 249-17, Pasadena, CA 91125 (United States)
2014-05-10
The intergalactic medium (IGM) is the dominant reservoir of baryons, delineates the large-scale structure of the universe at low to moderate overdensities, and provides gas from which galaxies form and evolve. Simulations of a cold-dark-matter- (CDM-) dominated universe predict that the IGM is distributed in a cosmic web of filaments and that galaxies should form along and at the intersections of these filaments. While observations of QSO absorption lines and the large-scale distribution of galaxies have confirmed the CDM paradigm, the cosmic web of IGM has never been confirmed by direct imaging. Here we report our observation of the Lyα blob 2 (LAB2) in SSA22 with the Cosmic Web Imager (CWI). This is an integral field spectrograph optimized for low surface brightness, extended emission. With 22 hr of total on- and off-source exposure, CWI has revealed that LAB2 has extended Lyα emission that is organized into azimuthal zones consistent with filaments. We perform numerous tests with simulations and the data to secure the robustness of this result, which relies on data with modest signal-to-noise ratios. We have developed a smoothing algorithm that permits visualization of data cube slices along image or spectral image planes. With both raw and smoothed data cubes we demonstrate that the filaments are kinematically associated with LAB2 and display double-peaked profiles characteristic of optically thick Lyα emission. The flux is 10-20 times brighter than expected for the average emission from the IGM but is consistent with boosted fluorescence from a buried QSO or gravitation cooling radiation. Using simple emission models, we infer a baryon mass in the filaments of at least 1-4 × 10{sup 11} M {sub ☉}, and the dark halo mass is at least 2 × 10{sup 12} M {sub ☉}. The spatial-kinematic morphology is more consistent with inflow from the cosmic web than outflow from LAB2, although an outflow feature maybe present at one azimuth. LAB2 and the surrounding gas
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Osinowo, Olawale O; Olayinka, A Idowu
2012-01-01
Groundwater exploration in either a basement or sedimentary environment is often fairly well defined and focuses on delineating weathered/fractured rocks or saturated formations, respectively. Conversely, unique geological structures, the complex coexistence of different rock types and poorly defined basal/lateral contacts between basement and sedimentary rocks make groundwater development in a geological transition environment very challenging. Ijebu-Ode and its environs lie within such a problematic transition zone, between the Precambrian basement rocks and Cretaceous sediments of the Dahomey Basin, in southwestern Nigeria, where associated acute groundwater development challenges require adequate subsurface information to maximize its groundwater resource potential. This study integrated very low frequency electromagnetic (VLF-EM) and electrical resistivity (ER) geophysical prospecting techniques for a detailed terrain study of Ijebu-Ode in order to establish the reasons for the low groundwater resource potential in the area. Thirty five VLF-EM profiles, 140 vertical electrical soundings (VES) and relevant hydrogeological data were acquired along grids and profiles. Data were filtered, inverted and enhanced using appropriate software packages. The current density and geoelectric parameters of the VLF-EM and VES data were employed to generate terrain maps, the conductivity distribution and a subsurface basement model of the study area. Current density plots and geoelectric parameters identified up to three layers in the basement complex terrain which comprised lateritic topsoil, weathered basement and fresh basement rocks. The five layers encountered in the sedimentary terrain were topsoil, a lateritic unit, a dry sandy unit, a saturated sandy unit and fresh basement rocks. The hydraulic conductivity of the thick (3–18 m) lateritic unit was determined to be 1.32 × 10 −5 mm s −1 , while that of the underlying sandy units ranged from 2.65 × 10 −4 to 1
-
Thiemann, Edward M. B.
Lightning detection and geolocation networks have found widespread use by the utility, air traffic control and forestry industries as a means of locating strikes and predicting imminent recurrence. Accurate lightning geolocation requires detecting VLF radio emissions at multiple sites using a distributed sensor network with typical baselines exceeding 150 km, along with precision time of arrival estimation to triangulate the origin of a strike. The trend has been towards increasing network accuracy without increasing sensor density by incorporating precision GPS synchronized clocks and faster front-end signal processing. Because lightning radio waveforms evolve as they propagate over a finitely conducting earth, and that measurements for a given strike may have disparate propagation path lengths, accurate models are required to determine waveform fiducials for precise strike location. The transition between the leader phase and return stroke phase may offer such a fiducial and warrants quantitative modeling to improve strike location accuracy. The VLF spectrum of the ubiquitous downward negative lightning strike is able to be modeled by the transfer of several Coulombs of negative charge from cloud to ground in a two-step process. The lightning stepped leader ionizes a plasma channel downward from the cloud at a velocity of approximately 0.05c, leaving a column of charge in its path. Upon connection with a streamer, the subsequent return stroke initiates at or near ground level and travels upward at an average but variable velocity of 0.3c. The return stroke neutralizes any negative charge along its path. Subsequent dart leader and return strokes often travel smoothly down the heated channel left by a preceding stroke, lacking the halting motion of the preceding initial stepped leader and initial return stroke. Existing lightning models often neglect the leader current and rely on approximations when solving for the return stroke. In this thesis, I present an
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pashchenko, M.I.; Rudnitskij, G.M.
1980-01-01
In 1978 observations of Herbig-Haro objects and R associations in the 1665 and 1667 MHz main lines of the ground state of the OH molecule have been carried out at the Large radio telescope of the Nancay Radio Astronomy Station (France). Out of the 63 objects searched, the OH emission has been observed in 36 directions. In most cases, the observed line profiles have a simple singlepeak structure, with the line widths of 1-3 km/s. This emission most probably originates in interstellar dust clouds surrounding the Herbig-Haro objects and R associations. Some consequences of the results obtained are briefly discussed. Results of observations show that the quantity of strong maser radio sources near Herbig-Haro objects is not large
-
Sakata, Akira; Wada, Setsuko; Narisawa, Takatoshi; Asano, Yoichi; Iijima, Yutaka; Onaka, Takashi; Tokunaga, Alan T.
1992-01-01
The photoluminescence (fluorescence) of a film of the laboratory-synthesized quenched carbonaceous composite (filmy QCC) is shown to have a single broad emission feature with a peak wavelength that varies from 670 to 725 nm, and coincides with that of the extended red emission observed in reflection nebulae. The rapid decay of the filmy QCC red fluorescence in air and of the stable blue fluorescence of the filmy QCC dissolved in liquid Freon suggests that the red fluorescence originates from the interaction of active chemical species and aromatic components in the filmy QCC. A material similar in nature to that of the filmy QCC may be a major component of interstellar dust.
-
Souri, Amir H.; Choi, Yunsoo; Pan, Shuai; Curci, Gabriele; Nowlan, Caroline R.; Janz, Scott J.; Kowalewski, Matthew G.; Liu, Junjie; Herman, Jay R.; Weinheimer, Andrew J.
2018-03-01
A number of satellite-based instruments have become an essential part of monitoring emissions. Despite sound theoretical inversion techniques, the insufficient samples and the footprint size of current observations have introduced an obstacle to narrow the inversion window for regional models. These key limitations can be partially resolved by a set of modest high-quality measurements from airborne remote sensing. This study illustrates the feasibility of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) columns from the Geostationary Coastal and Air Pollution Events Airborne Simulator (GCAS) to constrain anthropogenic NOx emissions in the Houston-Galveston-Brazoria area. We convert slant column densities to vertical columns using a radiative transfer model with (i) NO2 profiles from a high-resolution regional model (1 × 1 km2) constrained by P-3B aircraft measurements, (ii) the consideration of aerosol optical thickness impacts on radiance at NO2 absorption line, and (iii) high-resolution surface albedo constrained by ground-based spectrometers. We characterize errors in the GCAS NO2 columns by comparing them to Pandora measurements and find a striking correlation (r > 0.74) with an uncertainty of 3.5 × 1015 molecules cm-2. On 9 of 10 total days, the constrained anthropogenic emissions by a Kalman filter yield an overall 2-50% reduction in polluted areas, partly counterbalancing the well-documented positive bias of the model. The inversion, however, boosts emissions by 94% in the same areas on a day when an unprecedented local emissions event potentially occurred, significantly mitigating the bias of the model. The capability of GCAS at detecting such an event ensures the significance of forthcoming geostationary satellites for timely estimates of top-down emissions.
-
X-ray emission on hybird stars: ROSAT observations of alpha Trianguli Australis and iota Aurigae
Kashyap, V.; Rosner, R.; Harnden, F. R., Jr.; Maggio, A.; Micela, G.; Sciortino, S.
1994-01-01
We report on deep ROSAT observations of two Hybrid atmosphere stars, alpha TrA and iota Aur, and our analysis of these observations. We detect high-energy transient phenomena on alpha TrA and consider the implications of this discovery to the atmospheres of Hybrid stars. We detect iota Aur in the high-energy passband of ROSAT, implying the existence of multimillion degree plasma on the star. Our major results include the following: discovery of two large flare events, detected during pointed observations of alpha TrA; the demonstration that the flare emission most likely comes from the giant itself, rather than from a previously unseen low-mass companion star; the demonstration that the plasma characteristics associated with the flares and with the 'quiescent' component are essentially indistinguishable; and that the geometric dimensions of the emitting plasma are considerably smaller than the critical dimension characterizing stable 'hot' coronal loop structures. Our results suggest that alpha TrA does not have any steady X-ray emission consistent with theoretical expectations, and support the argument that Hybrid stars constitute a transitional type of object in which large-scale magnetic dynamo activity ceases, and the dominant spatial scales characterizing coronal structure rapidly decline as such stars evolve across the X-ray 'Dividing Line' in the H-R diagram.
-
Polarisation observations of VY Canis Majoris H2O 5 32-441 620.701 GHz maser emission with HIFI
Harwit, M.; Houde, M.; Sonnentrucker, P.; Boogert, A. C. A.; Cernicharo, J.; De Beck, E.; Decin, L.; Henkel, C.; Higgins, R. D.; Jellema, W.; Kraus, A.; McCoey, C.; Melnick, G. J.; Menten, K. M.; Risacher, C.; Teyssier, D.; Vaillancourt, J. E.; Alcolea, J.; Bujarrabal, V.; Dominik, C.; Justtanont, K.; de Koter, A.; Marston, A.P.; Olofsson, H.; Planesas, P.; Schmidt, M.; Schöier, F. L.; Szczerba, R.; Waters, L.B.F.M.
2010-01-01
Water vapour maser emission from evolved oxygen-rich stars remains poorly understood. Additional observations, including polarisation studies and simultaneous observation of different maser transitions may ultimately lead to greater insight. Aims. We have aimed to elucidate the nature and structure
-
Worldwide biogenic soil NOx emissions inferred from OMI NO2 observations
Vinken, G.C.M.; Boersma, K.F.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Adon, M.; Martin, R.V.
2014-01-01
Biogenic NOx emissions from soils are a large natural source with substantial uncertainties in global bottom-up estimates (ranging from 4 to 15 Tg N yr-1). We reduce this range in emission estimates, and present a top-down soil NOx emission inventory for 2005 based on retrieved tropospheric NO2
-
Worldwide biogenic soil NOx emissions inferred from OMI NO2 observations.
Vinken, G.C.M.; Boersma, K.F.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Adon, M.; Martin, R.V.
2014-01-01
Biogenic NOx emissions from soils are a large natural source with substantial uncertainties in global bottom-up estimates (ranging from 4 to 15 Tg N yr-1). We reduce this range in emission estimates, and present a top-down soil NOx emission inventory for 2005 based on retrieved tropospheric NO2
-
Multispectral Observations of Explosive Gas Emissions from Santiaguito, Guatemala
Carn, S. A.; Watson, M.; Thomas, H.; Rodriguez, L. A.; Campion, R.; Prata, F. J.
2016-12-01
Santiaguito volcano, Guatemala, has been persistently active for decades, producing frequent explosions from its actively growing lava dome. Repeated release of volcanic gases contains information about conduit processes during the cyclical explosions at Santiaguito, but the composition of the gas phase and the amount of volatiles released in each explosion remains poorly constrained. In addition to its persistent activity, Santiaguito offers an exceptional opportunity to investigate lava dome degassing processes since the upper surface of the active lava dome can be viewed from the summit of neighboring Santa Maria. In January 2016 we conducted multi-spectral observations of Santiaguito's explosive eruption plumes and passive degassing from multiple perspectives as part of the first NSF-sponsored `Workshop on Volcanoes' instrument deployment. Gas measurements included open-path Fourier-Transform infrared (OP-FTIR) spectroscopy from the Santa Maria summit, coincident with ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) camera and UV Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS) from the El Mirador site below Santiaguito's active Caliente lava dome. Using the OP-FTIR in passive mode with the Caliente lava dome as the source of IR radiation, we were able to collect IR spectra at high temporal resolution prior to and during two explosions of Santiaguito on 7-8 January, with volcanic SO2 and H2O emissions detected. UV and IR camera data provide constraints on the total SO2 burden in the emissions (and potentially the volcanic ash burden), which coupled with the FTIR gas ratios provides new constraints on the mass and composition of volatiles driving explosions at Santiaguito. All gas measurements indicate significant volatile release during explosions with limited degassing during repose periods. In this presentation we will present ongoing analysis of the unique Santiaguito gas dataset including estimation of the total volatile mass released in explosions and an
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
K. M. Emmerson
2018-05-01
Full Text Available One of the key challenges in atmospheric chemistry is to reduce the uncertainty of biogenic volatile organic compound (BVOC emission estimates from vegetation to the atmosphere. In Australia, eucalypt trees are a primary source of biogenic emissions, but their contribution to Australian air sheds is poorly quantified. The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN has performed poorly against Australian isoprene and monoterpene observations. Finding reasons for the MEGAN discrepancies and strengthening our understanding of biogenic emissions in this region is our focus. We compare MEGAN to the locally produced Australian Biogenic Canopy and Grass Emissions Model (ABCGEM, to identify the uncertainties associated with the emission estimates and the data requirements necessary to improve isoprene and monoterpene emissions estimates for the application of MEGAN in Australia. Previously unpublished, ABCGEM is applied as an online biogenic emissions inventory to model BVOCs in the air shed overlaying Sydney, Australia. The two models use the same meteorological inputs and chemical mechanism, but independent inputs of leaf area index (LAI, plant functional type (PFT and emission factors. We find that LAI, a proxy for leaf biomass, has a small role in spatial, temporal and inter-model biogenic emission variability, particularly in urban areas for ABCGEM. After removing LAI as the source of the differences, we found large differences in the emission activity function for monoterpenes. In MEGAN monoterpenes are partially light dependent, reducing their dependence on temperature. In ABCGEM monoterpenes are not light dependent, meaning they continue to be emitted at high rates during hot summer days, and at night. When the light dependence of monoterpenes is switched off in MEGAN, night-time emissions increase by 90–100 % improving the comparison with observations, suggesting the possibility that monoterpenes emitted from Australian
-
Northwestcape-induced Electron Precipitation and Theoretica Simulation
Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.
2017-12-01
Enhancement of the electron fluxes in the inner radiation belt, which is induced by the powerful North West Cape (NWC) very-low-frequency (VLF) transmitter, have been observed and analyzed by several research groups. However, all of the previous publications have focused on NWC-induced > 100-keV electrons only, based on observations from the Detection of Electro-Magnetic Emissions Transmitted from Earthquake Regions (DEMETER) and the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) satellites. Here, we present flux enhancements with 30-100-keV electrons related to NWC transmitter for the first time, which were observed by the GOES satellite at night. Similar to the 100- 300-keV precipitated-electron behavior, the low energy 30-100-keV electron precipitation is primarily located east of the transmitter. However, the latter does not drift eastward to the same extent as the former, possibly because of the lower electron velocity. The 30-100-keV electrons are distributed in the L = 1.8-2.1 L-shell range, in contrast to the 100-300-keVelectronswhichareatL=1.67-1.9. ThisisconsistentwiththeperspectivethattheenergyoftheVLF-waveinducedelectronfluxenhancementdecreaseswithhigherL-shellvalues. Weexpandupontherationalityofthesimultaneous enhancementofthe30-100-and100-300-keVelectronfluxesthroughcomparisonwiththecyclotronresonancetheoryfor the quasi-linear wave-particle interaction. In addition, we interpret the asymmetry characteristics of NWC electric power distribution in northand south hemisphere by ray tracing model. Finally, we present considerable discussionand showthat good agreement exists between the observation of satellites and theory.
-
Xu, Y.; Fan, M.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Chen, L.
2017-12-01
Open biomass burning which has adverse effects on air quality and human health is an important source of gas and particulate matter (PM) in China. Current emission estimations of open biomass burning are generally based on single source (alternative to statistical data and satellite-derived data) and thus contain large uncertainty due to the limitation of data. In this study, to quantify the 2015-based amount of open biomass burning, we established a new estimation method for open biomass burning activity levels by combining the bottom-up statistical data and top-down MODIS observations. And three sub-category sources which used different activity data were considered. For open crop residue burning, the "best estimate" of activity data was obtained by averaging the statistical data from China statistical yearbooks and satellite observations from MODIS burned area product MCD64A1 weighted by their uncertainties. For the forest and grassland fires, their activity levels were represented by the combination of statistical data and MODIS active fire product MCD14ML. Using the fire radiative power (FRP) which is considered as a better indicator of active fire level as the spatial allocation surrogate, coarse gridded emissions were reallocated into 3km ×3km grids to get a high-resolution emission inventory. Our results showed that emissions of CO, NOx, SO2, NH3, VOCs, PM2.5, PM10, BC and OC in mainland China were 6607, 427, 84, 79, 1262, 1198, 1222, 159 and 686 Gg/yr, respectively. Among all provinces of China, Henan, Shandong and Heilongjiang were the top three contributors to the total emissions. In this study, the developed open biomass burning emission inventory with a high-resolution could support air quality modeling and policy-making for pollution control.
-
The D-Region Ionospheric Response to the 2017 Solar Eclipse
Cohen, M.; McCormick, J.; Gross, N. C.; Higginson-Rollins, M. A.
2017-12-01
VLF/LF radio remote sensing (0.5-500 kHz) is an effective means for quantifying the D-region ionosphere (60-90 km altitude). Disturbances in the ionospheric electron density induce changes in the propagation of VLF/LF signals, so a network of transmitters and receivers can effectively "image" a disturbed region. VLF/LF signals can all be detected from 100s-1000s of km away. We utilize Georgia Tech's network of highly-sensitive VLF/LF receivers to quantify the lower ionospheric response to the "Great American Eclipse". Nine of these were deployed and operational across the Continental US, Alaska and Puerto Rico all operated successfully. Each receiver synchronously recorded the full radio spectrum between 0.5-470 kHz. The included figure shows the eclipse track at 80 km altitude with a green swath. The nine operational receivers are shown with blue stars, and operational VLF/LF transmitters in dark red. Gray lines are shown for each great-circle path linking a VLF/LF transmitter to a receiver. This constellation forms a dense spider's-web grid of radio links, with which we can effectively image the disturbed patch of the D-region ionosphere as it moves across the country. In addition, shown in yellow are NDGPS transmitters which lie between 285-325 kHz. The red dots are the 230,000 geolocated lightning strokes during the 90-mintue eclipse pass, each of which emitted an intense VLF/LF impulse. These are also detected by our receivers. We present our observations and comparison with a theoretical model, using a combination of three techniques established by a series of three 2017 journal papers: (1) Polarization measurements of VLF/LF transmitter signals, (2) Lightning-generated VLF sferics detected 1000s of km away, and (3) NDGPS beacons near 300 kHz for shorter-range sounding of a small patch of the ionosphere. We find evidence of large scale ionospheric changes which affect the D-region over the entire continental region with a slowly-varying signal perturbation
-
Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Crawford, J. H.; Fairlie, T. D.; Chen, G.; Chambers, S. D.; Kang, C. H.; Williams, A. G.; Zhang, K.; Considine, D. B.; Payer Sulprizio, M.; Yantosca, R.
2015-12-01
Convective and synoptic processes play a major role in determining the transport and distribution of trace gases and aerosols in the troposphere. The representation of these processes in global models (at ~100-1000 km horizontal resolution) is challenging, because convection is a sub-grid process and needs to be parameterized, while synoptic processes are close to the grid scale. Depending on the parameterization schemes used in climate models, the role of convection in transporting trace gases and aerosols may vary from model to model. 222Rn is a chemically inert and radioactive gas constantly emitted from soil and has a half-life (3.8 days) comparable to synoptic timescale, which makes it an effective tracer for convective and synoptic transport. In this study, we evaluate the convective and synoptic transport in two chemical transport models (GMI and GEOS-Chem), both driven by the NASA's MERRA reanalysis. Considering the uncertainties in 222Rn emissions, we incorporate two more recent scenarios with regionally varying 222Rn emissions into GEOS-Chem/MERRA and compare the simulation results with those using the relatively uniform 222Rn emissions in the standard model. We evaluate the global distribution and seasonality of 222Rn concentrations simulated by the two models against an extended collection of 222Rn observations from 1970s to 2010s. The intercomparison will improve our understanding of the spatial variability in global 222Rn emissions, including the suspected excessive 222Rn emissions in East Asia, and provide useful feedbacks on 222Rn emission models. We will assess 222Rn vertical distributions at different latitudes in the models using observations at surface sites and in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. Results will be compared with previous models driven by other meteorological fields (e.g., fvGCM and GEOS4). Since the decay of 222Rn is the source of 210Pb, a useful radionuclide tracer attached to submicron aerosols, improved
-
Karan, D. K.; Duggirala, P. R.
2017-12-01
The diurnal variations in daytime airglow emission intensity measurements at three wavelengths OI 777.4 nm, OI 630.0 nm, and OI 557.7 nm made from a low-latitude location, Hyderabad (Geographic 17.50 N, 78.40 E; 8.90 N Mag. Lat) in India have been investigated. The intensity patterns showed both symmetric and asymmetric behavior in their respective diurnal emission variability with respect to local noon. The asymmetric diurnal behavior is not expected considering the photochemical nature of the production mechanisms. The reason for this observed asymmetric diurnal behavior has been found to be predominantly the temporal variation in the equatorial electrodynamics. The plasma that is transported across latitudes due to the action of varying electric field strength over the magnetic equator in the daytime contributes to the asymmetric diurnal behavior in the neutral daytime airglow emissions. Independent magnetic and radio measurements support this finding. It is also noted that this asymmetric diurnal behavior in the neutral emission intensities has a solar cycle dependence with more number of days during high solar activity period showing asymmetric diurnal behavior compared to those during low-solar activity epoch. These intensity variations over long time scale demonstrate that the daytime neutral optical emissions are extremely sensitive to the changes in the eastward electric field over low- and equatorial-latitudes.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tucker, J.E.; Brake, M.L.; Gilgenbach, R.M.
1986-01-01
The authors present the results of axial and radial time resolved visible emission spectroscopy from the afterglow of a dense helium Z-pinch. These results show that the visible emissions in the pinch afterglow are dominated by line emissions from molecular helium and He II. Axial spectroscopy measurements show the occurrence of several absorption bands which cannot be identified as molecular or atomic helium nor impurities from the discharge chamber materials. The authors believe that these absorption bands are attributable to the molecular helium ion which is present in the discharge. The molecular ion has been observed by others in low pressure and temperature helium discharges directly by means of mass spectrometry and indirectly by the presence of helium atoms in the 2/sup 3/S state, (the He 2/sup 3/S state is believed to result from molecular helium ion recombination). However, the molecular helium ion has not previously been observed spectroscopically
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McHardy, I.M.; Pye, J.P.; Fairall, A.P.; Menzies, J.W.
1987-01-01
EXOSAT observations of the intermediate polar cataclysmic variable 3A0729+103 reveal a strong orbital modulation, with the 2-4KeV X-rays being significantly more modulated than the 4-6keV X-rays, indicative of photoelectric absorption. The 913 second modulation which is very prominent in the optical light curve, is weakly detected in the medium-energy X-ray light curve, confirming that it represents the white dwarf spin period. These observations are well explained by a combination of two sources of medium-energy X-ray emission. The presence of two emission regions is also clearly seen in the optical spectroscopy, particularly in the intensity of the He II4686 line which has two peaks during the orbit. The authors identify the two optical emission regions with the two X-ray emission regions. (author)
-
Observations on some thermoluminescence emission centres in geological quartz
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Scholefield, R.B.; Prescott, J.R.; Fox, P.J.; Franklin, A.D.
1994-01-01
We report measurements of three-dimensional thermoluminescence emission spectra of samples of geological quartz, derived from Australian sediments. The emphasis is on peaks of particular practical interest for thermoluminescence sediment dating, viz. the 110 o C peak, which is used for pre-dose dating and the peak at 325 o C, which is of significance for partial and selective bleach techniques and for optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating. Because the 325 o C peak can be bleached to essentially zero, it can be isolated in a given spectrum by subtracting the bleached spectrum from the unbleached spectrum. By including both peaks in the same spectrum, it is demonstrated that they do not emit at the same wavelength, although this does not necessarily mean that the emission is from different emission centres. The 375 o C peak, which is important in total bleach methods, emits at a distinguishable wavelength. The use of bleaching and subtraction in practical dating is discussed. (Author)
-
Greally, B. R.; Manning, A. J.; Reimann, S.; McCulloch, A.; Huang, J.; Dunse, B. L.; Simmonds, P. G.; Prinn, R. G.; Fraser, P. J.; Cunnold, D. M.; O'Doherty, S.; Porter, L. W.; Stemmler, K.; Vollmer, M. K.; Lunder, C. R.; Schmidbauer, N.; Hermansen, O.; Arduini, J.; Salameh, P. K.; Krummel, P. B.; Wang, R. H. J.; Folini, D.; Weiss, R. F.; Maione, M.; Nickless, G.; Stordal, F.; Derwent, R. G.
