
Sample records for surface currents predicted
-
Predictability of surface currents and fronts off the Mississippi Delta
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Walker, N.D.; Rouse, L.J.; Wiseman, W.J.
2001-01-01
The dynamic coastal region of the lower Mississippi River was examined under varying conditions of wind, river discharge and circulation patterns of the Gulf of Mexico. Nearly 7,000 deep-sea merchant vessels enter the port complex each year and the area boasts the highest concentration of offshore drilling rigs, rendering the Mississippi delta and adjacent coastal areas vulnerable to risk from oil spills. Satellite imagery has been useful in tracking movements of the Mississippi river plume as recognizable turbidity and temperature fronts are formed where river waters encounter ambient shelf waters. Oil spill modelers often base their predictions of oil movement on the surface wind field and surface currents, but past studies have indicated that this can be overly simplistic in regions affected by river flow because river fronts have significant control over the movement of oil in opposition to prevailing winds. Frontal zones, such as those found where river waters meet oceanic waters, are characterized by strong convergence of surface flow. These frontal zones can provide large and efficient traps or natural booms for spilled oil. In an effort to facilitate cleanup operations, this study made use of the National Ocean and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) AVHRR satellite imagery of temperature and reflectance to study front locations and their variability in space and time. The main objectives were to quantify surface temperature structure and locations of fronts throughout the year using satellite image data, to map the structure of the Mississippi sediment plume and to assess the forcing factors responsible for its variability over space and time. The final objective was to use in-situ measurements of surface currents together with satellite image data to better understand surface flow in this region of strong and variable currents. It was concluded that the main factors controlling circulation in the Mississippi River outflow region are river discharge and
-
Evaluation of OSCAR ocean surface current product in the tropical ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
Next, the evaluation has been carried out by comparing the OSCAR currents with currents measured by moored buoys ... measurements, to derive the surface current prod- uct, known ... ogy of surface currents based on drifter data. The ... and prediction (RAMA). ..... of satellite derived forcings on numerical ocean model sim-.
-
Messié, Monique; Chavez, Francisco P.
2017-09-01
A simple combination of wind-driven nutrient upwelling, surface currents, and plankton growth/grazing equations generates zooplankton patchiness and hotspots in coastal upwelling regions. Starting with an initial input of nitrate from coastal upwelling, growth and grazing equations evolve phytoplankton and zooplankton over time and space following surface currents. The model simulates the transition from coastal (large phytoplankton, e.g., diatoms) to offshore (picophytoplankton and microzooplankton) communities, and in between generates a large zooplankton maximum. The method was applied to four major upwelling systems (California, Peru, Northwest Africa, and Benguela) using latitudinal estimates of wind-driven nitrate supply and satellite-based surface currents. The resulting zooplankton simulations are patchy in nature; areas of high concentrations coincide with previously documented copepod and krill hotspots. The exercise highlights the importance of the upwelling process and surface currents in shaping plankton communities.
-
Belair, S.; Bernier, N.; Tong, L.; Mailhot, J.
2008-05-01
The 2010 Winter Olympic and Paralympic Games will take place in Vancouver, Canada, from 12 to 28 February 2010 and from 12 to 21 March 2010, respectively. In order to provide the best possible guidance achievable with current state-of-the-art science and technology, Environment Canada is currently setting up an experimental numerical prediction system for these special events. This system consists of a 1-km limited-area atmospheric model that will be integrated for 16h, twice a day, with improved microphysics compared with the system currently operational at the Canadian Meteorological Centre. In addition, several new and original tools will be used to adapt and refine predictions near and at the surface. Very high-resolution two-dimensional surface systems, with 100-m and 20-m grid size, will cover the Vancouver Olympic area. Using adaptation methods to improve the forcing from the lower-resolution atmospheric models, these 2D surface models better represent surface processes, and thus lead to better predictions of snow conditions and near-surface air temperature. Based on a similar strategy, a single-point model will be implemented to better predict surface characteristics at each station of an observing network especially installed for the 2010 events. The main advantage of this single-point system is that surface observations are used as forcing for the land surface models, and can even be assimilated (although this is not expected in the first version of this new tool) to improve initial conditions of surface variables such as snow depth and surface temperatures. Another adaptation tool, based on 2D stationnary solutions of a simple dynamical system, will be used to produce near-surface winds on the 100-m grid, coherent with the high- resolution orography. The configuration of the experimental numerical prediction system will be presented at the conference, together with preliminary results for winter 2007-2008.
-
Predictive Surface Complexation Modeling
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Sverjensky, Dimitri A. [Johns Hopkins Univ., Baltimore, MD (United States). Dept. of Earth and Planetary Sciences
2016-11-29
Surface complexation plays an important role in the equilibria and kinetics of processes controlling the compositions of soilwaters and groundwaters, the fate of contaminants in groundwaters, and the subsurface storage of CO2 and nuclear waste. Over the last several decades, many dozens of individual experimental studies have addressed aspects of surface complexation that have contributed to an increased understanding of its role in natural systems. However, there has been no previous attempt to develop a model of surface complexation that can be used to link all the experimental studies in order to place them on a predictive basis. Overall, my research has successfully integrated the results of the work of many experimentalists published over several decades. For the first time in studies of the geochemistry of the mineral-water interface, a practical predictive capability for modeling has become available. The predictive correlations developed in my research now enable extrapolations of experimental studies to provide estimates of surface chemistry for systems not yet studied experimentally and for natural and anthropogenically perturbed systems.
-
Gough, M.; Reniers, A.; MacMahan, J. H.; Howden, S. D.
2014-12-01
The continental shelf along the northeastern Gulf of Mexico is transected by the critical latitude (30°N) for inertial motions. At this latitude the inertial period is 24 hours and diurnal surface current oscillations can amplify due to resonance with diurnal wind and tidal forcing. Tidal amplitudes are relatively small in this region although K1 tidal currents can be strong over the shelf west of the DeSoto Canyon where the K1 tide propagates onshore as a Sverdrup wave. Other sources of diurnal motions include internal tidal currents, Poincaré waves, and basin resonance. It is therefore very difficult to separate inertial wind-driven motions from other diurnal motions. Spatiotemporal surface currents were measured using hourly 6 km resolution HF radar data collected in June 2010 during the Deepwater Horizon oil spill and July 2012 during the Grand Lagrangian Deployment (GLAD). Surface currents were also measured using GLAD GPS-tracked drifters. NDBC buoy wind data were used to determine wind-forcing, and OSU Tidal Inversion Software (OTIS) were used to predict tidal currents. The relative spatiotemporal influence of diurnal wind and tidal forcing on diurnal surface current oscillations is determined through a series of comparative analyses: phase and amplitude of bandpassed timeseries, wavelet analyses, wind-driven inertial oscillation calculations, and tidal current predictions. The wind-driven inertial ocean response is calculated by applying a simple "slab" model where wind-forcing is allowed to excite a layer of low-density water riding over high density water. The spatial variance of diurnal motions are found to be correlated with satellite turbidity imagery indicating that stratification influences the sea surface inertial response to wind-forcing. Surface dispersion is found to be minimized in regions of high diurnal variance suggesting that mean surface transport is restricted in regions of inertial motions associated with stratification.
-
Current in heavy-current planar diode with discrete emission surface
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Belomyttsev, S.Ya.; Korovin, S.D.; Pegel', I.V
1999-01-01
Dependence of current in a high-current planar diode on the size of emission centres was studied. Essential effect of emission surface microstructure on the current value in the planar diode was demonstrated. It was determined that if the distance between the emitter essentially exceeded their size then current dependence on the ratio of size to the value of the diode gap was an exponential function with 3/2 index. Current dependence on voltage obeyed the exponential law with 3/2 index up to higher voltage values in the planar diode with discrete emission surface in contrast to the case of a planar diode with homogeneous emission surface [ru
-
Towards an Airframe Noise Prediction Methodology: Survey of Current Approaches
Farassat, Fereidoun; Casper, Jay H.
2006-01-01
In this paper, we present a critical survey of the current airframe noise (AFN) prediction methodologies. Four methodologies are recognized. These are the fully analytic method, CFD combined with the acoustic analogy, the semi-empirical method and fully numerical method. It is argued that for the immediate need of the aircraft industry, the semi-empirical method based on recent high quality acoustic database is the best available method. The method based on CFD and the Ffowcs William- Hawkings (FW-H) equation with penetrable data surface (FW-Hpds ) has advanced considerably and much experience has been gained in its use. However, more research is needed in the near future particularly in the area of turbulence simulation. The fully numerical method will take longer to reach maturity. Based on the current trends, it is predicted that this method will eventually develop into the method of choice. Both the turbulence simulation and propagation methods need to develop more for this method to become useful. Nonetheless, the authors propose that the method based on a combination of numerical and analytical techniques, e.g., CFD combined with FW-H equation, should also be worked on. In this effort, the current symbolic algebra software will allow more analytical approaches to be incorporated into AFN prediction methods.
-
A robust empirical seasonal prediction of winter NAO and surface climate.
Wang, L; Ting, M; Kushner, P J
2017-03-21
A key determinant of winter weather and climate in Europe and North America is the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), the dominant mode of atmospheric variability in the Atlantic domain. Skilful seasonal forecasting of the surface climate in both Europe and North America is reflected largely in how accurately models can predict the NAO. Most dynamical models, however, have limited skill in seasonal forecasts of the winter NAO. A new empirical model is proposed for the seasonal forecast of the winter NAO that exhibits higher skill than current dynamical models. The empirical model provides robust and skilful prediction of the December-January-February (DJF) mean NAO index using a multiple linear regression (MLR) technique with autumn conditions of sea-ice concentration, stratospheric circulation, and sea-surface temperature. The predictability is, for the most part, derived from the relatively long persistence of sea ice in the autumn. The lower stratospheric circulation and sea-surface temperature appear to play more indirect roles through a series of feedbacks among systems driving NAO evolution. This MLR model also provides skilful seasonal outlooks of winter surface temperature and precipitation over many regions of Eurasia and eastern North America.
-
Measurement of neoclassically predicted edge current density at ASDEX Upgrade
Dunne, M. G.; McCarthy, P. J.; Wolfrum, E.; Fischer, R.; Giannone, L.; Burckhart, A.; the ASDEX Upgrade Team
2012-12-01
Experimental confirmation of neoclassically predicted edge current density in an ELMy H-mode plasma is presented. Current density analysis using the CLISTE equilibrium code is outlined and the rationale for accuracy of the reconstructions is explained. Sample profiles and time traces from analysis of data at ASDEX Upgrade are presented. A high time resolution is possible due to the use of an ELM-synchronization technique. Additionally, the flux-surface-averaged current density is calculated using a neoclassical approach. Results from these two separate methods are then compared and are found to validate the theoretical formula. Finally, several discharges are compared as part of a fuelling study, showing that the size and width of the edge current density peak at the low-field side can be explained by the electron density and temperature drives and their respective collisionality modifications.
-
Measurement of neoclassically predicted edge current density at ASDEX Upgrade
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dunne, M.G.; McCarthy, P.J.; Wolfrum, E.; Fischer, R.; Giannone, L.; Burckhart, A.
2012-01-01
Experimental confirmation of neoclassically predicted edge current density in an ELMy H-mode plasma is presented. Current density analysis using the CLISTE equilibrium code is outlined and the rationale for accuracy of the reconstructions is explained. Sample profiles and time traces from analysis of data at ASDEX Upgrade are presented. A high time resolution is possible due to the use of an ELM-synchronization technique. Additionally, the flux-surface-averaged current density is calculated using a neoclassical approach. Results from these two separate methods are then compared and are found to validate the theoretical formula. Finally, several discharges are compared as part of a fuelling study, showing that the size and width of the edge current density peak at the low-field side can be explained by the electron density and temperature drives and their respective collisionality modifications. (paper)
-
Xie, L.; Pietrafesa, L. J.; Wu, K.
2003-02-01
A three-dimensional wave-current coupled modeling system is used to examine the influence of waves on coastal currents and sea level. This coupled modeling system consists of the wave model-WAM (Cycle 4) and the Princeton Ocean Model (POM). The results from this study show that it is important to incorporate surface wave effects into coastal storm surge and circulation models. Specifically, we find that (1) storm surge models without coupled surface waves generally under estimate not only the peak surge but also the coastal water level drop which can also cause substantial impact on the coastal environment, (2) introducing wave-induced surface stress effect into storm surge models can significantly improve storm surge prediction, (3) incorporating wave-induced bottom stress into the coupled wave-current model further improves storm surge prediction, and (4) calibration of the wave module according to minimum error in significant wave height does not necessarily result in an optimum wave module in a wave-current coupled system for current and storm surge prediction.
-
The role of surface currents in plasma confinement
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Webster, Anthony J.
2011-01-01
During plasma instabilities, ''surface currents'' can flow at the interface between the plasma and the surrounding vacuum, and in most cases, they are a harmless symptom of the instability that is causing them. Large instabilities can lead to ''disruptions,'' an abrupt termination of the plasma with the potential to damage the machine in which it is contained. For disruptions, the correct calculation of surface currents is thought to be essential for modelling disruptions properly. Recently, however, there has been debate and disagreement about the correct way to calculate surface currents. The purpose of this paper is to clarify as simply as possible the role of surface currents for plasma confinement and to show that a commonly used representation for surface currents σ-vector with σ-vector=∇I and n-vector, I a scalar function, and n-vector the unit normal to the plasma surface, is only appropriate for the calculation of surface currents that are in magnetohydrodynamic equilibrium. Fortunately, this is the situation thought to be of most relevance for disruption calculations.
-
Land-surface initialisation improves seasonal climate prediction skill for maize yield forecast.
Ceglar, Andrej; Toreti, Andrea; Prodhomme, Chloe; Zampieri, Matteo; Turco, Marco; Doblas-Reyes, Francisco J
2018-01-22
Seasonal crop yield forecasting represents an important source of information to maintain market stability, minimise socio-economic impacts of crop losses and guarantee humanitarian food assistance, while it fosters the use of climate information favouring adaptation strategies. As climate variability and extremes have significant influence on agricultural production, the early prediction of severe weather events and unfavourable conditions can contribute to the mitigation of adverse effects. Seasonal climate forecasts provide additional value for agricultural applications in several regions of the world. However, they currently play a very limited role in supporting agricultural decisions in Europe, mainly due to the poor skill of relevant surface variables. Here we show how a combined stress index (CSI), considering both drought and heat stress in summer, can predict maize yield in Europe and how land-surface initialised seasonal climate forecasts can be used to predict it. The CSI explains on average nearly 53% of the inter-annual maize yield variability under observed climate conditions and shows how concurrent heat stress and drought events have influenced recent yield anomalies. Seasonal climate forecast initialised with realistic land-surface achieves better (and marginally useful) skill in predicting the CSI than with climatological land-surface initialisation in south-eastern Europe, part of central Europe, France and Italy.
-
Surface current density K: an introduction
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
McAllister, Iain Wilson
1991-01-01
The author discusses the vector surface of current density K used in electrical insulation studies. K is related to the vector tangential electric field Kt at the surface of a body by the vector equation K=ΓE t where Γ represents the surface conductivity. The author derives a surface continuity...
-
Rekik, Islem; Li, Gang; Lin, Weili; Shen, Dinggang
2016-02-01
Longitudinal neuroimaging analysis methods have remarkably advanced our understanding of early postnatal brain development. However, learning predictive models to trace forth the evolution trajectories of both normal and abnormal cortical shapes remains broadly absent. To fill this critical gap, we pioneered the first prediction model for longitudinal developing cortical surfaces in infants using a spatiotemporal current-based learning framework solely from the baseline cortical surface. In this paper, we detail this prediction model and even further improve its performance by introducing two key variants. First, we use the varifold metric to overcome the limitations of the current metric for surface registration that was used in our preliminary study. We also extend the conventional varifold-based surface registration model for pairwise registration to a spatiotemporal surface regression model. Second, we propose a morphing process of the baseline surface using its topographic attributes such as normal direction and principal curvature sign. Specifically, our method learns from longitudinal data both the geometric (vertices positions) and dynamic (temporal evolution trajectories) features of the infant cortical surface, comprising a training stage and a prediction stage. In the training stage, we use the proposed varifold-based shape regression model to estimate geodesic cortical shape evolution trajectories for each training subject. We then build an empirical mean spatiotemporal surface atlas. In the prediction stage, given an infant, we select the best learnt features from training subjects to simultaneously predict the cortical surface shapes at all later timepoints, based on similarity metrics between this baseline surface and the learnt baseline population average surface atlas. We used a leave-one-out cross validation method to predict the inner cortical surface shape at 3, 6, 9 and 12 months of age from the baseline cortical surface shape at birth. Our
-
Satellite Remote Sensing of Ocean Winds, Surface Waves and Surface Currents during the Hurricanes
Zhang, G.; Perrie, W. A.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.
2017-12-01
Hurricanes over the ocean have been observed by spaceborne aperture radar (SAR) since the first SAR images were available in 1978. SAR has high spatial resolution (about 1 km), relatively large coverage and capability for observations during almost all-weather, day-and-night conditions. In this study, seven C-band RADARSAT-2 dual-polarized (VV and VH) ScanSAR wide images from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) Hurricane Watch Program in 2017 are collected over five hurricanes: Harvey, Irma, Maria, Nate, and Ophelia. We retrieve the ocean winds by applying our C-band Cross-Polarization Coupled-Parameters Ocean (C-3PO) wind retrieval model [Zhang et al., 2017, IEEE TGRS] to the SAR images. Ocean waves are estimated by applying a relationship based on the fetch- and duration-limited nature of wave growth inside hurricanes [Hwang et al., 2016; 2017, J. Phys. Ocean.]. We estimate the ocean surface currents using the Doppler Shift extracted from VV-polarized SAR images [Kang et al., 2016, IEEE TGRS]. C-3PO model is based on theoretical analysis of ocean surface waves and SAR microwave backscatter. Based on the retrieved ocean winds, we estimate the hurricane center locations, maxima wind speeds, and radii of the five hurricanes by adopting the SHEW model (Symmetric Hurricane Estimates for Wind) by Zhang et al. [2017, IEEE TGRS]. Thus, we investigate possible relations between hurricane structures and intensities, and especially some possible effects of the asymmetrical characteristics on changes in the hurricane intensities, such as the eyewall replacement cycle. The three SAR images of Ophelia include the north coast of Ireland and east coast of Scotland allowing study of ocean surface currents respond to the hurricane. A system of methods capable of observing marine winds, surface waves, and surface currents from satellites is of value, even if these data are only available in near real-time or from SAR-related satellite images. Insight into high resolution ocean winds
-
Prediction and Migration of Surface-related Resonant Multiples
Guo, Bowen
2015-08-19
Surface-related resonant multiples can be migrated to achieve better resolution than migrating primary reflections. We now derive the formula for migrating surface-related resonant multiples, and show its super-resolution characteristics. Moreover, a method is proposed to predict surface-related resonant multiples with zero-offset primary reflections. The prediction can be used to indentify and extract the true resonant multiple from other events. Both synthetic and field data are used to validate this prediction.
-
Eddy current analysis by BEM utilizing loop electric and surface magnetic currents as unknowns
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ishibashi, Kazuhisa
2002-01-01
The surface integral equations whose unknowns are the surface electric and magnetic currents are widely used in eddy current analysis. However, when the skin depth is thick, computational error is increased especially in obtaining electromagnetic fields near the edge of the conductor. In order to obtain the electromagnetic field accurately, we propose an approach to solve surface integral equations utilizing loop electric and surface magnetic currents as unknowns. (Author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Naito, Susumu; Hirata, Yosuke; Izumi, Mikio; Sano, Akira; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Aoyama, Yoshio; Yamaguchi, Hiromi
2007-01-01
We present a reinforced ion current prediction model in alpha radioactivity measurement using ionized air transportation. Although our previous model explained the qualitative trend of the measured ion current values, the absolute values of the theoretical curves were about two times as large as the measured values. In order to accurately predict the measured values, we reinforced our model by considering columnar recombination and turbulent diffusion, which affects columnar recombination. Our new model explained the considerable ion loss in the early stage of ion diffusion and narrowed the gap between the theoretical and measured values. The model also predicted suppression of ion loss due to columnar recombination by spraying a high-speed air flow near a contaminated surface. This suppression was experimentally investigated and confirmed. In conclusion, we quantitatively clarified the theoretical relation between alpha radioactivity and ion current in laminar flow and turbulent pipe flow. (author)
-
Influence of orographically steered winds on Mutsu Bay surface currents
Yamaguchi, Satoshi; Kawamura, Hiroshi
2005-09-01
Effects of spatially dependent sea surface wind field on currents in Mutsu Bay, which is located at the northern end of Japanese Honshu Island, are investigated using winds derived from synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images and a numerical model. A characteristic wind pattern over the bay was evidenced from analysis of 118 SAR images and coincided with in situ observations. Wind is topographically steered with easterly winds entering the bay through the terrestrial gap and stronger wind blowing over the central water toward its mouth. Nearshore winds are weaker due to terrestrial blockages. Using the Princeton Ocean Model, we investigated currents forced by the observed spatially dependent wind field. The predicted current pattern agrees well with available observations. For a uniform wind field of equal magnitude and average direction, the circulation pattern departs from observations demonstrating that vorticity input due to spatially dependent wind stress is essential in generation of the wind-driven current in Mutsu Bay.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zhao, Mei; Wang, Guomin; Hendon, Harry H.; Alves, Oscar [Bureau of Meteorology, Centre for Australian Weather and Climate Research, Melbourne (Australia)
2011-04-15
Impacts on the coupled variability of the Indo-Pacific by including the effects of surface currents on surface stress are explored in four extended integrations of an experimental version of the Bureau of Meteorology's coupled seasonal forecast model POAMA. The first pair of simulations differs only in their treatment of momentum coupling: one version includes the effects of surface currents on the surface stress computation and the other does not. The version that includes the effect of surface currents has less mean-state bias in the equatorial Pacific cold tongue but produces relatively weak coupled variability in the Tropics, especially that related to the Indian Ocean dipole (IOD) and El Nino/Southern Oscillation (ENSO). The version without the effects of surface currents has greater bias in the Pacific cold tongue but stronger IOD and ENSO variability. In order to diagnose the role of changes in local coupling from changes in remote forcing by ENSO for causing changes in IOD variability, a second set of simulations is conducted where effects of surface currents are included only in the Indian Ocean and only in the Pacific Ocean. IOD variability is found to be equally reduced by inclusion of the local effects of surface currents in the Indian Ocean and by the reduction of ENSO variability as a result of including effects of surface currents in the Pacific. Some implications of these results for predictability of the IOD and its dependence on ENSO, and for ocean subsurface data assimilation are discussed. (orig.)
-
Surface ionization ion source with high current
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fang Jinqing; Lin Zhizhou; Yu Lihua; Zhan Rongan; Huang Guojun; Wu Jianhua
1986-04-01
The working principle and structure of a surface ionization ion source with high current is described systematically. Some technological keypoints of the ion source are given in more detail, mainly including: choosing and shaping of the material of the surface ionizer, heating of the ionizer, distributing of working vapour on the ionizer surface, the flow control, the cooling problem at the non-ionization surface and the ion optics, etc. This ion source has been used since 1972 in the electromagnetic isotope separator with 180 deg angle. It is suitable for separating isotopes of alkali metals and rare earth metals. For instance, in the case of separating Rubidium, the maximum ion current of Rbsup(+) extracted from the ion source is about 120 mA, the maximum ion current accepted by the receiver is about 66 mA, the average ion current is more than 25 mA. The results show that our ion source have advantages of high ion current, good characteristics of focusing ion beam, working stability and structure reliability etc. It may be extended to other fields. Finally, some interesting phenomena in the experiment are disccused briefly. Some problems which should be investigated are further pointed out
-
Multi-Objective Predictive Balancing Control of Battery Packs Based on Predictive Current
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wenbiao Li
2016-04-01
Full Text Available Various balancing topology and control methods have been proposed for the inconsistency problem of battery packs. However, these strategies only focus on a single objective, ignore the mutual interaction among various factors and are only based on the external performance of the battery pack inconsistency, such as voltage balancing and state of charge (SOC balancing. To solve these problems, multi-objective predictive balancing control (MOPBC based on predictive current is proposed in this paper, namely, in the driving process of an electric vehicle, using predictive control to predict the battery pack output current the next time. Based on this information, the impact of the battery pack temperature caused by the output current can be obtained. Then, the influence is added to the battery pack balancing control, which makes the present degradation, temperature, and SOC imbalance achieve balance automatically due to the change of the output current the next moment. According to MOPBC, the simulation model of the balancing circuit is built with four cells in Matlab/Simulink. The simulation results show that MOPBC is not only better than the other traditional balancing control strategies but also reduces the energy loss in the balancing process.
-
Predictive Toxicology: Current Status and Future Outlook (EBI ...
Slide presentation at the EBI-EMBL Industry Programme Workshop on Predictive Toxicology and the currently status of Computational Toxicology activities at the US EPA. Slide presentation at the EBI-EMBL Industry Programme Workshop on Predictive Toxicology and the currently status of Computational Toxicology activities at the US EPA.
-
Helicopter Rotor Noise Prediction: Background, Current Status, and Future Direction
Brentner, Kenneth S.
1997-01-01
Helicopter noise prediction is increasingly important. The purpose of this viewgraph presentation is to: 1) Put into perspective the recent progress; 2) Outline current prediction capabilities; 3) Forecast direction of future prediction research; 4) Identify rotorcraft noise prediction needs. The presentation includes an historical perspective, a description of governing equations, and the current status of source noise prediction.
-
Gravity current into an ambient fluid with an open surface
Ungarish, Marius
2017-11-01
Consider the steady-state gravity current of height h and density ρ1 that propagates into an ambient motionless fluid of height H and density ρ2 with an upper surface open to the atmosphere (open channel) at high Reynolds number. The current propagates with speed U and causes a depth decrease χ of the top surface. This is a significant extension of Benjamin's (1968) seminal solution for the fixed-top channel χ = 0 . Here the determination of χ is a part of the problem. The dimensionless parameters of the problem are a = h / H and r =ρ2 /ρ1 . We show that a control-volume analysis determines χ = χ / H and Fr = U / (g ' h)1/2 as functions of a , r , where g ' = (r-1 - 1) g is the reduced gravity. The system satisfies balance of volume and momentum (explicitly), and vorticity (implicitly). We present solutions. The predicted flows are in general dissipative, and thus physically valid only for a Frb (a) , but the reduction is not dramatic, typically a few percent. In the Boussinesq r 1 case, χ << 1 while Fr and dissipation are close to Benjamin's values.
-
Experimental study of neoclassical currents
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zarnstorff, M.C.; Prager, S.C.
1985-05-01
A detailed experimental study is presented of the bootstrap and Pfirsch-Schlueter currents that are predicted by neoclassical transport theory. In a toroidal octupole, on magnetic surfaces within the separatrix, the observed parallel plasma currents are in excellent quantitative agreement with neoclassical theory with regard to the spatial structure (along a magnetic surface), collisionality dependence and toroidal magnetic field dependence. On magnetic surfaces outside the separatrix, the ion portion of the parallel current is in agreement with neoclassical theory but the electron parallel current is observed to obtain a unidirectional component which deviates from and exceeds the theoretical prediction
-
Are we near the predictability limit of tropical Indo-Pacific sea surface temperatures?
Newman, Matthew; Sardeshmukh, Prashant D.
2017-08-01
The predictability of seasonal anomalies worldwide rests largely on the predictability of tropical sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies. Tropical forecast skill is also a key metric of climate models. We find, however, that despite extensive model development, the tropical SST forecast skill of the operational North American Multi-Model Ensemble (NMME) of eight coupled atmosphere-ocean models remains close both regionally and temporally to that of a vastly simpler linear inverse model (LIM) derived from observed covariances of SST, sea surface height, and wind fields. The LIM clearly captures the essence of the predictable SST dynamics. The NMME and LIM skills also closely track and are only slightly lower than the potential skill estimated using the LIM's forecast signal-to-noise ratios. This suggests that the scope for further skill improvement is small in most regions, except in the western equatorial Pacific where the NMME skill is currently much lower than the LIM skill.
-
Analysis of surface dark current dependent upon surface passivation in APD based on GaAs
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Song, Hong Joo; Roh, Cheong Hyun; Lee, Jun Ho; Choi, Hong Goo; Hahn, Cheol-Koo; Kim, Dong Ho; Park, Jung Ho
2009-01-01
In this paper, we investigated the dependence of reverse dark current on two types of surface passivation, one of which is polyimide and the other is SiN x , for InAs quantum dots/GaAs separate absorption, charge, multiplication avalanche photodiode (SACM APD). From the experimental results, we found that dark current was dominated by surface current, and not bulk current. It was also noted that SiN x passivation has a surface current that is lower by three to nine times in magnitude than that in polyimide passivation in the whole range of bias. To analyze the difference in dark current due to the passivation types, we propose the theoretical current components. This shows that the dark current of both passivation types is mainly composed of generation–recombination (G–R) and tunneling components, originating from the surface. However, each component has a different magnitude for passivation types, which can be explained by carrier concentration and trap density. The dependence of dark current on temperature shows the different behaviors between passivation types and supports a theoretical description of current components
-
Current-induced switching of magnetic molecules on topological insulator surfaces
Locane, Elina; Brouwer, Piet W.
2017-03-01
Electrical currents at the surface or edge of a topological insulator are intrinsically spin polarized. We show that such surface or edge currents can be used to switch the orientation of a molecular magnet weakly coupled to the surface or edge of a topological insulator. For the edge of a two-dimensional topological insulator as well as for the surface of a three-dimensional topological insulator the application of a well-chosen surface or edge current can lead to a complete polarization of the molecule if the molecule's magnetic anisotropy axis is appropriately aligned with the current direction. For a generic orientation of the molecule a nonzero but incomplete polarization is obtained. We calculate the probability distribution of the magnetic states and the switching rates as a function of the applied current.
-
Concentration polarization, surface currents, and bulk advection in a microchannel
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, Christoffer Peder; Bruus, Henrik
2014-01-01
. A remarkable outcome of the investigations is the discovery of strong couplings between bulk advection and the surface current; without a surface current, bulk advection is strongly suppressed. The numerical simulations are supplemented by analytical models valid in the long channel limit as well...... as in the limit of negligible surface charge. By including the effects of diffusion and advection in the diffuse part of the electric double layers, we extend a recently published analytical model of overlimiting current due to surface conduction....
-
Improved Modeling and Prediction of Surface Wave Amplitudes
2017-05-31
AFRL-RV-PS- AFRL-RV-PS- TR-2017-0162 TR-2017-0162 IMPROVED MODELING AND PREDICTION OF SURFACE WAVE AMPLITUDES Jeffry L. Stevens, et al. Leidos...data does not license the holder or any other person or corporation; or convey any rights or permission to manufacture, use, or sell any patented...SUBTITLE Improved Modeling and Prediction of Surface Wave Amplitudes 5a. CONTRACT NUMBER FA9453-14-C-0225 5b. GRANT NUMBER 5c. PROGRAM ELEMENT NUMBER
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
D. O. Topping
2007-01-01
Full Text Available In order to predict the physical properties of aerosol particles, it is necessary to adequately capture the behaviour of the ubiquitous complex organic components. One of the key properties which may affect this behaviour is the contribution of the organic components to the surface tension of aqueous particles in the moist atmosphere. Whilst the qualitative effect of organic compounds on solution surface tensions has been widely reported, our quantitative understanding on mixed organic and mixed inorganic/organic systems is limited. Furthermore, it is unclear whether models that exist in the literature can reproduce the surface tension variability for binary and higher order multi-component organic and mixed inorganic/organic systems of atmospheric significance. The current study aims to resolve both issues to some extent. Surface tensions of single and multiple solute aqueous solutions were measured and compared with predictions from a number of model treatments. On comparison with binary organic systems, two predictive models found in the literature provided a range of values resulting from sensitivity to calculations of pure component surface tensions. Results indicate that a fitted model can capture the variability of the measured data very well, producing the lowest average percentage deviation for all compounds studied. The performance of the other models varies with compound and choice of model parameters. The behaviour of ternary mixed inorganic/organic systems was unreliably captured by using a predictive scheme and this was dependent on the composition of the solutes present. For more atmospherically representative higher order systems, entirely predictive schemes performed poorly. It was found that use of the binary data in a relatively simple mixing rule, or modification of an existing thermodynamic model with parameters derived from binary data, was able to accurately capture the surface tension variation with concentration. Thus
-
Surface currents on the plasma-vacuum interface in MHD equilibria
Hanson, James
2017-10-01
The VMEC non-axisymmetric MHD equilibrium code can compute free-boundary equilibria. Since VMEC assumes that magnetic fields within the plasma form closed and nested flux surfaces, the plasma-vacuum interface is a flux surface, and the total magnetic field there has no normal component. VMEC imposes this condition of zero normal field using the potential formulation of Merkel, and solves a Neumann problem for the magnetic potential in the exterior region. This boundary condition necessarily admits the possibility of a surface current on the interface. While this surface current may be small in MHD equilibrium, it is readily computed in terms of the magnetic potentials in both the interior and exterior regions, evaluated on the surface. If only the external magnetic potential is known (as in VMEC), then the surface current can be computed from the discontinuity of the tangential field across the interface. Examples of the surface current for VMEC equilibria will be shown for a zero-pressure stellarator equilibrium. Field-line following of the vacuum magnetic field shows magnetic islands within the plasma region.
-
Modelling Monsoons: Understanding and Predicting Current and Future Behaviour
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Turner, A; Sperber, K R; Slingo, J M; Meehl, G A; Mechoso, C R; Kimoto, M; Giannini, A
2008-09-16
The global monsoon system is so varied and complex that understanding and predicting its diverse behaviour remains a challenge that will occupy modellers for many years to come. Despite the difficult task ahead, an improved monsoon modelling capability has been realized through the inclusion of more detailed physics of the climate system and higher resolution in our numerical models. Perhaps the most crucial improvement to date has been the development of coupled ocean-atmosphere models. From subseasonal to interdecadal timescales, only through the inclusion of air-sea interaction can the proper phasing and teleconnections of convection be attained with respect to sea surface temperature variations. Even then, the response to slow variations in remote forcings (e.g., El Nino-Southern Oscillation) does not result in a robust solution, as there are a host of competing modes of variability that must be represented, including those that appear to be chaotic. Understanding the links between monsoons and land surface processes is not as mature as that explored regarding air-sea interactions. A land surface forcing signal appears to dominate the onset of wet season rainfall over the North American monsoon region, though the relative role of ocean versus land forcing remains a topic of investigation in all the monsoon systems. Also, improved forecasts have been made during periods in which additional sounding observations are available for data assimilation. Thus, there is untapped predictability that can only be attained through the development of a more comprehensive observing system for all monsoon regions. Additionally, improved parameterizations - for example, of convection, cloud, radiation, and boundary layer schemes as well as land surface processes - are essential to realize the full potential of monsoon predictability. Dynamical considerations require ever increased horizontal resolution (probably to 0.5 degree or higher) in order to resolve many monsoon features
-
Current Density and Plasma Displacement Near Perturbed Rational Surface
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Boozer, A.H.; Pomphrey, N.
2010-01-01
The current density in the vicinity of a rational surface of a force-free magnetic field subjected to an ideal perturbation is shown to be the sum of both a smooth and a delta-function distribution, which give comparable currents. The maximum perturbation to the smooth current density is comparable to a typical equilibrium current density and the width of the layer in which the current flows is shown to be proportional to the perturbation amplitude. In the standard linearized theory, the plasma displacement has an unphysical jump across the rational surface, but the full theory gives a continuous displacement.
-
The Current State of Predicting Furrow Irrigation Erosion
There continues to be a need to predict furrow irrigation erosion to estimate on- and off-site impacts of irrigation management. The objective of this paper is to review the current state of furrow erosion prediction technology considering four models: SISL, WEPP, WinSRFR and APEX. SISL is an empiri...
-
Airborne Optical Remote Sensing of Ocean Surface Current Variability
Anderson, S. P.; Zuckerman, S.; Stuart, G.
2016-02-01
Accurate and timely knowledge of open ocean surface currents are needed for a variety of engineering and emergency missions, as well as for improving scientific understanding of ocean dynamics. This paper presents surface current observations from a new airborne current measurement capability called the Remote Ocean Current Imaging System (ROCIS). ROCIS exploits space-time processing of airborne ocean wave imagery to produce real-time maps of surface currents every 1 km along the flight track. Post-processing of the data allows for more in depth sensitivity studies than can be undertaken with the real-time measurements alone, providing swaths of current retrievals at higher spatial resolutions. Currents can be calculated on scales down to 100 m, across swaths 3 km wide, along the entire flight path. Here, we report on results for multiple ROCIS data collection flights over the Gulf of Mexico conducted in 2012, 2014 and 2015. We show comparisons to in situ current measurements, explore performance as a function of altitude, dwell, wind speed, and wave height, and discuss sources of error. We present examples of current retrievals revealing mesoscale and submesoscale variability. Lastly, we present horizontal kinetic energy spectra from select flights covering a range of spatial scales from hundreds of meters to hundreds of kilometers.
-
Climate-Induced Boreal Forest Change: Predictions versus Current Observations
Soja, Amber J.; Tchebakova, Nadezda M.; French, Nancy H. F.; Flannigan, Michael D.; Shugart, Herman H.; Stocks, Brian J.; Sukhinin, Anatoly I.; Parfenova, E. I.; Chapin, F. Stuart, III; Stackhouse, Paul W., Jr.
2007-01-01
For about three decades, there have been many predictions of the potential ecological response in boreal regions to the currently warmer conditions. In essence, a widespread, naturally occurring experiment has been conducted over time. In this paper, we describe previously modeled predictions of ecological change in boreal Alaska, Canada and Russia, and then we investigate potential evidence of current climate-induced change. For instance, ecological models have suggested that warming will induce the northern and upslope migration of the treeline and an alteration in the current mosaic structure of boreal forests. We present evidence of the migration of keystone ecosystems in the upland and lowland treeline of mountainous regions across southern Siberia. Ecological models have also predicted a moisture-stress-related dieback in white spruce trees in Alaska, and current investigations show that as temperatures increase, white spruce tree growth is declining. Additionally, it was suggested that increases in infestation and wildfire disturbance would be catalysts that precipitate the alteration of the current mosaic forest composition. In Siberia, five of the last seven years have resulted in extreme fire seasons, and extreme fire years have also been more frequent in both Alaska and Canada. In addition, Alaska has experienced extreme and geographically expansive multi-year outbreaks of the spruce beetle, which had been previously limited by the cold, moist environment. We suggest that there is substantial evidence throughout the circumboreal region to conclude that the biosphere within the boreal terrestrial environment has already responded to the transient effects of climate change. Additionally, temperature increases and warming-induced change are progressing faster than had been predicted in some regions, suggesting a potential non-linear rapid response to changes in climate, as opposed to the predicted slow linear response to climate change.
-
Mapping the Agulhas Current from space: an assessment of ASAR surface current velocities
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Rouault, MJ
2010-10-01
Full Text Available Over 2 years of surface current information collected in the Agulhas Current region and derived from the Doppler centroid anomalies of Envisat’s advanced synthetic aperture radar (ASAR) are examined. The sources of errors and potential use of ASAR...
-
Investigation of the surface current excitation by a relativistic electron electromagnetic field
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Naumenko, G; Shevelev, M; Potylitsyn, A; Popov, Yu; Sukhikh, L
2010-01-01
Surface current method and pseudo-photon ones are widely used in the problems of diffraction and transition radiation of relativistic electron in conductive targets. The simple analysis disclosed the contradiction between these methods in respect to the surface current excitation on target surfaces. This contradiction was resolved experimentally by the measurement of a surface current on the upstream and downstream target surfaces in diffraction radiation geometry. The experimental test showed, that no surface current is induced on the target downstream surface under the influence of a relativistic electron electromagnetic field in contrast to the upstream surface. This is important for the understanding of a forward transition and diffraction radiation nature and electromagnetic field evolution in interaction processes.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kumar, Sanjeev; Batish, Ajay [Thapar University, Patiala (India); Singh, Rupinder [GNDEC, Ludhiana (India); Singh, T. P. [Symbiosis Institute of Technology, Pune (India)
2014-07-15
In the present study, electric discharge machining process was used for machining of titanium alloys. Eight process parameters were varied during the process. Experimental results showed that current and pulse-on-time significantly affected the performance characteristics. Artificial neural network coupled with Taguchi approach was applied for optimization and prediction of surface roughness. The experimental results and the predicted results showed good agreement. SEM was used to investigate the surface integrity. Analysis for migration of different chemical elements and formation of compounds on the surface was performed using EDS and XRD pattern. The results showed that high discharge energy caused surface defects such as cracks, craters, thick recast layer, micro pores, pin holes, residual stresses and debris. Also, migration of chemical elements both from electrode and dielectric media were observed during EDS analysis. Presence of carbon was seen on the machined surface. XRD results showed formation of titanium carbide compound which precipitated on the machined surface.
-
Cheng, Jun; Gong, Yadong; Wang, Jinsheng
2013-11-01
The current research of micro-grinding mainly focuses on the optimal processing technology for different materials. However, the material removal mechanism in micro-grinding is the base of achieving high quality processing surface. Therefore, a novel method for predicting surface roughness in micro-grinding of hard brittle materials considering micro-grinding tool grains protrusion topography is proposed in this paper. The differences of material removal mechanism between convention grinding process and micro-grinding process are analyzed. Topography characterization has been done on micro-grinding tools which are fabricated by electroplating. Models of grain density generation and grain interval are built, and new predicting model of micro-grinding surface roughness is developed. In order to verify the precision and application effect of the surface roughness prediction model proposed, a micro-grinding orthogonally experiment on soda-lime glass is designed and conducted. A series of micro-machining surfaces which are 78 nm to 0.98 μm roughness of brittle material is achieved. It is found that experimental roughness results and the predicting roughness data have an evident coincidence, and the component variable of describing the size effects in predicting model is calculated to be 1.5×107 by reverse method based on the experimental results. The proposed model builds a set of distribution to consider grains distribution densities in different protrusion heights. Finally, the characterization of micro-grinding tools which are used in the experiment has been done based on the distribution set. It is concluded that there is a significant coincidence between surface prediction data from the proposed model and measurements from experiment results. Therefore, the effectiveness of the model is demonstrated. This paper proposes a novel method for predicting surface roughness in micro-grinding of hard brittle materials considering micro-grinding tool grains protrusion
-
Surface and near surface defect detection in thick copper EB-welds using eddy current testing
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pitkaenen, J.; Lipponen, A.
2010-01-01
The surface inspection of thick copper electron beam (EB) welds plays an important role in the acceptance of nuclear fuel disposal. The main reasons to inspect these components are related to potential manufacturing and handling defects. In this work the data acquisition software, visualising tools for eddy current (EC) measurements and eddy current sensors were developed for detection of unwanted defects. The eddy current equipment was manufactured by IZFP and the visualising software in active co-operation with Posiva and IZFP for the inspections. The inspection procedure was produced during the development of the inspection techniques. The inspection method development aims to qualify the method for surface and near surface defect detection and sizing according to ENIQ. The study includes technical justification to be carried out, and compilation of a defect catalogue and experience from measurements within the Posiva's research on issues related to manufacturing. The depth of penetration in copper components in eddy current testing is rather small. To detect surface breaking defects the eddy current inspection is a good solution. A simple approach was adopted using two techniques: higher frequency was used to detect surface defects and to determine the dimensions of the defects except depth, lower frequency was used to detect defects having a ligament and for sizing of deeper surface breaking defects. The higher frequency was 30 kHz and the lower frequency was 200 Hz. The higher frequency probes were absolute bobbing coils and lower frequency probes combined transmitter - several receiver coils. To evaluate both methods, calibration blocks were manufactured by FNS for weld inspections. These calibration specimens mainly consisted of electron discharge machined notches and holes of varying shapes, lengths and diameters in the range of 1 mm to 20 mm of depth. Also one copper lid specimen with 152 defects was manufactured and used for evaluation of weld inspection
-
Surface current measurements in Juan de Fuca Strait using the SeaSonde HF [high frequency] radar
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hodgins, D.O.
1994-09-01
The shore-based SeaSonde high-frequency (HF) radar was deployed for three weeks in summer 1993 to measure surface currents in the Strait of Georgia, British Columbia. Experimental objectives included documenting the complex flow regime generated by large tides and the brackish plume of the Fraser River, and determining the radar performance under low-wind, low-salinity conditions. The radar data showed that surface flows are dominated by the plume jet formed by the Fraser River outflow, giving rise to recurring, energetic eddies with scales of 8-12 km, strong flow meanders, and convergent fronts. These features were continuously modulated by the along-channel tidal flows. Comparisons with a detailed numerical model hindcast gave good correlation between observed and predicted flow fields, especially at tidal and low frequencies. Radar return was found to be correlated with local winds and radar performance was independent of salinity variations in the plume. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) provides a map of the radar scattering characteristics of the ocean surface on a capillary wave scale. ERS-1 satellite and airborne SAR images for July 28, 1993 were obtained and surface features were examined in the context of the HF radar current fields. Results show that SAR images alone cannot reliably provide the dynamical data required in this region by oil spill models. Under certain conditions, however, the radar imagery offers valuable physical information on phenomena affecting oil slick development. Interpretation of SAR imagery in conjunction with other remote sensing information would offer more quantitative prediction data. 28 refs., 334 figs., 1 tab
-
Surface currents in the Canary Basin from drifter observations
Zhou, Meng; Paduan, Jeffrey D.; Niiler, Pearn P.
2000-09-01
Satellite-tracked drifting buoys, deployed in the Canary Basin as part of the Subduction Experiment between July 1991 and October 1993 and the French Semaphore Experiment during October 1993, were used to obtain a description of surface currents and temperature in the Canary Basin. The study focuses on surface water convergence, eddy energy production, and heat transport. The Azores Current associated with the subtropical convergence zone is clearly visible at 34°N, and bifurcates around 22°W, with the major branch of the current circling the Madeira plateau and joining the Canary Current along the continental slope. Eddy kinetic energy maxima are found along the Azores Current. The mean current revealed a region of maximum convergence north of the Azores Current around longitude 29°W occurring with a negative heating anomaly and positive work done by the Reynolds stress. The southward meridional temperature fluxes in the Ekman layer (0-50 m) between 37°W and the African and European coast are estimated between -0.076±0.022×l015 W, produced by mean southward volume transport in our study area. The residual between local surface heat fluxes and horizontal convergence of heat implies a vertical heat convergence process associated with mesoscale temperature and flow fields.
-
Predicting Surface Runoff from Catchment to Large Region
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hongxia Li
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Predicting surface runoff from catchment to large region is a fundamental and challenging task in hydrology. This paper presents a comprehensive review for various studies conducted for improving runoff predictions from catchment to large region in the last several decades. This review summarizes the well-established methods and discusses some promising approaches from the following four research fields: (1 modeling catchment, regional and global runoff using lumped conceptual rainfall-runoff models, distributed hydrological models, and land surface models, (2 parameterizing hydrological models in ungauged catchments, (3 improving hydrological model structure, and (4 using new remote sensing precipitation data.
-
Surface Currents and Winds at the Delaware Bay Mouth
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Muscarella, P A; Barton, N P; Lipphardt, B L; Veron, D E; Wong, K C; Kirwan, A D
2011-04-06
Knowledge of the circulation of estuaries and adjacent shelf waters has relied on hydrographic measurements, moorings, and local wind observations usually removed from the region of interest. Although these observations are certainly sufficient to identify major characteristics, they lack both spatial resolution and temporal coverage. High resolution synoptic observations are required to identify important coastal processes at smaller scales. Long observation periods are needed to properly sample low-frequency processes that may also be important. The introduction of high-frequency (HF) radar measurements and regional wind models for coastal studies is changing this situation. Here we analyze synoptic, high-resolution surface winds and currents in the Delaware Bay mouth over an eight-month period (October 2007 through May 2008). The surface currents were measured by two high-frequency radars while the surface winds were extracted from a data-assimilating regional wind model. To illustrate the utility of these monitoring tools we focus on two 45-day periods which previously were shown to present contrasting pictures of the circulation. One, the low-outflow period is from 1 October through 14 November 2007; the other is the high-outflow period from 3 March through 16 April 2008. The large-scale characteristics noted by previous workers are clearly corroborated. Specifically the M2 tide dominates the surface currents, and the Delaware Bay outflow plume is clearly evident in the low frequency currents. Several new aspects of the surface circulation were also identified. These include a map of the spatial variability of the M2 tide (validating an earlier model study), persistent low-frequency cross-mouth flow, and a rapid response of the surface currents to a changing wind field. However, strong wind episodes did not persist long enough to set up a sustained Ekman response.
-
QCD predictions for weak neutral current structure functions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wu Jimin
1987-01-01
Employing the analytic expression (to the next leading order) for non-singlet component of structure function which the author got from QCD theory and putting recent experiment result of neutral current structure function at Q 2 = 11 (GeV/C) 2 as input, the QCD prediction for neutral current structure function of their scaling violation behaviours was given
-
Tuning and predicting the wetting of nanoengineered material surface
Ramiasa-MacGregor, M.; Mierczynska, A.; Sedev, R.; Vasilev, K.
2016-02-01
The wetting of a material can be tuned by changing the roughness on its surface. Recent advances in the field of nanotechnology open exciting opportunities to control macroscopic wetting behaviour. Yet, the benchmark theories used to describe the wettability of macroscopically rough surfaces fail to fully describe the wetting behaviour of systems with topographical features at the nanoscale. To shed light on the events occurring at the nanoscale we have utilised model gradient substrata where surface nanotopography was tailored in a controlled and robust manner. The intrinsic wettability of the coatings was varied from hydrophilic to hydrophobic. The measured water contact angle could not be described by the classical theories. We developed an empirical model that effectively captures the experimental data, and further enables us to predict the wetting of surfaces with nanoscale roughness by considering the physical and chemical properties of the material. The fundamental insights presented here are important for the rational design of advanced materials having tailored surface nanotopography with predictable wettability.The wetting of a material can be tuned by changing the roughness on its surface. Recent advances in the field of nanotechnology open exciting opportunities to control macroscopic wetting behaviour. Yet, the benchmark theories used to describe the wettability of macroscopically rough surfaces fail to fully describe the wetting behaviour of systems with topographical features at the nanoscale. To shed light on the events occurring at the nanoscale we have utilised model gradient substrata where surface nanotopography was tailored in a controlled and robust manner. The intrinsic wettability of the coatings was varied from hydrophilic to hydrophobic. The measured water contact angle could not be described by the classical theories. We developed an empirical model that effectively captures the experimental data, and further enables us to predict the
-
Sensitivity of point scale surface runoff predictions to rainfall resolution
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. J. Hearman
2007-01-01
Full Text Available This paper investigates the effects of using non-linear, high resolution rainfall, compared to time averaged rainfall on the triggering of hydrologic thresholds and therefore model predictions of infiltration excess and saturation excess runoff at the point scale. The bounded random cascade model, parameterized to three locations in Western Australia, was used to scale rainfall intensities at various time resolutions ranging from 1.875 min to 2 h. A one dimensional, conceptual rainfall partitioning model was used that instantaneously partitioned water into infiltration excess, infiltration, storage, deep drainage, saturation excess and surface runoff, where the fluxes into and out of the soil store were controlled by thresholds. The results of the numerical modelling were scaled by relating soil infiltration properties to soil draining properties, and in turn, relating these to average storm intensities. For all soil types, we related maximum infiltration capacities to average storm intensities (k* and were able to show where model predictions of infiltration excess were most sensitive to rainfall resolution (ln k*=0.4 and where using time averaged rainfall data can lead to an under prediction of infiltration excess and an over prediction of the amount of water entering the soil (ln k*>2 for all three rainfall locations tested. For soils susceptible to both infiltration excess and saturation excess, total runoff sensitivity was scaled by relating drainage coefficients to average storm intensities (g* and parameter ranges where predicted runoff was dominated by infiltration excess or saturation excess depending on the resolution of rainfall data were determined (ln g*<2. Infiltration excess predicted from high resolution rainfall was short and intense, whereas saturation excess produced from low resolution rainfall was more constant and less intense. This has important implications for the accuracy of current hydrological models that use time
-
Lim, S. J.; Choi, R. K.; Ahn, K. D.; Ha, J. C.; Cho, C. H.
2014-12-01
As the Korea Meteorology Administration (KMA) has operated Met Office Global and Regional Ensemble Prediction System (MOGREPS) with introduction of Unified Model (UM), many attempts have been made to improve predictability in temperature forecast in last years. In this study, post-processing method of MOGREPS for surface temperature prediction is developed with machine learning over 52 locations in South Korea. Past 60-day lag time was used as a training phase of Support Vector Regression (SVR) method for surface temperature forecast model. The selected inputs for SVR are followings: date and surface temperatures from Numerical Weather prediction (NWP), such as GDAPS, individual 24 ensemble members, mean and median of ensemble members for every 3hours for 12 days.To verify the reliability of SVR-based ensemble prediction (SVR-EP), 93 days are used (from March 1 to May 31, 2014). The result yielded improvement of SVR-EP by RMSE value of 16 % throughout entire prediction period against conventional ensemble prediction (EP). In particular, short range predictability of SVR-EP resulted in 18.7% better RMSE for 1~3 day forecast. The mean temperature bias between SVR-EP and EP at all test locations showed around 0.36°C and 1.36°C, respectively. SVR-EP is currently extending for more vigorous sensitivity test, such as increasing training phase and optimizing machine learning model.
-
Prediction of Tidal Elevations and Barotropic Currents in the Gulf of Bone
Purnamasari, Rika; Ribal, Agustinus; Kusuma, Jeffry
2018-03-01
Tidal elevation and barotropic current predictions in the gulf of Bone have been carried out in this work based on a two-dimensional, depth-integrated Advanced Circulation (ADCIRC-2DDI) model for 2017. Eight tidal constituents which were obtained from FES2012 have been imposed along the open boundary conditions. However, even using these very high-resolution tidal constituents, the discrepancy between the model and the data from tide gauge is still very high. In order to overcome such issues, Green’s function approach has been applied which reduced the root-mean-square error (RMSE) significantly. Two different starting times are used for predictions, namely from 2015 and 2016. After improving the open boundary conditions, RMSE between observation and model decreased significantly. In fact, RMSEs for 2015 and 2016 decreased 75.30% and 88.65%, respectively. Furthermore, the prediction for tidal elevations as well as tidal current, which is barotropic current, is carried out. This prediction was compared with the prediction conducted by Geospatial Information Agency (GIA) of Indonesia and we found that our prediction is much better than one carried out by GIA. Finally, since there is no tidal current observation available in this area, we assume that, when tidal elevations have been fixed, then the tidal current will approach the actual current velocity.
-
The prediction of BRDFs from surface profile measurements
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Church, E.L.; Takacs, P.Z.; Leonard, T.A.
1989-01-01
This paper discusses methods of predicting the BRDF of smooth surfaces from profile measurements of their surface finish. The conversion of optical profile data to the BRDF at the same wavelength is essentially independent of scattering models, while the conversion of mechanical measurements, and wavelength scaling in general, are model dependent. Procedures are illustrated for several surfaces, including two from the recent HeNe BRDF round robin, and results are compared with measured data. Reasonable agreement is found except for surfaces which involve significant scattering from isolated surface defects which are poorly sampled in the profile data
-
Surface current equilibria from a geometric point of view
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kaiser, R.; Salat, A.
1993-04-01
This paper addresses the inverse problem of the existence of surface current MHD equilibria in toroidal geometry with vanishing magnetic field inside. Inverse means that the plasma-vacuum interface rather than the external wall or conductors are given and the latter remain to be determined. This makes a reformulation of the problem possible in geometric terms: What toroidal surfaces with analytic parameterization allow a simple analytic covering by geodesics? If such a covering by geodesics (field lines) exists, their orthogonal trajectories (current lines) also form a simple covering and are described by a function satisfying a nonlinear partial differential equation of the Hamilton-Jacobi type whose coefficients are combinations of the metric elements of the surface. All known equilibria - equilibria with zero and infinite rotational transform and the symmetric ones in the case of finite rotational transform - turn out to be solutions of separable cases of that equation and allow a unified description if the toroidal surface is parametrized in the moving trihedral associated with a closed curve. Analogously to volume current equilibria, the only continuous symmetries compatible with separability are plane, helical and axial symmetry. In the nonseparable case numerical evidence is presented for cases with chaotic behaviour of geodesics, thus restricting possible equilibria for these surfaces. For weak deviation from axisymmetry KAM-type behaviour is observed, i.e. destruction of geodesic coverings with a low rational rotational transform and preservation of those with irrational rotational transform. A previous attempt to establish three-dimensional surface current equilibria on the basis of the KAM theorem is rejected as incomplete, and a complete proof of the existence of equilibria in the weakly nonaxisymmetric case, based on the twist theorem for mappings, is given. Finally, for a certain class of strong deviations from axisymmetry an analytic criterion is
-
Sea surface temperature predictions using a multi-ocean analysis ensemble scheme
Zhang, Ying; Zhu, Jieshun; Li, Zhongxian; Chen, Haishan; Zeng, Gang
2017-08-01
This study examined the global sea surface temperature (SST) predictions by a so-called multiple-ocean analysis ensemble (MAE) initialization method which was applied in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Climate Forecast System Version 2 (CFSv2). Different from most operational climate prediction practices which are initialized by a specific ocean analysis system, the MAE method is based on multiple ocean analyses. In the paper, the MAE method was first justified by analyzing the ocean temperature variability in four ocean analyses which all are/were applied for operational climate predictions either at the European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts or at NCEP. It was found that these systems exhibit substantial uncertainties in estimating the ocean states, especially at the deep layers. Further, a set of MAE hindcasts was conducted based on the four ocean analyses with CFSv2, starting from each April during 1982-2007. The MAE hindcasts were verified against a subset of hindcasts from the NCEP CFS Reanalysis and Reforecast (CFSRR) Project. Comparisons suggested that MAE shows better SST predictions than CFSRR over most regions where ocean dynamics plays a vital role in SST evolutions, such as the El Niño and Atlantic Niño regions. Furthermore, significant improvements were also found in summer precipitation predictions over the equatorial eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans, for which the local SST prediction improvements should be responsible. The prediction improvements by MAE imply a problem for most current climate predictions which are based on a specific ocean analysis system. That is, their predictions would drift towards states biased by errors inherent in their ocean initialization system, and thus have large prediction errors. In contrast, MAE arguably has an advantage by sampling such structural uncertainties, and could efficiently cancel these errors out in their predictions.
-
Comparison of HF radar measurements with Eulerian and Lagrangian surface currents
Röhrs, Johannes; Sperrevik, Ann Kristin; Christensen, Kai Håkon; Broström, Göran; Breivik, Øyvind
2015-05-01
High-frequency (HF) radar-derived ocean currents are compared with in situ measurements to conclude if the radar observations include effects of surface waves that are of second order in the wave amplitude. Eulerian current measurements from a high-resolution acoustic Doppler current profiler and Lagrangian measurements from surface drifters are used as references. Directional wave spectra are obtained from a combination of pressure sensor data and a wave model. Our analysis shows that the wave-induced Stokes drift is not included in the HF radar-derived currents, that is, HF radars measure the Eulerian current. A disputed nonlinear correction to the phase velocity of surface gravity waves, which may affect HF radar signals, has a magnitude of about half the Stokes drift at the surface. In our case, this contribution by nonlinear dispersion would be smaller than the accuracy of the HF radar currents, hence no conclusion can be made. Finally, the analysis confirms that the HF radar data represent an exponentially weighted vertical average where the decay scale is proportional to the wavelength of the transmitted signal.
-
Predicting the importance of current papers.
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Klavans, Richard (SciTech Strategies, Inc., Berwyn, PA); Boyack, Kevin W.
2005-01-01
This article examines how well one can predict the importance of a current paper (a paper that is recently published in the literature). We look at three factors--journal importance, reference importance and author reputation. Citation-based measures of importance are used for all variables. We find that journal importance is the best predictor (explaining 22.3% out of a potential 29.1% of the variance in the data), and that this correlation value varies significantly by discipline. Journal importance is a better predictor of citation in Computer Science than in any other discipline. While the finding supports the present policy of using journal impact statistics as a surrogate for the importance of current papers, it calls into question the present policy of equally weighting current documents in text-based analyses. We suggest that future researchers take into account the expected importance of a document when attempting to describe the cognitive structure of a field.
-
Flux surface shape and current profile optimization in tokamaks
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dobrott, D.R.; Miller, R.L.
1977-01-01
Axisymmetric tokamak equilibria of noncircular cross section are analyzed numerically to study the effects of flux surface shape and current profile on ideal and resistive interchange stability. Various current profiles are examined for circles, ellipses, dees, and doublets. A numerical code separately analyzes stability in the neighborhood of the magnetic axis and in the remainder of the plasma using the criteria of Mercier and Glasser, Greene, and Johnson. Results are interpreted in terms of flux surface averaged quantities such as magnetic well, shear, and the spatial variation in the magnetic field energy density over the cross section. The maximum stable β is found to vary significantly with shape and current profile. For current profiles varying linearly with poloidal flux, the highest β's found were for doublets. Finally, an algorithm is presented which optimizes the current profile for circles and dees by making the plasma everywhere marginally stable
-
Trauscht, Jacob; Pazmino, Eddy; Johnson, William P
2015-09-01
Despite several decades of research there currently exists no mechanistic theory to predict colloid attachment in porous media under environmental conditions where colloid-collector repulsion exists (unfavorable conditions for attachment). It has long been inferred that nano- to microscale surface heterogeneity (herein called discrete heterogeneity) drives colloid attachment under unfavorable conditions. Incorporating discrete heterogeneity into colloid-collector interaction calculations in particle trajectory simulations predicts colloid attachment under unfavorable conditions. As yet, discrete heterogeneity cannot be independently measured by spectroscopic or other approaches in ways directly relevant to colloid-surface interaction. This, combined with the fact that a given discrete heterogeneity representation will interact differently with differently sized colloids as well as different ionic strengths for a given sized colloid, suggests a strategy to back out representative discrete heterogeneity by a comparison of simulations to experiments performed across a range of colloid size, solution IS, and fluid velocity. This has recently been performed for interaction of carboxylate-modified polystyrene latex (CML) microsphere attachment to soda lime glass at pH 6.7 with NaCl electrolyte. However, extension to other surfaces, pH values, and electrolytes is needed. For this reason, the attachment of CML (0.25, 1.1, and 2.0 μm diameters) from aqueous suspension onto a variety of unfavorable mineral surfaces (soda lime glass, muscovite, and albite) was examined for pH values of 6.7 and 8.0), fluid velocities (1.71 × 10(-3) and 5.94 × 10(-3) m s(-1)), IS (6.0 and 20 mM), and electrolytes (NaCl, CaSO4, and multivalent mixtures). The resulting representative heterogeneities (heterodomain size and surface coverage, where heterodomain refers to nano- to microscale attractive domains) yielded colloid attachment predictions that were compared to predictions from existing
-
Improvement of gas entrainment prediction method. Introduction of surface tension effect
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ito, Kei; Sakai, Takaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Uchibori, Akihiro; Eguchi, Yuzuru; Monji, Hideaki; Xu, Yongze
2010-01-01
A gas entrainment (GE) prediction method has been developed to establish design criteria for the large-scale sodium-cooled fast reactor (JSFR) systems. The prototype of the GE prediction method was already confirmed to give reasonable gas core lengths by simple calculation procedures. However, for simplification, the surface tension effects were neglected. In this paper, the evaluation accuracy of gas core lengths is improved by introducing the surface tension effects into the prototype GE prediction method. First, the mechanical balance between gravitational, centrifugal, and surface tension forces is considered. Then, the shape of a gas core tip is approximated by a quadratic function. Finally, using the approximated gas core shape, the authors determine the gas core length satisfying the mechanical balance. This improved GE prediction method is validated by analyzing the gas core lengths observed in simple experiments. Results show that the analytical gas core lengths calculated by the improved GE prediction method become shorter in comparison to the prototype GE prediction method, and are in good agreement with the experimental data. In addition, the experimental data under different temperature and surfactant concentration conditions are reproduced by the improved GE prediction method. (author)
-
Applying machine learning to predict patient-specific current CD 4 ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
This work shows the application of machine learning to predict current CD4 cell count of an HIV-positive patient using genome sequences, viral load and time. A regression model predicting actual CD4 cell counts and a classification model predicting if a patient's CD4 cell count is less than 200 was built using a support ...
-
Baehr, J.; Fröhlich, K.; Botzet, M.; Domeisen, D. I. V.; Kornblueh, L.; Notz, D.; Piontek, R.; Pohlmann, H.; Tietsche, S.; Müller, W. A.
2015-05-01
A seasonal forecast system is presented, based on the global coupled climate model MPI-ESM as used for CMIP5 simulations. We describe the initialisation of the system and analyse its predictive skill for surface temperature. The presented system is initialised in the atmospheric, oceanic, and sea ice component of the model from reanalysis/observations with full field nudging in all three components. For the initialisation of the ensemble, bred vectors with a vertically varying norm are implemented in the ocean component to generate initial perturbations. In a set of ensemble hindcast simulations, starting each May and November between 1982 and 2010, we analyse the predictive skill. Bias-corrected ensemble forecasts for each start date reproduce the observed surface temperature anomalies at 2-4 months lead time, particularly in the tropics. Niño3.4 sea surface temperature anomalies show a small root-mean-square error and predictive skill up to 6 months. Away from the tropics, predictive skill is mostly limited to the ocean, and to regions which are strongly influenced by ENSO teleconnections. In summary, the presented seasonal prediction system based on a coupled climate model shows predictive skill for surface temperature at seasonal time scales comparable to other seasonal prediction systems using different underlying models and initialisation strategies. As the same model underlying our seasonal prediction system—with a different initialisation—is presently also used for decadal predictions, this is an important step towards seamless seasonal-to-decadal climate predictions.
