
Sample records for surveillance radar wind
-
1990-12-01
Overviev . ......................................... 9 2. Programs , Syr!ems, and Services ........................ 11 a. National Weather Service...Equipment Appropriation. ADA, a computer system developed and maintained by the Office of Aviation Policy and rlans, facilitates APS-I processing... Program Plan. The primary benefit of LLWAS, TDWR, and modified airport surveillance radar is reduced risk and expected incidence of wind shear-related
-
IFT&E Industry Report Wind Turbine-Radar Interference Test Summary.
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Karlson, Benjamin; LeBlanc, Bruce Philip.; Minster, David G; Estill, Milford; Miller, Bryan Edward; Busse, Franz (MIT LL); Keck, Chris (MIT LL); Sullivan, Jonathan (MIT LL); Brigada, David (MIT LL); Parker, Lorri (MIT LL); Younger, Richard (MIT LL); Biddle, Jason (MIT LL)
2014-10-01
Wind turbines have grown in size and capacity with today's average turbine having a power capacity of around 1.9 MW, reaching to heights of over 495 feet from ground to blade tip, and operating with speeds at the tip of the blade up to 200 knots. When these machines are installed within the line-of-sight of a radar system, they can cause significant clutter and interference, detrimentally impacting the primary surveillance radar (PSR) performance. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Lincoln Laboratory (MIT LL) and Sandia National Laboratories (SNL) were co-funded to conduct field tests and evaluations over two years in order to: I. Characterize the impact of wind turbines on existing Program-of-Record (POR) air surveillance radars; II. Assess near-term technologies proposed by industry that have the potential to mitigate the interference from wind turbines on radar systems; and III. Collect data and increase technical understanding of interference issues to advance development of long-term mitigation strategies. MIT LL and SNL managed the tests and evaluated resulting data from three flight campaigns to test eight mitigation technologies on terminal (short) and long-range (60 nmi and 250 nmi) radar systems. Combined across the three flight campaigns, more than 460 of hours of flight time were logged. This paper summarizes the Interagency Field Test & Evaluation (IFT&E) program and publicly- available results from the tests. It will also discuss the current wind turbine-radar interference evaluation process within the government and a proposed process to deploy mitigation technologies.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Davies, N.G.
1995-01-01
This report examines the possible degradations of radar performance that may be caused by the presence of a wind turbine generator within the radar coverage area. A brief literature survey reviews the previously published work, which is mainly concerned with degradation of broadcast TV reception. Estimates are made of wind turbine generator scattering cross-sections, and of the time and Doppler characteristics of the echo signals from representative wind turbine generator. The general characteristics of radar detection and tracking methods are described, and the behaviour of such systems in the presence of strong returns from a wind turbine generator (or an array of them) is discussed. (author)
-
Fusion of Radar and EO-sensors for Surveillance
Kester, L.J.H.M.; Theil, A.
2001-01-01
Fusion of radar and EO-sensors is investigated for the purpose of surveillance in littoral waters is. All sensors are considered to be co-located with respect to the distance, typically 1 to 10 km, of the area under surveillance. The sensor suite is a coherent polarimetric radar in combination with
-
Wind Turbine Radar Cross Section
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
David Jenn
2012-01-01
Full Text Available The radar cross section (RCS of a wind turbine is a figure of merit for assessing its effect on the performance of electronic systems. In this paper, the fundamental equations for estimating the wind turbine clutter signal in radar and communication systems are presented. Methods of RCS prediction are summarized, citing their advantages and disadvantages. Bistatic and monostatic RCS patterns for two wind turbine configurations, a horizontal axis three-blade design and a vertical axis helical design, are shown. The unique electromagnetic scattering features, the effect of materials, and methods of mitigating wind turbine clutter are also discussed.
-
Wind energy applications of synthetic aperture radar
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Badger, Merete
Synthetic aperture radars (SAR), mounted on satellites or aircraft, have proven useful for ocean wind mapping. Wind speeds at the height 10 m may be retrieved from measurements of radar backscatter using empirical model functions. The resulting windfields are valuable in offshore wind energy plan...
-
Wind farms impact on radar aviation interests - final report
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Poupart, G.J.
2003-09-01
The main objectives of the study were: to determine the effects of siting wind turbines adjacent to primary air traffic control radar; to gather the information required for the generation of guidelines by civil, military and wind farm developer stakeholders; to determine the extent to which the design of wind turbines influences their effects on radar systems and to determine the extent to which design of the radar processing influences the effects of wind turbines on radar systems. A computer model was developed to predict the Radar Cross Section (RCS) of wind turbines and understand the interaction of radar energy and turbines. The model was designed to predict and simulate the impact of wind farms on the primary radar display. Validation of the model was carried out in a full-scale trial and modelling process, with data collected from a number of sources. The model was validated against a single turbine scenario and showed an accurate prediction capability. Further validation of the model could be gained through a multiple turbine trial. The knowledge gained from the development and validation of the predictive computer model has been used to conduct a sensitivity analysis (of the sub-elements of the radar and wind farm interaction) and to compile a list of the key factors influencing the radar signature of wind turbines. The result is a more detailed quantification of the complex interactions between wind turbines and radar systems than was previously available. The key findings of how the design, size and construction materials of wind turbines affect RCS are summarised.
-
Radar-cross-section reduction of wind turbines. part 1.
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Brock, Billy C.; Loui, Hung; McDonald, Jacob J.; Paquette, Joshua A.; Calkins, David A.; Miller, William K.; Allen, Steven E.; Clem, Paul Gilbert; Patitz, Ward E.
2012-03-05
In recent years, increasing deployment of large wind-turbine farms has become an issue of growing concern for the radar community. The large radar cross section (RCS) presented by wind turbines interferes with radar operation, and the Doppler shift caused by blade rotation causes problems identifying and tracking moving targets. Each new wind-turbine farm installation must be carefully evaluated for potential disruption of radar operation for air defense, air traffic control, weather sensing, and other applications. Several approaches currently exist to minimize conflict between wind-turbine farms and radar installations, including procedural adjustments, radar upgrades, and proper choice of low-impact wind-farm sites, but each has problems with limited effectiveness or prohibitive cost. An alternative approach, heretofore not technically feasible, is to reduce the RCS of wind turbines to the extent that they can be installed near existing radar installations. This report summarizes efforts to reduce wind-turbine RCS, with a particular emphasis on the blades. The report begins with a survey of the wind-turbine RCS-reduction literature to establish a baseline for comparison. The following topics are then addressed: electromagnetic model development and validation, novel material development, integration into wind-turbine fabrication processes, integrated-absorber design, and wind-turbine RCS modeling. Related topics of interest, including alternative mitigation techniques (procedural, at-the-radar, etc.), an introduction to RCS and electromagnetic scattering, and RCS-reduction modeling techniques, can be found in a previous report.
-
Analysis of a Pareto Mixture Distribution for Maritime Surveillance Radar
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Graham V. Weinberg
2012-01-01
Full Text Available The Pareto distribution has been shown to be an excellent model for X-band high-resolution maritime surveillance radar clutter returns. Given the success of mixture distributions in radar, it is thus of interest to consider the effect of Pareto mixture models. This paper introduces a formulation of a Pareto intensity mixture distribution and investigates coherent multilook radar detector performance using this new clutter model. Clutter parameter estimates are derived from data sets produced by the Defence Science and Technology Organisation's Ingara maritime surveillance radar.
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — Clutter present in radar return signals as used for wind profiling is substantially removed by carrying out a Daubechies wavelet transformation on a time series of...
-
Detecting and mitigating wind turbine clutter for airspace radar systems.
Wang, Wen-Qin
2013-01-01
It is well recognized that a wind turbine has a large radar cross-section (RCS) and, due to the movement of the blades, the wind turbine will generate a Doppler frequency shift. This scattering behavior may cause severe interferences on existing radar systems including static ground-based radars and spaceborne or airborne radars. To resolve this problem, efficient techniques or algorithms should be developed to mitigate the effects of wind farms on radars. Herein, one transponder-based mitigation technique is presented. The transponder is not a new concept, which has been proposed for calibrating high-resolution imaging radars. It modulates the radar signal in a manner that the retransmitted signals can be separated from the scene echoes. As wind farms often occupy only a small area, mitigation processing in the whole radar operation will be redundant and cost inefficient. Hence, this paper uses a transponder to determine whether the radar is impacted by the wind farms. If so, the effects of wind farms are then mitigated with subsequent Kalman filtering or plot target extraction algorithms. Taking airborne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and pulse Doppler radar as the examples, this paper provides the corresponding system configuration and processing algorithms. The effectiveness of the mitigation technique is validated by numerical simulation results.
-
Detecting and Mitigating Wind Turbine Clutter for Airspace Radar Systems
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wen-Qin Wang
2013-01-01
Full Text Available It is well recognized that a wind turbine has a large radar cross-section (RCS and, due to the movement of the blades, the wind turbine will generate a Doppler frequency shift. This scattering behavior may cause severe interferences on existing radar systems including static ground-based radars and spaceborne or airborne radars. To resolve this problem, efficient techniques or algorithms should be developed to mitigate the effects of wind farms on radars. Herein, one transponder-based mitigation technique is presented. The transponder is not a new concept, which has been proposed for calibrating high-resolution imaging radars. It modulates the radar signal in a manner that the retransmitted signals can be separated from the scene echoes. As wind farms often occupy only a small area, mitigation processing in the whole radar operation will be redundant and cost inefficient. Hence, this paper uses a transponder to determine whether the radar is impacted by the wind farms. If so, the effects of wind farms are then mitigated with subsequent Kalman filtering or plot target extraction algorithms. Taking airborne synthetic aperture radar (SAR and pulse Doppler radar as the examples, this paper provides the corresponding system configuration and processing algorithms. The effectiveness of the mitigation technique is validated by numerical simulation results.
-
Comparison of FPS-16 radar/jimsphere and NASA's 50-MHz radar wind profiler turbulence indicators
Susko, Michael
1993-01-01
Measurements of the wind and turbulent regions from the surface to 16 km by the FPS-11 radar/jimsphere system are reported with particular attention given to the use of these turbulence and wind assessments to validate the NASA 50-MHz radar wind profiler. Wind profile statistics were compared at 150-m wavelengths, a wavelength validated from 20 jimspheres, simultaneously tracked by FPS-16 and FPQ-14 radar, and the resulting analysis of auto spectra, cross-spectra, and coherence squared spectra of the wind profiles. Results demonstrate that the NASA prototype wind profiler is an excellent monitoring device illustrating the measurements of the winds within 1/2 hour of launch zero.
-
Apparatus and method for using radar to evaluate wind flow fields for wind energy applications
Schroeder, John; Hirth, Brian; Guynes, Jerry
2017-02-21
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for obtaining data to determine one or more characteristics of a wind flow field using one or more radars. Data is collected from the one or more radars, and analyzed to determine the one or more characteristics of the wind flow field. The one or more radars are positioned to have a portion of the wind flow field within a scanning sector of the one or more radars.
-
Weather radars – the new eyes for offshore wind farms?
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Trombe, Pierre-Julien; Pinson, Pierre; Vincent, Claire Louise
2014-01-01
Offshore wind fluctuations are such that dedicated prediction and control systems are needed for optimizing the management of wind farms in real-time. In this paper, we present a pioneer experiment – Radar@Sea – in which weather radars are used for monitoring the weather at the Horns Rev offshore...... inputs to prediction systems for anticipating changes in the wind fluctuation dynamics, generating improved wind power forecasts and developing specific control strategies. However, integrating weather radar observations into automated decision support systems is not a plug-and-play task...... observed at Horns Rev and (iv) we discuss the future perspectives for weather radars in wind energy. Copyright © 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd....
-
Wind turbine clutter mitigation in coastal UHF radar.
Yang, Jing; Pan, Chao; Wang, Caijun; Jiang, Dapeng; Wen, Biyang
2014-01-01
Coastal UHF radar provides a unique capability to measure the sea surface dynamic parameters and detect small moving targets, by exploiting the low energy loss of electromagnetic waves propagating along the salty and good conducting ocean surface. It could compensate the blind zone of HF surface wave radar at close range and reach further distance than microwave radars. However, its performance is susceptible to wind turbines which are usually installed on the shore. The size of a wind turbine is much larger than the wavelength of radio waves at UHF band, which results in large radar cross section. Furthermore, the rotation of blades adds time-varying Doppler frequency to the clutter and makes the suppression difficult. This paper proposes a mitigation method which is based on the specific periodicity of wind turbine clutter and performed mainly in the time-frequency domain. Field experimental data of a newly developed UHF radar are used to verify this method, and the results prove its effectiveness.
-
PENGGUNAAN SECONDARY SURVEILLANCE RADAR UNTUK PENENTUAN POSISI PESAWAT UDARA
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Akhmad Hafidz Irfandi
2015-02-01
Full Text Available Republik Indonesia merupakan negara kepulauan terbesar di dunia yang memiliki lebih dari 17.000 pulau dengan pertumbuhan demografi yang sangat pesat, hal ini menjadikan Indonesia sebagai negara berpenduduk terbesar ke-empat di dunia. Pesawat udara merupakan alat transportasi yang paling efektif dalam mendukung mobilitas penduduk.Navigasi atau pandu arah adalah penentuan kedudukan (position dan arah perjalanan baik di medan sebenarnya atau di peta. Navigasi ini dilakukan pada pesawat udara yang dipandu dari darat melalui sinyal yang dipancarkan oleh instrumen terpasang pada menara (ground base maupun sinyal dari satelit (satellite base.Dalam navigasi ada beberapa macam radar yang umum digunakan yaitu Primary Surveillance Radar (PSR dan Secondary Surveillance Radar (SSR.Kedua jenis radar baik PSR maupun SSR mempunyai cara kerja berbeda. Pada PSR sifatnya aktif dan pesawat yang ditargetkan sifatnya pasif.Karena PSR hanya menerima pantulan gelombang radio dari refleksi pesawat tersebut (echo.Sedangkan pesawat itu sendiri tidak ikut aktif dengan pancaran sinyal radar di bawah. Pada SSR, baik radar maupun pesawat kedua-duanya aktif. Hal ini dapat dilakukan karena pesawat terbang telah dilengkapi dengan transponder. Pesawat-pesawat yang tidak dilengkapi transponder tidak akan dapat dilihat pada radar scope seperti identifikasi pesawat, ketinggiannya, dan lain-lain.SSR merupakan peralatan untuk mendeteksi dan mengetahui posisi dan data target yang ada di sekelilingnya secara aktif, dimana pesawat ikut aktif jika menerima pancaran sinyal Radio Frequency (RF radar sekunder. Pancaran radar ini berupa pulsa-pulsa mode, pesawat yang dipasangi transponder, akan menerima pulsa-pulsa tersebut dan akan menjawab berupa pulsa-pulsa code ke sistem penerima radar.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Trombe, Pierre-Julien; Pinson, Pierre; Madsen, Henrik
2011-01-01
The substantial impact of wind power fluctuations at large offshore wind farms calls for the development of dedicated monitoring and prediction approaches. Based on recent findings, a Local Area Weather Radar (LAWR) was installed at Horns Rev with the aim of improving predictability, controlability...... and potentially maintenance planning. Additional images are available from a Doppler radar covering the same area. The parallel analysis of rain events detection and of regime sequences in wind (and power) fluctuations demonstrates the interest of employing weather radars for a better operation and management...... of offshore wind farms....
-
Determination of the thermospheric neutral wind from incoherent scatter radar measurements
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Haeggstroem, I.; Murdin, J.; Rees, D.
1984-11-01
Measurements made by the EISCAT UHF incoherent scatter radar are used to derive thermospheric winds. The derived wind is compared to Fabry-Perot interferometer measurements of the neutral wind made simultaneously. The uncertainties in the radar derived wind are discussed. (author)
-
Automatic Classification of Offshore Wind Regimes With Weather Radar Observations
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Trombe, Pierre-Julien; Pinson, Pierre; Madsen, Henrik
2014-01-01
Weather radar observations are called to play an important role in offshore wind energy. In particular, they can enable the monitoring of weather conditions in the vicinity of large-scale offshore wind farms and thereby notify the arrival of precipitation systems associated with severe wind...... and amplitude) using reflectivity observations from a single weather radar system. A categorical sequence of most likely wind regimes is estimated from a wind speed time series by combining a Markov-Switching model and a global decoding technique, the Viterbi algorithm. In parallel, attributes of precipitation...... systems are extracted from weather radar images. These attributes describe the global intensity, spatial continuity and motion of precipitation echoes on the images. Finally, a CART classification tree is used to find the broad relationships between precipitation attributes and wind regimes...
-
Simplified formulae for the estimation of offshore wind turbines clutter on marine radars.
Grande, Olatz; Cañizo, Josune; Angulo, Itziar; Jenn, David; Danoon, Laith R; Guerra, David; de la Vega, David
2014-01-01
The potential impact that offshore wind farms may cause on nearby marine radars should be considered before the wind farm is installed. Strong radar echoes from the turbines may degrade radars' detection capability in the area around the wind farm. Although conventional computational methods provide accurate results of scattering by wind turbines, they are not directly implementable in software tools that can be used to conduct the impact studies. This paper proposes a simple model to assess the clutter that wind turbines may generate on marine radars. This method can be easily implemented in the system modeling software tools for the impact analysis of a wind farm in a real scenario.
-
Maritime target and sea clutter measurements with a coherent Doppler polarimetric surveillance radar
Smith, A.J.E.; Gelsema, S.J.; Kester, L.J.H.M.; Melief, H.W.; Premel Cabic, G.; Theil, A.; Woudenberg, E.
2002-01-01
Doppler polarimetry in a surveillance radar for the maritime surface picture is considered. This radar must be able to detect low-RCS targets in littoral environments. Measurements on such targets have been conducted with a coherent polarimetric measurement radar in March 2001 and preliminary
-
Assessing collision risk for birds and bats : radar survey
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Brunet, R. [Genivar SEC, Sherbrooke, PQ (Canada)
2010-07-01
This PowerPoint presentation described some of the inventories and instrumentation available for monitoring winged fauna in and around wind farms. In addition to visual observations, bird calls and songs can be recorded to determine the amount and different types of birds located at wind farm sites. Radio-telemetry devices are also used to evaluate bird activities, and nest searches are conducted to determine the amount of eggs or young birds that will soon add to the bird population. Between 90 and 100 percent of birds and bats migrate at night. Acoustic radar, Doppler radar, and maritime surveillance radar instruments are used to monitor night-time activities in wind farm locations. Doppler radar is also used to detect bird and bat migration corridors. Screen-shots of various radar interfaces were presented. tabs., figs.
-
A quantitative analysis of the impact of wind turbines on operational Doppler weather radar data
Norin, L.
2015-02-01
In many countries wind turbines are rapidly growing in numbers as the demand for energy from renewable sources increases. The continued deployment of wind turbines can, however, be problematic for many radar systems, which are easily disturbed by turbines located in the radar line of sight. Wind turbines situated in the vicinity of Doppler weather radars can lead to erroneous precipitation estimates as well as to inaccurate wind and turbulence measurements. This paper presents a quantitative analysis of the impact of a wind farm, located in southeastern Sweden, on measurements from a nearby Doppler weather radar. The analysis is based on 6 years of operational radar data. In order to evaluate the impact of the wind farm, average values of all three spectral moments (the radar reflectivity factor, absolute radial velocity, and spectrum width) of the nearby Doppler weather radar were calculated, using data before and after the construction of the wind farm. It is shown that all spectral moments, from a large area at and downrange from the wind farm, were impacted by the wind turbines. It was also found that data from radar cells far above the wind farm (near 3 km altitude) were affected by the wind farm. It is shown that this in part can be explained by detection by the radar sidelobes and by scattering off increased levels of dust and turbulence. In a detailed analysis, using data from a single radar cell, frequency distributions of all spectral moments were used to study the competition between the weather signal and wind turbine clutter. It is shown that, when weather echoes give rise to higher reflectivity values than those of the wind farm, the negative impact of the wind turbines is greatly reduced for all spectral moments.
-
An Assessment of Wind Plant Complex Flows Using Advanced Doppler Radar Measurements
Gunter, W. S.; Schroeder, J.; Hirth, B.; Duncan, J.; Guynes, J.
2015-12-01
As installed wind energy capacity continues to steadily increase, the need for comprehensive measurements of wind plant complex flows to further reduce the cost of wind energy has been well advertised by the industry as a whole. Such measurements serve diverse perspectives including resource assessment, turbine inflow and power curve validation, wake and wind plant layout model verification, operations and maintenance, and the development of future advanced wind plant control schemes. While various measurement devices have been matured for wind energy applications (e.g. meteorological towers, LIDAR, SODAR), this presentation will focus on the use of advanced Doppler radar systems to observe the complex wind flows within and surrounding wind plants. Advanced Doppler radars can provide the combined advantage of a large analysis footprint (tens of square kilometers) with rapid data analysis updates (a few seconds to one minute) using both single- and dual-Doppler data collection methods. This presentation demonstrates the utility of measurements collected by the Texas Tech University Ka-band (TTUKa) radars to identify complex wind flows occurring within and nearby operational wind plants, and provide reliable forecasts of wind speeds and directions at given locations (i.e. turbine or instrumented tower sites) 45+ seconds in advance. Radar-derived wind maps reveal commonly observed features such as turbine wakes and turbine-to-turbine interaction, high momentum wind speed channels between turbine wakes, turbine array edge effects, transient boundary layer flow structures (such as wind streaks, frontal boundaries, etc.), and the impact of local terrain. Operational turbine or instrumented tower data are merged with the radar analysis to link the observed complex flow features to turbine and wind plant performance.
-
TDMA X-band FMCW MIMO radar for short range surveillance applications
Belfiori, F.; Maas, A.P.M.; Hoogeboom, P.; Rossum, W.L. van
2011-01-01
The work presented in this paper was aimed at the design of a compact radar device to be used for private area surveillance applications. The radar is connected to a pan tilt zoom camera and it provides the camera system with high accuracy position information (bearing and range) of moving targets;
-
Spectral Polarimetric Features Analysis of Wind Turbine Clutter in Weather Radar
Yin, J.; Krasnov, O.A.; Unal, C.M.H.; Medagli, S.; Russchenberg, H.W.J.
2017-01-01
Wind turbine clutter has gradually become a concern for the radar community for its increasing size and quantity worldwide. Based on the S-band polarimetric Doppler PARSAX radar measurements, this paper demonstrates the micro-Doppler features and spectral-polarimetric characteristic of wind turbine
-
Reduction of radar cross-section of a wind turbine
McDonald, Jacob Jeremiah; Brock, Billy C.; Clem, Paul G.; Loui, Hung; Allen, Steven E.
2016-08-02
The various technologies presented herein relate to formation of a wind turbine blade having a reduced radar signature in comparison with a turbine blade fabricated using conventional techniques. Various techniques and materials are presented to facilitate reduction in radar signature of a wind turbine blade, where such techniques and materials are amenable for incorporation into existing manufacturing techniques without degradation in mechanical or physical performance of the blade or major alteration of the blade profile.
-
Radar Cross Section (RCS) Simulation for Wind Turbines
2013-06-01
wind turbines are unsafe to operate. Also, helical wind turbines generally have less environmental concerns such as killing birds , especially in...SECTION (RCS) SIMULATION FOR WIND TURBINES by Cuong Ton June 2013 Thesis Advisor: David C. Jenn Second Reader: Ric Romero THIS PAGE...TITLE AND SUBTITLE RADAR CROSS SECTION (RCS) SIMULATION FOR WIND TURBINES 5. FUNDING NUMBERS 6. AUTHOR(S) Cuong Ton 7. PERFORMING ORGANIZATION
-
Wind energy applications of synthetic aperture radar
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bruun Christiansen, M.
2006-11-15
Synthetic aperture radars (SAR), mounted on satellites or aircraft, have proven useful for ocean wind mapping. Wind speeds at the height 10 m may be retrieved from measurements of radar backscatter using empirical model functions. The resulting wind fields are valuable in offshore wind energy planning as a supplement to on site measurements, which are costly and sparse, and model wind fields, which are not fully validated. Two applications of SAR measurements in offshore wind energy planning are addressed here: the study of wind farm wake effects and the potential of using SAR winds in offshore wind resource assessment. Firstly, wind wakes behind two large offshore wind farms in Denmark Horns Rev and Nysted are identified. A region of reduced wind speed is found downstream of both wind farms from the SAR wind fields. The wake extent and magnitude depends on the wind speed, the atmospheric stability, and the fraction of turbines operating. Wind farm wake effects are detected up to 20 km downwind of the last turbine. This distance is longer than predicted by state-of-the art wake models. Wake losses are typically 10-20% near the wind farms. Secondly, the potential of using SAR wind maps in offshore wind resource assessment is investigated. The resource assessment is made through Weibull fitting to frequency observations of wind speed and requires at least 100 satellite observations per year for a given site of interest. Predictions of the energy density are very sensitive to the wind speed and the highest possible accuracy on SAR wind retrievals is therefore sought. A 1.1 m s{sup -1} deviation on the mean wind speed is found through comparison with mast measurements at Horns Rev. The accuracy on mean wind speeds and energy densities found from satellite measurements varies with different empirical model functions. Additional uncertainties are introduced by the infrequent satellite sampling at fixed times of the day. The accuracy on satellite based wind resource
-
Wind profile radar for study of Antarctic air circulation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ragaini, E.; Sarango, M.F.; Vasquez, E.H.
1992-01-01
After a brief discussion of meteorological methods used in the Antarctic, the paper gives an outline of a coordinated international research project whose objective is to set up a wind profiler radar station that would give meteorologists information regarding Antarctic atmospheric dynamics useful in their investigation of the causes and effects of the hole in the ozone layer. The radar instrumentation is to provide continuous readings of wind velocity at varying altitudes above the polar continent
-
An optimal beam alignment method for large-scale distributed space surveillance radar system
Huang, Jian; Wang, Dongya; Xia, Shuangzhi
2018-06-01
Large-scale distributed space surveillance radar is a very important ground-based equipment to maintain a complete catalogue for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) space debris. However, due to the thousands of kilometers distance between each sites of the distributed radar system, how to optimally implement the Transmitting/Receiving (T/R) beams alignment in a great space using the narrow beam, which proposed a special and considerable technical challenge in the space surveillance area. According to the common coordinate transformation model and the radar beam space model, we presented a two dimensional projection algorithm for T/R beam using the direction angles, which could visually describe and assess the beam alignment performance. Subsequently, the optimal mathematical models for the orientation angle of the antenna array, the site location and the T/R beam coverage are constructed, and also the beam alignment parameters are precisely solved. At last, we conducted the optimal beam alignment experiments base on the site parameters of Air Force Space Surveillance System (AFSSS). The simulation results demonstrate the correctness and effectiveness of our novel method, which can significantly stimulate the construction for the LEO space debris surveillance equipment.
-
Retrieving 3D Wind Field from Phased Array Radar Rapid Scans
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Xiaobin Qiu
2013-01-01
Full Text Available The previous two-dimensional simple adjoint method for retrieving horizontal wind field from a time sequence of single-Doppler scans of reflectivity and/or radial velocity is further developed into a new method to retrieve both horizontal and vertical winds at high temporal and spatial resolutions. This new method performs two steps. First, the horizontal wind field is retrieved on the conical surface at each tilt (elevation angle of radar scan. Second, the vertical velocity field is retrieved in a vertical cross-section along the radar beam with the horizontal velocity given from the first step. The method is applied to phased array radar (PAR rapid scans of the storm winds and reflectivity in a strong microburst event and is shown to be able to retrieve the three-dimensional wind field around a targeted downdraft within the storm that subsequently produced a damaging microburst. The method is computationally very efficient and can be used for real-time applications with PAR rapid scans.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ragaini, E.; Sarango, M.F.; Vasquez, E.H.
1992-10-01
After a brief discussion of meteorological methods used in the Antarctic, the paper gives an outline of a coordinated international research project whose objective is to set up a wind profiler radar station that would give meteorologists information regarding Antarctic atmospheric dynamics useful in their investigation of the causes and effects of the hole in the ozone layer. The radar instrumentation is to provide continuous readings of wind velocity at varying altitudes above the polar continent.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Takeyama, Yuko; Ohsawa, Teruo; Kozai, Katsutoshi
2013-01-01
Wind direction is required as input to the geophysical model function (GMF) for the retrieval of sea surface wind speed from a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images. The present study verifies the effectiveness of using the wind direction obtained from the weather research and forecasting model (...
-
Interval algebra - an effective means of scheduling surveillance radar networks
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Focke, RW
2015-05-01
Full Text Available Interval Algebra provides an effective means to schedule surveillance radar networks, as it is a temporal ordering constraint language. Thus it provides a solution to a part of resource management, which is included in the revised Data Fusion...
-
Interval algebra: an effective means of scheduling surveillance radar networks
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Focke, RW
2015-05-01
Full Text Available Interval Algebra provides an effective means to schedule surveillance radar networks, as it is a temporal ordering constraint language. Thus it provides a solution to a part of resource management, which is included in the revised Data Fusion...
-
Chandra*, Chandrasekar V.; the full DFW Team
2015-04-01
Currently, the National Weather Service (NWS) Next Generation Weather Radar (NEXRAD) provides observations updated every five-six minutes across the United States. However, at the maximum NEXRAD operating range of 230 km, the 0.5 degree radar beam (lowest tilt) height is about 5.4 km above ground level (AGL) because of the effect of Earth curvature. Consequently, much of the lower atmosphere (1-3 km AGL) cannot be observed by the NEXRAD. To overcome the fundamental coverage limitations of today's weather surveillance radars, and improve the spatial and temporal resolution issues, at urban scale, the National Science Foundation Engineering Research Center (NSF-ERC) for Collaborative Adaptive Sensing of the Atmosphere (CASA) has embarked the development of Dallas-Fort worth (DFW) urban remote sensing network to conduct high-resolution sensing in the lower atmosphere for a metropolitan environment, communicate high resolution observations and nowcasting of severe weather including flash floods, hail storms and high wind events. Being one of the largest inland metropolitan areas in the U.S., the DFW Metroplex is home to over 6.5 million people by 2012 according to the North Central Texas Council of Governments (NCTCOG). It experiences a wide range of natural weather hazards, including urban flash flood, high wind, tornado, and hail, etc. Successful monitoring of the rapid changing meteorological conditions in such a region is necessary for emergency management and decision making. Therefore, it is an ideal location to investigate the impacts of hazardous weather phenomena, to enhance resilience in an urban setting and demonstrate the CASA concept in a densely populated urban environment. The DFW radar network consists of 8 dual-polarization X-band weather radars and standard NEXRAD S-band radar, covering the greater DFW metropolitan region. This paper will present high resolution observation of tornado, urban flood, hail storm and damaging wind event all within the
-
Field campaign for the comparison of SOUSY radar wind measurements with rawinsonde and model data
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. Steinhagen
Full Text Available A field campaign was carried out from 26 October to 7 November 1992, using the SOUSY-VHF radar and a mobile rawinsonde system installed and operated nearby to produce vertical wind profiles. The purpose of this campaign was to compare the two types of wind measurements with one another and with results from forecast models. Numerical algorithms were developed and applied to the radar data in order to eliminate random errors, correct for velocity aliasing, and calculate the effective zenith angle of the off-vertical beams. Differences between wind profiler data and rawinsonde or model results depend not only upon the errors of the different systems, but also on temporal and spatial variations of the wind field. Therefore, methods for the comparison of radar and rawinsonde data were developed which take into consideration these variations. The practical potential of these methods is demonstrated by comparisons of rawinsonde and radar wind profiles. The comparison of radar data and model output shows excellent agreement in the direction and in the speed of the wind at virtually all altitudes. An evaluation of the quality of wind profiler measurements is possible using the estimation of variance and variability of wind components.
-
Field campaign for the comparison of SOUSY radar wind measurements with rawinsonde and model data
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. Steinhagen
1994-07-01
Full Text Available A field campaign was carried out from 26 October to 7 November 1992, using the SOUSY-VHF radar and a mobile rawinsonde system installed and operated nearby to produce vertical wind profiles. The purpose of this campaign was to compare the two types of wind measurements with one another and with results from forecast models. Numerical algorithms were developed and applied to the radar data in order to eliminate random errors, correct for velocity aliasing, and calculate the effective zenith angle of the off-vertical beams. Differences between wind profiler data and rawinsonde or model results depend not only upon the errors of the different systems, but also on temporal and spatial variations of the wind field. Therefore, methods for the comparison of radar and rawinsonde data were developed which take into consideration these variations. The practical potential of these methods is demonstrated by comparisons of rawinsonde and radar wind profiles. The comparison of radar data and model output shows excellent agreement in the direction and in the speed of the wind at virtually all altitudes. An evaluation of the quality of wind profiler measurements is possible using the estimation of variance and variability of wind components.
-
Kumar, Karanam Kishore; Ramkumar, Geetha; Shelbi, S. T.
2007-12-01
In the present communication, initial results from the allSKy interferometric METeor (SKiYMET) radar installed at Thumba (8.5°N, 77°E) are presented. The meteor radar system provides hourly zonal and meridional winds in the mesosphere lower thermosphere (MLT) region. The meteor radar measured zonal and meridional winds are compared with nearby MF radar at Tirunalveli (8.7°N, 77.8°E). The present study provided an opportunity to compare the winds measured by the two different techniques, namely, interferometry and spaced antenna drift methods. Simultaneous wind measurements for a total number of 273 days during September 2004 to May 2005 are compared. The comparison showed a very good agreement between these two techniques in the height region 82-90 km and poor agreement above this height region. In general, the zonal winds compare very well as compared to the meridional winds. The observed discrepancies in the wind comparison above 90 km are discussed in the light of existing limitations of both the radars. The detailed analysis revealed the consistency of the measured winds by both the techniques. However, the discrepancies are observed at higher altitudes and are attributed to the contamination of MF radar neutral wind measurements with Equatorial Electro Jet (EEJ) induced inospheric drifts rather than the limitations of the spaced antenna technique. The comparison of diurnal variation of zonal winds above 90 km measured by both the radars is in reasonably good agreement in the absence of EEJ (during local nighttime). It is also been noted that the difference in the zonal wind measurements by both the radars is directly related to the strength of EEJ, which is a noteworthy result from the present study.
-
Quality Control of Wind Data from 50-MHz Doppler Radar Wind Profiler
Vacek, Austin
2016-01-01
Upper-level wind profiles obtained from a 50-MHz Doppler Radar Wind Profiler (DRWP) instrument at Kennedy Space Center are incorporated in space launch vehicle design and day-of-launch operations to assess wind effects on the vehicle during ascent. Automated and manual quality control (QC) techniques are implemented to remove spurious data in the upper-level wind profiles caused from atmospheric and non-atmospheric artifacts over the 2010-2012 period of record (POR). By adding the new quality controlled profiles with older profiles from 1997-2009, a robust database will be constructed of upper-level wind characteristics. Statistical analysis will determine the maximum, minimum, and 95th percentile of the wind components from the DRWP profiles over recent POR and compare against the older database. Additionally, this study identifies specific QC flags triggered during the QC process to understand how much data is retained and removed from the profiles.
-
Toward an optimal inversion method for synthetic aperture radar wind retrieval
Portabella, M.; Stoffelen, A.; Johannessen, Johnny A.
2002-01-01
In recent years, particular efforts have been made to derive wind fields over the oceans from synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images. In contrast with the scatterometer, the SAR has a higher spatial resolution and therefore has the potential to provide higher resolution wind information. Since there are at least two geophysical parameters (wind speed and wind direction) modulating the single SAR backscatter measurements, the inversion of wind fields from SAR observations has an inherent proble...
-
Troitskaya, Yuliya; Abramov, Victor; Ermoshkin, Alexey; Zuikova, Emma; Kazakov, Vassily; Sergeev, Daniil; Kandaurov, Alexandr
2014-05-01
Satellite remote sensing is one of the main techniques of monitoring severe weather conditions over the ocean. The principal difficulty of the existing algorithms of retrieving wind based on dependence of microwave backscattering cross-section on wind speed (Geophysical Model Function, GMF) is due to its saturation at winds exceeding 25 - 30 m/s. Recently analysis of dual- and quad-polarization C-band radar return measured from satellite Radarsat-2 suggested that the cross-polarized radar return has much higher sensitivity to the wind speed than co-polarized back scattering [1] and conserved sensitivity to wind speed at hurricane conditions [2]. Since complete collocation of these data was not possible and time difference in flight legs and SAR images acquisition was up to 3 hours, these two sets of data were compared in [2] only statistically. The main purpose of this paper is investigation of the functional dependence of cross-polarized radar cross-section on the wind speed in laboratory experiment. Since cross-polarized radar return is formed due to scattering at small-scale structures of the air-sea interface (short-crested waves, foam, sprays, etc), which are well reproduced in laboratory conditions, then the approach based on laboratory experiment on radar scattering of microwaves at the water surface under hurricane wind looks feasible. The experiments were performed in the Wind-wave flume located on top of the Large Thermostratified Tank of the Institute of Applied Physics, where the airflow was produced in the flume with the straight working part of 10 m and operating cross section 0.40?0.40 sq. m, the axis velocity can be varied from 5 to 25 m/s. Microwave measurements were carried out by a coherent Doppler X-band (3.2 cm) scatterometer with the consequent receive of linear polarizations. Experiments confirmed higher sensitivity to the wind speed of the cross-polarized radar return. Simultaneously parameters of the air flow in the turbulent boundary layer
-
Autonomous soaring and surveillance in wind fields with an unmanned aerial vehicle
Gao, Chen
Small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) play an active role in developing a low-cost, low-altitude autonomous aerial surveillance platform. The success of the applications needs to address the challenge of limited on-board power plant that limits the endurance performance in surveillance mission. This thesis studies the mechanics of soaring flight, observed in nature where birds utilize various wind patterns to stay airborne without flapping their wings, and investigates its application to small UAVs in their surveillance missions. In a proposed integrated framework of soaring and surveillance, a bird-mimicking soaring maneuver extracts energy from surrounding wind environment that improves surveillance performance in terms of flight endurance, while the surveillance task not only covers the target area, but also detects energy sources within the area to allow for potential soaring flight. The interaction of soaring and surveillance further enables novel energy based, coverage optimal path planning. Two soaring and associated surveillance strategies are explored. In a so-called static soaring surveillance, the UAV identifies spatially-distributed thermal updrafts for soaring, while incremental surveillance is achieved through gliding flight to visit concentric expanding regions. A Gaussian-process-regression-based algorithm is developed to achieve computationally-efficient and smooth updraft estimation. In a so-called dynamic soaring surveillance, the UAV performs one cycle of dynamic soaring to harvest energy from the horizontal wind gradient to complete one surveillance task by visiting from one target to the next one. A Dubins-path-based trajectory planning approach is proposed to maximize wind energy extraction and ensure smooth transition between surveillance tasks. Finally, a nonlinear trajectory tracking controller is designed for a full six-degree-of-freedom nonlinear UAV dynamics model and extensive simulations are carried to demonstrate the effectiveness of
-
Surveillance Unattended Foliage Penetrating Radar for Border Control and Homeland Protection
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Felicia Amato
2013-06-01
Full Text Available The increasing request for safety, security and environment protection at local and national level reveal the deficiency of the traditional surveillance and control centers to satisfy the needs and requirements of modern border control systems for homeland protection where land border is expected to be monitored as well as the maritime one. This is, for instance, the case of any land border affected by hidden immigration and/or illegal traffics as well as any small areas such as critical infrastructures or military/ civilian posts in forest or jungle environment characterized by vegetation. In such challenging environment, logistics constraints strongly recommend to have very low power devices able to operate months or years without maintenance. A such scenario should be the perfect place for implementing an Unattended Ground Sensors (UGS network making use FOliage PENetration (FOPEN radar for border control. The paper aims to present the basic characteristics and preliminary results of a Surveillance Unattended FOPEN (SUF radar suitable for detecting moving targets, people or vehicles, in dense forest environment.
-
Measurement of the sea surface wind speed and direction by an airborne microwave radar altimeter
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nekrassov, A. [GKSS-Forschungszentrum Geesthacht GmbH (Germany). Inst. fuer Hydrophysik
2001-07-01
A pilot needs operational information about wind over sea as well as wave height to provide safety of a hydroplane landing on water. Near-surface wind speed and direction can be obtained with an airborne microwave scatterometer, radar designed for measuring the scatter characteristics of a surface. Mostly narrow-beam antennas are applied for such wind measurement. Unfortunately, a microwave narrow-beam antenna has considerable size that hampers its placing on flying apparatus. In this connection, a possibility to apply a conventional airborne radar altimeter as a scatterometer with a nadir-looking wide-beam antenna in conjunction with Doppler filtering for recovering the wind vector over sea is discussed, and measuring algorithms of sea surface wind speed and direction are proposed. The obtained results can be used for creation of an airborne radar system for operational measurement of the sea roughness characteristics and for safe landing of a hydroplane on water. (orig.)
-
Wind retrieval from synthetic aperture radar - an overview
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Dagestad, Knut-Frode; Horstmann, Jochen; Mouche, Alexis
2013-01-01
This paper represents a consensus on the state-of-the-art in wind retrieval using synthetic aperture radar (SAR), after the SEASAR 2012 workshop “Advances in SAR Oceanography” hosted by the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Norwegian Space Centre in Tromsø, Norway 18–22 June 2012. We document...
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Schroeder, John [Texas Tech Univ., Lubbock, TX (United States); Hirth, Brian [Texas Tech Univ., Lubbock, TX (United States); Guynes, Jerry [Texas Tech Univ., Lubbock, TX (United States)
2017-03-15
The National Wind Institute (NWI) at Texas Tech University (TTU) has had an impressive and well documented 46-year history of wind related research activities (http://www.depts.ttu.edu/nwi/). In 2011 with funding from the United States Department of Energy (DOE), an NWI team applied radar technologies and techniques to document the complex flows occurring across a wind plant. The resulting efforts yielded measurements that exceeded the capabilities of commercial lidar technologies with respect to maximum range, range resolution and scan speed. The NWI team was also the first to apply dual-Doppler synthesis and objective analysis techniques to resolve the full horizontal wind field (i.e. not just the line-of-sight wind speeds) to successfully define turbine inflow and wake flows across large segments of wind plants. While these successes advanced wind energy interests, the existing research radar platforms were designed to serve a diversity of meteorological applications, not specifically wind energy. Because of this broader focus and the design choices made during their development, the existing radars experienced technical limitations that inhibited their commercial viability and wide spread adoption. This DOE project enabled the development of a new radar prototype specifically designed for the purpose of documenting wind farm complex flows. Relative to other “off the shelf” radar technologies, the specialized transmitter and receiver chains were specifically designed to enhance data availability in non-precipitating atmospheres. The new radar prototype was integrated at TTU using components from various suppliers across the world, and installed at the Reese Technology Center in May 2016. Following installation, functionality and performance testing were completed, and subsequent comparative analysis indicated that the new prototype greatly enhances data availability by a factor of 3.5-50 in almost all atmospheric conditions. The new prototype also provided
-
High-resolution humidity profiles retrieved from wind profiler radar measurements
Saïd, Frédérique; Campistron, Bernard; Di Girolamo, Paolo
2018-03-01
The retrieval of humidity profiles from wind profiler radars has already been documented in the past 30 years and is known to be neither as straightforward and nor as robust as the retrieval of the wind velocity. The main constraint to retrieve the humidity profile is the necessity to combine measurements from the wind profiler and additional measurements (such as observations from radiosoundings at a coarser time resolution). Furthermore, the method relies on some assumptions and simplifications that restrict the scope of its application. The first objective of this paper is to identify the obstacles and limitations and solve them, or at least define the field of applicability. To improve the method, we propose using the radar capacity to detect transition levels, such as the top level of the boundary layer, marked by a maximum in the radar reflectivity. This forces the humidity profile from the free troposphere and from the boundary layer to coincide at this level, after an optimization of the calibration coefficients, and reduces the error. The resulting mean bias affecting the specific humidity profile never exceeds 0.25 g kg-1. The second objective is to explore the capability of the algorithm to retrieve the humidity vertical profiles for an operational purpose by comparing the results with observations from a Raman lidar.
-
Retrieval of Wind Speed Using an L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Monaldo, Frank M.; Thompson, Donald R.; Badger, Merete
2007-01-01
Retrieval of wind speed using L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is both an old and new endeavor. Although the Seasat L-band SAR in 1978 was not well calibrated, early results indicated a strong relationship between observed SAR image intensity and wind speed. The JERS-1 L-band SAR had limited...
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Chang, Rui; Zhu, Rong; Badger, Merete
2014-01-01
In view of the high cost and sparse spatial resolution of offshore meteorological observations, ocean winds retrieved from satellites are valuable in offshore wind resource assessment as a supplement to in situ measurements. This study examines satellite synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images from...... ENVISAT advanced SAR (ASAR) for mapping wind resources with high spatial resolution. Around 181 collected pairs of wind data from SAR wind maps and from 13 meteorological stations in Hangzhou Bay are compared. The statistical results comparing in situ wind speed and SAR-based wind speed show a standard...... density functions are compared at one meteorological station. The SAR-based results appear not to estimate the mean wind speed, Weibull scale and shape parameters and wind power density from the full in situ data set so well due to the lower number of satellite samples. Distributions calculated from...
-
Comparative study of MLT mean winds using MF radars located at ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
Medium Frequency Radar, Indian Institute of Geomagnetism, Shivaji University ... Research Laboratory, Indian Institute of Geomagnetism, Tirunelveli 627 011, India. ... paper is to describe mesosphere and lower thermosphere (MLT) wind field.
-
Sharma, A. K.; Gaikwad, H. P.; Ratnam, M. Venkat; Gurav, O. B.; Ramanjaneyulu, L.; Chavan, G. A.; Sathishkumar, S.
2018-04-01
Medium Frequency (MF) radar located at Kolhapur (16.8°N, 74.2°E) has been upgraded in August 2013. Since then continuous measurements of zonal and meridional winds are obtained covering larger altitudes from the Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere (MLT) region. Diurnal, monthly and seasonal variation of these mean winds is presented in this study using four years (2013-2017) of observations. The percentage occurrence of radar echoes show maximum between 80 and 105 km. The mean meridional wind shows Annual Oscillation (AO) between 80 and 90 km altitudes with pole-ward motion during December solstice and equatorial motion during June solstice. Quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) with weaker amplitudes are also observed between 90 and 104 km. Zonal winds show semi-annual oscillation (SAO) with westward winds during equinoxes and eastward winds during solstices between 80 and 90 km. AO with eastward winds during December solstice and westward wind in the June solstice is also observed in the mean zonal wind between 100 and 110 km. These results match well with that reported from other latitudes within Indian region between 80 and 90 km. However, above 90 km the results presented here provide true mean background winds for the first time over Indian low latitude region as the present station is away from equatorial electro-jet and are not contaminated by ionospheric processes. Further, the results presented earlier with an old version of this radar are found contaminated due to unknown reasons and are corrected in the present work. This upgraded MF radar together with other MLT radars in the Indian region forms unique network to investigate the vertical and lateral coupling.
-
Optimized variational analysis scheme of single Doppler radar wind data
Sasaki, Yoshi K.; Allen, Steve; Mizuno, Koki; Whitehead, Victor; Wilk, Kenneth E.
1989-01-01
A computer scheme for extracting singularities has been developed and applied to single Doppler radar wind data. The scheme is planned for use in real-time wind and singularity analysis and forecasting. The method, known as Doppler Operational Variational Extraction of Singularities is outlined, focusing on the principle of local symmetry. Results are presented from the application of the scheme to a storm-generated gust front in Oklahoma on May 28, 1987.
-
Diurnal evolution of wind structure and data availability measured by the DOE prototype radar system
Hirth, Brian D.; Schroeder, John L.; Guynes, Jerry G.
2017-11-01
A new Doppler radar prototype has been developed and deployed at Texas Tech University with a focus on enhancing the technologies’ capability to contribute to wind plant relevant complex flow measurements. In particular, improvements in data availability, total data coverage, and autonomous operation were targeted to enable contributions to a wider range of wind energy applications. Doppler radar offers rapid scan speeds, extended maximum range and excellent along-beam range resolution allowing for the simultaneous measurement of various wind phenomena ranging from regional and wind plant scales to inflow and wake flow assessment for an individual turbine. Data examples and performance improvements relative to a previous edition of the technology are presented, including insights into the influence of diurnal atmospheric stability evolution of wind structure and system performance.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. Murat Demirer
2012-01-01
Full Text Available The feasibility of using Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS sensor nodes is studied in a distributed network, aiming at dynamic surveillance and tracking of ground targets. Data acquisition by low-cost ( < $50 US miniature low-power radar through a wireless mote is described. We demonstrate the detection, ranging and velocity estimation, classification and tracking capabilities of the mini-radar, and compare results to simulations and manual measurements. Furthermore, we supplement the radar output with other sensor modalities, such as acoustic and vibration sensors. This method provides innovative solutions for detecting, identifying, and tracking vehicles and dismounts over a wide area in noisy conditions. This study presents a step towards distributed intelligent decision support and demonstrates effectiveness of small cheap sensors, which can complement advanced technologies in certain real-life scenarios.
-
Offshore Wind Potential in South India from Synthetic Aperture Radar
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Bingöl, Ferhat; Badger, Merete
are from Wide Swath Mode and each cover approximately 400 km by 400 km. The ocean wind speed maps are retrieved and processed at Risø DTU. The results show wind energy density from 200 W/m2 to 500 W/m2 at 10 m height above sea level. QuikSCAT ocean winds are included as background information on the 10......The offshore wind energy potential for pre-feasibility in South India in the area from 77° to 80° Eastern longitude and 7° to 10° Northern latitude is observed from a total of 164 ENVISAT Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ASAR) satellite images during the years 2002 to 2011. All satellite scenes......-year mean and a general description of the winds and climate with monsoons in India is presented....
-
Offshore wind potential in South India from synthetic aperture radar
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hasager, C.B.; Bingoel, F.; Badger, M.; Karagali, I.; Sreevalsan, E.
2011-10-15
The offshore wind energy potential for pre-feasibility in South India in the area from 77 deg. to 80 deg. Eastern longitude and 7 deg. to 10 deg. Northern latitude is observed from a total of 164 ENVISAT Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ASAR) satellite images during the years 2002 to 2011. All satellite scenes are from Wide Swath Mode and each cover approximately 400 km by 400 km. The ocean wind speed maps are retrieved and processed at Risoe DTU. The results show wind energy density from 200 W/m2 to 500 W/m2 at 10 m height above sea level. QuikSCAT ocean winds are included as background information on the 10-year mean and a general description of the winds and climate with monsoons in India is presented. (Author)
-
915-MHz Radar Wind Profiler (915RWP) Handbook
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Coulter, R
2005-01-01
The 915 MHz radar wind profiler/radio acoustic sounding system (RWP/RASS) measures wind profiles and backscattered signal strength between (nominally) 0.1 km and 5 km and virtual temperature profiles between 0.1 km and 2.5 km. It operates by transmitting electromagnetic energy into the atmosphere and measuring the strength and frequency of backscattered energy. Virtual temperatures are recovered by transmitting an acoustic signal vertically and measuring the electromagnetic energy scattered from the acoustic wavefront. Because the propagation speed of the acoustic wave is proportional to the square root of the virtual temperature of the air, the virtual temperature can be recovered by measuring the Doppler shift of the scattered electromagnetic wave.
-
A brief history of the development of wind-profiling or MST radars
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
T. E. Van Zandt
2000-07-01
Full Text Available The history of the development of the wind-profiling or MST radar technique is reviewed from its inception in the late 1960s to the present. Extensions of the technique by the development of boundary-layer radars and the radio-acoustic sounding system (RASS technique to measure temperature are documented. Applications are described briefly, particularly practical applications to weather forecasting, with data from networks of radars, and scientific applications to the study of rapidly varying atmospheric phenomena such as gravity waves and turbulence.Key words: Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (instruments and techniques · Radio science (remote sensing; instruments and techniques
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Johnson, R.M.
1987-01-01
Observations made by the Chatanika, Alaska, incoherent scatter radar during the summer months of 1976 to 1081 are analyzed to obtain high resolution lower-thermospheric neutral winds. Average winds and their tidal components are presented and compared to previous observational and model results. Upper-mesospheric neutral-wind observations obtained by the Poke Flat, Alaska Mesosphere-Stratosphere-Troposphere (MST) radar during the summer months of 1980 to 1982 are investigated statistically for evidence of variations due to geomagnetic activity. Observation of upper-mesospheric neutral winds made during two energetic Solar Proton Events (SPEs) by the Poker Flat, MST radar are presented. These results allow the low-altitude limits of magnetospheric coupling to the neutral atmosphere to be determined. Lower-thermospheric neutral winds are coupled to the ion convection driven by typical magnetospheric forcing above about 100 km. Coupling to lower atmospheric levels does not occur except during intervals of extreme disturbance of the magnetosphere-ionosphere-thermosphere system which are also accompanied by dramatically increased ionization in the high-latitude mesosphere, such as SPEs
-
Avian use of Norris Hill Wind Resource Area, Montana
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Harmata, A.; Podruzny, K.; Zelenak, J. [Montana State Univ., Bozeman, MT (United States). Biology Dept.
1998-07-01
This document presents results of a study of avian use and mortality in and near a proposed wind resource area in southwestern Montana. Data collected in autumn 1995 through summer 1996 represented preconstruction condition; it was compiled, analyzed, and presented in a format such that comparison with post-construction data would be possible. The primary emphasis of the study was recording avian migration in and near the wind resource area using state-of-the-art marine surveillance radar. Avian use and mortality were investigated during the breeding season by employing traditional avian sampling methods, radiotelemetry, radar, and direct visual observation. 61 figs., 34 tabs.
-
HF Radar Observations of Current, Wave and Wind Parameters in the South Australian Gulf
Middleditch, A.; Cosoli, S.
2016-12-01
The Australian Coastal Ocean Radar Network (ACORN) has been measuring metocean parameters from an array of HF radar systems since 2007. Current, wave and wind measurements from a WERA phased-array radar system in the South Australian Gulf are evaluated using current meter, wave buoy and weather station data over a 12-month period. The spatial and temporal scales of the radar deployment have been configured for the measurement of surface currents from the first order backscatter spectra. Quality control procedures are applied to the radar currents that relate to the geometric configurations, statistical properties, and diagnostic variables provided by the analysis software. Wave measurements are obtained through an iterative inversion algorithm that provides an estimate of the directional frequency spectrum. The standard static configurations and data sampling strategies are not optimised for waves and so additional signal processing steps need to be implemented in order to provide reliable estimates. These techniques are currently only applied in offline mode but a real-time approach is in development. Improvements in the quality of extracted wave data are found through increased averaging of the raw radar data but the impact of temporal non-stationarity and spatial inhomogeneities in the WERA measurement region needs to be taken into account. Validations of wind direction data from a weather station on Neptune Island show the potential of using HF radar to combat the spread of bushfires in South Australia.
-
A ground-base Radar network to access the 3D structure of MLT winds
Stober, G.; Chau, J. L.; Wilhelm, S.; Jacobi, C.
2016-12-01
The mesosphere/lower thermosphere (MLT) is a highly variable atmospheric region driven by wave dynamics at various scales including planetary waves, tides and gravity waves. Some of these propagate through the MLT into the thermosphere/ionosphere carrying energy and momentum from the middle atmosphere into the upper atmosphere. To improve our understanding of the wave energetics and momentum transfer during their dissipation it is essential to characterize their space time properties. During the last two years we developed a new experimental approach to access the horizontal structure of wind fields at the MLT using a meteor radar network in Germany, which we called MMARIA - Multi-static Multi-frequency Agile Radar for Investigation of the Atmosphere. The network combines classical backscatter meteor radars and passive forward scatter radio links. We present our preliminary results using up to 7 different active and passive radio links to obtain horizontally resolved wind fields applying a statistical inverse method. The wind fields are retrieved with 15-30 minutes temporal resolution on a grid with 30x30 km horizontal spacing. Depending on the number of observed meteors, we are able to apply the wind field inversion at heights between 84-94 km. The horizontally resolved wind fields provide insights of the typical horizontal gravity wave length and the energy cascade from large scales to small scales. We present first power spectra indicating the transition from the synoptic wave scale to the gravity wave scale.
-
A brief history of the development of wind-profiling or MST radars
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
T. E. Van Zandt
Full Text Available The history of the development of the wind-profiling or MST radar technique is reviewed from its inception in the late 1960s to the present. Extensions of the technique by the development of boundary-layer radars and the radio-acoustic sounding system (RASS technique to measure temperature are documented. Applications are described briefly, particularly practical applications to weather forecasting, with data from networks of radars, and scientific applications to the study of rapidly varying atmospheric phenomena such as gravity waves and turbulence.
Key words: Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (instruments and techniques · Radio science (remote sensing; instruments and techniques -
Application of wind-profiling radar data to the analysis of dust weather in the Taklimakan Desert.
Wang, Minzhong; Wei, Wenshou; Ruan, Zheng; He, Qing; Ge, Runsheng
2013-06-01
The Urumqi Institute of Desert Meteorology of the China Meteorological Administration carried out an atmospheric scientific experiment to detect dust weather using a wind-profiling radar in the hinterland of the Taklimakan Desert in April 2010. Based on the wind-profiling data obtained from this experiment, this paper seeks to (a) analyze the characteristics of the horizontal wind field and vertical velocity of a breaking dust weather in a desert hinterland; (b) calculate and give the radar echo intensity and vertical distribution of a dust storm, blowing sand, and floating dust weather; and (c) discuss the atmosphere dust counts/concentration derived from the wind-profiling radar data. Studies show that: (a) A wind-profiling radar is an upper-air atmospheric remote sensing system that effectively detects and monitors dust. It captures the beginning and ending of a dust weather process as well as monitors the sand and dust being transported in the air in terms of height, thickness, and vertical intensity. (b) The echo intensity of a blowing sand and dust storm weather episode in Taklimakan is about -1~10 dBZ while that of floating dust -1~-15 dBZ, indicating that the dust echo intensity is significantly weaker than that of precipitation but stronger than that of clear air. (c) The vertical shear of horizontal wind and the maintenance of low-level east wind are usually dynamic factors causing a dust weather process in Taklimakan. The moment that the low-level horizontal wind field finds a shear over time, it often coincides with the onset of a sand blowing and dust storm weather process. (d) When a blowing sand or dust storm weather event occurs, the atmospheric vertical velocity tends to be of upward motion. This vertical upward movement of the atmosphere supported with a fast horizontal wind and a dry underlying surface carries dust particles from the ground up to the air to form blown sand or a dust storm.
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)-derived high resolution wind products are calculated from high resolution SAR images of normalized radar cross section (NRCS) of the...
-
Zosel, Amy; Bartelson, Becki Bucher; Bailey, Elise; Lowenstein, Steven; Dart, Rick
2013-01-01
Objective: To describe the characteristics and health effects of adolescent (age 13-19 years) prescription drug abuse and misuse using the Researched Abuse Diversion and Addiction-Related Surveillance (RADARS[R])) System. Method: Secondary analysis of data collected from RADARS System participating poison centers was performed. Data for all…
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. Umemoto
2004-11-01
Full Text Available A special observation campaign (X-BAIU, using various instruments (wind profilers, C-band weather radars, X-band Doppler radars, rawinsondes, etc., was carried out in Kyushu (western Japan during the Baiu season, from 1998 to 2002. In the X-BAIU-99 and -02 observations, a line-shaped orographic rainband extending northeastward from the Koshikijima Islands appeared in the low-level strong wind with warm-moist airs. The weather radar observation indicated that the rainband was maintained for 11h. The maximum length and width of the rainband observed in 1999 was ~200km and ~20km, respectively. The rainband observed in 2002 was not so developed compared with the case in 1999. The Froude number averaged from sea level to the top of the Koshikijima Islands (~600m was large (>1, and the lifting condensation level was below the tops of the Koshikijima Islands. Thus, it is suggested that the clouds organizing the rainband are formed by the triggering of the mountains on the airflow passing over them. The vertical profile of horizontal wind in/around the rainband was investigated in the wind profiler observations. In the downdraft region 60km from the Koshikijima Islands, strong wind and its clockwise rotation with increasing height was observed below 3km altitude. In addition, a strong wind component perpendicular to the rainband was observed when the rainband was well developed. These wind behaviors were related to the evolution of the rainband.
-
Guimond, Stephen Richard; Tian, Lin; Heymsfield, Gerald M.; Frasier, Stephen J.
2013-01-01
Algorithms for the retrieval of atmospheric winds in precipitating systems from downward-pointing, conically-scanning airborne Doppler radars are presented. The focus in the paper is on two radars: the Imaging Wind and Rain Airborne Profiler(IWRAP) and the High-altitude IWRAP (HIWRAP). The IWRAP is a dual-frequency (Cand Ku band), multi-beam (incidence angles of 30 50) system that flies on the NOAAWP-3D aircraft at altitudes of 2-4 km. The HIWRAP is a dual-frequency (Ku and Kaband), dual-beam (incidence angles of 30 and 40) system that flies on the NASA Global Hawk aircraft at altitudes of 18-20 km. Retrievals of the three Cartesian wind components over the entire radar sampling volume are described, which can be determined using either a traditional least squares or variational solution procedure. The random errors in the retrievals are evaluated using both an error propagation analysis and a numerical simulation of a hurricane. These analyses show that the vertical and along-track wind errors have strong across-track dependence with values of 0.25 m s-1 at nadir to 2.0 m s-1 and 1.0 m s-1 at the swath edges, respectively. The across-track wind errors also have across-track structure and are on average, 3.0 3.5 m s-1 or 10 of the hurricane wind speed. For typical rotated figure four flight patterns through hurricanes, the zonal and meridional wind speed errors are 2 3 m s-1.Examples of measured data retrievals from IWRAP during an eyewall replacement cycle in Hurricane Isabel (2003) and from HIWRAP during the development of Tropical Storm Matthew (2010) are shown.
-
Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Jee, G.
