
Sample records for stratospheric mountain waves
-
Xu, Xin; Tang, Ying; Wang, Yuan; Xue, Ming
2018-03-01
The directional absorption of mountain waves in the Northern Hemisphere is assessed by examination of horizontal wind rotation using the 2.5° × 2.5° European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts ERA-Interim reanalysis between 2011 and 2016. In the deep layer of troposphere and stratosphere, the horizontal wind rotates by more than 120° all over the Northern Hemisphere primary mountainous areas, with the rotation mainly occurring in the troposphere (stratosphere) of lower (middle to high) latitudes. The rotation of tropospheric wind increases markedly in summer over the Tibetan Plateau and Iranian Plateau, due to the influence of Asian summer monsoonal circulation. The influence of directional absorption of mountain waves on the mountain wave momentum transport is also studied using a new parameterization scheme of orographic gravity wave drag (OGWD) which accounts for the effect of directional wind shear. Owing to the directional absorption, the wave momentum flux is attenuated by more than 50% in the troposphere of lower latitudes, producing considerable orographic gravity wave lift which is normal to the mean wind. Compared with the OGWD produced in traditional schemes assuming a unidirectional wind profile, the OGWD in the new scheme is suppressed in the lower stratosphere but enhanced in the upper stratosphere and lower mesosphere. This is because the directional absorption of mountain waves in the troposphere reduces the wave amplitude in the stratosphere. Consequently, mountain waves are prone to break at higher altitudes, which favors the production of stronger OGWD given the decrease of air density with height.
-
ST radar observations of atmospheric waves over mountainous areas: a review
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Röttger
2000-07-01
Full Text Available Lee and mountain waves are dominant dynamic processes in the atmosphere above mountain areas. ST VHF radars had been intensively used to investigate these wave processes. These studies are summarized in this work. After discussing features of long-period quasi-stationary lee waves, attention is drawn to the frequent occurrence of freely propagating waves of shorter periods, which seem to be more common and characteristic for wave processes generated over mountainous areas. Characteristics of these waves such as their relation to the topography and background winds, the possibility of trapping by and breaking in the tropopause region and their propagation into the stratosphere is investigated. These orographically produced waves transport energy and momentum into the troposphere and stratosphere, which is considered an important contribution to the kinetic energy of the lower atmosphere. The occurrence of inertia-gravity waves in the stratosphere had been confused with lee waves, which is discussed in conclusion. Finally further questions on mountain and lee waves are drawn up, which remain to be solved and where investigations with ST radars could play a fundamental role.Key words: Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (Middle atmosphere dynamics; Waves and tides; Instruments and techniques
-
Eckermann, S. D.; Wu, D. L.
2012-01-01
Orographic gravity-wave (OGW) parameterizations in models produce waves over subtropical mountain ranges in Australia and Africa that propagate into the stratosphere during austral winter and deposit momentum, affecting weather and climate. Satellite sensors have measured stratospheric GWs for over a decade, yet find no evidence of these waves. So are parameterizations failing here? Here we argue that the short wavelengths of subtropical OGWs place them near or below the detection limits of satellite sensors. To test this hypothesis, we reanalyze nine years of stratospheric radiances from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) on NASA's Aqua satellite during austral winter, applying new averaging techniques to maximize signal-to-noise and improve thresholds for OGW detection. Deep climatological enhancements in stratospheric OGW variance over specific mountain ranges in Australia and southern Africa are revealed for the first time, which exhibit temporal and vertical variations consistent with predicted OGW responses to varying background winds.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Dörnbrack
2012-04-01
Full Text Available The relatively warm 2009–2010 Arctic winter was an exceptional one as the North Atlantic Oscillation index attained persistent extreme negative values. Here, selected aspects of the Arctic stratosphere during this winter inspired by the analysis of the international field experiment RECONCILE are presented. First of all, and as a kind of reference, the evolution of the polar vortex in its different phases is documented. Special emphasis is put on explaining the formation of the exceptionally cold vortex in mid winter after a sequence of stratospheric disturbances which were caused by upward propagating planetary waves. A major sudden stratospheric warming (SSW occurring near the end of January 2010 concluded the anomalous cold vortex period. Wave ice polar stratospheric clouds were frequently observed by spaceborne remote-sensing instruments over the Arctic during the cold period in January 2010. Here, one such case observed over Greenland is analysed in more detail and an attempt is made to correlate flow information of an operational numerical weather prediction model to the magnitude of the mountain-wave induced temperature fluctuations. Finally, it is shown that the forecasts of the ECMWF ensemble prediction system for the onset of the major SSW were very skilful and the ensemble spread was very small. However, the ensemble spread increased dramatically after the major SSW, displaying the strong non-linearity and internal variability involved in the SSW event.
-
A global climatology of stratospheric gravity waves from Atmospheric Infrared Sounder observations
Hoffmann, Lars; Xue, Xianghui; Alexander, M. Joan
2014-05-01
We present the results of a new study that aims on the detection and classification of `hotspots' of stratospheric gravity waves on a global scale. The analysis is based on a nine-year record (2003 to 2011) of radiance measurements by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) aboard NASA's Aqua satellite. We detect the presence of stratospheric gravity waves based on 4.3 micron brightness temperature variances. Our method is optimized for peak events, i.e., strong gravity wave events for which the local variance considerably exceeds background levels. We estimated the occurrence frequencies of these peak events for different seasons and time of day and used the results to find local maxima of gravity wave activity. In addition, we use AIRS radiances at 8.1 micron to simultaneously detect convective events, including deep convection in the tropics and mesoscale convective systems at mid latitudes. We classified the gravity waves according to their sources, based on seasonal occurrence frequencies for convection and by means of topographic data. Our study reproduces well-known hotspots of gravity waves, e.g., the mountain wave hotspots at the Andes and the Antarctic Peninsula or the convective hotspot during the thunderstorm season over the North American Great Plains. However, the high horizontal resolution of the AIRS observations also helped us to locate several smaller hotspots, which were partly unknown or poorly studied so far. Most of these smaller hotspots are found near orographic features like small mountain ranges, in coastal regions, in desert areas, or near isolated islands. This new study will help to select the most promising regions and seasons for future observational studies of gravity waves. Reference: Hoffmann, L., X. Xue, and M. J. Alexander, A global view of stratospheric gravity wave hotspots located with Atmospheric Infrared Sounder observations, J. Geophys. Res., 118, 416-434, doi:10.1029/2012JD018658, 2013.
-
Imaging gravity waves in lower stratospheric AMSU-A radiances, Part 2: Validation case study
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. D. Eckermann
2006-01-01
Full Text Available Two-dimensional radiance maps from Channel 9 (~60–90 hPa of the Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU-A, acquired over southern Scandinavia on 14 January 2003, show plane-wave-like oscillations with a wavelength λh of ~400–500 km and peak brightness temperature amplitudes of up to 0.9 K. The wave-like pattern is observed in AMSU-A radiances from 8 overpasses of this region by 4 different satellites, revealing a growth in the disturbance amplitude from 00:00 UTC to 12:00 UTC and a change in its horizontal structure between 12:00 UTC and 20:00 UTC. Forecast and hindcast runs for 14 January 2003 using high-resolution global and regional numerical weather prediction (NWP models generate a lower stratospheric mountain wave over southern Scandinavia with peak 90 hPa temperature amplitudes of ~5–7 K at 12:00 UTC and a similar horizontal wavelength, packet width, phase structure and time evolution to the disturbance observed in AMSU-A radiances. The wave's vertical wavelength is ~12 km. These NWP fields are validated against radiosonde wind and temperature profiles and airborne lidar profiles of temperature and aerosol backscatter ratios acquired from the NASA DC-8 during the second SAGE III Ozone Loss and Validation Experiment (SOLVE II. Both the amplitude and phase of the stratospheric mountain wave in the various NWP fields agree well with localized perturbation features in these suborbital measurements. In particular, we show that this wave formed the type II polar stratospheric clouds measured by the DC-8 lidar. To compare directly with the AMSU-A data, we convert these validated NWP temperature fields into swath-scanned brightness temperatures using three-dimensional Channel 9 weighting functions and the actual AMSU-A scan patterns from each of the 8 overpasses of this region. These NWP-based brightness temperatures contain two-dimensional oscillations due to this resolved stratospheric mountain wave that have an amplitude, wavelength
-
Intercomparison of AIRS and HIRDLS stratospheric gravity wave observations
Meyer, Catrin I.; Ern, Manfred; Hoffmann, Lars; Trinh, Quang Thai; Alexander, M. Joan
2018-01-01
We investigate stratospheric gravity wave observations by the Atmospheric InfraRed Sounder (AIRS) aboard NASA's Aqua satellite and the High Resolution Dynamics Limb Sounder (HIRDLS) aboard NASA's Aura satellite. AIRS operational temperature retrievals are typically not used for studies of gravity waves, because their vertical and horizontal resolution is rather limited. This study uses data of a high-resolution retrieval which provides stratospheric temperature profiles for each individual satellite footprint. Therefore the horizontal sampling of the high-resolution retrieval is 9 times better than that of the operational retrieval. HIRDLS provides 2-D spectral information of observed gravity waves in terms of along-track and vertical wavelengths. AIRS as a nadir sounder is more sensitive to short-horizontal-wavelength gravity waves, and HIRDLS as a limb sounder is more sensitive to short-vertical-wavelength gravity waves. Therefore HIRDLS is ideally suited to complement AIRS observations. A calculated momentum flux factor indicates that the waves seen by AIRS contribute significantly to momentum flux, even if the AIRS temperature variance may be small compared to HIRDLS. The stratospheric wave structures observed by AIRS and HIRDLS often agree very well. Case studies of a mountain wave event and a non-orographic wave event demonstrate that the observed phase structures of AIRS and HIRDLS are also similar. AIRS has a coarser vertical resolution, which results in an attenuation of the amplitude and coarser vertical wavelengths than for HIRDLS. However, AIRS has a much higher horizontal resolution, and the propagation direction of the waves can be clearly identified in geographical maps. The horizontal orientation of the phase fronts can be deduced from AIRS 3-D temperature fields. This is a restricting factor for gravity wave analyses of limb measurements. Additionally, temperature variances with respect to stratospheric gravity wave activity are compared on a
-
Intercomparison of AIRS and HIRDLS stratospheric gravity wave observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. I. Meyer
2018-01-01
Full Text Available We investigate stratospheric gravity wave observations by the Atmospheric InfraRed Sounder (AIRS aboard NASA's Aqua satellite and the High Resolution Dynamics Limb Sounder (HIRDLS aboard NASA's Aura satellite. AIRS operational temperature retrievals are typically not used for studies of gravity waves, because their vertical and horizontal resolution is rather limited. This study uses data of a high-resolution retrieval which provides stratospheric temperature profiles for each individual satellite footprint. Therefore the horizontal sampling of the high-resolution retrieval is 9 times better than that of the operational retrieval. HIRDLS provides 2-D spectral information of observed gravity waves in terms of along-track and vertical wavelengths. AIRS as a nadir sounder is more sensitive to short-horizontal-wavelength gravity waves, and HIRDLS as a limb sounder is more sensitive to short-vertical-wavelength gravity waves. Therefore HIRDLS is ideally suited to complement AIRS observations. A calculated momentum flux factor indicates that the waves seen by AIRS contribute significantly to momentum flux, even if the AIRS temperature variance may be small compared to HIRDLS. The stratospheric wave structures observed by AIRS and HIRDLS often agree very well. Case studies of a mountain wave event and a non-orographic wave event demonstrate that the observed phase structures of AIRS and HIRDLS are also similar. AIRS has a coarser vertical resolution, which results in an attenuation of the amplitude and coarser vertical wavelengths than for HIRDLS. However, AIRS has a much higher horizontal resolution, and the propagation direction of the waves can be clearly identified in geographical maps. The horizontal orientation of the phase fronts can be deduced from AIRS 3-D temperature fields. This is a restricting factor for gravity wave analyses of limb measurements. Additionally, temperature variances with respect to stratospheric gravity wave activity are
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Joel Arnault
2012-02-01
Full Text Available Gravity waves generated by the Vestfjella Mountains (in western Droning Maud Land, Antarctica, southwest of the Finnish/Swedish Aboa/Wasa station have been observed with the Moveable atmospheric radar for Antarctica (MARA during the SWEDish Antarctic Research Programme (SWEDARP in December 2007/January 2008. These radar observations are compared with a 2-month Weather Research Forecast (WRF model experiment operated at 2 km horizontal resolution. A control simulation without orography is also operated in order to separate unambiguously the contribution of the mountain waves on the simulated atmospheric flow. This contribution is then quantified with a kinetic energy budget analysis computed in the two simulations. The results of this study confirm that mountain waves reaching lower-stratospheric heights break through convective overturning and generate inertia gravity waves with a smaller vertical wavelength, in association with a brief depletion of kinetic energy through frictional dissipation and negative vertical advection. The kinetic energy budget also shows that gravity waves have a strong influence on the other terms of the budget, i.e. horizontal advection and horizontal work of pressure forces, so evaluating the influence of gravity waves on the mean-flow with the vertical advection term alone is not sufficient, at least in this case. We finally obtain that gravity waves generated by the Vestfjella Mountains reaching lower stratospheric heights generally deplete (create kinetic energy in the lower troposphere (upper troposphere–lower stratosphere, in contradiction with the usual decelerating effect attributed to gravity waves on the zonal circulation in the upper troposphere–lower stratosphere.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Leutbecher, M. [DLR Deutsches Zentrum fuer Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., Wessling (Germany). Inst. fuer Physik der Atmosphaere
1998-07-01
Flow over mountains in the stably stratified atmosphere excites gravity waves. The three-dimensional propagation of these waves into the stratosphere is studied using linear theority as well as idealized and realistic numerical simulations. Stagnation, momentum fluxes and temperature anomalies are analyzed for idealized types of flow. Isolated mountains with elliptical contours are considered. The unperturbed atmosphere has constant wind speed and constant static stability or two layers (troposphere/stratosphere) of constant stability each. Real flow over orography is investigated where gravity waves in the stratosphere have been observed. Characteristics of the gravity wave event over the southern tip of Greenland on 6 January 1992 were recorded on a flight of the ER-2 at an altitude of 20 km. In the second case polar stratospheric clouds (PSC) were observed by an airborne Lidar over Northern Scandinavia on 9 January 1997. The PSC were induced by temperature anomalies in orographic gravity waves. (orig.)
-
On the role of the stratosphere in the process of overflow of mesoscale mountains
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
K. B. Moiseenko
2005-12-01
Full Text Available A 2-D, two- and three-layer stratified airflow over a mountain of arbitrary shape is considered on the assumptions that upstream wind velocity and static stability within each layer are constant (Long's model. The stratosphere is simulated by an infinitely deep upper layer with enhanced static stability.
The analytical solution for the stream function, as well as first (linear and second order approximations to the wave drag, are obtained in hydrostatic limit N1L/U0→∞, where N1 is the Brunt-Väsälä frequency in the troposphere, L is a characteristic length of the obstacle, and U0 is upstream velocity. The results of numerical computations show the principal role of long waves in the process of interaction between the model layers for a typical mesoscale mountains for which the hydrostatic approximation proves valid in a wide range of flow parameters, in accordance with the earlier conclusions of Klemp and Lilly (1975. Partial reflection of wave energy from the tropopause produces strong influence on the value of wave drag for typical middle and upper tropospheric lapse rates, leading to a quasi-periodic dependance of wave drag on a reduced frequency
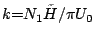 (
(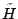 is tropopause height in the troposphere. The flow seems to be statically unstable for k≥2 for sufficiently large obstacles (whose height exceeds 1 km. In this case, vast regions of rotor motions and strong turbulence are predicted from model calculations in the middle troposphere and the lower stratosphere. The model calculations also point to a testify
is tropopause height in the troposphere. The flow seems to be statically unstable for k≥2 for sufficiently large obstacles (whose height exceeds 1 km. In this case, vast regions of rotor motions and strong turbulence are predicted from model calculations in the middle troposphere and the lower stratosphere. The model calculations also point to a testify -
Equatorial waves in the stratosphere of Uranus
Hinson, David P.; Magalhaes, Julio A.
1991-01-01
Analyses of radio occultation data from Voyager 2 have led to the discovery and characterization of an equatorial wave in the Uranus stratosphere. The observed quasi-periodic vertical atmospheric density variations are in close agreement with theoretical predictions for a wave that propagates vertically through the observed background structure of the stratosphere. Quantitative comparisons between measurements obtained at immersion and at emersion yielded constraints on the meridional and zonal structure of the wave; the fact that the two sets of measurements are correlated suggests a wave of planetary scale. Two equatorial wave models are proposed for the wave.
-
Detailed modeling of mountain wave PSCs
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Fueglistaler
2003-01-01
Full Text Available Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs play a key role in polar ozone depletion. In the Arctic, PSCs can occur on the mesoscale due to orographically induced gravity waves. Here we present a detailed study of a mountain wave PSC event on 25-27 January 2000 over Scandinavia. The mountain wave PSCs were intensively observed by in-situ and remote-sensing techniques during the second phase of the SOLVE/THESEO-2000 Arctic campaign. We use these excellent data of PSC observations on 3 successive days to analyze the PSCs and to perform a detailed comparison with modeled clouds. We simulated the 3-dimensional PSC structure on all 3 days with a mesoscale numerical weather prediction (NWP model and a microphysical box model (using best available nucleation rates for ice and nitric acid trihydrate particles. We show that the combined mesoscale/microphysical model is capable of reproducing the PSC measurements within the uncertainty of data interpretation with respect to spatial dimensions, temporal development and microphysical properties, without manipulating temperatures or using other tuning parameters. In contrast, microphysical modeling based upon coarser scale global NWP data, e.g. current ECMWF analysis data, cannot reproduce observations, in particular the occurrence of ice and nitric acid trihydrate clouds. Combined mesoscale/microphysical modeling may be used for detailed a posteriori PSC analysis and for future Arctic campaign flight and mission planning. The fact that remote sensing alone cannot further constrain model results due to uncertainities in the interpretation of measurements, underlines the need for synchronous in-situ PSC observations in campaigns.
-
Lubis, S. W.; Nakamura, N.
2017-12-01
Previous studies have shown that the monsoonal circulation plays an important role in planetary wave breaking (PWB). The highest frequency of breaking events occurs just downstream (east) of the monsoon region in summer. PWB induces mixing of potential vorticity (PV) and hence, alter the horizontal mixing in the atmosphere. Here, the authors hypothesize that the stratospheric easterlies in the boreal summer also play a significant role in the PWB and mixing associated with the summer monsoon. If the stratospheric winds were westerly in boreal summer, the frequency of PWB would be decreased due to more waves penetrating in the stratosphere, resulting in less horizontal PWB and thus reduced mixing in the subtropical tropopause region. The hypothesis is examined by using a set of idealized moist GFDL simulations. The monsoon circulation is produced by adding a land-sea contrast with a Gaussian-shaped mountains positioned in the midlatitudes. Other key ingredients for the monsoon, including albedo, oceanic warm pool, and Q-flux, were also ideally imposed in all simulations. Our control simulation produces a summer monsoon-like circulation similar to the observation. In particular, the thermally forced monsoonal circulation forms a prominent closed upper-level anticyclone that dominates the summertime upper-level flow. Associated with this circulation is an upward-bulging tropopause that forms a large reservoir of anomalously low PV. Consistent with previous studies, the well-defined tropospheric jet lies just poleward of the upper-level anticyclone, and acts as a dynamical barrier between the low-PV reservoir over the monsoonal region and the high-PV reservoir in the extratropics. This barrier disappears just northeast of the monsoon area in the jet exit region, allowing more quasi-planetary waves to break in this region. Repetitive wave breaking further weakens the PV gradient, leading to the formation of the surf zone and stronger mixing in this region. To quantify
-
Zhao, J.; Geraghty, I.; Chu, X.; Vadas, S.; Becker, E.; Harvey, V. L.; Jones, R. M.; Chen, C.; Lu, X.
2017-12-01
After Antarctic persistent gravity waves (GWs) in the Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere (MLT) were discovered from lidar observations [Chen et al., 2013, 2016], secondary wave generation theory was proposed to explain the source. Here we perform a source investigation of such persistent GWs through analyzing both stratospheric and MLT GWs at McMurdo using temperature measurements (30 - 50 km, year 2011 - 2015) obtained by Fe Boltzmann lidar. In the stratosphere, GW vertical wavelengths (λ) and periods exhibit seasonal cycles with winter maxima and summer minima, which linearly correlated with mean zonal wind velocities. GWs dissipate more in winter than in summer due to larger wave amplitudes. The potential energy density (Ep) are anti-correlated with wind rotation angles but positively correlated with surface and stratospheric winds. Critical level filtering, in-situ generation of GWs, and wave saturation changes play roles in Ep seasonal variations (winter maxima and summer minima). The large increase of Ep from summer to winter possibly results from the decrease in critical level filtering. The gradual variations of Ep from Mar to Oct are likely related both to the increased λ towards winter, allowing larger wave amplitudes before saturation, and to in-situ GW generation via geostrophic adjustment, secondary GW generation. Large Ep occur when McMurdo is inside the jet stream core 5-24º poleward from vortex edge. In winter MLT, the persistent GWs cause larger temperature perturbations (± 30 K, compared to ± 10 K in the stratosphere) with longer λ (23.5 km) and larger vertical phase speeds (1.8 m/s). More waves (95.4%) show downward phase progression compared to the stratospheric GWs (70.4%). Since the inferred horizontal wavelength of stratospheric GWs (350 - 450 km) are much shorter than those of the persistent GWs in the MLT (1000 - 2000 km), the dominant stratospheric GWs are not the direct source of the MLT persistent GWs. Secondary wave generation
-
Guerlet, S.; Fouchet, T.; Spiga, A.; Flasar, F. M.; Fletcher, L. N.; Hesman, B. E.; Gorius, N.
2018-01-01
Thermal infrared spectra acquired by Cassini/Composite InfraRed Spectrometer (CIRS) in limb-viewing geometry in 2015 are used to derive 2-D latitude-pressure temperature and thermal wind maps. These maps are used to study the vertical structure and evolution of Saturn's equatorial oscillation (SEO), a dynamical phenomenon presenting similarities with the Earth's quasi-biennal oscillation (QBO) and semi-annual oscillation (SAO). We report that a new local wind maximum has appeared in 2015 in the upper stratosphere and derive the descent rates of other wind extrema through time. The phase of the oscillation observed in 2015, as compared to 2005 and 2010, remains consistent with a ˜15 year period. The SEO does not propagate downward at a regular rate but exhibits faster descent rate in the upper stratosphere, combined with a greater vertical wind shear, compared to the lower stratosphere. Within the framework of a QBO-type oscillation, we estimate the absorbed wave momentum flux in the stratosphere to be on the order of ˜7 × 10-6 N m-2. On Earth, interactions between vertically propagating waves (both planetary and mesoscale) and the mean zonal flow drive the QBO and SAO. To broaden our knowledge on waves potentially driving Saturn's equatorial oscillation, we searched for thermal signatures of planetary waves in the tropical stratosphere using CIRS nadir spectra. Temperature anomalies of amplitude 1-4 K and zonal wave numbers 1 to 9 are frequently observed, and an equatorial Rossby (n = 1) wave of zonal wave number 3 is tentatively identified in November 2009.
-
Stratospheric gravity wave activities inferred through the GPS radio occultation technique
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wrasse, Cristiano Max; Takahashi, Hisao; Fechine, Joaquim; Denardini, Clezio Marcos; Wickert, Jens
2007-01-01
Stratospheric gravity wave activities were deduced from GPS radio occultation temperature profiles obtained by CHAMP satellite between 2001 and 2005. Potential energy profiles are used to analyze the gravity wave activity over South America. The results showed an inter-annual variation of the potential energy integrated between 24 and 34 km of altitude. The gravity wave activity is more concentrated around the equatorial region. In order to evaluate the seasonal variation of the gravity wave activity, a mean potential energy was determined over (10 deg N-10 deg S) and (100 deg W-20 deg W). The results showed a lower gravity wave activity during winter time, while during spring time the mean potential energy showed an increase in the wave activity. The results of the mean potential energy also showed that the gravity wave activity in the lower stratosphere exhibits a higher wave activity during 2002 and 2004 and a lower wave activity during 2003 and 2005. (author)
-
Hu, Yongyun; Kit Tung, Ka
2002-07-01
Using NCEP-NCAR 51-yr reanalysis data, the interannual and decadal variations of planetary wave activity and its relationship to stratospheric cooling, and the Northern Hemisphere Annular mode (NAM), are studied. It is found that winter stratospheric polar temperature is highly correlated on a year-to-year basis with the Eliassen-Palm (E-P) wave flux from the troposphere, implying a dynamical control of the former by the latter, as often suggested. Greater (lower) wave activity from the troposphere implies larger (smaller) poleward heat flux into the polar region, which leads to warmer (colder) polar temperature. A similar highly correlated antiphase relationship holds for E-P flux divergence and the strength of the polar vortex in the stratosphere. It is tempting to extrapolate these relationships found for interannual timescales to explain the recent stratospheric polar cooling trend in the past few decades as caused by decreased wave activity in the polar region. This speculation is not supported by the data. On timescales of decades the cooling trend is not correlated with the trend in planetary wave activity. In fact, it is found that planetary wave amplitude, E-P flux, and E-P flux convergence all show little statistical evidence of decrease in the past 51 yr, while the stratosphere is experiencing a cooling trend and the NAM index has a positive trend during the past 30 yr. This suggests that the trends in the winter polar temperature and the NAM index can reasonably be attributed to the radiative cooling of the stratosphere, due possibly to increasing greenhouse gases and ozone depletion. It is further shown that the positive trend of the NAM index in the past few decades is not through the inhibition of upward planetary wave propagation from the troposphere to the stratosphere, as previously suggested.
-
Intercomparison of stratospheric gravity wave observations with AIRS and IASI
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
L. Hoffmann
2014-12-01
Full Text Available Gravity waves are an important driver for the atmospheric circulation and have substantial impact on weather and climate. Satellite instruments offer excellent opportunities to study gravity waves on a global scale. This study focuses on observations from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS onboard the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Aqua satellite and the Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer (IASI onboard the European MetOp satellites. The main aim of this study is an intercomparison of stratospheric gravity wave observations of both instruments. In particular, we analyzed AIRS and IASI 4.3 μm brightness temperature measurements, which directly relate to stratospheric temperature. Three case studies showed that AIRS and IASI provide a clear and consistent picture of the temporal development of individual gravity wave events. Statistical comparisons based on a 5-year period of measurements (2008–2012 showed similar spatial and temporal patterns of gravity wave activity. However, the statistical comparisons also revealed systematic differences of variances between AIRS and IASI that we attribute to the different spatial measurement characteristics of both instruments. We also found differences between day- and nighttime data that are partly due to the local time variations of the gravity wave sources. While AIRS has been used successfully in many previous gravity wave studies, IASI data are applied here for the first time for that purpose. Our study shows that gravity wave observations from different hyperspectral infrared sounders such as AIRS and IASI can be directly related to each other, if instrument-specific characteristics such as different noise levels and spatial resolution and sampling are carefully considered. The ability to combine observations from different satellites provides an opportunity to create a long-term record, which is an exciting prospect for future climatological studies of stratospheric
-
Application of a planetary wave breaking parameterization to stratospheric circulation statistics
Randel, William J.; Garcia, Rolando R.
1994-01-01
The planetary wave parameterization scheme developed recently by Garcia is applied to statospheric circulation statistics derived from 12 years of National Meteorological Center operational stratospheric analyses. From the data a planetary wave breaking criterion (based on the ratio of the eddy to zonal mean meridional potential vorticity (PV) gradients), a wave damping rate, and a meridional diffusion coefficient are calculated. The equatorward flank of the polar night jet during winter is identified as a wave breaking region from the observed PV gradients; the region moves poleward with season, covering all high latitudes in spring. Derived damping rates maximize in the subtropical upper stratosphere (the 'surf zone'), with damping time scales of 3-4 days. Maximum diffusion coefficients follow the spatial patterns of the wave breaking criterion, with magnitudes comparable to prior published estimates. Overall, the observed results agree well with the parameterized calculations of Garcia.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. Romaniello
2007-06-01
Full Text Available Measurements of rotational lines emitted by middle atmospheric trace gases have been carried out from the Alpine station of Testa Grigia (45.9°N, 7.7°E, elev. 3500 m by means of a Ground-Based Millimeter-wave Spectrometer (GBMS. Observations of species such as O3, HNO3, CO, N2O, HCN, and HDO took place during 4 winter periods, from February 2004 to March 2007, for a total of 116 days of measurements grouped in about 18 field campaigns. By studying the pressure-broadened shape of emission lines the vertical distribution of the observed constituents is retrieved within an altitude range of ?17-75 km, constrained by the 600 MHz pass band and the 65 kHz spectral resolution of the back-end spectrometer. This work discusses the behavior of stratospheric O3 during the entire period of operation at Testa Grigia. Mid-latitude O3 columnar content as estimated using GBMS measurements can vary by large amounts over a period of very few days, with the largest variations observed in December 2005, February 2006, and March 2006, confirming that the northern winter of 2005-2006 was characterized by a particularly intense planetary wave activity. The largest rapid variation from maximum to minimum O3 column values over Testa Grigia took place in December 2006 and reached a relative value of 72% with respect to the average column content for that period. During most GBMS observation times much of the variability is concentrated in the column below 20 km, with tropospheric weather systems and advection of tropical tropospheric air into the lower stratosphere over Testa Grigia having a large impact on the observed variations in column contents. Nonetheless, a wide variability is also found in middle stratospheric GBMS O3 measurements, as expected for mid-latitude ozone. We find that O3 mixing ratios at ?32 km are very well correlated with the solar illumination experienced by air masses over the previous ?15 days, showing that already at 32 km
-
Gravity wave spectra in the lower stratosphere diagnosed from project loon balloon trajectories
Schoeberl, M. R.; Jensen, E.; Podglajen, A.; Coy, L.; Lodha, C.; Candido, S.; Carver, R.
2017-08-01
Project Loon has been launching superpressure balloons since January 2013 to provide worldwide Internet coverage. These balloons typically fly between 18 and 21 km and provide measurements of winds and pressure fluctuations in the lower stratosphere. We divide 1560 Loon flights into 3405 two-day segments for gravity wave analysis. We derive the kinetic energy spectrum from the horizontal balloon motion and estimate the temperature perturbation spectrum (proportional to the potential energy spectrum) from the pressure variations. We fit the temperature (and kinetic energy) data to the functional form T'2 = T'o2[ω/ωο)α, where ω is the wave frequency, ωο is daily frequency, T'o is the base temperature amplitude, and α is the spectral slope. Both the kinetic energy and temperature spectra show -1.9 ± 0.2 power-law dependence in the intrinsic frequency window 3-50 cycles/day. The temperature spectrum slope is weakly anticorrelated with the base temperature amplitude. We also find that the wave base temperature distribution is highly skewed. The tropical modal temperature is 0.77 K. The highest amplitude waves occur over the mountainous regions, the tropics, and the high southern latitudes. Temperature amplitudes show little height variation over our 18-21 km domain. Our results are consistent with other limited superpressure balloon analyses. The modal temperature is higher than the temperature currently used in high-frequency gravity wave parameterizations.
-
Numerical simulation of convective generated gravity waves in the stratosphere and MLT regions.
Heale, C. J.; Snively, J. B.
2017-12-01
Convection is an important source of gravity wave generation, especially in the summer tropics and midlatitudes, and coherent wave fields above convection are now routinely measured in the stratosphere and mesosphere [e.g. Hoffmann et al., JGR, 118, 2013; Gong et al., JGR, 120, 2015; Perwitasari et al., GRL, 42, 22, 2016]. Numerical studies have been performed to investigate the generation mechanisms, source spectra, and their effects on the middle and upper atmosphere [e.g. Fovell et al., AMS, 49,16, 1992; Alexander and Holton, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 4 2004; Vincent et al., JGR, 1118, 2013], however there is still considerable work needed to fully describe these parameters. GCMs currently lack the resolution to explicitly simulate convection generation and rely on simplified parameterizations while full cloud resolving models are computationally expensive and often only extend into the stratosphere. More recent studies have improved the realism of these simulations by using radar derived precipitation rates to drive latent heating in models that simulate convection [Grimsdell et al., AMS, 67, 2010; Stephan and Alexander., J. Adv. Model. Earth. Syst, 7, 2015], however they too only consider wave propagation in the troposphere and stratosphere. We use a 2D nonlinear, fully compressible model [Snively and Pasko., JGR, 113, 2008] to excite convectively generated waves, based on NEXRAD radar data, using the Stephan and Alexander [2015] algorithms. We study the propagation, and spectral evolution of the generated waves up into the MLT region. Ambient atmosphere parameters are derived from observations and MERRA-2 reanalysis data, and stratospheric (AIRS) and mesospheric (Lidar, OH airglow) observations enable comparisons with simulation results.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. Jia
2016-03-01
Full Text Available Spatial and temporal variabilities of Kelvin waves during stratospheric sudden warming (SSW events are investigated by the ERA-Interim reanalysis data, and the results are validated by the COSMIC temperature data. A case study on an exceptionally large SSW event in 2009, and a composite analysis comprising 18 events from 1980 to 2013 are presented. During SSW events, the average temperature increases by 20 K in the polar stratosphere, while the temperature in the tropical stratosphere decreases by about 4 K. Kelvin wave with wave numbers 1 and 2, and periods 10–20 days, clearly appear around the tropical tropopause layer (TTL during SSWs. The Kelvin wave activity shows obvious coupling with the convection localized in the India Ocean and western Pacific (Indo-Pacific region. Detailed analysis suggests that the enhanced meridional circulation driven by the extratropical planetary wave forcing during SSW events leads to tropical upwelling, which further produces temperature decrease in the tropical stratosphere. The tropical upwelling and cooling consequently result in enhancement of convection in the equatorial region, which excites the strong Kelvin wave activity. In addition, we investigated the Kelvin wave acceleration to the eastward zonal wind anomalies in the equatorial stratosphere during SSW events. The composite analysis shows that the proportion of Kelvin wave contribution ranges from 5 to 35 % during SSWs, much larger than in the non-SSW mid-winters (less than 5 % in the stratosphere. However, the Kelvin wave alone is insufficient to drive the equatorial eastward zonal wind anomalies during the SSW events, which suggests that the effects of other types of equatorial waves may not be neglected.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
U. Blum
2006-12-01
Full Text Available The importance of polar stratospheric clouds (PSC for polar ozone depletion is well established. Lidar experiments are well suited to observe and classify polar stratospheric clouds. On 5 January 2005 a PSC was observed simultaneously on the east and west sides of the Scandinavian mountains by ground-based lidars. This cloud was composed of liquid particles with a mixture of solid particles in the upper part of the cloud. Multi-colour measurements revealed that the liquid particles had a mode radius of r≈300 nm, a distribution width of σ≈1.04 and an altitude dependent number density of N≈2–20 cm−3. Simulations with a microphysical box model show that the cloud had formed about 20 h before observation. High HNO3 concentrations in the PSC of 40–50 weight percent were simulated in the altitude regions where the liquid particles were observed, while this concentration was reduced to about 10 weight percent in that part of the cloud where a mixture between solid and liquid particles was observed by the lidar. The model simulations also revealed a very narrow particle size distribution with values similar to the lidar observations. Below and above the cloud almost no HNO3 uptake was simulated. Although the PSC shows distinct wave signatures, no gravity wave activity was observed in the temperature profiles measured by the lidars and meteorological analyses support this observation. The observed cloud must have formed in a wave field above Iceland about 20 h prior to the measurements and the cloud wave pattern was advected by the background wind to Scandinavia. In this wave field above Iceland temperatures potentially dropped below the ice formation temperature, so that ice clouds may have formed which can act as condensation nuclei for the nitric acid trihydrate (NAT particles observed at the cloud top above Esrange.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
L. Thomas
Full Text Available Radar measurements at Aberystwyth (52.4° N, 4.1° W of winds at tropospheric and lower stratospheric heights are shown for 12-13 March 1994 in a region of highly curved flow, downstream of the jet maximum. The perturbations of horizontal velocity have comparable amplitudes in the troposphere and lower stratosphere with downward and upward phase propagation, respectively, in these two height regions. The sense of rotation with increasing height in hodographs of horizontal perturbation velocity derived for hourly intervals show downwards propagation of energy in the troposphere and upward propagation in the lower stratosphere with vertical wavelengths of 1.7 to 2.3 km. The results indicate inertia-gravity waves propagating in a direction similar to that of the jet stream but at smaller velocities. Some of the features observed contrast with those of previous observations of inertia-gravity waves propagating transverse to the jet stream. The interpretation of the hodographs to derive wave parameters has taken account of the vertical shear of the background wind transverse to the direction of wave propagation.
Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (mesoscale meteorology; middle atmosphere dynamics; waves and tides -
The interaction of katabatic winds and mountain waves
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Poulos, Gregory Steve [Colorado State Univ., Fort Collins, CO (United States)
1997-01-01
The variation in the oft-observed, thermally-forced, nocturnal katabatic winds along the east side of the Rocky Mountains can be explained by either internal variability or interactions with various other forcings. Though generally katabatic flows have been studied as an entity protected from external forcing by strong thermal stratification, this work investigates how drainage winds along the Colorado Front Range interact with, in particular, topographically forced mountain waves. Previous work has shown, based on measurements taken during the Atmospheric Studies in Complex Terrain 1993 field program, that the actual dispersion in katabatic flows is often greater than reflected in models of dispersion. The interaction of these phenomena is complicated and non-linear since the amplitude, wavelength and vertical structure of mountain waves developed by flow over the Rocky Mountain barrier are themselves partly determined by the evolving atmospheric stability in which the drainage flows develop. Perturbations to katabatic flow by mountain waves, relative to their more steady form in quiescent conditions, are found to be caused by both turbulence and dynamic pressure effects. The effect of turbulent interaction is to create changes to katabatic now depth, katabatic flow speed, katabatic jet height and, vertical thermal stratification. The pressure effect is found to primarily influence the variability of a given katabatic now through the evolution of integrated column wave forcing on surface pressure. Variability is found to occur on two scales, on the mesoscale due to meso-gamma scale mountain wave evolution, and on the microscale, due to wave breaking. Since existing parameterizations for the statically stable case are predominantly based on nearly flat terrain atmospheric measurements under idealized or nearly quiescent conditions, it is no surprise that these parameterizations often contribute to errors in prediction, particularly in complex terrain.
-
Broutman, Dave; Eckermann, Stephen D.; Knight, Harold; Ma, Jun
2017-01-01
A relatively general stationary phase solution is derived for mountain waves from localized topography. It applies to hydrostatic, nonhydrostatic, or anelastic dispersion relations, to arbitrary localized topography, and to arbitrary smooth vertically varying background temperature and vector wind profiles. A simple method is introduced to compute the ray Jacobian that quantifies the effects of horizontal geometrical spreading in the stationary phase solution. The stationary phase solution is applied to mesospheric mountain waves generated by Auckland Island during the Deep Propagating Gravity Wave Experiment. The results are compared to a Fourier solution. The emphasis is on interpretations involving horizontal geometrical spreading. The results show larger horizontal geometrical spreading for nonhydrostatic waves than for hydrostatic waves in the region directly above the island; the dominant effect of horizontal geometrical spreading in the lower ˜30 km of the atmosphere, compared to the effects of refraction and background density variation; and the enhanced geometrical spreading due to directional wind in the approach to a critical layer in the mesosphere.
-
Rocket Observations of Kelvin Waves in the Upper Stratosphere over India.
Devarajan, M.; Reddy, C. A.; Ragrava Reddi, C.
1985-09-01
The upper atmospheric winds (20-40 km) at two Indian stations, Sriharikota Range (SHAR 13.7°N, 80.2°E) and Balasore (2 1.5°N, 86.93°E) during the years 1979-80 were analyzed for short scale vertical variations (6-16 km) of the zonal wind. The analysis involves high-pass filtering of the wind profiles to extract the short-scale wavelike perturbations and Fourier analysis of the wave disturbances.The results of the analysis are presented. The dominant vertical wavelengths are in the 6-12 km range in 67% of the observed cases, and the amplitudes are significantly larger during the easterly background wind. The amplitudes are systematically larger by about a factor of 2 at Sriharikota (13.7°N) than at 1Wasore (21.5°N). Corresponding wave perturbations are absent in the meridional wind in as much as 70% of the observations. These characteristics lead to the conclusion that the observed wavelike disturbances are the manifestation of Kelvin waves in the upper stratosphere. In some cases, the periods of the waves are inferred to be in the range of 4-8 days. The short vertical wavelengths, together with the shorter periods, indicate the possible dominance of zonal wavenumber 2 during many disturbance events.The observations of the wave activity in relation to the semiannual oscillation (SAO) and the annual oscillation (AO) show that 1) the more active periods correspond to the easterly phase of the SAO in the middle stratosphere and that 2) the wave activity persists for a longer duration when both the AO and SAO are in easterly phase.
-
Tibetan Plateau glacier and hydrological change under stratospheric aerosol injection
Ji, D.
2017-12-01
As an important inland freshwater resource, mountain glaciers are highly related to human life, they provide water for many large rivers and play a very important role in regional water cycles. The response of mountain glaciers to future climate change is a topic of concern especially to the many people who rely on glacier-fed rivers for purposes such as irrigation. Geoengineering by stratospheric aerosol injection is a method of offsetting the global temperature rise from greenhouse gases. How the geoengineering by stratospheric aerosol injection affects the mass balance of mountain glaciers and adjacent river discharge is little understood. In this study, we use regional climate model WRF and catchment-based river model CaMa-Flood to study the impacts of stratospheric aerosol injection to Tibetan Plateau glacier mass balance and adjacent river discharge. To facilitate mountain glacier mass balance study, we improve the description of mountain glacier in the land surface scheme of WRF. The improvements include: (1) a fine mesh nested in WRF horizontal grid to match the highly non-uniform spatial distribution of the mountain glaciers, (2) revising the radiation flux at the glacier surface considering the surrounding terrain. We use the projections of five Earth system models for CMIP5 rcp45 and GeoMIP G4 scenarios to drive the WRF and CaMa-Flood models. The G4 scenario, which uses stratospheric aerosols to reduce the incoming shortwave while applying the rcp4.5 greenhouse gas forcing, starts stratospheric sulfate aerosol injection at a rate of 5 Tg per year over the period 2020-2069. The ensemble projections suggest relatively slower glacier mass loss rates and reduced river discharge at Tibetan Plateau and adjacent regions under geoengineering scenario by stratospheric aerosol injection.
-
Vadas, S.
2017-12-01
In this paper, we investigate the generation, propagation and effectsof secondary gravity waves (GWs) from momentum deposition in the stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and ionosphere in high-resolution GW-resolving models and in TEC/lidar/redline data. We show that secondary GWs generated from the dissipation of orographic GWs at McMurdo Station in Antarctica play a dominant role in the wave activity over McMurdo in the wintertime mesosphere. These secondary GWs are created in the stratosphere, and have been identified in models and data via their telltale "fishbone" appearance in z-t plots. We also show that secondary GWs from the dissipation of GWs excited by deep convectiongenerate concentric rings in the F-region ionosphere. These model results and data point to the importance of secondary GWs from momentumdeposition in the Earth's atmosphere and ionosphere.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
U. Blum
2006-12-01
Full Text Available The importance of polar stratospheric clouds (PSC for polar ozone depletion is well established. Lidar experiments are well suited to observe and classify polar stratospheric clouds. On 5 January 2005 a PSC was observed simultaneously on the east and west sides of the Scandinavian mountains by ground-based lidars. This cloud was composed of liquid particles with a mixture of solid particles in the upper part of the cloud. Multi-colour measurements revealed that the liquid particles had a mode radius of r≈300 nm, a distribution width of σ≈1.04 and an altitude dependent number density of N≈2–20 cm−3. Simulations with a microphysical box model show that the cloud had formed about 20 h before observation. High HNO3 concentrations in the PSC of 40–50 weight percent were simulated in the altitude regions where the liquid particles were observed, while this concentration was reduced to about 10 weight percent in that part of the cloud where a mixture between solid and liquid particles was observed by the lidar. The model simulations also revealed a very narrow particle size distribution with values similar to the lidar observations. Below and above the cloud almost no HNO3 uptake was simulated. Although the PSC shows distinct wave signatures, no gravity wave activity was observed in the temperature profiles measured by the lidars and meteorological analyses support this observation. The observed cloud must have formed in a wave field above Iceland about 20 h prior to the measurements and the cloud wave pattern was advected by the background wind to Scandinavia. In this wave field above Iceland temperatures potentially dropped below the ice formation temperature, so that ice clouds may have formed which can act as condensation nuclei for the nitric acid trihydrate (NAT particles observed at the cloud top above Esrange.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. Deepa
2006-10-01
Full Text Available The altitude profiles of temperature fluctuations in the stratosphere and mesosphere observed with the Rayleigh Lidar at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E on 30 nights during January to March 1999 and 21 nights during February to April 2000 were analysed to bring out the temporal and vertical propagation characteristics of gravity wave perturbations. The gravity wave perturbations showed periodicities in the 0.5–3-h range and attained large amplitudes (4–5 K in the mesosphere. The phase propagation characteristics of gravity waves with different periods showed upward wave propagation with a vertical wavelength of 5–7 km. The mean flow acceleration computed from the divergence of momentum flux of gravity waves is compared with that calculated from monthly values of zonal wind obtained from RH-200 rockets flights. Thus, the contribution of gravity waves towards the generation of Stratospheric Semi Annual Oscillation (SSAO is estimated.
-
Mountain Wave Analysis Using Fourier Methods
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Roadcap, John R
2007-01-01
...) their requirements for only a coarse horizontal background state. Common traits of Fourier mountain wave models include use of the Boussinesq approximation and neglect of moisture and Coriolis terms...
-
Turbulence and Mountain Wave Conditions Observed with an Airborne 2-Micron Lidar
Teets, Edward H., Jr.; Ehernberger, Jack; Bogue, Rodney; Ashburn, Chris
2007-01-01
Joint efforts by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the Department of Defense, and industry partners are enhancing the capability of airborne wind and turbulence detection. The Airborne Coherent Lidar for Advanced In-Flight Measurements (ACLAIM) was flown on three series of flights to assess its capability over a range of altitudes, air mass conditions, and gust phenomena. This paper describes the observation of mountain waves and turbulence induced by mountain waves over the Tehachapi and Sierra Nevada mountain ranges in southern California by lidar onboard the NASA Airborne Science DC-8 airplane. The examples in this paper compare lidar-predicted mountain waves and wave-induced turbulence to subsequent aircraft-measured true airspeed. Airplane acceleration data is presented describing the effects of the wave-induced turbulence on the DC-8 airplane. Highlights of the lidar-predicted airspeed from the two flights show increases of 12 m/s at the mountain wave interface and peak-to-peak airspeed changes of 10 m/s and 15 m/s in a span of 12 s in moderate turbulence.
-
Nath, Debashis; Chen, Wen; Zelin, Cai; Pogoreltsev, Alexander Ivanovich; Wei, Ke
2016-04-07
In the present study, we investigate the impact of stratospheric planetary wave reflection on tropospheric weather over Central Eurasia during the 2013 Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) event. We analyze EP fluxes and Plumb wave activity fluxes to study the two and three dimensional aspects of wave propagation, respectively. The 2013 SSW event is excited by the combined influence of wavenumber 1 (WN1) and wavenumber 2 (WN2) planetary waves, which makes the event an unusual one and seems to have significant impact on tropospheric weather regime. We observe an extraordinary development of a ridge over the Siberian Tundra and the North Pacific during first development stage (last week of December 2012) and later from the North Atlantic in the second development stage (first week of January 2013), and these waves appear to be responsible for the excitation of the WN2 pattern during the SSW. The wave packets propagated upward and were then reflected back down to central Eurasia due to strong negative wind shear in the upper stratospheric polar jet, caused by the SSW event. Waves that propagated downward led to the formation of a deep trough over Eurasia and brought extreme cold weather over Kazakhstan, the Southern part of Russia and the Northwestern part of China during mid-January 2013.
-
Observation of Mountain Lee Waves with MODIS NIR Column Water Vapor
Lyapustin, A.; Alexander, M. J.; Ott, L.; Molod, A.; Holben, B.; Susskind, J.; Wang, Y.
2014-01-01
Mountain lee waves have been previously observed in data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) "water vapor" 6.7 micrometers channel which has a typical peak sensitivity at 550 hPa in the free troposphere. This paper reports the first observation of mountain waves generated by the Appalachian Mountains in the MODIS total column water vapor (CWV) product derived from near-infrared (NIR) (0.94 micrometers) measurements, which indicate perturbations very close to the surface. The CWV waves are usually observed during spring and late fall or some summer days with low to moderate CWV (below is approx. 2 cm). The observed lee waves display wavelengths from3-4 to 15kmwith an amplitude of variation often comparable to is approx. 50-70% of the total CWV. Since the bulk of atmospheric water vapor is confined to the boundary layer, this indicates that the impact of thesewaves extends deep into the boundary layer, and these may be the lowest level signatures of mountain lee waves presently detected by remote sensing over the land.
-
Equatorial atmospheric Kelvin waves during El Niño episodes and their effect on stratospheric QBO
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Das, Uma; Pan, C.J.
2016-01-01
Equatorial atmospheric Kelvin waves are investigated during a positive El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) episode using temperature data retrieved from GPS Radio Occultation (RO) observations of FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC during the period from August 2006 to December 2013. Enhanced Kelvin wave amplitudes are observed during the El Niño episode of 2009–2010 and it is also observed that these amplitudes correlate with the Niño 3.4 index and also with outgoing longwave radiation and trade wind index. This study indicates that the enhanced equatorial atmospheric Kelvin wave amplitudes might be produced by geophysical processes that were involved in the onset and development of the El Niño episode. Further, easterly winds above the tropopause during this period favored the vertically upward propagation of these waves that induced a fast descending westerly regime by the end of 2010, where the zero-wind line is observed to take only 5 months to descend from 10 to 50 hPa. The current study presents observational evidence of enhanced Kelvin wave amplitudes during El Niño that has affected the stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) through wave–mean flow interactions. Earlier El Niño episodes of 1987 and 1998 are also qualitatively investigated, using reanalysis data. It is found that there might have been an enhancement in the equatorial Kelvin wave amplitudes during almost all El Niño episodes, however, an effect of a fast descending westerly is observed in the QBO only when the ambient zonal winds in the lower stratosphere favor the upward propagation of the Kelvin waves and consequently they interact with the mean flow. This study indicates that the El Niño and QBO are not linearly related and wave mean flow interactions play a very important role in connecting these two geophysical phenomena. - Highlights: • Enhanced atmospheric Kelvin Wave amplitudes observed during El Nino of 2010. • The waves are probably produced by processes generating El Nino. �
-
Equatorial atmospheric Kelvin waves during El Niño episodes and their effect on stratospheric QBO
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Das, Uma [Department of Physics, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton (Canada); Pan, C.J., E-mail: cjpan@jupiter.ss.ncu.edu.tw [Institute of Space Science, National Central University, Jhongli, Taiwan (China)
2016-02-15
Equatorial atmospheric Kelvin waves are investigated during a positive El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) episode using temperature data retrieved from GPS Radio Occultation (RO) observations of FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC during the period from August 2006 to December 2013. Enhanced Kelvin wave amplitudes are observed during the El Niño episode of 2009–2010 and it is also observed that these amplitudes correlate with the Niño 3.4 index and also with outgoing longwave radiation and trade wind index. This study indicates that the enhanced equatorial atmospheric Kelvin wave amplitudes might be produced by geophysical processes that were involved in the onset and development of the El Niño episode. Further, easterly winds above the tropopause during this period favored the vertically upward propagation of these waves that induced a fast descending westerly regime by the end of 2010, where the zero-wind line is observed to take only 5 months to descend from 10 to 50 hPa. The current study presents observational evidence of enhanced Kelvin wave amplitudes during El Niño that has affected the stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) through wave–mean flow interactions. Earlier El Niño episodes of 1987 and 1998 are also qualitatively investigated, using reanalysis data. It is found that there might have been an enhancement in the equatorial Kelvin wave amplitudes during almost all El Niño episodes, however, an effect of a fast descending westerly is observed in the QBO only when the ambient zonal winds in the lower stratosphere favor the upward propagation of the Kelvin waves and consequently they interact with the mean flow. This study indicates that the El Niño and QBO are not linearly related and wave mean flow interactions play a very important role in connecting these two geophysical phenomena. - Highlights: • Enhanced atmospheric Kelvin Wave amplitudes observed during El Nino of 2010. • The waves are probably produced by processes generating El Nino. �
-
What Controls the Arctic Lower Stratosphere Temperature?
Newman, Paul A.; Nash, Eric R.; Einaudi, Franco (Technical Monitor)
2001-01-01
The temperature of the Arctic lower stratosphere is critical for understanding polar ozone levels. As temperatures drop below about 195 K, polar stratospheric clouds form, which then convert HCl and ClONO2 into reactive forms that are catalysts for ozone loss reactions. Hence, the lower stratospheric temperature during the March period is a key parameter for understanding polar ozone losses. The temperature is basically understood to be a result of planetary waves which drive the polar temperature away from a cold "radiative equilibrium" state. This is demonstrated using NCEP/NCAR reanalysis calculations of the heat flux and the mean polar temperature. The temperature during the March period is fundamentally driven by the integrated impact of large scale waves moving from the troposphere to the stratosphere during the January through February period. We will further show that the recent cold years in the northern polar vortex are a result of this weakened wave driving of the stratosphere.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Mbatha, N. [South African National Space Agency, Hermanus (South Africa). Space Science; KwaZulu-Natal Univ., Durban (South Africa). School of Chemistry and Physics; Sivakumar, V. [KwaZulu-Natal Univ., Durban (South Africa). School of Chemistry and Physics; Bencherif, H. [La Reunion Univ. UMR 8105 CNRS, Saint-Denis (France). Lab. de l' Atmosphere et des Cyclones; Malinga, S. [South African National Space Agency, Hermanus (South Africa). Space Science
2013-11-01
Using absorption data measured by imaging riometer for ionospheric studies (IRIS) located at the South Africa National Antarctic Expedition (SANAE), Antarctica (72 S, 3 W), we extracted the parameters of gravity waves (GW) of periods between 40 and 50 min during late winter/ spring of the year 2002, a period of the unprecedented major sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) in the Southern Hemisphere middle atmosphere. During this period, an unprecedented substantial increase of temperature by about 25-30K throughout the stratosphere was observed. During the period of the occurrence of the major stratospheric warming, there was a reduction of both the GW horizontal phase speeds and the horizontal wavelengths at 90 km. The GW phase speeds and horizontal wavelengths were observed to reach minimum values of about 7ms{sup -1} and 19 km, respectively, while during the quiet period the average value of the phase speed and horizontal wavelength was approximately 23ms{sup -1} and 62 km, respectively. The observed event is discussed in terms of momentum flux and also a potential interaction of gravity waves, planetary waves and mean circulation.
-
Modulation of Precipitation in the Olympic Mountains by Trapped Gravity Waves
Heymsfield, G. M.; Tian, L.; Grecu, M.; McLinden, M.; Li, L.
2017-12-01
Precipitation over the Olympic Mountains was studied intensely with multiple aircraft and ground-based measurements during the Olympic Mountains Experiment (OLYMPEX) during the fall-winter season 2015-2016 as part of validation for the Global Precipitation Mission (GPM) (Houze et al. 2017) and the Radar Definition Experiment (RADEX) supported by the Aerosol Chemistry, Ecosystem (ACE) NASA Decadal Mission. This presentation focuses on observations of a broad frontal cloud system with strong flow over the mountains on 5 December 2015. Unique observations of trapped waves were obtained with in the three Goddard Space Flight Center nadir-looking, X- through W-band, Doppler radars on the NASA high-altitude ER-2: the High-altitude Wind and Rain Airborne Profiler (HIWRAP) at Ku and Ka-band, the W-band Cloud Radar System (CRS), and the ER-2 X-band Radar (EXRAD). Analysis of the aircraft measurements showed the presence of deep, trapped gravity waves on a scale ranging from 10-25 km in the nadir-looking Doppler and reflectivity observations. These waves cause localized vertical up/down motions on the order of 1-2 ms-1 and they are superimposed on the widespread south-southwest flow over the Olympic Mountains. While much of this widespread flow over the mountains produces copious amounts of snowfall, the gravity waves play an important role in modulating this precipitation indirectly through microphysical processes in the ice region. We will describe analyses of the interactions between the air motions and precipitation structure for this case and other cases we observed similar waves. We will present preliminary results from precipitation retrievals based on optimal estimation (Grecu et al. 2011).
-
Interannual variability of the stratospheric wave driving during northern winter
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. M. Kelder
2007-05-01
Full Text Available The strength of the stratospheric wave driving during northern winter is often quantified by the January–February mean poleward eddy heat flux at 100 hPa, averaged over 40°–80° N (or a similar area and period. Despite the dynamical and chemical relevance of the wave driving, the causes for its variability are still not well understood. In this study, ERA-40 reanalysis data for the period 1979–2002 are used to examine several factors that significantly affect the interannual variability of the wave driving. The total poleward heat flux at 100 hPa is poorly correlated with that in the troposphere, suggesting a decoupling between 100 hPa and the troposphere. However, the individual zonal wave-1 and wave-2 contributions to the wave driving at 100 hPa do exhibit a significant coupling with the troposphere, predominantly their stationary components. The stationary wave-1 contribution to the total wave driving significantly depends on the latitude of the stationary wave-1 source in the troposphere. The results suggest that this dependence is associated with the varying ability of stationary wave-1 activity to enter the tropospheric waveguide at mid-latitudes. The wave driving anomalies are separated into three parts: one part due to anomalies in the zonal correlation coefficient between the eddy temperature and eddy meridional wind, another part due to anomalies in the zonal eddy temperature amplitude, and a third part due to anomalies in the zonal eddy meridional wind amplitude. It is found that year-to-year variability in the zonal correlation coefficient between the eddy temperature and the eddy meridional wind is the most dominant factor in explaining the year-to-year variability of the poleward eddy heat flux.
-
What Controls the Temperature of the Arctic Stratosphere during the Spring?
Newman, Paul A.; Nash, Eric R.; Rosenfield, Joan E.; Einaudi, Franco (Technical Monitor)
2000-01-01
Understanding the mechanisms that control the temperature of the polar lower stratosphere during spring is key to understanding ozone loss in the Arctic polar vortex. Spring ozone loss rates are directly tied to polar stratospheric temperatures by the formation of polar stratospheric clouds, and the conversion of chlorine species to reactive forms on these cloud particle surfaces. In this paper, we study those factors that control temperatures in the polar lower stratosphere. We use the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP)/NCAR reanalysis data covering the last two decades to investigate how planetary wave driving of the stratosphere is connected to polar temperatures. In particular, we show that planetary waves forced in the troposphere in mid- to late winter (January-February) are principally responsible for the mean polar temperature during the March period. These planetary waves are forced by both thermal and orographic processes in the troposphere, and propagate into the stratosphere in the mid and high latitudes. Strong mid-winter planetary wave forcing leads to a warmer Arctic lower stratosphere in early spring, while weak mid-winter forcing leads to cooler Arctic temperatures.
-
The Temperature of the Arctic and Antarctic Lower Stratosphere
Newman, Paul A.; Nash, Eric R.; Bhartia, P. K. (Technical Monitor)
2002-01-01
The temperature of the polar lower stratosphere during spring is the key factor in changing the magnitude of ozone loss in the polar vortices. In this talk, we will review the results of Newman et al. [2000] that quantitatively demonstrate that the polar lower stratospheric temperature is primarily controlled by planetary-scale waves. In particular, the tropospheric eddy heat flux in middle to late winter (January--February) is highly correlated with the mean polar stratospheric temperature during March. Strong midwinter planetary wave forcing leads to a warmer spring Arctic lower stratosphere in early spring, while weak midwinter forcing leads to cooler spring Arctic temperatures. In addition, this planetary wave driving also has a strong impact on the strength of the polar vortex. These results from the Northern Hemisphere will be contrasted with the Southern Hemisphere.
-
Glacier evolution in high-mountain Asia under stratospheric sulfate aerosol injection geoengineering
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
L. Zhao
2017-06-01
Full Text Available Geoengineering by stratospheric sulfate aerosol injection may help preserve mountain glaciers by reducing summer temperatures. We examine this hypothesis for the glaciers in high-mountain Asia using a glacier mass balance model driven by climate simulations from the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP. The G3 and G4 schemes specify use of stratospheric sulfate aerosols to reduce the radiative forcing under the Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP 4.5 scenario for the 50 years between 2020 and 2069, and for a further 20 years after termination of geoengineering. We estimate and compare glacier volume loss for every glacier in the region using a glacier model based on surface mass balance parameterization under climate projections from three Earth system models under G3, five models under G4, and six models under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5. The ensemble projections suggest that glacier shrinkage over the period 2010–2069 is equivalent to sea-level rise of 9.0 ± 1.6 mm (G3, 9.8 ± 4.3 mm (G4, 15.5 ± 2.3 mm (RCP4.5, and 18.5 ± 1.7 mm (RCP8.5. Although G3 keeps the average temperature from increasing in the geoengineering period, G3 only slows glacier shrinkage by about 50 % relative to losses from RCP8.5. Approximately 72 % of glaciated area remains at 2069 under G3, as compared with about 30 % for RCP8.5. The widely reported reduction in mean precipitation expected for solar geoengineering is unlikely to be as important as the temperature-driven shift from solid to liquid precipitation for forcing Himalayan glacier change. The termination of geoengineering at 2069 under G3 leads to temperature rise of about 1.3 °C over the period 2070–2089 relative to the period 2050-2069 and corresponding increase in annual mean glacier volume loss rate from 0.17 to 1.1 % yr−1, which is higher than the 0.66 % yr−1 under RCP8.5 during 2070–2089.
-
Waves in the Red Sea: Response to monsoonal and mountain gap winds
Ralston, David K.
2013-08-01
An unstructured grid, phase-averaged wave model forced with winds from a high resolution atmospheric model is used to evaluate wind wave conditions in the Red Sea over an approximately 2-year period. The Red Sea lies in a narrow rift valley, and the steep topography surrounding the basin steers the dominant wind patterns and consequently the wave climate. At large scales, the model results indicated that the primary seasonal variability in waves was due to the monsoonal wind reversal. During the winter, monsoon winds from the southeast generated waves with mean significant wave heights in excess of 2. m and mean periods of 8. s in the southern Red Sea, while in the northern part of the basin waves were smaller, shorter period, and from northwest. The zone of convergence of winds and waves typically occurred around 19-20°N, but the location varied between 15 and 21.5°N. During the summer, waves were generally smaller and from the northwest over most of the basin. While the seasonal winds oriented along the axis of the Red Sea drove much of the variability in the waves, the maximum wave heights in the simulations were not due to the monsoonal winds but instead were generated by localized mountain wind jets oriented across the basin (roughly east-west). During the summer, a mountain wind jet from the Tokar Gap enhanced the waves in the region of 18 and 20°N, with monthly mean wave heights exceeding 2. m and maximum wave heights of 14. m during a period when the rest of the Red Sea was relatively calm. Smaller mountain gap wind jets along the northeast coast created large waves during the fall and winter, with a series of jets providing a dominant source of wave energy during these periods. Evaluation of the wave model results against observations from a buoy and satellites found that the spatial resolution of the wind model significantly affected the quality of the wave model results. Wind forcing from a 10-km grid produced higher skills for waves than winds from a
-
The MaCWAVE program to study gravity wave influences on the polar mesosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. A. Goldberg
2006-07-01
Full Text Available MaCWAVE (Mountain and Convective Waves Ascending VErtically was a highly coordinated rocket, ground-based, and satellite program designed to address gravity wave forcing of the mesosphere and lower thermosphere (MLT. The MaCWAVE program was conducted at the Norwegian Andøya Rocket Range (ARR, 69.3° N in July 2002, and continued at the Swedish Rocket Range (Esrange, 67.9° N during January 2003. Correlative instrumentation included the ALOMAR MF and MST radars and RMR and Na lidars, Esrange MST and meteor radars and RMR lidar, radiosondes, and TIMED (Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics satellite measurements of thermal structures. The data have been used to define both the mean fields and the wave field structures and turbulence generation leading to forcing of the large-scale flow. In summer, launch sequences coupled with ground-based measurements at ARR addressed the forcing of the summer mesopause environment by anticipated convective and shear generated gravity waves. These motions were measured with two 12-h rocket sequences, each involving one Terrier-Orion payload accompanied by a mix of MET rockets, all at ARR in Norway. The MET rockets were used to define the temperature and wind structure of the stratosphere and mesosphere. The Terrier-Orions were designed to measure small-scale plasma fluctuations and turbulence that might be induced by wave breaking in the mesosphere. For the summer series, three European MIDAS (Middle Atmosphere Dynamics and Structure rockets were also launched from ARR in coordination with the MaCWAVE payloads. These were designed to measure plasma and neutral turbulence within the MLT. The summer program exhibited a number of indications of significant departures of the mean wind and temperature structures from ``normal" polar summer conditions, including an unusually warm mesopause and a slowing of the formation of polar mesospheric summer echoes (PMSE and noctilucent clouds (NLC. This
-
Bleck, R.; Sun, S.; Benjamin, S.; Brown, J. M.
2017-12-01
Two- to four-week predictions of stratospheric sudden warming events during the winter seasons of 1999-2014, carried out with a high-resolution icosahedral NWP model using potential temperature as vertical coordinate, are inspected for commonalities in the evolution of both minor and major warmings. Emphasis is on the evolution of the potential vorticity field at different levels in the stratosphere, as well as on the sign and magnitude of the vertical component of the Eliassen-Palm flux vector suggestive of wave forcing in either direction. Material is presented shedding light on the skill of the model (FIM, developed at NOAA/ESRL) in predicting stratospheric warmings generally 2 weeks in advance. With an icosahedral grid ideally suited for studying polar processes, and a vertical coordinate faithfully reproducing details in the evolution of the potential vorticity and EP flux vector fields, FIM is found to be a good tool for investigating the SSW mechanism.
-
Hecht, J. H.; Fritts, D. C.; Wang, L.; Gelinas, L. J.; Rudy, R. J.; Walterscheid, R. L.; Taylor, M. J.; Pautet, P. D.; Smith, S.; Franke, S. J.
2018-01-01
Although mountain waves (MWs) are thought to be a ubiquitous feature of the wintertime southern Andes stratosphere, it was not known whether these waves propagated up to the mesopause region until Smith et al. (2009) confirmed their presence via airglow observations. The new Andes Lidar Observatory at Cerro Pachon in Chile provided the opportunity for a further study of these waves. Since MWs have near-zero phase speed, and zero wind lines often occur in the winter upper mesosphere (80 to 100 km altitude) region due to the reversal of the zonal mean and tidal wind, MW breakdown may routinely occur at these altitudes. Here we report on very high spatial/temporal resolution observations of the initiation of MW breakdown in the mesopause region. Because the waves are nearly stationary, the breakdown process was observed over several hours; a much longer interval than has previously been observed for any gravity wave breakdown. During the breakdown process observations were made of initial horseshoe-shaped vortices, leading to successive vortex rings, as is also commonly seen in Direct Numerical Simulations (DNS) of idealized and multiscale gravity wave breaking. Kelvin-Helmholtz instability (KHI) structures were also observed to form. Comparing the structure of observed KHI with the results of existing DNS allowed an estimate of the turbulent kinematic viscosity. This viscosity was found to be around 25 m2/s, a value larger than the nominal viscosity that is used in models.
-
Dynamical response of the Arctic winter stratosphere to global warming
Karpechko, A.; Manzini, E.
2017-12-01
Climate models often simulate dynamical warming of the Arctic stratosphere as a response to global warming in association with a strengthening of the deep branch of the Brewer-Dobson circulation; however until now, no satisfactory mechanism for such a response has been suggested. Here we investigate the role of stationary planetary waves in the dynamical response of the Arctic winter stratosphere circulation to global warming by analysing simulations performed with atmosphere-only Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5) models driven by prescribed sea surface temperatures (SSTs). We focus on December-February (DJF) because this is the period when the troposphere and stratosphere are strongly coupled. When forced by increased SSTs, all the models analysed here simulate Arctic stratosphere dynamical warming, mostly due to increased upward propagation of quasi-stationary wave number 1, as diagnosed by the meridional eddy heat flux. By analysing intermodel spread in the response we show that the stratospheric warming and increased wave flux to the stratosphere correlate with the strengthening of the zonal winds in subtropics and mid-latitudes near the tropopause- a robust response to global warming. These results support previous studies of future Arctic stratosphere changes and suggest a dynamical warming of the Arctic wintertime polar vortex as the most likely response to global warming.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Wrasse, Cristiano Max [Universidade do Vale do Paraiba (UNIVAP), Instituto de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento (IPeD), Sao Jose dos Campos, SP (Brazil); Takahashi, Hisao; Fechine, Joaquim; Denardini, Clezio Marcos [Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE), Sao Jose dos Campos, SP (Brazil); Wickert, Jens, E-mail: cmw@univap.br, E-mail: hisaotak@laser.inpe.br, E-mail: joaquim@laser.inpe.br, E-mail: denardin@dae.inpe.br, E-mail: jens.wickert@gfz-potsdam.de [GeoForschungsZentrum, Potsdam (GFZ), Department of Geodesy and Remote Sensing (Germany)
2007-07-01
Stratospheric gravity wave activities were deduced from GPS radio occultation temperature profiles obtained by CHAMP satellite between 2001 and 2005. Potential energy profiles are used to analyze the gravity wave activity over South America. The results showed an inter-annual variation of the potential energy integrated between 24 and 34 km of altitude. The gravity wave activity is more concentrated around the equatorial region. In order to evaluate the seasonal variation of the gravity wave activity, a mean potential energy was determined over (10 deg N-10 deg S) and (100 deg W-20 deg W). The results showed a lower gravity wave activity during winter time, while during spring time the mean potential energy showed an increase in the wave activity. The results of the mean potential energy also showed that the gravity wave activity in the lower stratosphere exhibits a higher wave activity during 2002 and 2004 and a lower wave activity during 2003 and 2005. (author)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lei Li
2013-01-01
Full Text Available This study of a lee wave event over three-dimensional (3D mountainous terrain in Lantau Island, Hong Kong, using a simulation combining mesoscale model and computational fluid dynamics (CFD model has shown that (1 3D steep mountainous terrain can trigger small scale lee waves under strong wind condition, and the horizontal extent of the wave structure is in a dimension of few kilometers and corresponds to the dimension of the horizontal cross-section of the mountain; (2 the life cycle of the lee wave is short, and the wave structures will continuously form roughly in the same location, then gradually move downstream, and dissipate over time; (3 the lee wave triggered by the mountainous terrain in this case can be categorized into “nonsymmetric vortex shedding” or “turbulent wake,” as defined before based on water tank experiments; (4 the magnitude of the wave is related to strength of wind shear. This study also shows that a simulation combining mesoscale model and CFD can capture complex wave structure in the boundary layer over realistic 3D steep terrain, and have a potential value for operational jobs on air traffic warning, wind energy utilization, and atmospheric environmental assessment.