2007-03-01
Ground-based in situ measurements of 1,1-difluoroethane (HFC-152a, CH3CHF2) which is regulated under the Kyoto Protocol are reported under the auspices of the AGAGE (Advanced Global Atmospheric Gases Experiment) and SOGE (System of Observation of halogenated Greenhouse gases in Europe) programs. Observations of HFC-152a at five locations (four European and one Australian) over a 10 year period were recorded. The annual average growth rate of HFC-152a in the midlatitude Northern Hemisphere has risen from 0.11 ppt/yr to 0.6 ppt/yr from 1994 to 2004. The Southern Hemisphere annual average growth rate has risen from 0.09 ppt/yr to 0.4 ppt/yr from 1998 to 2004. The 2004 average mixing ratio for HFC-152a was 5.0 ppt and 1.8 ppt in the Northern and Southern hemispheres, respectively. The annual cycle observed for this species in both hemispheres is approximately consistent with measured annual cycles at the same locations in other gases which are destroyed by OH. Yearly global emissions of HFC-152a from 1994 to 2004 are derived using the global mean HFC-152a observations and a 12-box 2-D model. The global emission of HFC-152a has risen from 7 Kt/yr to 28 Kt/yr from 1995 to 2004. On the basis of observations of above-baseline elevations in the HFC-152a record and a consumption model, regional emission estimates for Europe and Australia are calculated, indicating accelerating emissions from Europe since 2000. The overall European emission in 2004 ranges from 1.5 to 4.0 Kt/year, 5-15% of global emissions for 1,1-difluoroethane, while the Australian contribution is negligible at 5-10 tonnes/year, <0.05% of global emissions.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wada, A.; Matsueda, H.; Tsuboi, K.; Sawa, Y.; Murayama, S.; Taguchi, S.; Kamada, A.; Nosaka, M.
2012-01-01
We used the observed CO/"2"2"2Rn ratio in the Asian outflows at Minamitorishima (MNM), Yonagunijima (YON), and Ryori (RYO) in the western North Pacific from 2007 to 2011, together with a three-dimensional chemical transport model (STAG), in order to estimate anthropogenic emissions of CO in East Asia. The measurements captured high-frequency synoptic variations of enhanced "2"2"2Rn (ERN) events associated with the long-range transport of continental air masses. "2"2"2Rn and CO showed high correlation during the ERN events observed at MNM and YON in the winter and spring, but not at RYO. The STAG transport model reproduced well the concentrations of observed "2"2"2Rn when forced with a constant and uniform flux density of 1.0 atom cm"-"2 s"-"1, but underestimated the associated enhancement of synoptically variable CO caused by the underestimated flux values in the EDGAR ver. 4.1 emission database used in the model for East Asia. Better estimates for the East Asian emission were derived using a radon tracer method based on the difference in the enhancement ratio of CO/"2"2"2Rn between the observation and the model. The anthropogenic emissions of CO for China, Japan, and Korea were estimated to be 203 Tg CO yr"-"1, 91% of which originated in China. When compared with other estimated emissions of CO, our estimated result showed consistency with those of the inverse method, whereas the emission database of EDGAR was about 45% smaller than our anthropogenic estimation for China.
-
Kuhns, Hampden; Knipping, Eladio M; Vukovich, Jeffrey M
2005-05-01
The Big Bend Regional Aerosol and Visibility Observational (BRAVO) Study was commissioned to investigate the sources of haze at Big Bend National Park in southwest Texas. The modeling domain of the BRAVO Study includes most of the continental United States and Mexico. The BRAVO emissions inventory was constructed from the 1999 National Emission Inventory for the United States, modified to include finer-resolution data for Texas and 13 U.S. states in close proximity. The first regional-scale Mexican emissions inventory designed for air-quality modeling applications was developed for 10 northern Mexican states, the Tula Industrial Park in the state of Hidalgo, and the Popocatépetl volcano in the state of Puebla. Emissions data were compiled from numerous sources, including the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the Texas Natural Resources Conservation Commission (now Texas Commission on Environmental Quality), the Eastern Research Group, the Minerals Management Service, the Instituto Nacional de Ecología, and the Instituto Nacional de Estadistica Geografía y Informática. The inventory includes emissions for CO, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), ammonia, particulate matter (PM) < 10 microm in aerodynamic diameter, and PM < 2.5 microm in aerodynamic diameter. Wind-blown dust and biomass burning were not included in the inventory, although high concentrations of dust and organic PM attributed to biomass burning have been observed at Big Bend National Park. The SMOKE modeling system was used to generate gridded emissions fields for use with the Regional Modeling System for Aerosols and Deposition (REMSAD) and the Community Multiscale Air Quality model modified with the Model of Aerosol Dynamics, Reaction, Ionization and Dissolution (CMAQ-MADRID). The compilation of the inventory, supporting model input data, and issues encountered during the development of the inventory are documented. A comparison of the BRAVO emissions
-
Lee, Chulkyu; Martin Randall V.; vanDonkelaar, Aaron; Lee, Hanlim; Dickerson, RUssell R.; Hains, Jennifer C.; Krotkov, Nickolay; Richter, Andreas; Vinnikov, Konstantine; Schwab, James J.
2011-01-01
Top-down constraints on global sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions are inferred through inverse modeling using SO2 column observations from two satellite instruments (SCIAMACHY and OMI). We first evaluated the S02 column observations with surface SO2 measurements by applying local scaling factors from a global chemical transport model (GEOS-Chem) to SO2 columns retrieved from the satellite instruments. The resulting annual mean surface SO2 mixing ratios for 2006 exhibit a significant spatial correlation (r=0.86, slope=0.91 for SCIAMACHY and r=0.80, slope = 0.79 for OMI) with coincident in situ measurements from monitoring networks throughout the United States and Canada. We evaluate the GEOS-Chem simulation of the SO2 lifetime with that inferred from in situ measurements to verity the applicability of GEOS-Chem for inversion of SO2 columns to emissions. The seasonal mean SO2 lifetime calculated with the GEOS-Chem model over the eastern United States is 13 h in summer and 48 h in winter, compared to lifetimes inferred from in situ measurements of 19 +/- 7 h in summer and 58 +/- 20 h in winter. We apply SO2 columns from SCIAMACHY and OMI to derive a top-down anthropogenic SO2 emission inventory over land by using the local GEOS-Chem relationship between SO2 columns and emissions. There is little seasonal variation in the top-down emissions (SO2 emissions (52.4 Tg S/yr from SCIAMACHY and 49.9 Tg S / yr from OMI) closely agrees with the bottom-up emissions (54.6 Tg S/yr) in the GEOS-Chem model and exhibits consistency in global distributions with the bottom-up emissions (r = 0.78 for SCIAMACHY, and r = 0.77 for OMI). However, there are significant regional differences.
-
Aperture synthesis observations of solar and stellar radio emission
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bastian, T.S.
1987-01-01
The work presented in this thesis relied upon the radio astronomical instrument, The Very Large Array. The thesis is divided into three major sections. In the first the author applied maximum entropy-type image reconstruction techniques, using both single dish and iterferometer data, to generate full disk images of the Sun at a wavelength λ ∼ 21 cm. Using a set of six such images obtained during the Sun's decline from sunspot maximum to minimum, he has noted a number of previously unreported phenomena. Among these: (1) a systematic decrease in quiet Sun's brightness temperature as it declined to minimum; (2) a systematic decrease in the Sun's radius at 21 cm; (3) evidence for the evolution of polar coronal holes during the course of the solar cycle. The observed variation, though not noted previously at radio wavelengths, is entirely consistent with white light K coronagraph data. The results reported here explain the conflicting nature of a number of past observations. In the second section of the thesis, he presents the results of a long term survey of magnetic cataclysmic variables (CVs). Cataclysmic variables are close binary systems which contain a white dwarf accreting mass from a late-type secondary, typically a dwarf of spectral type, G, K, or M. The survey resulted in the detection of two out of the eighteen systems observed. In the third section of the thesis, he presents new results on flare stars in the solar neighborhood and in the Pleiades. He has successfully employed the technique of dynamic spectroscopy to constrain the mechanisms(s) for radio flaring on other stars. The second part of section three is devoted to a search for radio emission from flare stars in the Pleiades which was motivated by the evolutionary questions raised by flare stars and the Pleiades lower main sequence
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Gregoire, S. [CRITT Materiaux Alsace, 19 rue de St Junien, 67300 Schiltigheim (France); Laboratoire de Recherche des Monuments Historiques, 29 rue de Paris, 77420 Champs-sur-Marne (France); Institut Charles Sadron, CNRS and University of Strasbourg, 23 rue de Loess, 67034 Strasbourg Cedex (France); Motto-Ros, V.; Ma, Q.L.; Lei, W.Q.; Wang, X.C. [Universite de Lyon, F-69622, Lyon, France, Universite Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, CNRS, UMR5579, LASIM (France); Pelascini, F.; Surma, F. [CRITT Materiaux Alsace, 19 rue de St Junien, 67300 Schiltigheim (France); Detalle, V., E-mail: vincent.detalle@culture.gouv.fr [Laboratoire de Recherche des Monuments Historiques, 29 rue de Paris, 77420 Champs-sur-Marne (France); Yu, J. [Universite de Lyon, F-69622, Lyon, France, Universite Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, CNRS, UMR5579, LASIM (France)
2012-08-15
Emissions from C{sub 2} molecules and CN radicals in laser-induced plasmas on polymeric materials were observed with time-resolved spectroscopic imaging. More precisely, differential imaging with a pair of narrowband filters (one centered on the emission line and another out of the line) was used to extract emission images of interested molecules or radicals. The correlation between the molecular emission image of the plasma and the molecular structure of the polymer to be analyzed was studied for four different types of materials: polyamide (PA) with native CN bonds, polyethylene (PE) with simple CC bonds, polystyrene (PS) with delocalized double CC bonds, and polyoxymethylene (POM) which neither contains CC nor CN bonds. A clear correlation is demonstrated between emission and molecular structure of the material, allowing the identification of several organic compounds by differential spectroscopic imaging. - Highlights: Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Plasma imaging method to discriminate different type of polymers. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Molecular emissions (CN and C{sub 2}) are spatially and temporally correlated to native bonds. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Several formation processes of molecular fragments are observed.
-
Broad Line Radio Galaxies Observed with Fermi-LAT: The Origin of the GeV Gamma-Ray Emission
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kataoka, J.; /Waseda U., RISE; Stawarz, L.; /JAXA, Sagamihara /Jagiellonian U., Astron. Observ.; Takahashi, Y.; /Waseda U., RISE; Cheung, C.C.; /Natl. Acad. Sci. /Naval Research Lab, Wash., D.C.; Hayashida, M.; /SLAC /Stanford U., HEPL /KIPAC, Menlo Park; Grandi, P.; /Bologna Observ.; Burnett, T.H.; /Washington U., Seattle; Celotti, A.; /SISSA, Trieste; Fegan, S.J.; Fortin, P.; /Ecole Polytechnique; Maeda, K.; Nakamori, T.; /Waseda U., RISE; Taylor, G.B.; /New Mexico U.; Tosti, G.; /INFN, Perugia /Perugia U.; Digel, S.W.; /SLAC /Stanford U., HEPL /KIPAC, Menlo Park; McConville, W.; /NASA, Goddard /Maryland U.; Finke, J.; /Naval Research Lab, Wash., D.C.; D' Ammando, F.; /IASF, Palermo /INAF, Rome
2012-06-07
We report on a detailed investigation of the {gamma}-ray emission from 18 broad line radio galaxies (BLRGs) based on two years of Fermi Large Area Telescope (LAT) data. We confirm the previously reported detections of 3C 120 and 3C 111 in the GeV photon energy range; a detailed look at the temporal characteristics of the observed {gamma}-ray emission reveals in addition possible flux variability in both sources. No statistically significant {gamma}-ray detection of the other BLRGs was however found in the considered dataset. Though the sample size studied is small, what appears to differentiate 3C 111 and 3C 120 from the BLRGs not yet detected in {gamma}-rays is the particularly strong nuclear radio flux. This finding, together with the indications of the {gamma}-ray flux variability and a number of other arguments presented, indicate that the GeV emission of BLRGs is most likely dominated by the beamed radiation of relativistic jets observed at intermediate viewing angles. In this paper we also analyzed a comparison sample of high accretion-rate Seyfert 1 galaxies, which can be considered radio-quiet counterparts of BLRGs, and found none were detected in {gamma}-rays. A simple phenomenological hybrid model applied for the broad-band emission of the discussed radio-loud and radio-quiet type 1 active galaxies suggests that the relative contribution of the nuclear jets to the accreting matter is {ge} 1% on average for BLRGs, while {le} 0.1% for Seyfert 1 galaxies.
-
The High Energy Photons Emission from Solar Flares Observed by SZ2-XD
Wang, Huanyu; Li, Xinqiao; Ma, Yuqian; Zhang, Chengmo; Xu, Yupeng; Wang, Jingzhou; Chen, Guoming
The spectra and light curve of near a hundred Solar X-ray Flare events, which were observed by SZ2/XD in the energy band of 10-800 keV during 2001, have been investigated. The events covered from C to X-class flares, which are shown different characters of high energy photons emission. The results will be presented in this paper. The discussions will be made especially for 3 of the brightest X-class solar flares SF010402(X20),SF010406(X5.6) and SF010415 (X14.4, a GLE event).
-
Polarisation observations of VY Canis Majoris H2O 5(32)-4(41) 620.701 GHz maser emission with HIFI
Harwit, M.; Houde, M.; Sonnentrucker, P.; Boogert, A. C. A.; Cernicharo, J.; de Beck, E.; Decin, L.; Henkel, C.; Higgins, R. D.; Jellema, W.; Kraus, A.; McCoey, C.; Melnick, G. J.; Menten, K. M.; Risacher, C.; Teyssier, D.; Vaillancourt, J. E.; Alcolea, J.; Bujarrabal, V.; Dominik, C.; Justtanont, K.; de Koter, A.; Marston, A. P.; Olofsson, H.; Planesas, P.; Schmidt, M.; Schöier, F. L.; Szczerba, R.; Waters, L. B. F. M.
2010-01-01
Context. Water vapour maser emission from evolved oxygen-rich stars remains poorly understood. Additional observations, including polarisation studies and simultaneous observation of different maser transitions may ultimately lead to greater insight. Aims. We have aimed to elucidate the nature and
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Takahashi, H.; Sahai, Y.; Batista, P.P.
1984-01-01
The upper mesosphere airglow emissions OI 5577, NaD and OH have been observed at Cachoeira Paulista (22.7 deg S; 45.0 deg W) Brazil. Nocturnal variations and their seasonal dependencies in amplitude and phase, and the annual variations of these emissions are presented, analysing the data obtained from 1977 to 1982 during the ascending phase of the last solar cycle. The nocturnal variations of the OI 5577 emission and the OH rotational temperature showed a significant semidiurnal oscillation, with the phase of maximum moving from midnight in January to early morning in June. Semiannual variation of the OI 5577 and NaD emissions with the maximum intensities in April/May and October/November were observed. The OH rotational temperature, however, showed an annual variation, maximum in summer and minimum in winter, while no significant seasonal variation was found in the OH emission intensities. Long-term intensity variations are also presented with the solar sunspot numbers and the 10.7 cm flux. (author)
-
Hitomi observations of the LMC SNR N 132 D: Highly redshifted X-ray emission from iron ejecta
Hitomi Collaboration; Aharonian, Felix; Akamatsu, Hiroki; Akimoto, Fumie; Allen, Steven W.; Angelini, Lorella; Audard, Marc; Awaki, Hisamitsu; Axelsson, Magnus; Bamba, Aya; Bautz, Marshall W.; Blandford, Roger; Brenneman, Laura W.; Brown, Gregory V.; Bulbul, Esra; Cackett, Edward M.; Chernyakova, Maria; Chiao, Meng P.; Coppi, Paolo S.; Costantini, Elisa; de Plaa, Jelle; de Vries, Cor P.; den Herder, Jan-Willem; Done, Chris; Dotani, Tadayasu; Ebisawa, Ken; Eckart, Megan E.; Enoto, Teruaki; Ezoe, Yuichiro; Fabian, Andrew C.; Ferrigno, Carlo; Foster, Adam R.; Fujimoto, Ryuichi; Fukazawa, Yasushi; Furuzawa, Akihiro; Galeazzi, Massimiliano; Gallo, Luigi C.; Gandhi, Poshak; Giustini, Margherita; Goldwurm, Andrea; Gu, Liyi; Guainazzi, Matteo; Haba, Yoshito; Hagino, Kouichi; Hamaguchi, Kenji; Harrus, Ilana M.; Hatsukade, Isamu; Hayashi, Katsuhiro; Hayashi, Takayuki; Hayashida, Kiyoshi; Hiraga, Junko S.; Hornschemeier, Ann; Hoshino, Akio; Hughes, John P.; Ichinohe, Yuto; Iizuka, Ryo; Inoue, Hajime; Inoue, Yoshiyuki; Ishida, Manabu; Ishikawa, Kumi; Ishisaki, Yoshitaka; Iwai, Masachika; Kaastra, Jelle; Kallman, Tim; Kamae, Tsuneyoshi; Kataoka, Jun; Katsuda, Satoru; Kawai, Nobuyuki; Kelley, Richard L.; Kilbourne, Caroline A.; Kitaguchi, Takao; Kitamoto, Shunji; Kitayama, Tetsu; Kohmura, Takayoshi; Kokubun, Motohide; Koyama, Katsuji; Koyama, Shu; Kretschmar, Peter; Krimm, Hans A.; Kubota, Aya; Kunieda, Hideyo; Laurent, Philippe; Lee, Shiu-Hang; Leutenegger, Maurice A.; Limousin, Olivier; Loewenstein, Michael; Long, Knox S.; Lumb, David; Madejski, Greg; Maeda, Yoshitomo; Maier, Daniel; Makishima, Kazuo; Markevitch, Maxim; Matsumoto, Hironori; Matsushita, Kyoko; McCammon, Dan; McNamara, Brian R.; Mehdipour, Missagh; Miller, Eric D.; Miller, Jon M.; Mineshige, Shin; Mitsuda, Kazuhisa; Mitsuishi, Ikuyuki; Miyazawa, Takuya; Mizuno, Tsunefumi; Mori, Hideyuki; Mori, Koji; Mukai, Koji; Murakami, Hiroshi; Mushotzky, Richard F.; Nakagawa, Takao; Nakajima, Hiroshi; Nakamori, Takeshi; Nakashima, Shinya; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro; Nobukawa, Kumiko K.; Nobukawa, Masayoshi; Noda, Hirofumi; Odaka, Hirokazu; Ohashi, Takaya; Ohno, Masanori; Okajima, Takashi; Ota, Naomi; Ozaki, Masanobu; Paerels, Frits; Paltani, Stéphane; Petre, Robert; Pinto, Ciro; Porter, Frederick S.; Pottschmidt, Katja; Reynolds, Christopher S.; Safi-Harb, Samar; Saito, Shinya; Sakai, Kazuhiro; Sasaki, Toru; Sato, Goro; Sato, Kosuke; Sato, Rie; Sato, Toshiki; Sawada, Makoto; Schartel, Norbert; Serlemtsos, Peter J.; Seta, Hiromi; Shidatsu, Megumi; Simionescu, Aurora; Smith, Randall K.; Soong, Yang; Stawarz, Łukasz; Sugawara, Yasuharu; Sugita, Satoshi; Szymkowiak, Andrew; Tajima, Hiroyasu; Takahashi, Hiromitsu; Takahashi, Tadayuki; Takeda, Shin'ichiro; Takei, Yoh; Tamagawa, Toru; Tamura, Takayuki; Tanaka, Takaaki; Tanaka, Yasuo; Tanaka, Yasuyuki T.; Tashiro, Makoto S.; Tawara, Yuzuru; Terada, Yukikatsu; Terashima, Yuichi; Tombesi, Francesco; Tomida, Hiroshi; Tsuboi, Yohko; Tsujimoto, Masahiro; Tsunemi, Hiroshi; Tsuru, Takeshi Go; Uchida, Hiroyuki; Uchiyama, Hideki; Uchiyama, Yasunobu; Ueda, Shutaro; Ueda, Yoshihiro; Uno, Shin'ichiro; Urry, C. Megan; Ursino, Eugenio; Watanabe, Shin; Werner, Norbert; Wilkins, Dan R.; Williams, Brian J.; Yamada, Shinya; Yamaguchi, Hiroya; Yamaoka, Kazutaka; Yamasaki, Noriko Y.; Yamauchi, Makoto; Yamauchi, Shigeo; Yaqoob, Tahir; Yatsu, Yoichi; Yonetoku, Daisuke; Zhuravleva, Irina; Zoghbi, Abderahmen
2018-03-01
We present Hitomi observations of N 132 D, a young, X-ray bright, O-rich core-collapse supernova remnant in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). Despite a very short observation of only 3.7 ks, the Soft X-ray Spectrometer (SXS) easily detects the line complexes of highly ionized S K and Fe K with 16-17 counts in each. The Fe feature is measured for the first time at high spectral resolution. Based on the plausible assumption that the Fe K emission is dominated by He-like ions, we find that the material responsible for this Fe emission is highly redshifted at ˜ 800 km s-1 compared to the local LMC interstellar medium (ISM), with a 90% credible interval of 50-1500 km s-1 if a weakly informative prior is placed on possible line broadening. This indicates (1) that the Fe emission arises from the supernova ejecta, and (2) that these ejecta are highly asymmetric, since no blueshifted component is found. The S K velocity is consistent with the local LMC ISM, and is likely from swept-up ISM material. These results are consistent with spatial mapping that shows the He-like Fe concentrated in the interior of the remnant and the S tracing the outer shell. The results also show that even with a very small number of counts, direct velocity measurements from Doppler-shifted lines detected in extended objects like supernova remnants are now possible. Thanks to the very low SXS background of ˜ 1 event per spectral resolution element per 100 ks, such results are obtainable during short pointed or slew observations with similar instruments. This highlights the power of high-spectral-resolution imaging observations, and demonstrates the new window that has been opened with Hitomi and will be greatly widened with future missions such as the X-ray Astronomy Recovery Mission (XARM) and Athena.
-
Maury, A. J.; Girart, J. M.; Zhang, Q.; Hennebelle, P.; Keto, E.; Rao, R.; Lai, S.-P.; Ohashi, N.; Galametz, M.
2018-06-01
The role of the magnetic field during protostellar collapse is poorly constrained from an observational point of view, although it could be significant if we believe state-of-the-art models of protostellar formation. We present polarimetric observations of the 233 GHz thermal dust continuum emission obtained with ALMA in the B335 Class 0 protostar. Linearly polarized dust emission arising from the circumstellar material in the envelope of B335 is detected at all scales probed by our observations (50 to 1000 au). The magnetic field structure producing the dust polarization has a very ordered topology in the inner envelope, with a transition from a large-scale poloidal magnetic field, in the outflow direction, to strongly pinched in the equatorial direction. This is probably due to magnetic field lines being dragged along the dominating infall direction since B335 does not exhibit prominent rotation. Our data and their qualitative comparison to a family of magnetized protostellar collapse models show that, during the magnetized collapse in B335, the magnetic field is maintaining a high level of organization from scales 1000 au to 50 au: this suggests the field is dynamically relevant and capable of influencing the typical outcome of protostellar collapse, such as regulating the disc size in B335.
-
Maury, A. J.; Girart, J. M.; Zhang, Q.; Hennebelle, P.; Keto, E.; Rao, R.; Lai, S.-P.; Ohashi, N.; Galametz, M.
2018-03-01
The role of the magnetic field during protostellar collapse is poorly constrained from an observational point of view, although it could be significant if we believe state-of-the-art models of protostellar formation. We present polarimetric observations of the 233 GHz thermal dust continuum emission obtained with ALMA in the B335 Class 0 protostar. Linearly polarized dust emission arising from the circumstellar material in the envelope of B335 is detected at all scales probed by our observations, from radii of 50 to 1000 au. The magnetic field structure producing the dust polarization has a very ordered topology in the inner envelope, with a transition from a large-scale poloidal magnetic field, in the outflow direction, to strongly pinched in the equatorial direction. This is probably due to magnetic field lines being dragged along the dominating infall direction since B335 does not exhibit prominent rotation. Our data and their qualitative comparison to a family of magnetized protostellar collapse models show that, during the magnetized collapse in B335, the magnetic field is maintaining a high level of organization from scales 1000 au to 50 au: this suggests the field is dynamically relevant and capable of influencing the typical outcome of protostellar collapse, such as regulating the disk size in B335.
-
MILAGRO OBSERVATIONS OF MULTI-TeV EMISSION FROM GALACTIC SOURCES IN THE FERMI BRIGHT SOURCE LIST
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Abdo, A. A.; Linnemann, J. T.; Allen, B. T.; Chen, C.; Aune, T.; Berley, D.; Goodman, J. A.; Christopher, G. E.; Kolterman, B. E.; Mincer, A. I.; Nemethy, P.; DeYoung, T.; Dingus, B. L.; Hoffman, C. M.; Ellsworth, R. W.; Gonzalez, M. M.; Hays, E.; McEnery, J. E.; Huentemeyer, P. H.; Morgan, T.
2009-01-01
We present the result of a search of the Milagro sky map for spatial correlations with sources from a subset of the recent Fermi Bright Source List (BSL). The BSL consists of the 205 most significant sources detected above 100 MeV by the Fermi Large Area Telescope. We select sources based on their categorization in the BSL, taking all confirmed or possible Galactic sources in the field of view of Milagro. Of the 34 Fermi sources selected, 14 are observed by Milagro at a significance of 3 standard deviations or more. We conduct this search with a new analysis which employs newly optimized gamma-hadron separation and utilizes the full eight-year Milagro data set. Milagro is sensitive to gamma rays with energy from 1 to 100 TeV with a peak sensitivity from 10 to 50 TeV depending on the source spectrum and declination. These results extend the observation of these sources far above the Fermi energy band. With the new analysis and additional data, multi-TeV emission is definitively observed associated with the Fermi pulsar, J2229.0+6114, in the Boomerang pulsar wind nebula (PWN). Furthermore, an extended region of multi-TeV emission is associated with the Fermi pulsar, J0634.0+1745, the Geminga pulsar.
-
Zhang, B.; Yao, Y.; Xu, R.; Yang, J.; WANG, Z.; Pan, S.; Tian, H.