2013-12-01
For the first time, vertical winds near the mesopause region were estimated from radial velocities of meteor echoes detected by a VHF meteor radar at King Sejong Station (KSS) in 2011 and 2012. Since the radar usually detects more than a hundred echoes every hour in an altitude bin of 88 - 92 km, much larger than other radars, we were able to fit measured radial velocities of these echoes with a 6 component model that consists of horizontal winds, spatial gradients of horizontal winds and vertical wind. The conventional method of deriving horizontal winds from meteor echoes utilizes a 2 component model, assuming that vertical winds and spatial gradients of horizontal winds are negligible. We analyzed the radar data obtained for 8400 hours in 2012 and 8100 hours in 2011. We found that daily mean values of vertical winds are mostly within +/- 1 m/s, whereas those of zonal winds are a few tens m/s mostly eastward. The daily mean vertical winds sometimes stay positive or negative for more than 20 days, implying that the atmosphere near the mesopause experiences episodically a large scale low and high pressure environments, respectively, like the tropospheric weather system. By conducting Lomb-normalized periodogram analysis, we also found that the vertical winds have diurnal, semidiurnal and terdiurnal tidal components with about equal significance, in contrast to horizontal winds that show a dominant semidiurnal one. We will discuss about uncertainties of the estimated vertical wind and possible reasons of its tidal and daily variations.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Rui Chang
2014-05-01
Full Text Available In view of the high cost and sparse spatial resolution of offshore meteorological observations, ocean winds retrieved from satellites are valuable in offshore wind resource assessment as a supplement to in situ measurements. This study examines satellite synthetic aperture radar (SAR images from ENVISAT advanced SAR (ASAR for mapping wind resources with high spatial resolution. Around 181 collected pairs of wind data from SAR wind maps and from 13 meteorological stations in Hangzhou Bay are compared. The statistical results comparing in situ wind speed and SAR-based wind speed show a standard deviation (SD of 1.99 m/s and correlation coefficient of R = 0.67. The model wind directions, which are used as input for the SAR wind speed retrieval, show a high correlation coefficient (R = 0.89 but a large standard deviation (SD = 42.3° compared to in situ observations. The Weibull probability density functions are compared at one meteorological station. The SAR-based results appear not to estimate the mean wind speed, Weibull scale and shape parameters and wind power density from the full in situ data set so well due to the lower number of satellite samples. Distributions calculated from the concurrent 81 SAR and in situ samples agree well.
-
Kozma, Robert; Wang, Lan; Iftekharuddin, Khan; McCracken, Ernest; Khan, Muhammad; Islam, Khandakar; Bhurtel, Sushil R; Demirer, R Murat
2012-01-01
The feasibility of using Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) sensor nodes is studied in a distributed network, aiming at dynamic surveillance and tracking of ground targets. Data acquisition by low-cost (wireless mote is described. We demonstrate the detection, ranging and velocity estimation, classification and tracking capabilities of the mini-radar, and compare results to simulations and manual measurements. Furthermore, we supplement the radar output with other sensor modalities, such as acoustic and vibration sensors. This method provides innovative solutions for detecting, identifying, and tracking vehicles and dismounts over a wide area in noisy conditions. This study presents a step towards distributed intelligent decision support and demonstrates effectiveness of small cheap sensors, which can complement advanced technologies in certain real-life scenarios.
-
Design and manufacture of radar absorbing wind turbine blades - final report
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2005-02-15
This report describes the results of a collaborative project between QinetiQ Ltd and NOI (Scotland) Ltd to design and manufacture radar absorbent wind turbine blades. The main objectives were to: use predictive modelling to understand the contribution made by the blade to radar cross section (RCS) of the complete turbine; confirm that the turbine RCS could feasibility be reduced to appropriate levels through the use of radar absorbent material (RAM); and to demonstrate that introduction of stealth technology within current composite sections would allow RAM variants of the blade materials to be manufactured with minimal impact on the structure. The RCS of a turbine was predicted at frequencies at which representative air traffic control (ATC), weather and marine navigation radar systems operate. The material compositions that exist on the blades produced by NOI were studied and methods by which RAM could be introduced to each region were identified. RCS predictions for a blade having RAM over its surface were then repeated. The study showed that it was possible to modify all material regions of the NOI blades to create RAM with little or no degradation in structural properties, thus reducing detection by non-Doppler radar and ATC radars. A full practical demonstration of a stealthy turbine is recommended to allow the benefits of RCS reduction through the use of RAM to be quantified by all stakeholders.
-
A novel approach of collision assessment for coastal radar surveillance
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ma, Feng; Chen, Yu-wang; Huang, Zi-chao; Yan, Xin-ping; Wang, Jin
2016-01-01
For coastal radar surveillance, this paper proposes a data-driven approach to estimate a blip's collision probability preliminarily based on two factors: the probability of it being a moving vessel and the collision potential of its position. The first factor is determined by a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), whose nodes represent the blip's characteristics, including the velocity, direction and size. Additionally, the structure and conditional probability tables of the DAG can be learned from verified samples. Subsequently, obstacles in a waterway can be described as collision potential fields using an Artificial Potential Field model, and the corresponding coefficients can be trained in accordance with the historical vessel distribution. Then, the other factor, the positional collision potential of any position is obtained through overlapping all the collision potential fields. For simplicity, only static obstacles have been considered. Eventually, the two factors are characterised as evidence, and the collision probability of a blip is estimated by combining them with Dempster's rule. Through ranking blips on collision probabilities, those that pose high threat to safety can be picked up in advance to remind radar operators. Particularly, a good agreement between the proposed approach and the manual operation was found in a preliminary test. - Highlights: • Novel estimation approach of collision probability for radar blips. • Novel method to evaluate the positional collision potentials using the APF model. • Novel method to obtain the coefficients of potential fields with historical data.
-
Performance indicators modern surveillance radar
Nooij, P.N.C.; Theil, A.
2014-01-01
Blake chart computations are widely employed to rank detection coverage capabilities of competitive search radar systems. Developed for comparable 2D radar systems with a mechanically rotating reflector antenna, it was not necessary to regard update rate and plot quality in Blake's chart. To
-
Weissman, David E.; Davidson, Kenneth L.; Brown, Robert A.; Friehe, Carl A.; Li, Fuk
1994-01-01
The Frontal Air-Sea Interaction Experiment (FASINEX) provided a unique data set with coincident airborne scatterometer measurements of the ocean surface radar cross section (RCS)(at Ku band) and near-surface wind and wind stress. These data have been analyzed to study new model functions which relate wind speed and surface friction velocity (square root of the kinematic wind stress) to the radar cross section and to better understand the processes in the boundary layer that have a strong influence on the radar backscatter. Studies of data from FASINEX indicate that the RCS has a different relation to the friction velocity than to the wind speed. The difference between the RCS models using these two variables depends on the polarization and the incidence angle. The radar data have been acquired from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory airborne scatterometer. These data span 10 different flight days. Stress measurements were inferred from shipboard instruments and from aircraft flying at low altitudes, closely following the scatterometer. Wide ranges of radar incidence angles and environmental conditions needed to fully develop algorithms are available from this experiment.
-
An improvement of wind velocity estimation from radar Doppler spectra in the upper mesosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Takeda
2001-08-01
Full Text Available We have developed a new parameter estimation method for Doppler wind spectra in the mesosphere observed with an MST radar such as the MU radar in the DBS (Doppler Beam Swinging mode. Off-line incoherent integration of the Doppler spectra is carried out with a new algorithm excluding contamination by strong meteor echoes. At the same time, initial values on a least square fitting of the Gaussian function are derived using a larger number of integration of the spectra for a longer time and for multiple heights. As a result, a significant improvement has been achieved with the probability of a successful fitting and parameter estimation above 80 km. The top height for the wind estimation has been improved to around 95 km. A comparison between the MU radar and the High Resolution Doppler Imager (HRDI on the UARS satellite is shown and the capability of the new method for a validation of a future satellite mission is suggested.Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (middle atmosphere dynamics – Radio science (remote sensing; signal processing
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Gorsevski, Peter [Bowling Green State Univ., OH (United States); Afjeh, Abdollah [Univ. of Toledo, OH (United States); Jamali, Mohsin [Univ. of Toledo, OH (United States); Bingman, Verner [Bowling Green State Univ., OH (United States)
2014-04-04
reduced the wake size and enhanced the vortices in the flow downstream of the turbine-tower compared with the tower alone case. Mean and rms velocity distributions from hot wire anemometer data confirmed that in a downwind configuration, the wake of the tower dominates the flow, thus the flow fields of a tower alone and tower-turbine combinations are nearly the same. For the upwind configuration, the mean velocity shows a narrowing of the wake compared with the tower alone case. The downwind configuration wake persisted longer than that of an upwind configuration; however, it was not possible to quantify this difference because of the size limitation of the wind tunnel downstream of the test section. The water tunnel studies demonstrated that the scale model studies could be used to adequately produce accurate motions to model the motions of a wind turbine platform subject to large waves. It was found that the important factors that affect the platform is whether the platform is submerged or surface piercing. In the former, the loads on the platform will be relatively reduced whereas in the latter case, the structure pierces the wave free surface and gains stiffness and stability. The other important element that affects the movement of the platform is depth of the sea in which the wind turbine will be installed. Furthermore, the wildlife biology component evaluated migratory patterns by different monitoring systems consisting of marine radar, thermal IR camera and acoustic recorders. The types of radar used in the project are weather surveillance radar and marine radar. The weather surveillance radar (1988 Doppler), also known as Next Generation Radar (NEXRAD), provides a network of weather stations in the US. Data generated from this network were used to understand general migratory patterns, migratory stopover habitats, and other patterns caused by the effects of weather conditions. At a local scale our marine radar was used to complement the datasets from NEXRAD and
-
Spectral broadening of planetary radar signals by the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Harmon, J.K.; Coles, W.A.
1983-01-01
The microturbulence spectrum of the solar wind is estimated using the spectral broadening of planetary radar signals. Observations were made with the two radars (12.6 cm and 70 cm) at Arecibo Observatory during the 1979 and 1981 superior conjunctions of Venus. These observations, which span the solar distance range of 5.4 to 25.5 R/sub sun/, are the first of their type to be reported. The data are consistent with earlier observations where comparisons can be made. The flattening of the high-frequency portion of the spectrum near the Sun reported by Woo and Armstrong is confirmed. In one case clear evidence for an inner scale in the vicinity of 2 km is found. Two transients, 1979 August 15 and 1981 April 24-25, with rather different characteristics were observed
-
Typhoon 9707 observations with the MU radar and L-band boundary layer radar
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Teshiba
2001-08-01
Full Text Available Typhoon 9707 (Opal was observed with the VHF-band Middle and Upper atmosphere (MU radar, an L-band boundary layer radar (BLR, and a vertical-pointing C-band meteorological radar at the Shigaraki MU Observatory in Shiga prefecture, Japan on 20 June 1997. The typhoon center passed about 80 km southeast from the radar site. Mesoscale precipitating clouds developed due to warm-moist airmass transport from the typhoon, and passed over the MU radar site with easterly or southeasterly winds. We primarily present the wind behaviour including the vertical component which a conventional meteorological Doppler radar cannot directly observe, and discuss the relationship between the wind behaviour of the typhoon and the precipitating system. To investigate the dynamic structure of the typhoon, the observed wind was divided into radial and tangential wind components under the assumption that the typhoon had an axi-symmetric structure. Altitude range of outflow ascended from 1–3 km to 2–10 km with increasing distance (within 80–260 km range from the typhoon center, and in-flow was observed above and below the outflow. Outflow and inflow were associated with updraft and downdraft, respectively. In the tangential wind, the maximum speed of counterclockwise winds was confirmed at 1–2 km altitudes. Based on the vertical velocity and the reflectivity obtained with the MU radar and the C-band meteorological radar, respectively, precipitating clouds, accompanied by the wind behaviour of the typhoon, were classified into stratiform and convective precipitating clouds. In the stratiform precipitating clouds, a vertical shear of radial wind and the maximum speed of counterclockwise wind were observed. There was a strong reflectivity layer called a ‘bright band’ around the 4.2 km altitude. We confirmed strong updrafts and down-drafts below and above it, respectively, and the existence of a relatively dry layer around the bright band level from radiosonde
-
Typhoon 9707 observations with the MU radar and L-band boundary layer radar
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Teshiba
Full Text Available Typhoon 9707 (Opal was observed with the VHF-band Middle and Upper atmosphere (MU radar, an L-band boundary layer radar (BLR, and a vertical-pointing C-band meteorological radar at the Shigaraki MU Observatory in Shiga prefecture, Japan on 20 June 1997. The typhoon center passed about 80 km southeast from the radar site. Mesoscale precipitating clouds developed due to warm-moist airmass transport from the typhoon, and passed over the MU radar site with easterly or southeasterly winds. We primarily present the wind behaviour including the vertical component which a conventional meteorological Doppler radar cannot directly observe, and discuss the relationship between the wind behaviour of the typhoon and the precipitating system. To investigate the dynamic structure of the typhoon, the observed wind was divided into radial and tangential wind components under the assumption that the typhoon had an axi-symmetric structure. Altitude range of outflow ascended from 1–3 km to 2–10 km with increasing distance (within 80–260 km range from the typhoon center, and in-flow was observed above and below the outflow. Outflow and inflow were associated with updraft and downdraft, respectively. In the tangential wind, the maximum speed of counterclockwise winds was confirmed at 1–2 km altitudes. Based on the vertical velocity and the reflectivity obtained with the MU radar and the C-band meteorological radar, respectively, precipitating clouds, accompanied by the wind behaviour of the typhoon, were classified into stratiform and convective precipitating clouds. In the stratiform precipitating clouds, a vertical shear of radial wind and the maximum speed of counterclockwise wind were observed. There was a strong reflectivity layer called a ‘bright band’ around the 4.2 km altitude. We confirmed strong updrafts and down-drafts below and above it, respectively, and the existence of a relatively dry layer around the bright band level from radiosonde
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. R. John
2011-07-01
Full Text Available The All-Sky interferometric meteor (SKYiMET radar (MR derived winds in the vicinity of the equatorial electrojet (EEJ are discussed. As Thumba (8.5° N, 77° E; dip lat. 0.5° N is under the EEJ belt, there has been some debate on the reliability of the meteor radar derived winds near the EEJ height region. In this regard, the composite diurnal variations of zonal wind profiles in the mesosphere-lower thermosphere (MLT region derived from TIMED Doppler Interferometer (TIDI and ground based meteor radar at Thumba are compared. In this study, emphasis is given to verify the meteor radar observations at 98 km height region, especially during the EEJ peaking time (11:00 to 14:00 LT. The composite diurnal cycles of zonal winds over Thumba are constructed during four seasons of the year 2006 using TIDI and meteor radar observations, which showed good agreement especially during the peak EEJ hours, thus assuring the reliability of meteor radar measurements of neutral winds close to the EEJ height region. It is evident from the present study that on seasonal scales, the radar measurements are not biased by the EEJ. The day-time variations of HF radar measured E-region drifts at the EEJ region are also compared with MR measurements to show there are large differences between ionospheric drifts and MR measurements. The significance of the present study lies in validating the meteor radar technique over Thumba located at magnetic equator by comparing with other than the radio technique for the first time.
-
Radar ornithology and the conservation of migratory birds
Sidney A. Gauthreaux; Carroll G. Belser
2005-01-01
It is possible to study with surveillance radar the movements of migrating birds in the atmosphere at different spatial scales. At a spatial scale within a range of 6 kilometers, high-resolution, 3-centimeter wavelength surveillance radar (e.g. BIRDRAD) can detect the departure of migrants from different types of habitat within a few kilometers of the radar. The radar...
-
Examples of mesoscale structures and short-term wind variations detected by VHF Doppler radar
Forbes, G. S.
1986-01-01
The first of three wind profilers planned for operation in central and western Pennsylvania began full-time, high-quality operation during July 1985. It is located about 20 km south-southeast of University Park and operates at 50 MHz. Another 50-MHz radar and a 400-MHz radar are to be installed over the next few months, to complete a mesoscale triangle with sides of 120 to 160 km. During the period since early July, a number of weather systems have passed over the wind profiler. Those accompanied by thunderstorms caused data losses either because the Department computer system lost power or because power went out at the profiler site. A backup power supply and an automatic re-start program will be added to the profiler system to minimize such future losses. Data have normally been averaged over a one-hour period, although there have been some investigations of shorter-period averaging. In each case, preliminary examinations reveal that the profiler winds are indicative of meteorological phenomena. The only occasions of bad or missing data are obtained when airplane noise is occasionally experienced and when the returned power is nearly at the noise level, at the upper few gates, where a consensus wind cannot be determined. Jets streams, clouds, and diurnal variations of winds are discussed.
-
Barbre, Robert E., Jr.
2012-01-01
This paper presents the process used by the Marshall Space Flight Center Natural Environments Branch (EV44) to quality control (QC) data from the Kennedy Space Center's 50-MHz Doppler Radar Wind Profiler for use in vehicle wind loads and steering commands. The database has been built to mitigate limitations of using the currently archived databases from weather balloons. The DRWP database contains wind measurements from approximately 2.7-18.6 km altitude at roughly five minute intervals for the August 1997 to December 2009 period of record, and the extensive QC process was designed to remove spurious data from various forms of atmospheric and non-atmospheric artifacts. The QC process is largely based on DRWP literature, but two new algorithms have been developed to remove data contaminated by convection and excessive first guess propagations from the Median Filter First Guess Algorithm. In addition to describing the automated and manual QC process in detail, this paper describes the extent of the data retained. Roughly 58% of all possible wind observations exist in the database, with approximately 100 times as many complete profile sets existing relative to the EV44 balloon databases. This increased sample of near-continuous wind profile measurements may help increase launch availability by reducing the uncertainty of wind changes during launch countdown
-
A study of the radar backscattering from the breaking of wind waves on the sea
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ivanov, V.A.; Yurovskij, Yu.Yu.; Malinovskij, V.V.
2011-01-01
The results of a field study of the relationship between radar backscattering parameters and geometrical characteristics of the wind wave breaking are presented. The radar cross-section of a whitecap is found to be proportional to the breaking crest length. It is shown that the accounting for a change of the non-Bragg scattering in the presence of an oil slick on the sea surface allows one to interpret experimental data correctly.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Griffin, E.M.; Aruliah, A.; Mueller-Wodarg, I.C.F.; Aylward, A. [Atmospheric Physics Lab., Univ. Coll. London, London (United Kingdom)
2004-07-01
The climatological behaviour of the thermospheric meridional wind above Kiruna, Sweden (67.4 N, 20.4 E) has been investigated for seasonal and solar cycle dependence using six different techniques, comprising both model and experimental sources. Model output from both the empirical Horizontal Wind Model (HWM) (Hedin et al., 1988) and the numerical coupled thermosphere and ionosphere model (CTIM) are compared to the measured behaviour at kiruna, as a single site example. The empirical International Reference Ionosphere (IRI) model is used as input to an implementation of servo theory, to provide another climatology combining empirical input with a theoretical framework. The experimental techniques have been introduced in a companion paper in this issue and provide climatologies from direct measurements, using fabry-perot interferometers (FPI), together with 2 separate techniques applied to the European incoherent scatter radar (EISCAT) database to derive neutral winds. One of these techniques uses the same implementation of servo theory as has been used with the IRI model. Detailed comparisons for each season and solar activity category allow for conclusions to be drawn as to the major influences on the climatological behaviour of the wind at this latitude. Comparison of the incoherent scatter radar (ISR) derived neutral winds with FPI, empirical model and numerical model winds is important to our understanding and judgement of the validity of the techniques used to derive thermospheric wind databases. The comparisons also test model performance and indicate possible reasons for differences found between the models. In turn, the conclusions point to possible improvements in their formulation. In particular it is found that the empirical models are over-reliant on mid-latitude data in their formulation, and fail to provide accurate estimates of the winds at high-latitudes. (orig.)
-
Radar micro-Doppler of wind turbines : Simulation and analysis using rotating linear wire structures
Krasnov, O.A.; Yarovoy, A.
2015-01-01
A simple electromagnetic model of wind-turbine's main structural elements as the linear wired structures is developed to simulate the temporal patterns of observed radar return Doppler spectra (micro-Doppler). Using the model, the micro-Doppler for different combinations of the turbines rotation
-
The Orlando TDWR testbed and airborne wind shear date comparison results
Campbell, Steven; Berke, Anthony; Matthews, Michael
1992-01-01
The focus of this talk is on comparing terminal Doppler Weather Radar (TDWR) and airborne wind shear data in computing a microburst hazard index called the F factor. The TDWR is a ground-based system for detecting wind shear hazards to aviation in the terminal area. The Federal Aviation Administration will begin deploying TDWR units near 45 airports in late 1992. As part of this development effort, M.I.T. Lincoln Laboratory operates under F.A.A. support a TDWR testbed radar in Orlando, FL. During the past two years, a series of flight tests has been conducted with instrumented aircraft penetrating microburst events while under testbed radar surveillance. These tests were carried out with a Cessna Citation 2 aircraft operated by the University of North Dakota (UND) Center for Aerospace Sciences in 1990, and a Boeing 737 operated by NASA Langley Research Center in 1991. A large data base of approximately 60 instrumented microburst penetrations has been obtained from these flights.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. R. Jain
Full Text Available The turbulence refractivity structure constant (C2n is an important parameter of the atmosphere. VHF radars have been used extensively for the measurements of C2n. Presently, most of such observations are from mid and high latitudes and only very limited observations are available for equatorial and tropical latitudes. Indian MST radar is an excellent tool for making high-resolution measurements of atmospheric winds, associated shears and turbulence refractivity structure constant (C2n. This radar is located at Gadanki (13.45° N, 79.18° E, a tropical station in India. The objective of this paper is to bring out the height structure of C2n for different seasons using the long series of data (September 1995 – August 1999 from Indian MST radar. An attempt is also made to understand such changes in the height structure of C2n in relation to background atmospheric parameters such as horizontal winds and associated shears. The height structure of C2n, during the summer monsoon and post-monsoon season, shows specific height features that are found to be related to Tropical Easterly Jet (TEJ winds. It is important to examine the nature of the radar back-scatterers and also to understand the causative mechanism of such scatterers. Aspect sensitivity of the received radar echo is examined for this purpose. It is observed that radar back-scatterers at the upper tropospheric and lower stratospheric heights are more anisotropic, with horizontal correlation length of 10–20 m, as compared to those observed at lower and middle tropospheric heights.Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (climatology; tropical meteorology; turbulence
-
Dryden, Rachel L.
2011-01-01
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration s (NASA) Kennedy Space Center (KSC) has installed a five-instrument 915-Megahertz (MHz) Doppler Radar Wind Profiler (DRWP) system that records atmospheric wind profile properties. The purpose of these profilers is to fill data gaps between the top of the KSC wind tower network and the lowest measurement altitude of the KSC 50-MHz DRWP. The 915-MHz DRWP system has the capability to generate three-dimensional wind data outputs from approximately 150 meters (m) to 6,000 m at roughly 15-minute (min) intervals. NASA s long-term objective is to combine the 915-MHz and 50-MHz DRWP systems to create complete vertical wind profiles up to 18,300 m to be used in trajectory and loads analyses of space vehicles and by forecasters on day-of-launch (DOL). This analysis utilizes automated and manual quality control (QC) processes to remove erroneous and unrealistic wind data returned by the 915-MHz DRWP system. The percentage of data affected by each individual QC check in the period of record (POR) (i.e., January to April 2006) was computed, demonstrating the variability in the amount of data affected by the QC processes. The number of complete wind profiles available at given altitude thresholds for each profiler in the POR was calculated and outputted graphically, followed by an assessment of the number of complete wind profiles available for any profiler in the POR. A case study is also provided to demonstrate the QC process on a day of a known weather event.
-
Velazquez, F. A.; Martinez, J. A.; Durazo, R.; Flament, P.
2007-12-01
Most of the studies on coastal dynamics in the Gulf of Tehuatepec (GT) have been focused on mixing processes and mesoscale eddies generated due to strong off-shore wind events, know as Nortes or Tehuanos. In order to investigate the spatial and temporal mesoscale variability of surface dynamic in the GT in February 2005, two HF Radar model WERA were deployed along the shore of Oaxaca, Mexico. The spatial coverage of radars reaches up to 120 km off-shore. The radial velocities were processed to obtain total velocity maps every hour in a regular grid of 5.5 km. space resolution. The information of surface velocity and quickscat/NCEP wind obtained during the first sample days show that exist a coastal current toward the west and, during the wind events, is accelerated and steered toward the southwest. In this same period, we find that spatial density of kinetic energy and divergence of velocity field increase during wind events while the vorticity becomes negative. When strong wind events are not present the surface circulation is weakened, mainly for the zonal component of the wind that is mostly positive (westward). These results are in agreement with the upwelling processes observed on the coast and the anticyclonic eddie generation west of the GT during Tehuanos. Images of sea surface temperature and chlorophyll concentration are also used to observe the signature of wind events near the shore. Complementary to field observations, numerical simulation using a 3D primitive equations model (POM) are used to study the wind-driven circulation in the GT. It has been commonly accepted in previous studies that the strong wind events generate mesoscale eddies. We discuss the limited effect of the wind and the interaction of the wind with a coastal current required to generate long life eddies.
-
Fritts, D. C.; Janches, D.; Iimura, H.; Hocking, W. K.; Bageston, J. V.; Pene, N. M.
2011-01-01
A new-generation meteor radar was installed at the Brazilian Antarctic Comandante Ferraz Base (62.1degS) in March 2010. This paper describes the motivations for the radar location, its measurement capabilities, and comparisons of measured mean winds, tides, and gravity wave momentum fluxes from April to June of 2010 and 2011 with those by a similar radar on Tierra del Fuego (53.8degS). Motivations for the radars include the "hotspot" of small-scale gravity wave activity extending from the troposphere into the mesosphere and lower thermosphere (MLT) centered over the Drake Passage, the maximum of the semidiurnal tide at these latitudes, and the lack of other MLT wind measurements in this latitude band. Mean winds are seen to be strongly modulated at planetary wave and longer periods and to exhibit strong coherence over the two radars at shorter time scales as well as systematic seasonal variations. The semidiurnal tide contribute most to the large-scale winds over both radars, with maximum tidal amplitudes during May and maxima at the highest altitudes varying from approx.20 to >70 m/s. In contrast, the diurnal tide and various planetary waves achieve maximum winds of approx.10 to 20 m/s. Monthly-mean gravity wave momentum fluxes appear to reflect the occurrence of significant sources at lower altitudes, with relatively small zonal fluxes over both radars, but with significant, and opposite, meridional momentum fluxes below approx.85 km. These suggest gravity waves propagating away from the Drake Passage at both sites, and may indicate an important source region accounting in part for this "hotspot".
-
Kim, Yongha; Kim, Jeong-Han; Jee, Geonwha; Lee, Chang-Sup
2010-05-01
A VHF radar at King Sejong Station, Antarctica has been measuring meteor echoes since March 2007. Temperatures near the mesopause are derived from meteor decay times with an improved method of selecting meteor echo samples, and compared with airglow temperatures simultaneously observed by a spectral airglow temperature imager (SATI). The temperatures derived from meteor decay times are mostly consistent with the rotational temperatures of SATI OH(6-2) and O2(0-1) emissions from March through October. During southern summer when SATI cannot be operated due to brief night time, the meteor radar observation shows cold mesospheric temperatures, significantly lower than the CIRA86 model. The meteor radar observation also provides wind field information between 80 and 100 km of altitude. The measured meridional winds seem to follow the summer pole to winter pole circulation, and thus are correlated with the measured seasonal temperature change. However, the correlation between meridional winds and temperatures is not found in day by day base, as a previous study reported. Tidal characteristics of both zonal and meridional winds will also be compared with those of other Antarctic stations.
-
Kishore Kumar, G.; Nesse Tyssøy, H.; Williams, Bifford P.
2018-03-01
We investigate the possibility that sufficiently large electric fields and/or ionization during geomagnetic disturbed conditions may invalidate the assumptions applied in the retrieval of neutral horizontal winds from meteor and/or lidar measurements. As per our knowledge, the possible errors in the wind estimation have never been reported. In the present case study, we have been using co-located meteor radar and sodium resonance lidar zonal wind measurements over Andenes (69.27°N, 16.04°E) during intense substorms in the declining phase of the January 2005 solar proton event (21-22 January 2005). In total, 14 h of measurements are available for the comparison, which covers both quiet and disturbed conditions. For comparison, the lidar zonal wind measurements are averaged over the same time and altitude as the meteor radar wind measurements. High cross correlations (∼0.8) are found in all height regions. The discrepancies can be explained in light of differences in the observational volumes of the two instruments. Further, we extended the comparison to address the electric field and/or ionization impact on the neutral wind estimation. For the periods of low ionization, the neutral winds estimated with both instruments are quite consistent with each other. During periods of elevated ionization, comparatively large differences are noticed at the highermost altitude, which might be due to the electric field and/or ionization impact on the wind estimation. At present, one event is not sufficient to make any firm conclusion. Further study with more co-located measurements are needed to test the statistical significance of the result.
-
Ranger© - An Affordable, Advanced, Next-Generation, Dual-Pol, X-Band Weather Radar
Stedronsky, Richard
2014-05-01
The Enterprise Electronics Corporation (EEC) Ranger© system is a new generation, X-band (3 cm), Adaptive Polarization Doppler Weather Surveillance Radar that fills the gap between high-cost, high-power traditional radar systems and the passive ground station weather sensors. Developed in partnership with the University of Oklahoma Advanced Radar Research Center (ARRC), the system uses relatively low power solid-state transmitters and pulse compression technology to attain nearly the same performance capabilities of much more expensive traditional radar systems. The Ranger© also employs Adaptive Dual Polarization (ADP) techniques to allow Alternating or Simultaneous Dual Polarization capability with total control over the transmission polarization state using dual independent coherent transmitters. Ranger© has been designed using the very latest technology available in the industry and the technical and manufacturing experience gained through over four decades of successful radar system design and production at EEC. The entire Ranger© design concept emphasizes precision, stability, reliability, and value using proven solid state technology combined with the most advanced motion control system ever conceived for weather radar. Key applications include meteorology, hydrology, aviation, offshore oil/gas drilling, wind energy, and outdoor event situational awareness.
-
Summer planetary-scale oscillations: aura MLS temperature compared with ground-based radar wind
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. E. Meek
2009-04-01
Full Text Available The advent of satellite based sampling brings with it the opportunity to examine virtually any part of the globe. Aura MLS mesospheric temperature data are analysed in a wavelet format for easy identification of possible planetary waves (PW and aliases masquerading as PW. A calendar year, 2005, of eastward, stationary, and westward waves at a selected latitude is shown in separate panels for wave number range −3 to +3 for period range 8 h to 30 days (d. Such a wavelet analysis is made possible by Aura's continuous sampling at all latitudes 82° S–82° N. The data presentation is suitable for examination of years of data. However this paper focuses on the striking feature of a "dish-shaped" upper limit to periods near 2 d in mid-summer, with longer periods appearing towards spring and fall, a feature also commonly seen in radar winds. The most probable cause is suggested to be filtering by the summer jet at 70–80 km, the latter being available from ground based medium frequency radar (MFR. Classically, the phase velocity of a wave must be greater than that of the jet in order to propagate through it. As an attempt to directly relate satellite and ground based sampling, a PW event of period 8d and wave number 2, which appears to be the original rather than an alias, is compared with ground based radar wind data. An appendix discusses characteristics of satellite data aliases with regard to their periods and amplitudes.
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — This data set consists of high resolution sea surface winds data produced from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) on board Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-1B satellites. This...
-
Feasibility of mitigating the effects of windfarms on primary radar
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Butler, M.M.; Johnson, D.A.
2003-07-01
The objectives of the study were to investigate the feasibility of modifying civil and military radars to mitigate the effects from wind turbines, to provide costings for implementing changes to the radar and to produce guidelines for planning wind farms in the vicinity of radars. The effect of wind turbines on radar signals, assessed through computer modelling, is summarised. The key aspects of turbine design that can be modified to minimise these effects are described. A key issue is the fact that no two radar installations are alike, with settings being customised for local requirements. As a consequence, a detailed understanding of the design and features of each individual radar would be required in order to assess the impact of a wind farm proposal. The costs of a programme of modifications to the civil ATC (air traffic control) radar base will depend on many factors. An estimate of costs is provided, based on the assumption that only 30 of the UK radars would need modification and that a range of modifications from very simple to very complex will be required. A number of other approaches, outside of modification of the radar system, may require investigation during a windfarm planning application, such as layout and location of the wind farm or changing air traffic routes in the vicinity of the wind farm.
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — These data represent an inventory of the national impacts of wind turbine interference with NEXRAD radar stations. This inventory was developed by the NOAA Radar...
-
The monocular visual imaging technology model applied in the airport surface surveillance
Qin, Zhe; Wang, Jian; Huang, Chao
2013-08-01
At present, the civil aviation airports use the surface surveillance radar monitoring and positioning systems to monitor the aircrafts, vehicles and the other moving objects. Surface surveillance radars can cover most of the airport scenes, but because of the terminals, covered bridges and other buildings geometry, surface surveillance radar systems inevitably have some small segment blind spots. This paper presents a monocular vision imaging technology model for airport surface surveillance, achieving the perception of scenes of moving objects such as aircrafts, vehicles and personnel location. This new model provides an important complement for airport surface surveillance, which is different from the traditional surface surveillance radar techniques. Such technique not only provides clear objects activities screen for the ATC, but also provides image recognition and positioning of moving targets in this area. Thereby it can improve the work efficiency of the airport operations and avoid the conflict between the aircrafts and vehicles. This paper first introduces the monocular visual imaging technology model applied in the airport surface surveillance and then the monocular vision measurement accuracy analysis of the model. The monocular visual imaging technology model is simple, low cost, and highly efficient. It is an advanced monitoring technique which can make up blind spot area of the surface surveillance radar monitoring and positioning systems.
-
Radar Polarimetry and Interferometry (La polarimetrie et l'interferometrie radar) (CD-ROM)
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Keydel, W; Boerner, W. M; Pottier, E; Lee, J. S; Ferro-Famil, L; Hellmann, M; Cloude, S. R
2005-01-01
...: Scientists and engineers already engaged in the fields of radar surveillance, reconnaissance and scattering measurements, for instance, generally gain their specialist knowledge in both polarimetry...
-
Installation and Initial Operation of DOE's 449-MHz Wind Profiling Radars on the U.S. West Coast
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Flaherty, Julia E. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Shaw, William J. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Morris, Victor R. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Wilczak, J. M. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); White, A. B. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Ayers, Tom [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Jordan, Jim [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); King, Clark W. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States)
2015-10-30
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), in collaboration with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), has recently completed the installation of three new wind profiling radars on the Washington and Oregon coasts. These systems operate at a frequency of 449 MHz and provide mean wind profiles to a height of roughly 8 km, with the maximum measurement height depending on time-varying atmospheric conditions. This is roughly half the depth of the troposphere at these latitudes. Each system is also equipped with a radio acoustic sounding system (RASS), which provides a measure of the temperature profile to heights of approximately 2 km. Other equipment deployed alongside the radar includes a surface meteorological station and GPS for column water vapor. This project began in fiscal year 2014, starting with equipment procurements and site selection. In addition, environmental reviews, equipment assembly and testing, site access agreements, and infrastructure preparations have been performed. Finally, with equipment deployment with data collection and dissemination, the primary tasks of this project have been completed. The three new wind profiling radars have been deployed at airports near Coos Bay, OR, and Astoria, OR, and at an industrial park near Forks, WA. Data are available through the NOAA Earth Systems Research Laboratory Data Display website, and will soon be made available through the DOE Atmosphere to Electrons data archive and portal as well.
-
Ultra-wideband radar sensors and networks
Leach, Jr., Richard R; Nekoogar, Faranak; Haugen, Peter C
2013-08-06
Ultra wideband radar motion sensors strategically placed in an area of interest communicate with a wireless ad hoc network to provide remote area surveillance. Swept range impulse radar and a heart and respiration monitor combined with the motion sensor further improves discrimination.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Manson, A.H.; Meek, C.E.; Xu, X. [Saskatchewan Univ., Saskatoon (Canada). Inst. of Space and Atmospheric Studies; Aso, T.; Tsutsumi, M. [National Institute for Polar Research, Tokyo (Japan); Drummond, J.R. [Dalhousie Univ., Halifax (Canada). Physics and Atmospheric Science Dept.; Hall, C.M. [Tromsoe Univ. (Norway). Tromsoe Geophysical Observatory; Hocking, W.K. [Western Onatario Univ., London (Canada). Physics and Astronomy Dept.; Ward, W.E. [New Brunswick Univ., Fredericton (Canada). Physics and Astronomy Dept.
2011-07-01
Operation of a Meteor Wind Radar (MWR) at Eureka, Ellesmere Island (80 N, 86 W) began in February 2006; this is the location of the Polar Environmental and Atmospheric Research Laboratory (PEARL), operated by the ''Canadian Network for the Detection of Atmospheric Change'' (CANDAC). The first 36 months of wind data (82- 97 km) are here combined with contemporaneous winds from the Meteor Wind Radar at Adventdalen, Svalbard (78 N, 16 E), to provide the first evidence for substantial interannual variability (IAV) of longitudinally spaced observations of mean/background winds and waves at such High Arctic latitudes. The influences of ''Sudden Stratospheric Warmings'' (SSW) are also apparent. Monthly meridional (north-south, NS) 3-year means for each location/radar demonstrate that winds (82-97 km) differ significantly between Canada and Norway, with winterequinox values generally northward over Eureka and southward over Svalbard. Using January 2008 as case study, these oppositely directed meridional winds are related to mean positions of the Arctic mesospheric vortex. The vortex is from the Canadian Middle Atmosphere Model, with its Data Assimilation System (CMAM-DAS). The characteristics of ''Sudden stratospheric Warmings'' SSW in each of the three winters are noted, as well as their uniquely distinctive short-term mesospheric wind disturbances. Comparisons of the mean winds over 36 months at 78 and 80 N, with those within CMAM-DAS, are featured. E.g. for 2007, while both monthly mean EW and NS winds from CMAM/radar are quite similar over Eureka (82-88 km), the modeled autumn-winter NS winds over Svalbard (73-88 km) differ significantly from observations. The latter are southward, and the modeled winds over Svalbard are predominately northward. The mean positions of the winter polar vortex are related to these differences. (orig.)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Danny Scipión
2009-05-01
Full Text Available The daytime convective boundary layer (CBL is characterized by strong turbulence that is primarily forced by buoyancy transport from the heated underlying surface. The present study focuses on an example of flow structure of the CBL as observed in the U.S. Great Plains on June 8, 2007. The considered CBL flow has been reproduced using a numerical large eddy simulation (LES, sampled with an LES-based virtual boundary layer radar (BLR, and probed with an actual operational radar profiler. The LES-generated CBL flow data are then ingested by the virtual BLR and treated as a proxy for prevailing atmospheric conditions. The mean flow and turbulence parameters retrieved via each technique (actual radar profiler, virtual BLR, and LES have been cross-analyzed and reasonable agreement was found between the CBL wind parameters obtained from the LES and those measured by the actual radar. Averaged vertical velocity variance estimates from the virtual and actual BLRs were compared with estimates calculated from the LES for different periods of time. There is good agreement in the estimates from all three sources. Also, values of the vertical velocity skewness retrieved by all three techniques have been inter-compared as a function of height for different stages of the CBL evolution, showing fair agreement with each other. All three retrievals contain positively skewed vertical velocity structure throughout the main portion of the CBL. Radar estimates of the turbulence kinetic energy (eddy dissipation rate (ε have been obtained based on the Doppler spectral width of the returned signal for the vertical radar beam. The radar estimates were averaged over time in the same fashion as the LES output data. The agreement between estimates was generally good, especially within the mixing layer. Discrepancies observed above the inversion layer may be explained by a weak turbulence signal in particular flow configurations. The virtual BLR produces voltage
-
Lee, J. T.
1984-01-01
As part of continuing research on aviation related weather hazards, numerous experiments were incorporated into the 1983 Spring Observation Program. This year's program was an abbreviated one because of commitments made to the development of the Next Generation Radar (NEXRAD) project. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) P-3 Orion and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) RB-57B and U-2 were the main aircraft involved in the studies of lightning, wind shear, turbulence, and storm structure. A total of 14 flights were made by these aircraft during the period of May 16 through June 5, 1983. Aircraft instrumentation experiments are described, and resultant data sets available for research are detailed. Aircraft instrumentation and Doppler radar characteristics are detailed.
-
Experimentelles FMCW-Radar zur hochfrequenten Charakterisierung von Windenergieanlagen
Schubert, Karsten; Werner, Jens; Schwartau, Fabian
2017-09-01
During the increasing dissemination of renewable energy sources the potential and actual interference effects of wind turbine plants became obvious. Turbines reflect the signals of weather radar and other radar systems. In addition to the static radar echoes, in particular the Doppler echoes are to be mentioned as an undesirable impairment Keränen (2014). As a result, building permit is refused for numerous new wind turbines, as the potential interference can not be reliably predicted. As a contribution to the improvement of this predictability, measurements are planned which aim at the high-frequency characterisation of wind energy installations. In this paper, a cost-effective FMCW radar is presented, which is operated in the same frequency band (C-band) as the weather radars of the German weather service. Here, the focus is on the description of the hardware design including the considerations used for its dimensioning.
-
A Defender-Attacker Optimization of Port Radar Surveillance
2011-01-01
security; optimization; attacker-defender “And thence discover how with most advantage They may vex us with shot, or with assault.” Shakespeare , KingHenryVI...1. INTRODUCTION We introduce a new planning tool for locating shore radars and mobile picket boats with radar to maximize the probabil- ity that one
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Manson, A.H.; Meek, C.E.; Avery, S.K.; Fraser, G.J.; Vincent, R.A.; Phillips, A.; Clark, R.R.; Schminder, R.; Kurschner, D.; Kazimirovsky, E.S.
1991-01-01
Winds and tides were measured by nine MLT (mesophere, lower thermosphere) radars with locations between 70 degree N and 78 degree S, including an equatorial station at Christmas Island, 2 degree N (Avery et al., 1990). The mean winds were eastward (westward) in the northern (southern) hemisphere mesophere, consistent with midwinter circulations. For the 12-hour (semidiurnal) tide, observations and the model of Forbes and Vial (1989) were in generally good agreement: in both cases northward components were closer to being in phase in the two hemispheres, and winter wavelengths were shorter than those of the midlatitude summer. Major differences were large (small) amplitudes at 70 degree N for model(observations); and poor agreement of equatorial tidal profiles. For the 24-hour (diurnal tide), the radar observations and model of Forbes and Hagan (1988) were in useful agreement in the summer hemisphere. However, the short (long) wavelengths at mid (high) latitudes of the model's winter hemisphere were not observed during LTCS (lower Thermosphere Coupling Study) 2, nor in climatologies for December. Suggestions as to the reason for this disparity are presented
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Griffin, E.M.; Mueller-Wodarg, I.C.F.; Aruliah, A.; Aylward, A. [Atmospheric Physics Lab., Univ. Coll. London, London (United Kingdom)
2004-07-01
Thermospheric neutral winds at Kiruna, Sweden (67.4 N, 20.4 E) are compared using both direct optical fabry-perot interferometer (FPI) measurements and those derived from European incoherent scatter radar (EISCAT) measurements. This combination of experimental data sets, both covering well over a solar cycle of data, allows for a unique comparison of the thermospheric meridional component of the neutral wind as observed by different experimental techniques. Uniquely in this study the EISCAT measurements are used to provide winds for comparison using two separate techniques: the most popular method based on the work of Salah and Holt (1974) and the meridional wind model (MWM) (Miller et al., 1997) application of servo theory. The balance of forces at this location that produces the observed diurnal pattern are investigated using output from the coupled thermosphere and ionosphere (CTIM) numerical model. Along with detailed comparisons from short periods the climatological behaviour of the winds have been investigated for seasonal and solar cycle dependence using the experimental techniques. While there are features which are consistent between the 3 techniques, such as the evidence of the equinoctial asymmetry, there are also significant differences between the techniques both in terms of trends and absolute values. It is clear from this and previous studies that the high-latitude representation of the thermospheric neutral winds from the empirical horizontal wind model (HWM), though improved from earlier versions, lacks accuracy in many conditions. The relative merits of each technique are discussed and while none of the techniques provides the perfect data set to address model performance at high-latitude, one or more needs to be included in future HWM reformulations. (orig.)
-
Coherent Doppler Laser Radar: Technology Development and Applications
Kavaya, Michael J.; Arnold, James E. (Technical Monitor)
2000-01-01
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center has been investigating, developing, and applying coherent Doppler laser radar technology for over 30 years. These efforts have included the first wind measurement in 1967, the first airborne flights in 1972, the first airborne wind field mapping in 1981, and the first measurement of hurricane eyewall winds in 1998. A parallel effort at MSFC since 1982 has been the study, modeling and technology development for a space-based global wind measurement system. These endeavors to date have resulted in compact, robust, eyesafe lidars at 2 micron wavelength based on solid-state laser technology; in a factor of 6 volume reduction in near diffraction limited, space-qualifiable telescopes; in sophisticated airborne scanners with full platform motion subtraction; in local oscillator lasers capable of rapid tuning of 25 GHz for removal of relative laser radar to target velocities over a 25 km/s range; in performance prediction theory and simulations that have been validated experimentally; and in extensive field campaign experience. We have also begun efforts to dramatically improve the fundamental photon efficiency of the laser radar, to demonstrate advanced lower mass laser radar telescopes and scanners; to develop laser and laser radar system alignment maintenance technologies; and to greatly improve the electrical efficiency, cooling technique, and robustness of the pulsed laser. This coherent Doppler laser radar technology is suitable for high resolution, high accuracy wind mapping; for aerosol and cloud measurement; for Differential Absorption Lidar (DIAL) measurements of atmospheric and trace gases; for hard target range and velocity measurement; and for hard target vibration spectra measurement. It is also suitable for a number of aircraft operations applications such as clear air turbulence (CAT) detection; dangerous wind shear (microburst) detection; airspeed, angle of attack, and sideslip measurement; and fuel savings through
-
Mixing height measurements from UHF wind profiling radar
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Angevine, W.M.; Grimsdell, A.W. [CIRES, Univ. of Colorado, and NOAA Aeronomy Lab., Boulder, Colorado (United States)
1997-10-01
Mixing height in convective boundary layers can be detected by wind profiling radars (profilers) operating at or near 915 MHZ. We have made such measurements in a variety of settings including Alabama in 1992; Nova Scotia, Canada, during the North Atlantic Regional Experiment (NARE) 1993; Tennessee during the Southern Oxidant Study (SOS) 1994; near a 450 m tower in Wisconsin in 1995; and extensively in Illinois during the Flatland95, `96, and `97 experiments, as well as continuous operations at the Flatland Atmospheric Observatory. Profiler mixing height measurements, like all measurements, are subject to some limitations. The most important of these are due to rainfall, minimum height, and height resolution. Profilers are very sensitive to rain, which dominates the reflectivity and prevents the mixing height from being detected. Because the best height resolution is currently 60 m and the minimum height is 120-150 m AGL, the profiler is not suited for detecting mixing height in stable or nocturnal boundary layers. Problems may also arise in very dry or cold environments. (au) 12 refs.
-
Using radar wind profilers and RASS data to calculate power plant plume rise and transport
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ping, Y.J.; Gaynor, J.E.
1994-01-01
As the number of 915-MHz radar wind profilers and radio acoustic sounding systems (RASS) increases, their number of uses also increases. These systems have demonstrated particular utility in air quality studies and, more specifically, in complex terrain. One data set from the radar profilers that has not, to date, been utilized to any large extent is represented by the temperature profiles derived from the RASS. Normally, these profiles represent a 5-min average every hour with a height resolution of about 60 m, a minimum range of about 100 m, and a maximum range of about 1.5 km, although this varies substantially with meterological conditions. Such profiles have several potential applications. Among them are determinations of mixing height and stability. In this work, we use the stability, along with the hour-averaged wind profiles, to estimate plume rise heights at a power plant site in Laughlin, Nevada, about 200 km south of Lake Mead. The profiles are first stratified according to season and synoptic categories so that the calculated plume rise heights could be separated by background transport conditions. The data were taken during Project Measurement of Haze and Visual Effects (MOHAVE), which took place in 1992. This project is briefly discussed in the next section, along with the instrumentation and data used in this study
-
Using radar wind profilers and RASS data to calculate power plant plume rise and transport
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ping, Y.J. [Univ. of Colorado, Boulder, CO (United States); Gaynor, J.E. [NOAA/ERL Wave Propagation Lab., Boulder, CO (United States)
1994-12-31
As the number of 915-MHz radar wind profilers and radio acoustic sounding systems (RASS) increases, their number of uses also increases. These systems have demonstrated particular utility in air quality studies and, more specifically, in complex terrain. One data set from the radar profilers that has not, to date, been utilized to any large extent is represented by the temperature profiles derived from the RASS. Normally, these profiles represent a 5-min average every hour with a height resolution of about 60 m, a minimum range of about 100 m, and a maximum range of about 1.5 km, although this varies substantially with meterological conditions. Such profiles have several potential applications. Among them are determinations of mixing height and stability. In this work, we use the stability, along with the hour-averaged wind profiles, to estimate plume rise heights at a power plant site in Laughlin, Nevada, about 200 km south of Lake Mead. The profiles are first stratified according to season and synoptic categories so that the calculated plume rise heights could be separated by background transport conditions. The data were taken during Project Measurement of Haze and Visual Effects (MOHAVE), which took place in 1992. This project is briefly discussed in the next section, along with the instrumentation and data used in this study.
-
Wang, Minzhong; Ming, Hu; Ruan, Zheng; Gao, Lianhui; Yang, Di
2018-02-01
With the aim to achieve quantitative monitoring of sand-dust storms in real time, wind-profiling radar is applied to monitor and study the process of four sand-dust storms in the Tazhong area of the Taklimakan Desert. Through evaluation and analysis of the spatial-temporal distribution of reflectivity factor, it is found that reflectivity factor ranges from 2 to 18 dBz under sand-dust storm weather. Using echo power spectrum of radar vertical beams, sand-dust particle spectrum and sand-dust mass concentration at the altitude of 600 ˜ 1500 m are retrieved. This study shows that sand-dust mass concentration reaches 700 μg/m3 under blowing sand weather, 2000 μg/m3 under sand-dust storm weather, and 400 μg/m3 under floating dust weather. The following equations are established to represent the relationship between the reflectivity factor and sand-dust mass concentration: Z = 20713.5 M 0.995 under floating dust weather, Z = 22988.3 M 1.006 under blowing sand weather, and Z = 24584.2 M 1.013 under sand-dust storm weather. The retrieval results from this paper are almost consistent with previous monitoring results achieved by former researchers; thus, it is implied that wind-profiling radar can be used as a new reference device to quantitatively monitor sand-dust storms.
-
Low-resolution Airborne Radar Air/ground Moving Target Classification and Recognition
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wang Fu-you
2014-10-01
Full Text Available Radar Target Recognition (RTR is one of the most important needs of modern and future airborne surveillance radars, and it is still one of the key technologies of radar. The majority of present algorithms are based on wide-band radar signal, which not only needs high performance radar system and high target Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR, but also is sensitive to angle between radar and target. Low-Resolution Airborne Surveillance Radar (LRASR in downward-looking mode, slow flying aircraft and ground moving truck have similar Doppler velocity and Radar Cross Section (RCS, leading to the problem that LRASR air/ground moving targets can not be distinguished, which also disturbs detection, tracking, and classification of low altitude slow flying aircraft to solve these issues, an algorithm based on narrowband fractal feature and phase modulation feature is presented for LRASR air/ground moving targets classification. Real measured data is applied to verify the algorithm, the classification results validate the proposed method, helicopters and truck can be well classified, the average discrimination rate is more than 89% when SNR ≥ 15 dB.
-
Radar Target Classification using Recursive Knowledge-Based Methods
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Jochumsen, Lars Wurtz
The topic of this thesis is target classification of radar tracks from a 2D mechanically scanning coastal surveillance radar. The measurements provided by the radar are position data and therefore the classification is mainly based on kinematic data, which is deduced from the position. The target...... been terminated. Therefore, an update of the classification results must be made for each measurement of the target. The data for this work are collected throughout the PhD and are both collected from radars and other sensors such as GPS....
-
Britt, Charles L.; Bracalente, Emedio M.
1992-01-01
The algorithms used in the NASA experimental wind shear radar system for detection, characterization, and determination of windshear hazard are discussed. The performance of the algorithms in the detection of wet microbursts near Orlando is presented. Various suggested algorithms that are currently being evaluated using the flight test results from Denver and Orlando are reviewed.
-
A target recognition method for maritime surveillance radars based on hybrid ensemble selection
Fan, Xueman; Hu, Shengliang; He, Jingbo
2017-11-01
In order to improve the generalisation ability of the maritime surveillance radar, a novel ensemble selection technique, termed Optimisation and Dynamic Selection (ODS), is proposed. During the optimisation phase, the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II for multi-objective optimisation is used to find the Pareto front, i.e. a set of ensembles of classifiers representing different tradeoffs between the classification error and diversity. During the dynamic selection phase, the meta-learning method is used to predict whether a candidate ensemble is competent enough to classify a query instance based on three different aspects, namely, feature space, decision space and the extent of consensus. The classification performance and time complexity of ODS are compared against nine other ensemble methods using a self-built full polarimetric high resolution range profile data-set. The experimental results clearly show the effectiveness of ODS. In addition, the influence of the selection of diversity measures is studied concurrently.
-
Meteor detection on ST (MST) radars
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Avery, S.K.
1987-01-01
The ability to detect radar echoes from backscatter due to turbulent irregularities of the radio refractive index in the clear atmosphere has lead to an increasing number of established mesosphere - stratosphere - troposphere (MST or ST) radars. Humidity and temperature variations are responsible for the echo in the troposphere and stratosphere and turbulence acting on electron density gradients provides the echo in the mesosphere. The MST radar and its smaller version, the ST radar, are pulsed Doppler radars operating in the VHF - UHF frequency range. These echoes can be used to determine upper atmosphere winds at little extra cost to the ST radar configuration. In addition, the meteor echoes can supplement mesospheric data from an MST radar. The detection techniques required on the ST radar for delineating meteor echo returns are described
-
Using Satellite SAR to Characterize the Wind Flow around Offshore Wind Farms
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Vincent, Pauline; Badger, Jake
2015-01-01
Offshore wind farm cluster effects between neighboring wind farms increase rapidly with the large-scale deployment of offshore wind turbines. The wind farm wakes observed from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) are sometimes visible and atmospheric and wake models are here shown to convincingly repro...
-
Specification for a standard radar sea clutter model
Paulus, Richard A.
1990-09-01
A model for the average sea clutter radar cross section is proposed for the Oceanographic and Atmospheric Master Library. This model is a function of wind speed (or sea state), wind direction relative to the antenna, refractive conditions, radar antenna height, frequency, polarization, horizontal beamwidth, and compressed pulse length. The model is fully described, a FORTRAN 77 computer listing is provided, and test cases are given to demonstrate the proper operation of the program.
-
Performance test and verification of an off-the-shelf automated avian radar tracking system.
May, Roel; Steinheim, Yngve; Kvaløy, Pål; Vang, Roald; Hanssen, Frank
2017-08-01
Microwave radar is an important tool for observation of birds in flight and represents a tremendous increase in observation capability in terms of amount of surveillance space that can be covered at relatively low cost. Based on off-the-shelf radar hardware, automated radar tracking systems have been developed for monitoring avian movements. However, radar used as an observation instrument in biological research has its limitations that are important to be aware of when analyzing recorded radar data. This article describes a method for exploring the detection capabilities of a dedicated short-range avian radar system used inside the operational Smøla wind-power plant. The purpose of the testing described was to find the maximum detection range for various sized birds, while controlling for the effects of flight tortuosity, flight orientation relative to the radar and ground clutter. The method was to use a dedicated test target in form of a remotely controlled unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) with calibrated radar cross section (RCS), which enabled the design of virtually any test flight pattern within the area of interest. The UAV had a detection probability of 0.5 within a range of 2,340 m from the radar. The detection performance obtained by the RCS-calibrated test target (-11 dBm 2 , 0.08 m 2 RCS) was then extrapolated to find the corresponding performance of differently sized birds. Detection range depends on system sensitivity, the environment within which the radar is placed and the spatial distribution of birds. The avian radar under study enables continuous monitoring of bird activity within a maximum range up to 2 km dependent on the size of the birds in question. While small bird species may be detected up to 0.5-1 km, larger species may be detected up to 1.5-2 km distance from the radar.
-
2014-09-01
3D Antenna Gain 0 dB Azimuth Accuracy 20°/quadrant 52 51. ELT/750 Receiver Figure 51: ELT/750 Receiver/processor...71]) The Itata ELINT system has been developed by Desarrollo de Tecnologia y Sistemas (DTS) Ltd. and is a high-sensitivity electronic... 3D Long Range Surveillance Radar. [Online]. Available: https://www.thalesgroup.com/en/worldwide/defence/smart-l- 3d - long-range-surveillance-radar
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Chambers, D. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab., CA (United States)
1994-11-15
The ultimate goal of the Current Meter Array (CMA) is to be able to compare the current patterns detected with the array with radar images of the water surface. The internal wave current patterns modulate the waves on the water surface giving a detectable modulation of the radar cross-section (RCS). The function relating the RCS modulations to the current patterns is the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF). By comparing radar images directly with co-located CMA measurements the MTF can be determined. In this talk radar images and CMA measurements from a recent experiment at Loch Linnhe, Scotland, will be used to make the first direct determination of MTF for an X and S band radar at low grazing angles. The technical problems associated with comparing radar images to CMA data will be explained and the solution method discussed. The results suggest the both current and strain rate contribute equally to the radar modulation for X band. For S band, the strain rate contributes more than the current. The magnitude of the MTF and the RCS modulations are consistent with previous estimates when the wind is blowing perpendicular to the radar look direction.
-
Real-data tests of a single-Doppler radar assimilation system
Nehrkorn, Thomas; Hegarty, James; Hamill, Thomas M.
1994-06-01
Real data tests of a single-Doppler radar data assimilation and forecast system have been conducted for a Florida sea breeze case. The system consists of a hydrostatic mesoscale model used for prediction of the preconvective boundary layer, an objective analysis that combines model first guess fields with radar derived horizontal winds, a thermodynamic retrieval scheme that obtains temperature information from the three-dimensional wind field and its temporal evolution, and a Newtonian nudging scheme for forcing the model forecast to closer agreement with the analysis. As was found in earlier experiments with simulated data, assimilation using Newtonian nudging benefits from temperature data in addition to wind data. The thermodynamic retrieval technique was successful in retrieving a horizontal temperature gradient from the radar-derived wind fields that, when assimilated into the model, led to a significantly improved forecast of the seabreeze strength and position.
-
Progress in coherent laser radar
Vaughan, J. M.
1986-01-01
Considerable progress with coherent laser radar has been made over the last few years, most notably perhaps in the available range of high performance devices and components and the confidence with which systems may now be taken into the field for prolonged periods of operation. Some of this increasing maturity was evident at the 3rd Topical Meeting on Coherent Laser Radar: Technology and Applications. Topics included in discussions were: mesoscale wind fields, nocturnal valley drainage and clear air down bursts; airborne Doppler lidar studies and comparison of ground and airborne wind measurement; wind measurement over the sea for comparison with satellite borne microwave sensors; transport of wake vortices at airfield; coherent DIAL methods; a newly assembled Nd-YAG coherent lidar system; backscatter profiles in the atmosphere and wavelength dependence over the 9 to 11 micrometer region; beam propagation; rock and soil classification with an airborne 4-laser system; technology of a global wind profiling system; target calibration; ranging and imaging with coherent pulsed and CW system; signal fluctuations and speckle. Some of these activities are briefly reviewed.
-
Extracting bird migration information from C-band Doppler weather radars
van Gasteren, H.; Holleman, I.; Bouten, W.; van Loon, E.; Shamoun-Baranes, J.
2008-01-01
Although radar has been used in studies of bird migration for 60 years, there is still no network in Europe for comprehensive monitoring of bird migration. Europe has a dense network of military air surveillance radars but most systems are not directly suitable for reliable bird monitoring. Since
-
The effects of radar on avian behavior: Implications for wildlife management at airports
Sheridan, Eleanor R
2014-01-01
Airports are areas with a high availability of resources for wildlife to forage, breed, and roost. Airports also have different types of radars to assist with air traffic control as well as tracking of wildlife that could become a risk for aircraft. The effect of radar electromagnetic radiation on wildlife behavior is not well understood. The goal of this study was to determine if bird behavior is affected by radar in two contexts: static radar (e.g., surveillance radar) and approaching radar...
-
A User Guide for Smoothing Air Traffic Radar Data
Bach, Ralph E.; Paielli, Russell A.
2014-01-01
Matlab software was written to provide smoothing of radar tracking data to simulate ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) data in order to test a tactical conflict probe. The probe, called TSAFE (Tactical Separation-Assured Flight Environment), is designed to handle air-traffic conflicts left undetected or unresolved when loss-of-separation is predicted to occur within approximately two minutes. The data stream that is down-linked from an aircraft equipped with an ADS-B system would include accurate GPS-derived position and velocity information at sample rates of 1 Hz. Nation-wide ADS-B equipage (mandated by 2020) should improve surveillance accuracy and TSAFE performance. Currently, position data are provided by Center radar (nominal 12-sec samples) and Terminal radar (nominal 4.8-sec samples). Aircraft ground speed and ground track are estimated using real-time filtering, causing lags up to 60 sec, compromising performance of a tactical resolution tool. Offline smoothing of radar data reduces wild-point errors, provides a sample rate as high as 1 Hz, and yields more accurate and lag-free estimates of ground speed, ground track, and climb rate. Until full ADS-B implementation is available, smoothed radar data should provide reasonable track estimates for testing TSAFE in an ADS-B-like environment. An example illustrates the smoothing of radar data and shows a comparison of smoothed-radar and ADS-B tracking. This document is intended to serve as a guide for using the smoothing software.
-
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Grappel, Robert D; Harris, Garrett S; Kozar, Mark J; Wiken, Randall T
2008-01-01
...) and Enhanced Surveillance (ERS) data link applications. The intended audience for this report is an engineering staff assigned the task of implementing a monitoring system used to determine ELS and EHS compliance...