-
How stratospheric are deep stratospheric intrusions? LUAMI 2008
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
T. Trickl
2016-07-01
Full Text Available A large-scale comparison of water-vapour vertical-sounding instruments took place over central Europe on 17 October 2008, during a rather homogeneous deep stratospheric intrusion event (LUAMI, Lindenberg Upper-Air Methods Intercomparison. The measurements were carried out at four observational sites: Payerne (Switzerland, Bilthoven (the Netherlands, Lindenberg (north-eastern Germany, and the Zugspitze mountain (Garmisch-Partenkichen, German Alps, and by an airborne water-vapour lidar system creating a transect of humidity profiles between all four stations. A high data quality was verified that strongly underlines the scientific findings. The intrusion layer was very dry with a minimum mixing ratios of 0 to 35 ppm on its lower west side, but did not drop below 120 ppm on the higher-lying east side (Lindenberg. The dryness hardens the findings of a preceding study (“Part 1”, Trickl et al., 2014 that, e.g., 73 % of deep intrusions reaching the German Alps and travelling 6 days or less exhibit minimum mixing ratios of 50 ppm and less. These low values reflect values found in the lowermost stratosphere and indicate very slow mixing with tropospheric air during the downward transport to the lower troposphere. The peak ozone values were around 70 ppb, confirming the idea that intrusion layers depart from the lowermost edge of the stratosphere. The data suggest an increase of ozone from the lower to the higher edge of the intrusion layer. This behaviour is also confirmed by stratospheric aerosol caught in the layer. Both observations are in agreement with the idea that sections of the vertical distributions of these constituents in the source region were transferred to central Europe without major change. LAGRANTO trajectory calculations demonstrated a rather shallow outflow from the stratosphere just above the dynamical tropopause, for the first time confirming the conclusions in “Part 1” from the Zugspitze CO observations. The
-
Serva, Federico; Cagnazzo, Chiara; Riccio, Angelo
2016-04-01
The effects of the propagation and breaking of atmospheric gravity waves have long been considered crucial for their impact on the circulation, especially in the stratosphere and mesosphere, between heights of 10 and 110 km. These waves, that in the Earth's atmosphere originate from surface orography (OGWs) or from transient (nonorographic) phenomena such as fronts and convective processes (NOGWs), have horizontal wavelengths between 10 and 1000 km, vertical wavelengths of several km, and frequencies spanning from minutes to hours. Orographic and nonorographic GWs must be accounted for in climate models to obtain a realistic simulation of the stratosphere in both hemispheres, since they can have a substantial impact on circulation and temperature, hence an important role in ozone chemistry for chemistry-climate models. Several types of parameterization are currently employed in models, differing in the formulation and for the values assigned to parameters, but the common aim is to quantify the effect of wave breaking on large-scale wind and temperature patterns. In the last decade, both global observations from satellite-borne instruments and the outputs of very high resolution climate models provided insight on the variability and properties of gravity wave field, and these results can be used to constrain some of the empirical parameters present in most parameterization scheme. A feature of the NOGW forcing that clearly emerges is the intermittency, linked with the nature of the sources: this property is absent in the majority of the models, in which NOGW parameterizations are uncoupled with other atmospheric phenomena, leading to results which display lower variability compared to observations. In this work, we analyze the climate simulated in AMIP runs of the MAECHAM5 model, which uses the Hines NOGW parameterization and with a fine vertical resolution suitable to capture the effects of wave-mean flow interaction. We compare the results obtained with two
-
Hartley, Dana
1998-01-01
The main findings of this research project have been the following: (1) there is a significant feedback from the stratosphere on tropospheric dynamics, and (2) a detailed analysis of the interaction between tropical and polar wave breaking in controlling stratospheric mixing. Two papers are were written and are included. The first paper is titled, "A New Perspective on the Dynamical Link Between the Stratosphere and Troposphere." Atmospheric processes of tropospheric origin can perturb the stratosphere, but direct feedback in the opposite direction is usually assumed to be negligible, despite the troposphere's sensitivity to changes in the release of wave activity into the stratosphere. Here, however, we present evidence that such a feedback exists and can be significant. We find that if the wintertime Arctic polar stratospheric vortex is distorted, either by waves propagating upward from the troposphere or by eastward-travelling stratospheric waves, then there is a concomitant redistribution of stratospheric potential vorticity that induces perturbations in key meteorological fields in the upper troposphere. The feedback is large despite the much greater mass of the troposphere: it can account for up to half of the geopotential height anomaly at the tropopause. Although the relative strength of the feedback is partly due to a cancellation between contributions to these anomalies from lower altitudes, our results imply that stratospheric dynamics and its feedback on the troposphere are more significant for climate modelling and data assimilation than was previously assumed. The second article is titled "Diagnosing the Polar Excitation of Subtropical Waves in the Stratosphere". The poleward migration of planetary scale tongues of subtropical air has often been associated with intense polar vortex disturbances in the stratosphere. This question of vortex influence is reexamined from a potential vorticity (PV) perspective. Anomalous geopotential height and wind fields
-
Stratospheric Impact of Varying Sea Surface Temperatures
Newman, Paul A.; Nash, Eric R.; Nielsen, Jon E.; Waugh, Darryn; Pawson, Steven
2004-01-01
The Finite-Volume General Circulation Model (FVGCM) has been run in 50 year simulations with the: 1) 1949-1999 Hadley Centre sea surface temperatures (SST), and 2) a fixed annual cycle of SSTs. In this presentation we first show that the 1949-1999 FVGCM simulation produces a very credible stratosphere in comparison to an NCEP/NCAR reanalysis climatology. In particular, the northern hemisphere has numerous major and minor stratospheric warming, while the southern hemisphere has only a few over the 50-year simulation. During the northern hemisphere winter, temperatures are both warmer in the lower stratosphere and the polar vortex is weaker than is found in the mid-winter southern hemisphere. Mean temperature differences in the lower stratosphere are shown to be small (less than 2 K), and planetary wave forcing is found to be very consistent with the climatology. We then will show the differences between our varying SST simulation and the fixed SST simulation in both the dynamics and in two parameterized trace gases (ozone and methane). In general, differences are found to be small, with subtle changes in planetary wave forcing that lead to reduced temperatures in the SH and increased temperatures in the NH.
-
The 'surf zone' in the stratosphere
McIntyre, M. E.; Palmer, T. N.
Synoptic, coarse-grain, isentropic maps of Ertel's potential vorticity Q for the northern middle stratosphere, estimated using a large-Richardson-number approximation, are presented for a number of days in January-February 1979, together with some related isentropic trajectory calculations The effects of substituting FGGE for NMC base data are noted, as well as some slight corrections to maps published earlier. The combined evidence from the observations and from dynamical models strongly indicates the existence of planetary-wave breaking, a process in which material contours are rapidly and irreversibly deformed. In the winter stratosphere this occurs most spectacularly in a gigantic 'nonlinear critical layer', or 'surf zone', which surrounds the main polar vortex, and which tends to erode the vortex when wave amplitudes become large. Some of the FGGE-based Q maps suggest that we may be seeing glimpses of local dynamical instabilities and vortex-rollup phenomena within breaking planetary waves. Related phenomena in the troposphere are discussed. An objective definition of the area A( t) of the main vortex, as it appears on isentropic Q maps, is proposed. A smoothed time series of daily values of A( t) should be a statistically powerful 'circulation index' for the state of the winter-time middle stratosphere, which avoids the loss of information incurred by Eulerian space and time averaging.
-
The Unusual Southern Hemisphere Stratosphere Winter of 2002
Newman, Paul A.; Nash, Eric R.
2003-01-01
The southern hemisphere stratospheric winter of 2002 was the most unusual winter yet observed in the southern hemisphere climate record. Temperatures near the edge of the Antarctic polar vortex were considerably warmer than normal over the entire course of the winter. The polar night jet was considerably weaker than normal, and was displaced more poleward than has been observed in previous winters. These record high temperatures and weak jet resulted from a series of wave events that took place over the course of the winter. The first large event occurred on 15 May, and the final warming occurred on 25 October. The propagation of these wave events from the troposphere is diagnosed from time series of Eliassen-Palm flux vectors. The wave events tended to occur irregularly over the course of the winter, and pre-conditioned the polar night jet for the extremely large wave event of 22 September. This large wave event resulted in the first ever observed major stratospheric warming in the southern hemisphere. This wave event split the Antarctic ozone hole. The combined effect of the wave events of the 2002 winter resulted in the smallest ozone hole observed since 1988.
-
Selkirk, Henry B.; Pfister, Leonhard; Chan, K. Roland; Kritz, Mark; Kelly, Ken
1989-01-01
During January and February 1987, as part of the Stratosphere-Troposphere Exchange Project, the NASA ER-2 made 11 flights from Darwin, Australia to investigate dehydration mechanisms in the vicinity of the tropical tropopause. After the monsoon onset in the second week of January, steady easterly flow of 15-25 ms (exp -1) was established in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere over northern Australia and adjacent seas. Penetrating into this regime were elements of the monsoon convection such as overshooting convective turrets and extensive anvils including cyclone cloud shields. In cases of the latter, the resulting flow obstructions tended to produce mesoscale gravity waves. In several instances the ER- 2 meteorological and trace constituent measurements provide a detailed description of the structure of these gravity waves. Among these was STEP Flight 6, 22-23 January. It is of particular interest to STEP because of the close proximity of ice-laden and dehydrated air on the same isentropic surfaces. Convective events inject large amounts of ice into the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere which may not be completely removed by local precipitation processes. In the present instance, a gravity wave for removed from the source region appears to induce relativity rapid upward motion in the ice-laden air and subsequent dessication. Potential mechanisms for such a localized removal process are under investigation.
-
WAVE-E: The WAter Vapour European-Explorer Mission
Jimenez-LLuva, David; Deiml, Michael; Pavesi, Sara
2017-04-01
In the last decade, stratosphere-troposphere coupling processes in the Upper Troposphere Lower Stratosphere (UTLS) have been increasingly recognized to severely impact surface climate and high-impact weather phenomena. Weakened stratospheric circumpolar jets have been linked to worldwide extreme temperature and high-precipitation events, while anomalously strong stratospheric jets can lead to an increase in surface winds and tropical cyclone intensity. Moreover, stratospheric water vapor has been identified as an important forcing for global decadal surface climate change. In the past years, operational weather forecast and climate models have adapted a high vertical resolution in the UTLS region in order to capture the dynamical processes occurring in this highly stratified region. However, there is an evident lack of available measurements in the UTLS region to consistently support these models and further improve process understanding. Consequently, both the IPCC fifth assessment report and the ESA-GEWEX report 'Earth Observation and Water Cycle Science Priorities' have identified an urgent need for long-term observations and improved process understanding in the UTLS region. To close this gap, the authors propose the 'WAter Vapour European - Explorer' (WAVE-E) space mission, whose primary goal is to monitor water vapor in the UTLS at 1 km vertical, 25 km horizontal and sub-daily temporal resolution. WAVE-E consists of three quasi-identical small ( 500 kg) satellites (WAVE-E 1-3) in a constellation of Sun-Synchronous Low Earth Orbits, each carrying a limb sounding and cross-track scanning mid-infrared passive spectrometer (824 cm-1 to 829 cm-1). The core of the instruments builds a monolithic, field-widened type of Michelson interferometer without any moving parts, rendering it rigid and fault tolerant. Synergistic use of WAVE-E and MetOp-NG operational satellites is identified, such that a data fusion algorithm could provide water vapour profiles from the
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Park Sang Wook
2011-03-01
Full Text Available Objectives: The aim of this experiment is to know about Effect of pulse-wave factors in Middle Aged Women by Mountain Cultivated Ginseng Pharmacopuncture. Methods: First 20 Middle Aged women are diagnosed by pulse diagnosis, and then Mountain Cultivated Ginseng Pharmacopuncture(1 injection 20cc were injected. 30 minutes later, pulse diagnosis again performed. As a result, method of one-group pretest-posttes design were used for evaluation. Results: T(Total pulse cycle time statistically significant increased on both left and right chon, kwan,cheok. T4 time statistically significant increased on both left and right chon, kwan, cheok. T4-T1/T indexs except left cheokmaek, Right cheokmaek observation area decreased significantly in four sites.Wm(indicating high pressure retention time indexs increased significantly in the five sites were observed except right chon maek. Conclusions: Effect of pulse-wave factors in Middle Aged Women by Mountain Cultivated Ginseng Pharmacopuncture increased T, T4, Wm and decreased T4-T1/T indexs. The results of this experiment,Mountain Cultivated Ginseng Pharmacopuncture induced to increase the Pulse-wave's stability and strength.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
U. Raffalski
2005-01-01
Full Text Available We present ozone measurements from the millimetre wave radiometer installed at the Swedish Institute of Space Physics (Institutet för rymdfysik, IRF in Kiruna (67.8° N, 20.4° E, 420 m asl. Nearly continuous operation in the winter of 2002/2003 allows us to give an overview of ozone evolution in the stratosphere between 15 and 55 km. In this study we present a detailed analysis of the Arctic winter 2002/2003. By means of a methodology using equivalent latitudes we investigate the meteorological processes in the stratosphere during the entire winter/spring period. During the course of the winter strong mixing into the vortex took place in the middle and upper stratosphere as a result of three minor and one major warming event, but no evidence was found for significant mixing in the lower stratosphere. Ozone depletion in the lower stratosphere during this winter was estimated by measurements on those days when Kiruna was well inside the Arctic polar vortex. The days were carefully chosen using a definition of the vortex edge based on equivalent latitudes. At the 475 K isentropic level a cumulative ozone loss of about 0.5 ppmv was found starting in January and lasting until mid-March. The early ozone loss is probably a result of the very cold temperatures in the lower stratosphere in December and the geographical extension of the vortex to lower latitudes where solar irradiation started photochemical ozone loss in the pre-processed air. In order to correct for dynamic effects of the ozone variation due to diabatic subsidence of air masses inside the vortex, we used N2O measurements from the Odin satellite for the same time period. The derived ozone loss in the lower stratosphere between mid-December and mid-March varies between 1.1±0.1 ppmv on the 150 ppbv N2O isopleth and 1.7±0.1 ppmv on the 50 ppbv N2O isopleth.
-
Impact of major volcanic eruptions on stratospheric water vapour
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Löffler
2016-05-01
Full Text Available Volcanic eruptions can have a significant impact on the Earth's weather and climate system. Besides the subsequent tropospheric changes, the stratosphere is also influenced by large eruptions. Here changes in stratospheric water vapour after the two major volcanic eruptions of El Chichón in Mexico in 1982 and Mount Pinatubo on the Philippines in 1991 are investigated with chemistry–climate model simulations. This study is based on two simulations with specified dynamics of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Hamburg – Modular Earth Submodel System (ECHAM/MESSy Atmospheric Chemistry (EMAC model, performed within the Earth System Chemistry integrated Modelling (ESCiMo project, of which only one includes the long-wave volcanic forcing through prescribed aerosol optical properties. The results show a significant increase in stratospheric water vapour induced by the eruptions, resulting from increased heating rates and the subsequent changes in stratospheric and tropopause temperatures in the tropics. The tropical vertical advection and the South Asian summer monsoon are identified as sources for the additional water vapour in the stratosphere. Additionally, volcanic influences on tropospheric water vapour and El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO are evident, if the long-wave forcing is strong enough. Our results are corroborated by additional sensitivity simulations of the Mount Pinatubo period with reduced nudging and reduced volcanic aerosol extinction.
-
Shi, Chunhua; Gao, Yannan; Cai, Juan; Guo, Dong; Lu, Yan
2018-04-01
The response of the dynamic and thermodynamic structure of the stratosphere to the solar cycle in the boreal winter is investigated based on measurements of the solar cycle by the Spectral Irradiance Monitor onboard the SORCE satellite, monthly ERA-Interim Reanalysis data from the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, the radiative transfer scheme of the Beijing Climate Center (BCC-RAD) and a multiple linear regression model. The results show that during periods of strong solar activity, the solar shortwave heating anomaly from the climatology in the tropical upper stratosphere triggers a local warm anomaly and strong westerly winds in mid-latitudes, which strengthens the upward propagation of planetary wave 1 but prevents that of wave 2. The enhanced westerly jet makes a slight adjustment to the propagation path of wave 1, but prevents wave 2 from propagating upward, decreases the dissipation of wave 2 in the extratropical upper stratosphere and hence weakens the Brewer-Dobson circulation. The adiabatic heating term in relation to the Brewer-Dobson circulation shows anomalous warming in the tropical lower stratosphere and anomalous cooling in the mid-latitude upper stratosphere.
-
Variability of Irreversible Poleward Transport in the Lower Stratosphere
Olsen, Mark; Douglass, Anne; Newman, Paul; Nash, Eric; Witte, Jacquelyn; Ziemke, Jerry
2011-01-01
The ascent and descent of the Brewer-Dobson circulation plays a large role in determining the distributions of many constituents in the extratropical lower stratosphere. However, relatively fast, quasi-horizontal transport out of the tropics and polar regions also significantly contribute to determining these distributions. The tropical tape recorder signal assures that there must be outflow from the tropics into the extratropical lower stratosphere. The phase of the quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) and state of the polar vortex are known to modulate the transport from the tropical and polar regions, respectively. In this study we examine multiple years of ozone distributions in the extratropical lower stratosphere observed by the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) and the Aura High Resolution Dynamic Limb Sounder (HIRDLS). The distributions are compared with analyses of irreversible, meridional isentropic transport. We show that there is considerable year-to-year seasonal variability in the amount of irreversible transport from the tropics, which is related to both the phase of the QBO and the state of the polar vortex. The reversibility of the transport is consistent with the number of observed breaking waves. The variability of the atmospheric index of refraction in the lower stratosphere is shown to be significantly correlated with the wave breaking and amount of irreversible transport. Finally, we will show that the seasonal extratropical stratosphere to troposphere transport of ozone can be substantially modulated by the amount of irreversible meridional transport in the lower stratosphere and we investigate how observable these differences are in data of tropospheric ozone.
-
DeWit, R. J.; Janches, D.; Fritts, D. C.; Stockwell, R. G.; Coy, L.
2017-01-01
The Southern Argentina Agile MEteor Radar (SAAMER), located at Tierra del Fuego (53.7degS, 67.7degW), has been providing near-continuous high-resolution measurements of winds and high-frequency gravity wave (GW) momentum fluxes of the mesopause region since May 2008. As SAAMER is located in the lee of the largest seasonal GW hot spot on Earth, this is a key location to study GWs and their interaction with large-scale motions. GW momentum flux climatologies are shown for the first time for this location and discussed in light of these unique dynamics. Particularly, the large eastward GW momentum fluxes during local winter are surprising, as these observations cannot be explained by the direct upward propagation of expected large-amplitude mountain waves (MWs) through the eastward stratospheric jet. Instead, these results are interpreted as secondary GWs propagating away from stratospheric sources over the Andes accompanying MW breaking over the Southern Andes.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. M. Worthington
1999-02-01
Full Text Available A simple method is described, based on standard VHF wind-profiler data, where imbalances of echo power between four off-vertical radar beams, caused by mountain waves, can be used to calculate the orientation of the wave pattern. It is shown that the mountain wave azimuth (direction of the horizontal component of the wavevector, is given by the vector [ W (PE - P W ,W (PN - P S ]; PN, PS, PE, PW are radar echo powers, measured in dB, in beams pointed away from vertical by the same angle towards north, south, east and west respectively, and W is the vertical wind velocity. The method is applied to Aberystwyth MST radar data, and the calculated wave vector usually, but not always, points into the low-level wind direction. The mean vertical wind at Aberystwyth, which may also be affected by tilted aspect-sensitive layers, is investigated briefly using the entire radar output 1990-1997. The mean vertical-wind profile is inconsistent with existing theories, but a new mountain-wave interpretation is proposed.Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (middle atmosphere dynamics; waves and tides; instruments and techniques.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Garny, Hella
2011-05-13
The stratospheric meridional circulation is projected to be subject to changes due to enhanced greenhouse-gas concentrations in the atmosphere. This study aims to diagnose and explain long-term changes in the stratospheric meridional circulation using the chemistry-climate model E39CA. The diagnosed strengthening of the circulation is found to be driven by increases in tropical sea surface temperatures which lead to a strengthening and upward shift of the subtropical jets. This enables enhanced vertical propagation of large scale waves into the lower stratosphere, and therefore stronger local wave forcing of the meridional circulation in the tropical lower stratosphere. The impact of changes in transport on the ozone layer is analysed using a newly developed method that allows the separation of the effects of transport and chemistry changes on ozone. It is found that future changes of mean stratospheric ozone concentrations are largely determined by changes in chemistry, while changes in transport of ozone play a minor role. (orig.)
-
Can gravity waves significantly impact PSC occurrence in the Antarctic?
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. M. Woollands
2009-11-01
Full Text Available A combination of POAM III aerosol extinction and CHAMP RO temperature measurements are used to examine the role of atmospheric gravity waves in the formation of Antarctic Polar Stratospheric Clouds (PSCs. POAM III aerosol extinction observations and quality flag information are used to identify Polar Stratospheric Clouds using an unsupervised clustering algorithm.
A PSC proxy, derived by thresholding Met Office temperature analyses with the PSC Type Ia formation temperature (TNAT, shows general agreement with the results of the POAM III analysis. However, in June the POAM III observations of PSC are more abundant than expected from temperature threshold crossings in five out of the eight years examined. In addition, September and October PSC identified using temperature thresholding is often significantly higher than that derived from POAM III; this observation probably being due to dehydration and denitrification. Comparison of the Met Office temperature analyses with corresponding CHAMP observations also suggests a small warm bias in the Met Office data in June. However, this bias cannot fully explain the differences observed.
Analysis of CHAMP data indicates that temperature perturbations associated with gravity waves may partially explain the enhanced PSC incidence observed in June (relative to the Met Office analyses. For this month, approximately 40% of the temperature threshold crossings observed using CHAMP RO data are associated with small-scale perturbations. Examination of the distribution of temperatures relative to TNAT shows a large proportion of June data to be close to this threshold, potentially enhancing the importance of gravity wave induced temperature perturbations. Inspection of the longitudinal structure of PSC occurrence in June 2005 also shows that regions of enhancement are geographically associated with the Antarctic Peninsula; a known mountain wave "hotspot". The -
Climatology and energy budget of the northern hemisphere middle stratosphere during 1972
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tahnk, W R [Air Force Geophysics Lab., Bedforo, MA; Newell, R E
1975-01-01
The 10-2 mb (approx. 30 to 40 km) layer of the atmosphere in winter receives energy from two different sources: mechanical energy is carried up from the troposphere and lower stratosphere while energy is generated in situ by the gradients of radiative heating and cooling. We show here from data for 1972 that the latter primarily governs the energy budget of the middle stratosphere in early winter while the former becomes of comparable size, and often dominates, in the middle and late winter. Radiative energy sources for the summer hemisphere are very small, as there is considerable compensation between solar heating through ozone absorption and infrared cooling by carbon dioxide and ozone. Standing and travelling waves are quite clear-cut at 5 and 2 mb in winter, as much of the chaos of lower regions is filtered out in the lower stratosphere; the standing waves at 2 mb may reflect surface properties more effectively than flow patterns at lower levels. A westward-travelling wave, with a period of about a month, was evident in early 1972.
-
Coupling in the middle atmosphere related to the 2013 major sudden stratospheric warming
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. J. de Wit
2015-03-01
Full Text Available The previously reported observation of anomalous eastward gravity wave forcing at mesopause heights around the onset of the January 2013 major sudden stratospheric warming (SSW over Trondheim, Norway (63° N, 10° E, is placed in a global perspective using Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS temperature observations from the Aura satellite. It is shown that this anomalous forcing results in a clear cooling over Trondheim about 10 km below mesopause heights. Conversely, near the mesopause itself, where the gravity wave forcing was measured, observations with meteor radar, OH airglow and MLS show no distinct cooling. Polar cap zonal mean temperatures show a similar vertical profile. Longitudinal variability in the high northern-latitude mesosphere and lower thermosphere (MLT is characterized by a quasi-stationary wave-1 structure, which reverses phase at altitudes below ~ 0.1 hPa. This wave-1 develops prior to the SSW onset, and starts to propagate westward at the SSW onset. The latitudinal pole-to-pole temperature structure associated with the major SSW shows a warming (cooling in the winter stratosphere (mesosphere which extends to about 40° N. In the stratosphere, a cooling extending over the equator and far into the summer hemisphere is observed, whereas in the mesosphere an equatorial warming is noted. In the Southern Hemisphere mesosphere, a warm anomaly overlaying a cold anomaly is present, which is shown to propagate downward in time. This observed structure is in accordance with the temperature perturbations predicted by the proposed interhemispheric coupling mechanism for cases of increased winter stratospheric planetary wave activity, of which major SSWs are an extreme case. These results provide observational evidence for the interhemispheric coupling mechanism, and for the wave-mean flow interaction believed to be responsible for the establishment of the anomalies in the summer hemisphere.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hoffmann, P.; Serafimovich, A.; Peters, D.; Latteck, R. [Leibniz-Inst. fuer Atmosphaerenphysik, Kuehlungsborn (Germany); Dalin, P. [Swedish Inst. of Space Physics, Kiruna (Sweden); Goldberg, R. [NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD (United States)
2006-07-01
During the MaCWAVE campaign, combined rocket, radiosonde and ground-based measurements have been performed at the Norwegian Andoeya rocket range (ARR) near Andenes and the Swedish rocket range (ESRANGE) near Kiruna in January 2003 to study gravity waves in the vicinity of the Scandinavian mountain ridge. The investigations presented here are mainly based on the evaluation of continuous radar measurements with the ALWIN VHP radar in the upper troposphere/ lower stratosphere at Andenes (69.3 N, 16.0 E) and the ESRAD VHP radar near Kiruna (67.9 N, 21.9 E). Both radars are separated by about 260 km. Based on wavelet transformations of both data sets, the strongest activity of inertia gravity waves in the upper troposphere has been detected during the first period from 24-26 January 2003 with dominant vertical wavelengths of about 4-5 km as well as with dominant observed periods of about 13-14 h for the altitude range between 5 and 8 km under the additional influence of mountain waves. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia gravity waves with characteristic horizontal wavelengths of {proportional_to}200 km moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia gravity waves with intrinsic periods in the order of {proportional_to}5 h and with horizontal wavelengths of 200 km, moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind. From the derived downward energy propagation it is supposed, that these waves are likely generated by a jet streak in the upper troposphere. The parameters of the jet-induced gravity waves have been estimated at both sites separately. The identified gravity waves are coherent at both locations and show higher amplitudes on the east-side of the Scandinavian mountain ridge, as expected by the influence of mountains. (orig.)
-
Stratospheric dryness: model simulations and satellite observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Lelieveld
2007-01-01
Full Text Available The mechanisms responsible for the extreme dryness of the stratosphere have been debated for decades. A key difficulty has been the lack of comprehensive models which are able to reproduce the observations. Here we examine results from the coupled lower-middle atmosphere chemistry general circulation model ECHAM5/MESSy1 together with satellite observations. Our model results match observed temperatures in the tropical lower stratosphere and realistically represent the seasonal and inter-annual variability of water vapor. The model reproduces the very low water vapor mixing ratios (below 2 ppmv periodically observed at the tropical tropopause near 100 hPa, as well as the characteristic tape recorder signal up to about 10 hPa, providing evidence that the dehydration mechanism is well-captured. Our results confirm that the entry of tropospheric air into the tropical stratosphere is forced by large-scale wave dynamics, whereas radiative cooling regionally decelerates upwelling and can even cause downwelling. Thin cirrus forms in the cold air above cumulonimbus clouds, and the associated sedimentation of ice particles between 100 and 200 hPa reduces water mass fluxes by nearly two orders of magnitude compared to air mass fluxes. Transport into the stratosphere is supported by regional net radiative heating, to a large extent in the outer tropics. During summer very deep monsoon convection over Southeast Asia, centered over Tibet, moistens the stratosphere.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Hoffmann
2006-11-01
Full Text Available During the {MaCWAVE} campaign, combined rocket, radiosonde and ground-based measurements have been performed at the Norwegian Andøya Rocket Range (ARR near Andenes and the Swedish Rocket Range (ESRANGE near Kiruna in January 2003 to study gravity waves in the vicinity of the Scandinavian mountain ridge. The investigations presented here are mainly based on the evaluation of continuous radar measurements with the ALWIN VHF radar in the upper troposphere/ lower stratosphere at Andenes (69.3° N, 16.0° E and the ESRAD VHF radar near Kiruna (67.9° N, 21.9° E. Both radars are separated by about 260 km. Based on wavelet transformations of both data sets, the strongest activity of inertia gravity waves in the upper troposphere has been detected during the first period from 24–26 January 2003 with dominant vertical wavelengths of about 4–5 km as well as with dominant observed periods of about 13–14 h for the altitude range between 5 and 8 km under the additional influence of mountain waves. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia gravity waves with characteristic horizontal wavelengths of ~200 km moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia gravity waves with intrinsic periods in the order of ~5 h and with horizontal wavelengths of 200 km, moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind. From the derived downward energy propagation it is supposed, that these waves are likely generated by a jet streak in the upper troposphere. The parameters of the jet-induced gravity waves have been estimated at both sites separately. The identified gravity waves are coherent at both locations and show higher amplitudes on the east-side of the Scandinavian mountain ridge, as expected by the influence of mountains.
-
The effects of the Indo-Pacific warm pool on the stratosphere
Zhou, Xin; Li, Jianping; Xie, Fei; Ding, Ruiqiang; Li, Yanjie; Zhao, Sen; Zhang, Jiankai; Li, Yang
2017-03-01
Sea surface temperature (SST) in the Indo-Pacific warm pool (IPWP) plays a key role in influencing East Asian climate, and even affects global-scale climate change. This study defines IPWP Niño and IPWP Niña events to represent the warm and cold phases of IPWP SST anomalies, respectively, and investigates the effects of these events on stratospheric circulation and temperature. Results from simulations forced by observed SST anomalies during IPWP Niño and Niña events show that the tropical lower stratosphere tends to cool during IPWP Niño events and warm during IPWP Niña events. The responses of the northern and southern polar vortices to IPWP Niño events are fairly symmetric, as both vortices are significantly warmed and weakened. However, the responses of the two polar vortices to IPWP Niña events are of opposite sign: the northern polar vortex is warmed and weakened, but the southern polar vortex is cooled and strengthened. These features are further confirmed by composite analysis using reanalysis data. A possible dynamical mechanism connecting IPWP SST to the stratosphere is suggested, in which IPWP Niño and Niña events excite teleconnections, one similar to the Pacific-North America pattern in the Northern Hemisphere and a Rossby wave train in the Southern Hemisphere, which project onto the climatological wave in the mid-high latitudes, intensifying the upward propagation of planetary waves into the stratosphere and, in turn, affecting the polar vortex.
-
Correlative measurements of the stratospheric aerosols
Santer, R.; Brogniez, C.; Herman, M.; Diallo, S.; Ackerman, M.
1992-12-01
Joint experiments were organized or available during stratospheric flights of a photopolarimeter, referred to as RADIBAL (radiometer balloon). In May 1984, RADIBAL flew simultaneously with another balloonborne experiment conducted by the Institut d'Aeronomie Spatiale de Belgique (IASB), which provides multiwavelength vertical profiles of the aerosol scattering coefficient. At this time, the El Chichon layer was observable quite directly from mountain sites. A ground-based station set up at Pic du Midi allowed an extensive description of the aerosol optical properties. The IASB and the Pic du Midi observations are consistent with the aerosol properties derived from the RADIBAL measurement analysis.
-
Fiore, A. M.; Lin, M.; Cooper, O. R.; Horowitz, L. W.; Naik, V.; Levy, H.; Langford, A. O.; Johnson, B. J.; Oltmans, S. J.; Senff, C. J.
2011-12-01
As the National Ambient Air Quality (NAAQS) standard for ozone (O_{3}) is lowered, it pushes closer to policy-relevant background levels (O_{3} concentrations that would exist in the absence of North American anthropogenic emissions), making attainment more difficult with local controls. We quantify the Asian and stratospheric components of this North American background, with a primary focus on the western United States. Prior work has identified this region as a hotspot for deep stratospheric intrusions in spring. We conduct global simulations at 200 km and 50 km horizontal resolution with the GFDL AM3 model, including a stratospheric O_{3} tracer and two sensitivity simulations with anthropogenic emissions from Asia and North America turned off. The model is evaluated with a suite of in situ and satellite measurements during the NOAA CalNex campaign (May-June 2010). The model reproduces the principle features in the observed surface to near tropopause distribution of O_{3} along the California coast, including its latitudinal variation and the development of regional high-O_{3} episodes. Four deep tropopause folds are diagnosed and we find that the remnants of these stratospheric intrusions are transported to the surface of Southern California and Western U.S. Rocky Mountains, contributing 10-30 ppbv positive anomalies relative to the simulated campaign mean stratospheric component in the model surface layer. We further examine the contribution of North American background, including its stratospheric and Asian components, to the entire distribution of observed MDA8 O_{3} at 12 high-elevation CASTNet sites in the Mountain West. We find that the stratospheric O_{3} tracer constitutes 50% of the North American background, and can enhance surface maximum daily 8-hour average (MDA8) O_{3} by 20 ppb when observed surface O_{3} is in the range of 60-80 ppbv. Our analysis highlights the potential for natural sources such as deep stratospheric intrusions to contribute
-
Upper-mantle velocities below the Scandinavian Mountains from P- and S- wave traveltime tomography
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hejrani, Babak; Balling, N.; Jacobsen, B. H.
2017-01-01
More than 20000 arrival-times of teleseismic P- and S-waves were measured over a period of more than 10 years in five separate temporary and two permanent seismic networks covering the Scandinavian (Scandes) Mountains and adjacent areas of the Baltic Shield. The relative traveltime residuals were...... between Lofoten and the crest of the Northern Scandes Mountains and stays off the coast further north. Seismic velocities in the depth interval 100-300 km change across the UMVB from low relative VP and even lower relative VS on the western side to high relative VP and even higher relative VS to the east...
-
A warming tropical central Pacific dries the lower stratosphere
Ding, Qinghua; Fu, Qiang
2018-04-01
The amount of water vapor in the tropical lower stratosphere (TLS), which has an important influence on the radiative energy budget of the climate system, is modulated by the temperature variability of the tropical tropopause layer (TTL). The TTL temperature variability is caused by a complex combination of the stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO), tropospheric convective processes in the tropics, and the Brewer-Dobson circulation (BDC) driven by mid-latitude and subtropical atmospheric waves. In 2000, the TLS water vapor amount exhibited a stepwise transition to a dry phase, apparently caused by a change in the BDC. In this study, we present observational and modeling evidence that the epochal change of water vapor between the periods of 1992-2000 and 2001-2005 was also partly caused by a concurrent sea surface temperature (SST) warming in the tropical central Pacific. This SST warming cools the TTL above by enhancing the equatorial wave-induced upward motion near the tropopause, which consequently reduces the amount of water vapor entering the stratosphere. The QBO affects the TLS water vapor primarily on inter-annual timescales, whereas a classical El Niño southern oscillation (ENSO) event has small effect on tropical mean TLS water vapor because its responses are longitudinally out of phase. This study suggests that the tropical central Pacific SST is another driver of TLS water vapor variability on inter-decadal timescales and the tropical SST changes could contribute to about 30% of the step-wise drop of the lower stratospheric water vapor from 1992-2000 to 2001-2005.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rosen, J.; Ivanov, V.A.
1993-01-01
Stratospheric aerosol measurements can provide both spatial and temporal data of sufficient resolution to be of use in climate models. Relatively recent results from a wide range of instrument techniques for measuring stratospheric aerosol parameters are described. Such techniques include impactor sampling, lidar system sensing, filter sampling, photoelectric particle counting, satellite extinction-sensing using the sun as a source, and optical depth probing, at sites mainly removed from tropospheric aerosol sources. Some of these techniques have also had correlative and intercomparison studies. The main methods for determining the vertical profiles of stratospheric aerosols are outlined: lidar extinction measurements from satellites; impactor measurements from balloons and aircraft; and photoelectric particle counter measurements from balloons, aircraft, and rockets. The conversion of the lidar backscatter to stratospheric aerosol mass loading is referred to. Absolute measurements of total solar extinction from satellite orbits can be used to extract the aerosol extinction, and several examples of vertical profiles of extinction obtained with the SAGE satellite are given. Stratospheric mass loading can be inferred from extinction using approximate linear relationships but under restrictive conditions. Impactor sampling is essentially the only method in which the physical nature of the stratospheric aerosol is observed visually. Vertical profiles of stratospheric aerosol number concentration using impactor data are presented. Typical profiles using a dual-size-range photoelectric dustsonde particle counter are given for volcanically disturbed and inactive periods. Some measurements of the global distribution of stratospheric aerosols are also presented. Volatility measurements are described, indicating that stratospheric aerosols are composed primarily of about 75% sulfuric acid and 25% water
-
Methane as a Diagnostic Tracer of Changes in the Brewer-Dobson Circulation of the Stratosphere
Remsberg, E. E.
2015-01-01
This study makes use of time series of methane (CH4/ data from the Halogen Occultation Experiment (HALOE) to detect whether there were any statistically significant changes of the Brewer-Dobson circulation (BDC) within the stratosphere during 1992-2005. The HALOE CH4 profiles are in terms of mixing ratio versus pressure altitude and are binned into latitude zones within the Southern Hemisphere and the Northern Hemisphere. Their separate time series are then analyzed using multiple linear regression (MLR) techniques. The CH4 trend terms for the Northern Hemisphere are significant and positive at 10 N from 50 to 7 hPa and larger than the tropospheric CH4 trends of about 3%decade(exp -1) from 20 to 7 hPa. At 60 N the trends are clearly negative from 20 to 7 hPa. Their combined trends indicate an acceleration of the BDC in the middle stratosphere of the Northern Hemisphere during those years, most likely due to changes from the effects of wave activity. No similar significant BDC acceleration is found for the Southern Hemisphere. Trends from HALOE H2O are analyzed for consistency. Their mutual trends with CH4 are anti-correlated qualitatively in the middle and upper stratosphere, where CH4 is chemically oxidized to H2O. Conversely, their mutual trends in the lower stratosphere are dominated by their trends upon entry to the tropical stratosphere. Time series residuals for CH4 in the lower mesosphere also exhibit structures that are anti-correlated in some instances with those of the tracer-like species HCl. Their occasional aperiodic structures indicate the effects of transport following episodic, wintertime wave activity. It is concluded that observed multi-year, zonally averaged distributions of CH4 can be used to diagnose major instances of wave-induced transport in the middle atmosphere and to detect changes in the stratospheric BDC.
-
Yu, Yueyue; Cai, Ming; Ren, Rongcai
2017-08-01
We consider three indices to measure the polar stratospheric mass and stratospheric meridional mass circulation variability: anomalies of (1) total mass in the polar stratospheric cap (60-90°N, above the isentropic surface 400 K, PSM), (2) total adiabatic mass transport across 60°N into the polar stratosphere cap (AMT), (3) and total diabetic mass transport across 400 K from the polar stratosphere into the troposphere below (DMT). It is confirmed that the negative stratospheric Northern Annular Mode (NAM) and PSM indices have a nearly indistinguishable temporal evolution and a similar red-noise-like spectrum with a de-correlation timescale of 4 weeks. This enables us to examine the low-frequency nature of the NAM in the framework of mass circulation, namely, d/{dt}{PSM}={AMT} - {DMT} . The DMT index tends to be positively correlated with the PSM with a red-noise-like spectrum, representing slow radiative cooling processes giving rise to a de-correlation timescale of 3-4 weeks. The AMT is nearly perfectly correlated with the day-to-day tendency of PSM, reflecting a robust quasi 90° out-of-phase relation between the AMT and PSM at all frequency bands. Variations of vertically westward tilting of planetary waves contribute mainly to the high-frequency portion of AMT. It is the wave amplitude's slow vacillation that plays the leading role in the quasi 90° out-of-phase relation between the AMT and PSM. Based on this, we put forward a linear stochastic model with a low-frequency amplification feedback from low-frequency amplitude vacillations of planetary waves to explain the amplified low-frequency response of PSM/NAM to a stochastic forcing from the westward tilting variability.
-
Yang, Fanglin; Schlesinger, Michael E.; Andranova, Natasha; Zubov, Vladimir A.; Rozanov, Eugene V.; Callis, Lin B.
2003-01-01
The sensitivity of the middle atmospheric temperature and circulation to the treatment of mean- flow forcing due to breaking gravity waves was investigated using the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 40-layer Mesosphere-Stratosphere-Troposphere General Circulation Model (MST-GCM). Three GCM experiments were performed. The gravity-wave forcing was represented first by Rayleigh friction, and then by the Alexander and Dunkerton (AD) parameterization with weak and strong breaking effects of gravity waves. In all experiments, the Palmer et al. parameterization was included to treat the breaking of topographic gravity waves in the troposphere and lower stratosphere. Overall, the experiment with the strong breaking effect simulates best the middle atmospheric temperature and circulation. With Rayleigh friction and the weak breaking effect, a large warm bias of up to 60 C was found in the summer upper mesosphere and lower thermosphere. This warm bias was linked to the inability of the GCM to simulate the reversal of the zonal winds from easterly to westerly crossing the mesopause in the summer hemisphere. With the strong breaking effect, the GCM was able to simulate this reversal, and essentially eliminated the warm bias. This improvement was the result of a much stronger meridional transport circulation that possesses a strong vertical ascending branch in the summer upper mesosphere, and hence large adiabatic cooling. Budget analysis indicates that 'in the middle atmosphere the forces that act to maintain a steady zonal-mean zonal wind are primarily those associated with the meridional transport circulation and breaking gravity waves. Contributions from the interaction of the model-resolved eddies with the mean flow are small. To obtain a transport circulation in the mesosphere of the UIUC MST-GCM that is strong enough to produce the observed cold summer mesopause, gravity-wave forcing larger than 100 m/s/day in magnitude is required near the summer mesopause. In
-
Garcia, Rolando R.; Boville, Byron A.
1994-01-01
According to the 'downward control' principle, the extratropical mean vertical velocity on a given pressure level is approximately proportional to the meridional gradient of the vertically integrated zonal force per unit mass exerted by waves above that level. In this paper, a simple numerical model that includes parameterizations of both planetary and gravity wave breaking is used to explore the influence of gravity wave breaking in the mesosphere on the mean meridional circulation and temperature distribution at lower levels in the polar winter stratosphere. The results of these calculations suggest that gravity wave drag in the mesosphere can affect the state of the polar winter stratosphere down to altitudes below 30 km. The effect is most important when planetary wave driving is relatively weak: that is, during southern winter and in early northern winter. In southern winter, downwelling weakens by a factor of 2 near the stratospause and by 20% at 30 km when gravity wave drag is not included in the calculations. As a consequence, temperatures decrease considerably throughout the polar winter stratosphere (over 20 K above 40 km and as much as 8 K at 30 km, where the effect is enhanced by the long radiative relaxation timescale). The polar winter states obtained when gravity wave drag is omitted in this simple model resemble the results of simulations with some general circulation models and suggest that some of the shortcomings of the latter may be due to a deficit in mesospheric momentum deposition by small-scale gravity waves.
-
Stratospheric experiments on curing of composite materials
Chudinov, Viacheslav; Kondyurin, Alexey; Svistkov, Alexander L.; Efremov, Denis; Demin, Anton; Terpugov, Viktor; Rusakov, Sergey
2016-07-01
Future space exploration requires a large light-weight structure for habitats, greenhouses, space bases, space factories and other constructions. A new approach enabling large-size constructions in space relies on the use of the technology of polymerization of fiber-filled composites with a curable polymer matrix applied in the free space environment on Erath orbit. In orbit, the material is exposed to high vacuum, dramatic temperature changes, plasma of free space due to cosmic rays, sun irradiation and atomic oxygen (in low Earth orbit), micrometeorite fluence, electric charging and microgravitation. The development of appropriate polymer matrix composites requires an understanding of the chemical processes of polymer matrix curing under the specific free space conditions to be encountered. The goal of the stratospheric flight experiment is an investigation of the effect of the stratospheric conditions on the uncured polymer matrix of the composite material. The unique combination of low residual pressure, high intensity UV radiation including short-wave UV component, cosmic rays and other aspects associated with solar irradiation strongly influences the chemical processes in polymeric materials. We have done the stratospheric flight experiments with uncured composites (prepreg). A balloon with payload equipped with heater, temperature/pressure/irradiation sensors, microprocessor, carrying the samples of uncured prepreg has been launched to stratosphere of 25-30 km altitude. After the flight, the samples have been tested with FTIR, gel-fraction, tensile test and DMA. The effect of cosmic radiation has been observed. The composite was successfully cured during the stratospheric flight. The study was supported by RFBR grants 12-08-00970 and 14-08-96011.
-
An Atlantic streamer in stratospheric ozone observations and SD-WACCM simulation data
Hocke, Klemens; Schranz, Franziska; Maillard Barras, Eliane; Moreira, Lorena; Kämpfer, Niklaus
2017-03-01
Observation and simulation of individual ozone streamers are important for the description and understanding of non-linear transport processes in the middle atmosphere. A sudden increase in mid-stratospheric ozone occurred above central Europe on 4 December 2015. The GROund-based Millimeter-wave Ozone Spectrometer (GROMOS) and the Stratospheric Ozone MOnitoring RAdiometer (SOMORA) in Switzerland measured an ozone enhancement of about 30 % at 34 km altitude (8.3 hPa) from 1 to 4 December. A similar ozone increase is simulated by the Specified Dynamics Whole Atmosphere Community Climate (SD-WACCM) model. Further, the global ozone fields at 34 km altitude (8.3 hPa) from SD-WACCM and the satellite experiment Aura/MLS show a remarkable agreement for the location and timing of an ozone streamer (large-scale tongue-like structure) extending from the subtropics in northern America over the Atlantic to central Europe. This agreement indicates that SD-WACCM can inform us about the wind inside the Atlantic ozone streamer. SD-WACCM shows an eastward wind of about 100 m s-1 inside the Atlantic streamer in the mid-stratosphere. SD-WACCM shows that the Atlantic streamer flows along the edge of the polar vortex. The Atlantic streamer turns southward at an erosion region of the polar vortex located above the Caspian Sea. The spatial distribution of stratospheric water vapour indicates a filament outgoing from this erosion region. The Atlantic streamer, the polar vortex erosion region and the water vapour filament belong to the process of planetary wave breaking in the so-called surf zone of the northern midlatitude winter stratosphere.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Serafimovich, A.; Zuelicke, C.; Hoffmann, P.; Peters, D.; Singer, W. [Leibniz-Inst. fuer Atmosphaerenphysik, Kuehlungsborn (Germany); Dalin, P. [Swedish Inst. of Space Physics, Kiruna (Sweden)
2006-07-01
We present an experimental and modelling study of a strong gravity wave event in the upper troposphere/lower stratosphere near the Scandinavian mountain ridge. Continuous VHP radar measurements during the MaCWAVE rocket and ground-based measurement campaign were performed at the Norwegian Andoya rocket range (ARR) near Andenes (69.3 N, 16 E) in January 2003. Detailed gravity wave investigations based on PSU/NCAR fifth-generation mesoscale model (MM5) data have been used for comparison with experimentally obtained results. The model data show the presence of a mountain wave and of an inertia gravity wave generated by a jet streak near the tropopause region. Temporal and spatial dependencies of jet induced inertia gravity waves with dominant observed periods of about 13 h and vertical wavelengths of {proportional_to}4.5-5 km are investigated with wavelet transform applied on radar measurements and model data. The jet induced wave packet is observed to move upstream and downward in the upper troposphere. The model data agree with the experimentally obtained results fairly well. Possible reasons for the observed differences, e.g. in the time of maximum of the wave activity, are discussed. Finally, the vertical fluxes of horizontal momentum are estimated with different methods and provide similar amplitudes. We found indications that the derived positive vertical flux of the horizontal momentum corresponds to the obtained parameters of the jet-induced inertia gravity wave, but only at the periods and heights of the strongest wave activity. (orig.)
-
Kim, Yongha; Sunkara, Eswaraiah; Hong, Junseok; Ratnam, Venkat; Chandran, Amal; Rao, Svb; Riggin, Dennis
2015-04-01
The mesosphere-lower thermosphere (MLT) response to extremely rare minor sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) events was observed for the first time in the southern hemisphere (SH) during 2010 and is investigated using the meteor radar located at King Sejong Station (62.22°S, 58.78°W), Antarctica. Three episodic SSWs were noticed from early August to late October 2010. The mesospheric wind field was found to significantly differ from normal years due to enhanced planetary wave (PW) activity before the SSWs and secondary PWs in the MLT afterwards. The zonal winds in the mesosphere reversed approximately a week before the SSW occurrence in the stratosphere as has been observed 2002 major SSW, suggesting the downward propagation of disturbance during minor SSWs as well. Signatures of mesospheric cooling (MC) in association with SSWs are found in the Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) measurements. SD-WACCM simulations are able to produce these observed features.
-
ATMOS Stratospheric Deuterated Water and Implications for Tropospheric-Stratospheric Transport
Moyer, Elisabeth J.; Irion, Fredrick W.; Yung, Yuk L.; Gunson, Michael R.
1996-01-01
Measurements of the isotopic composition of stratospheric water by the ATMOS instrument are used to infer the convective history of stratospheric air. The average water vapor entering the stratosphere is found to be highly depleted of deuterium, with delta-D(sub w) of -670 +/- 80 (67% deuterium loss). Model calculations predict, however, that under conditions of thermodynamic equilibrium, dehydration to stratospheric mixing ratios should produce stronger depletion to delta-D(sub w) of -800 to 900 (80-90% deuterium loss). Deuterium enrichment of water vapor in ascending parcels can occur only in conditions of rapid convection; enrichments persisting into the stratosphere require that those conditions continue to near-tropopause altitudes. We conclude that either the predominant source of water vapor to the uppermost troposphere is enriched convective water, most likely evaporated cloud ice, or troposphere-stratosphere transport occurs closely associated with tropical deep convection.
-
Ramirez, C.; Nyblade, A.; Emry, E. L.; Julià, J.; Sun, X.; Anandakrishnan, S.; Wiens, D. A.; Aster, R. C.; Huerta, A. D.; Winberry, P.; Wilson, T.
2017-12-01
A uniform set of crustal parameters for seismic stations deployed on rock in West Antarctica and the Transantarctic Mountains (TAM) has been obtained to help elucidate similarities and differences in crustal structure within and between several tectonic blocks that make up these regions. P-wave receiver functions have been analysed using the H-κ stacking method to develop estimates of thickness and bulk Poisson's ratio for the crust, and jointly inverted with surface wave dispersion measurements to obtain depth-dependent shear wave velocity models for the crust and uppermost mantle. The results from 33 stations are reported, including three stations for which no previous results were available. The average crustal thickness is 30 ± 5 km along the TAM front, and 38 ± 2 km in the interior of the mountain range. The average Poisson's ratios for these two regions are 0.25 ± 0.03 and 0.26 ± 0.02, respectively, and they have similar average crustal Vs of 3.7 ± 0.1 km s-1. At multiple stations within the TAM, we observe evidence for mafic layering within or at the base of the crust, which may have resulted from the Ferrar magmatic event. The Ellsworth Mountains have an average crustal thickness of 37 ± 2 km, a Poisson's ratio of 0.27, and average crustal Vs of 3.7 ± 0.1 km s-1, similar to the TAM. This similarity is consistent with interpretations of the Ellsworth Mountains as a tectonically rotated TAM block. The Ross Island region has an average Moho depth of 25 ± 1 km, an average crustal Vs of 3.6 ± 0.1 km s-1 and Poisson's ratio of 0.30, consistent with the mafic Cenozoic volcanism found there and its proximity to the Terror Rift. Marie Byrd Land has an average crustal thickness of 30 ± 2 km, Poisson's ratio of 0.25 ± 0.04 and crustal Vs of 3.7 ± 0.1 km s-1. One station (SILY) in Marie Byrd Land is near an area of recent volcanism and deep (25-40 km) seismicity, and has a high Poisson's ratio, consistent with the presence of partial melt in the crust.
-
Servali, A.; Long, M. D.; Benoit, M.
2017-12-01
The eastern margin of North America has been affected by a series of mountain building and rifting events that have likely shaped the deep structure of the lithosphere. Observations of seismic anisotropy can provide insight into lithospheric deformation associated with these past tectonic events, as well as into present-day patterns of mantle flow beneath the passive margin. Previous work on SKS splitting beneath eastern North America has revealed fast splitting directions parallel to the strike of the Appalachian orogen in the central and southern Appalachians. A major challenge to the interpretation of SKS splitting measurements, however, is the lack of vertical resolution; isolating anisotropic structures at different depths is therefore difficult. Complementary constraints on the depth distribution of anisotropy can be provided by surface waves. In this study, we analyze the scattering of Love wave energy to Rayleigh waves, which is generated via sharp lateral gradients in anisotropic structure along the ray path. The scattered phases, known as quasi-Love (QL) waves, exhibit amplitude behavior that depend on the strength of the anisotropic contrast as well as the angle between the propagation azimuth and the anisotropic symmetry axis. We analyze data collected by the dense MAGIC seismic array across the central Appalachians. We examine teleseismic earthquakes of magnitude 6.7 and greater over a range of backazimuths, and isolate surface waves at periods between 100 and 500 seconds. We compare the data to synthetic seismograms generated by the Princeton Global ShakeMovie initiative to identify anomalous QL arrivals. We find evidence significant QL arrivals at MAGIC stations, with amplitudes depending on propagation azimuth and station location. Preliminary results are consistent with a sharp lateral gradient in seismic anisotropy across the Appalachian Mountains in the depth range between 100-200 km.
-
Coy, Lawrence; Pawson, Steven
2014-01-01
We examine the major stratosphere sudden warming (SSW) that occurred on 6 January 2013, using output from the NASA Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) GEOS-5 (Goddard Earth Observing System) near-real-time data assimilation system (DAS). Results show that the major SSW of January 2013 falls into the vortex splitting type of SSW, with the initial planetary wave breaking occurring near 10 hPa. The vertical flux of wave activity at the tropopause responsible for the SSW occurred mainly in the Pacific Hemisphere, including the a pulse associated with the preconditioning of the polar vortex by wave 1 identified on 23 December 2012. While most of the vertical wave activity flux was in the Pacific Hemisphere, a rapidly developing tropospheric weather system over the North Atlantic on 28 December is shown to have produced a strong transient upward wave activity flux into the lower stratosphere coinciding with the peak of the SSW event. In addition, the GEOS-5 5-day forecasts accurately predicted the major SSW of January 2013 as well as the upper tropospheric disturbances responsible for the warming. The overall success of the 5-day forecasts provides motivation to produce regular 10-day forecasts with GEOS-5, to better support studies of stratosphere-troposphere interaction.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Serafimovich
2005-01-01
Full Text Available A case study to investigate the properties of inertia-gravity waves in the upper troposphere/lower stratosphere has been carried out over Northern Germany during the occurrence of an upper tropospheric jet in connection with a poleward Rossby wave breaking event from 17-19 December 1999. The investigations are based on the evaluation of continuous radar measurements with the OSWIN VHF radar at Kühlungsborn (54.1 N, 11.8 E and the 482 MHz UHF wind profiler at Lindenberg (52.2 N, 14.1 E. Both radars are separated by about 265 km. Based on wavelet transformations of both data sets, the dominant vertical wavelengths of about 2-4 km for fixed times as well as the dominant observed periods of about 11 h and weaker oscillations with periods of 6 h for the altitude range between 5 and 8 km are comparable. Gravity wave parameters have been estimated at both locations separately and by a complex cross-spectral analysis of the data of both radars. The results show the appearance of dominating inertia-gravity waves with characteristic horizontal wavelengths of 300 km moving in the opposite direction than the mean background wind and a secondary less pronounced wave with a horizontal wavelength in the order of about 200 km moving with the wind. Temporal and spatial differences of the observed waves are discussed.
-
Rapp, Markus
conducted during five intensive observations periods, IOPs, where during two IOPs strong mountain wave generation was observed. In this paper we present an overview of the initial preliminary results of this first GW-LCYCLE campaign contrasting results from selected IOPs with and without strong mountain wave generation. We will discuss in how far observed tropospheric and lower stratospheric wave signatures can be reconciled with regional modelling and whether simultaneously observed mesospheric waves can be attributed to dedicated GW sources in the troposphere using GW ray tracing as well as high-resolution idealized modelling.
-
Kretschmer, M.; Cohen, J. L.; Runge, J.; Coumou, D.
2017-12-01
The stratospheric polar vortex in boreal winter can influence the tropospheric circulation and thereby surface weather in the mid-latitudes. Weak states of the vortex, e.g. associated with Sudden Stratospheric Warmings (SSWs), often precede a negative phase of the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), and thus increase the risk of mid-latitude cold-spells especially over Eurasia. Here we show using cluster analysis that next to the well-documented relationship between a zonally symmetric disturbed vortex and a negative NAO, there exists a zonally asymmetric pattern linked to a negative Western Pacific Oscillation (WPO) and cold-spells in the northeastern US, like for example observed in February 2014. The latter is more synoptic in time-scale but occurs more frequently than SSWs. A causal effect network (CEN) approach gives insights into the underlying physical pathways and time-lags showing that high-pressure around Greenland leads to vertical wave activity over eastern Siberia leading to downward propagating waves over Alaska and high pressure over the North Pacific. Moreover, composites propose that a rather strong mid-stratospheric vortex seems to be favorable for this zonally asymmetric and reflective mechanism. Overall, the mutual relationship between stratospheric circulation and high-latitude blocking in both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans is complex and involves mechanisms operating at different time-scales. Our results suggest that the stratospheric influence on winter circulation should not exclusively be analyzed in terms of a downward propagating Northern Annular Mode (NAM) signal and SSWs. In particular when studying the stratospheric impacts on North American temperature it is crucial to also consider the more transient and zonally asymmetric events which might help to improve seasonal winter predictions for this region.
-
Sudden Stratospheric Warming Compendium
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — Sudden Stratospheric Warming Compendium (SSWC) data set documents the stratospheric, tropospheric, and surface climate impacts of sudden stratospheric warmings. This...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Serafimovich
2006-11-01
Full Text Available We present an experimental and modelling study of a strong gravity wave event in the upper troposphere/lower stratosphere near the Scandinavian mountain ridge. Continuous VHF radar measurements during the MaCWAVE rocket and ground-based measurement campaign were performed at the Norwegian Andoya Rocket Range (ARR near Andenes (69.3° N, 16° E in January 2003. Detailed gravity wave investigations based on PSU/NCAR Fifth-Generation Mesoscale Model (MM5 data have been used for comparison with experimentally obtained results. The model data show the presence of a mountain wave and of an inertia gravity wave generated by a jet streak near the tropopause region. Temporal and spatial dependencies of jet induced inertia gravity waves with dominant observed periods of about 13 h and vertical wavelengths of ~4.5–5 km are investigated with wavelet transform applied on radar measurements and model data. The jet induced wave packet is observed to move upstream and downward in the upper troposphere. The model data agree with the experimentally obtained results fairly well. Possible reasons for the observed differences, e.g. in the time of maximum of the wave activity, are discussed. Finally, the vertical fluxes of horizontal momentum are estimated with different methods and provide similar amplitudes. We found indications that the derived positive vertical flux of the horizontal momentum corresponds to the obtained parameters of the jet-induced inertia gravity wave, but only at the periods and heights of the strongest wave activity.
-
Artificially ionized region as a source of ozone in the stratosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gurevich, Aleksandr V; Litvak, Aleksandr G; Vikharev, A L; Ivanov, O A; Borisov, Nikolai D; Sergeichev, Konstantin F
2000-01-01
A set of physical and chemical processes occurring in a microwave stratospheric discharge of nanosecond duration is discussed in connection with the effect they may have locally on the ozone layer in the artificially ionized region (AIR) in the stratosphere. The AIR, to be created at altitudes of 18 - 20 km by the microwave breakdown of air with ground-produced powerful electromagnetic wave beams, is planned for use in the natural physical experiment aimed at active monitoring of the ozone layer (its internal state and a set of plasma-chemical and photochemical processes) by controllably generating a considerable amount of ozone in the stratosphere. Results of relevant theoretical studies are presented, as are those of a large series of laboratory experiments performed under conditions similar to those prevailing in the stratosphere. Discharge regimes securing the efficient growth of ozone concentration are identified and studied in detail. It is demonstrated that such a stratospheric ozonizer is about as efficient as the best ground-based ozonizers used at present. For typical stratospheric conditions (low pressures and temperatures T ∼ 200 - 220 K), it is shown that the intense generation of ozone in a microwave breakdown effected by groups of short nanosecond pulses does not virtually increase the density of nitrogen oxides - gases that play a vital role in catalytic ozone-decomposing reactions. The possibility of effectively producing ozone in prebreakdown electric fields is established experimentally. It is demonstrated that due to its long lifetime, ozone produced locally at altitudes of 18 - 20 km may spread widely under the action of winds and turbulent diffusion, thus leading to an additional - artificial - ozonization of the stratosphere. (reviews of topical problems)
-
Sensitivity of Gravity Wave Fluxes to Interannual Variations in Tropical Convection and Zonal Wind.
Alexander, M Joan; Ortland, David A; Grimsdell, Alison W; Kim, Ji-Eun
2017-09-01
Using an idealized model framework with high-frequency tropical latent heating variability derived from global satellite observations of precipitation and clouds, the authors examine the properties and effects of gravity waves in the lower stratosphere, contrasting conditions in an El Niño year and a La Niña year. The model generates a broad spectrum of tropical waves including planetary-scale waves through mesoscale gravity waves. The authors compare modeled monthly mean regional variations in wind and temperature with reanalyses and validate the modeled gravity waves using satellite- and balloon-based estimates of gravity wave momentum flux. Some interesting changes in the gravity spectrum of momentum flux are found in the model, which are discussed in terms of the interannual variations in clouds, precipitation, and large-scale winds. While regional variations in clouds, precipitation, and winds are dramatic, the mean gravity wave zonal momentum fluxes entering the stratosphere differ by only 11%. The modeled intermittency in gravity wave momentum flux is shown to be very realistic compared to observations, and the largest-amplitude waves are related to significant gravity wave drag forces in the lowermost stratosphere. This strong intermittency is generally absent or weak in climate models because of deficiencies in parameterizations of gravity wave intermittency. These results suggest a way forward to improve model representations of the lowermost stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation winds and teleconnections.
-
Sridharan, S.; Raghunath, K.; Sathishkumar, S.; Nath, D.
2010-09-01
Rayleigh lidar observations at Gadanki (13.5°N, 79.2°E) show an enhancement of the nightly mean temperature by 10-15 K at altitudes 70-80 km and of gravity wave potential energy at 60-70 km during the 2009 major stratospheric warming event. An enhanced quasi-16-day wave activity is observed at 50-70 km in the wavelet spectrum of TIMED-SABER temperatures, possibly due to the absence of a critical level in the low-latitude stratosphere because of less westward winds caused by this warming event. The observed low-latitude mesospheric warming could be due to wave breaking, as waves are damped at 80 km.
-
Hurwitz, Margaret M.; Oman, Luke David; Newman, Paul A.; Song, InSun
2013-01-01
A Goddard Earth Observing System Chemistry- Climate Model (GEOSCCM) simulation with strong tropical non-orographic gravity wave drag (GWD) is compared to an otherwise identical simulation with near-zero tropical non-orographic GWD. The GEOSCCM generates a quasibiennial oscillation (QBO) zonal wind signal in response to a tropical peak in GWD that resembles the zonal and climatological mean precipitation field. The modelled QBO has a frequency and amplitude that closely resembles observations. As expected, the modelled QBO improves the simulation of tropical zonal winds and enhances tropical and subtropical stratospheric variability. Also, inclusion of the QBO slows the meridional overturning circulation, resulting in a generally older stratospheric mean age of air. Slowing of the overturning circulation, changes in stratospheric temperature and enhanced subtropical mixing all affect the annual mean distributions of ozone, methane and nitrous oxide. Furthermore, the modelled QBO enhances polar stratospheric variability in winter. Because tropical zonal winds are easterly in the simulation without a QBO, there is a relative increase in tropical zonal winds in the simulation with a QBO. Extratropical differences between the simulations with and without a QBO thus reflect the westerly shift in tropical zonal winds: a relative strengthening of the polar stratospheric jet, polar stratospheric cooling and a weak reduction in Arctic lower stratospheric ozone.
-
Petzoldt, K.
1989-04-01
For the MAP/WINE winter temperature and wind measurements of rockets were combined with SSU radiances (Stratospheric Sounder Unit onboard the NOAA satellites) and stratopause heights from the Solar Mesosphere Explorer (SME) to get a retrieved data set including all available information. By means of this data set a hemispheric geopotential height, temperature and geostrophic wind fields eddy transports for wave mean flow interaction and potential vorticity for the interpretation of nonlinear wave breaking could be computed. Wave reflection at critical lines was investigated with respect of stratospheric warmings. The meridional gradient of the potential vorticity and focusing of wave activity is compared with derived data from satellite observations during other winters.
-
Scherllin-Pirscher, Barbara; Randel, William J.; Kim, Joowan
2017-04-01
We investigate sub-seasonal temperature variability in the tropical upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) region using daily gridded fields of GPS radio occultation measurements. The unprecedented vertical resolution (from about 100 m in the troposphere to about 1.5 km in the stratosphere) and high accuracy and precision (0.7 K to 1 K between 8 km and 25 km) make these data ideal for characterizing temperature oscillations with short vertical wavelengths. Long-term behavior of sub-seasonal temperature variability is investigated using the entire RO record from January 2002 to December 2014 (13 years of data). Transient sub-seasonal waves including eastward-propagating Kelvin waves (isolated with space-time spectral analysis) dominate large-scale zonal temperature variability in the tropical tropopause region and in the lower stratosphere. Above 20 km, Kelvin waves are strongly modulated by the quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO). Enhanced wave activity can be found during the westerly shear phase of the QBO. In the tropical tropopause region, however, sub-seasonal waves are highly transient in time. Several peaks of Kelvin-wave activity coincide with short-term fluctuations in tropospheric deep convection, but other episodes are not evidently related. Also, there are no obvious relationships with zonal winds or stability fields near the tropical tropopause. Further investigations of convective forcing and atmospheric background conditions along the waves' trajectories are needed to better understand sub-seasonal temperature variability near the tropopause. For more details, see Scherllin-Pirscher, B., Randel, W. J., and Kim, J.: Tropical temperature variability and Kelvin-wave activity in the UTLS from GPS RO measurements, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 17, 793-806, doi:10.5194/acp-17-793-2017, 2017. http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/17/793/2017/acp-17-793-2017.html
-
Shao, Min
The troposphere and stratosphere are the two closest atmospheric layers to the Earth's surface. These two layers are separated by the so-called tropopause. On one hand, these two layers are largely distinguished, on the other hand, lots of evidences proved that connections are also existed between these two layers via various dynamical and chemical feedbacks. Both tropospheric and stratospheric waves can propagate through the tropopause and affect the down streams, despite the fact that this propagation of waves is relatively weaker than the internal interactions in both atmospheric layers. Major improvements have been made in numerical weather predictions (NWP) via data assimilation (DA) in the past 30 years. From optimal interpolation to variational methods and Kalman Filter, great improvements are also made in the development of DA technology. The availability of assimilating satellite radiance observation and the increasing amount of satellite measurements enabled the generation of better atmospheric initials for both global and regional NWP systems. The selection of DA schemes is critical for regional NWP systems. The performance of three major data assimilation (3D-Var, Hybrid, and EnKF) schemes on regional weather forecasts over the continental United States during winter and summer is investigated. Convergence rate in the variational methods can be slightly accelerated especially in summer by the inclusion of ensembles. When the regional model lid is set at 50-mb, larger improvements (10˜20%) in the initials are obtained over the tropopause and lower troposphere. Better forecast skills (˜10%) are obtained in all three DA schemes in summer. Among these three DA schemes, slightly better (˜1%) forecast skills are obtained in Hybrid configuration than 3D-Var. Overall better forecast skills are obtained in summer via EnKF scheme. An extra 22% skill in predicting summer surface pressure but 10% less skills in winter are given by EnKF when compared to 3D
-
Hu, Jinggao; Li, Tim; Xu, Haiming
2018-01-01
The seasonal timing or onset date of the stratospheric final warming (SFWOD) events has a considerable interannual variability. This paper reports a statistically significant relationship between the North Pacific Gyre Oscillation (NPGO) and SFWOD in the Northern Hemisphere in two sub-periods (1951-1978 and 1979-2015). Specifically, in the first (second) sub-period, the NPGO is negatively (positively) linked with SFWOD. Composite analyses associated with anomalous NPGO years are conducted to diagnose the dynamic processes of the NPGO-SFWOD link. During 1951-1978, positive NPGO years tend to strengthen the Pacific-North America (PNA) pattern in the mid-troposphere in boreal winter. The strengthened PNA pattern in February leads to strong planetary wave activity in the extratropical stratosphere from late February to March and causes the early onset of SFW in early April. By contrast, a strengthened Western Pacific pattern from January to early February in negative NPGO years causes a burst of planetary waves in both the troposphere and extratropical stratosphere from late January to mid-February and results in more winter stratospheric sudden warming events, which, in turn, leads to a dormant spring and a late onset of SFW in late April. During 1979-2015, positive (negative) NPGO years strongly strengthen (weaken) the mid-tropospheric Aleutian low and the Western Pacific pattern from January to mid-March, leading to increased (decreased) planetary wavenumber-1 activity in the stratosphere from mid- to late winter and thus more (less) winter stratospheric sudden warming events and late (early) onsets of SFW in early May (mid-April).
-
Wiley, Scott
2008-01-01
This viewgraph document reviews some mountain wave turbulence and operational hazards while soaring. Maps, photographs, and satellite images of the meteorological phenomena are included. Additionally, photographs of aircraft that sustained mountain wave damage are provided.
-
Characteristics of mid-latitude planetary waves in the lower atmosphere derived from radiosonde data
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. Wang
2012-10-01
Full Text Available The activities of mid-latitude planetary waves (PWs in the troposphere and lower stratosphere (TLS are presented by using the radiosonde data from 2000 to 2004 over four American stations (Miramar Nas, 32.9° N, 117.2° W; Santa Teresa, 31.9° N, 106.7° W; Fort Worth, 32.8° N, 97.3° W; and Birmingham, 33.1° N, 86.7° W and one Chinese station (Wuhan, 30.5° N, 114.4° E. Statistically, strong PWs mainly appear around subtropical jet stream in the troposphere and lower stratosphere. In the troposphere, the activities of the mid-latitude PWs are strong around the centre of the subtropical jet stream in winter and become small near the tropopause, which indicates that the subtropical jet stream may strengthen the propagation of PWs or even be one of the PW excitation sources. Among the three disturbance components of temperature, zonal and meridional winds, PWs at Wuhan are stronger in the temperature component, but weaker in the zonal wind component than at the other four American stations. While in the meridional wind component, the strengths of PW spectral amplitudes at the four American stations decrease from west to east, and their amplitudes are all larger than that of Wuhan. However, the PWs are much weaker in the stratosphere and only the lower frequency parts remain. The amplitudes of the PWs in the stratosphere increase with height and are strong in winter with the zonal wind component being the strongest. Using the refractive index, we found that whether the PWs could propagate upward to the stratosphere depends on the thickness of the tropopause reflection layer. In the case study of the 2000/2001 winter, it is observed that the quasi 16-day wave in the troposphere is a quasi standing wave in the vertical direction and propagates upward slowly with vertical wavelength greater than 24 km in the meridional component. It propagates eastward with the zonal numbers between 5 and 8, and the quasi 16-day wave at Wuhan is probably the same
-
2015-12-15
propagating , planetary-scale waves (wavenumber 1 and wavenumber 2) in the lower thermosphere that are associated with different stratospheric conditions. To...prominent meridional propagation of wave activity from the mid- latitudes toward the tropics. In combination with strong eastward meridional wind shear, our...Neutral and Ionized Atmosphere, Whole Atmosphere Model, and WACCM-X. The comparison focuses on the zonal mean, planetary wave , and tidal variability in
-
Global Distributions of Temperature Variances At Different Stratospheric Altitudes From Gps/met Data
Gavrilov, N. M.; Karpova, N. V.; Jacobi, Ch.
The GPS/MET measurements at altitudes 5 - 35 km are used to obtain global distribu- tions of small-scale temperature variances at different stratospheric altitudes. Individ- ual temperature profiles are smoothed using second order polynomial approximations in 5 - 7 km thick layers centered at 10, 20 and 30 km. Temperature inclinations from the averaged values and their variances obtained for each profile are averaged for each month of year during the GPS/MET experiment. Global distributions of temperature variances have inhomogeneous structure. Locations and latitude distributions of the maxima and minima of the variances depend on altitudes and season. One of the rea- sons for the small-scale temperature perturbations in the stratosphere could be internal gravity waves (IGWs). Some assumptions are made about peculiarities of IGW gener- ation and propagation in the tropo-stratosphere based on the results of GPS/MET data analysis.
-
First Successful Hindcasts of the 2016 Disruption of the Stratospheric Quasi-biennial Oscillation
Watanabe, S.; Hamilton, K.; Osprey, S.; Kawatani, Y.; Nishimoto, E.