-
Surface current double-heterogeneous multilayer multicell methodology
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Stepanek, J.; Segev, M.
1991-01-01
A surface current methodology is developed to respond to the need for treating the various levels of material heterogeneity in a double-heterogeneous multilayer multicell in processing neutron multigroup cross sections in the resonance as well as thermal energy range. First, the basic surface cosine current transport equations to calculate the energy-dependent neutron flux spatial distribution in the multilayered multicell are formulated. Slab, spherical and cylindrical geometries, as well as square and hexagonal lattices and pebble-bed configurations with white or reflective cell boundary conditions, are considered. Second, starting from the surface cosine-current formulation, a two-zone three-layer multicell formalism for reduction of heterogeneous flux expressions to equivalent homogeneous flux expression for table method was developed. This formalism allows an infinite, as well as a limited, number of second-heterogeneity cells within a partial first-heterogeneity cell layer to be considered. Also, the number of the first-and second-heterogeneity cell types is quite general. The 'outer' (right side) as well as 'inner' (left side) Dancoff probabilities can be calculated for any particular layer. An accurate, efficient, and compact interpolation procedure is developed to calculate the basic collision probabilities. These are transmission and escape probabilities for shells in slab, cylindrical, and spherical geometries, as well as Dancoff probabilities for cylinders in square and hexagonal lattices. The use of the interpolation procedure is exemplified in a multilayer multicell approximation for the Dancoff probability, enabling a routine evaluation of the equivalence-based shielded resonance integral in highly complex lattices of slab, cylindrical, or spherical cells. (author) 1 fig., 2 tabs., 10 refs
-
Predicting Nanocrystal Shape through Consideration of Surface-Ligand Interactions
Bealing, Clive R.
2012-03-27
Density functional calculations for the binding energy of oleic acid-based ligands on Pb-rich {100} and {111} facets of PbSe nanocrystals determine the surface energies as a function of ligand coverage. Oleic acid is expected to bind to the nanocrystal surface in the form of lead oleate. The Wulff construction predicts the thermodynamic equilibrium shape of the PbSe nanocrystals. The equilibrium shape is a function of the ligand surface coverage, which can be controlled by changing the concentration of oleic acid during synthesis. The different binding energy of the ligand on the {100} and {111} facets results in different equilibrium ligand coverages on the facets, and a transition in the equilibrium shape from octahedral to cubic is predicted when increasing the ligand concentration during synthesis. © 2012 American Chemical Society.
-
Kink modes and surface currents associated with vertical displacement events
Manickam, Janardhan; Boozer, Allen; Gerhardt, Stefan
2012-08-01
The fast termination phase of a vertical displacement event (VDE) in a tokamak is modeled as a sequence of shrinking equilibria, where the core current profile remains constant so that the safety-factor at the axis, qaxis, remains fixed and the qedge systematically decreases. At some point, the n = 1 kink mode is destabilized. Kink modes distort the magnetic field lines outside the plasma, and surface currents are required to nullify the normal component of the B-field at the plasma boundary and maintain equilibrium at finite pressure. If the plasma touches a conductor, the current can be transferred to the conductor, and may be measurable by the halo current monitors. This report describes a practical method to model the plasma as it evolves during a VDE, and determine the surface currents, needed to maintain equilibrium. The main results are that the onset conditions for the disruption are that the growth-rate of the n = 1 kink exceeds half the Alfven time and the associated surface current needed to maintain equilibrium exceeds one half of the core plasma current. This occurs when qedge drops below a low integer, usually 2. Application to NSTX provides favorable comparison with non-axisymmetric halo-current measurements. The model is also applied to ITER and shows that the 2/1 mode is projected to be the most likely cause of the final disruption.
-
The prediction of the hydrodynamic performance of tidal current turbines
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Xiao, B Y; Zhou, L J; Xiao, Y X; Wang, Z W
2013-01-01
Nowadays tidal current energy is considered to be one of the most promising alternative green energy resources and tidal current turbines are used for power generation. Prediction of the open water performance around tidal turbines is important for the reason that it can give some advice on installation and array of tidal current turbines. This paper presents numerical computations of tidal current turbines by using a numerical model which is constructed to simulate an isolated turbine. This paper aims at studying the installation of marine current turbine of which the hydro-environmental impacts influence by means of numerical simulation. Such impacts include free-stream velocity magnitude, seabed and inflow direction of velocity. The results of the open water performance prediction show that the power output and efficiency of marine current turbine varies from different marine environments. The velocity distribution should be clearly and the suitable unit installation depth and direction be clearly chosen, which can ensure the most effective strategy for energy capture before installing the marine current turbine. The findings of this paper are expected to be beneficial in developing tidal current turbines and array in the future
-
High performance predictive current control of a three phase VSI: An ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
... current control of a three phase VSI: An experimental assessment ... Voltage source inverter; two level inverter; predictive current control; weighting factor ... Conventionally, for reference current tracking control in a two level VSI, the objective ...
-
An Information Retrieval Approach for Robust Prediction of Road Surface States.
Park, Jae-Hyung; Kim, Kwanho
2017-01-28
Recently, due to the increasing importance of reducing severe vehicle accidents on roads (especially on highways), the automatic identification of road surface conditions, and the provisioning of such information to drivers in advance, have recently been gaining significant momentum as a proactive solution to decrease the number of vehicle accidents. In this paper, we firstly propose an information retrieval approach that aims to identify road surface states by combining conventional machine-learning techniques and moving average methods. Specifically, when signal information is received from a radar system, our approach attempts to estimate the current state of the road surface based on the similar instances observed previously based on utilizing a given similarity function. Next, the estimated state is then calibrated by using the recently estimated states to yield both effective and robust prediction results. To validate the performances of the proposed approach, we established a real-world experimental setting on a section of actual highway in South Korea and conducted a comparison with the conventional approaches in terms of accuracy. The experimental results show that the proposed approach successfully outperforms the previously developed methods.
-
New horizons in predictive toxicology: current status and application
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Wilson, A. G. E
2012-01-01
"In this comprehensive discussion of predictive toxicology and its applications, leading experts express their views on the technologies currently available and the potential for future developments...
-
Electric fields associated with transient surface currents
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
McAllister, Iain Wilson
1992-01-01
The boundary condition to be fulfilled by the potential functions associated with a transient surface current is derived and expressed in terms of generalized orthogonal coordinates. From the analysis, it can be deduced that the use of the method of separation of variables is restricted to three ...
-
Seasonal prediction of the Leeuwin Current using the POAMA dynamical seasonal forecast model
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hendon, Harry H.; Wang, Guomin [Centre for Australian Weather and Climate Research, Bureau of Meteorology, PO Box 1289, Melbourne (Australia)
2010-06-15
The potential for predicting interannual variations of the Leeuwin Current along the west coast of Australia is addressed. The Leeuwin Current flows poleward against the prevailing winds and transports warm-fresh tropical water southward along the coast, which has a great impact on local climate and ecosystems. Variations of the current are tightly tied to El Nino/La Nina (weak during El Nino and strong during La Nina). Skilful seasonal prediction of the Leeuwin Current to 9-month lead time is achieved by empirical downscaling of dynamical coupled model forecasts of El Nino and the associated upper ocean heat content anomalies off the north west coast of Australia from the Australian Bureau of Meteorology Predictive Ocean Atmosphere Model for Australia (POAMA) seasonal forecast system. Prediction of the Leeuwin Current is possible because the heat content fluctuations off the north west coast are the primary driver of interannual annual variations of the current and these heat content variations are tightly tied to the occurrence of El Nino/La Nina. POAMA can skilfully predict both the occurrence of El Nino/La Nina and the subsequent transmission of the heat content anomalies from the Pacific onto the north west coast. (orig.)
-
Observations of Near-Surface Current Shear Help Describe Oceanic Oil and Plastic Transport
Laxague, Nathan J. M.; Ö-zgökmen, Tamay M.; Haus, Brian K.; Novelli, Guillaume; Shcherbina, Andrey; Sutherland, Peter; Guigand, Cédric M.; Lund, Björn; Mehta, Sanchit; Alday, Matias; Molemaker, Jeroen
2018-01-01
Plastics and spilled oil pose a critical threat to marine life and human health. As a result of wind forcing and wave motions, theoretical and laboratory studies predict very strong velocity variation with depth over the upper few centimeters of the water column, an observational blind spot in the real ocean. Here we present the first-ever ocean measurements of the current vector profile defined to within 1 cm of the free surface. In our illustrative example, the current magnitude averaged over the upper 1 cm of the ocean is shown to be nearly four times the average over the upper 10 m, even for mild forcing. Our findings indicate that this shear will rapidly separate pieces of marine debris which vary in size or buoyancy, making consideration of these dynamics essential to an improved understanding of the pathways along which marine plastics and oil are transported.
-
Binding Ligand Prediction for Proteins Using Partial Matching of Local Surface Patches
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lee Sael
2010-12-01
Full Text Available Functional elucidation of uncharacterized protein structures is an important task in bioinformatics. We report our new approach for structure-based function prediction which captures local surface features of ligand binding pockets. Function of proteins, specifically, binding ligands of proteins, can be predicted by finding similar local surface regions of known proteins. To enable partial comparison of binding sites in proteins, a weighted bipartite matching algorithm is used to match pairs of surface patches. The surface patches are encoded with the 3D Zernike descriptors. Unlike the existing methods which compare global characteristics of the protein fold or the global pocket shape, the local surface patch method can find functional similarity between non-homologous proteins and binding pockets for flexible ligand molecules. The proposed method improves prediction results over global pocket shape-based method which was previously developed by our group.
-
Binding ligand prediction for proteins using partial matching of local surface patches.
Sael, Lee; Kihara, Daisuke
2010-01-01
Functional elucidation of uncharacterized protein structures is an important task in bioinformatics. We report our new approach for structure-based function prediction which captures local surface features of ligand binding pockets. Function of proteins, specifically, binding ligands of proteins, can be predicted by finding similar local surface regions of known proteins. To enable partial comparison of binding sites in proteins, a weighted bipartite matching algorithm is used to match pairs of surface patches. The surface patches are encoded with the 3D Zernike descriptors. Unlike the existing methods which compare global characteristics of the protein fold or the global pocket shape, the local surface patch method can find functional similarity between non-homologous proteins and binding pockets for flexible ligand molecules. The proposed method improves prediction results over global pocket shape-based method which was previously developed by our group.
-
Prediction of antigenic epitopes on protein surfaces by consensus scoring
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zhang Chi
2009-09-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background Prediction of antigenic epitopes on protein surfaces is important for vaccine design. Most existing epitope prediction methods focus on protein sequences to predict continuous epitopes linear in sequence. Only a few structure-based epitope prediction algorithms are available and they have not yet shown satisfying performance. Results We present a new antigen Epitope Prediction method, which uses ConsEnsus Scoring (EPCES from six different scoring functions - residue epitope propensity, conservation score, side-chain energy score, contact number, surface planarity score, and secondary structure composition. Applied to unbounded antigen structures from an independent test set, EPCES was able to predict antigenic eptitopes with 47.8% sensitivity, 69.5% specificity and an AUC value of 0.632. The performance of the method is statistically similar to other published methods. The AUC value of EPCES is slightly higher compared to the best results of existing algorithms by about 0.034. Conclusion Our work shows consensus scoring of multiple features has a better performance than any single term. The successful prediction is also due to the new score of residue epitope propensity based on atomic solvent accessibility.
-
Welling, D. T.; Manchester, W.; Savani, N.; Sokolov, I.; van der Holst, B.; Jin, M.; Toth, G.; Liemohn, M. W.; Gombosi, T. I.
2017-12-01
The future of space weather prediction depends on the community's ability to predict L1 values from observations of the solar atmosphere, which can yield hours of lead time. While both empirical and physics-based L1 forecast methods exist, it is not yet known if this nascent capability can translate to skilled dB/dt forecasts at the Earth's surface. This paper shows results for the first forecast-quality, solar-atmosphere-to-Earth's-surface dB/dt predictions. Two methods are used to predict solar wind and IMF conditions at L1 for several real-world coronal mass ejection events. The first method is an empirical and observationally based system to estimate the plasma characteristics. The magnetic field predictions are based on the Bz4Cast system which assumes that the CME has a cylindrical flux rope geometry locally around Earth's trajectory. The remaining plasma parameters of density, temperature and velocity are estimated from white-light coronagraphs via a variety of triangulation methods and forward based modelling. The second is a first-principles-based approach that combines the Eruptive Event Generator using Gibson-Low configuration (EEGGL) model with the Alfven Wave Solar Model (AWSoM). EEGGL specifies parameters for the Gibson-Low flux rope such that it erupts, driving a CME in the coronal model that reproduces coronagraph observations and propagates to 1AU. The resulting solar wind predictions are used to drive the operational Space Weather Modeling Framework (SWMF) for geospace. Following the configuration used by NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center, this setup couples the BATS-R-US global magnetohydromagnetic model to the Rice Convection Model (RCM) ring current model and a height-integrated ionosphere electrodynamics model. The long lead time predictions of dB/dt are compared to model results that are driven by L1 solar wind observations. Both are compared to real-world observations from surface magnetometers at a variety of geomagnetic latitudes
-
Prediction of surface tension of binary mixtures with the parachor method
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Němec Tomáš
2015-01-01
Full Text Available The parachor method for the estimation of the surface tension of binary mixtures is modified by considering temperature-dependent values of the parachor parameters. The temperature dependence is calculated by a least-squares fit of pure-solvent surface tension data to the binary parachor equation utilizing the Peng-Robinson equation of state for the calculation of equilibrium densities. A very good agreement between experimental binary surface tension data and the predictions of the modified parachor method are found for the case of the mixtures of carbon dioxide and butane, benzene, and cyclohexane, respectively. The surface tension is also predicted for three refrigerant mixtures, i.e. propane, isobutane, and chlorodifluoromethane, with carbon dioxide.
-
Surface CUrrents from a Diagnostic model (SCUD): Pacific
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — The SCUD data product is an estimate of upper-ocean velocities computed from a diagnostic model (Surface CUrrents from a Diagnostic model). This model makes daily...
-
Remote sensing of surface currents in the Fraser River plume with the SeaSonde HF radar
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hodgins, D.O.; Hardy, J.S.; Tinis, S.E.
1994-09-01
The SeaSonde 12.5-MHz radar system was deployed to measure surface currents in the Juan de Fuca Strait in July 1992. Reliable data were obtained from the two radars installed, and successful trials were conducted with the Infosat satellite link to transmit data from the remote site. Data recovery from the SeaSonde was generally good, with maximum ranges varying from 15 km to over 30 km. Sea echo return strength at both radars was correlated with wind, consistent with lower Bragg scattering at lower wind speeds. A simple surface current forecasting algorithm, based on decomposing the signal into tidal and residual bands, was examined. It was found that tides account for the greatest portion of currents in the study area, and could be forecasted out to 48 h with 1-2 d of input data. The nonpredictable, fluctuating part of the current signal was isolated and its statistics were calculated. The algorithm tests showed that the SeaSonde data can be used to measure and predict the slowly varying tidal and mean flow velocities, as well as the random part of the signal, both of which are important in oil spill modelling. Surface flow patterns and time-series data from the SeaSonde measurements, and from a three-dimensional hydrodynamic model, were compared from an oil spill modelling perspective. In general, surface flow patterns from the model were smoother than those observed. The differences were most noticeable in the cross-channel direction. The radar data indicate that a flow-dependent eddy viscosity formulation, with coefficients calibrated to reproduce the features observed with the radar, would improve agreement and yield a good model for data assimilation. 21 refs., 478 figs., 3 tabs
-
Surface Current Measurements In Terra Nova Bay By Hf Radar
Flocco, D.; Falco, P.; Wadhams, P.; Spezie, G.
We present the preliminary results of a field experiment carried out within frame- work of the CLIMA project of the Italian National Programme for Antarctic Research (PNRA) and in cooperation with the Scott Polar Research Institute of Cambridge. Dur- ing the second period (02/12/1999-23/01/2000) of the XV Italian expedition a coastal radar was used to characterize the current field in the area of Terra Nova Bay (TNB). One of the aims of the CLIMA (Climatic Long-term Interactions for the Mass balance in Antarctica) project is to determine the role of the polynya in the sea ice mass bal- ance, water structure and local climate. The OSCR-II experiment was planned in order to provide surface current measurements in the area of TNB polynya, one of the most important coastal polynya of the Ross Sea. OSCR (Ocean Surface Current Radar) is a shore based, remote sensing system designed to measure sea surface currents in coastal waters. Two radar sites (a master and a slave) provide with radial current mea- surements; data combined from both sites yield the total current vector. Unfortunately the master and slave stations did not work together throughout the whole period of the experiment. A description of the experiment and a discussion of the results, will be proposed.
-
Depletion region surface effects in electron beam induced current measurements
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Haney, Paul M.; Zhitenev, Nikolai B. [Center for Nanoscale Science and Technology, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland 20899 (United States); Yoon, Heayoung P. [Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah 84112 (United States); Gaury, Benoit [Center for Nanoscale Science and Technology, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland 20899 (United States); Maryland NanoCenter, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 20742 (United States)
2016-09-07
Electron beam induced current (EBIC) is a powerful characterization technique which offers the high spatial resolution needed to study polycrystalline solar cells. Current models of EBIC assume that excitations in the p-n junction depletion region result in perfect charge collection efficiency. However, we find that in CdTe and Si samples prepared by focused ion beam (FIB) milling, there is a reduced and nonuniform EBIC lineshape for excitations in the depletion region. Motivated by this, we present a model of the EBIC response for excitations in the depletion region which includes the effects of surface recombination from both charge-neutral and charged surfaces. For neutral surfaces, we present a simple analytical formula which describes the numerical data well, while the charged surface response depends qualitatively on the location of the surface Fermi level relative to the bulk Fermi level. We find that the experimental data on FIB-prepared Si solar cells are most consistent with a charged surface and discuss the implications for EBIC experiments on polycrystalline materials.
-
Towards predictive models for transitionally rough surfaces
Abderrahaman-Elena, Nabil; Garcia-Mayoral, Ricardo
2017-11-01
We analyze and model the previously presented decomposition for flow variables in DNS of turbulence over transitionally rough surfaces. The flow is decomposed into two contributions: one produced by the overlying turbulence, which has no footprint of the surface texture, and one induced by the roughness, which is essentially the time-averaged flow around the surface obstacles, but modulated in amplitude by the first component. The roughness-induced component closely resembles the laminar steady flow around the roughness elements at the same non-dimensional roughness size. For small - yet transitionally rough - textures, the roughness-free component is essentially the same as over a smooth wall. Based on these findings, we propose predictive models for the onset of the transitionally rough regime. Project supported by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
-
Predictive model for convective flows induced by surface reactivity contrast
Davidson, Scott M.; Lammertink, Rob G. H.; Mani, Ali
2018-05-01
Concentration gradients in a fluid adjacent to a reactive surface due to contrast in surface reactivity generate convective flows. These flows result from contributions by electro- and diffusio-osmotic phenomena. In this study, we have analyzed reactive patterns that release and consume protons, analogous to bimetallic catalytic conversion of peroxide. Similar systems have typically been studied using either scaling analysis to predict trends or costly numerical simulation. Here, we present a simple analytical model, bridging the gap in quantitative understanding between scaling relations and simulations, to predict the induced potentials and consequent velocities in such systems without the use of any fitting parameters. Our model is tested against direct numerical solutions to the coupled Poisson, Nernst-Planck, and Stokes equations. Predicted slip velocities from the model and simulations agree to within a factor of ≈2 over a multiple order-of-magnitude change in the input parameters. Our analysis can be used to predict enhancement of mass transport and the resulting impact on overall catalytic conversion, and is also applicable to predicting the speed of catalytic nanomotors.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Endal, A.S.; Sofia, S.
1979-01-01
Predicted surface rotation velocities are presented for Population I stars at 10, 7, 5, 3, and 1.5M/sub sun/. The surface velocities have been computed for three different cases of angular momentum redistribution: no radial redistribution (rotation on decoupled shells), complete redistribution (rigid-body rotation), and partial redistribution as predicted by detailed consideration of circulation currents in rotation stars. The velocities for these cases are compared to each other and to observed stellar rotation rates (upsilon sin i).Near the main sequence, rotational effects can substantially reduce the moment of inertia of a star, so nonrotating models consistently underestimate the expected velocities for evolving stars. The magnitude of these effects is sufficient to explain the large numbers of Be stars and, perhaps, to explain the bimodal distribution of velocities observed for the O stars.On the red giant branch, angular momentum redistribution reduces the surface velocity by a factor of 2 or more, relative to the velocity expected for no radial redistribution. This removes the discrepancy between predicted and observed rotation rates for the K giants and makes it unlikely that these stars lose significant amounts of angular momentum by stellar winds. Our calculations indicate that improved observations (by the Fourier-transform technique) of the red giants in the Hyades cluster can be used to determine how angular momentum is redistributed by convection
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ono, K [Mie Univ., Mie (Japan). Faculty of Biological and Resources
1991-12-01
In case a landslide occurs on a slope, grasping the area of influence (location and shape of the slip surface) is required to take a countermeasure against landslides. This paper describes a method developed by the author for predicting a slip surface by utilizing fuzzy theory. The method predicts a slip surface from observations on ground surface displacement vectors, and the validity of the method has been verified through slip experiments conducted on slopes with a centrifugal model experiment device. The developed method for predicting the location of a slip surface well matches the experiment results, indicating the validity of the method. It has been found that the difference between the predicted and observed locations of a slip surface mainly is due to the error of the prediction in the starting and ending locations of the slip surface. It is also pointed out that, in order to improve the prediction of the shape of a slip surface, the observation density must be increased at the location where the shape of the slip surface strongly varies, since the direction of the slip surface is determined by the direction of the ground surface displacement vectors. 4 refs., 7 figs.
-
Ka-band Doppler Scatterometer for Measurements of Ocean Vector Winds and Surface Currents
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — Ocean surface currents impact heat transport, surface momentum and gas fluxes, ocean productivity and marine biological communities. Ocean currents also have social...
-
Observation and modeling of tide- and wind-induced surface currents in Galway Bay
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lei REN
2015-10-01
Full Text Available A high-frequency radar system has been deployed in Galway Bay, a semi-enclosed bay on the west coast of Ireland. The system provides surface currents with fine spatial resolution every hour. Prior to its use for model validation, the accuracy of the radar data was verified through comparison with measurements from acoustic Doppler current profilers (ADCPs and a good correlation between time series of surface current speeds and directions obtained from radar data and ADCP data. Since Galway Bay is located on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, it is subject to relatively windy conditions, and surface currents are therefore strongly wind-driven. With a view to assimilating the radar data for forecasting purposes, a three-dimensional numerical model of Galway Bay, the Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code (EFDC, was developed based on a terrain-following vertical (sigma coordinate system. This study shows that the performance and accuracy of the numerical model, particularly with regard to tide- and wind-induced surface currents, are sensitive to the vertical layer structure. Results of five models using different layer structures are presented and compared with radar measurements. A variable vertical structure with thin layers at the bottom and the surface and thicker layers in the middle of the water column was found to be the optimal layer structure for reproduction of tide- and wind-induced surface currents. This structure ensures that wind shear can properly propagate from the surface layer to the sub-surface layers, thereby ensuring that wind forcing is not overdamped by tidal forcing. The vertical layer structure affects not only the velocities at the surface layer but also the velocities further down in the water column.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Thangam Chinnadurai
2016-12-01
Full Text Available This study focuses on investigating the effects of process parameters, namely, Peak current (Ip, Pulse on time (Ton, Pulse off time (Toff, Water pressure (Wp, Wire feed rate (Wf, Wire tension (Wt, Servo voltage (Sv and Servo feed setting (Sfs, on the Material Removal Rate (MRR and Surface Roughness (SR for Wire electrical discharge machining (Wire-EDM of nickel using Taguchi method. Response Surface Methodology (RSM is adopted to evolve mathematical relationships between the wire cutting process parameters and the output variables of the weld joint to determine the welding input parameters that lead to the desired optimal wire cutting quality. Besides, using response surface plots, the interaction effects of process parameters on the responses are analyzed and discussed. The statistical software Mini-tab is used to establish the design and to obtain the regression equations. The developed mathematical models are tested by analysis-of-variance (ANOVA method to check their appropriateness and suitability. Finally, a comparison is made between measured and calculated results, which are in good agreement. This indicates that the developed models can predict the responses accurately and precisely within the limits of cutting parameter being used.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chinnadurai, T.; Vendan, S.A.
2016-01-01
This study focuses on investigating the effects of process parameters, namely, Peak current (Ip), Pulse on time (Ton), Pulse off time (Toff), Water pressure (Wp), Wire feed rate (Wf), Wire tension (Wt), Servo voltage (Sv) and Servo feed setting (Sfs), on the Material Removal Rate (MRR) and Surface Roughness (SR) for Wire electrical discharge machining (Wire-EDM) of nickel using Taguchi method. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) is adopted to evolve mathematical relationships between the wire cutting process parameters and the output variables of the weld joint to determine the welding input parameters that lead to the desired optimal wire cutting quality. Besides, using response surface plots, the interaction effects of process parameters on the responses are analyzed and discussed. The statistical software Mini-tab is used to establish the design and to obtain the regression equations. The developed mathematical models are tested by analysis-of-variance (ANOVA) method to check their appropriateness and suitability. Finally, a comparison is made between measured and calculated results, which are in good agreement. This indicates that the developed models can predict the responses accurately and precisely within the limits of cutting parameter being used. (Author)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Chinnadurai, T.; Vendan, S.A.
2016-07-01
This study focuses on investigating the effects of process parameters, namely, Peak current (Ip), Pulse on time (Ton), Pulse off time (Toff), Water pressure (Wp), Wire feed rate (Wf), Wire tension (Wt), Servo voltage (Sv) and Servo feed setting (Sfs), on the Material Removal Rate (MRR) and Surface Roughness (SR) for Wire electrical discharge machining (Wire-EDM) of nickel using Taguchi method. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) is adopted to evolve mathematical relationships between the wire cutting process parameters and the output variables of the weld joint to determine the welding input parameters that lead to the desired optimal wire cutting quality. Besides, using response surface plots, the interaction effects of process parameters on the responses are analyzed and discussed. The statistical software Mini-tab is used to establish the design and to obtain the regression equations. The developed mathematical models are tested by analysis-of-variance (ANOVA) method to check their appropriateness and suitability. Finally, a comparison is made between measured and calculated results, which are in good agreement. This indicates that the developed models can predict the responses accurately and precisely within the limits of cutting parameter being used. (Author)
-
Predicting supramolecular self-assembly on reconstructed metal surfaces
Roussel, Thomas J.; Barrena, Esther; Ocal, Carmen; Faraudo, Jordi
2014-06-01
The prediction of supramolecular self-assembly onto solid surfaces is still challenging in many situations of interest for nanoscience. In particular, no previous simulation approach has been capable to simulate large self-assembly patterns of organic molecules over reconstructed surfaces (which have periodicities over large distances) due to the large number of surface atoms and adsorbing molecules involved. Using a novel simulation technique, we report here large scale simulations of the self-assembly patterns of an organic molecule (DIP) over different reconstructions of the Au(111) surface. We show that on particular reconstructions, the molecule-molecule interactions are enhanced in a way that long-range order is promoted. Also, the presence of a distortion in a reconstructed surface pattern not only induces the presence of long-range order but also is able to drive the organization of DIP into two coexisting homochiral domains, in quantitative agreement with STM experiments. On the other hand, only short range order is obtained in other reconstructions of the Au(111) surface. The simulation strategy opens interesting perspectives to tune the supramolecular structure by simulation design and surface engineering if choosing the right molecular building blocks and stabilising the chosen reconstruction pattern.The prediction of supramolecular self-assembly onto solid surfaces is still challenging in many situations of interest for nanoscience. In particular, no previous simulation approach has been capable to simulate large self-assembly patterns of organic molecules over reconstructed surfaces (which have periodicities over large distances) due to the large number of surface atoms and adsorbing molecules involved. Using a novel simulation technique, we report here large scale simulations of the self-assembly patterns of an organic molecule (DIP) over different reconstructions of the Au(111) surface. We show that on particular reconstructions, the molecule
-
Prediction of reservoir compaction and surface subsidence
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
De Waal, J.A.; Smits, R.M.M.
1988-06-01
A new loading-rate-dependent compaction model for unconsolidated clastic reservoirs is presented that considerably improves the accuracy of predicting reservoir rock compaction and surface subsidence resulting from pressure depletion in oil and gas fields. The model has been developed on the basis of extensive laboratory studies and can be derived from a theory relating compaction to time-dependent intergranular friction. The procedure for calculating reservoir compaction from laboratory measurements with the new model is outlined. Both field and laboratory compaction behaviors appear to be described by one single normalized, nonlinear compaction curve. With the new model, the large discrepancies usually observed between predictions based on linear compaction models and actual (nonlinear) field behavior can be explained.
-
Surface conductivity of Mercury provides current closure and may affect magnetospheric symmetry
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Janhunen
2004-04-01
Full Text Available We study what effect a possible surface conductivity of Mercury has on the closure of magnetospheric currents by making six runs with a quasi-neutral hybrid simulation. The runs are otherwise identical but use different synthetic conductivity models: run 1 has a fully conducting planet, run 2 has a poorly conducting planet ( m and runs 3-6 have one of the hemispheres either in the dawn-dusk or day-night directions, conducting well, the other one being conducting poorly. Although the surface conductivity is not known from observations, educated guesses easily give such conductivity values that magnetospheric currents may close partly within the planet, and as the conductivity depends heavily on the mineral composition of the surface, the possibility of significant horizontal variations cannot be easily excluded. The simulation results show that strong horizontal variations may produce modest magnetospheric asymmetries. Beyond the hybrid simulation, we also briefly discuss the possibility that in the nightside there may be a lack of surface electrons to carry downward current, which may act as a further source of surface-related magnetospheric asymmetry. Key words. Magnetospheric physics (planetary magnetospheres; current systems; solar wind-magnetosphere interactions.6
-
On the predictability of land surface fluxes from meteorological variables
Haughton, Ned; Abramowitz, Gab; Pitman, Andy J.
2018-01-01
Previous research has shown that land surface models (LSMs) are performing poorly when compared with relatively simple empirical models over a wide range of metrics and environments. Atmospheric driving data appear to provide information about land surface fluxes that LSMs are not fully utilising. Here, we further quantify the information available in the meteorological forcing data that are used by LSMs for predicting land surface fluxes, by interrogating FLUXNET data, and extending the benchmarking methodology used in previous experiments. We show that substantial performance improvement is possible for empirical models using meteorological data alone, with no explicit vegetation or soil properties, thus setting lower bounds on a priori expectations on LSM performance. The process also identifies key meteorological variables that provide predictive power. We provide an ensemble of empirical benchmarks that are simple to reproduce and provide a range of behaviours and predictive performance, acting as a baseline benchmark set for future studies. We reanalyse previously published LSM simulations and show that there is more diversity between LSMs than previously indicated, although it remains unclear why LSMs are broadly performing so much worse than simple empirical models.
-
Prediction of water droplet evaporation on zircaloy surface
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lee, Chi Young; In, Wang Kee
2014-01-01
In the present experimental study, the prediction of water droplet evaporation on a zircaloy surface was investigated using various initial droplet sizes. To the best of our knowledge, this may be the first valuable effort for understanding the details of water droplet evaporation on a zircaloy surface. The initial contact diameters of the water droplets tested ranged from 1.76 to 3.41 mm. The behavior (i.e., time-dependent droplet volume, contact angle, droplet height, and contact diameter) and mode-transition time of the water droplet evaporation were strongly influenced by the initial droplet size. Using the normalized contact angle (θ*) and contact diameter (d*), the transitions between evaporation modes were successfully expressed by a single curve, and their criteria were proposed. To predict the temporal droplet volume change and evaporation rate, the range of θ* > 0.25 and d* > 0.9, which mostly covered the whole evaporation period and the initial contact diameter remained almost constant during evaporation, was targeted. In this range, the previous contact angle functions for the evaporation model underpredicted the experimental data. A new contact angle function of a zircaloy surface was empirically proposed, which represented the present experimental data within a reasonable degree of accuracy. (author)
-
Wang, Chunbai; Mitra, Ambar K.
2016-01-01
Any boundary surface evolving in viscous fluid is driven with surface capillary currents. By step function defined for the fluid-structure interface, surface currents are found near a flat wall in a logarithmic form. The general flat-plate boundary layer is demonstrated through the interface kinematics. The dynamics analysis elucidates the relationship of the surface currents with the adhering region as well as the no-slip boundary condition. The wall skin friction coefficient, displacement thickness, and the logarithmic velocity-defect law of the smooth flat-plate boundary-layer flow are derived with the advent of the forced evolving boundary method. This fundamental theory has wide applications in applied science and engineering.
-
LIGSITEcsc: predicting ligand binding sites using the Connolly surface and degree of conservation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Schroeder Michael
2006-09-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background Identifying pockets on protein surfaces is of great importance for many structure-based drug design applications and protein-ligand docking algorithms. Over the last ten years, many geometric methods for the prediction of ligand-binding sites have been developed. Results We present LIGSITEcsc, an extension and implementation of the LIGSITE algorithm. LIGSITEcsc is based on the notion of surface-solvent-surface events and the degree of conservation of the involved surface residues. We compare our algorithm to four other approaches, LIGSITE, CAST, PASS, and SURFNET, and evaluate all on a dataset of 48 unbound/bound structures and 210 bound-structures. LIGSITEcsc performs slightly better than the other tools and achieves a success rate of 71% and 75%, respectively. Conclusion The use of the Connolly surface leads to slight improvements, the prediction re-ranking by conservation to significant improvements of the binding site predictions. A web server for LIGSITEcsc and its source code is available at scoppi.biotec.tu-dresden.de/pocket.
-
Historical Trust Levels Predict Current Welfare State Design
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Bergh, Andreas; Bjørnskov, Christian
Using cross-sectional data for 76 countries, we apply instrumental variable techniques based on pronoun drop, temperature and monarchies to demonstrate that historical trust levels predict several indicators of current welfare state design, including universalism and high levels of regulatory...... freedom. We argue that high levels of trust and trustworthiness are necessary, but not sufficient, conditions for societies to develop successful universal welfare states that would otherwise be highly vulnerable to free riding and fraudulent behavior. Our results do not exclude positive feedback from...... welfare state universalism to individual trust, although we claim that the important causal link runs from historically trust levels to current welfare state design....
-
Study of surface leakage current of AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistors
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen, YongHe; Zhang, Kai; Cao, MengYi; Zhao, ShengLei; Zhang, JinCheng; Hao, Yue; Ma, XiaoHua
2014-01-01
Temperature-dependent surface current measurements were performed to analyze the mechanism of surface conductance of AlGaN/GaN channel high-electron-mobility transistors by utilizing process-optimized double gate structures. Different temperatures and electric field dependence have been found in surface current measurements. At low electric field, the mechanism of surface conductance is considered to be two-dimensional variable range hopping. At elevated electric field, the Frenkel–Poole trap assisted emission governs the main surface electrons transportation. The extracted energy barrier height of electrons emitting from trapped state near Fermi energy level into a threading dislocations-related continuum state is 0.38 eV. SiN passivation reduces the surface leakage current by two order of magnitude and nearly 4 orders of magnitude at low and high electric fields, respectively. SiN also suppresses the Frenkel–Poole conductance at high temperature by improving the surface states of AlGaN/GaN. A surface treatment process has been introduced to further suppress the surface leakage current at high temperature and high field, which results in a decrease in surface current of almost 3 orders of magnitude at 476 K
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Razak, N H; Rahman, M M; Kadirgama, K
2012-01-01
This paper presents to develop of the response surface design model to predict the surface roughness for end-milling operation of Hastelloy C-2000 using uncoated carbide insert. Mathematical model is developed to study the effect of three input cutting parameters includes the feed rate, axial depth of cut and cutting speed. Design of experiments (DOE) was implemented with the aid of the statistical software package. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) has been performed to verify the fit and adequacy of the developed mathematical model. The result shows that the feed rate gave the more effect on the both prediction values of Ra compared to the cutting speed and axial depth of cut. SEM and EDX analyses were performed in different cutting conditions. It can be concluded that the feed rate and cutting force give the higher impact to influence the machining characteristics of surface roughness. Thus, the optimizing the cutting conditions are essential in order to improve the surface roughness in machining of Hastlelloy C-2000.
-
Prediction of incipient flow boiling from a uniformly heated surface
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yin, S.T.; Abdelmessih, A.H.
1977-01-01
This study was undertaken to investigate the phenomenon of liquid superheat during incipient boiling in a uniformly heated forced convection channel. Experimental data were obtained using Freon 11 as the test medium. Based on existing theories, an analytical method was developed for predicting the point of termination of nucleate boiling, observed during a decreasing heat flux process with a nucleation activated surface. The method may also be used to predict the point of boiling incipience, observed during an increasing heat flux process with a non-activated surface; this point does not appear to have been treated analytically in previous work. It can be shown that some of the existing models are special cases of the present formulation
-
Shear flow generation and transport barrier formation on rational surface current sheets in tokamaks
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wang Xiaogang; Xiao Chijie; Wang Jiaqi
2009-01-01
Full text: A thin current sheet with a magnetic field component in the same direction can form the electrical field perpendicularly pointing to the sheet, therefore an ExB flow with a strong shear across the current sheet. An electrical potential well is also found on the rational surface of RFP as well as the neutral sheet of the magnetotail with the E-field pointing to the rational (neutral) surface. Theoretically, a current singularity is found to be formed on the rational surface in ideal MHD. It is then very likely that the sheet current on the rational surfaces will generate the electrical potential well in its vicinity so the electrical field pointing to the sheet. It results in an ExB flow with a strong shear in the immediate neighborhood of the rational surface. It may be the cause of the transport barrier often seen near the low (m, n) rational surfaces with MHD signals. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Balasubramanian, M.; Jayabalan, V.; Balasubramanian, V.
2008-01-01
Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) alloy has gathered wide acceptance in the fabrication of light weight structures requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio, such as transportable bridge girders, military vehicles, road tankers and railway transport systems. The preferred welding process of titanium alloy is frequently gas tungsten arc (GTA) welding due to its comparatively easier applicability and better economy. In the case of single pass GTA welding of thinner section of this alloy, the pulsed current has been found beneficial due to its advantages over the conventional continuous current process. Many considerations come into the picture and one need to carefully balance various pulse current parameters to arrive at an optimum combination. Hence, in this investigation an attempt has been made to develop mathematical models to predict tensile properties of pulsed current GTA welded titanium alloy weldments. Four factors, five level, central composite, rotatable design matrix is used to optimise the required number of experiments. The mathematical models have been developed by response surface method (RSM). The adequacy of the models has been checked by ANOVA technique. By using the developed mathematical models, the tensile properties of the joints can be predicted with 99% confidence level
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Balasubramanian, M. [Department of Production Engineering, Sathyabama University, Old Mamallapuram Road, Chennai 600 119 (India)], E-mail: manianmb@rediffmail.com; Jayabalan, V. [Department of Manufacturing Engineering, Anna University, Guindy, Chennai 600 025 (India)], E-mail: jbalan@annauniv.edu; Balasubramanian, V. [Department of Manufacturing Engineering, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar 608 002 (India)], E-mail: visvabalu@yahoo.com
2008-07-01
Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) alloy has gathered wide acceptance in the fabrication of light weight structures requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio, such as transportable bridge girders, military vehicles, road tankers and railway transport systems. The preferred welding process of titanium alloy is frequently gas tungsten arc (GTA) welding due to its comparatively easier applicability and better economy. In the case of single pass GTA welding of thinner section of this alloy, the pulsed current has been found beneficial due to its advantages over the conventional continuous current process. Many considerations come into the picture and one need to carefully balance various pulse current parameters to arrive at an optimum combination. Hence, in this investigation an attempt has been made to develop mathematical models to predict tensile properties of pulsed current GTA welded titanium alloy weldments. Four factors, five level, central composite, rotatable design matrix is used to optimise the required number of experiments. The mathematical models have been developed by response surface method (RSM). The adequacy of the models has been checked by ANOVA technique. By using the developed mathematical models, the tensile properties of the joints can be predicted with 99% confidence level.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kilic, Tomislav; Milun, Stanko; Petrovic, Goran [FESB University of Split, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Machine Engineering and Naval Architecture, R. Boskovica bb, 21000, Split (Croatia)
2007-02-15
The shunt active power filters are used to attenuate the harmonic currents in power systems by injecting equal but opposite compensating currents. Successful control of the active filters requires an accurate current reference. In this paper the current reference determination based on predictive filtering structure is presented. Current reference was obtained by taking the difference of load current and its fundamental harmonic. For fundamental harmonic determination with no time delay a combination of digital predictive filter and low pass filter is used. The proposed method was implemented on a laboratory prototype of a three-phase active power filter. The algorithm for current reference determination was adapted and implemented on DSP controller. Simulation and experimental results show that the active power filter with implemented predictive filtering structure gives satisfactory performance in power system harmonic attenuation. (author)
-
Heuzé, Céline; Eriksson, Leif; Carvajal, Gisela
2017-04-01
Using sea surface temperature from satellite images to retrieve sea surface currents is not a new idea, but so far its operational near-real time implementation has not been possible. Validation studies are too region-specific or uncertain, due to the errors induced by the images themselves. Moreover, the sensitivity of the most common retrieval method, the maximum cross correlation, to the three parameters that have to be set is unknown. Using model outputs instead of satellite images, biases induced by this method are assessed here, for four different seas of Western Europe, and the best of nine settings and eight temporal resolutions are determined. For all regions, tracking a small 5 km pattern from the first image over a large 30 km region around its original location on a second image, separated from the first image by 6 to 9 hours returned the most accurate results. Moreover, for all regions, the problem is not inaccurate results but missing results, where the velocity is too low to be picked by the retrieval. The results are consistent both with limitations caused by ocean surface current dynamics and with the available satellite technology, indicating that automated sea surface current retrieval from sea surface temperature images is feasible now, for search and rescue operations, pollution confinement or even for more energy efficient and comfortable ship navigation.
-
Observation and modeling of tide- and wind-induced surface currents in Galway Bay
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lei Ren
2015-10-01
Full Text Available A high-frequency radar system has been deployed in Galway Bay, a semi-enclosed bay on the west coast of Ireland. The system provides surface currents with fine spatial resolution every hour. Prior to its use for model validation, the accuracy of the radar data was verified through comparison with measurements from acoustic Doppler current profilers (ADCPs and a good correlation between time series of surface current speeds and directions obtained from radar data and ADCP data. Since Galway Bay is located on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, it is subject to relatively windy conditions, and surface currents are therefore strongly wind-driven. With a view to assimilating the radar data for forecasting purposes, a three-dimensional numerical model of Galway Bay, the Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code (EFDC, was developed based on a terrain-following vertical (sigma coordinate system. This study shows that the performance and accuracy of the numerical model, particularly with regard to tide- and wind-induced surface currents, are sensitive to the vertical layer structure. Results of five models with different layer structures are presented and compared with radar measurements. A variable vertical structure with thin layers at the bottom and the surface and thicker layers in the middle of the water column was found to be the optimal layer structure for reproduction of tide- and wind-induced surface currents. This structure ensures that wind shear can properly propagate from the surface layer to the sub-surface layers, thereby ensuring that wind forcing is not overdamped by tidal forcing. The vertical layer structure affects not only the velocities at the surface layer but also the velocities further down in the water column.
-
Surface Complexation Modeling in Variable Charge Soils: Prediction of Cadmium Adsorption
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Giuliano Marchi
2015-10-01
Full Text Available ABSTRACT Intrinsic equilibrium constants for 22 representative Brazilian Oxisols were estimated from a cadmium adsorption experiment. Equilibrium constants were fitted to two surface complexation models: diffuse layer and constant capacitance. Intrinsic equilibrium constants were optimized by FITEQL and by hand calculation using Visual MINTEQ in sweep mode, and Excel spreadsheets. Data from both models were incorporated into Visual MINTEQ. Constants estimated by FITEQL and incorporated in Visual MINTEQ software failed to predict observed data accurately. However, FITEQL raw output data rendered good results when predicted values were directly compared with observed values, instead of incorporating the estimated constants into Visual MINTEQ. Intrinsic equilibrium constants optimized by hand calculation and incorporated in Visual MINTEQ reliably predicted Cd adsorption reactions on soil surfaces under changing environmental conditions.
-
Predicting the minimum liquid surface tension activity of pseudomonads expressing biosurfactants.
Mohammed, I U; Deeni, Y; Hapca, S M; McLaughlin, K; Spiers, A J
2015-01-01
Bacteria produce a variety of biosurfactants capable of significantly reducing liquid (aqueous) surface tension (γ) with a range of biological roles and biotechnological uses. To determine the lowest achievable surface tension (γMin ), we tested a diverse collection of Pseudomonas-like isolates from contaminated soil and activated sludge and identified those expressing biosurfactants by drop-collapse assay. Liquid surface tension-reducing ability was quantitatively determined by tensiometry, with 57 isolates found to significantly lower culture supernatant surface tensions to 24·5-49·1 mN m(-1) . Differences in biosurfactant behaviour determined by foaming, emulsion and oil-displacement assays were also observed amongst isolates producing surface tensions of 25-27 mN m(-1) , suggesting that a range of structurally diverse biosurfactants were being expressed. Individual distribution identification (IDI) analysis was used to identify the theoretical probability distribution that best fitted the surface tension data, which predicted a γMin of 24·24 mN m(-1) . This was in agreement with predictions based on earlier work of published mixed bacterial spp. data, suggesting a fundamental limit to the ability of bacterial biosurfactants to reduce surface tensions in aqueous systems. This implies a biological restriction on the synthesis and export of these agents or a physical-chemical restriction on their functioning once produced. Numerous surveys of biosurfactant-producing bacteria have been conducted, but only recently has an attempt been made to predict the minimum liquid surface tension these surface-active agents can achieve. Here, we determine a theoretical minimum of 24 mN m(-1) by statistical analysis of tensiometry data, suggesting a fundamental limit for biosurfactant activity in bacterial cultures incubated under standard growth conditions. This raises a challenge to our understanding of biosurfactant expression, secretion and function, as well as
-
InterProSurf: a web server for predicting interacting sites on protein surfaces
Negi, Surendra S.; Schein, Catherine H.; Oezguen, Numan; Power, Trevor D.; Braun, Werner
2009-01-01
Summary A new web server, InterProSurf, predicts interacting amino acid residues in proteins that are most likely to interact with other proteins, given the 3D structures of subunits of a protein complex. The prediction method is based on solvent accessible surface area of residues in the isolated subunits, a propensity scale for interface residues and a clustering algorithm to identify surface regions with residues of high interface propensities. Here we illustrate the application of InterProSurf to determine which areas of Bacillus anthracis toxins and measles virus hemagglutinin protein interact with their respective cell surface receptors. The computationally predicted regions overlap with those regions previously identified as interface regions by sequence analysis and mutagenesis experiments. PMID:17933856
-
Departure Queue Prediction for Strategic and Tactical Surface Scheduler Integration
Zelinski, Shannon; Windhorst, Robert
2016-01-01
A departure metering concept to be demonstrated at Charlotte Douglas International Airport (CLT) will integrate strategic and tactical surface scheduling components to enable the respective collaborative decision making and improved efficiency benefits these two methods of scheduling provide. This study analyzes the effect of tactical scheduling on strategic scheduler predictability. Strategic queue predictions and target gate pushback times to achieve a desired queue length are compared between fast time simulations of CLT surface operations with and without tactical scheduling. The use of variable departure rates as a strategic scheduler input was shown to substantially improve queue predictions over static departure rates. With target queue length calibration, the strategic scheduler can be tuned to produce average delays within one minute of the tactical scheduler. However, root mean square differences between strategic and tactical delays were between 12 and 15 minutes due to the different methods the strategic and tactical schedulers use to predict takeoff times and generate gate pushback clearances. This demonstrates how difficult it is for the strategic scheduler to predict tactical scheduler assigned gate delays on an individual flight basis as the tactical scheduler adjusts departure sequence to accommodate arrival interactions. Strategic/tactical scheduler compatibility may be improved by providing more arrival information to the strategic scheduler and stabilizing tactical scheduler changes to runway sequence in response to arrivals.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bouafia, Abdelouahab; Gaubert, Jean-Paul; Krim, Fateh
2010-01-01
This paper is concerned with the design and implementation of current control of three-phase PWM rectifier based on predictive control strategy. The proposed predictive current control technique operates with constant switching frequency, using space-vector modulation (SVM). The main goal of the designed current control scheme is to maintain the dc-bus voltage at the required level and to achieve the unity power factor (UPF) operation of the converter. For this purpose, two predictive current control algorithms, in the sense of deadbeat control, are developed for direct controlling input current vector of the converter in the stationary α-β and rotating d-q reference frame, respectively. For both predictive current control algorithms, at the beginning of each switching period, the required rectifier average voltage vector allowing the cancellation of both tracking errors of current vector components at the end of the switching period, is computed and applied during a predefined switching period by means of SVM. The main advantages of the proposed predictive current control are that no need to use hysteresis comparators or PI controllers in current control loops, and constant switching frequency. Finally, the developed predictive current control algorithms were tested both in simulations and experimentally, and illustrative results are presented here. Results have proven excellent performance in steady and transient states, and verify the validity of the proposed predictive current control which is compared to other control strategies.
-
Forced synchronization of large-scale circulation to increase predictability of surface states
Shen, Mao-Lin; Keenlyside, Noel; Selten, Frank; Wiegerinck, Wim; Duane, Gregory
2016-04-01
Numerical models are key tools in the projection of the future climate change. The lack of perfect initial condition and perfect knowledge of the laws of physics, as well as inherent chaotic behavior limit predictions. Conceptually, the atmospheric variables can be decomposed into a predictable component (signal) and an unpredictable component (noise). In ensemble prediction the anomaly of ensemble mean is regarded as the signal and the ensemble spread the noise. Naturally the prediction skill will be higher if the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is larger in the initial conditions. We run two ensemble experiments in order to explore a way to reduce the SNR of surface winds and temperature. One ensemble experiment is AGCM with prescribing sea surface temperature (SST); the other is AGCM with both prescribing SST and nudging the high-level temperature and winds to ERA-Interim. Each ensemble has 30 members. Larger SNR is expected and found over the tropical ocean in the first experiment because the tropical circulation is associated with the convection and the associated surface wind convergence as these are to a large extent driven by the SST. However, small SNR is found over high latitude ocean and land surface due to the chaotic and non-synchronized atmosphere states. In the second experiment the higher level temperature and winds are forced to be synchronized (nudged to reanalysis) and hence a larger SNR of surface winds and temperature is expected. Furthermore, different nudging coefficients are also tested in order to understand the limitation of both synchronization of large-scale circulation and the surface states. These experiments will be useful for the developing strategies to synchronize the 3-D states of atmospheric models that can be later used to build a super model.
-
Method of predicting surface deformation in the form of sinkholes
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Chudek, M.; Arkuszewski, J.
1980-06-01
Proposes a method for predicting probability of sinkhole shaped subsidence, number of funnel-shaped subsidences and size of individual funnels. The following factors which influence the sudden subsidence of the surface in the form of funnels are analyzed: geologic structure of the strata between mining workings and the surface, mining depth, time factor, and geologic disolocations. Sudden surface subsidence is observed only in the case of workings situated up to a few dozen meters from the surface. Using the proposed method is explained with some examples. It is suggested that the method produces correct results which can be used in coal mining and in ore mining. (1 ref.) (In Polish)
-
Disturbance estimator based predictive current control of grid-connected inverters
Al-Khafaji, Ahmed Samawi Ghthwan
2013-01-01
ABSTRACT: The work presented in my thesis considers one of the modern discrete-time control approaches based on digital signal processing methods, that have been developed to improve the performance control of grid-connected three-phase inverters. Disturbance estimator based predictive current control of grid-connected inverters is proposed. For inverter modeling with respect to the design of current controllers, we choose the d-q synchronous reference frame to make it easier to understand an...
-
Low Current Surface Flashover for Initiation of Electric Propulsion Devices
Dary, Omar G.
There has been a recent increase in interest in miniaturization of propulsion systems for satellites. These systems are needed to propel micro- and nano-satellites, where platforms are much smaller than conventional satellites and require smaller levels of thrust. Micro-propulsion systems for these satellites are in their infancy and they must manage with smaller power systems and smaller propellant volumes. Electric propulsion systems operating on various types of electric discharges are typically used for these needs. One of the central components of such electrical micropropulsion systems are ignitor subsystems, which are required for creation the breakdown and initiation of the main discharge. Ignitors have to provide reliable ignition for entire lifetime of the micropropulsion system. Electric breakdown in vacuum usually require high voltage potentials of hundreds of kilovolts per mm to induce breakdown. The breakdown voltage can be significantly decreased (down to several kVs per mm) if dielectric surface flashover is utilized. However, classical dielectric surface flashover operates at large electric current (100s of Amperes) and associated with overheating and damage of the electrodes/dielectric assembly after several flashover events. The central idea of this work was to eliminate the damage to the flashover electrode assembly by limiting the flashover currents to low values in milliampere range (Low Current Surface Flashover -LCSF) and utilize LCSF system as an ignition source for the main discharge on the micropropulsion system. The main objective of this research was to create a robust LCSF ignition system, capable producing a large number of surface flashover triggering events without significant damage to the LCSF electrode assembly. The thesis aims to characterize the plasma plume created at LCSF, study electrodes ablation and identify conditions required for robust triggering of main discharge utilized on micro-propulsion system. Conditioning of a
-
Robust Prediction of High Lift Using Surface Vorticity, Phase II
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — FlightStream has been developed a fast, accurate, aerodynamic prediction code based on vorticity computations on the surface of an aircraft. The code, though still a...
-
Sresht, Vishnu; Lewandowski, Eric P; Blankschtein, Daniel; Jusufi, Arben
2017-08-22
A molecular modeling approach is presented with a focus on quantitative predictions of the surface tension of aqueous surfactant solutions. The approach combines classical Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations with a molecular-thermodynamic theory (MTT) [ Y. J. Nikas, S. Puvvada, D. Blankschtein, Langmuir 1992 , 8 , 2680 ]. The MD component is used to calculate thermodynamic and molecular parameters that are needed in the MTT model to determine the surface tension isotherm. The MD/MTT approach provides the important link between the surfactant bulk concentration, the experimental control parameter, and the surfactant surface concentration, the MD control parameter. We demonstrate the capability of the MD/MTT modeling approach on nonionic alkyl polyethylene glycol surfactants at the air-water interface and observe reasonable agreement of the predicted surface tensions and the experimental surface tension data over a wide range of surfactant concentrations below the critical micelle concentration. Our modeling approach can be extended to ionic surfactants and their mixtures with both ionic and nonionic surfactants at liquid-liquid interfaces.
-
Applying machine learning to predict patient-specific current CD4 ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
Apple apple
This work shows the application of machine learning to predict current CD4 cell count of an HIV- .... Pre-processing ... remaining data elements of the PR and RT datasets. ... technique based on the structure of the human brain's neuron.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Saario, T.; Paine, J.P.N.
1995-01-01
The most widely used technique for NDE of steam generator tubing is eddy current. This technique can reliably detect cracks grown in sodium hydroxide environment only at depths greater than 50% through wall. However, cracking caused by thiosulphate solutions have been detected and sized at shallower depths. The disparity has been proposed to be caused by the different electric resistance of the crack wall surface films and corrosion products in the cracks formed in different environments. This work was undertaken to clarify the role of surface film electric resistance on the disparity found in eddy current detectability of surface cracks in alloy 600 tubes. The proposed model explaining the above mentioned disparity is the following. The detectability of tightly closed cracks by the eddy current technique depends on the electric resistance of the surface films of the crack walls. The nature and resistance of the films which form on the crack walls during operation depends on the composition of the solution inside the crack and close to the crack location. During cooling down of the steam generator, because of contraction and loss of internal pressurization, the cracks are rather tightly closed so that exchange of electrolyte and thus changes in the film properties become difficult. As a result, the surface condition prevailing at high temperature is preserved. If the environment is such that the films formed on the crack walls under operating conditions have low electric resistance, eddy current technique will fail to indicate these cracks or will underestimate the size of these cracks. However, if the electric resistance of the films is high, a tightly closed crack will resemble an open crack and will be easily indicated and correctly sized by eddy current technique
-
Surface characterization of current composites after toothbrush abrasion.
Takahashi, Rena; Jin, Jian; Nikaido, Toru; Tagami, Junji; Hickel, Reinhard; Kunzelmann, Karl-Heinz
2013-01-01
The present study was designed to evaluate the surface roughness and the gloss of current composites before and after toothbrush abrasion. We assessed forty dimensionally standardized composite specimens (n=8/group) from five composites: two nanohybrids (i. e., IPS Empress Direct Enamel and IPS Empress Direct Dentin), two microhybrids (i. e., Clearfil AP-X and Filtek Z250) and one organically modified ceramics (Admira). All of the specimens were polished with 4000-grid silicon carbide papers. Surface roughness was measured with a profilometer and gloss was measured with a glossmeter before and after powered toothbrush abrasion with a 1:1 slurry (dentifrice/tap water) at 12,000 strokes in a toothbrush simulator. There was a significant increase in the surface roughness and a reduction in gloss after toothbrush abrasion in all of the composites except Clearfil AP-X (pgloss (R(2)=0.191, p<0.001).
-
Biodiversity in environmental assessment-current practice and tools for prediction
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gontier, Mikael; Balfors, Berit; Moertberg, Ulla
2006-01-01
Habitat loss and fragmentation are major threats to biodiversity. Environmental impact assessment and strategic environmental assessment are essential instruments used in physical planning to address such problems. Yet there are no well-developed methods for quantifying and predicting impacts of fragmentation on biodiversity. In this study, a literature review was conducted on GIS-based ecological models that have potential as prediction tools for biodiversity assessment. Further, a review of environmental impact statements for road and railway projects from four European countries was performed, to study how impact prediction concerning biodiversity issues was addressed. The results of the study showed the existing gap between research in GIS-based ecological modelling and current practice in biodiversity assessment within environmental assessment
-
Modelling earth current precursors in earthquake prediction
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. Di Maio
1997-06-01
Full Text Available This paper deals with the theory of earth current precursors of earthquake. A dilatancy-diffusion-polarization model is proposed to explain the anomalies of the electric potential, which are observed on the ground surface prior to some earthquakes. The electric polarization is believed to be the electrokinetic effect due to the invasion of fluids into new pores, which are opened inside a stressed-dilated rock body. The time and space variation of the distribution of the electric potential in a layered earth as well as in a faulted half-space is studied in detail. It results that the surface response depends on the underground conductivity distribution and on the relative disposition of the measuring dipole with respect to the buried bipole source. A field procedure based on the use of an areal layout of the recording sites is proposed, in order to obtain the most complete information on the time and space evolution of the precursory phenomena in any given seismic region.
-
Can foot anthropometric measurements predict dynamic plantar surface contact area?
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Collins Natalie
2009-10-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background Previous studies have suggested that increased plantar surface area, associated with pes planus, is a risk factor for the development of lower extremity overuse injuries. The intent of this study was to determine if a single or combination of foot anthropometric measures could be used to predict plantar surface area. Methods Six foot measurements were collected on 155 subjects (97 females, 58 males, mean age 24.5 ± 3.5 years. The measurements as well as one ratio were entered into a stepwise regression analysis to determine the optimal set of measurements associated with total plantar contact area either including or excluding the toe region. The predicted values were used to calculate plantar surface area and were compared to the actual values obtained dynamically using a pressure sensor platform. Results A three variable model was found to describe the relationship between the foot measures/ratio and total plantar contact area (R2 = 0.77, p R2 = 0.76, p Conclusion The results of this study indicate that the clinician can use a combination of simple, reliable, and time efficient foot anthropometric measurements to explain over 75% of the plantar surface contact area, either including or excluding the toe region.
-
Surface Temperature Prediction of a Bridge for Tactical Decision Aide Modelling
1988-01-01
Roadway And Piling Surface Temperature Predictions (No Radiosity Incident on Lower Surface) Compared to Temperature Estimates...Heat gained from water = Heat lost by long wave radiosity radiation. Algebraically, with the conduction term expressed in the same manner as for...5 10 15 20 LOCAL TIME (hrs.) Figure 8. Effect of No Radiosity Incident on Lower Surface. 37 U 8a M OT U% 60-- 0- o.. 20- 0- 1 T I I 5 10 15 20 LOCAL
-
Poleward propagating subinertial alongshore surface currents off the U.S. West Coast
Kim, Sung Yong; Cornuelle, Bruce D.; Terrill, Eric J.; Jones, Burton; Washburn, Libe; Moline, Mark A.; Paduan, Jeffrey D.; Garfield, Newell; Largier, John L.; Crawford, Greg; Michael Kosro, P.
2013-01-01
The network comprising 61 high-frequency radar systems along the U.S. West Coast (USWC) provides a unique, high resolution, and broad scale view of ocean surface circulation. Subinertial alongshore surface currents show poleward propagating signals
-
Impact of data assimilation on ocean current forecasts in the Angola Basin
Phillipson, Luke; Toumi, Ralf
2017-06-01
The ocean current predictability in the data limited Angola Basin was investigated using the Regional Ocean Modelling System (ROMS) with four-dimensional variational data assimilation. Six experiments were undertaken comprising a baseline case of the assimilation of salinity/temperature profiles and satellite sea surface temperature, with the subsequent addition of altimetry, OSCAR (satellite-derived sea surface currents), drifters, altimetry and drifters combined, and OSCAR and drifters combined. The addition of drifters significantly improves Lagrangian predictability in comparison to the baseline case as well as the addition of either altimetry or OSCAR. OSCAR assimilation only improves Lagrangian predictability as much as altimetry assimilation. On average the assimilation of either altimetry or OSCAR with drifter velocities does not significantly improve Lagrangian predictability compared to the drifter assimilation alone, even degrading predictability in some cases. When the forecast current speed is large, it is more likely that the combination improves trajectory forecasts. Conversely, when the currents are weaker, it is more likely that the combination degrades the trajectory forecast.
-
Surface conductivity of Mercury provides current closure and may affect magnetospheric symmetry
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Janhunen
2004-04-01
Full Text Available We study what effect a possible surface conductivity of Mercury has on the closure of magnetospheric currents by making six runs with a quasi-neutral hybrid simulation. The runs are otherwise identical but use different synthetic conductivity models: run 1 has a fully conducting planet, run 2 has a poorly conducting planet (
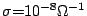 m
m and runs 3-6 have one of the hemispheres either in the dawn-dusk or day-night directions, conducting well, the other one being conducting poorly. Although the surface conductivity is not known from observations, educated guesses easily give such conductivity values that magnetospheric currents may close partly within the planet, and as the conductivity depends heavily on the mineral composition of the surface, the possibility of significant horizontal variations cannot be easily excluded. The simulation results show that strong horizontal variations may produce modest magnetospheric asymmetries. Beyond the hybrid simulation, we also briefly discuss the possibility that in the nightside there may be a lack of surface electrons to carry downward current, which may act as a further source of surface-related magnetospheric asymmetry.
and runs 3-6 have one of the hemispheres either in the dawn-dusk or day-night directions, conducting well, the other one being conducting poorly. Although the surface conductivity is not known from observations, educated guesses easily give such conductivity values that magnetospheric currents may close partly within the planet, and as the conductivity depends heavily on the mineral composition of the surface, the possibility of significant horizontal variations cannot be easily excluded. The simulation results show that strong horizontal variations may produce modest magnetospheric asymmetries. Beyond the hybrid simulation, we also briefly discuss the possibility that in the nightside there may be a lack of surface electrons to carry downward current, which may act as a further source of surface-related magnetospheric asymmetry.
Key words. Magnetospheric physics (planetary magnetospheres; current systems; solar wind-magnetosphere interactions.6 -
'Will I want these stickers tomorrow?' Preschoolers' ability to predict current and future needs.
Martin-Ordas, Gema
2017-11-01
Between 3 and 5 years of age, children develop the ability to plan for their own and others' future needs; however, they have great difficulty predicting future needs that conflict with current ones. Importantly, this ability has only been tested in the domain of physiological states (e.g., thirst). Therefore, it is still an open question whether in a different context preschoolers can disengage from their current needs to secure a different future one. In a Resource Allocation task, 4- and 5-year-olds had to distribute three types of rewards between themselves and another child for either 'right now' or 'tomorrow'. Children's current needs were manipulated by providing them (or not) with their preferred reward at beginning of the task. Only 5-year-olds could predict future needs that conflict with their current ones and act accordingly. Younger children's performance is discussed in the context of temporal and social distance. Statement of contribution What is already known on this subject? By the age of 4, children can plan for their own and others' future needs. Seven-year-old children still have difficulty predicting future physiological needs that conflict with their current ones. What does this study add? In a Resource Allocation task, preschoolers had to share rewards with another child for 'right now' or 'tomorrow'. Children's current needs were manipulated by providing them (or not) with their preferred reward. This study shows that 5-year-olds can predict future (non-physiological) needs that conflict with their current ones. © 2017 The British Psychological Society.