-
SeaWinds - Oceans, Land, Polar Regions
1999-01-01
The SeaWinds scatterometer on the QuikScat satellite makes global radar measurements -- day and night, in clear sky and through clouds. The radar data over the oceans provide scientists and weather forecasters with information on surface wind speed and direction. Scientists also use the radar measurements directly to learn about changes in vegetation and ice extent over land and polar regions.This false-color image is based entirely on SeaWinds measurements obtained over oceans, land, and polar regions. Over the ocean, colors indicate wind speed with orange as the fastest wind speeds and blue as the slowest. White streamlines indicate the wind direction. The ocean winds in this image were measured by SeaWinds on September 20, 1999. The large storm in the Atlantic off the coast of Florida is Hurricane Gert. Tropical storm Harvey is evident as a high wind region in the Gulf of Mexico, while farther west in the Pacific is tropical storm Hilary. An extensive storm is also present in the South Atlantic Ocean near Antarctica.The land image was made from four days of SeaWinds data with the aid of a resolution enhancement algorithm developed by Dr. David Long at Brigham Young University. The lightest green areas correspond to the highest radar backscatter. Note the bright Amazon and Congo rainforests compared to the dark Sahara desert. The Amazon River is visible as a dark line running horizontally though the bright South American rain forest. Cities appear as bright spots on the images, especially in the U.S. and Europe.The image of Greenland and the north polar ice cap was generated from data acquired by SeaWinds on a single day. In the polar region portion of the image, white corresponds to the largest radar return, while purple is the lowest. The variations in color in Greenland and the polar ice cap reveal information about the ice and snow conditions present.NASA's Earth Science Enterprise is a long-term research and technology program designed to examine Earth
-
Bringing satellite winds to hub-height
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Badger, Merete; Pena Diaz, Alfredo; Bredesen, Rolv Erlend
2012-01-01
Satellite observations of the ocean surface can provide detailed information about the spatial wind variability over large areas. This is very valuable for the mapping of wind resources offshore where other measurements are costly and sparse. Satellite sensors operating at microwave frequencies...... measure the amount of radar backscatter from the sea surface, which is a function of the instant wind speed, wind direction, and satellite viewing geometry. A major limitation related to wind retrievals from satellite observations is that existing empirical model functions relate the radar backscatter...... to wind speed at the height 10 m only. The extrapolation of satellite wind fields to higher heights, which are more relevant for wind energy, remains a challenge which cannot be addressed by means of satellite data alone. As part of the EU-NORSEWInD project (2008-12), a hybrid method has been developed...
-
Wind Shear Identification with the Retrieval Wind of Doppler Wearth Radar
Zhou, S.; Cui, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, T.
2018-05-01
A new method, which based on the wind field retrieval algorithm of Volume Velocity Process (VVP), has been used to identified the intensity of wind shear occurred in a severe convection process in Guangzhou. The intensity of wind shear's strength shown that new cells would be more likely to generate in areas where the magnitude generally larger than 3.0 m/(s*km). Moreover, in the areas of potential areas of rainfall, the wind shear's strength would larger than 4.5 m/(s*km). This wind shear identify method is very helpful to forecasting severe convections' moving and developments.
-
Ocean Surface Wind Speed of Hurricane Helene Observed by SAR
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Xu, Qing; Cheng, Yongcun; Li, Xiaofeng
2011-01-01
Prediction System (NOGAPS) model, C-band geophysical model functions (GMFs) which describe the normalized radar cross section (NRCS) dependence on the wind speed and the geometry of radar observations (i.e., incidence angle and azimuth angle with respect to wind direction) such as CMOD5 and newly developed......The hurricanes can be detected by many remote sensors, but synthetic aperture radar (SAR) can yield high-resolution (sub-kilometer) and low-level wind information that cannot be seen below the cloud by other sensors. In this paper, an assessment of SAR capability of monitoring high...
-
Yan, Qiushuang; Zhang, Jie; Fan, Chenqing; Wang, Jing; Meng, Junmin
2018-01-01
The collocated normalized radar backscattering cross-section measurements from the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Ku-band precipitation radar (KuPR) and the winds from the moored buoys are used to study the effect of different sea-surface slope probability density functions (PDFs), including the Gaussian PDF, the Gram-Charlier PDF, and the Liu PDF, on the geometrical optics (GO) model predictions of the radar backscatter at low incidence angles (0 deg to 18 deg) at different sea states. First, the peakedness coefficient in the Liu distribution is determined using the collocations at the normal incidence angle, and the results indicate that the peakedness coefficient is a nonlinear function of the wind speed. Then, the performance of the modified Liu distribution, i.e., Liu distribution using the obtained peakedness coefficient estimate; the Gaussian distribution; and the Gram-Charlier distribution is analyzed. The results show that the GO model predictions with the modified Liu distribution agree best with the KuPR measurements, followed by the predictions with the Gaussian distribution, while the predictions with the Gram-Charlier distribution have larger differences as the total or the slick filtered, not the radar filtered, probability density is included in the distribution. The best-performing distribution changes with incidence angle and changes with wind speed.
-
Comments on airborne ISR radar utilization
Doerry, A. W.
2016-05-01
A sensor/payload operator for modern multi-sensor multi-mode Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) platforms is often confronted with a plethora of options in sensors and sensor modes. This often leads an over-worked operator to down-select to favorite sensors and modes; for example a justifiably favorite Full Motion Video (FMV) sensor at the expense of radar modes, even if radar modes can offer unique and advantageous information. At best, sensors might be used in a serial monogamous fashion with some cross-cueing. The challenge is then to increase the utilization of the radar modes in a manner attractive to the sensor/payload operator. We propose that this is best accomplished by combining sensor modes and displays into `super-modes'.
-
Innovative SAR/MTI Concepts for Digital Radar
Wit, J.J.M. de
2008-01-01
Contemporary military operations make high demands on the capabilities of sensors. Modern sensors must have the capability to perform different tasks, such as ground surveillance and target tracking, simultaneously. Multifunction digital radar may provide the required capabilities and meet the
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
2008-01-01
Wind turbines and the movement of their blades can have penalizing effects on the processing of radars data. These disturbances can have a strong impact on the air, maritime and fluvial safety, on the protection of the territory and on the prevention of natural hazards. Reports made by the national agency of frequencies (ANFR) have established recommendations for the definition of protection areas (5 km) and coordination areas (5 to 30 km) which have to be taken into consideration prior to any project of wind turbine. (J.S.)
-
Global empirical wind model for the upper mesosphere/lower thermosphere. I. Prevailing wind
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. I. Portnyagin
Full Text Available An updated empirical climatic zonally averaged prevailing wind model for the upper mesosphere/lower thermosphere (70-110 km, extending from 80°N to 80°S is presented. The model is constructed from the fitting of monthly mean winds from meteor radar and MF radar measurements at more than 40 stations, well distributed over the globe. The height-latitude contour plots of monthly mean zonal and meridional winds for all months of the year, and of annual mean wind, amplitudes and phases of annual and semiannual harmonics of wind variations are analyzed to reveal the main features of the seasonal variation of the global wind structures in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Some results of comparison between the ground-based wind models and the space-based models are presented. It is shown that, with the exception of annual mean systematic bias between the zonal winds provided by the ground-based and space-based models, a good agreement between the models is observed. The possible origin of this bias is discussed.
Key words: Meteorology and Atmospheric dynamics (general circulation; middle atmosphere dynamics; thermospheric dynamics -
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Weiland, R.M.; Bowhill, S.A.
1981-12-01
The development and first observations of the partial-reflection drifts experiment at Urbana, Illinois (40 N) are described. The winds data from the drifts experiment are compared with electron concentration data obtained by the differential-absorption technique to study the possible meteorological causes of the winter anomaly in the mesosphere at midlatitudes. Winds data obtained by the meteor-radar experiment at Urbana are also compared with electron concentration data measured at Urban. A significant correlation is shown is both cases between southward winds and increasing electron concentration measured at the same location during winter. The possibility of stratospheric/mesospheric coupling is investigated by comparing satellite-measured 0.4 mbar geopotential data with mesospheric electron concentration data. No significant coupling was observed. The winds measured at Saskatoon, Saskatchewan (52 N) are compared with the electron concentrations measured at Urban, yielding constant fixed relationship, but significant correlations for short segments of the winter. A significant coherence is observed at discrete frequencies during segments of the winter
-
SAT-WIND project. Final report
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Astrup, Poul; Nielsen, Niels Morten
microwave, altimeter, scatterometer and imaging Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technologies for wind energy tools for wind resources and wind-indexing. The study area was the Danish Seas including the North Sea, interior seas and the Baltic Sea. The report describes technical details on the satellite data...
-
Low-Cost Mini Radar: Design Prototyping and Tests
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Dario Tarchi
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Radar systems are largely employed for surveillance of wide and remote areas; the recent advent of drones gives the opportunity to exploit radar sensors on board of unmanned aerial platforms. Nevertheless, whereas drone radars are currently available for military applications, their employment in the civilian domain is still limited. The present research focuses on design, prototyping, and testing of an agile, low-cost, mini radar system, to be carried on board of Remotely Piloted Aircraft (RPAs or tethered aerostats. In particular, the paper faces the challenge to integrate the in-house developed radar sensor with a low-cost navigation board, which is used to estimate attitude and positioning data. In fact, a suitable synchronization between radar and navigation data is essential to properly reconstruct the radar picture whenever the platform is moving or the radar is scanning different azimuthal sectors. Preliminary results, relative to tests conducted in preoperational conditions, are provided and exploited to assert the suitable consistency of the obtained radar pictures. From the results, there is a high consistency between the radar images and the picture of the current environment emerges; finally, the comparison of radar images obtained in different scans shows the stability of the platform.
-
Wind Resource Estimation using QuikSCAT Ocean Surface Winds
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Xu, Qing; Zhang, Guosheng; Cheng, Yongcun
2011-01-01
In this study, the offshore wind resources in the East China Sea and South China Sea were estimated from over ten years of QuikSCAT scatterometer wind products. Since the errors of these products are larger close to the coast due to the land contamination of radar backscatter signal...... and the complexity of air-sea interaction processes, an empirical relationship that adjusts QuikSCAT winds in coastal waters was first proposed based on vessel measurements. Then the shape and scale parameters of Weibull function are determined for wind resource estimation. The wind roses are also plotted. Results...
-
Sahawneh, Saleem; Farrar, Spencer; Johnson, James; Jones, W. Linwood; Roberts, Jason; Biswas, Sayak; Cecil, Daniel
2014-01-01
Microwave remote sensing observations of hurricanes, from NOAA and USAF hurricane surveillance aircraft, provide vital data for hurricane research and operations, for forecasting the intensity and track of tropical storms. The current operational standard for hurricane wind speed and rain rate measurements is the Stepped Frequency Microwave Radiometer (SFMR), which is a nadir viewing passive microwave airborne remote sensor. The Hurricane Imaging Radiometer, HIRAD, will extend the nadir viewing SFMR capability to provide wide swath images of wind speed and rain rate, while flying on a high altitude aircraft. HIRAD was first flown in the Genesis and Rapid Intensification Processes, GRIP, NASA hurricane field experiment in 2010. This paper reports on geophysical retrieval results and provides hurricane images from GRIP flights. An overview of the HIRAD instrument and the radiative transfer theory based, wind speed/rain rate retrieval algorithm is included. Results are presented for hurricane wind speed and rain rate for Earl and Karl, with comparison to collocated SFMR retrievals and WP3D Fuselage Radar images for validation purposes.
-
Research at the Stanford Center for Radar Astronomy
1972-01-01
The research is reported in the applications of radar and radio techniques to the study of the solar system, and to space programs. Experiments reported include: bistatic-radar on Apollo missions, development of an unmanned geophysical observatory in the Antartic, Bragg scattering probes of sea states, characteristics of dense solar wind disturbances, and satellite communications for Alaska.
-
Automatic identification of bird targets with radar via patterns produced by wing flapping
Zaugg, S.; Saporta, G.; van Loon, E.; Schmaljohann, H.; Liechti, F.
2008-01-01
Bird identification with radar is important for bird migration research, environmental impact assessments (e.g. wind farms), aircraft security and radar meteorology. In a study on bird migration, radar signals from birds, insects and ground clutter were recorded. Signals from birds show a typical
-
Meteor observation by the Kyoto meteor radar
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kato, S.; Tsuda, T.
1987-01-01
The Kyoto Meteor Radar is a monostatic coherent pulsed Doppler radar operating on the frequency of 31.57 MH. The system is computer controlled and uses radio interferometry for echo height determination. The antenna, an improvement, can be directed either to the north or the east. The system has been continuously collecting data on winds at meteor heights by radar observation. The meteor echo rate was also measured, the echo rate distribution with height and the daily variation in height integrated echo rate are discussed. Investigations of atmospheric tides are being pursued by cooperative observations. A novel approach to the study of gravity waves was attempted using the meteor radar which is able to detect the horizontal propagation of the waves by observing the changing phase through the region illuminated by the radar
-
Giangrande, S. E.; WANG, D.; Hardin, J. C.; Mitchell, J.
2017-12-01
As part of the 2 year Department of Energy Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) Observations and Modeling of the Green Ocean Amazon (GoAmazon2014/5) campaign, the ARM Mobile Facility (AMF) collected a unique set of observations in a region of strong climatic significance near Manacapuru, Brazil. An important example for the beneficial observational record obtained by ARM during this campaign was that of the Radar Wind Profiler (RWP). This dataset has been previously documented for providing critical convective cloud vertical air velocity retrievals and precipitation properties (e.g., calibrated reflectivity factor Z, rainfall rates) under a wide variety of atmospheric conditions. Vertical air motion estimates to within deep convective cores such as those available from this RWP system have been previously identified as critical constraints for ongoing global climate modeling activities and deep convective cloud process studies. As an extended deployment within this `green ocean' region, the RWP site and collocated AMF surface gauge instrumentation experienced a unique hybrid of tropical and continental precipitation conditions, including multiple wet and dry season precipitation regimes, convective and organized stratiform storm dynamics and contributions to rainfall accumulation, pristine aerosol conditions of the locale, as well as the effects of the Manaus, Brazil, mega city pollution plume. For hydrological applications and potential ARM products, machine learning methods developed using this dataset are explored to demonstrate advantages in geophysical retrievals when compared to traditional methods. Emphasis is on performance improvements when providing additional information on storm structure and regime or echo type classifications. Since deep convective cloud dynamic insights (core updraft/downdraft properties) are difficult to obtain directly by conventional radars that also observe radar reflectivity factor profiles similar to RWP systems, we also
-
Empirical wind retrieval model based on SAR spectrum measurements
Panfilova, Maria; Karaev, Vladimir; Balandina, Galina; Kanevsky, Mikhail; Portabella, Marcos; Stoffelen, Ad
The present paper considers polarimetric SAR wind vector applications. Remote-sensing measurements of the near-surface wind over the ocean are of great importance for the understanding of atmosphere-ocean interaction. In recent years investigations for wind vector retrieval using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data have been performed. In contrast with scatterometers, a SAR has a finer spatial resolution that makes it a more suitable microwave instrument to explore wind conditions in the marginal ice zones, coastal regions and lakes. The wind speed retrieval procedure from scatterometer data matches the measured radar backscattering signal with the geophysical model function (GMF). The GMF determines the radar cross section dependence on the wind speed and direction with respect to the azimuthal angle of the radar beam. Scatterometers provide information on wind speed and direction simultaneously due to the fact that each wind vector cell (WVC) is observed at several azimuth angles. However, SAR is not designed to be used as a high resolution scatterometer. In this case, each WVC is observed at only one single azimuth angle. That is why for wind vector determination additional information such as wind streak orientation over the sea surface is required. It is shown that the wind vector can be obtained using polarimetric SAR without additional information. The main idea is to analyze the spectrum of a homogeneous SAR image area instead of the backscattering normalized radar cross section. Preliminary numerical simulations revealed that SAR image spectral maxima positions depend on the wind vector. Thus the following method for wind speed retrieval is proposed. In the first stage of the algorithm, the SAR spectrum maxima are determined. This procedure is carried out to estimate the wind speed and direction with ambiguities separated by 180 degrees due to the SAR spectrum symmetry. The second stage of the algorithm allows us to select the correct wind direction
-
Overview of Experimental Pulse-Doppler Radar Data Collected Oct 1999
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Hughes, Steven
2000-01-01
The Defence Research Establishment Ottawa has designed and constructed an experimental air-to-air radar system as the first step in demonstrating an air-to-air surveillance capability for the Canadian...
-
A new approach to momentum flux determinations using SKiYMET meteor radars
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
W. K. Hocking
2005-10-01
Full Text Available The current primary radar method for determination of atmospheric momentum fluxes relies on multiple beam studies, usually using oppositely directed coplanar beams. Generally VHF and MF radars are used, and meteor radars have never been successfully employed. In this paper we introduce a new procedure that can be used for determination of gravity wave fluxes down to time scales of 2-3h, using the SKiYMET meteor radars. The method avoids the need for beam forming, and allows simultaneous determination of the three components of the wind averaged over the radar volume, as well as the variance and flux components
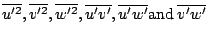 , where
, where 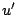 refers to the fluctuating eastward wind,
refers to the fluctuating eastward wind, 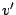 refers to the fluctuating northward wind, and
refers to the fluctuating northward wind, and 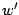 refers to the fluctuating vertical wind. Data from radars in New Mexico and Resolute Bay are used to illustrate the data quality, and demonstrate theoretically expected seasonal forcing.
refers to the fluctuating vertical wind. Data from radars in New Mexico and Resolute Bay are used to illustrate the data quality, and demonstrate theoretically expected seasonal forcing.
Keywords. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (Middle atmosphere dynamics; Waves and tides; Climatology -
Satellite Remote Sensing in Offshore Wind Energy
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Badger, Merete; Astrup, Poul
2013-01-01
Satellite remote sensing of ocean surface winds are presented with focus on wind energy applications. The history on operational and research-based satellite ocean wind mapping is briefly described for passive microwave, scatterometer and synthetic aperture radar (SAR). Currently 6 GW installed...
-
Localization Capability of Cooperative Anti-Intruder Radar Systems
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mauro Montanari
2008-06-01
Full Text Available System aspects of an anti-intruder multistatic radar based on impulse radio ultrawideband (UWB technology are addressed. The investigated system is composed of one transmitting node and at least three receiving nodes, positioned in the surveillance area with the aim of detecting and locating a human intruder (target that moves inside the area. Such systems, referred to also as UWB radar sensor networks, must satisfy severe power constraints worldwide imposed by, for example, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC and by the European Commission (EC power spectral density masks. A single transmitter-receiver pair (bistatic radar is considered at first. Given the available transmitted power and the capability of the receiving node to resolve the UWB pulses in the time domain, the surveillance area regions where the target is detectable, and those where it is not, are obtained. Moreover, the range estimation error for the transmitter-receiver pair is discussed. By employing this analysis, a multistatic system is then considered, composed of one transmitter and three or four cooperating receivers. For this multistatic system, the impact of the nodes location on area coverage, necessary transmitted power and localization uncertainty is studied, assuming a circular surveillance area. It is highlighted how area coverage and transmitted power, on one side, and localization uncertainty, on the other side, require opposite criteria of nodes placement. Consequently, the need for a system compromising between these factors is shown. Finally, a simple and effective criterion for placing the transmitter and the receivers is drawn.
-
Scanning ARM Cloud Radars. Part II: Data Quality Control and Processing
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kollias, Pavlos; Jo, Ieng; Borque, Paloma; Tatarevic, Aleksandra; Lamer, Katia; Bharadwaj, Nitin; Widener, Kevin B.; Johnson, Karen L.; Clothiaux, Eugene E.
2014-03-01
The Scanning ARM Cloud Radars (SACR’s) are the primary instruments for documenting the four-dimensional structure and evolution of clouds within a 20-30 km radius from the ARM fixed and mobile sites. Here, the post-processing of the calibrated SACR measurements is discussed. First, a feature mask algorithm that objectively determines the presence of significant radar returns is described. The feature mask algorithm is based on the statistical properties of radar receiver noise. It accounts for atmospheric emission and is applicable even for SACR profiles with few or no signal-free range gates. Using the nearest-in-time atmospheric sounding, the SACR radar reflectivities are corrected for gaseous attenuation (water vapor and oxygen) using a line-by-line absorption model. Despite having a high pulse repetition frequency, the SACR has a narrow Nyquist velocity limit and thus Doppler velocity folding is commonly observed. An unfolding algorithm that makes use of a first guess for the true Doppler velocity using horizontal wind measurements from the nearest sounding is described. The retrieval of the horizontal wind profile from the HS-RHI SACR scan observations and/or nearest sounding is described. The retrieved horizontal wind profile can be used to adaptively configure SACR scan strategies that depend on wind direction. Several remaining challenges are discussed, including the removal of insect and second-trip echoes. The described algorithms significantly enhance SACR data quality and constitute an important step towards the utilization of SACR measurements for cloud research.
-
Distributed radar network for real-time tracking of bullet trajectory
Zhang, Yimin; Li, Xin; Jin, Yuanwei; Amin, Moeness G.; Eydgahi, Ali
2009-05-01
Gunshot detection, sniper localization, and bullet trajectory prediction are of significant importance in military and homeland security applications. While the majority of existing work is based on acoustic and electro-optical sensors, this paper develops a framework of networked radar systems that uses distributed radar sensor networks to achieve the aforementioned objectives. The use of radio frequency radar systems allows the achievement of subtime- of-flight tracking response, enabling to response before the bullet reaches its target and, as such, effectively leading to the reduction of injuries and casualties in military and homeland security operations. The focus of this paper is to examine the MIMO radar concept with concurrent transmission of low-correlation waveforms from multiple radar sets to ensure wide surveillance coverage and maintain a high waveform repetition frequency for long coherent time interval required to achieve return signal concentration.
-
Microphysical retrievals from simultaneous polarimetric and profiling radar observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. P. Morris
2009-12-01
Full Text Available The character of precipitation detected at the surface is the final product of many microphysical interactions in the cloud above, the combined effects of which may be characterized by the observed drop size distribution (DSD. This necessitates accurate retrieval of the DSD from remote sensing data, especially radar as it offers large areal coverage, high spatial resolution, and rigorous quality control and testing. Combined instrument observations with a UHF wind profiler, an S-band polarimetric weather radar, and a video disdrometer are analyzed for two squall line events occuring during the calendar year 2007. UHF profiler Doppler velocity spectra are used to estimate the DSD aloft, and are complemented by DSDs retrieved from an exponential model applied to polarimetric data. Ground truth is provided by the disdrometer. A complicating factor in the retrieval from UHF profiler spectra is the presence of ambient air motion, which can be corrected using the method proposed by Teshiba et al. (2009, in which a comparison between idealized Doppler spectra calculated from the DSDs retrieved from KOUN and those retrieved from contaminated wind profiler spectra is performed. It is found that DSDs measured using the distrometer at the surface and estimated using the wind profiler and polarimetric weather radar generally showed good agreement. The DSD retrievals using the wind profiler were improved when the estimates of the vertical wind were included into the analysis, thus supporting the method of Teshiba et al. (2009. Furthermore, the the study presents a method of investigating the time and height structure of DSDs.
-
Reduction of snapshots for MIMO radar detection by block/group orthogonal matching pursuit
Ali, Hussain El Hosiny
2014-10-01
Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar works on the principle of transmission of independent waveforms at each element of its antenna array and is widely used for surveillance purposes. In this work, we investigate MIMO radar target localization problem with compressive sensing. Specifically, we try to solve the problem of estimation of target location in MIMO radar by group and block sparsity algorithms. It will lead us to a reduced number of snapshots required and also we can achieve better radar resolution. We will use group orthogonal matching pursuit (GOMP) and block orthogonal matching pursuit (BOMP) for our problem. © 2014 IEEE.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hasager, C.B.; Astrup, P.; Nielsen, M. (and others)
2007-04-15
The SAT-WIND project 'Winds from satellites for offshore and coastal wind energy mapping and wind-indexing' was a research project funded by STVF/DSF in the years 2003 to 2006 (Sagsnr. 2058-03-0006). The goal of the project was to verify the applicability of satellite wind maps derived from passive microwave, altimeter, scatterometer and imaging Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technologies for wind energy tools for wind resources and wind-indexing. The study area was the Danish Seas including the North Sea, interior seas and the Baltic Sea. The report describes technical details on the satellite data sources including: 1) passive microwave (SSM/I, AMSR-E), 2) passive microwave polarimetric (WindSat), 3) scatterometer (ERS, QuikSCAT, Midori-2 and NSCAT), 4) altimeter (ERS, Topex, Poseidon, GFO-1, Jason-1), 5) SAR (ERS, Envisat). The SAR wind maps were treated in S-WAsP developed by Risoe National Laboratory in cooperation with GRAS A/S in the innovative project SAT-WIND-SMV (Sagsnr. 2104-05-0084) in the years 2005 and 2006 in parallel with SAT-WIND. The results from the SAT-WIND project are presented. These include ocean wind statistics, offshore wind resource estimates and comparison results for wind-indexing. (au)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hasager, C B; Astrup, P; Nielsen, M [and others
2007-04-15
The SAT-WIND project 'Winds from satellites for offshore and coastal wind energy mapping and wind-indexing' was a research project funded by STVF/DSF in the years 2003 to 2006 (Sagsnr. 2058-03-0006). The goal of the project was to verify the applicability of satellite wind maps derived from passive microwave, altimeter, scatterometer and imaging Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technologies for wind energy tools for wind resources and wind-indexing. The study area was the Danish Seas including the North Sea, interior seas and the Baltic Sea. The report describes technical details on the satellite data sources including: 1) passive microwave (SSM/I, AMSR-E), 2) passive microwave polarimetric (WindSat), 3) scatterometer (ERS, QuikSCAT, Midori-2 and NSCAT), 4) altimeter (ERS, Topex, Poseidon, GFO-1, Jason-1), 5) SAR (ERS, Envisat). The SAR wind maps were treated in S-WAsP developed by Risoe National Laboratory in cooperation with GRAS A/S in the innovative project SAT-WIND-SMV (Sagsnr. 2104-05-0084) in the years 2005 and 2006 in parallel with SAT-WIND. The results from the SAT-WIND project are presented. These include ocean wind statistics, offshore wind resource estimates and comparison results for wind-indexing. (au)
-
Performance of the first European 482 MHz wind profiler radar with RASS under operational conditions
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Steinhagen, H.; Engelbart, D.; Goersdorf, U.; Lehmann, V.; Neisser, J. [Deutscher Wetterdienst, Lindenberg (Germany). Meteorologisches Observatorium; Dibbern, J.; Neuschaefer, J.W.
1998-10-01
The first 482 MHz wind profiler radar (WPR) in Europe completed with a radio-acoustic sounding system (RASS) has been operated at the meteorological observatory Lindenberg since July 3rd, 1996 after a comprehensive study regarding the investigation of frequency compatibility between the WPR and the television channel 22 (478-486 MHz). The WPR can operate with different height and time resolutions (e.g. 250 m in the so-called low mode or 500 m in the high mode). A height range of up to approximately 16 km can be realized in the high mode. The installed WPR/RASS combination allows also the measurement of profiles of the virtual temperature with the low mode resolution in the height range from 500 m up to approximately 4000 m. The main objective of this contribution is the investigation of the accuracy and the availability of this new remote sensing system. First results of the accuracy can be given on the base of about 1000 intercomparisons between WPR/RASS and rawinsonde data. The bias of the horizontal wind velocities is less than 0.4 m/s in the low mode and 0.7 m/s in the high mode (from 3 to 10 km) and therefore smaller than the average accuracy of both systems. The bias of the temperature measurements is less than 1 K and can be improved by some corrections in future. A first statistics of the data availability can be shown based on nearly 6000 profiles of wind and temperature. The 80% availability of the WPR/RASS was determined with 12.8 km for wind and 2.3 km for temperature measurements. The new possibilities of investigating the troposphere as well as the lowest part of the stratosphere are presented by measurement examples from February and March 1997. (orig.) 22 refs.
-
Wind Atlas of Bay of Bengal with Satellite Wind Measurement
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nadi, Navila Rahman
footstep towards offshore wind energy analysis for this region. Generally, it is difficult to find offshore wind data relative to the wind turbine hub heights, therefore a starting point is necessary to identify the possible wind power density of the region. In such scenario, Synthetic aperture radars (SAR......The objective of this study is to obtain appropriate offshore location in the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh for further development of wind energy. Through analyzing the previous published works, no offshore wind energy estimation has been found here. That is why, this study can be claimed as the first......) have proven useful. In this study, SAR based dataset- ENVISAT ASAR has been used for Wind Atlas generation. Furthermore, a comparative study has been performed with Global Wind Atlas (GWA) to determine a potential offshore wind farm. Additionally, the annual energy production of that offshore windfarm...
-
Basic study for tsunami detection with DBF ocean radar
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sakai, Shin'ichi; Matsuyama, Masafumi; Okuda, Kouzou; Uehara, Fumihiro
2015-01-01
To develop early tsunami warning system utilizing ocean radars, the evaluation of the variety of measuring coverage and data accuracy is indispensable in real oceans. The field observation was carried out at 5 minutes interval with two digital beam forming ocean radars with VHF band from 2012 to 2014 in the sea of Enshu. The high data acquisition areas are found in the extent of 17 km off the coast on a hill site and of 13 km on a low ground site. The measured current by the ocean radar were well correlated with that by the current-meter in the depth of 2 m near the coast with the correlation coefficient of ∼0.6. It is inferred that the main factor of difference in both data sets was due to the presence of wind-driven current through the multi-regression analysis with both current data and wind data. In addition, the order of the temporal current deviations as to the representative time-scale of one hour is about 5 cm/s under the ordinary sea conditions, which suggest that ocean radars could sufficiently detect the current deviation due to grant tsunami. (author)
-
Airborne Radar Observations of Severe Hailstorms: Implications for Future Spaceborne Radar
Heymsfield, Gerald M.; Tian, Lin; Li, Lihua; McLinden, Matthew; Cervantes, Jaime I.
2013-01-01
A new dual-frequency (Ku and Ka band) nadir-pointing Doppler radar on the high-altitude NASA ER-2 aircraft, called the High-Altitude Imaging Wind and Rain Airborne Profiler (HIWRAP), has collected data over severe thunderstorms in Oklahoma and Kansas during the Midlatitude Continental Convective Clouds Experiment (MC3E). The overarching motivation for this study is to understand the behavior of the dualwavelength airborne radar measurements in a global variety of thunderstorms and how these may relate to future spaceborne-radar measurements. HIWRAP is operated at frequencies that are similar to those of the precipitation radar on the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (Ku band) and the upcoming Global Precipitation Measurement mission satellite's dual-frequency (Ku and Ka bands) precipitation radar. The aircraft measurements of strong hailstorms have been combined with ground-based polarimetric measurements to obtain a better understanding of the response of the Ku- and Ka-band radar to the vertical distribution of the hydrometeors, including hail. Data from two flight lines on 24 May 2011 are presented. Doppler velocities were approx. 39m/s2at 10.7-km altitude from the first flight line early on 24 May, and the lower value of approx. 25m/s on a second flight line later in the day. Vertical motions estimated using a fall speed estimate for large graupel and hail suggested that the first storm had an updraft that possibly exceeded 60m/s for the more intense part of the storm. This large updraft speed along with reports of 5-cm hail at the surface, reflectivities reaching 70 dBZ at S band in the storm cores, and hail signals from polarimetric data provide a highly challenging situation for spaceborne-radar measurements in intense convective systems. The Ku- and Ka-band reflectivities rarely exceed approx. 47 and approx. 37 dBZ, respectively, in these storms.
-
Sentchev, Alexei; Forget, Philippe; Fraunié, Philippe
2017-04-01
Ocean surface boundary layer dynamics off the southern coast of France in the NW Mediterranean is investigated by using velocity observations by high-frequency (HF) radars, surface drifting buoys and a downward-looking drifting acoustic Doppler current profiler (ADCP). The analysis confirms that velocities measured by HF radars correspond to those observed by an ADCP at the effective depth z f = k -1, where k is wavenumber of the radio wave emitted by the radar. The radials provided by the radars were in a very good agreement with in situ measurements, with the relative errors of 1 and 9 % and root mean square (RMS) differences of 0.02 and 0.04 m/s for monostatic and bistatic radar, respectively. The total radar-based velocities appeared to be slightly underestimated in magnitude and somewhat biased in direction. At the end of the survey period, the difference in the surface current direction, based on HF radar and ADCP data, attained 10°. It was demonstrated that the surface boundary layer dynamics cannot be reconstructed successfully without taking into the account velocity variation with depth. A significant misalignment of ˜30° caused by the sea breeze was documented between the HF radar (HFR-derived) surface current and the background current. It was also found that the ocean response to a moderate wind forcing was confined to the 4-m-thick upper layer. The respective Ekman current attained the maximum value of 0.15 m/s, and the current rotation was found to be lagging the wind by approximately 40 min, with the current vector direction being 15-20° to the left of the wind. The range of velocity variability due to wind forcing was found comparable with the magnitude of the background current variability.
-
Wind Atlas of Aegean Sea with SAR data
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Bingöl, Ferhat; Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Badger, Merete
2013-01-01
The Global Wind Atlas project is established to create a “free-to-use” wind atlas of the whole globe. The modelling chain of the project includes micro-scale models and new reanalysis datasets. Local measurements are planed to be use for test and validation. Unfortunately, it is not always possible...... to find long term offshore measurement to make wind statistics. The main reason is the cost of setup and maintenance of an offshore mast. One of the regions which has high potential in wind resources but so far is without any long term offshore measurement is the Aegean sea. Recent developments...... in satellite radar technologies made it possible to use Synthetic Aperture Radars (SAR) for wind speed and direction measurements at offshore locations. In this study, a new technique of making wind atlases is applied to the region of Aegean Sea is presented. The method has been tested and validated...
-
Laser radar: historical prospective-from the East to the West
Molebny, Vasyl; McManamon, Paul; Steinvall, Ove; Kobayashi, Takao; Chen, Weibiao
2017-03-01
This article discusses the history of laser radar development in America, Europe, and Asia. Direct detection laser radar is discussed for range finding, designation, and topographic mapping of Earth and of extraterrestrial objects. Coherent laser radar is discussed for environmental applications, such as wind sensing and for synthetic aperture laser radar development. Gated imaging is discussed through scattering layers for military, medical, and security applications. Laser microradars have found applications in intravascular studies and in ophthalmology for vision correction. Ghost laser radar has emerged as a new technology in theoretical and simulation applications. Laser radar is now emerging as an important technology for applications such as self-driving cars and unmanned aerial vehicles. It is also used by police to measure speed, and in gaming, such as the Microsoft Kinect.
-
Scanning ARM Cloud Radars Part II. Data Quality Control and Processing
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kollias, Pavlos [McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Jo, Ieng [McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Borque, Paloma [McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Tatarevic, Aleksandra [McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Lamer, Katia [McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Bharadwaj, Nitin [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Widener, Kevin B. [Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States); Johnson, Karen [Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States); Clothiaux, Eugene E. [Pennsylvania State Univ., State College, PA (United States)
2013-10-04
The Scanning ARM Cloud Radars (SACR’s) are the primary instruments for documenting the four-dimensional structure and evolution of clouds within a 20-30 km radius from the ARM fixed and mobile sites. Here, the post-processing of the calibrated SACR measurements is discussed. First, a feature mask algorithm that objectively determines the presence of significant radar returns is described. The feature mask algorithm is based on the statistical properties of radar receiver noise. It accounts for atmospheric emission and is applicable even for SACR profiles with few or no signal-free range gates. Using the nearest-in-time atmospheric sounding, the SACR radar reflectivities are corrected for gaseous attenuation (water vapor and oxygen) using a line-by-line absorption model. Despite having a high pulse repetition frequency, the SACR has a narrow Nyquist velocity limit and thus Doppler velocity folding is commonly observed. An unfolding algorithm that makes use of a first guess for the true Doppler velocity using horizontal wind measurements from the nearest sounding is described. The retrieval of the horizontal wind profile from the Hemispherical Sky – Range Height Indicator SACR scan observations and/or nearest sounding is described. The retrieved horizontal wind profile can be used to adaptively configure SACR scan strategies that depend on wind direction. Several remaining challenges are discussed, including the removal of insect and second-trip echoes. The described algorithms significantly enhance SACR data quality and constitute an important step towards the utilization of SACR measurements for cloud research.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. A. Praskovsky
2004-11-01
Full Text Available The structure-function-based method (referred to as UCAR-STARS, a technique for estimating mean horizontal winds, variances of three turbulent velocity components and horizontal momentum flux was applied to the Middle and Upper atmosphere Radar (MUR operating in spaced antenna (SA profiling mode. The method is discussed and compared with the Holloway and Doviak (HAD correlation-function-based technique. Mean horizontal winds are estimated with the STARS and HAD techniques; the Doppler Beam Swinging (DBS method is used as a reference for evaluating the SA techniques. Reasonable agreement between SA and DBS techniques is found at heights from 5km to approximately 11km, where signal-to-noise ratio was rather high. The STARS and HAD produced variances of vertical turbulent velocity are found to be in fair agreement. They are affected by beam-broadening in a different way than the DBS-produced spectral width, and to a much lesser degree. Variances of horizontal turbulent velocity components and horizontal momentum flux are estimated with the STARS method, and strong anisotropy of turbulence is found. These characteristics cannot be estimated with correlation-function-based SA methods, which could make UCAR-STARS a useful alternative to traditional SA techniques.
-
MST radar and polarization lidar observations of tropical cirrus
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. Bhavani Kumar
2001-08-01
Full Text Available Significant gaps in our understanding of global cirrus effects on the climate system involve the role of frequently occurring tropical cirrus. Much of the cirrus in the atmosphere is largely due to frequent cumulus and convective activity in the tropics. In the Indian sub-tropical region, the deep convective activity is very prominent from April to December, which is a favorable period for the formation of deep cumulus clouds. The fibrous anvils of these clouds, laden with ice crystals, are one of the source mechanisms for much of the cirrus in the atmosphere. In the present study, several passages of tropical cirrus were investigated by simultaneously operating MST radar and a co-located polarization lidar at the National MST Radar Facility (NMRF, Gadanki (13.45° N, 79.18° E, India to understand its structure, the background wind field and the microphysics at the cloud boundaries. The lidar system used is capable of measuring the degree of depolarization in the laser backscatter. It has identified several different cirrus structures with a peak linear depolarization ratio (LDR in the range of 0.1 to 0.32. Simultaneous observations of tropical cirrus by the VHF Doppler radar indicated a clear enhancement of reflectivity detected in the vicinity of the cloud boundaries, as revealed by the lidar and are strongly dependent on observed cloud LDR. An inter-comparison of radar reflectivity observed for vertical and oblique beams reveals that the radar-enhanced reflectivity at the cloud boundaries is also accompanied by significant aspect sensitivity. These observations indicate the presence of anisotropic turbulence at the cloud boundaries. Radar velocity measurements show that boundaries of cirrus are associated with enhanced horizontal winds, significant vertical shear in the horizontal winds and reduced vertical velocity. Therefore, these measurements indicate that a circulation at the cloud boundaries suggest an entrainment taking place close to
-
MST radar and polarization lidar observations of tropical cirrus
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. Bhavani Kumar
Full Text Available Significant gaps in our understanding of global cirrus effects on the climate system involve the role of frequently occurring tropical cirrus. Much of the cirrus in the atmosphere is largely due to frequent cumulus and convective activity in the tropics. In the Indian sub-tropical region, the deep convective activity is very prominent from April to December, which is a favorable period for the formation of deep cumulus clouds. The fibrous anvils of these clouds, laden with ice crystals, are one of the source mechanisms for much of the cirrus in the atmosphere. In the present study, several passages of tropical cirrus were investigated by simultaneously operating MST radar and a co-located polarization lidar at the National MST Radar Facility (NMRF, Gadanki (13.45° N, 79.18° E, India to understand its structure, the background wind field and the microphysics at the cloud boundaries. The lidar system used is capable of measuring the degree of depolarization in the laser backscatter. It has identified several different cirrus structures with a peak linear depolarization ratio (LDR in the range of 0.1 to 0.32. Simultaneous observations of tropical cirrus by the VHF Doppler radar indicated a clear enhancement of reflectivity detected in the vicinity of the cloud boundaries, as revealed by the lidar and are strongly dependent on observed cloud LDR. An inter-comparison of radar reflectivity observed for vertical and oblique beams reveals that the radar-enhanced reflectivity at the cloud boundaries is also accompanied by significant aspect sensitivity. These observations indicate the presence of anisotropic turbulence at the cloud boundaries. Radar velocity measurements show that boundaries of cirrus are associated with enhanced horizontal winds, significant vertical shear in the horizontal winds and reduced vertical velocity. Therefore, these measurements indicate that a circulation at the cloud boundaries suggest an entrainment taking place close to
-
Danielson, E. F.; Hipskind, R. S.; Gaines, S. E.
1980-01-01
Results are presented from computer processing and digital filtering of radiosonde and radar tracking data obtained during the ITCZ experiment when coordinated measurements were taken daily over a 16 day period across the Panama Canal Zone. The temperature relative humidity and wind velocity profiles are discussed.
-
High-altitude wind prediction and measurement technology assessment
2009-06-30
The principles and operational characteristics of balloon and radar-based techniques for measuring upper air winds in support of launches and recoveries are presented. Though either a balloon or radar system could serve as a standalone system, the sa...
-
Enhancing Arctic Surveillance With Space-Based Radars
2013-06-01
180 degrees (Sellers, 2005). xvii Right Ascension of the Ascending Node: from a geocentric origin perspective, describes how an orbital plane...fascination with remote sensing and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance from space. • Dr. Ray Buettner, my co-advisor, whose positive approach ...48 N; 169 W (northwest maritime corner) • 74 43 N; 156 34 W (uppermost maritime point in the Beaufort Sea approaching the Arctic Ocean) • 72 53 N
-
A comprehensive review on intelligent surveillance systems
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sutrisno Warsono Ibrahim
2016-05-01
Full Text Available Intelligent surveillance system (ISS has received growing attention due to the increasing demand on security and safety. ISS is able to automatically analyze image, video, audio or other type of surveillance data without or with limited human intervention. The recent developments in sensor devices, computer vision, and machine learning have an important role in enabling such intelligent system. This paper aims to provide general overview of intelligent surveillance system and discuss some possible sensor modalities and their fusion scenarios such as visible camera (CCTV, infrared camera, thermal camera and radar. This paper also discusses main processing steps in ISS: background-foreground segmentation, object detection and classification, tracking, and behavioral analysis.
-
Improving ISR Radar Utilization (How I quit blaming the user and made the radar easier to use).
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Doerry, Armin Walter
2014-08-01
In modern multi - sensor multi - mode Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance ( ISR ) platforms, the plethora of options available to a sensor/payload operator are quite large, leading to an over - worked operator often down - selecting to favorite sensors an d modes. For example, Full Motion Video (FMV) is justifiably a favorite sensor at the expense of radar modes, even if radar modes can offer unique and advantageous information. The challenge is then to increase the utilization of the radar modes in a man ner attractive to the sensor/payload operator. We propose that this is best accomplished by combining sensor modes and displays into 'super - modes'. - 4 - Acknowledgements This report is the result of a n unfunded research and development activity . Sandia Natio nal Laboratories is a multi - program laboratory managed and operated by Sandia Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Lockheed Martin Corporation, for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration under contract DE - AC04 - 94AL850 00.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. M. Worthington
1999-02-01
Full Text Available A simple method is described, based on standard VHF wind-profiler data, where imbalances of echo power between four off-vertical radar beams, caused by mountain waves, can be used to calculate the orientation of the wave pattern. It is shown that the mountain wave azimuth (direction of the horizontal component of the wavevector, is given by the vector [ W (PE - P W ,W (PN - P S ]; PN, PS, PE, PW are radar echo powers, measured in dB, in beams pointed away from vertical by the same angle towards north, south, east and west respectively, and W is the vertical wind velocity. The method is applied to Aberystwyth MST radar data, and the calculated wave vector usually, but not always, points into the low-level wind direction. The mean vertical wind at Aberystwyth, which may also be affected by tilted aspect-sensitive layers, is investigated briefly using the entire radar output 1990-1997. The mean vertical-wind profile is inconsistent with existing theories, but a new mountain-wave interpretation is proposed.Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (middle atmosphere dynamics; waves and tides; instruments and techniques.
-
Energy-Aware Path Planning for UAS Persistent Sampling and Surveillance
Shaw-Cortez, Wenceslao
The focus of this work is to develop an energy-aware path planning algorithm that maximizes UAS endurance, while performing sampling and surveillance missions in a known, stationary wind environment. The energy-aware aspect is specifically tailored to extract energy from the wind to reduce thrust use, thereby increasing aircraft endurance. Wind energy extraction is performed by static soaring and dynamic soaring. Static soaring involves using upward wind currents to increase altitude and potential energy. Dynamic soaring involves taking advantage of wind gradients to exchange potential and kinetic energy. The path planning algorithm developed in this work uses optimization to combine these soaring trajectories with the overarching sampling and surveillance mission. The path planning algorithm uses a simplified aircraft model to tractably optimize soaring trajectories. This aircraft model is presented and along with the derivation of the equations of motion. A nonlinear program is used to create the soaring trajectories based on a given optimization problem. This optimization problem is defined using a heuristic decision tree, which defines appropriate problems given a sampling and surveillance mission and a wind model. Simulations are performed to assess the path planning algorithm. The results are used to identify properties of soaring trajectories as well as to determine what wind conditions support minimal thrust soaring. Additional results show how the path planning algorithm can be tuned between maximizing aircraft endurance and performing the sampling and surveillance mission. A means of trajectory stitching is demonstrated to show how the periodic soaring segments can be combined together to provide a full solution to an infinite/long horizon problem.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Oyama
2008-06-01
Full Text Available Lower-thermospheric winds at high latitudes during moderately-disturbed geomagnetic conditions were studied using data obtained with the European Incoherent Scatter (EISCAT Kiruna-Sodankylä-Tromsø (KST ultrahigh frequency (UHF radar system on 9–10 September 2004. The antenna-beam configuration was newly designed to minimize the estimated measurement error of the vertical neutral-wind speed in the lower thermosphere. This method was also available to estimate the meridional and zonal components. The vertical neutral-wind speed at 109 km, 114 km, and 120 km heights showed large upward motions in excess of 30 m s−1 in association with an ionospheric heating event. Large downward speeds in excess of −30 m s−1 were also observed before and after the heating event. The meridional neutral-wind speed suddenly changed its direction from equatorward to poleward when the heating event began, and then returned equatorward coinciding with a decrease in the heating event. The magnetometer data from northern Scandinavia suggested that the center of the heated region was located about 80 km equatorward of Tromsø. The pressure gradient caused the lower-thermospheric wind to accelerate obliquely upward over Tromsø in the poleward direction. Acceleration of the neutral wind flowing on a vertically tilted isobar produced vertical wind speeds larger by more than two orders of magnitude than previously predicted, but still an order of magnitude smaller than observed speeds.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Oyama
2008-06-01
Full Text Available Lower-thermospheric winds at high latitudes during moderately-disturbed geomagnetic conditions were studied using data obtained with the European Incoherent Scatter (EISCAT Kiruna-Sodankylä-Tromsø (KST ultrahigh frequency (UHF radar system on 9–10 September 2004. The antenna-beam configuration was newly designed to minimize the estimated measurement error of the vertical neutral-wind speed in the lower thermosphere. This method was also available to estimate the meridional and zonal components. The vertical neutral-wind speed at 109 km, 114 km, and 120 km heights showed large upward motions in excess of 30 m s−1 in association with an ionospheric heating event. Large downward speeds in excess of −30 m s−1 were also observed before and after the heating event. The meridional neutral-wind speed suddenly changed its direction from equatorward to poleward when the heating event began, and then returned equatorward coinciding with a decrease in the heating event. The magnetometer data from northern Scandinavia suggested that the center of the heated region was located about 80 km equatorward of Tromsø. The pressure gradient caused the lower-thermospheric wind to accelerate obliquely upward over Tromsø in the poleward direction. Acceleration of the neutral wind flowing on a vertically tilted isobar produced vertical wind speeds larger by more than two orders of magnitude than previously predicted, but still an order of magnitude smaller than observed speeds.
-
Ground Penetrating Radar for SMART CITIES
Soldovieri, Francesco; Catapano, Ilaria; Gennarelli, Gianluca
2016-04-01
The use of monitoring and surveillance technologies is now recognized as a reliable option of the overall smart cities management cycle, for the advantages that they offer in terms of: economically sustainable planning of the ordinary and extraordinary maintenance interventions; situational awareness of possible risks factors in view of a reliable early warning; improvement of the security of the communities especially in public environments. In this frame, the abstract will deal with the recent advances in the development and deployment of radar systems for the urban surveillance, exploitation of the subsurface resources and civil engineering structures. In particular, we will present the recent scientific developments and several examples of use of these systems in operational conditions.
-
Wind class sampling of satellite SAR imagery for offshore wind resource mapping
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Badger, Merete; Badger, Jake; Nielsen, Morten
2010-01-01
developed for mesoscale modeling of wind resources. Its performance in connection with sampling of SAR scenes is tested against two sets of random SAR samples and meteorological observations at three sites in the North Sea during 2005–08. Predictions of the mean wind speed and the Weibull scale parameter......High-resolution wind fields retrieved from satellite synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imagery are combined for mapping of wind resources offshore where site measurements are costly and sparse. A new sampling strategy for the SAR scenes is introduced, based on a method for statistical......-dynamical downscaling of large-scale wind conditions using a set of wind classes that describe representative wind situations. One or more SAR scenes are then selected to represent each wind class and the classes are weighted according to their frequency of occurrence. The wind class methodology was originally...
-
Offshore wind mapping Mediterranean area using SAR
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Calaudi, Rosamaria; Arena, Felice; Badger, Merete
2013-01-01
Satellite observations of the ocean surface, for example from Synthetic Aperture Radars (SAR), provide information about the spatial wind variability over large areas. This is of special interest in the Mediterranean Sea, where spatial wind information is only provided by sparse buoys, often with...
-
Progress with enhancing veterinary surveillance in the United Kingdom.
Lysons, R E; Gibbens, J C; Smith, L H
2007-01-27
The UK has experienced various animal health events that have had national impact in recent years. In response, a ;Veterinary Surveillance Strategy' (VSS) was published in 2003, with the objective of enhancing and coordinating national veterinary surveillance practice in a way that would enable important animal health events to be detected and assessed more rapidly and reliably. The VSS adopts an integrated UK-wide approach, which includes widespread engagement with interested parties both within government and beyond. It proposes enhancing surveillance through improved collaboration; transparent and defensible prioritisation of government resources to surveillance; deriving better value from existing resources, and assuring quality of the surveillance reports and source data. This article describes progress with implementing the VSS, in particular the methodology for developing a functional network and creating an effective, quality-assured, information management system, RADAR.
-
DOE's 449 MHz Wind Profiling Radars on the U.S. West Coast: Annual Report for Fiscal Year 2016
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Flaherty, Julia E.; Wilczak, J. M.; King, Clark W.; Shaw, William J.; White, A. B.; Ayers, Tom
2016-09-30
The three coastal wind profilers and associated meteorological instruments located in Forks, WA, Astoria, OR, and North Bend, OR, provide important observations at high temporal and vertical spatial resolution to characterize the meteorological inflow to the western region of the United States. These instruments have been operating for a year or more, and furnish boundary conditions for the modeling efforts of the WFIP2 project. The data have been delivered to archives at both NOAA and the DOE A2e DAP at a data recovery rate in excess of 98%. Site maintenance activities have been relatively minor, with a few component replacements and repairs to RASS foam. Bird mortality surveys have found no bird nests or carcasses, and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service has regularly been provided survey reports. This project represents a successful collaboration between PNNL and NOAA to procure, test, deploy, maintain, and operate three 449 MHz radar wind profilers.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jiang Tie-zhen
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Space target surveillance generally uses active radars. To take full advantage of passive radars, the idea of using spaceborne illuminators of opportunity for space target detection is presented in this paper. Analysis of the detectable time and direct wave suppression shows that passive radar using spaceborne illuminators of opportunity can effectively detect a Low-Earth-Orbit (LEO target. Meanwhile, Ku and L band bi-static radar cross section of passive radars that use spaceborne illuminators of opportunity are presented by simulation, providing the basis of choosing space target forward scatter. Finally the key parameters, mainly system gain, accumulation time and radiation source selection are studied. Results show that system size using satellite TV signals as illuminators of opportunity is relatively small. These encouraging results should stimulate the development of passive radar detection of space targets using spaceborne illuminators of opportunity.
-
Small Wind Turbine Installation Compatibility Demonstration Methodology
2013-08-01
wind turbine (HAWT) and one 2.9-kW vertical-axis wind turbine (VAWT), we planned to measure radar, acoustic and seismic, turbulence, bird and...non-issue for small turbines . The majority of studies of bat and bird interactions with wind turbines are for large turbines (BPA 2002; Whittam...et al. 2010). The majority of studies of bat and bird interactions with wind energy facil- ities are for utility-scale turbines (> 1 MW) with
-
Radar observations of field-aligned plasma irregularities in the SEEK-2 campaign
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Saito
2005-10-01
Full Text Available During the Sporadic E Experiment over Kyushu 2 (SEEK-2 campaign, field-aligned irregularities (FAIs associated with midlatitude sporadic-E (Es layers were observed with two backscatter radars, the Lower Thermosphere Profiler Radar (LTPR and the Frequency Agile Radar (FAR, which were located 40 km apart in Tanegashima, Japan. We conducted observations of FAI echoes from 31 July to 24 August 2002, and the radar data were used to determine launch timing of two sounding rockets on 3 August 2002. Our comparison of echoes obtained by the LTPR and the FAR revealed that echoes often appeared at the FAR about 10min earlier than they did at the LTPR and were well correlated. This indicates that echoing regions drift with a southward velocity component that maintains the spatial shape. Interferometry observations that were conducted with the LTPR from 3 to 8 August 2002, revealed that the quasi-periodic (QP striations in the Range-Time-Intensity (RTI plots were due to the apparent motion of echoing regions across the radar beam including both main and side lobes. In most cases, the echo moved to the east-southeast at an almost constant altitude of 100–110 km, which was along the locus of perpendicularity of the radar line-of-sight to the geomagnetic field line. We found that the QP pattern on the RTI plot reflects the horizontal structure and motion of the (Es layer, and that echoing regions seemed to be in one-dimensionally elongated shapes or in chains of patches. Neutral wind velocities from 75 to 105 km altitude were simultaneously derived with meteor echoes from the LTPR. This is the first time-continuous simultaneous observation FAIs and neutral wind with interferometry measurements. Assuming that the echoing regions were drifting with an ambient neutral wind, we found that the echoing region was aligned east-northeast-west-southwest in eight out of ten QP echo events during the SEEK-2 campaign. A range rate was
-
UK surveillance: provision of quality assured information from combined datasets.
Paiba, G A; Roberts, S R; Houston, C W; Williams, E C; Smith, L H; Gibbens, J C; Holdship, S; Lysons, R
2007-09-14
Surveillance information is most useful when provided within a risk framework, which is achieved by presenting results against an appropriate denominator. Often the datasets are captured separately and for different purposes, and will have inherent errors and biases that can be further confounded by the act of merging. The United Kingdom Rapid Analysis and Detection of Animal-related Risks (RADAR) system contains data from several sources and provides both data extracts for research purposes and reports for wider stakeholders. Considerable efforts are made to optimise the data in RADAR during the Extraction, Transformation and Loading (ETL) process. Despite efforts to ensure data quality, the final dataset inevitably contains some data errors and biases, most of which cannot be rectified during subsequent analysis. So, in order for users to establish the 'fitness for purpose' of data merged from more than one data source, Quality Statements are produced as defined within the overarching surveillance Quality Framework. These documents detail identified data errors and biases following ETL and report construction as well as relevant aspects of the datasets from which the data originated. This paper illustrates these issues using RADAR datasets, and describes how they can be minimised.
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — The Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT) sensor onboard the EUMETSAT MetOp polar-orbiting satellite provides ocean surface wind observations by means of radar...
-
Reduction and coding of synthetic aperture radar data with Fourier transforms
Tilley, David G.
1995-01-01
Recently, aboard the Space Radar Laboratory (SRL), the two roles of Fourier Transforms for ocean image synthesis and surface wave analysis have been implemented with a dedicated radar processor to significantly reduce Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) ocean data before transmission to the ground. The object was to archive the SAR image spectrum, rather than the SAR image itself, to reduce data volume and capture the essential descriptors of the surface wave field. SAR signal data are usually sampled and coded in the time domain for transmission to the ground where Fourier Transforms are applied both to individual radar pulses and to long sequences of radar pulses to form two-dimensional images. High resolution images of the ocean often contain no striking features and subtle image modulations by wind generated surface waves are only apparent when large ocean regions are studied, with Fourier transforms, to reveal periodic patterns created by wind stress over the surface wave field. Major ocean currents and atmospheric instability in coastal environments are apparent as large scale modulations of SAR imagery. This paper explores the possibility of computing complex Fourier spectrum codes representing SAR images, transmitting the coded spectra to Earth for data archives and creating scenes of surface wave signatures and air-sea interactions via inverse Fourier transformations with ground station processors.
-
Automated in situ monitoring of migratory birds at Germany's first offshore wind farm
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Coppack, Timothy; Kulemeyer, Christoph; Schulz, Axel; Steuri, Thomas; Liechti, Felix
2011-07-01
Full text: Offshore wind farms may negatively affect migrating birds, especially at night, by increased photo tactic attraction and risk of collision. Under favourable weather conditions (clear skies, tail wind) the majority of migrants probably fly well above the reach of wind turbine blades. Under unfavourable conditions (sea fog, precipitation, head wind), however, nocturnal migrants could get attracted by brightly lit wind farms, and the risk of collision would hence increase. To assess these potential effects, migration rates and collision probabilities need to be empirically quantified at existing wind farms. This is not an easy task, given the setting and dimension of an offshore wind farm and the sheer quantity and diversity of small-bodied birds potentially passing by. Nocturnal passerine migrants are impossible to count accurately over extended periods with observational methods, and even classic radar technology fails to pro-vide hard-wired information. Complementing the 'Standards for Environmental Impact Assessment' issued by Germany.s Federal Maritime and Hydrographic Agency (BSH), we have developed and installed a novel radar system (BirdScan) on the research platform FINO 1, situated around 50 km offshore next to the wind farm 'alpha ventus' in the German North Sea. BirdScan operates on the basis of defined detection volumes (fixed radar beam), allowing a precise quantification of passerine and non-passerine radar echoes. Our study design includes alternating measurements within and outside the wind farm in order to assess avoidance and/or photo tactic aggregation behaviour of migrants under various weather situations. At the same time, we are investigating the photo tactic attraction of birds at a smaller spatial scale using motion-controlled infrared cameras directly mounted on the nacelle and shaft of a wind turbine. Through this approach, disoriented birds (and even bats) can be automatically ground-proofed and set in
-
Dynamic neural network modeling of HF radar current maps for forecasting oil spill trajectories
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tissot, P.; Perez, J.; Kelly, F.J.; Bonner, J.; Michaud, P.
2001-01-01
This paper examined the concept of dynamic neural network (NN) modeling for short-term forecasts of coastal high-frequency (HF) radar current maps offshore of Galveston Texas. HF radar technology is emerging as a viable and affordable way to measure surface currents in real time and the number of users applying the technology is increasing. A 25 megahertz, two site, Seasonde HF radar system was used to map ocean and bay surface currents along the coast of Texas where wind and river discharge create complex and rapidly changing current patters that override the weaker tidal flow component. The HF radar system is particularly useful in this type of setting because its mobility makes it a good marine spill response tool that could provide hourly current maps. This capability helps improve deployment of response resources. In addition, the NN model recently developed by the Conrad Blucher Institute can be used to forecast water levels during storm events. Forecasted currents are based on time series of current vectors from HF radar plus wind speed, wind direction, and water levels, as well as tidal forecasts. The dynamic NN model was tested to evaluate its performance and the results were compared with a baseline model which assumes the currents do not change from the time of the forecast up to the forecasted time. The NN model showed improvements over the baseline model for forecasting time equal or greater than 3 hours, but the difference was relatively small. The test demonstrated the ability of the dynamic NN model to link meteorological forcing functions with HF radar current maps. Development of the dynamic NN modeling is still ongoing. 18 refs., 1 tab., 5 figs
-
Chinese HJ-1C SAR And Its Wind Mapping Capability
Huang, Weigen; Chen, Fengfeng; Yang, Jingsong; Fu, Bin; Chen, Peng; Zhang, Chan
2010-04-01
Chinese Huan Jing (HJ)-1C synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite has been planed to be launched in 2010. HJ-1C satellite will fly in a sun-synchronous polar orbit of 500-km altitude. SAR will be the only sensor on board the satellite. It operates in S band with VV polarization. Its image mode has the incidence angles 25°and 47°at the near and far sides of the swath respectively. There are two selectable SAR modes of operation, which are fine resolution beams and standard beams respectively. The sea surface wind mapping capability of the SAR has been examined using M4S radar imaging model developed by Romeiser. The model is based on Bragg scattering theory in a composite surface model expansion. It accounts for contributions of the full ocean wave spectrum to the radar backscatter from ocean surface. The model reproduces absolute normalized radar cross section (NRCS) values for wide ranges of wind speeds. The model results of HJ-1C SAR have been compared with the model results of Envisat ASAR. It shows that HJ-1C SAR is as good as Envisat ASAR at sea surface wind mapping.
-
Quantifying offshore wind resources from satellite wind maps: Study area the North Sea
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Barthelmie, Rebecca Jane; Christiansen, Merete B.
2006-01-01
Offshore wind resources are quantified from satellite synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and satellite scatterometer observations at local and regional scale respectively at the Horns Rev site in Denmark. The method for wind resource estimation from satellite observations interfaces with the wind atlas...... of the Horns Rev wind farm is quantified from satellite SAR images and compared with state-of-the-art wake model results with good agreement. It is a unique method using satellite observations to quantify the spatial extent of the wake behind large offshore wind farms. Copyright © 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd....... analysis and application program (WAsP). An estimate of the wind resource at the new project site at Horns Rev is given based on satellite SAR observations. The comparison of offshore satellite scatterometer winds, global model data and in situ data shows good agreement. Furthermore, the wake effect...
-
Radar-to-Radar Interference Suppression for Distributed Radar Sensor Networks
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wen-Qin Wang
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Radar sensor networks, including bi- and multi-static radars, provide several operational advantages, like reduced vulnerability, good system flexibility and an increased radar cross-section. However, radar-to-radar interference suppression is a major problem in distributed radar sensor networks. In this paper, we present a cross-matched filtering-based radar-to-radar interference suppression algorithm. This algorithm first uses an iterative filtering algorithm to suppress the radar-to-radar interferences and, then, separately matched filtering for each radar. Besides the detailed algorithm derivation, extensive numerical simulation examples are performed with the down-chirp and up-chirp waveforms, partially overlapped or inverse chirp rate linearly frequency modulation (LFM waveforms and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (ODFM chirp diverse waveforms. The effectiveness of the algorithm is verified by the simulation results.
-
Bianco, L.; Djalalova, I.; Konopleva-Akish, E.; Kenyon, J.; Olson, J. B.; Wilczak, J. M.