2018-02-01
In early 2016 the quasi-biennial oscillation in tropical stratospheric winds was disrupted by an anomalous easterly jet centered at 40 hPa, a development that was completely missed by all operational extended range weather forecast systems. This event and its predictability are investigated through 40 day ensemble hindcasts using a global model notable for its sophisticated representation of the upper atmosphere. Integrations starting at different times throughout January 2016—just before and during the initial development of the easterly jet—were performed. All integrations simulated the unusual developments in the stratospheric mean wind, despite considerable differences in other aspects of the flow evolution among the ensemble members, notably in the evolution of the winter polar vortex and the day-to-day variations in extratropical Rossby waves. Key to prediction of this event is simulating the slowly evolving mean winds in the winter subtropics that provide a waveguide for Rossby waves propagating from the winter hemisphere.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. Bossuet
Full Text Available Systematic westerly biases in the southern hemisphere wintertime flow and easterly equatorial biases are experienced in the Météo-France climate model. These biases are found to be much reduced when a simple parameterization is introduced to take into account the vertical momentum transfer through the gravity waves excited by deep convection. These waves are quasi-stationary in the frame of reference moving with convection and they propagate vertically to higher levels in the atmosphere, where they may exert a significant deceleration of the mean flow at levels where dissipation occurs. Sixty-day experiments have been performed from a multiyear simulation with the standard 31 levels for a summer and a winter month, and with a T42 horizontal resolution. The impact of this parameterization on the integration of the model is found to be generally positive, with a significant deceleration in the westerly stratospheric jet and with a reduction of the easterly equatorial bias. The sensitivity of the Météo-France climate model to vertical resolution is also investigated by increasing the number of vertical levels, without moving the top of the model. The vertical resolution is increased up to 41 levels, using two kinds of level distribution. For the first, the increase in vertical resolution concerns especially the troposphere (with 22 levels in the troposphere, and the second treats the whole atmosphere in a homogeneous way (with 15 levels in the troposphere; the standard version of 31 levels has 10 levels in the troposphere. A comparison is made between the dynamical aspects of the simulations. The zonal wind and precipitation are presented and compared for each resolution. A positive impact is found with the finer tropospheric resolution on the precipitation in the mid-latitudes and on the westerly stratospheric jet, but the general impact on the model climate is weak, the physical parameterizations used appear to be mostly independent to the
-
Stratospheric Aerosol Measurements
Pueschel, Rudolf, F.; Gore, Warren J. (Technical Monitor)
1998-01-01
Stratospheric aerosols affect the atmospheric energy balance by scattering and absorbing solar and terrestrial radiation. They also can alter stratospheric chemical cycles by catalyzing heterogeneous reactions which markedly perturb odd nitrogen, chlorine and ozone levels. Aerosol measurements by satellites began in NASA in 1975 with the Stratospheric Aerosol Measurement (SAM) program, to be followed by the Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE) starting in 1979. Both programs employ the solar occultation, or Earth limb extinction, techniques. Major results of these activities include the discovery of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs) in both hemispheres in winter, illustrations of the impacts of major (El Chichon 1982 and Pinatubo 1991) eruptions, and detection of a negative global trend in lower stratospheric/upper tropospheric aerosol extinction. This latter result can be considered a triumph of successful worldwide sulfur emission controls. The SAGE record will be continued and improved by SAGE III, currently scheduled for multiple launches beginning in 2000 as part of the Earth Observing System (EOS). The satellite program has been supplemented by in situ measurements aboard the ER-2 (20 km ceiling) since 1974, and from the DC-8 (13 km ceiling) aircraft beginning in 1989. Collection by wire impactors and subsequent electron microscopic and X-ray energy-dispersive analyses, and optical particle spectrometry have been the principle techniques. Major findings are: (1) The stratospheric background aerosol consists of dilute sulfuric acid droplets of around 0.1 micrometer modal diameter at concentration of tens to hundreds of monograms per cubic meter; (2) Soot from aircraft amounts to a fraction of one percent of the background total aerosol; (3) Volcanic eruptions perturb the sulfuric acid, but not the soot, aerosol abundance by several orders of magnitude; (4) PSCs contain nitric acid at temperatures below 195K, supporting chemical hypotheses
-
Temporal variability of gravity wave drag - vertical coupling and possible climate links
Miksovsky, Jiri; Sacha, Petr; Kuchar, Ales; Pisoft, Petr
2017-04-01
In the atmosphere, the internal gravity waves (IGW) are one of the fastest ways of natural information transfer in the vertical direction. Tropospheric changes that result in modification of sourcing, propagation or breaking conditions for IGWs almost immediately influence the distribution of gravity wave drag in the stratosphere. So far most of the related studies deal with IGW impacts higher in the upper stratospheric/mesospheric region and with the modulation of IGWs by planetary waves. This is most likely due to the fact that IGWs induce highest accelerations in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere region. However, the imposed drag force is much bigger in the stratosphere. In the presented analysis, we have assessed the relationship between the gravity wave activity in the stratosphere and other climatic phenomena through statistical techniques. Multivariable regression has been applied to investigate the IGW-related eastward and northward wind tendencies in the CMAM30-SD data, subject to the explanatory variables involving local circulation characteristics (derived from regional configuration of the thermobaric field) as well as the phases of the large-scale internal climate variability modes (ENSO, NAO, QBO). Our tests have highlighted several geographical areas with statistically significant responses of the orographic gravity waves effect to each of the variability modes under investigation; additional experiments have also indicated distinct signs of nonlinearity in some of the links uncovered. Furthermore, we have also applied composite analysis of displaced and split stratospheric polar vortex events (SPV) from CMAM30-SD to focus on how the strength and occurrence of the IGW hotspots can play a role in SPV occurrence and frequency.
-
Garfinkel, C. I.; Oman, L. D.
2018-01-01
The effect of small islands in the Southern Ocean on the atmospheric circulation in the Southern Hemisphere is considered with a series of simulations using the NASA Goddard Earth Observing System Chemistry-Climate Model in which the gravity wave stress generated by these islands is increased to resemble observed values. The enhanced gravity wave drag leads to a 2 K warming of the springtime polar stratosphere, partially ameliorating biases in this region. Resolved wave drag declines in the stratospheric region in which the added orographic gravity waves deposit their momentum, such that changes in gravity waves are partially compensated by changes in resolved waves, though resolved wave drag increases further poleward. The orographic drag from these islands has impacts for surface climate, as biases in tropospheric jet position are also partially ameliorated. These results suggest that these small islands are likely contributing to the missing drag near 60 degrees S in the upper stratosphere evident in many data assimilation products.
-
On the wave forcing of the semi-annual zonal wind oscillation
Nagpal, O. P.; Raghavarao, R.
1991-01-01
Observational evidence of rather large period waves (23-60 d) in the troposphere/stratosphere, particularly during the winter months, is presented. Wind data collected on a regular basis employing high-altitude balloons and meteorological rockets over the past few years are used. Maximum entropy methods applied to the time series of zonal wind data indicate the presence of 23-60-waves more prominently than shorter-period waves. The waves have substantial amplitudes in the stratosphere and lower mesosphere, often larger than those noted in the troposphere. The mean zonal wind in the troposphere (5-15 km altitude) during December, January, and February exhibits the presence of strong westerlies at latitudes between 8 and 21 deg N.
-
Dörnbrack, Andreas; Sharman, Robert
2015-04-01
Observational evidence indicates a higher incidence of turbulence near the tropopause, especially over mountainous terrain. Previous work by McHugh and Sharman (2013) indicate this may be due to nonlinear amplification of topographically-induced gravity waves as they impinge on the tropopause. However, that study did not consider nonlinear topography amplification effects, nor did it consider the more realistic case of a jet stream in the vicinity of the tropopause. This study extends the McHugh and Sharman study by considering these effects using fully nonlinear simulations with the jet modeled as a sech**2 profile. Sensitivity studies are performed to study such effects as the location of the nose of the jet relative to the tropopause height, the jet width, the height of the tropopause, and the size and shape of the obstacle. Momentum and energy flux profiles are used to deduce those configurations most conducive to gravity wave amplification, breakdown and turbulence near the tropopause. McHugh J., Sharman R., 2013: Generation of mountain wave-induced mean flows and turbulence near the tropopause. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 139: 1632-1642. DOI:10.1002/qj.2035
-
The Role of Gravity Waves in the Formation and Organization of Clouds during TWPICE
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Reeder, Michael J. [Monash University; Lane, Todd P. [University of Melbourne; Hankinson, Mai Chi Nguyen [Monash University
2013-09-27
All convective clouds emit gravity waves. While it is certain that convectively-generated waves play important parts in determining the climate, their precise roles remain uncertain and their effects are not (generally) represented in climate models. The work described here focuses mostly on observations and modeling of convectively-generated gravity waves, using the intensive observations from the DoE-sponsored Tropical Warm Pool International Cloud Experiment (TWP-ICE), which took place in Darwin, from 17 January to 13 February 2006. Among other things, the research has implications the part played by convectively-generated gravity waves in the formation of cirrus, in the initiation and organization of further convection, and in the subgrid-scale momentum transport and associated large-scale stresses imposed on the troposphere and stratosphere. The analysis shows two groups of inertia-gravity waves are detected: group L in the middle stratosphere during the suppressed monsoon period, and group S in the lower stratosphere during the monsoon break period. Waves belonging to group L propagate to the south-east with a mean intrinsic period of 35 h, and have vertical and horizontal wavelengths of about 5-6 km and 3000-6000 km, respectively. Ray tracing calculations indicate that these waves originate from a deep convective region near Indonesia. Waves belonging to group S propagate to the south-south-east with an intrinsic period, vertical wavelength and horizontal wavelength of about 45 h, 2 km and 2000-4000 km, respectively. These waves are shown to be associated with shallow convection in the oceanic area within about 1000 km of Darwin. The intrinsic periods of high-frequency waves are estimated to be between 20-40 minutes. The high-frequency wave activity in the stratosphere, defined by mass-weighted variance of the vertical motion of the sonde, has a maximum following the afternoon local convection indicating that these waves are generated by local convection
-
Li, F.; Newman, P. A.; Pawson, S.; Perlwitz, J.
2017-12-01
The strength of the stratospheric Brewer-Dobson circulation (BDC) in a changing climate has been extensively studied, but the relative importance of greenhouse gas (GHG) increases and stratospheric ozone depletion in driving the BDC changes remains uncertain. This study separates the impacts of GHG and stratospheric ozone forcings on stratospheric mean age of air in the 1960-2010 period using the Goddard Earth Observing System Model (GEOS) Chemistry-Climate Model (CCM). The experiment compares a set of controlled simulations using a coupled atmosphere-ocean version of the GEOS CCM, in which either GHGs, or stratospheric ozone, or both factors evolve over time. The model results show that GHGs and stratospheric ozone have about equal contributions to the simulated mean age decrease. It is also found that GHG increases account for about two thirds of the enhanced strength of the lower stratospheric residual circulation. The results show that ozone depletion causes an increase in the mean age of air in the Antarctic summer lower stratosphere through two processes: 1) a seasonal delay in the Antarctic polar vortex breakup, that inhibits young mid-latitude air from mixing with the older air inside the vortex; and 2) enhanced Antarctic downwelling, that brings older air from middle and upper stratosphere into the lower stratosphere.
-
Wu, J. F.; Xue, X. H.; Hoffmann, L.; Dou, X. K.; Li, H. M.; Chen, T. D.
2015-01-01
Atmospheric gravity waves (GWs) significantly influence global circulation. Deep convection, particularly that associated with typhoons, is believed to be an important source of gravity waves. Stratospheric gravity waves induced by Typhoon Mindulle (2004) were detected by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS). Semicircular GWs with horizontal wavelengths of 100–400 km were found over Taiwan through an inspection of AIRS radiances at 4.3 μm. Characteristics of the stratospheric gravity waves...
-
Upper-Level Waves of Synoptic Scale at Midlatitudes
Rivest, Chantal
1990-01-01
Upper-level waves of synoptic scale are important dynamical entities at midlatitudes. They often induce surface cyclogenesis (cf. Peterssen and Smebye, 1971), and their life duration is typically longer than time scales for disruption by the ambient shear (Sanders, 1988). The objectives of the present thesis are to explain the maintenance and genesis of upper-level synoptic-scale waves in the midlatitude flow. We develop an analytical model of waves on generalized Eady basic states that have uniform tropospheric and stratospheric potential vorticity, but allow for the decay of density with height. The Eady basic state represents the limiting case of infinite stratospheric stability and constant density. We find that the Eady normal mode characteristics hold in the presence of realistic tropopause and stratosphere. In particular, the basic states studied support at the synoptic scale upper-level normal modes. These modes provide simple models for the dynamics of upper-level synoptic-scale waves, as waves supported by the large latitudinal gradients of potential vorticity at the tropopause. In the presence of infinitesimal positive tropospheric gradients of potential vorticity, the upper-level normal mode solutions no longer exist, as was demonstrated in Green (1960). Disappearance of the normal mode solution when a parameter changes slightly represents a dilemma that we seek to understand. We examine what happens to the upper-level normal modes in the presence of tropospheric gradients of potential vorticity in a series of initial -value experiments. Our results show that the normal modes become slowly decaying quasi-modes. Mathematically the quasi-modes consist of a superposition of singular modes sharply peaked in the phase speed domain, and their decay proceeds as the modes interfere with one another. We repeat these experiments in basic states with a smooth tropopause in the presence of tropospheric and stratospheric gradients, and similar results are obtained
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brocard, Gilles Y.; Willenbring, Jane K.; Scatena, Frederick N.; Johnson, Art H.
2015-01-01
We document the long-term response of a tropical mountain stream to tectonics and show how this response exerts a first-order spatial control on the delivery of weatherable minerals to forest soils in its catchment. These minerals, in turn, affect nutrient availability and biogeochemical cycles. The Luquillo Mountains is a rainforest-covered isolated massif on Puerto Rico Island. Instead of displaying typical concave-up long profiles of most mountain streams, the rivers draining the southern flank of these mountains display a systematic downstream increase in gradient. Using concentrations of in situ-produced cosmogenic "1"0Be in quartz from river sediments, we find that the downstream steepening is due to the propagation of an erosion wave along the rivers from the coastal plain upstream, toward the headwaters. Decreased "1"0Be concentration along the steepened reaches (knickpoint faces or knickzones) results from faster denudation of the valley sides around the steepened reaches. The upper portions of the steepened reaches (knickpoint lips) cluster in elevation around the altitude of a flat-lying, dissected surface traceable around the Luquillo Mountains. Inspection of similar platforms over other parts of Puerto Rico and in the surrounding seas suggests that the dissected surface is an uplifted shore platform formed in the Early Pliocene (∼4 My ago). Upstream of the knickpoints, rivers possess alluvial reaches still graded to this uplifted platform. They represent relict profiles of the rivers that once drained an island that was surrounded by the now-uplifted platform. We conclude that the knickpoints initiated when the platform started to rise above the Caribbean Sea. The knickpoints then started propagating upstream, defining the front of a slow-moving wave of erosion. "1"0Be-derived catchment-scale denudation rates measured above and below the knickpoints indicate a 30–210% increase in denudation associated to the passage of the knickpoints
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. J. García-Garrido
2017-06-01
Full Text Available In this work, we study the Lagrangian footprint of the planetary waves present in the Southern Hemisphere stratosphere during the exceptional sudden Stratospheric warming event that took place during September 2002. Our focus is on constructing a simple kinematic model that retains the fundamental mechanisms responsible for complex fluid parcel evolution, during the polar vortex breakdown and its previous stages. The construction of the kinematic model is guided by the Fourier decomposition of the geopotential field. The study of Lagrangian transport phenomena in the ERA-Interim reanalysis data highlights hyperbolic trajectories, and these trajectories are Lagrangian objects that are the kinematic mechanism for the observed filamentation phenomena. Our analysis shows that the breaking and splitting of the polar vortex is justified in our model by the sudden growth of a planetary wave and the decay of the axisymmetric flow.
-
DYANA campaign results on long-period atmospheric waves over Thumba and Balasore
Reddi, C. Raghava; Rajeev, K.; Nair, S. Muraleedharan; Subbaraya, B. H.; Rama, G. V.; Appu, K. S.; Narayanan, V.; Apparao, B. V.; Chakravarty, S. C.; Nagpal, O. P.; Perov, S. P.; Kokin, G. A.
1994-12-01
The variation with altitude of the spectral amplitudes of the long period waves in the middle atmospheric zonal and meridional wind over Thumba (8.5°N, 76.9°E) and Balasore (21.5°N, 86.9°E) have shown clearly the enhanced dissipation of the atmospheric waves in the lower stratosphere and near the stratopause. The amplitudes are, in general, large for the lower frequency ( <0.1 cycles/day) waves in the troposphere. While propagating through the tropopause into the stratosphere and above, waves with periods in the range of 5-10 days suffer less attenuation. The dissipation of the atmospheric waves is found to be relatively large for frequencies below 0.1 cycles/day. The results are compared with earlier observational studies and theoretical computations on the propagation of equatorial waves through the middle atmosphere.
-
The influence of regional Arctic sea-ice decline on stratospheric and tropospheric circulation
McKenna, Christine; Bracegirdle, Thomas; Shuckburgh, Emily; Haynes, Peter
2016-04-01
Arctic sea-ice extent has rapidly declined over the past few decades, and most climate models project a continuation of this trend during the 21st century in response to greenhouse gas forcing. A number of recent studies have shown that this sea-ice loss induces vertically propagating Rossby waves, which weaken the stratospheric polar vortex and increase the frequency of sudden stratospheric warmings (SSWs). SSWs have been shown to increase the probability of a negative NAO in the following weeks, thereby driving anomalous weather conditions over Europe and other mid-latitude regions. In contrast, other studies have shown that Arctic sea-ice loss strengthens the polar vortex, increasing the probability of a positive NAO. Sun et al. (2015) suggest these conflicting results may be due to the region of sea-ice loss considered. They find that if only regions within the Arctic Circle are considered in sea-ice projections, the polar vortex weakens; if only regions outwith the Arctic Circle are considered, the polar vortex strengthens. This is because the anomalous Rossby waves forced in the former/latter scenario constructively/destructively interfere with climatological Rossby waves, thus enhancing/suppressing upward wave propagation. In this study, we investigate whether Sun et al.'s results are robust to a different model. We also divide the regions of sea-ice loss they considered into further sub-regions, in order to examine the regional differences in more detail. We do this by using the intermediate complexity climate model, IGCM4, which has a well resolved stratosphere and does a good job of representing stratospheric processes. Several simulations are run in atmosphere only mode, where one is a control experiment and the others are perturbation experiments. In the control run annually repeating historical mean surface conditions are imposed at the lower boundary, whereas in each perturbation run the model is forced by SST perturbations imposed in a specific
-
Equatorial wave activity during 2007 over Gadanki, a tropical station
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
been used to investigate the wave activity in the troposphere and lower stratosphere. Waves in the ...... Oltmans S J 2001 Water vapor control at the tropopause by equatorial Kelvin .... observed in UARS microwave limb sounder temperature.
-
Polar-Tropical Coupling in the Winter Stratosphere
Scott, R.
2017-12-01
A distinct pattern of enhanced equatorial potential vorticitygradients during QBO westerly anomalies, enhanced subtropicalgradients during QBO easterlies, is used to motivate a new formulationof dynamical coupling between the tropics and winter polar vortexbased on remote transfer of finite amplitude wave activity defined interms of lateral potential vorticity displacements. While the weakpotential vorticity gradients in the surf zone imply laterallyevanescent Rossby waves, transfer of wave activity from the polarvortex edge to the subtropical barrier or to the QBO westerly phaseequatorial gradients arises from nonlocality of potential vorticityinversion and the large horizontal displacements of the vortex edge.Our approach goes beyond the traditional description of the effect ofQBO wind anomalies on linear wave propagation through the stratospherevia wave reflection at the zero wind line; linear wave theory isappealing but neglects the long horizontal and vertical wavelengthsinvolved and the inhomogeneous background potential vorticity. Aparticular issue of outstanding interest is whether and how therelatively shallow QBO anomalies can influence the deep verticallypropagating waves on the edge of the winter stratospheric polarvortex. Process studies with a mechanistic model with prescribed QBOand carefully controlled high-latitude wave forcing are analyzed,guided by a reexamination of meteorological reanalysis, to address howsuch a dynamical linkage may influence in particular the resonantexcitation of the winter vortex, and the occurrence ofvortex-splitting sudden warming events. We quantify the associatedtransfer of wave activity from vortex edge to the tropics, considerunder what conditions this becomes a significant source of easterlymomentum in the driving of the QBO itself, and how the structure ofthe Brewer-Dobson circulation varies in response to the location ofthe QBO westerly winds in any given winter.
-
Surface pressure drag for hydrostatic two-layer flow over axisymmetric mountains
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Leutbecher, M.
2000-07-01
The effect of partial reflections on surface pressure drag is investigated for hydrostatic gravity waves in two-layer flow with piecewise constant buoyancy frequency. The variation of normalized surface pressure drag with interface height is analyzed for axisymmetric mountains. The results are compared with the familiar solution for infinitely long ridges. The drag for the two-layer flow is normalized with the drag of one-layer flow, which has the buoyancy frequency of the lower layer. An analytical expression for the normalized drag of axisymmetric mountains is derived from linear theory of steady flow. Additionally, two-layer flow over finite-height axisymmetric mountains is simulated numerically for flow with higher stability in the upper layer. The temporal evolution of the surface pressure drag is examined in a series of experiments with different interface and mountain heights. The focus is on the linear regime and the nonlinear regime of nonbreaking gravity waves. The dispersion of gravity waves in flow over isolated mountains prevents that the entire wave spectrum is in resonance at the same interface height, which is the case in hydrostatic flow over infinitely long ridges. In consequence, the oscillation of the normalized drag with interface height is smaller for axisymmetric mountains than for infinitely long ridges. However, even for a reflection coefficient as low as 1/3 the drag of an axisymmetric mountain can be amplified by 50% and reduced by 40%. The nonlinear drag becomes steady in the numerical experiments in which no wave breaking occurs. The steady state nonlinear drag agrees quite well with the prediction of linear theory if the linear drag is computed for a slightly lowered interface. (orig.)
-
Kondyurin, Alexey; Kondyurina, Irina; Bilek, Marcela; de Groh, Kim K.
2013-01-01
A cassette of uncured composite materials with epoxy resin matrixes was exposed in the stratosphere (40 km altitude) over three days. Temperature variations of -76 to 32.5C and pressure up to 2.1 torr were recorded during flight. An analysis of the chemical structure of the composites showed, that the polymer matrix exposed in the stratosphere becomes crosslinked, while the ground control materials react by way of polymerization reaction of epoxy groups. The space irradiations are considered to be responsible for crosslinking of the uncured polymers exposed in the stratosphere. The composites were cured on Earth after landing. Analysis of the cured composites showed that the polymer matrix remains active under stratospheric conditions. The results can be used for predicting curing processes of polymer composites in a free space environment during an orbital space flight.
-
QBO Modulation of the Mesopause Gravity Wave Momentum Flux over Tierra del Fuego
De Wit, R. J.; Janches, D.; Fritts, D. C.; Hibbins, R. E.
2016-01-01
The interannual variability of the mesosphere and lower thermosphere (MLT) gravity wave momentum flux over southern mid latitudes (53.7degS) has been studied using more than 7 years of meteor radar observations at Ro Grande, Argentina. A modulation, with periods similar to that of the equatorial stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO), is observed in the vertical flux of zonal as well as meridional momentum. The QBO signal is largest in the zonal component during summer and is in phase with the stratospheric QBO at 50 hPa (approx. 21 km). The relation between the stratospheric QBO and the QBO modulation in the MLT gravity wave forcing (derived from the divergence of the momentum flux) was found to be consistent with that expected from the Holton-Tan effect coupled to the interhemispheric coupling mechanism. These results provide the first observational support for the existence of the midlatitude gravity wave forcing anomalies as hypothesized in the interhemispheric coupling mechanism.
-
Sridharan, S.; Sathishkumar, S.; Raghunath, K.
2009-01-01
Rayleigh lidar observations of temperature structure and gravity wave activity were carried out at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E) during January-February 2006. A major stratospheric warming event occurred at high latitude during the end of January and early February. There was a sudden enhancement in the stratopause temperature over Gadanki coinciding with the date of onset of the major stratospheric warming event which occurred at high latitudes. The temperature enhancement persisted even after the end of the high latitude major warming event. During the same time, the UKMO (United Kingdom Meteorological Office) zonal mean temperature showed a similar warming episode at 10° N and cooling episode at 60° N around the region of stratopause. This could be due to ascending (descending) motions at high (low) latitudes above the critical level of planetary waves, where there was no planetary wave flux. The time variation of the gravity wave potential energy computed from the temperature perturbations over Gadanki shows variabilities at planetary wave periods, suggesting a non-linear interaction between gravity waves and planetary waves. The space-time analysis of UKMO temperature data at high and low latitudes shows the presence of similar periodicities of planetary wave of zonal wavenumber 1.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Sridharan
2009-01-01
Full Text Available Rayleigh lidar observations of temperature structure and gravity wave activity were carried out at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E during January–February 2006. A major stratospheric warming event occurred at high latitude during the end of January and early February. There was a sudden enhancement in the stratopause temperature over Gadanki coinciding with the date of onset of the major stratospheric warming event which occurred at high latitudes. The temperature enhancement persisted even after the end of the high latitude major warming event. During the same time, the UKMO (United Kingdom Meteorological Office zonal mean temperature showed a similar warming episode at 10° N and cooling episode at 60° N around the region of stratopause. This could be due to ascending (descending motions at high (low latitudes above the critical level of planetary waves, where there was no planetary wave flux. The time variation of the gravity wave potential energy computed from the temperature perturbations over Gadanki shows variabilities at planetary wave periods, suggesting a non-linear interaction between gravity waves and planetary waves. The space-time analysis of UKMO temperature data at high and low latitudes shows the presence of similar periodicities of planetary wave of zonal wavenumber 1.
-
Seasonal variation of equatorial wave momentum fluxes at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. N. Sasi
2001-08-01
Full Text Available The vertical flux of the horizontal momentum associated with the equatorial Kelvin and Rossby-gravity waves are estimated from the winds measured by the Indian MST radar located at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E during September 1995 to August 1996 in the tropospheric and lower stratospheric regions for all four seasons. The present study shows that momentum flux values are greater during equinox seasons than solstices, with values near the tropopause level being 16 × 10-3, 7.4 × 10-3, 27 × 10-3 and 5.5 × 10-3 m2 s-2 for Kelvin waves and 5.5 × 10-3, 3.5 × 10-3, 6.7 × 10-3 and 2.1 × 10-3 m2 s-2 for RG waves during autumnal equinox, winter, vernal equinox and summer seasons, respectively. Using these momentum flux values near the tropopause level, acceleration of the mean flow in the stratosphere up to a 29 km height were computed following Plumb (1984, by considering the wave-meanflow interaction and the deposition of the momentum through the radiative dissipation of the waves. A comparison of the estimated mean-flow acceleration in the stratosphere compares well, except at a few height levels, with the observed mean-flow accelerations in the stratosphere derived from the radiosonde data from a nearby station.Key words. Meteorology and atmosphenic dynamics (tropical meteorology; waves and tides
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Perlwitz, J.; Graf, H.F.
1994-01-01
The associated anomaly patterns of the stratospheric geopotential height field and the tropospheric geopotential and temperature height fields of the northern hemisphere are determined applying the Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA). With this linear multivariate technique the coupled modes of variability of time series of two fields are isolated in the EOF space. The one data set is the 50 hPa geopotential field, the other set consists of different height fields of the tropospheric pressure levels (200 hPa, 500 hPa, 700 hPa, 850 hPa) and the temperature of the 850 hPa pressure level. For the winter months (December, January, February) two natural coupled modes, a barotropic and a baroclinic one, of linear relationship between stratospheric and tropospheric circulation are found. The baroclinic mode describes a connection between the strength of the stratospheric cyclonic winter vortex and the tropospheric circulation over the North Atlantic. The corresponding temperature pattern for an anomalously strong stratospheric cyclonic vortex is characterized by positive temperature anomalies over higher latitudes of Eurasia. These 'Winter Warmings' are observed e.g. after violent volcanic eruptions. The barotropic mode is characterized by a zonal wave number one in the lower stratosphere and by a PNA-like pattern in the troposphere. It was shown by Labitzke and van Loon (1987) that this mode can be enhanced e.g. by El Ninos via the intensification of the Aleutian low. (orig.)
-
Wang, K.
2008-04-01
Previous studies of the exceptional 2002 Southern Hemisphere (SH) stratospheric warming event lead to some uncertainty, namely the question of whether excessive heat fluxes in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere are a symptom or cause of the 2002 SH warming event. In this work, we use a hemispheric version of the MM5 model with nudging capability and we devised a novel approach to separately test the significance of the stratosphere and troposphere for this year. We paired the flow conditions from 2002 in the stratosphere and troposphere, respectively, against the conditions in 1998 (a year with displaced polar vortex) and in 1948 (a year with strong polar vortex that coincided with the geographical South Pole). Our experiments show that the flow conditions from below determine the stratospheric flow features over the polar region. Regardless of the initial stratospheric conditions in 1998 or 1948, when we simulated these past stratospheres with the troposphere/lower stratosphere conditions constrained to 2002 levels, the simulated middle stratospheres resemble those observed in 2002 stratosphere over the polar region. On the other hand, when the 2002 stratosphere was integrated with the troposphere/lower stratosphere conductions constrained to 1948 and 1998, respectively, the simulated middle stratospheric conditions over the polar region shift toward those of 1948 and 1998. Thus, our experiments further support the wave-forcing theory as the cause of the 2002 SH warming event.
-
Statistical comparisons of gravity wave features derived from OH airglow and SABER data
Gelinas, L. J.; Hecht, J. H.; Walterscheid, R. L.
2017-12-01
The Aerospace Corporation's near-IR camera (ANI), deployed at Andes Lidar Observatory (ALO), Cerro Pachon Chile (30S,70W) since 2010, images the bright OH Meinel (4,2) airglow band. The imager provides detailed observations of gravity waves and instability dynamics, as described by Hecht et al. (2014). The camera employs a wide-angle lens that views a 73 by 73 degree region of the sky, approximately 120 km x 120 km at 85 km altitude. Image cadence of 30s allows for detailed spectral analysis of the horizontal components of wave features, including the evolution and decay of instability features. The SABER instrument on NASA's TIMED spacecraft provides remote soundings of kinetic temperature profiles from the lower stratosphere to the lower thermosphere. Horizontal and vertical filtering techniques allow SABER temperatures to be analyzed for gravity wave variances [Walterscheid and Christensen, 2016]. Here we compare the statistical characteristics of horizontal wave spectra, derived from airglow imagery, with vertical wave variances derived from SABER temperature profiles. The analysis is performed for a period of strong mountain wave activity over the Andes spanning the period between June and September 2012. Hecht, J. H., et al. (2014), The life cycle of instability features measured from the Andes Lidar Observatory over Cerro Pachon on March 24, 2012, J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 119, 8872-8898, doi:10.1002/2014JD021726. Walterscheid, R. L., and A. B. Christensen (2016), Low-latitude gravity wave variances in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere derived from SABER temperature observation and compared with model simulation of waves generated by deep tropical convection, J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 121, 11,900-11,912, doi:10.1002/2016JD024843.
-
Kenzelmann, P.; Weisenstein, D.; Peter, T.; Luo, B. P.; Rozanov, E.; Fueglistaler, S.; Thomason, L. W.
2009-04-01
Anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions tend to warm the global climate, calling for significant rapid emission reductions. As potential support measures various ideas for geoengineering are currently being discussed. The assessment of the possible manifold and as yet substantially unexplored repercussions of implementing geoengineering ideas to ameliorate climate change poses enormous challenges not least in the realm of aerosol-cloud-climate interactions. Sulphur aerosols cool the Earth's surface by reflecting short wave radiation. By increasing the amount of sulphur aerosols in the stratosphere, for example by sulphur dioxide injections, part of the anthropogenic climate warming might be compensated due to enhanced albedo. However, we are only at the beginning of understanding possible side effects. One such effect that such aerosol might have is the warming of the tropical tropopause and consequently the increase of the amount of stratospheric water vapour. Using the 2D AER Aerosol Model we calculated the aerosol distributions for yearly injections of 1, 2, 5 and 10 Mt sulphur into the lower tropical stratosphere. The results serve as input for the 3D chemistry-climate model SOCOL, which allows calculating the aerosol effect on stratospheric temperatures and chemistry. In the injection region the continuously formed sulphuric acid condensates rapidly on sulphate aerosol, which eventually grow to such extent that they sediment down to the tropical tropopause region. The growth of the aerosol particles depends on non-linear processes: the more sulphur is emitted the faster the particles grow. As a consequence for the scenario with continuous sulphur injection of totally 10 Mt per year, only 6 Mt sulphur are in the stratosphere if equilibrium is reached. According to our model calculations this amount of sulphate aerosols leads to a net surface forcing of -3.4 W/m2, which is less then expected radiative forcing by doubling of carbon dioxide concentration. Hence
-
Laboratory studies of stratospheric aerosol chemistry
Molina, Mario J.
1996-01-01
In this report we summarize the results of the two sets of projects funded by the NASA grant NAG2-632, namely investigations of various thermodynamic and nucleation properties of the aqueous acid system which makes up stratospheric aerosols, and measurements of reaction probabilities directly on ice aerosols with sizes corresponding to those of polar stratospheric cloud particles. The results of these investigations are of importance for the assessment of the potential stratospheric effects of future fleets of supersonic aircraft. In particular, the results permit to better estimate the effects of increased amounts of water vapor and nitric acid (which forms from nitrogen oxides) on polar stratospheric clouds and on the chemistry induced by these clouds.
-
Stratospheric Temperature Trends Observed by TIMED/SABER
Xian, T.; Tan, R.
2017-12-01
Trends in the stratospheric temperature are studied based on the temperature profile observation from the Sounding of the Atmosphere using Broadband Emission Radiometry (SABER). The spatially trends are evaluated in different time scales ranging from decadal to monthly resolved. The results indicate a signature of BDC acceleration. There are strong warming trends (up to 9 K/decade) in the middle to upper stratosphere in the high latitude spring, summer, and autumn seasons, accompanied by strong cooling trends in the lower stratosphere. Besides, strong warming trends occurs through the whole stratosphere over the Southern Hemisphere, which confirms Antarctic ozone layer healing since 2000. In addition, the results demonstrate a significant warming trends in the middle of tropical stratosphere, which becomes strongest during June-July-August.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Mueller, K P
2000-01-01
Temperatures in the polar middle atmosphere can fall to extremely low values leading to cloud formation in otherwise cloud-free regions: in summer near the mesopause i.e. noctiluent clouds (NLC) and in winter in the lower stratosphere, i.e. polar stratospheric clouds (PSC). Both clouds are environmentally important, PSCs in the ozone problem and NLCs as early indicators of climate change. To investigate these clouds and to measure temperature profiles the atmospheric physics group set up a backscatter lidar on the Esrange in northern Sweden. Based on our experience with a lidar in Norway the mechanics and optics were redesigned to allow for simultaneous measurements of the depolarization of the backscattered light, three colour measurements and measurements in daylight. A numerical simulation of the daylight filter characteristics suggests that the presently used tuning method should be replaced. The first measurements with this new lidar design on the Esrange were obtained in January 1997. PSCs were observed on 19 days from January to March. Surprisingly, PSCs of type 2 were detected several times even when though synoptic stratospheric temperatures were too warm for such clouds to exist. Temperatures in the lee of the Scandinavian mountains had been lowered by internal waves sufficiently to generate PSC type 2 clouds. Among the previous PSC-observations in January 1995 when the lidar was located on the Norwegian island Andoeya was a singular PSC of type 2 on on January 14, 1995, which had a surface area density two orders of magnitudes higher than typically assumed in theoretical models describing ozone depletion. (orig.)
-
Rapp, Markus; Dörnbrack, Andreas; Kaifler, Bernd
2018-02-01
Temperature profiles based on radio occultation (RO) measurements with the operational European METOP satellites are used to derive monthly mean global distributions of stratospheric (20-40 km) gravity wave (GW) potential energy densities (EP) for the period July 2014-December 2016. In order to test whether the sampling and data quality of this data set is sufficient for scientific analysis, we investigate to what degree the METOP observations agree quantitatively with ECMWF operational analysis (IFS data) and reanalysis (ERA-Interim) data. A systematic comparison between corresponding monthly mean temperature fields determined for a latitude-longitude-altitude grid of 5° by 10° by 1 km is carried out. This yields very low systematic differences between RO and model data below 30 km (i.e., median temperature differences is between -0.2 and +0.3 K), which increases with height to yield median differences of +1.0 K at 34 km and +2.2 K at 40 km. Comparing EP values for three selected locations at which also ground-based lidar measurements are available yields excellent agreement between RO and IFS data below 35 km. ERA-Interim underestimates EP under conditions of strong local mountain wave forcing over northern Scandinavia which is apparently not resolved by the model. Above 35 km, RO values are consistently much larger than model values, which is likely caused by the model sponge layer, which damps small-scale fluctuations above ˜ 32 km altitude. Another reason is the well-known significant increase of noise in RO measurements above 35 km. The comparison between RO and lidar data reveals very good qualitative agreement in terms of the seasonal variation of EP, but RO values are consistently smaller than lidar values by about a factor of 2. This discrepancy is likely caused by the very different sampling characteristics of RO and lidar observations. Direct comparison of the global data set of RO and model EP fields shows large correlation coefficients (0
-
Steinbrecht, W; Claude, H; Schönenborn, F; McDermid, I S; Leblanc, T; Godin, S; Song, T; Swart, D P J; Meijer, Y J; Bodeker, G E; Connor, B J; Kämpfer, N; Hocke, K; Calisesi, Y; Schneider, N; Noë, J de la; Parrish, A D; Boyd, I S; Brühl, C; Steil, B; Giorgetta, M A; Manzini, E; Thomason, L W; Zawodny, J M; McCormick, M P; Russell, J M; Bhartia, P K; Stolarski, R S; Hollandsworth-Frith, S M
2006-01-01
The long-term evolution of upper stratospheric ozone has been recorded by lidars and microwave radiometers within the ground-based Network for the Detection of Stratospheric Change (NDSC), and by the space-borne Solar Backscatter Ultra-Violet instruments (SBUV), Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas
-
Stratospheric Platforms for Monitoring Purposes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Konigorski, D.; Gratzel, U.; Obersteiner, M.; Schneidereit, M.
2010-01-01
Stratospheric platforms are emerging systems based on challenging technology. Goal is to create a platform, payload, and mission design which is able to complement satellite services on a local scale. Applications are close to traditional satellite business in telecommunication, navigation, science, and earth observation and include for example mobile telecommunications, navigation augmentation, atmospheric research, or border control. Stratospheric platforms could potentially support monitoring activities related to safeguards, e.g. by imagery of surfaces, operational conditions of nuclear facilities, and search for undeclared nuclear activities. Stratospheric platforms are intended to be flown in an altitude band between 16 and 30 km, above 16-20 km to take advantage of usually lower winds facilitating station keeping, below 30 km to limit the challenges to achieve a reasonable payload at acceptable platform sizes. Stratospheric platforms could substitute satellites which are expensive and lack upgrade capabilities for new equipment. Furthermore they have practically an unlimited time over an area of interest. It is intended to keep the platforms operational and maintenance free on a 24/7 basis with an average deployment time of 3 years. Geostationary satellites lack resolution. Potential customers like Armed Forces, National Agencies and commercial customers have indicated interest in the use of stratospheric platforms. Governmental entities are looking for cheaper alternatives to communications and surveillance satellites and stratospheric platforms could offer the following potential advantages: Lower operational cost than satellite or UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) constellation (fleet required); Faster deployment than satellite constellation; Repositioning capability and ability to loiter as required; Persistent long-term real-time services over a fairly large regional spot; Surge capability: Able to extend capability (either monitoring or communications
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Schnadt, C
2001-07-01
The impact of climate change and stratospheric chlorine loading on the stratospheric ozone layer is estimated by evaluating three multi-annual simulations of the interactively coupled global chemistry-climate model ECUAM4.L39 (DLR)/CHEM. Two experiments of the near past were carried out representing the early 1980s and 1990s, respectively. An additional scenario was conducted which is characterised by increased greenhouse gas concentrations and a slightly reduced stratospheric chlorine loading with respect to its value measured in the year 1990, according to current projections. The model is able to describe dynamic and chemical processes of the 1980s and 1990s realistically, and it is capable in reproducing the observed stratospheric temperature, water vapour, and ozone temperature trends of this time period. With increasing greenhouse gas concentrations, the model produces an enhancing stratospheric cooling for the years 1980 to 2015. Despite the reduced stratospheric chlorine loading in 2015, the decreased stratospheric temperatures will cause a continued reduction of stratospheric ozone in the southern hemisphere. In the northern hemisphere, tropospheric warming results in a changed excitation of planetary waves. Their vertical propagation and breaking in the stratosphere causes the polar vortex to become more unstable in 2015. This overcompensates the radiative stratospheric cooling so that stratospheric ozone recovers. (orig.)
-
VON CLARMANN, T.
2013-01-01
This paper reviews the various aspects of chlorine compounds in the stratosphere, both their roles as reactants and as tracers of dynamical processes. In the stratosphere, reactive chlorine is released from chlorofluorocarbons and other chlorine-containing organic source gases. To a large extent reactive chlorine is then sequestered in reservoir species ClONO2 and HCl. Re-activation of chlorine happens predominantly in polar winter vortices by heterogeneous reaction in combination with sunlig...
-
Deep Vs Profiling Along the Top of Yucca Mountain Using a Vibroseis Source and Surface Waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Stokoe, K.; Rosenblad, B.; Wong, I.; Bay, J.; Thomas, P.; Silva, W.
2004-01-01
Yucca Mountain, Nevada, was approved as the site for development of the geologic repository for high-level radioactive waste and spent nuclear fuel in the United States. The U.S. Department of Energy has been conducting studies to characterize the site and assess its future performance as a geologic repository. As part of these studies, a program of deep seismic profiling, to depths of 200 m, was conducted along the top of Yucca Mountain to evaluate the shear-wave velocity (V s ) structure of the repository block. The resulting V s data were used as input into the development of ground motions for the preclosure seismic design of the repository and for postclosure performance assessment. The noninvasive spectral-analysis-of-surface-waves (SASW) method was employed in the deep profiling. Field measurements involved the use of a modified Vibroseis as the seismic source. The modifications allowed the Vibroseis to be controlled by a signal analyzer so that slow frequency sweeps could be performed while simultaneous narrow-band filtering was performed on the receiver outputs. This process optimized input energy from the source and signal analysis of the receiver outputs. Six deep V s profiles and five intermediate-depth (about 100 m) profiles were performed along the top of Yucca Mountain over a distance of about 5 km. In addition, eleven shallower profiles (averaging about 45-m deep) were measured using a bulldozer source. The shallower profiles were used to augment the deeper profiles and to evaluate further the near-surface velocity structure. The V s profiles exhibit a strong velocity gradient within 5 m of the surface, with the mean V s value more than doubling. Below this depth, V s gradually increases from a mean value of about 900 to 1000 m/s at a depth of 150 m. Between the depths of 150 and 210 m, V s increases more rapidly to about 1350 m/s, but this trend is based on limited data. At depths less than 50 m, anisotropy in V s was measured for surveys conducted
-
Li, Feng; Newman, Paul; Pawson, Steven; Perlwitz, Judith
2018-01-01
The relative impacts of greenhouse gas (GHG) increase and stratospheric ozone depletion on stratospheric mean age of air in the 1960-2010 period are quantified using the Goddard Earth Observing System Chemistry-�Climate Model. The experiment compares controlled simulations using a coupled atmosphere-�ocean version of the Goddard Earth Observing System Chemistry-�Climate Model, in which either GHGs or ozone depleting substances, or both factors evolve over time. The model results show that GHGs and ozone-depleting substances have about equal contributions to the simulated mean age decrease, but GHG increases account for about two thirds of the enhanced strength of the lower stratospheric residual circulation. It is also found that both the acceleration of the diabatic circulation and the decrease of the mean age difference between downwelling and upwelling regions are mainly caused by GHG forcing. The results show that ozone depletion causes an increase in the mean age of air in the Antarctic summer lower stratosphere through two processes: (1) a seasonal delay in the Antarctic polar vortex breakup that inhibits young midlatitude air from mixing with the older air inside the vortex, and (2) enhanced Antarctic downwelling that brings older air from middle and upper stratosphere into the lower stratosphere.
-
VHF radar observations of gravity waves at a low latitude
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. Dutta
1999-08-01
Full Text Available Wind observations made at Gadanki (13.5°N by using Indian MST Radar for few days in September, October, December 1995 and January, 1996 have been analyzed to study gravity wave activity in the troposphere and lower stratosphere. Horizontal wind variances have been computed for gravity waves of period (2-6 h from the power spectral density (PSD spectrum. Exponential curves of the form eZ/H have been fitted by least squares technique to these variance values to obtain height variations of the irregular winds upto the height of about 15 km, where Z is the height in kilometers. The value of H, the scale height, as determined from curve fitting is found to be less than the theoretical value of scale height of neutral atmosphere in this region, implying that the waves are gaining energy during their passage in the troposphere. In other words, it indicates that the sources of gravity waves are present in the troposphere. The energy densities of gravity wave fluctuations have been computed. Polynomial fits to the observed values show that wave energy density increases in the troposphere, its source region, and then decreases in the lower stratosphere.Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (middle atmosphere dynamics; turbulence; waves and tides
-
Polar night vortex breakdown and large-scale stirring in the southern stratosphere
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Camara, Alvaro de la [Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Departamento de Geofisica y Meteorologia, Madrid (Spain); University of California, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, Los Angeles, CA (United States); Mechoso, C.R. [University of California, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, Los Angeles, CA (United States); Ide, K. [University of California, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, Los Angeles, CA (United States); University of Maryland, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Science, Collage Park, MD (United States); Walterscheid, R. [The Aerospace Corporation, Space Sciences Department, Los Angeles, CA (United States); Schubert, G. [University of California, Department of Earth and Space Sciences, Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, Los Angeles, CA (United States)
2010-11-15
The present paper examines the vortex breakdown and large-scale stirring during the final warming of the Southern Hemisphere stratosphere during the spring of 2005. A unique set of in situ observations collected by 27 superpressure balloons (SPBs) is used. The balloons, which were launched from McMurdo, Antarctica, by the Strateole/VORCORE project, drifted for several weeks on two different isopycnic levels in the lower stratosphere. We describe balloon trajectories and compare them with simulations obtained on the basis of the velocity field from the GEOS-5 and NCEP/NCAR reanalyses performed with and without VORCORE data. To gain insight on the mechanisms responsible for the horizontal transport of air inside and outside the well-isolated vortex we examine the balloon trajectories in the framework of the Lagrangian properties of the stratospheric flow. Coherent structures of the flow are visualized by computing finite-time Lyapunov exponents (FTLE). A combination of isentropic analysis and FTLE distributions reveals that air is stripped away from the vortex's interior as stable manifolds eventually cross the vortex's edge. It is shown that two SPBs escaped from the vortex within high potential vorticity tongues that developed in association with wave breaking at locations along the vortex's edge where forward and backward FTLE maxima approximately intersect. The trajectories of three SPBs flying as a group at the same isopycnic level are examined and their behavior is interpreted in reference to the FTLE field. These results support the concept of stable and unstable manifolds governing transport of air masses across the periphery of the stratospheric polar vortex. (orig.)
-
Condensed Acids In Antartic Stratospheric Clouds
Pueschel, R. F.; Snetsinger, K. G.; Toon, O. B.; Ferry, G. V.; Starr, W. L.; Oberbeck, V. R.; Chan, K. R.; Goodman, J. K.; Livingston, J. M.; Verma, S.;

1992-01-01
Report dicusses nitrate, sulfate, and chloride contents of stratospheric aerosols during 1987 Airborne Antarctic Ozone Experiment. Emphasizes growth of HNO3*3H2O particles in polar stratospheric clouds. Important in testing theories concerning Antarctic "ozone hole".
-
Stratospheric HTO perturbations 1980-1983
Mason, A. S.
1985-02-01
Three perturbations of the stratospheric tritiated water burden have occurred. An atmospheric nuclear detonation in 1980 injected about 2.1 MCi. The massive eruptions of the volcano El Chichon may have contributed to a doubling of the removal rate in 1982. An unusually large wintertime exchange with the upper stratosphere may have occurred between 1982 and 1983.
-
Seasonal variation of equatorial wave momentum fluxes at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. N. Sasi
Full Text Available The vertical flux of the horizontal momentum associated with the equatorial Kelvin and Rossby-gravity waves are estimated from the winds measured by the Indian MST radar located at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E during September 1995 to August 1996 in the tropospheric and lower stratospheric regions for all four seasons. The present study shows that momentum flux values are greater during equinox seasons than solstices, with values near the tropopause level being
16 × 10-3, 7.4 × 10-3, 27 × 10-3 and 5.5 × 10-3 m2 s-2 for Kelvin waves and 5.5 × 10-3, 3.5 × 10-3, 6.7 × 10-3 and 2.1 × 10-3 m2 s-2 for RG waves during autumnal equinox, winter, vernal equinox and summer seasons, respectively. Using these momentum flux values near the tropopause level, acceleration of the mean flow in the stratosphere up to a 29 km height were computed following Plumb (1984, by considering the wave-meanflow interaction and the deposition of the momentum through the radiative dissipation of the waves. A comparison of the estimated mean-flow acceleration in the stratosphere compares well, except at a few height levels, with the observed mean-flow accelerations in the stratosphere derived from the radiosonde data from a nearby station.
Key words. Meteorology and atmosphenic dynamics (tropical meteorology; waves and tides -
Dynamics and transport in the stratosphere : Simulations with a general circulation mode
van Aalst, Maarten Krispijn
2005-01-01
stratosphere, including the Antarctic temperature minima crucial for polar ozone chemistry, but failed to capture the precise timing and evolution of Arctic stratospheric warmings. We also identified an important model deficiency regarding tracer transport in the lower polar stratosphere. The success of the runs with tropospheric nudging in simulating the right stratospheric conditions, including the model capability to forecast major stratospheric warming events, bodes well for the model's representation of the dynamic coupling between the troposphere and the stratosphere, an important element of realistic simulation of the future climate of the middle atmosphere (which will partly depend on a changing wave forcing from the troposphere). However, for some aspects of stratospheric dynamics, such as the quasi-biennial oscillation, a higher vertical resolution is required, which might also help to reduce some of the transport problems identified in the lower polar vortex. The nudging technique applied and developed in this thesis offers excellent prospects for applications in coupled-chemistry simulations of the middle atmosphere, including for the interpretation of instantaneous measurements. In particular, it can be used to test and improve the new MA-ECHAM5/MESSy/MECCA coupled chemistry climate model system, in preparation for more reliable simulations of past and future climates.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ellsaesser, H.W.
1979-01-01
Documentation of the extreme aridity (approx. 3% relative humidity) of the lower stratosphere and the rapid decrease of mixing ratio with height just above the polar tropopause (20-fold in the 1st km) was begun by Dobson et al., (1946) in 1943. They recognized that this extreme and persistent aridity must be dynamically maintained else it would have been wiped out by turbulent diffusion. This led Brewer (1949) to hypothesize a stratospheric circulation in which all air enters through the tropical tropopause where it is freeze dried to a mass mixing ratio of 2 to 3 ppM. This dry air then spreads poleward and descends through the polar tropopauses overpowering upward transport of water vapor by diffusion which would otherwise be permitted by the much warmer temperatures of the polar tropopauses. Questions can indeed be raised as to the absolute magnitudes of stratospheric mixing ratios, the effective temperature of the tropical tropopause cold trap, the reality of winter pole freeze-dry sinks and the representativeness of the available observations suggesting an H 2 O mixing ratio maximum just above the tropical tropopause and a constant mixing ratio from the tropopause to 30 to 35 km. However, no model that better fits all of the available data is available, than does the Brewer (1949) hypothesis coupled with a lower stratosphere winter pole, freeze-dry sink, at least over Antarctica
-
Studying Stratospheric Temperature Variation with Cosmic Ray Measurements
Zhang, Xiaohang; He, Xiaochun
2015-04-01
The long term stratospheric cooling in recent decades is believed to be equally important as surface warming as evidence of influences of human activities on the climate system. Un- fortunatly, there are some discrepancies among different measurements of stratospheric tem- peratures, which could be partially caused by the limitations of the measurement techniques. It has been known for decades that cosmic ray muon flux is sensitive to stratospheric temperature change. Dorman proposed that this effect could be used to probe the tempera- ture variations in the stratophere. In this talk, a method for reconstructing stratospheric temperature will be discussed. We verify this method by comparing the stratospheric tem- perature measured by radiosonde with the ones derived from cosmic ray measurement at multiple locations around the globe.
-
The SAO and Kelvin waves in the EuroGRIPS GCMS and the UK Met. Office analyses
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Amodei
Full Text Available We compare the tropical oscillations and planetary scale Kelvin waves in four troposphere-stratosphere climate models and the assimilated dataset produced by the United Kingdom Meteorological Office (UKMO. The comparison has been made in the GRIPS framework "GCM-Reality Intercomparison Project for SPARC", where SPARC is Stratospheric Processes and their Role in Climate, a project of the World Climate Research Program. The four models evaluated are European members of GRIPS: the UKMO Unified Model (UM, the model of the Free University in Berlin (FUB–GCM, the ARPEGE-climat model of the French National Centre for Meteorological Research (CNRM, and the Extended UGAMP GCM (EUGCM of the Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling (CGAM. The integrations were performed with different, but annually periodic external conditions (e.g., sea-surface temperature, sea ice, and incoming solar radiation. The structure of the tropical winds and the strengths of the Kelvin waves are examined. In the analyses where the SAO (Semi-Annual Oscillation and the QBO (Quasi-Biennal Oscillation are reasonably well captured, the amplitude of these analysed Kelvin waves is close to that observed in independent data from UARS (Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite. In agreement with observations, the Kelvin waves generated in the models propagate into the middle atmosphere as wave packets, consistent with a convective forcing origin. In three of the models, slow Kelvin waves propagate too high and their amplitudes are overestimated in the upper stratosphere and in the mesosphere, the exception is the UM which has weaker waves. None of the modelled waves are sufficient to force realistic eastward phases of the QBO or SAO. Although the SAO is represented by all models, only two of them are able to generate westerlies between 10 hPa and 50 hPa. The importance of the role played in the SAO by unresolved gravity waves is emphasized. Although it exhibits some unrealistic features, the
-
The SAO and Kelvin waves in the EuroGRIPS GCMS and the UK Met. Office analyses
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Amodei
2001-01-01
Full Text Available We compare the tropical oscillations and planetary scale Kelvin waves in four troposphere-stratosphere climate models and the assimilated dataset produced by the United Kingdom Meteorological Office (UKMO. The comparison has been made in the GRIPS framework "GCM-Reality Intercomparison Project for SPARC", where SPARC is Stratospheric Processes and their Role in Climate, a project of the World Climate Research Program. The four models evaluated are European members of GRIPS: the UKMO Unified Model (UM, the model of the Free University in Berlin (FUB–GCM, the ARPEGE-climat model of the French National Centre for Meteorological Research (CNRM, and the Extended UGAMP GCM (EUGCM of the Centre for Global Atmospheric Modelling (CGAM. The integrations were performed with different, but annually periodic external conditions (e.g., sea-surface temperature, sea ice, and incoming solar radiation. The structure of the tropical winds and the strengths of the Kelvin waves are examined. In the analyses where the SAO (Semi-Annual Oscillation and the QBO (Quasi-Biennal Oscillation are reasonably well captured, the amplitude of these analysed Kelvin waves is close to that observed in independent data from UARS (Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite. In agreement with observations, the Kelvin waves generated in the models propagate into the middle atmosphere as wave packets, consistent with a convective forcing origin. In three of the models, slow Kelvin waves propagate too high and their amplitudes are overestimated in the upper stratosphere and in the mesosphere, the exception is the UM which has weaker waves. None of the modelled waves are sufficient to force realistic eastward phases of the QBO or SAO. Although the SAO is represented by all models, only two of them are able to generate westerlies between 10 hPa and 50 hPa. The importance of the role played in the SAO by unresolved gravity waves is emphasized. Although it exhibits some unrealistic features, the
-
Simulation of stratospheric water vapor trends: impact on stratospheric ozone chemistry
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Stenke
2005-01-01
Full Text Available A transient model simulation of the 40-year time period 1960 to 1999 with the coupled climate-chemistry model (CCM ECHAM4.L39(DLR/CHEM shows a stratospheric water vapor increase over the last two decades of 0.7 ppmv and, additionally, a short-term increase after major volcanic eruptions. Furthermore, a long-term decrease in global total ozone as well as a short-term ozone decline in the tropics after volcanic eruptions are modeled. In order to understand the resulting effects of the water vapor changes on lower stratospheric ozone chemistry, different perturbation simulations were performed with the CCM ECHAM4.L39(DLR/CHEM feeding the water vapor perturbations only to the chemistry part. Two different long-term perturbations of lower stratospheric water vapor, +1 ppmv and +5 ppmv, and a short-term perturbation of +2 ppmv with an e-folding time of two months were applied. An additional stratospheric water vapor amount of 1 ppmv results in a 5–10% OH increase in the tropical lower stratosphere between 100 and 30 hPa. As a direct consequence of the OH increase the ozone destruction by the HOx cycle becomes 6.4% more effective. Coupling processes between the HOx-family and the NOx/ClOx-family also affect the ozone destruction by other catalytic reaction cycles. The NOx cycle becomes 1.6% less effective, whereas the effectiveness of the ClOx cycle is again slightly enhanced. A long-term water vapor increase does not only affect gas-phase chemistry, but also heterogeneous ozone chemistry in polar regions. The model results indicate an enhanced heterogeneous ozone depletion during antarctic spring due to a longer PSC existence period. In contrast, PSC formation in the northern hemisphere polar vortex and therefore heterogeneous ozone depletion during arctic spring are not affected by the water vapor increase, because of the less PSC activity. Finally, this study shows that 10% of the global total ozone decline in the transient model run
-
Laboratory Investigations of Stratospheric Halogen Chemistry
Wine, Paul H.; Nicovich, J. Michael; Stickel, Robert E.; Hynes, Anthony J.
1997-01-01
A final report for the NASA-supported project on laboratory investigations of stratospheric halogen chemistry is presented. In recent years, this project has focused on three areas of research: (1) kinetic, mechanistic, and thermochemical studies of reactions which produce weakly bound chemical species of atmospheric interest; (2) development of flash photolysis schemes for studying radical-radical reactions of stratospheric interest; and (3) photochemistry studies of interest for understanding stratospheric chemistry. The first section of this paper contains a discussion of work which has not yet been published. All subsequent chapters contain reprints of published papers that acknowledge support from this grant.
-
Chen, Huilin; Paul, Dipayan; Meijer, Harro; Miller, John; Kivi, Rigel; Krol, Maarten
2016-04-01
Radiocarbon (14C) plays an important role in the carbon cycle studies to understand both natural and anthropogenic carbon fluxes, but also in atmospheric chemistry to constrain hydroxyl radical (OH) concentrations in the atmosphere. Apart from the enormous 14C emissions from nuclear bomb testing in the 1950s and 1960s, radiocarbon is primarily produced in the stratosphere due to the cosmogenic production. To this end, better understanding the stratospheric radiocarbon source is very useful to advance the use of radiocarbon for these applications. However, stratospheric 14C observations have been very limited so that there are large uncertainties on the magnitude and the location of the 14C production as well as the transport of radiocarbon from the stratosphere to the troposphere. Recently we have successfully made stratospheric 14C measurements using AirCore samples from Sodankylä, Northern Finland. AirCore is an innovative atmospheric sampling system, which passively collects atmospheric air samples into a long piece of coiled stainless steel tubing during the descent of a balloon flight. Due to the relatively low cost of the consumables, there is a potential to make such AirCore profiling in other parts of the world on a regular basis. In this study, we simulate the 14C in the atmosphere and assess the stratosphere-troposphere exchange of radiocarbon using the TM5 model. The Sodankylä radiocarbon measurements will be used to verify the performance of the model at high latitude. Besides this, we will also evaluate the influence of different cosmogenic 14C production scenarios and the uncertainties in the OH field on the seasonal cycles of radiocarbon and on the stratosphere-troposphere exchange, and based on the results design a strategy to set up a 14C measurement program using AirCore.
-
Condition of The Stratospheric and Mesospheric Ozone Layer Over Bulgaria for the Period 1996-2012
Kaleyna, Petya; Mukhtarov, Plamen; Miloshev, Nikolay
2014-05-01
A detailed analysis of the variations of the stratospheric and mesospheric ozone over Bulgaria, in the period 1996-2012, is presented in the article on the basis of ground and satellite measurements of the Total Ozone Content (TOC). The move of the most important components: yearly running mean values, amplitudes and phases of the first four harmonics of the seasonal cycle. Their mean values for the period and the existing long term trends have been found. An evaluation of the general characteristics of the short term variability of the Total Ozone Content (TOC) over Bulgaria also has been made in the article. The impact of the planetary wave activity of the stratosphere on the total ozone has been studied and the climatology of the oscillation amplitudes with periods of 4, 7, 11 and 25 days has been defined.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Colin C. Triplett
2017-01-01
Full Text Available The meteorological control of gravity wave activity through filtering by winds and generation by spontaneous adjustment of unbalanced flows is investigated. This investigation is based on a new analysis of Rayleigh LiDAR measurements of gravity wave activity in the upper stratosphere-lower mesosphere (USLM,40–50kmon 152 nights at Poker Flat Research Range (PFRR, Chatanika, Alaska (65◦ N, 147◦ W, over 13 years between 1998 and 2014. The LiDAR measurements resolve inertia-gravity waves with observed periods between 1 h and 4 h and vertical wavelengths between 2 km and 10 km. The meteorological conditions are defined by reanalysis data from the Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA. The gravity wave activity shows large night-to-night variability, but a clear annual cycle with a maximum in winter,and systematic interannual variability associated with stratospheric sudden warming events. The USLM gravity wave activity is correlated with the MERRA winds and is controlled by the winds in the lower stratosphere through filtering by critical layer filtering. The USLM gravity wave activity is also correlated with MERRA unbalanced flow as characterized by the residual of the nonlinear balance equation. This correlation with unbalanced flow only appears when the wind conditions are taken into account, indicating that wind filtering is the primary control of the gravity wave activity.
-
Dessler, A. E.; Ye, H.; Wang, T.; Schoeberl, M. R.; Oman, L. D.; Douglass, A. R.; Butler, A. H.; Rosenlof, K. H.; Davis, S. M.; Portmann, R. W.
2016-01-01
Climate models predict that tropical lower-stratospheric humidity will increase as the climate warms. We examine this trend in two state-of-the-art chemistry-climate models. Under high greenhouse gas emissions scenarios, the stratospheric entry value of water vapor increases by approx. 1 part per million by volume (ppmv) over this century in both models. We show with trajectory runs driven by model meteorological fields that the warming tropical tropopause layer (TTL) explains 50-80% of this increase. The remainder is a consequence of trends in evaporation of ice convectively lofted into the TTL and lower stratosphere. Our results further show that, within the models we examined, ice lofting is primarily important on long time scales - on interannual time scales, TTL temperature variations explain most of the variations in lower stratospheric humidity. Assessing the ability of models to realistically represent ice-lofting processes should be a high priority in the modeling community.
-
A case study of gravity waves in noctilucent clouds
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Dalin
2004-06-01
Full Text Available We present a case study of a noctilucent cloud (NLC display appearing on 10-11 August 2000 over Northern Sweden. Clear wave structures were visible in the clouds and time-lapse photography was used to derive the parameters characterising the gravity waves which could account for the observed NLC modulation. Using two nearby atmospheric radars, the Esrange MST Radar data and Andoya MF radar, we have identified gravity waves propagating upward from the upper stratosphere to NLC altitudes. The wave parameters derived from the radar measurements support the suggestion that gravity waves are responsible for the observed complex wave dynamics in the NLC.
-
Investigation of atmospheric waves on Neptune
Eshleman, Von R.; Hinson, David P.
1994-01-01
This document constitutes the final report for grant NAGW-2442 of the Neptune Data Analysis Program, which supported research concerning atmospheric dynamics on Neptune. Professor Von R. Eshleman was the principal investigator. David P. Hinson was a Co-Investigator. The grant covered the period 1 March 1991 through 31 August 1994, including a six month no-cost extension. Funding from this grant resulted in publication of one journal article and one book chapter as well as presentation of results at two conferences and in numerous seminars. A complete bibliography is given below. A copy of the journal article is attached along with abstracts from the book chapter and the conference presentations. With support from this grant we extended our analysis and interpretation of the Voyager Project. This research contributed to an improvement in our basic understanding of atmospheric dynamics on Neptune. The highlight was the discovery and characterization of inertio-gravity waves in the troposphere and stratosphere. Results include measures of basic wave properties, such as amplitudes and vertical wavelengths, as well as estimates of the effect of the waves on the photochemistry and momentum balance of the stratosphere. This investigation also yielded a better understanding of the potential of radio occultation experiments for studies of atmospheric waves. At the same time we developed new methods of data analysis for exploiting these capabilities. These are currently being applied to radio occultation data obtained with the Magellan spacecraft to study waves in the atmosphere of Venus. Future planetary missions, such as Mars Global Surveyor and Cassini, will benefit from these accomplishments.
-
Triton - Stratospheric molecules and organic sediments
Thompson, W. Reid; Singh, Sushil K.; Khare, B. N.; Sagan, Carl
1989-01-01
Continuous-flow plasma discharge techniques show production rates of hydrocarbons and nitriles in N2 + CH4 atmospheres appropriate to the stratosphere of Titan, and indicate that a simple eddy diffusion model together with the observed electron flux quantitatively matches the Voyager IRIS observations for all the hydrocarbons, except for the simplest ones. Charged particle chemistry is very important in Triton's stratosphere. In the more CH4-rich case of Titan, many hydrocarbons and nitriles are produced in high yield. If N2 is present, the CH4 fraction is low, but hydrocarbons and nitriles are produced in fair yield, abundances of HCN and C2H2 in Triton's stratosphere exceed 10 to the 19th molecules/sq cm per sec, and NCCN, C3H4, and other species are predicted to be present. These molecules may be detected by IRIS if the stratosphere is as warm as expected. Both organic haze and condensed gases will provide a substantial UV and visible opacity in Triton's atmosphere.
-
Trajectory tracking control for underactuated stratospheric airship
Zheng, Zewei; Huo, Wei; Wu, Zhe
2012-10-01
Stratospheric airship is a new kind of aerospace system which has attracted worldwide developing interests for its broad application prospects. Based on the trajectory linearization control (TLC) theory, a novel trajectory tracking control method for an underactuated stratospheric airship is presented in this paper. Firstly, the TLC theory is described sketchily, and the dynamic model of the stratospheric airship is introduced with kinematics and dynamics equations. Then, the trajectory tracking control strategy is deduced in detail. The designed control system possesses a cascaded structure which consists of desired attitude calculation, position control loop and attitude control loop. Two sub-loops are designed for the position and attitude control loops, respectively, including the kinematics control loop and dynamics control loop. Stability analysis shows that the controlled closed-loop system is exponentially stable. Finally, simulation results for the stratospheric airship to track typical trajectories are illustrated to verify effectiveness of the proposed approach.
-
Mahoney, M.; Hicke, J.; Rosenlof, K.; Tuck, A.; Hovde, S.
2000-01-01
On April 11, 1998 WB57F aircraft flew northwest at lower stratospheric altitudes from Houston, Texas, over eastern Wyoming as part of the WB57F Aerosol Mission to sample a vortex filament forecast to pass over that region.
-
Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE) IV Pathfinder
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — The Clean Air Act mandates NASA to monitor stratospheric ozone, and stratospheric aerosol measurements are vital to our understanding of climate. Maintaining...
-
Zhou, Xin; Li, Jianping; Xie, Fei; Chen, Quanliang; Ding, Ruiqiang; Zhang, Wenxia; Li, Yang
2018-03-01
A robust impact of El Niño on the Northern Hemisphere (NH) polar stratosphere has been demonstrated by previous studies, although whether this applies to extreme El Niño is uncertain. The time evolution of the response of the NH stratospheric vortex to extreme El Niño, compared with that to moderate eastern Pacific El Niño, is addressed by means of composite analysis using the National Centers for Environmental Prediction/Department of Energy reanalysis data set from 1980 to 2016. Lead-lag analysis indicates that the El Niño signal actually leads the stratospheric response by 2 months. Considering the time lag, the signal of December-January-February El Niño in the NH stratospheric vortex should mature in the February-March-April season (late winter/early spring). The patterns of circulation and temperature for late winter/early spring during extreme and moderate El Niño events are significant, exhibiting similar structure. The results are confirmed with the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model version 4 model, which is forced with observed SSTs of extreme and moderate El Niño in winter (December-January-February) to analyze the day-to-day propagation of their signals. Note that the magnitudes of the stratospheric responses are much larger in the case of extreme El Niño, as stronger upward propagation of planetary waves leads to a weaker northern polar vortex than during moderate El Niño events.
-
Zhang, Pengfei; Wu, Yutian; Smith, Karen L.
2018-01-01
To better understand the dynamical mechanism that accounts for the observed lead-lag correlation between the early winter Barents-Kara Sea (BKS) sea ice variability and the later winter midlatitude circulation response, a series of experiments are conducted using a simplified atmospheric general circulation model with a prescribed idealized near-surface heating over the BKS. A prolonged effect is found in the idealized experiments following the near-surface heating and can be explicitly attributed to the stratospheric pathway and the long time scale in the stratosphere. The analysis of the Eliassen-Palm flux shows that, as a result of the imposed heating and linear constructive interference, anomalous upward propagating planetary-scale waves are excited and weaken the stratospheric polar vortex. This stratospheric response persists for approximately 1-2 months accompanied by downward migration to the troposphere and the surface. This downward migration largely amplifies and extends the low-level jet deceleration in the midlatitudes and cold air advection over central Asia. The idealized model experiments also suggest that the BKS region is the most effective in affecting the midlatitude circulation than other regions over the Arctic.
-
Characteristics of equatorial gravity waves derived from mesospheric airglow imaging observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Suzuki
2009-04-01
Full Text Available We present the characteristics of small-scale (<100 km gravity waves in the equatorial mesopause region derived from OH airglow imaging observations at Kototabang (100.3° E, 0.2° S, Indonesia, from 2002 to 2005. We adopted a method that could automatically detect gravity waves in the airglow images using two-dimensional cross power spectra of gravity waves. The propagation directions of the waves were likely controlled by zonal filtering due to stratospheric mean winds that show a quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO and the presence of many wave sources in the troposphere.
-
Signals of El Niño Modoki in the tropical tropopause layer and stratosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. Xie
2012-06-01
Full Text Available The effects of El Niño Modoki events on the tropical tropopause layer (TTL and on the stratosphere were investigated using European Center for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (ECMWF reanalysis data, oceanic El Niño indices, and general climate model outputs. El Niño Modoki events tend to depress convective activities in the western and eastern Pacific but enhance convective activities in the central and northern Pacific. Consequently, during El Niño Modoki events, negative water vapor anomalies occur in the western and eastern Pacific upper troposphere, whereas there are positive anomalies in the central and northern Pacific upper troposphere. The spatial patterns of the outgoing longwave radiation (OLR and upper tropospheric water vapor anomalies exhibit a tripolar form. The empirical orthogonal function (EOF analysis of the OLR and upper tropospheric water vapor anomalies reveals that canonical El Niño events are associated with the leading mode of the EOF, while El Niño Modoki events correspond to the second mode. The composite analysis based on ERA-interim data indicate that El Niño Modoki events have a reverse effect on middle-high latitudes stratosphere, as compared with the effect of typical El Niño events, i.e., the northern polar vortex is stronger and colder but the southern polar vortex is weaker and warmer during El Niño Modoki events. According to the simulation' results, we found that the reverse effect on the middle-high latitudes stratosphere is resulted from a complicated interaction between quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO signal of east phase and El Niño Modoki signal. This interaction is not a simply linear overlay of QBO signal and El Niño Modoki signal in the stratosphere, it is El Niño Modoki that leads to different tropospheric zonal wind anomalies with QBO forcing from that caused by typical El Niño, thus, the planetary wave propagation from troposphere to the stratosphere during El Niño Modoki events is
-
Stratospheric BrONO2 observed by MIPAS
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. Fischer
2009-03-01
Full Text Available The first measurements of stratospheric bromine nitrate (BrONO2 are reported. Bromine nitrate has been clearly identified in atmospheric infrared emission spectra recorded with the Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS aboard the European Envisat satellite, and stratospheric concentration profiles have been determined for different conditions (day and night, different latitudes. The BrONO2 concentrations show strong day/night variations, with much lower concentrations during the day. Maximum volume mixing ratios observed during night are 20 to 25 pptv. The observed concentration profiles are in agreement with estimations from photochemical models and show that the current understanding of stratospheric bromine chemistry is generally correct.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
L. Schoon
2018-05-01
Full Text Available For the local diagnosis of wave properties, we develop, validate, and apply a novel method which is based on the Hilbert transform. It is called Unified Wave Diagnostics (UWaDi. It provides the wave amplitude and three-dimensional wave number at any grid point for gridded three-dimensional data. UWaDi is validated for a synthetic test case comprising two different wave packets. In comparison with other methods, the performance of UWaDi is very good with respect to wave properties and their location. For a first practical application of UWaDi, a minor sudden stratospheric warming on 30 January 2016 is chosen. Specifying the diagnostics for hydrostatic inertia–gravity waves in analyses from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, we detect the local occurrence of gravity waves throughout the middle atmosphere. The local wave characteristics are discussed in terms of vertical propagation using the diagnosed local amplitudes and wave numbers. We also note some hints on local inertia–gravity wave generation by the stratospheric jet from the detection of shallow slow waves in the vicinity of its exit region.
-
Internal gravity waves in Titan's atmosphere observed by Voyager radio occultation
Hinson, D. P.; Tyler, G. L.
1983-01-01
The radio scintillations caused by scattering from small-scale irregularities in Titan's neutral atmosphere during a radio occultation of Voyager 1 by Titan are investigated. Intensity and frequency fluctuations occurred on time scales from about 0.1 to 1.0 sec at 3.6 and 13 cm wavelengths whenever the radio path passed within 90 km of the surface, indicating the presence of variations in refractivity on length scales from a few hundred meters to a few kilometers. Above 25 km, the altitude profile of intensity scintillations closely agrees with the predictions of a simple theory based on the characteristics of internal gravity waves propagating with little or no attenuation through the vertical stratification in Titan's atmosphere. These observations support a hypothesis of stratospheric gravity waves, possibly driven by a cloud-free convective region in the lowest few kilometers of the stratosphere.
-
Seasonal variation and sources of atmospheric gravity waves in the Antarctic
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kaoru Sato
2010-12-01
Full Text Available In the last recent ten years, our knowledge of gravity waves in the Antarctic has been significantly improved through numerous studies using balloon and satellite observations and high-resolution model simulations. In this report, we introduce results from two studies which were performed as a part of the NIPR project "Integrated analysis of the material circulation in the Antarctic atmosphere-cryosphere-ocean" (2004-2009, i.e., Yoshiki et al. (2004 and Sato and Yoshiki (2008. These two studies focused on the seasonal variation and sources of the gravity waves in the Antarctic, because horizontal wavelengths and phase velocities depend largely on the wave sources. The former study used original high-resolution data from operational radiosonde observations at Syowa Station. In the lowermost stratosphere, gravity waves do not exhibit characteristic seasonal variation; instead, the wave energy is intensified when lower latitude air intrudes into the area near Syowa Station in the upper troposphere. This intrusion is associated with blocking events or developed synoptic-scale waves. In the lower and middle stratosphere, the gravity wave energy is maximized in spring and particularly intensified when the axis of the polar night jet approaches Syowa Station. The latter study is based on intensive radiosonde observation campaigns that were performed in 2002 at Syowa Station as an activity of JARE-43. Gravity wave propagation was statistically examined using two dimensional (i.e., vertical wavenumber versus frequency spectra in each season. It was shown that the gravity waves are radiated upward and downward from an unbalanced region of the polar night jet. This feature is consistent with the gravity-wave resolving GCM simulation.