2016-12-01
The atmospheric concentration of nitrous oxide (N2O), one of major greenhouse gases, has increased over 121% compared with the preindustrial level, and most of the increase arises from anthropogenic activities. Previous studies suggested that indirect emissions from global rivers remains a large source of uncertainty among all the N2O sources and restricted the assessment of N2O budget at both regional and global scales. Here, we have integrated a coupled biogeochemical model (DLEM) with observational data to quantify the magnitude and spatio-temporal variation of riverine N2O emission and attribute the environmental controls of indirect N2O emission from major rivers in the world. Our preliminary results indicate that the magnitude of indirect N2O emission from rivers is closely associated with the stream orders. To include N2O emissions from headwater streams is essential for reducing uncertainty in the estimation of indirect N2O emission. By implementing a set of factorial simulations, we have further quantified the relative contributions of climate, nitrogen deposition, nitrogen fertilizer use, and manure application to riverine N2O emission. Finally, this study has identified major knowledge gaps and uncertainties associated with model structure, parameters and input data that need to be improved in future research.
-
Cecconi, Baptiste; Hess, Sebastien; Le Sidaner, Pierre; Savalle, Renaud; Stéphane, Erard; Coffre, Andrée; Thétas, Emmanuel; André, Nicolas; Génot, Vincent; Thieman, Jim; Typinski, Dave; Sky, Jim; Higgins, Chuck; Imai, Masafumi
2016-04-01
In the frame of the preparation of the NASA/JUNO and ESA/JUICE (Jupiter Icy Moon Explorer) missions, and the development of a planetary sciences virtual observatory (VO), we are proposing a new set of tools directed to data providers as well as users, in order to ease data sharing and discovery. We will focus on ground based planetary radio observations (thus mainly Jupiter radio emissions), trying for instance to enhance the temporal coverage of jovian decametric emission. The data service we will be using is EPN-TAP, a planetary science data access protocol developed by Europlanet-VESPA (Virtual European Solar and Planetary Access). This protocol is derived from IVOA (International Virtual Observatory Alliance) standards. The Jupiter Routine Observations from the Nancay Decameter Array are already shared on the planetary science VO using this protocol, as well as data from the Iitate Low Frquency Radio Antenna, in Japan. Amateur radio data from the RadioJOVE project is also available. The attached figure shows data from those three providers. We will first introduce the VO tools and concepts of interest for the planetary radioastronomy community. We will then present the various data formats now used for such data services, as well as their associated metadata. We will finally show various prototypical tools that make use of this shared datasets.
-
Aging in autonomic control by multifractal studies of cardiac interbeat intervals in the VLF band
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Makowiec, Danuta; Kryszewski, Stanisław; Rynkiewicz, Andrzej; Wdowczyk-Szulc, Joanna; Żarczyńska-Buchowiecka, Marta; Gałąska, Rafał
2011-01-01
The heart rate responds dynamically to various intrinsic and environmental stimuli. The autonomic nervous system is said to play a major role in this response. Multifractal analysis offers a novel method to assess the response of cardiac interbeat intervals. Twenty-four hour ECG recordings of RR interbeat intervals (of 48 elderly volunteers (age 65–94), 40 middle-aged persons (age 45–53) and 36 young adults (age 18–26)) were investigated to study the effect of aging on autonomic regulation during normal activity in healthy adults. Heart RR-interval variability in the very low frequency (VLF) band (32–420 RR intervals) was evaluated by multifractal tools. The nocturnal and diurnal signals of 6 h duration were studied separately. For each signal, the analysis was performed twice: for a given signal and for the integrated signal. A multifractal spectrum was quantified by the h max value at which a multifractal spectrum attained its maximum, width of a spectrum, Hurst exponent, extreme events h left and distance between the maxima of a signal and its integrated counterpart. The following seven characteristics are suggested as quantifying the age-related decrease in the autonomic function ('int' refers to the integrated signal): (a) h sleep max − h max wake > 0.05 for a signal; (b) h int max > 1.15 for wake; (c) h int max − h max > 0.85 for sleep; (d) Hurst wake − Hurst sleep < 0.01; (e) width wake > 0.07; (f) width int < 0.30 for sleep; (g) h int left > 0.75. Eighty-one percent of elderly people had at least four of these properties, and ninety-two percent of young people had three or less. This shows that the multifractal approach offers a concise and reliable index of healthy aging for each individual. Additionally, the applied method yielded insights into dynamical changes in the autonomic regulation due to the circadian cycle and aging. Our observations support the hypothesis that imbalance in the autonomic control due to healthy aging could
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
L. Meng
2012-07-01
Full Text Available Methane emissions from natural wetlands and rice paddies constitute a large proportion of atmospheric methane, but the magnitude and year-to-year variation of these methane sources are still unpredictable. Here we describe and evaluate the integration of a methane biogeochemical model (CLM4Me; Riley et al., 2011 into the Community Land Model 4.0 (CLM4CN in order to better explain spatial and temporal variations in methane emissions. We test new functions for soil pH and redox potential that impact microbial methane production in soils. We also constrain aerenchyma in plants in always-inundated areas in order to better represent wetland vegetation. Satellite inundated fraction is explicitly prescribed in the model, because there are large differences between simulated fractional inundation and satellite observations, and thus we do not use CLM4-simulated hydrology to predict inundated areas. A rice paddy module is also incorporated into the model, where the fraction of land used for rice production is explicitly prescribed. The model is evaluated at the site level with vegetation cover and water table prescribed from measurements. Explicit site level evaluations of simulated methane emissions are quite different than evaluating the grid-cell averaged emissions against available measurements. Using a baseline set of parameter values, our model-estimated average global wetland emissions for the period 1993–2004 were 256 Tg CH4 yr−1 (including the soil sink and rice paddy emissions in the year 2000 were 42 Tg CH4 yr−1. Tropical wetlands contributed 201 Tg CH4 yr−1, or 78% of the global wetland flux. Northern latitude (>50 N systems contributed 12 Tg CH4 yr−1. However, sensitivity studies show a large range (150–346 Tg CH4 yr−1 in predicted global methane emissions (excluding emissions from rice paddies. The large range is
-
Propagation of a whistler wave incident from above on the lower nighttime ionosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Bespalov
2017-05-01
Full Text Available The problems of reflection and transmission of a whistler wave incident in the nighttime ionosphere from above are considered. Numerical solution of the wave equations for a typical condition of the lower ionosphere is found. The solution area comprises both the region of strong wave refraction and a sharp boundary of the nighttime ionosphere (∼ 100 km. The energy reflection coefficient and horizontal wave magnetic field on the ground surface are calculated. The results obtained are important for analysis of the extremely low-frequency and very low-frequency (ELF–VLF emission phenomena observed from both the satellites and the ground-based observatories.
-
Arnold, N. D.; Attig, J.; Banks, G.; Bechtold, R.; Beczek, K.; Benson, C.; Berg, S.; Berg, W.; Biedron, S. G.; Biggs, J. A.; Borland, M.; Boerste, K.; Bosek, M.; Brzowski, W. R.; Budz, J.; Carwardine, J. A.; Castro, P.; Chae, Y.-C.; Christensen, S.; Clark, C.; Conde, M.; Crosbie, E. A.; Decker, G. A.; Dejus, R. J.; DeLeon, H.; Den Hartog, P. K.; Deriy, B. N.; Dohan, D.; Dombrowski, P.; Donkers, D.; Doose, C. L.; Dortwegt, R. J.; Edwards, G. A.; Eidelman, Y.; Erdmann, M. J.; Error, J.; Ferry, R.; Flood, R.; Forrestal, J.; Freund, H.; Friedsam, H.; Gagliano, J.; Gai, W.; Galayda, J. N.; Gerig, R.; Gilmore, R. L.; Gluskin, E.; Goeppner, G. A.; Goetzen, J.; Gold, C.; Gorski, A. J.; Grelick, A. E.; Hahne, M. W.; Hanuska, S.; Harkay, K. C.; Harris, G.; Hillman, A. L.; Hogrefe, R.; Hoyt, J.; Huang, Z.; Jagger, J. M.; Jansma, W. G.; Jaski, M.; Jones, S. J.; Keane, R. T.; Kelly, A. L.; Keyser, C.; Kim, K.-J.; Kim, S. H.; Kirshenbaum, M.; Klick, J. H.; Knoerzer, K.; Koldenhoven, R. J.; Knott, M.; Labuda, S.; Laird, R.; Lang, J.; Lenkszus, F.; Lessner, E. S.; Lewellen, J. W.; Li, Y.; Lill, R. M.; Lumpkin, A. H.; Makarov, O. A.; Markovich, G. M.; McDowell, M.; McDowell, W. P.; McNamara, P. E.; Meier, T.; Meyer, D.; Michalek, W.; Milton, S. V.; Moe, H.; Moog, E. R.; Morrison, L.; Nassiri, A.; Noonan, J. R.; Otto, R.; Pace, J.; Pasky, S. J.; Penicka, J. M.; Pietryla, A. F.; Pile, G.; Pitts, C.; Power, J.; Powers, T.; Putnam, C. C.; Puttkammer, A. J.; Reigle, D.; Reigle, L.; Ronzhin, D.; Rotela, E. R.; Russell, E. F.; Sajaev, V.; Sarkar, S.; Scapino, J. C.; Schroeder, K.; Seglem, R. A.; Sereno, N. S.; Sharma, S. K.; Sidarous, J. F.; Singh, O.; Smith, T. L.; Soliday, R.; Sprau, G. A.; Stein, S. J.; Stejskal, B.; Svirtun, V.; Teng, L. C.; Theres, E.; Thompson, K.; Tieman, B. J.; Torres, J. A.; Trakhtenberg, E. M.; Travish, G.; Trento, G. F.; Vacca, J.; Vasserman, I. B.; Vinokurov, N. A.; Walters, D. R.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. J.; Warren, J.; Wesling, S.; Weyer, D. L.; Wiemerslage, G.; Wilhelmi, K.; Wright, R.; Wyncott, D.; Xu, S.; Yang, B.-X.; Yoder, W.; Zabel, R. B.
2001-12-01
Exponential growth of self-amplified spontaneous emission at 530 nm was first experimentally observed at the Advanced Photon Source low-energy undulator test line in December 1999. Since then, further detailed measurements and analysis of the results have been made. Here, we present the measurements and compare these with calculations based on measured electron beam properties and theoretical expectations.
-
Arnold, N D; Banks, G; Bechtold, R; Beczek, K; Benson, C; Berg, S; Berg, W; Biedron, S G; Biggs, J A; Boerste, K; Borland, M; Bosek, M; Brzowski, W R; Budz, J; Carwardine, J A; Castro, P; Chae, Y C; Christensen, S; Clark, C; Conde, M; Crosbie, E A; Decker, G A; Dejus, Roger J; Deleon, H; Den Hartog, P K; Deriy, B N; Dohan, D; Dombrowski, P; Donkers, D; Doose, C L; Dortwegt, R J; Edwards, G A; Eidelman, Y; Erdmann, M J; Error, J J; Ferry, R; Flood, R; Forrestal, J; Freund, H; Friedsam, H; Gagliano, J; Gai, W; Galayda, J N; Gerig, R; Gilmore, R L; Gluskin, E; Goeppner, G A; Goetzen, J; Gold, C; Grelick, A E; Hahne, M W; Hanuska, S; Harkay, K C; Harris, G; Hillman, A L; Hogrefe, R; Hoyt, J; Huang, Z; Jagger, J M; Jansma, W G; Jaski, M; Jones, S J; Keane, R T; Kelly, A L; Keyser, C; Kim, K J; Kim, S H; Kirshenbaum, M; Klick, J H; Knoerzer, K; Knott, M; Koldenhoven, R J; Labuda, S; Laird, R; Lang, J; Lenkszus, F R; Lessner, E S; Lewellen, J W; Li, Y; Lill, R M; Lumpkin, Alex H; Makarov, O A; Markovich, G M; McDowell, M; McDowell, W P; McNamara, P E; Meier, T; Meyer, D; Michalek, W; Milton, S V; Moe, H; Moog, E; Morrison, L; Nassiri, A; Noonan, J R; Otto, R; Pace, J; Pasky, S J; Penicka, J M; Pietryla, A F; Pile, G; Pitts, C; Power, J; Powers, T; Putnam, C C; Puttkammer, A J; Reigle, D; Reigle, L; Ronzhin, D; Rotela, E R; Russell, E F; Sajaev, Vadim; Sarkar, S; Scapino, J C; Schröder, K; Seglem, R A; Sereno, N S; Sharma, S K; Sidarous, J F; Singh, O; Smith, T L; Soliday, R; Sprau, G A; Stein, S J; Stejskal, B; Svirtun, V; Teng, L C; Theres, E; Thompson, K; Tieman, B J; Torres, J A; Trakhtenberg, E; Travish, G; Trento, G F; Vacca, J; Vasserman, I B; Vinokurov, N A; Walters, D R; Wang, J; Wang, X J; Warren, J; Wesling, S; Weyer, D L; Wiemerslage, G; Wilhelmi, K; Wright, R; Wyncott, D; Xu, S; Yang, B X; Yoder, W; Zabel, R B
2001-01-01
Exponential growth of self-amplified spontaneous emission at 530 nm was first experimentally observed at the Advanced Photon Source low-energy undulator test line in December 1999. Since then, further detailed measurements and analysis of the results have been made. Here, we present the measurements and compare these with calculations based on measured electron beam properties and theoretical expectations.
-
Zheng, Zhi-yuan; Wei, Zhi-gang; Wen, Zhi-ping; Dong, Wen-jie; Li, Zhen-chao; Wen, Xiao-hang; Zhu, Xian; Chen, Chen; Hu, Shan-shan
2018-02-01
Land surface emissivity is a significant variable in energy budgets, land cover assessments, and environment and climate studies. However, the assumption of an emissivity constant is being used in Gobi broadband emissivity (GbBE) parameterization scheme in numerical models because of limited knowledge surrounding the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of GbBE. To address this issue, we analyzed the variation characteristics of GbBE and possible impact factor-surface soil moisture based on long-term continuous and high temporal resolution field observational experiments over a typical Gobi underlying surface in arid and semiarid areas in northwestern China. The results indicate that GbBE has obvious daily and diurnal variation features, especially diurnal cycle characteristics. The multi-year average of the daily average of GbBE is in the range of 0.932 to 0.970 with an average of 0.951 ± 0.008, and the average diurnal GbBE is in the range of 0.880 to 0.940 with an average of 0.906 ± 0.018. GbBE varies with surface soil moisture content. We observed a slight decrease in GbBE with an increase in soil moisture, although this change was not very obvious because of the low soil moisture in this area. Nevertheless, we think that soil moisture must be one of the most significant impact factors on GbBE in arid and semiarid areas. Soil moisture must be taken into account into the parameterization schemes of bare soil broadband emissivity in land surface models. Additional field experiments and studies should be carried out in order to clarify this issue.
-
Gurnett, D. A.
2017-12-01
Voyager 1, which is now 140 AU (Astronomical Units) from the Sun, crossed the heliopause into interstellar space in 2012 at a heliospheric radial distance of 121 AU. Since crossing the heliopause the plasma wave instrument has on several occasions detected plasma oscillations and radio emissions at or near the electron plasma frequency. The most notable of these events occurred in Oct.-Nov. 2012, April-May 2013, Feb.-Nov. 2014, and Sept.-Nov. 2015. Most recently, a very weak emission has been observed at or near the electron plasma frequency through most of 2016. These emissions are all believed to be produced by shock waves propagating into the interstellar medium from energetic solar events. The oscillation frequency of the plasma indicates that the electron density in the interstellar plasma has gradually increased from about 0.06 cm-3 near the heliopause to about 0.12 cm-3 in the most recent data. The plasma wave instrument also continues to detect impacts of what are believed to be interstellar dust grains at an impact rate of a few per year. Comparisons with Ulysses observations of similar interstellar dust near 5 AU suggest that the dust grains have sizes in the range from about 0.1 to 1 micrometer. Although the statistics are poor due to the low count rate, the dust flux observed in the outer heliosphere appears to be as much as a factor of two greater than that observed in the interstellar medium. Since the dust particles are likely to be charged, this increase in the heliosphere suggests that there may be a significant electrodynamic interaction of the dust particles with the heliospheric magnetic field.
-
Singh, Dhananjali; Singh, Birbal; Pundhir, Devbrat
2018-04-01
Employing SoftPAL receiver, amplitude variations of VLF transmitter signals NWC (19.8 kHz) and NPM (21.4 kHz) are analyzed at Agra station in India (Geograph. lat. 27.2°N, long. 78°E) ±15 days from five major earthquakes of magnitude M = 6.9-8.5 occurred in Indian subcontinent during the years 2011-2013. We apply nighttime fluctuation (NF) method and show that in almost all cases the trend decreases and dispersion and NF increase on the same days corresponding to each earthquake about 11-15 days prior to the main shock. Assuming that the ionospheric perturbations are caused by atmospheric gravity waves (AGW), we also calculate AGW modulation index for each case and find its values increased on the days amplitude fluctuations take place. Its value is decreased in one case only where the perturbations may be attributed to penetration of seismogenic electric field. In order to support the above results we also present GPS-TEC data analyzed by us corresponding to three of the above earthquakes. We study the TEC anomalies (unusual enhancements) and find that in one case the precursory period is almost the same as that found in NF method.
-
Ground-based observation of emission lines from the corona of a red-dwarf star.
Schmitt, J H; Wichmann, R
2001-08-02
All 'solar-like' stars are surrounded by coronae, which contain magnetically confined plasma at temperatures above 106 K. (Until now, only the Sun's corona could be observed in the optical-as a shimmering envelope during a total solar eclipse.) As the underlying stellar 'surfaces'-the photospheres-are much cooler, some non-radiative process must be responsible for heating the coronae. The heating mechanism is generally thought to be magnetic in origin, but is not yet understood even for the case of the Sun. Ultraviolet emission lines first led to the discovery of the enormous temperature of the Sun's corona, but thermal emission from the coronae of other stars has hitherto been detectable only from space, at X-ray wavelengths. Here we report the detection of emission from highly ionized iron (Fe XIII at 3,388.1 A) in the corona of the red-dwarf star CN Leonis, using a ground-based telescope. The X-ray flux inferred from our data is consistent with previously measured X-ray fluxes, and the non-thermal line width of 18.4 km s-1 indicates great similarities between solar and stellar coronal heating mechanisms. The accessibility and spectral resolution (45,000) of the ground-based instrument are much better than those of X-ray satellites, so a new window to the study of stellar coronae has been opened.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. S. De
2010-04-01
Full Text Available The outcome of the results of some analyses of electromagnetic emissions recorded by VLF receivers at 6 kHz and 9 kHz over Agartala, Tripura, the North-Eastern state of India (Lat. 23° N, Long. 91.4° E during the large earthquake at Muzaffarabad (Lat. 34.53° N, Long. 73.58° E at Kashmir under Pakistan have been presented here. Spiky variations in integrated field intensity of atmospherics (IFIA at 6 and 9 kHz have been observed 10 days prior (from midnight of 28 September 2005 to the day of occurrence of the earthquake on 8 October 2005 and the effect continued, decayed gradually and eventually ceased on 16 October 2005. The spikes distinctly superimposed on the ambient level with mutual separation of 2–5 min. Occurrence number of spikes per hour and total duration of their occurrence have been found remarkably high on the day of occurrence of the earthquake. The spike heights are higher at 6 kHz than at 9 kHz. The results have been explained on the basis of generation of electromagnetic radiation associated with fracture of rocks, their subsequent penetration into the Earth's atmosphere and finally their propagation between Earth-ionosphere waveguide. The present observation shows that VLF anomaly is well-confined between 6 and 9 kHz.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gardelle, J.; Modin, P.; Donohue, J. T.
2012-01-01
An experiment at microwave frequencies confirms the recent prediction that a Smith-Purcell [S. J. Smith and E. M. Purcell, Phys. Rev. 92, 1069 (1953)] free-electron laser equipped with sidewalls can emit radiation at the frequency of the surface wave. The power output is considerably greater than for the previously observed emission at the second harmonic, in agreement with three-dimensional simulations. The dependence of frequency on beam energy and emission angle is in good agreement with three-dimensional theory and simulations. Provided that a reduction in scale can be achieved, a path is open to coherent Smith-Purcell radiation at terahertz frequency.
-
Gielen, Clio; Hendrick, Francois; Pinardi, Gaia; De Smedt, Isabelle; Stavrakou, Trissevgeni; Yu, Huan; Fayt, Caroline; Hermans, Christian; Bauwens, Maité; Ndenzako, Eugene; Nzohabonayo, Pierre; Akimana, Rachel; Niyonzima, Sébastien; Müller, Jean-Francois; Van Roozendael, Michel
2016-04-01
Central Africa is known for its strong biogenic, pyrogenic, and to a lesser extent anthropogenic emissions. Satellite observations of species like nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and formaldehyde (HCHO), as well as inverse modelling results have shown that there are large uncertainties associated with the emissions in this region. There is thus a need for additional measurements, especially from the ground, in order to better characterise the biomass-burning and biogenic products emitted in this area. We present MAX-DOAS measurements of NO2, HCHO, and aerosols performed in Central Africa, in the city of Bujumbura, Burundi (3°S, 29°E, 850m). A MAX-DOAS instrument has been operating at this location by BIRA-IASB since late 2013. Aerosol-extinction and trace-gases vertical profiles are retrieved by applying the optimal-estimation-based profiling tool bePRO to the measured O4, NO2 and HCHO slant-column densities. The MAX-DOAS vertical columns and profiles are used for investigating the diurnal and seasonal cycles of NO2, HCHO, and aerosols. Regarding the aerosols, the retrieved AODs are compared to co-located AERONET sun photometer measurements for verification purpose, while in the case of NO2 and HCHO, the MAX-DOAS vertical columns and profiles are used for validating GOME-2 and OMI satellite observations. To characterise the biomass-burning and biogenic emissions in the Bujumbura region, the trace gases and aerosol MAX-DOAS retrievals are used in combination to MODIS fire counts/radiative-power and GOME-2/OMI NO2 and HCHO satellite data, as well as simulations from the NOAA backward trajectory model HYSPLIT. First results show that HCHO seasonal variation around local noon is driven by the alternation of rain and dry periods, the latter being associated with intense biomass-burning agricultural activities and forest fires in the south/south-east and transport from this region to Bujumbura. In contrast, NO2 is seen to depend mainly on local emissions close to the city, due
-
Liu, Lei; Zhang, Xiuying; Xu, Wen; Liu, Xuejun; Li, Yi; Lu, Xuehe; Zhang, Yuehan; Zhang, Wuting
2017-08-01
China is experiencing intense air pollution caused in large part by anthropogenic emissions of reactive nitrogen (Nr). Atmospheric ammonia (NH3) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) are the most important precursors for Nr compounds (including N2O5, HNO3, HONO and particulate NO3- and NH4+) in the atmosphere. Understanding the changes in NH3 and NO2 has important implications for the regulation of anthropogenic Nr emissions and is a requirement for assessing the consequence of environmental impacts. We conducted the temporal trend analysis of atmospheric NH3 and NO2 on a national scale since 1980 based on emission data (during 1980-2010), satellite observation (for NH3 since 2008 and for NO2 since 2005) and atmospheric chemistry transport modeling (during 2008-2015).Based on the emission data, during 1980-2010, significant continuous increasing trends in both NH3 and NOx were observed in REAS (Regional Emission inventory in Asia, for NH3 0.17 and for NOx 0.16 kg N ha-1 yr-2) and EDGAR (Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research, for NH3 0.24 and for NOx 0.17 kg N ha-1 yr-2) over China. Based on the satellite data and atmospheric chemistry transport model (CTM) MOZART-4 (Model for Ozone and Related chemical Tracers, version 4), the NO2 columns over China increased significantly from 2005 to 2011 and then decreased significantly from 2011 to 2015; the satellite-retrieved NH3 columns from 2008 to 2014 increased at a rate of 2.37 % yr-1. The decrease in NO2 columns since 2011 may result from more stringent strategies taken to control NOx emissions during the 12th Five Year Plan, while no control policy has focused on NH3 emissions. Our findings provided an overall insight into the temporal trends of both NO2 and NH3 since 1980 based on emission data, satellite observations and atmospheric transport modeling. These findings can provide a scientific background for policy makers that are attempting to control atmospheric pollution in China. Moreover, the multiple datasets
-
Kangasaho, V. E.; Tsuruta, A.; Aalto, T.; Backman, L. B.; Houweling, S.; Krol, M. C.; Peters, W.; van der Laan-Luijkx, I. T.; Lienert, S.; Joos, F.; Dlugokencky, E. J.; Michael, S.; White, J. W. C.
2017-12-01
The atmospheric burden of CH4 has more than doubled since preindustrial time. Evaluating the contribution from anthropogenic and natural emissions to the global methane budget is of great importance to better understand the significance of different sources at the global scale, and their contribution to changes in growth rate of atmospheric CH4 before and after 2006. In addition, observations of δ13C-CH4 suggest an increase in natural sources after 2006, which matches the observed increase and variation of CH4 abudance. Methane emission sources can be identified using δ13C-CH4, because different sources produce methane with process-specific isotopic signatures. This study focuses on inversion model based estimates of global anthropogenic and natural methane emission rates to evaluate the existing methane emission estimates with a new δ13C-CH4 inversion system. In situ measurements of atmospheric methane and δ13C-CH4 isotopic signature, provided by the NOAA Global Monitoring Division and the Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research, will be assimilated into the CTDAS-13C-CH4. The system uses the TM5 atmospheric transport model as an observation operator, constrained by ECMWF ERA Interim meteorological fields, and off-line TM5 chemistry fields to account for the atmospheric methane sink. LPX-Bern DYPTOP ecosystem model is used for prior natural methane emissions from wetlands, peatlands and mineral soils, GFED v4 for prior fire emissions and EDGAR v4.2 FT2010 inventory for prior anthropogenic emissions. The EDGAR antropogenic emissions are re-divided into enteric fermentation and manure management, landfills and waste water, rice, coal, oil and gas, and residential emissions, and the trend of total emissions is scaled to match optimized anthropogenic emissions from CTE-CH4. In addition to these categories, emissions from termites and oceans are included. Process specific δ13C-CH4 isotopic signatures are assigned to each emission source to estimate 13CH4 fraction
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Liu, C.Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ma, J.G.; Liu, Y.C.