-
Surface currents associated with external kink modes in tokamak plasmas during a major disruption
Ng, C. S.; Bhattacharjee, A.
2017-10-01
The surface current on the plasma-vacuum interface during a disruption event involving kink instability can play an important role in driving current into the vacuum vessel. However, there have been disagreements over the nature or even the sign of the surface current in recent theoretical calculations based on idealized step-function background plasma profiles. We revisit such calculations by replacing step-function profiles with more realistic profiles characterized by a strong but finite gradient along the radial direction. It is shown that the resulting surface current is no longer a delta-function current density, but a finite and smooth current density profile with an internal structure, concentrated within the region with a strong plasma pressure gradient. Moreover, this current density profile has peaks of both signs, unlike the delta-function case with a sign opposite to, or the same as the plasma current. We show analytically and numerically that such current density can be separated into two parts, with one of them, called the convective current density, describing the transport of the background plasma density by the displacement, and the other part that remains, called the residual current density. It is argued that consideration of both types of current density is important and can resolve past controversies.
-
Novel structures of oxygen adsorbed on a Zr(0001) surface predicted from first principles
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Gao, Bo [State Key Laboratory of Superhard Materials, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012 (China); Beijing computational science research center, Beijing,100084 (China); Wang, Jianyun [State Key Laboratory of Superhard Materials, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012 (China); Lv, Jian [State Key Laboratory of Superhard Materials, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012 (China); College of Materials Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012 (China); Gao, Xingyu [Laboratory of Computational Physics, Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing, 100088 (China); CAEP Software Center for High Performance Numerical Simulation, Beijing, 100088 (China); Zhao, Yafan [CAEP Software Center for High Performance Numerical Simulation, Beijing, 100088 (China); Wang, Yanchao, E-mail: wyc@calypso.cn [State Key Laboratory of Superhard Materials, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012 (China); Beijing computational science research center, Beijing,100084 (China); College of Materials Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012 (China); Song, Haifeng, E-mail: song_haifeng@iapcm.ac.cn [Laboratory of Computational Physics, Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing, 100088 (China); CAEP Software Center for High Performance Numerical Simulation, Beijing, 100088 (China); Ma, Yanming [State Key Laboratory of Superhard Materials, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012 (China); Beijing computational science research center, Beijing,100084 (China)
2017-01-30
Highlights: • Two stable structures of O adsorbed on a Zr(0001) surface are predicted with SLAM. • A stable structure of O adsorbed on a Zr(0001) surface is proposed with MLAM. • The calculated work function change is agreement with experimental value. - Abstract: The structures of O atoms adsorbed on a metal surface influence the metal properties significantly. Thus, studying O chemisorption on a Zr surface is of great interest. We investigated O adsorption on a Zr(0001) surface using our newly developed structure-searching method combined with first-principles calculations. A novel structural prototype with a unique combination of surface face-centered cubic (SFCC) and surface hexagonal close-packed (SHCP) O adsorption sites was predicted using a single-layer adsorption model (SLAM) for a 0.5 and 1.0 monolayer (ML) O coverage. First-principles calculations based on the SLAM revealed that the new predicted structures are energetically favorable compared with the well-known SFCC structures for a low O coverage (0.5 and 1.0 ML). Furthermore, on basis of our predicted SFCC + SHCP structures, a new structure within multi-layer adsorption model (MLAM) was proposed to be more stable at the O coverage of 1.0 ML, in which adsorbed O atoms occupy the SFCC + SHCP sites and the substitutional octahedral sites. The calculated work functions indicate that the SFCC + SHCP configuration has the lowest work function of all known structures at an O coverage of 0.5 ML within the SLAM, which agrees with the experimental trend of work function with variation in O coverage.
-
Representation theory of current algebra and conformal field theory on Riemann surfaces
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yamada, Yasuhiko
1989-01-01
We study conformal field theories with current algebra (WZW-model) on general Riemann surfaces based on the integrable representation theory of current algebra. The space of chiral conformal blocks defined as solutions of current and conformal Ward identities is shown to be finite dimensional and satisfies the factorization properties. (author)
-
Prediction of Experimental Surface Heat Flux of Thin Film Gauges using ANFIS
Sarma, Shrutidhara; Sahoo, Niranjan; Unal, Aynur
2018-05-01
Precise quantification of surface heat fluxes in highly transient environment is of paramount importance from the design point of view of several engineering equipment like thermal protection or cooling systems. Such environments are simulated in experimental facilities by exposing the surface with transient heat loads typically step/impulsive in nature. The surface heating rates are then determined from highly transient temperature history captured by efficient surface temperature sensors. The classical approach is to use thin film gauges (TFGs) in which temperature variations are acquired within milliseconds, thereby allowing calculation of surface heat flux, based on the theory of one-dimensional heat conduction on a semi-infinite body. With recent developments in the soft computing methods, the present study is an attempt for the application of intelligent system technique, called adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) to recover surface heat fluxes from a given temperature history recorded by TFGs without having the need to solve lengthy analytical equations. Experiments have been carried out by applying known quantity of `impulse heat load' through laser beam on TFGs. The corresponding voltage signals have been acquired and surface heat fluxes are estimated through classical analytical approach. These signals are then used to `train' the ANFIS model, which later predicts output for `test' values. Results from both methods have been compared and these surface heat fluxes are used to predict the non-linear relationship between thermal and electrical properties of the gauges that are exceedingly pertinent to the design of efficient TFGs. Further, surface plots have been created to give an insight about dimensionality effect of the non-linear dependence of thermal/electrical parameters on each other. Later, it is observed that a properly optimized ANFIS model can predict the impulsive heat profiles with significant accuracy. This paper thus shows the
-
AN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE APPROACH FOR THE PREDICTION OF SURFACE ROUGHNESS IN CO2 LASER CUTTING
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
MILOŠ MADIĆ
2012-12-01
Full Text Available In laser cutting, the cut quality is of great importance. Multiple non-linear effects of process parameters and their interactions make very difficult to predict cut quality. In this paper, artificial intelligence (AI approach was applied to predict the surface roughness in CO2 laser cutting. To this aim, artificial neural network (ANN model of surface roughness was developed in terms of cutting speed, laser power and assist gas pressure. The experimental results obtained from Taguchi’s L25 orthogonal array were used to develop ANN model. The ANN mathematical model of surface roughness was expressed as explicit nonlinear function of the selected input parameters. Statistical results indicate that the ANN model can predict the surface roughness with good accuracy. It was showed that ANNs may be used as a good alternative in analyzing the effects of cutting parameters on the surface roughness.
-
Modelling of crater formation on anode surface by high-current vacuum arcs
Tian, Yunbo; Wang, Zhenxing; Jiang, Yanjun; Ma, Hui; Liu, Zhiyuan; Geng, Yingsan; Wang, Jianhua; Nordlund, Kai; Djurabekova, Flyura
2016-11-01
Anode melting and crater formation significantly affect interruption of high-current vacuum arcs. The primary objective of this paper is to theoretically investigate the mechanism of anode surface crater formation, caused by the combined effect of surface heating during the vacuum arc and pressure exerted on the molten surface by ions and electrons from the arc plasma. A model of fluid flow and heat transfer in the arc anode is developed and combined with a magnetohydrodynamics model of the vacuum arc plasma. Crater formation is observed in simulation for a peak arcing current higher than 15 kA on 40 mm diam. Cu electrodes spaced 10 mm apart. The flow of liquid metal starts after 4 or 5 ms of arcing, and the maximum velocities are 0.95 m/s and 1.39 m/s for 20 kA and 25 kA arcs, respectively. This flow redistributes thermal energy, and the maximum temperature of the anode surface does not remain in the center. Moreover, the condition for the liquid droplet formation on the anode surfaces is developed. The solidification process after current zero is also analyzed. The solidification time has been found to be more than 3 ms after 25 kA arcing. The long solidification time and sharp features on crater rims induce Taylor cone formation.
-
The current state of bearing surfaces in total hip replacement.
Rajpura, A; Kendoff, D; Board, T N
2014-02-01
We reviewed the literature on the currently available choices of bearing surface in total hip replacement (THR). We present a detailed description of the properties of articulating surfaces review the understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of existing bearing couples. Recent technological developments in the field of polyethylene and ceramics have altered the risk of fracture and the rate of wear, although the use of metal-on-metal bearings has largely fallen out of favour, owing to concerns about reactions to metal debris. As expected, all bearing surface combinations have advantages and disadvantages. A patient-based approach is recommended, balancing the risks of different options against an individual's functional demands.
-
Accurate Modelling of Surface Currents and Internal Tides in a Semi-enclosed Coastal Sea
Allen, S. E.; Soontiens, N. K.; Dunn, M. B. H.; Liu, J.; Olson, E.; Halverson, M. J.; Pawlowicz, R.
2016-02-01
The Strait of Georgia is a deep (400 m), strongly stratified, semi-enclosed coastal sea on the west coast of North America. We have configured a baroclinic model of the Strait of Georgia and surrounding coastal waters using the NEMO ocean community model. We run daily nowcasts and forecasts and publish our sea-surface results (including storm surge warnings) to the web (salishsea.eos.ubc.ca/storm-surge). Tides in the Strait of Georgia are mixed and large. The baroclinic model and previous barotropic models accurately represent tidal sea-level variations and depth mean currents. The baroclinic model reproduces accurately the diurnal but not the semi-diurnal baroclinic tidal currents. In the Southern Strait of Georgia, strong internal tidal currents at the semi-diurnal frequency are observed. Strong semi-diurnal tides are also produced in the model, but are almost 180 degrees out of phase with the observations. In the model, in the surface, the barotropic and baroclinic tides reinforce, whereas the observations show that at the surface the baroclinic tides oppose the barotropic. As such the surface currents are very poorly modelled. Here we will present evidence of the internal tidal field from observations. We will discuss the generation regions of the tides, the necessary modifications to the model required to correct the phase, the resulting baroclinic tides and the improvements in the surface currents.
-
Surface inspection technique with an eddy current testing array probe
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nishimizu, Akira; Endo, Hisashi; Tooma, Masahiro; Otani, Kenichi; Ouchi, Hirofumi; Yoshida, Isao; Nonaka, Yoshio
2010-01-01
An eddy current testing (ECT) system has been developed for inspecting weld surfaces of components in the reactor pressure vessel of nuclear plants. The system can be applied to curved surfaces with an ECT array probe, it can discriminate flaws from other signal factors by using a combination of arrayed coils signal-phase. The system is applied to a mock-up of core internal components and the signal discrimination using the signal-phase clearly separated flaw and noise signals. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Reuter, W.G.; Server, W.L.
1982-01-01
Data from flat-plate specimens containing either triangular-, ellipsoidal- or rectangular-shaped surface flaws were evaluated by several potential analytical techniques. These techniques were modified as needed to predict conditions for initiation of subcritical crack growth, for the defect to penetrate the 6.4 mm (0.25 in.) wall thickness, and for instability (plastic or unstable). The modified analytical techniques developed from the plate specimens were then used to make predictions which are compared with test results obtained from pipe specimens containing triangular-shaped surface flaws
-
The role of surface topography in predicting scattering at grazing incidence from optical surfaces
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rehn, V.; Jones, V.O.; Elson, J.M.; Bennett, J.M.
1980-01-01
Monochromator design and the design of optical experiments at XUV and X-ray wavelengths are frequently limited by scattering from optical components, yet theoretical treatments are few and untested experimentally. This is partly due to the failure of scattering models used in the visible and near UV when the wavelength becomes comparable to, or smaller than, the topographic features on the surface, and partly it is due to the difficulty in measuring the topography on the required size scale. We briefly review the theoretical problems and prospects for accurately predicting both the magnitude and angular distribution of scattering at grazing incidence from optical surfaces. Experimental methods for determining and representing the surface topography are also reviewed, together with their limitations and ranges of applicability. Finally, the first results of our experiments, conducted recently at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory on the angular distribution of scattering by surfaces of known topography are presented and discussed, along with their potential implications for the theory of scattering, and for XUV and X-ray optical components. (orig.)
-
Mathewson, Paul; Moyer-Horner, Lucas; Beever, Erik; Briscoe, Natalie; Kearney, Michael T.; Yahn, Jeremiah; Porter, Warren P.
2017-01-01
How climate constrains species’ distributions through time and space is an important question in the context of conservation planning for climate change. Despite increasing awareness of the need to incorporate mechanism into species distribution models (SDMs), mechanistic modeling of endotherm distributions remains limited in this literature. Using the American pika (Ochotona princeps) as an example, we present a framework whereby mechanism can be incorporated into endotherm SDMs. Pika distribution has repeatedly been found to be constrained by warm temperatures, so we used Niche Mapper, a mechanistic heat-balance model, to convert macroclimate data to pika-specific surface activity time in summer across the western United States. We then explored the difference between using a macroclimate predictor (summer temperature) and using a mechanistic predictor (predicted surface activity time) in SDMs. Both approaches accurately predicted pika presences in current and past climate regimes. However, the activity models predicted 8–19% less habitat loss in response to annual temperature increases of ~3–5 °C predicted in the region by 2070, suggesting that pikas may be able to buffer some climate change effects through behavioral thermoregulation that can be captured by mechanistic modeling. Incorporating mechanism added value to the modeling by providing increased confidence in areas where different modeling approaches agreed and providing a range of outcomes in areas of disagreement. It also provided a more proximate variable relating animal distribution to climate, allowing investigations into how unique habitat characteristics and intraspecific phenotypic variation may allow pikas to exist in areas outside those predicted by generic SDMs. Only a small number of easily obtainable data are required to parameterize this mechanistic model for any endotherm, and its use can improve SDM predictions by explicitly modeling a widely applicable direct physiological effect
-
Mathewson, Paul D; Moyer-Horner, Lucas; Beever, Erik A; Briscoe, Natalie J; Kearney, Michael; Yahn, Jeremiah M; Porter, Warren P
2017-03-01
How climate constrains species' distributions through time and space is an important question in the context of conservation planning for climate change. Despite increasing awareness of the need to incorporate mechanism into species distribution models (SDMs), mechanistic modeling of endotherm distributions remains limited in this literature. Using the American pika (Ochotona princeps) as an example, we present a framework whereby mechanism can be incorporated into endotherm SDMs. Pika distribution has repeatedly been found to be constrained by warm temperatures, so we used Niche Mapper, a mechanistic heat-balance model, to convert macroclimate data to pika-specific surface activity time in summer across the western United States. We then explored the difference between using a macroclimate predictor (summer temperature) and using a mechanistic predictor (predicted surface activity time) in SDMs. Both approaches accurately predicted pika presences in current and past climate regimes. However, the activity models predicted 8-19% less habitat loss in response to annual temperature increases of ~3-5 °C predicted in the region by 2070, suggesting that pikas may be able to buffer some climate change effects through behavioral thermoregulation that can be captured by mechanistic modeling. Incorporating mechanism added value to the modeling by providing increased confidence in areas where different modeling approaches agreed and providing a range of outcomes in areas of disagreement. It also provided a more proximate variable relating animal distribution to climate, allowing investigations into how unique habitat characteristics and intraspecific phenotypic variation may allow pikas to exist in areas outside those predicted by generic SDMs. Only a small number of easily obtainable data are required to parameterize this mechanistic model for any endotherm, and its use can improve SDM predictions by explicitly modeling a widely applicable direct physiological effect
-
Surface currents in the equatorial Indian Ocean during spring and fall - An altimetry based analysis
Digital Repository Service at National Institute of Oceanography (India)
Antony, M.K.; Somayajulu, Y.K.
This communication presents the results of a study aimed at investigating the nature and variability of surface currents in the equatorial Indian Ocean between 5 degrees N and 5 degrees S during spring and fall seasons. Geostrophic surface currents...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shen, Y.; Lo, C. C. H.; Frishman, A. M.; Lee, C.; Nakagawa, N.
2007-01-01
This paper describes an eddy current model-based method for inverting near-surface conductivity deviation profiles of surface treated materials from swept-high frequency eddy current (SHFEC) data. This work forms part of our current research directed towards the development of an electromagnetic nondestructive technique for assessing residual stress of shot-peened superalloy components. The inversion procedure is based on the use of a parameterized function to describe the near-surface conductivity as a function of depth for a shot-peened surface, and the laterally uniform multi-layer theory of Cheng, Dodd and Deeds to calculate the resulting coil impedance deviations. The convergence of the inversion procedure has been tested against synthesized eddy current data. As a demonstration, the conductivity deviation profiles of a series of Inconel 718 specimens, shot peened at various Almen intensities, have been obtained by inversion. Several consistency tests were conducted to examine the reliability of the inverted conductivity profiles. The results show that conductivity deviation profiles can be reliably determined from SHFEC data within the accuracy of the current measurement system
-
Surface waves on currents with arbitrary vertical shear
Smeltzer, Benjamin K.; Ellingsen, Simen Å.
2017-04-01
We study dispersion properties of linear surface gravity waves propagating in an arbitrary direction atop a current profile of depth-varying magnitude using a piecewise linear approximation and develop a robust numerical framework for practical calculation. The method has been much used in the past for the case of waves propagating along the same axis as the background current, and we herein extend and apply it to problems with an arbitrary angle between the wave propagation and current directions. Being valid for all wavelengths without loss of accuracy, the scheme is particularly well suited to solve problems involving a broad range of wave vectors, such as ship waves and Cauchy-Poisson initial value problems. We examine the group and phase velocities over different wavelength regimes and current profiles, highlighting characteristics due to the depth-variable vorticity. We show an example application to ship waves on an arbitrary current profile and demonstrate qualitative differences in the wake patterns between concave down and concave up profiles when compared to a constant shear profile with equal depth-averaged vorticity. We also discuss the nature of additional solutions to the dispersion relation when using the piecewise-linear model. These are vorticity waves, drifting vortical structures which are artifacts of the piecewise model. They are absent for a smooth profile and are spurious in the present context.
-
Observations of the sub-inertial, near-surface East India Coastal Current
Mukhopadhyay, S.; Shankar, D.; Aparna, S. G.; Mukherjee, A.
2017-09-01
We present surface current measurements made using two pairs of HF (high-frequency) radars deployed on the east coast of India. The radar data, used in conjunction with data from acoustic Doppler current profiler (ADCP) measurements on the shelf and slope off the Indian east coast, confirm that the East India Coastal Current (EICC) flows poleward as a deep current during February-March. During the summer monsoon, when the EICC flows poleward, and October-December, when the EICC flows equatorward, the current is shallow (art Ocean General Circulation Model, run at a resolution of 0.1 ° × 0.1 ° , shows that the model is able to simulate only the low-frequency variability.
-
Abu-Nabah, Bassam A.
Recent research results indicated that eddy current conductivity measurements can be exploited for nondestructive evaluation of near-surface residual stresses in surface-treated nickel-base superalloy components. Most of the previous experimental studies were conducted on highly peened (Almen 10-16A) specimens that exhibit harmful cold work in excess of 30% plastic strain. Such high level of cold work causes thermo-mechanical relaxation at relatively modest operational temperatures; therefore the obtained results were not directly relevant to engine manufacturers and end users. The main reason for choosing peening intensities in excess of recommended normal levels was that in low-conductivity engine alloys the eddy current penetration depth could not be forced below 0.2 mm without expanding the measurements above 10 MHz which is beyond the operational range of most commercial eddy current instruments. As for shot-peened components, it was initially felt that the residual stress effect was more difficult to separate from cold work, texture, and inhomogeneity effects in titanium alloys than in nickel-base superalloys. In addition, titanium alloys have almost 50% lower electric conductivity than nickel-base superalloys; therefore require proportionally higher inspection frequencies, which was not feasible until our recent breakthrough in instrument development. Our work has been focused on six main aspects of this continuing research, namely, (i) the development of an iterative inversion technique to better retrieve the depth-dependent conductivity profile from the measured frequency-dependent apparent eddy current conductivity (AECC), (ii) the extension of the frequency range up to 80 MHz to better capture the peak compressive residual stress in nickel-base superalloys using a new eddy current conductivity measuring system, which offers better reproducibility, accuracy and measurement speed than the previously used conventional systems, (iii) the lift-off effect on
-
Prediction of Sea Surface Temperature Using Long Short-Term Memory
Zhang, Qin; Wang, Hui; Dong, Junyu; Zhong, Guoqiang; Sun, Xin
2017-10-01
This letter adopts long short-term memory(LSTM) to predict sea surface temperature(SST), which is the first attempt, to our knowledge, to use recurrent neural network to solve the problem of SST prediction, and to make one week and one month daily prediction. We formulate the SST prediction problem as a time series regression problem. LSTM is a special kind of recurrent neural network, which introduces gate mechanism into vanilla RNN to prevent the vanished or exploding gradient problem. It has strong ability to model the temporal relationship of time series data and can handle the long-term dependency problem well. The proposed network architecture is composed of two kinds of layers: LSTM layer and full-connected dense layer. LSTM layer is utilized to model the time series relationship. Full-connected layer is utilized to map the output of LSTM layer to a final prediction. We explore the optimal setting of this architecture by experiments and report the accuracy of coastal seas of China to confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method. In addition, we also show its online updated characteristics.
-
Du, X.; Savich, G. R.; Marozas, B. T.; Wicks, G. W.
2018-02-01
Surface leakage and lateral diffusion currents in InAs-based nBn photodetectors have been investigated. Devices fabricated using a shallow etch processing scheme that etches through the top contact and stops at the barrier exhibited large lateral diffusion current but undetectably low surface leakage. Such large lateral diffusion current significantly increased the dark current, especially in small devices, and causes pixel-to-pixel crosstalk in detector arrays. To eliminate the lateral diffusion current, two different approaches were examined. The conventional solution utilized a deep etch process, which etches through the top contact, barrier, and absorber. This deep etch processing scheme eliminated lateral diffusion, but introduced high surface current along the device mesa sidewalls, increasing the dark current. High device failure rate was also observed in deep-etched nBn structures. An alternative approach to limit lateral diffusion used an inverted nBn structure that has its absorber grown above the barrier. Like the shallow etch process on conventional nBn structures, the inverted nBn devices were fabricated with a processing scheme that only etches the top layer (the absorber, in this case) but avoids etching through the barrier. The results show that inverted nBn devices have the advantage of eliminating the lateral diffusion current without introducing elevated surface current.
-
The Current and Future Use of Ridge Regression for Prediction in Quantitative Genetics
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ronald de Vlaming
2015-01-01
Full Text Available In recent years, there has been a considerable amount of research on the use of regularization methods for inference and prediction in quantitative genetics. Such research mostly focuses on selection of markers and shrinkage of their effects. In this review paper, the use of ridge regression for prediction in quantitative genetics using single-nucleotide polymorphism data is discussed. In particular, we consider (i the theoretical foundations of ridge regression, (ii its link to commonly used methods in animal breeding, (iii the computational feasibility, and (iv the scope for constructing prediction models with nonlinear effects (e.g., dominance and epistasis. Based on a simulation study we gauge the current and future potential of ridge regression for prediction of human traits using genome-wide SNP data. We conclude that, for outcomes with a relatively simple genetic architecture, given current sample sizes in most cohorts (i.e., N<10,000 the predictive accuracy of ridge regression is slightly higher than the classical genome-wide association study approach of repeated simple regression (i.e., one regression per SNP. However, both capture only a small proportion of the heritability. Nevertheless, we find evidence that for large-scale initiatives, such as biobanks, sample sizes can be achieved where ridge regression compared to the classical approach improves predictive accuracy substantially.
-
RIKEN 200 kV high current implanter for metal surface modification
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Iwaki, M.; Yoshida, K.; Sakudo, N.
1985-01-01
A high current, metal ion implanter was constructed in order to aid the formation of a new metastable surface alloy. This implanter, called a RIKEN 200 kV high current implanter, is a modified Lintott high current machine (Series III), which has the advantages of having its own microwave ion source and an extra target chamber. The microwave discharge ion source without a hot-filament has a comparatively long lifetime because the chloride ions and radicals in a plasma during discharge of metal chlorides might prevent metal to deposit on the inner walls of the discharge chamber by bombarding and chemically cleaning them. An extra target chamber for metal modification is able to control the surface composition by utilizing the sputtering effect of the ion beam during ion implantation. The use of this ion source and the extra target chamber is suggested to be suitable for the production of metallic ions and for the implantation into metals. The case study will be introduced for TI implantation into Fe. (orig.)
-
Eghlimi, Abbas; Shamanian, Morteza; Raeissi, Keyvan
2013-12-01
Super-duplex stainless steels have an excellent combination of mechanical properties and corrosion resistance at relatively low temperatures and can be used as a coating to improve the corrosion and wear resistance of low carbon and low alloy steels. Such coatings can be produced using weld cladding. In this study, pulsed current gas tungsten arc cladding process was utilized to deposit super-duplex stainless steel on high strength low alloy steel substrates. In such claddings, it is essential to understand how the dilution affects the composition and ferrite number of super-duplex stainless steel layer in order to be able to estimate its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. In the current study, the effect of pulsed current gas tungsten arc cladding process parameters on the dilution and ferrite number of super-duplex stainless steel clad layer was investigated by applying response surface methodology. The validity of the proposed models was investigated by using quadratic regression models and analysis of variance. The results showed an inverse relationship between dilution and ferrite number. They also showed that increasing the heat input decreases the ferrite number. The proposed mathematical models are useful for predicting and controlling the ferrite number within an acceptable range for super-duplex stainless steel cladding.
-
Numerically predicting horizontally oriented spent fuel rod surface temperatures
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wix, S.D.; Koski, J.A.
1993-01-01
A comparison between numerical calculations with use of commercial thermal analysis software packages and experimental data simulating a horizontally oriented spent fuel rod array was performed. Twelve cases were analyzed using air and helium for the fill gas, with three different heat dissipation levels. The numerically predicted temperatures are higher than the experimental data for all levels of heat dissipation with air as the fill gas. The temperature differences are 4 degrees C and 23 degrees C for the low heat dissipation and high dissipation, respectively. The temperature predictions using helium as a fill gas are lower than the experimental data for the low and medium heat dissipation levels. The temperature predictions are 1 degrees C and 6 degrees C lower than the experimental data for the low and medium heat dissipation, respectively. For the high heat dissipation level, the temperature predictions are 16 degrees C higher than the experimental data. Differences between the predicted and experimental temperatures can be attributed to several factors. These factors include a experimental uncertainity in the temperature and heat dissipation measurements, actual convection effects not included in the model, and axial heat flow in the experimental data. This works demonstrates that horizontally oriented spent fuel rod surface temperature predictions can be made using existing commercial software packages. This work also shows that end effects, such as axial heat transfer through the spent fuel rods, will be increasingly important as the amount of dissipated heat increases
-
Numerically predicting horizontally oriented spent fuel rod surface temperatures
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wix, S.D.; Koski, J.A.
1992-01-01
A comparison between numerical calculations with use of commercial thermal analysis software packages and experimental data simulating a horizontally oriented spent fuel rod array was performed. Twelve cases were analyzed using air and helium for the fill gas, with three different heat dissipation levels. The numerically predicted temperatures are higher than the experimental data for all levels of heat dissipation with air as the fill gas. The temperature differences are 4 degree C and 23 degree C for the low heat dissipation and high heat dissipation, respectively. The temperature predictions using helium as a fill gas are lower than the experimental data for the low and medium heat dissipation levels. The temperature predictions are 1 degree C and 6 degree C lower than the experimental data for the low and medium heat dissipation, respectively. For the high heat dissipation level, the temperature predictions are 16 degree C higher than the experimental data. Differences between the predicted and experimental temperatures can be attributed to several factors. These factors include experimental uncertainty in the temperature and heat dissipation measurements, actual convection effects not included in the model, and axial heat flow in the experimental data. This work demonstrates that horizontally oriented spent fuel rod surface temperature predictions can be made using existing commercial software packages. This work also shows that end effects, such as axial heat transfer through the spent fuel rods, will be increasingly important as the amount of dissipated heat increases
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Pal, Dipankar; Neogi, Sudarsan; De, Sirshendu, E-mail: sde@che.iitkgp.ernet.in
2015-12-31
Low temperature plasma treatment using pulsed direct current discharge of nitrogen gas was employed to enhance hydrophilicity of the polyacrylonitrile co-polymer membranes. The membranes were characterized in terms of morphology, structure, hydrophilicity, and membrane performance. Properties and functional groups on the surface of polyacrylonitrile co-polymer membranes were investigated by contact angle, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Effects of plasma conditions, namely, pulsed voltage, duty cycle and treatment time on increase in membrane hydrophilicity were studied. Permeability of treated membrane was increased by 47% and it was retained up to 70 days. Surface etching due to plasma treatment was confirmed by weight loss of the treated membranes. Due to surface etching, average pore size increased and rejection of 200 kDa polyethylene glycol decreased to about 70% for the treated membrane. Oxygen and nitrogen functional groups were responsible for surface hydrophilicity. - Highlights: • Surface modification of polyacrylonitrile co-polymer membranes by pulsed direct current nitrogen plasma • Hydrophilic functional groups incorporated on the membrane surface • Significant enhancement of the permeability and wettability of the membranes • Water contact angle increased with storage time and finally stabilized.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pal, Dipankar; Neogi, Sudarsan; De, Sirshendu
2015-01-01
Low temperature plasma treatment using pulsed direct current discharge of nitrogen gas was employed to enhance hydrophilicity of the polyacrylonitrile co-polymer membranes. The membranes were characterized in terms of morphology, structure, hydrophilicity, and membrane performance. Properties and functional groups on the surface of polyacrylonitrile co-polymer membranes were investigated by contact angle, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Effects of plasma conditions, namely, pulsed voltage, duty cycle and treatment time on increase in membrane hydrophilicity were studied. Permeability of treated membrane was increased by 47% and it was retained up to 70 days. Surface etching due to plasma treatment was confirmed by weight loss of the treated membranes. Due to surface etching, average pore size increased and rejection of 200 kDa polyethylene glycol decreased to about 70% for the treated membrane. Oxygen and nitrogen functional groups were responsible for surface hydrophilicity. - Highlights: • Surface modification of polyacrylonitrile co-polymer membranes by pulsed direct current nitrogen plasma • Hydrophilic functional groups incorporated on the membrane surface • Significant enhancement of the permeability and wettability of the membranes • Water contact angle increased with storage time and finally stabilized.
-
Near-surface current meter array measurements of internal gravity waves
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jones, H.B.E. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab., CA (United States)
1994-11-15
We have developed various processing algorithms used to estimate the wave forms produced by hydrodynamic Internal Waves. Furthermore, the estimated Internal Waves are used to calculate the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) which relates the current and strain rate subsurface fields to surface scattering phenomenon imaged by radar. Following a brief discussion of LLNL`s measurement platform (a 10 sensor current meter array) we described the generation of representative current and strain rate space-time images from measured or simulated data. Then, we present how our simulation capability highlighted limitations in estimating strain rate. These limitations spurred the application of beamforming techniques to enhance our estimates, albeit at the expense of collapsing our space-time images to 1-D estimates. Finally, we discuss progress with regard to processing the current meter array data captured during the recent Loch Linnhe field trials.
-
Harmonic current prediction by impedance modeling of grid-tied inverters
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Pereira, Heverton A.; Freijedo, Francisco D.; Silva, M. M.
2017-01-01
and harmonic voltage profiles. Results reinforce that impedance models can represent with relatively accuracy the harmonic current emitted by the PV plants at the point of common coupling (PCC). Lastly, a stress test is performed to show how a variation in the harmonic voltage phase angle impacts the PV plant...... impedance models when used in harmonic integration studies. It is aimed to estimate the harmonic current contribution as a function of the background harmonic voltages components. Time domain simulations based on detailed and average models are compared with the impedance model developed in frequency domain....... In grids with harmonic voltages, impedance models can predict the current distortion for all active power injection scenarios. Furthermore, measurements in a 1.4 MW PV plant connected in a distributed grid are used to validate the simulation based on impedance models during different power injections...
-
Nur, N.; Jahncke, J.; Herzog, M.P.; Howar, J.; Hyrenbach, K.D.; Zamon, J.E.; Ainley, D.G.; Wiens, J.A.; Morgan, K.; Balance, L.T.; Stralberg, D.
2011-01-01
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) provide an important tool for conservation of marine ecosystems. To be most effective, these areas should be strategically located in a manner that supports ecosystem function. To inform marine spatial planning and support strategic establishment of MPAs within the California Current System, we identified areas predicted to support multispecies aggregations of seabirds ("hotspot????). We developed habitat-association models for 16 species using information from at-sea observations collected over an 11-year period (1997-2008), bathymetric data, and remotely sensed oceanographic data for an area from north of Vancouver Island, Canada, to the USA/Mexico border and seaward 600 km from the coast. This approach enabled us to predict distribution and abundance of seabirds even in areas of few or no surveys. We developed single-species predictive models using a machine-learning algorithm: bagged decision trees. Single-species predictions were then combined to identify potential hotspots of seabird aggregation, using three criteria: (1) overall abundance among species, (2) importance of specific areas ("core area????) to individual species, and (3) predicted persistence of hotspots across years. Model predictions were applied to the entire California Current for four seasons (represented by February, May, July, and October) in each of 11 years. Overall, bathymetric variables were often important predictive variables, whereas oceanographic variables derived from remotely sensed data were generally less important. Predicted hotspots often aligned with currently protected areas (e.g., National Marine Sanctuaries), but we also identified potential hotspots in Northern California/Southern Oregon (from Cape Mendocino to Heceta Bank), Southern California (adjacent to the Channel Islands), and adjacent to Vancouver Island, British Columbia, that are not currently included in protected areas. Prioritization and identification of multispecies hotspots
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Poduval, B., E-mail: bpoduval@spacescience.org [Space Science Institute, Boulder, CO 80303 (United States)
2016-08-10
This Letter presents the results of an investigation into the controlling influence of large-scale magnetic field of the Sun in determining the solar wind outflow using two magnetostatic coronal models: current sheet source surface (CSSS) and potential field source surface. For this, we made use of the Wang and Sheeley inverse correlation between magnetic flux expansion rate (FTE) and observed solar wind speed (SWS) at 1 au. During the period of study, extended over solar cycle 23 and beginning of solar cycle 24, we found that the coefficients of the fitted quadratic equation representing the FTE–SWS inverse relation exhibited significant temporal variation, implying the changing pattern of the influence of FTE on SWS over time. A particularly noteworthy feature is an anomaly in the behavior of the fitted coefficients during the extended minimum, 2008–2010 (CRs 2073–2092), which is considered due to the particularly complex nature of the solar magnetic field during this period. However, this variation was significant only for the CSSS model, though not a systematic dependence on the phase of the solar cycle. Further, we noticed that the CSSS model demonstrated better solar wind prediction during the period of study, which we attribute to the treatment of volume and sheet currents throughout the corona and the more accurate tracing of footpoint locations resulting from the geometry of the model.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Loizu, J., E-mail: joaquim.loizu@ipp.mpg.de [Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-17491 Greifswald (Germany); Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, P.O. Box 451, Princeton New Jersey 08543 (United States); Hudson, S.; Bhattacharjee, A. [Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, P.O. Box 451, Princeton New Jersey 08543 (United States); Helander, P. [Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-17491 Greifswald (Germany)
2015-02-15
Using the recently developed multiregion, relaxed MHD (MRxMHD) theory, which bridges the gap between Taylor's relaxation theory and ideal MHD, we provide a thorough analytical and numerical proof of the formation of singular currents at rational surfaces in non-axisymmetric ideal MHD equilibria. These include the force-free singular current density represented by a Dirac δ-function, which presumably prevents the formation of islands, and the Pfirsch-Schlüter 1/x singular current, which arises as a result of finite pressure gradient. An analytical model based on linearized MRxMHD is derived that can accurately (1) describe the formation of magnetic islands at resonant rational surfaces, (2) retrieve the ideal MHD limit where magnetic islands are shielded, and (3) compute the subsequent formation of singular currents. The analytical results are benchmarked against numerical simulations carried out with a fully nonlinear implementation of MRxMHD.
-
Sparse approximation of currents for statistics on curves and surfaces.
Durrleman, Stanley; Pennec, Xavier; Trouvé, Alain; Ayache, Nicholas
2008-01-01
Computing, processing, visualizing statistics on shapes like curves or surfaces is a real challenge with many applications ranging from medical image analysis to computational geometry. Modelling such geometrical primitives with currents avoids feature-based approach as well as point-correspondence method. This framework has been proved to be powerful to register brain surfaces or to measure geometrical invariants. However, if the state-of-the-art methods perform efficiently pairwise registrations, new numerical schemes are required to process groupwise statistics due to an increasing complexity when the size of the database is growing. Statistics such as mean and principal modes of a set of shapes often have a heavy and highly redundant representation. We propose therefore to find an adapted basis on which mean and principal modes have a sparse decomposition. Besides the computational improvement, this sparse representation offers a way to visualize and interpret statistics on currents. Experiments show the relevance of the approach on 34 sets of 70 sulcal lines and on 50 sets of 10 meshes of deep brain structures.
-
Prediction of transverse asymmetries in MHD ducts with zero net Hall current
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Swean, T.F. Jr.; Oliver, D.A.; Maxwell, C.D.; Demetriades, S.T.
1981-01-01
A new class of fluid-electrical asymmetries in MHD generator channel flow are predicted. It is shown that the existence of interelectrode asymmetries is not confined to generators in which there exists a nonzero net axial current, but rather they are induced even in the case of the Faraday generators. Also demonstrated is the impact of these asymmetries upon the generator and diffuser flow. It is concluded that in MHD generators, the net axial current in the cross plane is identically zero, while at any given point in the plane, the local Hall current density is in general nonzero
-
Sahu, Neelesh Kumar; Andhare, Atul B.; Andhale, Sandip; Raju Abraham, Roja
2018-04-01
Present work deals with prediction of surface roughness using cutting parameters along with in-process measured cutting force and tool vibration (acceleration) during turning of Ti-6Al-4V with cubic boron nitride (CBN) inserts. Full factorial design is used for design of experiments using cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut as design variables. Prediction model for surface roughness is developed using response surface methodology with cutting speed, feed rate, depth of cut, resultant cutting force and acceleration as control variables. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is performed to find out significant terms in the model. Insignificant terms are removed after performing statistical test using backward elimination approach. Effect of each control variables on surface roughness is also studied. Correlation coefficient (R2 pred) of 99.4% shows that model correctly explains the experiment results and it behaves well even when adjustment is made in factors or new factors are added or eliminated. Validation of model is done with five fresh experiments and measured forces and acceleration values. Average absolute error between RSM model and experimental measured surface roughness is found to be 10.2%. Additionally, an artificial neural network model is also developed for prediction of surface roughness. The prediction results of modified regression model are compared with ANN. It is found that RSM model and ANN (average absolute error 7.5%) are predicting roughness with more than 90% accuracy. From the results obtained it is found that including cutting force and vibration for prediction of surface roughness gives better prediction than considering only cutting parameters. Also, ANN gives better prediction over RSM models.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Farkas, G.; Horvath, Z.G.; Toth, C.; Fotakis, C.; Hontzopoulos, E.
1987-01-01
Investigations were conducted on radiation-induced electron emission processes on a gold target surface with a high-intensity (2 MW/cm 2 ) KrF laser (λ = 248 nm). The single photon surface photoelectric emission obtained can be used for high-current density electron sources. The measured polarization dependence of electron current shows the dominance of the surface-type effect over that of the volume type, thereby making it possible to optimize the short, high-density electron current creation conditions. The advantage of the grazing light incidence and the multiphoton photoeffect giving rise to a 500 A/cm 2 electron current has been demonstrated
-
Stability of alternating current discharges between water drops on insulation surfaces
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rowland, S M; Lin, F C
2006-01-01
Discharges between water drops are important in the ageing of hydrophobic outdoor insulators. They may also be important in the processes leading up to flashover of these insulators in high pollution conditions. This paper considers discharges between drops when a limited alternating current is available, as experienced by an ageing insulator in service. A phenomenon is identified in which the length of a discharge between two drops is reduced through a particular type of distortion of the drops. This is visually characterized as a liquid protrusion from each of a pair of water drops along the insulator surface. This process is distinct from vibration of the drops, general distortion of their shape and the very fast emission of jet streams seen in very high fields. The process depends upon the discharge current, the resistivity of the moisture and the hydrophobicity of the insulation surface
-
Low Overpotential and High Current CO2 Reduction with Surface Reconstructed Cu Foam Electrodess
Min, Shixiong
2016-06-23
While recent reports have demonstrated that oxide-derived Cu-based electrodes exhibit high selectivity for CO2 reduction at low overpotential, the low catalytic current density (<2 mA/cm2 at -0.45 V vs. RHE) still largely limits its applications for large-scale fuel synthesis. Here we report an extremely high current density for CO2 reduction at low overpotential using a Cu foam electrode prepared by air-oxidation and subsequent electroreduction. Apart from possessing three-dimensional (3D) open frameworks, the resulting Cu foam electrodes prepared at higher temperatures exhibit enhanced electrochemically active surface area and distinct surface structures. In particular, the Cu foam electrode prepared at 500 °C exhibits an extremely high geometric current density of ~9.4 mA/cm2 in CO2-satrurated 0.1 M KHCO3 aqueous solution and achieving ~39% CO and ~23% HCOOH Faradaic efficiencies at -0.45 V vs. RHE. The high activity and significant selectivity enhancement are attributable to the formation of abundant grain-boundary supported active sites and preferable (100) and (111) facets as a result of reconstruction of Cu surface facets. This work demonstrates that the structural integration of Cu foam with open 3D frameworks and the favorable surface structures is a promising strategy to develop an advanced Cu electrocatalyst that can operate at high current density and low overpotential for CO2 reduction.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A Rohani
2015-09-01
Full Text Available Introduction: Fast and accurate determination of geometrical properties of agricultural products has many applications in agricultural operations like planting, cultivating, harvesting and post-harvesting. Calculations related to storing, shipping and storage-coating materials as well as peeling time and surface-microbial concentrations are some applications of estimating product volume and surface area. Sphericity is also a parameter by which the shape differences between fruits, vegetables, grains and seeds can be quantified. This parameter is important in grading systems and inspecting rolling capability of agricultural products. Bayram presented a new dimensional method and equation to calculate the sphericity of certain shapesand some granular food materials (Bayram, 2005. Kumar and Mathew proposed atheoretically soundmethod for estimating the surface area of ellipsoidal food materials (Kumar and Mathew, 2003. Clayton et al. used non-linear regression models for calculation of apple surface area using the fruit mass or volume (Clayton et al., 1995. Humeida and Hobani predicted surface area and volume of pomegranates based on the weight and geometrical diametermean (Humeida and Hobani, 1993. Wang and Nguang designeda low cost sensor system to automatically compute the volume and surface area of axi-symmetricagricultural products such as eggs, lemons, limes and tamarillos (Wang and Nguang, 2007. The main objective of this study was to investigate the potential of Artificial Neural Network (ANN technique as an alternative method to predict the volume, surface area and sphericity of pomegranates. Materials and methods: The water displacement method (WDM was used for measuring the actual volume of pomegranates. Also, the sphericity and surface area are computed by using analytical methods. In this study, the neural MLP models were designed based upon the three nominal diameters of pomegranatesas variable inputs, while the output model consisted
-
Nagaraja, Srinidhi; Di Prima, Matthew; Saylor, David; Takai, Erica
2017-08-01
In an effort to better understand current test practices and improve nonclinical testing of cardiovascular metallic implants, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) held a public workshop on Cardiovascular Metallic Implants: corrosion, surface characterization, and nickel leaching. The following topics were discussed: (1) methods used for corrosion assessments, surface characterization techniques, and nickel leach testing of metallic cardiovascular implant devices, (2) the limitations of each of these in vitro tests in predicting in vivo performance, (3) the need, utility, and circumstances when each test should be considered, and (4) the potential testing paradigms, including acceptance criteria for each test. In addition to the above topics, best practices for these various tests were discussed, and knowledge gaps were identified. Prior to the workshop, discussants had the option to provide feedback and information on issues relating to each of the topics via a voluntary preworkshop assignment. During the workshop, the pooled responses were presented and a panel of experts discussed the results. This article summarizes the proceedings of this workshop and background information provided by workshop participants. Published 2016. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. J Biomed Mater Res Part B: Appl Biomater, 105B: 1330-1341, 2017. Published 2016. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
-
Hodgson, Murray; Wareing, Andrew
2008-01-01
A combined beam-tracing and transfer-matrix model for predicting steady-state sound-pressure levels in rooms with multilayer bounding surfaces was used to compare the effect of extended- and local-reaction surfaces, and the accuracy of the local-reaction approximation. Three rooms—an office, a corridor and a workshop—with one or more multilayer test surfaces were considered. The test surfaces were a single-glass panel, a double-drywall panel, a carpeted floor, a suspended-acoustical ceiling, a double-steel panel, and glass fibre on a hard backing. Each test surface was modeled as of extended or of local reaction. Sound-pressure levels were predicted and compared to determine the significance of the surface-reaction assumption. The main conclusions were that the difference between modeling a room surface as of extended or of local reaction is not significant when the surface is a single plate or a single layer of material (solid or porous) with a hard backing. The difference is significant when the surface consists of multilayers of solid or porous material and includes a layer of fluid with a large thickness relative to the other layers. The results are partially explained by considering the surface-reflection coefficients at the first-reflection angles.
-
Electrodynamics of spin currents in superconductors
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hirsch, J.E.
2008-01-01
In recent work we formulated a new set of electrodynamic equations for superconductors as an alternative to the conventional London equations, compatible with the prediction of the theory of hole superconductivity that superconductors expel negative charge from the interior towards the surface. Charge expulsion results in a macroscopically inhomogeneous charge distribution and an electric field in the interior, and because of this a spin current is expected to exist. Furthermore, we have recently shown that a dynamical explanation of the Meissner effect in superconductors leads to the prediction that a spontaneous spin current exists near the surface of superconductors (spin Meissner effect). In this paper we extend the electrodynamic equations proposed earlier for the charge density and charge current to describe also the space and time dependence of the spin density and spin current. This allows us to determine the magnitude of the expelled negative charge and interior electric field as well as of the spin current in terms of other measurable properties of superconductors. We also provide a 'geometric' interpretation of the difference between type I and type II superconductors, discuss how superconductors manage to conserve angular momentum, discuss the relationship between our model and Slater's seminal work on superconductivity, and discuss the magnitude of the expected novel effects for elemental and other superconductors. (Abstract Copyright [2008], Wiley Periodicals, Inc.)
-
Swain, James H; Newman, Samuel M; Hunt, Janet R
2003-11-01
Foods are fortified with elemental forms of iron to reduce iron deficiency. However, the nutritional efficacy of current, commercially produced elemental iron powders has not been verified. We determined the bioavailability of six commercial elemental iron powders and examined how physicochemistry influences bioavailability. Relative biological value (RBV) of the iron powders was determined using a hemoglobin repletion/slope ratio method, treating iron-deficient rats with repletion diets fortified with graded quantities of iron powders, bakery-grade ferrous sulfate or no added iron. Iron powders were assessed physicochemically by measuring iron solubility in hydrochloric acid at pH 1.0 and 1.7, surface area by nitrogen gas adsorption and surface microstructure by electron microscopy. Bioavailability from the iron powders, based on absolute iron intake, was significantly less than from FeSO4 (100%; P Electrolytic (54%; A-131, U.S.) > Electrolytic (46%; Electrolytic Iron, India) > H-Reduced (42%; AC-325, U.S.) > Reduced (24%; ATOMET 95SP, Canada) > CO-Reduced (21%; RSI-325, Sweden). Solubility testing of the iron powders resulted in different relative rankings and better RBV predictability with increasing time at pH 1.7 (R2 = 0.65 at 150 min). The prediction was improved with less time and lower pH (R2 = 0.82, pH 1.0 at 30 min). Surface area, ranging from 90 to 370 m2/kg, was also highly predictive of RBV (R2 = 0.80). Bioavailability of iron powders is less than bakery-grade ferrous sulfate and varies up to three times among different commercial forms. Solubility at pH 1.0 and surface area were predictive of iron bioavailability in rats.
-
A Steel Ball Surface Quality Inspection Method Based on a Circumferential Eddy Current Array Sensor.
Zhang, Huayu; Xie, Fengqin; Cao, Maoyong; Zhong, Mingming
2017-07-01
To efficiently inspect surface defects on steel ball bearings, a new method based on a circumferential eddy current array (CECA) sensor was proposed here. The best probe configuration, in terms of the coil quality factor (Q-factor), magnetic field intensity, and induced eddy current density on the surface of a sample steel ball, was determined using 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6-coil probes, for analysis and comparison. The optimal lift-off from the measured steel ball, the number of probe coils, and the frequency of excitation current suitable for steel ball inspection were obtained. Using the resulting CECA sensor to inspect 46,126 steel balls showed a miss rate of ~0.02%. The sensor was inspected for surface defects as small as 0.05 mm in width and 0.1 mm in depth.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Plikhunov, V V; Petrov, L M; Grigorovich, K V
2016-01-01
The influence of current characteristics of the vacuum arc evaporator on the interaction process of plasma streams with the surface under treatment during generation of the physicochemical properties of the formed metal-coating composite is considered. It is shown that the interaction of plasma streams with the processed surface provides surface heating, defects elimination, change in energy properties, and mass transfer of plasma stream elements activating surface diffusion processes whose intensity is evaluated by the arc current magnitude and location of the processed surface relative to the cathode axis. (paper)
-
Sentchev, Alexei; Forget, Philippe; Fraunié, Philippe
2017-04-01
Ocean surface boundary layer dynamics off the southern coast of France in the NW Mediterranean is investigated by using velocity observations by high-frequency (HF) radars, surface drifting buoys and a downward-looking drifting acoustic Doppler current profiler (ADCP). The analysis confirms that velocities measured by HF radars correspond to those observed by an ADCP at the effective depth z f = k -1, where k is wavenumber of the radio wave emitted by the radar. The radials provided by the radars were in a very good agreement with in situ measurements, with the relative errors of 1 and 9 % and root mean square (RMS) differences of 0.02 and 0.04 m/s for monostatic and bistatic radar, respectively. The total radar-based velocities appeared to be slightly underestimated in magnitude and somewhat biased in direction. At the end of the survey period, the difference in the surface current direction, based on HF radar and ADCP data, attained 10°. It was demonstrated that the surface boundary layer dynamics cannot be reconstructed successfully without taking into the account velocity variation with depth. A significant misalignment of ˜30° caused by the sea breeze was documented between the HF radar (HFR-derived) surface current and the background current. It was also found that the ocean response to a moderate wind forcing was confined to the 4-m-thick upper layer. The respective Ekman current attained the maximum value of 0.15 m/s, and the current rotation was found to be lagging the wind by approximately 40 min, with the current vector direction being 15-20° to the left of the wind. The range of velocity variability due to wind forcing was found comparable with the magnitude of the background current variability.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Xaplanteris, Constantine L.; Filippaki, Eleni D.
2013-01-01
During the last decades many researchers have been occupied with other plasma applications apart from the big challenge which the thermonuclear fusion poses. Many experiments have been carried out on the plasma behavior in contact with a solid surface; when the surface material consists of chemical compounds (e.g. oxides of metals), then the plasma chemistry takes place. The present paper contains the final experimental and theoretical work of Plasma Laboratory at “Demokritos , which consists of an elaboration of plasma sheath parameters adapted to experimental conditions, a suitable choice of plasma gases (either H 2 or N 2 ), and an electric potential current enforcement on objects. Additionally, a brief theory is given to explain the results, with a short reference to both boundary phenomena in thermonuclear reactors and low pressure plasma of glow discharges, so as to reveal the similarities and differences of these two cases. An extensive examination of the treated objects by X-ray diffraction method (XRD) gives results in agreement with the theoretical predictions. Using this improvement on plasma restoration system, (a combination of electric current on metallic object into suitable plasma), it is shown that better results can be achieved on the cleaning and conservation of archaeological objects. (plasma technology)
-
Cane, M. A.; Cardone, V. J.; Halem, M.; Halberstam, I.
1981-01-01
The reported investigation has the objective to assess the potential impact on numerical weather prediction (NWP) of remotely sensed surface wind data. Other investigations conducted with similar objectives have not been satisfactory in connection with a use of procedures providing an unrealistic distribution of initial errors. In the current study, care has been taken to duplicate the actual distribution of information in the conventional observing system, thus shifting the emphasis from accuracy of the data to the data coverage. It is pointed out that this is an important consideration in assessing satellite observing systems since experience with sounder data has shown that improvements in forecasts due to satellite-derived information is due less to a general error reduction than to the ability to fill data-sparse regions. The reported study concentrates on the evaluation of the observing system simulation experimental design and on the assessment of the potential of remotely sensed marine surface wind data.
-
Chuang, Hsueh-Hua
The purpose of this dissertation is to develop an iterative model for the analysis of the current distribution in vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) using a circuit network modeling approach. This iterative model divides the VCSEL structure into numerous annular elements and uses a circuit network consisting of resistors and diodes. The measured sheet resistance of the p-distributed Bragg reflector (DBR), the measured sheet resistance of the layers under the oxide layer, and two empirical adjustable parameters are used as inputs to the iterative model to determine the resistance of each resistor. The two empirical values are related to the anisotropy of the resistivity of the p-DBR structure. The spontaneous current, stimulated current, and surface recombination current are accounted for by the diodes. The lateral carrier transport in the quantum well region is analyzed using drift and diffusion currents. The optical gain is calculated as a function of wavelength and carrier density from fundamental principles. The predicted threshold current densities for these VCSELs match the experimentally measured current densities over the wavelength range of 0.83 mum to 0.86 mum with an error of less than 5%. This model includes the effects of the resistance of the p-DBR mirrors, the oxide current-confining layer and spatial hole burning. Our model shows that higher sheet resistance under the oxide layer reduces the threshold current, but also reduces the current range over which single transverse mode operation occurs. The spatial hole burning profile depends on the lateral drift and diffusion of carriers in the quantum wells but is dominated by the voltage drop across the p-DBR region. To my knowledge, for the first time, the drift current and the diffusion current are treated separately. Previous work uses an ambipolar approach, which underestimates the total charge transferred in the quantum well region, especially under the oxide region. However, the total
-
Kondalkar, Vijay V; Li, Xiang; Park, Ikmo; Yang, Sang Sik; Lee, Keekeun
2018-02-05
A chipless, wireless current sensor system was developed using a giant magnetoimpedance (GMI) magnetic sensor and one-port surface acoustic wave (SAW) reflective delay line for real-time power monitoring in a current-carrying conductor. The GMI sensor has a high-quality crystalline structure in each layer, which contributes to a high sensitivity and good linearity in a magnetic field of 3-16 Oe. A 400 MHz RF energy generated from the interdigital transducer (IDT)-type reflector on the one-port SAW delay line was used as an activation source for the GMI magnetic sensor. The one-port SAW delay line replaces the presently existing transceiver system, which is composed of thousands of transistors, thus enabling chipless and wireless operation. We confirmed a large variation in the amplitude of the SAW reflection peak with a change in the impedance of the GMI sensor caused by the current flow through the conductor. Good linearity and sensitivity of ~0.691 dB/A were observed for currents in the range 1-12 A. Coupling of Mode (COM) modeling and impedance matching analysis were also performed to predict the device performance in advance and these were compared with the experimental results.
-
Suzuki, Kazuyoshi; Zupanski, Milija
2018-01-01
In this study, we investigate the uncertainties associated with land surface processes in an ensemble predication context. Specifically, we compare the uncertainties produced by a coupled atmosphere-land modeling system with two different land surface models, the Noah- MP land surface model (LSM) and the Noah LSM, by using the Maximum Likelihood Ensemble Filter (MLEF) data assimilation system as a platform for ensemble prediction. We carried out 24-hour prediction simulations in Siberia with 32 ensemble members beginning at 00:00 UTC on 5 March 2013. We then compared the model prediction uncertainty of snow depth and solid precipitation with observation-based research products and evaluated the standard deviation of the ensemble spread. The prediction skill and ensemble spread exhibited high positive correlation for both LSMs, indicating a realistic uncertainty estimation. The inclusion of a multiple snowlayer model in the Noah-MP LSM was beneficial for reducing the uncertainties of snow depth and snow depth change compared to the Noah LSM, but the uncertainty in daily solid precipitation showed minimal difference between the two LSMs. The impact of LSM choice in reducing temperature uncertainty was limited to surface layers of the atmosphere. In summary, we found that the more sophisticated Noah-MP LSM reduces uncertainties associated with land surface processes compared to the Noah LSM. Thus, using prediction models with improved skill implies improved predictability and greater certainty of prediction.
-
Jin, N.; Yang, F.; Shang, S. Y.; Tao, T.; Liu, J. S.
2016-08-01
According to the limitations of the LVRT technology of traditional photovoltaic inverter existed, this paper proposes a low voltage ride through (LVRT) control method based on model current predictive control (MCPC). This method can effectively improve the photovoltaic inverter output characteristics and response speed. The MCPC method of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter designed, the sum of the absolute value of the predictive current and the given current error is adopted as the cost function with the model predictive control method. According to the MCPC, the optimal space voltage vector is selected. Photovoltaic inverter has achieved automatically switches of priority active or reactive power control of two control modes according to the different operating states, which effectively improve the inverter capability of LVRT. The simulation and experimental results proves that the proposed method is correct and effective.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bonoli, P.T.; Barbato, E.; Imbeaux, F.
2003-01-01
This paper reviews the status of lower hybrid current drive (LHCD) simulation and modeling. We first discuss modules used for wave propagation, absorption, and current drive with particular emphasis placed on comparing exact numerical solutions of the Fokker Planck equation in 2-dimension with solution methods that employ 1-dimensional and adjoint approaches. We also survey model predictions for LHCD in past and present experiments showing detailed comparisons between simulated and observed current drive efficiencies and hard X-ray profiles. Finally we discuss several model predictions for lower hybrid current profile control in proposed next step reactor options. (authors)
-
A comparison of radiosity with current methods of sound level prediction in commercial spaces
Beamer, C. Walter, IV; Muehleisen, Ralph T.
2002-11-01
The ray tracing and image methods (and variations thereof) are widely used for the computation of sound fields in architectural spaces. The ray tracing and image methods are best suited for spaces with mostly specular reflecting surfaces. The radiosity method, a method based on solving a system of energy balance equations, is best applied to spaces with mainly diffusely reflective surfaces. Because very few spaces are either purely specular or purely diffuse, all methods must deal with both types of reflecting surfaces. A comparison of the radiosity method to other methods for the prediction of sound levels in commercial environments is presented. [Work supported by NSF.
-
A Steel Ball Surface Quality Inspection Method Based on a Circumferential Eddy Current Array Sensor
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Huayu Zhang
2017-07-01
Full Text Available To efficiently inspect surface defects on steel ball bearings, a new method based on a circumferential eddy current array (CECA sensor was proposed here. The best probe configuration, in terms of the coil quality factor (Q-factor, magnetic field intensity, and induced eddy current density on the surface of a sample steel ball, was determined using 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6-coil probes, for analysis and comparison. The optimal lift-off from the measured steel ball, the number of probe coils, and the frequency of excitation current suitable for steel ball inspection were obtained. Using the resulting CECA sensor to inspect 46,126 steel balls showed a miss rate of ~0.02%. The sensor was inspected for surface defects as small as 0.05 mm in width and 0.1 mm in depth.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hong Junjie, E-mail: hongjjie@mail.sysu.edu.cn [School of Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510006 (China); Li Liyi, E-mail: liliyi@hit.edu.cn [Dept. Electrical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150000 (China); Zong Zhijian; Liu Zhongtu [School of Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510006 (China)
2011-10-15
Highlights: {yields} The structure of the permanent magnet linear synchronous motor (SW-PMLSM) is new. {yields} A new current control method CEVPC is employed in this motor. {yields} The sectional power supply method is different to the others and effective. {yields} The performance gets worse with voltage and current limitations. - Abstract: To include features such as greater thrust density, higher efficiency without reducing the thrust stability, this paper proposes a section winding permanent magnet linear synchronous motor (SW-PMLSM), whose iron core is continuous, whereas winding is divided. The discrete system model of the motor is derived. With the definition of the current error vector and selection of the value function, the theory of the current error vector based prediction control (CEVPC) for the motor currents is explained clearly. According to the winding section feature, the motion region of the mover is divided into five zones, in which the implementation of the current predictive control method is proposed. Finally, the experimental platform is constructed and experiments are carried out. The results show: the current control effect has good dynamic response, and the thrust on the mover remains constant basically.
-
Prediction of viscosities and surface tensions of fuels using a new corresponding states model
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Queimada, A.J.; Rolo, L.I.; Caco, A.I.
2006-01-01
While some properties of diesels are cheap, easy and fast to measure, such as densities, others such as surface tensions and viscosities are expensive and time consuming. A new approach that uses some basic information such as densities to predict viscosities and surface tensions is here proposed......) 2005 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved....
-
Stryker, S. A.; Dimarco, S. F.; Stoessel, M. M.; Wang, Z.
2010-12-01
The northwest Indian Ocean is a region of complex circulation and atmospheric influence. The Persian (Arabian) Gulf and Red Sea contribute toward the complexity of the region. This study encompasses the surface and deep circulation in the region ranging from 0°N-35°N and 40°E-80°E from January 2002-December 2009. Emphasis is in the Persian Gulf, Oman Sea and Arabian Sea (roughly from 21°N-26°N and 56°E-63°E) using a variety of in situ and observation data sets. While there is a lot known about the Persian Gulf and Arabian Sea, little is known about the Oman Sea. Circulation in the northwest Indian Ocean is largely influenced by seasonal monsoon winds. From the winter monsoon to the summer monsoon, current direction reverses. Marginal sea inflow and outflow are also seasonally variable, which greatly impacts the physical water mass properties in the region. In situ and observation data sets include data from Argo floats (US GODAE), surface drifters (AOML) and an observation system consisting of 4 independent moorings and a cabled ocean observatory in the Oman Sea. The observing system in the Oman Sea was installed by Lighthouse R & D Enterprises, Inc. beginning in 2005, and measures current, temperature, conductivity, pressure, dissolved oxygen and turbidity, using the Aanderaa Recording Doppler Current Profiler (RDCP) 600 and the Aanderaa Recording Current Meter (RCM) 11. The cabled ocean observatory measures dissolved oxygen, temperature and salinity between 65 m and 1000 m and reports in real-time. Argo floats in the region have a parking depth range from 500 m to 2000 m. At 1000 m depth, 98% of the velocity magnitudes range from less than 1 cm/s to 20 cm/s. The Somali Current and Northeast/Southwest Monsoon Currents are present, reversing from summer to winter. At 2000 m depth, the Somali and Monsoon Currents are still present but have smaller velocities with 98% ranging from less than 1 cm/s to 13 cm/s. At both 1000 m and 2000 m, larger velocities occur
-
Predicting the effect of surface texture on the qualitative form of prehension.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ian John Flatters
Full Text Available Reach-to-grasp movements change quantitatively in a lawful (i.e. predictable manner with changes in object properties. We explored whether altering object texture would produce qualitative changes in the form of the precontact movement patterns. Twelve participants reached to lift objects from a tabletop. Nine objects were produced, each with one of three grip surface textures (high-friction, medium-friction and low-friction and one of three widths (50 mm, 70 mm and 90 mm. Each object was placed at three distances (100 mm, 300 mm and 500 mm, representing a total of 27 trial conditions. We observed two distinct movement patterns across all trials--participants either: (i brought their arm to a stop, secured the object and lifted it from the tabletop; or (ii grasped the object 'on-the-fly', so it was secured in the hand while the arm was moving. A majority of grasps were on-the-fly when the texture was high-friction and none when the object was low-friction, with medium-friction producing an intermediate proportion. Previous research has shown that the probability of on-the-fly behaviour is a function of grasp surface accuracy constraints. A finger friction rig was used to calculate the coefficients of friction for the objects and these calculations showed that the area available for a stable grasp (the 'functional grasp surface size' increased with surface friction coefficient. Thus, knowledge of functional grasp surface size is required to predict the probability of observing a given qualitative form of grasping in human prehensile behaviour.
-
Prediction of the surface roughness of AA6082 flow-formed tubes by design of experiments
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Srinivasulu, M.; Komaraiah, M.; Rao, C. S. Krishna Prasada
2013-01-01
Flow forming is a modern, chipless metal forming process that is employed for the production of thin-walled seamless tubes. Experiments are conducted on AA6082 alloy pre-forms to flow form into thin-walled tubes on a CNC flow-forming machine with a single roller. Design of experiments is used to predict the surface roughness of flow-formed tubes. The process parameters selected for this study are the roller axial feed, mandrel speed, and roller radius. A standard response surface methodology (RSM) called the Box Behnken design is used to perform the experimental runs. The regression model developed by RSM successfully predicts the surface roughness of AA6082 flow-formed tubes within the range of the selected process parameters.
-
Prediction of the surface roughness of AA6082 flow-formed tubes by design of experiments
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Srinivasulu, M. [Government Polytechnic for Women Badangpet, Hyderabad (India); Komaraiah, M. [Sreenidhi Institute of Science and Technology, Hyderabad (India); Rao, C. S. Krishna Prasada [Bharat Dynamics Limited, Hyderabad (India)
2013-06-15
Flow forming is a modern, chipless metal forming process that is employed for the production of thin-walled seamless tubes. Experiments are conducted on AA6082 alloy pre-forms to flow form into thin-walled tubes on a CNC flow-forming machine with a single roller. Design of experiments is used to predict the surface roughness of flow-formed tubes. The process parameters selected for this study are the roller axial feed, mandrel speed, and roller radius. A standard response surface methodology (RSM) called the Box Behnken design is used to perform the experimental runs. The regression model developed by RSM successfully predicts the surface roughness of AA6082 flow-formed tubes within the range of the selected process parameters.