2016-12-01
The Second Wind Forecast Improvement Project (WFIP2) is a DoE- and NOAA-sponsored program whose goal is to improve the accuracy of numerical weather prediction (NWP) forecasts in complex terrain. WFIP2 consists of an 18-month (October 2015 - March 2017) field campaign held in the Columbia River basin, in the Pacific Northwest of the U.S. As part of WFIP2 a large suite of in-situ and remote sensing instrumentation has been deployed, including, among several others, a network of eight 915-MHz wind profiling radars (WPRs) equipped with radio acoustic sounding systems (RASSs), and many surface meteorological stations. The diurnal evolution and annual variability of boundary layer height in the area of WFIP2 will be investigated through the `eye' of WPRs, employing state-of-the-art automated algorithms, based on fuzzy logic and artificial intelligence. The results will be used to evaluate possible errors in NWP models in this area of complex terrain.
-
Warm-season severe wind events in Germany
Gatzen, Christoph
2013-04-01
A 15-year data set of wind measurements was analyzed with regard to warm season severe wind gusts in Germany. For April to September of the years 1997 to 2011, 1035 wind measurements of 26 m/s or greater were found. These wind reports were associated with 268 wind events. In total, 252 convective wind events contributed to 837 (81%) of the wind reports, 16 non-convective synoptic-scale wind events contributed to 198 reports (19%). Severe wind events were found with synoptic situations characterized by rather strong mid-level flow and advancing mid-level troughs. Severe convective wind events were analyzed using radar images and classified with respect to the observed radar structure. The most important convective mode was squall lines that were associated with one third of all severe wind gusts, followed by groups, bow echo complexes, and bow echoes. Supercells and cells were not associated with many wind reports. The low contribution of isolated cells indicates that rather large-scale forcing by synoptic-scale features like fronts is important for German severe wind events. Bow echoes were found to be present for 58% of all wind reports. The movement speed of bow echoes indicated a large variation with a maximum speed of 33 m/s. Extreme wind events as well as events with more than 15 wind reports were found to be related to higher movement speeds. Concentrating on the most intense events, derechos seem to be very important to the warm season wind threat in Germany. Convective events with a path length of more than 400 km contributed to 36% of all warm-season wind gusts in this data set. Furthermore, eight of nine extreme gusts exceeding 40 m/s were recorded with derecho events.
-
An Initial Evaluation of Siting Considerations on Current and Future Wind Deployment
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tegen, Suzanne [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Lantz, Eric [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Mai, Trieu [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Heimiller, Donna [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Hand, Maureen [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Ibanez, Eduardo [GE Energy Consulting, Denver, CO (United States)
2016-07-01
This report provides a deeper understanding of the wind project development process, from desktop studies to a successful project in the ground. It examines three siting consideration categories that wind project sponsors must include in the development process: wildlife (species that live in, near, or migrate through the area where wind development is possible), radar (wind turbines can cause interference with radar signals), and public engagement (representing communities and stakeholders who live near wind power projects). The research shows that although this country's abundant wind resource provides numerous options for addressing siting considerations, actually siting individual projects is becoming more difficult because of regulatory and other uncertainties. Model results are based on the premise that developers will be able to site, permit, and build successful projects, which is not always the case in reality.
-
Multistatic Wireless Fidelity Network Based Radar – Results of the Chrcynno Experiment
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Rzewuski
2014-04-01
Full Text Available This paper presents the theory and experimental result of passive radar using WIFI transmitters as illuminators of opportunity. As a result of experiments conducted on 17th August 2013 at airfield Chrcynno a Cessna C208 airplane was detected and tracked using multistatic passive radar system based on low power signal from WIFI network nodes, which were acting as non cooperative illuminators of opportunity. In the experiment 3 wireless access points were communicating with each other and illuminating the radar scene (airfield. The direct reference and reflected (surveillance signals have been acquired and processed using specially developed algorithm presented in the paper. After signal processing using Passive Coherent Location methods target has been detected. This paper describes in details the algorithms and the results of the experiment for the multistatic passive radar based on the WIFI signal.
-
Sixteenth International Laser Radar Conference, Part 2
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mccormick, M.P.
1992-07-01
Given here are extended abstracts of papers presented at the 16th International Laser Radar Conference, held in Cambridge, Massachusetts, July 20-24, 1992. Topics discussed include the Mt. Pinatubo volcanic dust laser observations, global change, ozone measurements, Earth mesospheric measurements, wind measurements, imaging, ranging, water vapor measurements, and laser devices and technology
-
Session: Avian migration and implications for wind power development in the Eastern United States
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Mabey, Sarah; Cooper, Brian
2004-09-01
This session at the Wind Energy and Birds/Bats workshop consisted of two presentations followed by a discussion/question and answer period. The session was arranged to convey what is known about avian migration, particularly in the eastern US. The first presentation ''Migration Ecology: Issues of Scale and Behavior'' by Sarah Mabey frames the issue of migratory bird interactions with wind energy facilities from an ecological perspective: when, where, and why are migrant bird species vulnerable to wind turbine collision. The second presentation ''Radar Studies of Nocturnal Migration at Wind Sites in the Eastern US'' by Brian Cooper reported on radar studies conducted at wind sites in the eastern US, including Mount Storm, Clipper Wind, and others.
-
New Cloud and Precipitation Research Avenues Enabled by low-cost Phased-array Radar Technology
Kollias, P.; Oue, M.; Fridlind, A. M.; Matsui, T.; McLaughlin, D. J.
2017-12-01
For over half a century, radars operating in a wide range of frequencies have been the primary source of observational insights of clouds and precipitation microphysics and dynamics and contributed to numerous significant advancements in the field of cloud and precipitation physics. The development of multi-wavelength and polarization diversity techniques has further strengthened the quality of microphysical and dynamical retrievals from radars and has assisted in overcoming some of the limitations imposed by the physics of scattering. Atmospheric radars have historically employed a mechanically-scanning dish antenna and their ability to point to, survey, and revisit specific points or regions in the atmosphere is limited by mechanical inertia. Electronically scanned, or phased-array, radars capable of high-speed, inertialess beam steering, have been available for several decades, but the cost of this technology has limited its use to military applications. During the last 10 years, lower power and lower-cost versions of electronically scanning radars have been developed, and this presents an attractive and affordable new tool for the atmospheric sciences. The operational and research communities are currently exploring phased array advantages in signal processing (i.e. beam multiplexing, improved clutter rejection, cross beam wind estimation, adaptive sensing) and science applications (i.e. tornadic storm morphology studies). Here, we will present some areas of atmospheric research where inertia-less radars with ability to provide rapid volume imaging offers the potential to advance cloud and precipitation research. We will discuss the added value of single phased-array radars as well as networks of these radars for several problems including: multi-Doppler wind retrieval techniques, cloud lifetime studies and aerosol-convection interactions. The performance of current (dish) and future (e-scan) radar systems for these atmospheric studies will be evaluated using
-
Wind energy. To produce electricity with the wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bareau, Helene
2015-11-01
This guide addresses the different aspects of wind-based power generation. It outlines the role of wind energy to meet objectives related to the share of renewable energies in the French energy mix, that wind energy is actually replacing fossil energies, that it is based on local resources within higher safety and less wastage, that current advances are made to integrate wind energy production into the grid, and that it is a solution to diversify energy production. Some figures are presented and commented, regarding onshore wind energy production in France, the location of wind farms, and wind energy production in comparison with other renewable sources. The operation of a wind turbine is described and the different types of wind turbines are evoked. The issue of wind farm planning with citizen participation is addressed: regional planning, studies of pre-feasibility for location selection, procedure, and content of the impact study (radars, fauna and flora, landscapes, safety, health). Other features are outlined: a planned dismantling, and a globally favourable perception. The next part addresses offshore wind energy: the interesting potential of stronger and more reliable wind at sea (European situation, French opportunities, elements comprised in an offshore wind farm), impacts (on marine ecosystems, on neighbouring localities, and interests for visitors). Economic aspects are then addressed: cost and profitability, economic spin-offs, and perspectives. The last part concerns individuals and the possibilities to participate to wind farm projects or to invest in small wind turbines with some prerequisites (constant and steady winds, installation assessment, required expertise, indispensable preliminary steps, costs, aids and profitability)
-
SMAP RADAR Calibration and Validation
West, R. D.; Jaruwatanadilok, S.; Chaubel, M. J.; Spencer, M.; Chan, S. F.; Chen, C. W.; Fore, A.
2015-12-01
The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission launched on Jan 31, 2015. The mission employs L-band radar and radiometer measurements to estimate soil moisture with 4% volumetric accuracy at a resolution of 10 km, and freeze-thaw state at a resolution of 1-3 km. Immediately following launch, there was a three month instrument checkout period, followed by six months of level 1 (L1) calibration and validation. In this presentation, we will discuss the calibration and validation activities and results for the L1 radar data. Early SMAP radar data were used to check commanded timing parameters, and to work out issues in the low- and high-resolution radar processors. From April 3-13 the radar collected receive only mode data to conduct a survey of RFI sources. Analysis of the RFI environment led to a preferred operating frequency. The RFI survey data were also used to validate noise subtraction and scaling operations in the radar processors. Normal radar operations resumed on April 13. All radar data were examined closely for image quality and calibration issues which led to improvements in the radar data products for the beta release at the end of July. Radar data were used to determine and correct for small biases in the reported spacecraft attitude. Geo-location was validated against coastline positions and the known positions of corner reflectors. Residual errors at the time of the beta release are about 350 m. Intra-swath biases in the high-resolution backscatter images are reduced to less than 0.3 dB for all polarizations. Radiometric cross-calibration with Aquarius was performed using areas of the Amazon rain forest. Cross-calibration was also examined using ocean data from the low-resolution processor and comparing with the Aquarius wind model function. Using all a-priori calibration constants provided good results with co-polarized measurements matching to better than 1 dB, and cross-polarized measurements matching to about 1 dB in the beta release. During the
-
Specification for a surface-search radar-detection-range model
Hattan, Claude P.
1990-09-01
A model that predicts surface-search radar detection range versus a variety of combatants has been developed at the Naval Ocean Systems Center. This model uses a simplified ship radar cross section (RCS) model and the U.S. Navy Oceanographic and Atmospheric Mission Library Standard Electromagnetic Propagation Model. It provides the user with a method of assessing the effects of the environment of the performance of a surface-search radar system. The software implementation of the model is written in ANSI FORTRAN 77, with MIL-STD-1753 extensions. The program provides the user with a table of expected detection ranges when the model is supplied with the proper environmental radar system inputs. The target model includes the variation in RCS as a function of aspect angle and the distribution of reflected radar energy as a function of height above the waterline. The modeled propagation effects include refraction caused by a multisegmented refractivity profile, sea-surface roughness caused by local winds, evaporation ducting, and surface-based ducts caused by atmospheric layering.
-
Observation and modeling of tide- and wind-induced surface currents in Galway Bay
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lei REN
2015-10-01
Full Text Available A high-frequency radar system has been deployed in Galway Bay, a semi-enclosed bay on the west coast of Ireland. The system provides surface currents with fine spatial resolution every hour. Prior to its use for model validation, the accuracy of the radar data was verified through comparison with measurements from acoustic Doppler current profilers (ADCPs and a good correlation between time series of surface current speeds and directions obtained from radar data and ADCP data. Since Galway Bay is located on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, it is subject to relatively windy conditions, and surface currents are therefore strongly wind-driven. With a view to assimilating the radar data for forecasting purposes, a three-dimensional numerical model of Galway Bay, the Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code (EFDC, was developed based on a terrain-following vertical (sigma coordinate system. This study shows that the performance and accuracy of the numerical model, particularly with regard to tide- and wind-induced surface currents, are sensitive to the vertical layer structure. Results of five models using different layer structures are presented and compared with radar measurements. A variable vertical structure with thin layers at the bottom and the surface and thicker layers in the middle of the water column was found to be the optimal layer structure for reproduction of tide- and wind-induced surface currents. This structure ensures that wind shear can properly propagate from the surface layer to the sub-surface layers, thereby ensuring that wind forcing is not overdamped by tidal forcing. The vertical layer structure affects not only the velocities at the surface layer but also the velocities further down in the water column.
-
Surface current measurements in Juan de Fuca Strait using the SeaSonde HF [high frequency] radar
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hodgins, D.O.
1994-09-01
The shore-based SeaSonde high-frequency (HF) radar was deployed for three weeks in summer 1993 to measure surface currents in the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia. Experimental objectives included documenting the complex flow regime generated by large tides and the brackish plume of the Fraser River, and determining the radar performance under low-wind, low-salinity conditions. The radar data showed that surface flows are dominated by the plume jet formed by the Fraser River outflow, giving rise to recurring, energetic eddies with scales of 8-12 km, strong flow meanders, and convergent fronts. These features were continuously modulated by the along-channel tidal flows. Comparisons with a detailed numerical model hindcast gave good correlation between observed and predicted flow fields, especially at tidal and low frequencies. Radar return was found to be correlated with local winds and radar performance was independent of salinity variations in the plume. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) provides a map of the radar scattering characteristics of the ocean surface on a capillary wave scale. ERS-1 satellite and airborne SAR images for July 28, 1993 were obtained and surface features were examined in the context of the HF radar current fields. Results show that SAR images alone cannot reliably provide the dynamical data required in this region by oil spill models. Under certain conditions, however, the radar imagery offers valuable physical information on phenomena affecting oil slick development. Interpretation of SAR imagery in conjunction with other remote sensing information would offer more quantitative prediction data. 28 refs., 334 figs., 1 tab
-
Yearbook of wind energy law 2015
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brandt, Edmund
2016-01-01
In the yearbook 2015, the technical papers are dealing with the distance recommendations of the State Working Group of Bird Conservation Observatories, with aesthetics as a public interest in the planning and authorization regime for wind turbines, the prospect of the citizen and community participation law in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, the conflict between wind turbines and weather radars and with the higher court jurisdiction for feed management. [de
-
Jan, Shau-Shiun; Kao, Yu-Chun
2013-05-17
The current trend of the civil aviation technology is to modernize the legacy air traffic control (ATC) system that is mainly supported by many ground based navigation aids to be the new air traffic management (ATM) system that is enabled by global positioning system (GPS) technology. Due to the low receiving power of GPS signal, it is a major concern to aviation authorities that the operation of the ATM system might experience service interruption when the GPS signal is jammed by either intentional or unintentional radio-frequency interference. To maintain the normal operation of the ATM system during the period of GPS outage, the use of the current radar system is proposed in this paper. However, the tracking performance of the current radar system could not meet the required performance of the ATM system, and an enhanced tracking algorithm, the interacting multiple model and probabilistic data association filter (IMMPDAF), is therefore developed to support the navigation and surveillance services of the ATM system. The conventional radar tracking algorithm, the nearest neighbor Kalman filter (NNKF), is used as the baseline to evaluate the proposed radar tracking algorithm, and the real flight data is used to validate the IMMPDAF algorithm. As shown in the results, the proposed IMMPDAF algorithm could enhance the tracking performance of the current aviation radar system and meets the required performance of the new ATM system. Thus, the current radar system with the IMMPDAF algorithm could be used as an alternative system to continue aviation navigation and surveillance services of the ATM system during GPS outage periods.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Shau-Shiun Jan
2013-05-01
Full Text Available The current trend of the civil aviation technology is to modernize the legacy air traffic control (ATC system that is mainly supported by many ground based navigation aids to be the new air traffic management (ATM system that is enabled by global positioning system (GPS technology. Due to the low receiving power of GPS signal, it is a major concern to aviation authorities that the operation of the ATM system might experience service interruption when the GPS signal is jammed by either intentional or unintentional radio-frequency interference. To maintain the normal operation of the ATM system during the period of GPS outage, the use of the current radar system is proposed in this paper. However, the tracking performance of the current radar system could not meet the required performance of the ATM system, and an enhanced tracking algorithm, the interacting multiple model and probabilistic data association filter (IMMPDAF, is therefore developed to support the navigation and surveillance services of the ATM system. The conventional radar tracking algorithm, the nearest neighbor Kalman filter (NNKF, is used as the baseline to evaluate the proposed radar tracking algorithm, and the real flight data is used to validate the IMMPDAF algorithm. As shown in the results, the proposed IMMPDAF algorithm could enhance the tracking performance of the current aviation radar system and meets the required performance of the new ATM system. Thus, the current radar system with the IMMPDAF algorithm could be used as an alternative system to continue aviation navigation and surveillance services of the ATM system during GPS outage periods.
-
Bianco, L.; McCaffrey, K.; Wilczak, J. M.; Olson, J. B.; Kenyon, J.
2016-12-01
When forecasting winds at a wind plant for energy production, the turbulence parameterizations in the forecast models are crucial for understanding wind plant performance. Recent research shows that the turbulence (eddy) dissipation rate in planetary boundary layer (PBL) parameterization schemes introduces significant uncertainty in the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model. Thus, developing the capability to measure dissipation rates in the PBL will allow for identification of weaknesses in, and improvements to the parameterizations. During a preliminary field study at the Boulder Atmospheric Observatory in spring 2015, a 915-MHz wind profiling radar (WPR) measured dissipation rates concurrently with sonic anemometers mounted on a 300-meter tower. WPR set-up parameters (e.g., spectral resolution), post-processing techniques (e.g., filtering for non-atmospheric signals), and spectral averaging were optimized to capture the most accurate Doppler spectra for measuring spectral widths for use in the computation of the eddy dissipation rates. These encouraging results lead to the implementation of the observing strategy on a 915-MHz WPR in Wasco, OR, operating as part of the Wind Forecasting Improvement Project 2 (WFIP2). These observations are compared to dissipation rates calculated from the High-Resolution Rapid Refresh model, a WRF-based mesoscale numerical weather prediction model run for WFIP2 at 3000 m horizontal grid spacing and with a nest, which has 750-meter horizontal grid spacing, in the complex terrain region of the Columbia River Gorge. The observed profiles of dissipation rates are used to evaluate the PBL parameterization schemes used in the HRRR model, which are based on the modeled turbulent kinetic energy and a tunable length scale.
-
Using Satellite SAR to Characterize the Wind Flow around Offshore Wind Farms
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Charlotte Bay Hasager
2015-06-01
Full Text Available Offshore wind farm cluster effects between neighboring wind farms increase rapidly with the large-scale deployment of offshore wind turbines. The wind farm wakes observed from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR are sometimes visible and atmospheric and wake models are here shown to convincingly reproduce the observed very long wind farm wakes. The present study mainly focuses on wind farm wake climatology based on Envisat ASAR. The available SAR data archive covering the large offshore wind farms at Horns Rev has been used for geo-located wind farm wake studies. However, the results are difficult to interpret due to mainly three issues: the limited number of samples per wind directional sector, the coastal wind speed gradient, and oceanic bathymetry effects in the SAR retrievals. A new methodology is developed and presented. This method overcomes effectively the first issue and in most cases, but not always, the second. In the new method all wind field maps are rotated such that the wind is always coming from the same relative direction. By applying the new method to the SAR wind maps, mesoscale and microscale model wake aggregated wind-fields results are compared. The SAR-based findings strongly support the model results at Horns Rev 1.
-
Phased Array Radar Network Experiment for Severe Weather
Ushio, T.; Kikuchi, H.; Mega, T.; Yoshikawa, E.; Mizutani, F.; Takahashi, N.
2017-12-01
Phased Array Weather Radar (PAWR) was firstly developed in 2012 by Osaka University and Toshiba under a grant of NICT using the Digital Beamforming Technique, and showed a impressive thunderstorm behavior with 30 second resolution. After that development, second PAWR was installed in Kobe city about 60 km away from the first PAWR site, and Tokyo Metropolitan University, Osaka Univeristy, Toshiba and the Osaka Local Government started a new project to develop the Osaka Urban Demonstration Network. The main sensor of the Osaka Network is a 2-node Phased Array Radar Network and lightning location system. Data products that are created both in local high performance computer and Toshiba Computer Cloud, include single and multi-radar data, vector wind, quantitative precipitation estimation, VIL, nowcasting, lightning location and analysis. Each radar node is calibarated by the baloon measurement and through the comparison with the GPM (Global Precipitation Measurement)/ DPR (Dual Frequency Space borne Radar) within 1 dB. The attenuated radar reflectivities obtained by the Phased Array Radar Network at X band are corrected based on the bayesian scheme proposed in Shimamura et al. [2016]. The obtained high resolution (every 30 seconds/ 100 elevation angles) 3D reflectivity and rain rate fields are used to nowcast the surface rain rate up to 30 minutes ahead. These new products are transferred to Osaka Local Government in operational mode and evaluated by several section in Osaka Prefecture. Furthermore, a new Phased Array Radar with polarimetric function has been developed in 2017, and will be operated in the fiscal year of 2017. In this presentation, Phased Array Radar, network architecuture, processing algorithm, evalution of the social experiment and first Multi-Prameter Phased Array Radar experiment are presented.
-
Observation and modeling of tide- and wind-induced surface currents in Galway Bay
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lei Ren
2015-10-01
Full Text Available A high-frequency radar system has been deployed in Galway Bay, a semi-enclosed bay on the west coast of Ireland. The system provides surface currents with fine spatial resolution every hour. Prior to its use for model validation, the accuracy of the radar data was verified through comparison with measurements from acoustic Doppler current profilers (ADCPs and a good correlation between time series of surface current speeds and directions obtained from radar data and ADCP data. Since Galway Bay is located on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, it is subject to relatively windy conditions, and surface currents are therefore strongly wind-driven. With a view to assimilating the radar data for forecasting purposes, a three-dimensional numerical model of Galway Bay, the Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code (EFDC, was developed based on a terrain-following vertical (sigma coordinate system. This study shows that the performance and accuracy of the numerical model, particularly with regard to tide- and wind-induced surface currents, are sensitive to the vertical layer structure. Results of five models with different layer structures are presented and compared with radar measurements. A variable vertical structure with thin layers at the bottom and the surface and thicker layers in the middle of the water column was found to be the optimal layer structure for reproduction of tide- and wind-induced surface currents. This structure ensures that wind shear can properly propagate from the surface layer to the sub-surface layers, thereby ensuring that wind forcing is not overdamped by tidal forcing. The vertical layer structure affects not only the velocities at the surface layer but also the velocities further down in the water column.
-
Optimum radars and filters for the passive sphere system
Luers, J. K.; Soltes, A.
1971-01-01
Studies have been conducted to determine the influence of the tracking radar and data reduction technique on the accuracy of the meteorological measurements made in the 30 to 100 kilometer altitude region by the ROBIN passive falling sphere. A survey of accuracy requirements was made of agencies interested in data from this region of the atmosphere. In light of these requirements, various types of radars were evaluated to determine the tracking system most applicable to the ROBIN, and methods were developed to compute the errors in wind and density that arise from noise errors in the radar supplied data. The effects of launch conditions on the measurements were also examined. Conclusions and recommendations have been made concerning the optimum tracking and data reduction techniques for the ROBIN falling sphere system.
-
Monostatic radar cross section of flying wing delta planforms
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sevoor Meenakshisundaram Vaitheeswaran
2017-04-01
Full Text Available The design of the flying wing and its variants shapes continues to have a profound influence in the design of the current and future use of military aircraft. There is very little in the open literature available to the understanding and by way of comparison of the radar cross section of the different wing planforms, for obvious reasons of security and sensitivity. This paper aims to provide an insight about the radar cross section of the various flying wing planforms that would aid the need and amount of radar cross section suppression to escape detection from surveillance radars. Towards this, the shooting and bouncing ray method is used for analysis. In this, the geometric optics theory is first used for launching and tracing the electromagnetic rays to calculate the electromagnetic field values as the waves bounce around the target. The physical optics theory is next used to calculate the final scattered electric field using the far field integration along the observation direction. For the purpose of comparison, all the planform shapes are assumed to be having the same area, and only the aspect ratio and taper ratio are varied to feature representative airplanes.
-
Study of equatorial Kelvin waves using the MST radar and radiosonde observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Kishore
2005-06-01
Full Text Available In this paper an attempt has been made to study equatorial Kelvin waves using a high power coherent VHF radar located at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E, a tropical station in the Indian sub-continent. Simultaneous radiosonde observations taken from a nearby meteorological station located in Chennai (13.04° N, 80.17° E were also used to see the coherence in the observed structures. These data sets were analyzed to study the mean winds and equatorial waves in the troposphere and lower stratosphere. Equatorial waves with different periodicities were identified. In the present study, particular attention has been given to the fast Kelvin wave (6.5-day and slow Kelvin wave (16-day. Mean zonal wind structures were similar at both locations. The fast Kelvin wave amplitudes were somewhat similar in both observations and the maximum amplitude is about 8m/s. The phase profiles indicated a slow downward progression. The slow Kelvin wave (16-day amplitudes shown by the radiosonde measurements are a little larger than the radar derived amplitudes. The phase profiles showed downward phase progression and it translates into a vertical wavelength of ~10-12km. The radar and radiosonde derived amplitudes of fast and slow Kelvin waves are larger at altitudes near the tropopause (15-17km, where the mean wind attains westward maximum.
-
Simultaneous rocket and radar measurements of currents in an auroral arc
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Robinson, R.M.; Bering, E.A.; Vondrak, R.R.; Anderson, H.R.; Cloutier, P.A.
1981-01-01
A detailed study of electric field, current and conductivities associated with an auroral arc was made in a coordinated rocket and radar experiment in Alaska on March 9, 1978. The payload, designated 29.007 UE, was launched at 1013 p.m. local time. It penetrated the diffuse aurora on the upleg and at apogee traversed field lines connected to a stable auroral arc of 40 kR intensity. Among the instruments carried by the payload were a vector magnetometer, a set of electrostatic double probes and a set of electron and proton spectrometers. Simultaneous electron density and line-of-sight velocity measurements were made by Chatanika radar operating in an elevation scan mode in the magnetic meridian plane. Both the radar and rocket measurements indicated that the zonal electric field was westward and approximately constant across the arc with a magnitude of about 7 mV/m. Small differences between the rocket and radar zonal electric field measurements indicated the presence of upward drifting ions in the region of the arc. The meridional field was large and northward equatorward of the arc, but negligible within the arc. Conductivities computed from measured fluxes of energetic electrons agreed well with the conductivities derived from the radar measureements of electron density. The electric field and conductivity measurements indicated that the zonal currents were eastward equatorward of the arc and westward within the arc. These electrojet currents agreed well with those inferred from the rocket magnetometer data. Better agreement was obtained when a westward neutral wind was added. The westward wind was also consistent with differences between the rocket and radar meridional electric fields. The meridional currents computed from the electric field measurements were northward over the entire region
-
Offshore Wind Resource Estimation in Mediterranean Area Using SAR Images
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Calaudi, Rosamaria; Arena, Felice; Badger, Merete
Satellite observations of the ocean surface from Synthetic Aperture Radars (SAR) provide information about the spatial wind variability over large areas. This is of special interest in the Mediterranean, where spatial wind information is only provided by sparse buoys, often with long periods of m...
-
Development of wide band digital receiver for atmospheric radars using COTS board based SDR
Yasodha, Polisetti; Jayaraman, Achuthan; Thriveni, A.
2016-07-01
Digital receiver extracts the received echo signal information, and is a potential subsystem for atmospheric radar, also referred to as wind profiling radar (WPR), which provides the vertical profiles of 3-dimensional wind vector in the atmosphere. This paper presents the development of digital receiver using COTS board based Software Defined Radio technique, which can be used for atmospheric radars. The developmental work is being carried out at National Atmospheric Research Laboratory (NARL), Gadanki. The digital receiver consists of a commercially available software defined radio (SDR) board called as universal software radio peripheral B210 (USRP B210) and a personal computer. USRP B210 operates over a wider frequency range from 70 MHz to 6 GHz and hence can be used for variety of radars like Doppler weather radars operating in S/C bands, in addition to wind profiling radars operating in VHF, UHF and L bands. Due to the flexibility and re-configurability of SDR, where the component functionalities are implemented in software, it is easy to modify the software to receive the echoes and process them as per the requirement suitable for the type of the radar intended. Hence, USRP B210 board along with the computer forms a versatile digital receiver from 70 MHz to 6 GHz. It has an inbuilt direct conversion transceiver with two transmit and two receive channels, which can be operated in fully coherent 2x2 MIMO fashion and thus it can be used as a two channel receiver. Multiple USRP B210 boards can be synchronized using the pulse per second (PPS) input provided on the board, to configure multi-channel digital receiver system. RF gain of the transceiver can be varied from 0 to 70 dB. The board can be controlled from the computer via USB 3.0 interface through USRP hardware driver (UHD), which is an open source cross platform driver. The USRP B210 board is connected to the personal computer through USB 3.0. Reference (10 MHz) clock signal from the radar master oscillator
-
High resolution radar satellite imagery analysis for safeguards applications
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Minet, Christian; Eineder, Michael [German Aerospace Center, Remote Sensing Technology Institute, Department of SAR Signal Processing, Wessling, (Germany); Rezniczek, Arnold [UBA GmbH, Herzogenrath, (Germany); Niemeyer, Irmgard [Forschungszentrum Juelich, Institue of Energy and Climate Research, IEK-6: Nuclear Waste Management and Reactor Safety, Juelich, (Germany)
2011-12-15
For monitoring nuclear sites, the use of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery shows essential promises. Unlike optical remote sensing instruments, radar sensors operate under almost all weather conditions and independently of the sunlight, i.e. time of the day. Such technical specifications are required both for continuous and for ad-hoc, timed surveillance tasks. With Cosmo-Skymed, TerraSARX and Radarsat-2, high-resolution SAR imagery with a spatial resolution up to 1m has recently become available. Our work therefore aims to investigate the potential of high-resolution TerraSAR data for nuclear monitoring. This paper focuses on exploiting amplitude of a single acquisition, assessing amplitude changes and phase differences between two acquisitions, and PS-InSAR processing of an image stack.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2008-07-01
Wind turbines and the movement of their blades can have penalizing effects on the processing of radars data. These disturbances can have a strong impact on the air, maritime and fluvial safety, on the protection of the territory and on the prevention of natural hazards. Reports made by the national agency of frequencies (ANFR) have established recommendations for the definition of protection areas (5 km) and coordination areas (5 to 30 km) which have to be taken into consideration prior to any project of wind turbine. (J.S.)
-
A Machine Learning-based Rainfall System for GPM Dual-frequency Radar
Tan, H.; Chandrasekar, V.; Chen, H.
2017-12-01
Precipitation measurement produced by the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) plays an important role in researching the water circle and forecasting extreme weather event. Compare with its predecessor - Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) Precipitation Radar (PR), GRM DPR measures precipitation in two different frequencies (i.e., Ku and Ka band), which can provide detailed information on the microphysical properties of precipitation particles, quantify particle size distribution and quantitatively measure light rain and falling snow. This paper presents a novel Machine Learning system for ground-based and space borne radar rainfall estimation. The system first trains ground radar data for rainfall estimation using rainfall measurements from gauges and subsequently uses the ground radar based rainfall estimates to train GPM DPR data in order to get space based rainfall product. Therein, data alignment between space DPR and ground radar is conducted using the methodology proposed by Bolen and Chandrasekar (2013), which can minimize the effects of potential geometric distortion of GPM DPR observations. For demonstration purposes, rainfall measurements from three rain gauge networks near Melbourne, Florida, are used for training and validation purposes. These three gauge networks, which are located in Kennedy Space Center (KSC), South Florida Water Management District (SFL), and St. Johns Water Management District (STJ), include 33, 46, and 99 rain gauge stations, respectively. Collocated ground radar observations from the National Weather Service (NWS) Weather Surveillance Radar - 1988 Doppler (WSR-88D) in Melbourne (i.e., KMLB radar) are trained with the gauge measurements. The trained model is then used to derive KMLB radar based rainfall product, which is used to train GPM DPR data collected from coincident overpasses events. The machine learning based rainfall product is compared against the GPM standard products
-
Ionospheric Impacts on UHF Space Surveillance
Jones, J. C.
2017-12-01
Earth's atmosphere contains regions of ionized plasma caused by the interaction of highly energetic solar radiation. This region of ionization is called the ionosphere and varies significantly with altitude, latitude, local solar time, season, and solar cycle. Significant ionization begins at about 100 km (E layer) with a peak in the ionization at about 300 km (F2 layer). Above the F2 layer, the atmosphere is mostly ionized but the ion and electron densities are low due to the unavailability of neutral molecules for ionization so the density decreases exponentially with height to well over 1000 km. The gradients of these variations in the ionosphere play a significant role in radio wave propagation. These gradients induce variations in the index of refraction and cause some radio waves to refract. The amount of refraction depends on the magnitude and direction of the electron density gradient and the frequency of the radio wave. The refraction is significant at HF frequencies (3-30 MHz) with decreasing effects toward the UHF (300-3000 MHz) range. UHF is commonly used for tracking of space objects in low Earth orbit (LEO). While ionospheric refraction is small for UHF frequencies, it can cause errors in range, azimuth angle, and elevation angle estimation by ground-based radars tracking space objects. These errors can cause significant errors in precise orbit determinations. For radio waves transiting the ionosphere, it is important to understand and account for these effects. Using a sophisticated radio wave propagation tool suite and an empirical ionospheric model, we calculate the errors induced by the ionosphere in a simulation of a notional space surveillance radar tracking objects in LEO. These errors are analyzed to determine daily, monthly, annual, and solar cycle trends. Corrections to surveillance radar measurements can be adapted from our simulation capability.
-
Comparison between HF radar current data and moored ADCP currentmeter
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cosoli, S.
2005-01-01
A preliminary assessment of accuracy of a two-sites shore-based HF Radar network along the Venice Lagoon littoral was attempted by means of comparison with a 57.5 day-long ADCP current time series for the period September-October 2002. Results showed that radar measurements were accurate ( O . The main differences between the HF radar and surface ADCP currents can be explained in terms of random errors affecting the measurement technique and the daily sea breeze forcing, since low-pass filtering of current time series significantly improved the correlation and decreased the RMS of the differences between the two measured data set. Comparison of the semidiurnal (M2, S2) tidal band suggested good agreement between tidal ellipse amplitudes. Wind forcing on a daily time-scale (sea-breeze) was associated with larger differences between radar and ADCP currents at a diurnal band due to the presence of a vertical shear in the surface layer
-
Radar equations for modern radar
Barton, David K
2012-01-01
Based on the classic Radar Range-Performance Analysis from 1980, this practical volume extends that work to ensure applicability of radar equations to the design and analysis of modern radars. This unique book helps you identify what information on the radar and its environment is needed to predict detection range. Moreover, it provides equations and data to improve the accuracy of range calculations. You find detailed information on propagation effects, methods of range calculation in environments that include clutter, jamming and thermal noise, as well as loss factors that reduce radar perfo
-
High-Resolution Wind Measurements for Offshore Wind Energy Development
Nghiem, Son V.; Neumann, Gregory
2011-01-01
A mathematical transform, called the Rosette Transform, together with a new method, called the Dense Sampling Method, have been developed. The Rosette Transform is invented to apply to both the mean part and the fluctuating part of a targeted radar signature using the Dense Sampling Method to construct the data in a high-resolution grid at 1-km posting for wind measurements over water surfaces such as oceans or lakes.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ling, Hao [The University of Texas at Austin; Hamilton, Mark F. [The University of Texas at Austin Applied Research Laboratories; Bhalla, Rajan [Science Applications International Corporation; Brown, Walter E. [The University of Texas at Austin Applied Research Laboratories; Hay, Todd A. [The University of Texas at Austin Applied Research Laboratories; Whitelonis, Nicholas J. [The University of Texas at Austin; Yang, Shang-Te [The University of Texas at Austin; Naqvi, Aale R. [The University of Texas at Austin
2013-09-30
Offshore wind energy is a valuable resource that can provide a significant boost to the US renewable energy portfolio. A current constraint to the development of offshore wind farms is the potential for interference to be caused by large wind farms on existing electronic and acoustical equipment such as radar and sonar systems for surveillance, navigation and communications. The US Department of Energy funded this study as an objective assessment of possible interference to various types of equipment operating in the marine environment where offshore wind farms could be installed. The objective of this project was to conduct a baseline evaluation of electromagnetic and acoustical challenges to sea surface, subsurface and airborne electronic systems presented by offshore wind farms. To accomplish this goal, the following tasks were carried out: (1) survey electronic systems that can potentially be impacted by large offshore wind farms, and identify impact assessment studies and research and development activities both within and outside the US, (2) engage key stakeholders to identify their possible concerns and operating requirements, (3) conduct first-principle modeling on the interactions of electromagnetic signals with, and the radiation of underwater acoustic signals from, offshore wind farms to evaluate the effect of such interactions on electronic systems, and (4) provide impact assessments, recommend mitigation methods, prioritize future research directions, and disseminate project findings. This report provides a detailed description of the methodologies used to carry out the study, key findings of the study, and a list of recommendations derived based the findings.
-
Radar Rainfall Bias Correction based on Deep Learning Approach
Song, Yang; Han, Dawei; Rico-Ramirez, Miguel A.
2017-04-01
Radar rainfall measurement errors can be considerably attributed to various sources including intricate synoptic regimes. Temperature, humidity and wind are typically acknowledged as critical meteorological factors in inducing the precipitation discrepancies aloft and on the ground. The conventional practices mainly use the radar-gauge or geostatistical techniques by direct weighted interpolation algorithms as bias correction schemes whereas rarely consider the atmospheric effects. This study aims to comprehensively quantify those meteorological elements' impacts on radar-gauge rainfall bias correction based on a deep learning approach. The deep learning approach employs deep convolutional neural networks to automatically extract three-dimensional meteorological features for target recognition based on high range resolution profiles. The complex nonlinear relationships between input and target variables can be implicitly detected by such a scheme, which is validated on the test dataset. The proposed bias correction scheme is expected to be a promising improvement in systematically minimizing the synthesized atmospheric effects on rainfall discrepancies between radar and rain gauges, which can be useful in many meteorological and hydrological applications (e.g., real-time flood forecasting) especially for regions with complex atmospheric conditions.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mera, David; Cotos, José M.; Varela-Pet, José; Garcia-Pineda, Oscar
2012-01-01
Highlights: ► We present an adaptive thresholding algorithm to segment oil spills. ► The segmentation algorithm is based on SAR images and wind field estimations. ► A Database of oil spill confirmations was used for the development of the algorithm. ► Wind field estimations have demonstrated to be useful for filtering look-alikes. ► Parallel programming has been successfully used to minimize processing time. - Abstract: Satellite Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) has been established as a useful tool for detecting hydrocarbon spillage on the ocean’s surface. Several surveillance applications have been developed based on this technology. Environmental variables such as wind speed should be taken into account for better SAR image segmentation. This paper presents an adaptive thresholding algorithm for detecting oil spills based on SAR data and a wind field estimation as well as its implementation as a part of a functional prototype. The algorithm was adapted to an important shipping route off the Galician coast (northwest Iberian Peninsula) and was developed on the basis of confirmed oil spills. Image testing revealed 99.93% pixel labelling accuracy. By taking advantage of multi-core processor architecture, the prototype was optimized to get a nearly 30% improvement in processing time.
-
Validation of sentinel-1A SAR coastal wind speeds against scanning LiDAR
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Ahsbahs, Tobias Torben; Badger, Merete; Karagali, Ioanna
2017-01-01
High-accuracy wind data for coastal regions is needed today, e.g., for the assessment of wind resources. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is the only satellite borne sensor that has enough resolution to resolve wind speeds closer than 10 km to shore but the Geophysical Model Functions (GMF) used fo...
-
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Elkin, G
2001-01-01
.... The increased processing speed and memory size of the 9PAC hardware made it possible for new surveillance algorithms to be developed in software in order to provide improved primary radar and beacon...
-
Biaxial Testing of High-Strength Fabric Improves Design of Inflatable Radar Domes
Krause, David L.; Bartolotta, Paul A.
2001-01-01
Large radar installations around the globe continuously watch the skies, unobtrusively providing security to the United States; these systems have been in active use for the past 50 years. Often situated in extreme environments, the radar dishes require shielding from the harsh elements. Air-inflated domes (over 100 ft in diameter) are one structure of choice for providing this essential protection. The radomes are constructed from highstrength fabric that is strong enough to withstand the inflation pressure, high winds, and other environmental loads, yet transparent to the microwave signal to allow precise radar mapping. This fabric is woven from glass fibers for high strength and embedded in a polytetrafluoroethylene resin matrix, akin to the nonstick coatings used on cookware.
-
18th International Laser Radar Conference
Neuber, Roland; Rairoux, Patrick; Wandinger, Ulla
1997-01-01
Lidar or laser radar, the depth-resolved remote measurement of atmospheric parameters with optical means, has become an important tool in the field of atmospheric and environmental remote sensing. In this volume the latest progress in the development of lidar methods, experiments, and applications is described. The content is based on selected and thoroughly refereed papers presented at the 18th International Laser Radar Conference, Berlin, 22-26 July 1996. The book is divided into six parts which cover the topics of tropospheric aerosols and clouds, lidar in space, wind, water vapor, troposheric trace gases and plumes, and stratospheric and mesospheric profiling. As a supplement to fundamental lidar textbooks this volume may serve as a guide for scientists, engineers, and graduate students through the blossoming field of modern lidar techniques and their contribution to atmospheric and environmental research.
-
Wind mapping offshore in coastal Mediterranean area using SAR images
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Calaudi, Rosamaria; Arena, Felice; Badger, Merete
Satellite observations of the ocean surface from Synthetic Aperture Radars (SAR) provide information about the spatial wind variability over large areas. This is of special interest in the Mediterranean, where spatial wind information is only provided by sparse buoys, often with long periods...... of missing data. Here, we focus on evaluating the use of SAR for offshore wind mapping. Preliminary results from the analysis of SAR-based ocean winds in Mediterranean areas show interesting large scale wind flow features consistent with results from previous studies using numerical models and space borne...
-
Methods of quantitative and qualitative analysis of bird migration with a tracking radar
Bruderer, B.; Steidinger, P.
1972-01-01
Methods of analyzing bird migration by using tracking radar are discussed. The procedure for assessing the rate of bird passage is described. Three topics are presented concerning the grouping of nocturnal migrants, the velocity of migratory flight, and identification of species by radar echoes. The height and volume of migration under different weather conditions are examined. The methods for studying the directions of migration and the correlation between winds and the height and direction of migrating birds are presented.
-
AN/FPS-108 COBRA DANE Space Surveillance Mission Evolution
Chorman, P.; Boggs, J.
2013-09-01
It has been ten years since the COBRA DANE radar was restored to continuous full power operations in a more dedicated role of space debris tracking. Over this time, the satellite catalog population has grown and the overall average RCS value of cataloged objects has decreased dramatically, due to a combination of breakups and collisions together with the increased sensitivity offered by COBRA DANE's support to the network. This shift in catalog composition places new challenges on COBRA DANE and other debris tracking radars (PARCS and Eglin/FPS-85) to consistently track the ever-increasing number of small objects. Space Surveillance Network radars now operate at the limits of their detection performance, tracking several thousand new objects in a size category that only the most powerful and sensitive radars can observe (i.e., COBRA DANE's inherent Spacetrack mission software functionality remained better tuned for its original support role against the larger (known) orbital objects than for its more modern role in acquiring and reporting small debris in an appreciable number -- that is, until now. Several newly-identified software changes offer promise of significantly increased data yield that will make COBRA DANE an even more important asset for this evolving mission. In the course of assisting JSpOC, AFSPC, and USSTRATCOM with the ongoing challenges of lost satellite management, it was discovered that the radar's performance is being artificially restricted by mission software, rather than by the system's overall architectural design (power-aperture envelope and radar resources). This paper captures specific opportunities to improve COBRA DANE's Spacetrack mission performance, several of which are currently implemented and slated to become operational with the next two software releases. With one of the more prominent enhancements, COBRA DANE will be capable of autonomously 'fence tasking' all newly acquired small objects. Under the current operating paradigm
-
Zosel, Amy; Bartelson, Becki Bucher; Bailey, Elise; Lowenstein, Steven; Dart, Rick
2013-02-01
To describe the characteristics and health effects of adolescent (age 13-19 years) prescription drug abuse and misuse using the Researched Abuse Diversion and Addiction-Related Surveillance (RADARS(®)) System. Secondary analysis of data collected from RADARS System participating poison centers was performed. Data for all intentional exposures from 2007 through 2009 were used to describe adolescent prescription opioid (oxycodone, fentanyl, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, morphine, methadone, buprenorphine, and tramadol) and stimulant (methylphenidate and amphetamines) exposures. A total of 16,209 intentional adolescent exposures to prescription drugs were identified, 68% to opioids and 32% to stimulants. The mean age was 16.6 years (SD ± 1.7 years). Slightly more than half (52.4%) of drug mentions involved females. The five most frequently misused or abused drugs were hydrocodone (32%), amphetamines (18%), oxycodone (15%), methylphenidate (14%), and tramadol (11%). Of all exposures, 38% were classified as suspected suicidal. Of adolescents who intentionally exposed themselves to prescription drugs, 30% were treated in a health care facility, 2,792 of whom were admitted to the hospital, including 1,293 to the intensive care unit. A total of 17.2% of intentional exposures were associated with no effect, 38.9% minor effects, 23.3% moderate effects, 3.6% major effects, and 0.1% were associated with death. Oxycodone and methadone were associated with the most deaths. No deaths were associated with exposures to stimulants. Prescription drug misuse and abuse poses an important health problem and results in thousands of hospitalizations of adolescents per year. Further work is needed to develop focused interventions and educational programs to prevent prescription drug abuse and misuse by adolescents. Copyright © 2013 American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Green corona, geomagnetic activity and radar meteor rates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Prikryl, P.
1979-01-01
The short-term dependence of radar meteor rates on geomagnetic activity and/or central meridian passage (CMP) of bright or faint green corona regions is studied. A superimposed-epoch analysis was applied to radar meteor observations from the Ottawa patrol radar (Springhill, Ont.) and Ksub(p)-indices of geomagnetic activity for the period 1963 to 1967. During the minimum of solar activity (1963 to 1965) the CMP of bright coronal regions was followed by the maximum in the daily rates of persistent meteor echoes (>=4s), and the minimum in the daily sums of Ksub(p)-indices whereas the minimum or the maximum, respectively, occurs after the CMP of faint coronal regions. The time delay between the CMP of coronal structures and the corresponding maxima or minima is found to be 3 to 4 days. However, for the period immediately after the minimum of solar activity (1966 to 1967) the above correlation with the green corona is void both for the geomagnetic activity and radar meteor rates. An inverse correlation was found between the radar meteor rates and the geomagnetic activity irrespective of the solar activity. The observed effect can be ascribed to the solar-wind-induced ''geomagnetic'' heating of the upper atmosphere and to the subsequent change in the density gradient in the meteor zone. (author)
-
NORSEWInD satellite wind climatology
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Badger, Merete; Mouche, Alexis
The EU-NORSEWInD project www.norsewind.eu has taken place from August 2008 to July 2012 (4 years). NORSEWInD is short for Northern Seas Wind Index database. In the project ocean surface wind observations from space have been retrieved, processed and analysed. The overall aim of the work...... is to provide new offshore wind climatology map for the entire area of interest based on satellite remote sensing. This has been based on Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) from Envisat ASAR using 9000 scenes re-processed with ECMWF wind direction and CMOD-IFR. The number of overlapping samples range from 450...... in the Irish Sea to more than 1200 in most of the Baltic Sea. Wind resource statistics include maps at 2 km spatial resolution of mean wind speed, Weibull A and k, and energy density at 10 m above sea level. Uncertainty estimates on the number of available samples for each of the four parameters are presented...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Binod Pokharel
2017-02-01
Full Text Available This study describes a downslope wind storm event observed over the Medicine Bow range (Wyoming, USA on 11 January 2013. The University of Wyoming King Air (UWKA made four along-wind passes over a five-hour period over the mountain of interest. These passes were recognized as among the most turbulent ones encountered in many years by crew members. The MacCready turbulence meter aboard the UWKA measured moderate to severe turbulence conditions on each pass in the lee of the mountain range, with eddy dissipation rate values over 0.5 m2/3 s−1. Three rawinsondes were released from an upstream location at different times. This event is simulated using the non-hydrostatic Weather Research and Forecast (WRF model at an inner- domain resolution of 1 km. The model produces a downslope wind storm, notwithstanding some discrepancies between model and rawinsonde data in terms of upstream atmospheric conditions. Airborne Wyoming Cloud Radar (WCR vertical-plane Doppler velocity data from two beams, one pointing to the nadir and one pointing slant forward, are synthesized to obtain a two-dimensional velocity field in the vertical plane below flight level. This synthesis reveals the fine-scale details of an orographic wave breaking event, including strong, persistent downslope acceleration, a strong leeside updraft (up to 10 m·s−1 flanked by counter-rotating vortices, and deep turbulence, extending well above flight level. The analysis of WCR-derived cross-mountain flow in 19 winter storms over the same mountain reveals that cross-mountain flow acceleration and downslope wind formation are difficult to predict from upstream wind and stability profiles.
-
Cardone, V. J.; Pierson, W. J.
1975-01-01
On Skylab, a combination microwave radar-radiometer (S193) made measurements in a tropical hurricane (AVA), a tropical storm, and various extratropical wind systems. The winds at each cell scanned by the instrument were determined by objective numerical analysis techniques. The measured radar backscatter is compared to the analyzed winds and shown to provide an accurate method for measuring winds from space. An operational version of the instrument on an orbiting satellite will be able to provide the kind of measurements in tropical cyclones available today only by expensive and dangerous aircraft reconnaissance. Additionally, the specifications of the wind field in the tropical boundary layer should contribute to improved accuracy of tropical cyclone forecasts made with numerical weather predictions models currently being applied to the tropical atmosphere.
-
Field intercomparison of channel master ADCP with RiverSonde Radar for measuring river discharge
Spain, P.; Marsden, R.; Barrick, D.; Teague, C.; Ruhl, C.
2005-01-01
The RiverSonde radar makes non-contact measurement of a horizontal swath of surface velocity across a river section. This radar, which has worked successfully at several rivers in the Western USA, has shown encouraging correlation with simultaneous measurements of average currents at one level recorded by an acoustic travel-time system. This work reports a field study intercomparing data sets from a 600 kHz Channel Master ADCP with the RiverSonde radar. The primary goal was to begin to explore the robustness of the radar data as a reliable index of discharge. This site Is at Three Mile Slough in Northern California, USA. The larger intent of the work is to examine variability in space and time of the radar's surface currents compared with subsurface flows across the river section. Here we examine data from a couple of periods with strong winds. ?? 2005 IEEE.
-
Jenkins, Andrew R; Reid, Tim; du Plessis, Johan; Colyn, Robin; Benn, Grant; Millikin, Rhonda
2018-01-01
Pre-construction assessments of bird collision risk at proposed wind farms are often confounded by insufficient or poor quality data describing avian flight paths through the development area. These limitations can compromise the practical value of wind farm impact studies. We used radar- and observer-based methods to quantify great white pelican flights in the vicinity of a planned wind farm on the Cape west coast, South Africa, and modelled turbine collision risk under various scenarios. Model outputs were combined with pre-existing demographic data to evaluate the possible influence of the wind farm on the pelican population, and to examine impact mitigation options. We recorded high volumes of great white pelican movement through the wind farm area, coincident with the breeding cycle of the nearby colony and associated with flights to feeding areas located about 50 km away. Pelicans were exposed to collision risk at a mean rate of 2.02 High Risk flights.h-1. Risk was confined to daylight hours, highest during the middle of the day and in conditions of strong north-westerly winds, and 82% of High Risk flights were focused on only five of the proposed 35 turbine placements. Predicted mean mortality rates (22 fatalities.yr-1, 95% Cl, 16-29, with average bird and blade speeds and 95% avoidance rates) were not sustainable, resulting in a negative population growth rate (λ = 0.991). Models suggested that removal of the five highest risk turbines from the project, or institution of a curtailment regimen that shuts down at least these turbines at peak traffic times, could theoretically reduce impacts to manageable levels. However, in spite of the large quantities of high quality data used in our analyses, our collision risk model remains compromised by untested assumptions about pelican avoidance rates and uncertainties about the existing dynamics of the pelican population, and our findings are probably not reliable enough to ensure sustainable development.
-
Understanding the Role of Wind in Reducing the Surface Mass Balance Estimates over East Antarctica
Das, I.; Scambos, T. A.; Koenig, L.; Creyts, T. T.; Bell, R. E.; van den Broeke, M. R.; Lenaerts, J.; Paden, J. D.
2014-12-01
Accurate quantification of surface snow-accumulation over Antarctica is important for mass balance estimates and climate studies based on ice core records. An improved estimate of surface mass balance must include the significant role near-surface wind plays in the sublimation and redistribution of snow across Antarctica. We have developed an empirical model based on airborne radar and lidar observations, and modeled surface mass balance and wind fields to produce a continent-wide prediction of wind-scour zones over Antarctica. These zones have zero to negative surface mass balance, are located over locally steep ice sheet areas (>0.002) and controlled by bedrock topography. The near-surface winds accelerate over these zones, eroding and sublimating the surface snow. This scouring results in numerous localized regions (≤ 200 km2) with reduced surface accumulation. Each year, tens of gigatons of snow on the Antarctic ice sheet are ablated by persistent near-surface katabatic winds over these wind-scour zones. Large uncertainties remain in the surface mass balance estimates over East Antarctica as climate models do not adequately represent the small-scale physical processes that lead to mass loss through sublimation or redistribution over the wind-scour zones. In this study, we integrate Operation IceBridge's snow radar over the Recovery Ice Stream with a series of ice core dielectric and depth-density profiles for improved surface mass balance estimates that reflect the mass loss over the wind-scour zones. Accurate surface mass balance estimates from snow radars require spatially variable depth-density profiles. Using an ensemble of firn cores, MODIS-derived surface snow grain size, modeled accumulation rates and surface temperatures from RACMO2, we assemble spatially variable depth-density profiles and use our mapping of snow density variations to estimate layer mass and net accumulation rates from snow radar layer data. Our study improves the quantification of
-
Wind energy - Opinions of the ADEME
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
2016-04-01
This publication proposes brief presentations and discussions and some data related to the production of electricity by means of wind energy: principle and description, key data (international context, electric power production in France, economic development of the sector), status of knowledge regarding various aspects (assets of wind energy, a clean and local energy, a predictable and manageable source, an increasing competitiveness, a focus on offshore wind energy, control of acoustic and landscape impacts, protection of biodiversity, management of interactions with radars, a steady and clear regulation), perspectives of evolution (a sector of innovations, an opportunity for the development of circular economy, promotion of a participative and citizen wind energy), the case a small units, actions undertaken by the ADEME, and global opinion by the ADEME
-
Observation of snowfall with a low-power FM-CW K-band radar (Micro Rain Radar)
Kneifel, Stefan; Maahn, Maximilian; Peters, Gerhard; Simmer, Clemens
2011-06-01
Quantifying snowfall intensity especially under arctic conditions is a challenge because wind and snow drift deteriorate estimates obtained from both ground-based gauges and disdrometers. Ground-based remote sensing with active instruments might be a solution because they can measure well above drifting snow and do not suffer from flow distortions by the instrument. Clear disadvantages are, however, the dependency of e.g. radar returns on snow habit which might lead to similar large uncertainties. Moreover, high sensitivity radars are still far too costly to operate in a network and under harsh conditions. In this paper we compare returns from a low-cost, low-power vertically pointing FM-CW radar (Micro Rain Radar, MRR) operating at 24.1 GHz with returns from a 35.5 GHz cloud radar (MIRA36) for dry snowfall during a 6-month observation period at an Alpine station (Environmental Research Station Schneefernerhaus, UFS) at 2,650 m height above sea level. The goal was to quantify the potential and limitations of the MRR in relation to what is achievable by a cloud radar. The operational MRR procedures to derive standard radar variables like effective reflectivity factor ( Z e) or the mean Doppler velocity ( W) had to be modified for snowfall since the MRR was originally designed for rain observations. Since the radar returns from snowfall are weaker than from comparable rainfall, the behavior of the MRR close to its detection threshold has been analyzed and a method is proposed to quantify the noise level of the MRR based on clear sky observations. By converting the resulting MRR- Z e into 35.5 GHz equivalent Z e values, a remaining difference below 1 dBz with slightly higher values close to the noise threshold could be obtained. Due to the much higher sensitivity of MIRA36, the transition of the MRR from the true signal to noise can be observed, which agrees well with the independent clear sky noise estimate. The mean Doppler velocity differences between both radars
-
Estimation of wind stress using dual-frequency TOPEX data
Elfouhaily, Tanos; Vandemark, Douglas; Gourrion, Jéro‸me; Chapron, Bertrand
1998-10-01
The TOPEX/POSEIDON satellite carries the first dual-frequency radar altimeter. Monofrequency (Ku-band) algorithms are presently used to retrieve surface wind speed from the altimeter's radar cross-section measurement (σ0Ku). These algorithms work reasonably well, but it is also known that altimeter wind estimates can be contaminated by residual effects, such as sea state, embedded in the σ0Ku measurement. Investigating the potential benefit of using two frequencies for wind retrieval, it is shown that a simple evaluation of TOPEX data yields previously unavailable information, particularly for high and low wind speeds. As the wind speed increases, the dual-frequency data provides a measurement more directly linked to the short-scale surface roughness, which in turn is associated with the local surface wind stress. Using a global TOPEX σ0° data set and TOPEX's significant wave height (Hs) estimate as a surrogate for the sea state's degree of development, it is also shown that differences between the two TOPEX σ0 measurements strongly evidence nonlocal sea state signature. A composite scattering theory is used to show how the dual-frequency data can provide an improved friction velocity model, especially for winds above 7 m/s. A wind speed conversion is included using a sea state dependent drag coefficient fed with TOPEX Hs data. Two colocated TOPEX-buoy data sets (from the National Data Buoy Center (NDBC) and the Structure des Echanges Mer-Atmosphre, Proprietes des Heterogeneites Oceaniques: Recherche Expérimentale (SEMAPHORE) campaign) are employed to test the new wind speed algorithm. A measurable improvement in wind speed estimation is obtained when compared to the monofrequency Witter and Chelton [1991] model.
-
Phased-array radar design application of radar fundamentals
Jeffrey, Thomas
2009-01-01
Phased-Array Radar Design is a text-reference designed for electrical engineering graduate students in colleges and universities as well as for corporate in-house training programs for radar design engineers, especially systems engineers and analysts who would like to gain hands-on, practical knowledge and skills in radar design fundamentals, advanced radar concepts, trade-offs for radar design and radar performance analysis.
-
Upper wind observing systems used for meteorological operations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Nash
Full Text Available Methods of upper wind measurements used in operational meteorology have been reviewed to provide guidance to those developing wind profiler radar systems. The main limitations of the various methods of tracking weather balloons are identified using results from the WMO radiosonde comparisons and additional tests in the United Kingdom. Costs associated with operational balloon measurements are reviewed. The sampling and quality of operational aircraft wind observations are illustrated with examples from the ASDAR system. Measurement errors in horizontal winds are quantified wherever possible. When tracking equipment is functioning correctly, random errors in southerly and westerly wind component measurements from aircraft and weather balloons are usually in the range 0.5-2 m s-1.
-
MATSurv: multisensor air traffic surveillance system
Yeddanapudi, Murali; Bar-Shalom, Yaakov; Pattipati, Krishna R.; Gassner, Richard R.
1995-09-01
This paper deals with the design and implementation of MATSurv 1--an experimental Multisensor Air Traffic Surveillance system. The proposed system consists of a Kalman filter based state estimator used in conjunction with a 2D sliding window assignment algorithm. Real data from two FAA radars is used to evaluate the performance of this algorithm. The results indicate that the proposed algorithm provides a superior classification of the measurements into tracks (i.e., the most likely aircraft trajectories) when compared to the aircraft trajectories obtained using the measurement IDs (squawk or IFF code).
-
Observation of high-resolution wind fields and offshore wind turbine wakes using TerraSAR-X imagery
Gies, Tobias; Jacobsen, Sven; Lehner, Susanne; Pleskachevsky, Andrey
2014-05-01
1. Introduction Numerous large-scale offshore wind farms have been built in European waters and play an important role in providing renewable energy. Therefore, knowledge of behavior of wakes, induced by large wind turbines and their impact on wind power output is important. The spatial variation of offshore wind turbine wake is very complex, depending on wind speed, wind direction, ambient atmospheric turbulence and atmospheric stability. In this study we demonstrate the application of X-band TerraSAR-X (TS-X) data with high spatial resolution for studies on wind turbine wakes in the near and far field of the offshore wind farm Alpha Ventus, located in the North Sea. Two cases which different weather conditions and different wake pattern as observed in the TS-X image are presented. 2. Methods The space-borne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is a unique sensor that provides two-dimensional information on the ocean surface. Due to their high resolution, daylight and weather independency and global coverage, SARs are particularly suitable for many ocean and coastal applications. SAR images reveal wind variations on small scales and thus represent a valuable means in detailed wind-field analysis. The general principle of imaging turbine wakes is that the reduced wind speed downstream of offshore wind farms modulates the sea surface roughness, which in turn changes the Normalized Radar Cross Section (NRCS, denoted by σ0) in the SAR image and makes the wake visible. In this study we present two cases at the offshore wind farm Alpha Ventus to investigate turbine-induced wakes and the retrieved sea surface wind field. Using the wind streaks, visible in the TS-X image and the shadow behind the offshore wind farm, induced by turbine wake, the sea surface wind direction is derived and subsequently the sea surface wind speed is calculated using the latest generation of wind field algorithm XMOD2. 3. Case study alpha ventus Alpha Ventus is located approximately 45 km from the
-
Wave Tank Studies of Phase Velocities of Short Wind Waves
Ermakov, S.; Sergievskaya, I.; Shchegolkov, Yu.
Wave tank studies of phase velocities of short wind waves have been carried out using Ka-band radar and an Optical Spectrum Analyser. The phase velocities were retrieved from measured radar and optical Doppler shifts, taking into account measurements of surface drift velocities. The dispersion relationship was studied in centimetre (cm)- and millimetre(mm)-scale wavelength ranges at different fetches and wind speeds, both for a clean water surface and for water covered with surfactant films. It is ob- tained that the phase velocities do not follow the dispersion relation of linear capillary- gravity waves, increasing with fetch and, therefore, depending on phase velocities of dominant decimetre (dm)-centimetre-scale wind waves. One thus can conclude that nonlinear cm-mm-scale harmonics bound to the dominant wind waves and propagat- ing with the phase velocities of the decimetric waves are present in the wind wave spectrum. The resulting phase velocities of short wind waves are determined by re- lation between free and bound waves. The relative intensity of the bound waves in the spectrum of short wind waves is estimated. It is shown that this relation depends strongly on the surfactant concentration, because the damping effect due to films is different for free and bound waves; this results to changes of phase velocities of wind waves in the presence of surfactant films. This work was supported by MOD, UK via DERA Winfrith (Project ISTC 1774P) and by RFBR (Project 02-05-65102).