2014-01-01
In this work, ultraviolet (UV) electroluminescence (EL) is achieved from Au/MgO/Mg x Zn 1−x O heterojunction diodes. The EL mechanism and laser forming process are discussed based on the energy band diagram, impact-ionization process and disordered optical structure. For ZnO and low Mg-content MgZnO devices, their EL spectra show single near-band-edge (NBE) emission. While in high Mg-content MgZnO devices, the emission from self-formed Zn-rich MgZnO clusters is observed and also contribute to the UV EL band. These Zn-rich clusters can act as thermally-stable luminescence centers, suggesting a promising route for developing MgZnO-based UV light-emitting devices. -- Highlights: • A series of Au/MgO/Mg x Zn 1−x O heterojunction diodes with multiple Mg compositions are fabricated and ultraviolet electroluminescence is achieved. • EL mechanism and laser forming process are discussed based on energy band diagram, impact-ionization process and disordered optical structure. • The transition from spontaneous to stimulated emission is observed in these heterojunctions, and the lasing mode is random laser. • In high Mg-content MgZnO devices, the emission from self-formed Zn-rich clusters is observed, which are thermally stable luminescence centers
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Wakabayashi
2005-10-01
Full Text Available The SEEK-2 campaign was carried out over Kyushu Island in Japan on 3 August 2002, by using the two sounding rockets of S310-31 and S310-32. This campaign was planned to elucidate generation mechanisms of Quasi-Periodic Echoes (QPEs associated with mid-latitude sporadic-E (Es layers. Electron number densities were successfully measured in the Es layers by using the impedance probe on board two rockets. The plasma waves in the VLF and ELF ranges were also observed on board the S310-32 rocket. Results of electron density measurement showed that there were one or two major peaks in the Es layers along the rockets' trajectories near the altitude of about 10km. There were some smaller peaks associated with the main Es layers in the altitude range from 90 to 120 km. These density peaks were distributed in a very large extent during the SEEK-2 campaign. The Es layer structure is also measured by using the Fixed Bias Probe (FBP, which has a high spatial resolution of several meters (the impedance probe has an altitude resolution of about 400 m. The comparison with the total electron content (TEC measured by the Dual Band Beacon revealed that the Es layer was also modulated in the horizontal direction with the scale size of 30–40 km. It was shown that the QP echoes observed by the ground-based coherent radar come from the major density peak of the Es layer. The plasma wave instrument detected the enhancement of VLF and ELF plasma waves associated with the operation of the TMA release, and also with the passage of the Es layers. Keywords. Ionosphere (Ionospheric irregularities; Midlatitude ionosphere; Plasma temeperature and density
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lampert, M. [Wigner RCP, Euratom Association-HAS, Budapest (Hungary); BME NTI, Budapest (Hungary); Anda, G.; Réfy, D.; Zoletnik, S. [Wigner RCP, Euratom Association-HAS, Budapest (Hungary); Czopf, A.; Erdei, G. [Department of Atomic Physics, BME IOP, Budapest (Hungary); Guszejnov, D.; Kovácsik, Á.; Pokol, G. I. [BME NTI, Budapest (Hungary); Nam, Y. U. [National Fusion Research Institute, Daejeon (Korea, Republic of)
2015-07-15
A novel beam emission spectroscopy observation system was designed, built, and installed onto the Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research tokamak. The system is designed in a way to be capable of measuring beam emission either from a heating deuterium or from a diagnostic lithium beam. The two beams have somewhat complementary capabilities: edge density profile and turbulence measurement with the lithium beam and two dimensional turbulence measurement with the heating beam. Two detectors can be used in parallel: a CMOS camera provides overview of the scene and lithium beam light intensity distribution at maximum few hundred Hz frame rate, while a 4 × 16 pixel avalanche photo-diode (APD) camera gives 500 kHz bandwidth data from a 4 cm × 16 cm region. The optics use direct imaging through lenses and mirrors from the observation window to the detectors, thus avoid the use of costly and inflexible fiber guides. Remotely controlled mechanisms allow adjustment of the APD camera’s measurement location on a shot-to-shot basis, while temperature stabilized filter holders provide selection of either the Doppler shifted deuterium alpha or lithium resonance line. The capabilities of the system are illustrated by measurements of basic plasma turbulence properties.
-
Observations of Hα-emission stars in the young cluster NGC 2264
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rydgren, A.E.
1979-01-01
UBVRI photometry is given for a sample of 25 late-type Hα-emission stars in the young cluster NGC 2264. The stars are in the magnitude range 12< or =V<16. Some but not all appear to be T Tauri stars. The color--color diagrams support the view that the deviations from normal photospheric colors (due to ''spectral veiling'' and line emission) decrease with increasing wavelength between the U and I filters. In the (V, V-R) diagram, the Hα-emission stars lie in a well-defined pre-main-sequence band. Within this sample, there is a trend toward stronger line emission and spectral veiling with later spectral type. All of the likely legitimate T Tauri stars have inferred spectral types later than about K3. The question of cluster membership for stars in the cluster field with very small proper motions is considered
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hamaguchi, Kenji; Grosso, Nicolas; Kastner, Joel H.; Richmond, Michael; Weintraub, David A.
2010-01-01
The Suzaku X-ray satellite observed the young stellar object (YSO) V1647 Ori on 2008 October 8 during the new mass accretion outburst reported in 2008 August. During the 87 ks observation with a net exposure of 40 ks, V1647 Ori showed a high level of X-ray emission with a gradual decrease in flux by a factor of 5 and then displayed an abrupt flux increase by an order of magnitude. Such enhanced X-ray variability was also seen in XMM-Newton observations in 2004 and 2005 during the 2003-2005 outburst, but has rarely been observed for other YSOs. The spectrum clearly displays emission from Helium-like iron, which is a signature of hot plasma (kT ∼ 5 keV). It also shows a fluorescent iron Kα line with a remarkably large equivalent width (EW) of ∼600 eV. Such a large EW suggests that a part of the incident X-ray emission that irradiates the circumstellar material and/or the stellar surface is hidden from our line of sight. XMM-Newton spectra during the 2003-2005 outburst did not show a strong fluorescent iron Kα line, so that the structure of the circumstellar gas very close to the stellar core that absorbs and re-emits X-ray emission from the central object may have changed in between 2005 and 2008. This phenomenon may be related to changes in the infrared morphology of McNeil's nebula between 2004 and 2008.
-
France, Kevin; McCray, Richard; Penton, Steven V.; Kirshner, Robert P.; Challis, Peter; Laming, J. Martin; Bouchet, Patrice; Chevalier, Roger; Garnavich, Peter M.; Fransson, Claes;

2011-01-01
We present the most sensitive ultraviolet observations of Supernova 1987 A to date. Imaging spectroscopy from the Hubble Space Telescope-Cosmic Origins Spectrograph shows many narrow (Delta v approximates 300 km/s) emission lines from the circumstellar ring, broad Delta v approximates 10-20 x 10(exp 3) km/s) emission lines from the reverse shock, and ultraviolet continuum emission. The high signal-to-noise ratio (>40 per resolution element) broad Ly-alpha emission is excited by soft X-ray and EUV heating of mostly neutral gas in the circumstellar ring and outer supernova debris. The ultraviolet continuum at lambda > 1350 A can be explained by H-I two-photon (2s(exp 2)S(sub 1/2)-l(exp 2)S(sub 1/2)) emission from the same region. We confirm our earlier, tentative detection of N V lambda 1240 emission from the reverse shock and present the first detections of broad He II lambda1640, C IV lambda 1550, and N IV ] lambda1486 emission lines from the reverse shock. The helium abundance in the high-velocity material is He/H = 0.14 +/- 0.06. The N V /H alpha line ratio requires partial ion-electron equilibration (T(sub e)/T(sub p) approximately equal to 0.14-0.35). We find that the N/C abundance ratio in the gas crossing the reverse shock is significantly higher than that in the circumstellar ring, a result that may be attributed to chemical stratification in the outer envelope of the supernova progenitor. The N/C abundance may have been stratified prior to the ring expUlsion, or this result may indicate continued CNO processing in the progenitor subsequent to the expUlsion of the circumstellar ring.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Vivienne H. Payne
2011-11-01
Full Text Available We use the Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer (TES aboard the NASA Aura satellite to determine the concentrations of the trace gases ammonia (NH3 and formic acid (HCOOH within boreal biomass burning plumes, and present the first detection of peroxy acetyl nitrate (PAN and ethylene (C2H4 by TES. We focus on two fresh Canadian plumes observed by TES in the summer of 2008 as part of the Arctic Research of the Composition of the Troposphere from Aircraft and Satellites (ARCTAS-B campaign. We use TES retrievals of NH3 and HCOOH within the smoke plumes to calculate their emission ratios (1.0% ± 0.5% and 0.31% ± 0.21%, respectively relative to CO for these Canadian fires. The TES derived emission ratios for these gases agree well with previous aircraft and satellite estimates, and can complement ground-based studies that have greater surface sensitivity. We find that TES observes PAN mixing ratios of ~2 ppb within these mid-tropospheric boreal biomass burning plumes when the average cloud optical depth is low ( < 0.1 and that TES can detect C2H4 mixing ratios of ~2 ppb in fresh biomass burning smoke plumes.
-
Lightning impact on micro-second long ionospheric variability
Koh, Kuang Liang; Liu, Zhongjian; Fullekrug, Martin
2017-04-01
Lightning discharges cause electron heating and enhanced ionisation in the D region ionosphere which disturb the transmission of VLF communications [Inan et al., 2010]. A disturbance of such nature was measured in a VLF transmission with a sampling rate of 1 MHz, enabling much faster ionospheric variability to be observed when compared to previous studies which typically report results with a time resolution >5-20ms. The disturbance resembles "Long Recovery Early VLF" (LORE) events [Haldoupis et al. 2013, Cotts & Inan 2007]. LOREs exhibit observable ionospheric effects that last longer (>200s) than other lightning related disturbances. It was proposed that the mechanism behind the long-lasting effects of LOREs is different to shorter events [Gordillo-Vázquez et al. 2016]. The ionospheric variability inferred from the transmitted signal is seen to change dramatically after the lightning onset, suggesting that there are fast processes in the ionosphere affected or produced which have not been considered in previous research. The ionospheric variability inferred from the main two frequencies of the transmission is different. A possible explanation is a difference in the propagation paths of the two main frequencies of the transmission [Füllekrug et al., 2015]. References Inan, U.S., Cummer, S.A., Marshall, R.A., 2010. A survey of ELF and VLF research on lightning-ionosphere interactions and causative discharges. J. Geophys. Res. 115, A00E36. doi:10.1029/2009JA014775 Cotts, B.R.T., Inan, U.S., 2007. VLF observation of long ionospheric recovery events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L14809. doi:10.1029/2007GL030094 Haldoupis, C., Cohen, M., Arnone, E., Cotts, B., Dietrich, S., 2013. The VLF fingerprint of elves: Step-like and long-recovery early VLF perturbations caused by powerful ±CG lightning EM pulses. J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics 118, 5392-5402. doi:10.1002/jgra.50489 Gordillo-Vázquez, F.J., Luque, A., Haldoupis, C., 2016. Upper D region chemical kinetic modeling of
-
Randerson, J. T.; Chen, Y.; Giglio, L.; Rogers, B. M.; van der Werf, G.
2011-12-01
In several important biomes, including croplands and tropical forests, many small fires exist that have sizes that are well below the detection limit for the current generation of burned area products derived from moderate resolution spectroradiometers. These fires likely have important effects on greenhouse gas and aerosol emissions and regional air quality. Here we developed an approach for combining 1km thermal anomalies (active fires; MOD14A2) and 500m burned area observations (MCD64A1) to estimate the prevalence of these fires and their likely contribution to burned area and carbon emissions. We first estimated active fires within and outside of 500m burn scars in 0.5 degree grid cells during 2001-2010 for which MCD64A1 burned area observations were available. For these two sets of active fires we then examined mean fire radiative power (FRP) and changes in enhanced vegetation index (EVI) derived from 16-day intervals immediately before and after each active fire observation. To estimate the burned area associated with sub-500m fires, we first applied burned area to active fire ratios derived solely from within burned area perimeters to active fires outside of burn perimeters. In a second step, we further modified our sub-500m burned area estimates using EVI changes from active fires outside and within of burned areas (after subtracting EVI changes derived from control regions). We found that in northern and southern Africa savanna regions and in Central and South America dry forest regions, the number of active fires outside of MCD64A1 burned areas increased considerably towards the end of the fire season. EVI changes for active fires outside of burn perimeters were, on average, considerably smaller than EVI changes associated with active fires inside burn scars, providing evidence for burn scars that were substantially smaller than the 25 ha area of a single 500m pixel. FRP estimates also were lower for active fires outside of burn perimeters. In our
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Barbero, R; Abatzoglou, J T; Steel, E A; K Larkin, Narasimhan
2014-01-01
Very large-fires (VLFs) have widespread impacts on ecosystems, air quality, fire suppression resources, and in many regions account for a majority of total area burned. Empirical generalized linear models of the largest fires (>5000 ha) across the contiguous United States (US) were developed at ∼60 km spatial and weekly temporal resolutions using solely atmospheric predictors. Climate−fire relationships on interannual timescales were evident, with wetter conditions than normal in the previous growing season enhancing VLFs probability in rangeland systems and with concurrent long-term drought enhancing VLFs probability in forested systems. Information at sub-seasonal timescales further refined these relationships, with short-term fire weather being a significant predictor in rangelands and fire danger indices linked to dead fuel moisture being a significant predictor in forested lands. Models demonstrated agreement in capturing the observed spatial and temporal variability including the interannual variability of VLF occurrences within most ecoregions. Furthermore the model captured the observed increase in VLF occurrences across parts of the southwestern and southeastern US from 1984 to 2010 suggesting that, irrespective of changes in fuels and land management, climatic factors have become more favorable for VLF occurrence over the past three decades in some regions. Our modeling framework provides a basis for simulations of future VLF occurrences from climate projections. (letter)
-
Negative ion emission at field electron emission from amorphous (alpha-C:H) carbon
Bernatskij, D P; Ivanov-Omskij, V I; Pavlov, V G; Zvonareva, T K
2001-01-01
The study on the electrons field emission from the plane cathode surface on the basis of the amorphous carbon film (alpha-C:H) is carried out. The methodology, making it possible to accomplish simultaneously the registration of the emission currents and visually observe the distribution of the emission centers on the plane emitter surface is developed. The analysis of the oscillograms indicated that apart from the proper electron constituent the negative ions of hydrogen (H sup - and H sub 2 sup -), carbon (C sup -) and hydrocarbon (CH sub n sup -) are observed. The ions emission is connected with the processes of formation and degradation of the local emission centers
-
CONTINUUM OBSERVATIONS AT 350 MICRONS OF HIGH-REDSHIFT MOLECULAR EMISSION LINE GALAXIES
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wu Jingwen; Evans, Neal J.; Dunham, Michael M.; Vanden Bout, Paul A.
2009-01-01
We report observations of 15 high-redshift (z = 1 - 5) galaxies at 350 μm using the Caltech Submillimeter Observatory and Submillimeter High Angular Resolution Camera II array detector. Emission was detected from eight galaxies, for which far-infrared luminosities, star formation rates (SFRs), total dust masses, and minimum source size estimates are derived. These galaxies have SFRs and star formation efficiencies comparable to other high-redshift molecular emission line galaxies. The results are used to test the idea that star formation in these galaxies occurs in a large number of basic units, the units being similar to star-forming clumps in the Milky Way. The luminosity of these extreme galaxies can be reproduced in a simple model with (0.9-30)x10 6 dense clumps, each with a luminosity of 5 x 10 5 L sun , the mean value for such clumps in the Milky Way. Radiative transfer models of such clumps can provide reasonable matches to the overall spectral energy distributions (SEDs) of the galaxies. They indicate that the individual clumps are quite opaque in the far-infrared. Luminosity-to-mass ratios vary over two orders of magnitude, correlating strongly with the dust temperature derived from simple fits to the SED. The gas masses derived from the dust modeling are in remarkable agreement with those from CO luminosities, suggesting that the assumptions going into both calculations are reasonable.
-
Cluster observations of reflected EMIC-triggered emission
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Grison, Benjamin; Darrouzet, F.; Santolík, Ondřej; Cornilleau-Wehrlin, N.; Masson, A.
2016-01-01
Roč. 43, č. 9 (2016), s. 4164-4171 ISSN 0094-8276 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GAP209/12/2394; GA MŠk(CZ) LH15304 Grant - others:AV ČR(CZ) AP1401 Program:Akademická prémie - Praemium Academiae Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : EMIC * triggered emission * wave reflection * plasmapause Subject RIV: BN - Astronomy, Celestial Mechanics, Astrophysics Impact factor: 4.253, year: 2016 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2016GL069096/full
-
OBSERVATIONAL STUDY OF THE CONTINUUM AND WATER MASER EMISSION IN THE IRAS 19217+1651 REGION
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rodriguez-Esnard, T.; Trinidad, M. A. [Departamento de Astronomia, Universidad de Guanajuato, Apdo Postal 144, Guanajuato, GTO, Mexico CP 36000 (Mexico); Migenes, V., E-mail: tatiana@iga.cu, E-mail: trinidad@astro.ugto.mx, E-mail: vmigenes@byu.edu [Department of Physics and Astronomy, Brigham Young University, ESC-N145, Provo, UT 84602 (United States)
2012-12-20
We report interferometric observations of the high-mass star-forming region IRAS 19217+1651. We observed the radio continuum (1.3 cm and 3.6 cm) and water maser emission using the Very Large Array (VLA-EVLA) in transition mode (configuration A). Two radio continuum sources were detected at both wavelengths, I19217-A and I19217-B. In addition, 17 maser spots were observed distributed mainly in two groups, M1 and M2, and one isolated maser. This latter could be indicating the relative position of another continuum source which we did not detect. The results indicate that I19217-A appears to be consistent with an ultracompact H II region associated with a zero-age main-sequence B0-type star. Furthermore, the 1.3 cm continuum emission of this source suggests a cometary morphology. In addition, I19217-B appears to be an H II region consisting of at least two stars, which may be contributing to its complex structure. It was also found that the H{sub 2}O masers of the group M1 are apparently associated with the continuum source I19217-A. These are tracing motions which are not gravitationally bound according to their spatial distribution and kinematics. They also seem to be describing outflows in the direction of the elongated cometary region. On the other hand, the second maser group, M2, could be tracing the base of a jet. Finally, infrared data from Spitzer, Midcourse Space Experiment, and IRIS show that IRAS 19217+1651 is embedded inside a large open bubble, like a broken ring, which possibly has affected the morphology of the cometary H II region observed at 1.3 cm.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jones, Kevin C.; Solberg, Timothy D.; Avery, Stephen; Vander Stappen, François; Janssens, Guillaume; Prieels, Damien; Bawiec, Christopher R.; Lewin, Peter A.; Sehgal, Chandra M.
2015-01-01
Purpose: To measure the acoustic signal generated by a pulsed proton spill from a hospital-based clinical cyclotron. Methods: An electronic function generator modulated the IBA C230 isochronous cyclotron to create a pulsed proton beam. The acoustic emissions generated by the proton beam were measured in water using a hydrophone. The acoustic measurements were repeated with increasing proton current and increasing distance between detector and beam. Results: The cyclotron generated proton spills with rise times of 18 μs and a maximum measured instantaneous proton current of 790 nA. Acoustic emissions generated by the proton energy deposition were measured to be on the order of mPa. The origin of the acoustic wave was identified as the proton beam based on the correlation between acoustic emission arrival time and distance between the hydrophone and proton beam. The acoustic frequency spectrum peaked at 10 kHz, and the acoustic pressure amplitude increased monotonically with increasing proton current. Conclusions: The authors report the first observation of acoustic emissions generated by a proton beam from a hospital-based clinical cyclotron. When modulated by an electronic function generator, the cyclotron is capable of creating proton spills with fast rise times (18 μs) and high instantaneous currents (790 nA). Measurements of the proton-generated acoustic emissions in a clinical setting may provide a method for in vivo proton range verification and patient monitoring
-
Hernandez, E.; Mathur, S.; Fenton, A.; Behrend, C. C.; Bering, E., III
2017-12-01
As part of the Undergraduate Student Instrumentation Project (USIP) at the University of Houston, multiple Very Low Frequency (VLF) Radio Receivers will be set up during the 2017 solar eclipse. They will be taking data from Omaha, Nebraska and Casper, Wyoming. The receiver, using an air loop antenna, will record magnetic field fluctuations caused by VLF waves. The purpose of this experiment is to study the effects of the sudden change in electromagnetic radiation from the sun on the D-region of the ionosphere. VLF waves were chosen for measurement because naturally occurring VLF waves propagate through the Earth-ionosphere waveguide, which can be used to remotely observe the ionosphere. The D-region reduces the energy in propagating waves due to absorption. This means that any fluctuations in the D-region are inversely correlated to the strength of VLF waves being received. The experiment will focus on receiving waves transmitted from specific stations that are on the other side of totality. The amplitude and phase of the received waves will be measured and analyzed. It is hoped that this experiment will help us gain a better understanding of VLFs from the D-region during the solar eclipse, as well as increasing the overall data available for use by the community.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Reichardt I.
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Massive star-forming regions assemble a large number of young stars with remnants of stellar evolution and a very dense environment. Therefore, particles accelerated in supernova remnants and pulsar wind nebulae encounter optimal conditions for interacting with target material and photon fields, and thus produce gamma-ray emission. However, observations are challenging because multiple phenomena may appear entangled within the resolution of current gamma-ray telescopes. We report on MAGIC observations aimed to understand the nature of the emission from the star-forming region W51 and the unidentified source HESS J1857+026. While gamma-ray emission from W51 is dominated by the interaction of the supernova remnant W51C with dense molecular clouds, HESS J1857+026 is associated to the pulsar wind nebula from PSR J1856+0245. However, an additional source is resolved north of HESSJ1857+026, with sufficient separation to determine that it cannot be powered by the same pulsar. We search for multiwavelength data to determine the origin of the new source.
-
Initial Results from CASSIOPE/ePOP Satellite Overpasses above HAARP in 2014
Siefring, C. L.; Bernhardt, P. A.; Briczinski, S. J., Jr.; James, H. G.; Yau, A. W.; Knudsen, D. J.
2015-12-01
The High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program (HAARP) facility was operated in conjunction with overpasses of the enhanced Polar Outflow Probe (ePOP) instruments on the Canadian CASSIOPE satellite. During these overpasses HAARP was operated in several different heating modes and regimes as diagnosed by the characteristics of Stimulated Electromagnetic Emissions (SEE) using ground-based receivers while simultaneously ePOP monitored in-situ HF and VLF signals, looked for ion and electron heating, and provided VHF and UHF signals for propagation effects studies. The e-POP suite of instruments and particularly the ePOP Radio Receiver Instrument (RRI) offer a unique combination diagnostics appropriate for studying the non-linear plasma effects generated high-power HF waves in the ionosphere. In this presentation, the initial results from ePOP observations from two separate 2014 measurement campaigns at HAARP (April 16 to April 29 and May 25 to June 9) will be discussed. Several innovative experiments were performed during the campaign. Experiments explored a wide range of ionospheric effects. These include: 1) Penetration of HF pump waves into the ionosphere via large and small scale irregularities, 2) effects of gyro-harmonic heating and artificial ionization layers, 3) effects of HAARP beam shape with O- and X-mode transmissions, 4) coupling of Lower Hybrid modes into Whistler waves, 5) D/E-region VLF generation in the ionosphere using VLF modulation of the HF pump 6) scattering of VHF and UHF signals and 7) scattering and non-linear modulation of a 9.5 MHz probe wave propagating through the region of the ionosphere modified by HAARP. This work supported by the Naval Research Laboratory Base Program.
-
The evolution of interstellar medium mass probed by dust emission: Alma observations at z = 0.3-2
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Scoville, N.; Manohar, S.; Aussel, H.; Sheth, K.; Scott, K. S.; Sanders, D.; Ivison, R.; Pope, A.; Capak, P.; Vanden Bout, P.; Kartaltepe, J.; Robertson, B.; Lilly, S.
2014-01-01
The use of submillimeter dust continuum emission to probe the mass of interstellar dust and gas in galaxies is empirically calibrated using samples of local star-forming galaxies, Planck observations of the Milky Way, and high-redshift submillimeter galaxies. All of these objects suggest a similar calibration, strongly supporting the view that the Rayleigh-Jeans tail of the dust emission can be used as an accurate and very fast probe of the interstellar medium (ISM) in galaxies. We present ALMA Cycle 0 observations of the Band 7 (350 GHz) dust emission in 107 galaxies from z = 0.2 to 2.5. Three samples of galaxies with a total of 101 galaxies were stellar-mass-selected from COSMOS to have M * ≅ 10 11 M ☉ : 37 at z ∼ 0.4, 33 at z ∼ 0.9, and 31 at z = 2. A fourth sample with six infrared-luminous galaxies at z = 2 was observed for comparison with the purely mass-selected samples. From the fluxes detected in the stacked images for each sample, we find that the ISM content has decreased by a factor ∼6 from 1 to 2 × 10 10 M ☉ at both z = 2 and 0.9 down to ∼2 × 10 9 M ☉ at z = 0.4. The infrared-luminous sample at z = 2 shows a further ∼4 times increase in M ISM compared with the equivalent non-infrared-bright sample at the same redshift. The gas mass fractions are ∼2% ± 0.5%, 12% ± 3%, 14% ± 2%, and 53% ± 3% for the four subsamples (z = 0.4, 0.9, and 2 and infrared-bright galaxies).
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, Kræn V.; Blanke, Mogens; Eriksson, Lars
2017-01-01
Taking offspring in a problem of ship emission reduction by exhaust gas recirculation control for large diesel engines, an underlying generic estimation challenge is formulated as a problem of joint state and parameter estimation for a class of multiple-input single-output Hammerstein systems...... observer is shown on simulated cases, on tests with a large diesel engine on test bed and on tests with a container vessel....
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Němec, František; Parrot, M.; Santolík, Ondřej
2010-01-01
Roč. 115, - (2010), A11301/1-A11301/9 ISSN 0148-0227 R&D Projects: GA ČR GA205/09/1253; GA MŠk ME09107 Institutional research plan: CEZ:AV0Z30420517 Keywords : PLHR events * triggered emissions * DEMETER satellite Subject RIV: BL - Plasma and Gas Discharge Physics Impact factor: 3.303, year: 2010
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Inan, U.S.; Wolf, T.G.; Carpenter, D.L.