-
The coupling of mechanical dynamics and induced currents in plates and surfaces
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Weissenburger, D.W.; Bialek, J.M.
1986-10-01
Significant mechanical reactions and deflections may be produced when electrical eddy currents induced in a conducting structure by transformer-like electromotive forces interact with background magnetic fields. Additional eddy currents induced by structural motion through the background fields modify both the mechanical and electrical dynamic behavior of the system. The observed effects of these motional eddy currents are sometimes referred to as magnetic damping and magnetic stiffness. This paper addresses the coupled structural deformation and eddy currents in flat plates and simple two-dimensional surfaces in three-space. A coupled system of equations has been formulated using finite element techniques for the mechanical aspects and a mesh network method for the electrical aspects of the problem
-
Poleward propagating subinertial alongshore surface currents off the U.S. West Coast
Kim, Sung Yong
2013-12-01
The network comprising 61 high-frequency radar systems along the U.S. West Coast (USWC) provides a unique, high resolution, and broad scale view of ocean surface circulation. Subinertial alongshore surface currents show poleward propagating signals with phase speeds of O(10) and O(100-300) km d -1 that are consistent with historical in situ observations off the USWC and that can be possibly interpreted as coastally trapped waves (CTWs). The propagating signals in the slow mode are partly observed in southern California, which may result from scattering and reflection of higher-mode CTWs due to curvature of shoreline and bathymetry near Point Conception, California. On the other hand, considering the order of the phase speed in the slow mode, the poleward propagating signals may be attributed to alongshore advection or pressure-driven flows. A statistical regression of coastal winds at National Data Buoy Center buoys on the observed surface currents partitions locally and remotely wind-forced components, isolates footprints of the equatorward propagating storm events in winter off the USWC, and shows the poleward propagating signals year round. Key Points A unique resource to examine synoptic-scale alongshore variability Isolation of equatorward wind events in winter using a statistical model Poleward propagating surface signals year-round © 2013. American Geophysical Union. All Rights Reserved.
-
Surface science principles and current applications
Taglauer, E; Wandelt, K
1996-01-01
Modern technologies increasingly rely on low-dimensional physics at interfaces and in thin-films and nano-structures. Surface science holds a key position in providing the experimental methods and theoretical models for a basic understanding of these effects. This book includes case studies and status reports about research topics such as: surface structure determination by tensor-LEED and surface X-ray diffraction; the preparation and detection of low-dimensional electronic surface states; quantitative surface compositional analysis; the dynamics of adsorption and reaction of adsorbates, e.g. kinetic oscillations; the characterization and control of thin-film and multilayer growth including the influence of surfactants; a critical assessment of the surface physics approach to heterogeneous catalysis.
-
Mann, Michael E.; Steinman, Byron A.; Miller, Sonya K.; Frankcombe, Leela M.; England, Matthew H.; Cheung, Anson H.
2016-04-01
The temporary slowdown in large-scale surface warming during the early 2000s has been attributed to both external and internal sources of climate variability. Using semiempirical estimates of the internal low-frequency variability component in Northern Hemisphere, Atlantic, and Pacific surface temperatures in concert with statistical hindcast experiments, we investigate whether the slowdown and its recent recovery were predictable. We conclude that the internal variability of the North Pacific, which played a critical role in the slowdown, does not appear to have been predictable using statistical forecast methods. An additional minor contribution from the North Atlantic, by contrast, appears to exhibit some predictability. While our analyses focus on combining semiempirical estimates of internal climatic variability with statistical hindcast experiments, possible implications for initialized model predictions are also discussed.
-
Characterization of the Deep Water Surface Wave Variability in the California Current Region
Villas Bôas, Ana B.; Gille, Sarah T.; Mazloff, Matthew R.; Cornuelle, Bruce D.
2017-11-01
Surface waves are crucial for the dynamics of the upper ocean not only because they mediate exchanges of momentum, heat, energy, and gases between the ocean and the atmosphere, but also because they determine the sea state. The surface wave field in a given region is set by the combination of local and remote forcing. The present work characterizes the seasonal variability of the deep water surface wave field in the California Current region, as retrieved from over two decades of satellite altimetry data combined with wave buoys and wave model hindcast (WaveWatch III). In particular, the extent to which the local wind modulates the variability of the significant wave height, peak period, and peak direction is assessed. During spring/summer, regional-scale wind events of up to 10 m/s are the dominant forcing for waves off the California coast, leading to relatively short-period waves (8-10 s) that come predominantly from the north-northwest. The wave climatology throughout the California Current region shows average significant wave heights exceeding 2 m during most of the year, which may have implications for the planning and retrieval methods of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite mission.
-
Prediction Surface Morphology of Nanostructure Fabricated by Nano-Oxidation Technology.
Huang, Jen-Ching; Chang, Ho; Kuo, Chin-Guo; Li, Jeen-Fong; You, Yong-Chin
2015-12-04
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) was used for visualization of a nano-oxidation technique performed on diamond-like carbon (DLC) thin film. Experiments of the nano-oxidation technique of the DLC thin film include those on nano-oxidation points and nano-oxidation lines. The feature sizes of the DLC thin film, including surface morphology, depth, and width, were explored after application of a nano-oxidation technique to the DLC thin film under different process parameters. A databank for process parameters and feature sizes of thin films was then established, and multiple regression analysis (MRA) and a back-propagation neural network (BPN) were used to carry out the algorithm. The algorithmic results are compared with the feature sizes acquired from experiments, thus obtaining a prediction model of the nano-oxidation technique of the DLC thin film. The comparative results show that the prediction accuracy of BPN is superior to that of MRA. When the BPN algorithm is used to predict nano-point machining, the mean absolute percentage errors (MAPE) of depth, left side, and right side are 8.02%, 9.68%, and 7.34%, respectively. When nano-line machining is being predicted, the MAPEs of depth, left side, and right side are 4.96%, 8.09%, and 6.77%, respectively. The obtained data can also be used to predict cross-sectional morphology in the DLC thin film treated with a nano-oxidation process.
-
Rodrigues, Luis R. L.; Doblas-Reyes, Francisco J.; Coelho, Caio A. S.
2018-02-01
A Bayesian method known as the Forecast Assimilation (FA) was used to calibrate and combine monthly near-surface temperature and precipitation outputs from seasonal dynamical forecast systems. The simple multimodel (SMM), a method that combines predictions with equal weights, was used as a benchmark. This research focuses on Europe and adjacent regions for predictions initialized in May and November, covering the boreal summer and winter months. The forecast quality of the FA and SMM as well as the single seasonal dynamical forecast systems was assessed using deterministic and probabilistic measures. A non-parametric bootstrap method was used to account for the sampling uncertainty of the forecast quality measures. We show that the FA performs as well as or better than the SMM in regions where the dynamical forecast systems were able to represent the main modes of climate covariability. An illustration with the near-surface temperature over North Atlantic, the Mediterranean Sea and Middle-East in summer months associated with the well predicted first mode of climate covariability is offered. However, the main modes of climate covariability are not well represented in most situations discussed in this study as the seasonal dynamical forecast systems have limited skill when predicting the European climate. In these situations, the SMM performs better more often.
-
Tidal analysis of surface currents in the Porsanger fjord in northern Norway
Stramska, Malgorzata; Jankowski, Andrzej; Cieszyńska, Agata
2016-04-01
In this presentation we describe surface currents in the Porsanger fjord (Porsangerfjorden) located in the European Arctic in the vicinity of the Barents Sea. Our analysis is based on data collected in the summer of 2014 using High Frequency radar system. Our interest in this fjord comes from the fact that this is a region of high climatic sensitivity. One of our long-term goals is to develop an improved understanding of the undergoing changes and interactions between this fjord and the large-scale atmospheric and oceanic conditions. In order to derive a better understanding of the ongoing changes one must first improve the knowledge about the physical processes that create the environment of the fjord. The present study is the first step in this direction. Our main objective in this presentation is to evaluate the importance of tidal forcing. Tides in the Porsanger fjord are substantial, with tidal range on the order of about 3 meters. Tidal analysis attributes to tides about 99% of variance in sea level time series recorded in Honningsvåg. The most important tidal component based on sea level data is the M2 component (amplitude of ~90 cm). The S2 and N2 components (amplitude of ~ 20 cm) also play a significant role in the semidiurnal sea level oscillations. The most important diurnal component is K1 with amplitude of about 8 cm. Tidal analysis lead us to the conclusion that the most important tidal component in observed surface currents is also the M2 component. The second most important component is the S2 component. Our results indicate that in contrast to sea level, only about 10 - 20% of variance in surface currents can be attributed to tidal currents. This means that about 80-90% of variance can be credited to wind-induced and geostrophic currents. This work was funded by the Norway Grants (NCBR contract No. 201985, project NORDFLUX). Partial support for MS comes from the Institute of Oceanology (IO PAN).
-
Predictability of the California Current System
Miller, Arthur J.; Chereskin, T.; Cornuelle, B. D.; Niiler, P. P.; Moisan, J. R.; Lindstrom, Eric (Technical Monitor)
2001-01-01
The physical and biological oceanography of the Southern California Bight (SCB), a highly productive subregion of the California Current System (CCS) that extends from Point Conception, California, south to Ensenada, Mexico, continues to be extensively studied. For example, the California Cooperative Oceanic Fisheries Investigations (CalCOFI) program has sampled this region for over 50 years, providing an unparalleled time series of physical and biological data. However, our understanding of what physical processes control the large-scale and mesoscale variations in these properties is incomplete. In particular, the non-synoptic and relatively coarse spatial sampling (70km) of the hydrographic grid does not completely resolve the mesoscale eddy field (Figure 1a). Moreover, these unresolved physical variations exert a dominant influence on the evolution of the ecosystem. In recent years, additional datasets that partially sample the SCB have become available. Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP) measurements, which now sample upper-ocean velocity between stations, and sea level observations along TOPEX tracks give a more complete picture of the mesoscale variability. However, both TOPEX and ADCP are well-sampled only along the cruise or orbit tracks and coarsely sampled in time and between tracks. Surface Lagrangian drifters also sample the region, although irregularly in time and space. SeaWiFS provides estimates of upper-ocean chlorophyll-a (chl-alpha), usually giving nearly complete coverage for week-long intervals, depending on cloud coverage. Historical ocean color data from the Coastal Zone Color Scanner (CZCS) has been used extensively to determine phytoplankton patterns and variability, characterize the primary production across the SCB coastal fronts, and describe the seasonal and interannual variability in pigment concentrations. As in CalCOFI, these studies described much of the observed structures and their variability over relatively large space and
-
Lee, Jong-Chul; Lee, Won-Ho; Kim, Woun-Jea
2015-09-01
The design and development procedures of SF6 gas circuit breakers are still largely based on trial and error through testing although the development costs go higher every year. The computation cannot cover the testing satisfactorily because all the real processes arc not taken into account. But the knowledge of the arc behavior and the prediction of the thermal-flow inside the interrupters by numerical simulations are more useful than those by experiments due to the difficulties to obtain physical quantities experimentally and the reduction of computational costs in recent years. In this paper, in order to get further information into the interruption process of a SF6 self-blast interrupter, which is based on a combination of thermal expansion and the arc rotation principle, gas flow simulations with a CFD-arc modeling are performed during the whole switching process such as high-current period, pre-current zero period, and current-zero period. Through the complete work, the pressure-rise and the ramp of the pressure inside the chamber before current zero as well as the post-arc current after current zero should be a good criterion to predict the short-line fault interruption performance of interrupters.
-
Jian, Jhih-Wei; Elumalai, Pavadai; Pitti, Thejkiran; Wu, Chih Yuan; Tsai, Keng-Chang; Chang, Jeng-Yih; Peng, Hung-Pin; Yang, An-Suei
2016-01-01
Predicting ligand binding sites (LBSs) on protein structures, which are obtained either from experimental or computational methods, is a useful first step in functional annotation or structure-based drug design for the protein structures. In this work, the structure-based machine learning algorithm ISMBLab-LIG was developed to predict LBSs on protein surfaces with input attributes derived from the three-dimensional probability density maps of interacting atoms, which were reconstructed on the query protein surfaces and were relatively insensitive to local conformational variations of the tentative ligand binding sites. The prediction accuracy of the ISMBLab-LIG predictors is comparable to that of the best LBS predictors benchmarked on several well-established testing datasets. More importantly, the ISMBLab-LIG algorithm has substantial tolerance to the prediction uncertainties of computationally derived protein structure models. As such, the method is particularly useful for predicting LBSs not only on experimental protein structures without known LBS templates in the database but also on computationally predicted model protein structures with structural uncertainties in the tentative ligand binding sites. PMID:27513851
-
Investigation of surface related leakage current in AlGaN/GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kaushik, J.K., E-mail: janeshkaushik@sspl.drdo.in [Solid State Physics Laboratory, Delhi 110054 (India); Balakrishnan, V.R.; Mongia, D.; Kumar, U.; Dayal, S. [Solid State Physics Laboratory, Delhi 110054 (India); Panwar, B.S. [Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, Hauz Khas, New Delhi 110016 (India); Muralidharan, R. [Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560012 (India)
2016-08-01
This paper reports the study of surface-related mechanisms to explain the high reverse leakage current observed in the in-house fabricated Si{sub 3}N{sub 4} passivated AlGaN/GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors. We propose that the Si{sub 3}N{sub 4}/AlGaN interface in the un-gated regions provides an additional leakage path between the gate and source/drain and may constitute a large component of reverse current. This surface related leakage component of current exhibits both temperature and electric field dependence and its Arrhenius behavior has been experimentally verified using Conductance Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy and temperature dependent reverse leakage current measurements. A thin interfacial amorphous semiconductor layer formed due to inter diffusion at Si{sub 3}N{sub 4}/AlGaN interface has been presumed as the source for this surface related leakage. We, therefore, conclude that optimum Si{sub 3}N{sub 4} deposition conditions and careful surface preparation prior to passivation can limit the extent of surface leakage and can thus vastly improve the device performance. - Highlights: • Enhanced leakage in AlGaN/GaN High Electron Mobility Transistors after passivation • Experimental evidence of the presence of extrinsic traps at Si{sub 3}N{sub 4}/AlGaN interface • Electron hopping in shallower extended defects and band tail traps at the interface. • Reduction in current collapse due to the virtual gate inhibition by this conduction • However, limitation on the operating voltages due to decrease in breakdown voltage.
-
Finite Element Simulation of Shot Peening: Prediction of Residual Stresses and Surface Roughness
Gariépy, Alexandre; Perron, Claude; Bocher, Philippe; Lévesque, Martin
Shot peening is a surface treatment that consists of bombarding a ductile surface with numerous small and hard particles. Each impact creates localized plastic strains that permanently stretch the surface. Since the underlying material constrains this stretching, compressive residual stresses are generated near the surface. This process is commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries to improve fatigue life. Finite element analyses can be used to predict residual stress profiles and surface roughness created by shot peening. This study investigates further the parameters and capabilities of a random impact model by evaluating the representative volume element and the calculated stress distribution. Using an isotropic-kinematic hardening constitutive law to describe the behaviour of AA2024-T351 aluminium alloy, promising results were achieved in terms of residual stresses.
-
Yin, Xunqiang; Shi, Junqiang; Qiao, Fangli
2018-05-01
Due to the high cost of ocean observation system, the scientific design of observation network becomes much important. The current network of the high frequency radar system in the Gulf of Thailand has been studied using a three-dimensional coastal ocean model. At first, the observations from current radars have been assimilated into this coastal model and the forecast results have improved due to the data assimilation. But the results also show that further optimization of the observing network is necessary. And then, a series of experiments were carried out to assess the performance of the existing high frequency ground wave radar surface current observation system. The simulated surface current data in three regions were assimilated sequentially using an efficient ensemble Kalman filter data assimilation scheme. The experimental results showed that the coastal surface current observation system plays a positive role in improving the numerical simulation of the currents. Compared with the control experiment without assimilation, the simulation precision of surface and subsurface current had been improved after assimilated the surface currents observed at current networks. However, the improvement for three observing regions was quite different and current observing network in the Gulf of Thailand is not effective and a further optimization is required. Based on these evaluations, a manual scheme has been designed by discarding the redundant and inefficient locations and adding new stations where the performance after data assimilation is still low. For comparison, an objective scheme based on the idea of data assimilation has been obtained. Results show that all the two schemes of observing network perform better than the original network and optimal scheme-based data assimilation is much superior to the manual scheme that based on the evaluation of original observing network in the Gulf of Thailand. The distributions of the optimal network of radars could be a
-
Assessing Confidence in Pliocene Sea Surface Temperatures to Evaluate Predictive Models
Dowsett, Harry J.; Robinson, Marci M.; Haywood, Alan M.; Hill, Daniel J.; Dolan, Aisling. M.; Chan, Wing-Le; Abe-Ouchi, Ayako; Chandler, Mark A.; Rosenbloom, Nan A.; Otto-Bliesner, Bette L.;

2012-01-01
In light of mounting empirical evidence that planetary warming is well underway, the climate research community looks to palaeoclimate research for a ground-truthing measure with which to test the accuracy of future climate simulations. Model experiments that attempt to simulate climates of the past serve to identify both similarities and differences between two climate states and, when compared with simulations run by other models and with geological data, to identify model-specific biases. Uncertainties associated with both the data and the models must be considered in such an exercise. The most recent period of sustained global warmth similar to what is projected for the near future occurred about 3.33.0 million years ago, during the Pliocene epoch. Here, we present Pliocene sea surface temperature data, newly characterized in terms of level of confidence, along with initial experimental results from four climate models. We conclude that, in terms of sea surface temperature, models are in good agreement with estimates of Pliocene sea surface temperature in most regions except the North Atlantic. Our analysis indicates that the discrepancy between the Pliocene proxy data and model simulations in the mid-latitudes of the North Atlantic, where models underestimate warming shown by our highest-confidence data, may provide a new perspective and insight into the predictive abilities of these models in simulating a past warm interval in Earth history.This is important because the Pliocene has a number of parallels to present predictions of late twenty-first century climate.
-
A hybrid model to predict the onset of gas entrainment with surface tension effects
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Saleh, W.; Bowden, R.C.; Hassan, I.G.; Kadem, L.
2008-01-01
The onset of gas entrainment, in a single downward oriented discharge from a stratified gas-liquid region with was modeled. The assumptions made in the development of the model reduced the problem to that of a potential flow. The discharge was modeled as a point-sink. Through use of the Kelvin-Laplace equation the model included the effects of surface tension. The resulting model required further knowledge of the flow field, specifically the dip radius of curvature prior to the onset of gas entrainment. The dip shape and size was investigated experimentally and correlations were provided to characterize the dip in terms of the discharge Froude number. The experimental correlation was used in conjunction with the theoretical model to predict the critical height. The results showed that by including surface tension effects the predicted critical height showed excellent agreement with experimental data. Surface tension reduces the critical height through the Bond number
-
Predicting the behavioural impact of transcranial direct current stimulation: issues and limitations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Archy Otto De Berker
2013-10-01
Full Text Available The transcranial application of weak currents to the human brain has enjoyed a decade of success, providing a simple and powerful tool for non-invasively altering human brain function. However, our understanding of current delivery and its impact upon neural circuitry leaves much to be desired. We argue that the credibility of conclusions drawn with tDCS is contingent upon realistic explanations of how tDCS works, and that our present understanding of tDCS limits the technique’s use to localize function in the human brain. We outline two central issues where progress is required: the localization of currents, and predicting their functional consequence. We encourage experimenters to eschew simplistic explanations of mechanisms of transcranial current stimulation. We suggest the use of individualized current modelling, together with computational neurostimulation to inform mechanistic frameworks in which to interpret the physiological impact of tDCS. We hope that through mechanistically richer descriptions of current flow and action, insight into the biological processes by which transcranial currents influence behaviour can be gained, leading to more effective stimulation protocols and empowering conclusions drawn with tDCS.
-
Improvement of a land surface model for accurate prediction of surface energy and water balances
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Katata, Genki
2009-02-01
In order to predict energy and water balances between the biosphere and atmosphere accurately, sophisticated schemes to calculate evaporation and adsorption processes in the soil and cloud (fog) water deposition on vegetation were implemented in the one-dimensional atmosphere-soil-vegetation model including CO 2 exchange process (SOLVEG2). Performance tests in arid areas showed that the above schemes have a significant effect on surface energy and water balances. The framework of the above schemes incorporated in the SOLVEG2 and instruction for running the model are documented. With further modifications of the model to implement the carbon exchanges between the vegetation and soil, deposition processes of materials on the land surface, vegetation stress-growth-dynamics etc., the model is suited to evaluate an effect of environmental loads to ecosystems by atmospheric pollutants and radioactive substances under climate changes such as global warming and drought. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nasehi Tehrani, J; Wang, J; McEwan, A
2016-01-01
Purpose: In this study, we developed and evaluated a method for predicting lung surface deformation vector fields (SDVFs) based on surrogate signals such as chest and abdomen motion at selected locations and spirometry measurements. Methods: A Patient-specific 3D triangular surface mesh of the lung region at end-expiration (EE) phase was obtained by threshold-based segmentation method. For each patient, a spirometer recorded the flow volume changes of the lungs; and 192 selected points at a regular spacing of 2cm X 2cm matrix points over a total area of 34cm X 24cm on the surface of chest and abdomen was used to detect chest wall motions. Preprocessing techniques such as QR factorization with column pivoting (QRCP) were employed to remove redundant observations of the chest and abdominal area. To create a statistical model between the lung surface and the corresponding surrogate signals, we developed a predictive model based on canonical ridge regression (CRR). Two unique weighting vectors were selected for each vertex on the surface of the lung, and they were optimized during the training process using the all other phases of 4D-CT except the end-inspiration (EI) phase. These parameters were employed to predict the vertices locations of a testing data set, which was the EI phase of 4D-CT. Results: For ten lung cancer patients, the deformation vector field of each vertex of lung surface mesh was estimated from the external motion at selected positions on the chest wall surface plus spirometry measurements. The average estimation of 98th percentile of error was less than 1 mm (AP= 0.85, RL= 0.61, and SI= 0.82). Conclusion: The developed predictive model provides a non-invasive approach to derive lung boundary condition. Together with personalized biomechanical respiration modelling, the proposed model can be used to derive the lung tumor motion during radiation therapy accurately from non-invasive measurements.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nasehi Tehrani, J; Wang, J [UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX (United States); McEwan, A [The University of Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales (Australia)
2016-06-15
Purpose: In this study, we developed and evaluated a method for predicting lung surface deformation vector fields (SDVFs) based on surrogate signals such as chest and abdomen motion at selected locations and spirometry measurements. Methods: A Patient-specific 3D triangular surface mesh of the lung region at end-expiration (EE) phase was obtained by threshold-based segmentation method. For each patient, a spirometer recorded the flow volume changes of the lungs; and 192 selected points at a regular spacing of 2cm X 2cm matrix points over a total area of 34cm X 24cm on the surface of chest and abdomen was used to detect chest wall motions. Preprocessing techniques such as QR factorization with column pivoting (QRCP) were employed to remove redundant observations of the chest and abdominal area. To create a statistical model between the lung surface and the corresponding surrogate signals, we developed a predictive model based on canonical ridge regression (CRR). Two unique weighting vectors were selected for each vertex on the surface of the lung, and they were optimized during the training process using the all other phases of 4D-CT except the end-inspiration (EI) phase. These parameters were employed to predict the vertices locations of a testing data set, which was the EI phase of 4D-CT. Results: For ten lung cancer patients, the deformation vector field of each vertex of lung surface mesh was estimated from the external motion at selected positions on the chest wall surface plus spirometry measurements. The average estimation of 98th percentile of error was less than 1 mm (AP= 0.85, RL= 0.61, and SI= 0.82). Conclusion: The developed predictive model provides a non-invasive approach to derive lung boundary condition. Together with personalized biomechanical respiration modelling, the proposed model can be used to derive the lung tumor motion during radiation therapy accurately from non-invasive measurements.
-
Stage I surface crack formation in thermal fatigue: A predictive multi-scale approach
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Osterstock, S.; Robertson, C.; Sauzay, M.; Aubin, V.; Degallaix, S.
2010-01-01
A multi-scale numerical model is developed, predicting the formation of stage I cracks, in thermal fatigue loading conditions. The proposed approach comprises 2 distinct calculation steps. Firstly, the number of cycles to micro-crack initiation is determined, in individual grains. The adopted initiation model depends on local stress-strain conditions, relative to sub-grain plasticity, grain orientation and grain deformation incompatibilities. Secondly, 2-4 grains long surface cracks (stage I) is predicted, by accounting for micro-crack coalescence, in 3 dimensions. The method described in this paper is applied to a 500 grains aggregate, loaded in representative thermal fatigue conditions. Preliminary results provide quantitative insight regarding position, density, spacing and orientations of stage I surface cracks and subsequent formation of crack networks. The proposed method is fully deterministic, provided all grain crystallographic orientations and micro-crack linking thresholds are specified. (authors)
-
Analytical predictions of SGEMP response and comparisons with computer calculations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
de Plomb, E.P.
1976-01-01
An analytical formulation for the prediction of SGEMP surface current response is presented. Only two independent dimensionless parameters are required to predict the peak magnitude and rise time of SGEMP induced surface currents. The analysis applies to limited (high fluence) emission as well as unlimited (low fluence) emission. Cause-effect relationships for SGEMP response are treated quantitatively, and yield simple power law dependencies between several physical variables. Analytical predictions for a large matrix of SGEMP cases are compared with an array of about thirty-five computer solutions of similar SGEMP problems, which were collected from three independent research groups. The theoretical solutions generally agree with the computer solutions as well as the computer solutions agree with one another. Such comparisons typically show variations less than a ''factor of two.''
-
Predicting scour beneath subsea pipelines from existing small free span depths under steady currents
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jun Y. Lee
2017-06-01
Full Text Available An equation was developed to predict current-induced scour beneath subsea pipelines in areas with small span depths, S. Current equations for scour prediction are only applicable to partially buried pipelines. The existence of small span depths (i.e. S/D < 0.3 are of concern because the capacity for scour is higher at smaller span depths. Furthermore, it is impractical to perform rectification works, such as installing grout bags, under a pipeline with a small S/D. Full-scale two-dimensional computational fluid dynamics (CFD simulations were performed using the Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes approach and the Shear stress transport k–ω turbulence model. To predict the occurrence of scour, the computed maximum bed shear stress beneath the pipe was converted to the dimensionless Shields parameter, and compared with the critical Shields parameter based on the mean sediment grain size. The numerical setup was verified, and a good agreement was found between model-scale CFD data and experimental data. Field data were obtained to determine the mean grain size, far field current velocity and to measure the span depths along the surveyed pipe length. A trend line equation was fitted to the full-scale CFD data, whereby the maximum Shields parameter beneath the pipe can be calculated based on the undisturbed Shields parameter and S/D.
-
Nagata, Takahiro; Fukushi, Keisuke; Takahashi, Yoshio
2009-04-15
A deficiency in environmental iodine can cause a number of health problems. Understanding how iodine is sequestered by materials is helpful for evaluating and developing methods for minimizing human health effects related to iodine. In addition, (129)I is considered to be strategically important for safety assessment of underground radioactive waste disposal. To assess the long-term stability of disposed radioactive waste, an understanding of (129)I adsorption on geologic materials is essential. Therefore, the adsorption of I(-) on naturally occurring oxides is of environmental concern. The surface charges of hydrous ferric oxide (HFO) in NaI electrolyte solutions were measured by potentiometric acid-base titration. The surface charge data were analyzed by means of an extended triple-layer model (ETLM) for surface complexation modeling to obtain the I(-) adsorption reaction and its equilibrium constant. The adsorption of I(-) was determined to be an outer-sphere process from ETLM analysis, which was consistent with independent X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) observation of I(-) adsorbed on HFO. The adsorption equilibrium constants for I(-) on beta-TiO(2) and gamma-Al(2)O(3) were also evaluated by analyzing the surface charge data of these oxides in NaI solution as reported in the literature. Comparison of these adsorption equilibrium constants for HFO, beta-TiO(2), and gamma-Al(2)O(3) based on site-occupancy standard states permitted prediction of I(-) adsorption equilibrium constants for all oxides by means of the Born solvation theory. The batch adsorption data for I(-) on HFO and amorphous aluminum oxide were reasonably reproduced by ETLM with the predicted equilibrium constants, confirming the validity of the present approach. Using the predicted adsorption equilibrium constants, we calculated distribution coefficient (K(d)) values for I(-) adsorption on common soil minerals as a function of pH and ionic strength.
-
Predictive Trailing-Edge Modulation Average Current Control in DC-DC Converters
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
LASCU, D.
2013-11-01
Full Text Available The paper investigates predictive digital average current control (PDACC in dc/dc converters using trailing-edge modulation (TEM. The study is focused on the recurrence duty cycle equation and then stability analysis is performed. It is demonstrated that average current control using trailing-edge modulation is stable on the whole range of the duty cycle and thus design problems are highly reduced. The analysis is carried out in a general manner, independent of converter topology and therefore the results can then be easily applied for a certain converter (buck, boost, buck-boost, etc.. The theoretical considerations are confirmed for a boost converter first using the MATLAB program based on state-space equations and finally with the CASPOC circuit simulation package.
-
Predicting daylight illuminance on inclined surfaces using sky luminance data
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Li, D.H.W.; Lau, C.C.S.; Lam, J.C. [City University of Hong Kong, Kowloon (China). Dept. of Building and Construction
2005-07-01
Daylight illuminance, particularly on vertical surfaces, plays a major role in determining and evaluating the daylighting performance of a building. In many parts of the world, however, the basic daylight illuminance data for various vertical planes are not always readily available. The usual method to obtain diffuse illuminance on tilted planes would be based on inclined surface models using data from the horizontal measurements. Alternatively, the diffuse illuminance on a sloping plane can be computed by integrating the luminance distribution of the sky 'seen' by the plane. This paper presents an approach to estimate the vertical outdoor illuminance from sky luminance data and solar geometry. Sky luminance data recorded from January 1999 to December 2001 in Hong Kong and generated by two well-known sky luminance models (Kittler and Perez) were used to compute the outdoor illuminance for the four principal vertical planes (N, E, S and W). The performance of this approach was evaluated against data measured in the same period. Statistical analysis indicated that using sky luminance distributions to predict outdoor illuminance can give reasonably good agreement with measured data for all vertical surfaces. The findings provide an accurate alternative to determine the amount of daylight on vertical as well as other inclined surfaces when sky luminance data are available. (author)
-
Experimentation and Prediction of Temperature Rise in Turning ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
Experimentation and Prediction of Temperature Rise in Turning Process using Response Surface Methodology. ... Science, Technology and Arts Research Journal. Journal Home · ABOUT THIS JOURNAL · Advanced Search · Current Issue ...
-
Surface flaw evaluation by vectorized eddy current testing image
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Endo, Hisashi; Takagi, Toshiyuki
2006-01-01
A method of eddy current testing (ECT) data mapping for surface breaking evaluation is studied. The multicoil ECT probe utilized in this paper consists of Transmit-Receive (TR) type sensors as array elements to obtain the information on crack directions. Switching two directional scans, U- and T- modes, gives two-dimensional vector mapping as ECT images. The ECT signals of the TR type sensor also give the information on crack directions from their variation displayed on the complex number plane. Extracting a complex number component of the signals makes it possible to visualize directions of numerically simulated proximate EDM slits. (author)
-
Funk, Christopher C.; Hoell, Andrew; Shukla, Shraddhanand; Blade, Ileana; Liebmann, Brant; Roberts, Jason B.; Robertson, Franklin R.
2014-01-01
In southern Ethiopia, Eastern Kenya, and southern Somalia poor boreal spring rains in 1999, 2000, 2004, 2007, 2008, 2009 and 2011 contributed to severe food insecurity and high levels of malnutrition. Predicting rainfall deficits in this region on seasonal and decadal time frames can help decision makers support disaster risk reduction while guiding climate-smart adaptation and agricultural development. Building on recent research that links more frequent droughts to a stronger Walker Circulation, warming in the Indo-Pacific warm pool, and an increased western Pacific sea surface temperature (SST) gradient, we explore the dominant modes of East African rainfall variability, links between these modes and sea surface temperatures, and a simple index-based monitoring-prediction system suitable for drought early warning.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zhao, Bo; Chen, Fan; Jia, Xiao-feng; Zhao, Chong-yang; Wang, Xiao-bo [Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo (China)
2017-04-15
Ultrasonic vibration-assisted Electrolytic in-process dressing (ELID) grinding is a highly efficient and highly precise machining method. The surface quality prediction model in ultrasonic vibration-assisted ELID mirror grinding was studied. First, the interaction between grits and workpiece surface was analyzed according to kinematic mechanics, and the surface roughness model was developed. The variations in surface roughness under different parameters was subsequently calculated and analyzed by MATLAB. Results indicate that compared with the ordinary ELID grinding, ultrasonic vibration-assisted ELID grinding is superior, because it has more stable and better surface quality and has an improved range of ductile machining.
-
Threshold current for fireball generation
Dijkhuis, Geert C.
1982-05-01
Fireball generation from a high-intensity circuit breaker arc is interpreted here as a quantum-mechanical phenomenon caused by severe cooling of electrode material evaporating from contact surfaces. According to the proposed mechanism, quantum effects appear in the arc plasma when the radius of one magnetic flux quantum inside solid electrode material has shrunk to one London penetration length. A formula derived for the threshold discharge current preceding fireball generation is found compatible with data reported by Silberg. This formula predicts linear scaling of the threshold current with the circuit breaker's electrode radius and concentration of conduction electrons.
-
Yeh, Chun-Ping; Huang, Jiunn-Yuan
2018-04-01
Low-alloy steels used as structural materials in nuclear power plants are subjected to cyclic stresses during power plant operations. As a result, cracks may develop and propagate through the material. The alternating current potential drop technique is used to measure the lengths of cracks in metallic components. The depth of the penetration of the alternating current is assumed to be small compared to the crack length. This assumption allows the adoption of the unfolding technique to simplify the problem to a surface Laplacian field. The numerical modelling of the electric potential and current density distribution prediction model for a compact tension specimen and the unfolded crack model are presented in this paper. The goal of this work is to conduct numerical simulations to reduce deviations occurring in the crack length measurements. Numerical simulations were conducted on AISI 4340 low-alloy steel with different crack lengths to evaluate the electric potential distribution. From the simulated results, an optimised position for voltage measurements in the crack region was proposed.
-
Can current models of accommodation and vergence predict accommodative behavior in myopic children?
Sreenivasan, Vidhyapriya; Irving, Elizabeth L; Bobier, William R
2014-08-01
Investigations into the progression of myopia in children have long considered the role of accommodation as a cause and solution. Myopic children show high levels of accommodative adaptation, coupled with accommodative lag and high response AC/A (accommodative convergence per diopter of accommodation). This pattern differs from that predicted by current models of interaction between accommodation and vergence, where weakened reflex responses and a high AC/A would be associated with a low not high levels of accommodative adaptation. However, studies of young myopes were limited to only part of the accommodative vergence synkinesis and the reciprocal components of vergence adaptation and convergence accommodation were not studied in tandem. Accordingly, we test the hypothesis that the accommodative behavior of myopic children is not predicted by current models and whether that departure is explained by differences in the accommodative plant of the myopic child. Responses to incongruent stimuli (-2D, +2D adds, 10 prism diopter base-out prism) were investigated in 28 myopic and 25 non-myopic children aged 7-15 years. Subjects were divided into phoria groups - exo, ortho and eso based upon their near phoria. The school aged myopes showed high levels of accommodative adaptation but with reduced accommodation and high AC/A. This pattern is not explained by current adult models and could reflect a sluggish gain of the accommodative plant (ciliary muscle and lens), changes in near triad innervation or both. Further, vergence adaptation showed a predictable reciprocal relationship with the high accommodative adaptation, suggesting that departures from adult models were limited to accommodation not vergence behavior. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Adamczyk, J.; Horny, N.; Tricoteaux, A.; Jouan, P.-Y.; Zadam, M.
2008-01-01
This paper deals with experimental design applied to response surface methodology (RSM) in order to determine the influence of the discharge conditions on preferred c-axis orientation of sputtered AlN thin films. The thin films have been deposited by DC reactive magnetron sputtering on Si (1 0 0) substrates. The preferred orientation was evaluated using a conventional Bragg-Brentano X-ray diffractometer (θ-2θ) with the CuKα radiation. We have first determined the experimental domain for 3 parameters: sputtering pressure (2-6 mTorr), discharge current (312-438 mA) and nitrogen percentage (17-33%). For the setup of the experimental design we have used a three factors Doehlert matrix which allows the use of the statistical response surface methodology (RSM) in a spherical domain. A four dimensional surface response, which represents the (0 0 0 2) peak height as a function of sputtering pressure, discharge current and nitrogen percentage, was obtained. It has been found that the main interaction affecting the preferential c-axis orientation was the pressure-nitrogen percentage interaction. It has been proved that a Box-Cox transformation is a very useful method to interpret and discuss the experimental results and leads to predictions in good agreement with experiments
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Adamczyk, J.; Horny, N.; Tricoteaux, A. [IUT de Valenciennes, Departement Mesures Physiques, UVHC, Z.I. du Champ de l' Abbesse, 59600 Maubeuge (France); Jouan, P.-Y. [IUT de Valenciennes, Departement Mesures Physiques, UVHC, Z.I. du Champ de l' Abbesse, 59600 Maubeuge (France)], E-mail: pierre-yves.jouan@univ-valenciennes.fr; Zadam, M. [Electronic Department, Badji Mokhtar University, BP12 Annaba (Algeria)
2008-01-15
This paper deals with experimental design applied to response surface methodology (RSM) in order to determine the influence of the discharge conditions on preferred c-axis orientation of sputtered AlN thin films. The thin films have been deposited by DC reactive magnetron sputtering on Si (1 0 0) substrates. The preferred orientation was evaluated using a conventional Bragg-Brentano X-ray diffractometer ({theta}-2{theta}) with the CuK{alpha} radiation. We have first determined the experimental domain for 3 parameters: sputtering pressure (2-6 mTorr), discharge current (312-438 mA) and nitrogen percentage (17-33%). For the setup of the experimental design we have used a three factors Doehlert matrix which allows the use of the statistical response surface methodology (RSM) in a spherical domain. A four dimensional surface response, which represents the (0 0 0 2) peak height as a function of sputtering pressure, discharge current and nitrogen percentage, was obtained. It has been found that the main interaction affecting the preferential c-axis orientation was the pressure-nitrogen percentage interaction. It has been proved that a Box-Cox transformation is a very useful method to interpret and discuss the experimental results and leads to predictions in good agreement with experiments.
-
Study of leakage current behaviour on artificially polluted surface of ceramic insulator
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Subba Reddy, B.; Nagabhushana, G.R.
2003-01-01
This paper presents the results of the study concerning to the leakage current behaviour on artificially polluted ceramic insulator surface. From the present study it was observed that there is a reasonably well-defined inception of current i.e. scintillations at a finite voltage. The corresponding voltages for extinction of the current are in the range of 0.8 kV to 2.1 kV. Obviously, the dry band formed in the immediate vicinity of the pin prevents smooth current flow as the voltage rises from zero. Only when the voltage is adequate it causes a flashover of the dray band and current starts flowing. As is common in similar current extinction phenomena, here also, the extinction voltages are significantly lower than the inception voltages. Further, the voltage-current curves invariably show hysteresis-the leakage currents are lower in the reducing portion of the voltage. This is obviously due to drying of the wet pollutant layer thereby increasing its resistance. It is believed that this is the first time that such a direct quantitative evidence of drying in individual half cycles is experimentally visualized
-
Dynamics at Solid State Surfaces and Interfaces, Volume 1 Current Developments
Bovensiepen, Uwe; Wolf, Martin
2010-01-01
This two-volume work covers ultrafast structural and electronic dynamics of elementary processes at solid surfaces and interfaces, presenting the current status of photoinduced processes. Providing valuable introductory information for newcomers to this booming field of research, it investigates concepts and experiments, femtosecond and attosecond time-resolved methods, as well as frequency domain techniques. The whole is rounded off by a look at future developments.
-
Risk assessment based on current release standards for radioactive surface contamination
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen, S.Y.
1993-09-01
Standards for uncontrolled releases of radioactive surface contamination have been in existence in the United States for about two decades. Such standards have been issued by various agencies, including the US Department of Energy. This paper reviews the technical basis of published standards, identifies areas in need of revision, provides risk interpretations based on current technical knowledge and the regulatory environment, and offers suggestions for improvements
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ching-Tai Chen
Full Text Available Protein-protein interactions are key to many biological processes. Computational methodologies devised to predict protein-protein interaction (PPI sites on protein surfaces are important tools in providing insights into the biological functions of proteins and in developing therapeutics targeting the protein-protein interaction sites. One of the general features of PPI sites is that the core regions from the two interacting protein surfaces are complementary to each other, similar to the interior of proteins in packing density and in the physicochemical nature of the amino acid composition. In this work, we simulated the physicochemical complementarities by constructing three-dimensional probability density maps of non-covalent interacting atoms on the protein surfaces. The interacting probabilities were derived from the interior of known structures. Machine learning algorithms were applied to learn the characteristic patterns of the probability density maps specific to the PPI sites. The trained predictors for PPI sites were cross-validated with the training cases (consisting of 432 proteins and were tested on an independent dataset (consisting of 142 proteins. The residue-based Matthews correlation coefficient for the independent test set was 0.423; the accuracy, precision, sensitivity, specificity were 0.753, 0.519, 0.677, and 0.779 respectively. The benchmark results indicate that the optimized machine learning models are among the best predictors in identifying PPI sites on protein surfaces. In particular, the PPI site prediction accuracy increases with increasing size of the PPI site and with increasing hydrophobicity in amino acid composition of the PPI interface; the core interface regions are more likely to be recognized with high prediction confidence. The results indicate that the physicochemical complementarity patterns on protein surfaces are important determinants in PPIs, and a substantial portion of the PPI sites can be predicted
-
Chen, Ching-Tai; Peng, Hung-Pin; Jian, Jhih-Wei; Tsai, Keng-Chang; Chang, Jeng-Yih; Yang, Ei-Wen; Chen, Jun-Bo; Ho, Shinn-Ying; Hsu, Wen-Lian; Yang, An-Suei
2012-01-01
Protein-protein interactions are key to many biological processes. Computational methodologies devised to predict protein-protein interaction (PPI) sites on protein surfaces are important tools in providing insights into the biological functions of proteins and in developing therapeutics targeting the protein-protein interaction sites. One of the general features of PPI sites is that the core regions from the two interacting protein surfaces are complementary to each other, similar to the interior of proteins in packing density and in the physicochemical nature of the amino acid composition. In this work, we simulated the physicochemical complementarities by constructing three-dimensional probability density maps of non-covalent interacting atoms on the protein surfaces. The interacting probabilities were derived from the interior of known structures. Machine learning algorithms were applied to learn the characteristic patterns of the probability density maps specific to the PPI sites. The trained predictors for PPI sites were cross-validated with the training cases (consisting of 432 proteins) and were tested on an independent dataset (consisting of 142 proteins). The residue-based Matthews correlation coefficient for the independent test set was 0.423; the accuracy, precision, sensitivity, specificity were 0.753, 0.519, 0.677, and 0.779 respectively. The benchmark results indicate that the optimized machine learning models are among the best predictors in identifying PPI sites on protein surfaces. In particular, the PPI site prediction accuracy increases with increasing size of the PPI site and with increasing hydrophobicity in amino acid composition of the PPI interface; the core interface regions are more likely to be recognized with high prediction confidence. The results indicate that the physicochemical complementarity patterns on protein surfaces are important determinants in PPIs, and a substantial portion of the PPI sites can be predicted correctly with
-
Improving weather predictability by including land-surface model parameter uncertainty
Orth, Rene; Dutra, Emanuel; Pappenberger, Florian
2016-04-01
The land surface forms an important component of Earth system models and interacts nonlinearly with other parts such as ocean and atmosphere. To capture the complex and heterogenous hydrology of the land surface, land surface models include a large number of parameters impacting the coupling to other components of the Earth system model. Focusing on ECMWF's land-surface model HTESSEL we present in this study a comprehensive parameter sensitivity evaluation using multiple observational datasets in Europe. We select 6 poorly constrained effective parameters (surface runoff effective depth, skin conductivity, minimum stomatal resistance, maximum interception, soil moisture stress function shape, total soil depth) and explore their sensitivity to model outputs such as soil moisture, evapotranspiration and runoff using uncoupled simulations and coupled seasonal forecasts. Additionally we investigate the possibility to construct ensembles from the multiple land surface parameters. In the uncoupled runs we find that minimum stomatal resistance and total soil depth have the most influence on model performance. Forecast skill scores are moreover sensitive to the same parameters as HTESSEL performance in the uncoupled analysis. We demonstrate the robustness of our findings by comparing multiple best performing parameter sets and multiple randomly chosen parameter sets. We find better temperature and precipitation forecast skill with the best-performing parameter perturbations demonstrating representativeness of model performance across uncoupled (and hence less computationally demanding) and coupled settings. Finally, we construct ensemble forecasts from ensemble members derived with different best-performing parameterizations of HTESSEL. This incorporation of parameter uncertainty in the ensemble generation yields an increase in forecast skill, even beyond the skill of the default system. Orth, R., E. Dutra, and F. Pappenberger, 2016: Improving weather predictability by
-
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
XU Weiwei; DAI Songyuan; HU Linhua; ZHANG Changneng; XIAO Shangfeng; LUO Xiangdong; JING Weiping; WANG Kongjia
2007-01-01
The TiO2 nanoporous film photoelectrode, as a crucial component of dye-sensitized solar cells, has been investigated. The photovoltaic properties and the dark current were studied by two surface modification methods. One was to apply a compact layer between the conductive glass substrate and nanoporous TiO2 film. Another was to produce TiO2 nanoparticles among the microstructure by TiCU treatment. A suitable concentration and number of times for TiCU treatment were found in our experiment. The dark current is suppressed by surface modifications, leading to a significant improvement in the solar cells performance. An excessive concentration of TiCU will produce more surface states and introduce a larger dark current reversely. The dye is also regarded as a source of charge recombination in dark to some extent, due to an amount of surface protonations introduced by the interfacial link in the conductive glass substrate/dye interface and dye/TiO2 interface.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gutowski, W.J.; Gutzler, D.S.; Portman, D.; Wang, W.C.
1988-04-01
The surface energy balance simulated by state-of-the-art general circulation models at GFDL, GISS and NCAR for climates with current levels of atmospheric CO 2 concentration (control climate) and with twice the current levels. The work is part of an effort sponsored by the US Department of Energy to assess climate simulations produced by these models. The surface energy balance enables us to diagnose differences between models in surface temperature climatology and sensitivity to doubling CO 2 in terms of the processes that control surface temperature. Our analysis compares the simulated balances by averaging the fields of interest over a hierarchy of spatial domains ranging from the entire globe down to regions a few hundred kilometers across
-
Coupled assimilation for an intermediated coupled ENSO prediction model
Zheng, Fei; Zhu, Jiang
2010-10-01
The value of coupled assimilation is discussed using an intermediate coupled model in which the wind stress is the only atmospheric state which is slavery to model sea surface temperature (SST). In the coupled assimilation analysis, based on the coupled wind-ocean state covariance calculated from the coupled state ensemble, the ocean state is adjusted by assimilating wind data using the ensemble Kalman filter. As revealed by a series of assimilation experiments using simulated observations, the coupled assimilation of wind observations yields better results than the assimilation of SST observations. Specifically, the coupled assimilation of wind observations can help to improve the accuracy of the surface and subsurface currents because the correlation between the wind and ocean currents is stronger than that between SST and ocean currents in the equatorial Pacific. Thus, the coupled assimilation of wind data can decrease the initial condition errors in the surface/subsurface currents that can significantly contribute to SST forecast errors. The value of the coupled assimilation of wind observations is further demonstrated by comparing the prediction skills of three 12-year (1997-2008) hindcast experiments initialized by the ocean-only assimilation scheme that assimilates SST observations, the coupled assimilation scheme that assimilates wind observations, and a nudging scheme that nudges the observed wind stress data, respectively. The prediction skills of two assimilation schemes are significantly better than those of the nudging scheme. The prediction skills of assimilating wind observations are better than assimilating SST observations. Assimilating wind observations for the 2007/2008 La Niña event triggers better predictions, while assimilating SST observations fails to provide an early warning for that event.
-
Christman, Mary C; Doctor, Daniel H; Niemiller, Matthew L; Weary, David J; Young, John A; Zigler, Kirk S; Culver, David C
2016-01-01
One of the most challenging fauna to study in situ is the obligate cave fauna because of the difficulty of sampling. Cave-limited species display patchy and restricted distributions, but it is often unclear whether the observed distribution is a sampling artifact or a true restriction in range. Further, the drivers of the distribution could be local environmental conditions, such as cave humidity, or they could be associated with surface features that are surrogates for cave conditions. If surface features can be used to predict the distribution of important cave taxa, then conservation management is more easily obtained. We examined the hypothesis that the presence of major faunal groups of cave obligate species could be predicted based on features of the earth surface. Georeferenced records of cave obligate amphipods, crayfish, fish, isopods, beetles, millipedes, pseudoscorpions, spiders, and springtails within the area of Appalachian Landscape Conservation Cooperative in the eastern United States (Illinois to Virginia and New York to Alabama) were assigned to 20 x 20 km grid cells. Habitat suitability for these faunal groups was modeled using logistic regression with twenty predictor variables within each grid cell, such as percent karst, soil features, temperature, precipitation, and elevation. Models successfully predicted the presence of a group greater than 65% of the time (mean = 88%) for the presence of single grid cell endemics, and for all faunal groups except pseudoscorpions. The most common predictor variables were latitude, percent karst, and the standard deviation of the Topographic Position Index (TPI), a measure of landscape rugosity within each grid cell. The overall success of these models points to a number of important connections between the surface and cave environments, and some of these, especially soil features and topographic variability, suggest new research directions. These models should prove to be useful tools in predicting the
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cefalas, A.C., E-mail: ccefalas@eie.gr [National Hellenic Research Foundation, Theoretical and Physical Chemistry Institute, 48 Vassileos Constantinou Avenue, Athens 11635 (Greece); Kollia, Z.; Spyropoulos-Antonakakis, N.; Gavriil, V. [National Hellenic Research Foundation, Theoretical and Physical Chemistry Institute, 48 Vassileos Constantinou Avenue, Athens 11635 (Greece); Christofilos, D.; Kourouklis, G. [Physics Division, School of Technology, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki 54124 (Greece); Semashko, V.V.; Pavlov, V. [Kazan Federal University, Institute of Physics, 18 Kremljovskaja str., Kazan 420008 (Russian Federation); Sarantopoulou, E. [National Hellenic Research Foundation, Theoretical and Physical Chemistry Institute, 48 Vassileos Constantinou Avenue, Athens 11635 (Greece); Kazan Federal University, Institute of Physics, 18 Kremljovskaja str., Kazan 420008 (Russian Federation)
2017-02-28
Highlights: • The work links the surface morphology of amorphous semiconductors with both their electric-thermal properties and current stability at the nanoscale (<1 μm). • Measured high correlation value between surface morphological spatial gradient and conductive electron energy spatial gradient or thermal gradient. • Unidirectional current stability is associated with asymmetric nanodomains along nanosize conductive paths. • Bidirectional current stability is inherent with either long conductive paths or nanosize conductive paths along symmetric nanodomains. • Conclusion: Surface design improves current stability across nanoelectonic junctions. - Abstract: A link between the morphological characteristics and the electric properties of amorphous layers is established by means of atomic, conductive, electrostatic force and thermal scanning microscopy. Using amorphous Ta{sub 2}O{sub 5} (a-Ta{sub 2}O{sub 5}) semiconductive layer, it is found that surface profile gradients (morphological gradient), are highly correlated to both the electron energy gradient of trapped electrons in interactive Coulombic sites and the thermal gradient along conductive paths and thus thermal and electric properties are correlated with surface morphology at the nanoscale. Furthermore, morphological and electron energy gradients along opposite conductive paths of electrons intrinsically impose a current stability anisotropy. For either long conductive paths (L > 1 μm) or along symmetric nanodomains, current stability for both positive and negative currents i is demonstrated. On the contrary, for short conductive paths along non-symmetric nanodomains, the set of independent variables (L, i) is spanned by two current stability/intability loci. One locus specifies a stable state for negative currents, while the other locus also describes a stable state for positive currents.
-
Eddy current array probe for detection of surface breaking cracks in the extrados of feeder bends
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Obrutsky, L.S.; Cassidy, R.A.; Chaplin, K.; Martin, P.; Bureau, J.F.
2006-01-01
A new eddy current array probe has been implemented as a straightforward and promising technique for detection of outer diameter (OD) surface-breaking cracks on the extrados of feeder bends. The design is based on previous work performed at AECL, which had demonstrated that eddy current probes with laterally displaced transmit-receive coils can overcome some of the limitations of inspecting ferritic steel components for surface-breaking cracks. The Feeder Integrity Joint Program-CANDU Owners Group Inc. (FIJP-COG) Non-Destructive Evaluation (NDE) Team members commissioned AECL to work in collaboration with the probe manufacturer ZETEC, to develop a field usable eddy current array probe. The objective was to acquire a technique with the following capabilities: fast scanning non-contact inspection technique for surface breaking discontinuities; full inspection of the bend extrados OD surface in a single scan; ability to inspect first and second bends with similar settings and capabilities; permanent record for future reference; axial and circumferential crack detection in a single scan; capability to detect OD surface-breaking cracks, which can provide additional information to that provided by ultrasonic testing (UT) for flaw characterization, and detection threshold: Surface breaking cracks equivalent to a 0.5 mm deep, 10 mm long EDM notch located on the OD of the bend extrados. This paper discusses the basis for probe design, summarizes the experimental work to evaluate probe capabilities and analyzes the results from the field trial. (author)
-
Eddy current array probe for detection of surface breaking cracks in the extrados of feeder bends
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Obrutsky, L.S.; Cassidy, R.A.; Chaplin, K. [Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River, Ontario (Canada)]. E-mail: obrutskyl@aecl.ca; Martin, P. [NB Power, Point Lepreau NGS, Point Lepreau, New Brunswick (Canada)]. E-mail: PMartin@nbpower.com; Bureau, J.F. [Zetec, Quebec, Quebec (Canada)]. E-mail: jean-francois.bureau@zetec.com
2006-07-01
A new eddy current array probe has been implemented as a straightforward and promising technique for detection of outer diameter (OD) surface-breaking cracks on the extrados of feeder bends. The design is based on previous work performed at AECL, which had demonstrated that eddy current probes with laterally displaced transmit-receive coils can overcome some of the limitations of inspecting ferritic steel components for surface-breaking cracks. The Feeder Integrity Joint Program-CANDU Owners Group Inc. (FIJP-COG) Non-Destructive Evaluation (NDE) Team members commissioned AECL to work in collaboration with the probe manufacturer ZETEC, to develop a field usable eddy current array probe. The objective was to acquire a technique with the following capabilities: fast scanning non-contact inspection technique for surface breaking discontinuities; full inspection of the bend extrados OD surface in a single scan; ability to inspect first and second bends with similar settings and capabilities; permanent record for future reference; axial and circumferential crack detection in a single scan; capability to detect OD surface-breaking cracks, which can provide additional information to that provided by ultrasonic testing (UT) for flaw characterization, and detection threshold: Surface breaking cracks equivalent to a 0.5 mm deep, 10 mm long EDM notch located on the OD of the bend extrados. This paper discusses the basis for probe design, summarizes the experimental work to evaluate probe capabilities and analyzes the results from the field trial. (author)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Pouchly V.
2012-01-01
Full Text Available The sintering is a complex thermally activated process, thus any prediction of sintering behaviour is very welcome not only for industrial purposes. Presented paper shows the possibility of densification prediction based on concept of Master Sintering Surface (MSS for pressure assisted Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS. User friendly software for evaluation of the MSS is presented. The concept was used for densification prediction of alumina ceramics sintered by SPS.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Abdeen, Mostafa A. M.
2008-01-01
Most of the open water irrigation channels in Egypt suffer from the infestation of aquatic weeds, especially the submerged ones that cause numerous hydraulic problems for the open channels themselves and their water distributaries such as increasing water losses, obstructing water flow, and reducing channels' water distribution efficiencies. Accurate simulation and prediction of flow behavior in such channels is very essential for water distribution decision makers. Artificial neural networks (ANN) have proven to be very successful in the simulation of several physical phenomena, in general, and in the water research field in particular. Therefore, the current study aims towards introducing the utilization of ANN in simulating the impact of vegetation in main open channel, which supplies water to different distributaries, on the water surface profile in this main channel. Specifically, the study, presented in the current paper utilizes ANN technique for the development of various models to simulate the impact of different submerged weeds' densities, different flow discharges, and different distributaries operation scheduling on the water surface profile in an experimental main open channel that supplies water to different distributaries. In the investigated experiment, the submerged weeds were simulated as branched flexible elements. The investigated experiment was considered as an example for implementing the same methodology and technique in a real open channel system. The results showed that the ANN technique is very successful in simulating the flow behavior of the pre-mentioned open channel experiment with the existence of the submerged weeds. In addition, the developed ANN models were capable of predicting the open channel flow behavior in all the submerged weeds' cases that were considered in the ANN development process
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Toralf eNeuling
2012-09-01
Full Text Available Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS has been applied in numerous scientific studies over the past decade. However, the possibility to apply tDCS in therapy of neuropsychiatric disorders is still debated. While transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS has been approved for treatment of major depression in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA, tDCS is not as widely accepted. One of the criticisms against tDCS is the lack of spatial specificity. Focality is limited by the electrode size (35 cm2 are commonly used and the bipolar arrangement. However, a current flow through the head directly from anode to cathode is an outdated view. Finite element (FE models have recently been used to predict the exact current flow during tDCS. These simulations have demonstrated that the current flow depends on tissue shape and conductivity. Toface the challenge to predict the location, magnitude and direction of the current flow induced by tDCS and transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS, we used a refined realistic FE modeling approach. With respect to the literature on clinical tDCS and tACS, we analyzed two common setups for the location of the stimulation electrodes which target the frontal lobe and the occipital lobe, respectively. We compared lateral and medial electrode configuration with regard to theirusability. We were able to demonstrate that the lateral configurations yielded more focused stimulation areas as well as higher current intensities in the target areas. The high resolution of our simulation allows one to combine the modeled current flow with the knowledge of neuronal orientation to predict the consequences of tDCS and tACS. Our results not only offer a basis for a deeper understanding of the stimulation sites currently in use for clinical applications but also offer a better interpretation of observed effects.
-
Dyer, Joseph J.; Brewer, Shannon K.; Worthington, Thomas A.; Bergey, Elizabeth A.
2013-01-01
1.A major limitation to effective management of narrow-range crayfish populations is the paucity of information on the spatial distribution of crayfish species and a general understanding of the interacting environmental variables that drive current and future potential distributional patterns. 2.Maximum Entropy Species Distribution Modeling Software (MaxEnt) was used to predict the current and future potential distributions of four endemic crayfish species in the Ouachita Mountains. Current distributions were modelled using climate, geology, soils, land use, landform and flow variables thought to be important to lotic crayfish. Potential changes in the distribution were forecast by using models trained on current conditions and projecting onto the landscape predicted under climate-change scenarios. 3.The modelled distribution of the four species closely resembled the perceived distribution of each species but also predicted populations in streams and catchments where they had not previously been collected. Soils, elevation and winter precipitation and temperature most strongly related to current distributions and represented 6587% of the predictive power of the models. Model accuracy was high for all models, and model predictions of new populations were verified through additional field sampling. 4.Current models created using two spatial resolutions (1 and 4.5km2) showed that fine-resolution data more accurately represented current distributions. For three of the four species, the 1-km2 resolution models resulted in more conservative predictions. However, the modelled distributional extent of Orconectes leptogonopodus was similar regardless of data resolution. Field validations indicated 1-km2 resolution models were more accurate than 4.5-km2 resolution models. 5.Future projected (4.5-km2 resolution models) model distributions indicated three of the four endemic species would have truncated ranges with low occurrence probabilities under the low-emission scenario
-
Prediction of Outside Surface Aluminium Tank Corrosion on TRIGA Mark - IIResearch Reactor Bandung
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Soedardjo
2000-01-01
The prediction of outside surface aluminium tank corrosion on researchreactor design which coated by epoxy paint, has been assessed. The new TRIGAMark - II Bandung research reactor tank design separated by 3 section arebottom, middle and upper section then inserted into the existing old reactor.The separation carried out caused by the space constraint on top of old tank,so that the novel tank impossible inserted into old tank all at once. Thespace between novel and old tank is 10 mm. After bottom and middle section oftank welded then followed by epoxy painting and inserted partially into oldtank. From then on the middle and upper section welded and followed by epoxypainting then inserted into old tank. Based on prediction result, that theroot cause of corrosion would be took place on welding and on imperfectlyepoxy painting area. The outside surface novel tank would be generated by thereaction between imperfectly epoxy painting area and the highly basecondition on cement grout that available on novel and old tank gap. (author)
-
Preface: Current perspectives in modelling, monitoring, and predicting geophysical fluid dynamics
Mancho, Ana M.; Hernández-García, Emilio; López, Cristóbal; Turiel, Antonio; Wiggins, Stephen; Pérez-Muñuzuri, Vicente
2018-02-01
The third edition of the international workshop Nonlinear Processes in Oceanic and Atmospheric Flows was held at the Institute of Mathematical Sciences (ICMAT) in Madrid from 6 to 8 July 2016. The event gathered oceanographers, atmospheric scientists, physicists, and applied mathematicians sharing a common interest in the nonlinear dynamics of geophysical fluid flows. The philosophy of this meeting was to bring together researchers from a variety of backgrounds into an environment that favoured a vigorous discussion of concepts across different disciplines. The present Special Issue on Current perspectives in modelling, monitoring, and predicting geophysical fluid dynamics contains selected contributions, mainly from attendants of the workshop, providing an updated perspective on modelling aspects of geophysical flows as well as issues on prediction and assimilation of observational data and novel tools for describing transport and mixing processes in these contexts. More details on these aspects are discussed in this preface.
-
Model Predictive Current Control for High-Power Grid-Connected Converters with Output LCL Filter
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Delpino, Hernan Anres Miranda; Teodorescu, Remus; Rodriguez, Pedro
2009-01-01
A model predictive control strategy for a highpower, grid connected 3-level neutral clamped point converter is presented. Power losses constraints set a limit on commutation losses so reduced switching frequency is required, thus producing low frequency current harmonics. To reduce these harmonics...
-
Basu, Ishita; Graupe, Daniel; Tuninetti, Daniela; Shukla, Pitamber; Slavin, Konstantin V.; Metman, Leo Verhagen; Corcos, Daniel M.
2013-01-01
Objective We present a proof of concept for a novel method of predicting the onset of pathological tremor using non-invasively measured surface electromyogram (sEMG) and acceleration from tremor-affected extremities of patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Essential tremor (ET). Approach The tremor prediction algorithm uses a set of spectral (fourier and wavelet) and non-linear time series (entropy and recurrence rate) parameters extracted from the non-invasively recorded sEMG and acceleration signals. Main results The resulting algorithm is shown to successfully predict tremor onset for all 91 trials recorded in 4 PD patients and for all 91 trials recorded in 4 ET patients. The predictor achieves a 100% sensitivity for all trials considered, along with an overall accuracy of 85.7% for all ET trials and 80.2% for all PD trials. By using a Pearson’s chi-square test, the prediction results are shown to significantly differ from a random prediction outcome. Significance The tremor prediction algorithm can be potentially used for designing the next generation of non-invasive closed-loop predictive ON-OFF controllers for deep brain stimulation (DBS), used for suppressing pathological tremor in such patients. Such a system is based on alternating ON and OFF DBS periods, an incoming tremor being predicted during the time intervals when DBS is OFF, so as to turn DBS back ON. The prediction should be a few seconds before tremor re-appears so that the patient is tremor-free for the entire DBS ON-OFF cycle as well as the tremor-free DBS OFF interval should be maximized in order to minimize the current injected in the brain and battery usage. PMID:23658233
-
Basu, Ishita; Graupe, Daniel; Tuninetti, Daniela; Shukla, Pitamber; Slavin, Konstantin V.; Verhagen Metman, Leo; Corcos, Daniel M.
2013-06-01
Objective. We present a proof of concept for a novel method of predicting the onset of pathological tremor using non-invasively measured surface electromyogram (sEMG) and acceleration from tremor-affected extremities of patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and essential tremor (ET). Approach. The tremor prediction algorithm uses a set of spectral (Fourier and wavelet) and nonlinear time series (entropy and recurrence rate) parameters extracted from the non-invasively recorded sEMG and acceleration signals. Main results. The resulting algorithm is shown to successfully predict tremor onset for all 91 trials recorded in 4 PD patients and for all 91 trials recorded in 4 ET patients. The predictor achieves a 100% sensitivity for all trials considered, along with an overall accuracy of 85.7% for all ET trials and 80.2% for all PD trials. By using a Pearson’s chi-square test, the prediction results are shown to significantly differ from a random prediction outcome. Significance. The tremor prediction algorithm can be potentially used for designing the next generation of non-invasive closed-loop predictive ON-OFF controllers for deep brain stimulation (DBS), used for suppressing pathological tremor in such patients. Such a system is based on alternating ON and OFF DBS periods, an incoming tremor being predicted during the time intervals when DBS is OFF, so as to turn DBS back ON. The prediction should be a few seconds before tremor re-appears so that the patient is tremor-free for the entire DBS ON-OFF cycle and the tremor-free DBS OFF interval should be maximized in order to minimize the current injected in the brain and battery usage.