-
Is there any chlorine monoxide in the stratosphere?
Mumma, M. J.; Rogers, J. D.; Kostiuk, T.; Deming, D.; Hillman, J. J.; Zipoy, D.
1983-01-01
A ground-based search for stratospheric 35-ClO was carried out using an infrared heterodyne spectrometer in the solar absorption mode. Lines due to stratospheric HNO3 and tropospheric OCS were detected at about 0.2 percent absorptance levels, but the expected 0.1 percent lines of ClO in this same region were not seen. We find that stratospheric ClO is at least a factor of seven less abundant than is indicated by in situ measurements, and we set an upper limit of 2.3 x 10 to the 13th molecules/sq cm at the 95 percent confidence level for the integrated vertical column density of ClO. Our results imply that the release of chlorofluorocarbons may be significantly less important for the destruction of stratospheric ozone (O3) than is currently thought. Previously announced in STAR as N83-27518
-
Zhao, J.; Wang, S.
2017-12-01
Gravity wave drag (GWD) is among the drivers of meridional overturning in the middle atmosphere, also known as the Brewer-Dobson Circulation, and of the quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO). The small spatial scales and complications due to wave breaking require their effects to be parameterised. GWD parameterizations are usually divided into two parts, orographic and non-orographic. The basic dynamical and physical processes of the middle atmosphere and the mechanism of the interactions between the troposphere and the middle atmosphere were studied in the frame of a general circulation model. The model for the troposphere was expanded to a global model considering middle atmosphere with the capability of describing the basic processes in the middle atmosphere and the troposphere-middle atmosphere interactions. Currently, it is too costly to include full non-hydrostatic and rotational wave dynamics in an operational parameterization. The hydrostatic non-rotational wave dynamics which allow an efficient implementation that is suitably fast for operation. The simplified parameterization of non-orographic GWD follows from the WM96 scheme in which a framework is developed using conservative propagation of gravity waves, critical level filtering, and non-linear dissipation. In order to simulate and analysis the influence of non-orographic GWD on the stratospheric wind and temperature fields, experiments using Stratospheric Sudden Warming (SSW) event case occurred in January 2013 were carried out, and results of objective weather forecast verifications of the two months period were compared in detail. The verification of monthly mean of forecast anomaly correlation (ACC) and root mean square (RMS) errors shows consistently positive impact of non-orographic GWD on skill score of forecasting for the three to eight days, both in the stratosphere and troposphere, and visible positive impact on prediction of the stratospheric wind and temperature fields. Numerical simulation
-
On the development of the theory of the QBO. [Quasi-Biennial Oscillation
Lindzen, Richard S.
1987-01-01
The events that led to the discovery of the quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) of the equatorial stratosphere are described together with the development of current QBO theory. Three independent areas of inquiry led to this theory: (1) the observational and theoretical studies of equatorial waves, (2) the theoretical study of the behavior of mountain waves at critical levels where the mean flow speed went to zero, and (3) the semiempirical study of the momentum budget of the QBO. The efforts in each of these three areas are discussed.
-
Sources and sinks of stratospheric water vapor
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ellsaesser, H.W.
1979-11-01
A tutorial review of the understanding of stratospheric H 2 O and the processes controlling it is presented. Paradoxes posed by currently available observational data are cited and suggestions made as to how they might be resolved. Such resolution appears to require: that the bulk of our current data provides unrepresentative and misleading vertical and latitudinal H 2 O gradients immediately downstream from the tropical tropopause; and, that there exists within the troposphere a mechanism different from or in addition to the tropical tropopause cold trap for drying air to the mixing ratios found in the lower stratosphere. Satisfaction of these requirements will reconcile much heretofore puzzling observational data and will obviate the necessity for a stratospheric sink for H 2 O
-
Toohey, M.; Krüger, K.; Bittner, M.; Timmreck, C.; Schmidt, H.
2014-12-01
Observations and simple theoretical arguments suggest that the Northern Hemisphere (NH) stratospheric polar vortex is stronger in winters following major volcanic eruptions. However, recent studies show that climate models forced by prescribed volcanic aerosol fields fail to reproduce this effect. We investigate the impact of volcanic aerosol forcing on stratospheric dynamics, including the strength of the NH polar vortex, in ensemble simulations with the Max Planck Institute Earth System Model. The model is forced by four different prescribed forcing sets representing the radiative properties of stratospheric aerosol following the 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo: two forcing sets are based on observations, and are commonly used in climate model simulations, and two forcing sets are constructed based on coupled aerosol-climate model simulations. For all forcings, we find that simulated temperature and zonal wind anomalies in the NH high latitudes are not directly impacted by anomalous volcanic aerosol heating. Instead, high-latitude effects result from enhancements in stratospheric residual circulation, which in turn result, at least in part, from enhanced stratospheric wave activity. High-latitude effects are therefore much less robust than would be expected if they were the direct result of aerosol heating. Both observation-based forcing sets result in insignificant changes in vortex strength. For the model-based forcing sets, the vortex response is found to be sensitive to the structure of the forcing, with one forcing set leading to significant strengthening of the polar vortex in rough agreement with observation-based expectations. Differences in the dynamical response to the forcing sets imply that reproducing the polar vortex responses to past eruptions, or predicting the response to future eruptions, depends on accurate representation of the space-time structure of the volcanic aerosol forcing.
-
Stratospheric ozone: History and concepts and interactions with climate
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Bekki S.
2009-02-01
Full Text Available Although in relatively low concentration of a few molecules per million of e e air molecules, atmospheric ozone (trioxygen O3 is essential to sustaining life on the surface of the Earth. Indeed, by absorbing solar radiation between 240 and 320 nm, it shields living organisms including humans from the very harmful ultraviolet radiation UV-B. About 90% of the ozone resides in the stratosphere, a region that extends from the tropopause, whose altitude ranges from 7 km at the poles to 17 km in the tropics, to the stratopause located at about 50 km altitude. Stratospheric ozone is communally referred as the « ozone layer ». Unlike the atmosphere surrounding it, the stratosphere is vertically stratified and stable because the temperature increases with height within it. This particularity originates from heating produced by the absorption of UV radiation by stratospheric ozone. The present chapter describes the main mechanisms that govern the natural balance of ozone in the stratosphere, and its disruption under the influence of human activities.
-
Quantifying pollution transport from the Asian monsoon anticyclone into the lower stratosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. Ploeger
2017-06-01
Full Text Available Pollution transport from the surface to the stratosphere within the Asian monsoon circulation may cause harmful effects on stratospheric chemistry and climate. Here, we investigate air mass transport from the monsoon anticyclone into the stratosphere using a Lagrangian chemistry transport model. We show how two main transport pathways from the anticyclone emerge: (i into the tropical stratosphere (tropical pipe, and (ii into the Northern Hemisphere (NH extratropical lower stratosphere. Maximum anticyclone air mass fractions reach around 5 % in the tropical pipe and 15 % in the extratropical lowermost stratosphere over the course of a year. The anticyclone air mass fraction correlates well with satellite hydrogen cyanide (HCN and carbon monoxide (CO observations, confirming that pollution is transported deep into the tropical stratosphere from the Asian monsoon anticyclone. Cross-tropopause transport occurs in a vertical chimney, but with the pollutants transported quasi-horizontally along isentropes above the tropopause into the tropics and NH.
-
Stratospheric concentrations of N2O in July 1975
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Krey, P.W.; Lagomarsino, R.J.; Schonberg, M.
1977-01-01
The first measurement of the hemispheric distribution of N 2 O concentrations in the lower stratosphere of the Northern Hemisphere is reported for July 1975. This distribution is similar to those of CCl 3 F and SF 6 , although N 2 O is more stable in the stratosphere than either of the other trace gases. The inventory of N 2 O in the stratosphere of the Northern Hemisphere in July 1975 against which future observations can be compared is 136 Tg
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
D. Pancheva
2009-03-01
Full Text Available This paper is focused on the nonmigrating tidal activity seen in the SABER/TIMED temperatures that is related to the major sudden stratospheric warming (SSW taking place in the Arctic winter of 2003/2004. The emphasis is on the nonmigrating diurnal tides observed in the stratosphere and lower mesosphere which is usually accepted to be insignificant in comparison with that in the upper mesosphere and thermosphere. By using different independent spectral methods we found a significant amplification in December–January of the following nonmigrating 24-h tides: zonally symmetric (s=0, eastward propagating with zonal wavenumber 1 (E1, and westward propagating with zonal wavenumbers 2 and 3 (W2 and W3 tides. It has been found that the double peak nonmigrating tidal amplifications located in the stratosphere (~40 km and in the lower mesosphere (~70 km are a consequence of the maintained hydrostatic relation. By detailed comparison of the evolution and spatial structure of the nonmigrating diurnal tides with those of the migrating diurnal tide and stationary planetary waves (SPWs evidence for a SPW-migrating tide interaction as a source of nonmigrating tides has been presented. Therefore, the nonmigrating 24-h tides turn out to be an important component of the middle atmosphere dynamics during the major SSW in the Arctic winter of 2003/2004.
-
Sulphur-rich volcanic eruptions and stratospheric aerosols
Rampino, M. R.; Self, S.
1984-01-01
Data from direct measurements of stratospheric optical depth, Greenland ice-core acidity, and volcanological studies are compared, and it is shown that relatively small but sulfur-rich volcanic eruptions can have atmospheric effects equal to or even greater than much larger sulfur-poor eruptions. These small eruptions are probably the most frequent cause of increased stratospheric aerosols. The possible sources of the excess sulfur released in these eruptions are discussed.
-
Influence of an Internally-Generated QBO on Modeled Stratospheric Dynamics and Ozone
Hurwitz, M. M.; Newman, P. A.; Song, I. S.
2011-01-01
A GEOS V2 CCM simulation with an internally generated quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) signal is compared to an otherwise identical simulation without a QBO. In a present-day climate, inclusion of the modeled QBO makes a significant difference to stratospheric dynamics and ozone throughout the year. The QBO enhances variability in the tropics, as expected, but also in the polar stratosphere in some seasons. The modeled QBO also affects the mean stratospheric climate. Because tropical zonal winds in the baseline simulation are generally easterly, there is a relative increase in zonal wind magnitudes in tropical lower and middle stratosphere in the QBO simulation. Extra-tropical differences between the QBO and 'no QBO' simulations thus reflect a bias toward the westerly phase of the QBO: a relative strengthening and poleward shifting the polar stratospheric jets, and a reduction in Arctic lower stratospheric ozone.
-
New stratospheric UV/visible radiance measurements
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. J. Marceau
1994-01-01
Full Text Available A stratospheric balloon was launched on 12 October 1986 from the "CNES" base at Aire sur l'Adour (France to record twilight radiance in the stratosphere. The near-UV and visible radiances were continuously monitored by a photometer during sunrise. Some observations are presented for different viewing azimuthal planes and viewing elevation angles. They show the influence of aerosols layers and clouds which can be also seen on related photographs. The results as a whole may be used for testing some radiative models, especially for twilight conditions.
-
Benefits, risks, and costs of stratospheric geoengineering
Robock, Alan
2009-10-02
Injecting sulfate aerosol precursors into the stratosphere has been suggested as a means of geoengineering to cool the planet and reduce global warming. The decision to implement such a scheme would require a comparison of its benefits, dangers, and costs to those of other responses to global warming, including doing nothing. Here we evaluate those factors for stratospheric geoengineering with sulfate aerosols. Using existing U.S. military fighter and tanker planes, the annual costs of injecting aerosol precursors into the lower stratosphere would be several billion dollars. Using artillery or balloons to loft the gas would be much more expensive. We do not have enough information to evaluate more exotic techniques, such as pumping the gas up through a hose attached to a tower or balloon system. Anthropogenic stratospheric aerosol injection would cool the planet, stop the melting of sea ice and land-based glaciers, slow sea level rise, and increase the terrestrial carbon sink, but produce regional drought, ozone depletion, less sunlight for solar power, and make skies less blue. Furthermore it would hamper Earth-based optical astronomy, do nothing to stop ocean acidification, and present many ethical and moral issues. Further work is needed to quantify many of these factors to allow informed decision-making.
-
Tropical Gravity Wave Momentum Fluxes and Latent Heating Distributions
Geller, Marvin A.; Zhou, Tiehan; Love, Peter T.
2015-01-01
Recent satellite determinations of global distributions of absolute gravity wave (GW) momentum fluxes in the lower stratosphere show maxima over the summer subtropical continents and little evidence of GW momentum fluxes associated with the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ). This seems to be at odds with parameterizations forGWmomentum fluxes, where the source is a function of latent heating rates, which are largest in the region of the ITCZ in terms of monthly averages. The authors have examined global distributions of atmospheric latent heating, cloud-top-pressure altitudes, and lower-stratosphere absolute GW momentum fluxes and have found that monthly averages of the lower-stratosphere GW momentum fluxes more closely resemble the monthly mean cloud-top altitudes rather than the monthly mean rates of latent heating. These regions of highest cloud-top altitudes occur when rates of latent heating are largest on the time scale of cloud growth. This, plus previously published studies, suggests that convective sources for stratospheric GW momentum fluxes, being a function of the rate of latent heating, will require either a climate model to correctly model this rate of latent heating or some ad hoc adjustments to account for shortcomings in a climate model's land-sea differences in convective latent heating.
-
Stable Water Isotopologues in the Stratosphere Retrieved from Odin/SMR Measurements
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tongmei Wang
2018-01-01
Full Text Available Stable Water Isotopologues (SWIs are important diagnostic tracers for understanding processes in the atmosphere and the global hydrological cycle. Using eight years (2002–2009 of retrievals from Odin/SMR (Sub-Millimetre Radiometer, the global climatological features of three SWIs, H216O, HDO and H218O, the isotopic composition δD and δ18O in the stratosphere are analysed for the first time. Spatially, SWIs are found to increase with altitude due to stratospheric methane oxidation. In the tropics, highly depleted SWIs in the lower stratosphere indicate the effect of dehydration when the air comes through the cold tropopause, while, at higher latitudes, more enriched SWIs in the upper stratosphere during summer are produced and transported to the other hemisphere via the Brewer–Dobson circulation. Furthermore, we found that more H216O is produced over summer Northern Hemisphere and more HDO is produced over summer Southern Hemisphere. Temporally, a tape recorder in H216O is observed in the lower tropical stratosphere, in addition to a pronounced downward propagating seasonal signal in SWIs from the upper to the lower stratosphere over the polar regions. These observed features in SWIs are further compared to SWI-enabled model outputs. This helped to identify possible causes of model deficiencies in reproducing main stratospheric features. For instance, choosing a better advection scheme and including methane oxidation process in a specific model immediately capture the main features of stratospheric water vapor. The representation of other features, such as the observed inter-hemispheric difference of isotopic component, is also discussed.
-
Wang, Jack C.; Tsai-Lin, Rong; Chang, Loren C.; Wu, Qian; Lin, Charles C. H.; Yue, Jia
2018-06-01
The Quasi-biennial Oscillation (QBO) is a persistent oscillation in the zonal mean zonal winds of the low latitude middle atmosphere that is driven by breaking planetary and gravity waves with a period near two years. The atmospheric tides that dominate the dynamics of the mesosphere and lower thermosphere region (MLT, between heights of 70-120 km) are excited in the troposphere and stratosphere, and propagate through QBO-modulated zonal mean zonal wind fields. This allows the MLT tidal response to also be modulated by the QBO, with implications for ionospheric/thermospheric variability. Interannual oscillations in solar radiation can also directly drive the variations in the ionosphere with similar periodicities through the photoionization. Many studies have observed the connection between the solar activity and QBO signal in ionospheric features such as total electron content (TEC). In this research, we develop an empirical model to isolate stratospheric QBO-related tidal variability in the MLT diurnal and semidiurnal tides using values from assimilated TIMED satellite data. Migrating tidal fields corresponding to stratospheric QBO eastward and westward phases, as well as with the quasi-biennial variations in solar activity isolated by the Multi-dimensional Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (MEEMD) analysis from Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT), are then used to drive the NCAR Thermosphere-Ionosphere-Electrodynamics General Circulation Model (TIE-GCM). The numerical experiment results indicate that the ionospheric QBO is mainly driven by the solar quasi-biennial variations during the solar maximum, since the solar quasi-biennial variation amplitude is directly proportionate to the solar cycle. The ionospheric QBO in the model is sensitive to both the stratospheric QBO and solar quasi-biennial variations during the solar minimum, with solar effects still playing a stronger role.
-
The Limb Infrared Monitor of the Stratosphere (LIMS) experiment
Russell, J. M.; Gille, J. C.
1978-01-01
The Limb Infrared Monitor of the Stratosphere is used to obtain vertical profiles and maps of temperature and the concentration of ozone, water vapor, nitrogen dioxide, and nitric acid for the region of the stratosphere bounded by the upper troposphere and the lower mesosphere.
-
Impact of lower stratospheric ozone on seasonal prediction systems
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kelebogile Mathole
2014-03-01
Full Text Available We conducted a comparison of trends in lower stratospheric temperatures and summer zonal wind fields based on 27 years of reanalysis data and output from hindcast simulations using a coupled ocean-atmospheric general circulation model (OAGCM. Lower stratospheric ozone in the OAGCM was relaxed to the observed climatology and increasing greenhouse gas concentrations were neglected. In the reanalysis, lower stratospheric ozone fields were better represented than in the OAGCM. The spring lower stratospheric/ upper tropospheric cooling in the polar cap observed in the reanalysis, which is caused by a direct ozone depletion in the past two decades and is in agreement with previous studies, did not appear in the OAGCM. The corresponding summer tropospheric response also differed between data sets. In the reanalysis, a statistically significant poleward trend of the summer jet position was found, whereas no such trend was found in the OAGCM. Furthermore, the jet position in the reanalysis exhibited larger interannual variability than that in the OAGCM. We conclude that these differences are caused by the absence of long-term lower stratospheric ozone changes in the OAGCM. Improper representation or non-inclusion of such ozone variability in a prediction model could adversely affect the accuracy of the predictability of summer rainfall forecasts over South Africa.
-
Tiny Ultraviolet Polarimeter for Earth Stratosphere from Space Investigation
Nevodovskyi, P. V.; Morozhenko, O. V.; Vidmachenko, A. P.; Ivakhiv, O.; Geraimchuk, M.; Zbrutskyi, O.
2015-09-01
One of the reasons for climate change (i.e., stratospheric ozone concentrations) is connected with the variations in optical thickness of aerosols in the upper sphere of the atmosphere (at altitudes over 30 km). Therefore, aerosol and gas components of the atmosphere are crucial in the study of the ultraviolet (UV) radiation passing upon the Earth. Moreover, a scrupulous study of aerosol components of the Earth atmosphere at an altitude of 30 km (i.e., stratospheric aerosol), such as the size of particles, the real part of refractive index, optical thickness and its horizontal structure, concentration of ozone or the upper border of the stratospheric ozone layer is an important task in the research of the Earth climate change. At present, the Main Astronomical Observatory of the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) of Ukraine, the National Technical University of Ukraine "KPI"and the Lviv Polytechnic National University are engaged in the development of methodologies for the study of stratospheric aerosol by means of ultraviolet polarimeter using a microsatellite. So fare, there has been created a sample of a tiny ultraviolet polarimeter (UVP) which is considered to be a basic model for carrying out space experiments regarding the impact of the changes in stratospheric aerosols on both global and local climate.
-
Holmes, C. D.; Archibald, A. T.; Eastham, S. D.; Søvde, O. A.
2017-12-01
Methane is a direct and indirect greenhouse gas. The direct greenhouse effect comes from the radiation absorbed and emitted by methane itself. The indirect greenhouse effect comes from radiatively active gases that are produced during methane oxidation: principally O3, H2O, and CO2. Methane also suppresses tropospheric OH, which indirectly affects numerous greenhouses gases and aerosols. Traditionally, the methane global warming potential (GWP) has included the indirect effects on tropospheric O3 and OH and stratospheric H2O, with these effects estimated independently from unrelated tropospheric and stratospheric chemistry models and observations. Using this approach the CH4 is about 28 over 100 yr (without carbon cycle feedbacks, IPCC, 2013). Here we present a comprehensive analysis of the CH4 GWP in several 3-D global atmospheric models capable of simulating both tropospheric and stratospheric chemistry (GEOS-Chem, Oslo CTM3, UKCA). This enables us to include, for the first time, the indirect effects of CH4 on stratospheric O3 and stratosphere-troposphere coupling. We diagnose the GWP from paired simulations with and without a 5% perturbation to tropospheric CH4 concentrations. Including stratospheric chemistry nearly doubles the O3 contribution to CH4 GWP because of O3 production in the lower stratosphere and because CH4 inhibits Cl-catalyzed O3 loss in the upper stratosphere. In addition, stratosphere-troposphere coupling strengthens the chemical feedback on its own lifetime. In the stratosphere, this feedback operates by a CH4 perturbation thickening the stratospheric O3 layer, which impedes UV-driven OH production in the troposphere and prolongs the CH4 lifetime. We also quantify the impact of CH4-derived H2O on the stratospheric HOx cycles but these effects are small. Combining all of the above, these models suggest that the 100-yr GWP of CH4 is over 33.5, a 20% increase over the latest IPCC assessment.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. M. Khaykin
2013-07-01
Full Text Available Following recent studies evidencing the influence of deep convection on the chemical composition and thermal structure of the tropical lower stratosphere, we explore its impact on the temperature diurnal variation in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere using the high-resolution COSMIC GPS radio-occultation temperature measurements spanning from 2006 through 2011. The temperature in the lowermost stratosphere over land during summer displays a marked diurnal cycle characterized by an afternoon cooling. This diurnal cycle is shown collocated with most intense land convective areas observed by the Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission (TRMM precipitation radar and in phase with the maximum overshooting occurrence frequency in late afternoon. Two processes potentially responsible for that are identified: (i non-migrating tides, whose physical nature is internal gravity waves, and (ii local cross-tropopause mass transport of adiabatically cooled air by overshooting turrets. Although both processes can contribute, only the lofting of adiabatically cooled air is well captured by models, making it difficult to characterize the contribution of non-migrating tides. The impact of deep convection on the temperature diurnal cycle is found larger in the southern tropics, suggesting more vigorous convection over clean rain forest continents than desert areas and polluted continents in the northern tropics.
-
SAGE measurements of the stratospheric aerosol dispersion and loading from the Soufriere Volcano
Mccormick, M. P.; Kent, G. S.; Yue, G. K.; Cunnold, D. M.
1981-01-01
Explosions of the Soufriere volcano on the Caribbean Island of St. Vincent reduced two major stratospheric plumes which the stratospheric aerosol and gas experiment (SAGE) satellite tracked to West Africa and the North Atlantic Ocean. The total mass of the stratospheric ejecta measured is less than 0.5% of the global stratospheric aerosol burden. No significant temperature or climate perturbation is expected. It is found that the movement and dispersion of the plumes agree with those deduced from high altitude meteorological data and dispersion theory. The stratospheric aerosol dispersion and loading from the Soufrier volcano was measured.
-
Laboratory investigation of nitrile ices of Titan's stratospheric clouds
Nna Mvondo, D.; Anderson, C. M.; McLain, J. L.; Samuelson, R. E.
2017-09-01
Titan's mid to lower stratosphere contains complex cloud systems of numerous organic ice particles comprised of both hydrocarbon and nitrile compounds. Most of these stratospheric ice clouds form as a result of vapor condensation formation processes. However, there are additional ice emission features such as dicyanoacetylene (C4N2) and the 220 cm-1 ice emission feature (the "Haystack") that are difficult to explain since there are no observed vapor emission features associated with these ices. In our laboratory, using a high-vacuum chamber coupled to a FTIR spectrometer, we are engaged in a dedicated investigation of Titan's stratospheric ices to interpret and constrain Cassini Composite InfraRed Spectrometer (CIRS) far-IR data. We will present laboratory transmittance spectra obtained for propionitrile (CH3CH2CN), cyanogen (C2N2) and hydrogen cyanide (HCN) ices, as well as various combinations of their mixtures, to better understand the cloud chemistry occurring in Titan's stratosphere.
-
Sulfuric acid deposition from stratospheric geoengineering with sulfate aerosols
Kravitz, Ben
2009-07-28
We used a general circulation model of Earth\\'s climate to conduct geoengineering experiments involving stratospheric injection of sulfur dioxide and analyzed the resulting deposition of sulfate. When sulfur dioxide is injected into the tropical or Arctic stratosphere, the main additional surface deposition of sulfate occurs in midlatitude bands, because of strong cross-tropopause flux in the jet stream regions. We used critical load studies to determine the effects of this increase in sulfate deposition on terrestrial ecosystems by assuming the upper limit of hydration of all sulfate aerosols into sulfuric acid. For annual injection of 5 Tg of SO2 into the tropical stratosphere or 3 Tg of SO2 into the Arctic stratosphere, neither the maximum point value of sulfate deposition of approximately 1.5 mEq m−2 a−1 nor the largest additional deposition that would result from geoengineering of approximately 0.05 mEq m−2 a−1 is enough to negatively impact most ecosystems.
-
Sulfuric acid deposition from stratospheric geoengineering with sulfate aerosols
Kravitz, Ben; Robock, Alan; Oman, Luke; Stenchikov, Georgiy L.; Marquardt, Allison B.
2009-01-01
We used a general circulation model of Earth's climate to conduct geoengineering experiments involving stratospheric injection of sulfur dioxide and analyzed the resulting deposition of sulfate. When sulfur dioxide is injected into the tropical or Arctic stratosphere, the main additional surface deposition of sulfate occurs in midlatitude bands, because of strong cross-tropopause flux in the jet stream regions. We used critical load studies to determine the effects of this increase in sulfate deposition on terrestrial ecosystems by assuming the upper limit of hydration of all sulfate aerosols into sulfuric acid. For annual injection of 5 Tg of SO2 into the tropical stratosphere or 3 Tg of SO2 into the Arctic stratosphere, neither the maximum point value of sulfate deposition of approximately 1.5 mEq m−2 a−1 nor the largest additional deposition that would result from geoengineering of approximately 0.05 mEq m−2 a−1 is enough to negatively impact most ecosystems.
-
Anomalous high-frequency wave activity flux preceding anomalous changes in the Northern polar jet
Nakamura, Mototaka; Kadota, Minoru; Yamane, Shozo
2010-05-01
Anomalous forcing by quasi-geostrophic (QG) waves has been reported as an important forcing factor in the Northern Annular Mode (NAM) in recent literatures. In order to shed a light on the dynamics of the NAM from a different angle, we have examined anomalous behavior of the winter jets in the upper troposphere and stratosphere by focusing our diagnosis on not the anomalous geopotential height (Z) itself, but on the anomalous change in the Z (dZ) between two successive months and preceding transient QG wave activity flux during the cold season. We calculated EOFs of dZ between two successive months at 150hPa for a 46-year period, from 1958 to 2003, using the monthly mean NCEP reanalysis data. We then formed anomaly composites of changes in Z and the zonal velocity (U), as well as the preceding and following wave activity flux, Z, U, and temperature at various heights, for both positive and negative phases of the first EOF. For the wave forcing fields, we adopted the diagnostic system for the three-dimensional QG transient wave activity flux in the zonally-varying three-dimensional mean flow developed by Plumb (1986) with a slight modification in its application to the data. Our choice of the Plumb86 is based on the fact that the winter mean flow in the Northern Hemisphere is characterized by noticeable zonal asymmetry, and has a symbiotic relationship with waves in the extra-tropics. The Plumb86 flux was calculated for high-frequency (period of 2 to 7 days) and low-frequency (period of 10 to 20 days) waves with the ultra-low-frequency (period of 30 days or longer) flow as the reference state for each time frame of the 6 hourly NCEP reanalysis data from 1958 to 2003. By replacing the mean flow with the ultra-low-frequency flow in the application of the Plumb86 formula, the flux fields were calculated as time series at 6 hour intervals. The time series of the wave activity flux was then averaged for each month. The patterns of composited anomalous dZ and dU clearly
-
Stratospheric impact on tropospheric ozone variability and trends: 1990–2009
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. G. Hess
2013-01-01
Full Text Available The influence of stratospheric ozone on the interannual variability and trends in tropospheric ozone is evaluated between 30 and 90° N from 1990–2009 using ozone measurements and a global chemical transport model, the Community Atmospheric Model with chemistry (CAM-chem. Long-term measurements from ozonesondes, at 150 and 500 hPa, and the Measurements of OZone and water vapour by in-service Airbus aircraft programme (MOZAIC, at 500 hPa, are analyzed over Japan, Canada, the Eastern US and Northern and Central Europe. The measurements generally emphasize northern latitudes, although the simulation suggests that measurements over the Canadian, Northern and Central European regions are representative of the large-scale interannual ozone variability from 30 to 90° N at 500 hPa. CAM-chem is run with input meteorology from the National Center for Environmental Prediction; a tagging methodology is used to identify the stratospheric contribution to tropospheric ozone concentrations. A variant of the synthetic ozone tracer (synoz is used to represent stratospheric ozone. Both the model and measurements indicate that on large spatial scales stratospheric interannual ozone variability drives significant tropospheric variability at 500 hPa and the surface. In particular, the simulation and the measurements suggest large stratospheric influence at the surface sites of Mace Head (Ireland and Jungfraujoch (Switzerland as well as many 500 hPa measurement locations. Both the measurements and simulation suggest the stratosphere has contributed to tropospheric ozone trends. In many locations between 30–90° N 500 hPa ozone significantly increased from 1990–2000, but has leveled off since (from 2000–2009. The simulated global ozone budget suggests global stratosphere-troposphere exchange increased in 1998–1999 in association with a global ozone anomaly. Discrepancies between the simulated and measured ozone budget include a large underestimation of
-
Stratospheric Water and OzOne Satellite Homogenized (SWOOSH) data set
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — The Stratospheric Water and Ozone Satellite Homogenized (SWOOSH) data set is a merged record of stratospheric ozone and water vapor measurements taken by a number of...
-
An ultrahot gas-giant exoplanet with a stratosphere.
Evans, Thomas M; Sing, David K; Kataria, Tiffany; Goyal, Jayesh; Nikolov, Nikolay; Wakeford, Hannah R; Deming, Drake; Marley, Mark S; Amundsen, David S; Ballester, Gilda E; Barstow, Joanna K; Ben-Jaffel, Lotfi; Bourrier, Vincent; Buchhave, Lars A; Cohen, Ofer; Ehrenreich, David; García Muñoz, Antonio; Henry, Gregory W; Knutson, Heather; Lavvas, Panayotis; Etangs, Alain Lecavelier des; Lewis, Nikole K; López-Morales, Mercedes; Mandell, Avi M; Sanz-Forcada, Jorge; Tremblin, Pascal; Lupu, Roxana
2017-08-02
Infrared radiation emitted from a planet contains information about the chemical composition and vertical temperature profile of its atmosphere. If upper layers are cooler than lower layers, molecular gases will produce absorption features in the planetary thermal spectrum. Conversely, if there is a stratosphere-where temperature increases with altitude-these molecular features will be observed in emission. It has been suggested that stratospheres could form in highly irradiated exoplanets, but the extent to which this occurs is unresolved both theoretically and observationally. A previous claim for the presence of a stratosphere remains open to question, owing to the challenges posed by the highly variable host star and the low spectral resolution of the measurements. Here we report a near-infrared thermal spectrum for the ultrahot gas giant WASP-121b, which has an equilibrium temperature of approximately 2,500 kelvin. Water is resolved in emission, providing a detection of an exoplanet stratosphere at 5σ confidence. These observations imply that a substantial fraction of incident stellar radiation is retained at high altitudes in the atmosphere, possibly by absorbing chemical species such as gaseous vanadium oxide and titanium oxide.
-
Lee waves, benign and malignant
Wurtele, M. G.; Datta, A.
1992-01-01
The flow of an incompressible, stratified fluid over an obstacle will produce an oscillation in which buoyancy is the restoring force, called a gravity wave. For disturbances of this scale, the atmosphere may be treated as incompressible; and even the linear approximation will explain many of the phenomena observed in the lee of mountains. However, nonlinearities arise in two ways: (1) through the large (scaled) size of the mountain, and (2) from dynamically singular levels in the fluid field. These produce a complicated array of phenomena that present hazards to aircraft and to lee surface areas. If there is no dynamic barrier, these waves can penetrate vertically into the middle atmosphere (30-100 km attitude), where recent observations show them to be of a length scale that must involve the Coriolis force in any modeling. At these altitudes, the amplitude of the waves is very large, and the waves are studied with a view to their potential impact on the projected National Aerospace Plane. This paper presents the results of analyses and state-of-the-art numerical simulations, validated where possible by observational data.
-
Observations of Equatorial Kelvin Wave Modes in FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC GPS RO Temperature Profiles
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Potula Sree Brahmanandam
2010-01-01
Full Text Available In this study, we analyze FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC (F3/C GPS radio occultation (RO derived temperature components for the period September 2006 to February 2008. Results show the presence of slow Kelvin waves (wave period > 10 days with higher zonal wavenumbers (either one or two in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS. The vertical wavelengths of these waves are found to be in the range of 5 - 12 km. The predominant Kelvin waves observed in the temperature fluctuations are in the altitude range between 15 and 28 km and centered on the tropical tropopause. The downward phase progression of these waves suggests that the derived waves are propagating upward, with the source region located at lower altitudes possibly due to tropical convective heating. The zonal winds retrieved using radiosonde observations over Singapore (1¢XN, 104¢XE during this period show a periodicity of ~24 - 26 months in the stratosphere, and quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO characteristics with eastward zonal winds from March 2006 to May 2007 and westward winds from June 2007 to July 2008 respectively. Our results further show that the Kelvin wave characteristics are enhanced during the westward phase of QBO and diminish during the eastward phase, in line with the previous reported results. Furthermore, an examination of outgoing longwave radiation (OLR data shows that deep convection activity is developed episodically over the Indonesian archipelago during the observation period, thereby indicating that the Kelvin wave events observed in temperature fluctuations are either driven by convective activity (convectively coupled waves or by a broad spectrum of convective variability (free waves over the Indonesian region.
-
Barodka, S.; Krasovsky, A.; Shalamyansky, A.
2014-12-01
The height of the tropopause, which divided the stratosphere and the troposphere, is a result of two rival categories of processes: the tropospheric vertical convection and the radiative heating of the stratosphere resulting from the ozone cycle. Hence, it is natural that tropospheric and stratospheric phenomena can have effect each other in manifold processes of stratosphere-troposphere interactions. In the present study we focus our attention to the "top-down" side of the interaction: the impact of stratospheric ozone distribution on the features of tropospheric circulation and the associated weather patterns and regional climate conditions. We proceed from analyzes of the observational data performed at the A.I. Voeikov Main Geophysical Observatory, which suggest a distinct correlation between stratospheric ozone distribution, synoptic formations and air-masses boundaries in the upper troposphere and the temperature field of the lower stratosphere [1]. Furthermore, we analyze local features of atmospheric general circulation and stratospheric ozone distribution from the atmospheric reanalyses and general circulation model data, focusing our attention to instantaneous positions of subtropical and polar stationary atmospheric fronts, which define regional characteristics of the general circulation cells in the troposphere and separate global tropospheric air-masses, correspond to distinct meteorological regimes in the TOC field [2, 3]. We assume that by altering the tropopause height, stratospheric ozone-related processes can have an impact on the location of the stationary atmospheric fronts, thereby exerting influence on circulation processes in troposphere and lower stratosphere. For midlatitudes, the tropopause height controls the position of the polar stationary front, which has a direct impact on the trajectory of motion of active vortices on synoptic tropospheric levels, thereby controlling weather patterns in that region and the regional climate. This
-
Analysis of wave-like oscillations in parameters of sporadic E layer and neutral atmosphere
Mošna, Z.; Koucká Knížová, P.
2012-12-01
The present study mainly concerns the wave-like activity in the ionospheric sporadic E layer (Es) and in the lower lying stratosphere. The proposed analysis involves parameters describing the state of plasma in the sporadic E layer. Critical frequencies foEs and layer heights hEs were measured at the Pruhonice station (50°N, 14.5°E) during summer campaigns 2004, 2006 and 2008. Further, we use neutral atmosphere (temperature data at 10 hPa) data from the same time interval. The analysis concentrates on vertically propagating wave-like structures within distant atmospheric regions. By means of continuous wavelet transform (CWT) we have detected significant wave-like oscillation at periods covering tidal and planetary oscillation domains both in the Es layer parameters (some of them were reported earlier, for instance in works of Abdu et al., 2003; Pancheva and Mitchel, 2004; Pancheva et al., 2003; Šauli and Bourdillon, 2008) and in stratospheric temperature variations. Further analyses using cross wavelet transform (XWT) and wavelet coherence analysis (WTC) show that despite high wave-like activity in a wide period range, there are only limited coherent wave-like bursts present in both spectra. Such common coherent wave bursts occur on periods close to eigen-periods of the terrestrial atmosphere. We suppose that vertical coupling between atmospheric regions realized by vertically propagating planetary waves occurs predominantly on periods close to those of Rossby modes. Analysis of the phase shift between data from distant atmospheric regions reveals high variability and very likely supports the non-linear scenario of the vertical coupling provided by planetary waves.
-
Impacts of stratospheric sulfate geoengineering on tropospheric ozone
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
L. Xia
2017-10-01
Full Text Available A range of solar radiation management (SRM techniques has been proposed to counter anthropogenic climate change. Here, we examine the potential effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosols and solar insolation reduction on tropospheric ozone and ozone at Earth's surface. Ozone is a key air pollutant, which can produce respiratory diseases and crop damage. Using a version of the Community Earth System Model from the National Center for Atmospheric Research that includes comprehensive tropospheric and stratospheric chemistry, we model both stratospheric sulfur injection and solar irradiance reduction schemes, with the aim of achieving equal levels of surface cooling relative to the Representative Concentration Pathway 6.0 scenario. This allows us to compare the impacts of sulfate aerosols and solar dimming on atmospheric ozone concentrations. Despite nearly identical global mean surface temperatures for the two SRM approaches, solar insolation reduction increases global average surface ozone concentrations, while sulfate injection decreases it. A fundamental difference between the two geoengineering schemes is the importance of heterogeneous reactions in the photochemical ozone balance with larger stratospheric sulfate abundance, resulting in increased ozone depletion in mid- and high latitudes. This reduces the net transport of stratospheric ozone into the troposphere and thus is a key driver of the overall decrease in surface ozone. At the same time, the change in stratospheric ozone alters the tropospheric photochemical environment due to enhanced ultraviolet radiation. A shared factor among both SRM scenarios is decreased chemical ozone loss due to reduced tropospheric humidity. Under insolation reduction, this is the dominant factor giving rise to the global surface ozone increase. Regionally, both surface ozone increases and decreases are found for both scenarios; that is, SRM would affect regions of the world differently in terms of air
-
Impacts of stratospheric sulfate geoengineering on tropospheric ozone
Xia, Lili; Nowack, Peer J.; Tilmes, Simone; Robock, Alan
2017-10-01
A range of solar radiation management (SRM) techniques has been proposed to counter anthropogenic climate change. Here, we examine the potential effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosols and solar insolation reduction on tropospheric ozone and ozone at Earth's surface. Ozone is a key air pollutant, which can produce respiratory diseases and crop damage. Using a version of the Community Earth System Model from the National Center for Atmospheric Research that includes comprehensive tropospheric and stratospheric chemistry, we model both stratospheric sulfur injection and solar irradiance reduction schemes, with the aim of achieving equal levels of surface cooling relative to the Representative Concentration Pathway 6.0 scenario. This allows us to compare the impacts of sulfate aerosols and solar dimming on atmospheric ozone concentrations. Despite nearly identical global mean surface temperatures for the two SRM approaches, solar insolation reduction increases global average surface ozone concentrations, while sulfate injection decreases it. A fundamental difference between the two geoengineering schemes is the importance of heterogeneous reactions in the photochemical ozone balance with larger stratospheric sulfate abundance, resulting in increased ozone depletion in mid- and high latitudes. This reduces the net transport of stratospheric ozone into the troposphere and thus is a key driver of the overall decrease in surface ozone. At the same time, the change in stratospheric ozone alters the tropospheric photochemical environment due to enhanced ultraviolet radiation. A shared factor among both SRM scenarios is decreased chemical ozone loss due to reduced tropospheric humidity. Under insolation reduction, this is the dominant factor giving rise to the global surface ozone increase. Regionally, both surface ozone increases and decreases are found for both scenarios; that is, SRM would affect regions of the world differently in terms of air pollution. In conclusion
-
Kreyling, Daniel; Wohltmann, Ingo; Lehmann, Ralph; Rex, Markus
2015-01-01
The SWIFT model is a fast yet accurate chemistry scheme for calculating the chemistry of stratospheric ozone. It is mainly intended for use in Global Climate Models (GCMs), Chemistry Climate Models (CCMs) and Earth System Models (ESMs). For computing time reasons these models often do not employ full stratospheric chem- istry modules, but use prescribed ozone instead. This can lead to insufficient representation between stratosphere and troposphere. The SWIFT stratospheric ozone chem...
-
Forcing of stratospheric chemistry and dynamics during the Dalton Minimum
Anet, J. G.; Muthers, S.; Rozanov, E.; Raible, C. C.; Peter, T.; Stenke, A.; Shapiro, A. I.; Beer, J.; Steinhilber, F.; Brönnimann, S.; Arfeuille, F.; Brugnara, Y.; Schmutz, W.
2013-11-01
The response of atmospheric chemistry and dynamics to volcanic eruptions and to a decrease in solar activity during the Dalton Minimum is investigated with the fully coupled atmosphere-ocean chemistry general circulation model SOCOL-MPIOM (modeling tools for studies of SOlar Climate Ozone Links-Max Planck Institute Ocean Model) covering the time period 1780 to 1840 AD. We carried out several sensitivity ensemble experiments to separate the effects of (i) reduced solar ultra-violet (UV) irradiance, (ii) reduced solar visible and near infrared irradiance, (iii) enhanced galactic cosmic ray intensity as well as less intensive solar energetic proton events and auroral electron precipitation, and (iv) volcanic aerosols. The introduced changes of UV irradiance and volcanic aerosols significantly influence stratospheric dynamics in the early 19th century, whereas changes in the visible part of the spectrum and energetic particles have smaller effects. A reduction of UV irradiance by 15%, which represents the presently discussed highest estimate of UV irradiance change caused by solar activity changes, causes global ozone decrease below the stratopause reaching as much as 8% in the midlatitudes at 5 hPa and a significant stratospheric cooling of up to 2 °C in the mid-stratosphere and to 6 °C in the lower mesosphere. Changes in energetic particle precipitation lead only to minor changes in the yearly averaged temperature fields in the stratosphere. Volcanic aerosols heat the tropical lower stratosphere, allowing more water vapour to enter the tropical stratosphere, which, via HOx reactions, decreases upper stratospheric and mesospheric ozone by roughly 4%. Conversely, heterogeneous chemistry on aerosols reduces stratospheric NOx, leading to a 12% ozone increase in the tropics, whereas a decrease in ozone of up to 5% is found over Antarctica in boreal winter. The linear superposition of the different contributions is not equivalent to the response obtained in a simulation
-
Climate change projections and stratosphere-troposphere interaction
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Scaife, Adam A.; Fereday, David R.; Butchart, Neal; Hardiman, Steven C. [Met Office Hadley Centre, Exeter (United Kingdom); Spangehl, Thomas; Cubasch, Ulrich; Langematz, Ulrike [Freie Universitaet Berlin, Berlin (Germany); Akiyoshi, Hideharu [National Institute for Environmental Studies, Tsukuba (Japan); Bekki, Slimane [LATMOS-IPSL, UVSQ, UPMC, CNRS/INSU, Paris (France); Braesicke, Peter [University of Cambridge, Cambridge (United Kingdom); Chipperfield, Martyn P. [University of Leeds, School of Earth and Environment, Leeds (United Kingdom); Gettelman, Andrew [National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO (United States); Michou, Martine [GAME/CNRM (Meteo France, CNRS), Toulouse (France); Rozanov, Eugene [PMOD/WRC and ETHZ, Davos (Switzerland); Shepherd, Theodore G. [University of Toronto, Toronto, ON (Canada)
2012-05-15
Climate change is expected to increase winter rainfall and flooding in many extratropical regions as evaporation and precipitation rates increase, storms become more intense and storm tracks move polewards. Here, we show how changes in stratospheric circulation could play a significant role in future climate change in the extratropics through an additional shift in the tropospheric circulation. This shift in the circulation alters climate change in regional winter rainfall by an amount large enough to significantly alter regional climate change projections. The changes are consistent with changes in stratospheric winds inducing a change in the baroclinic eddy growth rate across the depth of the troposphere. A change in mean wind structure and an equatorward shift of the tropospheric storm tracks relative to models with poor stratospheric resolution allows coupling with surface climate. Using the Atlantic storm track as an example, we show how this can double the predicted increase in extreme winter rainfall over Western and Central Europe compared to other current climate projections. (orig.)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
D. BUESCH; K.H. STOKOE; M. SCHUHEN
2006-01-01
Evaluation of the seismic response of the proposed spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste repository at Yucca Mountain, Nevada, is in part based on the seismic properties of the host rock, the 12.8-million-year-old Topopah Spring Tuff. Because of the processes that formed the tuff, the densely welded and crystallized part has three lithophysal and three nonlithophysal zones, and each zone has characteristic variations in lithostratigraphic features and structures of the rocks. Lithostratigraphic features include lithophysal cavities, rims on lithophysae and some fractures, spots (which are similar to rims but without an associated cavity or aperture), amounts of porosity resulting from welding, crystallization, and vapor-phase corrosion and mineralization, and fractures. Seismic properties, including shear-wave velocity (V s ), have been measured on 38 pieces of core, and there is a good ''first order'' correlation with the lithostratigraphic zones; for example, samples from nonlithophysal zones have larger V s values compared to samples from lithophysal zones. Some samples have V s values that are beyond the typical range for the lithostratigraphic zone; however, these samples typically have one or more fractures, ''large'' lithophysal cavities, or ''missing pieces'' relative to the sample size. Shear-wave velocity data measured in the tunnels have similar relations to lithophysal and nonlithophysal rocks; however, tunnel-based values are typically smaller than those measured in core resulting from increased lithophysae and fracturing effects. Variations in seismic properties such as V s data from small-scale samples (typical and ''flawed'' core) to larger scale traverses in the tunnels provide a basis for merging our understanding of the distributions of lithostratigraphic features (and zones) with a method to scale seismic properties
-
A method for establishing a long duration, stratospheric platform for astronomical research
Fesen, Robert; Brown, Yorke
2015-10-01
During certain times of the year at middle and low latitudes, winds in the upper stratosphere move in nearly the opposite direction than the wind in the lower stratosphere. Here we present a method for maintaining a high-altitude balloon platform in near station-keeping mode that utilizes this stratospheric wind shear. The proposed method places a balloon-borne science platform high in the stratosphere connected by a lightweight, high-strength tether to a tug vehicle located in the lower or middle stratosphere. Using aerodynamic control surfaces, wind-induced aerodynamic forces on the tug can be manipulated to counter the wind drag acting on the higher altitude science vehicle, thus controlling the upper vehicle's geographic location. We describe the general framework of this station-keeping method, some important properties required for the upper stratospheric science payload and lower tug platforms, and compare this station-keeping approach with the capabilities of a high altitude airship and conventional tethered aerostat approaches. We conclude by discussing the advantages of such a platform for a variety of missions with emphasis on astrophysical research.
-
The natural stratosphere of 1974. CIAP monograph 1. Final report
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
1975-09-01
The Climatic Impact Assessment Program (CIAP) of the U.S. Department of Transportation is charged with the 'assessment' of the impact of future aircraft fleets and other vehicles operating in, or transiting through, the stratosphere. CIAP monograph 1 gives a survey, largely from an experimental standpoint, of what is known in 1974 about the unperturbed stratosphere with respect to an application to stratospheric flight. It reviews the overall structure of the stratosphere, its origin in terms of ozone photochemistry, solar irradiance and overall radiative energy balance, other chemically reactive minor species, and atmospheric motions on a variety of scales of time and distance. The limitations of our understanding are emphasized in the presentation. Also, the monograph examines briefly what is known about the effect of massive injections of nitrogen oxides (from atmospheric nuclear explosions) and sulfur oxides (from major volcanic eruptions)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. Pommrich
2014-12-01
Full Text Available Variations in the mixing ratio of trace gases of tropospheric origin entering the stratosphere in the tropics are of interest for assessing both troposphere to stratosphere transport fluxes in the tropics and the impact of these transport fluxes on the composition of the tropical lower stratosphere. Anomaly patterns of carbon monoxide (CO and long-lived tracers in the lower tropical stratosphere allow conclusions about the rate and the variability of tropical upwelling to be drawn. Here, we present a simplified chemistry scheme for the Chemical Lagrangian Model of the Stratosphere (CLaMS for the simulation, at comparatively low numerical cost, of CO, ozone, and long-lived trace substances (CH4, N2O, CCl3F (CFC-11, CCl2F2 (CFC-12, and CO2 in the lower tropical stratosphere. For the long-lived trace substances, the boundary conditions at the surface are prescribed based on ground-based measurements in the lowest model level. The boundary condition for CO in the lower troposphere (below about 4 km is deduced from MOPITT measurements. Due to the lack of a specific representation of mixing and convective uplift in the troposphere in this model version, enhanced CO values, in particular those resulting from convective outflow are underestimated. However, in the tropical tropopause layer and the lower tropical stratosphere, there is relatively good agreement of simulated CO with in situ measurements (with the exception of the TROCCINOX campaign, where CO in the simulation is biased low ≈10–15 ppbv. Further, the model results (and therefore also the ERA-Interim winds, on which the transport in the model is based are of sufficient quality to describe large scale anomaly patterns of CO in the lower stratosphere. In particular, the zonally averaged tropical CO anomaly patterns (the so called "tape recorder" patterns simulated by this model version of CLaMS are in good agreement with observations, although the simulations show a too rapid upwelling
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. R. Ziemke
2012-07-01
Full Text Available Ozone data beginning October 2004 from the Aura Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI and Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS are used to evaluate the accuracy of the Cloud Slicing technique in effort to develop long data records of tropospheric and stratospheric ozone and for studying their long-term changes. Using this technique, we have produced a 32-yr (1979–2010 long record of tropospheric and stratospheric column ozone from the combined Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS and OMI. Analyses of these time series suggest that the quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO is the dominant source of inter-annual variability of stratospheric ozone and is clearest in the Southern Hemisphere during the Aura time record with related inter-annual changes of 30–40 Dobson Units. Tropospheric ozone for the long record also indicates a QBO signal in the tropics with peak-to-peak changes varying from 2 to 7 DU. The most important result from our study is that global stratospheric ozone indicates signature of a recovery occurring with ozone abundance now approaching the levels of year 1980 and earlier. The negative trends in stratospheric ozone in both hemispheres during the first 15 yr of the record are now positive over the last 15 yr and with nearly equal magnitudes. This turnaround in stratospheric ozone loss is occurring about 20 yr earlier than predicted by many chemistry climate models. This suggests that the Montreal Protocol which was first signed in 1987 as an international agreement to reduce ozone destroying substances is working well and perhaps better than anticipated.
-
Stratospheric chlorine: Blaming it on nature
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Taube, G.
1993-01-01
Much of the bitter public debate over ozone depletion has centered on the claim that chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) pale into insignificance alongside natural sources of chlorine in the stratosphere. If so, goes the argument, chlorine could not be depleting ozone as atmospheric scientists claim, because the natural sources have been around since time immemorial, and the ozone layer is still there. The claim, put forward in a book by Rogelio Maduro and Ralf Schauerhammer, has since been touted by former Atomic Energy Commissioner Dixy Lee Ray and talk-show host Rush Limbaugh, and it forms the basis of much of the backlash now being felt by atmospheric scientists. The argument is simple: Maduro and Schauerhammer calculate that 600 million tons of chlorine enters the atmosphere annually from seawater, 36 million tons from volcanoes, 8.4 million tons from biomass burning, and 5 million tons from ocean biota. In contrast, CFCs account for a mere 750,000 tons of atmospheric chlorine a year. Besides disputing the numbers, scientists have both theoretical and observational bases for doubting that much of this chlorine is getting into the stratosphere, where it could affect the ozone layer. Linwood Callis of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Langley Research Center points out one crucial problem with the argument: Chlorine from natural sources is soluble, and so it gets rained out of the lower atmosphere. CFCs, in contrast, are insoluble and inert and thus make it to the stratosphere to release their chlorine. What's more, observations of stratospheric chemistry don't support the idea that natural sources are contributing much to the chlorine there
-
Evidence for a continuous decline in lower stratospheric ozone offsetting ozone layer recovery
Ball, William T.; Alsing, Justin; Mortlock, Daniel J.; Staehelin, Johannes; Haigh, Joanna D.; Peter, Thomas; Tummon, Fiona; Stübi, Rene; Stenke, Andrea; Anderson, John; Bourassa, Adam; Davis, Sean M.; Degenstein, Doug; Frith, Stacey; Froidevaux, Lucien; Roth, Chris; Sofieva, Viktoria; Wang, Ray; Wild, Jeannette; Yu, Pengfei; Ziemke, Jerald R.; Rozanov, Eugene V.
2018-02-01
Ozone forms in the Earth's atmosphere from the photodissociation of molecular oxygen, primarily in the tropical stratosphere. It is then transported to the extratropics by the Brewer-Dobson circulation (BDC), forming a protective ozone layer around the globe. Human emissions of halogen-containing ozone-depleting substances (hODSs) led to a decline in stratospheric ozone until they were banned by the Montreal Protocol, and since 1998 ozone in the upper stratosphere is rising again, likely the recovery from halogen-induced losses. Total column measurements of ozone between the Earth's surface and the top of the atmosphere indicate that the ozone layer has stopped declining across the globe, but no clear increase has been observed at latitudes between 60° S and 60° N outside the polar regions (60-90°). Here we report evidence from multiple satellite measurements that ozone in the lower stratosphere between 60° S and 60° N has indeed continued to decline since 1998. We find that, even though upper stratospheric ozone is recovering, the continuing downward trend in the lower stratosphere prevails, resulting in a downward trend in stratospheric column ozone between 60° S and 60° N. We find that total column ozone between 60° S and 60° N appears not to have decreased only because of increases in tropospheric column ozone that compensate for the stratospheric decreases. The reasons for the continued reduction of lower stratospheric ozone are not clear; models do not reproduce these trends, and thus the causes now urgently need to be established.
-
Evidence for a Continuous Decline in Lower Stratospheric Ozone Offsetting Ozone Layer Recovery
Ball, William T.; Alsing, Justin; Mortlock, Daniel J.; Staehelin, Johannes; Haigh, Joanna D.; Peter, Thomas; Tummon, Fiona; Stuebi, Rene; Stenke, Andrea; Anderson, John;

2018-01-01
Ozone forms in the Earth's atmosphere from the photodissociation of molecular oxygen, primarily in the tropical stratosphere. It is then transported to the extratropics by the Brewer-Dobson circulation (BDC), forming a protective "ozone layer" around the globe. Human emissions of halogen-containing ozone-depleting substances (hODSs) led to a decline in stratospheric ozone until they were banned by the Montreal Protocol, and since 1998 ozone in the upper stratosphere is rising again, likely the recovery from halogen-induced losses. Total column measurements of ozone between the Earth's surface and the top of the atmosphere indicate that the ozone layer has stopped declining across the globe, but no clear increase has been observed at latitudes between 60degS and 60degN outside the polar regions (60-90deg). Here we report evidence from multiple satellite measurements that ozone in the lower stratosphere between 60degS and 60degN has indeed continued to decline since 1998. We find that, even though upper stratospheric ozone is recovering, the continuing downward trend in the lower stratosphere prevails, resulting in a downward trend in stratospheric column ozone between 60degS and 60degN. We find that total column ozone between 60degS and 60degN appears not to have decreased only because of increases in tropospheric column ozone that compensate for the stratospheric decreases. The reasons for the continued reduction of lower stratospheric ozone are not clear; models do not reproduce these trends, and thus the causes now urgently need to be established.
-
Two-dimensional structure of mountain wave observed by aircraft during the PYREX experiment
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. L. Attié
Full Text Available This study presents an experimental analysis from aircraft measurements above the Pyrenees chain during the PYREX experiment. The Pyrenees chain, roughly WE oriented, is a major barrier for northerly and southerly airflows. We present a case of southerly flow (15 October 1990 and three successive cases of northerly flows above the Pyrenees (14, 15 and 16 November 1990 documented by two aircraft. The aircraft have described a vertical cross section perpendicular to the Pyrenean ridge. This area is described via the thermodynamical and dynamical fields which have a horizontal resolution of 10 km. Three methods for computing the vertical velocity of the air are presented. The horizontal advection terms which play a role in the budget equations are also evaluated. The altitude turbulence zone of 15 October are shown via turbulent fluxes, turbulent kinetic energy (TKE, dissipation rate of TKE and inertial length-scale. A comparison of results obtained by eddy-correlation and inertial-dissipation method is presented. The experimental results show a warm and dry downdraft for the southerly flow with large values for advection terms. All the mountain wave cases are also shown to present an important dynamical perturbation just above the Pyrenees at upper altitudes.
-
Representation of the tropical stratospheric zonal wind in global atmospheric reanalyses
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. Kawatani
2016-06-01
Full Text Available This paper reports on a project to compare the representation of the monthly-mean zonal wind in the equatorial stratosphere among major global atmospheric reanalysis data sets. The degree of disagreement among the reanalyses is characterized by the standard deviation (SD of the monthly-mean zonal wind and this depends on latitude, longitude, height, and the phase of the quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO. At each height the SD displays a prominent equatorial maximum, indicating the particularly challenging nature of the reanalysis problem in the low-latitude stratosphere. At 50–70 hPa the geographical distributions of SD are closely related to the density of radiosonde observations. The largest SD values are over the central Pacific, where few in situ observations are available. At 10–20 hPa the spread among the reanalyses and differences with in situ observations both depend significantly on the QBO phase. Notably the easterly-to-westerly phase transitions in all the reanalyses except MERRA are delayed relative to those directly observed in Singapore. In addition, the timing of the easterly-to-westerly phase transitions displays considerable variability among the different reanalyses and this spread is much larger than for the timing of the westerly-to-easterly phase changes. The eddy component in the monthly-mean zonal wind near the Equator is dominated by zonal wavenumber 1 and 2 quasi-stationary planetary waves propagating from midlatitudes in the westerly phase of the QBO. There generally is considerable disagreement among the reanalyses in the details of the quasi-stationary waves near the Equator. At each level, there is a tendency for the agreement to be best near the longitude of Singapore, suggesting that the Singapore observations act as a strong constraint on all the reanalyses. Our measures of the quality of the reanalysis clearly show systematic improvement over the period considered (1979–2012. The SD among the reanalysis
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Mieth
2004-09-01
Full Text Available We report the sensitivity of the Berlin Climate Middle Atmosphere Model (CMAM to different gravity-wave (GW parameterisations. We perform five perpetual January experiments: 1 Rayleigh friction (RF (control, 2 non-orographic GWs, 3 orographic GWs, 4 orographic and non-orographic GWs with no background stress, and 5 as for 4 but with background stress. We also repeat experiment 4 but for July conditions. Our main aim is to improve the model climatology by introducing orographic and non-orographic parameterisations and to investigate the individual effect of these schemes in the Berlin CMAM. We compare with an RF control to determine the improvement upon a previously-published model version employing RF. Results are broadly similar to previously-published works. The runs having both orographic and non-orographic GWs produce a statistically-significant warming of 4-8K in the wintertime polar lower stratosphere. These runs also feature a cooling of the warm summer pole in the mesosphere by 10-15K, more in line with observations. This is associated with the non-orographic GW scheme. This scheme is also associated with a heating feature in the winter polar upper stratosphere directly below the peak GW-breaking region. The runs with both orographic and non-orographic GWs feature a statistically-significant deceleration in the polar night jet (PNJ of 10-20ms-1 in the lower stratosphere. Both orographic and non-orographic GWs individually produce some latitudinal tilting of the polar jet with height, although the main effect comes from the non-orographic waves. The resulting degree of tilt, although improved, is nevertheless still weaker than that observed. Accordingly, wintertime variability in the zonal mean wind, which peaks at the edge of the vortex, tends to maximise too far polewards in the model compared with observations. Gravity-planetary wave interaction leads to a decrease in the amplitudes of stationary planetary waves 1 and 2 by up to 50% in
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Mieth
2004-09-01
Full Text Available We report the sensitivity of the Berlin Climate Middle Atmosphere Model (CMAM to different gravity-wave (GW parameterisations. We perform five perpetual January experiments: 1 Rayleigh friction (RF (control, 2 non-orographic GWs, 3 orographic GWs, 4 orographic and non-orographic GWs with no background stress, and 5 as for 4 but with background stress. We also repeat experiment 4 but for July conditions. Our main aim is to improve the model climatology by introducing orographic and non-orographic parameterisations and to investigate the individual effect of these schemes in the Berlin CMAM. We compare with an RF control to determine the improvement upon a previously-published model version employing RF. Results are broadly similar to previously-published works. The runs having both orographic and non-orographic GWs produce a statistically-significant warming of 4-8K in the wintertime polar lower stratosphere. These runs also feature a cooling of the warm summer pole in the mesosphere by 10-15K, more in line with observations. This is associated with the non-orographic GW scheme. This scheme is also associated with a heating feature in the winter polar upper stratosphere directly below the peak GW-breaking region. The runs with both orographic and non-orographic GWs feature a statistically-significant deceleration in the polar night jet (PNJ of 10-20ms-1 in the lower stratosphere. Both orographic and non-orographic GWs individually produce some latitudinal tilting of the polar jet with height, although the main effect comes from the non-orographic waves. The resulting degree of tilt, although improved, is nevertheless still weaker than that observed. Accordingly, wintertime variability in the zonal mean wind, which peaks at the edge of the vortex, tends to maximise too far polewards in the model compared with observations. Gravity-planetary wave interaction leads to a decrease in the amplitudes of stationary planetary waves 1 and 2 by
-
International Workshop on Stratospheric Aerosols: Measurements, Properties, and Effects
Pueschel, Rudolf F. (Editor)
1991-01-01
Following a mandate by the International Aerosol Climatology Program under the auspices of International Association of Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics International Radiation Commission, 45 scientists from five nations convened to discuss relevant issues associated with the measurement, properties, and effects of stratospheric aerosols. A summary is presented of the discussions on formation and evolution, transport and fate, effects on climate, role in heterogeneous chemistry, and validation of lidar and satellite remote sensing of stratospheric aerosols. Measurements are recommended of the natural (background) and the volcanically enhanced aerosol (sulfuric acid and silica particles), the exhaust of shuttle, civil aviation and supersonic aircraft operations (alumina, soot, and ice particles), and polar stratospheric clouds (ice, condensed nitric and hydrochloric acids).
-
Tropical stratospheric water vapor measured by the microwave limb sounder (MLS)
Carr, E. S.; Harwood, R. S.; Mote, P. W.; Peckham, G. E.; Suttie, R. A.; Lahoz, W. A.; O'Neill, A.; Froidevaux, L.; Jarnot, R. F.; Read, W. G.
1995-01-01
The lower stratospheric variability of equatorial water vapor, measured by the Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS), follows an annual cycle modulated by the quasi-biennial oscillation. At levels higher in the stratosphere, water vapor measurements exhibit a semi-annual oscillatory signal with the largest amplitudes at 2.2 and 1hPa. Zonal-mean cross sections of MLS water vapor are consistent with previous satellite measurements from the limb infrared monitor of the stratosphere (LIMS) and the stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment 2 (SAGE 2) instruments in that they show water vapor increasing upwards and the polewards from a well defined minimum in the tropics. The minimum values vary in height between the retrieved 46 and 22hPa pressure levels.
-
Impacts of Stratospheric Sulfate Geoengineering on PM2.5
Robock, A.; Xia, L.; Tilmes, S.; Mills, M. J.; Richter, J.; Kravitz, B.; MacMartin, D.
2017-12-01
Particulate matter (PM) includes sulfate, nitrate, organic carbon, elemental carbon, soil dust, and sea salt. The first four components are mostly present near the ground as fine particulate matter with a diameter less than 2.5 µm (PM2.5), and these are of the most concern for human health. PM is efficiently scavenged by precipitation, which is its main atmospheric sink. Here we examine the impact of stratospheric climate engineering on this important pollutant and health risk, taking advantage of two sets of climate model simulations conducted at the National Center for Atmospheric Research. We use the full tropospheric and stratospheric chemistry version of the Community Earth System Model - Community Atmospheric Model 4 (CESM CAM4-chem) with a horizontal resolution of 0.9° x 1.25° lat-lon to simulate a stratospheric sulfate injection climate intervention of 8 Tg SO2 yr-1 combined with an RCP6.0 global warming forcing, the G4 Specified Stratospheric Aerosol (G4SSA) scenario. We also analyze the output from a 20-member ensemble of Community Earth System Model, version 1 with the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model as its atmospheric component (CESM1(WACCM)) simulations, also at 0.9° x 1.25° lat-lon resolution, with sulfur dioxide injection at 15°N, 15°S, 30°N, and 30°S varying in time to balance RCP8.5 forcing. While the CESM CAM4-chem model has full tropospheric and stratospheric chemistry, CESM1(WACCM) has an internally generated quasi-biennial oscillation and a comprehensive tropospheric and stratospheric sulfate aerosol treatment, but only stratospheric chemistry. For G4SSA, there are a global temperature reduction of 0.8 K and global averaged precipitation decrease of 3% relative to RCP6.0. The global averaged surface PM2.5 reduces about 1% compared with RCP6.0, mainly over Eurasian and East Asian regions in Northern Hemisphere winter. The PM2.5 concentration change is a combination of effects from tropospheric chemistry and precipitation
-
A refined method for calculating equivalent effective stratospheric chlorine
Engel, Andreas; Bönisch, Harald; Ostermöller, Jennifer; Chipperfield, Martyn P.; Dhomse, Sandip; Jöckel, Patrick
2018-01-01
Chlorine and bromine atoms lead to catalytic depletion of ozone in the stratosphere. Therefore the use and production of ozone-depleting substances (ODSs) containing chlorine and bromine is regulated by the Montreal Protocol to protect the ozone layer. Equivalent effective stratospheric chlorine (EESC) has been adopted as an appropriate metric to describe the combined effects of chlorine and bromine released from halocarbons on stratospheric ozone. Here we revisit the concept of calculating EESC. We derive a refined formulation of EESC based on an advanced concept of ODS propagation into the stratosphere and reactive halogen release. A new transit time distribution is introduced in which the age spectrum for an inert tracer is weighted with the release function for inorganic halogen from the source gases. This distribution is termed the release time distribution. We show that a much better agreement with inorganic halogen loading from the chemistry transport model TOMCAT is achieved compared with using the current formulation. The refined formulation shows EESC levels in the year 1980 for the mid-latitude lower stratosphere, which are significantly lower than previously calculated. The year 1980 is commonly used as a benchmark to which EESC must return in order to reach significant progress towards halogen and ozone recovery. Assuming that - under otherwise unchanged conditions - the EESC value must return to the same level in order for ozone to fully recover, we show that it will take more than 10 years longer than estimated in this region of the stratosphere with the current method for calculation of EESC. We also present a range of sensitivity studies to investigate the effect of changes and uncertainties in the fractional release factors and in the assumptions on the shape of the release time distributions. We further discuss the value of EESC as a proxy for future evolution of inorganic halogen loading under changing atmospheric dynamics using simulations from
-
Wang, S.; Jun, Z.
2017-12-01
Climatic characteristics of tropical stratospheric methane have been well researched using various satellite data, and numerical simulations have furtherly conducted using chemical climatic models, while the impact of stratospheric methane oxidation on distribution of water vapor is not paid enough attention in general circulation models. Simulated values of water vapour in the tropical upper stratosphere, and throughout much of the extratropical stratosphere, were too low. Something must be done to remedy this deficiency in order to producing realistic stratospheric water vapor using a general circulation model including the whole stratosphere. Introduction of a simple parametrization of the upper-stratospheric moisture source due to methane oxidation and a sink due to photolysis in the mesosphere was conducted. Numerical simulations and analysis of the influence of stratospheric methane on the prediction of tropical stratospheric moisture and temperature fields were carried out. This study presents the advantages of methane oxidation parametrization in producing a realistic distribution of water vapour in the tropical stratosphere and analyzes the impact of methane chemical process on the general circulation model using two storm cases including a heavy rain in South China and a typhoon caused tropical storm.It is obvious that general circulation model with methane oxidation parametrization succeeds in simulating the water vapor and temperature in stratosphere. The simulating rain center value of contrast experiment is increased up to 10% than that of the control experiment. Introduction of methane oxidation parametrization has modified the distribution of water vapour and then producing a broadly realistic distribution of temperature. Objective weather forecast verifications have been performed using simulating results of one month, which demonstrate somewhat positive effects on the model skill. There is a certain extent impact of methane oxidation
-
Calvo, N.; Garcia, R. R.; Kinnison, D. E.
2017-04-01
The latest version of the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM), which includes a new chemistry scheme and an updated parameterization of orographic gravity waves, produces temperature trends in the Antarctic lower stratosphere in excellent agreement with radiosonde observations for 1969-1998 as regards magnitude, location, timing, and persistence. The maximum trend, reached in November at 100 hPa, is -4.4 ± 2.8 K decade-1, which is a third smaller than the largest trend in the previous version of WACCM. Comparison with a simulation without the updated orographic gravity wave parameterization, together with analysis of the model's thermodynamic budget, reveals that the reduced trend is due to the effects of a stronger Brewer-Dobson circulation in the new simulations, which warms the polar cap. The effects are both direct (a trend in adiabatic warming in late spring) and indirect (a smaller trend in ozone, hence a smaller reduction in shortwave heating, due to the warmer environment).
-
Lidar observations and transfer of stratospheric aerosol over Tomsk in summer period
Novikov, P. V.; Cheremisin, A. A.; Marichev, V. N.; Barashkov, T. O.
2015-11-01
The analysis of the stratospheric aerosol origin was carried out by the method of Lagrangian particle trajectories. Stratospheric aerosol was registered by lidar sounding of atmosphere above Tomsk in 2008-2013 in summer time. The analysis of the results had shown that the aerosol content at altitudes of 13-125 km with maximum at 16-18 km can be associated with aerosol transfer from tropical stratospheric reservoir.
-
Reduction of photosynthetically active radiation under extreme stratospheric-aerosol loads
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gerstl, S.A.W.; Zardecki, A.
1981-01-01
The recently published hypothesis that the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinctions might be caused by an obstruction of sunlight is tested by model calculations. First we compute the total mass of stratospheric aerosols under normal atmospheric conditions for four different (measured) aerosol size distributions and vertical profiles. For comparison, the stratospheric dust masses after four volcanic eruptions are also evaluated. Detailed solar radiative transfer calculations are then performed for artificially increased aerosol amounts until the postulated darkness scenario is obtained. Thus we find that a total stratospheric aerosol mass between 1 and 4 times 10 16 g is sufficient to reduce photosynthesis to 10 3 of normal. We also infer from this result that the impact of a 0.4- to 3-km-diameter asteroid or a close encounter with a Halley-size comet may deposit that amount of particulates into the stratosphere. The darkness scenario of Alvarez et al., is thus shown to be a possible extinction mechanism, even with smaller size asteroids or comets than previously estimated
-
Reduction of photosynthetically active radiation under extreme stratospheric aerosol loads
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gerstl, S.A.W.; Zardecki, A.
1981-08-01
The recently published hypothesis that the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinctions might be caused by an obstruction of sunlight is tested by model calculations. First we compute the total mass of stratospheric aerosols under normal atmospheric conditions for four different (measured) aerosol size distributions and vertical profiles. For comparison, the stratospheric dust masses after four volcanic eruptions are also evaluated. Detailed solar radiative transfer calculations are then performed for artificially increased aerosol amounts until the postulated darkness scenario is obtained. Thus we find that a total stratospheric aerosol mass between 1 and 4 times 10 1 g is sufficient to reduce photosynthesis to 10 -3 of normal. We also infer from this result tha the impact of a 0.4- to 3-km-diameter asteroid or a close encounter with a Halley-size comet may deposit that amount of particulates into the stratosphere. The darkness scenario of Alvarez et al. is thus shown to be a possible extinction mechanism, even with smaller size asteroids of comets than previously estimated
-
Possible effects of volcanic eruptions on stratospheric minor constituent chemistry
Stolarski, R. S.; Butler, D. M.
1979-01-01
Although stratosphere penetrating volcanic eruptions have been infrequent during the last half century, periods have existed in the last several hundred years when such eruptions were significantly more frequent. Several mechanisms exist for these injections to affect stratospheric minor constituent chemistry, both on the long-term average and for short-term perturbations. These mechanisms are reviewed and, because of the sensitivity of current models of stratospheric ozone to chlorine perturbations, quantitative estimates are made of chlorine injection rates. It is found that, if chlorine makes up as much as 0.5 to 1% of the gases released and if the total gases released are about the same magnitude as the fine ash, then a major stratosphere penetrating eruption could deplete the ozone column by several percent. The estimate for the Agung eruption of 1963 is just under 1% an amount not excluded by the ozone record but complicated by the peak in atmospheric nuclear explosions at about the same time.
-
The annual cycle of stratospheric water vapor in a general circulation model
Mote, Philip W.