1988-01-01
Expected occurrence characteristics of lightning-induced electron precipitation (LEP) events at longitudes of the western (110 0 W) versus eastern (71 0 W) Unted States are considered from the point of view of available trapped particle flux at the edge of the loss cone. Considered from the point of view of available trapped particle flux at the edge of the loss cone. Considering published data on nighttime fluxes of >68 keV electrons observed at L≅2.5, and for ''direct'' precipitation into the northern hemisphere induced by northern hemisphere lightning, the occurrence rate and flux levels are expected to a factor of 20--200 higher in the west than in the east, assuming no significant variation in lightning source activity with longitude. Again assuming lightning sources in the north, it is predicted that at 71 0 W, ''mirrored'' precipitation into the southern hemisphere would involve precipitation fluxes 30--300 times higher than ''direct'' precipitation into the noerthern hemisphere. However, at 110 0 W and again assuming lightning in the north, southern hemisphere precipitation would tend to be limited to that small fraction of particles that were initially scattered into the northern loss cone and that were then backscattered from the northern atmosphere so as to reach the south
-
France, Kevin; McCandliss, Stephan R.; Lupu, Roxana E.
2006-01-01
We present new infrared observations of the emission/reflection nebula IC 405 obtained with the Spitzer Space Telescope. Infrared images in the four IRAC bands (3.6, 4.5, 5.8, and 8.0 um) and two MIPS bands (24 and 70 um) are complemented by IRS spectroscopy (5-30 um) of two nebular filaments. The IRAC (8.0 um) and MIPS imaging shows evidence of a bow shock associated with the runaway O9.5V star, HD 34078, created by the interaction between the star and nebular material. The ratio of emission...
-
Chowdhury, P. K.; Rama Rao, K. V. S.; Mittal, J. P.
1994-02-01
In contrast to the photochemistry of electronically excited acrolein producing vinyl and formyl radicals via CC bond rupture, multiphoton vibrationally excited molecules undergo concerted dissociation generating CO and ethylene. Vibrational excitation in the CO product is detected immediately following the CO 2 laser pulse by observing IR emission at 4.7 μm. The decay of the IR emission was studied as a function of acrolein pressure. A vibrational-vibrational relaxation rate constant of CO ( v=1) by acrolein is found to be 1240 ± 200 Torr -1 s -1.
-
Magnetic field observations on the Akebono (KXOS-D) satellite
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fukunishi, H.; Fujii, R.; Kokubum, S.
1990-01-01
The Akebono (EXOS-D) satellite carries triaxial fluxgate and search coil magnetometers with sensors mounted on 5-and 3m masts, respectively. The fluxgate magnetometer has four automatically switchable ranges from ±1024 to ±65536 nT (full scale), and resolutions commensurate with a 16-bit A/D converter in each range (0.031 to 2 nT). The rate of sampling is 32 vectors per second. The triaxial search coil magnetometer has a frequency response up to 800 Hz. Signals in the frequency range higher than 100 Hz are used for VLF plasma wave experiments, while signals less than 100 Hz are used for magnetic field experiments. Both magnetometers have been operating consinuously since the 3- and 5-m masts were extended on March 7 and 8, 1989, respectively. Intense small-scale field-aligned currents embedded in the large-scale field-aligned current system were always observed at 1-2 Re altitudes in all local time regions. The region 0 currents which flow in the poleward region adjacent to the region 1 currents were also frequently observed. The search coil magnetometers measured ion cyclotron waves at 1-2 Re altitudes near the equator. (N.K.)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
L. Liu
2017-08-01
Full Text Available China is experiencing intense air pollution caused in large part by anthropogenic emissions of reactive nitrogen (Nr. Atmospheric ammonia (NH3 and nitrogen dioxide (NO2 are the most important precursors for Nr compounds (including N2O5, HNO3, HONO and particulate NO3− and NH4+ in the atmosphere. Understanding the changes in NH3 and NO2 has important implications for the regulation of anthropogenic Nr emissions and is a requirement for assessing the consequence of environmental impacts. We conducted the temporal trend analysis of atmospheric NH3 and NO2 on a national scale since 1980 based on emission data (during 1980–2010, satellite observation (for NH3 since 2008 and for NO2 since 2005 and atmospheric chemistry transport modeling (during 2008–2015.Based on the emission data, during 1980–2010, significant continuous increasing trends in both NH3 and NOx were observed in REAS (Regional Emission inventory in Asia, for NH3 0.17 and for NOx 0.16 kg N ha−1 yr−2 and EDGAR (Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research, for NH3 0.24 and for NOx 0.17 kg N ha−1 yr−2 over China. Based on the satellite data and atmospheric chemistry transport model (CTM MOZART-4 (Model for Ozone and Related chemical Tracers, version 4, the NO2 columns over China increased significantly from 2005 to 2011 and then decreased significantly from 2011 to 2015; the satellite-retrieved NH3 columns from 2008 to 2014 increased at a rate of 2.37 % yr−1. The decrease in NO2 columns since 2011 may result from more stringent strategies taken to control NOx emissions during the 12th Five Year Plan, while no control policy has focused on NH3 emissions. Our findings provided an overall insight into the temporal trends of both NO2 and NH3 since 1980 based on emission data, satellite observations and atmospheric transport modeling. These findings can provide a scientific background for policy makers that are attempting to control atmospheric
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. B. McQuaid
2008-04-01
Full Text Available Chemical and meteorological parameters measured on board the Facility for Airborne Atmospheric Measurements (FAAM BAe 146 Atmospheric Research Aircraft during the African Monsoon Multidisciplinary Analysis (AMMA campaign are presented to show the impact of NOx emissions from recently wetted soils in West Africa. NO emissions from soils have been previously observed in many geographical areas with different types of soil/vegetation cover during small scale studies and have been inferred at large scales from satellite measurements of NOx. This study is the first dedicated to showing the emissions of NOx at an intermediate scale between local surface sites and continental satellite measurements. The measurements reveal pronounced mesoscale variations in NOx concentrations closely linked to spatial patterns of antecedent rainfall. Fluxes required to maintain the NOx concentrations observed by the BAe-146 in a number of cases studies and for a range of assumed OH concentrations (1×106 to 1×107 molecules cm−3 are calculated to be in the range 8.4 to 36.1 ng N m−2 s−1. These values are comparable to the range of fluxes from 0.5 to 28 ng N m−2 s−1 reported from small scale field studies in a variety of non-nutrient rich tropical and sub-tropical locations reported in the review of Davidson and Kingerlee (1997. The fluxes calculated in the present study have been scaled up to cover the area of the Sahel bounded by 10 to 20 N and 10 E to 20 W giving an estimated emission of 0.03 to 0.30 Tg N from this area for July and August 2006. The observed chemical data also suggest that the NOx emitted from soils is taking part in ozone formation as ozone concentrations exhibit similar fine scale structure to the NOx, with enhancements over the wet soils. Such variability can not be explained on the basis of transport from other areas. Delon et al. (2008 is a companion paper to this one which models the impact of soil NOx emissions on the NOx and ozone
-
Prompt Emission Observations of Swift BAT Bursts
Barthelmy, Scott
2009-01-01
We review the prompt emission properties of Swift BAT gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). We present the global properties of BAT GRBs based on their spectral and temporal characteristics. The BAT T90 and T50 durations peak at 80 and 20 s, respectively. The peak energy (Epeak) of about 60% of BAT GRBs is very likely to be less than 1.00 keV. We also present the BAT characteristics of GRBs with soft spectra, so called Xray flashes (XRFs). We will compare the BAT GRBs and XRFs parameter distribution to the other missions.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Maissa, S
1996-11-26
This study investigates luminous emissions simultaneously to electron emissions and examines their features in order to better understand the field electron emission phenomenon. A RF cavity, operating at room temperature and in pulsed mode, joined to a sophisticated experimental apparatus has been especially developed. The electron and luminous emissions are investigated on cleaned or with metallic, graphitic and dielectric particles contaminated RF surfaces in order to study their influence on these phenomena. During the surface processing, unstable luminous spots glowing during one RF pulse are detected. Their apparition is promoted in the vicinity of the metallic particles or scratches. Two hypotheses could explain their origin: the presence of micro-plasmas associated to electronic explosive emission during processing or the thermal radiation of the melted metal during this emission. Stable luminous spots glowing during several RF pulses are also detected and appear to increase on RF surfaces contaminated with dielectric particles, leading to strong and explosive luminous emissions. Two interpretations are considered: the initiation of surface breakdowns on the dielectric particles or the heating by the RF field at temperatures sufficiently intense to provoke their thermal radiation then their explosion. Finally a superconducting cavity has been adapted to observe luminous spots, which differ from the former ones bu their star shape and could be associated to micro-plasmas, revealed by the starbursts observed on superconducting cavity walls. (author) 102 refs.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Budishchev
2014-09-01
Full Text Available Most plot-scale methane emission models – of which many have been developed in the recent past – are validated using data collected with the closed-chamber technique. This method, however, suffers from a low spatial representativeness and a poor temporal resolution. Also, during a chamber-flux measurement the air within a chamber is separated from the ambient atmosphere, which negates the influence of wind on emissions. Additionally, some methane models are validated by upscaling fluxes based on the area-weighted averages of modelled fluxes, and by comparing those to the eddy covariance (EC flux. This technique is rather inaccurate, as the area of upscaling might be different from the EC tower footprint, therefore introducing significant mismatch. In this study, we present an approach to validate plot-scale methane models with EC observations using the footprint-weighted average method. Our results show that the fluxes obtained by the footprint-weighted average method are of the same magnitude as the EC flux. More importantly, the temporal dynamics of the EC flux on a daily timescale are also captured (r2 = 0.7. In contrast, using the area-weighted average method yielded a low (r2 = 0.14 correlation with the EC measurements. This shows that the footprint-weighted average method is preferable when validating methane emission models with EC fluxes for areas with a heterogeneous and irregular vegetation pattern.
-
Xia, Yinmin; Zhao, Yu; Nielsen, Chris P.
2016-07-01
To evaluate the effectiveness of national air pollution control policies, the emissions of SO2, NOX, CO and CO2 in China are estimated using bottom-up methods for the most recent 15-year period (2000-2014). Vertical column densities (VCDs) from satellite observations are used to test the temporal and spatial patterns of emissions and to explore the ambient levels of gaseous pollutants across the country. The inter-annual trends in emissions and VCDs match well except for SO2. Such comparison is improved with an optimistic assumption in emission estimation that the emission standards for given industrial sources issued after 2010 have been fully enforced. Underestimation of emission abatement and enhanced atmospheric oxidization likely contribute to the discrepancy between SO2 emissions and VCDs. As suggested by VCDs and emissions estimated under the assumption of full implementation of emission standards, the control of SO2 in the 12th Five-Year Plan period (12th FYP, 2011-2015) is estimated to be more effective than that in the 11th FYP period (2006-2010), attributed to improved use of flue gas desulfurization in the power sector and implementation of new emission standards in key industrial sources. The opposite was true for CO, as energy efficiency improved more significantly from 2005 to 2010 due to closures of small industrial plants. Iron & steel production is estimated to have had particularly strong influence on temporal and spatial patterns of CO. In contrast to fast growth before 2011 driven by increased coal consumption and limited controls, NOX emissions decreased from 2011 to 2014 due to the penetration of selective catalytic/non-catalytic reduction systems in the power sector. This led to reduced NO2 VCDs, particularly in relatively highly polluted areas such as the eastern China and Pearl River Delta regions. In developed areas, transportation is playing an increasingly important role in air pollution, as suggested by the increased ratio of NO2 to SO
-
Cooper, Ruth E; Skirrow, Caroline; Tye, Charlotte; McLoughlin, Grainne; Rijsdijk, Fruhling; Banaschweski, Tobias; Brandeis, Daniel; Kuntsi, Jonna; Asherson, Philip
2014-04-01
Altered very low-frequency electroencephalographic (VLF-EEG) activity is an endophenotype of ADHD in children and adolescents. We investigated VLF-EEG case-control differences in adult samples and the effects of methylphenidate (MPH). A longitudinal case-control study was conducted examining the effects of MPH on VLF-EEG (.02-0.2Hz) during a cued continuous performance task. 41 untreated adults with ADHD and 47 controls were assessed, and 21 cases followed up after MPH treatment, with a similar follow-up for 38 controls (mean follow-up=9.4months). Cases had enhanced frontal and parietal VLF-EEG and increased omission errors. In the whole sample, increased parietal VLF-EEG correlated with increased omission errors. After controlling for subthreshold comorbid symptoms, VLF-EEG case-control differences and treatment effects remained. Post-treatment, a time by group interaction emerged; VLF-EEG and omission errors reduced to the same level as controls, with decreased inattentive symptoms in cases. Reduced VLF-EEG following MPH treatment provides preliminary evidence that changes in VLF-EEG may relate to MPH treatment effects on ADHD symptoms; and that VLF-EEG may be an intermediate phenotype of ADHD. Further studies of the treatment effect of MPH in larger controlled studies are required to formally evaluate any causal link between MPH, VLF-EEG and ADHD symptoms. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Occasional large emissions of nitrous oxide and methane observed in stormwater biofiltration systems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Grover, Samantha P.P.; Cohan, Amanda; Chan, Hon Sen; Livesley, Stephen J.; Beringer, Jason; Daly, Edoardo
2013-01-01
in the cell without the saturated zone CO 2 fluxes decreased as soil moisture increased. Other studies of CO 2 fluxes from urban soils have found both similar and larger CO 2 emissions than those measured in the biofilter. The results of this study suggest that the greenhouse gas footprint of stormwater treatment warrant consideration in the planning and implementation of engineered green infrastructures. - Highlights: ► First study of greenhouse gas fluxes from a stormwater biofilter. ► Observed occasional large emissions of nitrous oxide and methane. ► Biofilter designs with and without a saturated zone were net sinks for methane. ► Carbon dioxide emissions were four times less than those from lawns
-
CONSTRAINING RADIO EMISSION FROM MAGNETARS
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lazarus, P.; Kaspi, V. M.; Dib, R. [Department of Physics, Rutherford Physics Building, McGill University, 3600 University Street, Montreal, Quebec H3A 2T8 (Canada); Champion, D. J. [Max-Planck-Institut fuer Radioastronomie, Auf dem Huegel 69, 53121 Bonn (Germany); Hessels, J. W. T., E-mail: plazar@physics.mcgill.ca [Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy (ASTRON), Postbus 2, 7990 AA Dwingeloo (Netherlands)
2012-01-10
We report on radio observations of five magnetars and two magnetar candidates carried out at 1950 MHz with the Green Bank Telescope in 2006-2007. The data from these observations were searched for periodic emission and bright single pulses. Also, monitoring observations of magnetar 4U 0142+61 following its 2006 X-ray bursts were obtained. No radio emission was detected for any of our targets. The non-detections allow us to place luminosity upper limits of L{sub 1950} {approx}< 1.60 mJy kpc{sup 2} for periodic emission and L{sub 1950,single} {approx}< 7.6 Jy kpc{sup 2} for single pulse emission. These are the most stringent limits yet for the magnetars observed. The resulting luminosity upper limits together with previous results are discussed, as is the importance of further radio observations of radio-loud and radio-quiet magnetars.
-
Photometric Characteristics of Sprites and Elves Derived from JEM-GLIMS Nadir Observations (Invited)
Sato, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Adachi, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Mihara, M.; Ushio, T.; Morimoto, T.; Suzuki, M.; Yamazaki, A.; Inan, U.; Linscott, I.
2013-12-01
The main goal of the JEM-GLIMS mission is to identify the horizontal structures of Transient Luminous Events (TLEs) and spatiotemporal relationship between TLEs and their parent lightning discharges based on the nadir observations from the International Space Station (ISS). For this purpose JEM-GLIMS equips two sets of optical instruments (LSI: CMOS camera, and PH: spectrophotometers) and two sets of radio wave receivers (VLFR: VLF receiver, and VITF: VHF interferometer). As all these instruments are installed at the bottom plane of the bus module facing to the Earth, JEM-GLIMS can carry out the nadir observations continuously. JEM-GLIMS was launched by HTV3 and was successfully installed at the exposed facility of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) on August 9, 2012. After the initial checkout operations, JEM-GLIMS finally started continuous observations on November 20, 2012. In the period from November 20, 2012 to June 30, 2013, totally 1597 transient optical events related to lightning flashes and/or TLE emissions were detected by the optical instruments. In 578 of these events, both LSI and PH detected clear transient optical signals well above the noise level. In order to derive sprite events from the detected transient optical events, we analyzed PH light-curve data first and estimated the peak irradiance related to the transient optical flashes. Then, we compared these intensities with the atmospheric transmittance. Finally, LSI image data are examined to clarify the morphological properties of the optical emission. We analyzed a transient optical event detected at 00:56:29.198 UT on December 15, 2012. The peak intensities of PH channels are estimated to be 1.4E-2 W/m2 (150-280 nm), 2.3E-4 W/m2 (316 nm), 5.9E-4 W/m2 (337 nm), 4.0E-4 W/m2 (392 nm), 4.2E-4 W/m2 (762 nm), and 6.3E-2 W/m2 (600-900 nm), respectively. It is found that all these intensities are significantly stronger than the lightning emission affected by the atmospheric transmittance. This fact
-
C2 emission features in the Red Rectangle : A combined observational laboratory study
Wehres, N.; Romanzin, C.; Linnartz, H.; van Winckel, H.; Tielens, A. G. G. M.
Context. The Red Rectangle proto-planetary nebula (HD 44179) is known for a number of rather narrow emission features superimposed on a broad extended red emission (ERE) covering the 5000-7500 angstrom regime. The origin of these emission features is unknown. Aims. The aim of the present work is to
-
Coulomb scattering in field and photofield emission
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Donders, P.J.; Lee, M.J.G.
1987-01-01
An anomalous high-energy tail has been observed in the measured total energy distribution (TED) in photofield emission from tungsten. The strength of this tail is proportional to the product of the photofield emission current and the total emission current. Similar high- and low-energy tails in the TED's in field emission, which have previously been reported by several workers, are also observed. In any given measurement, the fraction of the total photofield-emission current in the anomalous photofield-emission tail is approximately equal to the fraction of the total field-emission current in the anomalous field-emission tail. Measurements of both the absolute strengths and energy dependences of the anomalous tails are reported. The experimental observations are consistent with the predictions of a classical calculation of the energy transfer that results from the Coulomb interaction between electrons in the vacuum near the field emitter. The various internal mechanisms that have previously been invoked to account for the tails in field-emission TED's do not appear to contribute significantly to the anomalous distributions observed in the present work
-
Kepa, Anna; Gburek, Szymon; Siarkowski, Marek; Sylwester, Barbara; Sylwester, Janusz; Kowalinski, Miroslaw
SphinX is a high-sensitivity soft X-ray spectrophotometer which measures soft X-ray spectra in the energy range between 0.8 keV and 15 keV. From February to November 2009 the instrument has observed unusually quiet solar coronal emission as well as a number of weak solar flares. Based on SphinX spectra it is possible to study the differential emission measure distributions (DEM) in the temperature range roughly between 1 MK and 10 MK. The aim of the present study is to unveil DEM plasma distributions for selected activity conditions and analyze their variability.
-
Sarin, S M; Singh, A; Sharma, N; Sharma, K; Shanmugum, P
2001-01-01
The tail pipe CO (carbon monoxide) and HC (hydrocarbon) emission characteristics of in-use petrol driven vehicles were evaluated between November 1996 through September 1997 in Delhi. A total of 4300 vehicles were checked at CRRI Pollution Checking Centre. Approximately 90% of the total vehicles meet the prescribed CO emission standards even without following routine I/M practices. The age of the vehicles appeared to have influence on the emission characteristics. The non-compliance level was found to be higher for older vehicles. Insignificant correlation was observed between CO and HC emissions for all categories of in-use petrol driven vehicles. The emission reduction (gain) in CO and HC emissions was observed for two wheelers equipped with four-stroke engines and four wheelers fitted with catalytic converters over their respective conventional vehicles. The observed high compliance levels indicate that existing tail pipe emission standards are lenient and need to be reviewed. The emission standards are proposed for different categories of in-use petrol driven vehicles.
-
Observations of low-frequency radio emissions in the Earth's magnetosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Filbert, P.C.; Kellogg, P.J.
1989-01-01
A study is made of electromagnetic radiation in the Earth's magnetosphere in the frequency range between 10 kHz and 80 kHz using data from the University of Minnesota Plasma Wave Experiment aboard the IMP 6 satellite. Two types of radio emissions are investigated. First is the nonthermal continuum radiation, it is found that discrete enhancements above ambient levels are correlated with enhancements of the magnetic substorm index AE and appear to follow the onset of the negative bay feature of the AU index by about 20 min or so. The directions of these discrete source regions of continuum radiation are measured as a function of time, and movement of the source region in a dusk-to-dawn direction is directly observed. This drift motion is used to measure the energy of the generating electrons by a time-of-flight method, and a range between 10 keV and 50 keV is found in agreement with previous studies. A second type of radiation is also observed which correlates with auroral kilometric radiation (AKR) on a time scale of ∼ 1 min. This radiation lies between 10 and 60 kHz with a spectral peak near 30 kHz and is found to have a source direction very near that of the coincident AKR. The lower frequency of the spectral peak, in conjunction with the analysis of the spin-modulated wave data, suggests a source location at a higher elevation than the higher-frequency AKR indicating a source altitude of roughly 3 Earth radii
-
The Story of Ever Diminishing Vehicle Tailpipe Emissions as Observed in the Chicago, Illinois Area.
Bishop, Gary A; Haugen, Molly J
2018-05-15
The University of Denver has collected on-road fuel specific vehicle emissions measurements in the Chicago area since 1989. This nearly 30 year record illustrates the large reductions in light-duty vehicle tailpipe emissions and the remarkable improvements in emissions control durability to maintain low emissions over increasing periods of time. Since 1989 fuel specific carbon monoxide (CO) emissions have been reduced by an order of magnitude and hydrocarbon (HC) emissions by more than a factor of 20. Nitric oxide (NO) emissions have only been collected since 1997 but have seen reductions of 79%. This has increased the skewness of the emissions distribution where the 2016 fleet's 99th percentile contributes ∼3 times more of the 1990 total for CO and HC emissions. There are signs that these reductions may be leveling out as the emissions durability of Tier 2 vehicles in use today has almost eliminated the emissions reduction benefit of fleet turnover. Since 1997, the average age of the Chicago on-road fleet has increased 2 model years and the percentage of passenger vehicles has dropped from 71 to 52% of the fleet. Emissions are now so well controlled that the influence of driving mode has been completely eliminated as a factor for fuel specific CO and NO emissions.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mende, S.B.; Arnoldy, R.L.; Cahill, L.J. Jr.; Doolittle, J.H.; Armstrong, W.C.; Fraser-Smith, A.C.
1980-01-01
Detailed correlations were observed between the amplitude envelope of Pc 1 pulsations and zenith 4278 N 2 + intensity at Siple Station, Antarctica, (L=4.2) on August 1, 1977. Conjugate Pc 1 data at Roberval show a similar amplitude envelope and an approximate antiphase relationship. The frequency-time spectrogram of the ULF data shows none of the increasing dispersion associated with bouncing waves; i.e., the Pc 1 pulsation event is a periodic hydromagnetic emission. Analysis of the time delay between the particle-induced optical emission and the wave (42 s) using the ion cyclotron resonance theory shows that the delay is consistent with the resonance of Pc 1 and MeV protons near the northern conjugate of the Siple field line. Alternately, resonance theory using He + or O + ions as the interacting hot particles does fit the data if the interaction region is off the equator. The intensity of the measured light is higher than that which can be expected from precipitation of ions of normally observed densities
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. J. E. van Marle
2017-09-01
Full Text Available Fires have influenced atmospheric composition and climate since the rise of vascular plants, and satellite data have shown the overall global extent of fires. Our knowledge of historic fire emissions has progressively improved over the past decades due mostly to the development of new proxies and the improvement of fire models. Currently, there is a suite of proxies including sedimentary charcoal records, measurements of fire-emitted trace gases and black carbon stored in ice and firn, and visibility observations. These proxies provide opportunities to extrapolate emission estimates back in time based on satellite data starting in 1997, but each proxy has strengths and weaknesses regarding, for example, the spatial and temporal extents over which they are representative. We developed a new historic biomass burning emissions dataset starting in 1750 that merges the satellite record with several existing proxies and uses the average of six models from the Fire Model Intercomparison Project (FireMIP protocol to estimate emissions when the available proxies had limited coverage. According to our approach, global biomass burning emissions were relatively constant, with 10-year averages varying between 1.8 and 2.3 Pg C yr−1. Carbon emissions increased only slightly over the full time period and peaked during the 1990s after which they decreased gradually. There is substantial uncertainty in these estimates, and patterns varied depending on choices regarding data representation, especially on regional scales. The observed pattern in fire carbon emissions is for a large part driven by African fires, which accounted for 58 % of global fire carbon emissions. African fire emissions declined since about 1950 due to conversion of savanna to cropland, and this decrease is partially compensated for by increasing emissions in deforestation zones of South America and Asia. These global fire emission estimates are mostly suited for global analyses and
-
Dima, G. I.; Kuhn, J. R.; Berdyugina, S.
2017-12-01
Measurements of the coronal magnetic field are difficult because of the intrinsically faint emission of coronal plasma and the large spurious background due to the bright solar disk. This work addresses the problem of resolving the confusion of the line-of-sight (LOS) integration through the optically-thin corona being observed. Work on developing new measuring techniques based on single-point inversions using the Hanle effect has already been described (Dima et al. 2016). It is important to develop a technique to assess when the LOS confusion makes comparing models and observations problematic. Using forward integration of synthetic emission through magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) models together with simultaneous linearly polarized observations of the FeXIII 1075nm and SiX 1430nm emission lines allows us to assess LOS confusion. Since the lines are both in the Hanle saturated regime their polarization angles are expected to be aligned as long as the gas is sampling the same magnetic field. If significant contributions to the emission is taking place from different regions along the LOS due to the additive nature of the polarized brightness the measured linear polarization between the two lines will be offset. The size of the resolution element is important for this determination since observing larger coronal regions will confuse the variation along the LOS with that in the plane-of-sky. We also present comparisons between synthetic linearly polarized emission through a global MHD model and observations of the same regions obtained using the 0.5m Scatter-free Observatory for Limb Active Regions and Coronae (SOLARC) telescope located on Haleakala, Maui. This work is being done in preparation for the type of observations that will become possible when the next generation 4m DKIST telescope comes online in 2020.