-
Eddy current technique for detecting and sizing surface cracks in steel components
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cecco, V.S.; Carter, J.R.; Sullivan, S.P.
1995-01-01
Cracking has occurred in pressure vessel nozzles and girth welds due to thermal fatigue. Pipe welds, welds in support structures, and welds in reactor vault liner panels in nuclear facilities have failed because of cracks. Cracking can also occur in turbine rotor bore surfaces due to high cycle fatigue. Dye penetrant, magnetic particle and other surface NDT methods are used to detect cracks but cannot be used for depth sizing. Crack depth can be measured with various NDT methods such as ultrasonic time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD), potential drop, and eddy current. The TOFD technique can be difficult to implement on nozzle welds and is best suited for sizing deep cracks (>5 mm). The conventional eddy current method is easy to implement, but crack sizing is normally limited to shallow cracks ( 2 mm) cracks. Eddy current testing (ET) techniques are readily amenable to remote/automatic inspections. These new probes could augment present magnetic particle (MT) and dye penetrant (PT) testing through provision of reliable defect depth information. Reliable crack sizing permits identification of critical cracks for plant life extension and licensing purposes. In addition, performing PT and MT generates low level radioactive waste in some inspection applications in nuclear facilities. Replacing these techniques with ET for some components will eliminate some of this radioactive waste. (author)
-
Aims and accomplishments of surface theory
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Feibelman, P.J.
1979-01-01
The goals of surface science include the understanding of surface structure, transport and chemistry. However, present activities are mainly focussed on the most basic problem, viz., what are the constituents of a given surface and where are they located. Theorists are approaching this surface characterization problem from two sides. To make better use of the data available from the many experimental surface probes, an understanding of the force laws which govern the motion of probe-particles near surfaces is being developed, and the relation between the excitation and ground state spectra of a solid are being studied. In order to develop a predictive capability regarding surface structure, a variety of intrinsic surface properties are being studied, including the nature of bonds at transition metal surfaces, the meaning of bond locality in extended systems, and the electronic factors underlying the forces which govern surface geometry. These studies often raise technical issues such as the validity of using local exchange-correlation potentials and the applicability of cluster calculations to the analysis of extended surface situations, which, however, should not obscure the main thrust of current work - empirical and predictive surface structure determination. These points are illustrated with examples from recent research and ways in which experimental surface work might assist theoretical efforts are indicated
-
Molecular adsorption of alkanes on platinum surfaces: A predictive theoretical model
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Stinnett, J.A.; Madix, R.J.
1996-01-01
The adsorption probabilities of methane and propane on Pt(111), and propane on Pt(110)-(1x2) have been successfully predicted for a wide range of incident energies and angles with classical stochastic trajectory simulations, using a pairwise additive Morse methyl endash platinum potential previously developed from the measured trapping probabilities of ethane on Pt(111). These predictions, along with those for ethane adsorption on Pt(110)endash(1x2), comprise a unified model for the molecular adsorption of alkanes on platinum surfaces. The simulations show the initial trapping probabilities of methane and propane on Pt(111) are determined to within approximately 10% by the fate of the first bounce. They also indicate that at normal incidence on Pt(111) energy conversions from perpendicular translational motion to both cartwheeling rotation and lattice phonons play increasingly important roles in increasing the trapping probability as the alkane increases in size and molecular weight. For methane itself excitation of parallel translational momentum after the first bounce serves as the most effective energy storage mechanism which facilitates trapping, whereas for propane cartwheel rotational motion plays the dominant role. Excessive excitation of these modes of motion, however, can cause scattering on subsequent bounces by reconversion of the energy into perpendicular translational energy. Collisions of methane with the hollow and bridge sites on the Pt(111) surface appear less effective in trapping than do atop sites. The simulations also suggest excitation of the C endash C endash C bending mode of propane has little effect on the trapping of propane on platinum surfaces for beam energies below 55 kJ/mol. copyright 1996 American Institute of Physics
-
Dose Prediction for surface nuclear explosions: case studies for Semipalatinsk and Lop Nur tests
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Takada, Jun
2008-01-01
Dose prediction method RAPS after surface nuclear explosion has been developed by using the empirical dose function of USA nuclear test. This method which provides us external total dose, dose rate at any distant, at any time for any yield of nuclear explosion, is useful for radiation protection in case of nuclear events such as terrorism and nuclear war. The validity of RAPS has been confirmed by application to historical surface nuclear test explosions. The first test case study which was done for the first test explosion of the former USSR at the Semipalatinsk Nuclear Test Site on August 29th 1949, shows a good agreement with luminescence dosimetry on a brick. This dose prediction method was applied nuclear tests in Lop Nur. The results indicate dangerous nuclear radiation influences including fatal risk in the wide Uygur area. (author)
-
Prediction of burnout of a conduction-cooled BSCCO current lead
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Seol, S.Y.; Cha, Y.S.; Niemann, R.C.; Hull, J.R.
1996-01-01
A one-dimensional heat conduction model is employed to predict burnout of a Bi 2 Sr 2 CaCu 2 O 8 current lead. The upper end of the lead is assumed to be at 77 K and the lower end is at 4 K. The results show that burnout always occurs at the warmer end of the lead. The lead reaches its burnout temperature in two distinct stage. Initially, the temperature rises slowly when part of the lead is in flux-flow state. As the local temperature reaches the critical temperature, it begins to increase sharply. Burnout time depends strongly on flux-flow resistivity
-
Ocean current surface measurement using dynamic elevations obtained by the GEOS-3 radar altimeter
Leitao, C. D.; Huang, N. E.; Parra, C. G.
1977-01-01
Remote Sensing of the ocean surface from the GEOS-3 satellite using radar altimeter data has confirmed that the altimeter can detect the dynamic ocean topographic elevations relative to an equipotential surface, thus resulting in a reliable direct measurement of the ocean surface. Maps of the ocean dynamic topography calculated over a one month period and with 20 cm contour interval are prepared for the last half of 1975. The Gulf Stream is observed by the rapid slope change shown by the crowding of contours. Cold eddies associated with the current are seen as roughly circular depressions.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Luo, Dian [State Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding and Joining, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001 (China); Tang, Guangze, E-mail: oaktang@hit.edu.cn [School of Material Science & Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001 (China); Ma, Xinxin [State Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding and Joining, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001 (China); Gu, Le [School of Mechatronics Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001 (China); Sun, Mingren [School of Material Science & Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001 (China); Wang, Liqin [School of Mechatronics Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001 (China)
2015-10-01
Highlights: • Four kinds of defects are found during surface alloying by high current electron beam. • Exploring the mechanism how these defects appear after irradiation. • Increasing pulsing cycles will help to get good surface quality. • Choosing proper energy density will increase surface quality. - Abstract: High current pulsed electron beam (HCPEB) is an attractive advanced materials processing method which could highly increase the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. However, how to eliminate different kinds of defects during irradiation by HCPEB especially in condition of adding new elements is a challenging task. In the present research, the titanium and TaNb-TiW composite films was deposited on the carburizing steel (SAE9310 steel) by DC magnetron sputtering before irradiation. The process of surface alloying was induced by HCPEB with pulse duration of 2.5 μs and energy density ranging from 3 to 9 J/cm{sup 2}. Investigation of the microstructure indicated that there were several forms of defects after irradiation, such as surface unwetting, surface eruption, micro-cracks and layering. How the defects formed was explained by the results of electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy. The results also revealed that proper energy density (∼6 J/cm{sup 2}) and multi-number of irradiation (≥50 times) contributed to high quality of alloyed layers after irradiation.
-
Determining the near-surface current profile from measurements of the wave dispersion relation
Smeltzer, Benjamin; Maxwell, Peter; Aesøy, Eirik; Ellingsen, Simen
2017-11-01
The current-induced Doppler shifts of waves can yield information about the background mean flow, providing an attractive method of inferring the current profile in the upper layer of the ocean. We present measurements of waves propagating on shear currents in a laboratory water channel, as well as theoretical investigations of inversion techniques for determining the vertical current structure. Spatial and temporal measurements of the free surface profile obtained using a synthetic Schlieren method are analyzed to determine the wave dispersion relation and Doppler shifts as a function of wavelength. The vertical current profile can then be inferred from the Doppler shifts using an inversion algorithm. Most existing algorithms rely on a priori assumptions of the shape of the current profile, and developing a method that uses less stringent assumptions is a focus of this study, allowing for measurement of more general current profiles. The accuracy of current inversion algorithms are evaluated by comparison to measurements of the mean flow profile from particle image velocimetry (PIV), and a discussion of the sensitivity to errors in the Doppler shifts is presented.
-
Predictive Surface Roughness Model for End Milling of Machinable Glass Ceramic
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Reddy, M Mohan; Gorin, Alexander [School of Engineering and Science, Curtin University of Technology, Sarawak (Malaysia); Abou-El-Hossein, K A, E-mail: mohan.m@curtin.edu.my [Mechanical and Aeronautical Department, Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University, Port Elegebeth, 6031 (South Africa)
2011-02-15
Advanced ceramics of Machinable glass ceramic is attractive material to produce high accuracy miniaturized components for many applications in various industries such as aerospace, electronics, biomedical, automotive and environmental communications due to their wear resistance, high hardness, high compressive strength, good corrosion resistance and excellent high temperature properties. Many research works have been conducted in the last few years to investigate the performance of different machining operations when processing various advanced ceramics. Micro end-milling is one of the machining methods to meet the demand of micro parts. Selecting proper machining parameters are important to obtain good surface finish during machining of Machinable glass ceramic. Therefore, this paper describes the development of predictive model for the surface roughness of Machinable glass ceramic in terms of speed, feed rate by using micro end-milling operation.
-
Predictive Surface Roughness Model for End Milling of Machinable Glass Ceramic
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Reddy, M Mohan; Gorin, Alexander; Abou-El-Hossein, K A
2011-01-01
Advanced ceramics of Machinable glass ceramic is attractive material to produce high accuracy miniaturized components for many applications in various industries such as aerospace, electronics, biomedical, automotive and environmental communications due to their wear resistance, high hardness, high compressive strength, good corrosion resistance and excellent high temperature properties. Many research works have been conducted in the last few years to investigate the performance of different machining operations when processing various advanced ceramics. Micro end-milling is one of the machining methods to meet the demand of micro parts. Selecting proper machining parameters are important to obtain good surface finish during machining of Machinable glass ceramic. Therefore, this paper describes the development of predictive model for the surface roughness of Machinable glass ceramic in terms of speed, feed rate by using micro end-milling operation.
-
Ahn, J. B.; Hur, J.
2015-12-01
The seasonal prediction of both the surface air temperature and the first-flowering date (FFD) over South Korea are produced using dynamical downscaling (Hur and Ahn, 2015). Dynamical downscaling is performed using Weather Research and Forecast (WRF) v3.0 with the lateral forcing from hourly outputs of Pusan National University (PNU) coupled general circulation model (CGCM) v1.1. Gridded surface air temperature data with high spatial (3km) and temporal (daily) resolution are obtained using the physically-based dynamical models. To reduce systematic bias, simple statistical correction method is then applied to the model output. The FFDs of cherry, peach and pear in South Korea are predicted for the decade of 1999-2008 by applying the corrected daily temperature predictions to the phenological thermal-time model. The WRF v3.0 results reflect the detailed topographical effect, despite having cold and warm biases for warm and cold seasons, respectively. After applying the correction, the mean temperature for early spring (February to April) well represents the general pattern of observation, while preserving the advantages of dynamical downscaling. The FFD predictabilities for the three species of trees are evaluated in terms of qualitative, quantitative and categorical estimations. Although FFDs derived from the corrected WRF results well predict the spatial distribution and the variation of observation, the prediction performance has no statistical significance or appropriate predictability. The approach used in the study may be helpful in obtaining detailed and useful information about FFD and regional temperature by accounting for physically-based atmospheric dynamics, although the seasonal predictability of flowering phenology is not high enough. Acknowledgements This work was carried out with the support of the Rural Development Administration Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development under Grant Project No. PJ009953 and
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zhang, PengFei; Qiu, Aici [State Key Laboratory of Electrical Insulation and Power Equipment, Xi' an Jiaotong University, Xi' an 710049 (China); State Key Laboratory of Intense Pulse Radiation of Simulation and Effect, Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology, Xi' an 710024 (China); Hu, Yang; Yang, HaiLiang; Sun, Jiang; Wang, Liangping; Cong, Peitian [State Key Laboratory of Intense Pulse Radiation of Simulation and Effect, Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology, Xi' an 710024 (China)
2016-03-15
The design of high-current density magnetically insulated transmission line (MITL) is a difficult problem of current large-scale Z-pinch device. In particular, a thorough understanding of the MITL electrode surface evolution process under high current density is lacking. On the “QiangGuang-I” accelerator, the load area possesses a low inductance short-circuit structure with a diameter of 2.85 mm at the cathode, and three reflux columns with a diameter of 3 mm and uniformly distributed circumference at the anode. The length of the high density MITL area is 20 mm. A laser interferometer is used to assess and analyze the state of the MITL cathode and anode gap, and their evolution process under high current density. Experimental results indicate that evident current loss is not observed in the current density area at pulse leading edge, and peak when the surface current density reaches MA/cm. Analysis on electrode surface working conditions indicates that when the current leading edge is at 71.5% of the peak, the total evaporation of MITL cathode structure can be realized by energy deposition caused by ohmic heating. The electrode state changes, and diffusion conditions are reflected in the laser interferometer image. The MITL cathode area mainly exists in metal vapor form. The metal vapor density in the cathode central region is higher than the upper limit of laser penetration density (∼4 × 10{sup 21}/cm{sup 3}), with an expansion velocity of ∼0.96 km/s. The metal vapor density in the electrode outer area may lead to evident distortion of fringes, and its expansion velocity is faster than that in the center area (1.53 km/s).
-
Isern-Fontanet, Jordi; Ballabrera-Poy, Joaquim; Turiel, Antonio; García-Ladona, Emilio
2017-10-01
Ocean currents play a key role in Earth's climate - they impact almost any process taking place in the ocean and are of major importance for navigation and human activities at sea. Nevertheless, their observation and forecasting are still difficult. First, no observing system is able to provide direct measurements of global ocean currents on synoptic scales. Consequently, it has been necessary to use sea surface height and sea surface temperature measurements and refer to dynamical frameworks to derive the velocity field. Second, the assimilation of the velocity field into numerical models of ocean circulation is difficult mainly due to lack of data. Recent experiments that assimilate coastal-based radar data have shown that ocean currents will contribute to increasing the forecast skill of surface currents, but require application in multidata assimilation approaches to better identify the thermohaline structure of the ocean. In this paper we review the current knowledge in these fields and provide a global and systematic view of the technologies to retrieve ocean velocities in the upper ocean and the available approaches to assimilate this information into ocean models.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Mjalli, Farouq S., E-mail: farouqsm@yahoo.com [Petroleum and Chemical Engineering Department, Sultan Qaboos University, 123 Sultanate of Oman (Oman); Vakili-Nezhaad, Gholamreza; Shahbaz, Kaveh [School of Engineering, Taylor' s University, 47500 Selangor (Malaysia); AlNashef, Inas M. [Chemical Engineering Department, King Saud University, Riyadh 11421 (Saudi Arabia)
2014-01-10
Highlights: • Critical temperatures of eight common DES were calculated using two methods. • Density and surface tension were calculated using the Rackett and Guggenheim equations. • The Rackett method should be used in the low temperature range only. • The Eötvos and Guggenheim methods gave best density and surface tension predictions. - Abstract: The recent continuing interest in deep eutectic solvents (DES) as ionic liquids analogues and their successful applications in different areas of separation necessities the existence of reliable physical and thermodynamic properties database. The scarcity of data on the physical properties of such solvents, increases the need for their prediction using reliable methods. In this study, first the critical temperatures of eight DES systems have been calculated based on the Eötvos empirical equation using the experimental data of the density and surface tension at various temperatures, then the density and surface tension values of these systems were predicted from the calculated critical temperatures. For the density prediction the Eötvos and Guggenheim equations were combined to introduce a simple power law equation using the estimated critical temperatures from the Eötvos and the Modified Lydersen–Joback–Reid group contribution methods. Finally, the estimated critical temperatures by these two methods were used in the Guggenheim empirical equation to calculate the surface tension of the DES systems. The prediction quality of the two physical properties under investigation were compared and proper recommendations were postulated.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mjalli, Farouq S.; Vakili-Nezhaad, Gholamreza; Shahbaz, Kaveh; AlNashef, Inas M.
2014-01-01
Highlights: • Critical temperatures of eight common DES were calculated using two methods. • Density and surface tension were calculated using the Rackett and Guggenheim equations. • The Rackett method should be used in the low temperature range only. • The Eötvos and Guggenheim methods gave best density and surface tension predictions. - Abstract: The recent continuing interest in deep eutectic solvents (DES) as ionic liquids analogues and their successful applications in different areas of separation necessities the existence of reliable physical and thermodynamic properties database. The scarcity of data on the physical properties of such solvents, increases the need for their prediction using reliable methods. In this study, first the critical temperatures of eight DES systems have been calculated based on the Eötvos empirical equation using the experimental data of the density and surface tension at various temperatures, then the density and surface tension values of these systems were predicted from the calculated critical temperatures. For the density prediction the Eötvos and Guggenheim equations were combined to introduce a simple power law equation using the estimated critical temperatures from the Eötvos and the Modified Lydersen–Joback–Reid group contribution methods. Finally, the estimated critical temperatures by these two methods were used in the Guggenheim empirical equation to calculate the surface tension of the DES systems. The prediction quality of the two physical properties under investigation were compared and proper recommendations were postulated
-
Garel, F.; Kaminski, E.; Tait, S.; Limare, A.
2011-12-01
During an effusive volcanic eruption, the crisis management is mainly based on the prediction of lava flows advance and its velocity. As the spreading of lava flows is mainly controlled by its rheology and the eruptive mass flux, the key question is how to evaluate them during the eruption (rather than afterwards.) A relationship between the heat flux lost by the lava at its surface and the eruption rate is likely to exist, based on the first-order argument that higher eruption rates should correspond to larger power radiated by a lava flow. The semi-empirical formula developed by Harris and co-workers (e.g. Harris et al., Bull. Volc. 2007) is currently used to estimate lava flow rate from satellite surveys yielding the surface temperatures and area of the lava flow field. However, this approach is derived from a static thermal budget of the lava flow and does not explicitly model the time-evolution of the surface thermal signal. Here we propose laboratory experiments and theoretical studies of the cooling of a viscous axisymmetric gravity current fed at constant flux rate. We first consider the isoviscous case, for which the spreading is well-know. The experiments using silicon oil and the theoretical model both reveal the establishment of a steady surface thermal structure after a transient time. The steady state is a balance between surface cooling and heat advection in the flow. The radiated heat flux in the steady regime, a few days for a basaltic lava flow, depends mainly on the effusion rate rather than on the viscosity. In this regime, one thermal survey of the radiated power could provide a consistent estimate of the flow rate if the external cooling conditions (wind) are reasonably well constrained. We continue to investigate the relationship between the thermal radiated heat flux and the effusion rate by using in the experiments fluids with temperature-dependent viscosity (glucose syrup) or undergoing solidification while cooling (PEG wax). We observe a
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Steskens, Paul Wilhelmus Maria Hermanus; Janssen, Hans; Rode, Carsten
2009-01-01
Current models to predict heat, air and moisture (HAM) conditions in buildings assume constant boundary conditions for the temperature and relative humidity of the neighbouring air and for the surface heat and moisture transfer coefficients. These assumptions may introduce errors in the predicted...... influence on the predicted hygrothermal conditions at the surface of a building component and on the heat and vapour exchange with the indoor environment....
-
On the surface recombination current of metal-insulator semiconductor inversion layer solar cells
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, Otto M.
1981-01-01
voltages Voc were found to be lower than for ~ cells. The measured differences in Voc were higher than expected from the dark characteristics which is explained as a difference in the surface recombination current due to a higher interface state density Nss of ~ cells. Journal of Applied Physics...
-
Analyses on the measurement of leakage currents in CdZnTe radiation detectors
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mescher, M.J.; Hoburg, J.F.; Schlesinger, T.E.; James, R.B.
1999-01-01
Models that place design constraints on devices which are used to measure the leakage currents in high-resistivity semiconductor materials are presented. If these design constraints are met, these models can then be used to quantitatively predict the surface sheet resistance of devices which are dominated by surface leakage currents. As a result, a means is provided to directly compare passivation techniques which are developed to decrease surface leakage currents. Furthermore, these models illustrate the necessity for inclusion of relevant geometrical data on sample size and shape and electrode configuration when reporting results of surface passivation techniques. These models specifically examine the case where a dc potential is applied across two electrodes on the surface of a semiconductor substrate which has a surface layer with lower resistivity than the bulk material. The authors describe several of the more common configurations used in analyzing passivation techniques for compounds of Cd 1-x Zn x Te (CZT) used for room-temperature radiation detection
-
Zhang, Daohong; Wu, Yunlong; Li, Ting; Huang, Yin; Zhang, Aiqing; Miao, Menghe
2015-11-25
Threadlike linear supercapacitors have demonstrated high potential for constructing fabrics to power electronic textiles (eTextiles). To improve the cyclic electrochemical performance and to produce power fabrics large enough for practical applications, a current collector has been introduced into the linear supercapcitors to transport charges produced by active materials along the length of the supercapacitor with high efficiency. Here, we first screened six candidate metal filaments (Pt, Au, Ag, AuAg, PtCu, and Cu) as current collectors for carbon nanotube (CNT) yarn-based linear supercapacitors. Although all of the metal filaments significantly improved the electrochemical performance of the linear supercapacitor, two supercapacitors constructed from Cu and PtCu filaments, respectively, demonstrate far better electrochemical performance than the other four supercapacitors. Further investigation shows that the surfaces of the two Cu-containing filaments are oxidized by the surrounding polymer electrolyte in the electrode. While the unoxidized core of the Cu-containing filaments remains highly conductive and functions as a current collector, the resulting CuO on the surface is an electrochemically active material. The linear supercapacitor architecture incorporating dual active materials CNT + Cu extends the potential window from 1.0 to 1.4 V, leading to significant improvement to the energy density and power density.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Li, Yanhao; Wang, Guangjun; Chen, Hong
2015-01-01
The predictive control theory is utilized for the research of a simultaneous estimation of heat fluxes through the upper, side and lower surface of a steel slab in a walking beam type rolling steel reheating furnace. An inverse algorithm based on dynamic matrix control (DMC) is established. That is, each surface heat flux of a slab is simultaneously estimated through rolling optimization on the basis of temperature measurements in selected points of its interior by utilizing step response function as predictive model of a slab's temperature. The reliability of the DMC results is enhanced without prior assuming specific functions of heat fluxes over a period of future time. The inverse algorithm proposed a respective regularization to effectively improve the stability of the estimated results by considering obvious strength differences between the upper as well as lower and side surface heat fluxes of the slab. - Highlights: • The predictive control theory is adopted. • An inversion scheme based on DMC is established. • Upper, side and lower surface heat fluxes of slab are estimated based DMC. • A respective regularization is proposed to improve the stability of results
-
Mendonça, Ana C F; Pádua, Agílio A H; Malfreyt, Patrice
2013-03-12
We report nonequilibrium molecular dynamics of ionic liquids interacting with metallic surfaces. A specific set of interaction parameters for ionic liquids composed of alkylammonium cations and alkylsulfonate anions with an iron surface, which has been previously developed (J. Chem. Theory Comput.2012, 8, 3348) is used here. We develop a procedure for a quantitative prediction of the friction coefficient at different loads and shear rates. The simulated friction coefficient agrees very well with the available experimental ones. The dependence of friction on the load, shear velocity, surface topology, and length of alkyl side chains in the ionic liquid is also investigated. The changes in the frictional forces are explained in terms of the specific arrangements and orientations of groups forming the ionic liquid at the vicinity of the surface.
-
Tolson, B.; Mai, J.; Kornelsen, K. C.; Coulibaly, P. D.; Anctil, F.; Fortin, V.; Leahy, M.; Hall, B.
2017-12-01
Environmental models are tools for the modern society for a wide range of applications such as flood and drought monitoring, carbon storage and release estimates, predictions of power generation amounts, or reservoir management amongst others. Environmental models differ in the types of processes they incorporate, where land surface models focus on the energy, water, and carbon cycle of the land and hydrological models concentrate mainly on the water cycle. All these models, however, have in common that they rely on environmental input data from ground observations such as temperature, precipitation and/or radiation to force the model. If the same model is run in forecast mode, numerical weather predictions (NWPs) are needed to replace these ground observations. Therefore, it is critical that NWP data be available to develop models and validate forecast performance. These data are provided by the Meteorological Service of Canada (MSC) on a daily basis. MSC provides multiple products ranging from large scale global models ( 33km/grid cell) to high resolution pan-Canadian models ( 2.5km/grid cell). Operational products providing forecasts in real-time are made publicly available only at the time of issue through various means with new forecasts issued 2-4 times per day. Unfortunately, long term storage of these data are offline and relatively inaccessible to the research and operational communities. The new Canadian Surface Prediction Archive (CaSPAr) platform is an accessible rolling archive of 10 of MSC's NWP products. The 500TB platform will allow users to extract specific time periods, regions of interest and variables of interest in an easy to access NetCDF format. CaSPAr and community contributed post-processing scripts and tools are being developed such that the users, for example, can interpolate the data due to their needs or auto-generate model forcing files. We will present the CaSPAr platform and provide some insights in the current development of the web
-
Ultrafast terahertz control of extreme tunnel currents through single atoms on a silicon surface
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Jelic, Vedran; Iwaszczuk, Krzysztof; Nguyen, Peter H.
2017-01-01
scanning tunnelling microscopy (THz-STM) in ultrahigh vacuum as a new platform for exploring ultrafast non-equilibrium tunnelling dynamics with atomic precision. Extreme terahertz-pulse-driven tunnel currents up to 10(7) times larger than steady-state currents in conventional STM are used to image...... terahertz-induced band bending and non-equilibrium charging of surface states opens new conduction pathways to the bulk, enabling extreme transient tunnel currents to flow between the tip and sample.......Ultrafast control of current on the atomic scale is essential for future innovations in nanoelectronics. Extremely localized transient electric fields on the nanoscale can be achieved by coupling picosecond duration terahertz pulses to metallic nanostructures. Here, we demonstrate terahertz...
-
Modeling of the anode surface deformation in high-current vacuum arcs with AMF contacts
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Huang, Xiaolong; Wang, Lijun; Deng, Jie; Jia, Shenli; Qin, Kang; Shi, Zongqian
2016-01-01
A high-current vacuum arc subjected to an axial magnetic field is maintained in a diffuse status. With an increase in arc current, the energy carried by the arc column to the anode becomes larger and finally leads to the anode temperature exceeding the melting point of the anode material. When the anode melting pool is formed, and the rotational plasma of the arc column delivers its momentum to the melting pool, the anode melting pool starts to rotate and also flow outwards along the radial direction, which has been photographed by some researchers using high-speed cameras. In this paper, the anode temperature and melting status is calculated using the melting and solidification model. The swirl flow of the anode melting pool and deformation of the anode is calculated using the magneto-hydrodynamic (MHD) model with the volume of fraction (VOF) method. All the models are transient 2D axial-rotational symmetric models. The influence of the impaction force of the arc plasma, electromagnetic force, viscosity force, and surface tension of the liquid metal are all considered in the model. The heat flux density injected into the anode and the arc pressure are obtained from the 3D numerical simulation of the high-current vacuum arc using the MHD model, which gives more realistic parameters for the anode simulation. Simulation results show that the depth of the anode melting pool increases with an increase in the arc current. Some droplets sputter out from the anode surface, which is caused by the inertial centrifugal force of the rotational melting pool and strong plasma pressure. Compared with the previous anode melting model without consideration of anode deformation, when the deformation and swirl flow of the anode melting pool are considered, the anode temperature is relatively lower, and just a little more than the melting point of Cu. This is because of liquid droplets sputtering out of the anode surface taking much of the energy away from the anode surface. The
-
Load Torque Compensator for Model Predictive Direct Current Control in High Power PMSM Drive Systems
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Preindl, Matthias; Schaltz, Erik
2010-01-01
In drive systems the most used control structure is the cascade control with an inner torque, i.e. current and an outer speed control loop. The fairly small converter switching frequency in high power applications, e.g. wind turbines lead to modest speed control performance. An improvement bring...... the use of a current controller which takes into account the discrete states of the inverter, e.g. DTC or a more modern approach: Model Predictive Direct Current Control (MPDCC). Moreover overshoots and oscillations in the speed are not desired in many applications, since they lead to mechanical stress...
-
GaInAsP/InP lateral-current-injection distributed feedback laser with a-Si surface grating.
Shindo, Takahiko; Okumura, Tadashi; Ito, Hitomi; Koguchi, Takayuki; Takahashi, Daisuke; Atsumi, Yuki; Kang, Joonhyun; Osabe, Ryo; Amemiya, Tomohiro; Nishiyama, Nobuhiko; Arai, Shigehisa
2011-01-31
We fabricated a novel lateral-current-injection-type distributed feedback (DFB) laser with amorphous-Si (a-Si) surface grating as a step to realize membrane lasers. This laser consists of a thin GaInAsP core layer grown on a semi-insulating InP substrate and a 30-nm-thick a-Si surface layer for DFB grating. Under a room-temperature continuous-wave condition, a low threshold current of 7.0 mA and high efficiency of 43% from the front facet were obtained for a 2.0-μm stripe width and 300-μm cavity length. A small-signal modulation bandwidth of 4.8 GHz was obtained at a bias current of 30 mA.
-
Prediction of abrupt reservoir compaction and surface subsidence due to pore collapse in carbonates
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Smits, R.M.M.; de Waal, A.; van Kooten, J.F.C.
1986-01-01
A new procedure has been developed to predict the abrupt in-situ compaction and the associated surface subsidence above high-porosity carbonate fields showing pore collapse. The approach is based on an extensive laboratory compaction study in which the effects of carbonate type, porosity, core preparation, pore saturant, horizontal to vertical stress ratio and loading rate on the pore collapse behaviour were investigated. For each carbonate type a trendline was established describing the relationship between the porosity after collapse and the vertical effective stress. This trendline concept, in combination with existing subsidence models, enables reservoir compaction and surface subsidence to be predicted on the basis of wireline porosity logs. Static and dynamic elastic constants were found to be uncorrelated during pore collapse. The position of the trendline depends strongly on carbonate type, pore saturant, loading rate and stress ratio. Therefore procedures are given to derive the correct in-situ trendline from laboratory compaction experiments.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Smits, R.M.M.; De Waal, J.A.; Van Kootan, J.F.C.
1988-06-01
A new procedure has been developed to predict the abrupt in-situ compaction and the associated surface subsidence above high-porosity carbonate fields that show pore collapse. The approach is based on an extensive laboratory compaction study in which the effects of carbonate type, porosity, core preparation, pore saturant, horizontal/vertical stress ratio, and loading rate on pore-collapse behavior were investigated. For a number of carbonate types, a trendline was established that describes the relationship between the porosity after collapse and the vertical effective stress. This trendline concept, in combination with existing subsidence models, enables reservoir compaction and surface subsidence to be predicted on the basis of wireline porosity logs. Static and dynamic elastic constants were found to be uncorrelated during pore collapse. The position of the trendline depends strongly on carbonate type, pore saturant, loading rate, and stress ratio. Therefore, procedures are given to derive the correct in-situ trendline from laboratory compaction experiments.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Wolters, A.
2003-07-01
Simulation of pesticide volatilization from plant and soil surfaces as an integral component of pesticide fate models is of utmost importance, especially as part of the PEC (predicted environmental concentrations) models used in the registration procedures for pesticides. Experimentally determined volatilization rates at different scales were compared to model predictions to improve recent approaches included in European registration models. To assess the influence of crucial factors affecting volatilization under well-defined conditions, a laboratory chamber was set-up and validated. Aerodynamic conditions were adjusted to fulfill the requirements of the German guideline on assessing pesticide volatilization for registration purposes. At the semi-field scale, volatilization rates were determined in a wind-tunnel study after soil surface application of pesticides to gleyic cambisol. The following descending order of cumulative volatilization was observed: chlorpyrifos > parathion-methyl > terbuthylazine > fenpropimorph. Parameterization of the models PEARL (pesticide emission assessment at regional and local scales) and PELMO (pesticide leaching model) was performed to mirror the experimental boundary conditions. (orig.)
-
Tong, Juxiu; Hu, Bill X; Yang, Jinzhong; Zhu, Yan
2016-06-01
The mixing layer theory is not suitable for predicting solute transfer from initially saturated soil to surface runoff water under controlled drainage conditions. By coupling the mixing layer theory model with the numerical model Hydrus-1D, a hybrid solute transfer model has been proposed to predict soil solute transfer from an initially saturated soil into surface water, under controlled drainage water conditions. The model can also consider the increasing ponding water conditions on soil surface before surface runoff. The data of solute concentration in surface runoff and drainage water from a sand experiment is used as the reference experiment. The parameters for the water flow and solute transfer model and mixing layer depth under controlled drainage water condition are identified. Based on these identified parameters, the model is applied to another initially saturated sand experiment with constant and time-increasing mixing layer depth after surface runoff, under the controlled drainage water condition with lower drainage height at the bottom. The simulation results agree well with the observed data. Study results suggest that the hybrid model can accurately simulate the solute transfer from initially saturated soil into surface runoff under controlled drainage water condition. And it has been found that the prediction with increasing mixing layer depth is better than that with the constant one in the experiment with lower drainage condition. Since lower drainage condition and deeper ponded water depth result in later runoff start time, more solute sources in the mixing layer are needed for the surface water, and larger change rate results in the increasing mixing layer depth.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jialong Wu
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Aiming at the surface defect inspection of carbon fiber reinforced composite, the differential and the direct measurement finite element simulation models of pulsed eddy current flaw detection were built. The principle of differential pulsed eddy current detection was analyzed and the sensitivity of defect detection was compared through two kinds of measurements. The validity of simulation results was demonstrated by experiments. The simulation and experimental results show that the pulsed eddy current detection method based on rectangular differential probe can effectively improve the sensitivity of surface defect detection of carbon fiber reinforced composite material.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Li, M.C.; Hao, S.Z.; Wen, H.; Huang, R.F.
2014-01-01
High current pulsed electron beam (HCPEB) treatment was conducted on an AZ91 cast magnesium alloy with accelerating voltage 27 kV, energy density 3 J/cm 2 and pulse duration 2.5 μs. The surface microstructure was characterized by optical microscope (OM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The surface corrosion property was tested with electrochemical method in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. It is found that after 1 pulse of HCPEB treatment, the initial eutectic α phase and Mg 17 Al 12 particles started to dissolve in the surface modified layer of depth ∼15 μm. When using 15 HCPEB pulses, the Al content in surface layer increased noticeably, and the phase structure was modified as composite nanostructures consisted of nano-grained Mg 3.1 Al 0.9 domains surrounded by network of Mg 17 Al 12 phase. The HCPEB treated samples showed an improved corrosion resistance with cathodic current density decreased by two orders of magnitude as compared to the initial AZ91 alloy.
-
Hertzberg, Jared B; Aksit, Mahmut; Otelaja, Obafemi O; Stewart, Derek A; Robinson, Richard D
2014-02-12
Thermal transport in nanostructures is strongly affected by phonon-surface interactions, which are expected to depend on the phonon's wavelength and the surface roughness. Here we fabricate silicon nanosheets, measure their surface roughness (∼ 1 nm) using atomic force microscopy (AFM), and assess the phonon scattering rate in the sheets with a novel technique: a microscale phonon spectrometer. The spectrometer employs superconducting tunnel junctions (STJs) to produce and detect controllable nonthermal distributions of phonons from ∼ 90 to ∼ 870 GHz. This technique offers spectral resolution nearly 10 times better than a thermal conductance measurement. We compare measured phonon transmission rates to rates predicted by a Monte Carlo model of phonon trajectories, assuming that these trajectories are dominated by phonon-surface interactions and using the Ziman theory to predict phonon-surface scattering rates based on surface topology. Whereas theory predicts a diffuse surface scattering probability of less than 40%, our measurements are consistent with a 100% probability. Our nanosheets therefore exhibit the so-called "Casimir limit" at a much lower frequency than expected if the phonon scattering rates follow the Ziman theory for a 1 nm surface roughness. Such a result holds implications for thermal management in nanoscale electronics and the design of nanostructured thermoelectrics.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Carmelo Nasello
2016-01-01
Full Text Available A new small drifter prototype for measuring current immediately below the free surface in a water basin is proposed in this paper. The drifter dimensions make it useful for shallow water applications. The drifter transmits its GPS location via GSM phone network. The drifter was used to study the trajectory of the surface current in the Muggia bay, the latter containing the industrial harbor of the city of Trieste (Italy. The analysis has been carried out under a wide variety of wind conditions. As regards the behavior of the drifter, the analysis has shown that it is well suited to detect the water current since its motion is marginally affected by the wind. The study has allowed detecting the main features of the surface circulation within the Muggia bay under different meteorological conditions. Also, the study has shown that the trajectory of the surface current within the bay is weakly affected by the Coriolis force.
-
Chen, Shuyi S.; Curcic, Milan
2016-07-01
Forecasting hurricane impacts of extreme winds and flooding requires accurate prediction of hurricane structure and storm-induced ocean surface waves days in advance. The waves are complex, especially near landfall when the hurricane winds and water depth varies significantly and the surface waves refract, shoal and dissipate. In this study, we examine the spatial structure, magnitude, and directional spectrum of hurricane-induced ocean waves using a high resolution, fully coupled atmosphere-wave-ocean model and observations. The coupled model predictions of ocean surface waves in Hurricane Ike (2008) over the Gulf of Mexico and Superstorm Sandy (2012) in the northeastern Atlantic and coastal region are evaluated with the NDBC buoy and satellite altimeter observations. Although there are characteristics that are general to ocean waves in both hurricanes as documented in previous studies, wave fields in Ike and Sandy possess unique properties due mostly to the distinct wind fields and coastal bathymetry in the two storms. Several processes are found to significantly modulate hurricane surface waves near landfall. First, the phase speed and group velocities decrease as the waves become shorter and steeper in shallow water, effectively increasing surface roughness and wind stress. Second, the bottom-induced refraction acts to turn the waves toward the coast, increasing the misalignment between the wind and waves. Third, as the hurricane translates over land, the left side of the storm center is characterized by offshore winds over very short fetch, which opposes incoming swell. Landfalling hurricanes produce broader wave spectra overall than that of the open ocean. The front-left quadrant is most complex, where the combination of windsea, swell propagating against the wind, increasing wind-wave stress, and interaction with the coastal topography requires a fully coupled model to meet these challenges in hurricane wave and surge prediction.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
O. Klemp
2006-01-01
Full Text Available In order to satisfy the stringent demand for an accurate prediction of MIMO channel capacity and diversity performance in wireless communications, more effective and suitable models that account for real antenna radiation behavior have to be taken into account. One of the main challenges is the accurate modeling of antenna correlation that is directly related to the amount of channel capacity or diversity gain which might be achieved in multi element antenna configurations. Therefore spherical wave theory in electromagnetics is a well known technique to express antenna far fields by means of a compact field expansion with a reduced number of unknowns that was recently applied to derive an analytical approach in the computation of antenna pattern correlation. In this paper we present a novel and efficient computational technique to determine antenna pattern correlation based on the evaluation of the surface current distribution by means of a spherical mode expansion.
-
Morphological features of the copper surface layer under sliding with high density electric current
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Fadin, V. V., E-mail: fvv@ispms.ru [Institute of Strength Physics and Materials Science SB RAS, Tomsk, 634055 (Russian Federation); Aleutdinova, M. I., E-mail: aleut@ispms.ru [Institute of Strength Physics and Materials Science SB RAS, Tomsk, 634055 (Russian Federation); Seversk Technological Institute, Branch of State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “National Research Nuclear University “MEPhI”, Seversk, 636036 (Russian Federation); Rubtsov, V. Ye., E-mail: rvy@ispms.ru [Institute of Strength Physics and Materials Science SB RAS, Tomsk, 634055 (Russian Federation); National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Tomsk, 634050 (Russian Federation); Aleutdinova, V. A., E-mail: valery-aleut@yandex.ru [National Research St. Petersburg State Polytechnical University, St. Petersburg, 195251 (Russian Federation)
2015-10-27
Conductivity and wear intensity of copper under the influence of dry friction and electric current with contact density higher 100 A/cm{sup 2} are presented. It is shown that an increase in hardness and heat outflow from a friction zone leads to the reduction of wear intensity and current contact density increase corresponding to the beginning of catastrophic wear. Structural changes, such as the formation of FeO oxide and α-Fe particles in the copper surface layer, have also been found. It is observed that a worn surface is deformed according to a viscous liquid mechanism. Such singularity is explained in terms of appearance of high-excited atomic states in deforming micro-volumes near contact spots that lead to easy stress relaxation by local plastic shears in the vicinity of stress concentrators. In common this effect allows to achieve high wear resistance.
-
A Methylmercury Prediction Too For Surface Waters Across The Contiguous United States (Invited)
Krabbenhoft, D. P.; Booth, N.; Lutz, M.; Fienen, M. N.; Saltman, T.
2009-12-01
About 20 years ago, researchers at a few locations across the globe discovered high levels of mercury in fish from remote settings lacking any obvious mercury source. We now know that for most locations atmospheric deposition is the dominant mercury source, and that mercury methylation is the key process that translates low mercury loading rates into relatively high levels in top predators of aquatic food webs. Presently, almost all US states have advisories for elevated levels of mercury in sport fish, and as a result there is considerable public awareness and concern for this nearly ubiquitous contaminant issue. In some states, “statewide” advisories have been issued because elevated fish mercury levels are so common, or the state has no effective way to monitor thousands of lakes, reservoirs, wetlands, and streams. As such, resource managers and public health officials have limited options for informing the public on of where elevated mercury concentrations in sport fish are more likely to occur than others. This project provides, for the first time, a national map of predicted (modeled) methylmercury concentrations in surface waters, which is the most toxic and bioaccumulative form of mercury in the environment. The map is the result of over two decades of research that resulted in the formulation of conceptual models of the mercury methylation process, which is strongly governed by environmental conditions - specifically hydrologic landscapes and water quality. The resulting predictive map shows clear regional trends in the distribution of methylmercury concentrations in surface waters. East of the Mississippi, the Gulf and southeastern Atlantic coast, the northeast, the lower Mississippi valley, and Great Lakes area are predicted to have generally higher environmental methylmercury levels. Higher-elevation, well-drained areas of Appalachia are predicted to have relatively lower methylmercury abundance. Other than the prairie pothole region, in the western
-
The effect of cathode bias (field effect) on the surface leakage current of CdZnTe detectors
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Bolotnikov, A.E.; Chen, C.M.H.; Cook, W.R.
2003-01-01
Surface resistivity is an important parameter of multi-electrode CZT detectors such as coplanar-grid, strip, or pixel detectors. Low surface resistivity results in a high leakage current and affects the charge collection efficiency in the areas near contacts. Thus, it is always desirable to have ...
-
Prediction of interannual climate variations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shukla, J.
1993-01-01
It has been known for some time that the behavior of the short-term fluctuations of the earth's atmosphere resembles that of a chaotic non-linear dynamical system, and that the day-to-day weather cannot be predicted beyond a few weeks. However, it has also been found that the interactions of the atmosphere with the underlying oceans and the land surfaces can produce fluctuations whose time scales are much longer than the limits of deterministic prediction of weather. It is, therefore, natural to ask whether it is possible that the seasonal and longer time averages of climate fluctuations can be predicted with sufficient skill to be beneficial for social and economic applications, even though the details of day-to-day weather cannot be predicted beyond a few weeks. The main objective of the workshop was to address this question by assessing the current state of knowledge on predictability of seasonal and interannual climate variability and to investigate various possibilities for its prediction. (orig./KW)
-
Ocular surface squamous neoplasia in HIV-infected patients: current perspectives
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Rathi SG
2018-03-01
Full Text Available Shweta Gupta Rathi, Anasua Ganguly Kapoor, Swathi Kaliki Operation Eyesight Universal Institute for Eye Cancer, LV Prasad Eye Institute, Hyderabad, India Abstract: Ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN refers to a spectrum of conjunctival and corneal epithelial tumors including dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, and invasive carcinoma. In this article, we discuss the current perspectives of OSSN associated with HIV infection, focusing mainly on the epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of these tumors in patients with HIV. Upsurge in the incidence of OSSN with the HIV pandemic most severely affected sub-Saharan Africa, due to associated risk factors, such as human papilloma virus and solar ultraviolet exposure. OSSN has been reported as the first presenting sign of HIV/AIDS in 26%–86% cases, and seropositivity is noted in 38%–92% OSSN patients. Mean age at presentation of OSSN has dropped to the third to fourth decade in HIV-positive patients in developing countries. HIV-infected patients reveal large aggressive tumors, higher-grade malignancy, higher incidence of corneal, scleral, and orbital invasion, advanced-stage T4 tumors, higher need for extended enucleation/exenteration, and increased risk of tumor recurrence. Current management of OSSN in HIV-positive individuals is based on standard treatment guidelines described for OSSN in the general population, as there is little information available about various treatment modalities or their outcomes in patients with HIV. OSSN can occur at any time in the disease course of HIV/AIDS, and no significant trend has been discovered between CD4 count and grade of OSSN. Furthermore, the effect of highly active antiretroviral therapy on OSSN is controversial. The current recommendation is to conduct HIV screening in all cases presenting with OSSN to rule out undiagnosed HIV infection. Patient counseling is crucial, with emphasis on regular follow-up to address
-
Attenborough, Keith; Horoshenkov, Kirill
2014-01-01
1. Introduction 2. The Propagation of Sound Near Ground Surfaces in a Homogeneous Medium 3. Predicting the Acoustical Properties of Outdoor Ground Surfaces 4. Measurements of the Acoustical Properties of Ground Surfaces and Comparisons with Models 5. Predicting Effects of Source Characteristics on Outdoor Sound 6. Predictions, Approximations and Empirical Results for Ground Effect Excluding Meteorological Effects 7. Influence of Source Motion on Ground Effect and Diffraction 8. Predicting Effects of Mixed Impedance Ground 9. Predicting the Performance of Outdoor Noise Barriers 10. Predicting Effects of Vegetation, Trees and Turbulence 11. Analytical Approximations including Ground Effect, Refraction and Turbulence 12. Prediction Schemes 13. Predicting Sound in an Urban Environment.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brennan, M.; Tolk, K.M.; Weldon, W.F.; Rylander, H.G.; Woodson, H.H.
1977-01-01
Test data is presented for one grade of copper graphite brush material, Morganite CMlS, over a wide range of surface velocities, atmospheres, and current densities that are expected for fast discharge (<100 ms) homopolar generators. The brushes were run on a copper coated 7075-T6 aluminum disk at surface speeds up to 277 m/sec. One electroplated copper and three flame sprayed copper coatings were used during the tests. Significant differences in contact voltage drops and surface mechanical properties of the copper coatings were observed
-
Surface modification of steels and magnesium alloy by high current pulsed electron beam
Hao, Shengzhi; Gao, Bo; Wu, Aimin; Zou, Jianxin; Qin, Ying; Dong, Chuang; An, Jian; Guan, Qingfeng
2005-11-01
High current pulsed electron beam (HCPEB) is now developing as a useful tool for surface modification of materials. When concentrated electron flux transferring its energy into a very thin surface layer within a short pulse time, superfast processes such as heating, melting, evaporation and consequent solidification, as well as dynamic stress induced may impart the surface layer with improved physico-chemical and mechanical properties. This paper presents our research work on surface modification of steels and magnesium alloy with HCPEB of working parameters as electron energy 27 keV, pulse duration ∼1 μs and energy density ∼2.2 J/cm2 per pulse. Investigations performed on carbon steel T8, mold steel D2 and magnesium alloy AZ91HP have shown that the most pronounced changes of phase-structure state and properties occurring in the near-surface layers, while the thickness of the modified layer with improved microhardness (several hundreds of micrometers) is significantly greater than that of the heat-affected zone. The formation mechanisms of surface cratering and non-stationary hardening effect in depth are discussed based on the elucidation of non-equilibrium temperature filed and different kinds of stresses formed during pulsed electron beam melting treatment. After the pulsed electron beam treatments, samples show significant improvements in measurements of wear and corrosion resistance.
-
Surface modification of steels and magnesium alloy by high current pulsed electron beam
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hao, Shengzhi; Gao, Bo; Wu, Aimin; Zou, Jianxin; Qin, Ying; Dong, Chuang; An, Jian; Guan, Qingfeng
2005-01-01
High current pulsed electron beam (HCPEB) is now developing as a useful tool for surface modification of materials. When concentrated electron flux transferring its energy into a very thin surface layer within a short pulse time, superfast processes such as heating, melting, evaporation and consequent solidification, as well as dynamic stress induced may impart the surface layer with improved physico-chemical and mechanical properties. This paper presents our research work on surface modification of steels and magnesium alloy with HCPEB of working parameters as electron energy 27 keV, pulse duration ∼1 μs and energy density ∼2.2 J/cm 2 per pulse. Investigations performed on carbon steel T8, mold steel D2 and magnesium alloy AZ91HP have shown that the most pronounced changes of phase-structure state and properties occurring in the near-surface layers, while the thickness of the modified layer with improved microhardness (several hundreds of micrometers) is significantly greater than that of the heat-affected zone. The formation mechanisms of surface cratering and non-stationary hardening effect in depth are discussed based on the elucidation of non-equilibrium temperature filed and different kinds of stresses formed during pulsed electron beam melting treatment. After the pulsed electron beam treatments, samples show significant improvements in measurements of wear and corrosion resistance
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mohammad Ramezani
2015-07-01
Full Text Available A number of factors, e.g. cutting speed and feed rate, affect the surface roughness in machining process. In this paper, an Artificial Neural Network model was used to forecast surface roughness with related inputs, including cutting speed and feed rate. The output of the ANN model input parameters related to the machined surface roughness parameters. In this research, twelve samples of experimental data were used to train the network. Moreover, four other experimental tests were implemented to test the network. The study concludes that ANN was a reliable and accurate method for predicting machining parameters in CNC turning operation of Particulate Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites (PAMCs specimens with 0%, 5%, 10% and 15% filler. The aim of this work is to decrease the production cost and consequently increase the production rate of these materials for industry without any trial and error method procedure.
-
Monte Carlo prediction of crater formation by single ion impact on solid surface
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Perez-Martin, A.M.C.; Dominguez-Vazquez, J.; Jimenez-Rodriguez, J.J.; Collins, R.; Gras-Marti, A.
1994-01-01
A method is presented for predicting the topography changes following the impact of one energetic ion on the plane surface of a monatomic amorphous solid. This is done in two stages. The first is a Monte Carlo calculation of the sputter yield and interior distribution relocated atoms, with no compensation for local departures from equilibrium density. In the second stage there is a systematic relaxation of the solid, in which the density returns to its previous constant value and a crater develops in the surface. Two alternative methods of carrying out stage two are compared. In the first the solid is subdivided into cells within which relaxation is carried out normal to the surface, as in previous one-dimensional studies. The second method treats the solid as a 3-dimensional incompressible medium. Both seem to reproduce quite well the main features found experimentally. (orig.)
-
ECMWF seasonal forecast system 3 and its prediction of sea surface temperature
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Stockdale, Timothy N.; Anderson, David L.T.; Balmaseda, Magdalena A.; Ferranti, Laura; Mogensen, Kristian; Palmer, Timothy N.; Molteni, Franco; Vitart, Frederic [ECMWF, Reading (United Kingdom); Doblas-Reyes, Francisco [ECMWF, Reading (United Kingdom); Institut Catala de Ciencies del Clima (IC3), Barcelona (Spain)
2011-08-15
The latest operational version of the ECMWF seasonal forecasting system is described. It shows noticeably improved skill for sea surface temperature (SST) prediction compared with previous versions, particularly with respect to El Nino related variability. Substantial skill is shown for lead times up to 1 year, although at this range the spread in the ensemble forecast implies a loss of predictability large enough to account for most of the forecast error variance, suggesting only moderate scope for improving long range El Nino forecasts. At shorter ranges, particularly 3-6 months, skill is still substantially below the model-estimated predictability limit. SST forecast skill is higher for more recent periods than earlier ones. Analysis shows that although various factors can affect scores in particular periods, the improvement from 1994 onwards seems to be robust, and is most plausibly due to improvements in the observing system made at that time. The improvement in forecast skill is most evident for 3-month forecasts starting in February, where predictions of NINO3.4 SST from 1994 to present have been almost without fault. It is argued that in situations where the impact of model error is small, the value of improved observational data can be seen most clearly. Significant skill is also shown in the equatorial Indian Ocean, although predictive skill in parts of the tropical Atlantic are relatively poor. SST forecast errors can be especially high in the Southern Ocean. (orig.)
-
Prediction of leakage current of non-ceramic insulators in early aging period
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
El-Hag, Ayman H. [Electrical Engineering Department, American University of Sharjah, Sharjah (United Arab Emirates); Jahromi, Ali Naderian [Kinectrics Inc., Transmission and Distribution Technologies, Toronto (Canada); Sanaye-Pasand, Majid [Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, University of Tehran (Iran)
2008-10-15
The paper presents a neural network based prediction technique for the leakage current (LC) of non-ceramic insulators during salt-fog test. Nearly 50 distribution class silicone rubber (SIR) insulators with three different voltage classes have been tested in a salt-fog chamber, where the LC has been continuously recorded for at least 100 h. A boundary for early aging period is defined by the rate of change of the LC instead of a fixed threshold value. Consequently, the Gaussian radial basis network has been adopted to predict the level of LC at the early stage of aging of the SIR insulators and is compared with a classical network. The initial values of LC and its rate of change at 10 min intervals for the first 5 h are selected as the input to the network, and the final value of LC of the early aging period is considered as the output of the network. It is found that Gaussian radial basis function network with a random optimizing training method is an appropriate network to predict the LC with a 3.5-5.3% accuracy, if the training data and the testing data are selected from the same type of SIR insulators. (author)
-
Gloss, B. B.; Johnson, F. T.
1976-01-01
The Boeing Commercial Airplane Company developed an inviscid three-dimensional lifting surface method that shows promise in being able to accurately predict loads, subsonic and supersonic, on wings with leading-edge separation and reattachment.
-
Bach, Martin; Diesner, Mirjam; Großmann, Dietlinde; Guerniche, Djamal; Hommen, Udo; Klein, Michael; Kubiak, Roland; Müller, Alexandra; Priegnitz, Jan; Reichenberger, Stefan; Thomas, Kai; Trapp, Matthias
2016-07-01
In 2001, the European Commission introduced a risk assessment project known as FOCUS (FOrum for the Coordination of pesticide fate models and their USe) for the surface water risk assessment of active substances in the European Union. Even for the national authorisation of plant protection products (PPPs), the vast majority of EU member states still refer to the four runoff and six drainage scenarios selected by the FOCUS Surface Water Workgroup. However, our study, as well as the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), has stated the need for various improvements. Current developments in pesticide exposure assessment mainly relate to two processes. Firstly, predicted environmental concentrations (PECs) of pesticides are calculated by introducing model input variables such as weather conditions, soil properties and substance fate parameters that have a probabilistic nature. Secondly, spatially distributed PECs for soil-climate scenarios are derived on the basis of an analysis of geodata. Such approaches facilitate the calculation of a spatiotemporal cumulative distribution function (CDF) of PECs for a given area of interest and are subsequently used to determine an exposure concentration endpoint as a given percentile of the CDF. For national PPP authorisation, we propose that, in the future, exposure endpoints should be determined from the overall known statistical PEC population for an area of interest, and derived for soil and climate conditions specific to the particular member state. © 2016 Society of Chemical Industry. © 2016 Society of Chemical Industry.
-
Basic research into eddy current testing of austenetic weld joints and surface claddings
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Meier, W.
1976-01-01
The result of research work has shown that the eddy-current testing method can be used for austenetic steel up to 10 mm thick to detect cracks in the material. An exception to this are laminations if they are parallel to the surface. Cracks in the various geometrical positions in the test specimen produce different results in the x-y plot. They are influenced by the direction of the material cracks. Research into the influence the geometric parameters have on the indications shows that the eddy-current method provides clearer interpretations of material cracks than any other non-destructive test method known. (orig.) [de
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yusa, Noritaka; Machida, Eiji; Janousek, Ladislav; Rebican, Mihai; Chen, Zhenmao; Miya, Kenzo
2005-01-01
This paper evaluates the applicability of eddy current inversion techniques to the sizing of defects in Inconel welds with rough surfaces. For this purpose, a plate Inconel weld specimen, which models the welding of a stub tube in a boiling water nuclear reactor is fabricated, and artificial notches machined into the specimen. Eddy current inspections using six different eddy current probes are conducted and efficiencies were evaluated for the six probes for weld inspection. It is revealed that if suitable probes are applied, an Inconel weld does not cause large noise levels during eddy current inspections even though the surface of the weld is rough. Finally, reconstruction of the notches is performed using eddy current signals measured using the uniform eddy current probe that showed the best results among the six probes in this study. A simplified configuration is proposed in order to consider the complicated configuration of the welded specimen in numerical simulations. While reconstructed profiles of the notches are slightly larger than the true profiles, quite good agreements are obtained in spite of the simple approximation of the configuration, which reveals that eddy current testing would be an efficient non-destructive testing method for the sizing of defects in Inconel welds
-
Surface modification of TA2 pure titanium by low energy high current pulsed electron beam treatments
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gao Yukui
2011-01-01
Surface integrity changes of TA2 pure titanium including surface topography, microstructure and nanohardness distribution along surface layer were investigated by different techniques of low energy high current pulsed electron beam treatments (LEHCPEBTs). The surface topography was characterized by SEM. Moreover, the TEM observation and X-ray diffraction analysis were performed to reveal the surface modification mechanism of TA2 pure titanium by LEHCPEBTs. The surface roughness was modified by electron beam treatment and the polishing mechanism was analyzed by studying the cross section microstructure of electron beam treated specimens by SEM and TEM. The results show that the surface finish obtains good polishing quality and there is no phase transformation but the dislocations by LEHCPEBT. Furthermore, the nanohardness in the surface modified layer is improved. The remelt and fine-grain microstructure of surface layer caused by LEHCPEBTs are the main polishing mechanism and the reason of modification of surface topography and the increment in nanohardness is mainly due to the dislocations and fine grains in the modified layer induced by LEHCPEBT.
-
Manzoor Hussain, M.; Pitchi Raju, V.; Kandasamy, J.; Govardhan, D.
2018-04-01
Friction surface treatment is well-established solid technology and is used for deposition, abrasion and corrosion protection coatings on rigid materials. This novel process has wide range of industrial applications, particularly in the field of reclamation and repair of damaged and worn engineering components. In this paper, we present the prediction of tensile and shear strength of friction surface treated tool steel using ANN for simulated results of friction surface treatment. This experiment was carried out to obtain tool steel coatings of low carbon steel parts by changing contribution process parameters essentially friction pressure, rotational speed and welding speed. The simulation is performed by a 33-factor design that takes into account the maximum and least limits of the experimental work performed with the 23-factor design. Neural network structures, such as the Feed Forward Neural Network (FFNN), were used to predict tensile and shear strength of tool steel sediments caused by friction.
-
Climate Prediction Center - Outlooks: Current UV Index Forecast Map
Weather Service NWS logo - Click to go to the NWS home page Climate Prediction Center Home Site Map News Service NOAA Center for Weather and Climate Prediction Climate Prediction Center 5830 University Research Court College Park, Maryland 20740 Page Author: Climate Prediction Center Internet Team Disclaimer
-
Jebri, Fatma; Zakardjian, Bruno; Birol, Florence; Bouffard, Jérôme; Jullion, Loïc.; Sammari, Cherif
2017-11-01
A 20 year coastal altimetry data set (X-TRACK) is used, for the first time, to gain insight into the long-term interannual variations of the surface circulation in the Sicily Channel. First, a spectral along with a time/space diagram analysis are applied to the monthly means. They reveal a regionally coherent current patterns from track to track with a marked interannual variability that is unequally shared between the Atlantic Tunisian Current and Atlantic Ionian Stream inflows in the Sicily Channel and the Bifurcation Tyrrhenian Current outflow northeast of Sicily. Second, an empirical altimetry-based transport-like technique is proposed to quantify volume budgets inside the closed boxes formed by the crossing of the altimetry tracks and coastlines over the study area. A set of hydrographic measurements is used to validate the method. The inferred altimetry transports give a well-balanced mean eastward Atlantic Waters baroclinic flow of 0.4 Sv and standard deviations of 0.2 Sv on a yearly basis throughout the Sicily Channel and toward the Ionian Sea, which is fairly coherent with those found in the literature. Furthermore, the analysis allows to quantify the intrusions of Atlantic Waters over the Tunisian Shelf (0.12 ± 0.1 Sv) and highlights two main modes of variability of the main surface waters path over the Sicily Channel through the Bifurcation Atlantic Tunisian Current and Atlantic Ionian Stream systems. Some physical mechanisms are finally discussed with regards to changes in the observed currents and transports.
-
Deterministic prediction of surface wind speed variations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. V. Drisya
2014-11-01
Full Text Available Accurate prediction of wind speed is an important aspect of various tasks related to wind energy management such as wind turbine predictive control and wind power scheduling. The most typical characteristic of wind speed data is its persistent temporal variations. Most of the techniques reported in the literature for prediction of wind speed and power are based on statistical methods or probabilistic distribution of wind speed data. In this paper we demonstrate that deterministic forecasting methods can make accurate short-term predictions of wind speed using past data, at locations where the wind dynamics exhibit chaotic behaviour. The predictions are remarkably accurate up to 1 h with a normalised RMSE (root mean square error of less than 0.02 and reasonably accurate up to 3 h with an error of less than 0.06. Repeated application of these methods at 234 different geographical locations for predicting wind speeds at 30-day intervals for 3 years reveals that the accuracy of prediction is more or less the same across all locations and time periods. Comparison of the results with f-ARIMA model predictions shows that the deterministic models with suitable parameters are capable of returning improved prediction accuracy and capturing the dynamical variations of the actual time series more faithfully. These methods are simple and computationally efficient and require only records of past data for making short-term wind speed forecasts within practically tolerable margin of errors.
-
Law, Caroline; Cupples, Linda
2017-03-01
Improving the reading performance of children with developmental surface dyslexia has proved challenging, with limited generalisation of reading skills typically reported after intervention. The aim of this study was to provide tailored, theoretically motivated intervention to two children with developmental surface dyslexia. Our objectives were to improve their reading performance, and to evaluate the utility of current reading models in therapeutic practice. Detailed reading and cognitive profiles for two male children with developmental surface dyslexia were compared to the results obtained by age-matched control groups. The specific area of single-word reading difficulty for each child was identified within the dual route model (DRM) of reading, following which a theoretically motivated intervention programme was devised. Both children showed significant improvements in single-word reading ability after training, with generalisation effects observed for untrained words. However, the assessment and intervention results also differed for each child, reinforcing the view that the causes and consequences of developmental dyslexia, even within subtypes, are not homogeneous. Overall, the results of the interventions corresponded more closely with the DRM than other current reading models, in that real word reading improved in the absence of enhanced nonword reading for both children.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Davari, Pooya; Yang, Yongheng; Zare, Firuz
2016-01-01
at the rectification stage to synthesize sinusoidal input currents. The input voltage sensing is avoided in order to minimize the number of required sensors, and the grid synchronization also has been implemented based on a common Phase-Locked-Loop (PLL) using the DC-link capacitor voltage ripple. Experimental results......The majority of the industrial motor drive systems are equipped with the conventional line-commutated front-end rectifiers, and being one of the main sources of harmonics in the power line. While a parallel combination of these drive units elevates current quality issues, a proper arrangement...... of them can lead to the cancellation of specific harmonics. This paper proposes a new cost-effective harmonic mitigation solution for multi-drive systems using a predictive pulse pattern current modulation control strategy. The proposed technique applies suitable interaction among parallel drive units...
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Mellor, A.; Domenech-Garret, J.L.; Chemisana, D.; Rosell, J.I. [Departament de Medi Ambient i C.S., University of Lleida, Av. Alcalde Rovira Roure 191, E25198 (Spain)
2009-09-15
A two-dimensional finite element model of current flow in the front surface of a PV cell is presented. In order to validate this model we perform an experimental test. Later, particular attention is paid to the effects of non-uniform illumination in the finger direction which is typical in a linear concentrator system. Fill factor, open circuit voltage and efficiency are shown to decrease with increasing degree of non-uniform illumination. It is shown that these detrimental effects can be mitigated significantly by reoptimization of the number of front surface metallization fingers to suit the degree of non-uniformity. The behavior of current flow in the front surface of a cell operating at open circuit voltage under non-uniform illumination is discussed in detail. (author)
-
Extended Range Prediction of Indian Summer Monsoon: Current status
Sahai, A. K.; Abhilash, S.; Borah, N.; Joseph, S.; Chattopadhyay, R.; S, S.; Rajeevan, M.; Mandal, R.; Dey, A.