-
a Study of Precipitation Using Dual-Frequency and Interferometric Doppler Radars.
Chilson, Phillip Bruce
The primary focus of this dissertation involves the investigation of precipitation using Doppler radar but using distinctly different methods. Each method will be treated separately. The first part describes an investigation of a tropical thunderstorm that occurred in the summer of 1991 over the National Astronomy and Ionosphere Center in Arecibo, Puerto Rico. Observations were made using a vertically pointing, dual-wavelength, collinear beam Doppler radar which permits virtually simultaneous observations of the same pulse volume using transmission and reception of coherent UHF and VHF signals on alternate pulses. This made it possible to measure directly the vertical wind within the sampling volume using the VHF signal while using the UHF signal to study the nature of the precipitation. The observed storm showed strong similarities with systems observed in the Global Atmospheric Research Program's (GARP) Atlantic Tropical Experiment (GATE) study. The experiment provided a means of determining various parameters associated with the storm, such as the vertical air velocity, the mean fall speeds of the precipitation, and the reflectivity. Rogers proposed a means of deducing the mean fall speed of precipitation particles using the radar reflectivity factor. Using the data from our experiment, the mean precipitation fall speeds were calculated and compared with those that would be inferred from Rogers' method. The results suggest the Rogers method of estimating mean precipitation fall speeds to be unreliable in turbulent environments. The second part reports observations made with the 50 MHz Middle and Upper Atmosphere (MU) radar located at Shigaraki, Japan during May of 1992. The facility was operated in a spatial interferometry (SI) mode while observing frontal precipitation. The data suggest that the presence of precipitation can produce a bias in the SI cross-spectral phase that in turn creates an overestimation of the horizontal wind. The process is likened to
-
Mass Processing of Sentinel-1 Images for Maritime Surveillance
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Carlos Santamaria
2017-07-01
Full Text Available The free, full and open data policy of the EU’s Copernicus programme has vastly increased the amount of remotely sensed data available to both operational and research activities. However, this huge amount of data calls for new ways of accessing and processing such “big data”. This paper focuses on the use of Copernicus’s Sentinel-1 radar satellite for maritime surveillance. It presents a study in which ship positions have been automatically extracted from more than 11,500 Sentinel-1A images collected over the Mediterranean Sea, and compared with ship position reports from the Automatic Identification System (AIS. These images account for almost all the Sentinel-1A acquisitions taken over the area during the two-year period from the start of the operational phase in October 2014 until September 2016. A number of tools and platforms developed at the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre (JRC that have been used in the study are described in the paper. They are: (1 Search for Unidentified Maritime Objects (SUMO, a tool for ship detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR images; (2 the JRC Earth Observation Data and Processing Platform (JEODPP, a platform for efficient storage and processing of large amounts of satellite images; and (3 Blue Hub, a maritime surveillance GIS and data fusion platform. The paper presents the methodology and results of the study, giving insights into the new maritime surveillance knowledge that can be gained by analysing such a large dataset, and the lessons learnt in terms of handling and processing the big dataset.
-
Fractionally Spaced Constant Modulus Equalizer with Recognition Capability for Digital Array Radar
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Feng Wang
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Fractionally spaced blind equalizer (BE based on constant modulus criteria is exploited to compensate for the channel-to-channel mismatch in a digital array radar. We apply the technique of recognition to improve the stability and reliability of the BE. The surveillance of the calibration signal and the convergence property of BE are both implemented with recognition description words. BE with cognitive capability is appropriate for the equalization of a digital array radar with thousands of channels and hundreds of working frequencies, where reliability becomes the most concerned indicator. The improvement of performance in the accidental scenarios is tested via numerical simulations with the cost of increased computational complexity.
-
Fpga based L-band pulse doppler radar design and implementation
Savci, Kubilay
As its name implies RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging) is an electromagnetic sensor used for detection and locating targets from their return signals. Radar systems propagate electromagnetic energy, from the antenna which is in part intercepted by an object. Objects reradiate a portion of energy which is captured by the radar receiver. The received signal is then processed for information extraction. Radar systems are widely used for surveillance, air security, navigation, weather hazard detection, as well as remote sensing applications. In this work, an FPGA based L-band Pulse Doppler radar prototype, which is used for target detection, localization and velocity calculation has been built and a general-purpose Pulse Doppler radar processor has been developed. This radar is a ground based stationary monopulse radar, which transmits a short pulse with a certain pulse repetition frequency (PRF). Return signals from the target are processed and information about their location and velocity is extracted. Discrete components are used for the transmitter and receiver chain. The hardware solution is based on Xilinx Virtex-6 ML605 FPGA board, responsible for the control of the radar system and the digital signal processing of the received signal, which involves Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR) detection and Pulse Doppler processing. The algorithm is implemented in MATLAB/SIMULINK using the Xilinx System Generator for DSP tool. The field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) implementation of the radar system provides the flexibility of changing parameters such as the PRF and pulse length therefore it can be used with different radar configurations as well. A VHDL design has been developed for 1Gbit Ethernet connection to transfer digitized return signal and detection results to PC. An A-Scope software has been developed with C# programming language to display time domain radar signals and detection results on PC. Data are processed both in FPGA chip and on PC. FPGA uses fixed
-
Remote Sensing of Surface Soil Moisture using Semi-Concurrent Radar and Radiometer Observations
Li, L.; Ouellette, J. D.; Colliander, A.; Cosh, M. H.; Caldwell, T. G.; Walker, J. P.
2017-12-01
Radar backscatter and radiometer brightness temperature both have well-documented sensitivity to surface soil moisture, particularly in the microwave regime. While radiometer-derived soil moisture retrievals have been shown to be stable and accurate, they are only available at coarse spatial resolutions on the order of tens of kilometers. Backscatter from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is similarly sensitive to soil moisture but can yield higher spatial resolutions, with pixel sizes about an order of magnitude smaller. Soil moisture retrieval from radar backscatter is more difficult, however, due to the combined sensitivity of radar scattering to surface roughness, vegetation structure, and soil moisture. The algorithm uses a time-series of SAR data to retrieval soil moisture information, constraining the SAR-derived soil moisture estimates with radiometer observations. This effectively combines the high spatial resolution offered by SAR with the precision offered by passive radiometry. The algorithm is a change detection approach which maps changes in the radar backscatter to changes in surface soil moisture. This new algorithm differs from existing retrieval techniques in that it does not require ancillary vegetation information, but assumes vegetation and surface roughness are stable between pairs of consecutive radar overpasses. Furthermore, this method does not require a radar scattering model for the vegetation canopy, nor the use of a training data set. The algorithm works over a long time series, and is constrained by hard bounds which are defined using a coarse-resolution radiometer soil moisture product. The presentation will include soil moisture retrievals from Soil Moisture Active/Passive (SMAP) SAR data. Two sets of optimization bounds will constrain the radar change detection algorithm: one defined by SMAP radiometer retrievals and one defined by WindSat radiometer retrievals. Retrieved soil moisture values will be presented on a world map and will
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
E. M. Griffin
2004-03-01
Full Text Available The climatological behaviour of the thermospheric meridional wind above Kiruna, Sweden (67.4°N, 20.4°E has been investigated for seasonal and solar cycle dependence using six different techniques, comprising both model and experimental sources. Model output from both the empirical Horizontal Wind Model (HWM (Hedin et al., 1988 and the numerical Coupled Thermosphere and Ionosphere Model (CTIM are compared to the measured behaviour at Kiruna, as a single site example. The empirical International Reference Ionosphere (IRI model is used as input to an implementation of servo theory, to provide another climatology combining empirical input with a theoretical framework. The experimental techniques have been introduced in a companion paper in this issue and provide climatologies from direct measurements, using Fabry-Perot Interferometers (FPI, together with 2 separate techniques applied to the European Incoherent Scatter radar (EISCAT database to derive neutral winds. One of these techniques uses the same implementation of servo theory as has been used with the IRI model. Detailed comparisons for each season and solar activity category allow for conclusions to be drawn as to the major influences on the climatological behaviour of the wind at this latitude. Comparison of the incoherent scatter radar (ISR derived neutral winds with FPI, empirical model and numerical model winds is important to our understanding and judgement of the validity of the techniques used to derive thermospheric wind databases. The comparisons also test model performance and indicate possible reasons for differences found between the models. In turn, the conclusions point to possible improvements in their formulation. In particular it is found that the empirical models are over-reliant on mid-latitude data in their formulation, and fail to provide accurate estimates of the winds at high-latitudes.
Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (thermospheric dynamics -
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
E. M. Griffin
2004-03-01
Full Text Available The climatological behaviour of the thermospheric meridional wind above Kiruna, Sweden (67.4°N, 20.4°E has been investigated for seasonal and solar cycle dependence using six different techniques, comprising both model and experimental sources. Model output from both the empirical Horizontal Wind Model (HWM (Hedin et al., 1988 and the numerical Coupled Thermosphere and Ionosphere Model (CTIM are compared to the measured behaviour at Kiruna, as a single site example. The empirical International Reference Ionosphere (IRI model is used as input to an implementation of servo theory, to provide another climatology combining empirical input with a theoretical framework. The experimental techniques have been introduced in a companion paper in this issue and provide climatologies from direct measurements, using Fabry-Perot Interferometers (FPI, together with 2 separate techniques applied to the European Incoherent Scatter radar (EISCAT database to derive neutral winds. One of these techniques uses the same implementation of servo theory as has been used with the IRI model. Detailed comparisons for each season and solar activity category allow for conclusions to be drawn as to the major influences on the climatological behaviour of the wind at this latitude. Comparison of the incoherent scatter radar (ISR derived neutral winds with FPI, empirical model and numerical model winds is important to our understanding and judgement of the validity of the techniques used to derive thermospheric wind databases. The comparisons also test model performance and indicate possible reasons for differences found between the models. In turn, the conclusions point to possible improvements in their formulation. In particular it is found that the empirical models are over-reliant on mid-latitude data in their formulation, and fail to provide accurate estimates of the winds at high-latitudes. Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (thermospheric dynamics
-
Non-Economic Obstacles to Wind Deployment: Issues and Regional Differences (Presentation)
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Baring-Gould, I.
2014-05-01
This presentation provides an overview of national obstacles to wind deployment, with regional assessments. A special mention of offshore projects and distributed wind projects is provided. Detailed maps examine baseline capacity, military and flight radar, golden and bald eagle habitat, bat habitat, whooping crane habitat, and public lands. Regional deployment challenges are also discussed.
-
Application of model-based spectral analysis to wind-profiler radar observations
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Boyer, E. [ENS, Cachan (France). LESiR; Petitdidier, M.; Corneil, W. [CETP, Velizy (France); Adnet, C. [THALES Air Dfense, Bagneux (France); Larzabal, P. [ENS, Cachan (France). LESiR; IUT, Cachan (France). CRIIP
2001-08-01
A classical way to reduce a radar's data is to compute the spectrum using FFT and then to identify the different peak contributions. But in case an overlapping between the different echoes (atmospheric echo, clutter, hydrometer echo..) exists, Fourier-like techniques provide poor frequency resolution and then sophisticated peak-identification may not be able to detect the different echoes. In order to improve the number of reduced data and their quality relative to Fourier spectrum analysis, three different methods are presented in this paper and applied to actual data. Their approach consists of predicting the main frequency-components, which avoids the development of very sophisticated peak-identification algorithms. The first method is based on cepstrum properties generally used to determine the shift between two close identical echoes. We will see in this paper that this method cannot provide a better estimate than Fourier-like techniques in an operational use. The second method consists of an autoregressive estimation of the spectrum. Since the tests were promising, this method was applied to reduce the radar data obtained during two thunderstorms. The autoregressive method, which is very simple to implement, improved the Doppler-frequency data reduction relative to the FFT spectrum analysis. The third method exploits a MUSIC algorithm, one of the numerous subspace-based methods, which is well adapted to estimate spectra composed of pure lines. A statistical study of performances of this method is presented, and points out the very good resolution of this estimator in comparison with Fourier-like techniques. Application to actual data confirms the good qualities of this estimator for reducing radar's data. (orig.)
-
Marine parameters from synergy of optical and radar satellite data
Lehner, S.; Hoja, D.; Schulz-Stellenfleth, J.
In 2001 the European Space Agency ESA will launch the earth observation satellite ENVISAT. It will carry several instruments that provide new opportunities to measure oceanographic variables. Together, they represent the main measurement techniques of satellite oceanography, and complement each other in an ideal manner. These instruments are to be used in synergy to: Improve the analysis of measured wind and ocean wave fields, and thereby improve weather forecasting at weather centers; Determine the extent and variables of sea ice and develop a five-day sea ice prediction model, to support maritime shipping and offshore activities; Monitor and map sediment and suspended matter transport in coastal regions, especially in areas with large river estuaries, which greatly affects shipping lanes, harbors, and dredging activities; Monitor hydrobiological and bio-geochemical variables related to water quality in coastal regions and large inland waters, which affects ecology, coastal development, aquaculture, drinking water supplies, and tourism. To prepare the oceanographic community to make best use of the ENVISAT sensors in the pre-launch phase, existing algorithms to derive marine parameters are used and validated using data from the ERS SAR, the ERS RA, SeaWiFS and IRS MOS sensors now in operation. Derived products are used to address problems that can best be tackled using the synergy of radar and optical data, such as the effect of surface slicks on radar wind measurements, of sea state on ocean color, of wind and waves on the resuspension of suspended matter, and of wind and waves on sea ice variables.
-
Aulenbacher, Uwe; Rech, Klaus; Sedlmeier, Johannes; Pratisto, Hans; Wellig, Peter
2014-10-01
Ground based millimeter wave radar sensors offer the potential for a weather-independent automatic ground surveillance at day and night, e.g. for camp protection applications. The basic principle and the experimental verification of a radar system concept is described, which by means of an extreme off-axis positioning of the antenna(s) combines azimuthal mechanical beam steering with the formation of a circular-arc shaped synthetic aperture (SA). In automatic ground surveillance the function of search and detection of moving ground targets is performed by means of the conventional mechanical scan mode. The rotated antenna structure designed as a small array with two or more RX antenna elements with simultaneous receiver chains allows to instantaneous track multiple moving targets (monopulse principle). The simultaneously operated SAR mode yields areal images of the distribution of stationary scatterers. For ground surveillance application this SAR mode is best suited for identifying possible threats by means of change detection. The feasibility of this concept was tested by means of an experimental radar system comprising of a 94 GHz (W band) FM-CW module with 1 GHz bandwidth and two RX antennas with parallel receiver channels, placed off-axis at a rotating platform. SAR mode and search/track mode were tested during an outdoor measurement campaign. The scenery of two persons walking along a road and partially through forest served as test for the capability to track multiple moving targets. For SAR mode verification an image of the area composed of roads, grassland, woodland and several man-made objects was reconstructed from the measured data.
-
Design and Implementation of a FPGA and DSP Based MIMO Radar Imaging System
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wei Wang
2015-06-01
Full Text Available The work presented in this paper is aimed at the implementation of a real-time multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO imaging radar used for area surveillance. In this radar, the equivalent virtual array method and time-division technique are applied to make 16 virtual elements synthesized from the MIMO antenna array. The chirp signal generater is based on a combination of direct digital synthesizer (DDS and phase locked loop (PLL. A signal conditioning circuit is used to deal with the coupling effect within the array. The signal processing platform is based on an efficient field programmable gates array (FPGA and digital signal processor (DSP pipeline where a robust beamforming imaging algorithm is running on. The radar system was evaluated through a real field experiment. Imaging capability and real-time performance shown in the results demonstrate the practical feasibility of the implementation.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
T. Rigo
2010-09-01
Full Text Available Monitoring thunderstorms activity is an essential part of operational weather surveillance given their potential hazards, including lightning, hail, heavy rainfall, strong winds or even tornadoes. This study has two main objectives: firstly, the description of a methodology, based on radar and total lightning data to characterise thunderstorms in real-time; secondly, the application of this methodology to 66 thunderstorms that affected Catalonia (NE Spain in the summer of 2006. An object-oriented tracking procedure is employed, where different observation data types generate four different types of objects (radar 1-km CAPPI reflectivity composites, radar reflectivity volumetric data, cloud-to-ground lightning data and intra-cloud lightning data. In the framework proposed, these objects are the building blocks of a higher level object, the thunderstorm.
The methodology is demonstrated with a dataset of thunderstorms whose main characteristics, along the complete life cycle of the convective structures (development, maturity and dissipation, are described statistically. The development and dissipation stages present similar durations in most cases examined. On the contrary, the duration of the maturity phase is much more variable and related to the thunderstorm intensity, defined here in terms of lightning flash rate. Most of the activity of IC and CG flashes is registered in the maturity stage. In the development stage little CG flashes are observed (2% to 5%, while for the dissipation phase is possible to observe a few more CG flashes (10% to 15%. Additionally, a selection of thunderstorms is used to examine general life cycle patterns, obtained from the analysis of normalized (with respect to thunderstorm total duration and maximum value of variables considered thunderstorm parameters. Among other findings, the study indicates that the normalized duration of the three stages of thunderstorm life cycle is similar in most thunderstorms -
Rigo, T.; Pineda, N.; Bech, J.
2010-09-01
Monitoring thunderstorms activity is an essential part of operational weather surveillance given their potential hazards, including lightning, hail, heavy rainfall, strong winds or even tornadoes. This study has two main objectives: firstly, the description of a methodology, based on radar and total lightning data to characterise thunderstorms in real-time; secondly, the application of this methodology to 66 thunderstorms that affected Catalonia (NE Spain) in the summer of 2006. An object-oriented tracking procedure is employed, where different observation data types generate four different types of objects (radar 1-km CAPPI reflectivity composites, radar reflectivity volumetric data, cloud-to-ground lightning data and intra-cloud lightning data). In the framework proposed, these objects are the building blocks of a higher level object, the thunderstorm. The methodology is demonstrated with a dataset of thunderstorms whose main characteristics, along the complete life cycle of the convective structures (development, maturity and dissipation), are described statistically. The development and dissipation stages present similar durations in most cases examined. On the contrary, the duration of the maturity phase is much more variable and related to the thunderstorm intensity, defined here in terms of lightning flash rate. Most of the activity of IC and CG flashes is registered in the maturity stage. In the development stage little CG flashes are observed (2% to 5%), while for the dissipation phase is possible to observe a few more CG flashes (10% to 15%). Additionally, a selection of thunderstorms is used to examine general life cycle patterns, obtained from the analysis of normalized (with respect to thunderstorm total duration and maximum value of variables considered) thunderstorm parameters. Among other findings, the study indicates that the normalized duration of the three stages of thunderstorm life cycle is similar in most thunderstorms, with the longest
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sadiel Novo
2008-03-01
Full Text Available Una de las principales aplicaciones del radar meteorológico es el pronóstico inmediato (decenas de minutos a unas pocas horas de antelación de los eventos de precipitación convectiva. Esto reviste gran importancia pues es precisamente en este lapso de tiempo donde son menos efectivos los pronósticos numéricos. Se repasan brevemente algunas de las técnicas de pronóstico inmediato reportadas en los últimos años, haciendo énfasis en aquellas que emplean solamente información de un radar convencional. Se distingue entre las que pronostican el movimiento de las tormentas como un todo y aquellas que permiten distinguir su movimiento interno, señalando sus ventajas y desventajas en situaciones meteorológicas concretas. Como ejemplo se presentan, para un caso de estudio escogido, aplicaciones simples de dos de estas técnicas. Por último se discute la utilidad de la técnica del sistema de referencia móvil para obtener las componentes del viento no observadas a partir de un solo radar Doppler o incluso un radar convencional, y sus implicaciones para la obtención de magnitudes termodinámicas.One of the main applications of the meteorological radar is the nowcasting (some tens of minutes to some hours forward of convective precipitation events. It has a great importance since this is the space of time in which the numerical forecasting is less effective. Some of the nowcasting techniques reported in the last years are reviewed shortly, making emphasis in those that use only information from a conventional radar. A distinction is made among those that predict the total movement of the storms and those that allow distinguishing their internal movement, pointing out their advantages and disadvantages in concrete meteorological situations. It is presented, for a chosen case of study, simple applications of two of these techniques. Finally, the utility of the moving frame of reference technique for obtaining the not observed wind components
-
The effect of stability on the coastal gradients at the Anholt wind farm
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Volker, Patrick; Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Badger, Merete
We use Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and SCADA measurements and mesoscale model simulations from the Weather Research and Forecast (WRF) model[3] to analyse the flow conditions at the Danish offshore wind farm at Anholt. The first Danish oshore wind farms have been installed in the North Sea of ...
-
Regional frequency analysis of extreme rainfall in Belgium based on radar estimates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
E. Goudenhoofdt
2017-10-01
Full Text Available In Belgium, only rain gauge time series have been used so far to study extreme rainfall at a given location. In this paper, the potential of a 12-year quantitative precipitation estimation (QPE from a single weather radar is evaluated. For the period 2005–2016, 1 and 24 h rainfall extremes from automatic rain gauges and collocated radar estimates are compared. The peak intensities are fitted to the exponential distribution using regression in Q-Q plots with a threshold rank which minimises the mean squared error. A basic radar product used as reference exhibits unrealistic high extremes and is not suitable for extreme value analysis. For 24 h rainfall extremes, which occur partly in winter, the radar-based QPE needs a bias correction. A few missing events are caused by the wind drift associated with convective cells and strong radar signal attenuation. Differences between radar and gauge rainfall values are caused by spatial and temporal sampling, gauge underestimations and radar errors. Nonetheless the fit to the QPE data is within the confidence interval of the gauge fit, which remains large due to the short study period. A regional frequency analysis for 1 h duration is performed at the locations of four gauges with 1965–2008 records using the spatially independent QPE data in a circle of 20 km. The confidence interval of the radar fit, which is small due to the sample size, contains the gauge fit for the two closest stations from the radar. In Brussels, the radar extremes are significantly higher than the gauge rainfall extremes, but similar to those observed by an automatic gauge during the same period. The extreme statistics exhibit slight variations related to topography. The radar-based extreme value analysis can be extended to other durations.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Mihalikova
2012-09-01
Full Text Available Tropopause folds are one of the mechanisms of stratosphere–troposphere exchange, which can bring ozone rich stratospheric air to low altitudes in the extra-tropical regions. They have been widely studied at northern mid- or high latitudes, but so far almost no studies have been made at mid- or high southern latitudes. The Moveable Atmospheric Radar for Antarctica (MARA, a 54.5 MHz wind-profiler radar, has operated at the Swedish summer station Wasa, Antarctica (73° S, 13.5° W during austral summer seasons from 2007 to 2011 and has observed on several occasions signatures similar to those caused by tropopause folds at comparable Arctic latitudes. Here a case study is presented of one of these events when an ozonesonde successfully sampled the fold. Analysis from European Center for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (ECMWF is used to study the circumstances surrounding the event, and as boundary conditions for a mesoscale simulation using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF model. The fold is well resolved by the WRF simulation, and occurs on the poleward side of the polar jet stream. However, MARA resolves fine-scale layering associated with the fold better than the WRF simulation.
-
Horizontal maps of echo power in the lower stratosphere using the MU radar
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Hirono
2004-03-01
Full Text Available In recent works, zenithal and azimuthal angle variations of echo power measured by VHF Stratosphere-Troposphere (ST radars have been analyzed in detail using different radar multi-beam configurations. It was found that the azimuthal angle corresponding to maximum echo power is closely related to the direction of the horizontal wind shear. These properties indicate that local wind shear affects the tilt of the scatterers. Moreover, horizontal maps of echo power collected using a large set of beams steered pulse-to-pulse up to 40 degrees off zenith revealed that the power distribution pattern in the troposphere is often skewed. In this work, a three-dimensional description of echo power variations up to 24 degrees off zenith is shown for measurements in the lower stratosphere (i.e. up to approximately 20km using a "sequential multi-beam" (SMB configuration. Such a description was not possible above the tropopause with classical multi-beam configurations because of the loss of radar sensitivity due to the limited integration time by the use of a large number of beams. This work attempts to complete previous descriptions of the phenomenon by some observations in the lower stratosphere discussed in association with complementary balloon measurements. Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (turbulence – Radio Science (remote sensing
-
Valencia, J. M.; Sepúlveda, J.; Hoyos, C.; Herrera, L.
2017-12-01
Characterization and identification of fire and hailstorm events using weather radar data in a tropical complex topography region is an important task in risk management and agriculture. Polarimetric variables from a C-Band Dual polarization weather radar have potential uses in particle classification, due to the relationship their sensitivity to shape, spatial orientation, size and fall behavior of particles. In this sense, three forest fires and two chemical fires were identified for the Áburra Valley regions. Measurements were compared between each fire event type and with typical data radar retrievals for liquid precipitation events. Results of this analysis show different probability density functions for each type of event according to the particles present in them. This is very important and useful result for early warning systems to avoid precipitation false alarms during fire events within the study region, as well as for the early detection of fires using radar retrievals in remote cases. The comparative methodology is extended to hailstorm cases. Complementary sensors like laser precipitation sensors (LPM) disdrometers and meteorological stations were used to select dates of solid precipitation occurrence. Then, in this dates weather radar data variables were taken in pixels surrounding the stations and solid precipitation polar values were statistically compared with liquid precipitation values. Spectrum precipitation measured by LPM disdrometer helps to define typical features like particles number, fall velocities and diameters for both precipitation types. In addition, to achieve a complete hailstorm characterization, other meteorological variables were analyzed: wind field from meteorological stations and radar wind profiler, profiling data from Micro Rain Radar (MRR), and thermodynamic data from a microwave radiometer.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Raynal, Ann Marie [Sandia National Laboratories (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States); Hensley, Jr., William H. [Sandia National Laboratories (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States); Burns, Bryan L. [Sandia National Laboratories (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States); Doerry, Armin Walter [Sandia National Laboratories (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States)
2014-11-01
The linear ground distance per unit time and ground area covered per unit time of producing synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imagery, termed rate of advance (ROA) and area coverage rate (ACR), are important metrics for platform and radar performance in surveillance applications. These metrics depend on many parameters of a SAR system such as wavelength, aircraft velocity, resolution, antenna beamwidth, imaging mode, and geometry. Often the effects of these parameters on rate of advance and area coverage rate are non-linear. This report addresses the impact of different parameter spaces as they relate to rate of advance and area coverage rate performance.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. Chandra
2008-09-01
Full Text Available A campaign to study turbulence in the mesosphere, over low latitudes in India, using rocket-borne measurements and Indian MST radar, was conducted during July 2004. A rocket-borne Langmuir probe detected a spectrum of electron density irregularities, with scale sizes in the range of about 1 m to 1 km, in 67.5–78.0 km and 84–89 km altitude regions over a low latitude station Sriharikota (13.6° N, 80.2° E. A rocket-borne chaff experiment measured zonal and meridional winds about 30 min after the Langmuir probe flight. The MST radar located at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E, which is about 100 km west of Sriharikota, also detected the presence of a strong scattering layer in 73.5–77.5 km region from which radar echoes corresponding to 3 m irregularities were received. Based on the region of occurrence of irregularities, which was highly collisional, presence of significant shears in zonal and meridional components of wind measured by the chaff experiment, 10 min periodicity in zonal and meridional winds obtained by the MST radar and the nature of wave number spectra of the irregularities, it is suggested that the observed irregularities were produced through the neutral turbulence mechanism. The percentage amplitude of fluctuations across the entire scale size range showed that the strength of turbulence was stronger in the lower altitude regions and decreased with increasing altitude. It was also found that the amplitude of fluctuations was large in regions of steeper electron density gradients. MST radar observations showed that at smaller scales of turbulence such as 3 m, (a the thickness of the turbulent layer was between 2 and 3 km and (b and fine structures, with layer thicknesses of about a km or less were also embedded in these layers. Rocket also detected 3-m fluctuations, which were very strong (a few percent in lower altitudes (67.5 to 71.0 km and small but clearly well above the noise floor at higher altitudes. Rocket and radar
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Chandra, H.; Sinha, H.S.S.; Das, U.; Misra, R.N.; Das, S.R. [Physical Research Lab., Ahmedabad (India); Datta, J.; Chakravarty, S.C. [ISRO Headquarters, Bangalore (India); Patra, A.K.; Vekateswara Rao, N.; Narayana Rao, D. [National Atmospheric Research Lab., Tirupati (India)
2008-07-01
A campaign to study turbulence in the mesosphere, over low latitudes in India, using rocket-borne measurements and Indian MST radar, was conducted during July 2004. A rocket-borne Langmuir probe detected a spectrum of electron density irregularities, with scale sizes in the range of about 1 m to 1 km, in 67.5-78.0 km and 84-89 km altitude regions over a low latitude station Sriharikota (13.6 N, 80.2 E). A rocket-borne chaff experiment measured zonal and meridional winds about 30 min after the Langmuir probe flight. The MST radar located at Gadanki (13.5 N, 79.2 E), which is about 100 km west of Sriharikota, also detected the presence of a strong scattering layer in 73.5-77.5 km region from which radar echoes corresponding to 3 m irregularities were received. Based on the region of occurrence of irregularities, which was highly collisional, presence of significant shears in zonal and meridional components of wind measured by the chaff experiment, 10 min periodicity in zonal and meridional winds obtained by the MST radar and the nature of wave number spectra of the irregularities, it is suggested that the observed irregularities were produced through the neutral turbulence mechanism. The percentage amplitude of fluctuations across the entire scale size range showed that the strength of turbulence was stronger in the lower altitude regions and decreased with increasing altitude. It was also found that the amplitude of fluctuations was large in regions of steeper electron density gradients. MST radar observations showed that at smaller scales of turbulence such as 3 m, (a) the thickness of the turbulent layer was between 2 and 3 km and (b) and fine structures, with layer thicknesses of about a km or less were also embedded in these layers. Rocket also detected 3-m fluctuations, which were very strong (a few percent) in lower altitudes (67.5 to 71.0 km) and small but clearly well above the noise floor at higher altitudes. Rocket and radar results also point to the
-
Improved Detection of Human Respiration Using Data Fusion Basedon a Multistatic UWB Radar
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hao Lv
2016-09-01
Full Text Available This paper investigated the feasibility for improved detection of human respiration using data fusion based on a multistatic ultra-wideband (UWB radar. UWB-radar-based respiration detection is an emerging technology that has great promise in practice. It can be applied to remotely sense the presence of a human target for through-wall surveillance, post-earthquake search and rescue, etc. In these applications, a human target’s position and posture are not known a priori. Uncertainty of the two factors results in a body orientation issue of UWB radar, namely the human target’s thorax is not always facing the radar. Thus, the radial component of the thorax motion due to respiration decreases and the respiratory motion response contained in UWB radar echoes is too weak to be detected. To cope with the issue, this paper used multisensory information provided by the multistatic UWB radar, which took the form of impulse radios and comprised one transmitting and four separated receiving antennas. An adaptive Kalman filtering algorithm was then designed to fuse the UWB echo data from all the receiving channels to detect the respiratory-motion response contained in those data. In the experiment, a volunteer’s respiration was correctly detected when he curled upon a camp bed behind a brick wall. Under the same scenario, the volunteer’s respiration was detected based on the radar’s single transmitting-receiving channels without data fusion using conventional algorithm, such as adaptive line enhancer and single-channel Kalman filtering. Moreover, performance of the data fusion algorithm was experimentally investigated with different channel combinations and antenna deployments. The experimental results show that the body orientation issue for human respiration detection via UWB radar can be dealt well with the multistatic UWB radar and the Kalman-filter-based data fusion, which can be applied to improve performance of UWB radar in real applications.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lin Ren
2017-11-01
Full Text Available This study analyzed the noise equivalent sigma zero (NESZ and ocean wind sensitivity for Chinese C-band Gaofen-3 (GF-3 quad-polarization synthetic aperture radar (SAR measurements to facilitate further operational wind extraction from GF-3 data. Data from the GF-3 quad-polarization SAR and collocated winds from both NOAA/NCEP Global Forecast System (GFS atmospheric model and National Data Buoy Center (NDBC buoys were used in the analysis. For NESZ, the co-polarization was slightly higher compared to the cross-polarization. Regarding co-polarization and cross-polarization, NESZ was close to RadarSAT-2 and Sentinel-1 A. Wind sensitivity was analyzed by evaluating the dependence on winds in terms of normalized radar cross-sections (NRCS and polarization combinations. The closest geophysical model function (GMF and the polarization ratio (PR model to GF-3 data were determined by comparing data and the model results. The dependence of co-polarized NRCS on wind speed and azimuth angle was consistent with the proposed GMF models. The combination of CMOD5 and CMOD5.N was considered to be the closest GMF in co-polarization. The cross-polarized NRCS exhibited a strong linear relationship with moderate wind speeds higher than 4 m·s−1, but a weak correlation with the azimuth angle. The proposed model was considered as the closest GMF in cross-polarization. For polarization combinations, PR and polarization difference (PD were considered. PR increased only with the incidence angle, whereas PD increased with wind speed and varied with azimuth angle. There were three very close PR models and each can be considered as the closest. Preliminary results indicate that GF-3 quad-polarization data are valid and have the ability to extract winds in each polarization.
-
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Mbatha, N
2010-01-01
Full Text Available . The mean zonal wind (from SANAE HF radar) at the MLT shows reversal in approximately 7 days before the reversal at 10 hPa (from NCEP). This indicates that there was a downwards propagation of circulation disturbance. Westerly zonal winds dominate the winter...
-
Mercier, François; Chazottes, Aymeric; Barthès, Laurent; Mallet, Cécile
2016-07-01
This paper presents a novel framework for retrieving the vertical raindrop size distribution (DSD) and vertical wind profiles during light rain events. This is also intended as a tool to better characterize rainfall microphysical processes. It consists in coupling K band Doppler spectra and ground disdrometer measurements (raindrop fluxes) in a 2-D numerical model propagating the DSD from the clouds to the ground level. The coupling is done via a 4-D-VAR data assimilation algorithm. As a first step, in this paper, the dynamical model and the geometry of the problem are quite simple. They do not allow the complexity implied by all rain microphysical processes to be encompassed (evaporation, coalescence breakup and horizontal air motion are not taken into account). In the end, the model is limited to the fall of droplets under gravity, modulated by the effects of vertical winds. The framework is thus illustrated with light, stratiform rain events. We firstly use simulated data sets (data assimilation twin experiment) to show that the algorithm is able to retrieve the DSD profiles and vertical winds. It also demonstrates the ability of the algorithm to deal with the atmospheric turbulence (broadening of the Doppler spectra) and the instrumental noise. The method is then applied to a real case study which was conducted in the southwest of France during the autumn 2013. The data set collected during a long, quiet event (6 h duration, rain rate between 2 and 7 mm h-1) comes from an optical disdrometer and a 24 GHz vertically pointing Doppler radar. We show that the algorithm is able to reproduce the observations and retrieve realistic DSD and vertical wind profiles, when compared to what could be expected for such a rain event. A goal for this study is to apply it to extended data sets for a validation with independent data, which could not be done with our limited 2013 data. Other data sets would also help to parameterize more processes needed in the model (evaporation
-
The Effect of Wind Forcing on Modeling Coastal Circulation at a Marine Renewable Test Site
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lei Ren
2017-12-01
Full Text Available The hydrodynamic circulation in estuaries is primarily driven by tides, river inflows and surface winds. While tidal and river data can be quite easily obtained for input to hydrodynamic models, sourcing accurate surface wind data is problematic. Inaccurate wind data can lead to inaccuracies in the surface currents computed by three-dimensional hydrodynamic models. In this research, a high-resolution wind model was coupled with a three-dimensional hydrodynamic model of Galway Bay, a semi-enclosed estuary on the west coast of Ireland, to investigate the effect of wind forcing on model accuracy. Two wind-forcing conditions were investigated: (1 using wind data measured onshore on the NUI Galway campus (NUIG and (2 using offshore wind data provided by a high resolution wind model (HR. A scenario with no wind forcing (NW was also assessed. The onshore wind data varied with time but the speed and direction were applied across the full model domain. The modeled offshore wind fields varied with both time and space. The effect of wind forcing on modeled hydrodynamics was assessed via comparison of modeled surface currents with surface current measurements obtained from a High-Frequency (HF radar Coastal Ocean Dynamics Applications Radar (CODAR observation system. Results indicated that winds were most significant in simulating the north-south surface velocity component. The model using high resolution temporally- and spatially-varying wind data achieved better agreement with the CODAR surface currents than the model using the onshore wind measurements and the model without any wind forcing.
-
Lanzagorta, Marco
2011-01-01
This book offers a concise review of quantum radar theory. Our approach is pedagogical, making emphasis on the physics behind the operation of a hypothetical quantum radar. We concentrate our discussion on the two major models proposed to date: interferometric quantum radar and quantum illumination. In addition, this book offers some new results, including an analytical study of quantum interferometry in the X-band radar region with a variety of atmospheric conditions, a derivation of a quantum radar equation, and a discussion of quantum radar jamming.This book assumes the reader is familiar w
-
Ecology of fall-migrating ducks in central Illinois: A radar perspective
O'Neal, Benjamin J.
Research from the last two decades has elucidated the importance of migration in the annual cycle of ducks, but many aspects of migration ecology remain poorly understood due to the difficulty of investigating movements that occur over large spatial scales, at substantial heights and at night. Weather surveillance radar (WSR) offers a unique tool for observing movements of birds aloft, but until now has been used primarily to address questions only relevant to broad taxonomic groups. Using thermal infrared imaging, portable radar, and natural history, I ground-truthed WSR echoes originating from a complex of wetlands in the central Illinois River valley to develop a technique for identifying and enumerating ducks as they emigrated from this important stopover area. With this technique, I quantified duck emigrations during 7 falls (1996, 1997, 2003, and 2005-2008). I used WSR-derived estimates of annual turnover in combination with aerial inventory estimates of duck use to estimate the average amount of time ducks spent at my study site during fall (stopover duration). The mean stopover duration estimate of 11 days (SD = 4 days) was much shorter than a historical estimate (28 days) that has been use for regional waterfowl conservation planning. I also regressed average annual stopover duration estimates against an index of annual foraging habitat quality and found a strong, positive relationship (r2 = 0.71), suggesting ducks assessed local habitat conditions and adjusted time spent at the site. Weather influences the timing of migration in many avian taxa, but this relationship is poorly understood for ducks. An evaluation of competing models including 15 years of data indicated following winds aloft, no precipitation, less cloud cover, decreasing temperatures, increasing barometric pressure and date best predicted emigration (R2 = 0.52). Based on this model, the odds of a duck emigration occurring when winds were following and precipitation was absent were 13.2 to
-
Trizna, D.; Hathaway, K.
2007-05-01
Two new radar systems have been developed for real-time measurement of near-shore processes, and results are presented for measurements of ocean wave spectra, near-shore sand bar structure, and ocean currents. The first is a non-coherent radar based on a modified version of the Sitex radar family, with a data acquisition system designed around an ISR digital receiver card. The card operates in a PC computer with inputs from a Sitex radar modified for extraction of analogue signals for digitization. Using a 9' antenna and 25 kW transmit power system, data were collected during 2007 at the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Field Research Facility (FRF), Duck, NC during winter and spring of 2007. The directional wave spectrum measurements made are based on using a sequence of 64 to 640 antenna rotations to form a snapshot series of radar images of propagating waves. A square window is extracted from each image, typically 64 x 64 pixels at 3-m resolution. Then ten sets of 64 windows are submitted to a three-dimensional Fast Fourier Transform process to generate radar image spectra in the frequency-wavenumber space. The relation between the radar image spectral intensity and wave spectral intensity derived from the FRF pressure gauge array was used for a test set of data, in order to establish a modulation transfer function (MTF) for each frequency component. For 640 rotations, 10 of such spectra are averaged for improved statistics. The wave spectrum so generated was compared for extended data sets beyond those used to establish the MTF, and those results are presented here. Some differences between the radar and pressure sensor data that are observed are found to be due to the influence of the wind field, as the radar echo image weakens for light winds. A model is developed to account for such an effect to improve the radar estimate of the directional wave spectrum. The radar ocean wave imagery is severely influenced only by extremely heavy rain-fall rates, so that
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Serafimovich
2005-01-01
Full Text Available A case study to investigate the properties of inertia-gravity waves in the upper troposphere/lower stratosphere has been carried out over Northern Germany during the occurrence of an upper tropospheric jet in connection with a poleward Rossby wave breaking event from 17-19 December 1999. The investigations are based on the evaluation of continuous radar measurements with the OSWIN VHF radar at Kühlungsborn (54.1 N, 11.8 E and the 482 MHz UHF wind profiler at Lindenberg (52.2 N, 14.1 E. Both radars are separated by about 265 km. Based on wavelet transformations of both data sets, the dominant vertical wavelengths of about 2-4 km for fixed times as well as the dominant observed periods of about 11 h and weaker oscillations with periods of 6 h for the altitude range between 5 and 8 km are comparable. Gravity wave parameters have been estimated at both locations separately and by a complex cross-spectral analysis of the data of both radars. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia-gravity waves with characteristic horizontal wavelengths of 300 km moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind and a secondary less pronounced wave with a horizontal wavelength in the order of about 200 km moving with the wind. Temporal and spatial differences of the observed waves are discussed.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kollias, Pavlos [Stony Brook Univ., NY (United States)
2017-04-23
With the vast upgrades to the ARM program radar measurement capabilities in 2010 and beyond, our ability to probe the 3D structure of clouds and associated precipitation has increased dramatically. This project build on the PI's and co-I's expertisein the analysis of radar observations. The first research thrust aims to document the 3D morphological (as depicted by the radar reflectivity structure) and 3D dynamical (cloud$-$scale eddies) structure of boundary layer clouds. Unraveling the 3D dynamical structure of stratocumulus and shallow cumulus clouds requires decomposition of the environmental wind contribution and particle sedimentation velocity from the observed radial Doppler velocity. The second thrust proposes to unravel the mechanism of cumulus entrainment (location, scales) and its impact on microphysics utilizing radar measurements from the vertically pointing and new scanning radars at the ARM sites. The third research thrust requires the development of a cloud$-$tracking algorithm that monitors the properties of cloud.
-
Radar-Derived Quantitative Precipitation Estimation Based on Precipitation Classification
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lili Yang
2016-01-01
Full Text Available A method for improving radar-derived quantitative precipitation estimation is proposed. Tropical vertical profiles of reflectivity (VPRs are first determined from multiple VPRs. Upon identifying a tropical VPR, the event can be further classified as either tropical-stratiform or tropical-convective rainfall by a fuzzy logic (FL algorithm. Based on the precipitation-type fields, the reflectivity values are converted into rainfall rate using a Z-R relationship. In order to evaluate the performance of this rainfall classification scheme, three experiments were conducted using three months of data and two study cases. In Experiment I, the Weather Surveillance Radar-1988 Doppler (WSR-88D default Z-R relationship was applied. In Experiment II, the precipitation regime was separated into convective and stratiform rainfall using the FL algorithm, and corresponding Z-R relationships were used. In Experiment III, the precipitation regime was separated into convective, stratiform, and tropical rainfall, and the corresponding Z-R relationships were applied. The results show that the rainfall rates obtained from all three experiments match closely with the gauge observations, although Experiment II could solve the underestimation, when compared to Experiment I. Experiment III significantly reduced this underestimation and generated the most accurate radar estimates of rain rate among the three experiments.
-
Influence of orographically steered winds on Mutsu Bay surface currents
Yamaguchi, Satoshi; Kawamura, Hiroshi
2005-09-01
Effects of spatially dependent sea surface wind field on currents in Mutsu Bay, which is located at the northern end of Japanese Honshu Island, are investigated using winds derived from synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images and a numerical model. A characteristic wind pattern over the bay was evidenced from analysis of 118 SAR images and coincided with in situ observations. Wind is topographically steered with easterly winds entering the bay through the terrestrial gap and stronger wind blowing over the central water toward its mouth. Nearshore winds are weaker due to terrestrial blockages. Using the Princeton Ocean Model, we investigated currents forced by the observed spatially dependent wind field. The predicted current pattern agrees well with available observations. For a uniform wind field of equal magnitude and average direction, the circulation pattern departs from observations demonstrating that vorticity input due to spatially dependent wind stress is essential in generation of the wind-driven current in Mutsu Bay.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chan, P W; Wong, K H
2008-01-01
Estimates of the wind gusts associated with intense convective weather could be obtained using empirical relationships such as GUSTEX based on radiosonde measurements. However, such data are only available a couple of times a day and may not reflect the rapidly changing atmospheric condition in spring and summer times. The feasibility of combining the thermodynamic profiles from a ground-based microwave radiometer and wind profiles given by radar wind profilers in the continuous estimation of wind gusts is studied in this paper. Based on the results of a 4-month trial of a microwave radiometer in Hong Kong in 2004, the estimated and the actual gusts are reasonably well correlated. It is also found that the wind gusts so estimated provide better indications of the strength of squalls compared with those based on radiosonde measurements and with a lead time of about one hour
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tang Jun
2015-08-01
Full Text Available In this paper, the definition and the key features of Software Radar, which is a new concept, are proposed and discussed. We consider the development of modern radar system technology to be divided into three stages: Digital Radar, Software radar and Intelligent Radar, and the second stage is just commencing now. A Software Radar system should be a combination of various modern digital modular components conformed to certain software and hardware standards. Moreover, a software radar system with an open system architecture supporting to decouple application software and low level hardware would be easy to adopt "user requirements-oriented" developing methodology instead of traditional "specific function-oriented" developing methodology. Compared with traditional Digital Radar, Software Radar system can be easily reconfigured and scaled up or down to adapt to the changes of requirements and technologies. A demonstration Software Radar signal processing system, RadarLab 2.0, which has been developed by Tsinghua University, is introduced in this paper and the suggestions for the future development of Software Radar in China are also given in the conclusion.
-
Small-scale wind shear definition for aerospace vehicle design.
Fichtl, G. H.
1972-01-01
Rawinsonde wind profile data provide adequate wind shear information for vertical height intervals greater than 1 km. To specify wind shears for intervals below 1 km for space vehicle design, detailed wind-profile information like that provided by the FPS-16 Radar/Jimsphere system or an extrapolation procedure is required. This paper is concerned with the latter alternative. It is assumed that any realization from an ensemble of wind profiles can be represented in terms of a Fourier integral. This permits the calculation of the ensemble standard deviation and mean of the corresponding shear ensemble for any altitude and shear interval in terms of the power spectrum of the ensemble of wind profiles. The results of these calculations show that the mean and standard deviation of the wind shear ensemble, as well as the wind shear for any percentile, asymptotically behave like the vertical interval to the 0.7 power. This result is in excellent agreement with shear data from Cape Kennedy, Fla.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Chang, Rui; Rong, Zhu; Badger, Merete
2015-01-01
offshore winds which can be used for offshore wind resource assessment. First, wind speeds retrieved from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and Scatterometer ASCAT images were validated against in situ measurements from seven coastal meteorological stations in South China Sea (SCS). The wind roses from...... (SD) of 2.09 m/s (1.83 m/s) and correlation coefficient of R 0.75 (0.80). When the offshore winds (i.e., winds directed from land to sea) are excluded, the comparison results for wind speeds show an improvement of SD and R, indicating that the satellite data are more credible over the open ocean...
-
Horizontal maps of echo power in the lower stratosphere using the MU radar
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Hirono
2004-03-01
Full Text Available In recent works, zenithal and azimuthal angle variations of echo power measured by VHF Stratosphere-Troposphere (ST radars have been analyzed in detail using different radar multi-beam configurations. It was found that the azimuthal angle corresponding to maximum echo power is closely related to the direction of the horizontal wind shear. These properties indicate that local wind shear affects the tilt of the scatterers. Moreover, horizontal maps of echo power collected using a large set of beams steered pulse-to-pulse up to 40 degrees off zenith revealed that the power distribution pattern in the troposphere is often skewed. In this work, a three-dimensional description of echo power variations up to 24 degrees off zenith is shown for measurements in the lower stratosphere (i.e. up to approximately 20km using a "sequential multi-beam" (SMB configuration. Such a description was not possible above the tropopause with classical multi-beam configurations because of the loss of radar sensitivity due to the limited integration time by the use of a large number of beams. This work attempts to complete previous descriptions of the phenomenon by some observations in the lower stratosphere discussed in association with complementary balloon measurements.
Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (turbulence – Radio Science (remote sensing -
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Miljko Erić
2004-05-01
Full Text Available Za sprovođenje savremenih operacija, kako na operativno-strategijskom, tako i na taktič kom nivou, izuzetno je važno da se obezbedi kontinuirani nadzor vazdušnog prostora. Poznato je da su aktivni radarski sistemi, na kojima se kod nas trenutno zasniva nadzor vazdušnog prostora, u ratnim uslovima veoma ranjivi i podložni elektronskim i borbenim dejstvima protivnika, što je u toku rata 1999. godine i praktično potvrđeno. Kao alternativa aktivnim radarskim sistemima nameće se koncept pasivnog nadzora vazdušnog prostora korišćenjem distribuiranih multisenzorskih sistema. Predmet širih istraživanja predstavljaju tehnička rešenja integrisanog multisenzorskog sistema za pasivan nadzor vazdušnog prostora, koji se sastoji od sledećih podsistema za nadzor vazdušnog prostora: na radio-gonimetarskom principu u frekvencijskom opsegu 20-3000 MHz, na zvukometrijskom principu, na principu vizuelnih osmatračkih stanica, na termovizijskom i televizijskom principu. U ovom radu analizirani su opšti principi pasivnog nadzora vazdušnog prostora multisenzorskim sistemima i predložena je tehnička koncepcija radio-goniometarskog i zvukometrijskog podsistema. / It is very important to provide continuous air surveillance in to realize modern operations on the operational-strategic level and tactical, as well. It is well known that active radar systems, on which air surveillance is based in our country, are very vulnerable in war times and susceptible to the electronic counter and combat attacks of the enemy, what is shown practically in 1999 war. Air surveillance by passive multi-sensor systems is a possible alternative to the air surveillance by the active radar systems. Subjects of our wider research are technical solutions of integrated multi-sensor systems for passive air surveillance which consists of the following subsystems: a subsystem for the air communication intelligence within the frequency range 20-3000 MHz based on intercept
-
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Uroden, M
2001-01-01
...) laser radar systems at MSSS. The paper reviews the first generation kilowatt class ladar/lidar HI-CLASS/LBD systems as the foundation for a second-generation ladar system that was developed under the AFRL/DE ALVA program...
-
Research on wind field algorithm of wind lidar based on BP neural network and grey prediction
Chen, Yong; Chen, Chun-Li; Luo, Xiong; Zhang, Yan; Yang, Ze-hou; Zhou, Jie; Shi, Xiao-ding; Wang, Lei
2018-01-01
This paper uses the BP neural network and grey algorithm to forecast and study radar wind field. In order to reduce the residual error in the wind field prediction which uses BP neural network and grey algorithm, calculating the minimum value of residual error function, adopting the residuals of the gray algorithm trained by BP neural network, using the trained network model to forecast the residual sequence, using the predicted residual error sequence to modify the forecast sequence of the grey algorithm. The test data show that using the grey algorithm modified by BP neural network can effectively reduce the residual value and improve the prediction precision.
-
Multi-Sensor Methods for Mobile Radar Motion Capture and Compensation
Nakata, Robert
Remote sensing has many applications, including surveying and mapping, geophysics exploration, military surveillance, search and rescue and counter-terrorism operations. Remote sensor systems typically use visible image, infrared or radar sensors. Camera based image sensors can provide high spatial resolution but are limited to line-of-sight capture during daylight. Infrared sensors have lower resolution but can operate during darkness. Radar sensors can provide high resolution motion measurements, even when obscured by weather, clouds and smoke and can penetrate walls and collapsed structures constructed with non-metallic materials up to 1 m to 2 m in depth depending on the wavelength and transmitter power level. However, any platform motion will degrade the target signal of interest. In this dissertation, we investigate alternative methodologies to capture platform motion, including a Body Area Network (BAN) that doesn't require external fixed location sensors, allowing full mobility of the user. We also investigated platform stabilization and motion compensation techniques to reduce and remove the signal distortion introduced by the platform motion. We evaluated secondary ultrasonic and radar sensors to stabilize the platform resulting in an average 5 dB of Signal to Interference Ratio (SIR) improvement. We also implemented a Digital Signal Processing (DSP) motion compensation algorithm that improved the SIR by 18 dB on average. These techniques could be deployed on a quadcopter platform and enable the detection of respiratory motion using an onboard radar sensor.
-
Radar Fundamentals, Presentation
Jenn, David
2008-01-01
Topics include: introduction, radar functions, antennas basics, radar range equation, system parameters, electromagnetic waves, scattering mechanisms, radar cross section and stealth, and sample radar systems.
-
Surface Currents and Winds at the Delaware Bay Mouth
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Muscarella, P A; Barton, N P; Lipphardt, B L; Veron, D E; Wong, K C; Kirwan, A D
2011-04-06
Knowledge of the circulation of estuaries and adjacent shelf waters has relied on hydrographic measurements, moorings, and local wind observations usually removed from the region of interest. Although these observations are certainly sufficient to identify major characteristics, they lack both spatial resolution and temporal coverage. High resolution synoptic observations are required to identify important coastal processes at smaller scales. Long observation periods are needed to properly sample low-frequency processes that may also be important. The introduction of high-frequency (HF) radar measurements and regional wind models for coastal studies is changing this situation. Here we analyze synoptic, high-resolution surface winds and currents in the Delaware Bay mouth over an eight-month period (October 2007 through May 2008). The surface currents were measured by two high-frequency radars while the surface winds were extracted from a data-assimilating regional wind model. To illustrate the utility of these monitoring tools we focus on two 45-day periods which previously were shown to present contrasting pictures of the circulation. One, the low-outflow period is from 1 October through 14 November 2007; the other is the high-outflow period from 3 March through 16 April 2008. The large-scale characteristics noted by previous workers are clearly corroborated. Specifically the M2 tide dominates the surface currents, and the Delaware Bay outflow plume is clearly evident in the low frequency currents. Several new aspects of the surface circulation were also identified. These include a map of the spatial variability of the M2 tide (validating an earlier model study), persistent low-frequency cross-mouth flow, and a rapid response of the surface currents to a changing wind field. However, strong wind episodes did not persist long enough to set up a sustained Ekman response.
-
Crowe, Christina C.; Schultz, Christopher J.; Kumjian, Matthew; Carey, Lawerence D.; Petersen, Walter A.
2011-01-01
The upgrade of the National Weather Service (NWS) network of S ]band dual-polarization radars is currently underway, and the incorporation of polarimetric information into the real ]time forecasting process will enhance the forecaster fs ability to assess thunderstorms and their near ]storm environments. Recent research has suggested that the combination of polarimetric variables differential reflectivity (ZDR) and specific differential phase (KDP) can be useful in the assessment of low level wind shear within a thunderstorm. In an environment with strong low ]level veering of the wind, ZDR values will be largest along the right inflow edge of the thunderstorm near a large gradient in horizontal reflectivity (indicative of large raindrops falling with a relative lack of smaller drops), and take the shape of an arc. Meanwhile, KDP values, which are proportional to liquid water content and indicative of a large number of smaller drops, are maximized deeper into the forward flank precipitation shield than the ZDR arc as the smaller drops are being advected further from the updraft core by the low level winds than the larger raindrops. Using findings from previous work, three severe weather events that occurred in North Alabama were examined in order to assess the utility of these signatures in determining the potential for tornadic activity. The first case is from October 26, 2010, where a large number of storms indicated tornadic potential from a standard reflectivity and velocity analysis but very few storms actually produced tornadoes. The second event is from February 28, 2011, where tornadic storms were present early on in the event, but as the day progressed, the tornado threat transitioned to a high wind threat. The third case is from April 27, 2011, where multiple rounds of tornadic storms ransacked the Tennessee Valley. This event provides a dataset including multiple modes of tornadic development, including QLCS and supercell structures. The overarching goal
-
Venkat Ratnam, Madineni; Karanam, Kishore Kumar; Sunkara, Eswaraiah; Vijaya Bhaskara Rao, S.; Subrahmanyam, K. V.; Ramanjaneyulu, L.
2016-07-01
Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere (MLT) mean winds, gravity waves, tidal and planetary wave characteristics are investigated using two years (2013-2015) of advanced meteor radar installed at Tirupathi (13.63oN, 79.4oE), India. The observations reveal the presence of high frequency gravity waves (30-120 minutes), atmospheric tides (diurnal, semi-diurnal and terr-diurnal) along with long period oscillations in both zonal and meridional winds. Background mean zonal winds show clear semi-annual oscillation in the mesosphere, whereas meridional winds are characterized by annual oscillation as expected. Diurnal tide amplitudes are significantly larger (60-80 m/s) than semi-diurnal (10-20 m/s) and terr-diurnal (5-8 m/s) tides and larger in meridional than zonal winds. The measured meridional components are in good agreement with Global Scale Wave Model (GSWM-09) predictions than zonal up to ~90 km in all the seasons, except fall equinox. Diurnal tidal phase matches well than the amplitudes between observations and model predictions. However, no similarity is being found in the semi-diurnal tides between observations and model. The measurements are further compared with nearby Thumba meteor radar (8.5oN, 77oE) observations. Some differences do exist between the measurements from Tirupati and Thumba meteor radar and model outputs at greater heights and the possible reasons are discussed. SVU meteor radar observations clearly showed the dominance of well-known ultra-fast kelvin waves (3.5 days), 5-8 day, 16 day, 27 day, and 30-40 day oscillations. Due to higher meteor count extending up to 110 km, we could investigate the variability of these PWs and oscillations covering wider range (70-110 km) for the first time. Significant change above 100 km is noticed in all the above mentioned PW activity and oscillations. We also used ERA-Interim reanalysis data sets available at 0.125x0.125 degree grids for investigating the characteristics of these PW right from surface to 1 h
-
Department of Homeland Security — These data represent Next-Generation Radar (NEXRAD) and Terminal Doppler Weather Radar (TDWR) weather radar stations within the US. The NEXRAD radar stations are...
-
Letter to the Editor: Complete maps of the aspect sensitivity of VHF atmospheric radar echoes
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. M. Worthington
1999-08-01
Full Text Available Using the MU radar at Shigaraki, Japan (34.85°N, 136.10°E, we measure the power distribution pattern of VHF radar echoes from the mid-troposphere. The large number of radar beam-pointing directions (320 allows the mapping of echo power from 0° to 40° from zenith, and also the dependence on azimuth, which has not been achieved before at VHF wavelengths. The results show how vertical shear of the horizontal wind is associated with a definite skewing of the VHF echo power distribution, for beam angles as far as 30° or more from zenith, so that aspect sensitivity cannot be assumed negligible at any beam-pointing angle that most existing VHF radars are able to use. Consequently, the use of VHF echo power to calculate intensity of atmospheric turbulence, which assumes only isotropic backscatter at large beam zenith angles, will sometimes not be valid.Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (middle atmosphere dynamics; turbulence; instruments and techniques
-
Random Forest Application for NEXRAD Radar Data Quality Control
Keem, M.; Seo, B. C.; Krajewski, W. F.
2017-12-01
Identification and elimination of non-meteorological radar echoes (e.g., returns from ground, wind turbines, and biological targets) are the basic data quality control steps before radar data use in quantitative applications (e.g., precipitation estimation). Although WSR-88Ds' recent upgrade to dual-polarization has enhanced this quality control and echo classification, there are still challenges to detect some non-meteorological echoes that show precipitation-like characteristics (e.g., wind turbine or anomalous propagation clutter embedded in rain). With this in mind, a new quality control method using Random Forest is proposed in this study. This classification algorithm is known to produce reliable results with less uncertainty. The method introduces randomness into sampling and feature selections and integrates consequent multiple decision trees. The multidimensional structure of the trees can characterize the statistical interactions of involved multiple features in complex situations. The authors explore the performance of Random Forest method for NEXRAD radar data quality control. Training datasets are selected using several clear cases of precipitation and non-precipitation (but with some non-meteorological echoes). The model is structured using available candidate features (from the NEXRAD data) such as horizontal reflectivity, differential reflectivity, differential phase shift, copolar correlation coefficient, and their horizontal textures (e.g., local standard deviation). The influence of each feature on classification results are quantified by variable importance measures that are automatically estimated by the Random Forest algorithm. Therefore, the number and types of features in the final forest can be examined based on the classification accuracy. The authors demonstrate the capability of the proposed approach using several cases ranging from distinct to complex rain/no-rain events and compare the performance with the existing algorithms (e
-
Cifelli, R.; Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V.
2017-12-01
A recent study by the State of California's Department of Water Resources has emphasized that the San Francisco Bay Area is at risk of catastrophic flooding. Therefore, accurate quantitative precipitation estimation (QPE) and forecast (QPF) are critical for protecting life and property in this region. Compared to rain gauge and meteorological satellite, ground based radar has shown great advantages for high-resolution precipitation observations in both space and time domain. In addition, the polarization diversity shows great potential to characterize precipitation microphysics through identification of different hydrometeor types and their size and shape information. Currently, all the radars comprising the U.S. National Weather Service (NWS) Weather Surveillance Radar-1988 Doppler (WSR-88D) network are operating in dual-polarization mode. Enhancement of QPE is one of the main considerations of the dual-polarization upgrade. The San Francisco Bay Area is covered by two S-band WSR-88D radars, namely, KMUX and KDAX. However, in complex terrain like the Bay Area, it is still challenging to obtain an optimal rainfall algorithm for a given set of dual-polarization measurements. In addition, the accuracy of rain rate estimates is contingent on additional factors such as bright band contamination, vertical profile of reflectivity (VPR) correction, and partial beam blockages. This presentation aims to improve radar QPE for the Bay area using advanced dual-polarization rainfall methodologies. The benefit brought by the dual-polarization upgrade of operational radar network is assessed. In addition, a pilot study of gap fill X-band radar performance is conducted in support of regional QPE system development. This paper also presents a detailed comparison between the dual-polarization radar-derived rainfall products with various operational products including the NSSL's Multi-Radar/Multi-Sensor (MRMS) system. Quantitative evaluation of various rainfall products is achieved
-
RADARSAT-1 synthetic aperture radar analysis
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Simecek-Beatty, D. [National Oceanic and Atmospheric Adminstration, National Ocean Service, Seattle, WA (United States). Office of Response and Restoration; Pichel, W.G. [National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Environmental Satellite, Data and Information Service, Camp Springs, MD (United States). Office of Research and Applications
2006-07-01
The M/V Selendang Ayu grounded off Unalaska Island in Alaska on December 8, 2004, and spilled over 1270 m{sup 3} of oil and an unknown quantity of soybeans. The freighter grounded nearshore in a high-wave energy zone along a remote and rugged coastline, a terrain which can cause difficulties for remote sensors in detecting oil slicks. In addition, guano, kelp beds, whale and fish sperm, and releases from fishing activities generated biogenic films on the sea surface that had a signature similar to that of petroleum films. RADARSAT-1 synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imagery was used as part of the response effort to assist in the pollution monitoring effort. This paper described the methodology and results of the RADARSAT-1 analysis. Detailed information on the spill response was reported daily, and provided an opportunity to compare field observations with RADARSAT-1 SAR imagery. Observers recorded observations onto electronic maps during 35 aerial surveillance flights. Fifty-seven incident reports describing the vessel status were also used for comparison. Using screening criteria for the favorable wind and wave conditions, 37 images were available for viewing the wreck, and 22 images were acceptable for oil slick viewing. Image analysis for the wreck suggested that the sensor has the resolution and capability to monitor a grounded freighter. Visual inspection of the images showed that SAR can capture changes in vessel status, such as the gradual sinking of the bow. However, SAR's oil slick detection capability was disappointing due to the significant number of biogenic films in the nearshore areas of Alaska. It was concluded that future work should concentrate on developing a ranking system to indicate analysis confidence that a particular image does in fact contain a petroleum pocket. 25 refs., 2 tabs., 10 figs.