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Parrot, M.; Němec, F.; Santolík, Ondřej
2014-01-01
Roč. 119, č. 7 (2014), s. 5744-5754 ISSN 2169-9380 R&D Projects: GA ČR GAP205/10/2279; GA MŠk LH12231 Institutional support: RVO:68378289 Keywords : man-made waves * ionosphere Subject RIV: BL - Plasma and Gas Discharge Physics Impact factor: 3.426, year: 2014 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2014JA020139/abstract
-
Krissinel, Boris
2018-03-01
The paper reports the results of calculations of the center-to-limb intensity of optically thin line emission in EUV and FUV wavelength ranges. The calculations employ a multicomponent model for the quiescent solar corona. The model includes a collection of loops of various sizes, spicules, and free (inter-loop) matter. Theoretical intensity values are found from probabilities of encountering parts of loops in the line of sight with respect to the probability of absence of other coronal components. The model uses 12 loops with sizes from 3200 to 210000 km with different values of rarefaction index and pressure at the loop base and apex. The temperature at loop apices is 1 400 000 K. The calculations utilize the CHIANTI database. The comparison between theoretical and observed emission intensity values for coronal and transition region lines obtained by the SUMER, CDS, and EIS telescopes shows quite satisfactory agreement between them, particularly for the solar disk center. For the data acquired above the limb, the enhanced discrepancies after the analysis refer to errors in EIS measurements.
-
A Climatology of dust emission in northern Africa using surface observations from 1984-2012
Cowie, Sophie; Knippertz, Peter; Marsham, John
2014-05-01
The huge quantity of mineral dust emitted annually from northern Africa makes this area crucial to the global dust cycle. Once in the atmosphere, dust aerosols have a significant impact on the global radiation budget, clouds, the carbon cycle and can even act as a fertilizer to rain forests in South America. Current model estimates of dust production from northern Africa are uncertain. At the heart of this problem is insufficient understanding of key dust emitting processes such as haboobs (cold pools generated through evaporation of convective precipitation), low-level jets (LLJs) and dry convection (dust devils and dust plumes). Scarce observations in this region, in particular in the Sahara, make model evaluation difficult. This work uses long-term surface observations from 70 stations situated in the Sahara and Sahel to explore the diurnal, seasonal and geographical variations in dust emission events and thresholds. Quality flags are applied to each station to indicate a day-time bias or gaps in the time period 1984-2012. The frequency of dust emission (FDE) is calculated using the present weather codes (WW) of SYNOP reports, where WW = 07,08,09,30-35 and 98. Thresholds are investigated by estimating the wind speeds for which there is a 25%, 50% and 75% probability of dust emission. The 50% threshold is used to calculate strong wind frequency (SWF) and the diagnostic parameter dust uplift potential (DUP); a thresholded cubic function of wind-speed which quantifies the dust generating power of winds. Stations are grouped into 6 areas (North Algeria, Central Sahara, Egypt, West Sahel, Central Sahel and Sudan) for more in-depth analysis of these parameters. Spatially, thresholds are highest in northern Algeria and lowest in the Sahel around the latitude band 16N-21N. Annual mean FDE is anti-correlated with the threshold, showing the importance of spatial variations in thresholds for mean dust emission. The annual cycles of FDE and SWF for the 6 grouped areas are
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kouveliotou, C.; Granot, J.; Racusin, J. L.; Gehrels, N.; McEnery, J. E.; Zhang, W. W.; Bellm, E.; Harrison, F. A.; Vianello, G.; Oates, S.; Fryer, C. L.; Boggs, S. E.; Craig, W. W.; Christensen, F. E.; Dermer, C. D.; Hailey, C. J.; Melandri, A.; Tagliaferri, G.; Mundell, C. G.; Stern, D. K.
2013-01-01
GRB 130427A occurred in a relatively nearby galaxy; its prompt emission had the largest GRB fluence ever recorded. The afterglow of GRB 130427A was bright enough for the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope ARray (NuSTAR) to observe it in the 3-79 keV energy range long after its prompt emission (∼1.5 and 5 days). This range, where afterglow observations were previously not possible, bridges an important spectral gap. Combined with Swift, Fermi, and ground-based optical data, NuSTAR observations unambiguously establish a single afterglow spectral component from optical to multi-GeV energies a day after the event, which is almost certainly synchrotron radiation. Such an origin of the late-time Fermi/Large Area Telescope >10 GeV photons requires revisions in our understanding of collisionless relativistic shock physics
-
Occasional large emissions of nitrous oxide and methane observed in stormwater biofiltration systems
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Grover, Samantha P.P., E-mail: samantha.grover@monash.edu [Department of Civil Engineering, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, 3800 (Australia); Cohan, Amanda, E-mail: acoh5@student.monash.edu [Department of Civil Engineering, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, 3800 (Australia); Chan, Hon Sen, E-mail: hon.sen.chan@gmail.com [Department of Civil Engineering, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, 3800 (Australia); Livesley, Stephen J., E-mail: sjlive@unimelb.edu.au [Department of Resource Management and Geography, The University of Melbourne, Richmond, Victoria, 3121 (Australia); Beringer, Jason, E-mail: jason.beringer@monash.edu [School of Geography and Environmental Science, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, 3800 (Australia); Monash Water for Liveability, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, 3800 (Australia); Daly, Edoardo, E-mail: edoardo.daly@monash.edu [Department of Civil Engineering, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, 3800 (Australia); Monash Water for Liveability, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, 3800 (Australia)
2013-11-01
inflow events, which were not seen in other urban systems. CO{sub 2} fluxes increased with soil temperature in both cells, and in the cell without the saturated zone CO{sub 2} fluxes decreased as soil moisture increased. Other studies of CO{sub 2} fluxes from urban soils have found both similar and larger CO{sub 2} emissions than those measured in the biofilter. The results of this study suggest that the greenhouse gas footprint of stormwater treatment warrant consideration in the planning and implementation of engineered green infrastructures. - Highlights: ► First study of greenhouse gas fluxes from a stormwater biofilter. ► Observed occasional large emissions of nitrous oxide and methane. ► Biofilter designs with and without a saturated zone were net sinks for methane. ► Carbon dioxide emissions were four times less than those from lawns.
-
Matsumoto, J.
2013-12-01
Nitrogen oxides, NOx (NO, NO2), and volatile organic compounds, VOCs, are important as precursors of photochemical oxidants (tropospheric ozone, O3). To predict and control photochemical oxidants, NOx emission should be captured precisely. In addition, the ratio of NO2/NOx in the exhaust gas is also important as the initial balance between NO and NO2 in the atmosphere. Monitoring the NO2/NOx ratio in the exhaust gases is essential. Especially, the influence of the NOx emission on the real atmosphere should be explored. However, conversion reactions among NO, NO2 and O3 are typically in the time scale of minutes. The NO2/NOx ratio can change rapidly just after emission. Real-time observations of these compounds in the second time scale are essential. In view of photochemical oxidant, near emission sources of NO, ozone concentration can be easily perturbed by reaction with locally emitted NO. As an index of oxidant, the sum of O3 and NO2 (Ox = O3 + NO2) is useful. In this study, a simultaneous and real-time analyzer of atmospheric Ox and NOx has been developed utilizing the dual NO2 detectors based on laser-induced fluorescence technique (LIF), and characterization of NOx emission was explored through the observations of Ox and NOx in the suburbs of Tokyo. The dual LIF detectors consisted of one laser head, two LIF cells, and one common vacuum pump. As the Ox monitor, the excess NO was added to the sample and O3 was converted to NO2, and then the sum of O3 and NO2 in the sample was quantified at the 1st LIF cell. As the NOx monitor, the excess O3 was added to the sample and NO was converted to NO2, and then the sum of NO and NO2 in the sample was quantified at the 2nd LIF cell. Both the ';Ox' and ';NOx' channels in the dual LIF analyzer were simultaneously monitoring Ox and NOx in the sample air, respectively. The temporal resolution of observed data was 1 s. Typical conversion efficiencies of O3 and NO to NO2 were more than 0.98. The lower detection limits were 0
-
Observation of damage process in RC beams under cucle bending by acoustic emission
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shigeishi, Mitsuhiro; Ohtsu, Masayasu; Tsuji, Nobuyuki; Yasuoka, Daisuke
1997-01-01
Reinforced concrete (RC) structures are generally applied to construction of buildings and bridges, and are imposed on cyclic loading incessantly. It is considered that detected acoustic emission (AE) waveforms are associated with the damage degree and the fracture mechanisms of RC structures. Therefor, the cyclic bending tests are applied to damaged RC beam specimens. To evaluate the interior of the damaged RC beams, the AE source kinematics are determined by 'SiGMA' procedure for AE moment tensor analysis. By using 'SiGMA' procedure, AE source kinematics, such as source locations, crack types, crack orientations and crack motions, can be identified. The results show the applicability to observation of the fracture process under cyclic bending load and evaluation the degree of damage of RC beam.
-
Observation of CH4 and other Non-CO2 Green House Gas Emissions from California
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Fischer, Marc L.; Zhao, Chuanfeng; Riley, William J.; Andrews, Arlyn C.
2009-01-09
In 2006, California passed the landmark assembly bill AB-32 to reduce California's emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs) that contribute to global climate change. AB-32 commits California to reduce total GHG emissions to 1990 levels by 2020, a reduction of 25 percent from current levels. To verify that GHG emission reductions are actually taking place, it will be necessary to measure emissions. We describe atmospheric inverse model estimates of GHG emissions obtained from the California Greenhouse Gas Emissions Measurement (CALGEM) project. In collaboration with NOAA, we are measuring the dominant long-lived GHGs at two tall-towers in central California. Here, we present estimates of CH{sub 4} emissions obtained by statistical comparison of measured and predicted atmospheric mixing ratios. The predicted mixing ratios are calculated using spatially resolved a priori CH{sub 4} emissions and surface footprints, that provide a proportional relationship between the surface emissions and the mixing ratio signal at tower locations. The footprints are computed using the Weather Research and Forecast (WRF) coupled to the Stochastic Time-Inverted Lagrangian Transport (STILT) model. Integral to the inverse estimates, we perform a quantitative analysis of errors in atmospheric transport and other factors to provide quantitative uncertainties in estimated emissions. Regressions of modeled and measured mixing ratios suggest that total CH{sub 4} emissions are within 25% of the inventory estimates. A Bayesian source sector analysis obtains posterior scaling factors for CH{sub 4} emissions, indicating that emissions from several of the sources (e.g., landfills, natural gas use, petroleum production, crops, and wetlands) are roughly consistent with inventory estimates, but livestock emissions are significantly higher than the inventory. A Bayesian 'region' analysis is used to identify spatial variations in CH{sub 4} emissions from 13 sub-regions within California
-
Observation of soft X-ray spectra from a Seyfert 1 and a narrow emission-line galaxy
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Singh, K.P.; Garmire, G.P.; Nousek, J.
1985-01-01
The 0.2-40 keV X-ray spectra of the Seyfert 1 galaxy Mrk 509 and the narrow emission-line galaxy NGC 2992 are analyzed. The results suggest the presence of a steep soft X-ray component in Mrk 509 in addition to the well-known Gamma = 1.7 component found in other active galactic nuclei in the 2-40 keV energy range. The soft X-ray component is interpreted as due to thermal emission from a hot gas, probably associated with the highly ionized gas observed to be outflowing from the galaxy. The X-ray spectrum of NGC 2992 does not show any steepening in the soft X-ray band and is consistent with a single power law (Gamma = 1.78) with very low absorbing column density of 4 x 10 to the 21st/sq cm. A model with partial covering of the nuclear X-ray source is preferred, however, to a simple model with a single power law and absorption. 34 references
-
Pallamraju, Duggirala; Das, Uma; Chakrabarti, Supriya
2011-01-01
We carried out high-cadence (5 min) and high-spatial resolution (2deg magnetic latitude) observations of daytime OI 630.0 nm airglow emission brightness from a low-latitude station to understand the behavior of neutral dynamics in the daytime. The results indicate that the wave periodicities of 12.20 min, and 2 h exist over a wide spatial range of around 8deg-12deg magnetic latitudes. The 20.80 min periodicities in the dayglow seem to appear more often in the measurements closer to the magnetic equator and not at latitudes farther away. Further, periodicities in that range are found to be frequent in the variations of the equatorial electrojet (EEJ) strength as well. We show that wave periodicities due to the neutral dynamics, at least until around 8deg magnetic latitude, are influenced by those that affect the EEJ strength variation as well. Furthermore, the average daily OI 630.0 nm emission brightness over 3 months varied in consonance with that of the sunspot numbers indicating a strong solar influence on the magnitudes of dayglow emissions.
-
Biogenic VOC Emissions from Tropical Landscapes
Guenther, A.; Greenberg, J.; Harley, P.; Otter, L.; Vanni Gatti, L.; Baker, B.
2003-04-01
Biogenic VOC have an important role in determining the chemical composition of atmosphere. As a result, these compounds are important for visibility, biogeochemical cycling, climate and radiative forcing, and the health of the biosphere. Tropical landscapes are estimated to release about 80% of total global biogenic VOC emissions but have been investigated to lesser extent than temperate regions. Tropical VOC emissions are particularly important due to the strong vertical transport and the rapid landuse change that is occurring there. This presentation will provide an overview of field measurements of biogenic VOC emissions from tropical landscapes in Amazonia (Large-scale Biosphere-atmosphere experiment in Amazonia, LBA) Central (EXPRESSO) and Southern (SAFARI 2000) Africa, Asia and Central America. Flux measurement methods include leaf-scale (enclosure measurements), canopy-scale (above canopy tower measurements), landscape-scale (tethered balloon), and regional-scale (aircraft measurements) observations. Typical midday isoprene emission rates for different landscapes vary by more than a factor of 20 with the lowest emissions observed from degraded forests. Emissions of alpha-pinene vary by a similar amount with the highest emissions associated with landscapes dominated by light dependent monoterpene emitting plants. Isoprene emissions tend to be higher for neotropical forests (Amazon and Costa Rica) in comparison to Africa and Asian tropical forests but considerable differences are observed within regions. Strong seasonal variations were observed in both the Congo and the Amazon rainforests with peak emissions during the dry seasons. Substantial emissions of light dependent monoterpenes, methanol and acetone are characteristic of at least some tropical landscapes.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ulrich, M.H.; Boksenberg, A.; Bromage, G.E.
1983-11-01
Observations of the variability of the three strong ultraviolet emission lines in the Seyfert galaxy NGC 4151 (CIV, CIII, and MgII) are used to study the structure of the broad line region and the nuclear energy source of this active galaxy. (author)
-
Usui, Harunobu; Nishida, Yusuke
2017-01-01
The very low-frequency (VLF) band of heart rate variability (HRV) has different characteristics compared with other HRV components. Here we investigated differences in HRV changes after a mental stress task. After the task, the high-frequency (HF) band and ratio of high- to low-frequency bands (LF/HF) immediately returned to baseline. We evaluated the characteristics of VLF band changes after a mental stress task. We hypothesized that the VLF band decreases during the Stroop color word task and there would be a delayed recovery for 2 h after the task (i.e., the VLF change would exhibit a "slow recovery"). Nineteen healthy, young subjects were instructed to rest for 10 min, followed by a Stroop color word task for 20 min. After the task, the subjects were instructed to rest for 120 min. For all subjects, R-R interval data were collected; analysis was performed for VLF, HF, and LF/HF ratio. HRV during the rest time and each 15-min interval of the recovery time were compared. An analysis of the covariance was performed to adjust for the HF band and LF/HF ratio as confounding variables of the VLF component. HF and VLF bands significantly decreased and the LF/HF ratio significantly increased during the task compared with those during rest time. During recovery, the VLF band was significantly decreased compared with the rest time. After the task, the HF band and LF/HF ratio immediately returned to baseline and were not significantly different from the resting values. After adjusting for HF and LF/HF ratio, the VLF band had significantly decreased compared with that during rest. The VLF band is the "slow recovery" component and the HF band and LF/HF ratio are the "quick recovery" components of HRV. This VLF characteristic may clarify the unexplained association of the VLF band in cardiovascular disease prevention.
-
Lightning Sensors for Observing, Tracking and Nowcasting Severe Weather
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Colin Price
2008-01-01
Full Text Available Severe and extreme weather is a major natural hazard all over the world, oftenresulting in major natural disasters such as hail storms, tornados, wind storms, flash floods,forest fires and lightning damages. While precipitation, wind, hail, tornados, turbulence,etc. can only be observed at close distances, lightning activity in these damaging stormscan be monitored at all spatial scales, from local (using very high frequency [VHF]sensors, to regional (using very low frequency [VLF] sensors, and even global scales(using extremely low frequency [ELF] sensors. Using sensors that detect the radio wavesemitted by each lightning discharge, it is now possible to observe and track continuouslydistant thunderstorms using ground networks of sensors. In addition to the number oflightning discharges, these sensors can also provide information on lightningcharacteristics such as the ratio between intra-cloud and cloud-to-ground lightning, thepolarity of the lightning discharge, peak currents, charge removal, etc. It has been shownthat changes in some of these lightning characteristics during thunderstorms are oftenrelated to changes in the severity of the storms. In this paper different lightning observingsystems are described, and a few examples are provided showing how lightning may beused to monitor storm hazards around the globe, while also providing the possibility ofsupplying short term forecasts, called nowcasting.
-
Study of luminous emissions associated to electron emissions in radiofrequency cavities
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Maissa, S.
1996-01-01
This study investigates luminous emissions simultaneously to electron emissions and examines their features in order to better understand the field electron emission phenomenon. A RF cavity, operating at room temperature and in pulsed mode, joined to a sophisticated experimental apparatus has been especially developed. The electron and luminous emissions are investigated on cleaned or with metallic, graphitic and dielectric particles contaminated RF surfaces in order to study their influence on these phenomena. During the surface processing, unstable luminous spots glowing during one RF pulse are detected. Their apparition is promoted in the vicinity of the metallic particles or scratches. Two hypotheses could explain their origin: the presence of micro-plasmas associated to electronic explosive emission during processing or the thermal radiation of the melted metal during this emission. Stable luminous spots glowing during several RF pulses are also detected and appear to increase on RF surfaces contaminated with dielectric particles, leading to strong and explosive luminous emissions. Two interpretations are considered: the initiation of surface breakdowns on the dielectric particles or the heating by the RF field at temperatures sufficiently intense to provoke their thermal radiation then their explosion. Finally a superconducting cavity has been adapted to observe luminous spots, which differ from the former ones bu their star shape and could be associated to micro-plasmas, revealed by the starbursts observed on superconducting cavity walls. (author)
-
Satellite observations of peroxyacetyl nitrate from the Aura Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. H. Payne
2014-11-01
Full Text Available We present a description of the algorithm used to retrieve peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN concentrations from the Aura Tropospheric Emission Spectrometer (TES. We describe the spectral microwindows, error analysis, and the utilization of a priori and initial guess information provided by the GEOS-Chem global chemical transport model. The TES PAN retrievals contain up to one degree of freedom for signal. In general, the retrievals are most sensitive to PAN in the mid-troposphere. Estimated single-measurement uncertainties are on the order of 30 to 50%. The detection limit for a single TES measurement is dependent on the atmospheric and surface conditions as well as on the instrument noise. For observations where the cloud optical depth is less than 0.5, we find that the TES detection limit for PAN is in the region of 200 to 300 pptv. We show that PAN retrievals capture plumes associated with boreal burning. Retrievals over the Northern Hemisphere Pacific in springtime show spatial features that are qualitatively consistent with the expected distribution of PAN in outflow of Asian pollution.
-
Extended emission sources observed via two-proton correlations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Awes, T.C.; Ferguson, R.L.; Obenshain, F.E.
1988-01-01
Two-proton correlations were measured as a function of the total energy and relative momentum of the proton. The correlation is analyzed for different orientations of the relative momentum, which allows information on the size and lifetime of the emission source to be extracted. The most energetic particles are emitted from a short- lived source of compound nucleus dimensions while the lower energy protons appear to be emitted from a source considerably larger than the compound nucleus. 9 refs., 3 figs
-
Regulated Emissions from Biodiesel Tested in Heavy-Duty Engines Meeting 2004 Emission Standards
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
McCormick, R. L.; Tennant, C. J.; Hayes, R. R.; Black, S.; Ireland, J.; McDaniel, T.; Williams, A.; Frailey, M.; Sharp, C. A.
2005-11-01
Biodiesel produced from soybean oil, canola oil, yellow grease, and beef tallow was tested in two heavy-duty engines. The biodiesels were tested neat and as 20% by volume blends with a 15 ppm sulfur petroleum-derived diesel fuel. The test engines were the following: 2002 Cummins ISB and 2003 DDC Series 60. Both engines met the 2004 U.S. emission standard of 2.5 g/bhp-h NO{sub x}+HC (3.35 g/kW-h) and utilized exhaust gas recirculation (EGR). All emission tests employed the heavy-duty transient procedure as specified in the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations. Reduction in PM emissions and increase in NO{sub x} emissions were observed for all biodiesels in all engines, confirming observations made in older engines. On average PM was reduced by 25% and NO{sub x} increased by 3% for the two engines tested for a variety of B20 blends. These changes are slightly larger in magnitude, but in the same range as observed in older engines. The cetane improver 2-ethyl hexyl nitrate was shown to have no measurable effect on NO{sub x} emissions from B20 in these engines, in contrast to observations reported for older engines. The effect of intake air humidity on NO{sub x} emissions from the Cummins ISB was quantified. The CFR NO{sub x}/humidity correction factor was shown to be valid for an engine equipped with EGR, operating at 1700 m above sea level, and operating on conventional or biodiesel.
-
Sarkar, Sohini; Sengupta, Abhigyan; Hazra, Partha; Mandal, Pankaj
2014-01-01
Recent literatures reported blue-green emission from amyloid fibril as exclusive signature of fibril formation. This unusual visible luminescence is regularly used to monitor fibril growth. Blue-green emission has also been observed in crystalline protein and in solution. However, the origin of this emission is not known exactly. Our spectroscopic study of serum proteins reveals that the blue-green emission is a property of protein monomer. Evidences suggest that semiconductor-like band struc...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Momose, Munetake; Ohashi, Nagayoshi; Kudo, Tomoyuki; Tamura, Motohide; Kitamura, Yoshimi
2010-01-01
FN Tau is a rare example of a very low-mass T Tauri star that exhibits a spatially resolved nebulosity in near-infrared scattering light. To directly derive the parameters of a circumstellar disk around FN Tau, observations of dust continuum emission at 340 GHz are carried out with the Submillimeter Array (SMA). A point-like dust continuum emission was detected with a synthesized beam of ∼0.''7 in FWHM. From the analysis of the visibility plot, the radius of the emission is estimated to be ≤0.''29, corresponding to 41 AU. This is much smaller than the radius of the nebulosity, 1.''85 for its brighter part at 1.6 μm. The 340 GHz continuum emission observed with the SMA and the photometric data at λ ≤ 70 μm are explained by a power-law disk model whose outer radius and mass are 41 AU and (0.24-5.9) x 10 -3 M sun , respectively, if the exponent of dust mass opacity (β) is assumed to be 0-2. The disk model cannot fully reproduce the flux density at 230 GHz obtained with the IRAM 30 m telescope, suggesting that there is another extended 'halo' component that is missed in the SMA observations. By requiring the halo not to be detected with the SMA, the lower limit to the size of the halo is evaluated to be between 174 AU and 574 AU, depending on the assumed β value. This size is comparable to the near-infrared nebulosity, implying that the halo unseen with the SMA corresponds to the origin of the near-infrared nebulosity. The halo can contain mass comparable to or at most 8 times greater than that of the inner power-law disk, but its surface density should be lower than that at the outer edge of the power-law disk by more than 1 order of magnitude. The physical nature of the halo is unclear, but it may be the periphery of a flared circumstellar disk that is not described well in terms of a power-law disk model, or a remnant of a protostellar envelope having flattened structure.
-
Chen, Z.; Griffis, T. J.; Lee, X.; Fu, C.; Dlugokencky, E. J.; Andrews, A. E.
2017-12-01
Mitigation of nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions requires a sound understanding of N2O production processes and a robust estimate of N2O budgets. It is critical to understand how emissions vary spatially and temporally, and how they are likely to change given future climate and land management decisions. To address these challenges we have coupled two models including WRF-Chem version 3.8.1 and CLM-GBC-CROP version 4.5 to simulate retrospective and future N2O emissions for the US Corn Belt. Using 7 years (2010-2016) of N2O mixing ratio data from 6 tall tower sites within the US Midwest, we ran the coupled model at a spatial resolution of 0.125o× 0.125o and tested and optimized the simulation of N2O emissions at hourly, seasonal, and inter-annual timescales. Our preliminary results indicate:1) The simulated tall tower mixing ratios for 6 tall towers were all significantly higher than the observations in the growing seasons, indicating a high bias of N2O emissions when using the default N2O production mechanisms in CLM. 2) Following the optimization of N2O production in CLM, the simulated tall tower mixing ratios were strongly correlated with the KCMP and WBI towers, and had moderate correlation with the BAO tower. Overall, the absolute biases in mixing ratios were relatively small. Our next step is to examine 7 years of simulations to assess the spatiotemporal variations of direct and indirect emissions within the US Corn Belt to help identify potential N2O hotspots and hot moments.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Noriega-Crespo, A.; Bohm, K.H.; Raga, A.C.