2014-12-01
added value to both deterministic and probability forecast compared to raw SME's and this better skill is probably flows from large spread and improved spread-error relationship. CGMME system is currently capable of generating ER prediction in real time and successfully delivering its experimental operational ER forecast of ISM for the last few years.
-
Decadel climate prediction: challenges and opportunities
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hurrell, J W
2008-01-01
The scientific understanding of climate change is now sufficiently clear to show that climate change from global warming is already upon us, and the rate of change as projected exceeds anything seen in nature in the past 10,000 years. Uncertainties remain, however, especially regarding how climate will change at regional and local scales where the signal of natural variability is large. Addressing many of these uncertainties will require a movement toward high resolution climate system predictions, with a blurring of the distinction between shorter-term predictions and longer-term climate projections. The key is the realization that climate system predictions, regardless of timescale, will require initialization of coupled general circulation models with best estimates of the current observed state of the atmosphere, oceans, cryosphere, and land surface. Formidable challenges exist: for instance, what is the best method of initialization given imperfect observations and systematic errors in models? What effect does initialization have on climate predictions? What predictions should be attempted, and how would they be verified? Despite such challenges, the unrealized predictability that resides in slowly evolving phenomena, such as ocean current systems, is of paramount importance for society to plan and adapt for the next few decades. Moreover, initialized climate predictions will require stronger collaboration with shared knowledge, infrastructure and technical capabilities among those in the weather and climate prediction communities. The potential benefits include improved understanding and predictions on all time scales
-
Case, Jonathan L.; Splitt, Michael E.; Fuell, Kevin K.; Santos, Pablo; Lazarus, Steven M.; Jedlovec, Gary J.
2009-01-01
The NASA Short-term Prediction Research and Transition (SPoRT) Center, the Florida Institute of Technology, and the NOAA/NWS Weather Forecast Office at Miami, FL (MFL) are collaborating on a project to investigate the impact of using high-resolution, 2-km Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) sea surface temperature (SST) composites within the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) prediction system. The NWS MFL is currently running WRF in real-time to support daily forecast operations, using the National Centers for Environmental Prediction Nonhydrostatic Mesoscale Model dynamical core within the NWS Science and Training Resource Center's Environmental Modeling System (EMS) software. Twenty-seven hour forecasts are run daily initialized at 0300, 0900, 1500, and 2100 UTC on a domain with 4-km grid spacing covering the southern half of Florida and adjacent waters of the Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic Ocean. The SSTs are initialized with the NCEP Real-Time Global (RTG) analyses at 1/12deg resolution. The project objective is to determine whether more accurate specification of the lower-boundary forcing over water using the MODIS SST composites within the 4-km WRF runs will result in improved sea fluxes and hence, more accurate e\\olutiono f coastal mesoscale circulations and the associated sensible weather elements. SPoRT conducted parallel WRF EMS runs from February to August 2007 identical to the operational runs at NWS MFL except for the use of MODIS SST composites in place of the RTG product as the initial and boundary conditions over water. During the course of this evaluation, an intriguing case was examined from 6 May 2007, in which lake breezes and convection around Lake Okeechobee evolved quite differently when using the high-resolution SPoRT MODIS SST composites versus the lower-resolution RTG SSTs. This paper will analyze the differences in the 6 May simulations, as well as examine other cases from the summer 2007 in which the WRF
-
Precise on-machine extraction of the surface normal vector using an eddy current sensor array
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wang, Yongqing; Lian, Meng; Liu, Haibo; Ying, Yangwei; Sheng, Xianjun
2016-01-01
To satisfy the requirements of on-machine measurement of the surface normal during complex surface manufacturing, a highly robust normal vector extraction method using an Eddy current (EC) displacement sensor array is developed, the output of which is almost unaffected by surface brightness, machining coolant and environmental noise. A precise normal vector extraction model based on a triangular-distributed EC sensor array is first established. Calibration of the effects of object surface inclination and coupling interference on measurement results, and the relative position of EC sensors, is involved. A novel apparatus employing three EC sensors and a force transducer was designed, which can be easily integrated into the computer numerical control (CNC) machine tool spindle and/or robot terminal execution. Finally, to test the validity and practicability of the proposed method, typical experiments were conducted with specified testing pieces using the developed approach and system, such as an inclined plane and cylindrical and spherical surfaces. (paper)
-
Precise on-machine extraction of the surface normal vector using an eddy current sensor array
Wang, Yongqing; Lian, Meng; Liu, Haibo; Ying, Yangwei; Sheng, Xianjun
2016-11-01
To satisfy the requirements of on-machine measurement of the surface normal during complex surface manufacturing, a highly robust normal vector extraction method using an Eddy current (EC) displacement sensor array is developed, the output of which is almost unaffected by surface brightness, machining coolant and environmental noise. A precise normal vector extraction model based on a triangular-distributed EC sensor array is first established. Calibration of the effects of object surface inclination and coupling interference on measurement results, and the relative position of EC sensors, is involved. A novel apparatus employing three EC sensors and a force transducer was designed, which can be easily integrated into the computer numerical control (CNC) machine tool spindle and/or robot terminal execution. Finally, to test the validity and practicability of the proposed method, typical experiments were conducted with specified testing pieces using the developed approach and system, such as an inclined plane and cylindrical and spherical surfaces.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Suresh V.
2016-02-01
Full Text Available In this paper, an analytical model is proposed to predict magnetic flux leakage (MFL signals from the surface defects in ferromagnetic tubes. The analytical expression consists of elliptic integrals of first kind based on the magnetic dipole model. The radial (Bz component of leakage fields is computed from the cylindrical holes in ferromagnetic tubes. The effectiveness of the model has been studied by analyzing MFL signals as a function of the defect parameters and lift-off. The model predicted results are verified with experimental results and a good agreement is observed between the analytical and the experimental results. This analytical expression could be used for quick prediction of MFL signals and also input data for defect reconstructions in inverse MFL problem.
-
Advanced Gas Tungsten Arc Weld Surfacing Current Status and Application
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Stephan Egerland
2015-09-01
Full Text Available Abstract Gas Shielded Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW – a process well-known providing highest quality weld results joined though by lower performance. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW is frequently chosen to increase productivity along with broadly accepted quality. Those industry segments, especially required to produce high quality corrosion resistant weld surfacing e.g. applying nickel base filler materials, are regularly in consistent demand to comply with "zero defect" criteria. In this conjunction weld performance limitations are overcome employing advanced 'hot-wire' GTAW systems. This paper, from a Welding Automation perspective, describes the technology of such devices and deals with the current status is this field – namely the application of dual-cathode hot-wire electrode GTAW cladding; considerably broadening achievable limits.
-
Simplified Approach to Predicting Rough Surface Transition
Boyle, Robert J.; Stripf, Matthias
2009-01-01
Turbine vane heat transfer predictions are given for smooth and rough vanes where the experimental data show transition moving forward on the vane as the surface roughness physical height increases. Consiste nt with smooth vane heat transfer, the transition moves forward for a fixed roughness height as the Reynolds number increases. Comparison s are presented with published experimental data. Some of the data ar e for a regular roughness geometry with a range of roughness heights, Reynolds numbers, and inlet turbulence intensities. The approach ta ken in this analysis is to treat the roughness in a statistical sense , consistent with what would be obtained from blades measured after e xposure to actual engine environments. An approach is given to determ ine the equivalent sand grain roughness from the statistics of the re gular geometry. This approach is guided by the experimental data. A roughness transition criterion is developed, and comparisons are made with experimental data over the entire range of experimental test co nditions. Additional comparisons are made with experimental heat tran sfer data, where the roughness geometries are both regular as well a s statistical. Using the developed analysis, heat transfer calculatio ns are presented for the second stage vane of a high pressure turbine at hypothetical engine conditions.
-
Eddy Current Nondestructive Residual Stress Assessment in Shot-Peened Nickel-Base Superalloys
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Blodgett, M.P.; Yu, F.; Nagy, P.B.
2005-01-01
Shot peening and other mechanical surface enhancement methods improve the fatigue resistance and foreign-object damage tolerance of metallic components by introducing beneficial near-surface compressive residual stresses and hardening the surface. However, the fatigue life improvement gained via surface enhancement is not explicitly accounted for in current engine component life prediction models because of the lack of accurate and reliable nondestructive methods that could verify the presence of compressive near-surface residual stresses in shot-peened hardware. In light of its frequency-dependent penetration depth, the measurement of eddy current conductivity has been suggested as a possible means to allow the nondestructive evaluation of subsurface residual stresses in surface-treated components. This technique is based on the so-called piezoresistivity effect, i.e., the stress-dependence of electrical resistivity. We found that, in contrast with most other materials, surface-treated nickel-base superalloys exhibit an apparent increase in electrical conductivity at increasing inspection frequencies, i.e., at decreasing penetration depths. Experimental results are presented to illustrate that the excess frequency-dependent apparent eddy current conductivity of shot-peened nickel-base superalloys can be used to estimate the absolute level and penetration depth of the compressive residual stress layer both before and after partial thermal relaxation
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zhong Jian; Dong Gang; Sun Yimei; Zhang Zhaoyang; Wu Yuqin
2016-01-01
The present work reports the development of nonlinear time series prediction method of genetic algorithm (GA) with singular spectrum analysis (SSA) for forecasting the surface wind of a point station in the South China Sea (SCS) with scatterometer observations. Before the nonlinear technique GA is used for forecasting the time series of surface wind, the SSA is applied to reduce the noise. The surface wind speed and surface wind components from scatterometer observations at three locations in the SCS have been used to develop and test the technique. The predictions have been compared with persistence forecasts in terms of root mean square error. The predicted surface wind with GA and SSA made up to four days (longer for some point station) in advance have been found to be significantly superior to those made by persistence model. This method can serve as a cost-effective alternate prediction technique for forecasting surface wind of a point station in the SCS basin. (paper)
-
Guérin, Charles-Antoine; Grilli, Stéphan T.
2018-01-01
We present a new method for inverting ocean surface currents from beam-forming HF radar data. In contrast with the classical method, which inverts radial currents based on shifts of the main Bragg line in the radar Doppler spectrum, the method works in the temporal domain and inverts currents from the amplitude modulation of the I and Q radar time series. Based on this principle, we propose a Maximum Likelihood approach, which can be combined with a Bayesian inference method assuming a prior current distribution, to infer values of the radial surface currents. We assess the method performance by using synthetic radar signal as well as field data, and systematically comparing results with those of the Doppler method. The new method is found advantageous for its robustness to noise at long range, its ability to accommodate shorter time series, and the possibility to use a priori information to improve the estimates. Limitations are related to current sign errors at far-ranges and biased estimates for small current values and very short samples. We apply the new technique to a data set from a typical 13.5 MHz WERA radar, acquired off of Vancouver Island, BC, and show that it can potentially improve standard synoptic current mapping.
-
The Search for Biosignatures on Mars: Using Predictive Geology to Optimize Exploration Targets
Oehler, Dorothy Z.; Allen, Carlton C.
2011-01-01
Predicting geologic context from satellite data is a method used on Earth for exploration in areas with limited ground truth. The method can be used to predict facies likely to contain organic-rich shales. Such shales concentrate and preserve organics and are major repositories of organic biosignatures on Earth [1]. Since current surface conditions on Mars are unfavorable for development of abundant life or for preservation of organic remains of past life, the chances are low of encountering organics in surface samples. Thus, focusing martian exploration on sites predicted to contain organic-rich shales would optimize the chances of discovering evidence of life, if it ever existed on that planet.
-
Biancamaria, S.; Clark, E.; Lettenmaier, D. P.
2010-12-01
More than 256 major global river basins, which cover about 45% of the continental land surface, are shared among two or more countries. The flow of such a large part of the global runoff across international boundaries has led to tension in many cases between upstream and downstream riparian countries. Among many examples, this is the case of the Ganges and the Brahmaputra Rivers, which cross the boundary between India and Bangladesh. Hydrological data (river discharge, reservoir storage) are viewed as sensitive by India (the upstream country) and are therefore not shared with Bangladesh, which can only monitor river discharge and water depth at the international border crossing. These measurements only allow forecasting of floods in the interior and southern portions of the country two to three days in advance. These forecasts are not long enough either for agricultural water management purposes (for which knowledge of upstream reservoir storage is essential) or for disaster preparedness purposes. Satellite observations of river spatial extent, surface slope, reservoir area and surface elevation have the potential to make tremendous changes in management of water within the basins. In this study, we examine the use of currently available satellite measurements (in India) and in-situ measurements in Bangladesh to increase forecast lead time in the Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers. Using nadir altimeters, we find that it is possible to forecast the discharge of the Ganges River at the Bangladesh border with lead time 3 days and mean absolute error of around 25%. On the Ganges River, 2-day forecasts are possible with a mean absolute error of around 20%. When combined with optical/infra-red MODIS images, it is possible to map water elevations along the river and its floodplain upstream of the boundary, and to compute water storage. However, the high frequency of clouds in this region results in relatively large errors in the water mask. Due to the nadir altimeter
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Maysonnave, T.; Bayol, F.; Demol, G.; Almeida, T. d'; Morell, A.; Lassalle, F.; Grunenwald, J.; Chuvatin, A.S.; Pecastaing, L.; De Ferron, A.S.
2013-01-01
SPHINX is a microsecond linear transformer driver located at Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) Gramat (France), which can deliver a current pulse of 6 MA within 800 ns in a Z-pinch load. Using the concept of the dynamic load current multiplier (DLCM), which was proposed by Chuvatin, we expect to increase the load current above 6 MA, while decreasing its rise time to ∼300 ns. The DLCM developed by the CEA Gramat and International Technologies for High Pulsed Power (ITHPP) is a compact system made up of concentric electrodes (auto-transformer), a dynamic flux extruder (cylindrical wire array), a vacuum convolute (eight post-hole rods), and a closing switch (compact vacuum surface switch). The latter is a key component of the system, which is used to prevent the current from flowing into the load until the inductance builds up due to the implosion of the wire array. This paper presents the design and testing of the DLCM surface switch, resulting from both electrostatic simulations and experiments on the SPHINX generator. These studies, carried out either with or without load (open circuit), were valuable for a first experimental evaluation of the DLCM scheme in a microsecond regime and provided detailed information on the surface switch behavior. (authors)
-
Existence of three-dimensional ideal-magnetohydrodynamic equilibria with current sheets
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Loizu, J. [Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-17491 Greifswald (Germany); Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, PO Box 451, Princeton, New Jersey 08543 (United States); Hudson, S. R.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Lazerson, S. [Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, PO Box 451, Princeton, New Jersey 08543 (United States); Helander, P. [Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, D-17491 Greifswald (Germany)
2015-09-15
We consider the linear and nonlinear ideal plasma response to a boundary perturbation in a screw pinch. We demonstrate that three-dimensional, ideal-MHD equilibria with continuously nested flux-surfaces and with discontinuous rotational-transform across the resonant rational-surfaces are well defined and can be computed both perturbatively and using fully nonlinear equilibrium calculations. This rescues the possibility of constructing MHD equilibria with current sheets and continuous, smooth pressure profiles. The results predict that, even if the plasma acts as a perfectly conducting fluid, a resonant magnetic perturbation can penetrate all the way into the center of a tokamak without being shielded at the resonant surface.
-
Modeling of surface stress effects on bending behavior of nanowires: Incremental deformation theory
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Song, F.; Huang, G.L.
2009-01-01
The surface stress effects on bending behavior of nanowires have recently attracted a lot of attention. In this letter, the incremental deformation theory is first applied to study the surface stress effects upon the bending behavior of the nanowires. Different from other linear continuum approaches, the local geometrical nonlinearity of the Lagrangian strain is considered, therefore, the contribution of the surface stresses is naturally derived by applying the Hamilton's principle, and influence of the surface stresses along all surfaces of the nanowires is captured. It is first shown that the surface stresses along all surfaces have contribution not only on the effective Young's modulus of the nanowires but also on the loading term in the governing equation. The predictions of the effective Young's modulus and the resonance shift of the nanowires from the current method are compared with those from the experimental measurement and other existing approaches. The difference with other models is discussed. Finally, based on the current theory, the resonant shift predictions by using both the modified Euler-Bernoulli beam and the modified Timoshenko beam theories of the nanowires are investigated and compared. It is noticed that the higher vibration modes are less sensitive to the surface stresses than the lower vibration modes.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Abdel Badie Sharkawy
2011-01-01
Full Text Available A study is presented to model surface roughness in end milling process. Three types of intelligent networks have been considered. They are (i radial basis function neural networks (RBFNs, (ii adaptive neurofuzzy inference systems (ANFISs, and (iii genetically evolved fuzzy inference systems (G-FISs. The machining parameters, namely, the spindle speed, feed rate, and depth of cut have been used as inputs to model the workpiece surface roughness. The goal is to get the best prediction accuracy. The procedure is illustrated using experimental data of end milling 6061 aluminum alloy. The three networks have been trained using experimental training data. After training, they have been examined using another set of data, that is, validation data. Results are compared with previously published results. It is concluded that ANFIS networks may suffer the local minima problem, and genetic tuning of fuzzy networks cannot insure perfect optimality unless suitable parameter setting (population size, number of generations etc. and tuning range for the FIS, parameters are used which can be hardly satisfied. It is shown that the RBFN model has the best performance (prediction accuracy in this particular case.
-
The artificial object detection and current velocity measurement using SAR ocean surface images
Alpatov, Boris; Strotov, Valery; Ershov, Maksim; Muraviev, Vadim; Feldman, Alexander; Smirnov, Sergey
2017-10-01
Due to the fact that water surface covers wide areas, remote sensing is the most appropriate way of getting information about ocean environment for vessel tracking, security purposes, ecological studies and others. Processing of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images is extensively used for control and monitoring of the ocean surface. Image data can be acquired from Earth observation satellites, such as TerraSAR-X, ERS, and COSMO-SkyMed. Thus, SAR image processing can be used to solve many problems arising in this field of research. This paper discusses some of them including ship detection, oil pollution control and ocean currents mapping. Due to complexity of the problem several specialized algorithm are necessary to develop. The oil spill detection algorithm consists of the following main steps: image preprocessing, detection of dark areas, parameter extraction and classification. The ship detection algorithm consists of the following main steps: prescreening, land masking, image segmentation combined with parameter measurement, ship orientation estimation and object discrimination. The proposed approach to ocean currents mapping is based on Doppler's law. The results of computer modeling on real SAR images are presented. Based on these results it is concluded that the proposed approaches can be used in maritime applications.
-
De Conti, Alberto; Silveira, Fernando H.; Visacro, Silvério
2014-05-01
This paper investigates the influence of corona on currents and electromagnetic fields predicted by a return-stroke model that represents the lightning channel as a nonuniform transmission line with time-varying (nonlinear) resistance. The corona model used in this paper allows the calculation of corona currents as a function of the radial electric field in the vicinity of the channel. A parametric study is presented to investigate the influence of corona parameters, such as the breakdown electric field and the critical electric field for the stable propagation of streamers, on predicted currents and electromagnetic fields. The results show that, regardless of the assumed corona parameters, the incorporation of corona into the nonuniform and nonlinear transmission line model under investigation modifies the model predictions so that they consistently reproduce most of the typical features of experimentally observed lightning electromagnetic fields and return-stroke speed profiles. In particular, it is shown that the proposed model leads to close vertical electric fields presenting waveforms, amplitudes, and decay with distance in good agreement with dart leader electric field changes measured in triggered lightning experiments. A comparison with popular engineering return-stroke models further confirms the model's ability to predict consistent electric field waveforms in the close vicinity of the channel. Some differences observed in the field amplitudes calculated with the different models can be related to the fact that current distortion, while present in the proposed model, is ultimately neglected in the considered engineering return-stroke models.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kossyi, I.A.; Silakov, V.P.; Tarasova, N.M.
2001-01-01
Results are presented from experimental studies of the destruction of chlorofluorocarbon (CF 2 Cl 2 ) molecules in a methane-oxygen (air) gas mixture whose combustion is initiated by a high-current slipping surface discharge. It is found that a three-component CH 4 + O 2 (air)+ CF 2 Cl 2 gas mixture (even with a considerable amount of the third component) demonstrates properties of explosive combustion involving chain reactions that are typical of two-component CH 4 + O 2 mixtures. Experiments show the high degree of destruction (almost complete decomposition) of chlorofluorocarbons contained in the mixture during one combustion event. The combustion dynamics is studied. It is shown that the combustion initiated by a slipping surface discharge has a number of characteristic features that make it impossible to identify the combustion dynamics with the formation of a combustion or detonation wave. The features of the effects observed can be related to intense UV radiation produced by a pulsed high-current surface discharge
-
Multifrequency eddy current examination for surface defects detection of hot steel products
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hiroshima, Tatsuo; Sakamoto, Takahide; Takahashi, Akio; Miyata, Kenichi.
1985-01-01
Multifrequency eddy current testing method using probe coils has been studied for surface defects detection in hot steel products at high temperature over the magnetic Curie point. The conventional signal processing method is not available for suppression of an undesirable signal caused by lift-off variation or unevenness in inspected surfaces, because the undesirable signal pattern is similar to a defect signal pattern. In order to suppress the undesirable signal a new dual frequency signal processing method using three phase rotators has been developed, and was applied to several hot steel inspections. The results are as follows. 1. In the rotating eddy current machine for hot steel rods, the lift-off variation signal caused by a wobble of rods or the difference between rotating center and pass center of rods can be suppressed. A long seam or crack whose depth is more than 0.5mm can be detected. 2. In the hot inspection for continuously cast slabs, the signal caused by oscillation mark whose depth is under 1 mm can be suppressed. A fine transversal crack whose depth is 2 mm can be detected. 3. In the hot inspection for round billets, the lift-off variation signal caused by oval shape can be eliminated, and a crack which is deeper than 1.5 mm can be clearly detected. The detectability of defects can be improved by the analysis of dual frequency signal pattern. (author)
-
Normand, Frédéric; Lauri, Pierre-Éric
2012-03-01
Accurate and reliable predictive models are necessary to estimate nondestructively key variables for plant growth studies such as leaf area and leaf, stem, and total biomass. Predictive models are lacking at the current-year branch scale despite the importance of this scale in plant science. We calibrated allometric models to estimate leaf area and stem and branch (leaves + stem) mass of current-year branches, i.e., branches several months old studied at the end of the vegetative growth season, of four mango cultivars on the basis of their basal cross-sectional area. The effects of year, site, and cultivar were tested. Models were validated with independent data and prediction accuracy was evaluated with the appropriate statistics. Models revealed a positive allometry between dependent and independent variables, whose y-intercept but not the slope, was affected by the cultivar. The effects of year and site were negligible. For each branch characteristic, cultivar-specific models were more accurate than common models built with pooled data from the four cultivars. Prediction quality was satisfactory but with data dispersion around the models, particularly for large values. Leaf area and stem and branch mass of mango current-year branches could be satisfactorily estimated on the basis of branch basal cross-sectional area with cultivar-specific allometric models. The results suggested that, in addition to the heteroscedastic behavior of the variables studied, model accuracy was probably related to the functional plasticity of branches in relation to the light environment and/or to the number of growth units composing the branches.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Mikami, T. [Japan Automobile Research Institute Inc., Tsukuba (Japan)
1999-07-01
A method for tire/road noise prediction is studied based on the result of road surface profile measurement (horizontal direction measurement interval 3mm, horizontal direction measurement accuracy 8{mu}m, distance measured 1655m, using a laser-aided profile meter). The obtained road surface profile is used for the calculation of contact pressure that occurs between the tire tread and road surface (using the 2-dimensional calculation model of Clapp et al.). For the examination of the relationship between the contact pressure and generated noise, tire noise is measured using a microphone array provided near the tire circumference. The frequency spectral ratio between the generated noise and contact pressure is determined as a transmission function. It may be said that the transmission function is unique to the tire, not dependent on the road surface profile. The road surface profile is determined by use of the transmission function, and this enables the prediction of the noise from the tire. Noises were measured on several kinds of road surfaces different in coarseness for a passenger car and truck, and the values from these actual measurements are compared with the predicted values, and then it is found that the prediction model is valid. (NEDO)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Taller, Stephen A. [School of Nuclear Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907 (United States); Bai, Xian-Ming, E-mail: xianming.bai@inl.gov [Fuels Modeling and Simulation Department, Idaho National Laboratory, Idaho Falls, ID 83415 (United States)
2013-11-15
The irradiation in nuclear reactors creates many point defects and defect clusters in uranium dioxide (UO{sub 2}) and their evolution severely degrades the thermal and mechanical properties of the nuclear fuels. Previously many empirical interatomic potentials have been developed for modeling defect production and evolution in UO{sub 2}. However, the properties of defect clusters and extended defects are usually not fitted into these potentials. In this work nine interatomic potentials for UO{sub 2} are examined by using molecular statics and molecular dynamics to assess their applicability in predicting the properties of various types of defect clusters in UO{sub 2}. The binding energies and structures for these defect clusters have been evaluated for each potential. In addition, the surface energies of voids of different radii and (1 1 0) flat surfaces predicted by these potentials are also evaluated. It is found that both good agreement and significant discrepancies exist for these potentials in predicting these properties. For oxygen interstitial clusters, these potentials predict significantly different defect cluster structures and stabilities; For defect clusters consisting of both uranium and oxygen defects, the prediction is in better agreement; The surface energies predicted by these potentials have significant discrepancies, and some of them are much higher than the experimentally measured values. The results from this work can provide insight on interpreting the outcome of atomistic modeling of defect production using these potentials and may provide guidelines for choosing appropriate potential models to study problems of interest in UO{sub 2}.
-
Analysis of energy flow during playground surface impacts.
Davidson, Peter L; Wilson, Suzanne J; Chalmers, David J; Wilson, Barry D; Eager, David; McIntosh, Andrew S
2013-10-01
The amount of energy dissipated away from or returned to a child falling onto a surface will influence fracture risk but is not considered in current standards for playground impact-attenuating surfaces. A two-mass rheological computer simulation was used to model energy flow within the wrist and surface during hand impact with playground surfaces, and the potential of this approach to provide insights into such impacts and predict injury risk examined. Acceleration data collected on-site from typical playground surfaces and previously obtained data from children performing an exercise involving freefalling with a fully extended arm provided input. The model identified differences in energy flow properties between playground surfaces and two potentially harmful surface characteristics: more energy was absorbed by (work done on) the wrist during both impact and rebound on rubber surfaces than on bark, and rubber surfaces started to rebound (return energy to the wrist) while the upper limb was still moving downward. Energy flow analysis thus provides information on playground surface characteristics and the impact process, and has the potential to identify fracture risks, inform the development of safer impact-attenuating surfaces, and contribute to development of new energy-based arm fracture injury criteria and tests for use in conjunction with current methods.
-
Nguyen, Caroline K; Stone, Kendall R; Dudi, Abhijeet; Edwards, Marc A
2010-09-15
As stagnant water contacts copper pipe and lead solder (simulated soldered joints), a corrosion cell is formed between the metals in solder (Pb, Sn) and the copper. If the resulting galvanic current exceeds about 2 μA/cm(2), a highly corrosive microenvironment can form at the solder surface, with pH chloride concentrations at least 11 times higher than bulk water levels. Waters with relatively high chloride tend to sustain high galvanic currents, preventing passivation of the solder surface, and contributing to lead contamination of potable water supplies. The total mass of lead corroded was consistent with predictions based on the galvanic current, and lead leaching to water was correlated with galvanic current. If the concentration of sulfate in the water increased relative to chloride, galvanic currents and associated lead contamination could be greatly reduced, and solder surfaces were readily passivated.
-
Predicting wettability behavior of fluorosilica coated metal surface using optimum neural network
Taghipour-Gorjikolaie, Mehran; Valipour Motlagh, Naser
2018-02-01
The interaction between variables, which are effective on the surface wettability, is very complex to predict the contact angles and sliding angles of liquid drops. In this paper, in order to solve this complexity, artificial neural network was used to develop reliable models for predicting the angles of liquid drops. Experimental data are divided into training data and testing data. By using training data and feed forward structure for the neural network and using particle swarm optimization for training the neural network based models, the optimum models were developed. The obtained results showed that regression index for the proposed models for the contact angles and sliding angles are 0.9874 and 0.9920, respectively. As it can be seen, these values are close to unit and it means the reliable performance of the models. Also, it can be inferred from the results that the proposed model have more reliable performance than multi-layer perceptron and radial basis function based models.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zou Yang; Cai Jie; Wan Ming-Zhen; Lv Peng; Guan Qing-Feng
2011-01-01
The mechanism of micropores formed on the surface of polycrystalline pure aluminum under high-current pulsed electron beam (HCPEB) irradiation is explained. It is discovered that dispersed micropores with sizes of 0.1–1 μm on the irradiated surface of pure aluminum can be successfully fabricated after HCPEB irradiation. The dominant formation mechanism of the surface micropores should be attributed to the formation of supersaturation vacancies within the near surface during the HCPEB irradiation and the migration of vacancies along grain boundaries and/or dislocations towards the irradiated surface. It is expected that the HCPEB technique will become a new method for the rapid synthesis of surface porous materials. (condensed matter: structure, mechanical and thermal properties)
-
Sources, occurrence and predicted aquatic impact of legacy and contemporary pesticides in streams.
McKnight, Ursula S; Rasmussen, Jes J; Kronvang, Brian; Binning, Philip J; Bjerg, Poul L
2015-05-01
We couple current findings of pesticides in surface and groundwater to the history of pesticide usage, focusing on the potential contribution of legacy pesticides to the predicted ecotoxicological impact on benthic macroinvertebrates in headwater streams. Results suggest that groundwater, in addition to precipitation and surface runoff, is an important source of pesticides (particularly legacy herbicides) entering surface water. In addition to current-use active ingredients, legacy pesticides, metabolites and impurities are important for explaining the estimated total toxicity attributable to pesticides. Sediment-bound insecticides were identified as the primary source for predicted ecotoxicity. Our results support recent studies indicating that highly sorbing chemicals contribute and even drive impacts on aquatic ecosystems. They further indicate that groundwater contaminated by legacy and contemporary pesticides may impact adjoining streams. Stream observations of soluble and sediment-bound pesticides are valuable for understanding the long-term fate of pesticides in aquifers, and should be included in stream monitoring programs. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kelly P Nevin
Full Text Available The mechanisms by which Geobacter sulfurreducens transfers electrons through relatively thick (>50 microm biofilms to electrodes acting as a sole electron acceptor were investigated. Biofilms of Geobacter sulfurreducens were grown either in flow-through systems with graphite anodes as the electron acceptor or on the same graphite surface, but with fumarate as the sole electron acceptor. Fumarate-grown biofilms were not immediately capable of significant current production, suggesting substantial physiological differences from current-producing biofilms. Microarray analysis revealed 13 genes in current-harvesting biofilms that had significantly higher transcript levels. The greatest increases were for pilA, the gene immediately downstream of pilA, and the genes for two outer c-type membrane cytochromes, OmcB and OmcZ. Down-regulated genes included the genes for the outer-membrane c-type cytochromes, OmcS and OmcT. Results of quantitative RT-PCR of gene transcript levels during biofilm growth were consistent with microarray results. OmcZ and the outer-surface c-type cytochrome, OmcE, were more abundant and OmcS was less abundant in current-harvesting cells. Strains in which pilA, the gene immediately downstream from pilA, omcB, omcS, omcE, or omcZ was deleted demonstrated that only deletion of pilA or omcZ severely inhibited current production and biofilm formation in current-harvesting mode. In contrast, these gene deletions had no impact on biofilm formation on graphite surfaces when fumarate served as the electron acceptor. These results suggest that biofilms grown harvesting current are specifically poised for electron transfer to electrodes and that, in addition to pili, OmcZ is a key component in electron transfer through differentiated G. sulfurreducens biofilms to electrodes.
-
Influence of the surface drag coefficient (young waves) on the current structure of the Berre lagoon
Alekseenko, Elena; Roux, Bernard; Kharif, Christian; Sukhinov, Alexander; Kotarba, Richard; Fougere, Dominique; Chen, Paul Gang
2013-04-01
Due to the shallowness, currents and hydrodynamics of Berre lagoon (South of France) are closely conditioned by the bottom topography, and wind affects the entire water column, as for many other Mediterranean lagoons (Perez-Ruzafa, 2011). Wind stress, which is caused by moving atmospheric disturbance, is known to have a major influence in lagoon water circulation. According to the numerical simulation for the main directions of the wind: N-NW, S-SE and W (wind speed of 80 km/h) it is observed that the current is maximal alongshore in the wind direction; the bottom nearshore current being larger in shallower area. This fact is coherent with fundamental principle of wind-driven flows in closed or partially closed basins which states that in shallow water the dominant force balance is between surface wind stress and bottom friction, yielding a current in the direction of the wind (Mathieu et al, 2002, Hunter and Hearn, 1987; Hearn and Hunter,1990). A uniform wind stress applied at the surface of a basin of variable depth sets up a circulation pattern characterized by relatively strong barotropic coastal currents in the direction of the wind, with return flow occurring over the deeper regions (Csanady, 1967; Csanady, 1971). One of the key parameters characterizing the wind stress formulation is a surface drag coefficient (Cds). Thus, an effect of a surface drag coefficient, in the range 0.0016 - 0.0032, will be analyzed in this work. The value of surface drag coefficient Cds = 0.0016 used in our previous studies (Alekseenko et al., 2012), would correspond to mature waves (open sea). But, in the case of semi-closed lagoonal ecosystem, it would be more appropriate to consider "young waves" mechanism. A dependency of this coefficient in terms of the wind speed is given by Young (1999) in both cases of mature waves and young waves. For "young waves" generated at a wind speed of 80 km/h, Cds = 0.0032. So, the influence of Cds on the vertical profile of the velocity in the
-
Simulations of vertical disruptions with VDE code: Hiro and Evans currents
Li, Xujing; Di Hu Team; Leonid Zakharov Team; Galkin Team
2014-10-01
The recently created numerical code VDE for simulations of vertical instability in tokamaks is presented. The numerical scheme uses the Tokamak MHD model, where the plasma inertia is replaced by the friction force, and an adaptive grid numerical scheme. The code reproduces well the surface currents generated at the plasma boundary by the instability. Five regimes of the vertical instability are presented: (1) Vertical instability in a given plasma shaping field without a wall; (2) The same with a wall and magnetic flux ΔΨ|plX< ΔΨ|Xwall(where X corresponds to the X-point of a separatrix); (3) The same with a wall and magnetic flux ΔΨ|plX> ΔΨ|Xwall; (4) Vertical instability without a wall with a tile surface at the plasma path; (5) The same in the presence of a wall and a tile surface. The generation of negative Hiro currents along the tile surface, predicted earlier by the theory and measured on EAST in 2012, is well-reproduced by simulations. In addition, the instability generates the force-free Evans currents at the free plasma surface. The new pattern of reconnection of the plasma with the vacuum magnetic field is discovered. This work is supported by US DoE Contract No. DE-AC02-09-CH11466.
-
Wen, Huan Fei; Li, Yan Jun; Arima, Eiji; Naitoh, Yoshitaka; Sugawara, Yasuhiro; Xu, Rui; Cheng, Zhi Hai
2017-03-10
We propose a new multi-image method for obtaining the frequency shift, tunneling current and local contact potential difference (LCPD) on a TiO 2 (110) surface with atomic resolution. The tunneling current image reveals rarely observed surface oxygen atoms contrary to the conventional results. We analyze how the surface and subsurface defects affect the distribution of the LCPD. In addition, the subsurface defects are observed clearly in the tunneling current image, in contrast to a topographic image. To clarify the origin of the atomic contrast, we perform site-dependent spectroscopy as a function of the tip-sample distance. The multi-image method is expected to be widely used to investigate the charge transfer phenomena between the nanoparticles and surface sites, and it is useful for elucidating the mechanisms of catalytic reactions.
-
Shikin, A. M.; Voroshin, V. Yu; Rybkin, A. G.; Kokh, K. A.; Tereshchenko, O. E.; Ishida, Y.; Kimura, A.
2018-01-01
A new kind of 2D photovoltaic effect (PVE) with the generation of anomalously large surface photovoltage up to 210 meV in magnetically doped topological insulators (TIs) has been studied by the laser time-resolved pump-probe angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy. The PVE has maximal efficiency for TIs with high occupation of the upper Dirac cone (DC) states and the Dirac point located inside the fundamental energy gap. For TIs with low occupation of the upper DC states and the Dirac point located inside the valence band the generated surface photovoltage is significantly reduced. We have shown that the observed giant PVE is related to the laser-generated electron-hole asymmetry followed by accumulation of the photoexcited electrons at the surface. It is accompanied by the 2D relaxation process with the generation of zero-bias spin-polarized currents flowing along the topological surface states (TSSs) outside the laser beam spot. As a result, the spin-polarized current generates an effective in-plane magnetic field that is experimentally confirmed by the k II-shift of the DC relative to the bottom non-spin-polarized conduction band states. The realized 2D PVE can be considered as a source for the generation of zero-bias surface spin-polarized currents and the laser-induced local surface magnetization developed in such kind 2D TSS materials.
-
Forcing and variability of nonstationary rip currents
Long, Joseph W.; H.T. Özkan-Haller,
2016-01-01
Surface wave transformation and the resulting nearshore circulation along a section of coast with strong alongshore bathymetric gradients outside the surf zone are modeled for a consecutive 4 week time period. The modeled hydrodynamics are compared to in situ measurements of waves and currents collected during the Nearshore Canyon Experiment and indicate that for the entire range of observed conditions, the model performance is similar to other studies along this stretch of coast. Strong alongshore wave height gradients generate rip currents that are observed by remote sensing data and predicted qualitatively well by the numerical model. Previous studies at this site have used idealized scenarios to link the rip current locations to undulations in the offshore bathymetry but do not explain the dichotomy between permanent offshore bathymetric features and intermittent rip current development. Model results from the month‐long simulation are used to track the formation and location of rip currents using hourly statistics, and results show that the direction of the incoming wave energy strongly controls whether rip currents form. In particular, most of the offshore wave spectra were bimodal and we find that the ratio of energy contained in each mode dictates rip current development, and the alongshore rip current position is controlled by the incident wave period. Additionally, model simulations performed with and without updating the nearshore morphology yield no significant change in the accuracy of the predicted surf zone hydrodyanmics indicating that the large‐scale offshore features (e.g., submarine canyon) predominately control the nearshore wave‐circulation system.
-
The effect of cathode bias (field effect) on the surface leakage current of CdZnTe detectors
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bolotnikov, A.E.; Hubert Chen, C.M.; Cook, W.R.; Harrison, F.A.; Kuvvetli, I.; Schindler, S.M.; Stahle, C.M.; Parker, B.H.
2003-01-01
Surface resistivity is an important parameter of multi-electrode CZT detectors such as coplanar-grid, strip, or pixel detectors. Low surface resistivity results in a high leakage current and affects the charge collection efficiency in the areas near contacts. Thus, it is always desirable to have the surface resistivity of the detector as high as possible. In the past the most significant efforts were concentrated to develop passivation techniques for CZT detectors. However, as we found, the field-effect caused by a bias applied on the cathode can significantly reduce the surface resistivity even though the detector surface was carefully passivated. In this paper we illustrate that the field-effect is a common feature of the CZT multi-electrode detectors, and discuss how to take advantage of this effect to improve the surface resistivity of CZT detectors
-
Noether Current of the Surface Term of Einstein-Hilbert Action, Virasoro Algebra, and Entropy
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Bibhas Ranjan Majhi
2013-01-01
Full Text Available A derivation of Noether current from the surface term of Einstein-Hilbert action is given. We show that the corresponding charge, calculated on the horizon, is related to the Bekenstein-Hawking entropy. Also using the charge, the same entropy is found based on the Virasoro algebra and Cardy formula approach. In this approach, the relevant diffeomorphisms are found by imposing a very simple physical argument: diffeomorphisms keep the horizon structure invariant. This complements similar earlier results (Majhi and Padmanabhan (2012 (arXiv:1204.1422 obtained from York-Gibbons-Hawking surface term. Finally we discuss the technical simplicities and improvements over the earlier attempts and also various important physical implications.
-
Laepple, Thomas; Jewson, Stephen; Meagher, Jonathan; O'Shay, Adam; Penzer, Jeremy
2007-01-01
We are developing schemes that predict future hurricane numbers by first predicting future sea surface temperatures (SSTs), and then apply the observed statistical relationship between SST and hurricane numbers. As part of this overall goal, in this study we compare the historical performance of three simple statistical methods for making five-year SST forecasts. We also present SST forecasts for 2006-2010 using these methods and compare them to forecasts made from two structural time series ...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Williams, E D; Bondarchuk, O; Tao, C G; Yan, W; Cullen, W G; Rous, P J; Bole, T
2007-01-01
Scattering of charge carriers from surface structures will become an increasing factor in the resistivity as the structure decreases in size to the nanoscale. The effects of scattering at the most basic surface defect, a kink in a step edge, are here analyzed using the continuum step model. Using a Langevin analysis, it has been shown that the electromigration force on the atoms at the step edge causes changes in the temporal evolution of the step-edge. For an electromigration force acting perpendicular to the average step edge and mass-transport dominated by step-edge diffusion, significant deviations from the usual t 1/4 scaling of the displacement correlation function occur dependent on a critical time τ and the direction of the force relative to the step edge (i.e. uphill or downhill). Experimental observations of step fluctuations on Ag(111) show the predicted changes among step fluctuations without current, and with current in the up- and down-hill directions for a current density of order 10 5 A cm -2 . The results yield the magnitude of the electromigration force acting on kinked sites at the step-edge. This in turn yields the contribution of the fluctuating steps to the surface resistivity, which exceeds 1% of the bulk resistivity as wire diameters decrease below 10s of nanometres. The temporal fluctuations of kink density can thus also be related to resistivity noise. Relating the known fluctuation spectrum of the step displacements to fluctuations in their lengths, the corresponding resistivity noise is predicted to show spectral signatures of ∼f -1/2 for step fluctuations governed by random attachment/detachment, and ∼f -3/4 for step fluctuations governed by step-edge diffusion
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Desiree Tommasi
2017-06-01
Full Text Available Decisions made by fishers and fisheries managers are informed by climate and fisheries observations that now often span more than 50 years. Multi-annual climate forecasts could further inform such decisions if they were skillful in predicting future conditions relative to the 50-year scope of past variability. We demonstrate that an existing multi-annual prediction system skillfully forecasts the probability of next year, the next 1–3 years, and the next 1–10 years being warmer or cooler than the 50-year average at the surface in coastal ecosystems. Probabilistic forecasts of upper and lower seas surface temperature (SST terciles over the next 3 or 10 years from the GFDL CM 2.1 10-member ensemble global prediction system showed significant improvements in skill over the use of a 50-year climatology for most Large Marine Ecosystems (LMEs in the North Atlantic, the western Pacific, and Indian oceans. Through a comparison of the forecast skill of initialized and uninitialized hindcasts, we demonstrate that this skill is largely due to the predictable signature of radiative forcing changes over the 50-year timescale rather than prediction of evolving modes of climate variability. North Atlantic LMEs stood out as the only coastal regions where initialization significantly contributed to SST prediction skill at the 1 to 10 year scale.
-
Luke, K. L.; Cheng, L.-J.
1984-01-01
A chopped electron beam induced current (EBIC) technique for the chacterization of back-surface field (BSF) solar cells is presented. It is shown that the effective recombination velocity of the low-high junction forming the back-surface field of BSF cells, in addition to the diffusion length and the surface recombination velocity of the surface perpendicular to both the p-n and low-high junctions, can be determined from the data provided by a single EBIC scan. The method for doing so is described and illustrated. Certain experimental considerations taken to enhance the quality of the EBIC data are also discussed.
-
The interaction of pulsed eddy current with metal surface crack for various coils
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yang, H.-C.; Tai, C.-C.
2002-01-01
We study the interaction of pulsed eddy current (PEC) with metal surface cracks using various coils that have different geometric sizes. In the previous work, we have showed that the PEC technique can be used to inspect electrical-discharge-machined (EDM) notches with depth from 0.5 mm to 9 mm. The results showed that the relationship between PEC signals and crack depth is obvious. In this work, we further try a series of coils with different radii, heights, turns and shapes. We will discuss the effects of these coil parameters on the PEC signal. Some other critical problems of PEC measurements such as signal drift that caused by heating effect of coil currents will be studied. We also show more experiments on fatigue cracks to demonstrate the capability of PEC technique for cracks inspection
-
Fluorine-plasma surface treatment for gate forward leakage current reduction in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen Wanjun; Zhang Jing; Zhang Bo; Chen, Kevin Jing
2013-01-01
The gate forward leakage current in AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs) is investigated. It is shown that the current which originated from the forward biased Schottky-gate contributed to the gate forward leakage current. Therefore, a fluorine-plasma surface treatment is presented to induce the negative ions into the AlGaN layer which results in a higher metal—semiconductor barrier. Consequently, the gate forward leakage current shrinks. Experimental results confirm that the gate forward leakage current is decreased by one order magnitude lower than that of HEMT device without plasma treatment. In addition, the DC characteristics of the HEMT device with plasma treatment have been studied. (semiconductor devices)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hao, Shengzhi, E-mail: ebeam@dlut.edu.cn; Li, Mincai
2016-05-15
Highlights: • HCPEB surface treatment was conducted on AZ91 magnesium alloy. • Surface modified microstructure and phase composition were characterized. • Preferential evaporation of Mg and dissolution of Mg{sub 17}Al{sub 12} phase occurred. • Nano-grained and Al-enriched surface layer was produced of depth ∼8 μm. • Surface microhardness and corrosion resistance were improved simultaneously. - Abstract: Surface treatment of AZ91 magnesium alloy was carried out by high current pulsed electron beam (HCPEB) with accelerating voltage 27 kV and energy density 3 J/cm{sup 2}. The surface microstructure and phase composition were characterized by using optical microscope (OM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). The surface microhardness and corrosion resistance were measured. Under HCPEB treatments, the preferential evaporation of Mg element occurred intensively on irradiated surface and the initial large Mg{sub 17}Al{sub 12} phases were dissolved. The nano-grained and Al-enriched surface modified layer was ultimately formed of depth ∼8 μm. According to the testing results, the surface microhardness increased from 63 to 141 HK after 30 pulses of HCPEB treatment, while the best improvement of corrosion resistance was obtained by 15 pulses of HCPEB treatment with a cathodic current density decreased by two orders of magnitude as compared with the initial AZ91 sample.
-
Patteson, R. N.
2017-12-01
Mixing mechanisms of the Arctic Ocean have profound impacts on sea ice, global ocean dynamics, and arctic communities. This project used a two-year long time series of ocean current velocities collected from eight moorings located on the Eurasian basin, as well as ERA-interim wind data, to compare and assess relationships between current and wind velocities at different depths. Determining the strength of these correlations will further scientific understanding of the degree to which wind influences mixing, with implications for heat flux, diffusion, and sea ice changes. Using statistical analysis, I calculated whether a significant relationship between wind velocity and ocean currents existed beginning at the surface level ( 50m) .The final correlation values, ranging from R = 0.11 to R = 0.28, indicated a weak relationship between wind velocity and ocean currents at the surface for all eight mooring sites. The results for the surface depth imply that correlation likely decreases with increasing depths, and thus further testing of deeper depth levels was unnecessary. This finding suggests that there is another dominant factor at play in the ocean; we postulate that topography exerts a significant influence on subsurface mixing. This study highlights the need for further research of the different mechanisms and their importance in influencing the dynamic structure of the ocean.
-
Elshayeb, Ayman A; Ahmed, Abdelazim A; El Siddig, Marmar A; El Hussien, Adil A
2017-11-14
Enteric fever has persistence of great impact in Sudanese public health especially during rainy season when the causative agent Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi possesses pan endemic patterns in most regions of Sudan - Khartoum. The present study aims to assess the recent state of antibiotics susceptibility of Salmonella Typhi with special concern to multidrug resistance strains and predict the emergence of new resistant patterns and outbreaks. Salmonella Typhi strains were isolated and identified according to the guidelines of the International Standardization Organization and the World Health Organization. The antibiotics susceptibilities were tested using the recommendations of the Clinical Laboratories Standards Institute. Predictions of emerging resistant bacteria patterns and outbreaks in Sudan were done using logistic regression, forecasting linear equations and in silico simulations models. A total of 124 antibiotics resistant Salmonella Typhi strains categorized in 12 average groups were isolated, different patterns of resistance statistically calculated by (y = ax - b). Minimum bactericidal concentration's predication of resistance was given the exponential trend (y = n e x ) and the predictive coefficient R 2 > 0 current antimicrobial drug resistance patterns of community-acquired agents causing outbreaks.
-
Safety-related problems continue to be one of the major reasons of attrition in drug development. Non-testing approaches to predict toxicity could form part of the solution. This review provides a perspective of current status of non-testing approaches available for the predictio...
-
Hsieh, Po-Fan; Wang, Yu-De; Huang, Chi-Ping; Wu, Hsi-Chin; Yang, Che-Rei; Chen, Guang-Heng; Chang, Chao-Hsiang
2016-07-01
We proposed a mathematical formula to calculate contact surface area between a tumor and renal parenchyma. We examined the applicability of using contact surface area to predict renal function after partial nephrectomy. We performed this retrospective study in patients who underwent partial nephrectomy between January 2012 and December 2014. Based on abdominopelvic computerized tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, we calculated the contact surface area using the formula (2*π*radius*depth) developed by integral calculus. We then evaluated the correlation between contact surface area and perioperative parameters, and compared contact surface area and R.E.N.A.L. (Radius/Exophytic/endophytic/Nearness to collecting system/Anterior/Location) score in predicting a reduction in renal function. Overall 35, 26 and 45 patients underwent partial nephrectomy with open, laparoscopic and robotic approaches, respectively. Mean ± SD contact surface area was 30.7±26.1 cm(2) and median (IQR) R.E.N.A.L. score was 7 (2.25). Spearman correlation analysis showed that contact surface area was significantly associated with estimated blood loss (p=0.04), operative time (p=0.04) and percent change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (p contact surface area and R.E.N.A.L. score independently affected percent change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (p contact surface area was a better independent predictor of a greater than 10% change in estimated glomerular filtration rate compared to R.E.N.A.L. score (AUC 0.86 vs 0.69). Using this simple mathematical method, contact surface area was associated with surgical outcomes. Compared to R.E.N.A.L. score, contact surface area was a better predictor of functional change after partial nephrectomy. Copyright © 2016 American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Wind effect on currents in a thin surface layer of coastal waters faced open-sea
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nakano, Masanao; Isozaki, Hisaaki; Isozaki, Tokuju; Nemoto, Masashi; Hasunuma, Keiichi; Kitamura, Takashi
2009-01-01
Two-years of continuous observation of wind and current were carried out to investigate the relationship between them in the coastal waters off Tokai-mura, Ibaraki prefecture. Three instruments to measure the current were set in a thin surface layer of 3 m above the strong pycnocline, which is a common feature in coastal waters. Both of the power spectra of wind and currents showed very similar features, an outstanding high peak at 24-hour period and a range of high peaks longer than several-days period. The long term variation of the wind field always contained north-wind component, which contributed to forming the southward current along the shore throughout the year. A high correlation coefficient (0.64) was obtained between the wind and the current at a depth of 0.5 m on the basis of the two-year observation. Harmonic analysis revealed that an outstanding current with 24-hour period was the S 1 component (meteorological tide), and was driven by land and sea breezes. These breezes also contained solar tidal components such as K 1 , P 1 and S 2 . These wind components added their own wind driven currents on the original tidal currents. This meant that land and sea breezes generated wind driven currents with solar tidal periods which behaved like astronomical tidal currents. As result, coastal currents contained pseudo tidal currents which behaved like astronomical tidal currents. (author)
-
Numerical Studies of Friction Between Metallic Surfaces and of its Dependence on Electric Currents
Meintanis, Evangelos; Marder, Michael
2009-03-01
We will present molecular dynamics simulations that explore the frictional mechanisms between clean metallic surfaces. We employ the HOLA molecular dynamics code to run slider-on-block experiments. Both objects are allowed to evolve freely. We recover realistic coefficients of friction and verify the importance of cold-welding and plastic deformations in dry sliding friction. We also find that plastic deformations can significantly affect both objects, despite a difference in hardness. Metallic contacts have significant technological applications in the transmission of electric currents. To explore the effects of the latter to sliding, we had to integrate an electrodynamics solver into the molecular dynamics code. The disparate time scales involved posed a challenge, but we have developed an efficient scheme for such an integration. A limited electrodynamic solver has been implemented and we are currently exploring the effects of currents in the friction and wear of metallic contacts.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Sharma, Ashutosh; Bhattacharya, Sumit; Das, Siddhartha; Das, Karabi, E-mail: karabi@metal.iitkgp.ernet.in
2014-01-30
Bulk polycrystalline tin films have been processed by pulse electrodeposition technique from a simple solution containing triammonium citrate and stannous chloride. The cathodic investigations have been carried out by galvanostatic methods. As deposited samples are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). XRD analysis of the deposited films shows microcrystalline grains having β-Sn form. The surface morphology is very rough at lower current density, but becomes smooth at higher current density, and exhibits pyramid type morphology at all the current densities. The effect of current density on microhardness, melting behavior, and electrical resistivity are also reported here.
-
Labudda, Kirsten; Illies, Dominik; Herzig, Cornelia; Schröder, Katharina; Bien, Christian G; Neuner, Frank
2017-09-01
Childhood maltreatment has been shown to be a risk factor for the development of psychiatric disorders. Although the prevalence of psychiatric disorders is high in epilepsy patients, it is unknown if childhood maltreatment experiences are elevated compared to the normal population and if early maltreatment is a risk factor for current psychiatric comorbidities in epilepsy patients. This is the main purpose of this study. Structured interviews were used to assess current Axis I diagnoses in 120 epilepsy patients from a tertiary Epilepsy Center (34 TLE patients, 86 non-TLE patients). Childhood maltreatment in the family and peer victimization were assessed with validated questionnaires. Patients' maltreatment scores were compared with those of a representative matched control group. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to assess the potential impact of childhood maltreatment on current psychiatric comorbidity in epilepsy patients. Compared to a matched control group, epilepsy patients had higher emotional and sexual maltreatment scores. Patients with a current psychiatric diagnosis reported more family and peer maltreatment than patients without a psychiatric disorder. Family maltreatment scores predicted the likelihood of a current psychiatric disorder. TLE patients did not differ from non-TLE patients according to maltreatment experiences and rates of current psychiatric disorders. Our findings suggest that in epilepsy patients emotional and sexual childhood maltreatment is experienced more often than in the normal population and that early maltreatment is a general risk factor for psychiatric comorbidities in this group. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Translation of Land Surface Model Accuracy and Uncertainty into Coupled Land-Atmosphere Prediction
Santanello, Joseph A.; Kumar, Sujay; Peters-Lidard, Christa D.; Harrison, Kenneth W.; Zhou, Shuija
2012-01-01
Land-atmosphere (L-A) Interactions playa critical role in determining the diurnal evolution of both planetary boundary layer (PBL) and land surface heat and moisture budgets, as well as controlling feedbacks with clouds and precipitation that lead to the persistence of dry and wet regimes. Recent efforts to quantify the strength of L-A coupling in prediction models have produced diagnostics that integrate across both the land and PBL components of the system. In this study, we examine the impact of improved specification of land surface states, anomalies, and fluxes on coupled WRF forecasts during the summers of extreme dry (2006) and wet (2007) land surface conditions in the U.S. Southern Great Plains. The improved land initialization and surface flux parameterizations are obtained through the use of a new optimization and uncertainty estimation module in NASA's Land Information System (US-OPT/UE), whereby parameter sets are calibrated in the Noah land surface model and classified according to a land cover and soil type mapping of the observation sites to the full model domain. The impact of calibrated parameters on the a) spinup of the land surface used as initial conditions, and b) heat and moisture states and fluxes of the coupled WRF Simulations are then assessed in terms of ambient weather and land-atmosphere coupling along with measures of uncertainty propagation into the forecasts. In addition, the sensitivity of this approach to the period of calibration (dry, wet, average) is investigated. Finally, tradeoffs of computational tractability and scientific validity, and the potential for combining this approach with satellite remote sensing data are also discussed.
-
Translation of Land Surface Model Accuracy and Uncertainty into Coupled Land-Atmosphere Prediction
Santanello, J. A.; Kumar, S.; Peters-Lidard, C. D.; Harrison, K. W.; Zhou, S.
2012-12-01
Land-atmosphere (L-A) interactions play a critical role in determining the diurnal evolution of both planetary boundary layer (PBL) and land surface heat and moisture budgets, as well as controlling feedbacks with clouds and precipitation that lead to the persistence of dry and wet regimes. Recent efforts to quantify the strength of L-A coupling in prediction models have produced diagnostics that integrate across both the land and PBL components of the system. In this study, we examine the impact of improved specification of land surface states, anomalies, and fluxes on coupled WRF forecasts during the summers of extreme dry (2006) and wet (2007) land surface conditions in the U.S. Southern Great Plains. The improved land initialization and surface flux parameterizations are obtained through the use of a new optimization and uncertainty estimation module in NASA's Land Information System (LIS-OPT/UE), whereby parameter sets are calibrated in the Noah land surface model and classified according to a land cover and soil type mapping of the observation sites to the full model domain. The impact of calibrated parameters on the a) spinup of the land surface used as initial conditions, and b) heat and moisture states and fluxes of the coupled WRF simulations are then assessed in terms of ambient weather and land-atmosphere coupling along with measures of uncertainty propagation into the forecasts. In addition, the sensitivity of this approach to the period of calibration (dry, wet, average) is investigated. Finally, tradeoffs of computational tractability and scientific validity, and the potential for combining this approach with satellite remote sensing data are also discussed.
-
Developments in outburst prediction by microseismic monitoring from the surface
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Davies, A W; Styles, P; Jones, V K
1987-01-01
Violent outbursts of coal and firedamp affect production operations in most of the coal producing countries of the world, often leading to heavy loss of life. Significant changes in the pattern of Welsh outbursts from 1978 onwards are described with a far larger proportion occurring on longwall faces than was previously the case and with a much higher incidence of spontaneous outbursts, which carry a greater risk than those which are deliberately induced. The elaborate defences in use appeared inadequate to deal with the changing circumstances as methane based alarms only operated after the outburst phenomenon had initiated. An earlier warning of an incipient outburst was required and evidence suggested that seismic monitoring might provide this early warning. A surface located seismometer was installed giving radio transmitted signals to a tape recorder in the colliery control room. This provided promising historical records and led to five surface seismometer stations being commissioned feeding signals, suitably treated, to a micro-processor located in the mine control room. The programming of the micro-processor was arranged to give a real time alarm at pre-set levels of seismic activity in defined areas of the mine. Experience with the new predictive tool is described, as well as the use made of the new facility by management, including changed methods of outburst stress relief.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Abdul’Azeez Abdu Aliyu
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Surface treatment remained a key solution to numerous problems of synthetic hard tissues. The basic methods of implant surface modification include various physical and chemical deposition techniques. However, most of these techniques have several drawbacks such as excessive cost and surface cracks and require very high sintering temperature. Additive mixed-electric discharge machining (AM-EDM is an emerging technology which simultaneously acts as a machining and surface modification technique. Aside from the mere molds, dies, and tool fabrication, AM-EDM is materializing to finishing of automobiles and aerospace, nuclear, and biomedical components, through the concept of material migrations. The mechanism of material transfer by AM-EDM resembles electrophoretic deposition, whereby the additives in the AM-EDM dielectric fluids are melted and migrate to the machined surface, forming a mirror-like finishing characterized by extremely hard, nanostructured, and nanoporous layers. These layers promote the bone in-growth and strengthen the cell adhesion. Implant shaping and surface treatment through AM-EDM are becoming a key research focus in recent years. This paper reports and summarizes the current advancement of AM-EDM as a potential tool for orthopedic and dental implant fabrication. Towards the end of this paper, the current challenges and future research trends are highlighted.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Olariu Tudor
2015-01-01
Full Text Available A quantitative structure - property relationship (QSPR modeling of vapor pressure at 298.15 K, expressed as log (VP / Pa was performed for a series of 84 hydrocarbons (63 alkanes and 21 cycloalkanes using the van der Waals (vdW surface area, SW/Å2, calculated by the Monte Carlo method, as the molecular descriptor. The QSPR model developed from the subset of 63 alkanes (C1-C16, deemed as the training set, was successfully used for the prediction of the log (VP / Pa values of the 21 cycloalkanes, which was the external prediction (test subset. A QSPR model was also developed for a series composed of all 84 hydrocarbons. Both QSPR models were statistically tested for their ability to fit the data and for prediction. The results showed that the vdW molecular surface used as molecular descriptor (MD explains the variance of the majority of the log (VP / Pa values in this series of 84 hydrocarbons. This MD describes very well the intermolecular forces that hold neutral molecules together. The clear physical meaning of the molecular surface values, SW/Å2, could explain the success of the QSPR models obtained with a single structural molecular descriptor.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zotova, N V; Karandashev, S A; Matveev, B. A., E-mail: Bmat@iropt3.ioffe.ru; Remennyy, M A; Rybal' chenko, A Yu; Stus' , N M [Russian Academy of Sciences, Ioffe Physical Technical Institute (Russian Federation)
2011-04-15
Current-voltage characteristics of surface-irradiated photodiodes based on the InAsSbP/InAs structures are analyzed using experimental data on the distribution of electroluminescence intensity over the diode surface and taking into account thickening the current streamlines near the contacts. The influence of the potential barrier associated with the N-InAsSbP/n-InAs junction in double heterostructures on the differential resistance of diodes under zero bias, the value of the reverse current, and spreading of the forward current is discussed.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zotova, N. V.; Karandashev, S. A.; Matveev, B. A.; Remennyy, M. A.; Rybal’chenko, A. Yu.; Stus’, N. M.
2011-01-01
Current-voltage characteristics of surface-irradiated photodiodes based on the InAsSbP/InAs structures are analyzed using experimental data on the distribution of electroluminescence intensity over the diode surface and taking into account thickening the current streamlines near the contacts. The influence of the potential barrier associated with the N-InAsSbP/n-InAs junction in double heterostructures on the differential resistance of diodes under zero bias, the value of the reverse current, and spreading of the forward current is discussed.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sergio Saludes-Rodil
2015-04-01
Full Text Available An unsupervised approach to classify surface defects in wire rod manufacturing is developed in this paper. The defects are extracted from an eddy current signal and classified using a clustering technique that uses the dynamic time warping distance as the dissimilarity measure. The new approach has been successfully tested using industrial data. It is shown that it outperforms other classification alternatives, such as the modified Fourier descriptors.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jahangir, Vafa; Riahifar, Reza; Sahba Yaghmaee, Maziar
2016-01-01
In order to predict as well as study the surface melting phenomena in contradiction to surface overheating, a generalized thermodynamics model including the surface free energy of solid and the melt state along with the interfacial energy of solid–liquid (melt on substrate) has been introduced. In addition, the effect of different crystal structures of surfaces in fcc, bcc and hcp metals was included in surface energies as well as in the atomistic model. These considerations lead us to predict surface melting and overheating as two contradictory melting phenomena. The results of the calculation are demonstrated on the example of Pb and Al thin films in three groups of (100), (110) and (111) surface planes. Our conclusions show good agreement with experimental results and other theoretical investigations. Moreover, a computational algorithm has been developed which enables users to investigate the surface melt or overheating of single component metallic thin film with variable crystal structures and different crystalline planes. This model and developed software can be used for studying all related surface phenomena. - Highlights: • Investigating the surface melting and overheating phenomena • Effect of crystal orientations, surface energies, geometry and different atomic surface layers • Developing a computational algorithm and its related code (free-software SMSO-Ver1) • Thickness and orientation of surface plane dominate the surface melting or overheating. • Total excess surface energy as a function of thickness and temperature explains melting.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jahangir, Vafa, E-mail: vafa.jahangir@yahoo.com; Riahifar, Reza, E-mail: reza_rfr@yahoo.com; Sahba Yaghmaee, Maziar, E-mail: fkmsahba@uni-miskolc.hu
2016-03-31
In order to predict as well as study the surface melting phenomena in contradiction to surface overheating, a generalized thermodynamics model including the surface free energy of solid and the melt state along with the interfacial energy of solid–liquid (melt on substrate) has been introduced. In addition, the effect of different crystal structures of surfaces in fcc, bcc and hcp metals was included in surface energies as well as in the atomistic model. These considerations lead us to predict surface melting and overheating as two contradictory melting phenomena. The results of the calculation are demonstrated on the example of Pb and Al thin films in three groups of (100), (110) and (111) surface planes. Our conclusions show good agreement with experimental results and other theoretical investigations. Moreover, a computational algorithm has been developed which enables users to investigate the surface melt or overheating of single component metallic thin film with variable crystal structures and different crystalline planes. This model and developed software can be used for studying all related surface phenomena. - Highlights: • Investigating the surface melting and overheating phenomena • Effect of crystal orientations, surface energies, geometry and different atomic surface layers • Developing a computational algorithm and its related code (free-software SMSO-Ver1) • Thickness and orientation of surface plane dominate the surface melting or overheating. • Total excess surface energy as a function of thickness and temperature explains melting.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zalina Laili; Muhamat Omar; Woo, Y.M.