-
Satellite based wind resource assessment over the South China Sea
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Badger, Merete; Astrup, Poul; Hasager, Charlotte Bay
2014-01-01
variations are clearly visible across the domain; for instance sheltering effects caused by the land masses. The satellite based wind resource maps have two shortcomings. One is the lack of information at the higher vertical levels where wind turbines operate. The other is the limited number of overlapping...... years of WRF data – specifically the parameters heat flux, air temperature, and friction velocity – are used to calculate a long-term correction for atmospheric stability effects. The stability correction is applied to the satellite based wind resource maps together with a vertical wind profile...... from satellite synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data are particularly suitable for offshore wind energy applications because they offer a spatial resolution up to 500 m and include coastal seas. In this presentation, satellite wind maps are used in combination with mast observations and numerical...
-
Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Jee, G.
2010-12-01
We have analyzed wind data from individual meteor echoes detected by a meteor radar at King Sejong Station, Antarctica to measure gravity wave activity in the mesopause region. Wind data in the meteor altitudes has been obtained routinely by the meteor radar since its installation in March 2007. The mean variances in the wind data that were filtered for large scale motions (mean winds and tides) can be regarded as the gravity wave activity. Monthly mean gravity wave activities show strong seasonal and height dependences in the altitude range of 80 to 100 km. The gravity wave activities except summer monotonically increase with altitude, which is expected since decreasing atmospheric densities cause wave amplitudes to increase. During summer (Dec. - Feb.) the height profiles of gravity wave activities show a minimum near 90 - 95 km, which may be due to different zonal wind and strong wind shear near 80 - 95 km. Our gravity wave activities are generally stronger than those of the Rothera station, implying sensitive dependency on location. The difference may be related to gravity wave sources in the lower atmosphere near Antarctic vortex.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gao eHu
2016-02-01
Full Text Available Most insect migrants fly at considerable altitudes (hundreds of meters above the ground where they utilize fast-flowing winds to achieve rapid and comparatively long-distance transport. The nocturnal aerial migrant fauna has been well studied with entomological radars, and many studies have demonstrated that flight orientations are frequently grouped around a common direction in a range of nocturnal insect migrants. Common orientation typically occurs close to the downwind direction (thus ensuring that a large component of the insects’ self-powered speed is directed downstream, and in nocturnal insects at least, the downwind headings are seemingly maintained by direct detection of wind-related turbulent cues. Despite being far more abundant and speciose, the day-flying windborne migrant fauna has been much less studied by radar; thus the frequency of wind-related common orientation patterns and the sensory mechanisms involved in their formation remain to be established. Here we analyze a large dataset of >600,000 radar-detected ‘medium-sized’ windborne insect migrants (body mass from 10 to 70 mg, flying hundreds of meters above southern UK, during the afternoon, in the period around sunset, and in the middle of the night. We found that wind-related common orientation was almost ubiquitous during the day (present in 97% of all ‘migration events’ analyzed, and was also frequent at sunset (85% and at night (81%. Headings were systematically offset to the right of the flow at night-time (as predicted from the use of turbulence cues for flow assessment, but there was no directional bias in the offsets during the day or at sunset. Orientation ‘performance’ significantly increased with increasing flight altitude throughout the day and night. We conclude by discussing sensory mechanisms which most likely play a role in the selection and maintenance of wind-related flight headings.
-
Universal Library for Building Radar Operator Interface
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. A. Karankevich
2014-01-01
Full Text Available The article contains the results of the development of a software library, used for building software interfaces for radars being developed in BMSTU Radioelectronic Technics Scientific and Research Institute. The library is a software application library written in C++ using Qt and OpenGL libraries.The article describes the requirements, that the library is supposed to meet, in particular — cross-platform capabilities and versatility of the solution. The data types, that library uses, are described. The description of theinterface elements developed is shown, and some pictures of their operation are given.The article shows the main interface elements used. They are: «Matrix» that shows twodimensional data, «Waterfall», that is used for time scanning of the parameter specified, and «Plan Position Indicator» that shows circular scan from surveillance radar without geometric distortions.The part «Library implementation» shows the example of radiolocation station interface, that was based on this library, used in the working model of ultrashortpulse radar. Some results of the operation of this interface are also shown. The experiment shows the system working with two people in the field. As people start to move, the system becomes capable of distinguishing moving targets and stationary surface. The article shows the system operation the same way as the system operator can see it through his interface.The conclusion contains brief results of the development, the sphere of application of the software, and the prospects of the further development of the library.
-
Improving Weather Radar Precipitation Estimates by Combining two Types of Radars
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, Jesper Ellerbæk; Thorndahl, Søren Liedtke; Rasmussen, Michael R.
2014-01-01
This paper presents a demonstration of how Local Area Weather Radar (LAWR) X-band measurements can be combined with meteorological C–band measurements into a single radar product. For this purpose, a blending method has been developed which combines the strengths of the two radar systems. Combining...... the two radar types achieves a radar product with both long range and high temporal resolution. It is validated that the blended radar product performs better than the individual radars based on ground observations from laser disdrometers. However, the data combination is challenged by lower performance...... of the LAWR. Although both radars benefits from the data combination, it is also found that advection based temporal interpolation is a more favourable method for increasing the temporal resolution of meteorological C–band measurements....
-
Temperature sheets and aspect sensitive radar echoes
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. Luce
Full Text Available here have been years of discussion and controversy about the existence of very thin and stable temperature sheets and their relationship to the VHF radar aspect sensitivity. It is only recently that very high-resolution in situ temperature observations have brought credence to the reality and ubiquity of these structures in the free atmosphere and to their contribution to radar echo enhancements along the vertical. Indeed, measurements with very high-resolution sensors are still extremely rare and rather difficult to obtain outside of the planetary boundary layer. They have only been carried out up to the lower stratosphere by Service d’A´ eronomie (CNRS, France for about 10 years. The controversy also persisted due to the volume resolution of the (Mesosphere-Stratosphere-Troposphere VHF radars which is coarse with respect to sheet thickness, although widely sufficient for meteorological or mesoscale investigations. The contribution within the range gate of many of these structures, which are advected by the wind, and decay and grow at different instants and could be distorted either by internal gravity waves or turbulence fields, could lead to radar echoes with statistical properties similar to those produced by anisotropic turbulence. Some questions thus remain regarding the manner in which temperature sheets contribute to VHF radar echoes. In particular, the zenithal and azimuthal angular dependence of the echo power may not only be produced by diffuse reflection on stable distorted or corrugated sheets, but also by extra contributions from anisotropic turbulence occurring in the stratified atmosphere. Thus, for several years, efforts have been put forth to improve the radar height resolution in order to better describe thin structures. Frequency interferometric techniques are widely used and have been recently further developed with the implementation of high-resolution data processings. We begin by reviewing briefly some characteristics
-
Temperature sheets and aspect sensitive radar echoes
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. Luce
2001-08-01
Full Text Available here have been years of discussion and controversy about the existence of very thin and stable temperature sheets and their relationship to the VHF radar aspect sensitivity. It is only recently that very high-resolution in situ temperature observations have brought credence to the reality and ubiquity of these structures in the free atmosphere and to their contribution to radar echo enhancements along the vertical. Indeed, measurements with very high-resolution sensors are still extremely rare and rather difficult to obtain outside of the planetary boundary layer. They have only been carried out up to the lower stratosphere by Service d’A´ eronomie (CNRS, France for about 10 years. The controversy also persisted due to the volume resolution of the (Mesosphere-Stratosphere-Troposphere VHF radars which is coarse with respect to sheet thickness, although widely sufficient for meteorological or mesoscale investigations. The contribution within the range gate of many of these structures, which are advected by the wind, and decay and grow at different instants and could be distorted either by internal gravity waves or turbulence fields, could lead to radar echoes with statistical properties similar to those produced by anisotropic turbulence. Some questions thus remain regarding the manner in which temperature sheets contribute to VHF radar echoes. In particular, the zenithal and azimuthal angular dependence of the echo power may not only be produced by diffuse reflection on stable distorted or corrugated sheets, but also by extra contributions from anisotropic turbulence occurring in the stratified atmosphere. Thus, for several years, efforts have been put forth to improve the radar height resolution in order to better describe thin structures. Frequency interferometric techniques are widely used and have been recently further developed with the implementation of high-resolution data processings. We begin by reviewing briefly some characteristics
-
Development of a Wind Plant Large-Eddy Simulation with Measurement-Driven Atmospheric Inflow
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Quon, Eliot W.; Churchfield, Matthew J.; Cheung, Lawrence; Kern, Stefan
2017-01-09
This paper details the development of an aeroelastic wind plant model with large-eddy simulation (LES). The chosen LES solver is the Simulator for Wind Farm Applications (SOWFA) based on the OpenFOAM framework, coupled to NREL's comprehensive aeroelastic analysis tool, FAST. An atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) precursor simulation was constructed based on assessments of meteorological tower, lidar, and radar data over a 3-hour window. This precursor was tuned to the specific atmospheric conditions that occurred both prior to and during the measurement campaign, enabling capture of a night-to-day transition in the turbulent ABL. In the absence of height-varying temperature measurements, spatially averaged radar data were sufficient to characterize the atmospheric stability of the wind plant in terms of the shear profile, and near-ground temperature sensors provided a reasonable estimate of the ground heating rate describing the morning transition. A full aeroelastic simulation was then performed for a subset of turbines within the wind plant, driven by the precursor. Analysis of two turbines within the array, one directly waked by the other, demonstrated good agreement with measured time-averaged loads.
-
Satellite information for wind energy applications
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, M.; Astrup, Poul; Hasager, Charlotte Bay
2004-01-01
An introduction to satellite information relevant for wind energy applications is given. It includes digital elevation model (DEM) data based on satellite observations. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is useful for regional scale wind resourcestudies. Comparison results from complex...... terrain in Spain and flat terrain in Denmark are found to be acceptable for both sites. Also land cover type information can be retrieved from satellite observations. Land cover type maps have to be combined withroughness data from field observation or literature values. Land cover type maps constitute...... an aid to map larger regions within shorter time. Field site observations of obstacles and hedges are still necessary. The raster-based map information from DEMand land cover maps can be converted for use in WASP. For offshore locations it is possible to estimate the wind resources based on ocean surface...
-
Cassini RADAR at Titan : Results in 2013/2014
Lorenz, Ralph D.; Cassini RadarTeam
2014-05-01
Since the last EGU meeting, several Cassini flybys of Titan have featured significant RADAR observations. These include T91 and T92 (May/July 2013) with SAR and altimetry observations of Ligeia Mare. The latter have placed tight constraints on surface roughness (Zebker et al., in press), showing that wind-driven waves were not present. A remarkable altimetry analysis by Mastrogiuseppe et al. (submitted) detects a bottom echo from the bed of Ligeia, only possible if the liquid is exceptionally radar-transparent. This opens the way to wider radar bathymetry analyses of the northern seas. SAR coverage, augmented by some distant HiSAR observations, has now allowed construction of a more-or-less complete map of the northern polar region. This map now defines the extent of the northern lakes and seas, permitting oceanographic studies. T95 (October 2013) made SAR observations of the impact crater Selk (previously observed by VIMS and RADAR). As well as a closer view of this rather polygonal crater, the observation shows dramatic change in the dune orientation around the crater and its ejecta blanket. The T98 encounter is due to occur in February 2014, and will feature the last prime SAR observation of Ontario Lacus, giving a good baseline for change detection against prior observations. Additionally, close-approach observations (mandated to avoid solar heating constraints on other instruments) will give high-resolution altimetry data on the Shangri-La dunes. Preliminary results may be available in time for the meeting, at which this solicted talk will review analyses of these and other observations.
-
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Smith, Margaret
1997-01-01
.... Trajectories produced by the NOAA/HAZMAT On-Scene Spill Model, using different combinations of surface currents and winds, were compared to trajectories generated using HF radar-derived surface currents...
-
Fingerprints of a riming event on cloud radar Doppler spectra: observations and modeling
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. Kalesse
2016-03-01
Full Text Available Radar Doppler spectra measurements are exploited to study a riming event when precipitating ice from a seeder cloud sediment through a supercooled liquid water (SLW layer. The focus is on the "golden sample" case study for this type of analysis based on observations collected during the deployment of the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Program's (ARM mobile facility AMF2 at Hyytiälä, Finland, during the Biogenic Aerosols – Effects on Clouds and Climate (BAECC field campaign. The presented analysis of the height evolution of the radar Doppler spectra is a state-of-the-art retrieval with profiling cloud radars in SLW layers beyond the traditional use of spectral moments. Dynamical effects are considered by following the particle population evolution along slanted tracks that are caused by horizontal advection of the cloud under wind shear conditions. In the SLW layer, the identified liquid peak is used as an air motion tracer to correct the Doppler spectra for vertical air motion and the ice peak is used to study the radar profiles of rimed particles. A 1-D steady-state bin microphysical model is constrained using the SLW and air motion profiles and cloud top radar observations. The observed radar moment profiles of the rimed snow can be simulated reasonably well by the model, but not without making several assumptions about the ice particle concentration and the relative role of deposition and aggregation. This suggests that in situ observations of key ice properties are needed to complement the profiling radar observations before process-oriented studies can effectively evaluate ice microphysical parameterizations.
-
Kumar, Karanam Kishore; Antonita, T. Maria; Shelbi, S. T.
2007-12-01
In the present communication, allSKy interferometric METeor (SKiYMET) radar observations of gravity wave activity in the mesosphere lower thermosphere (MLT) region over Thumba (8.5°N, 77°E) are presented. The present meteor radar system provides hourly zonal and meridional winds in the MLT region, which can be readily used for studying the tides, planetary waves, gravity waves of periods 2-6 hours, and other long period oscillations in this region. However, these hourly winds are not sufficient for studying short period gravity waves having periods less than an hour, which demand high temporal resolution measurements. Even though the winds are estimated on an hourly basis, information such as zenith angle, azimuth angle, and radial velocity of each detected meteor are archived. Using these details of the meteor, an algorithm is developed to obtain the 15-min temporal resolution wind data. The output of the algorithm is compared with hourly wind data, and it showed a good agreement during the high meteor shower periods. Most of the times high meteor counts are observed during late night and early morning hours (local) over this latitude. Continuous wind measurements during the high meteor shower periods are used for studying the gravity wave activity in the MLT region. As the wave activity is intermittent and nonstationary, wavelet analysis has been used for delineating the wave features. The results showed the upward propagating intermittent gravity waves with periods 1-2 and 4-5 hours. The new aspect of the present communication is the usage of meteor radar for gravity wave studies for the first time over this latitude and studying their seasonal variability.
-
Radar sensing via a Micro-UAV-borne system
Catapano, Ilaria; Ludeno, Giovanni; Gennarelli, Gianluca; Soldovieri, Francesco; Rodi Vetrella, Amedeo; Fasano, Giancarmine
2017-04-01
In recent years, the miniaturization of flight control systems and payloads has contributed to a fast and widespread diffusion of micro-UAV (Unmanned Aircraft Vehicle). While micro-UAV can be a powerful tool in several civil applications such as environmental monitoring and surveillance, unleashing their full potential for societal benefits requires augmenting their sensing capability beyond the realm of active/passive optical sensors [1]. In this frame, radar systems are drawing attention since they allow performing missions in all-weather and day/night conditions and, thanks to the microwave ability to penetrate opaque media, they enable the detection and localization not only of surface objects but also of sub-surface/hidden targets. However, micro-UAV-borne radar imaging represents still a new frontier, since it is much more than a matter of technology miniaturization or payload installation, which can take advantage of the newly developed ultralight systems. Indeed, micro-UAV-borne radar imaging entails scientific challenges in terms of electromagnetic modeling and knowledge of flight dynamics and control. As a consequence, despite Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging is a traditional remote sensing tool, its adaptation to micro-UAV is an open issue and so far only few case studies concerning the integration of SAR and UAV technologies have been reported worldwide [2]. In addition, only early results concerning subsurface imaging by means of an UAV-mounted radar are available [3]. As a contribution to radar imaging via autonomous micro-UAV, this communication presents a proof-of-concept experiment. This experiment represents the first step towards the development of a general methodological approach that exploits expertise about (sub-)surface imaging and aerospace systems with the aim to provide high-resolution images of the surveyed scene. In details, at the conference, we will present the results of a flight campaign carried out by using a single radar
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Fontán
2013-04-01
Full Text Available Two high-frequency (HF radar stations were installed on the coast of the south-eastern Bay of Biscay in 2009, providing high spatial and temporal resolution and large spatial coverage of currents in the area for the first time. This has made it possible to quantitatively assess the air–sea interaction patterns and timescales for the period 2009–2010. The analysis was conducted using the Barnett–Preisendorfer approach to canonical correlation analysis (CCA of reanalysis surface winds and HF radar-derived surface currents. The CCA yields two canonical patterns: the first wind–current interaction pattern corresponds to the classical Ekman drift at the sea surface, whilst the second describes an anticyclonic/cyclonic surface circulation. The results obtained demonstrate that local winds play an important role in driving the upper water circulation. The wind–current interaction timescales are mainly related to diurnal breezes and synoptic variability. In particular, the breezes force diurnal currents in waters of the continental shelf and slope of the south-eastern Bay. It is concluded that the breezes may force diurnal currents over considerably wider areas than that covered by the HF radar, considering that the northern and southern continental shelves of the Bay exhibit stronger diurnal than annual wind amplitudes.
-
Application of HF Radar in Hazard Management
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mal Heron
2016-01-01
Full Text Available A review is given of the impact that HF radars are having on the management of coastal hazards. Maps of surface currents can be produced every 10–20 minutes which, in real time, improve navigation safety in restricted areas commonly found near ports and harbours. The time sequence of surface current maps enables Lagrangian tracking of small parcels of surface water, which enables hazard mitigation in managing suspended sediments in dredging, in emergency situations where flotsam and other drifting items need to be found, and in pollution control. The surface current measurement capability is used to assist tsunami warnings as shown by the phased-array data from Chile following the Great Tohoku Earthquake in 2011. The newly launched Tsunami Warning Center in Oman includes a network of phased-array HF radars to provide real-time tsunami monitoring. Wind direction maps can be used to locate the position of cold fronts in the open ocean and to monitor the timing and strength of sea-breeze fronts in key locations.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Edward Natenberg
2013-01-01
Full Text Available A three-dimensional variational (3DVAR assimilation technique developed for a convective-scale NWP model—advanced regional prediction system (ARPS—is used to analyze the 8 May 2003, Moore/Midwest City, Oklahoma tornadic supercell thunderstorm. Previous studies on this case used only one or two radars that are very close to this storm. However, three other radars observed the upper-level part of the storm. Because these three radars are located far away from the targeted storm, they were overlooked by previous studies. High-frequency intermittent 3DVAR analyses are performed using the data from five radars that together provide a more complete picture of this storm. The analyses capture a well-defined mesocyclone in the midlevels and the wind circulation associated with a hook-shaped echo. The analyses produced through this technique are used as initial conditions for a 40-minute storm-scale forecast. The impact of multiple radars on a short-term NWP forecast is most evident when compared to forecasts using data from only one and two radars. The use of all radars provides the best forecast in which a strong low-level mesocyclone develops and tracks in close proximity to the actual tornado damage path.
-
Inner Core Structure of Hurricane Alicia from Airborne Doppler Radar Observations.
Marks, Frank D., Jr.; Houze, Robert A., Jr.
1987-05-01
Airborne Doppler radar measurements are used to determine the horizontal winds, vertical air motions, radar reflectivity and hydrometer fallspeeds over much of the inner-core region (within 40 km of the eye) of Hurricane Alicia (1983). The reconstructed flow field is more complete and detailed than any obtained previously. The data show both the primary (azimuthal) and secondary (radial-height) circulations. The primary circulation was characterized by an outward sloping maximum of tangential wind. The secondary circulation was characterized by a deep layer of radial inflow in the lower troposphere and a layer of intense outflow above 10 km altitude. The rising branch of the secondary circulation was located in the eyewall and sloped radially outward. Discrete convective-scale bubbles of more intense upward motion were superimposed on this mean rising current, and convective-scale downdrafts were located throughout and below the core of maximum precipitation in the eyewall.Precipitation particles in the eyewall rainshaft circulated 18-20 km downwind as they fell, consistent with the typical upwind slope with increasing altitude of eyewall precipitation cores Outside the eyewall, the precipitation was predominantly stratiform. A radar bright band was evident at the melting level. Above the melting level, ice particles were advected into the stratiform region from the upper levels of the eyewall and drifted downward through a mesoscale region of ascent. Hypothetical precipitation particle trajectories showed that as these particles fell slowly through the mesoscale updraft toward the melting level, they were carried azimuthally as many as 1 1/2 times around the storm. During this spiraling descent, the particles evidently grew vigorously. The amount of water condensed by the ambient mesoscale ascent exceeded that transported into the stratiform region by the eyewall outflow by a factor of 3. As the particles fell into the lower troposphere, they entered a mesoscale
-
Remote sensing of surface currents in the Fraser River plume with the SeaSonde HF radar
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hodgins, D.O.; Hardy, J.S.; Tinis, S.E.
1994-09-01
The SeaSonde 12.5-MHz radar system was deployed to measure surface currents in the Juan de Fuca Strait in July 1992. Reliable data were obtained from the two radars installed, and successful trials were conducted with the Infosat satellite link to transmit data from the remote site. Data recovery from the SeaSonde was generally good, with maximum ranges varying from 15 km to over 30 km. Sea echo return strength at both radars was correlated with wind, consistent with lower Bragg scattering at lower wind speeds. A simple surface current forecasting algorithm, based on decomposing the signal into tidal and residual bands, was examined. It was found that tides account for the greatest portion of currents in the study area, and could be forecasted out to 48 h with 1-2 d of input data. The nonpredictable, fluctuating part of the current signal was isolated and its statistics were calculated. The algorithm tests showed that the SeaSonde data can be used to measure and predict the slowly varying tidal and mean flow velocities, as well as the random part of the signal, both of which are important in oil spill modelling. Surface flow patterns and time-series data from the SeaSonde measurements, and from a three-dimensional hydrodynamic model, were compared from an oil spill modelling perspective. In general, surface flow patterns from the model were smoother than those observed. The differences were most noticeable in the cross-channel direction. The radar data indicate that a flow-dependent eddy viscosity formulation, with coefficients calibrated to reproduce the features observed with the radar, would improve agreement and yield a good model for data assimilation. 21 refs., 478 figs., 3 tabs
-
The determination of time-stationary two-dimensional convection patterns with single-station radars
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Freeman, M.P.; Ruohoniemi, J.M.; Greenwald, R.A.
1991-01-01
At the present time, most ground-based radar estimations of ionospheric convection use observations from single-station facilities. This approach requires certain assumptions as to the spatial and/or temporal uniformity of the convection. In this paper the authors present a critical examination of the accuracy of these vector velocity determinations, using realistic modeled flow patterns that are time-stationary but not spatially uniform. They find that under certain circumstances the actual and inferred flow fields show considerable discrepancy, sometimes not even agreeing in the sense of flow direction. Specifically, they show that the natural curvature present in ionospheric convection on varying spatial scales can introduce significant error in the velocity estimate, particularly when the radius of curvature of the flow structure is less than or equal to the radar range to the scattering volume. The presence of flow curvature cannot be detected by radars which determine velocities from measurements in two viewing directions, and it might not be detected by radars using azimuth scanning techniques. Thus they argue that every effort should be made to measure the ionospheric convection by bidirectional or multidirectional observations of a common ionospheric volume and that a synthesis of coherent and incoherent radar observations from different sites is preferable to multidirectional single-station observations using either radar alone. These conclusions are applicable to any Doppler measurement technique and are equally valid for high-latitude wind patterns using Fabry-Perot interferometer techniques
-
76 FR 76333 - Notification for Airborne Wind Energy Systems (AWES)
2011-12-07
... conventional ground-based wind turbines cannot reach. As part of their research, the energy community is... defines a kite as a ``framework, covered with paper, cloth, metal, or other material, intended to be flown... design, how it operates, necessary airspace utilized, radar cross-section, and reflection coefficient...
-
Pinales, J. C.; Graber, H. C.; Hargrove, J. T.; Caruso, M. J.
2016-02-01
Previous studies have demonstrated the ability to detect and classify marine hydrocarbon films with spaceborne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imagery. The dampening effects of hydrocarbon discharges on small surface capillary-gravity waves renders the ocean surface "radar dark" compared with the standard wind-borne ocean surfaces. Given the scope and impact of events like the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, the need for improved, automated and expedient monitoring of hydrocarbon-related marine anomalies has become a pressing and complex issue for governments and the extraction industry. The research presented here describes the development, training, and utilization of an algorithm that detects marine oil spills in an automated, semi-supervised manner, utilizing X-, C-, or L-band SAR data as the primary input. Ancillary datasets include related radar-borne variables (incidence angle, etc.), environmental data (wind speed, etc.) and textural descriptors. Shapefiles produced by an experienced human-analyst served as targets (validation) during the training portion of the investigation. Training and testing datasets were chosen for development and assessment of algorithm effectiveness as well as optimal conditions for oil detection in SAR data. The algorithm detects oil spills by following a 3-step methodology: object detection, feature extraction, and classification. Previous oil spill detection and classification methodologies such as machine learning algorithms, artificial neural networks (ANN), and multivariate classification methods like partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) are evaluated and compared. Statistical, transform, and model-based image texture techniques, commonly used for object mapping directly or as inputs for more complex methodologies, are explored to determine optimal textures for an oil spill detection system. The influence of the ancillary variables is explored, with a particular focus on the role of strong vs. weak wind forcing.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Quon, Eliot; Churchfield, Matthew; Cheung, Lawrence; Kern, Stefan
2017-02-01
This paper details the development of an aeroelastic wind plant model with large-eddy simulation (LES). The chosen LES solver is the Simulator for Wind Farm Applications (SOWFA) based on the OpenFOAM framework, coupled to NREL's comprehensive aeroelastic analysis tool, FAST. An atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) precursor simulation was constructed based on assessments of meteorological tower, lidar, and radar data over a 3-hour window. This precursor was tuned to the specific atmospheric conditions that occurred both prior to and during the measurement campaign, enabling capture of a night-to-day transition in the turbulent ABL. In the absence of height-varying temperature measurements, spatially averaged radar data were sufficient to characterize the atmospheric stability of the wind plant in terms of the shear profile, and near-ground temperature sensors provided a reasonable estimate of the ground heating rate describing the morning transition. A full aeroelastic simulation was then performed for a subset of turbines within the wind plant, driven by the precursor. Analysis of two turbines within the array, one directly waked by the other, demonstrated good agreement with measured time-averaged loads.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
N. Engler
2005-06-01
Full Text Available During the MIDAS/MaCWAVE campaign in summer 2002 we have observed turbulence using Doppler beam steering measurements obtained from the ALWIN VHF radar at Andøya/Northern Norway. This radar was operated in the Doppler beam steering mode for turbulence investigations during the campaign, as well as in spaced antenna mode, for continuously measuring the background wind field. The real-time data analysis of the Doppler radar backscattering provided the launch conditions for the sounding rockets. The spectral width data observed during the occurrence of PMSE were corrected for beam and shear broadening caused by the background wind field to obtain the turbulent part of the spectral width. The turbulent energy dissipation rates determined from the turbulent spectral width vary between 5 and 100mW kg-1 in the altitude range of 80-92km and increase with altitude. These estimations agree well with the in-situ measurements using the CONE sensor which was launched on 3 sounding rockets during the campaign.
-
Simulation of a weather radar display for over-water airborne radar approaches
Clary, G. R.
1983-01-01
Airborne radar approach (ARA) concepts are being investigated as a part of NASA's Rotorcraft All-Weather Operations Research Program on advanced guidance and navigation methods. This research is being conducted using both piloted simulations and flight test evaluations. For the piloted simulations, a mathematical model of the airborne radar was developed for over-water ARAs to offshore platforms. This simulated flight scenario requires radar simulation of point targets, such as oil rigs and ships, distributed sea clutter, and transponder beacon replies. Radar theory, weather radar characteristics, and empirical data derived from in-flight radar photographs are combined to model a civil weather/mapping radar typical of those used in offshore rotorcraft operations. The resulting radar simulation is realistic and provides the needed simulation capability for ongoing ARA research.
-
Flood Monitoring using X-band Dual-polarization Radar Network
Chandrasekar, V.; Wang, Y.; Maki, M.; Nakane, K.
2009-09-01
A dense weather radar network is an emerging concept advanced by the Center for Collaborative Adaptive Sensing of the Atmosphere (CASA). Using multiple radars observing over a common will create different data outcomes depending on the characteristics of the radar units employed and the network topology. To define this a general framework is developed to describe the radar network space, and formulations are obtained that can be used for weather radar network characterization. Current weather radar surveillance networks are based upon conventional sensing paradigm of widely-separated, standalone sensing systems using long range radars that operate at wavelengths in 5-10 cm range. Such configuration has limited capability to observe close to the surface of the earth because of the earth's curvature but also has poorer resolution at far ranges. The dense network radar system, observes and measures weather phenomenon such as rainfall and severe weather close to the ground at higher spatial and temporal resolution compared to the current paradigm. In addition the dense network paradigm also is easily adaptable to complex terrain. Flooding is one of the most common natural hazards in the world. Especially, excessive development decreases the response time of urban watersheds and complex terrain to rainfall and increases the chance of localized flooding events over a small spatial domain. Successful monitoring of urban floods requires high spatiotemporal resolution, accurate precipitation estimation because of the rapid flood response as well as the complex hydrologic and hydraulic characteristics in an urban environment. This paper reviews various aspects in radar rainfall mapping in urban coverage using dense X-band dual-polarization radar networks. By reducing the maximum range and operating at X-band, one can ensure good azimuthal resolution with a small-size antenna and keep the radar beam closer to the ground. The networked topology helps to achieve satisfactory
-
Shi, Chenguang; Wang, Fei; Salous, Sana; Zhou, Jianjiang
2017-11-25
In this paper, we investigate a low probability of intercept (LPI)-based optimal power allocation strategy for a joint bistatic radar and communication system, which is composed of a dedicated transmitter, a radar receiver, and a communication receiver. The joint system is capable of fulfilling the requirements of both radar and communications simultaneously. First, assuming that the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) corresponding to the target surveillance path is much weaker than that corresponding to the line of sight path at radar receiver, the analytically closed-form expression for the probability of false alarm is calculated, whereas the closed-form expression for the probability of detection is not analytically tractable and is approximated due to the fact that the received signals are not zero-mean Gaussian under target presence hypothesis. Then, an LPI-based optimal power allocation strategy is presented to minimize the total transmission power for information signal and radar waveform, which is constrained by a specified information rate for the communication receiver and the desired probabilities of detection and false alarm for the radar receiver. The well-known bisection search method is employed to solve the resulting constrained optimization problem. Finally, numerical simulations are provided to reveal the effects of several system parameters on the power allocation results. It is also demonstrated that the LPI performance of the joint bistatic radar and communication system can be markedly improved by utilizing the proposed scheme.
-
NASA's Newest SeaWinds Instrument Breezes Into Operation
2003-01-01
One of NASA's newest Earth-observing instruments, the SeaWinds scatterometer aboard Japan's Advanced Earth Observing Satellite (Adeos) 2--now renamed Midori 2--has successfully transmitted its first radar data to our home planet, generating its first high-quality images.From its orbiting perch high above Earth, SeaWinds on Midori 2 ('midori' is Japanese for the color green, symbolizing the environment) will provide the world's most accurate, highest resolution and broadest geographic coverage of ocean wind speed and direction, sea ice extent and properties of Earth's land surfaces. It will complement and eventually replace an identical instrument orbiting since June 1999 on NASA's Quick Scatterometer (QuikScat) satellite. Its three- to five-year mission will augment a long-term ocean surface wind data series that began in 1996 with launch of the NASA Scatterometer on Japan's first Adeos spacecraft.Climatologists, meteorologists and oceanographers will soon routinely use data from SeaWinds on Midori 2 to understand and predict severe weather patterns, climate change and global weather abnormalities like El Nino. The data are expected to improve global and regional weather forecasts, ship routing and marine hazard avoidance, measurements of sea ice extent and the tracking of icebergs, among other uses.'Midori 2, its SeaWinds instrument and associated ground processing systems are functioning very smoothly,' said Moshe Pniel, scatterometer projects manager at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 'Following initial checkout and calibration, we look forward to continuous operations, providing vital data to scientists and weather forecasters around the world.' 'These first images show remarkable detail over land, ice and oceans,' said Dr. Michael Freilich, Ocean Vector Winds Science Team Leader, Oregon State University, Corvallis, Ore. 'The combination of SeaWinds data and measurements from other instruments on Midori 2 with data from other international
-
Neish, Catherine D.; Carter, Lynn M.
2015-01-01
This chapter describes the principles of planetary radar, and the primary scientific discoveries that have been made using this technique. The chapter starts by describing the different types of radar systems and how they are used to acquire images and accurate topography of planetary surfaces and probe their subsurface structure. It then explains how these products can be used to understand the properties of the target being investigated. Several examples of discoveries made with planetary radar are then summarized, covering solar system objects from Mercury to Saturn. Finally, opportunities for future discoveries in planetary radar are outlined and discussed.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shershakov, V.M.; Zukov, G.P.; Kosykh, V.S.
2003-01-01
radiation monitoring laboratory and the LDU was on the bank of the cooling pond. The main characteristics of a cloud of substances are standard deviations in the spatial concentration distributions in the cloud along mutually perpendicular directions, which are representative spatial scales of the cloud in these directions. The squares of these values are relative variances of the cloud. These characteristics were the first to determine and are among the most important input parameters in different models assessing transport and dispersion of hazardous substances. Dispersion of a cloud of substances is influenced by turbulence and vertical shifts of the mean wind speed, with the patterns of dispersion being different depending an diffusion time (or distance to a source). The results of the conducted experiments have revealed an important advantage of the used radar complex in terms of support to predictions of possible contamination in case of release of hazardous materials. As the chaff cloud moves with the wind and is dispersed, it echoes the meteorological situation at a given time moment (vertical wind distribution and air temperature, turbulence level, boundary layer thickness, type of underlying surface) and any changes occurring in the conditions on its way. Based on obtained radar data, the radar complex is capable of assessing the dispersion parameters which can then be used in the mathematical transport and dispersion models. What's more, determination of these parameters does not require any meteorological measurements. In addition, using data about movement of the cloud centroid, the wind speed and direction is estimated at the release height by the radar complex itself. The conducted experiments have shown that the developed technology makes possible measuring key parameters of a cloud of substances at the height of dispersion and taking into account local features of the distribution of meteorological quantities occurring in the vicinity of a source. This
-
Kingsley, Simon
1999-01-01
What is radar? What systems are currently in use? How do they work? This book provides engineers and scientists with answers to these critical questions, focusing on actual radar systems in use today. It is a perfect resource for those just entering the field, or as a quick refresher for experienced practitioners. The book leads readers through the specialized language and calculations that comprise the complex world of radar engineering as seen in dozens of state-of-the-art radar systems. An easy to read, wide ranging guide to the world of modern radar systems.
-
Alabaster, Clive
2012-01-01
This book is a practitioner's guide to all aspects of pulse Doppler radar. It concentrates on airborne military radar systems since they are the most used, most complex, and most interesting of the pulse Doppler radars; however, ground-based and non-military systems are also included. It covers the fundamental science, signal processing, hardware issues, systems design and case studies of typical systems. It will be a useful resource for engineers of all types (hardware, software and systems), academics, post-graduate students, scientists in radar and radar electronic warfare sectors and milit
-
Radar orthogonality and radar length in Finsler and metric spacetime geometry
Pfeifer, Christian
2014-09-01
The radar experiment connects the geometry of spacetime with an observers measurement of spatial length. We investigate the radar experiment on Finsler spacetimes which leads to a general definition of radar orthogonality and radar length. The directions radar orthogonal to an observer form the spatial equal time surface an observer experiences and the radar length is the physical length the observer associates to spatial objects. We demonstrate these concepts on a forth order polynomial Finsler spacetime geometry which may emerge from area metric or premetric linear electrodynamics or in quantum gravity phenomenology. In an explicit generalization of Minkowski spacetime geometry we derive the deviation from the Euclidean spatial length measure in an observers rest frame explicitly.
-
BIRDS’ FLIGHT ENERGY PREDICTIONS AND APPLICATION TO RADAR-TRACKING STUDY
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Matsyura Alex
2013-12-01
Full Text Available In ofered research, we propose to observe diurnal soaring birds to check, whether there the positions of birds in formations are such, that the wing tip interval and depth met the predictions of aerodynamic theory for achievement of maximal conservation of energy or predictions of the hypothesis of communication. We also can estimate, whether adverse conditions of a wind influence the abilty of birds to support formation. We can asume that windy conditions during flight might make precision flight more dificult by inducing both unpredictable bird and vortex positions. To this, we ned to found change in wing-tip spacing variation with increasing wind sped, sugesting or rejecting that in high winds bird skeins maintained similar variation to that on calm days. The interelation betwen variation of mean depth and wind sped should prove this hypothesis. Litle is known about the importance of depth, but in high winds the vortex is likely to break up more rapidly and its location become unpredictable the further back a bird flies; therefore, a shift towards skeins with more regular depths at high wind speds may compensate for the unpredictabilty of the vortex locations. Any significant relationship betwen the standard deviation of wing-tip spacing and wind sped sugests that wind has a major efect on optimal positioning. Results of proposed study wil be used also as the auxilary tol in radar research of bird migration, namely in research of flight features of soaring birds. It is extremely important to determine al pertinent characteristics of flock for model species, namely flocking birds
-
Wave Tank Studies of Strong Modulation of Wind Ripples Due To Long Waves
Ermakov, S.; Sergievskaya, I.; Shchegolkov, Yu.
Modulation of wind capillary-gravity ripples due to long waves has been studied in wave tank experiment at low wind speeds using Ka-band radar. The experiments were carried out both for clean water and the water surface covered with surfactant films. It is obtained that the modulation of radar signals is quite strong and can increase with surfactant concentration and fetch. It is shown that the hydrodynamic Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) calculated for free wind ripples and taking into account the kinematic (straining) effect, variations of the wind stress and variations of surfactant concentration strongly underestimates experimental MTF-values. The effect of strong modulation is assumed to be connected with nonlinear harmonics of longer dm-cm- scale waves - bound waves ("parasitic ripples"). The intensity of bound waves depends strongly on the amplitude of decimetre-scale waves, therefore even weak modulation of the dm-scale waves due to long waves results to strong ("cascade") modulation of bound waves. Modulation of the system of "free/bound waves" is estimated using results of wave tank studies of bound waves generation and is shown to be in quali- tative agreement with experiment. This work was supported by MOD, UK via DERA Winfrith (Project ISTC 1774P) and by RFBR (Project 02-05-65102).
-
Surveillance and remote sensing: ITOPF participation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nichols, J.A.
1992-01-01
Although the Federation does not sponsor or undertake surveillance and remote sensing research and development projects, it is a potential user of remote sensing equipment when responding to oil spills. Indeed, the Federation has already made use of suitably equipped aircraft on a number of occasions in Europe. Several countries in north west Europe, viz. France, Germany, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and the U.K., operate aircraft fitted with broadly similar systems comprising side-looking airborne radar (SLAR), infra-red line scanners (IRLS) and ultra-violet line scanners (UVLS). These aircraft are used routinely for the detection of operational discharges of oil from ships in violation of the International Convention on the Prevention of Pollution from Ships 73/78 (MARPOL 73/78)
-
Li, Xiaowen; Janiga, Matthew A.; Wang, Shuguang; Tao, Wei-Kuo; Rowe, Angela; Xu, Weixin; Liu, Chuntao; Matsui, Toshihisa; Zhang, Chidong
2018-04-01
Evolution of precipitation structures are simulated and compared with radar observations for the November Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) event during the DYNAmics of the MJO (DYNAMO) field campaign. Three ground-based, ship-borne, and spaceborne precipitation radars and three cloud-resolving models (CRMs) driven by observed large-scale forcing are used to study precipitation structures at different locations over the central equatorial Indian Ocean. Convective strength is represented by 0-dBZ echo-top heights, and convective organization by contiguous 17-dBZ areas. The multi-radar and multi-model framework allows for more stringent model validations. The emphasis is on testing models' ability to simulate subtle differences observed at different radar sites when the MJO event passed through. The results show that CRMs forced by site-specific large-scale forcing can reproduce not only common features in cloud populations but also subtle variations observed by different radars. The comparisons also revealed common deficiencies in CRM simulations where they underestimate radar echo-top heights for the strongest convection within large, organized precipitation features. Cross validations with multiple radars and models also enable quantitative comparisons in CRM sensitivity studies using different large-scale forcing, microphysical schemes and parameters, resolutions, and domain sizes. In terms of radar echo-top height temporal variations, many model sensitivity tests have better correlations than radar/model comparisons, indicating robustness in model performance on this aspect. It is further shown that well-validated model simulations could be used to constrain uncertainties in observed echo-top heights when the low-resolution surveillance scanning strategy is used.
-
Willis, Nick
2007-01-01
Advances in Bistatic Radar updates and extends bistatic and multistatic radar developments since publication of Willis' Bistatic Radar in 1991. New and recently declassified military applications are documented. Civil applications are detailed including commercial and scientific systems. Leading radar engineers provide expertise to each of these applications. Advances in Bistatic Radar consists of two major sections: Bistatic/Multistatic Radar Systems and Bistatic Clutter and Signal Processing. Starting with a history update, the first section documents the early and now declassified military
-
Recommendation on Transition from Primary/Secondary Radar to Secondary- Only Radar Capability
1994-10-01
Radar Beacon Performance Monitor RCIU Remote Control Interface Unit RCL Remote Communications Link R E&D Research, Engineering and Development RML Radar...rate. 3.1.2.5 Maintenance The current LRRs have limited remote maintenance monitoring (RMM) capabilities via the Remote Control Interface Unit ( RCIU ...1, -2 and FPS-20 radars required an upgrade of some of the radar subsystems, namely the RCIU to respond as an RMS and the CD to interface with radar
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Badger, Merete; Nawri, Nikolai
2015-01-01
effects, gap flow, coastal barrier jets, and atmospheric gravity waves are not only observed in SAR, but are also modeled well from HARMONIE. Offshore meteorological observations are not available, but wind speed and wind direction measurements from coastal meteorological masts are found to compare well...... to nearby offshore locations observed by SAR. More than 2500 SAR scenes from the Envisat ASAR wide swathmode are used for wind energy resource estimation. The wind energy potential observed from satellite SAR shows high values above 1000 Wm −2 in coastal regions in the south, east, and west, with lower...
-
Jorgensen, David P.; Hanshaw, Maiana N.; Schmidt, Kevin M.; Laber, Jayme L; Staley, Dennis M.; Kean, Jason W.; Restrepo, Pedro J.
2011-01-01
A portable truck-mounted C-band Doppler weather radar was deployed to observe rainfall over the Station Fire burn area near Los Angeles, California, during the winter of 2009/10 to assist with debris-flow warning decisions. The deployments were a component of a joint NOAA–U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) research effort to improve definition of the rainfall conditions that trigger debris flows from steep topography within recent wildfire burn areas. A procedure was implemented to blend various dual-polarized estimators of precipitation (for radar observations taken below the freezing level) using threshold values for differential reflectivity and specific differential phase shift that improves the accuracy of the rainfall estimates over a specific burn area sited with terrestrial tipping-bucket rain gauges. The portable radar outperformed local Weather Surveillance Radar-1988 Doppler (WSR-88D) National Weather Service network radars in detecting rainfall capable of initiating post-fire runoff-generated debris flows. The network radars underestimated hourly precipitation totals by about 50%. Consistent with intensity–duration threshold curves determined from past debris-flow events in burned areas in Southern California, the portable radar-derived rainfall rates exceeded the empirical thresholds over a wider range of storm durations with a higher spatial resolution than local National Weather Service operational radars. Moreover, the truck-mounted C-band radar dual-polarimetric-derived estimates of rainfall intensity provided a better guide to the expected severity of debris-flow events, based on criteria derived from previous events using rain gauge data, than traditional radar-derived rainfall approaches using reflectivity–rainfall relationships for either the portable or operational network WSR-88D radars. Part of the reason for the improvement was due to siting the radar closer to the burn zone than the WSR-88Ds, but use of the dual-polarimetric variables
-
An Improved Semi-Empirical Model for Radar Backscattering from Rough Sea Surfaces at X-Band
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Taekyeong Jin
2018-04-01
Full Text Available We propose an improved semi-empirical scattering model for X-band radar backscattering from rough sea surfaces. This new model has a wider validity range of wind speeds than does the existing semi-empirical sea spectrum (SESS model. First, we retrieved the small-roughness parameters from the sea surfaces, which were numerically generated using the Pierson-Moskowitz spectrum and measurement datasets for various wind speeds. Then, we computed the backscattering coefficients of the small-roughness surfaces for various wind speeds using the integral equation method model. Finally, the large-roughness characteristics were taken into account by integrating the small-roughness backscattering coefficients multiplying them with the surface slope probability density function for all possible surface slopes. The new model includes a wind speed range below 3.46 m/s, which was not covered by the existing SESS model. The accuracy of the new model was verified with two measurement datasets for various wind speeds from 0.5 m/s to 14 m/s.
-
Adaptive radar resource management
Moo, Peter
2015-01-01
Radar Resource Management (RRM) is vital for optimizing the performance of modern phased array radars, which are the primary sensor for aircraft, ships, and land platforms. Adaptive Radar Resource Management gives an introduction to radar resource management (RRM), presenting a clear overview of different approaches and techniques, making it very suitable for radar practitioners and researchers in industry and universities. Coverage includes: RRM's role in optimizing the performance of modern phased array radars The advantages of adaptivity in implementing RRMThe role that modelling and
-
Bole, A G
2013-01-01
Radar and ARPA Manual focuses on the theoretical and practical aspects of electronic navigation. The manual first discusses basic radar principles, including principles of range and bearing measurements and picture orientation and presentation. The text then looks at the operational principles of radar systems. Function of units; aerial, receiver, and display principles; transmitter principles; and sitting of units on board ships are discussed. The book also describes target detection, Automatic Radar Plotting Aids (ARPA), and operational controls of radar systems, and then discusses radar plo
-
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Naicker, K
2011-04-01
Full Text Available Maritime border safeguarding is a vital component in the protection of a countries resources and interests against illegal activities. With the increasing asymmetric nature of today’s threats, a primary requirement of any coastal surveillance system...
-
2012-01-01
RTA HFM-201/RSM PAPER 3 - 1 © 2012 The MITRE Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Social Radar Barry Costa and John Boiney MITRE Corporation...defenders require an integrated set of capabilities that we refer to as a “ social radar.” Such a system would support strategic- to operational-level...situation awareness, alerting, course of action analysis, and measures of effectiveness for each action undertaken. Success of a social radar
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tegen, Suzanne
2017-05-24
This presentation provides an overview of findings from a report published in 2016 by researchers at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, An Initial Evaluation of Siting Considerations on Current and Future Wind Deployment. The presentation covers the background for research, the Energy Department's Wind Vision, research methods, siting considerations, the wind project deployment process, and costs associated with siting considerations.
-
Performance of wind energy in 2015 and future perspectives - Press file
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Allenet, Tiffany; Resse, Bastien; Kari, Cynthia
2016-01-01
This document first proposes a press release which outlines the steady growth of the wind energy installed power in France, the conditions to be met for a continuous progression of wind energy, the necessary development of offshore wind energy production, and the necessity of an agreement with military authorities who still limit wind farm projects because of constraints related to air force training and to military radars. Data are then presented regarding the installed and connected power (manufacturer shares), technical characteristics of the main installed models, installed capacity per region. Brief articles comment the implications of the COP21 for the wind energy sector and French territories, the project of multi-annual planning of energy for 2016-2023, the military constraints and propositions to reduce them, and the rather high growth of employment in the sector
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. Chisham
2000-02-01
Full Text Available We present data from conjugate SuperDARN radars describing the high-latitude ionosphere's response to changes in the direction of IMF By during a period of steady IMF Bz southward and Bx positive. During this interval, the radars were operating in a special mode which gave high-time resolution data (30 s sampling period on three adjacent beams with a full scan every 3 min. The location of the radars around magnetic local noon at the time of the event allowed detailed observations of the variations in the ionospheric convection patterns close to the cusp region as IMF By varied. A significant time delay was observed in the ionospheric response to the IMF By changes between the two hemispheres. This is explained as being partially a consequence of the location of the dominant merging region on the magnetopause, which is ~8-12RE closer to the northern ionosphere than to the southern ionosphere (along the magnetic field line due to the dipole tilt of the magnetosphere and the orientation of the IMF. This interpretation supports the anti-parallel merging hypothesis and highlights the importance of the IMF Bx component in solar wind-magnetosphere coupling.Key words: Ionosphere (plasma convection - Magnetospheric physics (magnetopause, cusp, and boundary layers; solar wind - magnetosphere interactions
-
Design and development of correlation techniques to maintain a space surveillance system catalogue
Olmedo, E.; Sánchez Ortiz, Noelia; Lerate, Mercedes; Belló-Mora, Miguel; Klinkrad, H.
2009-10-01
A growing interest exists in a future, autonomous European Space Surveillance System (ESSS). Currently, most of the knowledge about Earth-orbiting space objects is based on information provided by the USASPACECOM. This paper presents the required initial orbit determination (IOD) and correlation techniques to process optical measurements. Former studies were focused on the handling of radar measurements, which are summarised with the aim of describing a global procedure for processing hybrid measurement types (combination of radar and optic data for catalogue maintenance). The introduction of manoeuvres are presented due to their importance in the space object catalogue maintenance. The detection of uncatalogued objects and the successful correlation of already catalogued objects involve two different tasks for telescopes: survey and tasking. Assumptions for both strategies are developed on the basis of the previous work developed at the University of Berne (see [T. Flohrer, T. Schildknecht, R. Musci, E. Stöveken, Performance estimation for GEO space surveillance, Advances in Space Research 35 (2005). [1]; T. Flohrer, T. Schildknecht, R. Musci, Proposed strategies for optical observations in a future European Space Surveillance Network, presented in the 36th COSPAR Scientific Assembly (2006). [2]; R. Musci, T. Schildknecht, M. Ploner, Orbit improvement for GEO objects using follow-up observations, Advances in Space Research 34 (2004). [3]; R. Musci, T. Schildknecht, M. Ploner, G. Beutler, Orbit improvement for GTO objects using follow-up observations, Advances in Space Research 35 (2005). [4]; R. Musci, T. Schildknecht, T. Flohrer, G. Beutler, Concept for a catalogue of space debris in GEO, Proceedings of the Fourth European Conference on Space Debris, (ESA SP-587, 2005). [5
-
Novel radar techniques and applications
Klemm, Richard; Lombardo, Pierfrancesco; Nickel, Ulrich
2017-01-01
Novel Radar Techniques and Applications presents the state-of-the-art in advanced radar, with emphasis on ongoing novel research and development and contributions from an international team of leading radar experts. This volume covers: Real aperture array radar; Imaging radar and Passive and multistatic radar.
-
Albers, Cerese; Sippel, Jason A.; Braun, Scott A.; Miller, Timothy
2012-01-01
Previous studies (e.g., Zhang et al. 2009, Weng et al. 2011) have shown that radial velocity data from airborne and ground-based radars can be assimilated into ensemble Kalman filter (EnKF) systems to produce accurate analyses of tropical cyclone vortices, which can reduce forecast intensity error. Recently, wind speed data from SFMR technology has also been assimilated into the same types of systems and has been shown to improve the forecast intensity of mature tropical cyclones. Two instruments that measure these properties were present during the NASA Genesis and Rapid Intensification Processes (GRIP) field experiment in 2010 which sampled Hurricane Karl, and will next be co-located on the same aircraft for the subsequent NASA HS3 experiment. The High Altitude Wind and Rain Profiling Radar (HIWRAP) is a conically scanning Doppler radar mounted upon NASAs Global Hawk unmanned aerial vehicle, and the usefulness of its radial velocity data for assimilation has not been previously examined. Since the radar scans from above with a fairly large fixed elevation angle, it observes a large component of the vertical wind, which could degrade EnKF analyses compared to analyses with data taken from lesser elevation angles. The NASA Hurricane Imaging Radiometer (HIRAD) is a passive microwave radiometer similar to SFMR, and measures emissivity and retrieves hurricane surface wind speeds and rain rates over a much wider swath. Thus, this study examines the impact of assimilating simulated HIWRAP radial velocity data into an EnKF system, simulated HIRAD wind speed, and HIWRAP+HIRAD with the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model and compares the results to no data assimilation and also to the Truth from which the data was simulated for both instruments.
-
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Anderson, F
2008-11-01
Full Text Available of an S&T capability based on international technology trends in persistent, ubiquitous surveillance. The ultimate aim of this programme is to develop and produce a series of South African innovations that can be used by departments and agencies...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. G. Yoe
Full Text Available The aspect sensitivity of SOUSY-VHF-radar oblique-beam echoes from the troposphere and lower stratosphere has been examined for a number of jet stream passages during the years 1990 - 1992. When the core of the jet is overhead or nearly so, vertical profiles of the aspect sensitivity display two notable features. First, the distinction between mainly isotropic and strongly aspect-sensitive echoes in the troposphere and the lower stratosphere, respectively, often reported for measurements made during calm conditions, does not necessarily prevail in the vicinity of the jet stream. Second, echoes obtained at altitudes near the height of the horizontal wind maximum are found to be more aspect sensitive for beams directed parallel to the horizontal flow or nearly so, than for other beam directions. It is demonstrated that time-averaged horizontal wind speeds estimated from the radar data, taking into account the reduced effective oblique-beam zenith angle resulting from aspect sensitivity, may exceed uncorrected wind speeds by as much as 10 m s-1 in these circumstances. Implications for wind profiling and for describing the backscattering process are discussed. Doppler spectral widths examined for one jet stream passage are found to be narrower in a beam aligned with the horizontal wind at heights near the wind speed maximum than corresponding widths measured in a beam projected at right angles to the jet. The narrowest spectra thus coincide with the most aspect-sensitive echoes, consistent with the hypothesis that such returns result from specular backscattering processes.
-
Minimum redundancy MIMO radars
Chen, Chun-Yang; Vaidyanathan, P. P.
2008-01-01
The multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) radar concept has drawn considerable attention recently. In the traditional single-input multiple-output (SIMO) radar system, the transmitter emits scaled versions of a single waveform. However, in the MIMO radar system, the transmitter transmits independent waveforms. It has been shown that the MIMO radar can be used to improve system performance. Most of the MIMO radar research so far has focused on the uniform array. However, i...
-
The Offshore New European Wind Atlas
Karagali, I.; Hahmann, A. N.; Badger, M.; Hasager, C.; Mann, J.
2017-12-01
The New European Wind Atlas (NEWA) is a joint effort of research agencies from eight European countries, co-funded under the ERANET Plus Program. The project is structured around two areas of work: development of dynamical downscaling methodologies and measurement campaigns to validate these methodologies, leading to the creation and publication of a European wind atlas in electronic form. This atlas will contain an offshore component extending 100 km from the European coasts. To achieve this, mesoscale models along with various observational datasets are utilised. Scanning lidars located at the coastline were used to compare the coastal wind gradient reproduced by the meso-scale model. Currently, an experimental campaign is occurring in the Baltic Sea, with a lidar located in a commercial ship sailing from Germany to Lithuania, thus covering the entire span of the south Baltic basin. In addition, satellite wind retrievals from scatterometers and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) instruments were used to generate mean wind field maps and validate offshore modelled wind fields and identify the optimal model set-up parameters.The aim of this study is to compare the initial outputs from the offshore wind atlas produced by the Weather & Research Forecasting (WRF) model, still in pre-operational phase, and the METOP-A/B Advanced Scatterometer (ASCAT) wind fields, reprocessed to stress equivalent winds at 10m. Different experiments were set-up to evaluate the model sensitivity for the various domains covered by the NEWA offshore atlas. ASCAT winds were utilised to assess the performance of the WRF offshore atlases. In addition, ASCAT winds were used to create an offshore atlas covering the years 2007 to 2016, capturing the signature of various spatial wind features, such as channelling and lee effects from complex coastal topographical elements.
-
2007-09-01
Analysis and Design. Wiley- Interscience, 111 River Street, Hoboken, NJ, 3 edition, 2005. ISBN 0-471-66782. 2. Carlos A. Coello Coello, David A. Van ... Veldhuizen and Gary B. Lamont. Evolu- tionary Algorithms for solving Multi-Objective Problems. Kluwer Academic Pub- lishers, 233 Spring Street, New York...Building, Suite 1035, 150 South Independence Mall West, Philadelphia, PA 19106, 2000. 27. Van Blaricum, G. F. “Tactical Air Surveillance RADAR Netting
-
Principles of modern radar systems
Carpentier, Michel H
1988-01-01
Introduction to random functions ; signal and noise : the ideal receiver ; performance of radar systems equipped with ideal receivers ; analysis of the operating principles of some types of radar ; behavior of real targets, fluctuation of targets ; angle measurement using radar ; data processing of radar information, radar coverage ; applications to electronic scanning antennas to radar ; introduction to Hilbert spaces.
-
Decker, Ryan; Barbre, Robert E., Jr.
2011-01-01
Impact of winds to space launch vehicle include Design, Certification Day-of-launch (DOL) steering commands (1)Develop "knockdowns" of load indicators (2) Temporal uncertainty of flight winds. Currently use databases from weather balloons. Includes discrete profiles and profile pair datasets. Issues are : (1)Larger vehicles operate near design limits during ascent 150 discrete profiles per month 110-217 seasonal 2.0 and 3.5-hour pairs Balloon rise time (one hour) and drift (up to 100 n mi) Advantages of the Alternative approach using Doppler Radar Wind Profiler (DRWP) are: (1) Obtain larger sample size (2) Provide flexibility for assessing trajectory changes due to winds (3) Better representation of flight winds.
-
The Next Generation Airborne Polarimetric Doppler Radar
Vivekanandan, J.; Lee, Wen-Chau; Loew, Eric; Salazar, Jorge; Chandrasekar, V.
2013-04-01
NCAR's Electra Doppler radar (ELDORA) with a dual-beam slotted waveguide array using dual-transmitter, dual-beam, rapid scan and step-chirped waveform significantly improved the spatial scale to 300m (Hildebrand et al. 1996). However, ELDORA X-band radar's penetration into precipitation is limited by attenuation and is not designed to collect polarimetric measurements to remotely estimate microphysics. ELDORA has been placed on dormancy because its airborne platform (P3 587) was retired in January 2013. The US research community has strongly voiced the need to continue measurement capability similar to the ELDORA. A critical weather research area is quantitative precipitation estimation/forecasting (QPE/QPF). In recent years, hurricane intensity change involving eye-eyewall interactions has drawn research attention (Montgomery et al., 2006; Bell and Montgomery, 2006). In the case of convective precipitation, two issues, namely, (1) when and where convection will be initiated, and (2) determining the organization and structure of ensuing convection, are key for QPF. Therefore collocated measurements of 3-D winds and precipitation microphysics are required for achieving significant skills in QPF and QPE. Multiple radars in dual-Doppler configuration with polarization capability estimate dynamical and microphysical characteristics of clouds and precipitation are mostly available over land. However, storms over complex terrain, the ocean and in forest regions are not observable by ground-based radars (Bluestein and Wakimoto, 2003). NCAR/EOL is investigating potential configurations for the next generation airborne radar that is capable of retrieving dynamic and microphysical characteristics of clouds and precipitation. ELDORA's slotted waveguide array radar is not compatible for dual-polarization measurements. Therefore, the new design has to address both dual-polarization capability and platform requirements to replace the ELDORA system. NCAR maintains a C-130
-
Automated intelligent video surveillance system for ships
Wei, Hai; Nguyen, Hieu; Ramu, Prakash; Raju, Chaitanya; Liu, Xiaoqing; Yadegar, Jacob
2009-05-01
To protect naval and commercial ships from attack by terrorists and pirates, it is important to have automatic surveillance systems able to detect, identify, track and alert the crew on small watercrafts that might pursue malicious intentions, while ruling out non-threat entities. Radar systems have limitations on the minimum detectable range and lack high-level classification power. In this paper, we present an innovative Automated Intelligent Video Surveillance System for Ships (AIVS3) as a vision-based solution for ship security. Capitalizing on advanced computer vision algorithms and practical machine learning methodologies, the developed AIVS3 is not only capable of efficiently and robustly detecting, classifying, and tracking various maritime targets, but also able to fuse heterogeneous target information to interpret scene activities, associate targets with levels of threat, and issue the corresponding alerts/recommendations to the man-in- the-loop (MITL). AIVS3 has been tested in various maritime scenarios and shown accurate and effective threat detection performance. By reducing the reliance on human eyes to monitor cluttered scenes, AIVS3 will save the manpower while increasing the accuracy in detection and identification of asymmetric attacks for ship protection.
-
Transmission of wave energy through an offshore wind turbine farm
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Christensen, Erik Damgaard; Johnson, Martin; Sørensen, Ole Rene
2013-01-01
condition at infinity. From airborne and Satellite SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) a model has been derived for the change of the water surface friction C) inside and on the lee side of the offshore wind farm. The effects have been implemented in a spectral wind wave model,MIKE21 SW, and a parametric study......The transmission of wave energy passing an offshore wind farm is studied. Three effects that can change the wave field are analysed, which is the A) energy dissipation due to drag resistance, B) wave reflection/diffraction from structures, and C) the effect of a modified wind field inside...... and on the lee side of the wind farm. The drag dissipation, A), is quantified by a quadratic resistance law. The effect of B) is parameterised based on 1st order potential theory. A method to find the amount of reflected and transmitted wave energy is developed based on the panel method WAMIT™ and a radiation...