1995-01-01
The application of general circulation models (GCM's) to stratospheric chemistry and transport both permits and requires a thorough investigation of stratospheric water vapor. The National Center for Atmospheric Research has redesigned its GCM, the Community Climate Model (CCM2), to enable studies of the chemistry and transport of tracers including water vapor; the importance of water vapor to the climate and chemistry of the stratosphere requires that it be better understood in the atmosphere and well represented in the model. In this study, methane is carried as a tracer and converted to water; this simple chemistry provides an adequate representation of the upper stratospheric water vapor source. The cold temperature bias in the winter polar stratosphere, which the CCM2 shares with other GCM's, produces excessive dehydration in the southern hemisphere, but this dry bias can be ameliorated by setting a minimum vapor pressure. The CCM2's water vapor distribution and seasonality compare favorably with observations in many respects, though seasonal variations including the upper stratospheric semiannual oscillation are generally too small. Southern polar dehydration affects midlatitude water vapor mixing ratios by a few tenths of a part per million, mostly after the demise of the vortex. The annual cycle of water vapor in the tropical and northern midlatitude lower stratosphere is dominated by drying at the tropical tropopause. Water vapor has a longer adjustment time than methane and had not reached equilibrium at the end of the 9 years simulated here.
-
Effects of stratospheric perturbations on the solar radiation budget
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Luther, F.M.
1978-04-01
The changes in solar absorption and in local heating rates due to perturbations to O 3 and NO 2 concentrations caused by stratospheric injection of NO/sub x/ and CFM pollutants are assessed. The changes in species concentration profiles are derived from theoretical calculations using a transport-kinetics model. Because of significant changes in our understanding of stratospheric chemistry during the past year, the assessment of the effect of stratospheric perturbations on the solar radiation budget differs from previous assessments. Previously, a reduction in O 3 due to an NO/sub x/ injection caused a net decrease in the gaseous solar absorption;now the same perturbation leads to a net increase. The implication of these changes on the surface temperature is also discussed
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
D. Putero
2016-11-01
Full Text Available Stratospheric intrusion (SI events are a topic of ongoing research, especially because of their ability to change the oxidation capacity of the troposphere and their contribution to tropospheric ozone levels. In this work, a novel tool called STEFLUX (Stratosphere-to-Troposphere Exchange Flux is presented, discussed, and used to provide a first long-term investigation of SI over two global hot-spot regions for climate change and air pollution: the southern Himalayas and the central Mediterranean Basin. The main purpose of STEFLUX is to obtain a fast-computing and reliable identification of the SI events occurring at a specific location and during a specified time window. It relies on a compiled stratosphere-to-troposphere exchange (STE climatology, which makes use of the ERA-Interim reanalysis dataset from the ECMWF, as well as a refined version of a well-established Lagrangian methodology. STEFLUX results are compared to the SI observations (SIO at two high-mountain WMO/GAW global stations in these climate hot spots, i.e., the Nepal Climate Observatory-Pyramid (NCO-P, 5079 m a.s.l. and Mt. Cimone (2165 m a.s.l., which are often affected by SI events. Compared to the observational datasets at the two specific measurement sites, STEFLUX is able to detect SI events on a regional scale. Furthermore, it has the advantage of retaining additional information concerning the pathway of stratospheric-affected air masses, such as the location of tropopause crossing and other meteorological parameters along the trajectories. However, STEFLUX neglects mixing and dilution that air masses undergo along their transport within the troposphere. Therefore, the regional-scale STEFLUX events cannot be expected to perfectly reproduce the point measurements at NCO-P and Mt. Cimone, which are also affected by small-scale (orographic circulations. Still, the seasonal variability in SI events according to SIO and STEFLUX agrees fairly well. By exploiting the
-
Parameterization of planetary wave breaking in the middle atmosphere
Garcia, Rolando R.
1991-01-01
A parameterization of planetary wave breaking in the middle atmosphere has been developed and tested in a numerical model which includes governing equations for a single wave and the zonal-mean state. The parameterization is based on the assumption that wave breaking represents a steady-state equilibrium between the flux of wave activity and its dissipation by nonlinear processes, and that the latter can be represented as linear damping of the primary wave. With this and the additional assumption that the effect of breaking is to prevent further amplitude growth, the required dissipation rate is readily obtained from the steady-state equation for wave activity; diffusivity coefficients then follow from the dissipation rate. The assumptions made in the derivation are equivalent to those commonly used in parameterizations for gravity wave breaking, but the formulation in terms of wave activity helps highlight the central role of the wave group velocity in determining the dissipation rate. Comparison of model results with nonlinear calculations of wave breaking and with diagnostic determinations of stratospheric diffusion coefficients reveals remarkably good agreement, and suggests that the parameterization could be useful for simulating inexpensively, but realistically, the effects of planetary wave transport.
-
Breaking strain of neutron star crust and gravitational waves.
Horowitz, C J; Kadau, Kai
2009-05-15
Mountains on rapidly rotating neutron stars efficiently radiate gravitational waves. The maximum possible size of these mountains depends on the breaking strain of the neutron star crust. With multimillion ion molecular dynamics simulations of Coulomb solids representing the crust, we show that the breaking strain of pure single crystals is very large and that impurities, defects, and grain boundaries only modestly reduce the breaking strain to around 0.1. Because of the collective behavior of the ions during failure found in our simulations, the neutron star crust is likely very strong and can support mountains large enough so that their gravitational wave radiation could limit the spin periods of some stars and might be detectable in large-scale interferometers. Furthermore, our microscopic modeling of neutron star crust material can help analyze mechanisms relevant in magnetar giant flares and microflares.
-
Space-time patterns of trends in stratospheric constituents derived from UARS measurements
Randel, William J.; Wu, Fei; Russell, James M.; Waters, Joe
1999-02-01
The spatial and temporal behavior of low-frequency changes (trends) in stratospheric constituents measured by instruments on the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS) during 1991-98 is investigated. The data include CH4, H2O, HF, HCl, O3, and NO2 from the Halogen Occultation Experiment (HALOE), and O3, ClO, and HNO3 from the Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS). Time series of global anomalies are analyzed by linear regression and empirical orthogonal function analysis. Each of the constituents show significant linear trends over at least some region of the stratosphere, and the spatial patterns exhibit coupling between the different species. Several of the constituents (namely CH4, H2O, HF, HCl, O3, and NO2) exhibit a temporal change in trend rates, with strong changes prior to 1996 and weaker (or reversed) trends thereafter. Positive trends are observed in upper stratospheric ClO, with a percentage rate during 1993-97 consistent with stratospheric HCl increases and with tropospheric chlorine emission rates. Significant negative trends in ozone in the tropical middle stratosphere are found in both HALOE and MLS data during 1993-97, together with positive trends in the tropics near 25 km. These trends are very different from the decadal-scale ozone trends observed since 1979, and this demonstrates the variability of trends calculated over short time periods. Positive trends in NO2 are found in the tropical middle stratosphere, and spatial coincidence to the observed ozone decreases suggests the ozone is responding to the NO2 increase. Significant negative trends in HNO3 are found in the lower stratosphere of both hemispheres. These coupled signatures offer a fingerprint of chemical evolution in the stratosphere for the UARS time frame.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Mihalikova
2016-05-01
Full Text Available Inertia-gravity waves (IGWs are an important component for the dynamics of the middle atmosphere. However, observational studies needed to constrain their forcing are still insufficient especially in the remote areas of the Antarctic region. One year of observational data (January to December 2013 by the PANSY radar of the wind components (vertical resolution of 150 m and temporal resolution of 30 min are used to derive statistical analysis of the properties of IGWs with short vertical wavelengths ( ≤ 4 km and ground-based periods longer than 4 h in the lowermost stratosphere (height range 10 to 12 km with the help of the hodograph method. The annual change of the IGWs parameters are inspected but no pronounced year cycle is found. The year is divided into two seasons (summer and winter based on the most prominent difference in the ratio of Coriolis parameter (f to intrinsic frequency (ω^ distribution. Average of f∕ω^ for the winter season is 0.40 and for the summer season 0.45 and the average horizontal wavelengths are 140 and 160 km respectively. Vertical wavelengths have an average of 1.85 km through the year. For both seasons the properties of IGWs with upward and downward propagation of the energy are also derived and compared. The percentage of downward propagating waves is 10.7 and 18.4 % in the summer and winter season respectively. This seasonal change is more than the one previously reported in the studies from mid-latitudes and model-based studies. It is in agreement with the findings of past radiosonde data-based studies from the Antarctic region. In addition, using the so-called dual-beam technique, vertical momentum flux and the variance of the horizontal perturbation velocities of IGWs are examined. Tropospheric disturbances of synoptic-scale are suggested as a source of episodes of IGWs with large variance of horizontal perturbation velocities, and this is shown in a number of cases.
-
Is 239+240Pu the new tracer for soil erosion assessment in mountain grasslands?
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Alewell, Christine; Meusburger, Katrin; Juretzko, Gregor; Mabit, Lionel; Ketterer, Michael E.
2015-01-01
Soil erosion is a major threat to mountain ecosystems worldwide. However, there has been limited scientific interest in this significant environmental problem. Minimal attention has been given towards its mitigation by policy makers. Limited information in this area is partly due to the difficulty of quantifying soil erosion in mountain environments having un-ploughed soils, steep, complex topography, and harsh climates. In many environments, fallout radionuclides (FRNs) have been widely used to quantify soil particle movement and net erosion rates. A wide variety of artificial radionuclides have been deposited globally via nuclear weapons testing, nuclear accidents, nuclear weapons fabrication, and nuclear fuel reprocessing. Large-scale atmospheric tests of thermonuclear weapons resulted in the injection of debris into the stratosphere; following which isotopes such as 137 Cs, 239 Pu and 240 Pu deposited relatively uniformly on a local scale. While it is unfortunate that these isotopes were released into the environment, it is at the same time fortuitous that these FRNs can serve as valuable tracers of recent earth surface processes, including assessing soil erosion
-
Rastgoo, Mehdi; Rahimi, Habib; Motaghi, Khalil; Shabanian, Esmaeil; Romanelli, Fabio; Panza, Giuliano F.
2018-04-01
The Alborz Mountains represent a tectonically and seismically active convergent boundary in the Arabia - Eurasia collision zone, in western Asia. The orogenic belt has undergone a long-lasted tectono-magmatic history since the Cretaceous. The relationship between shallow and deep structures in this complex tectonic domain is not straightforward. We present a 2D velocity model constructed by the assemblage of 1D shear wave velocity (Vs) models from 26 seismic stations, mainly distributed along the southern flank of the Alborz Mountains. The shear wave velocity structure has been estimated beneath each station using joint inversion of P-waves receiver functions and Rayleigh wave dispersion curves. A substantiation of the Vs inversion results sits on the modeling of Bouguer gravity anomaly data. Our velocity and density models show low velocity/density anomalies in uppermost mantle of western and central Alborz at a depth range of ∼50-100 km. In deeper parts of the uppermost mantle (depth range of 100-150 km), a high velocity/density anomaly is located beneath most of the Mountain range. The spatial pattern of these low and high velocity/density structures in the upper mantle is interpreted as the result of post collisional delamination of lower part of the western and central Alborz lithosphere.
-
On the detection of the solar signal in the tropical stratosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. Chiodo
2014-06-01
Full Text Available We investigate the relative role of volcanic eruptions, El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO, and the quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO in the quasi-decadal signal in the tropical stratosphere with regard to temperature and ozone commonly attributed to the 11 \\unit{yr} solar cycle. For this purpose, we perform transient simulations with the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model forced from 1960 to 2004 with an 11 yr solar cycle in irradiance and different combinations of other forcings. An improved multiple linear regression technique is used to diagnose the 11 yr solar signal in the simulations. One set of simulations includes all observed forcings, and is thereby aimed at closely reproducing observations. Three idealized sets exclude ENSO variability, volcanic aerosol forcing, and QBO in tropical stratospheric winds, respectively. Differences in the derived solar response in the tropical stratosphere in the four sets quantify the impact of ENSO, volcanic events and the QBO in attributing quasi-decadal changes to the solar cycle in the model simulations. The novel regression approach shows that most of the apparent solar-induced lower-stratospheric temperature and ozone increase diagnosed in the simulations with all observed forcings is due to two major volcanic eruptions (i.e., El Chichón in 1982 and Mt. Pinatubo in 1991. This is caused by the alignment of these eruptions with periods of high solar activity. While it is feasible to detect a robust solar signal in the middle and upper tropical stratosphere, this is not the case in the tropical lower stratosphere, at least in a 45 yr simulation. The present results suggest that in the tropical lower stratosphere, the portion of decadal variability that can be unambiguously linked to the solar cycle may be smaller than previously thought.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Lambert
2012-03-01
Full Text Available A-train Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP and Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS observations are used to investigate the development of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs and the gas-phase nitric acid distribution in the early 2008 Antarctic winter. Observational evidence of gravity-wave activity is provided by Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS radiances and infrared spectroscopic detection of nitric acid trihydrate (NAT in PSCs is obtained from the Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS. Goddard Earth Observing System Data Assimilation System (GEOS-5 DAS analyses are used to derive Lagrangian trajectories and to determine temperature-time histories of air parcels. We use CALIOP backscatter and depolarization measurements to classify PSCs and the MLS measurements to determine the corresponding gas-phase HNO3 as a function of temperature. For liquid PSCs the uptake of HNO3 follows the theoretical equilibrium curve for supercooled ternary solutions (STS, but at temperatures about 1 K lower as determined from GEOS-5. In the presence of solid phase PSCs, above the ice frost-point, the HNO3 depletion occurs over a wider range of temperatures (+2 to −7 K distributed about the NAT equilibrium curve. Rapid gas-phase HNO3 depletion is first seen by MLS from from 23–25 May 2008, consisting of a decrease in the volume mixing ratio from 14 ppbv (parts per billion by volume to 7 ppbv on the 46–32 hPa (hectopascal pressure levels and accompanied by a 2–3 ppbv increase by renitrification at the 68 hPa pressure level. The observed region of depleted HNO3 is substantially smaller than the region bounded by the NAT existence temperature threshold. Temperature-time histories of air parcels demonstrate that the depletion is more clearly correlated with prior exposure to temperatures a few kelvin above the frost-point. From the combined data we infer the presence
-
Long-term trends in stratospheric ozone, temperature, and water vapor over the Indian region
Thankamani Akhil Raj, Sivan; Venkat Ratnam, Madineni; Narayana Rao, Daggumati; Venkata Krishna Murthy, Boddam
2018-01-01
We have investigated the long-term trends in and variabilities of stratospheric ozone, water vapor and temperature over the Indian monsoon region using the long-term data constructed from multi-satellite (Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS MLS and HALOE, 1993-2005), Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS, 2004-2015), Sounding of the Atmosphere using Broadband Emission Radiometry (SABER, 2002-2015) on board TIMED (Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics Dynamics)) observations covering the period 1993-2015. We have selected two locations, namely, Trivandrum (8.4° N, 76.9° E) and New Delhi (28° N, 77° E), covering northern and southern parts of the Indian region. We also used observations from another station, Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E), for comparison. A decreasing trend in ozone associated with NOx chemistry in the tropical middle stratosphere is found, and the trend turned to positive in the upper stratosphere. Temperature shows a cooling trend in the stratosphere, with a maximum around 37 km over Trivandrum (-1.71 ± 0.49 K decade-1) and New Delhi (-1.15 ± 0.55 K decade-1). The observed cooling trend in the stratosphere over Trivandrum and New Delhi is consistent with Gadanki lidar observations during 1998-2011. The water vapor shows a decreasing trend in the lower stratosphere and an increasing trend in the middle and upper stratosphere. A good correlation between N2O and O3 is found in the middle stratosphere (˜ 10 hPa) and poor correlation in the lower stratosphere. There is not much regional difference in the water vapor and temperature trends. However, upper stratospheric ozone trends over Trivandrum and New Delhi are different. The trend analysis carried out by varying the initial year has shown significant changes in the estimated trend.
-
Lidar observations of stratospheric aerosol layer after the Mt. Pinatubo volcanic eruption
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nagai, Tomohiro; Uchino, Osamu; Fujimoto, Toshifumi.
1992-01-01
The volcano Mt. Pinatubo located on the Luzon Island, Philippines, had explosively erupted on June 15, 1991. The volcanic eruptions such as volcanic ash, SO2 and H2O reached into the stratosphere over 30 km altitude by the NOAA-11 satellite observation and this is considered one of the biggest volcanic eruptions in this century. A grandiose volcanic eruption influences the atmosphere seriously and causes many climatic effects globally. There had been many impacts on radiation, atmospheric temperature and stratospheric ozone after some past volcanic eruptions. The main cause of volcanic influence depends on stratospheric aerosol, that stay long enough to change climate and other meteorological conditions. Therefore it is very important to watch stratospheric aerosol layers carefully and continuously. Standing on this respect, we do not only continue stratospheric aerosol observation at Tsukuba but also have urgently developed another lidar observational point at Naha in Okinawa Island. This observational station could be thought valuable since there is no lidar observational station in this latitudinal zone and it is much nearer to Mt. Pinatubo. Especially, there is advantage to link up these two stations on studying the transportation mechanism in the stratosphere. In this paper, we present the results of lidar observations at Tsukuba and Naha by lidar systems with Nd:YAG laser
-
Lidar Observations of Stratospheric Aerosol Layer After the Mt. Pinatubo Volcanic Eruption
Nagai, Tomohiro; Uchino, Osamu; Fujimoto, Toshifumi
1992-01-01
The volcano Mt. Pinatubo located on the Luzon Island, Philippines, had explosively erupted on June 15, 1991. The volcanic eruptions such as volcanic ash, SO2 and H2O reached into the stratosphere over 30 km altitude by the NOAA-11 satellite observation and this is considered one of the biggest volcanic eruptions in this century. A grandiose volcanic eruption influences the atmosphere seriously and causes many climatic effects globally. There had been many impacts on radiation, atmospheric temperature and stratospheric ozone after some past volcanic eruptions. The main cause of volcanic influence depends on stratospheric aerosol, that stay long enough to change climate and other meteorological conditions. Therefore it is very important to watch stratospheric aerosol layers carefully and continuously. Standing on this respect, we do not only continue stratospheric aerosol observation at Tsukuba but also have urgently developed another lidar observational point at Naha in Okinawa Island. This observational station could be thought valuable since there is no lidar observational station in this latitudinal zone and it is much nearer to Mt. Pinatubo. Especially, there is advantage to link up these two stations on studying the transportation mechanism in the stratosphere. In this paper, we present the results of lidar observations at Tsukuba and Naha by lidar systems with Nd:YAG laser.
-
Manzini, E.; Karpechko, A.Yu.; Anstey, J.; Shindell, Drew Todd; Baldwin, M.P.; Black, R.X.; Cagnazzo, C.; Calvo, N.; Charlton-Perez, A.; Christiansen, B.;

2014-01-01
Future changes in the stratospheric circulation could have an important impact on northern winter tropospheric climate change, given that sea level pressure (SLP) responds not only to tropospheric circulation variations but also to vertically coherent variations in troposphere-stratosphere circulation. Here we assess northern winter stratospheric change and its potential to influence surface climate change in the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project-Phase 5 (CMIP5) multimodel ensemble. In the stratosphere at high latitudes, an easterly change in zonally averaged zonal wind is found for the majority of the CMIP5 models, under the Representative Concentration Pathway 8.5 scenario. Comparable results are also found in the 1% CO2 increase per year projections, indicating that the stratospheric easterly change is common feature in future climate projections. This stratospheric wind change, however, shows a significant spread among the models. By using linear regression, we quantify the impact of tropical upper troposphere warming, polar amplification, and the stratospheric wind change on SLP. We find that the intermodel spread in stratospheric wind change contributes substantially to the intermodel spread in Arctic SLP change. The role of the stratosphere in determining part of the spread in SLP change is supported by the fact that the SLP change lags the stratospheric zonally averaged wind change. Taken together, these findings provide further support for the importance of simulating the coupling between the stratosphere and the troposphere, to narrow the uncertainty in the future projection of tropospheric circulation changes.
-
Long-term Global Morphology of Gravity Wave Activity Using UARS Data
Eckermann, Stephen D.; Jackman, C. (Technical Monitor)
2000-01-01
This quarter was largely devoted to a detailed study of temperature data acquired by the Cryogenic Limb Array Etalon Spectrometer (CLAES) on UARS. Our analysis used the same sequence of methods that have been developed, tested and refined on a more limited subset of temperature data acquired by the CRISTA instrument. We focused on a limited subset of our reasoning that geographical and vertical trends in the small-scale temperature variability could be compared with similar trends observed in November 1994 by the CRISTA-SPAS satellite. Results, backed up with hindcasts from the Mountain Wave Forecast Model (MWFM), reveal strong evidence of mountain waves, most persuasively in the Himalayas on 16-17 November, 1992. These CLAES results are coherent over the 30-50 km range and compare well with MWFM hindcasts for the same period. This constitutes, we believe, the first clear evidence that CLAES explicitly resolved long wavelength gravity waves in its CO2 temperature channel. A series of other tasks, related to mesoscale modeling of mountain waves in CRISTA data and fitting of ground-based and HRDI data on global scales, were seen through to publication stage in peer-reviewed journals.
-
Zonally resolved impact of ENSO on the stratospheric circulation and water vapor entry values
Konopka, Paul; Ploeger, Felix; Tao, Mengchu; Riese, Martin
2016-10-01
Based on simulations with the Chemical Lagrangian Model of the Stratosphere (CLaMS) for the period 1979-2013, with model transport driven by the ECMWF ERA-Interim reanalysis, we discuss the impact of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) on the variability of the dynamics, water vapor, ozone, and mean age of air (AoA) in the tropical lower stratosphere during boreal winter. Our zonally resolved analysis at the 390 K potential temperature level reveals that not only (deseasonalized) ENSO-related temperature anomalies are confined to the tropical Pacific (180-300°E) but also anomalous wave propagation and breaking, as quantified in terms of the Eliassen-Palm (EP) flux divergence, with strongest local contribution during the La Niña phase. This anomaly is coherent with respective anomalies of water vapor (±0.5 ppmv) and ozone (±100 ppbv) derived from CLaMS being in excellent agreement with the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder observations. Thus, during El Niño a more zonally symmetric wave forcing drives a deep branch of the Brewer-Dobson (BD) circulation. During La Niña this forcing increases at lower levels (≈390 K) over the tropical Pacific, likely influencing the shallow branch of the BD circulation. In agreement with previous studies, wet (dry) and young (old) tape recorder anomalies propagate upward in the subsequent months following El Niño (La Niña). Using CLaMS, these anomalies are found to be around +0.3 (-0.2) ppmv and -4 (+4) months for water vapor and AoA, respectively. The AoA ENSO anomaly is more strongly affected by the residual circulation (≈2/3) than by eddy mixing (≈1/3).
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
E. Castelli
2013-10-01
Full Text Available MARSCHALS (Millimetre-wave Airborne Receivers for Spectroscopic CHaracterisation in Atmospheric Limb Sounding is a limb viewing instrument working in the millimetre and sub-millimetre spectral regions (from 294 to 349 GHz. The scientific rationale of MARSCHALS is the study of the Upper Troposphere and Lower Stratosphere region. In March 2010 MARSCHALS was deployed on-board the M-55 Geophysica stratospheric aircraft during the PREMIER(PRocess Exploration through Measurements of Infrared and millimetre-wave Emitted Radiation-Ex field campaign. From the campaign base at Kiruna, Sweden, a research flight to investigate the Arctic atmosphere was conducted. For the first time the instrument fully exploited the three spectral bands. In this paper, we present results of the analysis of MARSCHALS measurements acquired during the PREMIER-Ex flight as processed by the Millimetre-wave Atmospheric Retrieval Code. For the second time after the SCOUT-O3 flight in 2005, MARSCHALS measured vertical distributions of temperature, water vapour, ozone and nitric acid over an altitude range of 4 to 24 km. In addition, vertical profiles of carbon monoxide and nitrous oxide were obtained for the first time. The measurements were performed in clear sky conditions and in presence of low and high altitude clouds (that were able to obscure measurements in the middle infrared spectroscopic region and some information about thick clouds were extracted from the data. The capabilities to derive information on upper tropospheric and lower stratospheric vertical profiles of temperature and minor constituents from millimetre-wave limb sounding observations in the northern polar region are presented and discussed for each of the individual targets. The results of MARSCHALS data analysis contributed to demonstrate the scientific relevance and technical feasibility of millimetre-wave limb-sounding of the UTLS proposed for the ESA Earth Explorer 7 candidate Core Mission PREMIER
-
Drift-corrected Odin-OSIRIS ozone product: algorithm and updated stratospheric ozone trends
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. E. Bourassa
2018-01-01
Full Text Available A small long-term drift in the Optical Spectrograph and Infrared Imager System (OSIRIS stratospheric ozone product, manifested mostly since 2012, is quantified and attributed to a changing bias in the limb pointing knowledge of the instrument. A correction to this pointing drift using a predictable shape in the measured limb radiance profile is implemented and applied within the OSIRIS retrieval algorithm. This new data product, version 5.10, displays substantially better both long- and short-term agreement with Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS ozone throughout the stratosphere due to the pointing correction. Previously reported stratospheric ozone trends over the time period 1984–2013, which were derived by merging the altitude–number density ozone profile measurements from the Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE II satellite instrument (1984–2005 and from OSIRIS (2002–2013, are recalculated using the new OSIRIS version 5.10 product and extended to 2017. These results still show statistically significant positive trends throughout the upper stratosphere since 1997, but at weaker levels that are more closely in line with estimates from other data records.
-
Titan's Stratospheric Condensibles at High Northern Latitudes During Northern Winter
Anderson, Carrie; Samuelson, R.; Achterberg, R.
2012-01-01
The Infrared Interferometer Spectrometer (IRIS) instrument on board Voyager 1 caught the first glimpse of an unidentified particulate feature in Titan's stratosphere that spectrally peaks at 221 per centimeter. Until recently, this feature that we have termed 'the haystack,' has been seen persistently at high northern latitudes with the Composite Infrared Spectrometer (CIRS) instrument onboard Cassini, The strength of the haystack emission feature diminishes rapidly with season, becoming drastically reduced at high northern latitudes, as Titan transitions from northern winter into spring, In contrast to IRIS whose shortest wavenumber was 200 per centimeter, CIRS extends down to 10 per centimeter, thus revealing an entirely unexplored spectral region in which nitrile ices have numerous broad lattice vibration features, Unlike the haystack, which is only found at high northern latitudes during northern winter/early northern spring, this geometrically thin nitrile cloud pervades Titan's lower stratosphere, spectrally peaking at 160 per centimeter, and is almost global in extent spanning latitudes 85 N to 600 S, The inference of nitrile ices are consistent with the highly restricted altitude ranges over which these features are observed, and appear to be dominated by a mixture of HCN and HC3N, The narrow range in altitude over which the nitrile ices extend is unlike the haystack, whose vertical distribution is significantly broader, spanning roughly 70 kilometers in altitude in Titan's lower stratosphere, The nitrile clouds that CIRS observes are located in a dynamically stable region of Titan's atmosphere, whereas CH4 clouds, which ordinarily form in the troposphere, form in a more dynamically unstable region, where convective cloud systems tend to occur. In the unusual situation where Titan's tropopause cools significantly from the HASI 70.5K temperature minimum, CH4 should condense in Titan's lower stratosphere, just like the aforementioned nitrile clouds, although
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Kleinböhl
2005-01-01
Full Text Available We present observations of unusually high values of ozone and N2O in the middle stratosphere that were observed by the airborne submillimeter radiometer ASUR in the Arctic. The observations took place in the meteorological situation of a major stratospheric warming that occurred in mid-January 2003 and was dominated by a wave 2 event. On 23 January 2003 the observed N2O and O3 mixing ratios around 69° N in the middle stratosphere reached maximum values of ~190 ppb and ~10 ppm, respectively. The similarities of these N2O profiles in a potential temperature range between 800 and 1200 K with N2O observations around 20° N on 1 March 2003 by the same instrument suggest that the observed Arctic airmasses were transported from the tropics quasi-isentropically. This is confirmed by 5-day back trajectory calculations which indicate that the airmasses between about 800 and 1000 K had been located around 20° N 3–5 days prior to the measurement in the Arctic. Calculations with a linearized ozone chemistry model along calculated as well as idealized trajectories, initialized with the low-latitude ASUR ozone measurements, give reasonable agreement with the Arctic ozone measurement by ASUR. PV distributions suggest that these airmasses did not stay confined in the Arctic region which makes it unlikely that this dynamical situation lead to the formation of dynamically caused pockets of low ozone.
-
Stratospheric mean ages and transport rates from observations of CO{sub 2} and N{sub 2}O
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Boering, K A; Wofsy, S C; Daube, B C; Schneider, H R [Harvard Univ., Cambridge, MA (United States). Div. of Engineering and Applied Sciences; Loewenstein, M; Podolske, J R [NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA (United States); Conway, T J [National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Boulder, CO (United States)
1998-12-31
Measurements of CO{sub 2} and N{sub 2}O concentrations are reported and analyzed to investigate stratospheric transport rates. Temporal variations in tropospheric CO{sub 2} are observed to propagate into the stratosphere, showing that tropospheric air enters the lower tropical stratosphere continuously, ascends, and is transported rapidly (in less than 1 month) to both hemispheres. The mean age of stratospheric air determined from CO{sub 2} data is approximately 5 years in the mid-stratosphere. It is shown that the mean age is mathematically equivalent to a conserved tracer analogous to exhaust from stratospheric aircraft. Comparison of the mean age from models and observations indicates that current model simulations likely underestimate pollutant concentrations from proposed stratospheric aircraft by 25-100%. (author) 36 refs.
-
Stratospheric mean ages and transport rates from observations of CO{sub 2} and N{sub 2}O
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Boering, K.A.; Wofsy, S.C.; Daube, B.C.; Schneider, H.R. [Harvard Univ., Cambridge, MA (United States). Div. of Engineering and Applied Sciences; Loewenstein, M.; Podolske, J.R. [NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA (United States); Conway, T.J. [National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Boulder, CO (United States)
1997-12-31
Measurements of CO{sub 2} and N{sub 2}O concentrations are reported and analyzed to investigate stratospheric transport rates. Temporal variations in tropospheric CO{sub 2} are observed to propagate into the stratosphere, showing that tropospheric air enters the lower tropical stratosphere continuously, ascends, and is transported rapidly (in less than 1 month) to both hemispheres. The mean age of stratospheric air determined from CO{sub 2} data is approximately 5 years in the mid-stratosphere. It is shown that the mean age is mathematically equivalent to a conserved tracer analogous to exhaust from stratospheric aircraft. Comparison of the mean age from models and observations indicates that current model simulations likely underestimate pollutant concentrations from proposed stratospheric aircraft by 25-100%. (author) 36 refs.
-
Long-term trends in stratospheric ozone, temperature, and water vapor over the Indian region
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. T. Akhil Raj
2018-01-01
Full Text Available We have investigated the long-term trends in and variabilities of stratospheric ozone, water vapor and temperature over the Indian monsoon region using the long-term data constructed from multi-satellite (Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS MLS and HALOE, 1993–2005, Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS, 2004–2015, Sounding of the Atmosphere using Broadband Emission Radiometry (SABER, 2002–2015 on board TIMED (Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics Dynamics observations covering the period 1993–2015. We have selected two locations, namely, Trivandrum (8.4° N, 76.9° E and New Delhi (28° N, 77° E, covering northern and southern parts of the Indian region. We also used observations from another station, Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E, for comparison. A decreasing trend in ozone associated with NOx chemistry in the tropical middle stratosphere is found, and the trend turned to positive in the upper stratosphere. Temperature shows a cooling trend in the stratosphere, with a maximum around 37 km over Trivandrum (−1.71 ± 0.49 K decade−1 and New Delhi (−1.15 ± 0.55 K decade−1. The observed cooling trend in the stratosphere over Trivandrum and New Delhi is consistent with Gadanki lidar observations during 1998–2011. The water vapor shows a decreasing trend in the lower stratosphere and an increasing trend in the middle and upper stratosphere. A good correlation between N2O and O3 is found in the middle stratosphere (∼ 10 hPa and poor correlation in the lower stratosphere. There is not much regional difference in the water vapor and temperature trends. However, upper stratospheric ozone trends over Trivandrum and New Delhi are different. The trend analysis carried out by varying the initial year has shown significant changes in the estimated trend.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Belova
2008-11-01
Full Text Available A number of studies have shown that 5-day planetary waves modulate noctilucent clouds and the closely related Polar Mesosphere Summer Echoes (PMSE at the summer mesopause. Summer stratospheric winds should inhibit wave propagation through the stratosphere and, although some numerical models (Geisler and Dickinson, 1976 do show a possibility for upward wave propagation, it has also been suggested that the upward propagation may in practice be confined to the winter hemisphere with horizontal propagation of the wave from the winter to the summer hemisphere at mesosphere heights causing the effects observed at the summer mesopause. It has further been proposed (Garcia et al., 2005 that 5-day planetary waves observed in the summer mesosphere could be excited in-situ by baroclinic instability in the upper mesosphere. In this study, we first extract and analyze 5-day planetary wave characteristics on a global scale in the middle atmosphere (up to 54 km in temperature, and up to 68 km in ozone concentration using measurements by the Odin satellite for selected days during northern hemisphere summer from 2003, 2004, 2005 and 2007. Second, we show that 5-day temperature fluctuations consistent with westward-traveling 5-day waves are present at the summer mesopause, using local ground-based meteor-radar observations. Finally we examine whether any of three possible sources of the detected temperature fluctuations at the summer mesopause can be excluded: upward propagation from the stratosphere in the summer-hemisphere, horizontal propagation from the winter-hemisphere or in-situ excitation as a result of the baroclinic instability. We find that in one case, far from solstice, the baroclinic instability is unlikely to be involved. In one further case, close to solstice, upward propagation in the same hemisphere seems to be ruled out. In all other cases, all or any of the three proposed mechanisms are consistent with the observations.
-
Decade of stratospheric sulfate measurements compared with observations of volcanic eruptions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sedlacek, W.A.; Mroz, E.J.; Lazrus, A.L.; Gandrud, B.W.
1983-01-01
Sulfate aerosol concentrations in the stratosphere have been measured for 11 years (1971--1981) using portions of filters collected by the Department of Energy's High Altitude Sampling Program. Data collected seasonally at altitudes between 13 km and 20 km spanning latitudes from 75 0 N to 51 0 S are reported. These data are compared with the reported altitudes of volcanic eruption plumes during the same decade. From this comparison it is concluded that (1) several unreported volcanic eruptions or eruptions to altitudes higher than reported did occur during the decade, (2) the e-fold removal time for sulfate aerosol from the stratosphere following the eruption of Volcan Fuego in 1974 was 11.2 +- 1.2 months, (3) the volcanic contribution to the average stratospheric sulfate concentration over the decade was greater than 50%, and (4) there may be evidence for an anthropogenic contribution to stratospheric sulfate that increases at the rate of 6 to 8% per year
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
JOEL Arnault
2013-03-01
Full Text Available The case study of a mountain wave triggered by the Antarctic Peninsula on 6 October 2005, which has already been documented in the literature, is chosen here to quantify the associated gravity wave forcing on the large-scale flow, with a budget analysis of the horizontal wind components and horizontal kinetic energy. In particular, a numerical simulation using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF model is compared to a control simulation with flat orography to separate the contribution of the mountain wave from that of other synoptic processes of non-orographic origin. The so-called differential budgets of horizontal wind components and horizontal kinetic energy (after subtracting the results from the simulation without orography are then averaged horizontally and vertically in the inner domain of the simulation to quantify the mountain wave dynamical influence at this scale. This allows for a quantitative analysis of the simulated mountain wave's dynamical influence, including the orographically induced pressure drag, the counterbalancing wave-induced vertical transport of momentum from the flow aloft, the momentum and energy exchanges with the outer flow at the lateral and upper boundaries, the effect of turbulent mixing, the dynamics associated with geostrophic re-adjustment of the inner flow, the deceleration of the inner flow, the secondary generation of an inertia–gravity wave and the so-called baroclinic conversion of energy between potential energy and kinetic energy.
-
The Polar Stratosphere in a Changing Climate (POLSTRACC)
Oelhaf, Hermann; Sinnhuber, Björn-Martin; Woiwode, Wolfgang; Rapp, Markus; Dörnbrack, Andreas; Engel, Andreas; Boenisch, Harald
2015-04-01
The POLSTRACC mission aims at providing new scientific knowledge on the Arctic lowermost stratosphere (LMS) and upper troposphere under the present load of halogens and state of climate variables. POLSTRACC is the only HALO (High Altitude and LOng Range Research Aircraft, German Research Community) mission dedicated to study the UTLS at high latitudes several years after the last intensive Arctic campaigns. The scientific scope of POLSTRACC will be broadened by its combination with the SALSA (Seasonality of Air mass transport and origin in the Lowermost Stratosphere using the HALO Aircraft) and GW-LCYCLE (Gravity Wave Life Cycle Experiment, a BMBF/ROMIC project) missions, which address complementary scientific goals sharing the same HALO payload. POLSTRACC, SALSA and GW-LCYCLE will offer the unique opportunity to study the bottom of the polar vortex and the high-latitude UTLS along with their impact on lower latitudes throughout an entire winter/spring cycle. The POLSTRACC consortium includes national (KIT, Forschungszentrum Jülich, DLR, Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, Universities of Frankfurt, Heidelberg, Mainz and Wuppertal) and international partners (e.g. NASA). The payload for the combined POLSTRACC, SALSA and GW-LCYCLE campaigns comprises an innovative combination of remote sensing techniques providing 2- and 3-D distributions of temperature and a large number of substances, and precise in-situ instruments measuring T, O3, H2O, tracers of different lifetimes and chemically active species at the aircraft level with high time-resolution. Drop sondes will add information about temperature, humidity and wind in the atmosphere underneath the aircraft. The field campaign will be divided into three phases for addressing (i) the early polar vortex and its wide-scale vicinity in December 2015 (from Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany), (ii) the mid-winter vortex from January to March 2016 (from Kiruna, Sweden), and (iii) the late dissipating vortex and its wide
-
Key aspects of stratospheric tracer modeling using assimilated winds
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. Bregman
2006-01-01
Full Text Available This study describes key aspects of global chemistry-transport models and their impact on stratospheric tracer transport. We concentrate on global models that use assimilated winds from numerical weather predictions, but the results also apply to tracer transport in general circulation models. We examined grid resolution, numerical diffusion, air parcel dispersion, the wind or mass flux update frequency, and time interpolation. The evaluation is performed with assimilated meteorology from the "operational analyses or operational data" (OD from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF. We also show the effect of the mass flux update frequency using the ECMWF 40-year re-analyses (ERA40. We applied the three-dimensional chemistry-transport Tracer Model version 5 (TM5 and a trajectory model and performed several diagnoses focusing on different transport regimes. Covering different time and spatial scales, we examined (1 polar vortex dynamics during the Arctic winter, (2 the large-scale stratospheric meridional circulation, and (3 air parcel dispersion in the tropical lower stratosphere. Tracer distributions inside the Arctic polar vortex show considerably worse agreement with observations when the model grid resolution in the polar region is reduced to avoid numerical instability. The results are sensitive to the diffusivity of the advection. Nevertheless, the use of a computational cheaper but diffusive advection scheme is feasible for tracer transport when the horizontal grid resolution is equal or smaller than 1 degree. The use of time interpolated winds improves the tracer distributions, particularly in the middle and upper stratosphere. Considerable improvement is found both in the large-scale tracer distribution and in the polar regions when the update frequency of the assimilated winds is increased from 6 to 3 h. It considerably reduces the vertical dispersion of air parcels in the tropical lower stratosphere. Strong
-
A Semi-empirical Model of the Stratosphere in the Climate System
Sodergren, A. H.; Bodeker, G. E.; Kremser, S.; Meinshausen, M.; McDonald, A.
2014-12-01
Chemistry climate models (CCMs) currently used to project changes in Antarctic ozone are extremely computationally demanding. CCM projections are uncertain due to lack of knowledge of future emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs) and ozone depleting substances (ODSs), as well as parameterizations within the CCMs that have weakly constrained tuning parameters. While projections should be based on an ensemble of simulations, this is not currently possible due to the complexity of the CCMs. An inexpensive but realistic approach to simulate changes in stratospheric ozone, and its coupling to the climate system, is needed as a complement to CCMs. A simple climate model (SCM) can be used as a fast emulator of complex atmospheric-ocean climate models. If such an SCM includes a representation of stratospheric ozone, the evolution of the global ozone layer can be simulated for a wide range of GHG and ODS emissions scenarios. MAGICC is an SCM used in previous IPCC reports. In the current version of the MAGICC SCM, stratospheric ozone changes depend only on equivalent effective stratospheric chlorine (EESC). In this work, MAGICC is extended to include an interactive stratospheric ozone layer using a semi-empirical model of ozone responses to CO2and EESC, with changes in ozone affecting the radiative forcing in the SCM. To demonstrate the ability of our new, extended SCM to generate projections of global changes in ozone, tuning parameters from 19 coupled atmosphere-ocean general circulation models (AOGCMs) and 10 carbon cycle models (to create an ensemble of 190 simulations) have been used to generate probability density functions of the dates of return of stratospheric column ozone to 1960 and 1980 levels for different latitudes.
-
Temperature thresholds for chlorine activation and ozone loss in the polar stratosphere
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Drdla, K. [NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA (United States); Mueller, R. [Forschungszentrum Juelich (DE). Inst. of Energy and Climate Research (IEK-7)
2012-07-01
Low stratospheric temperatures are known to be responsible for heterogeneous chlorine activation that leads to polar ozone depletion. Here, we discuss the temperature threshold below which substantial chlorine activation occurs. We suggest that the onset of chlorine activation is dominated by reactions on cold binary aerosol particles, without the formation of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs), i.e. without any significant uptake of HNO{sub 3} from the gas phase. Using reaction rates on cold binary aerosol in a model of stratospheric chemistry, a chlorine activation threshold temperature, T{sub ACL}, is derived. At typical stratospheric conditions, T{sub ACL} is similar in value to T{sub NAT} (within 1-2 K), the highest temperature at which nitric acid trihydrate (NAT) can exist. T{sub NAT} is still in use to parameterise the threshold temperature for the onset of chlorine activation. However, perturbations can cause T{sub ACL} to differ from T{sub NAT}: T{sub ACL} is dependent upon H{sub 2} O and potential temperature, but unlike T{sub NAT} is not dependent upon HNO3. Furthermore, in contrast to T{sub NAT}, T{sub ACL} is dependent upon the stratospheric sulfate aerosol loading and thus provides a means to estimate the impact on polar ozone of strong volcanic eruptions and some geo-engineering options, which are discussed. A parameterisation of T{sub ACL} is provided here, allowing it to be calculated for low solar elevation (or high solar zenith angle) over a comprehensive range of stratospheric conditions. Considering T{sub ACL} as a proxy for chlorine activation cannot replace a detailed model calculation, and polar ozone loss is influenced by other factors apart from the initial chlorine activation. However, T{sub ACL} provides a more accurate description of the temperature conditions necessary for chlorine activation and ozone loss in the polar stratosphere than T{sub NAT}. (orig.)
-
Airborne Arctic Stratospheric Expedition II: An overview
Anderson, James G.; Toon, Owen B.
1993-11-01
The sudden onset of ozone depletion in the antarctic vortex set a precedent for both the time scale and the severity of global change. The Airborne Antarctic Ozone Experiment (AAOE), staged from Punta Arenas, Chile, in 1987, established that CFCs, halons, and methyl bromide, the dominant sources of chlorine and bromine radicals in the stratosphere, control the rate of ozone destruction over the Antarctic; that the vortex is depleted in reactive nitrogen and water vapor; and that diabatic cooling during the Antarctic winter leads to subsidence within the vortex core, importing air from higher altitudes and lower latitudes. This last conclusion is based on observed dramatic distortion in the tracer fields, most notably N2O.In 1989, the first Airborne Arctic Stratospheric Expedition (AASE-I), staged from Stavanger, Norway, and using the same aircraft employed for AAOE (the NASA ER-2 and the NASA DC-8), discovered that while NOx and to some degree NOy were perturbed within the arctic vortex, there was little evidence for desiccation. Under these (in contrast to the antarctic) marginally perturbed conditions, however, ClO was found to be dramatically enhanced such that a large fraction of the available (inorganic) chlorine resided in the form of ClO and its dimer ClOOCl.This leaves two abiding issues for the northern hemisphere and the mission of the second Airborne Arctic Stratospheric Expedition (AASE-II): (1) Will significant ozone erosion occur within the arctic vortex in the next ten years as chlorine loading in the stratosphere exceeds four parts per billion by volume? (2) Which mechanisms are responsible for the observed ozone erosion poleward of 30°N in the winter/spring northern hemisphere reported in satellite observations?
-
Stratospheric aerosol effects from Soufriere Volcano as measured by the SAGE satellite system
Mccormick, M. P.; Kent, G. S.; Yue, G. K.; Cunnold, D. M.
1982-01-01
During its April 1979 eruption series, Soufriere Volcano produced two major stratospheric plumes that the SAGE (Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment) satellite system tracked to West Africa and the North Atlantic Ocean. The total mass of these plumes, whose movement and dispersion are in agreement with those deduced from meteorological data and dispersion theory, was less than 0.5 percent of the global stratospheric aerosol burden; no significant temperature or climate perturbation is therefore expected.
-
Garfinkel, C I; Schwartz, C
2017-10-16
The effect of the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) on the Northern Hemisphere wintertime stratospheric polar vortex in the period preceding stratospheric sudden warmings is evaluated in operational subseasonal forecasting models. Reforecasts which simulate stronger MJO-related convection in the Tropical West Pacific also simulate enhanced heat flux in the lowermost stratosphere and a more realistic vortex evolution. The time scale on which vortex predictability is enhanced lies between 2 and 4 weeks for nearly all cases. Those stratospheric sudden warmings that were preceded by a strong MJO event are more predictable at ∼20 day leads than stratospheric sudden warmings not preceded by a MJO event. Hence, knowledge of the MJO can contribute to enhanced predictability, at least in a probabilistic sense, of the Northern Hemisphere polar stratosphere.
-
Mortality tradeoff between air quality and skin cancer from changes in stratospheric ozone
Eastham, Sebastian D.; Keith, David W.; Barrett, Steven R. H.
2018-03-01
Skin cancer mortality resulting from stratospheric ozone depletion has been widely studied. Similarly, there is a deep body of literature on surface ozone and its health impacts, with modeling and observational studies demonstrating that surface ozone concentrations can be increased when stratospheric air mixes to the Earth’s surface. We offer the first quantitative estimate of the trade-off between these two effects, comparing surface air quality benefits and UV-related harms from stratospheric ozone depletion. Applying an idealized ozone loss term in the stratosphere of a chemistry-transport model for modern-day conditions, we find that each Dobson unit of stratospheric ozone depletion results in a net decrease in the global annual mortality rate of ~40 premature deaths per billion population (d/bn/DU). The impacts are spatially heterogeneous in sign and magnitude, composed of a reduction in premature mortality rate due to ozone exposure of ~80 d/bn/DU concentrated in Southeast Asia, and an increase in skin cancer mortality rate of ~40 d/bn/DU, mostly in Western Europe. This is the first study to quantify air quality benefits of stratospheric ozone depletion, and the first to find that marginal decreases in stratospheric ozone around modern-day values could result in a net reduction in global mortality due to competing health impact pathways. This result, which is subject to significant methodological uncertainty, highlights the need to understand the health and environmental trade-offs involved in policy decisions regarding anthropogenic influences on ozone chemistry over the 21st century.
-
On the Climate Impacts of Upper Tropospheric and Lower Stratospheric Ozone
Xia, Yan; Huang, Yi; Hu, Yongyun
2018-01-01
The global warming simulations of the general circulation models (GCMs) are generally performed with different ozone prescriptions. We find that the differences in ozone distribution, especially in the upper tropospheric and lower stratospheric (UTLS) region, account for important model discrepancies shown in the ozone-only historical experiment of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5). These discrepancies include global high cloud fraction, stratospheric temperature, and stratospheric water vapor. Through a set of experiments conducted by an atmospheric GCM with contrasting UTLS ozone prescriptions, we verify that UTLS ozone not only directly radiatively heats the UTLS region and cools the upper parts of the stratosphere but also strongly influences the high clouds due to its impact on relative humidity and static stability in the UTLS region and the stratospheric water vapor due to its impact on the tropical tropopause temperature. These consequences strongly affect the global mean effective radiative forcing of ozone, as noted in previous studies. Our findings suggest that special attention should be paid to the UTLS ozone when evaluating the climate effects of ozone depletion in the 20th century and recovery in the 21st century. UTLS ozone difference may also be important for understanding the intermodel discrepancy in the climate projections of the CMIP6 GCMs in which either prescribed or interactive ozone is used.
-
Effects of intense stratospheric ionisation events
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Reid, G.C.; McAfee, J.R.; Crutzen, P.J.
1978-01-01
High levels of ionising radiation in the Earth's stratosphere will lead to increased concentrations of nitrogen oxides and decreased concentrations of ozone. Changes in the surface environment will include an increased level, of biologically harmful UV radiation, caused by the ozone depletion, and a decreased level of visible solar radiation, due to the presence of major enhancements in the stratospheric concentration of nitrogen dioxide. These changes have been studied quantitatively, using the passage of the Solar System through a supernova remnant shell as an example. Some of the potential environmental changes are a substantial global cooling, abnormally dry conditions, a reduction in global photosynthesis and a large increase in the flux of atmospheric fixed nitrogen to the surface of the Earth. Such events might have been the cause of mass extinctions in the distant past. (Author)
-
On the cryogenic removal of NOy from the Antarctic polar stratosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Smyshlyaev
2003-06-01
Full Text Available We review current knowledge about the annual cycle of transport of nitrogen oxides to, and removal from, the polar stratosphere, with particular attention to Antarctica where the annual winter denitrifi cation process is both regular in occurrence and severe in effect. Evidence for a large downward fl ux of NOy from the mesosphere to the stratosphere, fi rst seen briefl y in the Limb Infrared Monitor of the Stratosphere (LIMS data from the Arctic winter of 1978-1979, has been found during the 1990s in both satellite and ground-based observations, though this still seems to be omitted from many atmospheric models. When incorporated in the Stony Brook- St. Petersburg two dimensional (2D transport and chemistry model, more realistic treatment of the NOy fl ux, along with sulfate transport from the mesosphere, sulfate aerosol formation where temperature is favorable, and the inclusion of a simple ion-cluster reaction, leads to good agreement with observed HNO3 formation in the mid-winter middle to upper stratosphere. To further emphasize the importance of large fl uxes of thermospheric and mesospheric NOy into the polar stratosphere, we have used observations, supplemented with model calculations, to defi ne new altitude dependent correlation curves between N2O and NOy. These are more suitable than those previously used in the literature to represent conditions within the Antarctic vortex region prior to and during denitrifi cation by Polar Stratospheric Cloud (PSC particles. Our NOy -N2O curves lead to a 40% increase in the average amount of NOy removed during the Antarctic winter with respect to estimates calculated using NOy-N2O curves from the Atmospheric Trace Molecule Spectroscopy (ATMOS/ATLAS-3 data set.
-
Brief communication "Stratospheric winds, transport barriers and the 2011 Arctic ozone hole"
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. J. Olascoaga
2012-12-01
Full Text Available The Arctic stratosphere throughout the late winter and early spring of 2011 was characterized by an unusually severe ozone loss, resulting in what has been described as an ozone hole. The 2011 ozone loss was made possible by unusually cold temperatures throughout the Arctic stratosphere. Here we consider the issue of what constitutes suitable environmental conditions for the formation and maintenance of a polar ozone hole. Our discussion focuses on the importance of the stratospheric wind field and, in particular, the importance of a high latitude zonal jet, which serves as a meridional transport barrier both prior to ozone hole formation and during the ozone hole maintenance phase. It is argued that stratospheric conditions in the boreal winter/spring of 2011 were highly unusual inasmuch as in that year Antarctic-like Lagrangian dynamics led to the formation of a boreal ozone hole.
-
An investigation of the processes controlling ozone in the upper stratosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Patten, K.O. Jr.; Connell, P.S.; Kinnison, D.E.; Wuebbles, D.J.; Waters, J.; Froidevaux, L.; Slanger, T.G.
1992-01-01
Photolysis of vibrationally excited oxygen produced by ultraviolet photolysis of ozone in the upper stratosphere is incorporated into the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 2-D zonally averaged chemical-radiative-transport model of the troposphere and stratosphere. The importance of this potential contributor of odd oxygen to the concentration of ozone is evaluated based upon recent information on vibrational distributions of excited oxygen and upon preliminary studies of energy transfer from the excited oxygen. When the energy transfer rate constants of previous work are assumed, increases in model ozone concentrations of up to 40 percent in the upper stratosphere are found, and the ozone concentrations of the model agree with measurements, including data from the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite. However, the increase is about 0.4 percent when the larger energy transfer rate constants suggested by more recent experimental work are applied in the model. This indicates the importance of obtaining detailed information on vibrationally excited oxygen properties, particularly the state-specific energy transfer rate constants, to evaluation of tills precess for stratospheric modeling
-
Stratospheric ozone reduction and its relation to natural and man made sources
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Isaksen, I S [Oslo Univ. (Norway). Dept. of Geophysics
1996-12-31
Approximately 90 % of the total ozone mass is in the stratosphere (between approximately 12 and 50 km), the rest is in the troposphere (below 12 km). The global distribution of ozone in the stratosphere and its variation over time have been studied extensively over several decades. These studies include observations by ground based instruments (e.g. Dobson instruments), instruments on airborne platforms (e.g. ozone sondes) and on satellites, and model studies which simulate the chemical and dynamical behaviour of the stratosphere. These studies have given good information about the processes which determine the ozone distribution, and how man made emissions affect the distribution. Observations have revealed that there are large year to year variations in stratospheric ozone above a particular location. These variations are difficult to predict as they are connected to irregular weather patterns. However, the observations have shown that there has been a long term decrease in stratospheric ozone on a global scale during the last two decades. The decrease has been most pronounced during the last five to six years and is seen both in the Northern and the Southern Hemispheres. The strong decrease in stratospheric ozone over the Antarctic continent, which has been observed since the mid 80s, and which has reduced the total ozone column with more than 50 % compared with earlier observations, is proven to be a result of increased man made emissions of CFCs. There are also mounting evidences that Northern Hemispheric ozone reductions observed since 1980 are connected to man made emissions of CFCs
-
Stratospheric ozone reduction and its relation to natural and man made sources
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Isaksen, I.S. [Oslo Univ. (Norway). Dept. of Geophysics
1995-12-31
Approximately 90 % of the total ozone mass is in the stratosphere (between approximately 12 and 50 km), the rest is in the troposphere (below 12 km). The global distribution of ozone in the stratosphere and its variation over time have been studied extensively over several decades. These studies include observations by ground based instruments (e.g. Dobson instruments), instruments on airborne platforms (e.g. ozone sondes) and on satellites, and model studies which simulate the chemical and dynamical behaviour of the stratosphere. These studies have given good information about the processes which determine the ozone distribution, and how man made emissions affect the distribution. Observations have revealed that there are large year to year variations in stratospheric ozone above a particular location. These variations are difficult to predict as they are connected to irregular weather patterns. However, the observations have shown that there has been a long term decrease in stratospheric ozone on a global scale during the last two decades. The decrease has been most pronounced during the last five to six years and is seen both in the Northern and the Southern Hemispheres. The strong decrease in stratospheric ozone over the Antarctic continent, which has been observed since the mid 80s, and which has reduced the total ozone column with more than 50 % compared with earlier observations, is proven to be a result of increased man made emissions of CFCs. There are also mounting evidences that Northern Hemispheric ozone reductions observed since 1980 are connected to man made emissions of CFCs
-
On the aliasing of the solar cycle in the lower stratospheric tropical temperature
Kuchar, Ales; Ball, William T.; Rozanov, Eugene V.; Stenke, Andrea; Revell, Laura; Miksovsky, Jiri; Pisoft, Petr; Peter, Thomas
2017-09-01
The double-peaked response of the tropical stratospheric temperature profile to the 11 year solar cycle (SC) has been well documented. However, there are concerns about the origin of the lower peak due to potential aliasing with volcanic eruptions or the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) detected using multiple linear regression analysis. We confirm the aliasing using the results of the chemistry-climate model (CCM) SOCOLv3 obtained in the framework of the International Global Atmospheric Chemisty/Stratosphere-troposphere Processes And their Role in Climate Chemistry-Climate Model Initiative phase 1. We further show that even without major volcanic eruptions included in transient simulations, the lower stratospheric response exhibits a residual peak when historical sea surface temperatures (SSTs)/sea ice coverage (SIC) are used. Only the use of climatological SSTs/SICs in addition to background stratospheric aerosols removes volcanic and ENSO signals and results in an almost complete disappearance of the modeled solar signal in the lower stratospheric temperature. We demonstrate that the choice of temporal subperiod considered for the regression analysis has a large impact on the estimated profile signal in the lower stratosphere: at least 45 consecutive years are needed to avoid the large aliasing effect of SC maxima with volcanic eruptions in 1982 and 1991 in historical simulations, reanalyses, and observations. The application of volcanic forcing compiled for phase 6 of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP6) in the CCM SOCOLv3 reduces the warming overestimation in the tropical lower stratosphere and the volcanic aliasing of the temperature response to the SC, although it does not eliminate it completely.
-
Pautet, P. D.; Taylor, M.; Kaifler, B.
2016-12-01
The Gravity Wave Life Cycle (GW-LCYCLE) project took place in Northern Scandinavia during the winter 2015-16. This international program focused on investigating the generation and deep propagation of atmospheric gravity waves, especially the orographic waves generated over the Scandinavian mountain range. A series of instruments was operated at several ground-based locations and on-board the DLR HALO Gulfstream V and Falcon aircrafts. As part of this project, Utah State University (USU) deployed 3 Advanced Mesospheric Temperature Mappers (AMTM) at the ALOMAR facility, Norway (operational since December 2010), at the IRF institute in Kiruna, Sweden, and at the FMI institute in Sodankylä, Finland. Each of these instruments measures the OH (3,1) rotational temperature over a large region (200x160km) at 87km altitude. During the campaign, their total coverage extended across the Scandinavian Mountain Range, from the wind side in the west to 500 km to the east in the lee of the mountains, allowing the investigation of the occurrence and evolution of gravity waves (GWs) over this part of Scandinavia. Furthermore, the AMTM in Sodankylä operated in the container housing a DLR Rayleigh lidar. Both instruments ran simultaneously and autonomously from November 2015 to April 2016, providing an unprecedented complementary high-quality data set. This presentation will introduce preliminary results obtained during this campaign, in particular the evolution of the mesospheric temperature through the winter, the analysis of mountain waves occurrence and dynamics at mesospheric altitude, as well as the investigation of interesting individual GW cases.
-
Effect of Recent Sea Surface Temperature Trends on the Arctic Stratospheric Vortex
Garfinkel, Chaim I.; Oman, Luke; Hurwitz, Margaret
2015-01-01
The springtime Arctic polar vortex has cooled significantly over the satellite era, with consequences for ozone concentrations in the springtime transition season. The causes of this cooling trend are deduced by using comprehensive chemistry-climate model experiments. Approximately half of the satellite era early springtime cooling trend in the Arctic lower stratosphere was caused by changing sea surface temperatures (SSTs). An ensemble of experiments forced only by changing SSTs is compared to an ensemble of experiments in which both the observed SSTs and chemically- and radiatively-active trace species are changing. By comparing the two ensembles, it is shown that warming of Indian Ocean, North Pacific, and North Atlantic SSTs, and cooling of the tropical Pacific, have strongly contributed to recent polar stratospheric cooling in late winter and early spring, and to a weak polar stratospheric warming in early winter. When concentrations of ozone-depleting substances and greenhouse gases are fixed, polar ozone concentrations show a small but robust decline due to changing SSTs. Ozone changes are magnified in the presence of changing gas concentrations. The stratospheric changes can be understood by examining the tropospheric height and heat flux anomalies generated by the anomalous SSTs. Finally, recent SST changes have contributed to a decrease in the frequency of late winter stratospheric sudden warmings.
-
Wave-equation dispersion inversion of surface waves recorded on irregular topography
Li, Jing; Schuster, Gerard T.; Lin, Fan-Chi; Alam, Amir
2017-01-01
Significant topographic variations will strongly influence the amplitudes and phases of propagating surface waves. Such effects should be taken into account, otherwise the S-velocity model inverted from the Rayleigh dispersion curves will contain significant inaccuracies. We now show that the recently developed wave-equation dispersion inversion (WD) method naturally takes into account the effects of topography to give accurate S-velocity tomograms. Application of topographic WD to demonstrates that WD can accurately invert dispersion curves from seismic data recorded over variable topography. We also apply this method to field data recorded on the crest of mountainous terrain and find with higher resolution than the standard WD tomogram.
-
Wave-equation dispersion inversion of surface waves recorded on irregular topography
Li, Jing
2017-08-17
Significant topographic variations will strongly influence the amplitudes and phases of propagating surface waves. Such effects should be taken into account, otherwise the S-velocity model inverted from the Rayleigh dispersion curves will contain significant inaccuracies. We now show that the recently developed wave-equation dispersion inversion (WD) method naturally takes into account the effects of topography to give accurate S-velocity tomograms. Application of topographic WD to demonstrates that WD can accurately invert dispersion curves from seismic data recorded over variable topography. We also apply this method to field data recorded on the crest of mountainous terrain and find with higher resolution than the standard WD tomogram.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. J. Sica
2007-11-01
Full Text Available The Purple Crow Lidar (PCL is a large power-aperture product monostatic Rayleigh-Raman-Sodium-resonance-fluorescence lidar, which has been in operation at the Delaware Observatory (42.9° N, 81.4° W, 237 m elevation near the campus of The University of Western Ontario since 1992. Kinetic-energy density has been calculated from the Rayleigh-scatter system measurements of density fluctuations at temporal-spatial scales relevant for gravity waves, e.g. soundings at 288 m height resolution and 9 min temporal resolution in the upper stratosphere and mesosphere. The seasonal averages from 10 years of measurements show in all seasons some loss of gravity-wave energy in the upper stratosphere. During the equinox periods and summer the measurements are consistent with gravity waves growing in height with little saturation, in agreement with the classic picture of the variations in the height at which gravity waves break given by Lindzen (1981. The mean values compare favourably to previous measurements when computed as nightly averages, but the high temporal-spatial resolution measurements show considerable day-to-day variability. The variability over a night is often extremely large, with typical RMS fluctuations of 50 to 100% at all heights and seasons common. These measurements imply that using a daily or nightly-averaged gravity-wave energy density in numerical models may be highly unrealistic.
-
Solar wind control of stratospheric temperatures in Jupiter's auroral regions?
Sinclair, James Andrew; Orton, Glenn; Kasaba, Yasumasa; Sato, Takao M.; Tao, Chihiro; Waite, J. Hunter; Cravens, Thomas; Houston, Stephen; Fletcher, Leigh; Irwin, Patrick; Greathouse, Thomas K.
2017-10-01
Auroral emissions are the process through which the interaction of a planet’s atmosphere and its external magnetosphere can be studied. Jupiter exhibits auroral emission at a multitude of wavelengths including the X-ray, ultraviolet and near-infrared. Enhanced emission of CH4 and other stratospheric hydrocarbons is also observed coincident with Jupiter’s shorter-wavelength auroral emission (e.g. Caldwell et al., 1980, Icarus 44, 667-675, Kostiuk et al., 1993, JGR 98, 18823). This indicates that auroral processes modify the thermal structure and composition of the auroral stratosphere. The exact mechanism responsible for this auroral-related heating of the stratosphere has however remained elusive (Sinclair et al., 2017a, Icarus 292, 182-207, Sinclair et al., 2017b, GRL, 44, 5345-5354). We will present an analysis of 7.8-μm images of Jupiter measured by COMICS (Cooled Mid-Infrared Camera and Spectrograph, Kataza et al., 2000, Proc. SPIE(4008), 1144-1152) on the Subaru telescope. These images were acquired on January 11th, 12th, 13th, 14th, February 4, 5th and May 17th, 18th, 19th and 20th in 2017, allowing the daily variability of Jupiter’s auroral-related stratospheric heating to be tracked. Preliminary results suggest lower stratospheric temperatures are directly forced by the solar wind dynamical pressure. The southern auroral hotspot exhibited a significant increase in brightness temperature over a 24-hour period. Over the same time period, a solar wind propagation model (Tao et al. 2005, JGR 110, A11208) predicts a strong increase in the solar wind dynamical pressure at Jupiter.
-
A consistent definition of the Arctic polar vortex breakup in both the lower and upper stratosphere
Choi, W.; Seo, J.
2014-12-01
Breakup of the polar vortex is a dominant feature of the seasonal transition from winter to summer in the stratosphere, which significantly affects stratospheric O3 concentration and tropospheric weather. Previously several criteria for the vortex breakup have been suggested based on the potential vorticity (PV) and wind speed, however, those mainly have focused on the lower stratospheric vortex of which spatiotemporal evolution and decay are more continuous than those of the upper stratospheric vortex. To find a consistent criterion for the vortex breakup in both the lower and upper stratosphere, the present study defined a polar vortex breakup day as when PV gradient at the polar vortex edge becomes lower than that at the subtropical edge on the area equivalent latitude based on PV. With applying the new definition to the UK Met Office reanalysis data, the breakup days of the Arctic polar vortices on 18 isentropic levels from 450 K to 1300 K were calculated for the period of 1993-2005. In comparison with CH4, N2O and O3 measured by the ILAS and POAM II/III satellite instruments, the breakup days are well consistent with changes in the distribution of such tracers as well as their zonal standard deviations associated with the vortex structure breaking and irreversible mixing. The vortex breakup in the upper stratosphere occurs more or less a month prior to that in the middle and lower stratosphere while the stratospheric final warming events occurs simultaneously in the upper and lower stratosphere.
-
Tritium Records to Trace Stratospheric Moisture Inputs in Antarctica
Fourré, E.; Landais, A.; Cauquoin, A.; Jean-Baptiste, P.; Lipenkov, V.; Petit, J.-R.
2018-03-01
Better assessing the dynamic of stratosphere-troposphere exchange is a key point to improve our understanding of the climate dynamic in the East Antarctica Plateau, a region where stratospheric inputs are expected to be important. Although tritium (3H or T), a nuclide naturally produced mainly in the stratosphere and rapidly entering the water cycle as HTO, seems a first-rate tracer to study these processes, tritium data are very sparse in this region. We present the first high-resolution measurements of tritium concentration over the last 50 years in three snow pits drilled at the Vostok station. Natural variability of the tritium records reveals two prominent frequencies, one at about 10 years (to be related to the solar Schwabe cycles) and the other one at a shorter periodicity: despite dating uncertainty at this short scale, a good correlation is observed between 3H and Na+ and an anticorrelation between 3H and δ18O measured on an individual pit. The outputs from the LMDZ Atmospheric General Circulation Model including stable water isotopes and tritium show the same 3H-δ18O anticorrelation and allow further investigation on the associated mechanism. At the interannual scale, the modeled 3H variability matches well with the Southern Annular Mode index. At the seasonal scale, we show that modeled stratospheric tritium inputs in the troposphere are favored in winter cold and dry conditions.
-
Stratospheric aerosols and precursor gases
1982-01-01
Measurements were made of the aerosol size, height and geographical distribution, their composition and optical properties, and their temporal variation with season and following large volcanic eruptions. Sulfur-bearing gases were measured in situ in the stratosphere, and studied of the chemical and physical processes which control gas-to-particle conversion were carried out in the laboratory.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mohamed Naaim, Gérard Degoutte et François Delorme
2010-09-01
Full Text Available Édifiées dans les stations de loisirs de montagne pour la production de neige de culture, les retenues d'altitude, comme tout ouvrage hydraulique, sont soumises aux aléas météorologiques qui peuvent générer des risques pour la sécurité publique. Les auteurs s'intéressent ici aux conséquences des vagues provoquées par le vent et les mouvements gravitaires rapides sur de tels ouvrages et étudient les moyens de protection à mettre en place.The load of the wind and the impact of rapid mass movements in a reservoir generate waves whose nature and properties depend on the magnitude of the load and the water depth in the reservoir. In this paper we summarized the main existing scaling laws allowing assessing the resulting hydrodynamic effects, focusing not only on the amplitude of the waves, but also on its nature. The wind and the slow movements produce sinusoidal waves while rapid mass movements produce steeper water waves such as tsunamis. Given the limited extension of the mountain lakes, the produced water waves rapidly meet the shores or the dam on which they generate a run-up whose amplitude depends on the characteristics of the incident wave and the slope of the shore. We have undertaken a theoretical analysis and collected several experimental data in order to show the similarities and the differences between the sinusoidal waves and the solitary waves in terms of run-up. We finally, choose simple formulas and produced a chart enabling any engineer to make a first diagnosis.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Connell, P.S.; Kinnison, D.E.; Wuebbles, D.J.; Burley, J.D.; Johnston, H.S.
1992-01-01
We have investigated the effects of incorporating representations of heterogeneous chemical processes associated with stratospheric sulfuric acid aerosol into the LLNL two-dimensional, zonally averaged, model of the troposphere and stratosphere. Using distributions of aerosol surface area and volume density derived from SAGE 11 satellite observations, we were primarily interested in changes in partitioning within the Cl- and N- families in the lower stratosphere, compared to a model including only gas phase photochemical reactions
-
The Impact of Stratospheric Circulation Extremes on Minimum Arctic Sea Ice Extent
Smith, K. L.; Polvani, L. M.; Tremblay, B.
2017-12-01
The interannual variability of summertime Arctic sea ice extent (SIE) is anti-correlated with the leading mode of extratropical atmospheric variability in preceding winter, the Arctic Oscillation (AO). Given this relationship and the need for better seasonal predictions of Arctic SIE, we here examine the role of stratospheric circulation extremes and stratosphere-troposphere coupling in linking the AO and Arctic SIE variability. We show that extremes in the stratospheric circulation during the winter season, namely stratospheric sudden warming (SSW) and strong polar vortex (SPV) events, are associated with significant anomalies in sea ice concentration in the Bering Straight and the Sea of Okhotsk in winter, the Barents Sea in spring and along the Eurasian coastline in summer in both observations and a fully-coupled, stratosphere-resolving general circulation model. The accompanying figure shows the composite mean sea ice concentration anomalies from the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) for SSWs (N = 126, top row) and SPVs (N = 99, bottom row) for winter (a,d), spring (b,e) and summer (c,f). Consistent with previous work on the AO, we find that SSWs, which are followed by the negative phase of the AO at the surface, result in sea ice growth, whereas SPVs, which are followed by the positive phase of the AO at the surface, result in sea ice loss, although the dynamic and thermodynamic processes driving these sea ice anomalies in the three Arctic regions, noted above, are different. Our analysis suggests that the presence or absence of stratospheric circulation extremes in winter may play a non-trivial role in determining total September Arctic SIE when combined with other factors.
-
Assessing the long-term variability of acetylene and ethane in the stratosphere of Jupiter
Melin, Henrik; Fletcher, L. N.; Donnelly, P. T.; Greathouse, T. K.; Lacy, J. H.; Orton, G. S.; Giles, R. S.; Sinclair, J. A.; Irwin, P. G. J.
2018-05-01
Acetylene (C2H2) and ethane (C2H6) are both produced in the stratosphere of Jupiter via photolysis of methane (CH4). Despite this common source, the latitudinal distribution of the two species is radically different, with acetylene decreasing in abundance towards the pole, and ethane increasing towards the pole. We present six years of NASA IRTF TEXES mid-infrared observations of the zonally-averaged emission of methane, acetylene and ethane. We confirm that the latitudinal distributions of ethane and acetylene are decoupled, and that this is a persistent feature over multiple years. The acetylene distribution falls off towards the pole, peaking at ∼ 30°N with a volume mixing ratio (VMR) of ∼ 0.8 parts per million (ppm) at 1 mbar and still falling off at ± 70° with a VMR of ∼ 0.3 ppm. The acetylene distributions are asymmetric on average, but as we move from 2013 to 2017, the zonally-averaged abundance becomes more symmetric about the equator. We suggest that both the short term changes in acetylene and its latitudinal asymmetry is driven by changes to the vertical stratospheric mixing, potentially related to propagating wave phenomena. Unlike acetylene, ethane has a symmetric distribution about the equator that increases toward the pole, with a peak mole fraction of ∼ 18 ppm at about ± 50° latitude, with a minimum at the equator of ∼ 10 ppm at 1 mbar. The ethane distribution does not appear to respond to mid-latitude stratospheric mixing in the same way as acetylene, potentially as a result of the vertical gradient of ethane being much shallower than that of acetylene. The equator-to-pole distributions of acetylene and ethane are consistent with acetylene having a shorter lifetime than ethane that is not sensitive to longer advective timescales, but is augmented by short-term dynamics, such as vertical mixing. Conversely, the long lifetime of ethane allows it to be transported to higher latitudes faster than it can be chemically depleted.
-
Early work on the stratospheric ozone depletion-CFC issue
Molina, M.