1989-01-01
In this paper, it is shown that most of the spatial intensity distribution of 11 selected emission lines for Herbig-Haro 1 (including the forbidden S II emission lines at 6731 A and 4069 A, the forbidden O III line at 5007 A, and the forbidden O II line at 3727 A) can be explained by a bow shock with a shock velocity of about 150-200 km/sec at the stagnation point, and under the assumption that the gas entering the shock is fully preionized. The results are based on three spectrograms (with a total exposure time of 180 min) obtained consecutively. Specifically, the ratios of each of the forbidden lines to H-alpha were studied, which permitted a critical test of the model. The agreement between the theoretical predictions and the observations was found to be remarkable, considering the complex geometry that a bow shock could have. 38 refs
-
Herrera, S.; Diskin, G. S.; Pusede, S.
2016-12-01
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a long-lived and highly potent greenhouse gas that also destroys stratospheric ozone. Largely attributed to changes in agricultural sources, N2O concentrations are increasing at a steady rate of 0.8 ppb y-1 globally. Emission rates of N2O remain poorly constrained, with N2O sources arguably among the most uncertain of the long-lived greenhouse gases. This study quantifies N2O emissions at the kilometer-spatial scale in the wintertime in a region with both agricultural and urban sources, the San Joaquin Valley of California. To do this, we use the large number vertical profiles of N2O and other relevant trace gases measured by the P3 aircraft during the NASA DISCOVER-AQ campaign that took place throughout the San Joaquin Valley in January-February 2013. We exploit the observed variability in profile shape by time of day, day to day, and location (over urban versus agricultural sources), along with chemical and physical constraints on mixing and the timing of decoupling between the surface boundary layer and residual layers aloft.
-
CLASP/SJ Observations of Rapid Time Variations in the Ly α Emission in a Solar Active Region
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ishikawa, Shin-nosuke [Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, 3-1-1 Yoshinodai, Chuo-ku, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 252–5210 (Japan); Kubo, Masahito; Katsukawa, Yukio; Kano, Ryouhei; Narukage, Noriyuki; Ishikawa, Ryohko; Bando, Takamasa [National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, 2-21-1 Osawa, Mitaka, Tokyo 181-8588 (Japan); Winebarger, Amy; Kobayashi, Ken [NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, AL 35812 (United States); Trujillo Bueno, Javier [Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, E-38205 La Laguna, Tenerife (Spain); Auchère, Frédéric, E-mail: s.ishikawa@solar.isas.jaxa.jp [Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale, CNRS/Univ. Paris-Sud 11, Bätiment 121, F-91405 Orsay (France)
2017-09-10
The Chromospheric Ly α SpectroPolarimeter (CLASP) is a sounding rocket experiment launched on 2015 September 3 to investigate the solar chromosphere and transition region. The slit-jaw (SJ) optical system captured Ly α images with a high time cadence of 0.6 s. From the CLASP/SJ observations, many variations in the solar chromosphere and transition region emission with a timescale of <1 minute were discovered. In this paper, we focus on the active region within the SJ field of view and investigate the relationship between short (<30 s) temporal variations in the Ly α emission and the coronal structures observed by Solar Dynamics Observatory/Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA). We compare the Ly α temporal variations at the coronal loop footpoints observed in the AIA 211 Å (≈2 MK) and AIA 171 Å (≈0.6 MK) channels with those in the regions with bright Ly α features without a clear association with the coronal loop footpoints. We find more short (<30 s) temporal variations in the Ly α intensity in the footpoint regions. Those variations did not depend on the temperature of the coronal loops. Therefore, the temporal variations in the Ly α intensity at this timescale range could be related to the heating of the coronal structures up to temperatures around the sensitivity peak of 171 Å. No signature was found to support the scenario that these Ly α intensity variations were related to the nanoflares. Waves or jets from the lower layers (lower chromosphere or photosphere) are possible causes for this phenomenon.
-
Nighttime ionospheric D region: Equatorial and nonequatorial
Thomson, Neil R.; McRae, Wayne M.
2009-08-01
Nighttime ionospheric D region parameters are found to be generally well modeled by the traditional H‧ and β as used by Wait and by the U.S. Navy in their Earth-ionosphere VLF radio waveguide programs. New comparisons with nonequatorial, mainly all-sea VLF path observations reported over several decades are shown to be consistent with the previously determined height H‧ ˜ 85.0 km and sharpness β ˜ 0.63 km-1. These paths include NPM (Hawaii) to Washington, D. C., Omega Hawaii and NLK (Seattle) to Japan, NWC (N.W. Australia) to Madagascar, and NBA (Panama) to Colorado. In marked contrast, transequatorial path observations (even when nearly all-sea) are found to be often not well modeled: for example, for Omega Japan and JJI (Japan) to Dunedin, New Zealand, the observed amplitudes are markedly lower than those which would be expected from H‧ ˜ 85.0 km and β ˜ 0.63 km-1, or any other realistic values of H‧ and β. Other transequatorial observations compared with modeling include NWC to Japan, Omega Hawaii to Dunedin, and NPM (Hawaii) to Dunedin. It is suggested that the effects of irregularities in the equatorial electrojet may extend down into the nighttime D region and so account for the observed equatorial VLF perturbations through scattering or mode conversion.
-
Analysis of hard X-ray emission from selected very high energy γ-ray sources observed with INTEGRAL
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hoffmann, Agnes Irene Dorothee
2009-01-01
A few years ago, the era of very high energy γ-ray astronomy started, when the latest generation of Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes (IACT) like H.E.S.S. began to operate and to resolve the sources of TeV emission. Identifications via multi-wavelength studies reveal that the detected sources are supernova remnants and active galactic nuclei, but also pulsar wind nebulae and a few binaries. One widely discussed open question is, how these sources are able to accelerate particles to such high energies. The understanding of the underlying particle distribution, the acceleration processes taking place, and the knowledge of the radiation processes which produce the observed emission, is, therefore, of crucial interest. Observations in the hard X-ray domain can be a key to get information on these particle distributions and processes. Important for this thesis are the TeV and the hard X-ray range. The two instruments, H.E.S.S. and INTEGRAL, whose data were used, are, therefore, described in detail. The main part of this thesis is focused on the X-ray binary system LS 5039/RX J1826.2-1450. It was observed in several energy ranges. The nature of the compact object is still not known, and it was proposed either to be a microquasar system or a non-accreting pulsar system. The observed TeV emission is modulated with the orbital cycle. Several explanations for this variability have been discussed in recent years. The observations with INTEGRAL presented in this thesis have provided new information to solve this question. Therefore, a search for a detection in the hard X-ray range and for its orbital dependence was worthwhile. Since LS 5039 is a faint source and the sky region where it is located is crowded, a very careful, non-standard handling of the INTEGRAL data was necessary, and a cross-checking with other analysis methods was essential to provide reliable results. We found that LS 5039 is emitting in the hard X-ray energy range. A flux rate and an upper flux
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hoffmann, Agnes Irene Dorothee
2009-11-13
A few years ago, the era of very high energy {gamma}-ray astronomy started, when the latest generation of Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes (IACT) like H.E.S.S. began to operate and to resolve the sources of TeV emission. Identifications via multi-wavelength studies reveal that the detected sources are supernova remnants and active galactic nuclei, but also pulsar wind nebulae and a few binaries. One widely discussed open question is, how these sources are able to accelerate particles to such high energies. The understanding of the underlying particle distribution, the acceleration processes taking place, and the knowledge of the radiation processes which produce the observed emission, is, therefore, of crucial interest. Observations in the hard X-ray domain can be a key to get information on these particle distributions and processes. Important for this thesis are the TeV and the hard X-ray range. The two instruments, H.E.S.S. and INTEGRAL, whose data were used, are, therefore, described in detail. The main part of this thesis is focused on the X-ray binary system LS 5039/RX J1826.2-1450. It was observed in several energy ranges. The nature of the compact object is still not known, and it was proposed either to be a microquasar system or a non-accreting pulsar system. The observed TeV emission is modulated with the orbital cycle. Several explanations for this variability have been discussed in recent years. The observations with INTEGRAL presented in this thesis have provided new information to solve this question. Therefore, a search for a detection in the hard X-ray range and for its orbital dependence was worthwhile. Since LS 5039 is a faint source and the sky region where it is located is crowded, a very careful, non-standard handling of the INTEGRAL data was necessary, and a cross-checking with other analysis methods was essential to provide reliable results. We found that LS 5039 is emitting in the hard X-ray energy range. A flux rate and an upper
-
Source mechanism of Saturn narrowband emission
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. D. Menietti
2010-04-01
Full Text Available Narrowband emission (NB is observed at Saturn centered near 5 kHz and 20 kHz and harmonics. This emission appears similar in many ways to Jovian kilometric narrowband emission observed at higher frequencies, and therefore may have a similar source mechanism. Source regions of NB near 20 kHz are believed to be located near density gradients in the inner magnetosphere and the emission appears to be correlated with the occurrence of large neutral plasma clouds observed in the Saturn magnetotail. In this work we present the results of a growth rate analysis of NB emission (~20 kHz near or within a probable source region. This is made possible by the sampling of in-situ wave and particle data. The results indicate waves are likely to be generated by the mode-conversion of directly generated Z-mode emission to O-mode near a density gradient. When the local hybrid frequency is close n fce (n is an integer and fce is the electron cyclotron frequency with n=4, 5 or 6 in our case, electromagnetic Z-mode and weak ordinary (O-mode emission can be directly generated by the cyclotron maser instability.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kroon, P.S.
2010-09-01
About 30% of the increased greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) are related to land use changes and agricultural activities. In order to select effective measures, knowledge is required about GHG emissions from these ecosystems and how these emissions are influenced by management and meteorological conditions. Accurate emission values are therefore needed for all three GHGs to compile the full GHG balance. However, the current annual estimates of CH4 and N2O emissions from ecosystems have significant uncertainties, even larger than 50%. The present study showed that an advanced technique, micrometeorological eddy covariance flux technique, could obtain more accurate estimates with uncertainties even smaller than 10%. The current regional and global trace gas flux estimates of CH4 and N2O are possibly seriously underestimated due to incorrect measurement procedures. Accurate measurements of both gases are really important since they could even contribute for more than two-third to the total GHG emission. For example: the total GHG emission of a dairy farm site was estimated at 16.10 3 kg ha -1 yr -1 in CO2-equivalents from which 25% and 45% was contributed by CH4 and N2O, respectively. About 60% of the CH4 emission was emitted by ditches and their bordering edges. These emissions are not yet included in the national inventory reports. We recommend including these emissions in coming reports.
-
3 mm GMVA Observations of Total and Polarized Emission from Blazar and Radio Galaxy Core Regions
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Carolina Casadio
2017-10-01
Full Text Available We present total and linearly polarized 3 mm Global mm-VLBI Array (GMVA; mm-VLBI: Very Long Baseline Interferometry observations at millimetre wavelengths images of a sample of blazars and radio galaxies from the VLBA-BU-BLAZAR 7 mm monitoring program designed to probe the innermost regions of active galactic nuclei (AGN jets and locate the sites of gamma-ray emission observed by the Fermi-LAT. The lower opacity at 3 mm and improved angular resolution—on the order of 50 microarcseconds—allow us to distinguish features in the jet not visible in the 7 mm VLBA data. We also compare two different methods used for the calibration of instrumental polarisation and we analyze the resulting images for some of the sources in the sample.
-
Observation of disturbance in the lower ionosphere due to standard very low frequency transmission
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Muraoka, Yoshikazu; Murata, Hiroo; Sato, Teruo
1976-01-01
A number of trials to make clear the disturbance phenomena of the lower ionosphere have been carried out by observing the phase and intensity of standard very low frequency waves. Here, the sudden phase anomaly (SPA) and the storm after-effect are discussed, based on the data obtained so far. In the observation of VLF waves, the height of reflecting point of the ionosphere is lowered by the ionization with solar X-ray accompanying flares, and the phase angle generally advances. The SPS was observed to determine the quantitative relation between this phase deviation and the solar X-ray flux as a function of solar zenith angle. The lower ionosphere disturbance which occurs subsequently to magnetic storm is a phenomenon specific to middle latitudes, and called storm after-effect. The observations were carried out to clarify the form of the after-effect by comparing its characteristics with the result of theoretical discussions. Concerning the storm after-effect, it was made clear that its duration considerably changed with the value of Dst, and it showed a different aspect during winter. It was also made clear that a part of the complicated aspect of phase angle change in winter was caused by the storm after-effect. (Wakatsuki, Y.)
-
Simmonds, P. G.; Rigby, M.; Manning, A. J.; Lunt, M. F.; O'Doherty, S.; McCulloch, A.; Fraser, P. J.; Henne, S.; Vollmer, M. K.; Mühle, J.; Weiss, R. F.; Salameh, P. K.; Young, D.; Reimann, S.; Wenger, A.; Arnold, T.; Harth, C. M.; Krummel, P. B.; Steele, L. P.; Dunse, B. L.; Miller, B. R.; Lunder, C. R.; Hermansen, O.; Schmidbauer, N.; Saito, T.; Yokouchi, Y.; Park, S.; Li, S.; Yao, B.; Zhou, L. X.; Arduini, J.; Maione, M.; Wang, R. H. J.; Ivy, D.; Prinn, R. G.
2016-01-01
High frequency, in situ observations from 11 globally distributed sites for the period 1994-2014 and archived air measurements dating from 1978 onward have been used to determine the global growth rate of 1,1-difluoroethane (HFC-152a, CH3CHF2). These observations have been combined with a range of atmospheric transport models to derive global emission estimates in a top-down approach. HFC-152a is a greenhouse gas with a short atmospheric lifetime of about 1.5 years. Since it does not contain chlorine or bromine, HFC-152a makes no direct contribution to the destruction of stratospheric ozone and is therefore used as a substitute for the ozone depleting chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs). The concentration of HFC-152a has grown substantially since the first direct measurements in 1994, reaching a maximum annual global growth rate of 0.84 ± 0.05 ppt yr-1 in 2006, implying a substantial increase in emissions up to 2006. However, since 2007, the annual rate of growth has slowed to 0.38 ± 0.04 ppt yr-1 in 2010 with a further decline to an annual average rate of growth in 2013-2014 of -0.06 ± 0.05 ppt yr-1. The annual average Northern Hemisphere (NH) mole fraction in 1994 was 1.2 ppt rising to an annual average mole fraction of 10.1 ppt in 2014. Average annual mole fractions in the Southern Hemisphere (SH) in 1998 and 2014 were 0.84 and 4.5 ppt, respectively. We estimate global emissions of HFC-152a have risen from 7.3 ± 5.6 Gg yr-1 in 1994 to a maximum of 54.4 ± 17.1 Gg yr-1 in 2011, declining to 52.5 ± 20.1 Gg yr-1 in 2014 or 7.2 ± 2.8 Tg-CO2 eq yr-1. Analysis of mole fraction enhancements above regional background atmospheric levels suggests substantial emissions from North America, Asia, and Europe. Global HFC emissions (so called "bottom up" emissions) reported by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are based on cumulative national emission data reported to the UNFCCC, which in turn are based on
-
Ganguli, G.; Crabtree, C. E.; Rudakov, L.; Mithaiwala, M.
2014-12-01
Velocity ring instabilities are a common naturally occuring magnetospheric phenomenon that can also be generated by man made ionospheric experiments. These instabilities are known to generate lower-hybrid waves, which generally cannot propagte out of the source region. However, nonlinear wave physics can convert these linearly driven electrostatic lower-hybrid waves into electromagnetic waves that can escape the source region. These nonlinearly generated waves can be an important source of VLF turbulence that controls the trapped electron lifetime in the radiation belts. We develop numerical solutions to the wave-kinetic equation in a periodic box including the effects of nonlinear (NL) scattering (nonlinear Landau damping) of Lower-hybrid waves giving the evolution of the wave-spectra in wavenumber space. Simultaneously we solve the particle diffusion equation of both the background plasma particles and the ring ions, due to both linear and nonlinear Landau resonances. At initial times for cold ring ions, an electrostatic beam mode is excited, while the kinetic mode is stable. As the instability progresses the ring ions heat, the beam mode is stabilized, and the kinetic mode destabilizes. When the amplitude of the waves becomes sufficient the lower-hybrid waves are scattered (by either nearly unmagnetized ions or magnetized electrons) into electromagnetic magnetosonic waves [Ganguli et al 2010]. The effect of NL scattering is to limit the amplitude of the waves, slowing down the quasilinear relaxation time and ultimately allowing more energy from the ring to be liberated into waves [Mithaiwala et al. 2011]. The effects of convection out of the instability region are modeled, additionally limiting the amplitude of the waves, allowing further energy to be liberated from the ring [Scales et al., 2012]. Results are compared to recent 3D PIC simulations [Winske and Duaghton 2012].
-
Gruzinov, Andrei
2013-01-01
Emission spectrum is calculated for a weak axisymmetric pulsar. Also calculated are the observed spectrum, efficiency, and the observed efficiency. The underlying flow of electrons and positrons turns out to be curiously intricate.
-
The Annual Cycle of Water Vapor on Mars as Observed by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer
Smith, Michael D.; Vondrak, Richard R. (Technical Monitor)
2001-01-01
Spectra taken by the Mars Global Surveyor Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) have been used to monitor the latitude, longitude, and seasonal dependence of water vapor for over one full Martian year (March 1999-March 2001). A maximum in water vapor abundance is observed at high latitudes during mid-summer in both hemispheres, reaching a maximum value of approximately 100 pr-micrometer in the north and approximately 50 pr-micrometer in the south. Low water vapor abundance (water vapor. The latitudinal and seasonal dependence of the decay of the northern summer water vapor maximum implies cross-equatorial transport of water to the southern hemisphere, while there is little or no corresponding transport during the decay of the southern hemisphere summer maximum. The latitude-longitude dependence of annually-averaged water vapor (corrected for topography) has a significant positive correlation with albedo and significant negative correlations with thermal inertia and surface pressure. Comparison of TES results with those retrieved from the Viking Orbiter Mars Atmospheric Water Detectors (MAWD) experiments shows some similar features, but also many significant differences. The southern hemisphere maximum observed by TES was not observed by MAWD and the large latitudinal gradient in annually-averaged water vapor observed by MAWD does not appear in the TES results.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Harunobu Usui
Full Text Available The very low-frequency (VLF band of heart rate variability (HRV has different characteristics compared with other HRV components. Here we investigated differences in HRV changes after a mental stress task. After the task, the high-frequency (HF band and ratio of high- to low-frequency bands (LF/HF immediately returned to baseline. We evaluated the characteristics of VLF band changes after a mental stress task. We hypothesized that the VLF band decreases during the Stroop color word task and there would be a delayed recovery for 2 h after the task (i.e., the VLF change would exhibit a "slow recovery". Nineteen healthy, young subjects were instructed to rest for 10 min, followed by a Stroop color word task for 20 min. After the task, the subjects were instructed to rest for 120 min. For all subjects, R-R interval data were collected; analysis was performed for VLF, HF, and LF/HF ratio. HRV during the rest time and each 15-min interval of the recovery time were compared. An analysis of the covariance was performed to adjust for the HF band and LF/HF ratio as confounding variables of the VLF component. HF and VLF bands significantly decreased and the LF/HF ratio significantly increased during the task compared with those during rest time. During recovery, the VLF band was significantly decreased compared with the rest time. After the task, the HF band and LF/HF ratio immediately returned to baseline and were not significantly different from the resting values. After adjusting for HF and LF/HF ratio, the VLF band had significantly decreased compared with that during rest. The VLF band is the "slow recovery" component and the HF band and LF/HF ratio are the "quick recovery" components of HRV. This VLF characteristic may clarify the unexplained association of the VLF band in cardiovascular disease prevention.
-
Photon emission from massive projectile impacts on solids.
Fernandez-Lima, F A; Pinnick, V T; Della-Negra, S; Schweikert, E A
2011-01-01
First evidence of photon emission from individual impacts of massive gold projectiles on solids for a number of projectile-target combinations is reported. Photon emission from individual impacts of massive Au(n) (+q) (1 ≤ n ≤ 400; q = 1-4) projectiles with impact energies in the range of 28-136 keV occurs in less than 10 ns after the projectile impact. Experimental observations show an increase in the photon yield from individual impacts with the projectile size and velocity. Concurrently with the photon emission, electron emission from the impact area has been observed below the kinetic emission threshold and under unlikely conditions for potential electron emission. We interpret the puzzling electron emission and correlated luminescence observation as evidence of the electronic excitation resulting from the high-energy density deposited by massive cluster projectiles during the impact.
-
Synthesis of silver hollow nanoparticles and observation of photoluminescence emission properties
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Desarkar, H.S.; Kumbhakar, P.; Mitra, A.K.
2013-01-01
Preparation of hollow silver nanoparticles (HSNs) along-with solid silver nanoparticles are reported by Nd:YAG laser ablation of solid silver target immersed in water medium with a laser ablation time (LAT) duration of 50 min and with the incident laser fluence of 151 J/cm 2 . It is found that only solid silver nanoparticles are produced when the experiment is carried out with smaller values of LAT duration. The synthesized samples are characterized by using transmission electron microscopy and UV–Visible absorption spectroscopy. The UV–Visible absorption spectra of the samples show sharp absorptions in the ultraviolet and in visible regions due to interband transition and surface plasmon resonance oscillations in Ag nanoparticles, respectively. It is found that all samples exhibit photoluminescence (PL) emission, at room temperature, in the UV–Visible region peaked at ∼346 nm, due to the recombination of electrons with holes from sp conduction band to d band of Ag. The sample containing HSNs exhibits strong PL emission and the value of peak PL emission intensity is enhanced by the factor of 2.4 in comparison to that obtained from the sample synthesized with LAT duration of 20 min. The synthesized HSNs may find applications in catalysis and in chemical sensing. - Highlights: ►Hollow silver nanoparticles of 15–60 nm particle sizes are prepared by laser ablation. ►Prepared Ag nanoparticles show sharp absorptions in the UV and visible regions. ►Strong interband transition along-with SPR oscillations is reported. ►Enhancement (2.4 times) in photoluminescence emission in the UV region is reported.
-
Ilić, L.; Kuzmanoski, M.; Kolarž, P.; Nina, A.; Srećković, V.; Mijić, Z.; Bajčetić, J.; Andrić, M.
2018-06-01
Measurements of atmospheric parameters were carried out during the partial solar eclipse (51% coverage of solar disc) observed in Belgrade on 20 March 2015. The measured parameters included height of the planetary boundary layer (PBL), meteorological parameters, solar radiation, surface ozone and air ions, as well as Very Low Frequency (VLF, 3-30 kHz) and Low Frequency (LF, 30-300 kHz) signals to detect low-ionospheric plasma perturbations. The observed decrease of global solar and UV-B radiation was 48%, similar to the solar disc coverage. Meteorological parameters showed similar behavior at two measurement sites, with different elevations and different measurement heights. Air temperature change due to solar eclipse was more pronounced at the lower measurement height, showing a decrease of 2.6 °C, with 15-min time delay relative to the eclipse maximum. However, at the other site temperature did not decrease; its morning increase ceased with the start of the eclipse, and continued after the eclipse maximum. Relative humidity at both sites remained almost constant until the eclipse maximum and then decreased as the temperature increased. The wind speed decreased and reached minimum 35 min after the last contact. The eclipse-induced decrease of PBL height was about 200 m, with minimum reached 20 min after the eclipse maximum. Although dependent on UV radiation, surface ozone concentration did not show the expected decrease, possibly due to less significant influence of photochemical reactions at the measurement site and decline of PBL height. Air-ion concentration decreased during the solar eclipse, with minimum almost coinciding with the eclipse maximum. Additionally, the referential Line-of-Sight (LOS) radio link was set in the area of Belgrade, using the carrier frequency of 3 GHz. Perturbation of the receiving signal level (RSL) was observed on March 20, probably induced by the solar eclipse. Eclipse-related perturbations in ionospheric D-region were detected
-
The detectability of radio emission from exoplanets
Lynch, C. R.; Murphy, Tara; Lenc, E.; Kaplan, D. L.
2018-05-01
Like the magnetised planets in our Solar System, magnetised exoplanets should emit strongly at radio wavelengths. Radio emission directly traces the planetary magnetic fields and radio detections can place constraints on the physical parameters of these features. Large comparative studies of predicted radio emission characteristics for the known population of exoplanets help to identify what physical parameters could be key for producing bright, observable radio emission. Since the last comparative study, many thousands of exoplanets have been discovered. We report new estimates for the radio flux densities and maximum emission frequencies for the current population of known exoplanets orbiting pre-main sequence and main-sequence stars with spectral types F-M. The set of exoplanets predicted to produce observable radio emission are Hot Jupiters orbiting young stars. The youth of these system predicts strong stellar magnetic fields and/or dense winds, which are key for producing bright, observable radio emission. We use a new all-sky circular polarisation Murchison Widefield Array survey to place sensitive limits on 200 MHz emission from exoplanets, with 3σ values ranging from 4.0 - 45.0 mJy. Using a targeted Giant Metre Wave Radio Telescope observing campaign, we also report a 3σ upper limit of 4.5 mJy on the radio emission from V830 Tau b, the first Hot Jupiter to be discovered orbiting a pre-main sequence star. Our limit is the first to be reported for the low-frequency radio emission from this source.
-
Biophoton emission induced by heat shock.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Katsuhiro Kobayashi
Full Text Available Ultraweak biophoton emission originates from the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS that are produced in mitochondria as by-products of cellular respiration. In healthy cells, the concentration of ROS is minimized by a system of biological antioxidants. However, heat shock changes the equilibrium between oxidative stress and antioxidant activity, that is, a rapid rise in temperature induces biophoton emission from ROS. Although the rate and intensity of biophoton emission was observed to increase in response to elevated temperatures, pretreatment at lower high temperatures inhibited photon emission at higher temperatures. Biophoton measurements are useful for observing and evaluating heat shock.