-
Lhermitte, R. M.; Conte, D.; Pasqualucci, F.; Lennon, C.; Serafin, R. J.
1978-01-01
Storm data obtained on August 1, 1977 are examined in an attempt to interpret the relationship between lightning occurrence and the thunderstorm inner dynamics and precipitation processes. Horizontal maps are presented which indicated the position of radiation sources detected by the Lightning Detection and Ranging (LDAR) network, together with the horizontal motion fields and radar reflectivity data. Detailed inspection of these fields showed that, although radiation sources are found in the vicinity of precipitation cells, they are not located in the heavy precipitation areas, but rather on their rear side in regions where the configuration of the wind fields suggests the presence of updrafts.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
N. F. Arnold
2001-04-01
Full Text Available The Doppler shifts of meteor echoes measured by the SuperDARN HF radar network have been used in several studies to observe neutral winds in the upper mesosphere and lower thermosphere region. In the absence of accurate height information for individual meteors, it has been necessary to assume a statistical mean meteor layer where the variations in altitude were not correlated to changes in the horizontal winds. Observations of spectral width distribution variations made by the radars allow an independent determination of the systematic error in the height. We have investigated the dependence of this distribution on a number of factors including the radar geometry, diurnal and seasonal cycles, variations in solar UV irradiance and geomagnetic activity. Changes in the altitude of the mean meteor layer observed at different radar ranges provide us with some insight into the structure of the upper mesosphere and the lower thermosphere within which the meteors are being ablated. An examination of the spectral widths, as measured by the CUT-LASS Finland radar, in the days preceding and following a Storm Sudden Commencement in April 1997, illustrates how the spectral properties of the observed region can be affected. The variations in the widths were consistent with model calculations of the changes to the temperature profile over this interval. Further refinements in the determination of the spectral width are outlined for future experiments.Key words. Meterology and atmospheric dynamics (middle atmosphere dynamics; thermospheric dynamics; instruments and techniques
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
N. F. Arnold
Full Text Available The Doppler shifts of meteor echoes measured by the SuperDARN HF radar network have been used in several studies to observe neutral winds in the upper mesosphere and lower thermosphere region. In the absence of accurate height information for individual meteors, it has been necessary to assume a statistical mean meteor layer where the variations in altitude were not correlated to changes in the horizontal winds. Observations of spectral width distribution variations made by the radars allow an independent determination of the systematic error in the height. We have investigated the dependence of this distribution on a number of factors including the radar geometry, diurnal and seasonal cycles, variations in solar UV irradiance and geomagnetic activity. Changes in the altitude of the mean meteor layer observed at different radar ranges provide us with some insight into the structure of the upper mesosphere and the lower thermosphere within which the meteors are being ablated. An examination of the spectral widths, as measured by the CUT-LASS Finland radar, in the days preceding and following a Storm Sudden Commencement in April 1997, illustrates how the spectral properties of the observed region can be affected. The variations in the widths were consistent with model calculations of the changes to the temperature profile over this interval. Further refinements in the determination of the spectral width are outlined for future experiments.
Key words. Meterology and atmospheric dynamics (middle atmosphere dynamics; thermospheric dynamics; instruments and techniques -
A comparison of mixing depths observed by ground-based wind profilers and an airborne lidar
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
White, A.B.; Senff, C. [Univ. of Colorado/NOAA Environmental Technology Lab., Cooperative Inst. for Research in Environmental Sciences, Boulder, CO (United States); Banta, R.M. [NOAA Environmental Technology Lab., Boulder, CO (United States)
1997-10-01
The mixing depth is one of the most important parameters in air pollution studies because it determines the vertical extent of the `box` in which pollutants are mixed and dispersed. During the 1995 Southern Oxidants Study (SOS95), scientists from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Environmental Technology Laboratory (NOAA/ETL) deployed four 915-MHz boundary-layer radar/wind profilers (hereafter radars) in and around the Nashville, Tennessee metropolitan area. Scientists from NOAA/ETL also operated an ultraviolet differential absorption lidar (DIAL) onboard a CASA-212 aircraft. Profiles from radar and DIAL can be used to derive estimates of the mixing depth. The methods used for both instruments are similar in that they depend on information derived from the backscattered power. However, different scattering mechanisms for the radar and DIAL mean that different tracers of mixing depth are measured. In this paper we compare the mixing depth estimates obtained from the radar and DIAL and discuss the similarities and differences that occur. (au)
-
A millimetre-wave MIMO radar system for threat detection in urban environments
Kirschner, A. J.; Guetlein, J.; Bertl, S.; Detlefsen, J.
2012-10-01
The European Defence Agency (EDA) engages countermeasures against Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) by funding several scientific programs on threat awareness, countermeasures IEDs or land-mine detection, in which this work is only one of numerous projects. The program, denoted as Surveillance in an urban environment using mobile sensors (SUM), covers the idea of equipping one or more vehicles of a patrol or a convoy with a set of sensors exploiting different physical principles in order to gain detailed insights of the road situation ahead. In order to give an added value to a conventional visual camera system, measurement data from an infra-red (IR) camera, a radiometer and a millimetre-wave radar are fused with data from an optical image and are displayed on a human-machine-interface (HMI) which shall assist the vehicle's co-driver to identify suspect objects or persons on or next to the road without forcing the vehicle to stop its cruise. This paper shall especially cover the role of the millimetre-wave radar sensor and its different operational modes. Measurement results are discussed. It is possible to alter the antenna mechanically which gives two choices for a field of view and angular resolution trade-off. Furthermore a synthetic aperture radar mode is possible and has been tested successfully. MIMO radar principles like orthogonal signal design were exploited tofrom a virtual array by 4 transmitters and 4 receivers. In joint evaluation, it was possible to detect e.g. grenade shells under cardboard boxes or covered metal barrels which were invisible for optical or infra-red detection.
-
Sensor-Oriented Path Planning for Multiregion Surveillance with a Single Lightweight UAV SAR
Li, Jincheng; Chen, Jie; Wang, Pengbo; Li, Chunsheng
2018-01-01
In the surveillance of interested regions by unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), system performance relies greatly on the motion control strategy of the UAV and the operation characteristics of the onboard sensors. This paper investigates the 2D path planning problem for the lightweight UAV synthetic aperture radar (SAR) system in an environment of multiple regions of interest (ROIs), the sizes of which are comparable to the radar swath width. Taking into account the special requirements of the SAR system on the motion of the platform, we model path planning for UAV SAR as a constrained multiobjective optimization problem (MOP). Based on the fact that the UAV route can be designed in the map image, an image-based path planner is proposed in this paper. First, the neighboring ROIs are merged by the morphological operation. Then, the parts of routes for data collection of the ROIs can be located according to the geometric features of the ROIs and the observation geometry of UAV SAR. Lastly, the route segments for ROIs surveillance are connected by a path planning algorithm named the sampling-based sparse A* search (SSAS) algorithm. Simulation experiments in real scenarios demonstrate that the proposed sensor-oriented path planner can improve the reconnaissance performance of lightweight UAV SAR greatly compared with the conventional zigzag path planner. PMID:29439447
-
Sensor-Oriented Path Planning for Multiregion Surveillance with a Single Lightweight UAV SAR.
Li, Jincheng; Chen, Jie; Wang, Pengbo; Li, Chunsheng
2018-02-11
In the surveillance of interested regions by unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), system performance relies greatly on the motion control strategy of the UAV and the operation characteristics of the onboard sensors. This paper investigates the 2D path planning problem for the lightweight UAV synthetic aperture radar (SAR) system in an environment of multiple regions of interest (ROIs), the sizes of which are comparable to the radar swath width. Taking into account the special requirements of the SAR system on the motion of the platform, we model path planning for UAV SAR as a constrained multiobjective optimization problem (MOP). Based on the fact that the UAV route can be designed in the map image, an image-based path planner is proposed in this paper. First, the neighboring ROIs are merged by the morphological operation. Then, the parts of routes for data collection of the ROIs can be located according to the geometric features of the ROIs and the observation geometry of UAV SAR. Lastly, the route segments for ROIs surveillance are connected by a path planning algorithm named the sampling-based sparse A* search (SSAS) algorithm. Simulation experiments in real scenarios demonstrate that the proposed sensor-oriented path planner can improve the reconnaissance performance of lightweight UAV SAR greatly compared with the conventional zigzag path planner.
-
Offshore wind resource mapping for Europe by Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellite data
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hasager, Charlotte Bay; Badger, Merete
2015-01-01
For the New European Wind Atlas (NEWA) project with 8 participating countries during5 years (March 2015 – March 2020) we will develop a new wind atlas covering most of the European countries as well as most of the offshore areas in Europe. For the offshore atlas we will rely on a combination of s...
-
Comparison of Geophysical Model Functions for SAR Wind Speed Retrieval in Japanese Coastal Waters
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Takeyama, Yuko; Ohsawa, Teruo; Kozai, Katsutoshi
2013-01-01
This work discusses the accuracies of geophysical model functions (GMFs) for retrieval of sea surface wind speed from satellite-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images in Japanese coastal waters characterized by short fetches and variable atmospheric stability conditions. In situ observations...
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — The Radar Chart collection is an archived product of summarized radar data. The geographic coverage is the 48 contiguous states of the United States. These hourly...
-
The production of wind-generated electricity
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
2013-11-01
After some key data on installed wind power and its evolution in the World (notably in China and in the USA), in European countries and in France, an overview of the sector economic evolution in France in terms of jobs in different fields (fabrication, electricity production, studies and installations), this publication comments the various benefits of wind energy and its necessary framework for a sane development. Strengths are discussed: a local and clean energy source, a predictable and manageable energy source, an increasing competitiveness. Issues to be considered are also discussed: control of acoustic and landscape impacts, protection of biodiversity, management of interactions with military, meteorological and civil aviation radars, a necessary more steady and coherent regulation. After a discussion of the possibilities offered by small wind energy installations (between 1 and 36 kW), actions undertaken by the ADEME are overviewed. A conclusion outlines the role of wind energy on the supply-demand balance in the French power system, its contribution to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, the positive environmental impact, the importance of societal appropriation, and the importance of developing this sector while keeping on reducing consumptions
-
A Wing Pod-based Millimeter Wave Cloud Radar on HIAPER
Vivekanandan, Jothiram; Tsai, Peisang; Ellis, Scott; Loew, Eric; Lee, Wen-Chau; Emmett, Joanthan
2014-05-01
One of the attractive features of a millimeter wave radar system is its ability to detect micron-sized particles that constitute clouds with lower than 0.1 g m-3 liquid or ice water content. Scanning or vertically-pointing ground-based millimeter wavelength radars are used to study stratocumulus (Vali et al. 1998; Kollias and Albrecht 2000) and fair-weather cumulus (Kollias et al. 2001). Airborne millimeter wavelength radars have been used for atmospheric remote sensing since the early 1990s (Pazmany et al. 1995). Airborne millimeter wavelength radar systems, such as the University of Wyoming King Air Cloud Radar (WCR) and the NASA ER-2 Cloud Radar System (CRS), have added mobility to observe clouds in remote regions and over oceans. Scientific requirements of millimeter wavelength radar are mainly driven by climate and cloud initiation studies. Survey results from the cloud radar user community indicated a common preference for a narrow beam W-band radar with polarimetric and Doppler capabilities for airborne remote sensing of clouds. For detecting small amounts of liquid and ice, it is desired to have -30 dBZ sensitivity at a 10 km range. Additional desired capabilities included a second wavelength and/or dual-Doppler winds. Modern radar technology offers various options (e.g., dual-polarization and dual-wavelength). Even though a basic fixed beam Doppler radar system with a sensitivity of -30 dBZ at 10 km is capable of satisfying cloud detection requirements, the above-mentioned additional options, namely dual-wavelength, and dual-polarization, significantly extend the measurement capabilities to further reduce any uncertainty in radar-based retrievals of cloud properties. This paper describes a novel, airborne pod-based millimeter wave radar, preliminary radar measurements and corresponding derived scientific products. Since some of the primary engineering requirements of this millimeter wave radar are that it should be deployable on an airborne platform
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dabis, H.S.; Chignell, R.J.
1997-01-01
The potential for wind turbines to interfere with radio systems can be a source of conflict between radio operators and the wind energy community. In this report, the problem of accurately predicting the effects of wind turbines on radio systems with the aim of establishing guidelines for their installation is investigated. Initially models for the scatter mechanisms that occur at the wind turbine are developed. These models predict the wind turbine radar cross section and the modulation effects due to the rotation of the blades. Initial validation of these models is established by comparing the predicted results with a set of measurements obtained from experiments performed on a 20:1 scale model wind turbine. It is shown that generally these results agree well. These results are then used in the guideline formulation to compute, for specific radio systems, regions where wind turbines cannot be installed. Examples using realistic parameters for various radio systems are presented. Further validation of the derived models is required. (author)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2011-07-01
The island of Gotland has a large potential for wind power production. An existing weather radar system, however, causes extensive restrictions for further development of wind power on Gotland. In a joint project during 2011 the County Administration Board of Gotland, the Municipality of Gotland and the Swedish Armed Forces have explored ways to overcome the existing conflicts. The project has been sponsored by the Swedish Energy Agency. Through the collaboration, the participants have gained a better understanding of various aspects of the conflicting interests. Studies have been carried out with the prospect to modelling alternative solutions to reduce the conflicts. The study regarding the radar system has been carried out by the Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Inst.. This report present some practical solutions to avoid conflict in most of areas which are planned for wind power by the municipality. It is suggested that a complimentary radar can be built. A number of alternative localizations for the complimentary radar have been suggested and the potential effects for wind power production estimated. Costs for the suggested solutions have been calculated.
-
Combined radar and telemetry system
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rodenbeck, Christopher T.; Young, Derek; Chou, Tina; Hsieh, Lung-Hwa; Conover, Kurt; Heintzleman, Richard
2017-08-01
A combined radar and telemetry system is described. The combined radar and telemetry system includes a processing unit that executes instructions, where the instructions define a radar waveform and a telemetry waveform. The processor outputs a digital baseband signal based upon the instructions, where the digital baseband signal is based upon the radar waveform and the telemetry waveform. A radar and telemetry circuit transmits, simultaneously, a radar signal and telemetry signal based upon the digital baseband signal.
-
Effects of Abrupt Variations of Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure on the High-Latitude Ionosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Igino Coco
2011-01-01
Full Text Available We show the results of a statistical study on the effects in the high-latitude ionosphere of abrupt variations of solar wind dynamic pressure, using Super Dual Auroral Radar Network (SuperDARN data in both hemispheres. We find that, during periods of quiet ionospheric conditions, the amount of radar backscatter increases when a variation in the dynamic pressure occurs, both positive (increase of the pressure and negative (decrease of the pressure. We also investigate the behaviour of the Cross-Polar Cap Potential (CPCP during pressure variations and show preliminary results.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. S. Rodrigues
2008-10-01
Full Text Available The 30 MHz coherent backscatter radar located at the equatorial observatory in São Luís, Brazil (2.59° S, 44.21° W, −2.35° dip lat has been upgraded to perform coherent backscatter radar imaging. The wide field-of-view of this radar makes it well suited for radar imaging studies of ionospheric irregularities. Radar imaging observations were made in support to the spread F Experiment (SpreadFEx campaign. This paper describes the system and imaging technique and presents results from a bottom-type layer that preceded fully-developed radar plumes on 25 October 2005. The radar imaging technique was able to resolve decakilometric structures within the bottom-type layer. These structures indicate the presence of large-scale waves (~35 km in the bottomside F-region with phases that are alternately stable and unstable to wind-driven gradient drift instabilities. The observations suggest that these waves can also cause the initial perturbation necessary to initiate the Generalized Rayleigh-Taylor instability leading to spread F. The electrodynamic conditions and the scale length of the bottom-type layer structures suggest that the waves were generated by the collisional shear instability. These results indicate that monitoring bottom-type layers may provide helpful diagnostics for spread F forecasting.
-
Full polarimetric millimetre wave radar for stand-off security screening
Blackhurst, Eddie; Salmon, Neil; Southgate, Matthew
2017-10-01
The development and measurements are described of a frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) mono-static millimetre wave full polarimetric radar, operating at k-band (18 to 26 GHz). The system has been designed to explore the feasibility of using full polarimetry for the detection of concealed weapons, and person borne improvised explosive devices (PBIED). The philosophy of this scheme is a means to extract the maximum information content from a target which is normally in the single spatial pixel (sometimes sub-pixel) configuration in stand-off (tens of metres) and crowd surveillance scenarios. The radar comprises a vector network analyser (VNA), an orthomode transducer and a conical horn antenna. A calibration strategy is discussed and demonstrated using a variety of known calibration targets with known reflective properties, including a flat metal plate, dihedral reflector, metal sphere, helix and dipole. The orthomode transducer is based on a high performance linear polarizer of the turnstile type with isolation better than - 35dB between orthogonal polarisations. The calibration enables the polarimetric Sinclair scattering matrix to be measured at each frequency for coherent polarimetry, and this can be extended using multiple measurements via the Kennaugh matrix to investigate incoherent full polarimetry.
-
Exploring inner structure of Titan's dunes from Cassini Radar observations
Sharma, P.; Heggy, E.; Farr, T. G.
2013-12-01
Linear dunes discovered in the equatorial regions of Titan by the Cassini-Huygens mission are morphologically very similar to many terrestrial linear dune fields. These features have been compared with terrestrial longitudinal dune fields like the ones in Namib desert in western Africa. This comparison is based on the overall parallel orientation of Titan's dunes to the predominant wind direction on Titan, their superposition on other geomorphological features and the way they wrap around topographic obstacles. Studying the internal layering of dunes has strong implications in understanding the hypothesis for their origin and evolution. In Titan's case, although the morphology of the dunes has been studied from Cassini Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images, it has not been possible to investigate their internal structure in detail as of yet. Since no radar sounding data is available for studying Titan's subsurface yet, we have developed another technique to examine the inner layering of the dunes. In this study, we utilize multiple complementary radar datasets, including radar imaging data for Titan's and Earth's dunes and Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)/radar sounding data for terrestrial dunes. Based on dielectric mixing models, we suggest that the Cassini Ku-band microwaves should be able to penetrate up to ~ 3 m through Titan's dunes, indicating that the returned radar backscatter signal would include contributions from both surface and shallow subsurface echoes. This implies that the shallow subsurface properties can be retrieved from the observed radar backscatter (σ0). In our analysis, the variation of the radar backscatter as a function of dune height is used to provide an insight into the layering in Titan's dunes. We compare the variation of radar backscatter with elevation over individual dunes on Titan and analogous terrestrial dunes in three sites (Great Sand Sea, Siwa dunes and Qattaniya dunes) in the Egyptian Sahara. We observe a strong, positive
-
SAR-Based Wind Resource Statistics in the Baltic Sea
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Alfredo Peña
2011-01-01
Full Text Available Ocean winds in the Baltic Sea are expected to power many wind farms in the coming years. This study examines satellite Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR images from Envisat ASAR for mapping wind resources with high spatial resolution. Around 900 collocated pairs of wind speed from SAR wind maps and from 10 meteorological masts, established specifically for wind energy in the study area, are compared. The statistical results comparing in situ wind speed and SAR-based wind speed show a root mean square error of 1.17 m s−1, bias of −0.25 m s−1, standard deviation of 1.88 m s−1 and correlation coefficient of R2 0.783. Wind directions from a global atmospheric model, interpolated in time and space, are used as input to the geophysical model function CMOD-5 for SAR wind retrieval. Wind directions compared to mast observations show a root mean square error of 6.29° with a bias of 7.75°, standard deviation of 20.11° and R2 of 0.950. The scale and shape parameters, A and k, respectively, from the Weibull probability density function are compared at only one available mast and the results deviate ~2% for A but ~16% for k. Maps of A and k, and wind power density based on more than 1000 satellite images show wind power density values to range from 300 to 800 W m−2 for the 14 existing and 42 planned wind farms.
-
Description and evaluation of the CASA dual-Doppler system
Martinez, Matthew
2011-12-01
Long range weather surveillance radars are designed for observing weather events for hundreds of kilometers from the radar and operate over a large coverage domain independently of weather conditions. As a result a loss in spatial resolution and limited temporal sampling of the weather phenomenon occurs. Due to the curvature of the Earth, long-range weather radars tend to make the majority of their precipitation and wind observations in the middle to upper troposphere, resulting in missed features associates with severe weather occurring in the lowest three kilometers of the troposphere. The spacing of long-range weather radars in the United States limits the feasibility of using dual-Doppler wind retrievals that would provide valuable information on the kinematics of weather events to end-users and researchers. The National Science Foundation Center for Collaborative Adapting Sensing of the Atmosphere (CASA) aims to change the current weather sensing model by increasing coverage of the lowest three kilometers of the troposphere by using densely spaced networked short-range weather radars. CASA has deployed a network of these radars in south-western Oklahoma, known as Integrated Project 1 (IP1). The individual radars are adaptively steered by an automated system known as the Meteorological Command and Control (MCC). The geometry of the IP1 network is such that the coverage domains of the individual radars are overlapping. A dual-Doppler system has been developed for the IP1 network which takes advantage of the overlapping coverage domains. The system is comprised of two subsystems, scan optimization and wind field retrieval. The scan strategy subsystem uses the DCAS model and the number of dual-Doppler pairs in the IP1 network to minimizes the normalized standard deviation in the wind field retrieval. The scan strategy subsystem also minimizes the synchronization error between two radars. The retrieval itself is comprised of two steps, data resampling and the
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — RADAR PPI Scope Overlays are used to position a RADAR image over a station at the correct resolution. The archive maintains several different RADAR resolution types,...
-
Jones, Thomas A.; Stensrud, David; Wicker, Louis; Minnis, Patrick; Palikonda, Rabindra
2015-01-01
Assimilating high-resolution radar reflectivity and radial velocity into convection-permitting numerical weather prediction models has proven to be an important tool for improving forecast skill of convection. The use of satellite data for the application is much less well understood, only recently receiving significant attention. Since both radar and satellite data provide independent information, combing these two sources of data in a robust manner potentially represents the future of high-resolution data assimilation. This research combines Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite 13 (GOES-13) cloud water path (CWP) retrievals with Weather Surveillance Radar-1988 Doppler (WSR-88D) reflectivity and radial velocity to examine the impacts of assimilating each for a severe weather event occurring in Oklahoma on 24 May 2011. Data are assimilated into a 3-km model using an ensemble adjustment Kalman filter approach with 36 members over a 2-h assimilation window between 1800 and 2000 UTC. Forecasts are then generated for 90 min at 5-min intervals starting at 1930 and 2000 UTC. Results show that both satellite and radar data are able to initiate convection, but that assimilating both spins up a storm much faster. Assimilating CWP also performs well at suppressing spurious precipitation and cloud cover in the model as well as capturing the anvil characteristics of developed storms. Radar data are most effective at resolving the 3D characteristics of the core convection. Assimilating both satellite and radar data generally resulted in the best model analysis and most skillful forecast for this event.
-
Li, Qiang; Rapp, Markus; Stober, Gunter; Latteck, Ralph
2018-04-01
The Middle Atmosphere Alomar Radar System (MAARSY) installed at the island of Andøya has been run for continuous probing of atmospheric winds in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) region. In the current study, we present high-resolution wind measurements during the period between 2010 and 2013 with MAARSY. The spectral analysis applying the Lomb-Scargle periodogram method has been carried out to determine the frequency spectra of vertical wind velocity. From a total of 522 days of observations, the statistics of the spectral slope have been derived and show a dependence on the background wind conditions. It is a general feature that the observed spectra of vertical velocity during active periods (with wind velocity > 10 m s-1) are much steeper than during quiet periods (with wind velocity wind conditions considered together the general spectra are obtained and their slopes are compared with the background horizontal winds. The comparisons show that the observed spectra become steeper with increasing wind velocities under quiet conditions, approach a spectral slope of -5/3 at a wind velocity of 10 m s-1 and then roughly maintain this slope (-5/3) for even stronger winds. Our findings show an overall agreement with previous studies; furthermore, they provide a more complete climatology of frequency spectra of vertical wind velocities under different wind conditions.
-
Systems and Methods for Radar Data Communication
Bunch, Brian (Inventor); Szeto, Roland (Inventor); Miller, Brad (Inventor)
2013-01-01
A radar information processing system is operable to process high bandwidth radar information received from a radar system into low bandwidth radar information that may be communicated to a low bandwidth connection coupled to an electronic flight bag (EFB). An exemplary embodiment receives radar information from a radar system, the radar information communicated from the radar system at a first bandwidth; processes the received radar information into processed radar information, the processed radar information configured for communication over a connection operable at a second bandwidth, the second bandwidth lower than the first bandwidth; and communicates the radar information from a radar system, the radar information communicated from the radar system at a first bandwidth.
-
Intercalibration of HRDI and WINDII wind measurements
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. D. Burrage
1997-09-01
Full Text Available The High Resolution Doppler Imager (HRDI and the Wind Imaging Interferometer (WINDII in- struments, which are both on the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite, measure winds by sensing the Doppler shift in atmospheric emission features. Because the two observation sets are frequently nearly coincident in space and time, each provides a very e.ective validation test of the other. Discrepancies due to geophysical di.erences should be much smaller than for comparisons with other techniques (radars, rockets, etc., and the very large sizes of the coincident data sets provide excellent statistics for the study. Issues that have been examined include relative systematic o.sets and the wind magnitudes obtained with the two systems. A significant zero wind position di.erence of ~6 m s–1 is identified for the zonal component, and it appears that this arises from an absolute perturbation in WINDII winds of –4 m s–1 and in HRDI of +2 m s–1. Altitude o.sets appear to be relatively small, and do not exceed 1 km. In addition, no evidence is found for the existence of a systematic wind speed bias between HRDI and WINDII. However, considerable day-to-day variability is found in the quality of the agreement, and RMS di.erences are surprisingly large, typically in the range of 20±30 m s–1.
-
Zaczek, Mariusz P.
2005-01-01
Java Radar Analysis Tool (JRAT) is a computer program for analyzing two-dimensional (2D) scatter plots derived from radar returns showing pieces of the disintegrating Space Shuttle Columbia. JRAT can also be applied to similar plots representing radar returns showing aviation accidents, and to scatter plots in general. The 2D scatter plots include overhead map views and side altitude views. The superposition of points in these views makes searching difficult. JRAT enables three-dimensional (3D) viewing: by use of a mouse and keyboard, the user can rotate to any desired viewing angle. The 3D view can include overlaid trajectories and search footprints to enhance situational awareness in searching for pieces. JRAT also enables playback: time-tagged radar-return data can be displayed in time order and an animated 3D model can be moved through the scene to show the locations of the Columbia (or other vehicle) at the times of the corresponding radar events. The combination of overlays and playback enables the user to correlate a radar return with a position of the vehicle to determine whether the return is valid. JRAT can optionally filter single radar returns, enabling the user to selectively hide or highlight a desired radar return.
-
Synthetic impulse and aperture radar (SIAR) a novel multi-frequency MIMO radar
Chen, Baixiao
2014-01-01
Analyzes and discusses the operating principle, signal processing method, and experimental results of this advanced radar technology This book systematically discusses the operating principle, signal processing method, target measurement technology, and experimental results of a new kind of radar called synthetic impulse and aperture radar (SIAR). The purpose is to help readers acquire an insight into the concept and principle of the SIAR, to know its operation mode, signal processing method, the difference between the traditional radar and itself, the designing ideals, and the developing me
-
Hansen, L.G.; Lading, Lars
2002-01-01
This report contains the results of a cost-benefit analysis for the use of embed-ded sensors for damage detection in large wind turbine blades - structural health monitoring - (in connection with remote surveillance) of large wind turbine placedoff-shore. The total operating costs of a three-bladed 2MW turbine placed offshore either without sensors or with sensors are compared. The price of a structural health monitoring system of a price of 100 000 DKK (per tur-bine) results in a break-event...
-
A conceptual framework for using Doppler radar acquired atmospheric data for flight simulation
Campbell, W.
1983-01-01
A concept is presented which can permit turbulence simulation in the vicinity of microbursts. The method involves a large data base, but should be fast enough for use with flight simulators. The model permits any pilot to simulate any flight maneuver in any aircraft. The model simulates a wind field with three-component mean winds and three-component turbulent gusts, and gust variation over the body of an aircraft so that all aerodynamic loads and moments can be calculated. The time and space variation of mean winds and turbulent intensities associated with a particular atmospheric phenomenon such as a microburst is used in the model. In fact, Doppler radar data such as provided by JAWS is uniquely suited for use with the proposed model. The concept is completely general and is not restricted to microburst studies. Reentry and flight in terrestrial or planetary atmospheres could be realistically simulated if supporting data of sufficient resolution were available.
-
Wind Turbines Adaptation to the Variability of the Wind Field
Ulianov, Yuriy; Martynenko, Gennadii; Misaylov, Vitaliy; Soliannikova, Iuliia
2010-05-01
WIND TURBINES ADAPTATION TO THE VARIABILITY OF THE WIND FIELD The subject of our scientific research is wind power turbines (WPT) with the horizontal axis which were now common in the world. Efficient wind turbines work is largely determined by non-stationarity of the wind field, expressed in its gustiness, the presence of vertical and horizontal shifts of wind speed and direction. At critical values of the wind parameters WPT has aerodynamic and mechanical overload, leading to breakdowns, premature wear and reduce the life of the wind turbine. To prevent accidents at the peak values of wind speed it is used the regulatory system of windwheels. WPT control systems provide a process orientation of the wind turbine rotor axis in the line of the mean wind. Wind turbines are also equipped with braking device used to protect against breakdowns when a significant increase in the wind. In general, all these methods of regulation are not always effective. Thus, in practice there may be situations when the wind speed is many times greater than the stated limit. For example, if there are microbursts in the atmospheric boundary layer, low-level wind shears caused by its gust front, storms, etc. It is required for a wind power turbine adaptation to intensive short-term wind impulses and considerable vertical wind shifts that the data about them shall be obtained ahead of time. To do this it is necessary to have the information on the real structure of the wind field in the area of the blade sweep for the minimum range against the wind that is determined by the mean speed and the system action time. The implementation of acoustic and laser traditional wind sounding systems is limited by ambient acoustic noise, by heavy rain, snowfall and by fog. There are free of these disadvantages the inclined radioacoustic sounding (IRASS) technique which works for a system of remote detection and control of wind gusts. IRASS technique is realized as low-potential Doppler pulse radar
-
Probabilities of False Alarm for Vital Sign Detection on the Basis of a Doppler Radar System
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Nguyen Thi Phuoc Van
2018-02-01
Full Text Available Vital detection on the basis of Doppler radars has drawn a great deal of attention from researchers because of its high potential for applications in biomedicine, surveillance, and finding people alive under debris during natural hazards. In this research, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR of the remote vital-sign detection system is investigated. On the basis of different types of noise, such as phase noise, Gaussian noise, leakage noise between the transmitting and receiving antennae, and so on, the SNR of the system has first been examined. Then the research has focused on the investigation of the detection and false alarm probabilities of the system when the transmission link between the human and the radar sensor system took the Nakagami-m channel model. The analytical model for the false alarm and the detection probabilities of the system have been derived. The proposed theoretical models for the SNR and detection probability match with the simulation and measurement results. These theoretical models have the potential to be used as good references for the hardware development of the vital-sign detection radar sensor system.
-
Array-Based Ultrawideband through-Wall Radar: Prediction and Assessment of Real Radar Abilities
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Nadia Maaref
2013-01-01
Full Text Available This paper deals with a new through-the-wall (TTW radar demonstrator for the detection and the localisation of people in a room (in a noncooperative way with the radar situated outside but in the vicinity of the first wall. After modelling the propagation through various walls and quantifying the backscattering by the human body, an analysis of the technical considerations which aims at defining the radar design is presented. Finally, an ultrawideband (UWB frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW radar is proposed, designed, and implemented. Some representative trials show that this radar is able to localise and track moving people behind a wall in real time.
-
Sixteenth International Laser Radar Conference, Part 1
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mccormick, M.P.
1992-07-01
This publication contains extended abstracts of papers presented at the 16th International Laser Radar Conference. One-hundred ninety-five papers were presented in both oral and poster sessions. The topics of the conference sessions were: (1) Mt. Pinatubo Volcanic Dust Layer Observations; (2) Global Change/Ozone Measurements; (3) GLOBE/LAWS/LITE; (4) Mesospheric Measurements and Measurement Systems; (5) Middle Atmosphere; (6) Wind Measurements and Measurement Systems; (7) Imaging and Ranging; (8) Water Vapor Measurements; (9) Systems and Facilities; and (10) Laser Devices and Technology. This conference reflects the breadth of research activities being conducted in the lidar field. These abstracts address subjects from lidar-based atmospheric investigations relating to global change to the development of new lidar systems and technology
-
Novel radar techniques and applications
Klemm, Richard; Koch, Wolfgang
2017-01-01
Novel Radar Techniques and Applications presents the state-of-the-art in advanced radar, with emphasis on ongoing novel research and development and contributions from an international team of leading radar experts. This volume covers: Waveform diversity and cognitive radar and Target tracking and data fusion.
-
Montopoli, Mario; Vulpiani, Gianfranco; Riccci, Matteo; Corradini, Stefano; Merucci, Luca; Marzano, Frank S.
2015-04-01
Ground based weather radar observations of volcanic ash clouds are gaining momentum after recent works which demonstrated their potential use either as stand alone tool or in combination with satellite retrievals. From an operational standpoint, radar data have been mainly exploited to derive the height of ash plume and its temporal-spatial development, taking into account the radar limitation of detecting coarse ash particles (from approximately 20 microns to 10 millimeters and above in terms of particle's radius). More sophisticated radar retrievals can include airborne ash concentration, ash fall rate and out-flux rate. Marzano et al. developed several volcanic ash radar retrieval (VARR) schemes, even though their practical use is still subject to a robust validation activity. The latter is made particularly difficult due to the lack of field campaigns with multiple observations and the scarce repetition of volcanic events. The radar variable, often used to infer the physical features of actual ash clouds, is the radar reflectivity named ZHH. It is related to ash particle size distribution and it shows a nice power law relationship with ash concentration. This makes ZHH largely used in radar-volcanology studies. However, weather radars are often able to detect Doppler frequency shifts and, more and more, they have a polarization-diversity capability. The former means that wind speed spectrum of the ash cloud is potentially inferable, whereas the latter implies that variables other than ZHH are available. Theoretically, these additional radar variables are linked to the degree of eccentricity of ash particles, their orientation and density as well as the presence of strong turbulence effects. Thus, the opportunity to refine the ash radar estimates so far developed can benefit from the thorough analysis of radar Doppler and polarization diversity. In this work we show a detailed analysis of Doppler shifts and polarization variables measured by the X band radar
-
Yearbook of wind energy law 2015; Jahrbuch Windenergierecht 2015
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Brandt, Edmund (ed.) [Technische Univ. Braunschweig (Germany). Lehrstuhl Staats- und Verwaltungsrecht sowie Verwaltungswissenschaften; Koordinierungsstelle Windenergierecht k:wer, Braunschweig (Germany)
2016-08-01
In the yearbook 2015, the technical papers are dealing with the distance recommendations of the State Working Group of Bird Conservation Observatories, with aesthetics as a public interest in the planning and authorization regime for wind turbines, the prospect of the citizen and community participation law in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, the conflict between wind turbines and weather radars and with the higher court jurisdiction for feed management. [German] Im Jahrbuch 2015 beschaeftigen sich die Fachbeitraege mit den Abstandsempfehlungen der Laenderarbeitsgemeinschaft der Vogelschutzwarten, mit Aesthetik als oeffentlichem Belang im Planungs- und Genehmigungsregime fuer Windenergieanlagen, dem Entwurf zum Buerger- und Gemeindenbeteiligungsgesetz Mecklenburg-Vorpommerns, dem Konflikt zwischen Windenergieanlagen und Wetterradaren und mit der obergerichtlichen Rechtsprechung zum Einspeisemanagement.
-
A statistical survey of dayside pulsed ionospheric flows as seen by the CUTLASS Finland HF radar
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
K. A. McWilliams
2000-04-01
Full Text Available Nearly two years of 2-min resolution data and 7- to 21-s resolution data from the CUTLASS Finland HF radar have undergone Fourier analysis in order to study statistically the occurrence rates and repetition frequencies of pulsed ionospheric flows in the noon-sector high-latitude ionosphere. Pulsed ionospheric flow bursts are believed to be the ionospheric footprint of newly reconnected geomagnetic field lines, which occur during episodes of magnetic flux transfer to the terrestrial magnetosphere - flux transfer events or FTEs. The distribution of pulsed ionospheric flows were found to be well grouped in the radar field of view, and to be in the vicinity of the radar signature of the cusp footprint. Two thirds of the pulsed ionospheric flow intervals included in the statistical study occurred when the interplanetary magnetic field had a southward component, supporting the hypothesis that pulsed ionospheric flows are a reconnection-related phenomenon. The occurrence rate of the pulsed ionospheric flow fluctuation period was independent of the radar scan mode. The statistical results obtained from the radar data are compared to occurrence rates and repetition frequencies of FTEs derived from spacecraft data near the magnetopause reconnection region, and to ground-based optical measurements of poleward moving auroral forms. The distributions obtained by the various instruments in different regions of the magnetosphere were remarkably similar. The radar, therefore, appears to give an unbiased sample of magnetopause activity in its routine observations of the cusp footprint.Key words: Magnetospheric physics (magnetosphere-ionosphere interactions; plasma convection; solar wind-magnetosphere interactions
-
Characterizing the surface circulation in the Ebro Delta using a HF radar data-model approach
Lorente Jimenez, Pablo; Piedracoba Varela, Silvia; Soto-Navarro, Javier; Garcia-Sotillo, Marcos; Alvarez Fanjul, Enrique
2016-04-01
One year-long (2014) quality-controlled current observations from a CODAR SeaSonde High Frequency (HF) radar network deployed in the Ebro Delta (northwestern Mediterranean) were combined with operational products provided by a regional ocean forecasting system named IBI (Iberia-Biscay-Ireland) in order to comprehensively portray the ocean state and its variability. First, accurate HF radar data were used as benchmark for the rigorous validation of IBI performance by means of the computation of skill metrics and quality indicators. The analysis of the monthly averaged current maps for 2014 showed that IBI properly captured the prevailing dynamic features of the coastal circulation observed by the HF radar, according to the resemblance of circulation patterns and the eddy kinetic energy spatial distribution. The model skill assessment was completed with an exploration of dominant modes of variability both in time and space. The EOF analysis confirmed that the modeled surface current field evolved in space and time according to three significantly dominant modes of variability which accounted for the 49.2% of the total variance, in close agreement with the results obtained for the HF radar (46.1%). The response of the subtidal surface current field to prevalent wind regimes in the study area was examined in terms of induced circulation structures by performing a conditional averaging approach. This data-model synergistic approach has proved to be valid to operationally monitor and describe the complex coastal circulation in Ebro Delta despite the observed model drawbacks in terms of reduced energy content in surface currents and some inaccuracies in the wind-driven low frequency response. This integrated methodology constitutes a powerful tool for improving operational ocean forecasting systems at European level within the frame of the Copernicus Marine Environment Monitoring Service (CMEMS). It also facilitates high-stakes decision-making for coastal management and
-
Transport Infrastructure Surveillance and Monitoring by Electromagnetic Sensing: The ISTIMES Project
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Marie Bost
2010-11-01
Full Text Available The ISTIMES project, funded by the European Commission in the frame of a joint Call “ICT and Security” of the Seventh Framework Programme, is presented and preliminary research results are discussed. The main objective of the ISTIMES project is to design, assess and promote an Information and Communication Technologies (ICT-based system, exploiting distributed and local sensors, for non-destructive electromagnetic monitoring of critical transport infrastructures. The integration of electromagnetic technologies with new ICT information and telecommunications systems enables remotely controlled monitoring and surveillance and real time data imaging of the critical transport infrastructures. The project exploits different non-invasive imaging technologies based on electromagnetic sensing (optic fiber sensors, Synthetic Aperture Radar satellite platform based, hyperspectral spectroscopy, Infrared thermography, Ground Penetrating Radar-, low-frequency geophysical techniques, Ground based systems for displacement monitoring. In this paper, we show the preliminary results arising from the GPR and infrared thermographic measurements carried out on the Musmeci bridge in Potenza, located in a highly seismic area of the Apennine chain (Southern Italy and representing one of the test beds of the project.
-
Radar remote sensing in biology
Moore, Richard K.; Simonett, David S.
1967-01-01
The present status of research on discrimination of natural and cultivated vegetation using radar imaging systems is sketched. The value of multiple polarization radar in improved discrimination of vegetation types over monoscopic radars is also documented. Possible future use of multi-frequency, multi-polarization radar systems for all weather agricultural survey is noted.
-
Two applications of time reversal mirrors: Seismic radio and seismic radar
Hanafy, Sherif M.
2011-07-08
Two seismic applications of time reversal mirrors (TRMs) are introduced and tested with field experiments. The first one is sending, receiving, and decoding coded messages similar to a radio except seismic waves are used. The second one is, similar to radar surveillance, detecting and tracking a moving object(s) in a remote area, including the determination of the objects speed of movement. Both applications require the prior recording of calibrationGreen’s functions in the area of interest. This reference Green’s function will be used as a codebook to decrypt the coded message in the first application and as a moving sensor for the second application. Field tests show that seismicradar can detect the moving coordinates ( x(t), y(t), z(t)) of a person running through a calibration site. This information also allows for a calculation of his velocity as a function of location. Results with the seismic radio are successful in seismically detecting and decoding coded pulses produced by a hammer. Both seismic radio and radar are highly robust to signals in high noise environments due to the super-stacking property of TRMs.
-
Signal processing in noise waveform radar
Kulpa, Krzysztof
2013-01-01
This book is devoted to the emerging technology of noise waveform radar and its signal processing aspects. It is a new kind of radar, which use noise-like waveform to illuminate the target. The book includes an introduction to basic radar theory, starting from classical pulse radar, signal compression, and wave radar. The book then discusses the properties, difficulties and potential of noise radar systems, primarily for low-power and short-range civil applications. The contribution of modern signal processing techniques to making noise radar practical are emphasized, and application examples
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — Radar Weather Observation is a set of archived historical manuscripts stored on microfiche. The primary source of these radar weather observations manuscript records...
-
Brookner, E.
1981-10-01
Achievements in the area of array radars are illustrated by such activities as the operational deployment of the large high-power, high-range-resolution Cobra Dane; the operational deployment of two all-solid-state high-power, large UHF Pave Paws radars; and the development of the SAM multifunction Patriot radar. This paper reviews the following topics: array radars steered in azimuth and elevation by phase shifting (phase-phase steered arrays); arrays steered + or - 60 deg, limited scan arrays, hemispherical coverage, and omnidirectional coverage arrays; array radars steering electronically in only one dimension, either by frequency or by phase steering; and array radar antennas which use no electronic scanning but instead use array antennas for achieving low antenna sidelobes.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Gade
2017-11-01
Full Text Available We show that high-resolution space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR imagery with pixel sizes well below 1 m2 can be used to complement archaeological surveys in areas that are difficult to access. After major storm surges in the 14th and 17th centuries, vast areas on the German North Sea coast were lost to the sea. Areas of former settlements and historical land use were buried under sediments for centuries, but when the surface layer is driven away under the permanent action of wind, currents, and waves, they appear again on the Wadden Sea surface. However, the frequent flooding and erosion of the intertidal flats make any archaeological monitoring a difficult task, so that remote sensing techniques appear to be an efficient and cost-effective instrument for any archaeological surveillance of that area. Space-borne SAR images clearly show remnants of farmhouse foundations and of former systems of ditches, dating back to the 14th and to the 16th/17th centuries. In particular, the very high-resolution acquisition (staring spotlight mode of the German TerraSAR/ TanDEM-X satellites allows for the detection of various kinds of residuals of historical land use with high precision. In addition, we also investigate the capability of SARs working at lower microwave frequencies (on Radarsat-2 to complement our archaeological survey of historical cultural traces, some of which have been unknown so far.
-
Doppler radar physiological sensing
Lubecke, Victor M; Droitcour, Amy D; Park, Byung-Kwon; Singh, Aditya
2016-01-01
Presents a comprehensive description of the theory and practical implementation of Doppler radar-based physiological monitoring. This book includes an overview of current physiological monitoring techniques and explains the fundamental technology used in remote non-contact monitoring methods. Basic radio wave propagation and radar principles are introduced along with the fundamentals of physiological motion and measurement. Specific design and implementation considerations for physiological monitoring radar systems are then discussed in detail. The authors address current research and commercial development of Doppler radar based physiological monitoring for healthcare and other applications.
-
Development of Radar Control system for Multi-mode Active Phased Array Radar for atmospheric probing
Yasodha, Polisetti; Jayaraman, Achuthan; Thriveni, A.
2016-07-01
Modern multi-mode active phased array radars require highly efficient radar control system for hassle free real time radar operation. The requirement comes due to the distributed architecture of the active phased array radar, where each antenna element in the array is connected to a dedicated Transmit-Receive (TR) module. Controlling the TR modules, which are generally few hundreds in number, and functioning them in synchronisation, is a huge task during real time radar operation and should be handled with utmost care. Indian MST Radar, located at NARL, Gadanki, which is established during early 90's, as an outcome of the middle atmospheric program, is a remote sensing instrument for probing the atmosphere. This radar has a semi-active array, consisting of 1024 antenna elements, with limited beam steering, possible only along the principle planes. To overcome the limitations and difficulties, the radar is being augmented into fully active phased array, to accomplish beam agility and multi-mode operations. Each antenna element is excited with a dedicated 1 kW TR module, located in the field and enables to position the radar beam within 20° conical volume. A multi-channel receiver makes the radar to operate in various modes like Doppler Beam Swinging (DBS), Spaced Antenna (SA), Frequency Domain Interferometry (FDI) etc. Present work describes the real-time radar control (RC) system for the above described active phased array radar. The radar control system consists of a Spartan 6 FPGA based Timing and Control Signal Generator (TCSG), and a computer containing the software for controlling all the subsystems of the radar during real-time radar operation and also for calibrating the radar. The main function of the TCSG is to generate the control and timing waveforms required for various subsystems of the radar. Important components of the RC system software are (i) TR module configuring software which does programming, controlling and health parameter monitoring of the
-
Rosen, Paul A.
2012-01-01
This lecture was just a taste of radar remote sensing techniques and applications. Other important areas include Stereo radar grammetry. PolInSAR for volumetric structure mapping. Agricultural monitoring, soil moisture, ice-mapping, etc. The broad range of sensor types, frequencies of observation and availability of sensors have enabled radar sensors to make significant contributions in a wide area of earth and planetary remote sensing sciences. The range of applications, both qualitative and quantitative, continue to expand with each new generation of sensors.
-
Imaging radar observations of Farley Buneman waves during the JOULE II experiment
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
D. L. Hysell
2008-07-01
Full Text Available Vector electric fields and associated E×B drifts measured by a sounding rocket in the auroral zone during the NASA JOULE II experiment in January 2007, are compared with coherent scatter spectra measured by a 30 MHz radar imager in a common volume. Radar imaging permits precise collocation of the spectra with the background electric field. The Doppler shifts and spectral widths appear to be governed by the cosine and sine of the convection flow angle, respectively, and also proportional to the presumptive ion acoustic speed. The neutral wind also contributes to the Doppler shifts. These findings are consistent with those from the JOULE I experiment and also with recent numerical simulations of Farley Buneman waves and instabilities carried out by Oppenheim et al. (2008. Simple linear analysis of the waves offers some insights into the spectral moments. A formula relating the spectral width to the flow angle, ion acoustic speed, and other ionospheric parameters is derived.
-
Li, Yanpeng; Li, Xiang; Wang, Hongqiang; Deng, Bin; Qin, Yuliang
2016-01-06
Radar is a very important sensor in surveillance applications. Near-space vehicle-borne radar (NSVBR) is a novel installation of a radar system, which offers many benefits, like being highly suited to the remote sensing of extremely large areas, having a rapidly deployable capability and having low vulnerability to electronic countermeasures. Unfortunately, a target detection challenge arises because of complicated scenarios, such as nuclear blackout, rain attenuation, etc. In these cases, extra care is needed to evaluate the detection performance in blackout situations, since this a classical problem along with the application of an NSVBR. However, the existing evaluation measures are the probability of detection and the receiver operating curve (ROC), which cannot offer detailed information in such a complicated application. This work focuses on such requirements. We first investigate the effect of blackout on an electromagnetic wave. Performance evaluation indexes are then built: three evaluation indexes on the detection capability and two evaluation indexes on the robustness of the detection process. Simulation results show that the proposed measure will offer information on the detailed performance of detection. These measures are therefore very useful in detecting the target of interest in a remote sensing system and are helpful for both the NSVBR designers and users.
-
Bridge Testing With Ground-Based Interferometric Radar: Experimental Results
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chiara, P.; Morelli, A.
2010-01-01
The research of innovative non-contact techniques aimed at the vibration measurement of civil engineering structures (also for damage detection and structural health monitoring) is continuously directed to the optimization of measures and methods. Ground-Based Radar Interferometry (GBRI) represents the more recent technique available for static and dynamic control of structures and ground movements.Dynamic testing of bridges and buildings in operational conditions are currently performed: (a) to assess the conformity of the structure to the project design at the end of construction; (b) to identify the modal parameters (i.e. natural frequencies, mode shapes and damping ratios) and to check the variation of any modal parameters over the years; (c) to evaluate the amplitude of the structural response to special load conditions (i.e. strong winds, earthquakes, heavy railway or roadway loads). If such tests are carried out by using a non-contact technique (like GBRI), the classical issues of contact sensors (like accelerometers) are easily overtaken.This paper presents and discusses the results of various tests carried out on full-scale bridges by using a Stepped Frequency-Continuous Wave radar system.
-
Bridge Testing With Ground-Based Interferometric Radar: Experimental Results
Chiara, P.; Morelli, A.
2010-05-01
The research of innovative non-contact techniques aimed at the vibration measurement of civil engineering structures (also for damage detection and structural health monitoring) is continuously directed to the optimization of measures and methods. Ground-Based Radar Interferometry (GBRI) represents the more recent technique available for static and dynamic control of structures and ground movements. Dynamic testing of bridges and buildings in operational conditions are currently performed: (a) to assess the conformity of the structure to the project design at the end of construction; (b) to identify the modal parameters (i.e. natural frequencies, mode shapes and damping ratios) and to check the variation of any modal parameters over the years; (c) to evaluate the amplitude of the structural response to special load conditions (i.e. strong winds, earthquakes, heavy railway or roadway loads). If such tests are carried out by using a non-contact technique (like GBRI), the classical issues of contact sensors (like accelerometers) are easily overtaken. This paper presents and discusses the results of various tests carried out on full-scale bridges by using a Stepped Frequency-Continuous Wave radar system.
-
Principles of modern radar radar applications
Scheer, James A
2013-01-01
Principles of Modern Radar: Radar Applications is the third of the three-volume seriesof what was originally designed to be accomplished in one volume. As the final volumeof the set, it finishes the original vision of a complete yet bounded reference for radartechnology. This volume describes fifteen different system applications or class ofapplications in more detail than can be found in Volumes I or II.As different as the applications described, there is a difference in how these topicsare treated by the authors. Whereas in Volumes I and II there is strict adherence tochapter format and leve
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Blew, J.; Hoffmann, M.; Nehls, G. [BioConsult SH (Germany)
2007-07-01
This study investigates the collision risks of birds in operating offshore wind farms, focussing on all bird species present in the direct vicinity of the wind farms, their altitude distribution and reactions. The project was conducted jointly by BioConsult SH and the University of Hamburg in the two Danish offshore wind farms Horns Rev (North Sea) and Nysted (Baltic Sea) in the framework of a Danish-German cooperation and financed by the German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU). Data were collected between March 2005 and November 2006, using a ship anchored at the edge of the offshore wind farms. In this way, bird species of all sizes could be considered. Daytime observations yielded data on species composition, flight routes and potential reactions of the birds. Radar observations provided altitude distributions inside and outside the wind farm area and also reactions. The results shall help to further describe and assess the collision risk of different species groups. Since data analysis is still running, exemplary results will be presented here. 114 species have been recorded in Nysted and 99 in Horns Rev, approximately 65% of which have been observed inside the wind farm areas. Migrating birds seem to avoid flying into the wind farms, whereas individuals present in the areas for extended time periods utilize areas within the wind farms. While a barrier effect exists for species on migration, resident species probably have a higher collision risk. Raptors migrating during daylight frequently enter the wind farm area on their flight routes, correcting their flight paths in order to avoid collisions. Radar results show that during times of intensive migration, the proportion of birds flying at high altitudes and thus above windmill height is higher than in times of low migration intensity. Consequently, there is a lower proportion of migrating birds flying within the risk area. Data will be further analysed to
-
Intercalibration of HRDI and WINDII wind measurements
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. D. Burrage
Full Text Available The High Resolution Doppler Imager (HRDI and the Wind Imaging Interferometer (WINDII in- struments, which are both on the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite, measure winds by sensing the Doppler shift in atmospheric emission features. Because the two observation sets are frequently nearly coincident in space and time, each provides a very e.ective validation test of the other. Discrepancies due to geophysical di.erences should be much smaller than for comparisons with other techniques (radars, rockets, etc., and the very large sizes of the coincident data sets provide excellent statistics for the study. Issues that have been examined include relative systematic o.sets and the wind magnitudes obtained with the two systems. A significant zero wind position di.erence of ~6 m s–1 is identified for the zonal component, and it appears that this arises from an absolute perturbation in WINDII winds of –4 m s–1 and in HRDI of +2 m s–1. Altitude o.sets appear to be relatively small, and do not exceed 1 km. In addition, no evidence is found for the existence of a systematic wind speed bias between HRDI and WINDII. However, considerable day-to-day variability is found in the quality of the agreement, and RMS di.erences are surprisingly large, typically in the range of 20±30 m s–1.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Fichaux, N.
2003-12-15
Offshore wind energy may help to contribute to the respect of the Kyoto objectives by Europe. It is a key issue to struggle against global change. To sit the future offshore wind parks, it is necessary to accurately evaluate the spatial repartition of the wind potential. We demonstrate that the offshore wind potential shall be represented by maps of wind statistics. As remote sensing is a tool for measuring space physical phenomena, we evaluate its potentialities for mapping wind statistics. Space-borne scatterometers enables the obtention of wind statistics, but far from our areas of interest and at low spatial resolution. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) enables the computation of high resolution wind maps over our areas of interest, but are unsuitable to compute wind statistics. We define the mathematical framework of a statistical method. That method enables to take advantage of both scatterometer and SAR to compute maps of wind statistics at high spatial resolution over the areas of interest. It enables remote sensing to be used operationally to map the offshore wind potential. (author)
-
Russell, Robert William
I studied the ecology of aerial insects and birds (the "aerofauna") during the Convection and Precipitation/Electrification (CaPE) Experiment in Florida during the summer of 1991. Visual observations were coordinated with simultaneous measurements of atmospheric motions, permitting novel explorations of: (1) patterns and processes in the distribution of "aerial plankton" (i.e., small, weakly flying insects that drift with boundary-layer winds); (2) the feeding ecology of "aerial planktivores" (i.e., predators that feed on aerial plankton); and (3) the flight tactics of soaring birds. Sensitive Doppler radars regularly detected fine lines of enhanced reflectivity in boundary-layer convergence zones. These "fine lines" were attributable to dense concentrations of aerial plankton entrained by the convergent airflow. Insect densities were inferred to be about an order of magnitude higher inside convergence zones then elsewhere. Anecdotal observations suggested that large quantities of aerial plankton entrained in convergence zones were sometimes "scrubbed" from the boundary layer by precipitation. Radar images clearly depicted the rapid aeolian transport of aerial plankton across the landscape, but also showed that densities of aerial plankton became concentrated along coastlines when winds blew toward the sea. In contrast, airspace over the adjacent ocean remained largely free of radar echoes under all wind conditions. The coastal concentrations, together with the absence of overwater echoes, indicate that the organisms comprising the aerial plankton respond behaviorally to coastlines to avoid being blown out to sea. Several species of aerial insectivorous predators commonly exploited boundary-layer fine lines as food resources. Chimney swifts (Chaetura pelagica), barn swallows (Hirundo rustica), and wandering gliders (Pantala flavescens) showed significant responses to fine lines. Details of these responses differed, but this variation clearly reflected species
-
Anisotropy of Doppler spectral parameters in the VHF radar observations at MU and White Sands
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. D. Nastrom
2001-08-01
Full Text Available Significant differences are found between the mean spectral widths from beams in the meridional plane and in the zonal plane at both the MU and the White Sands VHF radars. The spectral width in the beam directed perpendicular to the prevailing wind is greater than that in the beam parallel to the wind. The magnitudes of the differences in spectral width show a linear relationship with wind speed, with the greatest differences at the greatest wind speeds. The differences in spectral width show a positive correlation with the differences in backscattered power. The anisotropy in backscattered power is well-known and is usually attributed to aspect sensitivity effects. However, the anisotropy in spectral width does not appear to be due to the same mechanism, and while several hypotheses to account for this are considered, including finite range-volume effects, effects from the tilting of isentropic layers, and anisotropic turbulence effects, it is seen that each of these suggestions has its shortcomings.Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (turbulence; instruments and techniques
-
All-weather volume imaging of the boundary layer and troposphere using the MU radar
Worthington , R. M.
2004-01-01
This paper shows the first volume-imaging radar that can run in any weather, revealing the turbulent three-dimensional structure and airflow of convective cells, rain clouds, breaking waves and deep convection as they evolve and move. Precipitation and clear air can be volume-imaged independently. Birds are detected as small high-power echoes moving near horizontal, at different speeds and directions from background wind. The volume-imaging method could be used to create a real-time virtual-r...
-
Survey of Ultra-wideband Radar
Mokole, Eric L.; Hansen, Pete
The development of UWB radar over the last four decades is very briefly summarized. A discussion of the meaning of UWB is followed by a short history of UWB radar developments and discussions of key supporting technologies and current UWB radars. Selected UWB radars and the associated applications are highlighted. Applications include detecting and imaging buried mines, detecting and mapping underground utilities, detecting and imaging objects obscured by foliage, through-wall detection in urban areas, short-range detection of suicide bombs, and the characterization of the impulse responses of various artificial and naturally occurring scattering objects. In particular, the Naval Research Laboratory's experimental, low-power, dual-polarized, short-pulse, ultra-high resolution radar is used to discuss applications and issues of UWB radar. Some crucial issues that are problematic to UWB radar are spectral availability, electromagnetic interference and compatibility, difficulties with waveform control/shaping, hardware limitations in the transmission chain, and the unreliability of high-power sources for sustained use above 2 GHz.
-
Climatological lower thermosphere winds as seen by ground-based and space-based instruments
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. M. Forbes
2004-06-01
Full Text Available Comparisons are made between climatological dynamic fields obtained from ground-based (GB and space-based (SB instruments with a view towards identifying SB/GB intercalibration issues for TIMED and other future aeronomy satellite missions. SB measurements are made from the High Resolution Doppler Imager (HRDI instrument on the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS. The GB data originate from meteor radars at Obninsk, (55° N, 37° E, Shigaraki (35° N, 136° E and Jakarta (6° S, 107° E and MF spaced-antenna radars at Hawaii (22° N, 160° W, Christmas I. (2° N, 158° W and Adelaide (35° S, 138° E. We focus on monthly-mean prevailing, diurnal and semidiurnal wind components at 96km, averaged over the 1991-1999 period. We perform space-based (SB analyses for 90° longitude sectors including the GB sites, as well as for the zonal mean. Taking the monthly prevailing zonal winds from these stations as a whole, on average, SB zonal winds exceed GB determinations by ~63%, whereas meridional winds are in much better agreement. The origin of this discrepancy remains unknown, and should receive high priority in initial GB/SB comparisons during the TIMED mission. We perform detailed comparisons between monthly climatologies from Jakarta and the geographically conjugate sites of Shigaraki and Adelaide, including some analyses of interannual variations. SB prevailing, diurnal and semidiurnal tides exceed those measured over Jakarta by factors, on the average, of the order of 2.0, 1.6, 1.3, respectively, for the eastward wind, although much variability exists. For the meridional component, SB/GB ratios for the diurnal and semidiurnal tide are about 1.6 and 1.7. Prevailing and tidal amplitudes at Adelaide are significantly lower than SB values, whereas similar net differences do not occur at the conjugate Northern Hemisphere location of Shigaraki. Adelaide diurnal phases lag SB phases by several hours, but excellent agreement between the two data
-
German Radar Observation Shuttle Experiment (ROSE)
Sleber, A. J.; Hartl, P.; Haydn, R.; Hildebrandt, G.; Konecny, G.; Muehlfeld, R.
1984-01-01
The success of radar sensors in several different application areas of interest depends on the knowledge of the backscatter of radar waves from the targets of interest, the variance of these interaction mechanisms with respect to changing measurement parameters, and the determination of the influence of he measuring systems on the results. The incidence-angle dependency of the radar cross section of different natural targets is derived. Problems involved by the combination of data gained with different sensors, e.g., MSS-, TM-, SPOTand SAR-images are analyzed. Radar cross-section values gained with ground-based radar spectrometers and spaceborne radar imaging, and non-imaging scatterometers and spaceborne radar images from the same areal target are correlated. The penetration of L-band radar waves into vegetated and nonvegetated surfaces is analyzed.
-
Multi-Instrument Observations of Prolonged Stratified Wind Layers at Iqaluit, Nunavut
Mariani, Zen; Dehghan, Armin; Gascon, Gabrielle; Joe, Paul; Hudak, David; Strawbridge, Kevin; Corriveau, Julien
2018-02-01
Data collected between October 2015 and May 2016 at Environment and Climate Change Canada's Iqaluit research site (64°N, 69°W) have revealed a high frequency (40% of all days for which observations were available) of stratified wind layer events that occur from near the surface up to about 7.2 km above sea level. These stratified wind layers are clearly visible as wind shifts (90 to 180°) with height in range-height indicator scans from the Doppler lidar and Ka-band radar and in wind direction profiles from the Doppler lidar and radiosonde. During these events, the vertical structure of the flow appears to be a stack of 4 to 10 layers ranging in vertical width from 0.1 to 4.4 km. The stratification events that were observed occurred predominantly (81%) during light precipitation and lasted up to 27.5 h. The integrated measurement platforms at Iqaluit permitted continuous observations of the evolution of stratification events in different meteorological conditions.