2012-12-01
I became involved with the atmospheric chemistry of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) shortly after joining Sherry Rowland's research group at the University of California, Irvine, in 1973. CFCs had been detected in the troposphere by James Lovelock in 1971, and the question we set out to answer was the fate of these compounds of industrial origin in the environment, as well as possibly identifying any consequences of their accumulation in the atmosphere. After examining many potential sinks for these compounds we realized that because of their unusual stability the most likely destruction process was photolysis in the stratosphere. I carried out measurements of the absorption spectra of these compounds in the near ultraviolet; previous work involved only spectra in the far ultraviolet, not relevant for atmospheric chemistry. The results indicated that photolysis would take place in the upper stratosphere. I subsequently carried out calculations using one-dimensional atmospheric models to estimate their atmospheric residence times, which turned out to be many decades. We realized that the chlorine atoms generated by photolysis of the CFCs would participate in a catalytic chain reaction that would efficiently destroy ozone. Furthermore, we estimated that the amount of CFCs produced industrially was comparable to the amount of nitric oxide produced naturally in the stratosphere by the decomposition of nitrous oxide; work by Paul Crutzen and Harold Johnston had indicated that the abundance of ozone in the stratosphere was controlled by nitric oxide. We then formulated the hypothesis that the continued release of CFCs to the environment posed a threat to the stability of the ozone layer, and published our results in the journal Nature in 1974. The publication was noticed almost exclusively by the community of experts in stratospheric chemistry, and hence Sherry Rowland and I decided at that time that it was our responsibility to communicate this finding to society at large
-
Gu, Myojeong; Enell, Carl-Fredrik; Hendrick, François; Pukite, Janis; Van Roozendael, Michel; Platt, Ulrich; Raffalski, Uwe; Wagner, Thomas
2014-05-01
Stratospheric NO2 destroys ozone and acts as a buffer against halogen-catalyzed ozone loss through the formation of reservoir species (ClONO2, BrONO2). Since the importance of both mechanisms depends on the altitude, the investigation of stratospheric NO2 vertical distribution can provide more insight into the role of nitrogen compounds in the destruction of ozone. Here we present stratospheric NO2 vertical profiles retrieved from twilight ground-based zenith-sky DOAS observations at Kiruna, Sweden (68.84°N, 20.41°E) covering 1997 - 2013 periods. This instrument observes zenith scattered sunlight. The sensitivity for stratospheric trace gases is highest during twilight due to the maximum altitude of the scattering profile and the light path through the stratosphere, which vary with the solar zenith angle. The profiling algorithm, based on the Optimal Estimation Method, has been developed by IASB-BIRA and successfully applied at other stations (Hendrick et al., 2004). The basic principle behind this profiling approach is that during twilight, the mean Rayleigh scattering altitude scans the stratosphere rapidly, providing height-resolved information on the absorption by stratospheric NO2. In this study, the long-term evolution of the stratospheric NO2 profile at polar latitude will be investigated. Hendrick, F., B. Barret, M. Van Roozendael, H. Boesch, A. Butz, M. De Mazière, F. Goutail, C. Hermans, J.-C. Lambert, K. Pfeilsticker, and J.-P. Pommereau, Retrieval of nitrogen dioxide stratospheric profiles from ground-based zenith-sky UV-visible observations: Validation of the technique through correlative comparisons, Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 4, 2091-2106, 2004
-
Stratospheric ozone: an introduction to its study
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nicolet, M.
1975-01-01
An analysis is made of the various reactions in which ozone and atomic oxygen are involved in the stratosphere. At the present time, hydrogen, nitrogen, and chlorine compounds in the ranges parts per million, parts per billion, and parts per trillion may have significant chemical effects. In the upper stratosphere, above the ozone peak, where there is no strong departure from photochemical equilibrium conditions, the action of hydroxyl and hydroperoxyl radicals of nitrogen dioxide and chlorine monoxide on atomic oxygen and of atomic chlorine on ozone can be introduced. A precise determination of their exact effects requires knowledge of the vertical distribution of the H 2 O, CH 4 , and H 2 dissociation by reaction of these molecules with electronically excited oxygen atom O( 1 D); the ratio of the OH and HO 2 concentrations and their absolute values, which depend on insufficiently known rate coefficients; the various origins of nitric oxide production, with their vertical distributions related to latitude and season; and the various sources giving different chlorine compounds that may be dissociated in the stratosphere. In the lower stratosphere, below the ozone peak, there is no important photochemical production of O 3 , but there exist various possibilities of transport. The predictability of the action of chemical reactions depends strongly on important interactions between OH and HO 2 radicals with CO and NO, respectively, which affect the ratio n(OH)/n(HO 2 ) at the tropopause level; between OH and NO 2 , which lead to the formation of nitric acid with its downward transport toward the troposphere; between NO and HO 2 , which lead to NO 2 and its subsequent photodissociation; between ClO and NO, which also lead to NO 2 and become more important than the reaction of ClO with O; and between Cl and various molecules, such as CH 4 and H 2 , which lead to HCl with its downward transportation toward the troposphere
-
The ASSET intercomparison of stratosphere and lower mesosphere humidity analyses
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. E. Thornton
2009-02-01
Full Text Available This paper presents results from the first detailed intercomparison of stratosphere-lower mesosphere water vapour analyses; it builds on earlier results from the EU funded framework V "Assimilation of ENVISAT Data" (ASSET project. Stratospheric water vapour plays an important role in many key atmospheric processes and therefore an improved understanding of its daily variability is desirable. With the availability of high resolution, good quality Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS water vapour profiles, the ability of four different atmospheric models to assimilate these data is tested. MIPAS data have been assimilated over September 2003 into the models of the European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF, the Belgian Institute for Space and Aeronomy (BIRA-IASB, the French Service d'Aéronomie (SA-IPSL and the UK Met Office. The resultant middle atmosphere humidity analyses are compared against independent satellite data from the Halogen Occultation Experiment (HALOE, the Polar Ozone and Aerosol Measurement (POAM III and the Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE II. The MIPAS water vapour profiles are generally well assimilated in the ECMWF, BIRA-IASB and SA systems, producing stratosphere-mesosphere water vapour fields where the main features compare favourably with the independent observations. However, the models are less capable of assimilating the MIPAS data where water vapour values are locally extreme or in regions of strong humidity gradients, such as the southern hemisphere lower stratosphere polar vortex. Differences in the analyses can be attributed to the choice of humidity control variable, how the background error covariance matrix is generated, the model resolution and its complexity, the degree of quality control of the observations and the use of observations near the model boundaries. Due to the poor performance of the Met Office analyses the results are not included in
-
The ASSET intercomparison of stratosphere and lower mesosphere humidity analyses
Thornton, H. E.; Jackson, D. R.; Bekki, S.; Bormann, N.; Errera, Q.; Geer, A. J.; Lahoz, W. A.; Rharmili, S.
2009-02-01
This paper presents results from the first detailed intercomparison of stratosphere-lower mesosphere water vapour analyses; it builds on earlier results from the EU funded framework V "Assimilation of ENVISAT Data" (ASSET) project. Stratospheric water vapour plays an important role in many key atmospheric processes and therefore an improved understanding of its daily variability is desirable. With the availability of high resolution, good quality Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS) water vapour profiles, the ability of four different atmospheric models to assimilate these data is tested. MIPAS data have been assimilated over September 2003 into the models of the European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), the Belgian Institute for Space and Aeronomy (BIRA-IASB), the French Service d'Aéronomie (SA-IPSL) and the UK Met Office. The resultant middle atmosphere humidity analyses are compared against independent satellite data from the Halogen Occultation Experiment (HALOE), the Polar Ozone and Aerosol Measurement (POAM III) and the Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE II). The MIPAS water vapour profiles are generally well assimilated in the ECMWF, BIRA-IASB and SA systems, producing stratosphere-mesosphere water vapour fields where the main features compare favourably with the independent observations. However, the models are less capable of assimilating the MIPAS data where water vapour values are locally extreme or in regions of strong humidity gradients, such as the southern hemisphere lower stratosphere polar vortex. Differences in the analyses can be attributed to the choice of humidity control variable, how the background error covariance matrix is generated, the model resolution and its complexity, the degree of quality control of the observations and the use of observations near the model boundaries. Due to the poor performance of the Met Office analyses the results are not included in the intercomparison
-
WASP-121b: An ultrahot gas-giant exoplanet with a stratosphere
Kataria, Tiffany; Evans, Thomas M.; Sing, David; Goyal, Jayesh; Nikolov, Nikolay; Wakeford, Hannah R.; Deming, Drake; Marley, Mark S.; PanCET Team
2018-01-01
Stratospheres are ubiquitous in the atmospheres of solar system planets, and provide crucial information about an atmosphere’s chemical composition, vertical temperature structure, and energy budget. While it has been suggested that stratospheres could form in highly irradiated exoplanets, the extent to which this occurs has so far been unresolved both theoretically and observationally. Here we present secondary eclipse observations of the ultra-hot (Teq ~ 2500 K) gas giant exoplanet WASP-121b made using HST/WFC3 in spectroscopic mode across the 1.12-1.64 micron wavelength range. The spectrum is inconsistent with an isothermal atmosphere and has spectrally-resolved water features in emission, providing a detection of an exoplanet stratosphere at 5-sigma confidence. WASP-121b is one of the standout exoplanets available for atmospheric characterization, both in transmission and emission, due to its large radius (1.8 Rjup), high temperature, and bright host star (H=9.4mag). As such, we will also discuss follow-up observations of WASP-121b with HST and JWST to probe the longitudinal extent of its stratosphere, and the molecular absorbers that may produce it.
-
Detection and mapping of polar stratospheric clouds using limb scattering observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. von Savigny
2005-01-01
Full Text Available Satellite-based measurements of Visible/NIR limb-scattered solar radiation are well suited for the detection and mapping of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs. This publication describes a method to detect PCSs from limb scattering observations with the Scanning Imaging Absorption spectroMeter for Atmospheric CartograpHY (SCIAMACHY on the European Space Agency's Envisat spacecraft. The method is based on a color-index approach and requires a priori knowledge of the stratospheric background aerosol loading in order to avoid false PSC identifications by stratospheric background aerosol. The method is applied to a sample data set including the 2003 PSC season in the Southern Hemisphere. The PSCs are correlated with coincident UKMO model temperature data, and with very few exceptions, the detected PSCs occur at temperatures below 195–198 K. Monthly averaged PSC descent rates are about 1.5 km/month for the −50° S to −75° S latitude range and assume a maximum between August and September with a value of about 2.5 km/month. The main cause of the PSC descent is the slow descent of the lower stratospheric temperature minimum.
-
Unexpected variations in the triple oxygen isotope composition of stratospheric carbon dioxide
Wiegel, Aaron A.; Cole, Amanda S.; Hoag, Katherine J.; Atlas, Elliot L.; Schauffler, Sue M.; Boering, Kristie A.
2013-10-01
We report observations of stratospheric CO2 that reveal surprisingly large anomalous enrichments in 17O that vary systematically with latitude, altitude, and season. The triple isotope slopes reached 1.95 ± 0.05(1σ) in the middle stratosphere and 2.22 ± 0.07 in the Arctic vortex versus 1.71 ± 0.03 from previous observations and a remarkable factor of 4 larger than the mass-dependent value of 0.52. Kinetics modeling of laboratory measurements of photochemical ozone-CO2 isotope exchange demonstrates that non-mass-dependent isotope effects in ozone formation alone quantitatively account for the 17O anomaly in CO2 in the laboratory, resolving long-standing discrepancies between models and laboratory measurements. Model sensitivities to hypothetical mass-dependent isotope effects in reactions involving O3, O(1D), or CO2 and to an empirically derived temperature dependence of the anomalous kinetic isotope effects in ozone formation then provide a conceptual framework for understanding the differences in the isotopic composition and the triple isotope slopes between the laboratory and the stratosphere and between different regions of the stratosphere. This understanding in turn provides a firmer foundation for the diverse biogeochemical and paleoclimate applications of 17O anomalies in tropospheric CO2, O2, mineral sulfates, and fossil bones and teeth, which all derive from stratospheric CO2.
-
The stratospheric ozone and the ozone layer
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zea Mazo, Jorge Anibal; Leon Aristizabal Gloria Esperanza; Eslava Ramirez Jesus Antonio
2000-01-01
An overview is presented of the principal characteristics of the stratospheric ozone in the Earth's atmosphere, with particular emphasis on the tropics and the ozone hole over the poles. Some effects produced in the atmosphere as a consequence of the different human activities will be described, and some data on stratospheric ozone will be shown. We point out the existence of a nucleus of least ozone in the tropics, stretching from South America to central Africa, with annual mean values less than 240 DU, a value lower than in the middle latitudes and close to the mean values at the South Pole. The existence of such a minimum is confirmed by mean values from measurements made on satellites or with earthbound instruments, for different sectors in Colombia, like Medellin, Bogota and Leticia
-
Odin-OSIRIS stratospheric aerosol data product and SAGE III intercomparison
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. E. Bourassa
2012-01-01
Full Text Available The scattered sunlight measurements made by the Optical Spectrograph and InfraRed Imaging System (OSIRIS on the Odin spacecraft are used to retrieve vertical profiles of stratospheric aerosol extinction at 750 nm. The recently released OSIRIS Version 5 data product contains the first publicly released stratospheric aerosol extinction retrievals, and these are now available for the entire Odin mission, which extends from the present day back to launch in 2001. A proof-of-concept study for the retrieval of stratospheric aerosol extinction from limb scatter measurements was previously published and the Version 5 data product retrievals are based on this work, but incorporate several important improvements to the algorithm. One of the primary changes is the use of a new retrieval vector that greatly improves the sensitivity to aerosol scattering by incorporating a forward modeled calculation of the radiance from a Rayleigh atmosphere. Additional improvements include a coupled retrieval of the effective albedo, a new method for normalization of the retrieval vector to improve signal-to-noise, and the use of an initial guess that is representative of very low background aerosol loading conditions, which allows for maximal retrieval range. Furthermore, the Version 5 data set is compared to Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE III 755 nm extinction profiles during the almost four years of mission overlap from 2002 to late 2005. The vertical structure in coincident profile measurements is well correlated and the statistics on a relatively large set of tight coincident measurements show agreement between the measurements from the two instruments to within approximately 10% throughout the 15 to 25 km altitude range, which covers the bulk of the stratospheric aerosol layer for the mid and high latitude cases studied here.
-
Lee, Changsup; Kim, Yong Ha; Kim, Jeong-Han; Jee, Geonhwa; Won, Young-In; Wu, Dong L.
2013-12-01
We analyzed the neutral wind data at altitudes of 80-100 km obtained from a VHF meteor radar at King Sejong Station (KSS, 62.22°S, 58.78°W), a key location to study wave activities above the stratospheric vortex near the Antarctic Peninsula. The seasonal behavior of the semidiurnal tides is generally consistent with the prediction of Global Scale Wave Model (GSWM02) except in the altitude region above ~96 km. Gravity wave (GW) activities inferred from the neutral wind variances show a seasonal variation very similar to the semidiurnal tide amplitudes, suggesting a strong interaction between gravity waves and the tide. Despite the consistent seasonal variations of the GW wind variances observed at the adjacent Rothera station, the magnitudes of the wind variance obtained at KSS are much larger than those at Rothera, especially during May-September. The enhanced GW activity at KSS is also observed by Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) from space in its temperature variance. The observed large wind variances at KSS imply that the Antarctic vortex in the stratosphere may act as an effective filter and source for the GWs in the upper atmosphere.
-
Climatology and trends in the forcing of the stratospheric zonal-mean flow
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
E. Monier
2011-12-01
Full Text Available The momentum budget of the Transformed Eulerian-Mean (TEM equation is calculated using the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF reanalysis (ERA-40 and the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP Reanalysis 2 (R-2. This study outlines the considerable contribution of unresolved waves, deduced to be gravity waves, to the forcing of the zonal-mean flow. A trend analysis, from 1980 to 2001, shows that the onset and break down of the Northern Hemisphere (NH stratospheric polar night jet has a tendency to occur later in the season in the more recent years. This temporal shift follows long-term changes in planetary wave activity that are mainly due to synoptic waves, with a lag of one month. In the Southern Hemisphere (SH, the polar vortex shows a tendency to persist further into the SH summertime. This also follows a statistically significant decrease in the intensity of the stationary EP flux divergence over the 1980–2001 period. Ozone depletion is well known for strengthening the polar vortex through the thermal wind balance. However, the results of this work show that the SH polar vortex does not experience any significant long-term changes until the month of December, even though the intensification of the ozone hole occurs mainly between September and November. This study suggests that the decrease in planetary wave activity in November provides an important feedback to the zonal wind as it delays the breakdown of the polar vortex. In addition, the absence of strong eddy feedback before November explains the lack of significant trends in the polar vortex in the SH early spring. A long-term weakening in the Brewer-Dobson (B-D circulation in the polar region is identified in the NH winter and early spring and during the SH late spring and is likely driven by the decrease in planetary wave activity previously mentioned. During the rest of the year, there are large discrepancies in the representation of the B
-
Stratospheric tritium sampling. Final progress report
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mason, A.S.; Oestlund, H.G.
1985-09-01
Stratospheric tritium sampling was part of Project Airstream (sponsored by the US Department of Energy) between 1975 and 1983. Data from the final deployment in November 1983 are reported here, and the results of the 9 years of effort are summarized. 9 refs., 2 figs., 2 tabs
-
Stratospheric ozone - Impact of human activity
Mcelroy, Michael B.; Salawitch, Ross J.
1989-01-01
The current knowledge of the chemistry of the stratosphere is reviewed, with particular consideration given to the measurements from the Atmospheric Trace Molecule Spectroscopy (ATMOS) experiment and from the Airborne Antarctic Ozone Experiment. Analysis of the ATMOS data at 30 deg N suggests that the current understanding of the contemporary-stratosphere chemistry at mid-latitudes is relatively complete, except for possible problems with the diurnal variations of N2O5 at low altitudes, and with ClNO3 at higher altitudes. Except for some difficulties with these two compounds, the data from ATMOS agree well with the gas phase models for nitrogen and chlorine species at 30 deg N in spring. It is emphasized that, in addition to the HOCl mechanism proposed by Solomon et al. (1986), the ClO-BrO scheme proposed by McElroy et al. (1986), and the ClO dimer mechanism introduced by Molina and Molina (1987), other processes exist that are responsible for ozone removal.
-
A new formulation of equivalent effective stratospheric chlorine (EESC
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. A. Newman
2007-09-01
Full Text Available Equivalent effective stratospheric chlorine (EESC is a convenient parameter to quantify the effects of halogens (chlorine and bromine on ozone depletion in the stratosphere. We show, discuss, and analyze a new formulation of EESC that now includes the effects of age-of-air dependent fractional release values and an age-of-air spectrum. This EESC can be more appropriately applied to various parts of the stratosphere because of this dependence on mean age-of-air. This new formulation provides quantitative estimates of EESC that can be directly related to inorganic chlorine and bromine throughout the stratosphere. In this paper, we first provide a detailed description of the EESC calculation. We then use this EESC formulation to estimate that human-produced ozone depleting substances will recover to 1980 levels in 2041 in the midlatitudes, and 2067 over Antarctica. These recovery dates are based upon the assumption that the international agreements for regulating ozone-depleting substances are adhered to. In addition to recovery dates, we also estimate the uncertainties and possible problems in the estimated times of recovery. The midlatitude recovery of 2041 has a 95% confidence uncertainty from 2028 to 2049, while the 2067 Antarctic recovery has a 95% confidence uncertainty from 2056 to 2078. The principal uncertainties are from the estimated mean age-of-air and fractional release values, and the assumption that these quantities are time independent. Using other model estimates of age decrease due to climate change, we estimate that midlatitude recovery may be significantly accelerated.
-
Stratospheric role in interdecadal changes of El Niño impacts over Europe
Ayarzagüena, B.; López-Parages, J.; Iza, M.; Calvo, N.; Rodríguez-Fonseca, B.
2018-04-01
The European precipitation response to El Niño (EN) has been found to present interdecadal changes, with alternated periods of important or negligible EN impact in late winter. These periods are associated with opposite phases of multi-decadal sea surface temperature (SST) variability, which modifies the tropospheric background and EN teleconnections. In addition, other studies have shown how SST anomalies in the equatorial Pacific, and in particular, the location of the largest anomalous SST, modulate the stratospheric response to EN. Nevertheless, the role of the stratosphere on the stationarity of EN response has not been investigated in detail so far. Using reanalysis data, we present a comprehensive study of EN teleconnections to Europe including the role of the ocean background and the stratosphere in the stationarity of the signal. The results reveal multidecadal variability in the location of EN-related SST anomalies that determines different teleconnections. In periods with relevant precipitation signal over Europe, the EN SST pattern resembles Eastern Pacific EN and the stratospheric pathway plays a key role in transmitting the signal to Europe in February, together with two tropospheric wavetrains that transmit the signal in February and April. Conversely, the stratospheric pathway is not detected in periods with a weak EN impact on European precipitation, corresponding to EN-related SST anomalies primarily located over the central Pacific. SST mean state and its associated atmospheric background control the location of EN-related SST anomalies in different periods and modulate the establishment of the aforementioned stratospheric pathway of EN teleconnection to Europe too.
-
Ho-Fang, TSAI; Toshitaka, TSUDA; George A., HAJJ; Jens, WICKERT; Yuichi, AOYAMA; Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere (RASC), Kyoto University :National Space Program Office(NSPO); Radio Science Center for Space and Atmosphere (RASC), Kyoto University; Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), California Institute of Technology; GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam (GFZ), Department 1:Geodesy and Remote Sensing; RASC, Kyoto University
2004-01-01
Structure and propagation of equatorial Kelvin waves during May 2001 and December 2002 are observed from the temperature profiles in the upper troposphere and the lower stratosphere using CHAMP and SAC-C GPS radio occultation data. Kelvin waves derived from temperature fluctuations characterize eastward phase propagation in time-longitude section and eastward phase tilts with height in altitude-longitude section between 10 and 30 km. The phase progression spans the range indicating the contin...
-
Chemical and Dynamical Impacts of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings on Arctic Ozone Variability
Strahan, S. E.; Douglass, A. R.; Steenrod, S. D.
2016-01-01
We use the Global Modeling Initiative (GMI) chemistry and transport model with Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA) meteorological fields to quantify heterogeneous chemical ozone loss in Arctic winters 2005-2015. Comparisons to Aura Microwave Limb Sounder N2O and O3 observations show the GMI simulation credibly represents the transport processes and net heterogeneous chemical loss necessary to simulate Arctic ozone. We find that the maximum seasonal ozone depletion varies linearly with the number of cold days and with wave driving (eddy heat flux) calculated from MERRA fields. We use this relationship and MERRA temperatures to estimate seasonal ozone loss from 1993 to 2004 when inorganic chlorine levels were in the same range as during the Aura period. Using these loss estimates and the observed March mean 63-90N column O3, we quantify the sensitivity of the ozone dynamical resupply to wave driving, separating it from the sensitivity of ozone depletion to wave driving. The results show that about 2/3 of the deviation of the observed March Arctic O3 from an assumed climatological mean is due to variations in O3 resupply and 13 is due to depletion. Winters with a stratospheric sudden warming (SSW) before mid-February have about 1/3 the depletion of winters without one and export less depletion to the midlatitudes. However, a larger effect on the spring midlatitude ozone comes from dynamical differences between warm and cold Arctic winters, which can mask or add to the impact of exported depletion.
-
On particles in the Arctic stratosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
T. S. Jørgensen
2003-06-01
Full Text Available Soon after the discovery of the Antarctic ozone hole it became clear that particles in the polar stratosphere had an infl uence on the destruction of the ozone layer. Two major types of particles, sulphate aerosols and Polar Stratospheric Clouds (PSCs, provide the surfaces where fast heterogeneous chemical reactions convert inactive halogen reservoir species into potentially ozone-destroying radicals. Lidar measurements have been used to classify the PSCs. Following the Mt. Pinatubo eruption in June 1991 it was found that the Arctic stratosphere was loaded with aerosols, and that aerosols observed with lidar and ozone observed with ozone sondes displayed a layered structure, and that the aerosol and ozone contents in the layers frequently appeared to be negatively correlated. The layered structure was probably due to modulation induced by the dynamics at the edge of the polar vortex. Lidar observations of the Mt. Pinatubo aerosols were in several cases accompanied by balloon-borne backscatter soundings, whereby backscatter measurements in three different wavelengths made it possible to obtain information about the particle sizes. An investigation of the infl uence of synoptic temperature histories on the physical properties of PSC particles has shown that most of the liquid type 1b particles were observed in the process of an ongoing, relatively fast, and continuous cooling from temperatures clearly above the nitric acid trihydrate condensation temperature (TNAT. On the other hand, it appeared that a relatively long period, with a duration of at least 1-2 days, at temperatures below TNAT provide the conditions which may lead to the production of solid type 1a PSCs.
-
Page, William A.
1982-01-01
The following six papers report preliminary results obtained from a field experiment designed to study the role of tropical cumulo-nimbus clouds in the transfer of water vapor from the troposphere to the stratosphere over the region of Panama. The measurements were made utilizing special NOAA enhanced IR satellite images, radiosonde-ozonesondes and a NASA U-2 aircraft carrying. nine experiments. The experiments were provided by a group of NASA, NOAA, industry, and university scientists. Measurements included atmospheric humidity, air and cloud top temperatures, atmospheric tracer constituents, cloud particle characteristics and cloud morphology. The aircraft made a total of eleven flights from August 30 through September 18, 1980, from Howard Air Force Base, Panama; the pilots obtained horizontal and vertical profiles in and near convectively active regions and flew around and over cumulo-nimbus towers and through the extended anvils in the stratosphere. Cumulo-nimbus clouds in the tropics appear to play an important role in upward water vapor transport and may represent the principal source influencing the stratospheric water vapor budget. The clouds provide strong vertical circulation in the troposphere, mixing surface air and its trace materials (water vapor, CFM's sulfur compounds, etc.) quickly up to the tropopause. It is usually assumed that large scale mean motions or eddy scale motions transport the trace materials through the tropopause and into the stratosphere where they are further dispersed and react with other stratospheric constituents. The important step between the troposphere and stratosphere for water vapor appears to depend upon the processes occurring at or near the tropopause at the tops of the cumulo-nimbus towers. Several processes have been sugested: (1) The highest towers penetrate the tropopause and carry water in the form of small ice particles directly into the stratosphere. (2) Water vapor from the tops of the cumulonimbus clouds is
-
Stratospheric measurements of ozone-depleting substances and greenhouse gases using AirCores
Laube, Johannes; Leedham Elvidge, Emma; Kaiser, Jan; Sturges, Bill; Heikkinen, Pauli; Laurila, Tuomas; Hatakka, Juha; Kivi, Rigel; Chen, Huilin; Fraser, Paul; van der Veen, Carina; Röckmann, Thomas
2017-04-01
Retrieving air samples from the stratosphere has previously required aircraft or large balloons, both of which are expensive to operate. The novel "AirCore" technique (Karion et al., 2010) enables stratospheric sampling using weather balloons, which is much more cost effective. AirCores are long (up to 200 m) stainless steel tubes which are placed as a payload on a small balloon, can ascend to over 30 km and fill upon descent, collecting a vertical profile of the atmosphere. Retrieved volumes are much smaller though, which presents a challenge for trace gas analysis. To date, only the more abundant trace gases such as carnon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) have been quantified in AirCores. Halogenated trace gases are also important greenhouse gases and many also deplete stratospheric ozone. Their concentrations are however much lower i.e. typically in the part per trillion (ppt) molar range. We here present the first stratospheric measurements of halocarbons in AirCores obtained using UEA's highly sensitive (detection limits of 0.01-0.1 ppt in 10 ml of air) gas chromatography mass spectrometry system. The analysed air originates from a Stratospheric Air Sub-sampler (Mrozek et al., 2016) which collects AirCore segments after the non-destructive CO2 and CH4 analysis. Successfully measured species include CFC-11, CFC-12, CFC-113, CFC-115, H-1211, H-1301, HCFC-22, HCFC-141b, HCFC-142b, HCFC-133a, and sulphur hexafluoride (SF6). We compare the observed mixing ratios and precisions with data obtained from samples collected during various high-altitude aircraft campaigns between 2009 and 2016 as well as with southern hemisphere tropospheric long-term trends. As part of the ERC-funded EXC3ITE (EXploring stratospheric Composition, Chemistry and Circulation with Innovative Techniques) project more than 40 AirCore flights are planned in the next 3 years with an expanded range of up to 30 gases in order to explore seasonal and interannual variability in the stratosphere
-
Tunable Far Infrared Studies in Support of Stratospheric Measurements
Chance, Kelly V.; Park, K.; Nolt, I. G.; Evenson, K. M.
2001-01-01
determined from Stark effect measurements; exceptions include some molecules with large vibration-rotation interactions (NO2) and internal motions (H2O2 above the lowest torsional state). The line parameters that are still the least well determined are pressure broadening coefficients, and their temperature coefficients, These are strongly dependent on the quantum states involved in the transitions, in a way that is much more complex than the simple projection by directional cosine matrix elements involved in determination of rotational line strengths from static dipole moments. The following molecules have now been measured or detected in the atmosphere using far infrared and millimeter-wave emission spectroscopy from balloon- and satellite-borne spectrometers: OH, HO2, H2O (including minor isotopomers and hot band lines), H2O2, O3P, O2 (including minor isotopomers), O3 (including minor isotopomers and hot band lines), HOCl, HCl, HF, HBr, CIO, CO, CO2, N2O, NO2, N2O5, HNO3, ClNO3, and HCN. Many of these species have spectral lines that are saturated in stratospheric spectra. In these cases, the measured line equivalent widths are proportional to (line strength x Lorentz width) (exp 1/2) so that the pressure broadening coefficients are as important as the line intensities in determining concentration profiles. Interpretation of field measurements for these species have required ongoing measurement programs of pressure broadening measurements. Other species (HO2, HGCl, H2O2, HBr, and NO2, as examples) have required further line position studies in order to fully analyze the field measurements.
-
Lambert, Alyn; Santee, Michelle L.
2018-02-01
compare how the wave amplitudes are reproduced by each reanalysis dataset. We find that the spatial and temporal distribution of temperatures below the ice frost point, and hence the potential to form ice polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs) in model studies driven by the reanalyses, varies significantly because of the underlying differences in the representation of mountain wave activity. High-accuracy COSMIC temperatures are used as a common reference to intercompare the reanalysis temperatures. Over the 68-21 hPa pressure range, the biases of the reanalyses with respect to COSMIC temperatures for both polar regions fall within the narrow range of -0.6 K to +0.5 K. GEOS-5.9.1, MERRA, MERRA-2, and JRA-55 have predominantly cold biases, whereas ERA-I has a predominantly warm bias. NCEP-CFSR has a warm bias in the Arctic but becomes substantially colder in the Antarctic. Reanalysis temperatures are also compared with the PSC reference temperatures. Over the 68-21 hPa pressure range, the reanalysis temperature biases are in the range -1.6 to -0.3 K with standard deviations ˜ 0.6 K for the CALIOP STS reference, and in the range -0.9 to +0.1 K with standard deviations ˜ 0.7 K for the CALIOP ice reference. Comparisons of MLS temperatures with the PSC reference temperatures reveal vertical oscillations in the MLS temperatures and a significant low bias in MLS temperatures of up to 3 K.
-
Benefits, risks, and costs of stratospheric geoengineering
Robock, Alan; Marquardt, Allison; Kravitz, Ben; Stenchikov, Georgiy L.
2009-01-01
Injecting sulfate aerosol precursors into the stratosphere has been suggested as a means of geoengineering to cool the planet and reduce global warming. The decision to implement such a scheme would require a comparison of its benefits, dangers
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
1991-01-01
The Peer Review Panel was charged with deciding whether seismic methods, which had been utilized at Yucca Mountain with mixed results in the past, could provide useful information about the Tertiary structure in the Yucca Mountain area. The objectives of using seismic methods at Yucca Mountain are to: (a) obtain information about the structural character of the Paleozoic-Tertiary (Pz-T) contact, and (b) obtain information about the structural and volcanic details within the Tertiary and Quaternary section. The Panel recommends that a four part program be undertaken to test the utility of seismic reflection data for characterizing the structural setting of the Yucca Mountain area. The Panel feels strongly that all four parts of the program must be completed in order to provide the highest probability of success. The four parts of the program are: (a) drill or extend a deep hole in Crater Flat to provide depth control and allow for the identification of seismic reflectors in an area where good quality seismic reflection data are expected; (b) undertake a full seismic noise test in Crater Flat, test 2D receiver arrays as well as linear arrays; perform an expanding spread test using both P and S wave sources to obtain a quick look at the reflection quality in the area and see if shear wave reflections might provide structural information in areas of unsaturated rock; (c) acquire a P wave seismic reflection profile across Crater Flat through the deep control well, across Yucca Mountain, and continuing into Jackass Flats; and (d) acquire a standard VSP (vertical seismic profiling) in the deep control well to tie the seismic data into depth and to identify reflectors correctly
-
Commentary on using equivalent latitude in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
L. L. Pan
2012-10-01
Full Text Available We discuss the use of potential vorticity (PV based equivalent latitude (EqLat and potential temperature (θ coordinates in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS for chemical transport studies. The main objective is to provide a cautionary note on using EqLat-θ coordinates for aggregating chemical tracers in the UTLS. Several examples are used to show 3-D distributions of EqLat together with chemical constituents for a range of θ. We show that the use of PV-θ coordinates may not be suitable for several reasons when tropospheric processes are an important part of a study. Due to the different static stability structures between the stratosphere and troposphere, the use of θ as a vertical coordinate does not provide equal representations of the UT and LS. Since the θ surfaces in the troposphere often intersect the surface of the Earth, the θ variable does not work well distinguishing the UT from the boundary layer when used globally as a vertical coordinate. We further discuss the duality of PV/EqLat as a tracer versus as a coordinate variable. Using an example, we show that while PV/EqLat serves well as a transport tracer in the UTLS region, it may conceal the chemical structure associated with wave breaking when used as a coordinate to average chemical tracers. Overall, when choosing these coordinates, considerations need to be made not only based on the time scale of PV being a conservative tracer, but also the specific research questions to be addressed.
-
Lower stratospheric observations from aircraft and satellite during the 2015/2016 El Nino
Rosenlof, K. H.; Avery, M. A.; Davis, S. M.; Gao, R. S.; Thornberry, T. D.
2016-12-01
Winter 2015/2016 experienced a strong El Nino that was heavily observed by aircraft, radiosonde and satellite platforms. During the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Sensing Hazards with Operational Unmanned Technology (SHOUT)/El Nino Rapid Response (ENRR) flights of the NASA Global Hawk, in situ ozone measurements were made in the lower stratosphere over the Pacific. These will be contrasted with ozone measurements taken during La Nina and ENSO neutral conditions during past Global Hawk aircraft campaigns. Additionally, lower stratospheric water vapor and ozone measurements from the Microwave Limb Sounder satellite instrument and stratospheric ice measurements above the tropopause from the Cloud-Aerosol Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP) will be presented. Our aircraft ozone measurements are higher for the El Nino flights than during other missions previously sampled, while zonally averaged lower stratospheric water vapor and central Pacific ice path above the tropopause reached record highs. Implications and possible reasons for these anomalous observations will be discussed. Winter 2015/2016 experienced a strong El Nino that was heavily observed by aircraft, radiosonde and satellite platforms. During the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Sensing Hazards with Operational Unmanned Technology (SHOUT)/El Nino Rapid Response (ENRR) flights of the NASA Global Hawk, in situ ozone measurements were made in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) over the Pacific. These will be contrasted with ozone measurements made during La Nina and ENSO neutral conditions during past Global Hawk aircraft campaigns. Additionally, UTLS water vapor and ozone measurements from the Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) satellite instrument and stratospheric ice measurements above the tropopause from the Cloud-Aerosol Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP) will be presented. Our aircraft ozone
-
Meteorological Conditions of Floods In The Chilean Andes Mountains
Vergara, J.
Catastrophic floods occurred on mountains River during 2000 and 2001. The meteo- rological conditions of flood during the last five years have analyzed. For example, the flood of June 29 of 2000 occurred after one of extremely wettest June of the last 40 years were snowfall was 991cm in the Aconcagua Valley. Infrequently storms activ- ity generated a huge snowfall and rainfall over the Andes mountains on June of 2000 (1525mm in El Maule Valley) and the end of the unusually period, the flood was trig- gered by rising temperatures on the mountains and heavy rain (199mm in 24 hours) fall over the fresh snow on the morning of June 29 and floods wave developed and moved down along of the all river located on Central part of Chile, the foods peak was 2970.5m3/s on the El Maule basin in the morning of June 29. The regional meteoro- logical models with the hydrological forecasting was used for alert of the floods.
-
Dinh, Tra; Fueglistaler, Stephan
2016-04-01
Thin cirrus clouds in the tropical tropopause layer (TTL) are of great interest due to their role in the control of water vapor and temperature in the TTL. Previous research on TTL cirrus clouds has focussed mainly on microphysical processes, specifically the ice nucleation mechanism and dehydration efficiency. Here, we use a cloud resolving model to analyse the sensitivity of TTL cirrus characteristics and impacts with respect to microphysical and radiative processes. A steady-state TTL cirrus cloud field is obtained in the model forced with dynamical conditions typical for the TTL (2-dimensional setup with a Kelvin-wave temperature perturbation). Our model results show that the dehydration efficiency (as given by the domain average relative humidity in the layer of cloud occurrence) is relatively insensitive to the ice nucleation mechanism, i.e. homogeneous versus heterogeneous nucleation. Rather, TTL cirrus affect the water vapor entering the stratosphere via an indirect effect associated with the cloud radiative heating and dynamics. Resolving the cloud radiative heating and the radiatively induced circulations approximately doubles the domain average ice mass. The cloud radiative heating is proportional to the domain average ice mass, and the observed increase in domain average ice mass induces a domain average temperature increase of a few Kelvin. The corresponding increase in water vapor entering the stratosphere is estimated to be about 30 to 40%.
-
Study nonlinear dynamics of stratospheric ozone concentration at Pakistan Terrestrial region
Jan, Bulbul; Zai, Muhammad Ayub Khan Yousuf; Afradi, Faisal Khan; Aziz, Zohaib
2018-03-01
This study investigates the nonlinear dynamics of the stratospheric ozone layer at Pakistan atmospheric region. Ozone considered now the most important issue in the world because of its diverse effects on earth biosphere, including human health, ecosystem, marine life, agriculture yield and climate change. Therefore, this paper deals with total monthly time series data of stratospheric ozone over the Pakistan atmospheric region from 1970 to 2013. Two approaches, basic statistical analysis and Fractal dimension (D) have adapted to study the nature of nonlinear dynamics of stratospheric ozone level. Results obtained from this research have shown that the Hurst exponent values of both methods of fractal dimension revealed an anti-persistent behavior (negatively correlated), i.e. decreasing trend for all lags and Rescaled range analysis is more appropriate as compared to Detrended fluctuation analysis. For seasonal time series all month follows an anti-persistent behavior except in the month of November which shown persistence behavior i.e. time series is an independent and increasing trend. The normality test statistics also confirmed the nonlinear behavior of ozone and the rejection of hypothesis indicates the strong evidence of the complexity of data. This study will be useful to the researchers working in the same field in the future to verify the complex nature of stratospheric ozone.
-
20 Years of ClO Measurements in the Antarctic Lower Stratosphere
Nedoluha, Gerald E.; Connor, Brian J.; Mooney, Thomas; Barrett, James W.; Parrish, Alan; Gomez, R. Michael; Boyd, Ian; Allen, Douglas R.; Kotkamp, Michael; Kremser, Stefanie;

2016-01-01
We present 20 years (1996-2015) of austral springtime measurements of chlorine monoxide (ClO) over Antarctica from the Chlorine Oxide Experiment (ChlOEl) ground-based millimeter wave spectrometer at Scott Base, Antarctica, as well 12 years (2004-2015) of ClO measurements from the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS). From August onwards we observe a strong increase in lower stratospheric ClO, with a peak column amount usually occurring in early September. From mid-September onwards we observe a strong decrease in ClO. In order to study interannual differences, we focus on a 3-week period from 28 August to 17 September for each year and compare the average column ClO anomalies. These column ClO anomalies are shown to be highly correlated with the average ozone mass deficit for September and October of each year. We also show that anomalies in column ClO are strongly anti-correlated with 30 hPa temperature anomalies, both on a daily and an interannual timescale. Making use of this anti-correlation we calculate the linear dependence of the interannual variations in column C1O on interannual variations in temperature. By making use of this relationship, we can better estimate the underlying trend in the total chlorine (Cl(sub y) = HCl + ClONO2 + HOCl + 2 x Cl2 + 2 x Cl2+ ClO + Cl). The resultant trends in Cl(sub y), which determine the long-term trend in ClO, are estimated to be -0.5 +/-0.2, -1.40.9, and -0.60.4% per year, for zonal MLS, Scott Base MLS (both 2004-2015), and ChlOE (1996-2015) respectively. These trends are within 1sigma of trends in stratospheric Cl(sub y) previously found at other latitudes. The decrease in ClO is consistent with the trend expected from regulations enacted under the Montreal Protocol.
-
Simulating the Snowball Stratosphere and Its Influence On CO2 Inference
Graham, R. J.; Shaw, T.; Abbot, D. S.
2017-12-01
According to the snowball Earth hypothesis, a large quantity of CO2 must build up during an event in order to cause eventual deglaciation. One prediction of this model is a depletion in atmospheric oxygen-17 as a result of stratospheric chemical reactions, which has been observed in preserved barite minerals. This represents one of the most dramatic and compelling pieces of evidence in support of the snowball Earth hypothesis. The inference of anomalous atmospheric oxygen-17 based on measurements of barite minerals, however, was made by assuming that the stratosphere-troposphere mass exchange rate and mixing within the stratosphere were the same as the present. In this contribution we test these assumptions with simulations of modern and snowball atmospheric conditions using the global climate model ECHAM5. Our simulations are still running, but we will have results to report by December.
-
A case study of formation and maintenance of a lower stratospheric cirrus cloud over the tropics
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Sandhya
2015-05-01
Full Text Available A rare occurrence of stratospheric cirrus at 18.6 km height persisting for about 5 days during 3–7 March 2014 is inferred from the ground-based Mie lidar observations over Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E and spaceborne observations. Due to the vertical transport by large updrafts on 3 March in the troposphere, triggered by a potential vorticity intrusion, the water vapour mixing ratio shows an increase around the height of 18.6 km. Relative humidity with respect to ice is ~ 150%, indicating that the cirrus cloud may be formed though homogeneous nucleation of sulfuric acid. The cirrus cloud persists due to the cold anomaly associated with the presence of a 4-day wave.
-
Rietmeijer, Frans J. M.
1995-01-01
Some fraction of Zn, Cu, Se, Ga and Ge in chondritic interplanetary dust particles (IDPs) collected in the lower stratosphere between 1981 May and 1984 June has a volcanic origin. I present a method to evaluate the extent of this unavoidable type of stratospheric contamination for individual particles. The mass-normalized abundances for Cu and Ge as a function of mass-normalized stratospheric residence time show their time-integrated stratospheric aerosol abundances. The Zn, Se and Ga abundances show a subdivision into two groups that span approximately two-year periods following the eruptions of the Mount St. Helens (1980 May) and El Chichon (1982 April) volcanoes. Elemental abundances in particles collected at the end of each two-year period indicate low, but not necessarily ambient, volcanic stratospheric abundances. Using this time-integrated baseline, I calculate the straospheric contaminant fractions in nine IDPs and show that Zn, SE and Ga abundances in chondritic IDPs derive in part from stratospheric aerosol contaminants. Post-entry elemental abundances (i.e., the amount that survived atmospheric entry heating of the IDP) show enrichments relative to the CI abundances but in a smaller number of particles than previously suggested.
-
Global assimilation of X Project Loon stratospheric balloon observations
Coy, L.; Schoeberl, M. R.; Pawson, S.; Candido, S.; Carver, R. W.
2017-12-01
Project Loon has an overall goal of providing worldwide internet coverage using a network of long-duration super-pressure balloons. Beginning in 2013, Loon has launched over 1600 balloons from multiple tropical and middle latitude locations. These GPS tracked balloon trajectories provide lower stratospheric wind information over the oceans and remote land areas where traditional radiosonde soundings are sparse, thus providing unique coverage of lower stratospheric winds. To fully investigate these Loon winds we: 1) compare the Loon winds to winds produced by a global data assimilation system (DAS: NASA GEOS) and 2) assimilate the Loon winds into the same comprehensive DAS. Results show that in middle latitudes the Loon winds and DAS winds agree well and assimilating the Loon winds have only a small impact on short-term forecasting of the Loon winds, however, in the tropics the loon winds and DAS winds often disagree substantially (8 m/s or more in magnitude) and in these cases assimilating the loon winds significantly improves the forecast of the loon winds. By highlighting cases where the Loon and DAS winds differ, these results can lead to improved understanding of stratospheric winds, especially in the tropics.
-
Stratospheric General Circulation with Chemistry Model (SGCCM)
Rood, Richard B.; Douglass, Anne R.; Geller, Marvin A.; Kaye, Jack A.; Nielsen, J. Eric; Rosenfield, Joan E.; Stolarski, Richard S.
1990-01-01
In the past two years constituent transport and chemistry experiments have been performed using both simple single constituent models and more complex reservoir species models. Winds for these experiments have been taken from the data assimilation effort, Stratospheric Data Analysis System (STRATAN).
-
Age and gravitational separation of the stratospheric air over Indonesia
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Sugawara
2018-02-01
Full Text Available The gravitational separation of major atmospheric components, in addition to the age of air, would provide additional useful information about stratospheric circulation. However, observations of the age of air and gravitational separation are still geographically sparse, especially in the tropics. In order to address this issue, air samples were collected over Biak, Indonesia in February 2015 using four large plastic balloons, each loaded with two compact cryogenic samplers. With a vertical resolution of better than 2 km, air samples from seven different altitudes were analyzed for CO2 and SF6 mole fractions, δ15N of N2, δ18O of O2, and δ(Ar∕N2 to examine the vertically dependent age and gravitational separation of air in the tropical tropopause layer (TTL and the equatorial stratosphere. By comparing their measured mole fractions with aircraft observations in the upper tropical troposphere, we have found that CO2 and SF6 ages increase gradually with increasing altitude from the TTL to 22 km, and then rapidly from there up to 29 km. The CO2 and SF6 ages agree well with each other in the TTL and in the lower stratosphere, but show a significant difference above 24 km. The average values of δ15N of N2, δ18O of O2, and δ(Ar∕N2 all show a small but distinct upward decrease due to the gravitational separation effect. Simulations with a two-dimensional atmospheric transport model indicate that the gravitational separation effect decreases as tropical upwelling is enhanced. From the model calculations with enhanced eddy mixing, it is also found that the upward increase in air age is magnified by horizontal mixing. These model simulations also show that the gravitational separation effect remains relatively constant in the lower stratosphere. The results of this study strongly suggest that the gravitational separation, combined with the age of air, can be used to diagnose air transport processes in the stratosphere.
-
Stratospheric ozone measurements at Arosa (Switzerland): history and scientific relevance
Staehelin, Johannes; Viatte, Pierre; Stübi, Rene; Tummon, Fiona; Peter, Thomas
2018-05-01
Climatic Observatory (LKO) in Arosa (Switzerland), marking the beginning of the world's longest series of total (or column) ozone measurements. They were driven by the recognition that atmospheric ozone is important for human health, as well as by scientific curiosity about what was, at the time, an ill characterised atmospheric trace gas. From around the mid-1950s to the beginning of the 1970s studies of high atmosphere circulation patterns that could improve weather forecasting was justification for studying stratospheric ozone. In the mid-1970s, a paradigm shift occurred when it became clear that the damaging effects of anthropogenic ozone-depleting substances (ODSs), such as long-lived chlorofluorocarbons, needed to be documented. This justified continuing the ground-based measurements of stratospheric ozone. Levels of ODSs peaked around the mid-1990s as a result of a global environmental policy to protect the ozone layer, implemented through the 1987 Montreal Protocol and its subsequent amendments and adjustments. Consequently, chemical destruction of stratospheric ozone started to slow around the mid-1990s. To some extent, this raises the question as to whether continued ozone observation is indeed necessary. In the last decade there has been a tendency to reduce the costs associated with making ozone measurements globally including at Arosa. However, the large natural variability in ozone on diurnal, seasonal, and interannual scales complicates the capacity for demonstrating the success of the Montreal Protocol. Chemistry-climate models also predict a super-recovery of the ozone layer at mid-latitudes in the second half of this century, i.e. an increase of ozone concentrations beyond pre-1970 levels, as a consequence of ongoing climate change. These factors, and identifying potentially unexpected stratospheric responses to climate change, support the continued need to document stratospheric ozone changes. This is particularly valuable at the Arosa site, due
-
An introduction to atmospheric gravity waves
Nappo, Carmen J
2012-01-01
Gravity waves exist in all types of geophysical fluids, such as lakes, oceans, and atmospheres. They play an important role in redistributing energy at disturbances, such as mountains or seamounts and they are routinely studied in meteorology and oceanography, particularly simulation models, atmospheric weather models, turbulence, air pollution, and climate research. An Introduction to Atmospheric Gravity Waves provides readers with a working background of the fundamental physics and mathematics of gravity waves, and introduces a wide variety of applications and numerous recent advances. Nappo provides a concise volume on gravity waves with a lucid discussion of current observational techniques and instrumentation.An accompanying website contains real data, computer codes for data analysis, and linear gravity wave models to further enhance the reader's understanding of the book's material. Companion web site features animations and streaming video Foreword by George Chimonas, a renowned expert on the interac...
-
Piecewise Delamination Drives Uplift in the Atlas Mountains Region of Morocco
Bezada, M. J.; Humphreys, E.; Martin Davila, J.; mimoun, H.; Josep, G.; Palomeras, I.
2013-12-01
The elevation of the intra-continental Atlas Mountains of Morocco and surrounding regions requires a mantle component of buoyancy, and there is consensus that this buoyancy results from an abnormally thin lithosphere. Lithospheric delamination under the Atlas Mountains and thermal erosion caused by upwelling mantle have each been suggested as thinning mechanisms. We use seismic tomography to image the upper mantle of Morocco by inverting teleseimic p-wave delay times, complemented with local delays, recorded on a dense array of stations in the Iberian peninsula and Morocco. A surface wave model provides constraint on the shallower layers. We determine the geometry of lithospheric cavities and mantle upwelling beneath the Middle Atlas and central High Atlas, and image delaminated lithosphere at ~400 km beneath the Middle Atlas. We propose discontinuous delamination of an intrinsically unstable Atlas lithosphere, enabled by the presence of anomalously hot mantle, as a mechanism for producing the imaged structures. The Atlas lithosphere was made unstable by a combination of tectonic shortening and eclogite loading during Mesozoic rifting and Cenozoic magmatism. The presence of hot mantle, sourced from regional upwellings in northern Africa or the Canary Islands, enabled the mobilization of this lithosphere. Flow around the retreating Alboran slab focused upwelling mantle under the Middle Atlas, where we image the most recent delamination. The Atlas Mountains of Morocco stand as an example of mantle-generated uplift and large-scale lithospheric loss in a mildly contractional orogen.
-
Stratospheric contribution to the global bomb radiocarbon inventory: Model versus observation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Broecker, W.S.; Peng, T.H.
1994-01-01
An attempt is made, through modeling, to account for the decline in the 14 C/C ratio in atmospheric CO 2 after its bomb-test induced peak in 1963. The model suggests that as of 1964 about one third of the bomb 14 C remained in the stratosphere and that it was released to the troposphere with an e-folding time of about seven years. By contrast, measurements carried out in the stratosphere suggest that at that time the excess was closer to one quarter of the total and that e-folding time for its decline was 3±1 years. The anomaly between model and observation cannot be attributed solely to an inadequacy in the representation of the terrestrial biosphere. Rather, it must reflect either an inadequacy in the ocean model or in the measured stratospheric inventories. 24 refs., 9 figs., 4 tabs
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Considine, D. B.; Douglass, A. R.; Connell, P. S.; Kinnison, D. E.; Rotman, D. A.
2000-01-01
We describe a new parameterization of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs) which was written for and incorporated into the three-dimensional (3-D) chemistry and transport model (CTM) developed for NASA's Atmospheric Effects of Aviation Project (AEAP) by the Global Modeling Initiative (GMI). The parameterization was designed to respond to changes in NO y and H 2 O produced by high-speed civilian transport (HSCT) emissions. The parameterization predicts surface area densities (SADs) of both Type 1 and Type 2 PSCs for use in heterogeneous chemistry calculations. Type 1 PSCs are assumed to have a supercooled ternary sulfate (STS) composition, and Type 2 PSCs are treated as water ice with a coexisting nitric acid trihydrate (NAT) phase. Sedimentation is treated by assuming that the PSC particles obey lognormal size distributions, resulting in a realistic mass flux of condensed phase H 2 O and HNO 3 . We examine a simulation of the Southern Hemisphere high-latitude lower stratosphere winter and spring seasons driven by temperature and wind fields from a modified version of the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Middle Atmosphere Community Climate Model Version 2 (MACCM2). Predicted PSC SADs and median radii for both Type 1 and Type 2 PSCs are consistent with observations. Gas phase HNO 3 and H 2 O concentrations in the high-latitude lower stratosphere qualitatively agree with Cryogenic Limb Array Etalon Spectrometer (CLAES) HNO 3 and Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) H 2 O observations. The residual denitrification and dehydration of the model polar vortex after polar winter compares well with atmospheric trace molecule spectroscopy (ATMOS) observations taken during November 1994. When the NO x and H 2 O emissions of a standard 500-aircraft HSCT fleet with a NO x emission index of 5 are added, NO x and H 2 O concentrations in the Southern Hemisphere polar vortex before winter increase by up to 3%. This results in earlier onset of PSC formation, denitrification, and
-
The isotopic composition of methane in the stratosphere: high-altitude balloon sample measurements
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
T. Röckmann
2011-12-01
Full Text Available The isotopic composition of stratospheric methane has been determined on a large suite of air samples from stratospheric balloon flights covering subtropical to polar latitudes and a time period of 16 yr. 154 samples were analyzed for δ13C and 119 samples for δD, increasing the previously published dataset for balloon borne samples by an order of magnitude, and more than doubling the total available stratospheric data (including aircraft samples published to date. The samples also cover a large range in mixing ratio from tropospheric values near 1800 ppb down to only 250 ppb, and the strong isotope fractionation processes accordingly increase the isotopic composition up to δ13C = −14‰ and δD = +190‰, the largest enrichments observed for atmospheric CH4 so far. When analyzing and comparing kinetic isotope effects (KIEs derived from single balloon profiles, it is necessary to take into account the residence time in the stratosphere in combination with the observed mixing ratio and isotope trends in the troposphere, and the range of isotope values covered by the individual profile. The isotopic composition of CH4 in the stratosphere is affected by both chemical and dynamical processes. This severely hampers interpretation of the data in terms of the relative fractions of the three important sink mechanisms (reaction with OH, O(1D and Cl. It is shown that a formal sink partitioning using the measured data severely underestimates the fraction removed by OH, which is likely due to the insensitivity of the measurements to the kinetic fractionation in the lower stratosphere. Full quantitative interpretation of the CH4 isotope data in terms of the three sink reactions requires a global model.
-
Influence of Aerosol Heating on the Stratospheric Transport of the Mt. Pinatubo Eruption
Aquila, Valentina; Oman, Luke D.; Stolarski, Richard S.
2011-01-01
On June 15th, 1991 the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo (15.1 deg. N, 120.3 Deg. E) in the Philippines injected about 20 Tg of sulfur dioxide in the stratosphere, which was transformed into sulfuric acid aerosol. The large perturbation of the background aerosol caused an increase in temperature in the lower stratosphere of 2-3 K. Even though stratospheric winds climatological]y tend to hinder the air mixing between the two hemispheres, observations have shown that a large part of the SO2 emitted by Mt. Pinatubo have been transported from the Northern to the Southern Hemisphere. We simulate the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo with the Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS) version 5 global climate model, coupled to the aerosol module GOCART and the stratospheric chemistry module StratChem, to investigate the influence of the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo on the stratospheric transport pattern. We perform two ensembles of simulations: the first ensemble consists of runs without coupling between aerosol and radiation. In these simulations the plume of aerosols is treated as a passive tracer and the atmosphere is unperturbed. In the second ensemble of simulations aerosols and radiation are coupled. We show that the set of runs with interactive aerosol produces a larger cross-equatorial transport of the Pinatubo cloud. In our simulations the local heating perturbation caused by the sudden injection of volcanic aerosol changes the pattern of the stratospheric winds causing more intrusion of air from the Northern into the Southern Hemisphere. Furthermore, we perform simulations changing the injection height of the cloud, and study the transport of the plume resulting from the different scenarios. Comparisons of model results with SAGE II and AVHRR satellite observations will be shown.
-
The Polar Stratosphere in a Changing Climate (POLSTRACC): Mission overview and first results
Oelhaf, Hermann; Sinnhuber, Björn-Martin; Woiwode, Wolfgang; Rapp, Markus; Dörnbrack, Andreas; Engel, Andreas; Bönisch, Harald
2016-04-01
The POLSTRACC mission aims at providing new scientific knowledge on the Arctic lowermost stratosphere and upper troposphere under the present load of halogens and state of climate variables. POLSTRACC employs the German High Altitude and LOng Range Research Aircraft (HALO) and is the only HALO mission dedicated to study the UTLS at high latitudes several years after the last intensive Arctic campaigns. The scientific scope of POLSTRACC is broadened by its combination with the SALSA (Seasonality of Air mass transport and origin in the Lowermost Stratosphere using the HALO Aircraft) and GW-LCYCLE (Gravity Wave Life Cycle Experiment, a BMBF/ROMIC project) missions, which address complementary scientific goals sharing the same HALO payload. POLSTRACC, SALSA and GW-LCYCLE offer the unique opportunity to study the bottom of the polar vortex and the high-latitude UTLS along with their impact on lower latitudes throughout an entire winter/spring cycle. The payload for the combined POLSTRACC, SALSA and GW-LCYCLE campaigns comprises an innovative combination of remote sensing techniques providing 2- and 3-D distributions of temperature and a large number of substances, and precise in-situ instruments measuring T, O3, H2O, tracers of different lifetimes and chemically active species at the aircraft level with high time-resolution. Drop sondes will add information about temperature, humidity and wind in the atmosphere underneath the aircraft. The POLSTRACC consortium includes national (KIT, Forschungszentrum Jülich, DLR, Universities of Frankfurt, Heidelberg, Mainz and Wuppertal; PTB) and international partners (e.g. NASA). The field campaign is divided into three phases for addressing (i) the early polar vortex and its wide-scale vicinity in December 2015 (from Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany), (ii) the mid-winter vortex from January to March 2016 (from Kiruna, Sweden), and (iii) the late dissipating vortex and its wide-scale vicinity in March 2016 (from Kiruna and
-
La, I.; Yum, S. S.; Yeom, J. M.; Gultepe, I.
2017-12-01
Since microphysical and dynamical processes of fog are not well-known and have non-linear relationships among processes that are related to fog formation, improving the accuracy of the fog forecasting/nowcasting system is challenging. For these reasons, understanding the fog mechanism is needed to develop the fog forecasting system. So, we focus on understanding fog-turbulence interactions and fog-gravity wave interactions. Many studies noted that turbulence plays important roles in fog. However, a discrepancy between arguments for the effect of turbulent mixing on fog formation exists. Several studies suggested that turbulent mixing suppresses fog formation. Some other studies reported that turbulent mixing contributes to fog formation. On the other hand, several quasi-periodic oscillations of temperature, visibility, and vertical velocity, which have period of 10-20 minutes, were observed to be related to gravity waves in fog; because gravity waves play significant dynamic roles in the atmosphere. Furthermore, a numerical study suggested that gravity waves, simulated near the top of the fog layer, may affect fog microphysics. Thus, we investigate the effects of turbulent mixing on fog formation and the influences of gravity waves on fog microphysics to understand fog structure in Pyeongchang. In these studies, we analyze the data that are obtained from doppler lidar and 3.5 m meteorological observation tower including 3D-ultrasonic anemometer, IR sensor, and fog monitor during ICE-POP (International Collaborative Experiments for Pyeongchang 2018 Olympic and Paralympic winter games) campaign. In these instruments, doppler lidar is a good instrument to observe the gravity waves near the fog top, while in situ measurements have small spatial coverage. The instruments are installed at the mountainous terrain of Pyeongchang, Korea. More details will be presented at the conference.
-
Ability of the CCSR-NIES atmospheric general circulation model in the stratosphere. Chapter 3
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sugata, S.
1997-01-01
A quantitative evaluation of climate change such as global warming is impossible without a high-quality numerical model which describes the dynamics of the climate system and the circulation of energy and materials. The Center for Climate Research - National Institute for Environmental Studies (CCSR-NIES) atmospheric general circulation model (hereafter, GCM for a general circulation model) has been developed to obtain such a high-quality model. The emphasis of the development has been laid on the troposphere and the lower stratosphere below about 30 km altitude. This is natural because human beings live on the Earth's surface and the condition of the lower atmosphere directly affects human life. However, the stratosphere and the upper atmosphere beyond it have recently been the focus even in investigations of climate change, because they are relevant to many issues which relate closely to tropospheric climate change, such as the ozone hole, material exchange between the stratosphere and the troposphere, and physical interaction between the stratosphere and troposphere. This study extended the region of the CCSR-NIES GCM to the lower mesosphere (about 70 km from the surface). This is our first attempt to investigate this GCM's climatology in the upper atmosphere, although some studies for QBO in the middle and lower stratosphere had been done with the GCM
-
Goncharenko, L. P.; Panasenko, S.; Aksonova, K.; Erickson, P. J.; Domnin, I. F.
2016-12-01
Travelling ionospheric disturbances (TIDs) play a key role in the coupling of different ionospheric regions through momentum an energy transfer. They are thought to be mostly associated with atmospheric gravity waves and are known to strongly affect radio propagation conditions. The incoherent scatter (IS) method enables TIDs detection in such ionospheric parameters as electron density, ion and electron temperatures, and plasma velocity along radar beam, thus providing critical information needed to examine different hypothesis about association of TIDs with their sources. In 2016, several joint measuring campaigns were conducted using Kharkiv (49.6 N, 36.4 E) and Millstone Hill (42.6 N, 288.5 E) IS radars. These campaigns covered the periods of sudden stratospheric warnings (SSW) in February, vernal equinox and summer solstice. For consistency, the data acquired by radars were processed using the same data analysis methods. The results obtained show the TIDs to be detected throughout all observation intervals in February measurements. The differences found in the behavior of TIDs over Kharkiv and Millstone Hill sites may be partially explained by variations in stratospheric wind velocity vectors during SSW period. As for March equinox and June solstice, the prevailing TIDs are observed near solar terminators. Their periods vary mostly in the range of 40 - 80 minutes, relative amplitudes are about 0.05 - 0.3 of the background electron density, and the maximum values are observed at the heights of 200 - 250 km. Systematic long-term observations of wave processes in the ionosphere with multiple IS facilities can reveal interhemispheric variability in TID parameters, give better understanding the mechanisms of TID generation and propagation, and improve regional and global ionospheric models.
-
Exposing Microorganisms in the Stratosphere for Planetary Protection
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — Earth’s stratosphere is similar to the surface of Mars: rarified air which is dry, cold, and irradiated. E-MIST is a balloon payload that has 4 independently...
-
A stratospheric aerosol increase
Rosen, J. M.; Hofmann, D. J.
1980-01-01
Large disturbances were noted in the stratospheric aerosol content in the midlatitude Northern Hemisphere commencing about 7 months after the eruption of La Soufriere and less than 1 month after the eruption of Sierra Negra. The aerosol was characterized by a very steep size distribution in the 0.15 to 0.25 micron radius range and contained a volatile component. Measurements near the equator and at the South Pole indicate that the disturbance was widespread. These observations were made before the May 18 eruption of Mt. St. Helens.
-
Stratospheric ethane on Neptune - Comparison of groundbased and Voyager IRIS retrievals
Kostiuk, Theodor; Romani, Paul; Espenak, Fred; Bezard, Bruno
1992-01-01
Near-simultaneous ground and spacecraft measurements of 12-micron ethane emission spectra during the Voyager encounter with Neptune have furnished bases for the determination of stratospheric ethane abundance and the testing and constraining of Neptune methane-photochemistry models. The ethane retrievals were sensitive to the thermal profile used. Contribution functions for warm thermal profiles peaked at higher altitudes, as expected, with the heterodyne functions covering lower-pressure regions. Both constant- and nonconstant-with-height profiles remain candidate distributions for Neptune's stratospheric ethane.
-
Stratospheric cooling and polar ozone loss due to H2 emissions of a global hydrogen economy
Feck, T.; Grooß, J.-U.; Riese, M.; Vogel, B.
2009-04-01
"Green" hydrogen is seen as a major element of the future energy supply to reduce greenhouse gas emissions substantially. However, due to the possible interactions of hydrogen (H2) with other atmospheric constituents there is a need to analyse the implications of additional atmospheric H2 that could result from hydrogen leakage of a global hydrogen infrastructure. Emissions of molecular H2 can occur along the whole hydrogen process chain which increase the tropospheric H2 burden. Across the tropical tropopause H2 reaches the stratosphere where it is oxidised and forms water vapour (H2O). This causes increased IR-emissions into space and hence a cooling of the stratosphere. Both effects, the increase of stratospheric H2O and the cooling, enhances the potential of chlorine activation on liquid sulfate aerosol and polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs), which increase polar ozone destruction. Hence a global hydrogen economy could provoke polar ozone loss and could lead to a substantial delay of the current projected recovery of the stratospheric ozone layer. Our investigations show that even if 90% of the current global fossil primary energy input could be replaced by hydrogen and approximately 9.5% of the product gas would leak to the atmosphere, the ozone loss would be increased between 15 to 26 Dobson Units (DU) if the stratospheric CFC loading would retain unchanged. A consistency check of the used approximation methods with the Chemical Lagrangian Model of the Stratosphere (CLaMS) shows that this additional ozone loss can probably be treated as an upper limit. Towards more realistic future H2 leakage rate assumptions (< 3%) the additional ozone loss would be rather small (? 10 DU). However, in all cases the full damage would only occur if stratospheric CFC-levels would retain unchanged. Due to the CFC-prohibition as a result of the Montreal Protocol the forecasts suggest a decline of the stratospheric CFC loading about 50% until 2050. In this case our calculations
-
Banda, Narcissa; Krol, Maarten; van Noije, Twan; van Weele, Michiel; Williams, Jason E.; Sager, Philippe Le; Niemeier, Ulrike; Thomason, Larry; Röckmann, Thomas
2015-01-01
The eruption of Mount Pinatubo in 1991 injected a large amount of SO2 into the stratosphere, which formed sulfate aerosols. Increased scattering and absorption of UV radiation by the enhanced stratospheric SO2 and aerosols decreased the amount of UV radiation reaching the troposphere, causing
-
Pal, S.; Hobara, Y.; Chakrabarti, S. K.; Schnoor, P. W.
2017-07-01
This paper presents effects of the major sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) event of 2009 on the subionospheric very low frequency/low frequency (VLF/LF) radio signals propagating in the Earth-ionosphere waveguide. Signal amplitudes from four transmitters received by VLF/LF radio networks of Germany and Japan corresponding to the major SSW event are investigated for possible anomalies and atmospheric influence on the high- to middle-latitude ionosphere. Significant anomalous increase or decrease of nighttime and daytime amplitudes of VLF/LF signals by ˜3-5 dB during the SSW event have been found for all propagation paths associated with stratospheric temperature rise at 10 hPa level. Increase or decrease in VLF/LF amplitudes during daytime and nighttime is actually due to the modification of the lower ionospheric boundary conditions in terms of electron density and electron-neutral collision frequency profiles and associated modal interference effects between the different propagating waveguide modes during the SSW period. TIMED/SABER mission data are also used to investigate the upper mesospheric conditions over the VLF/LF propagation path during the same time period. We observe a decrease in neutral temperature and an increase in pressure at the height of 75-80 km around the peak time of the event. VLF/LF anomalies are correlated and in phase with the stratospheric temperature and mesospheric pressure variation, while minimum of mesospheric cooling shows a 2-3 day delay with maximum VLF/LF anomalies. Simulations of VLF/LF diurnal variation are performed using the well-known Long Wave Propagating Capability (LWPC) code within the Earth-ionosphere waveguide to explain the VLF/LF anomalies qualitatively.
-
Contrasting Effects of Central Pacific and Eastern Pacific El Nino on Stratospheric Water Vapor
Garfinkel, Chaim I.; Hurwitz, Margaret M.; Oman, Luke D.; Waugh, Darryn W.
2013-01-01
Targeted experiments with a comprehensive chemistry-climate model are used to demonstrate that seasonality and the location of the peak warming of sea surface temperatures dictate the response of stratospheric water vapor to El Nino. In spring, El Nino events in which sea surface temperature anomalies peak in the eastern Pacific lead to a warming at the tropopause above the warm pool region, and subsequently to more stratospheric water vapor (consistent with previous work). However, in fall and in early winter, and also during El Nino events in which the sea surface temperature anomaly is found mainly in the central Pacific, the response is qualitatively different: temperature changes in the warm pool region are nonuniform and less water vapor enters the stratosphere. The difference in water vapor in the lower stratosphere between the two variants of El Nino approaches 0.3 ppmv, while the difference between the winter and spring responses exceeds 0.5 ppmv.
-
Measurements of stratospheric Pinatubo aerosol extinction profiles by a Raman lidar
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Abo, Makoto; Nagasawa, Chikao.
1992-01-01
The Raman lidar has been used for remote measurements of water vapor, ozone and atmospheric temperature in the lower troposphere because the Raman cross section is three orders smaller than the Rayleigh cross section. The authors estimated the extinction coefficients of the Pinatubo volcanic aerosol in the stratosphere using a Raman lidar. If the precise aerosol extinction coefficients are derived, the backscatter coefficient of a Mie scattering lidar will be more accurately estimated. The Raman lidar has performed to measure density profiles of some species using Raman scattering. Here the authors used a frequency-doubled Nd:YAG laser for transmitter and received nitrogen vibrational Q-branch Raman scattering signal. Ansmann et al. (1990) derived tropospherical aerosol extinction profiles with a Raman lidar. The authors think that this method can apply to dense stratospheric aerosols such as Pinatubo volcanic aerosols. As dense aerosols are now accumulated in the stratosphere by Pinatubo volcanic eruption, the error of Ramen lidar signal regarding the fluctuation of air density can be ignored
-
Impact and mitigation of stratospheric ozone depletion by chemical rockets
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mcdonald, A.J.
1992-03-01
The American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) conducted a workshop in conjunction with the 1991 AIAA Joint Propulsion Conference in Sacramento, California, to assess the impact of chemical rocket propulsion on the environment. The workshop included recognized experts from the fields of atmospheric physics and chemistry, solid rocket propulsion, liquid rocket propulsion, government, and environmental agencies, and representatives from several responsible environmental organizations. The conclusion from this workshop relative to stratospheric ozone depletion was that neither solid nor liquid rocket launchers have a significant impact on stratospheric ozone depletion, and that there is no real significant difference between the two
-
Haase, S.; Matthes, K. B.
2017-12-01
Changes in stratospheric ozone can trigger tropospheric circulation changes. In the Southern hemisphere (SH), the observed shift of the Southern Annular Mode was attributed to the observed trend in lower stratospheric ozone. In the Northern Hemisphere (NH), a recent study showed that extremely low stratospheric ozone conditions during spring produce robust anomalies in the troposphere (zonal wind, temperature and precipitation). This could only be reproduced in a coupled chemistry climate model indicating that chemical-dynamical feedbacks are also important on the NH. To further investigate the importance of interactive chemistry for surface climate, we conducted a set of experiments using NCAR's Community Earth System Model (CESM1) with the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM) as the atmosphere component. WACCM contains a fully interactive stratospheric chemistry module in its standard configuration. It also allows for an alternative configuration, referred to as SC-WACCM, in which the chemistry (O3, NO, O, O2, CO2 and chemical and shortwave heating rates) is specified as a 2D field in the radiation code. A comparison of the interactive vs. the specified chemistry version enables us to evaluate the relative importance of interactive chemistry by systematically inhibiting the feedbacks between chemistry and dynamics. To diminish the effect of temporal interpolation when prescribing ozone, we use daily resolved zonal mean ozone fields for the specified chemistry run. Here, we investigate the differences in stratosphere-troposphere coupling between the interactive and specified chemistry simulations for the mainly chemically driven SH as well as for the mainly dynamically driven NH. We will especially consider years that are characterized by extremely low stratospheric ozone on the one hand and by large dynamical disturbances, i.e. Sudden Stratospheric Warmings, on the other hand.
-
Davis, Sean M.; Hegglin, Michaela I.; Fujiwara, Masatomo; Dragani, Rossana; Harada, Yayoi; Kobayashi, Chiaki; Long, Craig; Manney, Gloria L.; Nash, Eric R.; Potter, Gerald L.; Tegtmeier, Susann; Wang, Tao; Wargan, Krzysztof; Wright, Jonathon S.