2011-01-01
Surface wipe samples of aircraft and container from Japan that were exposed to radioactive dust fallout due to Fukushima nuclear accident has been analysed using gamma spectrometry systems. The samples were analysed to determine their contamination levels. The surface of aircraft and container might be exposed to short and long lived fission and activation products. Thus, good evaluations, as well as a reliable and reasonable judgment were needed in order to determine the presence of fission and activation products. A work procedure has been developed to evaluate and predict the presence of fission and activation products in surface wipe samples. Good references, skilled and experienced level in analysis, a well calibrated and validated detector system were the important factors in determining the presence of fission and activation products in surface wipe samples. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Burzynski, T; Papini, M
2012-01-01
A previous implementation of narrow-band level set methodology developed by the authors was extended to allow for the modelling of mask erosive wear in abrasive jet micro-machining (AJM). The model permits the prediction of the surface evolution of both the mask and the target simultaneously, by representing them as a hybrid and continuous mask–target surface. The model also accounts for the change in abrasive mass flux incident to both the target surface and, for the first time, the eroding mask edge, that is brought about by the presence of the mask edge itself. The predictions of the channel surface and eroded mask profiles were compared with measurements on channels machined in both glass and poly-methyl-methacrylate (PMMA) targets at both normal and oblique incidence, using tempered steel and elastomeric masks. A much better agreement between the predicted and measured profiles was found when mask wear was taken into account. Mask wear generally resulted in wider and deeper glass target profiles and wider PMMA target profiles, respectively, when compared to cases where no mask wear was present. This work has important implications for the AJM of complex MEMS and microfluidic devices that require longer machining times. (paper)
-
Developing Metamodels for Fast and Accurate Prediction of the Draping of Physical Surfaces
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Christensen, Esben Toke; Forrester, AIJ.; Lund, Erik
2018-01-01
In this paper, the use of methods from the meta- or surrogate modeling literature, for building models predicting the draping of physical surfaces, is examined. An example application concerning modeling of the behavior of a variable shape mold is treated. Four different methods are considered...... and local variants, are compared in terms of accuracy and numerical efficiency on data sets of different sizes for the treated application. It is shown that the POD-based methods are vastly superior to models based on kriging alone, and that the use of a difference model structure is advantageous...
-
Sharif, M.S.U.; Davis, R.K.; Steele, K.F.; Kim, B.; Hays, P.D.; Kresse, T.M.; Fazio, J.A.
2011-01-01
The potential health impact of As in drinking water supply systems in the Mississippi River Valley alluvial aquifer in the state of Arkansas, USA is significant. In this context it is important to understand the occurrence, distribution and mobilization of As in the Mississippi River Valley alluvial aquifer. Application of surface complexation models (SCMs) to predict the sorption behavior of As and hydrous Fe oxides (HFO) in the laboratory has increased in the last decade. However, the application of SCMs to predict the sorption of As in natural sediments has not often been reported, and such applications are greatly constrained by the lack of site-specific model parameters. Attempts have been made to use SCMs considering a component additivity (CA) approach which accounts for relative abundances of pure phases in natural sediments, followed by the addition of SCM parameters individually for each phase. Although few reliable and internally consistent sorption databases related to HFO exist, the use of SCMs using laboratory-derived sorption databases to predict the mobility of As in natural sediments has increased. This study is an attempt to evaluate the ability of the SCMs using the geochemical code PHREEQC to predict solid phase As in the sediments of the Mississippi River Valley alluvial aquifer in Arkansas. The SCM option of the double-layer model (DLM) was simulated using ferrihydrite and goethite as sorbents quantified from chemical extractions, calculated surface-site densities, published surface properties, and published laboratory-derived sorption constants for the sorbents. The model results are satisfactory for shallow wells (10.6. m below ground surface), where the redox condition is relatively oxic or mildly suboxic. However, for the deep alluvial aquifer (21-36.6. m below ground surface) where the redox condition is suboxic to anoxic, the model results are unsatisfactory. ?? 2011 Elsevier Ltd.
-
Decadal prediction skill in the ocean with surface nudging in the IPSL-CM5A-LR climate model
Mignot, Juliette; García-Serrano, Javier; Swingedouw, Didier; Germe, Agathe; Nguyen, Sébastien; Ortega, Pablo; Guilyardi, Eric; Ray, Sulagna
2016-08-01
Two decadal prediction ensembles, based on the same climate model (IPSL-CM5A-LR) and the same surface nudging initialization strategy are analyzed and compared with a focus on upper-ocean variables in different regions of the globe. One ensemble consists of 3-member hindcasts launched every year since 1961 while the other ensemble benefits from 9 members but with start dates only every 5 years. Analysis includes anomaly correlation coefficients and root mean square errors computed against several reanalysis and gridded observational fields, as well as against the nudged simulation used to produce the hindcasts initial conditions. The last skill measure gives an upper limit of the predictability horizon one can expect in the forecast system, while the comparison with different datasets highlights uncertainty when assessing the actual skill. Results provide a potential prediction skill (verification against the nudged simulation) beyond the linear trend of the order of 10 years ahead at the global scale, but essentially associated with non-linear radiative forcings, in particular from volcanoes. At regional scale, we obtain 1 year in the tropical band, 10 years at midlatitudes in the North Atlantic and North Pacific, and 5 years at tropical latitudes in the North Atlantic, for both sea surface temperature (SST) and upper-ocean heat content. Actual prediction skill (verified against observational or reanalysis data) is overall more limited and less robust. Even so, large actual skill is found in the extratropical North Atlantic for SST and in the tropical to subtropical North Pacific for upper-ocean heat content. Results are analyzed with respect to the specific dynamics of the model and the way it is influenced by the nudging. The interplay between initialization and internal modes of variability is also analyzed for sea surface salinity. The study illustrates the importance of two key ingredients both necessary for the success of future coordinated decadal
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Czanderna, A.W.; Landgrebe, A.R. [eds.
1992-09-01
Goal of surface processing is to develop innovative methods of surface modification and characterization for optimum performance and environmental protection for cost-effective operational lifetimes of systems, materials, and components used in transportation and utilities. These proceedings document the principal discussions and conclusions reached at the workshop; they document chapters about the current status of surface characterization with focus on composition, structure, bonding, and atomic-scale topography of surfaces. Also documented are chapters on the current status of surface modification techniques: electrochemical, plasma-aided, reactive and nonreactive physical vapor deposition, sol-gel coatings, high-energy ion implantation, ion-assisted deposition, organized molecular assemblies, solar energy. Brief chapters in the appendices document basic research in surface science by NSF, Air Force, and DOE. Participants at the workshop were invited to serve on 10 working groups. Separate abstracts were prepared for the data base where appropriate.
-
Surface forces between rough and topographically structured interfaces
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Thormann, Esben
2017-01-01
Within colloidal science, direct or indirect measurements of surface forces represent an important tool for developing a fundamental understanding of colloidal systems, as well as for predictions of the stability of colloidal suspensions. While the general understanding of colloidal interactions...... and manufactured materials, which possess topographical variations. Further, with technological advances in nanotechnology, fabrication of nano- or micro-structured surfaces has become increasingly important for many applications, which calls for a better understanding of the effect of surface topography...... on the interaction between interfaces. This paper presents a review of the current state of understanding of the effect of surface roughness on DLVO forces, as well as on the interactions between topographically structured hydrophobic surfaces in water. While the first case is a natural choice because it represents...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Vigneron, Audrey
2015-01-01
The thesis addresses the numerical simulation of non-destructive testing (NDT) using eddy currents, and more precisely the computation of induced electromagnetic fields by a transmitter sensor in a healthy part. This calculation is the first step of the modeling of a complete control process in the CIVA software platform developed at CEA LIST. Currently, models integrated in CIVA are restricted to canonical (modal computation) or axially-symmetric geometries. The need for more diverse and complex configurations requires the introduction of new numerical modeling tools. In practice the sensor may be composed of elements with different shapes and physical properties. The inspected parts are conductive and may contain dielectric or magnetic elements. Due to the cohabitation of different materials in one configuration, different regimes (static, quasi-static or dynamic) may coexist. Under the assumption of linear, isotropic and piecewise homogeneous material properties, the surface integral equation (SIE) approach allows to reduce a volume-based problem to an equivalent surface-based problem. However, the usual SIE formulations for the Maxwell's problem generally suffer from numerical noise in asymptotic situations, and especially at low frequencies. The objective of this study is to determine a version that is stable for a range of physical parameters typical of eddy-current NDT applications. In this context, a block-iterative scheme based on a physical decomposition is proposed for the computation of primary fields. This scheme is accurate and well-conditioned. An asymptotic study of the integral Maxwell's problem at low frequencies is also performed, allowing to establish the eddy-current integral problem as an asymptotic case of the corresponding Maxwell problem. (author) [fr
-
Station-keeping control of an unmanned surface vehicle exposed to current and wind disturbances
Sarda, Edoardo I.; Qu, Huajin; Bertaska, Ivan R.; von Ellenrieder, Karl D.
2017-01-01
Field trials of a 4 meter long, 180 kilogram, unmanned surface vehicle (USV) have been conducted to evaluate the performance of station-keeping heading and position controllers in an outdoor marine environment disturbed by wind and current. The USV has a twin hull configuration and a custom-designed propulsion system, which consists of two azimuthing thrusters, one for each hull. Nonlinear proportional derivative, backstepping and sliding mode feedback controllers were tested in winds of abou...
-
Reiman, Allan H.
2016-07-01
In toroidal, magnetically confined plasmas, the heat and particle transport is strongly anisotropic, with transport along the field lines sufficiently strong relative to cross-field transport that the equilibrium pressure can generally be regarded as constant on the flux surfaces in much of the plasma. The regions near small magnetic islands, and those near the X-lines of larger islands, are exceptions, having a significant variation of the pressure within the flux surfaces. It is shown here that the variation of the equilibrium pressure within the flux surfaces in those regions has significant consequences for the pressure driven currents. It is further shown that the consequences are strongly affected by the symmetry of the magnetic field if the field is invariant under combined reflection in the poloidal and toroidal angles. (This symmetry property is called "stellarator symmetry.") In non-stellarator-symmetric equilibria, the pressure-driven currents have logarithmic singularities at the X-lines. In stellarator-symmetric MHD equilibria, the singular components of the pressure-driven currents vanish. These equilibria are to be contrasted with equilibria having B ṡ∇p =0 , where the singular components of the pressure-driven currents vanish regardless of the symmetry. They are also to be contrasted with 3D MHD equilibrium solutions that are constrained to have simply nested flux surfaces, where the pressure-driven current goes like 1 /x near rational surfaces, where x is the distance from the rational surface, except in the case of quasi-symmetric flux surfaces. For the purpose of calculating the pressure-driven currents near magnetic islands, we work with a closed subset of the MHD equilibrium equations that involves only perpendicular force balance, and is decoupled from parallel force balance. It is not correct to use the parallel component of the conventional MHD force balance equation, B ṡ∇p =0 , near magnetic islands. Small but nonzero values of B �
-
Detection of milled 100Cr6 steel surface by eddy current and incremental permeance methods
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Perevertov, Oleksiy; Neslušan, M.; Stupakov, Alexandr
2017-01-01
Roč. 87, Apr (2017), s. 15-23 ISSN 0963-8695 R&D Projects: GA ČR GB14-36566G; GA ČR GA13-18993S Institutional support: RVO:68378271 Keywords : Eddy currents * hard milling * incremental permeance * magnetic materials * surface characterization Subject RIV: JB - Sensors, Measurment, Regulation OBOR OECD: Electrical and electronic engineering Impact factor: 2.726, year: 2016
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Siyuan He
2012-01-01
Full Text Available The range profiles of a two-dimension (2 D perfect electric conductor (PEC ship on a wind-driven rough sea surface are derived by performing an inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT on the wide band backscattered field. The rough sea surface is assuming to be a PEC surface. The back scattered field is computed based on EM numerical simulation when the frequencies are sampled between 100 MHz and 700 MHz. Considering the strong coupling interactions between the ship and sea, the complicated multipath effect to the range profile characteristics is fully analyzed based on the multipath imaging mechanisms. The coupling mechanisms could be explained by means of ray theory prediction and numerical extraction of the coupling currents. The comparison of the range profile locations between ray theory prediction and surface current simulation is implemented and analyzed in this paper. Finally, the influence of different sea states on the radar target signatures has been examined and discussed.
-
Sources, occurrence and predicted aquatic impact of legacy and contemporary pesticides in streams
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McKnight, Ursula S.; Rasmussen, Jes J.; Kronvang, Brian; Binning, Philip J.; Bjerg, Poul L.
2015-01-01
We couple current findings of pesticides in surface and groundwater to the history of pesticide usage, focusing on the potential contribution of legacy pesticides to the predicted ecotoxicological impact on benthic macroinvertebrates in headwater streams. Results suggest that groundwater, in addition to precipitation and surface runoff, is an important source of pesticides (particularly legacy herbicides) entering surface water. In addition to current-use active ingredients, legacy pesticides, metabolites and impurities are important for explaining the estimated total toxicity attributable to pesticides. Sediment-bound insecticides were identified as the primary source for predicted ecotoxicity. Our results support recent studies indicating that highly sorbing chemicals contribute and even drive impacts on aquatic ecosystems. They further indicate that groundwater contaminated by legacy and contemporary pesticides may impact adjoining streams. Stream observations of soluble and sediment-bound pesticides are valuable for understanding the long-term fate of pesticides in aquifers, and should be included in stream monitoring programs. - Highlights: • Findings comprised a range of contemporary and banned legacy pesticides in streams. • Groundwater is a significant pathway for some herbicides entering streams. • Legacy pesticides increased predicted aquatic toxicity by four orders of magnitude. • Sediment-bound insecticides were identified as the primary source for ecotoxicity. • Stream monitoring programs should include legacy pesticides to assess impacts. - Legacy pesticides, particularly sediment-bound insecticides were identified as the primary source for predicted ecotoxicity impacting benthic macroinvertebrates in headwater streams
-
Liu, Yonggang; Weisberg, Robert H.; Vignudelli, Stefano; Mitchum, Gary T.
2014-05-01
Lagrangian particle trajectory models based on several altimetry-derived surface current products are used to hindcast the drifter trajectories observed in the eastern Gulf of Mexico during May to August 2010 (the Deepwater Horizon oil spill incident). The performances of the trajectory models are gauged in terms of Lagrangian separation distances (d) and a nondimensional skill score (s), respectively. A series of numerical experiments show that these altimetry-based trajectory models have about the same performance, with a certain improvement by adding surface wind Ekman components, especially over the shelf region. However, their hindcast skills are slightly better than those of the data assimilative numerical model output. After 3 days' simulation the altimetry-based trajectory models have mean d values of 75-83 and 34-42 km (s values of 0.49-0.51 and 0.35-0.43) in the Gulf of Mexico deep water area and on the West Florida Continental Shelf, respectively. These satellite altimetry data products are useful for providing essential information on ocean surface currents of use in water property transports, offshore oil and gas operations, hazardous spill mitigation, search and rescue, etc.
-
A residual life prediction model based on the generalized σ -N curved surface
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zongwen AN
2016-06-01
Full Text Available In order to investigate change rule of the residual life of structure under random repeated load, firstly, starting from the statistic meaning of random repeated load, the joint probability density function of maximum stress and minimum stress is derived based on the characteristics of order statistic (maximum order statistic and minimum order statistic; then, based on the equation of generalized σ -N curved surface, considering the influence of load cycles number on fatigue life, a relationship among minimum stress, maximum stress and residual life, that is the σmin(n- σmax(n-Nr(n curved surface model, is established; finally, the validity of the proposed model is demonstrated by a practical case. The result shows that the proposed model can reflect the influence of maximum stress and minimum stress on residual life of structure under random repeated load, which can provide a theoretical basis for life prediction and reliability assessment of structure.
-
Tong, Qiaoling; Chen, Chen; Zhang, Qiao; Zou, Xuecheng
2015-04-28
To realize accurate current control for a boost converter, a precise measurement of the inductor current is required to achieve high resolution current regulating. Current sensors are widely used to measure the inductor current. However, the current sensors and their processing circuits significantly contribute extra hardware cost, delay and noise to the system. They can also harm the system reliability. Therefore, current sensorless control techniques can bring cost effective and reliable solutions for various boost converter applications. According to the derived accurate model, which contains a number of parasitics, the boost converter is a nonlinear system. An Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is proposed for inductor current estimation and output voltage filtering. With this approach, the system can have the same advantages as sensored current control mode. To implement EKF, the load value is necessary. However, the load may vary from time to time. This can lead to errors of current estimation and filtered output voltage. To solve this issue, a load variation elimination effect elimination (LVEE) module is added. In addition, a predictive average current controller is used to regulate the current. Compared with conventional voltage controlled system, the transient response is greatly improved since it only takes two switching cycles for the current to reach its reference. Finally, experimental results are presented to verify the stable operation and output tracking capability for large-signal transients of the proposed algorithm.
-
Detection of flaws below curved surfaces
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Elsley, R.K.; Addison, R.C.; Graham, L.J.
1983-01-01
A measurement model has been developed to describe ultrasonic measurements made with circular piston transducers in parts with flat or cylindrically curved surfaces. The model includes noise terms to describe electrical noise, scatterer noise and echo noise as well as effects of attenuation, diffraction and Fresnel loss. An experimental procedure for calibrating the noise terms of the model was developed. Experimental measurements were made on a set of known flaws located beneath a cylindrically curved surface. The model was verified by using it to correct the experimental measurements to obtain the absolute scattering amplitude of the flaws. For longitudinal wave propagation within the part, the derived scattering amplitudes were consistent with predictions at internal angles of less than 30 0 . At larger angles, focusing and aberrations caused a lack of agreement; the model needs further refinement in this case. For shear waves, it was found that the frequency for optimum flaw detection in the presence of material noise is lower than that for longitudinal waves; lower frequency measurements are currently in progress. The measurement model was then used to make preliminary predictions of the best experimental measurement technique for the detection of cracks located under cylindrically curved surfaces
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sera, Takehiko; Hirano, Shinro; Chigusa, Naoki; Okano, Shigetaka; Saida, Kazuyoshi; Mochizuki, Masahito; Nishimoto, Kazutoshi
2012-01-01
Surface finishing methods, such as Water Jet Peening (WJP), have been applied to welds in some major components of nuclear power plants as a counter measure to Primary Water Stress Corrosion Cracking (PWSCC). In addition, the methods of surface finishing (buffing treatment) is being standardized, and thus the buffing treatment has been also recognized as the well-established method of improving stress. On the other hand, the long-term stability of peening techniques has been confirmed by accelerated test. However, the effectiveness of stress improvement by surface treatment is limited to thin layers and the effect of complicated residual stress distribution in the weld metal beneath the surface is not strictly taken into account for long-term stability. This paper, therefore, describes the accelerated tests, which confirmed that the long-term stability of the layer subjected to buffing treatment was equal to that subjected to WJP. The long-term reliability of very thin stress improved layer was also confirmed through a trial evaluation by thermal elastic-plastic creep analysis, even if the effect of complicated residual stress distribution in the weld metal was excessively taken into account. Considering the above findings, an approach is proposed for constructing the prediction method of the long-term reliability of stress improvement by surface finishing. (author)
-
Computational prediction of chemical reactions: current status and outlook.
Engkvist, Ola; Norrby, Per-Ola; Selmi, Nidhal; Lam, Yu-Hong; Peng, Zhengwei; Sherer, Edward C; Amberg, Willi; Erhard, Thomas; Smyth, Lynette A
2018-06-01
Over the past few decades, various computational methods have become increasingly important for discovering and developing novel drugs. Computational prediction of chemical reactions is a key part of an efficient drug discovery process. In this review, we discuss important parts of this field, with a focus on utilizing reaction data to build predictive models, the existing programs for synthesis prediction, and usage of quantum mechanics and molecular mechanics (QM/MM) to explore chemical reactions. We also outline potential future developments with an emphasis on pre-competitive collaboration opportunities. Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Life Sciences Implications of Lunar Surface Operations
Chappell, Steven P.; Norcross, Jason R.; Abercromby, Andrew F.; Gernhardt, Michael L.
2010-01-01
The purpose of this report is to document preliminary, predicted, life sciences implications of expected operational concepts for lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). Algorithms developed through simulation and testing in lunar analog environments were used to predict crew metabolic rates and ground reaction forces experienced during lunar EVA. Subsequently, the total metabolic energy consumption, the daily bone load stimulus, total oxygen needed, and other variables were calculated and provided to Human Research Program and Exploration Systems Mission Directorate stakeholders. To provide context to the modeling, the report includes an overview of some scenarios that have been considered. Concise descriptions of the analog testing and development of the algorithms are also provided. This document may be updated to remain current with evolving lunar or other planetary surface operations, assumptions and concepts, and to provide additional data and analyses collected during the ongoing analog research program.
-
ProtPOS: a python package for the prediction of protein preferred orientation on a surface.
Ngai, Jimmy C F; Mak, Pui-In; Siu, Shirley W I
2016-08-15
Atomistic molecular dynamics simulation is a promising technique to investigate the energetics and dynamics in the protein-surface adsorption process which is of high relevance to modern biotechnological applications. To increase the chance of success in simulating the adsorption process, favorable orientations of the protein at the surface must be determined. Here, we present ProtPOS which is a lightweight and easy-to-use python package that can predict low-energy protein orientations on a surface of interest. It combines a fast conformational sampling algorithm with the energy calculation of GROMACS. The advantage of ProtPOS is it allows users to select any force fields suitable for the system at hand and provide structural output readily available for further simulation studies. ProtPOS is freely available for academic and non-profit uses at http://cbbio.cis.umac.mo/software/protpos Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online. shirleysiu@umac.mo. © The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ayman A. Elshayeb
2017-11-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background Enteric fever has persistence of great impact in Sudanese public health especially during rainy season when the causative agent Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi possesses pan endemic patterns in most regions of Sudan - Khartoum. Objectives The present study aims to assess the recent state of antibiotics susceptibility of Salmonella Typhi with special concern to multidrug resistance strains and predict the emergence of new resistant patterns and outbreaks. Methods Salmonella Typhi strains were isolated and identified according to the guidelines of the International Standardization Organization and the World Health Organization. The antibiotics susceptibilities were tested using the recommendations of the Clinical Laboratories Standards Institute. Predictions of emerging resistant bacteria patterns and outbreaks in Sudan were done using logistic regression, forecasting linear equations and in silico simulations models. Results A total of 124 antibiotics resistant Salmonella Typhi strains categorized in 12 average groups were isolated, different patterns of resistance statistically calculated by (y = ax − b. Minimum bactericidal concentration’s predication of resistance was given the exponential trend (y = n ex and the predictive coefficient R2 > 0 < 1 are approximately alike. It was assumed that resistant bacteria occurred with a constant rate of antibiotic doses during the whole experimental period. Thus, the number of sensitive bacteria decreases at the same rate as resistant occur following term to the modified predictive model which solved computationally. Conclusion This study assesses the prediction of multi-drug resistance among S. Typhi isolates by applying low cost materials and simple statistical methods suitable for the most frequently used antibiotics as typhoid empirical therapy. Therefore, bacterial surveillance systems should be implemented to present data on the aetiology and current
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kozlowski, K.K. [Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (DESY), Hamburg (Germany); Terras, V. [CNRS, ENS Lyon (France). Lab. de Physique
2010-12-15
We present a new method allowing us to derive the long-time and large-distance asymptotic behavior of the correlations functions of quantum integrable models from their exact representations. Starting from the form factor expansion of the correlation functions in finite volume, we explain how to reduce the complexity of the computation in the so-called interacting integrable models to the one appearing in free fermion equivalent models. We apply our method to the time-dependent zero-temperature current-current correlation function in the non-linear Schroedinger model and compute the first few terms in its asymptotic expansion. Our result goes beyond the conformal field theory based predictions: in the time-dependent case, other types of excitations than the ones on the Fermi surface contribute to the leading orders of the asymptotics. (orig.)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kozlowski, K.K.; Terras, V.
2010-12-01
We present a new method allowing us to derive the long-time and large-distance asymptotic behavior of the correlations functions of quantum integrable models from their exact representations. Starting from the form factor expansion of the correlation functions in finite volume, we explain how to reduce the complexity of the computation in the so-called interacting integrable models to the one appearing in free fermion equivalent models. We apply our method to the time-dependent zero-temperature current-current correlation function in the non-linear Schroedinger model and compute the first few terms in its asymptotic expansion. Our result goes beyond the conformal field theory based predictions: in the time-dependent case, other types of excitations than the ones on the Fermi surface contribute to the leading orders of the asymptotics. (orig.)
-
McWilliams, J. C.; Lane, E.; Melville, K.; Restrepo, J.; Sullivan, P.
2004-12-01
Oceanic surface gravity waves are approximately irrotational, weakly nonlinear, and conservative, and they have a much shorter time scale than oceanic currents and longer waves (e.g., infragravity waves) --- except where the primary surface waves break. This provides a framework for an asymptotic theory, based on separation of time (and space) scales, of wave-averaged effects associated with the conservative primary wave dynamics combined with a stochastic representation of the momentum transfer and induced mixing associated with non-conservative wave breaking. Such a theory requires only modest information about the primary wave field from measurements or operational model forecasts and thus avoids the enormous burden of calculating the waves on their intrinsically small space and time scales. For the conservative effects, the result is a vortex force associated with the primary wave's Stokes drift; a wave-averaged Bernoulli head and sea-level set-up; and an incremental material advection by the Stokes drift. This can be compared to the "radiation stress" formalism of Longuet-Higgins, Stewart, and Hasselmann; it is shown to be a preferable representation since the radiation stress is trivial at its apparent leading order. For the non-conservative breaking effects, a population of stochastic impulses is added to the current and infragravity momentum equations with distribution functions taken from measurements. In offshore wind-wave equilibria, these impulses replace the conventional surface wind stress and cause significant differences in the surface boundary layer currents and entrainment rate, particularly when acting in combination with the conservative vortex force. In the surf zone, where breaking associated with shoaling removes nearly all of the primary wave momentum and energy, the stochastic forcing plays an analogous role as the widely used nearshore radiation stress parameterizations. This talk describes the theoretical framework and presents some
-
Rodriguez-Fonseca, Belen; Mohino, Elsa; Mechoso, Carlos R.; Caminade, Cyril; Biasutti, Michela; Gaetani, Marco; Garcia-Serrano, J.; Vizy, Edward K.; Cook, Kerry; Xue, Yongkang;

2015-01-01
The Sahel experienced a severe drought during the 1970s and 1980s after wet periods in the 1950s and 1960s. Although rainfall partially recovered since the 1990s, the drought had devastating impacts on society. Most studies agree that this dry period resulted primarily from remote effects of sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies amplified by local land surface-atmosphere interactions. This paper reviews advances made during the last decade to better understand the impact of global SST variability on West African rainfall at interannual to decadal time scales. At interannual time scales, a warming of the equatorial Atlantic and Pacific/Indian Oceans results in rainfall reduction over the Sahel, and positive SST anomalies over the Mediterranean Sea tend to be associated with increased rainfall. At decadal time scales, warming over the tropics leads to drought over the Sahel, whereas warming over the North Atlantic promotes increased rainfall. Prediction systems have evolved from seasonal to decadal forecasting. The agreement among future projections has improved from CMIP3 to CMIP5, with a general tendency for slightly wetter conditions over the central part of the Sahel, drier conditions over the western part, and a delay in the monsoon onset. The role of the Indian Ocean, the stationarity of teleconnections, the determination of the leader ocean basin in driving decadal variability, the anthropogenic role, the reduction of the model rainfall spread, and the improvement of some model components are among the most important remaining questions that continue to be the focus of current international projects.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Han, Z.; Zou, H.; Wang, Z.; Ji, I.; Cai, J.; Guan, Q.
2013-01-01
The nanocrystalline surface was produced on 3Cr13 martensite stainless steel surface using high-current pulsed electron beam (HCPEB) technique. The structures of the nano crystallized surface were characterized by X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy. Two nano structures consisting of fine austenite grains (50-150 nm) and very fine carbides precipitates are formed in melted surface layer after multiple bombardments via dissolution of carbides and crater eruption. It is demonstrated that the dissolution of the carbides and the formation of the supersaturated Fe (C) solid solution play a determining role on the microstructure evolution. Additionally, the formation of fine austenite structure is closely related to the thermal stresses induced by the HCPEB irradiation. The effects of both high carbon content and high value of stresses increase the stability of the austenite, which leads to the complete suppression of martensitic transformation.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gao, Yu-kui
2013-01-01
Highlights: •The hardness changes were determined by nanoindention method. •The surface integrity changes were investigated by different techniques. •The mechanism was analyzed based on AFM and TEM investigations. -- Abstract: Surface changes including surface topography and nanohardness distribution along surface layer were investigated for TC4 titanium alloy by different energy densities of high current pulsed electron beam (HCPEB). The surface topography was characterized by SEM and AFM, and cross-sectional TEM observation was performed to reveal the surface modification mechanism of TC4 titanium alloy by HCPEB. The surface roughness was modified by HCPEB and the polishing mechanism was analyzed by studying the cross section microstructure of electron beam treated specimens by SEM. The fine grain structure inherited from the rapid solidification of the melted layer as well as the strain hardening of the sub-surface are two of the factors responsible the increase in nanohardness
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Valíček J.
2014-06-01
Full Text Available The paper is based on results obtained from topography of surfaces of sheets rolled from deep-drawing steel of the type KOHAL grade 697, non-alloy low-carbon structural steel EN 10263-2:2004 and aluminium. The presented results document correctness of the assumption that the rolling force Froll increases with the increasing reduction Δh and the quality of the rolled surface is improved at the simultaneous increasing of strength of rolled sheets and the decreasing of size of structural grains. The experiment was performed on the two-high rolling stand DUO 210 SVa, which enables only non-continuous technology in contrast to the rolling mill with continuous reduction on one sheet in several degrees on rolling trains, in consequence of which the obtained height parameters of the section are in close correlation with the predicted dependence. Contribution of the work consists in the creation of a mathematical model (algorithm for predicting technological parameters of the two-high rolling stand DUO 210 SVa at change of the absolute reduction Δh, for example for a deep-drawing steel of the type KOHAL grade 697 and non-alloy lowcarbon structural steel PN EN 10263-2:2004 and aluminium, and also in the development of a method of calculation applicable to any material being rolled in general, because the authors have found that various materials can be differentiated by a derived analytical criterion IKP. This criterion is a function of ratio between the modulus of elasticity of reference material and that of actually rolled material. The reference material is here deep-drawing steel of the type KOHAL grade 697. Verification was carried out by measuring changes of final surface roughness profile and final strength of rolled sheets of the stated materials in relation to reductions and those were compared with theoretically predicted values. It is possible to identify and predict on the basis of this algorithm an instant state of surface topography in
-
Su, Ji Guo; Qi, Li Sheng; Li, Chun Hua; Zhu, Yan Ying; Du, Hui Jing; Hou, Yan Xue; Hao, Rui; Wang, Ji Hua
2014-08-01
Allostery is a rapid and efficient way in many biological processes to regulate protein functions, where binding of an effector at the allosteric site alters the activity and function at a distant active site. Allosteric regulation of protein biological functions provides a promising strategy for novel drug design. However, how to effectively identify the allosteric sites remains one of the major challenges for allosteric drug design. In the present work, a thermodynamic method based on the elastic network model was proposed to predict the allosteric sites on the protein surface. In our method, the thermodynamic coupling between the allosteric and active sites was considered, and then the allosteric sites were identified as those where the binding of an effector molecule induces a large change in the binding free energy of the protein with its ligand. Using the proposed method, two proteins, i.e., the 70 kD heat shock protein (Hsp70) and GluA2 alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptor, were studied and the allosteric sites on the protein surface were successfully identified. The predicted results are consistent with the available experimental data, which indicates that our method is a simple yet effective approach for the identification of allosteric sites on proteins.
-
Thomson, Alan W.P.; McKay, Allan J.; Clarke, Ellen; Reay, Sarah J.
2005-01-01
A surface electric field model is used to estimate the UK surface E field during the 30 October 2003 severe geomagnetic storm. This model is coupled with a power grid model to determine the flow of geomagnetically induced currents (GIC) through the Scottish part of the UK grid. Model data are compared with GIC measurements at four sites in the power network. During this storm, measured and modeled GIC levels exceeded 40 A, and the surface electric field reached 5 V/km at sites in ...
-
Power Prediction Model for Turning EN-31 Steel Using Response Surface Methodology
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Hameedullah
2010-01-01
Full Text Available Power consumption in turning EN-31 steel (a material that is most extensively used in automotive industry with tungstencarbide tool under different cutting conditions was experimentally investigated. The experimental runs were planned accordingto 24+8 added centre point factorial design of experiments, replicated thrice. The data collected was statisticallyanalyzed using Analysis of Variance technique and first order and second order power consumption prediction models weredeveloped by using response surface methodology (RSM. It is concluded that second-order model is more accurate than thefirst-order model and fit well with the experimental data. The model can be used in the automotive industries for decidingthe cutting parameters for minimum power consumption and hence maximum productivity
-
A two-parameter model to predict fracture in the transition
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
DeAquino, C.T.; Landes, J.D.; McCabe, D.E.
1995-01-01
A model is proposed that uses a numerical characterization of the crack tip stress field modified by the J - Q constraint theory and a weak link assumption to predict fracture behavior in the transition for reactor vessel steels. This model predicts the toughness scatter band for a component model from a toughness scatter band measured on a test specimen geometry. The model has been applied previously to two-dimensional through cracks. Many applications to actual components structures involve three-dimensional surface flaws. These cases require a more difficult level of analysis and need additional information. In this paper, both the current model for two-dimensional cracks and an approach needed to extend the model for the prediction of transition fracture behavior in three-dimensional surface flaws are discussed. Examples are presented to show how the model can be applied and in some cases to compare with other test results. (author). 13 refs., 7 figs
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Johnson, M.J.; Nakagawa, N.; Wendt, S.E.; Hentscher, S.R.; Nelson, D.L.; Buhr, K.T.; Kilbugh, B.A.; Raithel, D.C.
2005-01-01
Eddy-current scans have been carried out on two Inconel-718 specimens following the application of various levels of shot peening and heat treatments. The conventional analysis of roughened or shot peened surfaces looks at multi-frequency impedance measurements and interprets the data as a change in conductivity or liftoff. An approach involving the statistical analysis of scanned eddy-current impedance data is suggested as an alternative that may provide a more sensitive way of determining the treatment history of a component. It is possible that an analysis of these statistical distributions in spatial eddy-current data could be used to determine the level of remaining residual stress in engine components
-
Zodiatis, George; Galanis, George; Nikolaidis, Andreas; Stylianoy, Stavros; Liakatas, Aristotelis
2015-04-01
The use of wave energy as an alternative renewable is receiving attention the last years under the shadow of the economic crisis in Europe and in the light of the promising corresponding potential especially for countries with extended coastline. Monitoring and studying the corresponding resources is further supported by a number of critical advantages of wave energy compared to other renewable forms, like the reduced variability and the easier adaptation to the general grid, especially when is jointly approached with wind power. Within the framework, a number of countries worldwide have launched research and development projects and a significant number of corresponding studies have been presented the last decades. However, in most of them the impact of wave-sea surface currents interaction on the wave energy potential has not been taken into account neglecting in this way a factor of potential importance. The present work aims at filling this gap for a sea area with increased scientific and economic interest, the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Based on a combination of high resolution numerical modeling approach with advanced statistical tools, a detailed analysis is proposed for the quantification of the impact of sea surface currents, which produced from downscaling the MyOcean-FO regional data, to wave energy potential. The results although spatially sensitive, as expected, prove beyond any doubt that the wave- sea surface currents interaction should be taken into account for similar resource analysis and site selection approaches since the percentage of impact to the available wave power may reach or even exceed 20% at selected areas.
-
Development and application of an oil spill model with wave–current interactions in coastal areas
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Guo, WeiJun; Hao, Yanni; Zhang, Li; Xu, Tiaojian; Ren, Xiaozhong; Cao, Feng; Wang, Shoudong
2014-01-01
Highlights: • Numerical oil spill developed by incorporating wave–current interactions and applied to hindcasting the Dalian oil spill. • Numerical model results taking into wave–current coupling shows better conformity with the observed data. • Oil dispersion will be enhanced due to the gradient of surface wave radiation stress in the coastal waters. - Abstract: The present paper focuses on developing a numerical oil spill model that incorporates the full three-dimensional wave–current interactions for a better representation of the spilled oil transport mechanics in complicated coastal environments. The incorporation of surface wave effects is not only imposing a traditional drag coefficient formulation at the free surface, but also the 3D momentum equations are adjusted to include the impact of the vertically dependent radiation stresses on the currents. Based on the current data from SELFE and wave data from SWAN, the oil spill model utilizes oil particle method to predict the trajectory of individual droplets and the oil concentration. Compared with the observations in Dalian New Port oil spill event, the developed model taking into account wave–current coupling administers to giving better conformity than the one without. The comparisons demonstrates that 3D radiation stress impacts the spill dynamics drastically near the sea surface and along the coastline, while having less impact in deeper water
-
Submerged Fixed Floating Structure under the Action of Surface Current
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zhen Cui
2018-01-01
Full Text Available The implementation of floating structures has increased with the construction of new sluices for flood control. The overturning moment of floating structure and its influencing factors are the important parameters that determine the structural safety. It is essential to understand the overturning characteristics of these structures in currents. Based on hydrodynamic theory and equilibrium analysis, the hydraulic characteristics of a floating structure are discussed by means of theoretical analysis and experiments. A formula for the overturning moment is developed in terms of the time-averaged pressure on the structure. The corresponding parametric study aims to assess the effects of flow velocities, vertical positions, shape ratios and water levels on the overturning moment. The experimental results show that hydrodynamic factors have a significant influence on the overturning of the structure. Furthermore, a relationship is obtained between the overturning moment and the contributing parameters according to dimensional analysis and the linear fitting method of multidimensional ordinary least squares (OLS. The results predicted by the formula agree with the experimental results, demonstrating the potential for general applicability.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Vicca, S.; Bahn, M.; Estiarte, M.
2014-01-01
dependencies of SCE. Hence, the most justified answer to the question of whether current moisture responses of SCE can be extrapolated to predict SCE under altered precipitation regimes is 'no' - as based on the most reliable data sets available. We strongly recommend that future experiments focus more...
-
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — Navigation, surface current, sea surface temperature, wind, and atmospheric pressure data collected by the Mar Mostro during the around-the-world Volvo Ocean Race...
-
Current density profile inside q=1 on Tore Supra
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Joffrin, E.; Desgranges, C.; Sabot, R.; Dubois, M.A.
1995-01-01
The Tore Supra polarimeter used to measure the poloidal field distribution is described. The current density profiles are computed in two different ways using the interferometric and polarimetric data in conjunction with the magnetic data and the location of the inversion radius determined by the soft X-ray camera. The current density inside the q=1 surface is investigated for normal and monster sawteeth. Its variation are also measured by the polarimeter and compared with that predicted by the current diffusion equation assuming complete reconnection. Finally, the safety factor profile is compared with that obtained with the striation data of the pellet ablation. The results of the evolution of the q profile during sawteeth are in good agreement with those obtained in other devices. (author) 9 refs.; 4 figs
-
Ocular surface squamous neoplasia in HIV-infected patients: current perspectives.
Rathi, Shweta Gupta; Ganguly Kapoor, Anasua; Kaliki, Swathi
2018-01-01
Ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN) refers to a spectrum of conjunctival and corneal epithelial tumors including dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, and invasive carcinoma. In this article, we discuss the current perspectives of OSSN associated with HIV infection, focusing mainly on the epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of these tumors in patients with HIV. Upsurge in the incidence of OSSN with the HIV pandemic most severely affected sub-Saharan Africa, due to associated risk factors, such as human papilloma virus and solar ultraviolet exposure. OSSN has been reported as the first presenting sign of HIV/AIDS in 26%-86% cases, and seropositivity is noted in 38%-92% OSSN patients. Mean age at presentation of OSSN has dropped to the third to fourth decade in HIV-positive patients in developing countries. HIV-infected patients reveal large aggressive tumors, higher-grade malignancy, higher incidence of corneal, scleral, and orbital invasion, advanced-stage T4 tumors, higher need for extended enucleation/exenteration, and increased risk of tumor recurrence. Current management of OSSN in HIV-positive individuals is based on standard treatment guidelines described for OSSN in the general population, as there is little information available about various treatment modalities or their outcomes in patients with HIV. OSSN can occur at any time in the disease course of HIV/AIDS, and no significant trend has been discovered between CD4 count and grade of OSSN. Furthermore, the effect of highly active antiretroviral therapy on OSSN is controversial. The current recommendation is to conduct HIV screening in all cases presenting with OSSN to rule out undiagnosed HIV infection. Patient counseling is crucial, with emphasis on regular follow-up to address high recurrence rates and early presentation to an ophthalmologist for of any symptoms in the unaffected eye. Effective evidence-based interventions are needed to allow early diagnosis
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gao Xiang
2017-04-01
Full Text Available A model for predicting the size ranges of different potential inclusions initiating damage on the surface of fused silica has been presented. This accounts for the heating of nanometric inclusions whose absorptivity is described based on Mie Theory. The depth profile of impurities has been measured by ICP-OES. By the measured temporal pulse profile on the surface of fused silica, the temperature and thermal stress has been calculated. Furthermore, considering the limit conditions of temperature and thermal stress strength for different damage morphologies, the size range of potential inclusions for fused silica is discussed.
-
Schultz, A.; Bonner, L. R., IV
2016-12-01
Existing methods to predict Geomagnetically Induced Currents (GICs) in power grids, such as the North American Electric Reliability Corporation standard adopted by the power industry, require explicit knowledge of the electrical resistivity structure of the crust and mantle to solve for ground level electric fields along transmission lines. The current standard is to apply regional 1-D resistivity models to this problem, which facilitates rapid solution of the governing equations. The systematic mapping of continental resistivity structure from projects such as EarthScope reveals several orders of magnitude of lateral variations in resistivity on local, regional and continental scales, resulting in electric field intensifications relative to existing 1-D solutions that can impact GICs to first order. The computational burden on the ground resistivity/GIC problem of coupled 3-D solutions inhibits the prediction of GICs in a timeframe useful to protecting power grids. In this work we reduce the problem to applying a set of filters, recognizing that the magnetotelluric impedance tensors implicitly contain all known information about the resistivity structure beneath a given site, and thus provides the required relationship between electric and magnetic fields at each site. We project real-time magnetic field data from distant magnetic observatories through a robustly calculated multivariate transfer function to locations where magnetotelluric impedance tensors had previously been obtained. This provides a real-time prediction of the magnetic field at each of those points. We then project the predicted magnetic fields through the impedance tensors to obtain predictions of electric fields induced at ground level. Thus, electric field predictions can be generated in real-time for an entire array from real-time observatory data, then interpolated onto points representing a power transmission line contained within the array to produce a combined electric field prediction
-
Air-Sea Interaction in the Somali Current Region
Jensen, T. G.; Rydbeck, A.
2017-12-01
The western Indian Ocean is an area of high eddy-kinetic energy generated by local wind-stress curl, instability of boundary currents as well as Rossby waves from the west coast of India and the equatorial wave guide as they reflect off the African coast. The presence of meso-scale eddies and coastal upwelling during the Southwest Monsoon affects the air-sea interaction on those scales. The U.S. Navy's Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Mesoscale Prediction System (COAMPS) is used to understand and quantify the surface flux, effects on surface waves and the role of Sea Surface Temperature anomalies on ocean-atmosphere coupling in that area. The COAMPS atmosphere model component with 9 km resolution is fully coupled to the Navy Coastal Ocean Model (NCOM) with 3.5 km resolution and the Simulating WAves Nearshore (SWAN) wave model with 10 km resolution. Data assimilation using a 3D-variational approach is included in hindcast runs performed daily since June 1, 2015. An interesting result is that a westward jet associated with downwelling equatorial Rossy waves initiated the reversal from the southward Somali Current found during the northeast monsoon to a northward flow in March 2016 more than a month before the beginning of the southwest monsoon. It is also found that warm SST anomalies in the Somali Current eddies, locally increase surface wind speed due to an increase in the atmospheric boundary layer height. This results in an increase in significant wave height and also an increase in heat flux to the atmosphere. Cold SST anomalies over upwelling filaments have the opposite impacts on air-sea fluxes.
-
Broglia, Riccardo; Durante, Danilo
2017-11-01
This paper focuses on the analysis of a challenging free surface flow problem involving a surface vessel moving at high speeds, or planing. The investigation is performed using a general purpose high Reynolds free surface solver developed at CNR-INSEAN. The methodology is based on a second order finite volume discretization of the unsteady Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes equations (Di Mascio et al. in A second order Godunov—type scheme for naval hydrodynamics, Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 253-261, 2001; Proceedings of 16th international offshore and polar engineering conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006; J Mar Sci Technol 14:19-29, 2009); air/water interface dynamics is accurately modeled by a non standard level set approach (Di Mascio et al. in Comput Fluids 36(5):868-886, 2007a), known as the single-phase level set method. In this algorithm the governing equations are solved only in the water phase, whereas the numerical domain in the air phase is used for a suitable extension of the fluid dynamic variables. The level set function is used to track the free surface evolution; dynamic boundary conditions are enforced directly on the interface. This approach allows to accurately predict the evolution of the free surface even in the presence of violent breaking waves phenomena, maintaining the interface sharp, without any need to smear out the fluid properties across the two phases. This paper is aimed at the prediction of the complex free-surface flow field generated by a deep-V planing boat at medium and high Froude numbers (from 0.6 up to 1.2). In the present work, the planing hull is treated as a two-degree-of-freedom rigid object. Flow field is characterized by the presence of thin water sheets, several energetic breaking waves and plungings. The computational results include convergence of the trim angle, sinkage and resistance under grid refinement; high-quality experimental data are used for the purposes of validation, allowing to
-
Ardhuin, Fabrice; Aksenov, Yevgueny; Benetazzo, Alvise; Bertino, Laurent; Brandt, Peter; Caubet, Eric; Chapron, Bertrand; Collard, Fabrice; Cravatte, Sophie; Delouis, Jean-Marc; Dias, Frederic; Dibarboure, Gérald; Gaultier, Lucile; Johannessen, Johnny; Korosov, Anton; Manucharyan, Georgy; Menemenlis, Dimitris; Menendez, Melisa; Monnier, Goulven; Mouche, Alexis; Nouguier, Frédéric; Nurser, George; Rampal, Pierre; Reniers, Ad; Rodriguez, Ernesto; Stopa, Justin; Tison, Céline; Ubelmann, Clément; van Sebille, Erik; Xie, Jiping
2018-05-01
We propose a satellite mission that uses a near-nadir Ka-band Doppler radar to measure surface currents, ice drift and ocean waves at spatial scales of 40 km and more, with snapshots at least every day for latitudes 75 to 82°, and every few days for other latitudes. The use of incidence angles of 6 and 12° allows for measurement of the directional wave spectrum, which yields accurate corrections of the wave-induced bias in the current measurements. The instrument's design, an algorithm for current vector retrieval and the expected mission performance are presented here. The instrument proposed can reveal features of tropical ocean and marginal ice zone (MIZ) dynamics that are inaccessible to other measurement systems, and providing global monitoring of the ocean mesoscale that surpasses the capability of today's nadir altimeters. Measuring ocean wave properties has many applications, including examining wave-current interactions, air-sea fluxes, the transport and convergence of marine plastic debris and assessment of marine and coastal hazards.
-
Critical current density of BiSrCaCuO superconductors: effect of surface barriers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Konczykowski, M.; Chikumoto, N.
1992-01-01
Effects of surface barriers on vortex motion in BiSrCaCuO-2212 high-temperature superconducting crystals is summarized. Characteristic features of this phenomenon appear in the hysteresis loop (shape of its ascending and descending branches), in the effect of 2.5 MeV electron irradiation, and in flux creep measurements (magnetization dependence to the crystal lateral dimension, size of the flux-creep barrier and the crossover as a function of temperature and time persistent current density). (A.B.). 25 refs., 3 figs
-
Halpern, David
1995-01-01
The relative accuracies of three surface wind data products for the tropical Pacific Ocean during April 1992 to March 1994 were examined by analyzing temperature and current fields along the equator, which were simulated with an ocean general circulation model. Simulations were made with and without assimilation of surface and subsurface temperature data. Simulated currents were compared with observations at three sites (170oW, 140oW, 110oW) at the equator. Model-generated currents and temperatures indicated that the ERS-1 westward wind speeds were low compared to the FSU and NMC winds. With data assimilation, the agreement between simulated and observed currents was highest at 170oW and lowest at 110oW.
-
Current trends of surface science and catalysis
Park, Jeong Young
2014-01-01
Including detail on applying surface science in renewable energy conversion, this book covers the latest results on model catalysts including single crystals, bridging "materials and pressure gaps", and hot electron flows in heterogeneous catalysis.
-
Liver Surface Nodularity Score Allows Prediction of Cirrhosis Decompensation and Death.
Smith, Andrew D; Zand, Kevin A; Florez, Edward; Sirous, Reza; Shlapak, Darya; Souza, Frederico; Roda, Manohar; Bryan, Jason; Vasanji, Amit; Griswold, Michael; Lirette, Seth T
2017-06-01
Purpose To determine whether use of the liver surface nodularity (LSN) score, a quantitative biomarker derived from routine computed tomographic (CT) images, allows prediction of cirrhosis decompensation and death. Materials and Methods For this institutional review board-approved HIPAA-compliant retrospective study, adult patients with cirrhosis and Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score within 3 months of initial liver CT imaging between January 3, 2006, and May 30, 2012, were identified from electronic medical records (n = 830). The LSN score was measured by using CT images and quantitative software. Competing risk regression was used to determine the association of the LSN score with hepatic decompensation and overall survival. A risk model combining LSN scores (<3 or ≥3) and MELD scores (<10 or ≥10) was created for predicting liver-related events. Results In patients with compensated cirrhosis, 40% (129 of 326) experienced decompensation during a median follow-up period of 4.22 years. After adjustment for competing risks including MELD score, LSN score (hazard ratio, 1.38; 95% confidence interval: 1.06, 1.79) was found to be independently predictive of hepatic decompensation. Median times to decompensation of patients at high (1.76 years, n = 48), intermediate (3.79 years, n = 126), and low (6.14 years, n = 152) risk of hepatic decompensation were significantly different (P < .001). Among the full cohort with compensated or decompensated cirrhosis, 61% (504 of 830) died during the median follow-up period of 2.26 years. After adjustment for competing risks, LSN score (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval: 1.11, 1.33) and MELD score (hazard ratio, 1.08; 95% confidence interval: 1.06, 1.11) were found to be independent predictors of death. Median times to death of patients at high (0.94 years, n = 315), intermediate (2.79 years, n = 312), and low (4.69 years, n = 203) risk were significantly different (P < .001). Conclusion The LSN score
-
Gotto, Geoffrey T.; Yu, Changhong; Bernstein, Melanie; Eastham, James A.; Kattan, Michael W.
2014-01-01
Purpose: To develop a nomogram predictive of current bone scan positivity in patients receiving androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) for advanced prostate cancer; to augment clinical judgment and highlight patients in need of additional imaging investigations. Materials and methods: A retrospective chart review of bone scan records (conventional 99mTc-scintigraphy) of 1,293 patients who received ADT at the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center from 2000 to 2011. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to identify variables suitable for inclusion in the nomogram. The probability of current bone scan positivity was determined using these variables and the predictive accuracy of the nomogram was quantified by concordance index. Results: In total, 2,681 bone scan records were analyzed and 636 patients had a positive result. Overall, the median pre-scan prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level was 2.4 ng/ml; median PSA doubling time (PSADT) was 5.8 months. At the time of a positive scan, median PSA level was 8.2 ng/ml; 53% of patients had PSA <10 ng/ml; median PSADT was 4.0 months. Five variables were included in the nomogram: number of previous negative bone scans after initiating ADT, PSA level, Gleason grade sum, and history of radical prostatectomy and radiotherapy. A concordance index value of 0.721 was calculated for the nomogram. This was a retrospective study based on limited data in patients treated in a large cancer center who underwent conventional 99mTc bone scans, which themselves have inherent limitations. Conclusion: This is the first nomogram to predict current bone scan positivity in ADT-treated prostate cancer patients, providing high predictive accuracy. PMID:25386410
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Michael eKattan
2014-10-01
Full Text Available Purpose: To develop a nomogram predictive of current bone scan positivity in patients receiving androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT for advanced prostate cancer; to augment clinical judgment and highlight patients in need of additional imaging investigations.Materials and Methods: A retrospective chart review of bone scan records (conventional 99mTc-scintigraphy of 1,293 patients who received ADT at the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center from 2000 to 2011. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to identify variables suitable for inclusion in the nomogram. The probability of current bone scan positivity was determined using these variables and the predictive accuracy of the nomogram was quantified by concordance index.Results: In total, 2,681 bone scan records were analyzed and 636 patients had a positive result. Overall, the median pre-scan prostate-specific antigen (PSA level was 2.4 ng/ml; median PSA doubling time (PSADT was 5.8 months. At the time of a positive scan, median PSA level was 8.2 ng/ml; 53% of patients had PSA <10 ng/ml; median PSADT was 4.0 months. Five variables were included in the nomogram: number of previous negative bone scans after initiating ADT, PSA level, Gleason grade sum, and history of radical prostatectomy and radiotherapy. A concordance index value of 0.721 was calculated for the nomogram. This was a retrospective study based on limited data in patients treated in a large cancer centre who underwent conventional 99mTc bone scans, which themselves have inherent limitations. Conclusions: This is the first nomogram to predict current bone scan positivity in ADT-treated prostate cancer patients, providing high predictive accuracy.
-
A Seamless Framework for Global Water Cycle Monitoring and Prediction
Sheffield, J.; Wood, E. F.; Chaney, N.; Fisher, C. K.; Caylor, K. K.
2013-12-01
The Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS) Water Strategy ('From Observations to Decisions') recognizes that 'water is essential for ensuring food and energy security, for facilitating poverty reduction and health security, and for the maintenance of ecosystems and biodiversity', and that water cycle data and observations are critical for improved water management and water security - especially in less developed regions. The GEOSS Water Strategy has articulated a number of goals for improved water management, including flood and drought preparedness, that include: (i) facilitating the use of Earth Observations for water cycle observations; (ii) facilitating the acquisition, processing, and distribution of data products needed for effective management; (iii) providing expertise, information systems, and datasets to the global, regional, and national water communities. There are several challenges that must be met to advance our capability to provide near real-time water cycle monitoring, early warning of hydrological hazards (floods and droughts) and risk assessment under climate change, regionally and globally. Current approaches to monitoring and predicting hydrological hazards are limited in many parts of the world, and especially in developing countries where national capacity is limited and monitoring networks are inadequate. This presentation describes the development of a seamless monitoring and prediction framework at all time scales that allows for consistent assessment of water variability from historic to current conditions, and from seasonal and decadal predictions to climate change projections. At the center of the framework is an experimental, global water cycle monitoring and seasonal forecast system that has evolved out of regional and continental systems for the US and Africa. The system is based on land surface hydrological modeling that is driven by satellite remote sensing precipitation to predict current hydrological conditions
-
Space-charge-limited currents for cathodes with electric field enhanced geometry
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lai, Dingguo, E-mail: laidingguo@nint.ac.cn; Qiu, Mengtong; Xu, Qifu [State Key Laboratory of Intense Pulsed Radiation Simulation and Effect, Northwest Institute of Nuclear Technology, Xi' an 701124 (China); Huang, Zhongliang [Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084 (China)
2016-08-15
This paper presents the approximate analytic solutions of current density for annulus and circle cathodes. The current densities of annulus and circle cathodes are derived approximately from first principles, which are in agreement with simulation results. The large scaling laws can predict current densities of high current vacuum diodes including annulus and circle cathodes in practical applications. In order to discuss the relationship between current density and electric field on cathode surface, the existing analytical solutions of currents for concentric cylinder and sphere diodes are fitted from existing solutions relating with electric field enhancement factors. It is found that the space-charge-limited current density for the cathode with electric-field enhanced geometry can be written in a general form of J = g(β{sub E}){sup 2}J{sub 0}, where J{sub 0} is the classical (1D) Child-Langmuir current density, β{sub E} is the electric field enhancement factor, and g is the geometrical correction factor depending on the cathode geometry.
-
Stability of alternating current gliding arcs
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Kusano, Yukihiro; Salewski, Mirko; Leipold, Frank
2014-01-01
on Ohm’s law indicates that the critical length of alternating current (AC) gliding arc discharge columns can be larger than that of a corresponding direct current (DC) gliding arc. This finding is supported by previously published images of AC and DC gliding arcs. Furthermore, the analysis shows......A gliding arc is a quenched plasma that can be operated as a non-thermal plasma at atmospheric pressure and that is thus suitable for large-scale plasma surface treatment. For its practical industrial use the discharge should be extended stably in ambient air. A simple analytical calculation based...... that the critical length can be increased by increasing the AC frequency, decreasing the serial resistance and lowering the gas flow rate. The predicted dependence of gas flow rate on the arc length is experimentally demonstrated. The gap width is varied to study an optimal electrode design, since the extended non...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Vitte J.
2004-06-01
Full Text Available There is much interest in predicting and controlling the outcome of interaction between artificial surfaces and living cells. However, although there is an impressive amount of information on the behaviour of many cell populations deposited on a variety of surfaces, there is presently no available theory to explain or even summarize these data. Indeed, it is not even obvious that such a theory may exist. The aim of the present review is to emphasize the problems encountered when one attempts to build such a theory. Three sequential steps of cell surface interactions are considered: 1 protein adsorption is a preliminary step liable to involve irreversible interaction between the surface and several hundreds of molecular species occurring in blood or plasma. 2 the second step is the formation of adhesive bonds. Several theoretical frameworks were suggested to account for this step, including DLVO theory, physical chemistry of surfaces, and formation of specific ligandreceptor bonds. It is concluded that present evidence supports the latter approach, although this involves serious difficulties. 3 The last step is the triggering of a specific cell program such as apoptosis, proliferation, migration, differentiation or activation. Recent evidence suggests that in addition to the nature and amount of stimulated surface receptors, additional cues such as substratum mechanical or topographical properties may significantly affect cell behaviour.
-
Bunte, K.; Abt, S. R.; Swingle, K. W.; Cenderelli, D. A.; Gaeuman, D. A.
2014-12-01
Bedload transport and flow competence relations are difficult to predict in coarse-bedded steep streams where widely differing sediment supply, bed stability, and complex flow hydraulics greatly affect amounts and sizes of transported gravel particles. This study explains how properties of bed material surface and subsurface size distributions are directly related to gravel transport and may be used for prediction of gravel transport and flow competence relations. Gravel transport, flow competence, and bed material size were measured in step-pool and plane-bed streams. Power functions were fitted to gravel transport QB=aQb and flow competence Dmax=cQd relations; Q is water discharge. Frequency distributions of surface FDsurf and subsurface FDsub bed material were likewise described by power functions FDsurf=hD j and FDsub=kDm fitted over six 0.5-phi size classes within 4 to 22.4 mm. Those gravel sizes are typically mobile even in moderate floods. Study results show that steeper subsurface bed material size distributions lead to steeper gravel transport and flow competence relations, whereas larger amounts of sediment contained in those 6 size bedmaterial classes (larger h and k) flatten the relations. Similarly, steeper surface size distributions decrease the coefficients of the gravel transport and flow competence relations, whereas larger amounts of sediment within the six bed material classes increase the intercepts of gravel transport and flow competence relations. Those relations are likely causative in streams where bedload stems almost entirely from the channel bed as opposed to direct (unworked) contributions from hillslopes and tributaries. The exponent of the subsurface bed material distribution m predicted the gravel transport exponent b with r2 near 0.7 and flow competence exponent d with r2 near 0.5. The intercept of bed surface distributions h increased the intercept a of gravel transport and c of the flow competence relations with r2 near 0.6.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Su Jian; Silva Freire, Atila P.
2002-01-01
A simple analytical method was developed for the prediction of the friction factor, f, of fully developed turbulent flow and the Nusselt number, Nu, of fully developed turbulent forced convection in rod bundles arranged in square or hexagonal arrays. The friction factor equation for smooth rod bundles was presented in a form similar to the friction factor equation for turbulent flow in a circular pipe. An explicit equation for the Nusselt number of turbulent forced convection in rod bundles with smooth surface was developed. In addition, we extended the analysis to rod bundles with rough surface and provided a method for the prediction of the friction factor and the Nusselt number. The method was based on the law of the wall for velocity and the law of the wall for the temperature, which were integrated over the entire flow area to yield algebraic equations for the prediction of f and Nu. The present method is applicable to infinite rod bundles in square and hexagonal arrays with low pitch to rod diameter ratio, P/D<1.2
-
Wang, Fan; Zhao, Hongwei; Xiang, Haiying; Wu, Lijun; Men, Xiao; Qi, Chang; Chen, Guoqiang; Zhang, Haibo; Wang, Yi; Xian, Mo
2018-06-05
Microbes on aging flue-cured tobaccos (ATFs) improve the aroma and other qualities desirable in products. Understanding the relevant organisms would picture microbial community diversity, metabolic potential, and their applications. However, limited efforts have been made on characterizing the microbial quality and functional profiling. Herein, we present our investigation of the bacterial diversity and predicted potential genetic capability of the bacteria from two AFTs using 16S rRNA gene sequences and phylogenetic investigation of communities by reconstruction of unobserved states (PICRUSt) software. The results show that dominant bacteria from AFT surfaces were classified into 48 genera, 36 families, and 7 phyla. In addition, Bacillus spp. was found prevalent on both ATFs. Furthermore, PICRUSt predictions of bacterial community functions revealed many attractive metabolic capacities in the AFT microbiota, including several involved in the biosynthesis of flavors and fragrances and the degradation of harmful compounds, such as nicotine and nitrite. These results provide insights into the importance of AFT bacteria in determining product qualities and indicate specific microbial species with predicted enzymatic capabilities for the production of high-efficiency flavors, the degradation of undesirable compounds, and the provision of nicotine and nitrite tolerance which suggest fruitful areas of investigation into the manipulation of AFT microbiota for AFT and other product improvements.
-
Chabrillat, Sabine; Foerster, Saskia; Steinberg, Andreas; Stevens, Antoine; Segl, Karl
2016-04-01
There is a renewed awareness of the finite nature of the world's soil resources, growing concern about soil security, and significant uncertainties about the carrying capacity of the planet. As a consequence, soil scientists are being challenged to provide regular assessments of soil conditions from local through to global scales. However, only a few countries have the necessary survey and monitoring programs to meet these new needs and existing global data sets are out-of-date. A particular issue is the clear demand for a new area-wide regional to global coverage with accurate, up-to-date, and spatially referenced soil information as expressed by the modeling scientific community, farmers and land users, and policy and decision makers. Soil spectroscopy from remote sensing observations based on studies from the laboratory scale to the airborne scale has been shown to be a proven method for the quantitative prediction of key soil surface properties in local areas for exposed soils in appropriate surface conditions such as low vegetation cover and low water content. With the upcoming launch of the next generation of hyperspectral satellite sensors in the next 3 to 5 years (EnMAP, HISUI, PRISMA, SHALOM), a great potential for the global mapping and monitoring of soil properties is appearing. Nevertheless, the capabilities to extend the soil properties current spectral modeling from local to regional scales are still to be demonstrated using robust methods. In particular, three central questions are at the forefront of research nowadays: a) methodological developments toward improved algorithms and operational tools for the extraction of soil properties, b) up scaling from the laboratory into space domain, and c) demonstration of the potential of upcoming satellite systems and expected accuracy of soil maps. In this study, airborne imaging spectroscopy data from several test sites are used to simulate EnMAP satellite images at 30 m scale. Then, different soil
-
Kourafalou, V.; Kang, H.; Perlin, N.; Le Henaff, M.; Lamkin, J. T.
2016-02-01
Connectivity around the South Florida coastal regions and between South Florida and Cuba are largely influenced by a) local coastal processes and b) circulation in the Florida Straits, which is controlled by the larger scale Florida Current variability. Prediction of the physical connectivity is a necessary component for several activities that require ocean forecasts, such as oil spills, fisheries research, search and rescue. This requires a predictive system that can accommodate the intense coastal to offshore interactions and the linkages to the complex regional circulation. The Florida Straits, South Florida and Florida Keys Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model is such a regional ocean predictive system, covering a large area over the Florida Straits and the adjacent land areas, representing both coastal and oceanic processes. The real-time ocean forecast system is high resolution ( 900m), embedded in larger scale predictive models. It includes detailed coastal bathymetry, high resolution/high frequency atmospheric forcing and provides 7-day forecasts, updated daily (see: http://coastalmodeling.rsmas.miami.edu/). The unprecedented high resolution and coastal details of this system provide value added on global forecasts through downscaling and allow a variety of applications. Examples will be presented, focusing on the period of a 2015 fisheries cruise around the coastal areas of Cuba, where model predictions helped guide the measurements on biophysical connectivity, under intense variability of the mesoscale eddy field and subsequent Florida Current meandering.
-
Measuring Light Reflectance of BGO Crystal Surfaces
Janecek, Martin; Moses, William W.
2008-10-01
A scintillating crystal's surface reflectance has to be well understood in order to accurately predict and optimize the crystal's light collection through Monte Carlo simulations. In this paper, we measure the inner surface reflectance properties for BGO. The measurements include BGO crystals with a mechanically polished surface, rough-cut surface, and chemically etched surface, and with various reflectors attached, both air-coupled and with coupling compound. The measurements are performed with a laser aimed at the center of a hemispherical shaped BGO crystal. The hemispherical shape eliminates any non-perpendicular angles for light entering and exiting the crystal. The reflected light is collected with an array of photodiodes. The laser can be set at an arbitrary angle, and the photodiode array is rotated to fully cover 2pi of solid angle. The current produced in the photodiodes is readout with a digital multimeter connected through a multiplexer. The two rows of photodiodes achieve 5-degree by 4-degree resolution, and the current measurement has a dynamic range of 105:1. The acquired data was not described by the commonly assumed linear combination of specular and diffuse (Lambertian) distributions, except for a very few surfaces. Surface roughness proved to be the most important parameter when choosing crystal setup. The reflector choice was of less importance and of almost no consequence for rough-cut surfaces. Pure specular reflection distribution for all incidence angles was measured for polished surfaces with VM2000 film, while the most Lambertian distribution for any surface finish was measured for titanium dioxide paint. The distributions acquired in this paper will be used to create more accurate Monte Carlo models for light reflection distribution within BGO crystals.