-
Jia, Jianjun; Ptak, Andrew; Heckman, Timothy M.; Braito, Valentina; Reeves, James
2012-01-01
We present a Chandra observation of IRAS 19254-7245, a nearby ultraluminous infrared galaxy also known as the Superantennae. The high spatial resolution of Chandra allows us to disentangle for the first time the diffuse starburst (SB) emission from the embedded Compton-thick active galactic nucleus (AGN) in the southern nucleus. No AGN activity is detected in the northern nucleus. The 2-10 keV spectrum of the AGN emission is fitted by a flat power law (TAU = 1.3) and an He-like Fe Kalpha line with equivalent width 1.5 keV, consistent with previous observations. The Fe K line profile could be resolved as a blend of a neutral 6.4 keV line and an ionized 6.7 keV (He-like) or 6.9 keV (H-like) line. Variability of the neutral line is detected compared with the previous XMM-Newton and Suzaku observations, demonstrating the compact size of the iron line emission. The spectrum of the galaxy-scale extended emission excluding the AGN and other bright point sources is fitted with a thermal component with a best-fit kT of approximately 0.8 keV. The 2-10 keV luminosity of the extended emission is about one order of magnitude lower than that of the AGN. The basic physical and structural properties of the extended emission are fully consistent with a galactic wind being driven by the SB. A candidate ultraluminous X-ray source is detected 8 south of the southern nucleus. The 0.3 - 10 keV luminosity of this off-nuclear point source is approximately 6 x 10(exp 40) erg per second if the emission is isotropic and the source is associated with the Superantennae.
-
Optimization study of direct morphology observation by cold field emission SEM without gold coating.
He, Dan; Fu, Cheng; Xue, Zhigang
2018-06-01
Gold coating is a general operation that is generally applied on non-conductive or low conductive materials, during which the morphology of the materials can be examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). However, fatal deficiencies in the materials can result in irreversible distortion and damage. The present study directly characterized different low conductive materials such as hydroxyapatite, modified poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) fiber, and zinc oxide nanopillar by cold field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) without a gold coating. According to the characteristics of the low conductive materials, various test conditions, such as different working signal modes, accelerating voltages, electron beam spots, and working distances, were characterized to determine the best morphological observations of each sample. Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Variability of OH(3-1) and OH(6-2) emission altitude and volume emission rate from 2003 to 2011
Teiser, Georg; von Savigny, Christian
2017-08-01
In this study we report on variability in emission rate and centroid emission altitude of the OH(3-1) and OH(6-2) Meinel bands in the terrestrial nightglow based on spaceborne nightglow measurements with the SCIAMACHY (SCanning Imaging Absorption spectroMeter for Atmospheric CHartographY) instrument on the Envisat satellite. The SCIAMACHY observations cover the time period from August 2002 to April 2012 and the nighttime observations used in this study are performed at 10:00 p.m. local solar time. Characterizing variability in OH emission altitude - particularly potential long-term variations - is important for an appropriate interpretation of ground-based OH rotational temperature measurements, because simultaneous observations of the vertical OH volume emission rate profile are usually not available for these measurements. OH emission altitude and vertically integrated emission rate time series with daily resolution for the OH(3-1) band and monthly resolution for the OH(6-2) band were analyzed using a standard multilinear regression approach allowing for seasonal variations, QBO-effects (Quasi-Biennial Oscillation), solar cycle (SC) variability and a linear long-term trend. The analysis focuses on low latitudes, where SCIAMACHY nighttime observations are available all year. The dominant sources of variability for both OH emission rate and altitude are the semi-annual and annual variations, with emission rate and altitude being highly anti-correlated. There is some evidence for a 11-year solar cycle signature in the vertically integrated emission rate and in the centroid emission altitude of both the OH(3-1) and OH(6-2) bands.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bandis, C.; Pate, B.B.
1995-01-01
We have recently reported that bound electron-hole pairs (Mott-Wannier excitons) are the dominant source of photoelectron emission from specially prepared [''as-polished'' C(111)-(1x1):H] negative-electron-affinity diamond surfaces for near-band-gap excitation up to 0.5 eV above threshold [C. Bandis and B. B. Pate, Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 777 (1995)]. It was found that photoexcited excitons transport to the surface, break up, and emit their electron. In this paper, we extend the study of exciton-derived emission to include partial yield (constant final-state) analysis as well as angular distribution measurements of the photoelectric emission. In addition, we find that exciton-derived emission does not always dominate. Photoelectric emission properties of the in situ ''rehydrogenated'' (111)-(1x1):H diamond surface are characteristically different than emission observed from the as-polished (111)-(1x1):H surface. The rehydrogenated surface has additional downward band bending as compared to the as-polished surface. In confirmation of the assignment of photoelectric yield to exciton breakup emission, we find a significant enhancement of the total electron yield when the downward band bending of the hydrogenated surface is increased. The functional form of the observed total electron yield demonstrates that, in contrast to the as-polished surface, conduction-band electrons are a significant component of the observed photoelectric yield from the in situ hydrogenated (111)-(1x1):H surface. Furthermore, electron emission characteristics of the rehydrogenated surface confirms our assignment of a Fan phonon-cascade mechanism for thermalization of excitons
-
Observations of OH(3,1) airglow emission using a Michelson interferometer at 62° S
Won, Young-In; Cho, Young-Min; Niciejewski, Rick J.; Kim, Jhoon
A Michelson interferometer was used to observe the hydroxyl (OH) emission in the upper mesosphere at the King Sejong Station (62.22° S, 301.25° E), Antarctica. The instrument was installed in February 1999 and has been in routine operation since then. An intensive operational effort has resulted in a substantial data set between April and June, 1999. A spectral analysis was performed on individual data to examine the information of dominant waves. A harmonic analysis was also carried out on the monthly average data to investigate the characteristics of the major low frequency oscillations. The 12-hr temperature oscillations exhibit a striking agreement with a theoretical tidal model, supporting the tidal (migrating) origin. The 8-hr wave is found to be persistent and dominant, reflecting its major role in the upper mesospheric dynamics at the given latitude. The 6-hr oscillation is observed only in May with its value close to the prediction for zonally symmetric tides.
-
Zhang, X.; Jones, D. B. A.; Keller, M.; Jiang, Z.; Bourassa, A. E.; Degenstein, D. A.; Clerbaux, C.; Pierre-Francois, C.
2017-12-01
Atmospheric carbon monoxide (CO) emissions estimated from inverse modeling analyses exhibit large uncertainties, due, in part, to discrepancies in the tropospheric chemistry in atmospheric models. We attempt to reduce the uncertainties in CO emission estimates by constraining the modeled abundance of ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitric acid (HNO3), and formaldehyde (HCHO), which are constituents that play a key role in tropospheric chemistry. Using the GEOS-Chem four-dimensional variational (4D-Var) data assimilation system, we estimate CO emissions by assimilating observations of CO from the Measurement of Pollution In the Troposphere (MOPITT) and the Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer (IASI), together with observations of O3 from the Optical Spectrograph and InfraRed Imager System (OSIRIS) and IASI, NO2 and HCHO from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI), and HNO3 from the Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS). Our experiments evaluate the inferred CO emission estimates from major anthropogenic, biomass burning and biogenic sources. Moreover, we also infer surface emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx = NO + NO2) and isoprene. Our results reveal that this multiple species chemical data assimilation produces a chemical consistent state that effectively adjusts the CO-O3-OH coupling in the model. The O3-induced changes in OH are particularly large in the tropics. Overall, our analysis results in a better constrained tropospheric chemical state.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Sato, H; Utsugi, M; Hirano, K; Doi, T; Nishida, Y; Arita, K [Hokkaido University, Sapporo (Japan)
1996-05-01
An MT observation was conducted in the Hidaka district, Hokkaido, for the estimation of the 2D resistivity structure in the southern part of the metamorphic belt, when frequencies of the VLF, ELF, and ULF bands were used. An approximately 42km-long traverse line was set to cross the Hidaka metamorphic belt from east to west. As for the observation points, 48 VLF points, 16 ELF points, and 4 ULF points were provided. During the data processing, impedance tensor was calculated in the frequency domain for the determination of the apparent resistivity relative to frequency and the phase difference. As the result, it was found that there is a fairly large resistivity gap between observation spots MNS and KWR and that the boundary corresponds to the Hidaka metamorphic belt, that the metamorphic belt that is reflected as a conspicuous high-resistivity layer in the VLF-, ELF-MT slopes down toward the east and has a distribution as deep as 10km in the vicinity of observation point KWR, that this high-resistivity layer sandwiches a low-resistivity layer at a depth of 5-7km, and that on the east side of the metamorphic belt there is a medium-resistivity layer creeping under the belt from the east side toward the west side. 5 refs., 6 figs.
-
Exciplex emission from amphiphilic polysilanes bearing ammonium moieties
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yamaki, T.; Nakashiba, Y.; Asai, K.; Ishigure, K.; Shibata, H.
1997-01-01
We were the first to observe two emission bands in the visible region for some kinds of ammonium-type amphiphilic polysilanes both in solutions and in thin films. One, a broad emission band at 400-500 nm not due to a σ * →σ transition, was observed only for methylphenylsilane-based polymer solutions. The appearance of this low-energy emission is reasonably explained by considering the intramolecular exciplex formation between a Si-conjugated main chain and an ammonium site in the same monomer unit. The other, an emission band at the longer wavelength (around 560 nm), was found in the solvent-cast films where each molecule is randomly located, in addition to that observed for the solutions. This emission, which was not observed for the oriented LB films, is considered to originate from an intermolecular interaction. (orig.)
-
Acoustic emission technique and its applications
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sato, Ichiya; Sasaki, Soji
1976-01-01
Acoustic emission technique is described. The characteristics of acoustic emission signal, measurement techniques, and its application are explained. The acoustic signals are grouped into continuous and burst types. The continuous signal is due to plastic deformation, and the burst type is due to the generation and growth of cracks. The latter can be used for the identification of the position of cracks. The frequency of the acoustic emission is in the range from several tens of KHz to two MHz. Piezoelectric ceramics are used as the oscillators of sensors. The dynamic behavior of acoustic emission can be observed with a two-channel acoustic emission measuring apparatus. Multi-channel method was developed at Hitachi, Ltd., and is used for large structures. General computer identification method and simple zone identification method are explained. Noise elimination is important for the measurement, and the methods were studied. Examples of application are the observation of acoustic emission in the plastic deformation of steel, the tensile test of large welded material with natural defects, and others. The method will be used for the diagnosis and observation of large structures, the test and quality control of products. (Kato, T.)
-
Kauffmann, Jens; Goldsmith, Paul F.; Melnick, Gary; Tolls, Volker; Guzman, Andres; Menten, Karl M.
2017-09-01
Trends observed in galaxies, such as the Gao & Solomon relation, suggest a linear relationship between the star formation rate and the mass of dense gas available for star formation. Validation of such trends requires the establishment of reliable methods to trace the dense gas in galaxies. One frequent assumption is that the HCN (J = 1-0) transition is unambiguously associated with gas at H2 densities ≫ 104 cm-3. If so, the mass of gas at densities ≫ 104 cm-3 could be inferred from the luminosity of this emission line, LHCN (1-0). Here we use observations of the Orion A molecular cloud to show that the HCN (J = 1-0) line traces much lower densities 103 cm-3 in cold sections of this molecular cloud, corresponding to visual extinctions AV ≈ 6 mag. We also find that cold and dense gas in a cloud like Orion produces too little HCN emission to explain LHCN (1-0) in star forming galaxies, suggesting that galaxies might contain a hitherto unknown source of HCN emission. In our sample of molecules observed at frequencies near 100 GHz (also including 12CO, 13CO, C18O, CN, and CCH), N2H+ is the only species clearly associated with relatively dense gas.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. G. Simmonds
2016-01-01
Full Text Available High frequency, in situ observations from 11 globally distributed sites for the period 1994–2014 and archived air measurements dating from 1978 onward have been used to determine the global growth rate of 1,1-difluoroethane (HFC-152a, CH3CHF2. These observations have been combined with a range of atmospheric transport models to derive global emission estimates in a top-down approach. HFC-152a is a greenhouse gas with a short atmospheric lifetime of about 1.5 years. Since it does not contain chlorine or bromine, HFC-152a makes no direct contribution to the destruction of stratospheric ozone and is therefore used as a substitute for the ozone depleting chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs. The concentration of HFC-152a has grown substantially since the first direct measurements in 1994, reaching a maximum annual global growth rate of 0.84 ± 0.05 ppt yr−1 in 2006, implying a substantial increase in emissions up to 2006. However, since 2007, the annual rate of growth has slowed to 0.38 ± 0.04 ppt yr−1 in 2010 with a further decline to an annual average rate of growth in 2013–2014 of −0.06 ± 0.05 ppt yr−1. The annual average Northern Hemisphere (NH mole fraction in 1994 was 1.2 ppt rising to an annual average mole fraction of 10.1 ppt in 2014. Average annual mole fractions in the Southern Hemisphere (SH in 1998 and 2014 were 0.84 and 4.5 ppt, respectively. We estimate global emissions of HFC-152a have risen from 7.3 ± 5.6 Gg yr−1 in 1994 to a maximum of 54.4 ± 17.1 Gg yr−1 in 2011, declining to 52.5 ± 20.1 Gg yr−1 in 2014 or 7.2 ± 2.8 Tg-CO2 eq yr−1. Analysis of mole fraction enhancements above regional background atmospheric levels suggests substantial emissions from North America, Asia, and Europe. Global HFC emissions (so called “bottom up” emissions reported by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC
-
Pulsed, atmospheric pressure plasma source for emission spectrometry
Duan, Yixiang; Jin, Zhe; Su, Yongxuan
2004-05-11
A low-power, plasma source-based, portable molecular light emission generator/detector employing an atmospheric pressure pulsed-plasma for molecular fragmentation and excitation is described. The average power required for the operation of the plasma is between 0.02 W and 5 W. The features of the optical emission spectra obtained with the pulsed plasma source are significantly different from those obtained with direct current (dc) discharge higher power; for example, strong CH emission at 431.2 nm which is only weakly observed with dc plasma sources was observed, and the intense CN emission observed at 383-388 nm using dc plasma sources was weak in most cases. Strong CN emission was only observed using the present apparatus when compounds containing nitrogen, such as aniline were employed as samples. The present apparatus detects dimethylsulfoxide at 200 ppb using helium as the plasma gas by observing the emission band of the CH radical. When coupled with a gas chromatograph for separating components present in a sample to be analyzed, the present invention provides an apparatus for detecting the arrival of a particular component in the sample at the end of the chromatographic column and the identity thereof.
-
Verrecchia, F.; Tavani, M.; Donnarumma, I.; Bulgarelli, A.; Evangelista, Y.; Pacciani, L.; Ursi, A.; Piano, G.; Pilia, M.; Cardillo, M.; Parmiggiani, N.; Giuliani, A.; Pittori, C.; Longo, F.; Lucarelli, F.; Minervini, G.; Feroci, M.; Argan, A.; Fuschino, F.; Labanti, C.; Marisaldi, M.; Fioretti, V.; Trois, A.; Del Monte, E.; Antonelli, L. A.; Barbiellini, G.; Caraveo, P.; Cattaneo, P. W.; Colafrancesco, S.; Costa, E.; D'Amico, F.; Ferrari, A.; Giommi, P.; Morselli, A.; Paoletti, F.; Pellizzoni, A.; Picozza, P.; Rappoldi, A.; Soffitta, P.; Vercellone, S.; Baroncelli, L.; Zollino, G.
2017-12-01
The LIGO-Virgo Collaboration (LVC) detected, on 2017 August 17, an exceptional gravitational-wave (GW) event temporally consistent within ˜ 1.7 {{s}} with the GRB 1708117A observed by Fermi-GBM and INTEGRAL. The event turns out to be compatible with a neutron star-neutron star (NS-NS) coalescence that subsequently produced a radio/optical/X-ray transient detected at later times. We report the main results of the observations by the AGILE satellite of the GW170817 localization region (LR) and its electromagnetic (EM) counterpart. At the LVC detection time T 0, the GW170817 LR was occulted by the Earth. The AGILE instrument collected useful data before and after the GW/GRB event because in its spinning observation mode it can scan a given source many times per hour. The earliest exposure of the GW170817 LR by the gamma-ray imaging detector started about 935 s after T 0. No significant X-ray or gamma-ray emission was detected from the LR that was repeatedly exposed over timescales of minutes, hours, and days before and after GW170817, also considering Mini-calorimeter and Super-AGILE data. Our measurements are among the earliest ones obtained by space satellites on GW170817 and provide useful constraints on the precursor and delayed emission properties of the NS-NS coalescence event. We can exclude with high confidence the existence of an X-ray/gamma-ray emitting magnetar-like object with a large magnetic field of {10}15 {{G}}. Our data are particularly significant during the early stage of evolution of the EM remnant.
-
Roiger, A.; Klausner, T.; Schlager, H.; Ziereis, H.; Huntrieser, H.; Baumann, R.; Eirenschmalz, L.; Joeckel, P.; Mertens, M.; Fisher, R.; Bauguitte, S.; Young, S.; Andrés Hernández, M. D.
2017-12-01
Urban environments represent large and diffuse area sources of CH4 including emissions from pipeline leaks, industrial/sewage treatment plants, and landfills. However, there is little knowledge about the exact magnitude of these emissions and their contribution to total anthropogenic CH4. Especially in the context of an urbanizing world, a better understanding of the methane footprint of urban areas is crucial, both with respect to mitigation and projection of climate impacts. Aircraft-borne in-situ measurements are particularly useful to both quantify emissions from such area sources, as well as to study their impact on the regional distribution. However, airborne CH4 observations downstream of European cities are especially sparse.Here we report from aircraft-borne CH4 in-situ measurements as conducted during the HALO aircraft campaign EMeRGe (Effect of Megacities on the Transport and Transformation of Pollutants on the Regional to Global Scales) in July 2017, which was led by the University of Bremen, Germany. During seven research flights, emissions from a variety of European (Mega)-cities were probed at different altitudes from 3km down to 500m, including measurements in the outflows of London, Rome, Po Valley, Ruhr and Benelux. We will present and compare the CH4 distribution measured downstream of the various studied urban hot-spots. With the help of other trace gas measurements (including e.g. CO2, CO, O3, SO2), observed methane enhancements will be attributed to the different potential source types. Finally, by the combination of in-situ measurements and regional model simulations using the EMAC-MECO(n) model, the contribution of emissions from urban centers to the regional methane budget over Europe will be discussed.
-
Continuum emission of excited sodium dimer
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pardo, A.; Poyato, J.M.L.; Alonso, J.I.; Rico, F.R.
1980-01-01
A study has been made of the behaviour of excited molecular sodium using high-power Ar + laser radiation. A continuum emission was observed in the red wavelength region. This emission was thought to be caused by the formation of excited triatomic molecules. Energy transfer was observed from excited molecules to atoms. (orig.)
-
Lei, L.; Zhong, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, S., Sr.
2016-12-01
The growth of the global anthropogenic carbon emission stalled in 2014, according to data from International Energy Agency (IEA). This paper presents a practical application of satellite observation for detecting the regional enhancement of CO2 induced by underlying anthropogenic CO2 emissions especially during the 2014 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) summit. We collected the column averaged dry air mole fraction (XCO2) data from Greenhouse Observation SATellite (GOSAT) from Jan. 2010 to Dec. 2015, which are provided by Japan GOSAT project team. The spatial change of the 5-year averaged XCO2 derived by gap filling [Zeng et al., TGRS, 2014], as shown in Fig.1, demonstrated that high XCO2prefer to correspond to the most intensive power plants. We calculated the regional contrasts between source and almost without emission (Fig.2), which are defined based on emission and potential temperature. The source, which is defined around Beijing, has many big power plants (Fig.1). The regional contrast showed 1-3 ppm with large seasonal variations while it is the lowest in summer due to influence of biospheric fluxes and especially show abnormal fluctuation in autumn 2014 (Fig.3). XCO2 fell from 398.9 ppm in 15-30 Oct. before APEC to 395.7 ppm during 1-11 Nov. 2014 APEC in source area around Beijing, and the contrast decreased from 4.5 ppm to 1.0 ppm (Table 1). This abnormal decline of XCO2 likely indicate the effects of controlling action for strong local source emissions such as closed many small inefficient coal-fired power plants from the beginning of 2014, banned on burning straw, especially in addition to temporally shut down the big coal-power plants and limiting the number of vehicles running during the APEC summit within the large zone covering the six provinces around Beijing. The large reduction was reported in aerosol of 50% above during the APEC summit (Sun et al., Sci. report, 2016). Our results agree to the potential of satellite observations to
-
A flare observed in coronal, transition region, and helium I 10830 Å emissions
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zeng, Zhicheng; Cao, Wenda [Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research, New Jersey Institute of Technology, 323 Martin Luther King Boulevard, Newark, NJ 07102 (United States); Qiu, Jiong [Department of Physics, Montana State University, Bozeman, MT 59717-3840 (United States); Judge, Philip G. [High Altitude Observatory, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO 80307-3000 (United States)
2014-10-01
On 2012 June 17, we observed the evolution of a C-class flare associated with the eruption of a filament near a large sunspot in the active region NOAA 11504. We obtained high spatial resolution filtergrams using the 1.6 m New Solar Telescope at the Big Bear Solar Observatory in broadband TiO at 706 nm (bandpass: 10 Å) and He I 10830 Å narrow band (bandpass: 0.5 Å, centered 0.25 Å to the blue). We analyze the spatio-temporal behavior of the He I 10830 Å data, which were obtained over a 90''×90'' field of view with a cadence of 10 s. We also analyze simultaneous data from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly and Extreme Ultraviolet Variability Experiment instruments on board the Solar Dynamics Observatory spacecraft, and data from the Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager and GOES spacecrafts. Non-thermal effects are ignored in this analysis. Several quantitative aspects of the data, as well as models derived using the '0D' enthalpy-based thermal evolution of loops model code, indicate that the triplet states of the 10830 Å multiplet are populated by photoionization of chromospheric plasma followed by radiative recombination. Surprisingly, the He II 304 Å line is reasonably well matched by standard emission measure calculations, along with the C IV emission which dominates the Atmosphere Imaging Assembly 1600 Å channel during flares. This work lends support to some of our previous work combining X-ray, EUV, and UV data of flares to build models of energy transport from corona to chromosphere.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Samantha J Broyd
Full Text Available BACKGROUND: The default-mode network (DMN is characterised by coherent very low frequency (VLF brain oscillations. The cognitive significance of this VLF profile remains unclear, partly because of the temporally constrained nature of the blood oxygen-level dependent (BOLD signal. Previously we have identified a VLF EEG network of scalp locations that shares many features of the DMN. Here we explore the intracranial sources of VLF EEG and examine their overlap with the DMN in adults with high and low ADHD ratings. METHODOLOGY/PRINCIPAL FINDINGS: DC-EEG was recorded using an equidistant 66 channel electrode montage in 25 adult participants with high- and 25 participants with low-ratings of ADHD symptoms during a rest condition and an attention demanding Eriksen task. VLF EEG power was calculated in the VLF band (0.02 to 0.2 Hz for the rest and task condition and compared for high and low ADHD participants. sLORETA was used to identify brain sources associated with the attention-induced deactivation of VLF EEG power, and to examine these sources in relation to ADHD symptoms. There was significant deactivation of VLF EEG power between the rest and task condition for the whole sample. Using s-LORETA the sources of this deactivation were localised to medial prefrontal regions, posterior cingulate cortex/precuneus and temporal regions. However, deactivation sources were different for high and low ADHD groups: In the low ADHD group attention-induced VLF EEG deactivation was most significant in medial prefrontal regions while for the high ADHD group this deactivation was predominantly localised to the temporal lobes. CONCLUSIONS/SIGNIFICANCE: Attention-induced VLF EEG deactivations have intracranial sources that appear to overlap with those of the DMN. Furthermore, these seem to be related to ADHD symptom status, with high ADHD adults failing to significantly deactivate medial prefrontal regions while at the same time showing significant attenuation of
-
Noise storm coordinated observations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Elgaroey, Oe.; Tlamicha, A.
1983-01-01
The usually accepted bipolar model of noise storm centers is irrelevant for the present observations. An alternative model has been proposed in which the different sources of a noise storm center are located in different flux tubes connecting active regions with their surroundings. Radio emission is observed from the wide, descending branch of the flux tubes, opposite to the flaring site. The relation between the sense of circular polarization of the radio emission and the magnetic polarity, has been more precisely defined. The radiation is in the ordinary mode with respect to the underlying large scale photospheric magnetic polarity. Thus the ''irregular'' polarity of noice storm center ''B'' is explained. As regards center ''C'', one should note that although the observed radio emission is polarized in the ordinary mode with respect to the leading spot of region HR 17653, center ''C'' is not situated in flux tubes originating from the leading part of this region according to the proposed model. Rather, the radio sources are located in the wide and descending part of flux tubes connecting a large, quiet area of south magnetic polarity with the following part of the region HR 17653 (of north magnetic polarity). Thus it is the polarity of the extended area which determines the polarization of the radio emission. The observed polarization should result rather from the emission process than from complicated conditions of propagation for the radio waves
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. G. Kapiris
2003-01-01
Full Text Available In analogy to the study of critical phase transitions in statistical physics, it has been argued recently that the fracture of heterogeneous materials could be viewed as a critical phenomenon, either at laboratory or at geophysical scales. If the picture of the development of the fracture is correct one may guess that the precursors may reveal the critical approach of the main-shock. When a heterogeneous material is stretched, its evolution towards breaking is characterized by the appearance of microcracks before the final break-up. Microcracks produce both acoustic and electromagnetic(EM emission in the frequency range from VLF to VHF. The microcracks and the associated acoustic and EM activities constitute the so-called precursors of general fracture. These precursors are detectable not only at laboratory but also at geophysical scales. VLF and VHF acoustic and EM emissions have been reported resulting from volcanic and seismic activities in various geologically distinct regions of the world. In the present work we attempt to establish the hypothesis that the evolution of the Earth's crust towards the critical point takes place not only in a mechanical but also in an electromagnetic sense. In other words, we focus on the possible electromagnetic criticality, which is reached while the catastrophic rupture in the Earth's crust approaches. Our main tool is the monitoring of micro-fractures that occur before the final breakup, by recording their radio-electromagnetic emissions. We show that the spectral power law analysis of the electromagnetic precursors reveals distinguishing signatures of underlying critical dynamics, such as: (i the emergence of memory effects; (ii the decrease with time of the anti-persistence behaviour; (iii the presence of persistence properties in the tail of the sequence of the precursors; and (iv the acceleration of the precursory electro-magnetic energy release. Moreover, the statistical analysis of the amplitudes of