2017-10-01
Reanalysis data sets are widely used to understand atmospheric processes and past variability, and are often used to stand in as "observations" for comparisons with climate model output. Because of the central role of water vapor (WV) and ozone (O3) in climate change, it is important to understand how accurately and consistently these species are represented in existing global reanalyses. In this paper, we present the results of WV and O3 intercomparisons that have been performed as part of the SPARC (Stratosphere-troposphere Processes and their Role in Climate) Reanalysis Intercomparison Project (S-RIP). The comparisons cover a range of timescales and evaluate both inter-reanalysis and observation-reanalysis differences. We also provide a systematic documentation of the treatment of WV and O3 in current reanalyses to aid future research and guide the interpretation of differences amongst reanalysis fields.The assimilation of total column ozone (TCO) observations in newer reanalyses results in realistic representations of TCO in reanalyses except when data coverage is lacking, such as during polar night. The vertical distribution of ozone is also relatively well represented in the stratosphere in reanalyses, particularly given the relatively weak constraints on ozone vertical structure provided by most assimilated observations and the simplistic representations of ozone photochemical processes in most of the reanalysis forecast models. However, significant biases in the vertical distribution of ozone are found in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere in all reanalyses.In contrast to O3, reanalysis estimates of stratospheric WV are not directly constrained by assimilated data. Observations of atmospheric humidity are typically used only in the troposphere, below a specified vertical level at or near the tropopause. The fidelity of reanalysis stratospheric WV products is therefore mainly dependent on the reanalyses' representation of the physical drivers that
-
Satellite observations of middle atmosphere–thermosphere vertical coupling by gravity waves
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Q. T. Trinh
2018-03-01
Full Text Available Atmospheric gravity waves (GWs are essential for the dynamics of the middle atmosphere. Recent studies have shown that these waves are also important for the thermosphere/ionosphere (T/I system. Via vertical coupling, GWs can significantly influence the mean state of the T/I system. However, the penetration of GWs into the T/I system is not fully understood in modeling as well as observations. In the current study, we analyze the correlation between GW momentum fluxes observed in the middle atmosphere (30–90 km and GW-induced perturbations in the T/I. In the middle atmosphere, GW momentum fluxes are derived from temperature observations of the Sounding of the Atmosphere using Broadband Emission Radiometry (SABER satellite instrument. In the T/I, GW-induced perturbations are derived from neutral density measured by instruments on the Gravity field and Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE and CHAllenging Minisatellite Payload (CHAMP satellites. We find generally positive correlations between horizontal distributions at low altitudes (i.e., below 90 km and horizontal distributions of GW-induced density fluctuations in the T/I (at 200 km and above. Two coupling mechanisms are likely responsible for these positive correlations: (1 fast GWs generated in the troposphere and lower stratosphere can propagate directly to the T/I and (2 primary GWs with their origins in the lower atmosphere dissipate while propagating upwards and generate secondary GWs, which then penetrate up to the T/I and maintain the spatial patterns of GW distributions in the lower atmosphere. The mountain-wave related hotspot over the Andes and Antarctic Peninsula is found clearly in observations of all instruments used in our analysis. Latitude–longitude variations in the summer midlatitudes are also found in observations of all instruments. These variations and strong positive correlations in the summer midlatitudes suggest that GWs with origins related to convection also
-
Satellite observations of middle atmosphere-thermosphere vertical coupling by gravity waves
Trinh, Quang Thai; Ern, Manfred; Doornbos, Eelco; Preusse, Peter; Riese, Martin
2018-03-01
Atmospheric gravity waves (GWs) are essential for the dynamics of the middle atmosphere. Recent studies have shown that these waves are also important for the thermosphere/ionosphere (T/I) system. Via vertical coupling, GWs can significantly influence the mean state of the T/I system. However, the penetration of GWs into the T/I system is not fully understood in modeling as well as observations. In the current study, we analyze the correlation between GW momentum fluxes observed in the middle atmosphere (30-90 km) and GW-induced perturbations in the T/I. In the middle atmosphere, GW momentum fluxes are derived from temperature observations of the Sounding of the Atmosphere using Broadband Emission Radiometry (SABER) satellite instrument. In the T/I, GW-induced perturbations are derived from neutral density measured by instruments on the Gravity field and Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE) and CHAllenging Minisatellite Payload (CHAMP) satellites. We find generally positive correlations between horizontal distributions at low altitudes (i.e., below 90 km) and horizontal distributions of GW-induced density fluctuations in the T/I (at 200 km and above). Two coupling mechanisms are likely responsible for these positive correlations: (1) fast GWs generated in the troposphere and lower stratosphere can propagate directly to the T/I and (2) primary GWs with their origins in the lower atmosphere dissipate while propagating upwards and generate secondary GWs, which then penetrate up to the T/I and maintain the spatial patterns of GW distributions in the lower atmosphere. The mountain-wave related hotspot over the Andes and Antarctic Peninsula is found clearly in observations of all instruments used in our analysis. Latitude-longitude variations in the summer midlatitudes are also found in observations of all instruments. These variations and strong positive correlations in the summer midlatitudes suggest that GWs with origins related to convection also propagate up to the T
-
Bândə, Narcisa; Krol, Maarten; Noije, Van Twan; Weele, Van Michiel; Williams, Jason E.; Sager, Philippe Le; Niemeier, Ulrike; Thomason, Larry; Röckmann, Thomas
2015-01-01
The eruption of Mount Pinatubo in 1991 injected a large amount of SO2 into the stratosphere, which formed sulfate aerosols. Increased scattering and absorption of UV radiation by the enhanced stratospheric SO2 and aerosols decreased the amount of UV radiation reaching the
-
A New Formulation of Equivalent Effective Stratospheric Chlorine (EESC)
Newman, P. A.; Daniel, J. S.; Waugh, D. W.; Nash, E. R.
2007-01-01
Equivalent effective stratospheric chlorine (EESC) is a convenient parameter to quantify the effects of halogens (chlorine and bromine) on ozone depletion in the stratosphere. We show and discuss a new formulation of EESC that now includes the effects of age-of-air dependent fractional release values and an age-of-air spectrum. This new formulation provides quantitative estimates of EESC that can be directly related to inorganic chlorine and bromine throughout the stratosphere. Using this EESC formulation, we estimate that human-produced ozone depleting substances will recover to 1980 levels in 2041 in the midlatitudes, and 2067 over Antarctica. These recovery dates are based upon the assumption that the international agreements for regulating ozone-depleting substances are adhered to. In addition to recovery dates, we also estimate the uncertainties in the estimated time of recovery. The midlatitude recovery of 2041 has a 95% confidence uncertainty from 2028 to 2049, while the 2067 Antarctic recovery has a 95% confidence uncertainty from 2056 to 2078. The principal uncertainties are from the estimated mean age-of-air, and the assumption that the mean age-of-air and fractional release values are time independent. Using other model estimates of age decrease due to climate change, we estimate that midlatitude recovery may be accelerated from 2041 to 2031.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Froidevaux, L.; Waters, J. W.; Read, W. G.; Connell, P. S.; Kinnison, D. E.; Russell, J. M. III
2000-01-01
Remote sensing of chlorine monoxide (ClO) by the Microwave Limb Sounder experiment aboard the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS) has provided global measurements of variations in stratospheric free chlorine for 1991-1997. Linear trends were obtained from a multiple regression analysis of this data set at low latitudes and midlatitudes. ClO increases in the upper stratosphere (2 hPa) are significantly larger than expected from trends in chlorine source gases alone. Much of the upper stratospheric ClO variability can be explained by changes in CH 4 , as measured by the UARS Halogen Occultation Experiment. Decreasing ClO in the lower stratosphere is consistent with a relaxation from a chemically perturbed state attributed to the 1991 Mt. Pinatubo eruption. (c) 2000 American Geophysical Union
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Daniels, R.C. [ed.
1995-09-22
Surface measurements of solar irradiance of the atmosphere were made by a multipurpose computer-controlled scanning photometer at the Rattlesnake Mountain Observatory. The observatory is located at 46.4{degrees}N, 119.6{degrees}W at an elevation of 1088 m above mean sea level. The photometer measures the attenuation of direct solar radiation for different wavelengths using 12 filters. Five of these filters (ie., at 428 nm, 486 nm, 535 nm, 785 nm, and 1010 nm, with respective half-power widths of 2, 2, 3, 18, and 28 nm) are suitable for monitoring variations in the total optical depth of the atmosphere. Total optical depths for the five wavelength bands were derived from solar irradiance measurements taken at the observatory from August 5, 1979, to September 2, 1994; these total optical depth data are distributed with this numeric data package (NDP). To determine the contribution of atmospheric aerosols to the total optical depths, the effects of Rayleigh scattering and ozone absorption were subtracted (other molecular scattering was minimal for the five filters) to obtain total column aerosol optical depths. The total aerosol optical depths were further decomposed into tropospheric and stratospheric components by calculating a robustly smoothed mean background optical depth (tropospheric component) for each wavelength using data obtained during periods of low stratospheric aerosol loading. By subtracting the smoothed background tropospheric aerosol optical depths from the total aerosol optical depths, residual aerosol optical depths were obtained. These residuals are good estimates of the stratospheric aerosol optical depth at each wavelength and may be used to monitor the long-term effects of volcanic eruptions on the atmosphere. These data are available as an NDP from the Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC), and the NDP consists of this document and a set of computerized data files.
-
A global space-based stratospheric aerosol climatology: 1979-2016
Thomason, Larry W.; Ernest, Nicholas; Millán, Luis; Rieger, Landon; Bourassa, Adam; Vernier, Jean-Paul; Manney, Gloria; Luo, Beiping; Arfeuille, Florian; Peter, Thomas
2018-03-01
We describe the construction of a continuous 38-year record of stratospheric aerosol optical properties. The Global Space-based Stratospheric Aerosol Climatology, or GloSSAC, provided the input data to the construction of the Climate Model Intercomparison Project stratospheric aerosol forcing data set (1979-2014) and we have extended it through 2016 following an identical process. GloSSAC focuses on the Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE) series of instruments through mid-2005, and on the Optical Spectrograph and InfraRed Imager System (OSIRIS) and the Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation (CALIPSO) data thereafter. We also use data from other space instruments and from ground-based, air, and balloon borne instruments to fill in key gaps in the data set. The end result is a global and gap-free data set focused on aerosol extinction coefficient at 525 and 1020 nm and other parameters on an "as available" basis. For the primary data sets, we developed a new method for filling the post-Pinatubo eruption data gap for 1991-1993 based on data from the Cryogenic Limb Array Etalon Spectrometer. In addition, we developed a new method for populating wintertime high latitudes during the SAGE period employing a latitude-equivalent latitude conversion process that greatly improves the depiction of aerosol at high latitudes compared to earlier similar efforts. We report data in the troposphere only when and where it is available. This is primarily during the SAGE II period except for the most enhanced part of the Pinatubo period. It is likely that the upper troposphere during Pinatubo was greatly enhanced over non-volcanic periods and that domain remains substantially under-characterized. We note that aerosol levels during the OSIRIS/CALIPSO period in the lower stratosphere at mid- and high latitudes is routinely higher than what we observed during the SAGE II period. While this period had nearly continuous low-level volcanic activity, it
-
A global analysis of the ozone deficit in the upper stratosphere and lower mesosphere
Eluszkiewicz, Janusz; Allen, Mark
1993-01-01
The global measurements of temperature, ozone, water vapor, and nitrogen dioxide acquired by the Limb Infrared Monitor of the Stratosphere (LIMS), supplemented by a precomputed distribution of chlorine monoxide, are used to test the balance between odd oxygen production and loss in the upper stratosphere and lower mesosphere. An efficient photochemical equilibrium model, whose validity is ascertained by comparison with the results from a fully time-dependent one-dimensional model at selected latitudes, is used in the calculations. The computed ozone abundances are systematically lower than observations for May 1-7, 1979, which suggests, contrary to the conclusions of other recent studies, a real problem in model simulations of stratospheric ozone.
-
Laboratory chemistry and stratospheric clouds
Molina, Mario J.
1989-01-01
Results are presented from laboratory experiments on the chemistry of ice particles to study the role of HCl and ClONO2 from CFCs in stratospheric ozone depletion over Antarctica. It is found that gaseous HCl is scavenged with high efficiency by the ice and the gas phase chlorine nitrate may react with the HCL-containing ice to produce Cl2. Also, consideration is given ot the behavior of solid nitric acid trihydrate and sulfuric acid aerosols.
-
Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment III on the International Space Station (SAGE III/ISS)
Gasbarre, Joseph; Walker, Richard; Cisewski, Michael; Zawodny, Joseph; Cheek, Dianne; Thornton, Brooke
2015-01-01
The Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment III on the International Space Station (SAGE III/ISS) mission will extend the SAGE data record from the ideal vantage point of the International Space Station (ISS). The ISS orbital inclination is ideal for SAGE measurements providing coverage between 70 deg north and 70 deg south latitude. The SAGE data record includes an extensively validated data set including aerosol optical depth data dating to the Stratospheric Aerosol Measurement (SAM) experiments in 1975 and 1978 and stratospheric ozone profile data dating to the Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE) in 1979. These and subsequent data records, notably from the SAGE II experiment launched on the Earth Radiation Budget Satellite in 1984 and the SAGE III experiment launched on the Russian Meteor-3M satellite in 2001, have supported a robust, long-term assessment of key atmospheric constituents. These scientific measurements provide the basis for the analysis of five of the nine critical constituents (aerosols, ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), water vapor (H2O), and air density using O2) identified in the U.S. National Plan for Stratospheric Monitoring. SAGE III on ISS was originally scheduled to fly on the ISS in the same timeframe as the Meteor-3M mission, but was postponed due to delays in ISS construction. The project was re-established in 2009.
-
Stratospheric temperatures and tracer transport in a nudged 4-year middle atmosphere GCM simulation
van Aalst, M. K.; Lelieveld, J.; Steil, B.; Brühl, C.; Jöckel, P.; Giorgetta, M. A.; Roelofs, G.-J.
2005-02-01
We have performed a 4-year simulation with the Middle Atmosphere General Circulation Model MAECHAM5/MESSy, while slightly nudging the model's meteorology in the free troposphere (below 113 hPa) towards ECMWF analyses. We show that the nudging 5 technique, which leaves the middle atmosphere almost entirely free, enables comparisons with synoptic observations. The model successfully reproduces many specific features of the interannual variability, including details of the Antarctic vortex structure. In the Arctic, the model captures general features of the interannual variability, but falls short in reproducing the timing of sudden stratospheric warmings. A 10 detailed comparison of the nudged model simulations with ECMWF data shows that the model simulates realistic stratospheric temperature distributions and variabilities, including the temperature minima in the Antarctic vortex. Some small (a few K) model biases were also identified, including a summer cold bias at both poles, and a general cold bias in the lower stratosphere, most pronounced in midlatitudes. A comparison 15 of tracer distributions with HALOE observations shows that the model successfully reproduces specific aspects of the instantaneous circulation. The main tracer transport deficiencies occur in the polar lowermost stratosphere. These are related to the tropopause altitude as well as the tracer advection scheme and model resolution. The additional nudging of equatorial zonal winds, forcing the quasi-biennial oscillation, sig20 nificantly improves stratospheric temperatures and tracer distributions.
-
Satellite studies of the stratospheric aerosol
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McCormick, M.P.; Hamill, P.; Pepin, T.J.; Chu, W.P.; Swissler, T.J.; McMaster, L.R.
1979-01-01
The potential climatological and environmental importance of the stratospheric aerosol layer has prompted great interest in measuring the properties of this aerosol. In this paper we report on two recently deployed NASA satellite systems (SAM II and SAGE) that are monitoring the stratospheric aerosol. The satellite orbits are such that nearly global coverage is obtained. The instruments mounted in the spacecraft are sun photometers that measure solar intensity at specific wavelengths as it is moderated by atmospheric particulates and gases during each sunrise and sunset encountered by the satellites. The data obtained are ''inverted'' to yield vertical aerosol and gaseous (primarily ozone) extinction profiles with 1 km vertical resolution. Thus, latitudinal, longitudinal, and temporal variations in the aerosol layer can be evaluated. The satellite systems are being validated by a series of ground truth experiments using airborne and ground lidar, balloon-borne dustsondes, aircraft-mounted impactors, and other correlative sensors. We describe the SAM II and SAGE satellite systems, instrument characteristics, and mode of operation; outline the methodology of the experiments; and describe the ground truth experiments. We present preliminary results from these measurements
-
Influence of vertically and obliquely propagating gravity waves on the polar summer mesosphere
Thurairajah, B.; Siskind, D. E.; Bailey, S. M.
2017-12-01
Polar Mesospheric Clouds (PMCs) are sensitive to changes in temperature of the cold polar summer mesosphere, which in turn are modulated by gravity waves (GWs). In this study we investigate the link between PMCs and GWs that propagate both vertically (i.e. wave propagation is directly above the source region) and obliquely (lateral or non-vertical propagation upward but away from the source region). Several observational studies have analyzed the link between PMCs and vertically propagating GWs and have reported both positive and negative correlations. Moreover, while modelling studies have noted the possibility of oblique propagation of GWs from the low-latitude stratosphere to the high-latitude mesosphere, observational studies of the influence of these waves on the polar summer mesosphere are sparse. We present a comprehensive analysis of the influence of vertically and obliquely propagating GWs on the northern hemisphere (NH) polar summer mesosphere using data from 8 PMC seasons. Temperature data from the SOFIE experiment on the AIM satellite and SABER instrument on the TIMED satellite are used to derive GW parameters. SOFIE PMC data in terms of Ice Water Content (IWC) are used to quantify the changes in the polar summer mesosphere. At high latitudes, preliminary analysis of vertically propagating waves indicate a weak but positive correlation between GWs at 50 km and GWs at the PMC altitude of 84 km. Overall there is a negative correlation between GWs at 50 km and IWC and a positive correlation between GWs at 84 km and IWC. These results and the presence of a slanted structure (slanted from the low-latitude stratosphere to the high-latitude mesosphere) in GW momentum flux suggest the possibility of a significant influence of obliquely propagating GWs on the polar summer mesosphere
-
Development of the Multi-Angle Stratospheric Aerosol Radiometer (MASTAR) Instrument
DeLand, M. T.; Colarco, P. R.; Kowalewski, M. G.; Gorkavyi, N.; Ramos-Izquierdo, L.
2017-12-01
Aerosol particles in the stratosphere ( 15-25 km altitude), both produced naturally and perturbed by volcanic eruptions and anthropogenic emissions, continue to be a source of significant uncertainty in the Earth's energy budget. Stratospheric aerosols can offset some of the warming effects caused by greenhouse gases. These aerosols are currently monitored using measurements from the Ozone Mapping and Profiling Suite (OMPS) Limb Profiler (LP) instrument on the Suomi NPP satellite. In order to improve the sensitivity and spatial coverage of these aerosol data, we are developing an aerosol-focused compact version of the OMPS LP sensor called Multi-Angle Stratospheric Aerosol Radiometer (MASTAR) to fly on a 3U Cubesat satellite, using a NASA Instrument Incubator Program (IIP) grant. This instrument will make limb viewing measurements of the atmosphere in multiple directions simultaneously, and uses only a few selected wavelengths to reduce size and cost. An initial prototype version has been constructed using NASA GSFC internal funding and tested in the laboratory. Current design work is targeted towards a preliminary field test in Spring 2018. We will discuss the scientific benefits of MASTAR and the status of the project.
-
Forecast, observation and modelling of a deep stratospheric intrusion event over Europe
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Zanis
2003-01-01
Full Text Available A wide range of measurements was carried out in central and southeastern Europe within the framework of the EU project STACCATO (Influence of Stratosphere-Troposphere Exchange in a Changing Climate on Atmospheric Transport and Oxidation Capacity with the principle goal to create a comprehensive data set on stratospheric air intrusions into the troposphere along a rather frequently observed pathway over central Europe from the North Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. The measurements were based on predictions by suitable quasi-operational trajectory calculations using ECMWF forecast data. A predicted deep Stratosphere to Troposphere Transport (STT event, encountered during the STACCATO period on 20-21 June 2001, was followed by the measurements network almost from its inception. Observations provide evidence that the intrusion affected large parts of central and southeastern Europe. Especially, the ozone lidar observations on 20-21 June 2001 at Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany captured the evolution of two marked tongues of high ozone with the first one descending to nearly 2 km, thus providing an excellent data set for model intercomparisons and validation. In addition, for the first time to our knowledge concurrent surface measurements of the cosmogenic radionuclides 10Be and 7Be and their ratio 10Be/7Be are presented together as stratospheric tracers in a case study of a stratospheric intrusion. The ozone tracer columns calculated with the FLEXPART model were found to be in good agreement with water vapour satellite images, capturing the evolution of the observed dry streamers of stratospheric origin. Furthermore, the time-height cross section of ozone tracer simulated with FLEXPART over Garmisch-Partenkirchen captures many details of the evolution of the two observed high-ozone filaments measured with the IFU lidar, thus demonstrating the considerable progress in model simulations. Finally, the modelled ozone (operationally available since October
-
Solar variations and their influence on trends in upper stratospheric ozone and temperature
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wuebbles, D.J.; Kinnison, D.E.; Lean, J.L.
1990-10-01
Over the past decade, knowledge of the magnitude and temporal structure of the variations in the sun's ultraviolet irradiance has increased steadily. A number of theoretical modeling studies have shown that changes in the solar ultraviolet flux during the 11-year solar cycle can have a significant effect on stratospheric ozone concentrations. With the exception of Brasseur et al., who examined a very broad range of solar flux variations, all of these studies assumed much larger changes in the ultraviolet flux than measurements now indicate. These studies either calculated the steady-state effect at solar maximum and solar minimum or assumed sinusoidal variations in the solar flux changes with time. It is now possible to narrow the uncertainty range of the expected effects on upper stratospheric ozone and temperature resulting from the 11-year solar cycle. A more accurate representation of the solar flux changes with time is used in this analysis, as compared to previous published studies. This study also evaluates the relative roles of solar flux variations and increasing concentrations of long-lived trace gases in determining the observed trends in upper stratospheric ozone and temperature. The LLNL two-dimensional chemical-radiative-transport model of the global atmosphere is used to evaluate the combined effects on the stratosphere from changes in solar ultraviolet irradiances and trace gas concentrations over the last several decades. Derived trends in upper stratospheric ozone concentrations and temperature are then compared with available analyses of ground-based and satellite measurements over this time period
-
The extrapolar SWIFT-model: Fast stratospheric ozone chemistry for global climate models
Kreyling, Daniel
2016-01-01
The goal of this PhD-thesis was the development of a fast yet accurate chemistry scheme for an interactive calculation of the extrapolar stratospheric ozone layer. The SWIFT-model is mainly intended for use in Global Climate Models (GCMs). For computing-time reasons GCMs often do not employ full stratospheric chemistry modules, but use prescribed ozone instead. This method does not consider the interaction between atmospheric dynamics and the ozone layer and can neither resolve the inter-annu...
-
Eswaraiah, S.; Kim, Yong Ha; Hong, Junseok; Kim, Jeong-Han; Ratnam, M. Venkat; Chandran, A.; Rao, S. V. B.; Riggin, Dennis
2016-03-01
A minor stratospheric sudden warming (SSW) event was noticed in the southern hemisphere (SH) during September (day 259) 2010 along with two episodic warmings in early August (day 212) and late October (day 300) 2010. Among the three warming events, the signature of mesosphere response was detected only for the September event in the mesospheric wind dataset from both meteor radar and MF radar located at King Sejong Station (62°S, 59°W) and Rothera (68°S, 68°W), Antarctica, respectively. The zonal winds in the mesosphere reversed approximately a week before the September SSW event, as has been observed in the 2002 major SSW. Signatures of mesospheric cooling (MC) in association with stratospheric warmings are found in temperatures measured by the Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS). Simulations of specified dynamics version of Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (SD-WACCM) are able to reproduce these observed features. The mesospheric wind field was found to differ significantly from that of normal years probably due to enhanced planetary wave (PW) activity before the SSW. From the wavelet analysis of wind data of both stations, we find that strong 14-16 day PWs prevailed prior to the SSW and disappeared suddenly after the SSW in the mesosphere. Our study provides evidence that minor SSWs in SH can result in significant effects on the mesospheric dynamics as in the northern hemisphere.
-
Waxler, R.; Talmadge, C. L.; Blom, P.
2009-12-01
Theory predicts that for ground to ground infrasound propagation along paths which travel downwind, relative to the stratospheric jet, there is a shadow zone which ends about 200 km from the source where the first return from the stratosphere strikes the earth. With increasing range the single stratospheric arrival splits into two distinct arrivals, a fast arrival with the trace velocity of the effective sound speed at the stratopause, and a slower arrival with the trace velocity of the sound speed on the ground. To test the theory we have deployed eight infrasound arrays along an approximate line directly west of the site of the US Navy's Trident Missile rocket motor eliminations. The arrays were deployed during the summer of 2009 spaced roughly 10 km apart along a segment from 180 to 260 km west of the site. Comparisons between the theoretical predictions and the received data will be presented.
-
Mechanism and Kinetics of the Formation and Transport of Aerosol Particles in the Lower Stratosphere
Aloyan, A. E.; Ermakov, A. N.; Arutyunyan, V. O.
2018-03-01
Field and laboratory observation data on aerosol particles in the lower stratosphere are considered. The microphysics of their formation, mechanisms of heterogeneous chemical reactions involving reservoir gases (e.g., HCl, ClONO2, etc.) and their kinetic characteristics are analyzed. A new model of global transport of gaseous and aerosol admixtures in the lower stratosphere is described. The preliminary results from a numerical simulation of the formation of sulfate particles of the Junge layer and particles of polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs, types Ia, Ib, and II) are presented, and their effect on the gas and aerosol composition is analyzed.
-
Sridharan, S.
2017-10-01
The Global Positioning System deduced total electron content (TEC) data at 15°N (geomagnetic), which is the crest region of equatorial ionization anomaly, are used to study tidal variabilities during the 2013 sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) event. The results from space-time spectral analysis reveal that the amplitudes of migrating diurnal (DW1) and semidiurnal (SW2) tides are larger than those of nonmigrating tides. After the SSW onset, the amplitudes of DW1, SW2, SW1, and DS0 increase. Moreover, they show 16 day variations similar to the periodicity of the high-latitude stratospheric planetary wave (PW), suggesting that the nonmigrating tides (SW1 and DS0) are possibly generated due to nonlinear interaction of migrating tides with PW. Similar spectral analysis on temperature at 10°N obtained from the Sounding of Atmosphere by Broadband Emission Radiometry (SABER) shows that the SW2 enhances at stratospheric heights and the SW2 is more dominant at 80-90 km, but its amplitude decreases around 100 km. The amplitudes of nonmigrating tides become comparable to those of SW2 around 100 km, and their contribution becomes increasingly important at higher heights. This suggests that the nonlinear interaction between migrating tides and PW occurs at low-latitude upper mesospheric heights, as SW2 exhibits 16 day periodicity in SABER temperature at 100 km as observed in TEC. Besides, it is observed that the eastward propagating tides are less dominant than westward propagating tides in both TEC and SABER temperatures.
-
CERN: Antiprotons probe the nuclear stratosphere
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Anon.
1995-06-15
The outer periphery of heavy stable nuclei is notoriously difficult to study experimentally. While the well understood electromagnetic interaction between electrons (or muons) and protons has given the nuclear charge (or proton) distribution with high precision for almost all stable nuclei, neutron distribution studies are much less precise. This is especially true for large nuclear distances, where the nuclear density is small. A few previous experiments probing the nuclear ''stratosphere'' suggested that far from the centre of the nucleus (of the order of 2 nuclear radii) this stratosphere may be composed predominantly of neutrons. At the end of the sixties the term ''neutron halo'' was introduced to describe this phenomenon, but experimental evidence was scarce or even controversial, and remained so for almost a quarter of a century. Recently, the Warsaw/Munich/Berlin collaboration working within the PS203 experiment at CERN's LEAR low energy antiproton ring, proposed a new method to study the nuclear periphery using stopped antiprotons. The halo now looks firmer. A 200 MeV/c beam of antiprotons was slowed down by interactions with atomic electrons. When antiproton kinetic energy drops well below 1 keV, the particles are captured in the outermost orbits of ''exotic atoms'', where the antiprotons take the place of the usual orbital electrons. With the lower orbits in this antiprotonic atom empty, the antiproton drops toward the nuclear surface, first emitting Auger electrons and later predominantly antiprotonic X-rays. Due to the strong interaction between antiprotons and nucleons, the antiproton succumbs to annihilation with a nucleon in the rarified nuclear stratosphere, far above the innermost Bohr orbit of the atom. The annihilation probability in heavy nuclei is maximal where the nuclear density is about 3% of its central value and extends to densities many orders of magnitude smaller. Antiproton annihilation on a proton or on a neutron at the nuclear
-
STRATOSPHERIC TEMPERATURES AND WATER LOSS FROM MOIST GREENHOUSE ATMOSPHERES OF EARTH-LIKE PLANETS
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kasting, James F.; Kopparapu, Ravi K. [Department of Geosciences, The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA 16801 (United States); Chen, Howard, E-mail: jfk4@psu.edu, E-mail: hwchen@bu.edu [Department of Astronomy, Boston University, 725 Commonwealth Ave., Boston, MA 02215 (United States)
2015-11-01
A radiative-convective climate model is used to calculate stratospheric temperatures and water vapor concentrations for ozone-free atmospheres warmer than that of modern Earth. Cold, dry stratospheres are predicted at low surface temperatures, in agreement with recent 3D calculations. However, at surface temperatures above 350 K, the stratosphere warms and water vapor becomes a major upper atmospheric constituent, allowing water to be lost by photodissociation and hydrogen escape. Hence, a moist greenhouse explanation for loss of water from Venus, or some exoplanet receiving a comparable amount of stellar radiation, remains a viable hypothesis. Temperatures in the upper parts of such atmospheres are well below those estimated for a gray atmosphere, and this factor should be taken into account when performing inverse climate calculations to determine habitable zone boundaries using 1D models.
-
STRATOSPHERIC TEMPERATURES AND WATER LOSS FROM MOIST GREENHOUSE ATMOSPHERES OF EARTH-LIKE PLANETS
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kasting, James F.; Kopparapu, Ravi K.; Chen, Howard
2015-01-01
A radiative-convective climate model is used to calculate stratospheric temperatures and water vapor concentrations for ozone-free atmospheres warmer than that of modern Earth. Cold, dry stratospheres are predicted at low surface temperatures, in agreement with recent 3D calculations. However, at surface temperatures above 350 K, the stratosphere warms and water vapor becomes a major upper atmospheric constituent, allowing water to be lost by photodissociation and hydrogen escape. Hence, a moist greenhouse explanation for loss of water from Venus, or some exoplanet receiving a comparable amount of stellar radiation, remains a viable hypothesis. Temperatures in the upper parts of such atmospheres are well below those estimated for a gray atmosphere, and this factor should be taken into account when performing inverse climate calculations to determine habitable zone boundaries using 1D models
-
Regina M. Rochefort; Laurie L. Kurth; Tara W. Carolin; Robert R. Mierendorf; Kimberly Frappier; David L. Steenson
2006-01-01
This chapter concentrates on subalpine parklands and alpine meadows of southern British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and western Montana. These areas lie on the flanks of several mountain ranges including the Olympics, the Cascades of Oregon and Washington, and the Coast Mountains in British Columbia.
-
Lee waves: Benign and malignant
Wurtele, M. G.; Datta, A.; Sharman, R. D.
1993-01-01
The flow of an incompressible fluid over an obstacle will produce an oscillation in which buoyancy is the restoring force, called a gravity wave. For disturbances of this scale, the atmosphere may be treated as dynamically incompressible, even though there exists a mean static upward density gradient. Even in the linear approximation - i.e., for small disturbances - this model explains a great many of the flow phenomena observed in the lee of mountains. However, nonlinearities do arise importantly, in three ways: (1) through amplification due to the decrease of mean density with height; (2) through the large (scaled) size of the obstacle, such as a mountain range; and (3) from dynamically singular levels in the fluid field. These effects produce a complicated array of phenomena - large departure of the streamlines from their equilibrium levels, high winds, generation of small scales, turbulence, etc. - that present hazards to aircraft and to lee surface areas. The nonlinear disturbances also interact with the larger-scale flow in such a manner as to impact global weather forecasts and the climatological momentum balance. If there is no dynamic barrier, these waves can penetrate vertically into the middle atmosphere (30-100 km), where recent observations show them to be of a length scale that must involve the coriolis force in any modeling. At these altitudes, the amplitude of the waves is very large, and the phenomena associated with these wave dynamics are being studied with a view to their potential impact on high performance aircraft, including the projected National Aerospace Plane (NASP). The presentation shows the results of analysis and of state-of-the-art numerical simulations, validated where possible by observational data, and illustrated with photographs from nature.
-
Vernier, Jean-Paul; Thomason, Larry W.; Pommereau, J.-P.; Bourassa, Adam; Pelon, Jacques; Garnier, Anne; Hauchecorne, A.; Blanot, L.; Trepte, Charles R.; Degenstein, Doug;

2011-01-01
The variability of stratospheric aerosol loading between 1985 and 2010 is explored with measurements from SAGE II, CALIPSO, GOMOS/ENVISAT, and OSIRIS/Odin space-based instruments. We find that, following the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo, stratospheric aerosol levels increased by as much as two orders of magnitude and only reached background levels between 1998 and 2002. From 2002 onwards, a systematic increase has been reported by a number of investigators. Recently, the trend, based on ground-based lidar measurements, has been tentatively attributed to an increase of SO2 entering the stratosphere associated with coal burning in Southeast Asia. However, we demonstrate with these satellite measurements that the observed trend is mainly driven by a series of moderate but increasingly intense volcanic eruptions primarily at tropical latitudes. These events injected sulfur directly to altitudes between 18 and 20 km. The resulting aerosol particles are slowly lofted into the middle stratosphere by the Brewer-Dobson circulation and are eventually transported to higher latitudes.
-
SEASONAL DISAPPEARANCE OF FAR-INFRARED HAZE IN TITAN'S STRATOSPHERE
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jennings, Donald E.; Anderson, C. M.; Flasar, F. M.; Cottini, V. [Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 (United States); Samuelson, R. E.; Nixon, C. A.; Kunde, V. G.; Achterberg, R. K. [Department of Astronomy, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742 (United States); De Kok, R. [SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research, Sorbonnelaan 2, 3584 CA Utrecht (Netherlands); Coustenis, A.; Vinatier, S. [LESIA, Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, 92195 Meudon Cedex (France); Calcutt, S. B., E-mail: donald.e.jennings@nasa.gov [Department of Physics, University of Oxford, Parks Road, Oxford OX1 3PU (United Kingdom)
2012-07-20
A far-infrared emission band attributed to volatile or refractory haze in Titan's stratosphere has been decreasing in intensity since Cassini's arrival in 2004. The 220 cm{sup -1} feature, first seen by the Voyager Infrared Interferometer Spectrometer, has only been found in Titan's winter polar region. The emission peaks at about 140 km altitude near the winter stratospheric temperature minimum. Observations recorded over the period 2004-2012 by the Composite Infrared Spectrometer on Cassini show a decrease in the intensity of this feature by about a factor of four. Possible seasonal causes of this decline are an increase in photolytic destruction of source chemicals at high altitude, a lessening of condensation as solar heating increased, or a weakening of downwelling of vapors. As of early 2012, the 220 cm{sup -1} haze has not yet been detected in the south. The haze composition is unknown, but its decrease is similar to that of HC{sub 3}N gas in Titan's polar stratosphere, pointing to a nitrile origin.
-
Waves in the Red Sea: Response to monsoonal and mountain gap winds
Ralston, David K.; Jiang, Houshuo; Farrar, J. Thomas
2013-01-01
An unstructured grid, phase-averaged wave model forced with winds from a high resolution atmospheric model is used to evaluate wind wave conditions in the Red Sea over an approximately 2-year period. The Red Sea lies in a narrow rift valley
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ferraro, Angus J; Griffiths, Hannah G
2016-01-01
The reduction in global-mean precipitation when stratospheric aerosol geoengineering is used to counterbalance global warming from increasing carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) concentrations has been mainly attributed to the temperature-independent effect of CO 2 on atmospheric radiative cooling. We demonstrate here that stratospheric sulphate aerosol itself also acts to reduce global-mean precipitation independent of its effects on temperature. The temperature-independent effect of stratospheric aerosol geoenginering on global-mean precipitation is calculated by removing temperature-dependent effects from climate model simulations of the Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project (GeoMIP). When sulphate aerosol is injected into the stratosphere at a rate of 5 Tg SO 2 per year the aerosol reduces global-mean precipitation by approximately 0.2 %, though multiple ensemble members are required to separate this effect from internal variability. For comparison, the precipitation reduction from the temperature-independent effect of increasing CO 2 concentrations under the RCP4.5 scenario of the future is approximately 0.5 %. The temperature-independent effect of stratospheric sulphate aerosol arises from the aerosol’s effect on tropospheric radiative cooling. Radiative transfer calculations show this is mainly due to increasing downward emission of infrared radiation by the aerosol, but there is also a contribution from the stratospheric warming the aerosol causes. Our results suggest climate model simulations of solar dimming can capture the main features of the global-mean precipitation response to stratospheric aerosol geoengineering. (letter)
-
Meraner, Katharina; Schmidt, Hauke
2018-01-01
Energetic particles enter the polar atmosphere and enhance the production of nitrogen oxides and hydrogen oxides in the winter stratosphere and mesosphere. Both components are powerful ozone destroyers. Recently, it has been inferred from observations that the direct effect of energetic particle precipitation (EPP) causes significant long-term mesospheric ozone variability. Satellites observe a decrease in mesospheric ozone up to 34 % between EPP maximum and EPP minimum. Stratospheric ozone decreases due to the indirect effect of EPP by about 10-15 % observed by satellite instruments. Here, we analyze the climate impact of winter boreal idealized polar mesospheric and polar stratospheric ozone losses as caused by EPP in the coupled Max Planck Institute Earth System Model (MPI-ESM). Using radiative transfer modeling, we find that the radiative forcing of mesospheric ozone loss during polar night is small. Hence, climate effects of mesospheric ozone loss due to energetic particles seem unlikely. Stratospheric ozone loss due to energetic particles warms the winter polar stratosphere and subsequently weakens the polar vortex. However, those changes are small, and few statistically significant changes in surface climate are found.
-
Strong modification of stratospheric ozone forcing by cloud and sea-ice adjustments
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. Xia
2016-06-01
Full Text Available We investigate the climatic impact of stratospheric ozone recovery (SOR, with a focus on the surface temperature change in atmosphere–slab ocean coupled climate simulations. We find that although SOR would cause significant surface warming (global mean: 0.2 K in a climate free of clouds and sea ice, it causes surface cooling (−0.06 K in the real climate. The results here are especially interesting in that the stratosphere-adjusted radiative forcing is positive in both cases. Radiation diagnosis shows that the surface cooling is mainly due to a strong radiative effect resulting from significant reduction of global high clouds and, to a lesser extent, from an increase in high-latitude sea ice. Our simulation experiments suggest that clouds and sea ice are sensitive to stratospheric ozone perturbation, which constitutes a significant radiative adjustment that influences the sign and magnitude of the global surface temperature change.
-
Dust ablation on the giant planets: Consequences for stratospheric photochemistry
Moses, Julianne I.; Poppe, Andrew R.
2017-11-01
Ablation of interplanetary dust supplies oxygen to the upper atmospheres of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Using recent dynamical model predictions for the dust influx rates to the giant planets (Poppe et al., 2016), we calculate the ablation profiles and investigate the subsequent coupled oxygen-hydrocarbon neutral photochemistry in the stratospheres of these planets. We find that dust grains from the Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt, Jupiter-family comets, and Oort-cloud comets supply an effective oxygen influx rate of 1.0-0.7+2.2 ×107 O atoms cm-2 s-1 to Jupiter, 7.4-5.1+16 ×104 cm-2 s-1 to Saturn, 8.9-6.1+19 ×104 cm-2 s-1 to Uranus, and 7.5-5.1+16 ×105 cm-2 s-1 to Neptune. The fate of the ablated oxygen depends in part on the molecular/atomic form of the initially delivered products, and on the altitude at which it was deposited. The dominant stratospheric products are CO, H2O, and CO2, which are relatively stable photochemically. Model-data comparisons suggest that interplanetary dust grains deliver an important component of the external oxygen to Jupiter and Uranus but fall far short of the amount needed to explain the CO abundance currently seen in the middle stratospheres of Saturn and Neptune. Our results are consistent with the theory that all of the giant planets have experienced large cometary impacts within the last few hundred years. Our results also suggest that the low background H2O abundance in Jupiter's stratosphere is indicative of effective conversion of meteoric oxygen to CO during or immediately after the ablation process - photochemistry alone cannot efficiently convert the H2O into CO on the giant planets.
-
Solitary waves for a coupled nonlinear Schrodinger system with dispersion management
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Panayotis Panayotaros
2010-08-01
Full Text Available We consider a system of coupled nonlinear Schrodinger equations with periodically varying dispersion coefficient that arises in the context of fiber-optics communication. We use Lions's Concentration Compactness principle to show the existence of standing waves with prescribed L^2 norm in an averaged equation that approximates the coupled system. We also use the Mountain Pass Lemma to prove the existence of standing waves with prescribed frequencies.
-
Observing Trace Gases Of The Arctic And Subarctic Stratosphere By TELIS
Xu, Jian; Schreier, Franz; Doicu, Adrian; Vogt, Peter; Birk, Manfred; Wagner, Georg; Trautmann, Thomas
2013-12-01
The Terahertz and submillimeter Limb Sounder (TELIS) is a balloon-borne cryogenic heterodyne spectrometer developed by a consortium of European institutes, which was mounted together with the Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding - Balloon (MIPAS- B) and the mini- Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (mini-DOAS) instruments on a stratospheric gondola. The TELIS instrument is designed to monitor the vertical distribution of stratospheric state parameters associated with ozone destruction and climate change in Arctic and subarctic areas. The broad spectral coverage of TELIS is achieved by utilizing three frequency channels: a tunable 1.8THz channel based on a solid state local oscillator and a hot electron bolometer as mixer, a 480-650GHz channel with the Superconducting Integrated Receiver (SIR) technology, and a highly compact 500 GHz channel developed by the German Aerospace Center (DLR), the Netherlands Institute for Space Research (SRON), and the Rutherford Apple- ton Laboratory (RAL), respectively. Furthermore, an ex- tended spectral range is observed by the combination of TELIS and MIPAS-B, which can be employed for cross validation of several gas concentrations. Between 2009 and 2011 three successful scientific flights have been launched in Kiruna, Sweden and all relevant atmospheric gas species were seen by TELIS over an altitude range of 10-32.5 km. For estimation of concentration profiles from TELIS measurements, a constrained nonlinear least squares fitting framework along with var- ious Tikhonov-type regularization methods has been developed. In this work we present recent retrieval results from latest calibrated spectra during the 2010 flight. Emphasis is placed on ozone (O3) and hydrogen chloride (HCl), and error issues pertaining to the main instrumental uncertainty terms including nonlinearity in the calibration procedure, sideband ratio and pointing offset are investigated. The retrieved profiles are validated against
-
20 years of ClO measurements in the Antarctic lower stratosphere
Nedoluha, Gerald E.; Connor, Brian J.; Mooney, Thomas; Barrett, James W.; Parrish, Alan; Gomez, R. Michael; Boyd, Ian; Allen, Douglas R.; Kotkamp, Michael; Kremser, Stefanie; Deshler, Terry; Newman, Paul; Santee, Michelle L.
2016-08-01
We present 20 years (1996-2015) of austral springtime measurements of chlorine monoxide (ClO) over Antarctica from the Chlorine Oxide Experiment (ChlOE1) ground-based millimeter wave spectrometer at Scott Base, Antarctica, as well 12 years (2004-2015) of ClO measurements from the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS). From August onwards we observe a strong increase in lower stratospheric ClO, with a peak column amount usually occurring in early September. From mid-September onwards we observe a strong decrease in ClO. In order to study interannual differences, we focus on a 3-week period from 28 August to 17 September for each year and compare the average column ClO anomalies. These column ClO anomalies are shown to be highly correlated with the average ozone mass deficit for September and October of each year. We also show that anomalies in column ClO are strongly anti-correlated with 30 hPa temperature anomalies, both on a daily and an interannual timescale. Making use of this anti-correlation we calculate the linear dependence of the interannual variations in column ClO on interannual variations in temperature. By making use of this relationship, we can better estimate the underlying trend in the total chlorine (Cly = HCl + ClONO2 + HOCl + 2 × Cl2 + 2 × Cl2O2 + ClO + Cl). The resultant trends in Cly, which determine the long-term trend in ClO, are estimated to be -0.5 ± 0.2, -1.4 ± 0.9, and -0.6 ± 0.4 % year-1, for zonal MLS, Scott Base MLS (both 2004-2015), and ChlOE (1996-2015) respectively. These trends are within 1σ of trends in stratospheric Cly previously found at other latitudes. The decrease in ClO is consistent with the trend expected from regulations enacted under the Montreal Protocol.
-
Wind tunnel tests of stratospheric airship counter rotating propellers
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yaxi Chen
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Aerodynamic performance of the high-altitude propeller, especially the counter rotation effects, is experimentally studied. Influences of different configurations on a stratospheric airship, included 2-blade counter-rotating propeller (CRP, dual 2-blade single rotation propellers (SRPs and 4-blade SRP, are also indicated. This research indicates that the effect of counter rotation can greatly improve the efficiency. It shows that the CRP configuration results in a higher efficiency than the dual 2-blade SRPs configuration or 4-blade SRP configuration under the same advance ratio, and the CRP configuration also gains the highest efficiency whether under the situation of providing the same trust or absorbing the same power. It concludes that, for a stratospheric airship, the CRP configuration is better than the multiple SRPs configuration or a multi-blade SRP one.
-
Future changes in large-scale transport and stratosphere-troposphere exchange
Abalos, M.; Randel, W. J.; Kinnison, D. E.; Garcia, R. R.
2017-12-01
Future changes in large-scale transport are investigated in long-term (1955-2099) simulations of the Community Earth System Model - Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (CESM-WACCM) under an RCP6.0 climate change scenario. We examine artificial passive tracers in order to isolate transport changes from future changes in emissions and chemical processes. The model suggests enhanced stratosphere-troposphere exchange in both directions (STE), with decreasing tropospheric and increasing stratospheric tracer concentrations in the troposphere. Changes in the different transport processes are evaluated using the Transformed Eulerian Mean continuity equation, including parameterized convective transport. Dynamical changes associated with the rise of the tropopause height are shown to play a crucial role on future transport trends.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. L. Manney
2016-12-01
Full Text Available The 2015/16 Northern Hemisphere winter stratosphere appeared to have the greatest potential yet seen for record Arctic ozone loss. Temperatures in the Arctic lower stratosphere were at record lows from December 2015 through early February 2016, with an unprecedented period of temperatures below ice polar stratospheric cloud thresholds. Trace gas measurements from the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS show that exceptional denitrification and dehydration, as well as extensive chlorine activation, occurred throughout the polar vortex. Ozone decreases in 2015/16 began earlier and proceeded more rapidly than those in 2010/11, a winter that saw unprecedented Arctic ozone loss. However, on 5–6 March 2016 a major final sudden stratospheric warming ("major final warming", MFW began. By mid-March, the mid-stratospheric vortex split after being displaced far off the pole. The resulting offspring vortices decayed rapidly preceding the full breakdown of the vortex by early April. In the lower stratosphere, the period of temperatures low enough for chlorine activation ended nearly a month earlier than that in 2011 because of the MFW. Ozone loss rates were thus kept in check because there was less sunlight during the cold period. Although the winter mean volume of air in which chemical ozone loss could occur was as large as that in 2010/11, observed ozone values did not drop to the persistently low values reached in 2011.We use MLS trace gas measurements, as well as mixing and polar vortex diagnostics based on meteorological fields, to show how the timing and intensity of the MFW and its impact on transport and mixing halted chemical ozone loss. Our detailed characterization of the polar vortex breakdown includes investigations of individual offspring vortices and the origins and fate of air within them. Comparisons of mixing diagnostics with lower-stratospheric N2O and middle-stratospheric CO from MLS (long-lived tracers show rapid vortex erosion and
-
Persistence of Antarctic polar stratospheric clouds
Mccormick, M. Patrick; Trepte, C. R.
1988-01-01
The persistence of Polar Stratospheric Clouds (PSCs) observed by the Stratospheric Aerosol Measurement (SAM) 2 satellite sensor over a 9-year period is compared and contrasted. Histograms of the SAM 2 1.0 micron extinction ratio data (aerosol extinction normalized by the molecular extinction) at an altitude of 18 km in the Antarctic have been generated for three 10-day periods in the month of September. Statistics for eight different years (1979 to 1982 and 1984 to 1987) are shown in separate panels for each figure. Since the SAM 2 system is a solar occultation experiment, observations are limited to the edge of the polar night and no measurements are made deep within the vortex where temperatures could be colder. For this reason, use is made of the NMC global gridded fields and the known temperature-extinction relationship to infer additional information on the occurrence and areal coverage of PSCs. Calculations of the daily areal coverage of the 195 K isotherm will be presented for this same period of data. This contour level lies in the range of the predicted temperature for onset of the Type 1 particle enhancement mode at 50 mb (Poole and McCormick, 1988b) and should indicate approximately when formation of the binary HNO3-H2O particles begins.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Holzworth, R.H.
1981-01-01
Stratospheric electric field and conductivity measurements during a wide variety of weather and solar conditions are presented. These data are all from high latitude sites in the months of either April or August. The vector electric field is determined by orthogonal double probes connected through high impedance inputs to differential electrometers. The direct conductivity measurement involves determining the relaxation time constant of the medium after refloating a shorted pair of separated probes. Vertical electric field data from several balloon flights with average duration of 18 h at ceiling in fair weather are shown to be well modeled by a simple exponential altitude dependent equation. Examples of solar flare and magnetospheric effects on stratospheric electric fields are shown. Data collected over electrified clouds and thunderstorms are presented along with a discussion of the thunderstorm related electric currents. Lightning stroke signatures in the stratosphere during a large thunderstorm are identified in the electric field data. Current surges through the stratosphere due to DC currents as well as the sferic are calculated. In nearly 1000 h of balloon data no direct solar influence is identified in these data except during major flares. (author)
-
Aerosol particle size distribution in the stratosphere retrieved from SCIAMACHY limb measurements
Malinina, Elizaveta; Rozanov, Alexei; Rozanov, Vladimir; Liebing, Patricia; Bovensmann, Heinrich; Burrows, John P.
2018-04-01
health, stratospheric aerosol plays an important role in atmospheric chemistry and climate change. In particular, information about the amount and distribution of stratospheric aerosols is required to initialize climate models, as well as validate aerosol microphysics models and investigate geoengineering. In addition, good knowledge of stratospheric aerosol loading is needed to increase the retrieval accuracy of key trace gases (e.g. ozone or water vapour) when interpreting remote sensing measurements of the scattered solar light. The most commonly used characteristics to describe stratospheric aerosols are the aerosol extinction coefficient and Ångström coefficient. However, the use of particle size distribution parameters along with the aerosol number density is a more optimal approach. In this paper we present a new retrieval algorithm to obtain the particle size distribution of stratospheric aerosol from space-borne observations of the scattered solar light in the limb-viewing geometry. While the mode radius and width of the aerosol particle size distribution are retrieved, the aerosol particle number density profile remains unchanged. The latter is justified by a lower sensitivity of the limb-scattering measurements to changes in this parameter. To our knowledge this is the first data set providing two parameters of the particle size distribution of stratospheric aerosol from space-borne measurements of scattered solar light. Typically, the mode radius and w can be retrieved with an uncertainty of less than 20 %. The algorithm was successfully applied to the tropical region (20° N-20° S) for 10 years (2002-2012) of SCIAMACHY observations in limb-viewing geometry, establishing a unique data set. Analysis of this new climatology for the particle size distribution parameters showed clear increases in the mode radius after the tropical volcanic eruptions, whereas no distinct behaviour of the absolute distribution width could be identified. A tape recorder
-
Recent population trends of mountain goats in the Olympic Mountains, Washington
Jenkins, Kurt J.; Happe, Patricia J.; Beirne, Katherine F.; Hoffman, Roger A.; Griffin, Paul C.; Baccus, William T.; Fieberg, John
2012-01-01
Mountain goats (Oreamnos americanus) were introduced in Washington's Olympic Mountains during the 1920s. The population subsequently increased in numbers and expanded in range, leading to concerns by the 1970s over the potential effects of non-native mountain goats on high-elevation plant communities in Olympic National Park. The National Park Service (NPS) transplanted mountain goats from the Olympic Mountains to other ranges between 1981 and 1989 as a means to manage overabundant populations, and began monitoring population trends of mountain goats in 1983. We estimated population abundance of mountain goats during 18–25 July 2011, the sixth survey of the time series, to assess current population status and responses of the population to past management. We surveyed 39 sample units, comprising 39% of the 59,615-ha survey area. We estimated a population of 344 ± 72 (90% confidence interval [CI]) mountain goats in the survey area. Retrospective analysis of the 2004 survey, accounting for differences in survey area boundaries and methods of estimating aerial detection biases, indicated that the population increased at an average annual rate of 4.9% since the last survey. That is the first population growth observed since the cessation of population control measures in 1990. We postulate that differences in population trends observed in western, eastern, and southern sections of the survey zone reflected, in part, a variable influence of climate change across the precipitation gradient in the Olympic Mountains.
-
A global space-based stratospheric aerosol climatology: 1979–2016
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
L. W. Thomason
2018-03-01
Full Text Available We describe the construction of a continuous 38-year record of stratospheric aerosol optical properties. The Global Space-based Stratospheric Aerosol Climatology, or GloSSAC, provided the input data to the construction of the Climate Model Intercomparison Project stratospheric aerosol forcing data set (1979–2014 and we have extended it through 2016 following an identical process. GloSSAC focuses on the Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE series of instruments through mid-2005, and on the Optical Spectrograph and InfraRed Imager System (OSIRIS and the Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation (CALIPSO data thereafter. We also use data from other space instruments and from ground-based, air, and balloon borne instruments to fill in key gaps in the data set. The end result is a global and gap-free data set focused on aerosol extinction coefficient at 525 and 1020 nm and other parameters on an "as available" basis. For the primary data sets, we developed a new method for filling the post-Pinatubo eruption data gap for 1991–1993 based on data from the Cryogenic Limb Array Etalon Spectrometer. In addition, we developed a new method for populating wintertime high latitudes during the SAGE period employing a latitude-equivalent latitude conversion process that greatly improves the depiction of aerosol at high latitudes compared to earlier similar efforts. We report data in the troposphere only when and where it is available. This is primarily during the SAGE II period except for the most enhanced part of the Pinatubo period. It is likely that the upper troposphere during Pinatubo was greatly enhanced over non-volcanic periods and that domain remains substantially under-characterized. We note that aerosol levels during the OSIRIS/CALIPSO period in the lower stratosphere at mid- and high latitudes is routinely higher than what we observed during the SAGE II period. While this period had nearly continuous low
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
W. H. Daffer
2009-07-01
Full Text Available An unusually strong and prolonged stratospheric sudden warming (SSW in January 2006 was the first major SSW for which globally distributed long-lived trace gas data are available covering the upper troposphere through the lower mesosphere. We use Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS, Atmospheric Chemistry Experiment-Fourier Transform Spectrometer (ACE-FTS data, the SLIMCAT Chemistry Transport Model (CTM, and assimilated meteorological analyses to provide a comprehensive picture of transport during this event. The upper tropospheric ridge that triggered the SSW was associated with an elevated tropopause and layering in trace gas profiles in conjunction with stratospheric and tropospheric intrusions. Anomalous poleward transport (with corresponding quasi-isentropic troposphere-to-stratosphere exchange at the lowest levels studied in the region over the ridge extended well into the lower stratosphere. In the middle and upper stratosphere, the breakdown of the polar vortex transport barrier was seen in a signature of rapid, widespread mixing in trace gases, including CO, H2O, CH4 and N2O. The vortex broke down slightly later and more slowly in the lower than in the middle stratosphere. In the middle and lower stratosphere, small remnants with trace gas values characteristic of the pre-SSW vortex lingered through the weak and slow recovery of the vortex. The upper stratospheric vortex quickly reformed, and, as enhanced diabatic descent set in, CO descended into this strong vortex, echoing the fall vortex development. Trace gas evolution in the SLIMCAT CTM agrees well with that in the satellite trace gas data from the upper troposphere through the middle stratosphere. In the upper stratosphere and lower mesosphere, the SLIMCAT simulation does not capture the strong descent of mesospheric CO and H2O values into the reformed vortex; this poor CTM performance in the upper stratosphere and lower mesosphere results
-
Rays, waves, and scattering topics in classical mathematical physics
Adam, John A
2017-01-01
This one-of-a-kind book presents many of the mathematical concepts, structures, and techniques used in the study of rays, waves, and scattering. Panoramic in scope, it includes discussions of how ocean waves are refracted around islands and underwater ridges, how seismic waves are refracted in the earth's interior, how atmospheric waves are scattered by mountains and ridges, how the scattering of light waves produces the blue sky, and meteorological phenomena such as rainbows and coronas. Rays, Waves, and Scattering is a valuable resource for practitioners, graduate students, and advanced undergraduates in applied mathematics, theoretical physics, and engineering. Bridging the gap between advanced treatments of the subject written for specialists and less mathematical books aimed at beginners, this unique mathematical compendium features problems and exercises throughout that are geared to various levels of sophistication, covering everything from Ptolemy's theorem to Airy integrals (as well as more technica...
-
Study of stratosphere-troposphere exchange via 10Be/7Be isotope ratios
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Priller, A.; Berger, M.; Golser, R.; Kutschera, W.; Steier, P.; Vockenhuber, C.; Wild, E.M.
2001-01-01
Full text: The present study is part of the European project STACCATO (influence of stratosphere-troposphere exchange in a changing climate on atmospheric transport and oxidation capacity). Stratosphere-troposphere exchange (STE) is one of the key factors controlling the budgets of ozone, water vapor and other substances in both the troposphere and the lower stratosphere. However, its contribution to their ozone budget relative to photo-chemical ozone formation from natural and anthropogenic precursor emissions is still uncertain. An international effort is made to estimate the strength of STE and its impact on tropospheric chemistry. The two cosmogenic radioisotopes of beryllium, 10 Be and 7 Be have very different half-lives of 1.51 Ma and 53.4 d, respectively. The combination of production rates, half-lives and different residence times in the stratosphere and troposphere, respectively, results in 10 Be/ 7 Be isotope ratios which can be used as fingerprints for STE. This ratio helps to give a much improved estimate of STE. However, only few 10 Be measurements exist, because its detection requires the rather elaborate method of accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS). At the AMS facility VERA we are now measuring the 10 Be content of air filters from the high-alpine stations 'Hoher Sonnblick', Austria, and 'Zugspitze', Germany. The TBe content is measured separately by decay counting. In this presentation, we want to describe the method of measuring 10 Be with AMS, and to discuss the results of first 10 Be/ 7 Be ratios. (author)
-
Yu, Pengfei; Rosenlof, Karen H.; Liu, Shang; Telg, Hagen; Thornberry, Troy D.; Rollins, Andrew W.; Portmann, Robert W.; Bai, Zhixuan; Ray, Eric A.; Duan, Yunjun; Pan, Laura L.; Toon, Owen B.; Bian, Jianchun; Gao, Ru-Shan
2017-07-01
An enhanced aerosol layer near the tropopause over Asia during the June-September period of the Asian summer monsoon (ASM) was recently identified using satellite observations. Its sources and climate impact are presently not well-characterized. To improve understanding of this phenomenon, we made in situ aerosol measurements during summer 2015 from Kunming, China, then followed with a modeling study to assess the global significance. The in situ measurements revealed a robust enhancement in aerosol concentration that extended up to 2 km above the tropopause. A climate model simulation demonstrates that the abundant anthropogenic aerosol precursor emissions from Asia coupled with rapid vertical transport associated with monsoon convection leads to significant particle formation in the upper troposphere within the ASM anticyclone. These particles subsequently spread throughout the entire Northern Hemispheric (NH) lower stratosphere and contribute significantly (˜15%) to the NH stratospheric column aerosol surface area on an annual basis. This contribution is comparable to that from the sum of small volcanic eruptions in the period between 2000 and 2015. Although the ASM contribution is smaller than that from tropical upwelling (˜35%), we find that this region is about three times as efficient per unit area and time in populating the NH stratosphere with aerosol. With a substantial amount of organic and sulfur emissions in Asia, the ASM anticyclone serves as an efficient smokestack venting aerosols to the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere. As economic growth continues in Asia, the relative importance of Asian emissions to stratospheric aerosol is likely to increase.
-
Aquila, V.; Swartz, W. H.; Waugh, D. W.; Colarco, P. R.; Pawson, S.; Polvani, L. M.; Stolarski, R. S.
2016-01-01
Satellite instruments show a cooling of global stratospheric temperatures over the whole data record (1979-2014). This cooling is not linear and includes two descending steps in the early 1980s and mid-1990s. The 1979-1995 period is characterized by increasing concentrations of ozone depleting substances (ODS) and by the two major volcanic eruptions of El Chichon (1982) and Mount Pinatubo (1991). The 1995-present period is characterized by decreasing ODS concentrations and by the absence of major volcanic eruptions. Greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations increase over the whole time period. In order to isolate the roles of different forcing agents in the global stratospheric temperature changes, we performed a set of AMIP-style simulations using the NASA Goddard Earth Observing System Chemistry-Climate Model (GEOSCCM). We find that in our model simulations the cooling of the stratosphere from 1979 to present is mostly driven by changes in GHG concentrations in the middle and upper stratosphere and by GHG and ODS changes in the lower stratosphere. While the cooling trend caused by increasing GHGs is roughly constant over the satellite era, changing ODS concentrations cause a significant stratospheric cooling only up to the mid-1990s, when they start to decrease because of the implementation of the Montreal Protocol. Sporadic volcanic events and the solar cycle have a distinct signature in the time series of stratospheric temperature anomalies but do not play a statistically significant role in the long-term trends from 1979 to 2014. Several factors combine to produce the step-like behavior in the stratospheric temperatures: in the lower stratosphere, the flattening starting in the mid-1990s is due to the decrease in ozone-depleting substances; Mount Pinatubo and the solar cycle cause the abrupt steps through the aerosol-associated warming and the volcanically induced ozone depletion. In the middle and upper stratosphere, changes in solar irradiance are largely
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zhang, S.D.; Yi, F. [Wuhan Univ., Hubei (China). School of Electronic Information; Ministry of Education, Wuhan, Hubei (China). Key Lab. of Geospace Environment and Geodesy; State Observatory for Atmospheric Remote Sensing, Wuhan (China); Huang, C.M. [Wuhan Univ., Hubei (China). School of Electronic Information; Ministry of Education, Wuhan, Hubei (China). Key Lab. of Geospace Environment and Geodesy; State Observatory for Atmospheric Remote Sensing, Wuhan (China); Miami Univ., Oxford, OH (United States). Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept.; Zhou, Q. [Miami Univ., Oxford, OH (United States). Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept.
2010-07-01
The latitudinal and seasonal variations of gravity wave (GW) potential energy density (E{sub P}), kinetic energy density (E{sub K}), and total energy density (E{sub T}), i.e, the sum of potential and kinetic energy densities in the tropospheric (typically 2-10 km) and lower stratospheric (typically 18- 25 km) segments have been derived from 10 years (1998- 2007) of radiosonde observations over 92 United States stations in the Northern Hemisphere. The latitudinal variation of E{sub P} in the lower stratosphere is in good agreement with satellite observations. However, E{sub K} and E{sub T} in the lower stratosphere are different from satellite observations and the difference is believed to be linked with the latitudinal dependence of GW sources. Our analysis reveals that GW energy properties exhibit distinctive latitudinal and seasonal variations. The upward-propagating GW energy in the troposphere is larger than that in the lower stratosphere at low latitudes but the opposite holds true at high latitudes. The transition latitude, where the upward- propagating energies in the two altitude regions are the same, occurs at 35 N throughout the year. So striking differences between GW activity in the troposphere and lower stratosphere are not likely explained only by the background wind Doppler shifting due to strong tropospheric jets. Our analysis indicates that the region around tropopause, roughly from 10 km to 18 km, is an important source region, especially at latitudes below 35 N. Our studies strongly suggest that in order to fully understand the global GW activity in the lower atmosphere, the GW kinetic energy and its geographical and seasonal variations should be included, and more attention should be given to GWs in the troposphere and GW sources within the intermediate region, especially the upper troposphere. (orig.)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. D. Zhang
2010-05-01
Full Text Available The latitudinal and seasonal variations of gravity wave (GW potential energy density (EP, kinetic energy density (EK, and total energy density (ET, i.e, the sum of potential and kinetic energy densities in the tropospheric (typically 2–10 km and lower stratospheric (typically 18–25 km segments have been derived from 10 years (1998–2007 of radiosonde observations over 92 United States stations in the Northern Hemisphere. The latitudinal variation of EP in the lower stratosphere is in good agreement with satellite observations. However, EK and ET in the lower stratosphere are different from satellite observations and the difference is believed to be linked with the latitudinal dependence of GW sources. Our analysis reveals that GW energy properties exhibit distinctive latitudinal and seasonal variations. The upward-propagating GW energy in the troposphere is larger than that in the lower stratosphere at low latitudes but the opposite holds true at high latitudes. The transition latitude, where the upward- propagating energies in the two altitude regions are the same, occurs at 35° N throughout the year. So striking differences between GW activity in the troposphere and lower stratosphere are not likely explained only by the background wind Doppler shifting due to strong tropospheric jets. Our analysis indicates that the region around tropopause, roughly from 10 km to 18 km, is an important source region, especially at latitudes below 35° N. Our studies strongly suggest that in order to fully understand the global GW activity in the lower atmosphere, the GW kinetic energy and its geographical and seasonal variations should be included, and more attention should be given to GWs in the troposphere and GW sources within the intermediate region, especially the upper troposphere.
-
Particulate sulfur in the upper troposphere and lowermost stratosphere – sources and climate forcing
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. G. Martinsson
2017-09-01
Full Text Available This study is based on fine-mode aerosol samples collected in the upper troposphere (UT and the lowermost stratosphere (LMS of the Northern Hemisphere extratropics during monthly intercontinental flights at 8.8–12 km altitude of the IAGOS-CARIBIC platform in the time period 1999–2014. The samples were analyzed for a large number of chemical elements using the accelerator-based methods PIXE (particle-induced X-ray emission and PESA (particle elastic scattering analysis. Here the particulate sulfur concentrations, obtained by PIXE analysis, are investigated. In addition, the satellite-borne lidar aboard CALIPSO is used to study the stratospheric aerosol load. A steep gradient in particulate sulfur concentration extends several kilometers into the LMS, as a result of increasing dilution towards the tropopause of stratospheric, particulate sulfur-rich air. The stratospheric air is diluted with tropospheric air, forming the extratropical transition layer (ExTL. Observed concentrations are related to the distance to the dynamical tropopause. A linear regression methodology handled seasonal variation and impact from volcanism. This was used to convert each data point into stand-alone estimates of a concentration profile and column concentration of particulate sulfur in a 3 km altitude band above the tropopause. We find distinct responses to volcanic eruptions, and that this layer in the LMS has a significant contribution to the stratospheric aerosol optical depth and thus to its radiative forcing. Further, the origin of UT particulate sulfur shows strong seasonal variation. We find that tropospheric sources dominate during the fall as a result of downward transport of the Asian tropopause aerosol layer (ATAL formed in the Asian monsoon, whereas transport down from the Junge layer is the main source of UT particulate sulfur in the first half of the year. In this latter part of the year, the stratosphere is the clearly dominating source of
-
Siddiqui, T. A.; Yamazaki, Y.; Stolle, C.; Lühr, H.; Matzka, J.
2017-12-01
A number of studies in recent years have reported about the lunar tidal enhancements in the equatorial electrojet (EEJ) from ground- and space-based magnetometer measurements during stratospheric sudden warming (SSW) events. In this study, we make use of the ground magnetometer recordings at Huancayo observatory in Peru for the years 1978 - 2013 to derive a relationship between the lunar tidal enhancements in the EEJ and tropospheric eddy heat fluxes at 100 hPa during the SSW events. Tropospheric eddy heat fluxes are used to quantify the amount of wave activity entering the stratosphere. Anomalously large upward wave activity is known to precede the polar vortex breakdown during SSWs. We make use of the superposed epoch analysis method to determine the temporal relations between lunar tidal enhancements and eddy heat flux anomalies during SSWs, in order to demonstrate the causal relationship between these two phenomena. We also compare the lunar tidal enhancements and eddy heat flux anomalies for vortex split and for vortex displaced SSWs. It is found that larger lunar tidal enhancements are recorded for vortex split events, as compared to vortex displaced events. This confirms earlier observation; larger heat flux anomalies are recorded during vortex split SSW events than the heat flux anomalies during vortex displaced SSW events. Further, the temporal relations of lunar tidal enhancements in the EEJ have been compared separately for both the QBO phases and with the phases of the moon with respect to the central epoch of SSWs by means of the superposed epoch analysis approach. The EEJ lunar tidal enhancements in the east phase of QBO are found to be larger than the lunar tidal enhancements in the west phase of QBO. The phase of moon relative to the central SSW epoch also affects the lunar tidal enhancement in the EEJ. It is found that the lunar tidal enhancements are significantly larger when the day of new or full moon lies near the central SSW epoch, as compared
-
Tsuda, Toshitaka
2014-01-01
The wind velocity and temperature profiles observed in the middle atmosphere (altitude: 10-100 km) show perturbations resulting from superposition of various atmospheric waves, including atmospheric gravity waves. Atmospheric gravity waves are known to play an important role in determining the general circulation in the middle atmosphere by dynamical stresses caused by gravity wave breaking. In this paper, we summarize the characteristics of atmospheric gravity waves observed using the middle and upper atmosphere (MU) radar in Japan, as well as novel satellite data obtained from global positioning system radio occultation (GPS RO) measurements. In particular, we focus on the behavior of gravity waves in the mesosphere (50-90 km), where considerable gravity wave attenuation occurs. We also report on the global distribution of gravity wave activity in the stratosphere (10-50 km), highlighting various excitation mechanisms such as orographic effects, convection in the tropics, meteorological disturbances, the subtropical jet and the polar night jet.
-
Navas-Guzmán, Francisco; Kämpfer, Niklaus; Haefele, Alexander; Keckhut, Philippe; Hauchecorne, Alain
2015-04-01
The importance of the knowledge of the temperature structure in the atmosphere has been widely recognized. Temperature is a key parameter for dynamical, chemical and radiative processes in the atmosphere. The cooling of the stratosphere is an indicator for climate change as it provides evidence of natural and anthropogenic climate forcing just like surface warming ( [1] and references therein). However, our understanding of the observed stratospheric temperature trend and our ability to test simulations of the stratospheric response to emissions of greenhouse gases and ozone depleting substances remains limited. Stratospheric long-term datasets are sparse and obtained trends differ from one another [1]. Therefore it is important that in the future such datasets are generated. Different techniques allow to measure stratospheric temperature profiles as radiosonde, lidar or satellite. The main advantage of microwave radiometers against these other instruments is a high temporal resolution with a reasonable good spatial resolution. Moreover, the measurement at a fixed location allows to observe local atmospheric dynamics over a long time period, which is crucial for climate research. TEMPERA (TEMPERature RAdiometer) is a newly developed ground-based microwave radiometer designed, built and operated at the University of Bern. The instrument and the retrieval of temperature profiles has been described in detail in [2]. TEMPERA is measuring a pressure broadened oxygen line at 53.1 GHz in order to determine stratospheric temperature profiles. The retrieved profiles of TEMPERA cover an altitude range of approximately 20 to 45 km with a vertical resolution in the order of 15 km. The lower limit is given by the instrumental baseline and the bandwidth of the measured spectrum. The upper limit is given by the fact that above 50 km the oxygen lines are splitted by the Zeeman effect in the terrestrial magnetic field. In this study we present a comparison of stratospheric
-
Advances in global mountain geomorphology
Slaymaker, Olav; Embleton-Hamann, Christine
2018-05-01
Three themes in global mountain geomorphology have been defined and reinforced over the past decade: (a) new ways of measuring, sensing, and analyzing mountain morphology; (b) a new emphasis on disconnectivity in mountain geomorphology; and (c) the emergence of concerns about the increasing influence of anthropogenic disturbance of the mountain geomorphic environment, especially in intertropical mountains where population densities are higher than in any other mountain region. Anthropogenically induced hydroclimate change increases geomorphic hazards and risks but also provides new opportunities for mountain landscape enhancement. Each theme is considered with respect to the distinctiveness of mountain geomorphology and in relation to important advances in research over the past decade. The traditional reliance on the high energy condition to define mountain geomorphology seems less important than the presence of unique mountain landforms and landscapes and the distinctive ways in which human activity and anthropogenically induced hydroclimate change are transforming mountain landscapes.
-
Aerosol-associated changes in tropical stratospheric ozone following the eruption of Mount Pinatubo
Grant, William B.; Browell, Edward V.; Fishman, Jack; Brackett, Vincent G.; Veiga, Robert E.; Nganga, Dominique; Minga, A.; Cros, Bernard; Butler, Carolyn F.; Fenn, Marta A.
1994-01-01
The large amount of sulfuric acid aerosol formed in the stratosphere by conversion of sulfur dioxide emitted by the eruption of Mount Pinatubo (15.14 deg N, 120.35 deg E) in the Philippines around June 15, 1991, has had a pronounced effect on lower stratospheric ozone in the tropics. Measurements of stratospheric ozone in the tropics using electrochemical concentration cell (ECC) sondes before and after the eruption and the airborne UV differential absorption lidar (DIAL) system after the eruption are compared with Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment II (SAGE II) measurements from several years before the eruption and ECC sonde measurements from the year prior to the eruption to determine the resulting changes. Ozone decreases of up to 33 % compared with SAGE II climatological values were found to be directly correlated with altitude regions of enhanced aerosol loading in the 16- to 28-km range. A maximum partial-column decrease of 29 +/- Dobson units (DU) was found over the 16- to 28-km range in September 1991 along with small increases (to 5.9 +/- 2 DU) from 28 to 31.5 km. A large decrease of ozone was also found at 4 deg to 8 deg S from May to August 1992, with a maximum decrease of 33 +/- 7 DU found above Brazzaville in July. Aerosol data form the visible channel of the advanced very high resolution radiometer (AVHRR) and the visible wavelength of the UV DIAL system were used to examine the relationship between aerosol (surface area) densities and ozone changes. The tropical stratospheric ozone changes we observed in 1991 and 1992 are likely be explained by a combination of dynamical (vertical transport) perturbations, radiative perturbations on ozone photochemistry, and heterogeneous chemistry.