-
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — The TOGA radar dataset consists of browse and radar data collected from the TOGA radar during the CAMEX-4 experiment. TOGA is a C-band linear polarized doppler radar...
-
Long-period variations of wind parameters in the mesopause region and the solar cycle dependence
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Greisiger, K.M.; Schminder, R.; Kuerschner, D.
1987-01-01
The solar cycle dependence of wind parameters below 100 km on the basis of long term continuous ionospheric drift measurements in the low frequency range is discussed. For the meridional prevailing wind no significant variation was found. The same comparison as for winter was done for summer where the previous investigations gave no correlation. Now the radar meteor wind measurement values, too, showed a significant negative correlation of the zonal prevailing wind with solar activity for the years 1976 to 1983. The ionospheric drift measurement results of Collm have the same tendency but a larger dispersion due to the lower accuracy of the harmonic analysis because of the shorter daily measuring interval in summer. Continuous wind observations in the upper mesopause region over more than 20 years revealed distinct long term variations, the origin of which cannot be explained with the present knowledge
-
Meng, Zhiyong; Yao, Dan; Bai, Lanqiang; Zheng, Yongguang; Xue, Ming; Zhang, Xiaoling; Zhao, Kun; Tian, Fuyou; Wang, Mingjun
Based on observational analyses and on-site ground and aerial damage surveys, this work aims to reveal the weather phenomena-especially the wind situation-when Oriental Star capsized in the Yangtze River on June 1, 2015. Results demonstrate that the cruise ship capsized when it encountered strong winds at speeds of at least 31 m s -1 near the apex of a bow echo embedded in a squall line. As suggested by the fallen trees within a 2-km radius around the wreck location, such strong winds were likely caused by microburst straight-line wind and/or embedded small vortices, rather than tornadoes.
-
Radar Plan Position Indicator Scope
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — Radar Plan Position Indicator Scope is the collection of weather radar imagery for the period prior to the beginning of the Next Generation Radar (NEXRAD) system...
-
Wind turbines and aviation interests - European experience and practice
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jago, P.; Taylor, N.
2002-07-01
The approach of other European countries to the effects of wind turbines on civil and military aviation has been studied in order to determine the applicability of these experiences to UK stakeholders. The background to the study is traced, and the restriction on the siting of turbines due to the hazards posed to aviation and defence interests, and the potential effects on radar for air traffic control, defence and low flying aircraft are examined. The planning and siting issues in different European countries, the planning system in the UK, and the safeguarding of aerodromes and military sites are discussed along with issues involved in low flying aircraft and search and rescue operations, and the marking and illumination of wind farms.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hoffmann, P.; Serafimovich, A.; Peters, D.; Latteck, R. [Leibniz-Inst. fuer Atmosphaerenphysik, Kuehlungsborn (Germany); Dalin, P. [Swedish Inst. of Space Physics, Kiruna (Sweden); Goldberg, R. [NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD (United States)
2006-07-01
During the MaCWAVE campaign, combined rocket, radiosonde and ground-based measurements have been performed at the Norwegian Andoeya rocket range (ARR) near Andenes and the Swedish rocket range (ESRANGE) near Kiruna in January 2003 to study gravity waves in the vicinity of the Scandinavian mountain ridge. The investigations presented here are mainly based on the evaluation of continuous radar measurements with the ALWIN VHP radar in the upper troposphere/ lower stratosphere at Andenes (69.3 N, 16.0 E) and the ESRAD VHP radar near Kiruna (67.9 N, 21.9 E). Both radars are separated by about 260 km. Based on wavelet transformations of both data sets, the strongest activity of inertia gravity waves in the upper troposphere has been detected during the first period from 24-26 January 2003 with dominant vertical wavelengths of about 4-5 km as well as with dominant observed periods of about 13-14 h for the altitude range between 5 and 8 km under the additional influence of mountain waves. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia gravity waves with characteristic horizontal wavelengths of {proportional_to}200 km moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia gravity waves with intrinsic periods in the order of {proportional_to}5 h and with horizontal wavelengths of 200 km, moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind. From the derived downward energy propagation it is supposed, that these waves are likely generated by a jet streak in the upper troposphere. The parameters of the jet-induced gravity waves have been estimated at both sites separately. The identified gravity waves are coherent at both locations and show higher amplitudes on the east-side of the Scandinavian mountain ridge, as expected by the influence of mountains. (orig.)
-
The effect of the Sep wind park near Oosterbierum, Friesland, The Netherlands, on birds
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Winkelman, J.E.
1992-01-01
The title study concerns the period 1984-1991. The wind park consists of 18 three-bladed 300 kW horizontal axis wind turbines of 35 meters height, and a rotor diameter of 30 meters, seven meteorological towers, and three cluster and control buildings. Aspects studied included disturbance of breeding, resting or feeding, and migrating birds, behavior of birds approaching the wind turbines during the day and night, and bird victims due to collision with the wind turbines and the meteorological towers. In this report data on the number of birds passing the wind park at night and the flight behavior of these birds during their passage are presented and discussed. The numbers were determined in the period 1985-1988 by using a search approach radar, two passive image intensifiers in combination with infrared spot lights, and a thermal image intensifier. Illumination of the wind turbines to avoid collisions is not believed to be necessary, because birds seem to be quite good at spotting the wind turbines, even during conditions of moderate visibility at night. 30 figs., 23 tabs., 18 app., 109 refs
-
VHF radar observations of gravity waves at a low latitude
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. Dutta
1999-08-01
Full Text Available Wind observations made at Gadanki (13.5°N by using Indian MST Radar for few days in September, October, December 1995 and January, 1996 have been analyzed to study gravity wave activity in the troposphere and lower stratosphere. Horizontal wind variances have been computed for gravity waves of period (2-6 h from the power spectral density (PSD spectrum. Exponential curves of the form eZ/H have been fitted by least squares technique to these variance values to obtain height variations of the irregular winds upto the height of about 15 km, where Z is the height in kilometers. The value of H, the scale height, as determined from curve fitting is found to be less than the theoretical value of scale height of neutral atmosphere in this region, implying that the waves are gaining energy during their passage in the troposphere. In other words, it indicates that the sources of gravity waves are present in the troposphere. The energy densities of gravity wave fluctuations have been computed. Polynomial fits to the observed values show that wave energy density increases in the troposphere, its source region, and then decreases in the lower stratosphere.Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (middle atmosphere dynamics; turbulence; waves and tides
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. L. Parkinson
2006-03-01
Full Text Available Akasofu's solar wind ε parameter describes the coupling of solar wind energy to the magnetosphere and ionosphere. Analysis of fluctuations in ε using model independent scaling techniques including the peaks of probability density functions (PDFs and generalised structure function (GSF analysis show the fluctuations were self-affine (mono-fractal, single exponent scaling over 9 octaves of time scale from ~46 s to ~9.1 h. However, the peak scaling exponent α0 was a function of the fluctuation bin size, so caution is required when comparing the exponents for different data sets sampled in different ways. The same generic scaling techniques revealed the organisation and functional form of concurrent fluctuations in azimuthal magnetospheric electric fields implied by SuperDARN HF radar measurements of line-of-sight Doppler velocity, vLOS, made in the high-latitude austral ionosphere. The PDFs of vLOS fluctuation were calculated for time scales between 1 min and 256 min, and were sorted into noon sector results obtained with the Halley radar, and midnight sector results obtained with the TIGER radar. The PDFs were further sorted according to the orientation of the interplanetary magnetic field, as well as ionospheric regions of high and low Doppler spectral width. High spectral widths tend to occur at higher latitude, mostly on open field lines but also on closed field lines just equatorward of the open-closed boundary, whereas low spectral widths are concentrated on closed field lines deeper inside the magnetosphere. The vLOS fluctuations were most self-affine (i.e. like the solar wind ε parameter on the high spectral width field lines in the noon sector ionosphere (i.e. the greater cusp, but suggested multi-fractal behaviour on closed field lines in the midnight sector (i.e. the central plasma sheet. Long tails in the PDFs imply that "microbursts" in ionospheric convection occur far more frequently, especially on open field lines, than can be
-
Satellite information for wind energy applications
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nielsen, M.; Astrup, P.; Bay Hasager, C.
2004-11-01
An introduction to satellite information relevant for wind energy applications is given. It includes digital elevation model (DEM) data based on satellite observations. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) is useful for regional scale wind resource studies. Comparison results from complex terrain in Spain and flat terrain in Denmark are found to be acceptable for both sites. Also land cover type information can be retrieved from satellite observations. Land cover type maps have to be combined with roughness data from field observation or literature values. Land cover type maps constitute an aid to map larger regions within shorter time. Field site observations of obstacles and hedges are still necessary. The raster-based map information from DEM and land cover maps can be converted for use in WASP. For offshore locations it is possible to estimate the wind resources based on ocean surface wind data from several types of satellite observations. The RWT software allows an optimal calculation of SAR wind resource statistics. A tab-file with SAR-based observed wind climate (OWC) data can be obtained for 10 m above sea level and used in WASP. RWT uses a footprint averaging technique to obtain data as similar as possible to mast observations. Maximum-likelihood fitting is used to calculate the Weibull A and k parameters from the constrained data set. Satellite SAR wind maps cover the coastal zone from 3 km and offshore with very detailed information of 400 m by 400 m grid resolution. Spatial trends in mean wind, energy density, Weibull A and k and uncertainty values are provided for the area of interest. Satellite scatterometer wind observations have a spatial resolution of 25 km by 25 km. These data typically represent a site further offshore, and the tab-file statistics should be used in WASP combined with topography and roughness information to assess the coastal wind power potential. Scatterometer wind data are observed {approx} twice per day, whereas SAR only
-
Wind power and bats : Ontario guideline
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
McGuiness, F. [Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources, Peterborough, ON (Canada). Renewable Energy Resources; Stewart, J. [Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources, Toronto, ON (Canada). Wildlife Section
2008-07-01
None of the 8 species of bats in Ontario are considered as species at risk. However, all bats in Ontario are protected under the Fish and Wildlife Conservation Act. The Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources (MNR) is responsible for identifying significant wildlife habitat for bats, including hibernacula and maternity roosts. The MNR's role in wind development includes environmental assessments (EA) and surveys. The MNR bat guideline includes a summary of Ontario species, a literature review of research related to wind turbines and bats, and a review of methods for assessing and monitoring bats. Guideline development includes a bat working group responsible for obtaining data on risk factors and monitoring requirements. The MNR has determined that site selection is critical for minimizing potential impacts. Wind farm proponents can use MNR data, information, and maps for their site selection process. Information requirements include bat species data; habitat data; and meteorological data. The presence of risk factors results in a sensitivity rating. The MNR is also developing a site sensitivity mapping project in order to assist proponents in making siting decisions. All proposed sites are required to conduct pre-construction site surveys. Acoustic detectors and radar are used to determine bat activity at the site. Monitoring and mitigation strategies include selective wind turbine shutdown during key periods or weather conditions. tabs., figs.
-
The use of radar for bathymetry assessment
Aardoom, J.H.; Greidanus, H.S.F.
1998-01-01
The bottom topography in shallow seas can be observed by air- and spaceborne imaging radar. Bathymetric information derived from radar data is limited in accuracy, but radar has a good spatial coverage. The accuracy can be increased by assimilating the radar imagery into existing or insitu gathered bathymetric data. The paper reviews the concepts of bathymetry assessment by radar, the radar imaging mechanism, and the possibilities and limitations of the use of radar data in rapid assessment.
-
Wavelet based methods for improved wind profiler signal processing
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. Lehmann
2001-08-01
Full Text Available In this paper, we apply wavelet thresholding for removing automatically ground and intermittent clutter (airplane echoes from wind profiler radar data. Using the concept of discrete multi-resolution analysis and non-parametric estimation theory, we develop wavelet domain thresholding rules, which allow us to identify the coefficients relevant for clutter and to suppress them in order to obtain filtered reconstructions.Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (instruments and techniques – Radio science (remote sensing; signal processing
-
SAR Observation and Modeling of Gap Winds in the Prince William Sound of Alaska.
Liu, Haibo; Olsson, Peter Q; Volz, Karl
2008-08-22
Alaska's Prince William Sound (PWS) is a unique locale tending to have strong gap winds, especially in the winter season. To characterize and understand these strong surface winds, which have great impacts on the local marine and aviation activities, the surface wind retrieval from the Synthetic Aperture Radar data (SAR-wind) is combined with a numerical mesoscale model. Helped with the SAR-wind observations, the mesoscale model is used to study cases of strong winds and relatively weak winds to depict the nature of these winds, including the area of extent and possible causes of the wind regimes. The gap winds from the Wells Passage and the Valdez Arm are the most dominant gap winds in PWS. Though the Valdez Arm is north-south trending and Wells Passage is east-west oriented, gap winds often develop simultaneously in these two places when a low pressure system is present in the Northern Gulf of Alaska. These two gap winds often converge at the center of PWS and extend further out of the Sound through the Hinchinbrook Entrance. The pressure gradients imposed over these areas are the main driving forces for these gap winds. Additionally, the drainage from the upper stream glaciers and the blocking effect of the banks of the Valdez Arm probably play an important role in enhancing the gap wind.
-
SAR Observation and Modeling of Gap Winds in the Prince William Sound of Alaska
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Karl Volz
2008-08-01
Full Text Available Alaska’s Prince William Sound (PWS is a unique locale tending to have strong gap winds, especially in the winter season. To characterize and understand these strong surface winds, which have great impacts on the local marine and aviation activities, the surface wind retrieval from the Synthetic Aperture Radar data (SAR-wind is combined with a numerical mesoscale model. Helped with the SAR-wind observations, the mesoscale model is used to study cases of strong winds and relatively weak winds to depict the nature of these winds, including the area of extent and possible causes of the wind regimes. The gap winds from the Wells Passage and the Valdez Arm are the most dominant gap winds in PWS. Though the Valdez Arm is north-south trending and Wells Passage is east-west oriented, gap winds often develop simultaneously in these two places when a low pressure system is present in the Northern Gulf of Alaska. These two gap winds often converge at the center of PWS and extend further out of the Sound through the Hinchinbrook Entrance. The pressure gradients imposed over these areas are the main driving forces for these gap winds. Additionally, the drainage from the upper stream glaciers and the blocking effect of the banks of the Valdez Arm probably play an important role in enhancing the gap wind.
-
Fusion of imaging and nonimaging data for surveillance aircraft
Shahbazian, Elisa; Gagnon, Langis; Duquet, Jean Remi; Macieszczak, Maciej; Valin, Pierre
1997-06-01
This paper describes a phased incremental integration approach for application of image analysis and data fusion technologies to provide automated intelligent target tracking and identification for airborne surveillance on board an Aurora Maritime Patrol Aircraft. The sensor suite of the Aurora consists of a radar, an identification friend or foe (IFF) system, an electronic support measures (ESM) system, a spotlight synthetic aperture radar (SSAR), a forward looking infra-red (FLIR) sensor and a link-11 tactical datalink system. Lockheed Martin Canada (LMCan) is developing a testbed, which will be used to analyze and evaluate approaches for combining the data provided by the existing sensors, which were initially not designed to feed a fusion system. Three concurrent research proof-of-concept activities provide techniques, algorithms and methodology into three sequential phases of integration of this testbed. These activities are: (1) analysis of the fusion architecture (track/contact/hybrid) most appropriate for the type of data available, (2) extraction and fusion of simple features from the imaging data into the fusion system performing automatic target identification, and (3) development of a unique software architecture which will permit integration and independent evolution, enhancement and optimization of various decision aid capabilities, such as multi-sensor data fusion (MSDF), situation and threat assessment (STA) and resource management (RM).
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
D. A. Neudegg
1999-06-01
Full Text Available Observations of a flux transfer event (FTE have been made simultaneously by the Equator-S spacecraft near the dayside magnetopause whilst corresponding transient plasma flows were seen in the near-conjugate polar ionosphere by the CUTLASS Finland HF radar. Prior to the occurrence of the FTE, the magnetometer on the WIND spacecraft ~226 RE upstream of the Earth in the solar wind detected a southward turning of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF which is estimated to have reached the subsolar magnetopause ~77 min later. Shortly afterwards the Equator-S magnetometer observed a typical bipolar FTE signature in the magnetic field component normal to the magnetopause, just inside the magnetosphere. Almost simultaneously the CUTLASS Finland radar observed a strong transient flow in the F region plasma between 78° and 83° magnetic latitude, near the ionospheric region predicted to map along geomagnetic field lines to the spacecraft. The flow signature (and the data set as a whole is found to be fully consistent with the view that the FTE was formed by a burst of magnetopause reconnection.Key words. Interplanetary physics (ionosphere-magnetosphere interaction · Magnetospheric physics (magnetopause · cusp · and boundary layers; solar wind-magnetosphere interactions
-
The SUMO Ship Detector Algorithm for Satellite Radar Images
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Harm Greidanus
2017-03-01
Full Text Available Search for Unidentified Maritime Objects (SUMO is an algorithm for ship detection in satellite Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR images. It has been developed over the course of more than 15 years, using a large amount of SAR images from almost all available SAR satellites operating in L-, C- and X-band. As validated by benchmark tests, it performs very well on a wide range of SAR image modes (from Spotlight to ScanSAR and resolutions (from 1–100 m and for all types and sizes of ships, within the physical limits imposed by the radar imaging. This paper describes, in detail, the algorithmic approach in all of the steps of the ship detection: land masking, clutter estimation, detection thresholding, target clustering, ship attribute estimation and false alarm suppression. SUMO is a pixel-based CFAR (Constant False Alarm Rate detector for multi-look radar images. It assumes a K distribution for the sea clutter, corrected however for deviations of the actual sea clutter from this distribution, implementing a fast and robust method for the clutter background estimation. The clustering of detected pixels into targets (ships uses several thresholds to deal with the typically irregular distribution of the radar backscatter over a ship. In a multi-polarization image, the different channels are fused. Azimuth ambiguities, a common source of false alarms in ship detection, are removed. A reliability indicator is computed for each target. In post-processing, using the results of a series of images, additional false alarms from recurrent (fixed targets including range ambiguities are also removed. SUMO can run in semi-automatic mode, where an operator can verify each detected target. It can also run in fully automatic mode, where batches of over 10,000 images have successfully been processed in less than two hours. The number of satellite SAR systems keeps increasing, as does their application to maritime surveillance. The open data policy of the EU�
-
Use of ground-based wind profiles in mesoscale forecasting
Schlatter, Thomas W.
1985-01-01
A brief review is presented of recent uses of ground-based wind profile data in mesoscale forecasting. Some of the applications are in real time, and some are after the fact. Not all of the work mentioned here has been published yet, but references are given wherever possible. As Gage and Balsley (1978) point out, sensitive Doppler radars have been used to examine tropospheric wind profiles since the 1970's. It was not until the early 1980's, however, that the potential contribution of these instruments to operational forecasting and numerical weather prediction became apparent. Profiler winds and radiosonde winds compare favorably, usually within a few m/s in speed and 10 degrees in direction (see Hogg et al., 1983), but the obvious advantage of the profiler is its frequent (hourly or more often) sampling of the same volume. The rawinsonde balloon is launched only twice a day and drifts with the wind. In this paper, I will: (1) mention two operational uses of data from a wind profiling system developed jointly by the Wave Propagation and Aeronomy Laboratories of NOAA; (2) describe a number of displays of these same data on a workstation for mesoscale forecasting developed by the Program for Regional Observing and Forecasting Services (PROFS); and (3) explain some interesting diagnostic calculations performed by meteorologists of the Wave Propagation Laboratory.
-
A new approach to wind energy: Opportunities and challenges
Dabiri, John O.; Greer, Julia R.; Koseff, Jeffrey R.; Moin, Parviz; Peng, Jifeng
2015-03-01
Despite common characterizations of modern wind energy technology as mature, there remains a persistent disconnect between the vast global wind energy resource—which is 20 times greater than total global power consumption—and the limited penetration of existing wind energy technologies as a means for electricity generation worldwide. We describe an approach to wind energy harvesting that has the potential to resolve this disconnect by geographically distributing wind power generators in a manner that more closely mirrors the physical resource itself. To this end, technology development is focused on large arrays of small wind turbines that can harvest wind energy at low altitudes by using new concepts of biology-inspired engineering. This approach dramatically extends the reach of wind energy, as smaller wind turbines can be installed in many places that larger systems cannot, especially in built environments. Moreover, they have lower visual, acoustic, and radar signatures, and they may pose significantly less risk to birds and bats. These features can be leveraged to attain cultural acceptance and rapid adoption of this new technology, thereby enabling significantly faster achievement of state and national renewable energy targets than with existing technology alone. Favorable economics stem from an orders-of-magnitude reduction in the number of components in a new generation of simple, mass-manufacturable (even 3D-printable), vertical-axis wind turbines. However, this vision can only be achieved by overcoming significant scientific challenges that have limited progress over the past three decades. The following essay summarizes our approach as well as the opportunities and challenges associated with it, with the aim of motivating a concerted effort in basic and applied research in this area.
-
Interception of LPI radar signals
Lee, Jim P.
1991-11-01
Most current radars are designed to transmit short duration pulses with relatively high peak power. These radars can be detected easily by the use of relatively modest EW intercept receivers. Three radar functions (search, anti-ship missile (ASM) seeker, and navigation) are examined to evaluate the effectiveness of potential low probability of intercept (LPI) techniques, such as waveform coding, antenna profile control, and power management that a radar may employ against current Electronic Warfare (EW) receivers. The general conclusion is that it is possible to design a LPI radar which is effective against current intercept EW receivers. LPI operation is most easily achieved at close ranges and against a target with a large radar cross section. The general system sensitivity requirement for the detection of current and projected LPI radars is found to be on the order of -100 dBmi which cannot be met by current EW receivers. Finally, three potential LPI receiver architectures, using channelized, superhet, and acousto-optic receivers with narrow RF and video bandwidths are discussed. They have shown some potential in terms of providing the sensitivity and capability in an environment where both conventional and LPI signals are present.
-
Air and spaceborne radar systems an introduction
Lacomme, Philippe; Hardange, Jean-Philippe; Normant, Eric
2001-01-01
A practical tool on radar systems that will be of major help to technicians, student engineers and engineers working in industry and in radar research and development. The many users of radar as well as systems engineers and designers will also find it highly useful. Also of interest to pilots and flight engineers and military command personnel and military contractors. """"This introduction to the field of radar is intended for actual users of radar. It focuses on the history, main principles, functions, modes, properties and specific nature of modern airborne radar. The book examines radar's
-
Spectral Properties of ENVISAT ASAR and QuikSCAT Surface Winds in the North Sea
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Karagali, Ioanna; Larsén, Xiaoli Guo; Badger, Merete
2013-01-01
as an increase in spectral density over similar wavenumber ranges as the spatial resolution increases. The 600-m SAR wind product reveals a range of wavenumbers in which the exchange processes between micro- and meso-scales occur; this range is not captured by the wind products with a resolution of 1.5 km......Spectra derived from ENVISAT Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ASAR) and QuikSCAT near-surface ocean winds are investigated over the North Sea. The two sensors offer a wide range of spatial resolutions, from 600 m to 25 km, with different spatial coverage over the area of interest. This provides...... a unique opportunity to study the impact of the spatial resolution on the spectral properties of the wind over a wide range of length scales. Initially, a sub-domain in the North Sea is chosen, due to the overlap of 87 wind scenes from both sensors. The impact of the spatial resolution is manifested...
-
Human walking estimation with radar
Dorp, Ph. van; Groen, F.C.A.
2003-01-01
Radar can be used to observe humans that are obscured by objects such as walls. These humans cannot be visually observed. The radar measurements are used to animate an obscured human in virtual reality. This requires detailed information about the motion. The radar measurements give detailed
-
FMWC Radar for Breath Detection
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Suhr, Lau Frejstrup; Tafur Monroy, Idelfonso; Vegas Olmos, Juan José
We report on the experimental demonstration of an FMCW radar operating in the 25.7 - 26.6 GHz range with a repetition rate of 500 sweeps per second. The radar is able to track the breathing rate of an adult human from a distance of 1 meter. The experiments have utilized a 50 second recording window...... to accurately track the breathing rate. The radar utilizes a saw tooth modulation format and a low latency receiver. A breath tracking radar is useful both in medical scenarios, diagnosing disorders such as sleep apnea, and for home use where the user can monitor its health. Breathing is a central part of every...... radar chip which, through the use of a simple modulation scheme, is able to measure the breathing rate of an adult human from a distance. A high frequency output makes sure that the radar cannot penetrate solid obstacles which is a wanted feature in private homes where people therefore cannot measure...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Hoffmann
2006-11-01
Full Text Available During the {MaCWAVE} campaign, combined rocket, radiosonde and ground-based measurements have been performed at the Norwegian Andøya Rocket Range (ARR near Andenes and the Swedish Rocket Range (ESRANGE near Kiruna in January 2003 to study gravity waves in the vicinity of the Scandinavian mountain ridge. The investigations presented here are mainly based on the evaluation of continuous radar measurements with the ALWIN VHF radar in the upper troposphere/ lower stratosphere at Andenes (69.3° N, 16.0° E and the ESRAD VHF radar near Kiruna (67.9° N, 21.9° E. Both radars are separated by about 260 km. Based on wavelet transformations of both data sets, the strongest activity of inertia gravity waves in the upper troposphere has been detected during the first period from 24–26 January 2003 with dominant vertical wavelengths of about 4–5 km as well as with dominant observed periods of about 13–14 h for the altitude range between 5 and 8 km under the additional influence of mountain waves. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia gravity waves with characteristic horizontal wavelengths of ~200 km moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia gravity waves with intrinsic periods in the order of ~5 h and with horizontal wavelengths of 200 km, moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind. From the derived downward energy propagation it is supposed, that these waves are likely generated by a jet streak in the upper troposphere. The parameters of the jet-induced gravity waves have been estimated at both sites separately. The identified gravity waves are coherent at both locations and show higher amplitudes on the east-side of the Scandinavian mountain ridge, as expected by the influence of mountains.
-
Radar meteor rates and solar activity
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Prikryl, P.
1983-01-01
The short-term variation of diurnal radar meteor rates with solar activity represented by solar microwave flux Fsub(10.7), and sunspots relative number Rsub(z), is investigated. Applying the superposed-epoch analysis to the observational material of radar meteor rates from Christchurch (1960-61 and 1963-65), a decrease in the recorded radar rates is found during days of enhanced solar activity. No effect of geomagnetic activity similar to the one reported for the Swedish and Canadian radar meteor data was found by the author in the Christchurch data. A possible explanation of the absence of the geomagnetic effect on radar meteor rates from New Zealand due to a lower echo ceiling height of the Christchurch radar is suggested. The variation of the atmospheric parameters as a possible cause of the observed variation in radar meteor rates is also discussed. (author)
-
Hogan, Patrick; Maxwell, Christopher; Kim, Randolph; Gaskins, Tom
2007-01-01
World Wind allows users to zoom from satellite altitude down to any place on Earth, leveraging high-resolution LandSat imagery and SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) elevation data to experience Earth in visually rich 3D. In addition to Earth, World Wind can also visualize other planets, and there are already comprehensive data sets for Mars and the Earth's moon, which are as easily accessible as those of Earth. There have been more than 20 million downloads to date, and the software is being used heavily by the Department of Defense due to the code s ability to be extended and the evolution of the code courtesy of NASA and the user community. Primary features include the dynamic access to public domain imagery and its ease of use. All one needs to control World Wind is a two-button mouse. Additional guides and features can be accessed through a simplified menu. A JAVA version will be available soon. Navigation is automated with single clicks of a mouse, or by typing in any location to automatically zoom in to see it. The World Wind install package contains the necessary requirements such as the .NET runtime and managed DirectX library. World Wind can display combinations of data from a variety of sources, including Blue Marble, LandSat 7, SRTM, NASA Scientific Visualization Studio, GLOBE, and much more. A thorough list of features, the user manual, a key chart, and screen shots are available at http://worldwind.arc.nasa.gov.
-
Environmental considerations of offshore wind energy
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ryckman, A. [Natural Resource Solutions Inc., Kitchener, ON (Canada)
2010-07-01
The environmental considerations of offshore wind energy projects in the Great Lakes region were discussed from the viewpoint of an environmental consulting firm. Existing projects and proposals were discussed in relation to site-specific conditions and the environmental studies required at the proposed sites. North American facilities that are now undergoing baseline studies in the Great Lakes include the Cape Wind and Nai Kun wind farms. Impact to fisheries in the lakes is expected to occur largely during the construction phases of the developments. However, additional noise, sedimentation, and lakebed losses have the potential to impact local fish populations. Some turbine foundations create a a reef effect that increases local fish populations. Baseline fisheries data as well as substrate and habitat assessments of the lakebed are required. Impacts on birds include collision and displacement impacts. Migratory birds and staging or wintering waterfowl may be displaced from feeding areas. Radar- and plane-based surveys should be used to identify large rafts of birds in offshore habitats, while boat surveys can be used to confirm species and identify diurnal migrants. The migratory paths of bats over the Great Lakes are not well-understood. It is expected that offshore wind developments will have little impact on terrestrial vegetation. Impacts will be localized at shoreline connection points and construction areas. Shoreline habitats, wetlands, dunes and beach habitats may also be impacted. Post-construction surveys should include avian and bat mortality, waterfowl usage, and fish habitat and substrates. Further studies were recommended, as there are limited guidelines for determining the effects of offshore wind energy developments. tabs., figs.
-
Assessing Upper-Level Winds on Day-of-Launch
Bauman, William H., III; Wheeler, Mark M.
2012-01-01
On the day-or-launch. the 45th Weather Squadron Launch Weather Officers (LWOS) monitor the upper-level winds for their launch customers to include NASA's Launch Services Program (LSP). During launch operations, the payload launch team sometimes asks the LWO if they expect the upper level winds to change during the countdown but the LWOs did not have the capability to quickly retrieve or display the upper-level observations and compare them to the numerical weather prediction model point forecasts. The LWOs requested the Applied Meteorology Unit (AMU) develop a capability in the form of a graphical user interface (GUI) that would allow them to plot upper-level wind speed and direction observations from the Kennedy Space Center Doppler Radar Wind Profilers and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station rawinsondes and then overlay model point forecast profiles on the observation profiles to assess the performance of these models and graphically display them to the launch team. The AMU developed an Excel-based capability for the LWOs to assess the model forecast upper-level winds and compare them to observations. They did so by creating a GUI in Excel that allows the LWOs to first initialize the models by comparing the O-hour model forecasts to the observations and then to display model forecasts in 3-hour intervals from the current time through 12 hours.
-
Characteristics of radar-derived hailstreaks across Central Europe
Kunz, Michael; Fluck, Elody; Schmidberger, Manuel; Jürgen Punge, Heinz; Baumstark, Sven
2017-04-01
Hailstorms are among the most damaging natural disasters in various parts of Europe. For example, two supercells in Germany, on 27 and 28 July 2013, bearing hailstones with a diameter of up to 10 cm, caused economic losses of around 4.0 billion EUR. Despite the large damage potential of severe hailstorms, knowledge about the probability and severity of hail events and hailstorm-favoring conditions in Europe still is limited. A large event set of past severe thunderstorms that occurred between 2004 and 2014 was identified for Germany, France, Belgium, and Luxembourg from radar data considering a lower threshold of 55 dBZ of the maximum Constant Altitude Plan Position Indicator (maxCAPPI). Additional filtering with lightning data and applying a cell tracking algorithm improves the reliability of the detected severe thunderstorm tracks. The obtained statistics show a gradual increase of the track density with increasing distance to the Atlantic and several local-scale maxima, mostly around the mountains. Both the seasonal and daily cycle of severe thunderstorms show large differences across the investigation area. For example, while in Southern France most events occur in June, the peak month in Northern Germany is August, which can be plausibly explained by differences in convective energy due to the large-scale circulation. Furthermore, ambient conditions in terms of convection-related quantities (e.g., CAPE, wind shear, lapse rate) and prevailing synoptic scale fronts were studied both for the entire event set and a subset, where radar-derived storm tracks were combined with hail observations provided by the European Severe Weather Database ESWD. Over Northern Germany, for example, up to 40% of all radar-derived thunderstorm tracks were associated with cold fronts, while in Southern Germany the ratio is only around 20%. Overall, around 25% of all hail streaks were associated with cold fronts.
-
Knott, Gene; Tuley, Michael
2004-01-01
This is the second edition of the first and foremost book on this subject for self-study, training, and course work. Radar cross section (RCS) is a comparison of two radar signal strengths. One is the strength of the radar beam sweeping over a target, the other is the strength of the reflected echo sensed by the receiver. This book shows how the RCS ?gauge? can be predicted for theoretical objects and how it can be measured for real targets. Predicting RCS is not easy, even for simple objects like spheres or cylinders, but this book explains the two ?exact? forms of theory so well that even a
-
Classification and correction of the radar bright band with polarimetric radar
Hall, Will; Rico-Ramirez, Miguel; Kramer, Stefan
2015-04-01
The annular region of enhanced radar reflectivity, known as the Bright Band (BB), occurs when the radar beam intersects a layer of melting hydrometeors. Radar reflectivity is related to rainfall through a power law equation and so this enhanced region can lead to overestimations of rainfall by a factor of up to 5, so it is important to correct for this. The BB region can be identified by using several techniques including hydrometeor classification and freezing level forecasts from mesoscale meteorological models. Advances in dual-polarisation radar measurements and continued research in the field has led to increased accuracy in the ability to identify the melting snow region. A method proposed by Kitchen et al (1994), a form of which is currently used operationally in the UK, utilises idealised Vertical Profiles of Reflectivity (VPR) to correct for the BB enhancement. A simpler and more computationally efficient method involves the formation of an average VPR from multiple elevations for correction that can still cause a significant decrease in error (Vignal 2000). The purpose of this research is to evaluate a method that relies only on analysis of measurements from an operational C-band polarimetric radar without the need for computationally expensive models. Initial results show that LDR is a strong classifier of melting snow with a high Critical Success Index of 97% when compared to the other variables. An algorithm based on idealised VPRs resulted in the largest decrease in error when BB corrected scans are compared to rain gauges and to lower level scans with a reduction in RMSE of 61% for rain-rate measurements. References Kitchen, M., R. Brown, and A. G. Davies, 1994: Real-time correction of weather radar data for the effects of bright band, range and orographic growth in widespread precipitation. Q.J.R. Meteorol. Soc., 120, 1231-1254. Vignal, B. et al, 2000: Three methods to determine profiles of reflectivity from volumetric radar data to correct
-
A NEW METHOD TO DETECT REGIONS ENDANGERED BY HIGH WIND SPEEDS
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Fischer
2016-06-01
Full Text Available In this study we evaluate whether the methodology of Boosted Regression Trees (BRT suits for accurately predicting maximum wind speeds. As predictors a broad set of parameters derived from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM acquired within the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM is used. The derived parameters describe the surface by means of quantities (e.g. slope, aspect and quality (landform classification. Furthermore land cover data from the CORINE dataset is added. The response variable is maximum wind speed, measurements are provided by a network of weather stations. The area of interest is Switzerland, a country which suits perfectly for this study because of its highly dynamic orography and various landforms.
-
2010-10-01
... within one mile of land must be fitted with a FCC Type Accepted general marine radar system for surface... Federal Communications Commission (FCC) type accepted general marine radar system for surface navigation... 46 Shipping 7 2010-10-01 2010-10-01 false Radars. 184.404 Section 184.404 Shipping COAST GUARD...
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Albrechtslund, Anders; Coeckelbergh, Mark; Matzner, Tobias
Studying surveillance involves raising questions about the very nature of concepts such as information, technology, identity, space and power. Besides the maybe all too obvious ethical issues often discussed with regard to surveillance, there are several other angles and approaches that we should...... like to encourage. Therefore, our panel will focus on the philosophical, yet non-ethical issues of surveillance in order to stimulate an intense debate with the audience on the ethical implications of our enquiries. We also hope to provide a broader and deeper understanding of surveillance....
-
Radar network communication through sensing of frequency hopping
Dowla, Farid; Nekoogar, Faranak
2013-05-28
In one embodiment, a radar communication system includes a plurality of radars having a communication range and being capable of operating at a sensing frequency and a reporting frequency, wherein the reporting frequency is different than the sensing frequency, each radar is adapted for operating at the sensing frequency until an event is detected, each radar in the plurality of radars has an identification/location frequency for reporting information different from the sensing frequency, a first radar of the radars which senses the event sends a reporting frequency corresponding to its identification/location frequency when the event is detected, and all other radars in the plurality of radars switch their reporting frequencies to match the reporting frequency of the first radar upon detecting the reporting frequency switch of a radar within the communication range. In another embodiment, a method is presented for communicating information in a radar system.
-
Developing Lightning Prediction Tools for the CCAFS Dual-Polarimetric Radar
Petersen, W. A.; Carey, L. D.; Deierling, W.; Johnson, E.; Bateman, M.
2009-01-01
NASA Marshall Space Flight Center and the University of Alabama Huntsville are collaborating with the 45th Weather Squadron (45WS) to develop improved lightning prediction capabilities for the new C-band dual-polarimetric weather radar being acquired for use by 45WS and launch weather forecasters at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). In particular, these algorithms will focus on lightning onset, cessation and combined lightning-radar applications for convective winds assessment. Research using radar reflectivity (Z) data for prediction of lightning onset has been extensively discussed in the literature and subsequently applied by launch weather forecasters as it pertains to lightning nowcasting. Currently the forecasters apply a relatively straight forward but effective temperature-Z threshold algorithm for assessing the likelihood of lightning onset in a given storm. In addition, a layered VIL above the freezing level product is used as automated guidance for the onset of lightning. Only limited research and field work has been conducted on lightning cessation using Z and vertically-integrated Z for determining cessation. Though not used operationally vertically-integrated Z (basis for VIL) has recently shown promise as a tool for use in nowcasting lightning cessation. The work discussed herein leverages and expands upon these and similar reflectivity-threshold approaches via the application/addition of over two decades of polarimetric radar research focused on distinct multi-parameter radar signatures of ice/mixed-phase initiation and ice-crystal orientation in highly electrified convective clouds. Specifically, our approach is based on numerous previous studies that have observed repeatable patterns in the behavior of the vertical hydrometeor column as it relates to the temporal evolution of differential reflectivity and depolarization (manifested in either LDR or p(sub hv)), development of in-situ mixed and ice phase microphysics, electric fields, and
-
Sensor management in RADAR/IRST track fusion
Hu, Shi-qiang; Jing, Zhong-liang
2004-07-01
In this paper, a novel radar management strategy technique suitable for RADAR/IRST track fusion, which is based on Fisher Information Matrix (FIM) and fuzzy stochastic decision approach, is put forward. Firstly, optimal radar measurements' scheduling is obtained by the method of maximizing determinant of the Fisher information matrix of radar and IRST measurements, which is managed by the expert system. Then, suggested a "pseudo sensor" to predict the possible target position using the polynomial method based on the radar and IRST measurements, using "pseudo sensor" model to estimate the target position even if the radar is turned off. At last, based on the tracking performance and the state of target maneuver, fuzzy stochastic decision is used to adjust the optimal radar scheduling and retrieve the module parameter of "pseudo sensor". The experiment result indicates that the algorithm can not only limit Radar activity effectively but also keep the tracking accuracy of active/passive system well. And this algorithm eliminates the drawback of traditional Radar management methods that the Radar activity is fixed and not easy to control and protect.
-
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Stryjewski, John
1998-01-01
The BMDO Innovative Science and Technology Experimentation Facility (BMDO/ISTEF) laser radar program is engaged in an ongoing program to develop and demonstrate advanced laser radar concepts for Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD...
-
Meng, Zhiyong; Yao, Dan; Bai, Lanqiang; Zheng, Yongguang; Xue, Ming; Zhang, Xiaoling; Zhao, Kun; Tian, Fuyou; Wang, Mingjun
2016-01-01
Based on observational analyses and on-site ground and aerial damage surveys, this work aims to reveal the weather phenomena?especially the wind situation?when Oriental Star capsized in the Yangtze River on June 1, 2015. Results demonstrate that the cruise ship capsized when it encountered strong winds at speeds of at least 31?m?s?1 near the apex of a bow echo embedded in a squall line. As suggested by the fallen trees within a 2-km radius around the wreck location, such strong winds were lik...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
E. M. Griffin
2004-03-01
Full Text Available Thermospheric neutral winds at Kiruna, Sweden (67.4°N, 20.4°E are compared using both direct optical Fabry-Perot Interferometer (FPI measurements and those derived from European incoherent scatter radar (EISCAT measurements. This combination of experimental data sets, both covering well over a solar cycle of data, allows for a unique comparison of the thermospheric meridional component of the neutral wind as observed by different experimental techniques. Uniquely in this study the EISCAT measurements are used to provide winds for comparison using two separate techniques: the most popular method based on the work of Salah and Holt (1974 and the Meridional Wind Model (MWM (Miller et al., 1997 application of servo theory. The balance of forces at this location that produces the observed diurnal pattern are investigated using output from the Coupled Thermosphere and Ionosphere (CTIM numerical model. Along with detailed comparisons from short periods the climatological behaviour of the winds have been investigated for seasonal and solar cycle dependence using the experimental techniques. While there are features which are consistent between the 3 techniques, such as the evidence of the equinoctial asymmetry, there are also significant differences between the techniques both in terms of trends and absolute values. It is clear from this and previous studies that the high-latitude representation of the thermospheric neutral winds from the empirical Horizontal Wind Model (HWM, though improved from earlier versions, lacks accuracy in many conditions. The relative merits of each technique are discussed and while none of the techniques provides the perfect data set to address model performance at high-latitude, one or more needs to be included in future HWM reformulations.
Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (thermospheric dynamics, Ionosphere (ionosphere-atmosphere interactions, auroral ionosphere
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
E. M. Griffin
2004-03-01
Full Text Available Thermospheric neutral winds at Kiruna, Sweden (67.4°N, 20.4°E are compared using both direct optical Fabry-Perot Interferometer (FPI measurements and those derived from European incoherent scatter radar (EISCAT measurements. This combination of experimental data sets, both covering well over a solar cycle of data, allows for a unique comparison of the thermospheric meridional component of the neutral wind as observed by different experimental techniques. Uniquely in this study the EISCAT measurements are used to provide winds for comparison using two separate techniques: the most popular method based on the work of Salah and Holt (1974 and the Meridional Wind Model (MWM (Miller et al., 1997 application of servo theory. The balance of forces at this location that produces the observed diurnal pattern are investigated using output from the Coupled Thermosphere and Ionosphere (CTIM numerical model. Along with detailed comparisons from short periods the climatological behaviour of the winds have been investigated for seasonal and solar cycle dependence using the experimental techniques. While there are features which are consistent between the 3 techniques, such as the evidence of the equinoctial asymmetry, there are also significant differences between the techniques both in terms of trends and absolute values. It is clear from this and previous studies that the high-latitude representation of the thermospheric neutral winds from the empirical Horizontal Wind Model (HWM, though improved from earlier versions, lacks accuracy in many conditions. The relative merits of each technique are discussed and while none of the techniques provides the perfect data set to address model performance at high-latitude, one or more needs to be included in future HWM reformulations. Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (thermospheric dynamics, Ionosphere (ionosphere-atmosphere interactions, auroral ionosphere
-
Radar and electronic navigation
Sonnenberg, G J
2013-01-01
Radar and Electronic Navigation, Sixth Edition discusses radar in marine navigation, underwater navigational aids, direction finding, the Decca navigator system, and the Omega system. The book also describes the Loran system for position fixing, the navy navigation satellite system, and the global positioning system (GPS). It reviews the principles, operation, presentations, specifications, and uses of radar. It also describes GPS, a real time position-fixing system in three dimensions (longitude, latitude, altitude), plus velocity information with Universal Time Coordinated (UTC). It is accur
-
Solar Cycle variations in Earth's open flux content measured by the SuperDARN radar network
Imber, S. M.; Milan, S. E.; Lester, M.
2013-09-01
We present a long term study, from 1996 - 2012, of the latitude of the Heppner-Maynard Boundary (HMB) determined using the northern hemisphere SuperDARN radars. The HMB represents the equatorward extent of ionospheric convection and is here used as a proxy for the amount of open flux in the polar cap. The mean HMB latitude (measured at midnight) is found to be at 64 degrees during the entire period, with secondary peaks at lower latitudes during the solar maximum of 2003, and at higher latitudes during the recent extreme solar minimum of 2008-2011. We associate these large scale statistical variations in open flux content with solar cycle variations in the solar wind parameters leading to changes in the intensity of the coupling between the solar wind and the magnetosphere.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Watermann, J.; Delabeaujardiere, O.; Lummerzheim, D.; Woch, J.; Newell, P.T.; Potemra, T.A.; Rich, F.J.; Shapshak, M.
1992-01-01
A case study involving data from three satellites and a ground-based radar are presented. Focus is on a detailed discussion of observations of the dynamic cusp made on 24 Sep. 1986 in the dayside high-latitude ionosphere and interior magnetosphere. The relevant data from space-borne and ground-based sensors is presented. They include in-situ particle and field measurements from the DMSP-F7 and Viking spacecraft and Sondrestrom radar observations of the ionosphere. These data are augmented by observations of the IMF and the solar wind plasma. The observations are compared with predictions about the ionospheric response to the observed particle precipitation, obtained from an auroral model. It is shown that observations and model calculations fit well and provide a picture of the ionospheric footprint of the cusp in an invariant latitude versus local time frame. The combination of Viking, Sondrestrom radar, and IMP-8 data suggests that an ionospheric signature of the dynamic cusp was observed. Its spatial variation over time which appeared closely related to the southward component of the IMF was monitored
-
X-band COSMO-SkyMed wind field retrieval, with application to coastal circulation modeling
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Montuori
2013-02-01
Full Text Available In this paper, X-band COSMO-SkyMed© synthetic aperture radar (SAR wind field retrieval is investigated, and the obtained data are used to force a coastal ocean circulation model. The SAR data set consists of 60 X-band Level 1B Multi-Look Ground Detected ScanSAR Huge Region COSMO-SkyMed© SAR data, gathered in the southern Tyrrhenian Sea during the summer and winter seasons of 2010. The SAR-based wind vector field estimation is accomplished by resolving both the SAR-based wind speed and wind direction retrieval problems independently. The sea surface wind speed is retrieved by means of a SAR wind speed algorithm based on the azimuth cut-off procedure, while the sea surface wind direction is provided by means of a SAR wind direction algorithm based on the discrete wavelet transform multi-resolution analysis. The obtained wind fields are compared with ground truth data provided by both ASCAT scatterometer and ECMWF model wind fields. SAR-derived wind vector fields and ECMWF model wind data are used to construct a blended wind product regularly sampled in both space and time, which is then used to force a coastal circulation model of a southern Tyrrhenian coastal area to simulate wind-driven circulation processes. The modeling results show that X-band COSMO-SkyMed© SAR data can be valuable in providing effective wind fields for coastal circulation modeling.
-
Pocket radar guide key facts, equations, and data
Curry, G Richard
2010-01-01
ThePocket Radar Guideis a concise collection of key radar facts and important radar data that provides you with necessary radar information when you are away from your office or references. It includes statements and comments on radar design, operation, and performance; equations describing the characteristics and performance of radar systems and their components; and tables with data on radar characteristics and key performance issues.It is intended to supplement other radar information sources by providing a pocket companion to refresh memory and provide details whenever you need them such a
-
Synthetic aperture radar capabilities in development
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Miller, M. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab., CA (United States)
1994-11-15
The Imaging and Detection Program (IDP) within the Laser Program is currently developing an X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) to support the Joint US/UK Radar Ocean Imaging Program. The radar system will be mounted in the program`s Airborne Experimental Test-Bed (AETB), where the initial mission is to image ocean surfaces and better understand the physics of low grazing angle backscatter. The Synthetic Aperture Radar presentation will discuss its overall functionality and a brief discussion on the AETB`s capabilities. Vital subsystems including radar, computer, navigation, antenna stabilization, and SAR focusing algorithms will be examined in more detail.
-
Extended Target Recognition in Cognitive Radar Networks
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Xiqin Wang
2010-11-01
Full Text Available We address the problem of adaptive waveform design for extended target recognition in cognitive radar networks. A closed-loop active target recognition radar system is extended to the case of a centralized cognitive radar network, in which a generalized likelihood ratio (GLR based sequential hypothesis testing (SHT framework is employed. Using Doppler velocities measured by multiple radars, the target aspect angle for each radar is calculated. The joint probability of each target hypothesis is then updated using observations from different radar line of sights (LOS. Based on these probabilities, a minimum correlation algorithm is proposed to adaptively design the transmit waveform for each radar in an amplitude fluctuation situation. Simulation results demonstrate performance improvements due to the cognitive radar network and adaptive waveform design. Our minimum correlation algorithm outperforms the eigen-waveform solution and other non-cognitive waveform design approaches.
-
Ionospheric cusp flows pulsed by solar wind Alfvén waves
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Prikryl
2002-02-01
Full Text Available Pulsed ionospheric flows (PIFs in the cusp foot-print have been observed by the SuperDARN radars with periods between a few minutes and several tens of minutes. PIFs are believed to be a consequence of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF reconnection with the magnetospheric magnetic field on the dayside magnetopause, ionospheric signatures of flux transfer events (FTEs. The quasiperiodic PIFs are correlated with Alfvénic fluctuations observed in the upstream solar wind. It is concluded that on these occasions, the FTEs were driven by Alfvén waves coupling to the day-side magnetosphere. Case studies are presented in which the dawn-dusk component of the Alfvén wave electric field modulates the reconnection rate as evidenced by the radar observations of the ionospheric cusp flows. The arrival of the IMF southward turning at the magnetopause is determined from multipoint solar wind magnetic field and/or plasma measurements, assuming plane phase fronts in solar wind. The cross-correlation lag between the solar wind data and ground magnetograms that were obtained near the cusp footprint exceeded the estimated spacecraft-to-magnetopause propagation time by up to several minutes. The difference can account for and/or exceeds the Alfvén propagation time between the magnetopause and ionosphere. For the case of short period ( < 13 min PIFs, the onset times of the flow transients appear to be further delayed by at most a few more minutes after the IMF southward turning arrived at the magnetopause. For the case of long period (30 – 40 min PIFs, the observed additional delays were 10–20 min. We interpret the excess delay in terms of an intrinsic time scale for reconnection (Russell et al., 1997 which can be explained by the surface-wave induced magnetic reconnection mechanism (Uberoi et al., 1999. Here, surface waves with wavelengths larger than the thickness of the neutral layer induce a tearing-mode instability whose rise time explains the
-
Detection of Weather Radar Clutter
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Bøvith, Thomas
2008-01-01
classification and use a range of different techniques and input data. The first method uses external information from multispectral satellite images to detect clutter. The information in the visual, near-infrared, and infrared parts of the spectrum can be used to distinguish between cloud and cloud-free areas......Weather radars provide valuable information on precipitation in the atmosphere but due to the way radars work, not only precipitation is observed by the weather radar. Weather radar clutter, echoes from non-precipitating targets, occur frequently in the data, resulting in lowered data quality....... Especially in the application of weather radar data in quantitative precipitation estimation and forecasting a high data quality is important. Clutter detection is one of the key components in achieving this goal. This thesis presents three methods for detection of clutter. The methods use supervised...
-
Talich, Milan
2017-12-01
The paper describes possibilities of the relatively new technics - ground based radar interferometry for precise determining of deformation of structures. Special focus on the vertical deflection of bridge structures and on the horizontal movements of high-rise buildings and structural objects is presented. The technology of ground based radar interferometry can be used in practice to the contactless determination of deformations of structures with accuracy up to 0.01 mm in real time. It is also possible in real time to capture oscillations of the object with a frequency up to 50 Hz. Deformations can be determined simultaneously in multiple places of the object, for example a bridge structure at points distributed on the bridge deck at intervals of one or more meters. This allows to obtain both overall and detailed information about the properties of the structure during the dynamic load and monitoring the impact of movements either individual vehicles or groups. In the case of high-rise buildings, it is possible to monitor the horizontal vibration of the whole object at its different height levels. It is possible to detect and determine the compound oscillations that occur in some types of buildings. Then prevent any damage or even disasters in these objects. In addition to the necessary theory basic principles of using radar interferometry for determining of deformation of structures are given. Practical examples of determining deformation of bridge structures, water towers reservoirs, factory chimneys and wind power plants are also given. The IBIS-S interferometric radar of the Italian IDS manufacturer was used for the measurements.
-
Penn State Radar Systems: Implementation and Observations
Urbina, J. V.; Seal, R.; Sorbello, R.; Kuyeng, K.; Dyrud, L. P.
2014-12-01
Software Defined Radio/Radar (SDR) platforms have become increasingly popular as researchers, hobbyists, and military seek more efficient and cost-effective means for radar construction and operation. SDR platforms, by definition, utilize a software-based interface for configuration in contrast to traditional, hard-wired platforms. In an effort to provide new and improved radar sensing capabilities, Penn State has been developing advanced instruments and technologies for future radars, with primary objectives of making such instruments more capable, portable, and more cost effective. This paper will describe the design and implementation of two low-cost radar systems and their deployment in ionospheric research at both low and mid-latitudes. One radar has been installed near Penn State campus, University Park, Pennsylvania (77.97°W, 40.70°N), to make continuous meteor observations and mid-latitude plasma irregularities. The second radar is being installed in Huancayo (12.05°S, -75.33°E), Peru, which is capable of detecting E and F region plasma irregularities as well as meteor reflections. In this paper, we examine and compare the diurnal and seasonal variability of specular, non- specular, and head-echoes collected with these two new radar systems and discuss sampling biases of each meteor observation technique. We report our current efforts to validate and calibrate these radar systems with other VHF radars such as Jicamarca and SOUSY. We also present the general characteristics of continuous measurements of E-region and F-region coherent echoes using these modern radar systems and compare them with coherent radar events observed at other geographic mid-latitude radar stations.
-
Thiebaud, P.; Cross, D. C.
1980-07-01
A new solid-state radar switchboard equipped with 16 input ports which will output data to 16 displays is presented. Each of the ports will handle a single two-dimensional radar input, or three ports will accommodate a three-dimensional radar input. A video switch card of the switchboard is used to switch all signals, with the exception of the IFF-mode-control lines. Each card accepts inputs from up to 16 sources and can pass a signal with bandwidth greater than 20 MHz to the display assigned to that card. The synchro amplifier of current systems has been eliminated and in the new design each PPI receives radar data via a single coaxial cable. This significant reduction in cabling is achieved by adding a serial-to-parallel interface and a digital-to-synchro converter located at the PPI.
-
Bierstedt, Svenja E.; Hünicke, Birgit; Zorita, Eduardo; Ludwig, Juliane
2017-07-01
We statistically analyse the relationship between the structure of migrating dunes in the southern Baltic and the driving wind conditions over the past 26 years, with the long-term aim of using migrating dunes as a proxy for past wind conditions at an interannual resolution. The present analysis is based on the dune record derived from geo-radar measurements by Ludwig et al. (2017). The dune system is located at the Baltic Sea coast of Poland and is migrating from west to east along the coast. The dunes present layers with different thicknesses that can be assigned to absolute dates at interannual timescales and put in relation to seasonal wind conditions. To statistically analyse this record and calibrate it as a wind proxy, we used a gridded regional meteorological reanalysis data set (coastDat2) covering recent decades. The identified link between the dune annual layers and wind conditions was additionally supported by the co-variability between dune layers and observed sea level variations in the southern Baltic Sea. We include precipitation and temperature into our analysis, in addition to wind, to learn more about the dependency between these three atmospheric factors and their common influence on the dune system. We set up a statistical linear model based on the correlation between the frequency of days with specific wind conditions in a given season and dune migration velocities derived for that season. To some extent, the dune records can be seen as analogous to tree-ring width records, and hence we use a proxy validation method usually applied in dendrochronology, cross-validation with the leave-one-out method, when the observational record is short. The revealed correlations between the wind record from the reanalysis and the wind record derived from the dune structure is in the range between 0.28 and 0.63, yielding similar statistical validation skill as dendroclimatological records.
-
Observations of peculiar sporadic sodium structures and their relation with wind variations
Sridharan, S.; Prasanth, P. Vishnu; Kumar, Y. Bhavani; Ramkumar, Geetha; Sathishkumar, S.; Raghunath, K.
2009-04-01
Resonance lidar observations of sodium density in the upper mesosphere region over Gadanki (13.5°N, 79.2°E) rarely show complex structures with rapid enhancements of sodium density, completely different from normal sporadic sodium structures. The hourly averaged meteor radar zonal winds over Trivandrum (8.5°N, 76.5°E) show an eastward shear with altitude during the nights, when these events are formed. As suggested by Kane et al. [2001. Joint observations of sodium enhancements and field-aligned ionospheric irregularities. Geophysical Research Letters 28, 1375-1378], our observations show that the complex structures may be formed due to Kelvin-Helmholtz instability, which can occur in the region of strong wind shear.
-
ST radar observations of atmospheric waves over mountainous areas: a review
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Röttger
2000-07-01
Full Text Available Lee and mountain waves are dominant dynamic processes in the atmosphere above mountain areas. ST VHF radars had been intensively used to investigate these wave processes. These studies are summarized in this work. After discussing features of long-period quasi-stationary lee waves, attention is drawn to the frequent occurrence of freely propagating waves of shorter periods, which seem to be more common and characteristic for wave processes generated over mountainous areas. Characteristics of these waves such as their relation to the topography and background winds, the possibility of trapping by and breaking in the tropopause region and their propagation into the stratosphere is investigated. These orographically produced waves transport energy and momentum into the troposphere and stratosphere, which is considered an important contribution to the kinetic energy of the lower atmosphere. The occurrence of inertia-gravity waves in the stratosphere had been confused with lee waves, which is discussed in conclusion. Finally further questions on mountain and lee waves are drawn up, which remain to be solved and where investigations with ST radars could play a fundamental role.Key words: Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (Middle atmosphere dynamics; Waves and tides; Instruments and techniques
-
Introduction to surveillance studies
Petersen, JK
2012-01-01
Introduction & OverviewIntroduction Brief History of Surveillance Technologies & TechniquesOptical SurveillanceAerial Surveillance Audio Surveillance Radio-Wave SurveillanceGlobal Positioning Systems Sensors Computers & the Internet Data Cards Biochemical Surveillance Animal Surveillance Biometrics Genetics Practical ConsiderationsPrevalence of Surveillance Effectiveness of Surveillance Freedom & Privacy IssuesConstitutional Freedoms Privacy Safeguards & Intrusions ResourcesReferences Glossary Index
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hansen, L.G.; Lading, Lars
2002-01-01
-bladed 2MW turbine placed offshore either without sensors or with sensors are compared. The price of a structural health monitoring system of a price of 100 000 DKK (per tur-bine) results in a break-eventime of about 3 years. For a price of 300 000 DKK the break-even time is about 8 years. However......This report contains the results of a cost-benefit analysis for the use of embed-ded sensors for damage detection in large wind turbine blades - structural health monitoring - (in connection with remote surveillance) of large wind turbine placedoff-shore. The total operating costs of a three......, the cost/benefit analysis has large uncertainties....
-
The use of radar for bathymetry assessment
Aardoom, J.H.; Greidanus, H.S.F.
1998-01-01
The bottom topography in shallow seas can be observed by air- and spaceborne imaging radar. Bathymetric information derived from radar data is limited in accuracy, but radar has a good spatial coverage. The accuracy can be increased by assimilating the radar imagery into existing or insitu gathered
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Bonelli
2008-10-01
Full Text Available Thunderstorms and their ground effects, such as flash floods, hail, lightning, strong winds, and tornadoes, are responsible for most weather damages in northern Italy, especially in the warm season from May to September. A nowcasting and warning system focused on severe thunderstorm events would be useful to reduce risks for people involved in outside activities and for electric, telecommunication, and sensitive industrial business. C-band radar and Lighting Location Systems provide useful, fast and high resolution data for the detection of convective systems and for following their dynamics. The whole of northern Italy is covered by radar with a resolution of 1 km and by a lightning network with a mean accuracy of 0.5 km on the single point of impact. The authors present an algorithm developed for tracking high intensity storm cells by means of radar and lightning data. Application to northern Italy reveals that tracking thunderstorm cells can be used as an alert system that may help prevent damages from extreme weather, as well as allowing for studying the correlation among lightning, rainfall and tornado occurrence. Assessing the algorithm skill is also discussed, and a forecast verification method is described and applied for the duration of a thunderstorm season.
-
Radar Observations of Convective Systems from a High-Altitude Aircraft
Heymsfield, G.; Geerts, B.; Tian, L.
1999-01-01
. Both TEFLUN-A and B were amply supported by surface data, in particular a dense raingauge network, a polarization radar, wind profilers, a mobile radiosonde system, a cloud physics aircraft penetrating the overflown storms, and a network of 10 cm Doppler radars(WSR-88D). This presentation will show some preliminary comparisons between TRMM, EDOP, and WSR-88D reflectivity fields in the case of an MCS, a hurricane, and less organized convection in central Florida. A validation of TRMM reflectivity is important, because TRMM's primary objective is to estimate the rainfall climatology with 35 degrees of the equator. Rainfall is estimated from the radar reflectivity, as well from TRMM's Microwave Imager, which measures at 10.7, 19.4, 21.3, 37, and 85.5 GHz over a broader swath (78 km). While the experiments lasted about three months the cumulative period of near simultaneous observations of storms by ground-based, airborne and space borne radars is only about an hour long. Therefore the comparison is case-study-based, not climatological. We will highlight fundamental differences in the typical reflectivity profiles in stratiform regions of MCS's, Florida convection and hurricanes and will explain why Z-R relationships based on ground-based radar data for convective systems over land should be different from those for hurricanes. These catastrophically intense rainfall from hurricane Georges in Hispaniola and from Mitch in Honduras highlights the importance of accurate Z-R relationships, It will be shown that a Z-R relationship that uses the entire reflectivity profile (rather than just a 1 level) works much better in a variety of cases, making an adjustment of the constants for different precipitation system categories redundant.
-
Willis, Nick
2004-01-01
Annotation his book is a major extension of a chapter on bistatic radar written by the author for the Radar Handbook, 2nd edition, edited by Merrill Skolnik. It provides a history of bistatic systems that points out to potential designers the applications that have worked and the dead-ends not worth pursuing. The text reviews the basic concepts and definitions, and explains the mathematical development of relationships, such as geometry, Ovals of Cassini, dynamic range, isorange and isodoppler contours, target doppler, and clutter doppler spread.Key Features * All development and analysis are