-
Load Torque Compensator for Model Predictive Direct Current Control in High Power PMSM Drive Systems
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Preindl, Matthias; Schaltz, Erik
2011-01-01
The widely used cascade speed and torque controllers have a limited control performance in most high power applications due to the low switching frequency of power electronic converters and the convenience to avoid speed overshoots and oscillations for lifetime considerations. Model Predictive...... Direct Current Control (MPDCC) leads to an increase of torque control performance taking into account the discrete nature of inverters but temporary offsets and poor responses to load torque variations are still issues in speed control. A load torque estimator is proposed in this paper in order...
-
Surface Temperature Variation Prediction Model Using Real-Time Weather Forecasts
Karimi, M.; Vant-Hull, B.; Nazari, R.; Khanbilvardi, R.
2015-12-01
Combination of climate change and urbanization are heating up cities and putting the lives of millions of people in danger. More than half of the world's total population resides in cities and urban centers. Cities are experiencing urban Heat Island (UHI) effect. Hotter days are associated with serious health impacts, heart attaches and respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Densely populated cities like Manhattan, New York can be affected by UHI impact much more than less populated cities. Even though many studies have been focused on the impact of UHI and temperature changes between urban and rural air temperature, not many look at the temperature variations within a city. These studies mostly use remote sensing data or typical measurements collected by local meteorological station networks. Local meteorological measurements only have local coverage and cannot be used to study the impact of UHI in a city and remote sensing data such as MODIS, LANDSAT and ASTER have with very low resolution which cannot be used for the purpose of this study. Therefore, predicting surface temperature in urban cities using weather data can be useful.Three months of Field campaign in Manhattan were used to measure spatial and temporal temperature variations within an urban setting by placing 10 fixed sensors deployed to measure temperature, relative humidity and sunlight. Fixed instrument shelters containing relative humidity, temperature and illumination sensors were mounted on lampposts in ten different locations in Manhattan (Vant-Hull et al, 2014). The shelters were fixed 3-4 meters above the ground for the period of three months from June 23 to September 20th of 2013 making measurements with the interval of 3 minutes. These high resolution temperature measurements and three months of weather data were used to predict temperature variability from weather forecasts. This study shows that the amplitude of spatial and temporal variation in temperature for each day can be predicted
-
S. Vicca; M. Bahn; M. Estiarte; E. E. van Loon; R. Vargas; G. Alberti; P. Ambus; M. A. Arain; C. Beier; L. P. Bentley; W. Borken; N. Buchmann; S. L. Collins; G. de Dato; J. S. Dukes; C. Escolar; P. Fay; G. Guidolotti; P. J. Hanson; A. Kahmen; G. Kröel-Dulay; T. Ladreiter-Knauss; K. S. Larsen; E. Lellei-Kovacs; E. Lebrija-Trejos; F. T. Maestre; S. Marhan; M. Marshall; P. Meir; Y. Miao; J. Muhr; P. A. Niklaus; R. Ogaya; J. Peñuelas; C. Poll; L. E. Rustad; K. Savage; A. Schindlbacher; I. K. Schmidt; A. R. Smith; E. D. Sotta; V. Suseela; A. Tietema; N. van Gestel; O. van Straaten; S. Wan; U. Weber; I. A. Janssens
2014-01-01
As a key component of the carbon cycle, soil CO2 efflux (SCE) is being increasingly studied to improve our mechanistic understanding of this important carbon flux. Predicting ecosystem responses to climate change often depends an extrapolation of current relationships between ecosystem processes and their climatic drivers to conditions not yet experienced by the...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Smith, A C; Pei, X; Oliver, A; Husband, M; Rindfleisch, M
2012-01-01
A prototype resistive superconducting fault current limiter (SFCL) was developed using single-strand round magnesium diboride (MgB 2 ) wire. The MgB 2 wire was wound with an interleaved arrangement to minimize coil inductance and provide adequate inter-turn voltage withstand capability. The temperature profile from 30 to 40 K and frequency profile from 10 to 100 Hz at 25 K were tested and reported. The quench properties of the prototype coil were tested using a high current test circuit. The fault current was limited by the prototype coil within the first quarter-cycle. The prototype coil demonstrated reliable and repeatable current limiting properties and was able to withstand a potential peak current of 372 A for one second without any degradation of performance. A three-strand SFCL coil was investigated and demonstrated scaled-up current capacity. An analytical model to predict the behaviour of the prototype single-strand SFCL coil was developed using an adiabatic boundary condition on the outer surface of the wire. The predicted fault current using the analytical model showed very good correlation with the experimental test results. The analytical model and a finite element thermal model were used to predict the temperature rise of the wire during a fault. (paper)
-
Nayamatullah, M.; Rao Pillalamarri, Narasimha; Bhaganagar, Kiran
2018-04-01
A numerical investigation was performed to understand the flow dynamics of 2D density currents over sloping surfaces. Large eddy simulation was conducted for lock-exchange (L-E) release currents and overflows. 2D Navier-Stokes equations were solved using the Boussinesq approximation. The effects of the lock aspect-ratio (height/length of lock), slope, and Reynolds number on the flow structures and turbulence mixing have been analyzed. Results have confirmed buoyancy within the head of the two-dimensional currents is not conserved which contradicts the classical thermal theory. The lock aspect-ratio dictates the fraction of initial buoyancy which is carried by the head of the current at the beginning of the slumping (horizontal) and accelerating phase (over a slope), which has important implications on turbulence kinetic energy production, and hence mixing in the current. For L-E flows over a slope, increasing slope angle enhances the turbulence production. Increasing slope results in shear reversal within the density current resulting in shear-instabilities. Differences in turbulence production mechanisms and flow structures exist between the L-E and constant-flux release currents resulting in significant differences in the flow characteristics between different releases.
-
Marek K. Jakubowksi; Qinghua Guo; Brandon Collins; Scott Stephens; Maggi. Kelly
2013-01-01
We compared the ability of several classification and regression algorithms to predict forest stand structure metrics and standard surface fuel models. Our study area spans a dense, topographically complex Sierra Nevada mixed-conifer forest. We used clustering, regression trees, and support vector machine algorithms to analyze high density (average 9 pulses/m
-
Technology and economics of near-surface geothermal resources exploitation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Э. И. Богуславский
2017-04-01
Full Text Available The paper presents economic justification for applicability of near-surface geothermal installations in Luga region, based on results of techno-economic calculations as well as integrated technical and economic comparison of different prediction scenarios of heat supply, both conventional and using geothermal heat pumps (GHP. Construction costs of a near-surface geothermal system can exceed the costs of central heating by 50-100 %. However, operation and maintenance (O&M costs of heat production for geothermal systems are 50-70 % lower than for conventional sources of heating. Currently this technology is very important, it is applied in various countries (USA, Germany, Japan, China etc., and depending on the region both near-surface and deep boreholes are being used. World practice of near-surface geothermal systems application is reviewed in the paper.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Payne, J.R. [Payne Environmental Consultants Inc., Encinitas, CA (United States); Terrill, E.; Carter, M.; Otero, M.; Middleton, W.; Chen, A. [Scripps Inst. of Oceanography, La Jolla, CA (United States); French McCay, D.; Mueller, C.; Jayko, K. [Applied Science Associates Inc., Narragansett, RI (United States); Nordhausen, W.; Lewis, R.; Lampinen, M.; Evans, T. [California Dept. of Fish and Game, San Diego, CA (United States). Office of Spill Prevention and Response; Ohlmann, C. [California Univ., Santa Barbara, CA (United States); Via, G.L.; Ruiz-Santana, H.; Maly, M.; Willoughby, B.; Varela, C. [United States Coast Guard Pacific Strike Team, Novato, CA (United States); Lynch, P.; Sanchez, P. [Marine Spill Response Corp., San Diego, CA (United States)
2007-07-01
Extensive coastal areas in the United States have been designated as pre-approved zones for dispersant applications in the event of an oil spill. Although the use of dispersants may reduce impacts to wildlife and shoreline habitats, it is recognized that the dispersed oil may cause impacts to organisms in the water column. The State of California Department of Fish and Game Office of Spill Prevention and Response is currently using oil spill fate and transport modeling to address this issue. The purpose is to develop the time and spatial scales, and equipment needs for a formal dispersed oil monitoring plan (DOMP) to document hydrocarbon water column concentrations, potentially exposed zooplankton, and the impact of the oil spills with and without dispersant use. A series of 7 fluorescein dye releases were completed off the coast of San Diego, California in order to test the operational framework for repeated sampling of dispersed oil plumes as outlined in the DOMP. The ability of high-frequency radar to provide surface current input data to oil spill models was also evaluated. The dye concentrations were measured over three spatial dimensions and time in order to verify the model-predicted movement of subsurface dye. Surface current fields at varying depths were also measured and the subsurface dye plume structure was mapped using a GPS coupled towed-fluorometer equipped with pressure sensors. Measurements were compared with data from traditional special monitoring of applied response technology (SMART). The database acquired through this program represents a technical resource that can help physical and chemical oceanographers, modelers, spill response and contingency planners involved in the debate of whether or not to use dispersants to mitigate near shore and open ocean marine oil spills. 14 refs., 2 tabs., 14 figs.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Holden, S J [Defence Science and Technology Laboratory, Porton Down, Salisbury, Wiltshire SP4 0JQ (United Kingdom); Sheridan, R D [Defence Science and Technology Laboratory, Porton Down, Salisbury, Wiltshire SP4 0JQ (United Kingdom); Coffey, T J [Mathshop Ltd, Porton Down Science Park, Salisbury, Wiltshire SP4 0JQ (United Kingdom); Scaramuzza, R A [Flomerics Ltd, Electromagnetic Division, TLM House, Percy Street, Nottingham NG16 3EP (United Kingdom); Diamantopoulos, P [Bio-Medical Modelling Unit, School of Engineering, University of Sussex, Falmer, Sussex BN1 9QT (United Kingdom)
2007-12-21
Increasing use by law enforcement agencies of the M26 and X26 TASER electrical incapacitation devices has raised concerns about the arrhythmogenic potential of these weapons. Using a numerical phantom constructed from medical images of the human body in which the material properties of the tissues are represented, computational electromagnetic modelling has been used to predict the currents arising at the heart following injection of M26 and X26 waveforms at the anterior surface of the chest (with one TASER 'barb' directly overlying the ventricles). The modelling indicated that the peak absolute current densities at the ventricles were 0.66 and 0.11 mA mm{sup -2} for the M26 and X26 waveforms, respectively. When applied during the vulnerable period to the ventricular epicardial surface of guinea-pig isolated hearts, the M26 and X26 waveforms induced ectopic beats, but only at current densities greater than 60-fold those predicted by the modelling. When applied to the ventricles in trains designed to mimic the discharge patterns of the TASER devices, neither waveform induced ventricular fibrillation at peak currents >70-fold (for the M26 waveform) and >240-fold (for the X26) higher than the modelled current densities. This study provides evidence for a lack of arrhythmogenic action of the M26 and X26 TASER devices.
-
In the last decade three new techniques scanning probe microscopy (SPM), virtual reality (YR) and computational chemistry ave emerged with the combined capability of a priori predicting the chemically reactivity of environmental surfaces. Computational chemistry provides the cap...
-
Stabilization of the (2,1) tearing mode and of the current disruption in the W VII-A stellarator
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bartlett, D.V.; Cannici, G.; Cattanei, G.
1980-01-01
A numerical code based on a Δ'-analysis is applied to calculate the saturated amplitude of tearing modes dependent on the current density profile. The only stellarator effect included is the additional, shearless external rotational transform in the safety factor profile q(r). In this way, the stellarator field shifts the resonant q=2 surface toward the outside, where the current density gradient is smaller, and stabilizes the (2,1) mode as observed experimentally. Also the measured dependence of the (2,1) mode amplitude on electron density and plasma current can be absolutely predicted by the calculations. - In addition to stabilizing the (2,1) tearing mode, the current disruption is suppressed in Ohmically heated W VII-A discharges for approximately >0.15. The experimental findings, together with the calculated island widths, are compared with the predictions of a theoretical model proposed by several authors to explain the current disruption. (author)
-
Dippe, Tina; Greatbatch, Richard; Ding, Hui
2016-04-01
The dominant mode of interannual variability in tropical Atlantic sea surface temperatures (SSTs) is the Atlantic Niño or Zonal Mode. Akin to the El Niño-Southern Oscillation in the Pacific sector, it is able to impact the climate both of the adjacent equatorial African continent and remote regions. Due to heavy biases in the mean state climate of the equatorial-to-subtropical Atlantic, however, most state-of-the-art coupled global climate models (CGCMs) are unable to realistically simulate equatorial Atlantic variability. In this study, the Kiel Climate Model (KCM) is used to investigate the impact of a simple bias alleviation technique on the predictability of equatorial Atlantic SSTs. Two sets of seasonal forecasting experiments are performed: An experiment using the standard KCM (STD), and an experiment with additional surface heat flux correction (FLX) that efficiently removes the SST bias from simulations. Initial conditions for both experiments are generated by the KCM run in partially coupled mode, a simple assimilation technique that forces the KCM with observed wind stress anomalies and preserves SST as a fully prognostic variable. Seasonal predictions for both sets of experiments are run four times yearly for 1981-2012. Results: Heat flux correction substantially improves the simulated variability in the initialization runs for boreal summer and fall (June-October). In boreal spring (March-May), however, neither the initialization runs of the STD or FLX-experiments are able to capture the observed variability. FLX-predictions show no consistent enhancement of skill relative to the predictions of the STD experiment over the course of the year. The skill of persistence forecasts is hardly beat by either of the two experiments in any season, limiting the usefulness of the few forecasts that show significant skill. However, FLX-forecasts initialized in May recover skill in July and August, the peak season of the Atlantic Niño (anomaly correlation
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. Ardhuin
2018-05-01
Full Text Available We propose a satellite mission that uses a near-nadir Ka-band Doppler radar to measure surface currents, ice drift and ocean waves at spatial scales of 40 km and more, with snapshots at least every day for latitudes 75 to 82°, and every few days for other latitudes. The use of incidence angles of 6 and 12° allows for measurement of the directional wave spectrum, which yields accurate corrections of the wave-induced bias in the current measurements. The instrument's design, an algorithm for current vector retrieval and the expected mission performance are presented here. The instrument proposed can reveal features of tropical ocean and marginal ice zone (MIZ dynamics that are inaccessible to other measurement systems, and providing global monitoring of the ocean mesoscale that surpasses the capability of today's nadir altimeters. Measuring ocean wave properties has many applications, including examining wave–current interactions, air–sea fluxes, the transport and convergence of marine plastic debris and assessment of marine and coastal hazards.
-
Exchange currents in nuclear physics
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Truglik, Eh.
1980-01-01
Starting from Adler's low-energy theorem for the soft pion production amplitudes the predictions of the meson exchange currents theory for the nuclear physics are discussed. The results are reformulated in terms of phenomenological lagrangians. This method allows one to pass naturally to the more realistic case of hard mesons. The predictions are critically compared with the existing experimental data. The main processes in which vector isovector exchange currents, vector isoscalar exchange currents and axial exchange currents take place are pointed out
-
Atteia, Olivier; Höhener, Patrick
2010-08-15
Volatilization of toxic organic contaminants from groundwater to the soil surface is often considered an important pathway in risk analysis. Most of the risk models use simplified linear solutions that may overpredict the volatile flux. Although complex numerical models have been developed, their use is restricted to experienced users and for sites where field data are known in great detail. We present here a novel semianalytical model running on a spreadsheet that simulates the volatilization flux and vertical concentration profile in a soil based on the Van Genuchten functions. These widely used functions describe precisely the gas and water saturations and movement in the capillary fringe. The analytical model shows a good accuracy over several orders of magnitude when compared to a numerical model and laboratory data. The effect of barometric pumping is also included in the semianalytical formulation, although the model predicts that barometric pumping is often negligible. A sensitivity study predicts significant fluxes in sandy vadose zones and much smaller fluxes in other soils. Fluxes are linked to the dimensionless Henry's law constant H for H < 0.2 and increase by approximately 20% when temperature increases from 5 to 25 degrees C.
-
Image analysis from surface scanning with an absolute eddy current coil
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Attaoui, P.
1994-01-01
The aim of this work is to implement processing and analysis tools applied to eddy current imaging. These cartographies are issued from steam generator tubes testing using an absolute coil. The first is to eliminate the perturbations due to probe lift-off changes which generate low frequency oscillations on the image. The principle of the processing is to rebuild a complete surface of the noise using only the points around the defect area. The geometric origin of these perturbations led to a model based on sinusoidal functions. The method consists of gradually decomposing the image into a sum of basic sinusoidal surfaces. In order to take into account all kind of cartographies (especially rolling zone) some preprocessing must be applied. The results obtained with this 'cartography flattening'are satisfactory and the phase of analysis could begin with good condition of signal ratio. The second part of this work dealt with the choice and the perfection of image processing tools which would fit the most with the defect characterization. The aim of this characterization is to give the orientation and main size of the detected defect. A morphological skeleton representation has been chosen to illustrate the defect architecture and to allow sizing. A set of tools has been elaborated to obtain an (automatic) processing according to threshold. The results for single defect are satisfactory since the sizing error is around ± 25% and orientation is nearly always correctly given. The processing for area with several defects is more complex and new complementary research directions are proposed. (author)
-
Nikolaidis, Andreas; Stylianou, Stavros; Georgiou, Georgios; Hajimitsis, Diofantos; Gravanis, Elias; Akylas, Evangelos
2015-04-01
During the last decade, Rixen (2005) and Alvera-Azkarate (2010) presented the DINEOF (Data Interpolating Empirical Orthogonal Functions) method, a EOF-based technique to reconstruct missing data in satellite images. The application of DINEOF method, proved to provide relative success in various experimental trials (Wang and Liu, 2013; Nikolaidis et al., 2013;2014), and tends to be an effective and computationally affordable solution, on the problem of data reconstruction, for missing data from geophysical fields, such as chlorophyll-a, sea surface temperatures or salinity and geophysical fields derived from satellite data. Implementation of this method in a GIS system will provide with a more complete, integrated approach, permitting the expansion of the applicability over various aspects. This may be especially useful in studies where various data of different kind, have to be examined. For this purpose, in this study we have implemented and present a GIS toolbox that aims to automate the usage of the algorithm, incorporating the DINEOF codes provided by GHER (GeoHydrodynamics and Environment Research Group of University of Liege) into the ArcGIS®. ArcGIS® is a well known standard on Geographical Information Systems, used over the years for various remote sensing procedures, in sea and land environment alike. A case-study of filling the missing satellite derived current data in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea area, for a monthly period is analyzed, as an example for the effectiveness and simplicity of the usage of this toolbox. The specific study focuses to OSCAR satellite data (http://www.oscar.noaa.gov/) collected by NOAA/NESDIS Operational Surface Current Processing and Data Center, from the respective products of OSCAR Project Office Earth and Space Research organization, that provides free online access to unfiltered (1/3 degree) resolution. All the 5-day mean products data coverage were successfully reconstructed. KEY WORDS: Remote Sensing, Cyprus
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Batchelor, D.B.; Baity, F.W.; Carter, M.D.
1994-01-01
The objective of the advanced tokamak program is to optimize plasma performance leading to a compact tokamak reactor through active, steady state control of the current profile using non-inductive current drive and profile control. To achieve these objectives requires compatibility and flexibility in the use of available heating and current drive systems--ion cyclotron radio frequency (ICRF), neutral beams, and lower hybrid. For any advanced tokamak, the following are important challenges to effective use of fast waves in various roles of direct electron heating, minority ion heating, and current drive: (1) to employ the heating and current drive systems to give self-consistent pressure and current profiles leading to the desired advanced tokamak operating modes; (2) to minimize absorption of the fast waves by parasitic resonances, which limit current drive; (3) to optimize and control the spectrum of fast waves launched by the antenna array for the required mix of simultaneous heating and current drive. The authors have addressed these issues using theoretical and computational tools developed at a number of institutions by benchmarking the computations against available experimental data and applying them to the specific case of TPX
-
Current-Sensitive Path Planning for an Underactuated Free-Floating Ocean Sensorweb
Dahl, Kristen P.; Thompson, David R.; McLaren, David; Chao, Yi; Chien, Steve
2011-01-01
This work investigates multi-agent path planning in strong, dynamic currents using thousands of highly under-actuated vehicles. We address the specific task of path planning for a global network of ocean-observing floats. These submersibles are typified by the Argo global network consisting of over 3000 sensor platforms. They can control their buoyancy to float at depth for data collection or rise to the surface for satellite communications. Currently, floats drift at a constant depth regardless of the local currents. However, accurate current forecasts have become available which present the possibility of intentionally controlling floats' motion by dynamically commanding them to linger at different depths. This project explores the use of these current predictions to direct float networks to some desired final formation or position. It presents multiple algorithms for such path optimization and demonstrates their advantage over the standard approach of constant-depth drifting.
-
Computer modelling of eddy current probes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sullivan, S.P.
1992-01-01
Computer programs have been developed for modelling impedance and transmit-receive eddy current probes in two-dimensional axis-symmetric configurations. These programs, which are based on analytic equations, simulate bobbin probes in infinitely long tubes and surface probes on plates. They calculate probe signal due to uniform variations in conductor thickness, resistivity and permeability. These signals depend on probe design and frequency. A finite element numerical program has been procured to calculate magnetic permeability in non-linear ferromagnetic materials. Permeability values from these calculations can be incorporated into the above analytic programs to predict signals from eddy current probes with permanent magnets in ferromagnetic tubes. These programs were used to test various probe designs for new testing applications. Measurements of magnetic permeability in magnetically biased ferromagnetic materials have been performed by superimposing experimental signals, from special laboratory ET probes, on impedance plane diagrams calculated using these programs. (author). 3 refs., 2 figs
-
Japan Tsunami Current Flows Observed by HF Radars on Two Continents
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Toshiyuki Awaji
2011-08-01
Full Text Available Quantitative real-time observations of a tsunami have been limited to deep-water, pressure-sensor observations of changes in the sea surface elevation and observations of sea level fluctuations at the coast, which are essentially point measurements. Constrained by these data, models have been used for predictions and warning of the arrival of a tsunami, but to date no detailed verification of flow patterns nor area measurements have been possible. Here we present unique HF-radar area observations of the tsunami signal seen in current velocities as the wave train approaches the coast. Networks of coastal HF-radars are now routinely observing surface currents in many countries and we report clear results from five HF radar sites spanning a distance of 8,200 km on two continents following the magnitude 9.0 earthquake off Sendai, Japan, on 11 March 2011. We confirm the tsunami signal with three different methodologies and compare the currents observed with coastal sea level fluctuations at tide gauges. The distance offshore at which the tsunami can be detected, and hence the warning time provided, depends on the bathymetry: the wider the shallow continental shelf, the greater this time. Data from these and other radars around the Pacific rim can be used to further develop radar as an important tool to aid in tsunami observation and warning as well as post-processing comparisons between observation and model predictions.
-
Prediction and Migration of Surface-related Resonant Multiples
Guo, Bowen; Schuster, Gerard T.; Huang, Yunsong
2015-01-01
Surface-related resonant multiples can be migrated to achieve better resolution than migrating primary reflections. We now derive the formula for migrating surface-related resonant multiples, and show its super-resolution characteristics. Moreover
-
Plasma current profile during current reversal in a tokamak
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Huang Jianguo; Yang Xuanzong; Zheng Shaobai; Feng Chunhua; Zhang Houxian; Wang Long
1999-01-01
Alternating current operation with one full cycle and a current level of 2.5 kA have been achieved in the CT-6B tokamak. The poloidal magnetic field in the plasma is measured with two internal magnetic probes in repeated discharges. The current distribution is reconstructed with an inversion algorithm. The inverse current first appears on the weak field side. The existence of magnetic surfaces and rotational transform provide particle confinement in the current reversal phase
-
Lázaro y De Mercado, Pablo; Blasco Bravo, Antonio Javier; Lázaro y De Mercado, Ignacio; Castañeda, Santos; López Robledillo, Juan Carlos
2013-01-01
To: 1) describe the distribution of the public sector rheumatologists; 2) identify variables on which the workload in Rheumatology depends; and 3) build a predictive model on the need of rheumatologists for the next 10 years, in the Community of Madrid (CM). The information was obtained through structured questionnaires sent to all services/units of Rheumatology of public hospitals in the CM. The population figures, current and forecasted, were obtained from the National Statistics Institute. A predictive model was built based on information about the current and foreseeable supply, current and foreseeable demand, and the assumptions and criteria used to match supply with demand. The underlying uncertainty in the model was assessed by sensitivity analysis. In the CM in 2011 there were 150 staff rheumatologists and 49 residents in 27 centers, which is equivalent to one rheumatologist for every 33,280 inhabitants in the general population, and one for every 4,996 inhabitants over 65 years. To keep the level of assistance of 2011 in 2021 in the general population, it would be necessary to train more residents or hire more rheumatologists in scenarios of demand higher than 15%. However, to keep the level of assistance in the population over 65 years of age it would be necessary to train more residents or hire more specialists even without increased demand. The model developed may be very useful for planning, with the CM policy makers, the needs of human resources in Rheumatology in the coming years. Copyright © 2012 Elsevier España, S.L. All rights reserved.
-
Schober, P; Krage, R; Lagerburg, V; Van Groeningen, D; Loer, S A; Schwarte, L A
2014-04-01
Current cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)-guidelines recommend an increased chest compression depth and rate compared to previous guidelines, and the use of automatic feedback devices is encouraged. However, it is unclear whether this compression depth can be maintained at an increased frequency. Moreover, the underlying surface may influence accuracy of feedback devices. We investigated compression depths over time and evaluated the accuracy of a feedback device on different surfaces. Twenty-four volunteers performed four two-minute blocks of CPR targeting at current guideline recommendations on different surfaces (floor, mattress, 2 backboards) on a patient simulator. Participants rested for 2 minutes between blocks. Influences of time and different surfaces on chest compression depth (ANOVA, mean [95% CI]) and accuracy of a feedback device to determine compression depth (Bland-Altman) were assessed. Mean compression depth did not reach recommended depth and decreased over time during all blocks (first block: from 42 mm [39-46 mm] to 39 mm [37-42 mm]). A two-minute resting period was insufficient to restore compression depth to baseline. No differences in compression depth were observed on different surfaces. The feedback device slightly underestimated compression depth on the floor (bias -3.9 mm), but markedly overestimated on the mattress (bias +12.6 mm). This overestimation was eliminated after correcting compression depth by a second sensor between manikin and mattress. Strategies are needed to improve chest compression depth, and more than two providers should alternate with chest compressions. The underlying surface does not necessarily adversely affect CPR performance but influences accuracy of feedback devices. Accuracy is improved by a second, posterior, sensor.
-
Kravtsov, Sergey; Kamenkovich, Igor; Hogg, Andrew M.; Peters, John M.
2011-11-01
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), with its associated three-dimensional circulation, plays an important role in global climate. This study concentrates on surface signatures of recent climate change in the ACC region and on mechanisms that control this change. Examination of climate model simulations shows that they match the observed late 20th century sea-surface temperature (SST) trends averaged over this region quite well, despite underestimating the observed surface-wind increases. Such wind increases, however, are expected to lead to significant cooling of the region, contradicting the observed SST trends. Motivated by recent theories of the ACC response to variable wind and radiative forcing, the authors used two idealized models to assess contributions of various dynamical processes to the SST evolution in the region. In particular, a high-resolution channel model of the ACC responds to increasing winds by net surface ACC warming due to enhanced mesoscale turbulence and associated heat transports in the mixed layer. These fluxes, modeled, in a highly idealized fashion, via increased lateral surface mixing in a coarse-resolution hybrid climate model, substantially offset zonally non-uniform surface cooling due to air-sea flux and Ekman-transport anomalies. These results suggest that the combination of these opposing effects must be accounted for when estimating climate response to any external forcing in the ACC region.
-
Fuel particles in the Chernobyl cooling pond: current state and prediction for remediation options
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bulgakov, A.; Konoplev, A.; Smith, J.; Laptev, G.; Voitsekhovich, O.
2009-01-01
During the coming years, a management and remediation strategy for the Chernobyl cooling pond (CP) will be implemented. Remediation options include a controlled reduction in surface water level of the cooling pond and stabilisation of exposed sediments. In terrestrial soils, fuel particles deposited during the Chernobyl accident have now almost completely disintegrated. However, in the CP sediments the majority of 90 Sr activity is still in the form of fuel particles. Due to the low dissolved oxygen concentration and high pH, dissolution of fuel particles in the CP sediments is significantly slower than in soils. After the planned cessation of water pumping from the Pripyat River to the Pond, significant areas of sediments will be drained and exposed to the air. This will significantly enhance the dissolution rate and, correspondingly, the mobility and bioavailability of radionuclides will increase with time. The rate of acidification of exposed bottom sediments was predicted on the basis of acidification of similar soils after liming. Using empirical equations relating the fuel particle dissolution rate to soil and sediment pH allowed prediction of fuel particle dissolution and 90 Sr mobilisation for different remediation scenarios. It is shown that in exposed sediments, fuel particles will be almost completely dissolved in 15-25 years, while in parts of the cooling pond which remain flooded, fuel particle dissolution will take about a century
-
Watt, D.A.
1956-07-01
A current transfer system is described for transferring current between a rotating member and a co-axial stationary member. The particular area of application for the invention is in connection with homopolar generators where a low voltage and high current are generated. The current tramsfer system of the invention comprises a rotor member and a co-axial stator member wherein one of the members is shaped to provide a circumferential surface concave in section and the other member is shaped to have a peripheral portion in close proximity to the surface, whereby a liquid metal can be stably supported between the two members when they are moving relative to one another to establish an electrical conducting path between the members.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Olesen, Laurits Højgaard; Bruus, Henrik; Ajdari, A.
2006-01-01
therefore extend the latter theories to account for three experimentally relevant effects: (i) vertical confinement of the pumping channel, (ii) Faradaic currents from electrochemical reactions at the electrodes, and (iii) nonlinear surface capacitance of the Debye layer. We report here that these effects......Recent experiments have demonstrated that ac electrokinetic micropumps permit integrable, local, and fast pumping (velocities similar to mm/s) with low driving voltage of a few volts only. However, they also displayed many quantitative and qualitative discrepancies with existing theories. We...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Baker, L.A.; Kaufmann, P.R.; Brakke, D.F.; Herlihy, A.T.; Eilers, J.M.
1990-09-01
The report is based largely upon the National Surface Water Survey (NSWS), augmented by numerous smaller state and university surveys and many detailed watershed studies. In describing the current status of surface waters, the authors go far beyond the description of population statistics, although some of this is necessary, and direct their attention to the interpretation of these data. They address the question of the sources of acidity to surface waters in order to determine the relative importance of acidic deposition compared with other sources, such as naturally produced organic acids and acid mine drainage. They also examine in some detail what they call 'high interest' populations-the specific groups of lakes and streams most likely to be impacted by acidic deposition. The authors then turn to the general question of uncertainty, and finally examine low alkalinity surface waters in several other parts of the world to develop further inferences about the acid-base status of surface waters in the United States
-
Ocean Surface Current Vectors from MODIS Terra/Aqua Sea Surface Temperature Image Pairs, Phase I
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — Satellites that record imagery of the same sea surface area, at times separated by a few hours, can be used to estimate ocean surface velocity fields based on the...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. O. Babiak
2009-07-01
Full Text Available The process of mutual moving and contacting of surfaces of current collecting pantograph elements and contact network is considered taking into account the particularities of inf1uence of speed and acceleration parameters, determination of which will allow to forecast mathematically the wear-out degree of contacting elements.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Su, Guo-Qiang; Wang, Yi-Bo; Song, Bai-Peng; Mu, Hai-Bao, E-mail: haibaomu@xjtu.edu.cn, E-mail: gjzhang@xjtu.edu.cn; Zhang, Guan-Jun, E-mail: haibaomu@xjtu.edu.cn, E-mail: gjzhang@xjtu.edu.cn [State Key Laboratory of Electrical Insulation and Power Equipment, School of Electrical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710049 (China); Li, Feng; Wang, Meng [Institute of Fluid Physics, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang, Sichuan 621900 (China)
2016-06-15
The luminescence evolution phenomena from alumina ceramic surface in vacuum under high voltage of direct and alternating current are reported, with the voltage covering a large range from far below to close to the flashover voltage. Its time resolved and spatial distributed behaviors are examined by a photon counting system and an electron-multiplying charge-coupled device (EMCCD) together with a digital camera, respectively. The luminescence before flashover exhibits two stages as voltage increasing, i.e., under a relative low voltage (Stage A), the luminescence is ascribed to radiative recombination of hetero-charges injected into the sample surface layer by Schottky effect; under a higher voltage (Stage B), a stable secondary electron emission process, resulting from the Fowler-Nordheim emission at the cathode triple junction (CTJ), is responsible for the luminescence. Spectrum analysis implies that inner secondary electrons within the surface layer of alumina generated during the SSEE process also participate in the luminescence of Stage B. A comprehensive interpretation of the flashover process is formulated, which might promote a better understanding of flashover issue in vacuum.
-
Lorenzo, M. N.; Iglesias, I.; Taboada, J. J.; Gómez-Gesteira, M.; Ramos, A. M.
2009-04-01
This work assesses the possibility of doing a forecast of rainfall and the main teleconnections patterns that influences climate in Southwest Europe by using sea surface temperature anomalies (SSTA). The area under study is located in the NW Iberian Peninsula. This region has a great oceanic influence on its climate and has an important dependency of the water resources. In this way if the different SST patterns are known, the different rainfall situations can be predicted. On the other hand, the teleconnection patterns, which have strong weight on rainfall, are influenced by the SSTA of different areas. In the light of this, the aim of this study is to explore the relationship between global SSTAs, rainfall and the main teleconnection patterns influencing on Europe. The SST data with a 2.0 degree resolution was provided by the NOAA/OAR/ESRL PSD, Boulder, Colorado, USA. A monthly averaged data from 1 January 1951 through December 2006 was considered. The monthly precipitation data from 1951-2006 were obtained from the database CLIMA of the University of Santiago de Compostela with data from the Meteorological State Agency (AEMET) and the Regional Government of Galicia. The teleconnection indices were taken of the Climate Prediction Center of the NOAA between 1950 and 2006. A monthly and seasonal study was analysed considering up to three months of delay in the first case and up to four seasons of delay in the second case. The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient r was considered to quantify linear associations between SSTA and precipitation and/or SSTA and teleconnection indices. A test for field-significance was applied considering the properties of finiteness and interdependence of the spatial grid to avoid spurious correlations. Analysing the results obtained with the global SSTA and the teleconnection indices, a great number of ocean regions with high correlations can be found. The spatial patterns show very high correlations with Indian Ocean waters
-
Combined RF current drive and bootstrap current in tokamaks
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Schultz, S. D.; Bers, A.; Ram, A. K.
1999-01-01
By calculating radio frequency current drive (RFCD) and the bootstrap current in a consistent kinetic manner, we find synergistic effects in the total noninductive current density in tokamaks [1]. We include quasilinear diffusion in the Drift Kinetic Equation (DKE) in order to generalize neoclassical theory to highly non-Maxwellian electron distributions due to RFCD. The parallel plasma current is evaluated numerically with the help of the FASTEP Fokker-Planck code [2]. Current drive efficiency is found to be significantly affected by neoclassical effects, even in cases where only circulating electrons interact with the waves. Predictions of the current drive efficiency are made for lower hybrid and electron cyclotron wave current drive scenarios in the presence of bootstrap current
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ali Khazaei
2014-07-01
Full Text Available In this work, artificial neural network (ANN has been employed to propose a practical model for predicting the surface tension of multi-component mixtures. In order to develop a reliable model based on the ANN, a comprehensive experimental data set including 15 ternary liquid mixtures at different temperatures was employed. These systems consist of 777 data points generally containing hydrocarbon components. The ANN model has been developed as a function of temperature, critical properties, and acentric factor of the mixture according to conventional corresponding-state models. 80% of the data points were employed for training ANN and the remaining data were utilized for testing the generated model. The average absolute relative deviations (AARD% of the model for the training set, the testing set, and the total data points were obtained 1.69, 1.86, and 1.72 respectively. Comparing the results with Flory theory, Brok-Bird equation, and group contribution theory has proved the high prediction capability of the attained model.
-
Taxi Time Prediction at Charlotte Airport Using Fast-Time Simulation and Machine Learning Techniques
Lee, Hanbong
2016-01-01
Accurate taxi time prediction is required for enabling efficient runway scheduling that can increase runway throughput and reduce taxi times and fuel consumptions on the airport surface. Currently NASA and American Airlines are jointly developing a decision-support tool called Spot and Runway Departure Advisor (SARDA) that assists airport ramp controllers to make gate pushback decisions and improve the overall efficiency of airport surface traffic. In this presentation, we propose to use Linear Optimized Sequencing (LINOS), a discrete-event fast-time simulation tool, to predict taxi times and provide the estimates to the runway scheduler in real-time airport operations. To assess its prediction accuracy, we also introduce a data-driven analytical method using machine learning techniques. These two taxi time prediction methods are evaluated with actual taxi time data obtained from the SARDA human-in-the-loop (HITL) simulation for Charlotte Douglas International Airport (CLT) using various performance measurement metrics. Based on the taxi time prediction results, we also discuss how the prediction accuracy can be affected by the operational complexity at this airport and how we can improve the fast time simulation model before implementing it with an airport scheduling algorithm in a real-time environment.
-
Wood, William A.; Kleb, William L.; Tang, chun Y.; Palmer, Grant E.; Hyatt, Andrew J.; Wise, Adam J.; McCloud, Peter L.
2010-01-01
Surface temperature measurements from the STS-119 boundary-layer transition experiment on the space shuttle orbiter Discovery provide a rare opportunity to assess turbulent CFD models at hypersonic flight conditions. This flight data was acquired by on-board thermocouples and by infrared images taken off-board by the Hypersonic Thermodynamic Infrared Measurements (HYTHIRM) team, and is suitable for hypersonic CFD turbulence assessment between Mach 6 and 14. The primary assessment is for the Baldwin-Lomax and Cebeci-Smith algebraic turbulence models in the DPLR and LAURA CFD codes, respectively. A secondary assessment is made of the Shear-Stress Transport (SST) two-equation turbulence model in the DPLR code. Based upon surface temperature comparisons at eleven thermocouple locations, the algebraic-model turbulent CFD results average 4% lower than the measurements for Mach numbers less than 11. For Mach numbers greater than 11, the algebraic-model turbulent CFD results average 5% higher than the three available thermocouple measurements. Surface temperature predictions from the two SST cases were consistently 3 4% higher than the algebraic-model results. The thermocouple temperatures exhibit a change in trend with Mach number at about Mach 11; this trend is not reflected in the CFD results. Because the temperature trends from the turbulent CFD simulations and the flight data diverge above Mach 11, extrapolation of the turbulent CFD accuracy to higher Mach numbers is not recommended.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lohr, J.; Harvey, R.W.; Luce, T.C.; Matsuda, Kyoko; Moeller, C.P.; Petty, C.C.; Prater, R.; James, R.A.; Giruzzi, G.; Gorelov, Y.; DeHaas, J.
1990-11-01
Electron cyclotron current drive has been demonstrated on the DIII-D tokamak in an experiment in which ∼1 MW of microwave power generated ∼50 kA of non-inductive current. The rf-generated portion was about 15% of the total current. On the T-10 tokamak, more than 3 MW of microwave power will be available for current generation, providing the possibility that all the plasma current could be maintained by this method. Fokker-Planck calculations using the code CQL3D and ray tracing calculations using TORAY have been performed to model both experiments. For DIII-D the agreement between the calculations and measurements is good, producing confidence in the validity of the computational models. The same calculations using the T-10 geometry predict that for n e (0) ∼ 1.8 x 10 13 cm -3 , and T e (0) ∼ 7 keV, 1.2 MW, that is, the power available from only three gyrotrons, could generate as much as 150 kA of non-inductive current. Parameter space scans in which temperature, density and resonance location were varied have been performed to indicate the current drive expected under different experimental conditions. The residual dc electric field was considered in the DIII-D analysis because of its nonlinear effect on the electron distribution, which complicates the interpretation of the results. A 110 GHz ECH system is being installed on DIII-D. Initial operations, planned for late 1991, will use four gyrotrons with 500 kW each and 10 second output pulses. Injection will be from the low field side from launchers which can be steered to heat at the desired location. These launchers, two of which are presently installed, are set at 20 degrees to the radial and rf current drive studies are planned for the initial operation. 8 refs., 10 figs
-
Magnetic induction strength on surface of a ferro-medium circular cylinder
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Jin
2016-09-01
Full Text Available Based on the Ampere molecular current hypothesis and the Biot–Savart law, a magnetic model on the metal magnetic memory (MMM testing of a specimen is proposed. Relation between magnetic flux leakage (MFL and magnetization of a ferro-medium circular cylinder is set up. We can predict magnetization of material according to the MFL on surface of the circular cylinder.
-
Multilayer Relaxation and Surface Energies of Metallic Surfaces
Bozzolo, Guillermo; Rodriguez, Agustin M.; Ferrante, John
1994-01-01
The perpendicular and parallel multilayer relaxations of fcc (210) surfaces are studied using equivalent crystal theory (ECT). A comparison with experimental and theoretical results is made for AI(210). The effect of uncertainties in the input parameters on the magnitudes and ordering of surface relaxations for this semiempirical method is estimated. A new measure of surface roughness is proposed. Predictions for the multilayer relaxations and surface energies of the (210) face of Cu and Ni are also included.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McGuffie, K.; Henderson-Sellers, A.
2002-01-01
Global climate model (GCM) predictions of the impact of large-scale land-use change date back to 1984 as do the earliest isotopic studies of large-basin hydrology. Despite this coincidence in interest and geography, with both papers focussed on the Amazon, there have been few studies that have tried to exploit isotopic information with the goal of improving climate model simulations of the land-surface. In this paper we analyze isotopic results from the IAEA global data base specifically with the goal of identifying signatures of potential value for improving global and regional climate model simulations of the land-surface. Evaluation of climate model predictions of the impacts of deforestation of the Amazon has been shown to be of significance by recent results which indicate impacts occurring distant from the Amazon i.e. tele-connections causing climate change elsewhere around the globe. It is suggested that these could be similar in magnitude and extent to the global impacts of ENSO events. Validation of GCM predictions associated with Amazonian deforestation are increasingly urgently required because of the additional effects of other aspects of climate change, particularly synergies occurring between forest removal and greenhouse gas increases, especially CO 2 . Here we examine three decades distributions of deuterium excess across the Amazon and use the results to evaluate the relative importance of the fractionating (partial evaporation) and non-fractionating (transpiration) processes. These results illuminate GCM scenarios of importance to the regional climate and hydrology: (i) the possible impact of increased stomatal resistance in the rainforest caused by higher levels of atmospheric CO2 [4]; and (ii) the consequences of the combined effects of deforestation and global warming on the regions climate and hydrology
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Babak. B. Naghshine
2017-02-01
Full Text Available Laser processing is one of the most popular small-scale patterning methods and has many applications in semiconductor device fabrication and biomedical engineering. Numerical modelling of this process can be used for better understanding of the process, optimization, and predicting the quality of the final product. An accurate 3D model is presented here for short laser pulses that can predict the ablation depth and temperature distribution on any section of the material in a minimal amount of time. In this transient model, variations of thermal properties, plasma shielding, and phase change are considered. Ablation depth was measured using a 3D optical profiler. Calculated depths are in good agreement with measured values on laser treated titanium surfaces. The proposed model can be applied to a wide range of materials and laser systems.
-
Hybrid Back Surface Reflector GaInAsSb Thermophotovoltaic Devices
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
RK Huang; CA Wang; MK Connors; GW Turner; M Dashiell
2004-01-01
Back surface reflectors have the potential to improve thermophotovoltaic (TPV) device performance though the recirculation of infrared photons. The ''hybrid'' back-surface reflector (BSR) TPV cell approach allows one to construct BSRs for TPV devices using conventional, high efficiency, GaInAsSb-based TPV material. The design, fabrication, and measurements of hybrid BSR-TPV cells are described. The BSR was shown to provide a 4 mV improvement in open-circuit voltage under a constant shortcircuit current, which is comparable to the 5 mV improvement theoretically predicted. Larger improvements in open-circuit voltage are expected in the future with materials improvements
-
Kirk, Ansgar Thomas; Kobelt, Tim; Spehlbrink, Hauke; Zimmermann, Stefan
2018-05-01
Corona discharge ionization sources are often used in ion mobility spectrometers (IMS) when a non-radioactive ion source with high ion currents is required. Typically, the corona discharge is followed by a reaction region where analyte ions are formed from the reactant ions. In this work, we present a simple yet sufficiently accurate model for predicting the ion current available at the end of this reaction region when operating at reduced pressure as in High Kinetic Energy Ion Mobility Spectrometers (HiKE-IMS) or most IMS-MS instruments. It yields excellent qualitative agreement with measurement results and is even able to calculate the ion current within an error of 15%. Additional interesting findings of this model are the ion current at the end of the reaction region being independent from the ion current generated by the corona discharge and the ion current in High Kinetic Energy Ion Mobility Spectrometers (HiKE-IMS) growing quadratically when scaling down the length of the reaction region. [Figure not available: see fulltext.
-
Climate modelling, uncertainty and responses to predictions of change
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Henderson-Sellers, A.
1996-01-01
Article 4.1(F) of the Framework Convention on Climate Change commits all parties to take climate change considerations into account, to the extent feasible, in relevant social, economic and environmental policies and actions and to employ methods such as impact assessments to minimize adverse effects of climate change. This could be achieved by, inter alia, incorporating climate change risk assessment into development planning processes, i.e. relating climatic change to issues of habitability and sustainability. Adaptation is an ubiquitous and beneficial natural and human strategy. Future adaptation (adjustment) to climate is inevitable at the least to decrease the vulnerability to current climatic impacts. An urgent issue is the mismatch between the predictions of global climatic change and the need for information on local to regional change in order to develop adaptation strategies. Mitigation efforts are essential since the more successful mitigation activities are, the less need there will be for adaptation responses. And, mitigation responses can be global (e.g. a uniform percentage reduction in greenhouse gas emissions) while adaptation responses will be local to regional in character and therefore depend upon confident predictions of regional climatic change. The dilemma facing policymakers is that scientists have considerable confidence in likely global climatic changes but virtually zero confidence in regional changes. Mitigation and adaptation strategies relevant to climatic change can most usefully be developed in the context of sound understanding of climate, especially the near-surface continental climate, permitting discussion of societally relevant issues. But, climate models can't yet deliver this type of regionally and locationally specific prediction and some aspects of current research even seem to indicate increased uncertainty. These topics are explored in this paper using the specific example of the prediction of land-surface climate changes
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Prakash Maran
2013-09-01
Full Text Available In this study, a comparative approach was made between artificial neural network (ANN and response surface methodology (RSM to predict the mass transfer parameters of osmotic dehydration of papaya. The effects of process variables such as temperature, osmotic solution concentration and agitation speed on water loss, weight reduction, and solid gain during osmotic dehydration were investigated using a three-level three-factor Box-Behnken experimental design. Same design was utilized to train a feed-forward multilayered perceptron (MLP ANN with back-propagation algorithm. The predictive capabilities of the two methodologies were compared in terms of root mean square error (RMSE, mean absolute error (MAE, standard error of prediction (SEP, model predictive error (MPE, chi square statistic (χ2, and coefficient of determination (R2 based on the validation data set. The results showed that properly trained ANN model is found to be more accurate in prediction as compared to RSM model.
-
Heavy-Ion Injector for the High Current Experiment
Bieniosek, F. M.; Henestroza, E.; Kwan, J. W.; Prost, L.; Seidl, P.
2001-10-01
We report on progress in development of the Heavy-Ion Injector at LBNL, which is being prepared for use as an injector for the High Current Experiment (HCX). It is composed of a 10-cm-diameter surface ionization source, an extraction diode, and an electrostatic quadrupole (ESQ) accelerator, with a typical operating current of 0.6 A of potassium ions at 1.8 MeV, and a beam pulse length of 4.5 microsecs. We have improved the Injector equipment and diagnostics, and have characterized the source emission and radial beam profiles at the diode and ESQ regions. We find improved agreement with EGUN predictions, and improved compatibility with the downstream matching section. Plans are to attach the matching section and the initial ESQ transport section of HCX. Results will be presented and compared with EGUN and WARP simulations.
-
Alzahrani, Majed; Alsolami, Fawaz; Chikalov, Igor; Algharbi, Salem; Aboudi, Faisal; Khudiri, Musab
2016-01-01
Disclosed are various embodiments for a prediction application to predict a stuck pipe. A linear regression model is generated from hook load readings at corresponding bit depths. A current hook load reading at a current bit depth is compared with a normal hook load reading from the linear regression model. A current hook load greater than a normal hook load for a given bit depth indicates the likelihood of a stuck pipe.
-
Alzahrani, Majed
2016-03-10
Disclosed are various embodiments for a prediction application to predict a stuck pipe. A linear regression model is generated from hook load readings at corresponding bit depths. A current hook load reading at a current bit depth is compared with a normal hook load reading from the linear regression model. A current hook load greater than a normal hook load for a given bit depth indicates the likelihood of a stuck pipe.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Carlson, Daniel Frazier
2015-01-01
The Institute of Marine Sciences (ISMAR) of the National Research Council of Italy (CNR) established a High Frequency (HF) Coastal Radar Network for the measurement of the velocity of surface currents in coastal seas. The network consists of four HF radar systems located on the coast of the Gargano...... Promontory (Southern Adriatic, Italy). The network has been operational since May 2013 and covers an area of approximately 1700 square kilometers in the Gulf of Manfredonia. Quality Assessment (QA) procedures are applied for the systems deployment and maintenance and Quality Control (QC) procedures...
-
Gálvez, Rosa; Musella, Vicenzo; Descalzo, Miguel A; Montoya, Ana; Checa, Rocío; Marino, Valentina; Martín, Oihane; Cringoli, Giuseppe; Rinaldi, Laura; Miró, Guadalupe
2017-09-19
The cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis, is the most prevalent flea species detected on dogs and cats in Europe and other world regions. The status of flea infestation today is an evident public health concern because of their cosmopolitan distribution and the flea-borne diseases transmission. This study determines the spatial distribution of the cat flea C. felis infesting dogs in Spain. Using geospatial tools, models were constructed based on entomological data collected from dogs during the period 2013-2015. Bioclimatic zones, covering broad climate and vegetation ranges, were surveyed in relation to their size. The models builded were obtained by negative binomial regression of several environmental variables to show impacts on C. felis infestation prevalence: land cover, bioclimatic zone, mean summer and autumn temperature, mean summer rainfall, distance to urban settlement and normalized difference vegetation index. In the face of climate change, we also simulated the future distributions of C. felis for the global climate model (GCM) "GFDL-CM3" and for the representative concentration pathway RCP45, which predicts their spread in the country. Predictive models for current climate conditions indicated the widespread distribution of C. felis throughout Spain, mainly across the central northernmost zone of the mainland. Under predicted conditions of climate change, the risk of spread was slightly greater, especially in the north and central peninsula, than for the current situation. The data provided will be useful for local veterinarians to design effective strategies against flea infestation and the pathogens transmitted by these arthropods.
-
Improving NOAA's NWLON Through Enhanced Data Inputs from NASA's Ocean Surface Topography
Guest, DeNeice C.
2010-01-01
This report assesses the benefit of incorporating NASA's OSTM (Ocean Surface Topography Mission) altimeter data (C- and Ku-band) into NOAA's (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) NWLON (National Water Level Observation Network) DSS (Decision Support System). This data will enhance the NWLON DSS by providing additional inforrnation because not all stations collect all meteorological parameters (sea-surface height, ocean tides, wave height, and wind speed over waves). OSTM will also provide data where NWLON stations are not present. OSTM will provide data on seasurface heights for determining sea-level rise and ocean circulation. Researchers and operational users currently use satellite altimeter data products with the GSFCOO NASA data model to obtain sea-surface height and ocean circulation inforrnation. Accurate and tirnely inforrnation concerning sea-level height, tide, and ocean currents is needed to irnprove coastal tidal predictions, tsunarni and storm surge warnings, and wetland restoration.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
2000-04-01
This was a detailed plan after fiscal year 2000 on the first stage of the Research stage at investigating prediction from ground surface' in three researches carried out at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) according to the 'Basic plan on research of underground science at MIU', based on progress of investigation and research before fiscal year 1999. This project contains following three items as its general targets; establishment of general investigating techniques for geological environment, collection of informations on deep underground environment, and development on foundation of engineering technology at super-deep underground. And, targets at investigating prediction stage from ground surface contain acquisition of geological environment data through investigations from ground surface to predict changes of the environment accompanied with underground geological environment and construction of experimental tunnel, to determine evaluating method on prediction results, and to determine plannings of an investigating stage accompanied with excavation of the tunnel by carrying out detail design of the tunnel. Here were introduced about results and problems on the investigation of the first phase, the integration of investigating results, and the investigation and researches on geology/geological structure, hydrology and geochemistry of groundwater, mechanical properties of rocks, and the mass transfer. (G.K.)
-
Choi, Byoung-Ju; Cho, Seong Hun; Jung, Hee Seok; Lee, Sang-Ho; Byun, Do-Seong; Kwon, Kyungman
2018-03-01
The interannual variation of surface ocean currents can be as large as seasonal variation in the Japan/East Sea (JES). To identify the major factors that cause such interannual variability of surface ocean circulation in the JES, surface circulation was simulated from 1998 to 2009 using a three-dimensional model. Contributions of atmospheric forcing (ATM), open boundary data (OBC), and intrinsic variability (ITV) of the surface flow in the JES on the interannual variability of surface ocean circulation were separately examined using numerical simulations. Variability in surface circulation was quantified in terms of variance in sea surface height, 100-m depth water temperature, and surface currents. ITV was found to be the dominant factor that induced interannual variabilities of surface circulation, the main path of the East Korea Warm Current (EKWC), and surface kinetic energy on a time scale of 2-4 years. OBC and ATM were secondary factors contributing to the interannual variation of surface circulation. Interannual variation of ATM changed the separation latitude of EKWC and increased the variability of surface circulation in the Ulleung Basin. Interannual variation of OBC enhanced low-frequency changes in surface circulation and eddies in the Yamato Basin. It also modulated basin-wide uniform oscillations of sea level. This study suggests that precise estimation of initial conditions using data assimilation is essential for long-term prediction of surface circulation in the JES.
-
Snedden, Gregg A.; Steyer, Gregory D.
2013-02-01
Understanding plant community zonation along estuarine stress gradients is critical for effective conservation and restoration of coastal wetland ecosystems. We related the presence of plant community types to estuarine hydrology at 173 sites across coastal Louisiana. Percent relative cover by species was assessed at each site near the end of the growing season in 2008, and hourly water level and salinity were recorded at each site Oct 2007-Sep 2008. Nine plant community types were delineated with k-means clustering, and indicator species were identified for each of the community types with indicator species analysis. An inverse relation between salinity and species diversity was observed. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) effectively segregated the sites across ordination space by community type, and indicated that salinity and tidal amplitude were both important drivers of vegetation composition. Multinomial logistic regression (MLR) and Akaike's Information Criterion (AIC) were used to predict the probability of occurrence of the nine vegetation communities as a function of salinity and tidal amplitude, and probability surfaces obtained from the MLR model corroborated the CCA results. The weighted kappa statistic, calculated from the confusion matrix of predicted versus actual community types, was 0.7 and indicated good agreement between observed community types and model predictions. Our results suggest that models based on a few key hydrologic variables can be valuable tools for predicting vegetation community development when restoring and managing coastal wetlands.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
T. Aly Saandy
2015-08-01
Full Text Available Abstract This article presents to an analytical calculation methodology of the Steinmetz coefficient applied to the prediction of Eddy current loss in a single-phase transformer. Based on the electrical circuit theory the active power consumed by the core is expressed analytically in function of the electrical parameters as resistivity and the geometrical dimensions of the core. The proposed modeling approach is established with the duality parallel series. The required coefficient is identified from the empirical Steinmetz data based on the experimented active power expression. To verify the relevance of the model validations both by simulations with two in two different frequencies and measurements were carried out. The obtained results are in good agreement with the theoretical approach and the practical results.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Fallah Ardashir
2017-06-01
Full Text Available This paper proposes a new single phase transformerless Photovoltaic (PV inverter for grid connected systems. It consists of six power switches, two diodes, one capacitor and filter at the output stage. The neutral of the grid is directly connected to the negative terminal of the source. This results in constant common mode voltage and zero leakage current. Model Predictive Controller (MPC technique is used to modulate the converter to reduce the output current ripple and filter requirements. The main advantages of this inverter are compact size, low cost, flexible grounding configuration. Due to brevity, the operating principle and analysis of the proposed circuit are presented in brief. Simulation and experimental results of 200W prototype are shown at the end to validate the proposed topology and concept. The results obtained clearly verifies the performance of the proposed inverter and its practical application for grid connected PV systems.
-
A Bingham-plastic model for fluid mud transport under waves and currents
Liu, Chun-rong; Wu, Bo; Huhe, Ao-de
2014-04-01
Simplified equations of fluid mud motion, which is described as Bingham-Plastic model under waves and currents, are presented by order analysis. The simplified equations are non-linear ordinary differential equations which are solved by hybrid numerical-analytical technique. As the computational cost is very low, the effects of wave current parameters and fluid mud properties on the transportation velocity of the fluid mud are studied systematically. It is found that the fluid mud can move toward one direction even if the shear stress acting on the fluid mud bed is much smaller than the fluid mud yield stress under the condition of wave and current coexistence. Experiments of the fluid mud motion under current with fluctuation water surface are carried out. The fluid mud transportation velocity predicted by the presented mathematical model can roughly match that measured in experiments.
-
Using reweighting and free energy surface interpolation to predict solid-solid phase diagrams
Schieber, Natalie P.; Dybeck, Eric C.; Shirts, Michael R.
2018-04-01
Many physical properties of small organic molecules are dependent on the current crystal packing, or polymorph, of the material, including bioavailability of pharmaceuticals, optical properties of dyes, and charge transport properties of semiconductors. Predicting the most stable crystalline form at a given temperature and pressure requires determining the crystalline form with the lowest relative Gibbs free energy. Effective computational prediction of the most stable polymorph could save significant time and effort in the design of novel molecular crystalline solids or predict their behavior under new conditions. In this study, we introduce a new approach using multistate reweighting to address the problem of determining solid-solid phase diagrams and apply this approach to the phase diagram of solid benzene. For this approach, we perform sampling at a selection of temperature and pressure states in the region of interest. We use multistate reweighting methods to determine the reduced free energy differences between T and P states within a given polymorph and validate this phase diagram using several measures. The relative stability of the polymorphs at the sampled states can be successively interpolated from these points to create the phase diagram by combining these reduced free energy differences with a reference Gibbs free energy difference between polymorphs. The method also allows for straightforward estimation of uncertainties in the phase boundary. We also find that when properly implemented, multistate reweighting for phase diagram determination scales better with the size of the system than previously estimated.
-
Using Google Earth Surface Metrics to Predict Plant Species Richness in a Complex Landscape
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sebastián Block
2016-10-01
Full Text Available Google Earth provides a freely available, global mosaic of high-resolution imagery from different sensors that has become popular in environmental and ecological studies. However, such imagery lacks the near-infrared band often used in studying vegetation, thus its potential for estimating vegetation properties remains unclear. In this study, we assess the potential of Google Earth imagery to describe and predict vegetation attributes. Further, we compare it to the potential of SPOT imagery, which has additional spectral information. We measured basal area, vegetation height, crown cover, density of individuals, and species richness in 60 plots in the oak forests of a complex volcanic landscape in central Mexico. We modelled each vegetation attribute as a function of surface metrics derived from Google Earth and SPOT images, and selected the best-supported linear models from each source. Total species richness was the best-described and predicted variable: the best Google Earth-based model explained nearly as much variation in species richness as its SPOT counterpart (R2 = 0.44 and 0.51, respectively. However, Google Earth metrics emerged as poor predictors of all remaining vegetation attributes, whilst SPOT metrics showed potential for predicting vegetation height. We conclude that Google Earth imagery can be used to estimate species richness in complex landscapes. As it is freely available, Google Earth can broaden the use of remote sensing by researchers and managers in low-income tropical countries where most biodiversity hotspots are found.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Minero, C.; Lauri, V.; Maurino, V.; Pelizzetti, E.; Vione, D.
2007-01-01
A model was developed to predict the steady-state [·OH] in the surface layer of natural waters as a function of nitrate, inorganic carbon (IC) and dissolved organic matter (DOM). The parameter values were studied in the range detected in shallow high-mountain lakes, to which the model results are most relevant. Calculations indicate that [·OH] increases with increasing nitrate and decreasing IC, and conditions are also identified where [·OH] is directly proportional, inversely proportional or independent of DOM. Based on the model results it is possible to predict the half-life time, due to reaction with ·OH, of given dissolved compounds, including organic pollutants, from the water composition data
-
Resonances and surface waves in bounded plasmas
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bowers, K.J.; Qui, D.W.; Smith, H.B.; Birdsall, C.K.
1999-01-01
Surface waves provide a promising means of creating large, area plasmas. These waves can uniformly distribute the excitation energy and while presenting a small resistance and zero reactance to the driving source. Experimentally and in the simulations, the electron temperature is low (like 1--3 eV) as is the plasma potential (like 10 Te). The use of surface waves experimentally, and now industrially, to sustain large area plasma sources with device size is comparable to free space wavelength have motivated the authors to refine the theories of [1] and [2] to be fully electromagnetic. The wave dispersion predicted by the electromagnetic theory differs from the predictions of the prior theories and the results illuminate limitations of the electrostatic model. The use of surface waves have also motivated them to explore the mechanisms by which surface waves heat the plasma. In the 1d electrostatic simulations high velocity electron bunches are formed in the sheaths and are alternatively accelerated from each sheath into the bulk plasma each RF cycle. They speculate similar mechanisms provide the ionization in surface wave discharges. They also see in these simulations the plasma makes an abrupt transition from capacitively coupled to resistively coupled and the series resonance locks onto the drive frequency; these abrupt transitions resemble mode-jumping seen experimentally in large area sources. Furthermore, the density profile of the plasma tracks the drive frequency while in the resonant mode giving a new mechanism by which the plasma parameters can be controlled. They are currently investigating the effect of the driving electrode shape has on these resonances and conducting 2d simulations of a large area surface wave source to explore the ignition of surface wave devices and how the plasma fills in the device
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jenkins, Thomas G.; Schnack, Dalton D.; Kruger, Scott E.; Hegna, C. C.; Sovinec, Carl R.
2010-01-01
A model which incorporates the effects of electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) into the magnetohydrodynamic equations is implemented in the NIMROD code [C. R. Sovinec et al., J. Comput. Phys. 195, 355 (2004)] and used to investigate the effect of ECCD injection on the stability, growth, and dynamical behavior of magnetic islands associated with resistive tearing modes. In addition to qualitatively and quantitatively agreeing with numerical results obtained from the inclusion of localized ECCD deposition in static equilibrium solvers [A. Pletzer and F. W. Perkins, Phys. Plasmas 6, 1589 (1999)], predictions from the model further elaborate the role which rational surface motion plays in these results. The complete suppression of the (2,1) resistive tearing mode by ECCD is demonstrated and the relevant stabilization mechanism is determined. Consequences of the shifting of the mode rational surface in response to the injected current are explored, and the characteristic short-time responses of resistive tearing modes to spatial ECCD alignments which are stabilizing are also noted. We discuss the relevance of this work to the development of more comprehensive predictive models for ECCD-based mitigation and control of neoclassical tearing modes.
-
Deane, R. P.; Obreschkow, D.; Heywood, I.
2015-09-01
Strong gravitational lensing provides some of the deepest views of the Universe, enabling studies of high-redshift galaxies only possible with next-generation facilities without the lensing phenomenon. To date, 21-cm radio emission from neutral hydrogen has only been detected directly out to z ˜ 0.2, limited by the sensitivity and instantaneous bandwidth of current radio telescopes. We discuss how current and future radio interferometers such as the Square Kilometre Array (SKA) will detect lensed H I emission in individual galaxies at high redshift. Our calculations rely on a semi-analytic galaxy simulation with realistic H I discs (by size, density profile and rotation), in a cosmological context, combined with general relativistic ray tracing. Wide-field, blind H I surveys with the SKA are predicted to be efficient at discovering lensed H I systems, increasingly so at z ≳ 2. This will be enabled by the combination of the magnification boosts, the steepness of the H I luminosity function at the high-mass end, and the fact that the H I spectral line is relatively isolated in frequency. These surveys will simultaneously provide a new technique for foreground lens selection and yield the highest redshift H I emission detections. More near term (and existing) cm-wave facilities will push the high-redshift H I envelope through targeted surveys of known lenses.