-
Study of equatorial Kelvin waves using the MST radar and radiosonde observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Kishore
2005-06-01
Full Text Available In this paper an attempt has been made to study equatorial Kelvin waves using a high power coherent VHF radar located at Gadanki (13.5° N, 79.2° E, a tropical station in the Indian sub-continent. Simultaneous radiosonde observations taken from a nearby meteorological station located in Chennai (13.04° N, 80.17° E were also used to see the coherence in the observed structures. These data sets were analyzed to study the mean winds and equatorial waves in the troposphere and lower stratosphere. Equatorial waves with different periodicities were identified. In the present study, particular attention has been given to the fast Kelvin wave (6.5-day and slow Kelvin wave (16-day. Mean zonal wind structures were similar at both locations. The fast Kelvin wave amplitudes were somewhat similar in both observations and the maximum amplitude is about 8m/s. The phase profiles indicated a slow downward progression. The slow Kelvin wave (16-day amplitudes shown by the radiosonde measurements are a little larger than the radar derived amplitudes. The phase profiles showed downward phase progression and it translates into a vertical wavelength of ~10-12km. The radar and radiosonde derived amplitudes of fast and slow Kelvin waves are larger at altitudes near the tropopause (15-17km, where the mean wind attains westward maximum.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pawson, S.; Labitzke, K.; Lenschow, R.; Naujokat, B.; Rajewski, B.; Wiesner, M.; Wohlfart, R.C.
1993-01-01
This work presents a climatology of the northern hemisphere lower and middle stratosphere derived from daily radiosonde observations subjectively analysed in the Stratospheric Research Group of the 'Meteorologisches Institut der Freien Universitaet Berlin'. Previous climatologies from these data were presented by Labitzke (1972), van Loon et al. (1972), and by Labitzke and Goretzki (1982). Although some more recent climatological fields have been presented in several works by members of the group, no complete atlas has been compiled for some time. The work is intended to serve as a reference for people interested in the stratosphere and, particularly, the climate analysis and modelling communities, which require contemporary analyses of the available data in order to interpret their products. In this first part of the climatological atlas, monthly mean data are presented. (orig./KW)
-
H2SO4-HNO3-H2O ternary system in the stratosphere
Kiang, C. S.; Hamill, P.
1974-01-01
Estimation of the equilibrium vapor pressure over the ternary system H2SO4-HNO3-H2O to study the possibility of stratospheric aerosol formation involving HNO3. It is shown that the vapor pressures for the ternary system H2SO4-HNO3-H2O with weight composition around 70-80% H2SO4, 10-20% HNO3, 10-20% H2O at -50 C are below the order of 10 to the minus 8th mm Hg. It is concluded that there exists more than sufficient nitric acid and water vapor in the stratosphere to participate in ternary system aerosol formation at -50 C. Therefore, HNO3 should be present in stratospheric aerosols, provided that H2SO4 is also present.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Pawson, S; Labitzke, K; Lenschow, R; Naujokat, B; Rajewski, B; Wiesner, M; Wohlfart, R C
1933-01-01
This work presents a climatology of the northern hemisphere lower and middle stratosphere derived from daily radiosonde observations subjectively analysed in the Stratospheric Research Group of the 'Meteorologisches Institut der Freien Universitaet Berlin'. Previous climatologies from these data were presented by Labitzke (1972), van Loon et al. (1972), and by Labitzke and Goretzki (1982). Although some more recent climatological fields have been presented in several works by members of the group, no complete atlas has been compiled for some time. The work is intended to serve as a reference for people interested in the stratosphere and, particularly, the climate analysis and modelling communities, which require contemporary analyses of the available data in order to interpret their products. In this first part of the climatological atlas, monthly mean data are presented. (orig./KW)
-
Eight years of stratospheric ozone observations at Marambio, Antarctica
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Damski, J; Taalas, P [Finnish Meteorological Inst., Helsinki (Finland). Section of Ozone and UV Research
1996-12-31
In this work behaviour of the stratospheric ozone using the total ozone and ozone sounding measurements from Marambio (64 deg 14`S, 56 deg 37`W) at Antarctic Peninsula has been studied. The effects of depleted stratospheric ozone to the UV-B-radiation are investigated employing a radiative transfer model, and the Marambio total ozone measurements. The levels of UV-B radiation have been studied from the point of the erythemal UV-B-doses on the horizontal human epidermis. The low values of total ozone at Marambio are also reflected to the received UV-doses which have increased roughly 20-80% (compared to long term average) during austral spring and summer. In respective to the total amount of ozone, the model calculations show that during October the UV-B-doses can be at the same level they should be during normal summer
-
Eight years of stratospheric ozone observations at Marambio, Antarctica
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Damski, J.; Taalas, P. [Finnish Meteorological Inst., Helsinki (Finland). Section of Ozone and UV Research
1995-12-31
In this work behaviour of the stratospheric ozone using the total ozone and ozone sounding measurements from Marambio (64 deg 14`S, 56 deg 37`W) at Antarctic Peninsula has been studied. The effects of depleted stratospheric ozone to the UV-B-radiation are investigated employing a radiative transfer model, and the Marambio total ozone measurements. The levels of UV-B radiation have been studied from the point of the erythemal UV-B-doses on the horizontal human epidermis. The low values of total ozone at Marambio are also reflected to the received UV-doses which have increased roughly 20-80% (compared to long term average) during austral spring and summer. In respective to the total amount of ozone, the model calculations show that during October the UV-B-doses can be at the same level they should be during normal summer
-
The Evolution and Fate of Saturn's Stratospheric Vortex: Infrared Spectroscopy from Cassini
Fletcher, Leigh N.; Hesman, B. E.; Arhterberg, R. K.; Bjoraker, G.; Irwin, P. G. J.; Hurley, J.; Sinclair, J.; Gorius, N.; Orton, G. S.; Read, P. L.;

2012-01-01
The planet-encircling springtime storm in Saturn's troposphere (December 2010-July 2011) produced dramatic perturbations to stratospheric temperatures, winds and composition at mbar pressures that persisted long after the tropospheric disturbance had abated. Observations from the Cassini Composite Infrared Spectrometer (CIRS), supported by ground-based imaging from the VISIR instrument on the Very Large Telescope,is used to track the evolution of a large, hot stratospheric anticyclone between January 2011 and the present day. The evolutionary sequence can be divided into three phases: (I) the formation and intensification of two distinct warm airmasses near 0.5 mbar between 25 and 35N (one residing directly above the convective storm head) between January-April 2011, moving westward with different zonal velocities; (II) the merging of the warm airmasses to form the large single 'stratospheric beacon' near 40N between April and June 2011, dissociated from the storm head and at a higher pressure (2 mbar) than the original beacons; and (III) the mature phase characterized by slow cooling and longitudinal shrinkage of the anticyclone since July 2011, moving west with a near-constant velocity of 2.70+/-0.04 deg/day (-24.5+/-0.4 m/s at 40N). Peak temperatures of 220 K at 2 mbar were measured on May 5th 2011 immediately after the merger, some 80 K warmer than the quiescent surroundings. Thermal winds hear calculations in August 2011 suggest clockwise peripheral velocities of 200400 mls at 2 mbar, defining a peripheral collar with a width of 65 degrees longitude (50,000 km in diameter) and 25 degrees latitude. Stratospheric acetylene (C2H2) was uniformly enhanced by a factor of three within the vortex, whereas ethane (C2H6) remained unaffected. We will discuss the thermal and chemical characteristics of Saturn's beacon in its mature phase, and implications for stratospheric vortices on other giant planets.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
K. Meraner
2018-01-01
Full Text Available Energetic particles enter the polar atmosphere and enhance the production of nitrogen oxides and hydrogen oxides in the winter stratosphere and mesosphere. Both components are powerful ozone destroyers. Recently, it has been inferred from observations that the direct effect of energetic particle precipitation (EPP causes significant long-term mesospheric ozone variability. Satellites observe a decrease in mesospheric ozone up to 34 % between EPP maximum and EPP minimum. Stratospheric ozone decreases due to the indirect effect of EPP by about 10–15 % observed by satellite instruments. Here, we analyze the climate impact of winter boreal idealized polar mesospheric and polar stratospheric ozone losses as caused by EPP in the coupled Max Planck Institute Earth System Model (MPI-ESM. Using radiative transfer modeling, we find that the radiative forcing of mesospheric ozone loss during polar night is small. Hence, climate effects of mesospheric ozone loss due to energetic particles seem unlikely. Stratospheric ozone loss due to energetic particles warms the winter polar stratosphere and subsequently weakens the polar vortex. However, those changes are small, and few statistically significant changes in surface climate are found.
-
Liang, Q.; Douglass, A. R.; Duncan, B. N.; Stolarski, R. S.; Witte, J. C.
2009-01-01
We used the seasonality of a combination of atmospheric trace gases and idealized tracers to examine stratosphere-to-troposphere transport and its influence on tropospheric composition in the Arctic. Maximum stratosphere-to-troposphere transport of CFCs and O3 occurs in April as driven by the Brewer-Dobson circulation. Stratosphere-troposphere exchange (STE) occurs predominantly between 40 deg N to 80 deg N with stratospheric influx in the mid-latitudes (30-70 deg N) accounting for 67.81 percent of the air of stratospheric origin in the Northern Hemisphere extratropical troposphere. Transport from the lower stratosphere to the lower troposphere (LT) takes three months on average, one month to cross the tropopause, the second month to travel from the upper troposphere (UT) to the middle troposphere (MT), and the third month to reach the LT. During downward transport, the seasonality of a trace gas can be greatly impacted by wet removal and chemistry. A comparison of idealized tracers with varying lifetimes suggests that when initialized with the same concentrations and seasonal cycles at the tropopause, trace gases that have shorter lifetimes display lower concentrations, smaller amplitudes, and earlier seasonal maxima during transport to the LT. STE contributes to O3 in the Arctic troposphere directly from the transport of O3 and indirectly from the transport of NOy . Direct transport of O3 from the stratosphere accounts for 78 percent of O3 in the Arctic UT with maximum contributions occurring from March to May. The stratospheric contribution decreases significantly in the MT/LT (20.25 percent of total O3) and shows a very weak March.April maximum. Our NOx budget analysis in the Arctic UT shows that during spring and summer, the stratospheric injection of NO y-rich air increases NOx concentrations above the 20 pptv threshold level, thereby shifting the Arctic UT from a regime of net photochemical ozone loss to one of net production with rates as high as +16 ppbv/month.
-
Liang, Q.; Douglass, A. R.; Duncan, B. N.; Stolarski, R. S.; Witte, J. C.
2009-05-01
We used the seasonality of a combination of atmospheric trace gases and idealized tracers to examine stratosphere-to-troposphere transport and its influence on tropospheric composition in the Arctic. Maximum stratosphere-to-troposphere transport of CFCs and O3 occurs in April as driven by the Brewer-Dobson circulation. Stratosphere-troposphere exchange (STE) occurs predominantly between 40° N to 80° N with stratospheric influx in the mid-latitudes (30-70° N) accounting for 67-81% of the air of stratospheric origin in the Northern Hemisphere extratropical troposphere. Transport from the lower stratosphere to the lower troposphere (LT) takes three months on average, one month to cross the tropopause, the second month to travel from the upper troposphere (UT) to the middle troposphere (MT), and the third month to reach the LT. During downward transport, the seasonality of a trace gas can be greatly impacted by wet removal and chemistry. A comparison of idealized tracers with varying lifetimes suggests that when initialized with the same concentrations and seasonal cycles at the tropopause, trace gases that have shorter lifetimes display lower concentrations, smaller amplitudes, and earlier seasonal maxima during transport to the LT. STE contributes to O3 in the Arctic troposphere directly from the transport of O3 and indirectly from the transport of NOy. Direct transport of O3 from the stratosphere accounts for 78% of O3 in the Arctic UT with maximum contributions occurring from March to May. The stratospheric contribution decreases significantly in the MT/LT (20-25% of total O3) and shows a very weak March-April maximum. Our NOx budget analysis in the Arctic UT shows that during spring and summer, the stratospheric injection of NOy-rich air increases NOx concentrations above the 20 pptv threshold level, thereby shifting the Arctic UT from a regime of net photochemical ozone loss to one of net production with rates as high as +16 ppbv/month.
-
Observed temporal evolution of global mean age of stratospheric air for the 2002 to 2010 period
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. P. Stiller
2012-04-01
Full Text Available An extensive observational data set, consisting of more than 106 SF6 vertical profiles from MIPAS measurements distributed over the whole globe has been condensed into monthly zonal means of mean age of air for the period September 2002 to January 2010, binned at 10° latitude and 1–2 km altitude. The data were analysed with respect to their temporal variation by fitting a regression model consisting of a constant and a linear increase term, 2 proxies for the QBO variation, sinusoidal terms for the seasonal and semi-annual variation and overtones for the correction of the shapes to the observed data set. The impact of subsidence of mesospheric SF6-depleted air and in-mixing into non-polar latitudes on mid-latitudinal absolute age of air and its linear increase was assessed and found to be small.
The linear increase of mean age of stratospheric air was found to be positive and partly larger than the trend derived by Engel et al. (2009 for most of the Northern mid-latitudes, the middle stratosphere in the tropics, and parts of the Southern mid-latitudes, as well as for the Southern polar upper stratosphere. Multi-year decrease of age of air was found for the lowermost and the upper stratospheric tropics, for parts of Southern mid-latitudes, and for the Northern polar regions. Analysis of the amplitudes and phases of the seasonal variation shed light on the coupling of stratospheric regions to each other. In particular, the Northern mid-latitude stratosphere is well coupled to the tropics, while the Northern lowermost mid-latitudinal stratosphere is decoupled, confirming the separation of the shallow branch of the Brewer-Dobson circulation from the deep branch. We suggest an overall increased tropical upwelling, together with weakening of mixing barriers, especially in the Northern Hemisphere, as a hypothetical model to explain the observed pattern of linear multi-year increase/decrease, and amplitudes
-
Holt, L A; Alexander, M J; Coy, L; Liu, C; Molod, A; Putman, W; Pawson, S
2017-07-01
In this study, gravity waves (GWs) in the high-resolution GEOS-5 Nature Run are first evaluated with respect to satellite and other model results. Southern Hemisphere winter sources of non-orographic GWs in the model are then investigated by linking measures of tropospheric non-orographic gravity wave generation tied to precipitation and frontogenesis with absolute gravity wave momentum flux in the lower stratosphere. Finally, non-orographic GW momentum flux is compared to orographic gravity wave momentum flux and compared to previous estimates. The results show that the global patterns in GW amplitude, horizontal wavelength, and propagation direction are realistic compared to observations. However, as in other global models, the amplitudes are weaker and horizontal wavelengths longer than observed. The global patterns in absolute GW momentum flux also agree well with previous model and observational estimates. The evaluation of model non-orographic GW sources in the Southern Hemisphere winter shows that strong intermittent precipitation (greater than 10 mm h -1 ) is associated with GW momentum flux over the South Pacific, whereas frontogenesis and less intermittent, lower precipitation rates (less than 10 mm h -1 ) are associated with GW momentum flux near 60°S. In the model, orographic GWs contribute almost exclusively to a peak in zonal mean momentum flux between 70 and 75°S, while non-orographic waves dominate at 60°S, and non-orographic GWs contribute a third to a peak in zonal mean momentum flux between 25 and 30°S.
-
Sassi, F.; McDonald, S. E.; McCormack, J. P.; Tate, J.; Liu, H.; Kuhl, D.
2017-12-01
The 2015-2016 boreal winter and spring is a dynamically very interesting time in the lower atmosphere: a minor high latitude stratospheric warming occurred in February 2016; an interrupted descent of the QBO was found in the tropical stratosphere; and a large warm ENSO took place in the tropical Pacific Ocean. The stratospheric warming, the QBO and ENSO are known to affect in different ways the meteorology of the upper atmosphere in different ways: low latitude solar tides and high latitude planetary-scale waves have potentially important implications on the structure of the ionosphere. In this study, we use global atmospheric analyses from a high-altitude version of the High-Altitude Navy Global Environmental Model (HA-NAVGEM) to constrain the meteorology of numerical simulations of the Specified Dynamics Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model, extended version (SD-WACCM-X). We describe the large-scale behavior of tropical tides and mid-latitude planetary waves that emerge in the lower thermosphere. The effect on the ionosphere is captured by numerical simulations of the Navy Highly Integrated Thermosphere Ionosphere Demonstration System (Navy-HITIDES) that uses the meteorology generated by SD-WACCM-X to drive ionospheric simulations during this time period. We will analyze the impact of various dynamical fields on the zonal behavior of the ionosphere by selectively filtering the relevant dynamical modes.
-
Brühl, C; Lelieveld, J; Tost, H; Höpfner, M; Glatthor, N
2015-03-16
Multiyear simulations with the atmospheric chemistry general circulation model EMAC with a microphysical modal aerosol module at high vertical resolution demonstrate that the sulfur gases COS and SO 2 , the latter from low-latitude and midlatitude volcanic eruptions, predominantly control the formation of stratospheric aerosol. Marine dimethyl sulfide (DMS) and other SO 2 sources, including strong anthropogenic emissions in China, are found to play a minor role except in the lowermost stratosphere. Estimates of volcanic SO 2 emissions are based on satellite observations using Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer and Ozone Monitoring Instrument for total injected mass and Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS) on Envisat or Stratospheric Aerosol and Gases Experiment for the spatial distribution. The 10 year SO 2 and COS data set of MIPAS is also used for model evaluation. The calculated radiative forcing of stratospheric background aerosol including sulfate from COS and small contributions by DMS oxidation, and organic aerosol from biomass burning, is about 0.07W/m 2 . For stratospheric sulfate aerosol from medium and small volcanic eruptions between 2005 and 2011 a global radiative forcing up to 0.2W/m 2 is calculated, moderating climate warming, while for the major Pinatubo eruption the simulated forcing reaches 5W/m 2 , leading to temporary climate cooling. The Pinatubo simulation demonstrates the importance of radiative feedback on dynamics, e.g., enhanced tropical upwelling, for large volcanic eruptions.
-
CERN: Antiprotons probe the nuclear stratosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Anon.
1995-01-01
The outer periphery of heavy stable nuclei is notoriously difficult to study experimentally. While the well understood electromagnetic interaction between electrons (or muons) and protons has given the nuclear charge (or proton) distribution with high precision for almost all stable nuclei, neutron distribution studies are much less precise. This is especially true for large nuclear distances, where the nuclear density is small. A few previous experiments probing the nuclear ''stratosphere'' suggested that far from the centre of the nucleus (of the order of 2 nuclear radii) this stratosphere may be composed predominantly of neutrons. At the end of the sixties the term ''neutron halo'' was introduced to describe this phenomenon, but experimental evidence was scarce or even controversial, and remained so for almost a quarter of a century. Recently, the Warsaw/Munich/Berlin collaboration working within the PS203 experiment at CERN's LEAR low energy antiproton ring, proposed a new method to study the nuclear periphery using stopped antiprotons. The halo now looks firmer. A 200 MeV/c beam of antiprotons was slowed down by interactions with atomic electrons. When antiproton kinetic energy drops well below 1 keV, the particles are captured in the outermost orbits of ''exotic atoms'', where the antiprotons take the place of the usual orbital electrons. With the lower orbits in this antiprotonic atom empty, the antiproton drops toward the nuclear surface, first emitting Auger electrons and later predominantly antiprotonic X-rays. Due to the strong interaction between antiprotons and nucleons, the antiproton succumbs to annihilation with a nucleon in the rarified nuclear stratosphere, far above the innermost Bohr orbit of the atom. The annihilation probability in heavy nuclei is maximal where the nuclear density is about 3% of its central value and extends to densities many orders of magnitude smaller
-
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Vollmer, David R
2008-01-01
... advection, forming an intense inversion. Such a configuration may be associated with vertically-intersecting ageostrophic jet circulations or trough-induced differential vertical motions leading to cold air undercutting a warm layer aloft...
-
Comparison of the long-term trends in stratospheric dynamics of four reanalyses
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Kozubek
2017-02-01
Full Text Available Since the long-term trends of different atmospheric parameters have been already studied separately in many papers, this study is focused on the stratospheric wind (zonal and meridional components and temperature over the whole globe at 10 hPa during 1979–2015. We present the trends for the whole winter (October–March, for each individual month of winter and separately for the period before and after the ozone trend turnaround during the mid-1990s. The change of ozone trends has a clear impact on trends in other investigated stratospheric parameters. Four reanalyses (MERRA, ERA-Interim, JRA-55 and NCEP-DOE are used for comparison. Every grid point is analysed, not zonal averages. The comparison of trends in meridional wind, which is closely connected with Brewer–Dobson circulation, shows a good agreement for all four reanalyses (main features and amplitudes of the trends in terms of winter averages, but there are some differences in individual months, particularly in trend amplitude. These results could be important for studying dynamics (transport in the whole stratosphere.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Huang, Bohua; Kinter, James L. [George Mason University, Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic, and Earth Sciences, College of Science, Fairfax, VA (United States); Center for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies, Calverton, MD (United States); Hu, Zeng-Zhen [Center for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies, Calverton, MD (United States); Climate Prediction Center (suite 605), NCEP/NWS/NOAA, Camp Springs, MD (United States); Wu, Zhaohua [Florida State University, Department of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric Science, and Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Tallahassee, FL (United States); Kumar, Arun [Climate Prediction Center (suite 605), NCEP/NWS/NOAA, Camp Springs, MD (United States)
2012-01-15
The stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) and its association with the interannual variability in the stratosphere and troposphere, as well as in tropical sea surface temperature anomalies (SSTA), are examined in the context of a QBO life cycle. The analysis is based on the ERA40 and NCEP/NCAR reanalyses, radiosonde observations at Singapore, and other observation-based datasets. Both reanalyses reproduce the QBO life cycle and its associated variability in the stratosphere reasonably well, except that some long-term changes are detected only in the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. In order to separate QBO from variability on other time scales and to eliminate the long-term changes, a scale separation technique [Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (EEMD)] is applied to the raw data. The QBO component of zonal wind anomalies at 30 hPa, extracted using the EEMD method, is defined as a QBO index. Using this index, the QBO life cycle composites of stratosphere and troposphere variables, as well as SSTA, are constructed and examined. The composite features in the stratosphere are generally consistent with previous investigations. The correlations between the QBO and tropical Pacific SSTA depend on the phase in a QBO life cycle. On average, cold (warm) SSTA peaks about half a year after the maximum westerlies (easterlies) at 30 hPa. The connection of the QBO with the troposphere seems to be associated with the differences of temperature anomalies between the stratosphere and troposphere. While the anomalies in the stratosphere propagate downward systematically, some anomalies in the troposphere develop and expand vertically. Therefore, it is possible that the temperature difference between the troposphere and stratosphere may alter the atmospheric stability and tropical deep convection, which modulates the Walker circulation and SSTA in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. (orig.)
-
Huang, Bohua; Hu, Zeng-Zhen; Kinter, James L.; Wu, Zhaohua; Kumar, Arun
2012-01-01
The stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) and its association with the interannual variability in the stratosphere and troposphere, as well as in tropical sea surface temperature anomalies (SSTA), are examined in the context of a QBO life cycle. The analysis is based on the ERA40 and NCEP/NCAR reanalyses, radiosonde observations at Singapore, and other observation-based datasets. Both reanalyses reproduce the QBO life cycle and its associated variability in the stratosphere reasonably well, except that some long-term changes are detected only in the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. In order to separate QBO from variability on other time scales and to eliminate the long-term changes, a scale separation technique [Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (EEMD)] is applied to the raw data. The QBO component of zonal wind anomalies at 30 hPa, extracted using the EEMD method, is defined as a QBO index. Using this index, the QBO life cycle composites of stratosphere and troposphere variables, as well as SSTA, are constructed and examined. The composite features in the stratosphere are generally consistent with previous investigations. The correlations between the QBO and tropical Pacific SSTA depend on the phase in a QBO life cycle. On average, cold (warm) SSTA peaks about half a year after the maximum westerlies (easterlies) at 30 hPa. The connection of the QBO with the troposphere seems to be associated with the differences of temperature anomalies between the stratosphere and troposphere. While the anomalies in the stratosphere propagate downward systematically, some anomalies in the troposphere develop and expand vertically. Therefore, it is possible that the temperature difference between the troposphere and stratosphere may alter the atmospheric stability and tropical deep convection, which modulates the Walker circulation and SSTA in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
-
High-Resolution Body Wave Tomography of the Ross Sea Embayment, Antarctica
White-Gaynor, A.; Nyblade, A.; Wiens, D. A.; Aster, R. C.; Gerstoft, P.; Bromirski, P. D.; Stephen, R. A.
2017-12-01
The West Antarctic Rift System (WARS) is one of the least understood continental rift system on the planet. The 1000 km wide WARS includes the Ross Sea Embayment between Marie Byrd Land and the Transantarctic Mountains (TAMS). Active volcanism on Ross Island continues to challenge our understanding of the generally quiescent rift system. Previous regional-scale body wave tomographic investigations have identified areas of low seismic wave speeds to 200 km depth beneath Ross Island. However, the spatial extent of the low velocity structure across the entirety of the WARS remains poorly constrained due to the insufficient resolution of upper mantle structure under the Ross Sea Embayment away from Ross Island. We utilize teleseismic P wave observations recorded on the RIS/DRIS network, which consists of 34 seismometers deployed across the Ross Ice Shelf, along with data from nearby POLENET and TAMSEIS stations to better resolve this region. Relative P wave travel time residuals from 1300 teleseismic events, obtained using a multichannel cross-correlation method, have been inverted for a seismic velocity model of the upper mantle throughout the Ross Sea Embayment. Our results suggest that the low wave speed structure under Ross Island extends roughly halfway across the Embayment and south along the Transantarctic Mountains. This observation is consistent with a two-phase rifting history for the WARS in which broad, late Cretaceous rifting between Marie Byrd Land and the TAMS transitioned to more focused rifting along the TAMS margin in the Cenozoic.
-
Interpretation of DIAL Measurements of Lower Stratospheric Ozone in Regions with Pinatubo Aerosols
Grant, William B.; Browell, Edward V.; Fenn, Marta A.; Butler, Carolyn F.; Brackett, Vincent G.; Veiga, Robert E.; Mayor, Shane D.; Fishman, Jack; Nganga, D.; Minga, A.
1992-01-01
The influence of volcanic aerosols on stratospheric ozone is a topic of current interest, especially with the June 15, 1991 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo in the Philippines. Lidar has been used in the past to provide aerosol profiles which could be compared with ozone profiles measured using ozonesondes to look for coincidences between volcanic aerosols and ozone decreases. The differential absorption lidar (DIAL) technique has the advantages of being able to measure ozone and aerosol profiles simultaneously as well as being able to cover large geographical regions rapidly. While there are problems associated with correcting the ozone profiles for the presence of aerosols, the corrections can be made reliably when the wavelengths are closely spaced and the Bernoulli method is applied. The DIAL measurements considered in this paper are those obtained in the tropical stratosphere in January 1992 during the Airborne Arctic Stratospheric Expedition (AASE-II). The determination of ozone profiles in the presence of Pinatubo aerosols is discussed in a companion paper.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wuebbles, D.J.
1981-09-01
Since the LLNL one-dimensional coupled transport and chemical kinetics model of the troposphere and stratosphere was originally developed in 1972 (Chang et al., 1974), there have been many changes to the model's representation of atmospheric physical and chemical processes. A brief description is given of the current LLNL one-dimensional coupled transport and chemical kinetics model of the troposphere and stratosphere
-
Homeyer, C. R.
2017-12-01
Deep convection reaching the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) and its impact on atmospheric composition through rapid vertical transport of lower troposphere air and stratosphere-troposphere exchange has received increasing attention in the past 5-10 years. Most efforts focused on convection have been directed toward storms that reach and/or penetrate the coincident environmental lapse-rate tropopause. However, convection has also been shown to reach into large-scale stratospheric intrusions (depressions of stratospheric air lying well below the lapse-rate tropopause on the cyclonic side of upper troposphere jet streams). Such convective penetration of stratospheric intrusions is not captured by studies of lapse-rate tropopause-penetrating convection. In this presentation, it will be shown using hourly, high-quality mergers of ground-based radar observations from 2004 to 2013 in the contiguous United States (CONUS) and forward large-scale trajectory analysis that convective penetration of stratospheric intrusions: 1) is more frequent than lapse-rate tropopause-penetrating convection, 2) occurs over a broader area of the CONUS than lapse-rate tropopause-penetrating convection, and 3) can influence the composition of the lower stratosphere through large-scale advection of convectively influenced air to altitudes above the lapse-rate tropopause, which we find to occur for about 8.5% of the intrusion volumes reached by convection.
-
Gravitational waves from color-magnetic "mountains" in neutron stars.
Glampedakis, K; Jones, D I; Samuelsson, L
2012-08-24
Neutron stars may harbor the true ground state of matter in the form of strange quark matter. If present, this type of matter is expected to be a color superconductor, a consequence of quark pairing with respect to the color and flavor degrees of freedom. The stellar magnetic field threading the quark core becomes a color-magnetic admixture and, in the event that superconductivity is of type II, leads to the formation of color-magnetic vortices. In this Letter, we show that the volume-averaged color-magnetic vortex tension force should naturally lead to a significant degree of nonaxisymmetry in systems such as radio pulsars. We show that gravitational radiation from such color-magnetic "mountains" in young pulsars, such as the Crab and Vela, could be observable by the future Einstein Telescope, thus, becoming a probe of paired quark matter in neutron stars. The detectability threshold can be pushed up toward the sensitivity level of Advanced LIGO if we invoke an interior magnetic field about a factor ten stronger than the surface polar field.
-
Hygienic estimation of population doses due to stratospheric fallout
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Marej, A.N.; Knizhnikov, V.A.
1980-01-01
The hygienic estimation of external and internal irradiation of the USSR population due to stratospheric global fallouts of fission products after nuclear explosions and weapon tests, is carried out. Numerical values which characterize the dose-effect dependence in the case of radiation of marrow, bone tissue and whole body are presented. Values of mean individual and population doses of irradiation due to global fallouts within 1963-1975, types of injury and the number of mortal cases due to malignant neoplasms are presented. A conclusion is made that the contribution of radiation due to stratospheric fallouts in the mortality due to malignant neoplasms is insignificant. Annual radiation doses, conditioned by global fallouts within the period of 1963-1975 constitute but several percent from the dose of radiation of the natural radiation background. Results of estimation of genetic consequences of irradiation due to atmospheric fallouts are presented
-
Stratospheric chlorine injection by volcanic eruptions - HCl scavenging and implications for ozone
Tabazadeh, A.; Turco, R. P.
1993-01-01
Because the output of volatile chlorine during a major volcanic event can greatly exceed the annual anthropogenic emissions of chlorine to the atmosphere, the fate of volcanic chlorine must be known. Although numerous observations have shown that volcanoes do not significantly contribute to the stratospheric chlorine burden, no quantitative explanation has been published. Hydrogen chloride (HCl) scavenging processes during the early phases of a volcanic eruption are discussed. A plume dynamics and thermodynamics model is used to show that HCl removal in condensed supercooled water can reduce HCl vapor concentrations by up to four orders of magnitude, preventing substantial stratospheric chlorine injection.
-
Solar UV radiation variations and their stratospheric and climatic effects
Donnelly, R. F.; Heath, D. F.
1985-01-01
Nimbus-7 SBUV measurements of the short-term solar UV variations caused by solar rotation and active-region evolution have determined the amplitude and wavelength dependence for the active-region component of solar UV variations. Intermediate-term variations lasting several months are associated with rounds of major new active regions. The UV flux stays near the peak value during the current solar cycle variation for more than two years and peaks about two years later than the sunspot number. Nimbus-7 measurements have observed the concurrent stratospheric ozone variations caused by solar UV variations. There is now no doubt that solar UV variations are an important cause of short- and long-term stratospheric variations, but the strength of the coupling to the troposphere and to climate has not yet been proven.
-
Chemical characterization of local and stratospheric plutonium in Ohio soils
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Muller, R.N.
1978-01-01
The chemical nature of plutonium derived from stratospheric fallout and industrial sources was studied in three agricultural soils. The majority of the soil plutonium was associated with a reductant-soluble, hydrous oxide phase that, under most conditions of terrestrial ecosystems, remains essentially immobile. The proportion of plutonium associated with organic matter (0.1N NaOH-extractable) varied among soils, and increased with decreasing particle size in the same soil. In a soil containing 238 Pu from a local fabrication facility and 239 , 240 Pu from stratospheric fallout, isotopic ratios between the NaOH-extractable and residual phases were essentially constant, indicating that, in these soils, plutonium from both sources behaves similarly. The distribution of soil plutonium with particle size appears to be most directly related to the mass of the soil particle
-
Müller, Rolf; Grooß, Jens-Uwe; Mannan Zafar, Abdul; Robrecht, Sabine; Lehmann, Ralph
2018-03-01
The Antarctic ozone hole arises from ozone destruction driven by elevated levels of ozone destroying (active) chlorine in Antarctic spring. These elevated levels of active chlorine have to be formed first and then maintained throughout the period of ozone destruction. It is a matter of debate how this maintenance of active chlorine is brought about in Antarctic spring, when the rate of formation of HCl (considered to be the main chlorine deactivation mechanism in Antarctica) is extremely high. Here we show that in the heart of the ozone hole (16-18 km or 85-55 hPa, in the core of the vortex), high levels of active chlorine are maintained by effective chemical cycles (referred to as HCl null cycles hereafter). In these cycles, the formation of HCl is balanced by immediate reactivation, i.e. by immediate reformation of active chlorine. Under these conditions, polar stratospheric clouds sequester HNO3 and thereby cause NO2 concentrations to be low. These HCl null cycles allow active chlorine levels to be maintained in the Antarctic lower stratosphere and thus rapid ozone destruction to occur. For the observed almost complete activation of stratospheric chlorine in the lower stratosphere, the heterogeneous reaction HCl + HOCl is essential; the production of HOCl occurs via HO2 + ClO, with the HO2 resulting from CH2O photolysis. These results are important for assessing the impact of changes of the future stratospheric composition on the recovery of the ozone hole. Our simulations indicate that, in the lower stratosphere, future increased methane concentrations will not lead to enhanced chlorine deactivation (through the reaction CH4 + Cl → HCl + CH3) and that extreme ozone destruction to levels below ≈ 0.1 ppm will occur until mid-century.
-
Li, Feng; Newman, Paul; Pawson, Steven; Waugh, Darryn
2014-01-01
Stratospheric ozone depletion has played a dominant role in driving Antarctic climate change in the last decades. In order to capture the stratospheric ozone forcing, many coupled atmosphere-ocean general circulation models (AOGCMs) prescribe the Antarctic ozone hole using monthly and zonally averaged ozone field. However, the prescribed ozone hole has a high ozone bias and lacks zonal asymmetry. The impacts of these biases on model simulations, particularly on Southern Ocean and the Antarctic sea ice, are not well understood. The purpose of this study is to determine the effects of using interactive stratospheric chemistry instead of prescribed ozone on Antarctic and Southern Ocean climate change in an AOGCM. We compare two sets of ensemble simulations for the 1960-2010 period using different versions of the Goddard Earth Observing System 5 - AOGCM: one with interactive stratospheric chemistry, and the other with prescribed monthly and zonally averaged ozone and 6 other stratospheric radiative species calculated from the interactive chemistry simulations. Consistent with previous studies using prescribed sea surface temperatures and sea ice concentrations, the interactive chemistry runs simulate a deeper Antarctic ozone hole and consistently larger changes in surface pressure and winds than the prescribed ozone runs. The use of a coupled atmosphere-ocean model in this study enables us to determine the impact of these surface changes on Southern Ocean circulation and Antarctic sea ice. The larger surface wind trends in the interactive chemistry case lead to larger Southern Ocean circulation trends with stronger changes in northerly and westerly surface flow near the Antarctica continent and stronger upwelling near 60S. Using interactive chemistry also simulates a larger decrease of sea ice concentrations. Our results highlight the importance of using interactive chemistry in order to correctly capture the influences of stratospheric ozone depletion on climate
-
Vertical sounding balloons for stratospheric photochemistry
Pommereau, J. P.
The use of vertical sounding balloons for stratospheric photochemistry studies is illustrated by the use of a vertical piloted gas balloon for the search of NO2 diurnal variations. It is shown that the use of montgolfieres (hot air balloons) can enhance the vertical sounding technique. Particular attention is given to a sun-heated montgolfiere and to the more sophisticated infrared montgolfiere that is able to perform three to four vertical excursions per day and to remain aloft for weeks or months.
-
Mountain goat abundance and population trends in the Olympic Mountains, Washington, 2011
Jenkins, Kurt; Happe, Patricia; Griffin, Paul C.; Beirne, Katherine; Hoffman, Roger; Baccus, William
2011-01-01
We conducted an aerial helicopter survey between July 18 and July 25, 2011, to estimate abundance and trends of introduced mountain goats (Oreamnos americanus) in the Olympic Mountains. The survey was the first since we developed a sightability correction model in 2008, which provided the means to estimate the number of mountain goats present in the surveyed areas and not seen during the aerial surveys, and to adjust for undercounting biases. Additionally, the count was the first since recent telemetry studies revealed that the previously defined survey zone, which was delineated at lower elevations by the 1,520-meter elevation contour, did not encompass all lands used by mountain goats during summer. We redefined the lower elevation boundary of survey units before conducting the 2011 surveys in an effort to more accurately estimate the entire mountain goat population. We surveyed 39 survey units, comprising 39 percent of the 59,615-hectare survey area. We estimated a mountain goat population of 344±44 (standard error, SE) in the expanded survey area. Based on this level of estimation uncertainty, the 95-percent confidence interval ranged from 258 to 430 mountain goats at the time of the survey. To permit comparisons of mountain goat populations between the 2004 and 2011 surveys, we recomputed population estimates derived from the 2004 survey using the newly developed bias correction methods, and we computed the 2004 and 2011 surveys based on comparable survey zone definitions (for example, using the boundaries of the 2004 survey). The recomputed estimates of mountain goat populations were 217±19 (SE) in 2004 and 303±41(SE) in 2011. The difference between the current 2011 population estimate (344±44[SE]) and the recomputed 2011 estimate (303±41[SE]) reflects the number of mountain goats counted in the expanded lower elevation portions of the survey zone added in 2011. We conclude that the population of mountain goats has increased in the Olympic Mountains at
-
Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tilmes, S.
2016-12-01
Water vapor maxima are found in the upper troposphere lower stratosphere (UTLS) over Asian and North America monsoon regions during Northern Hemisphere (NH) summer months. High concentrations of stratospheric water vapor are associated with the upper-level anticyclonic circulation and they play an important role in the radiative forcing for the climate system. However, discrepancies in the simulation of stratospheric water vapor are found among different models. In this study, we use both observational data: Aura Microwave Limb Sounder satellite observations (MLS), the Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications version 2 (MERRA-2) and chemistry climate model outputs: different configurations of the Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model (WACCM), including standard configuration of WACCM, WACCM L110, specified chemistry (SC) WACCM and specified dynamics (SD) WACCM. We find that WACCM L110 with finer vertical resolution better simulates the stratospheric water vapor maxima over the summer monsoon regions. To better understand the mechanism, we examine the simulated temperature at around 100 hPa since 100 hPa is known to act as a dehydration mechanism, i.e. the warmer the temperature, the wetter the stratospheric water vapor. We find that both WACCM L110 and SD-WACCM better simulate the temperature at 100 hPa as compared to that of MERRA2. This suggests that improving model vertical resolution and dynamical processes in the UTLS is crucial in simulating the stratospheric water vapor concentrations.
-
Observation of stratospheric ozone with NIES lidar system in Tsukuba, Japan
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nakane, H.; Hayashida, S.; Sasano, Y.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsui, I.; Minato, A.
1992-01-01
Lidars are expected to play important roles in an international monitoring network of the stratosphere such as the Network for the Detection of Stratospheric Change (NDSC). The National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES) in Tsukuba constructed an ozone lidar system in March 1988 and started observation in August 1988. The lidar system has a 2-m telescope and injection locked XeCl and XeF excimer lasers which can measure ozone profiles (15-45 km) and temperature profiles (30-80 km). From December 1991, lidar observations have been carried out in which the second Stokes line of the stimulated Raman scattering of a KrF laser has been used. Ozone profiles obtained with the NIES lidar system are compared with the data provided by the SAGE II satellite sensor. Results showed good agreement for the individual and the zonal mean profiles. Variations of ozone with various time scales at each altitude can be studied using the data obtained with the NIES ozone lidar system. Seasonal variations are easily found at 20 km, 30 km, and 35 km, which are qualitatively understood as a result of dynamical and photochemical effects. Systematic errors of ozone profiles due to the Pinatubo stratospheric aerosols have been detected using multi-wavelength observation
-
Salinas, Cornelius Csar Jude H.; Chang, Loren C.
2018-06-01
This work presents the results of a Conventional Empirical Orthogonal Function Analysis on daily global zonal mean temperature profiles in the Upper Troposphere and Lower Stratosphere (15-35 km), as measured by the FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC mission from January 2007 to June 2013. For validation, results were compared with ERA-Interim reanalysis. Results show that, the leading global EOF mode (27%) from COSMIC is consistent with temperature anomalies due to the tropical cooling associated with boreal winter Sudden Stratospheric Warmings (SSW). The second global EOF mode from COSMIC (15.3%) is consistent with temperature anomalies due to the Quasi-biennial Oscillation (QBO). The third global mode from COSMIC (10.9%) is consistent with temperature anomalies due to the El Nino Southern Oscillation. This work also shows that the second northern hemisphere EOF mode from COSMIC (16.8%) is consistent with temperature anomalies due Rossby-wave breaking (RWB) which is expected to only be resolved by a high vertical and temporal resolution dataset like COSMIC. Our work concludes that the use of a high vertical and temporal resolution dataset like COSMIC yields non-seasonal EOF modes that are consistent with relatively more intricate temperature anomalies due to the SSW, QBO, ENSO and RWB.
-
Multi-model assessment of stratospheric ozone return dates and ozone recovery in CCMVal-2 models
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. Eyring
2010-10-01
Full Text Available Projections of stratospheric ozone from a suite of chemistry-climate models (CCMs have been analyzed. In addition to a reference simulation where anthropogenic halogenated ozone depleting substances (ODSs and greenhouse gases (GHGs vary with time, sensitivity simulations with either ODS or GHG concentrations fixed at 1960 levels were performed to disaggregate the drivers of projected ozone changes. These simulations were also used to assess the two distinct milestones of ozone returning to historical values (ozone return dates and ozone no longer being influenced by ODSs (full ozone recovery. The date of ozone returning to historical values does not indicate complete recovery from ODSs in most cases, because GHG-induced changes accelerate or decelerate ozone changes in many regions. In the upper stratosphere where CO2-induced stratospheric cooling increases ozone, full ozone recovery is projected to not likely have occurred by 2100 even though ozone returns to its 1980 or even 1960 levels well before (~2025 and 2040, respectively. In contrast, in the tropical lower stratosphere ozone decreases continuously from 1960 to 2100 due to projected increases in tropical upwelling, while by around 2040 it is already very likely that full recovery from the effects of ODSs has occurred, although ODS concentrations are still elevated by this date. In the midlatitude lower stratosphere the evolution differs from that in the tropics, and rather than a steady decrease in ozone, first a decrease in ozone is simulated from 1960 to 2000, which is then followed by a steady increase through the 21st century. Ozone in the midlatitude lower stratosphere returns to 1980 levels by ~2045 in the Northern Hemisphere (NH and by ~2055 in the Southern Hemisphere (SH, and full ozone recovery is likely reached by 2100 in both hemispheres. Overall, in all regions except the tropical lower stratosphere, full ozone recovery from ODSs occurs significantly later than the
-
The ten-year pattern (1978-1987) of stratospheric aerosol loading using ground-based radiometry
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Michalsky, J.J.; Pearson, E.W.; LeBaron, B.A.
1988-09-01
In this paper the procedures used to obtain a stratospheric measurement with ground-based sun radiometry are reviewed briefly. The five-wavelength optical depths are then used to study the evolution of aerosol size during the decade. The time history of loading from the instruments described are compared. Particular emphasis will be placed on the Garmisch-Partenkirchen data because their latitude is very nearly that of the PNL site. The most useful data for this study are those observational records that measure total stratospheric aerosol burden and include the early period and continue throughout the eruption and decay of El Chichon. The lidar data from Langley Research Center and Fraunhofer-Institute for Atmospheric Environmental Research at Garmisch-Partenkirchen, the SAM II satellite data, and the Pacific Northwest Laboratory (PNL) sun radiometry are the published contiguous measurements of the stratosphere aerosol burden during this period. 16 refs., 6 figs
-
Impact of H{sub 2} emissions of a global hydrogen economy on the stratosphere
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Grooss, Jens-Uwe; Feck, Thomas; Vogel, Baerbel; Riese, Martin [Forschungszentrum Juelich (Germany)
2010-07-01
''Green'' hydrogen is seen as a major element of the future energy supply to reduce greenhouse gas emissions substantially. However, due to the possible interactions of hydrogen (H{sub 2}) with other atmospheric constituents there is a need to analyse the implications of additional atmospheric H{sub 2} that could result from hydrogen leakage of a global hydrogen infrastructure. Emissions of molecular H{sub 2} can occur along the whole hydrogen process chain which increase the tropospheric H{sub 2} burden. The impact of these emissions is investigated. Figure 1 is a sketch that clarifies the path way and impact of hydrogen in the stratosphere. The air follows the Brewer-Dobson circulation in which air enters the stratosphere through the tropical tropopause, ascends then to the upper stratosphere and finally descends in polar latitudes within a typical transport time frame of 4 to 8 years. (orig.)
-
Atmospheric gravity waves observed by an international network of micro-barographs
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Marty, Julien
2010-01-01
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) manages an international network of forty-two operational infra-sound stations recording the pressure fluctuations produced at the ground surface by infrasonic waves. This thesis demonstrates that most of these stations also accurately detect the pressure fluctuations in the entire gravity wave band. This work includes carrying out and analyzing several metrological laboratory experiments and a field campaign (M2008) in Mongolia in 2008. The layout of the experiments as well as the interpretation of their results gave rise to the development of a new linear spectral numerical model able to simulate the generation and propagation of gravity waves. This model was used to quantify the gravity waves produced by the atmospheric cooling that occurs during solar eclipses. The pressure fluctuations expected at ground level were estimated and compared to the data recorded during the 1 August 2008 solar eclipse by the CTBTO and M2008 stations. A detailed data analysis reveals two waves with similar time-frequency characteristics to those simulated for a stratospheric and tropospheric cooling. This constitutes, to our knowledge, a unique result. The validation of worldwide and pluri-annual pressure measurements in the entire gravity wave band allowed the statistical study of gravity wave spectra and atmospheric tides. The work presented throughout this thesis has led to the publication of two articles. A third one is in the drafting process. (author)
-
Ozone zonal asymmetry and planetary wave characterization during Antarctic spring
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
I. Ialongo
2012-03-01
Full Text Available A large zonal asymmetry of ozone has been observed over Antarctica during winter-spring, when the ozone hole develops. It is caused by a planetary wave-driven displacement of the polar vortex. The total ozone data by OMI (Ozone Monitoring Instrument and the ozone profiles by MLS (Microwave Limb Sounder and GOMOS (Global Ozone Monitoring by Occultation of Stars were analysed to characterize the ozone zonal asymmetry and the wave activity during Antarctic spring. Both total ozone and profile data have shown a persistent zonal asymmetry over the last years, which is usually observed from September to mid-December. The largest amplitudes of planetary waves at 65° S (the perturbations can achieve up to 50% of zonal mean values is observed in October. The wave activity is dominated by the quasi-stationary wave 1 component, while the wave 2 is mainly an eastward travelling wave. Wave numbers 1 and 2 generally explain more than the 90% of the ozone longitudinal variations. Both GOMOS and MLS ozone profile data show that ozone zonal asymmetry covers the whole stratosphere and extends up to the altitudes of 60–65 km. The wave amplitudes in ozone mixing ratio decay with altitude, with maxima (up to 50% below 30 km.
The characterization of the ozone zonal asymmetry has become important in the climate research. The inclusion of the polar zonal asymmetry in the climate models is essential for an accurate estimation of the future temperature trends. This information might also be important for retrieval algorithms that rely on ozone a priori information. -
UV spectroscopy applied to stratospheric chemistry, methods and results
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Karlsen, K.
1996-03-01
The publication from the Norwegian Institute for Air Research (NILU) deals with an investigation done on stratospheric chemistry by UV spectroscopy. The scientific goals are briefly discussed, and it gives the results from the measuring and analysing techniques used in the investigation. 6 refs., 11 figs.
-
Herman, Robert L.; Ray, Eric A.; Rosenlof, Karen H.; Bedka, Kristopher M.; Schwartz, Michael J.; Read, William G.; Troy, Robert F.; Chin, Keith; Christensen, Lance E.; Fu, Dejian; Stachnik, Robert A.; Bui, T. Paul; Dean-Day, Jonathan M.
2017-05-01
The NASA ER-2 aircraft sampled the lower stratosphere over North America during the field mission for the NASA Studies of Emissions and Atmospheric Composition, Clouds and Climate Coupling by Regional Surveys (SEAC4RS). This study reports observations of convectively influenced air parcels with enhanced water vapor in the overworld stratosphere over the summertime continental United States and investigates three case studies in detail. Water vapor mixing ratios greater than 10 ppmv, which is much higher than the background 4 to 6 ppmv of the overworld stratosphere, were measured by the JPL Laser Hygrometer (JLH Mark2) at altitudes between 16.0 and 17.5 km (potential temperatures of approximately 380 to 410 K). Overshooting cloud tops (OTs) are identified from a SEAC4RS OT detection product based on satellite infrared window channel brightness temperature gradients. Through trajectory analysis, we make the connection between these in situ water measurements and OT. Back trajectory analysis ties enhanced water to OT 1 to 7 days prior to the intercept by the aircraft. The trajectory paths are dominated by the North American monsoon (NAM) anticyclonic circulation. This connection suggests that ice is convectively transported to the overworld stratosphere in OT events and subsequently sublimated; such events may irreversibly enhance stratospheric water vapor in the summer over Mexico and the United States. A regional context is provided by water observations from the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS).
-
Nonlinear response of tropical lower-stratospheric temperature and water vapor to ENSO
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. I. Garfinkel
2018-04-01
Full Text Available A series of simulations using the NASA Goddard Earth Observing System Chemistry–Climate Model are analyzed in order to aid in the interpretation of observed interannual and sub-decadal variability in the tropical lower stratosphere over the past 35 years. The impact of El Niño–Southern Oscillation on temperature and water vapor in this region is nonlinear in boreal spring. While moderate El Niño events lead to cooling in this region, strong El Niño events lead to warming, even as the response of the large-scale Brewer–Dobson circulation appears to scale nearly linearly with El Niño. This nonlinearity is shown to arise from the response in the Indo-West Pacific to El Niño: strong El Niño events lead to tropospheric warming extending into the tropical tropopause layer and up to the cold point in this region, where it allows for more water vapor to enter the stratosphere. The net effect is that both strong La Niña and strong El Niño events lead to enhanced entry water vapor and stratospheric moistening in boreal spring and early summer. These results lead to the following interpretation of the contribution of sea surface temperatures to the decline in water vapor in the early 2000s: the very strong El Niño event in 1997/1998, followed by more than 2 consecutive years of La Niña, led to enhanced lower-stratospheric water vapor. As this period ended in early 2001, entry water vapor concentrations declined. This effect accounts for approximately one-quarter of the observed drop.
-
Nonlinear response of tropical lower-stratospheric temperature and water vapor to ENSO
Garfinkel, Chaim I.; Gordon, Amit; Oman, Luke D.; Li, Feng; Davis, Sean; Pawson, Steven
2018-04-01
A series of simulations using the NASA Goddard Earth Observing System Chemistry-Climate Model are analyzed in order to aid in the interpretation of observed interannual and sub-decadal variability in the tropical lower stratosphere over the past 35 years. The impact of El Niño-Southern Oscillation on temperature and water vapor in this region is nonlinear in boreal spring. While moderate El Niño events lead to cooling in this region, strong El Niño events lead to warming, even as the response of the large-scale Brewer-Dobson circulation appears to scale nearly linearly with El Niño. This nonlinearity is shown to arise from the response in the Indo-West Pacific to El Niño: strong El Niño events lead to tropospheric warming extending into the tropical tropopause layer and up to the cold point in this region, where it allows for more water vapor to enter the stratosphere. The net effect is that both strong La Niña and strong El Niño events lead to enhanced entry water vapor and stratospheric moistening in boreal spring and early summer. These results lead to the following interpretation of the contribution of sea surface temperatures to the decline in water vapor in the early 2000s: the very strong El Niño event in 1997/1998, followed by more than 2 consecutive years of La Niña, led to enhanced lower-stratospheric water vapor. As this period ended in early 2001, entry water vapor concentrations declined. This effect accounts for approximately one-quarter of the observed drop.
-
Polar Processes in a 50-year Simulation of Stratospheric Chemistry and Transport
Kawa, S.R.; Douglass, A. R.; Patrick, L. C.; Allen, D. R.; Randall, C. E.
2004-01-01
The unique chemical, dynamical, and microphysical processes that occur in the winter polar lower stratosphere are expected to interact strongly with changing climate and trace gas abundances. Significant changes in ozone have been observed and prediction of future ozone and climate interactions depends on modeling these processes successfully. We have conducted an off-line model simulation of the stratosphere for trace gas conditions representative of 1975-2025 using meteorology from the NASA finite-volume general circulation model. The objective of this simulation is to examine the sensitivity of stratospheric ozone and chemical change to varying meteorology and trace gas inputs. This presentation will examine the dependence of ozone and related processes in polar regions on the climatological and trace gas changes in the model. The model past performance is base-lined against available observations, and a future ozone recovery scenario is forecast. Overall the model ozone simulation is quite realistic, but initial analysis of the detailed evolution of some observable processes suggests systematic shortcomings in our description of the polar chemical rates and/or mechanisms. Model sensitivities, strengths, and weaknesses will be discussed with implications for uncertainty and confidence in coupled climate chemistry predictions.
-
A Model of the Effect of Ozone Depletion on Lower-Stratospheric Structure
Olsen, Mark A.; Stolarski, Richard S.; Gupta, Mohan L.; Nielsen, J. Eric; Pawson, Steven
2005-01-01
We have run two twenty-year integrations of a global circulation model using 1978-1980 and 1998-2000 monthly mean ozone climatologies. The ozone climatology is used solely in the radiation scheme of the model. Several key differences between the model runs will be presented. The temperature and potential vorticity (PV) structure of the lower stratosphere, particularly in the Southern Hemisphere, is significantly changed using the 1998-2000 ozone climatology. In the Southern Hemisphere summer, the lapse rate and PV-defined polar tropopauses are both at altitudes on the order of several hundred meters greater than the 1978-1980 climatological run. The 380 K potential temperature surf= is likewise at a greater altitude. The mass of the extratropical lowermost stratosphere (between the tropopause and 380 K surface) remains unchanged. The altitude differences are not observed in the Northern Hemisphere. The different ozone fields do not produce a significant change in the annual extratropical stratosphere-troposphere exchange of mass although slight variations in the spatial distribution of the exchange exist. We are also investigating a delay in the breakup of the Southern Hemisphere polar vortex due to the differing ozone climatologies.
-
THERMAL AND CHEMICAL STRUCTURE VARIATIONS IN TITAN'S STRATOSPHERE DURING THE CASSINI MISSION
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bampasidis, Georgios; Coustenis, A.; Vinatier, S. [Laboratoire d' Etudes Spatiales et d' Instrumentation en Astrophysique (LESIA), Observatoire de Paris, CNRS, UPMC Univ. Paris 06, Univ. Paris-Diderot, 5, place Jules Janssen, F-92195 Meudon Cedex (France); Achterberg, R. K. [Department of Astronomy, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742 (United States); Lavvas, P. [GSMA, Universite Reims Champagne-Ardenne, F-51687 Reims Cedex 2 (France); Nixon, C. A.; Jennings, D. E.; Flasar, F. M.; Carlson, R. C.; Romani, P. N.; Guandique, E. A. [Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 (United States); Teanby, N. A. [School of Earth Sciences, University of Bristol, Bristol BS8 1RJ (United Kingdom); Moussas, X.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Stamogiorgos, S., E-mail: gbabasid@phys.uoa.gr [Faculty of Physics, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Panepistimioupolis, GR 15783 Zographos, Athens (Greece)
2012-12-01
We have developed a line-by-line Atmospheric Radiative Transfer for Titan code that includes the most recent laboratory spectroscopic data and haze descriptions relative to Titan's stratosphere. We use this code to model Cassini Composite Infrared Spectrometer data taken during the numerous Titan flybys from 2006 to 2012 at surface-intercepting geometry in the 600-1500 cm{sup -1} range for latitudes from 50 Degree-Sign S to 50 Degree-Sign N. We report variations in temperature and chemical composition in the stratosphere during the Cassini mission, before and after the Northern Spring Equinox (NSE). We find indication for a weakening of the temperature gradient with warming of the stratosphere and cooling of the lower mesosphere. In addition, we infer precise concentrations for the trace gases and their main isotopologues and find that the chemical composition in Titan's stratosphere varies significantly with latitude during the 6 years investigated here, with increased mixing ratios toward the northern latitudes. In particular, we monitor and quantify the amplitude of a maximum enhancement of several gases observed at northern latitudes up to 50 Degree-Sign N around mid-2009, at the time of the NSE. We find that this rise is followed by a rapid decrease in chemical inventory in 2010 probably due to a weakening north polar vortex with reduced lateral mixing across the vortex boundary.
-
A one-dimensional model of the semiannual oscillation driven by convectively forced gravity waves
Sassi, Fabrizio; Garcia, Rolando R.
1994-01-01
A one-dimensional model that solves the time-dependent equations for the zonal mean wind and a wave of specified zonal wavenumber has been used to illustrate the ability of gravity waves forced by time-dependent tropospheric heating to produce a semiannual oscillation (SAO) in the middle atmosphere. When the heating has a strong diurnal cycle, as observed over tropical landmasses, gravity waves with zonal wavelengths of a few thousand kilometers and phase velocities in the range +/- 40-50 m/sec are excited efficiently by the maximum vertical projection criterion (vertical wavelength approximately equals 2 x forcing depth). Calculations show that these waves can account for large zonal mean wind accelerations in the middle atmosphere, resulting in realistic stratopause and mesopause oscillations. Calculations of the temporal evolution of a quasi-conserved tracer indicate strong down-welling in the upper stratosphere near the equinoxes, which is associated with the descent of the SAO westerlies. In the upper mesosphere, there is a semiannual oscillation in tracer mixing ratio driven by seasonal variability in eddy mixing, which increases at the solstices and decreases at the equinoxes.
-
Ou-Yang, C. F.; Lin, J. R.; Yen, M. C.; Sheu, G. R.; Wang, J. L.; Lin, N. H.
2017-12-01
Stratospheric intrusion (SI) is mainly induced by tropopause folds, frontal passages, cutoff lows, and surface pressure systems. Ozone can be increased rapidly by the SI with decreased humidity and other primary air pollutants in the lower free troposphere. We present 5 years of ozone observed at Lulin Atmospheric Background Station (LABS, 23.47°N, 120.87°E, 2862 m a.s.l.) as a representative regional mountain site located in subtropical East Asia from April 2006 to March 2011. A fast-screening algorithm was proposed to sift the SI events at the LABS. The ozone was increased approximately 13.5±6.1 ppb on average during the 54 detected SI events, whereas the mean ozone mixing ratio was calculated to be 32.8±15.2 ppb over the 5 years. Distinct seasonal variation of ozone was observed with a maximum in spring and a minimum in summer, which was predominately shaped by the long-range transport of biomass burning air masses from Southeast Asia and oceanic influences from the Pacific, respectively. By contrast, the SI events were observed at the LABS mainly during wintertime. The characteristics of the SI events were also investigated in association with Modern Era Retrospective Analysis - 2 (MERRA-2) assimilated data provided by NASA/GSFC in this study.
-
The impact of atmospheric data assimilation on wave simulations in the Red Sea
Langodan, Sabique
2016-03-11
Although wind and wave modeling is rather successful in the open ocean, modeling enclosed seas, particularly seas with small basins and complex orography, presents challenges. Here, we use data assimilation to improve wind and wave simulations in the Red Sea. We generated two sets of wind fields using a nested, high-resolution Weather Research and Forecasting model implemented with (VARFC) and without (CTL) assimilation of observations. Available conventional and satellite data were assimilated using the consecutive integration method with daily initializations over one year (2009). By evaluating the two wind products against in-situ data from synoptic stations, buoys, scatterometers, and altimeters, we found that seasonal patterns of wind and wave variability were well reproduced in both experiments. Statistical scores for simulated winds computed against QuikSCAT, buoy, and synoptic station observations suggest that data assimilation decreases the root-mean-square error to values between 1 and 2 m s-1 and reduces the scatter index by 30% compared to the CTL. Sensitivity clearly increased around mountain gaps, where the channeling effect is better described by VARFC winds. The impact of data assimilation is more pronounced in wave simulations, particularly during extreme winds and in the presence of mountain jets. © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Study of photolytic aerosols at stratospheric pressures
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Delattre, Patrick.
1975-07-01
An experimental study of photolytic aerosol formation at stratospheric pressure (60 Torr) and laboratory temperature, was carried out previous to the exact simulation of photolytic aerosol formation in real stratospheric conditions. An experimental simulation device, techniques of generation of known mixtures of inert gases with SO 2 and NOsub(x) traces at low concentration (below 1 ppm volume) and H 2 O traces (a few ppm), and techniques for the determination and counting of aerosol particles at low pressures were perfected. The following results were achieved: the rate of vapor condensation on nuclei was reduced when total pressure decreased. At low pressure the working of condensation nuclei counters and the formation of photolytic aerosols is influenced by this phenomenon. An explanation is proposed, as well as means to avoid this unpleasant effect on the working of nuclei counters at low pressure. No photolytic aerosol production was ascertained at 60 Torr when water concentration was below 100 ppm whatever the concentration of SO 2 or NOsub(x) traces. With water concentration below 1200ppm and SO 2 trace concentration below 1ppm, the aerosol particles produced could not consist of sulfuric acid drops but probably of nitrosyl sulfate acide crystals [fr
-
Rigorous determination of stratospheric water vapor trends from MIPAS observations.
Ceccherini, Simone; Carli, Bruno; Raspollini, Piera; Ridolfi, Marco
2011-05-09
The trend of stratospheric water vapor as a function of latitude is estimated by the MIPAS measurements by means of a new method that uses the measurement space solution. The method uses all the information provided by the observations avoiding the artifacts introduced by the a priori information and by the interpolation to different vertical grids. The analysis provides very precise values of the trends that, however, are limited by a relatively large systematic error induced by the radiometric calibration error of the instrument. The results show in the five years from 2005 to 2009 a dependence on latitude of the stratospheric (from 37 to 53 km) water vapor trend with a positive value of (0.41 ± 0.16)%yr-1 in the northern hemisphere and less than 0.16%yr-1 in the southern hemisphere.
-
Treatment of dynamical processes in two-dimensional models of the troposphere and stratosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wuebbles, D.J.
1980-07-01
The physical structure of the troposphere and stratosphere is the result of an intricate interplay among a large number of radiative, chemical, and dynamical processes. Because it is not possible to model the global environment in the laboratory, theoretical models must be relied on, subject to observational verification, to simulate atmospheric processes. Of particular concern in recent years has been the modeling of those processes affecting the structure of ozone and other trace species in the stratosphere and troposphere. Zonally averaged two-dimensional models with spatial resolution in the vertical and meridional directions can provide a much more realistic representation of tracer transport than one-dimensional models, yet are capable of the detailed representation of chemical and radiative processes contained in the one-dimensional models. The purpose of this study is to describe and analyze existing approaches to representing global atmospheric transport processes in two-dimensional models and to discuss possible alternatives to these approaches. A general description of the processes controlling the transport of trace constituents in the troposphere and stratosphere is given
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. F. Sofieva
2017-10-01
Full Text Available In this paper, we present a merged dataset of ozone profiles from several satellite instruments: SAGE II on ERBS, GOMOS, SCIAMACHY and MIPAS on Envisat, OSIRIS on Odin, ACE-FTS on SCISAT, and OMPS on Suomi-NPP. The merged dataset is created in the framework of the European Space Agency Climate Change Initiative (Ozone_cci with the aim of analyzing stratospheric ozone trends. For the merged dataset, we used the latest versions of the original ozone datasets. The datasets from the individual instruments have been extensively validated and intercompared; only those datasets which are in good agreement, and do not exhibit significant drifts with respect to collocated ground-based observations and with respect to each other, are used for merging. The long-term SAGE–CCI–OMPS dataset is created by computation and merging of deseasonalized anomalies from individual instruments. The merged SAGE–CCI–OMPS dataset consists of deseasonalized anomalies of ozone in 10° latitude bands from 90° S to 90° N and from 10 to 50 km in steps of 1 km covering the period from October 1984 to July 2016. This newly created dataset is used for evaluating ozone trends in the stratosphere through multiple linear regression. Negative ozone trends in the upper stratosphere are observed before 1997 and positive trends are found after 1997. The upper stratospheric trends are statistically significant at midlatitudes and indicate ozone recovery, as expected from the decrease of stratospheric halogens that started in the middle of the 1990s and stratospheric cooling.
-
Annual Copper Mountain Conferences on Multigrid and Iterative Methods, Copper Mountain, Colorado
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McCormick, Stephen F.
2016-01-01
This project supported the Copper Mountain Conference on Multigrid and Iterative Methods, held from 2007 to 2015, at Copper Mountain, Colorado. The subject of the Copper Mountain Conference Series alternated between Multigrid Methods in odd-numbered years and Iterative Methods in even-numbered years. Begun in 1983, the Series represents an important forum for the exchange of ideas in these two closely related fields. This report describes the Copper Mountain Conference on Multigrid and Iterative Methods, 2007-2015. Information on the conference series is available at http://grandmaster.colorado.edu/~copper/
-
Annual Copper Mountain Conferences on Multigrid and Iterative Methods, Copper Mountain, Colorado
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
McCormick, Stephen F. [Front Range Scientific, Inc., Lake City, CO (United States)
2016-03-25
This project supported the Copper Mountain Conference on Multigrid and Iterative Methods, held from 2007 to 2015, at Copper Mountain, Colorado. The subject of the Copper Mountain Conference Series alternated between Multigrid Methods in odd-numbered years and Iterative Methods in even-numbered years. Begun in 1983, the Series represents an important forum for the exchange of ideas in these two closely related fields. This report describes the Copper Mountain Conference on Multigrid and Iterative Methods, 2007-2015. Information on the conference series is available at http://grandmaster.colorado.edu/~copper/.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hausel, W.D.
1983-01-01
The Copper Mountain metamorphic complex lies within a westerly trending belt of Precambrian exposures known as the Owl Creek Mountains uplift. The metamorphic complex at Copper Mountain is part of a larger complex known as the Owl Creek Mountains greenstone belt. Until more detailed mapping and petrographic studies can be completed, the Copper Mountain area is best referred to as a complex, even though it has some characteristics of a greestone belt. At least three episodes of Precambrian deformation have affected the supracrustals, and two have disturbed the granites. The final Precambrian deformation event was preceded by a weak thermal event expressed by retrogressive metamorphism and restricted metasomatic alteration. During this event, a second phase of pegmatization was accompanied by hydrothermal solutions. During the Laramide orogeny, Copper Mountain was again modified by deformation. Laramide deformation produced complex gravity faults and keystone grabens. Uranium deposits were formed following major Laramide deformation. The genesis of these deposits is attributable to either the leaching of granites or the leaching of overlying tuffaceous sediments during the Tertiary. Production of metals and industrial minerals has been limited, although some gold, copper, silver, tungsten, beryl, feldspar, and lithium ore have been shipped from Copper Mountain. A large amount of uranium was produced from the Copper Mountain district in the 1950s
-
20 years of ClO measurements in the Antarctic lower stratosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
G. E. Nedoluha
2016-08-01
Full Text Available We present 20 years (1996–2015 of austral springtime measurements of chlorine monoxide (ClO over Antarctica from the Chlorine Oxide Experiment (ChlOE1 ground-based millimeter wave spectrometer at Scott Base, Antarctica, as well 12 years (2004–2015 of ClO measurements from the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS. From August onwards we observe a strong increase in lower stratospheric ClO, with a peak column amount usually occurring in early September. From mid-September onwards we observe a strong decrease in ClO. In order to study interannual differences, we focus on a 3-week period from 28 August to 17 September for each year and compare the average column ClO anomalies. These column ClO anomalies are shown to be highly correlated with the average ozone mass deficit for September and October of each year. We also show that anomalies in column ClO are strongly anti-correlated with 30 hPa temperature anomalies, both on a daily and an interannual timescale. Making use of this anti-correlation we calculate the linear dependence of the interannual variations in column ClO on interannual variations in temperature. By making use of this relationship, we can better estimate the underlying trend in the total chlorine (Cly = HCl + ClONO2 + HOCl + 2 × Cl2 + 2 × Cl2O2 + ClO + Cl. The resultant trends in Cly, which determine the long-term trend in ClO, are estimated to be −0.5 ± 0.2, −1.4 ± 0.9, and −0.6 ± 0.4 % year−1, for zonal MLS, Scott Base MLS (both 2004–2015, and ChlOE (1996–2015 respectively. These trends are within 1σ of trends in stratospheric Cly previously found at other latitudes. The decrease in ClO is consistent with the trend expected from regulations enacted under the Montreal Protocol.
-
2012-03-23
... procedure, Air pollution control, Reporting and recordkeeping requirements, Stratospheric ozone layer. Dated... FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT: Margaret Sheppard, Stratospheric Protection Division, Office of Atmospheric... Reduction Act, 44 U.S.C. 3501 et seq. and has assigned OMB control numbers 2060-0226 (EPA ICR No. 1596.08...
-
Browell, Edward V.; Butler, Carolyn F.; Fenn, Marta A.; Grant, William B.; Ismail, Syed; Carter, Arlen F.
1994-01-01
The NASA Langley airborne differential absorption lidar system was operated from the NASA Ames DC-8 aircraft during the 1992 Airborne Arctic Stratospheric Expedition to investigate the distribution of stratospheric aerosols and ozone (O3) across the Arctic vortex from January to March 1992. Aerosols from the Mt. Pinatubo eruption were found outside and inside the Arctic vortex with distinctly different scattering characteristics and spatial distributions in the two regions. The aerosol and O3 distributions clearly identified the edge of the vortex and provided additional information on vortex dynamics and transport processes. Few polar stratospheric clouds were observed during the AASE-2; however, those that were found had enhanced scattering and depolarization over the background Pinatubo aerosols. The distribution of aerosols inside the vortex exhibited relatively minor changes during the AASE-2. Ozone depletion inside the vortex as limited to less than or equal to 20 percent in the altitude region from 15-20 km.
-
Ugolnikov, O. S.; Maslov, I. A.
2018-03-01
The first results of multiwave measurements of twilight background and the all-sky camera with a color (RGB) CCD matrix conducted in the spring and summer of 2016 in Central Russia (55.2° N, 37.5° E) have been discussed. The observations reveal the effect of aerosol scattering at heights of up to 35 km, which is substantially enhanced in the long-wave part of the spectrum (R band with an effective wavelength of 624 nm). An analysis of the behavior of the sky color during light period of twilight with allowance for the absorption by ozone in the Chappuis bands make it possible to restore the angular dependences of the intensity of the aerosol scattering of the light. This is used to determine the parameters of the lognormal distribution of aerosol particles over their sizes with a mean radius of 0.08 μm and a width of 1.5-1.6 for the stratospheric height interval.
-
Air Revitalization System Enables Excursions to the Stratosphere
2015-01-01
Paragon Space Development Corporation, based in Tucson, Arizona has had a long history of collaboration with NASA, including developing a modular air purification system under the Commercial Crew Development Program, designed to support the commercial space sector. Using that device and other NASA technology, startup company World View is now gearing up to take customers on helium balloon rides to the stratosphere.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. Brühl
2012-02-01
Full Text Available Globally, carbonyl sulphide (COS is the most abundant sulphur gas in the atmosphere. Our chemistry-climate model (CCM of the lower and middle atmosphere with aerosol module realistically simulates the background stratospheric sulphur cycle, as observed by satellites in volcanically quiescent periods. The model results indicate that upward transport of COS from the troposphere largely controls the sulphur budget and the aerosol loading of the background stratosphere. This differs from most previous studies which indicated that short-lived sulphur gases are also important. The model realistically simulates the modulation of the particulate and gaseous sulphur abundance in the stratosphere by the quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO. In the lowermost stratosphere organic carbon aerosol contributes significantly to extinction. Further, using a chemical radiative convective model and recent spectra, we compute that the direct radiative forcing efficiency by 1 kg of COS is 724 times that of 1 kg CO2. Considering an anthropogenic fraction of 30% (derived from ice core data, this translates into an overall direct radiative forcing by COS of 0.003 W m−2. The direct global warming potentials of COS over time horizons of 20 and 100 yr are GWP(20 yr = 97 and GWP(100 yr = 27, respectively (by mass. Furthermore, stratospheric aerosol particles produced by the photolysis of COS (chemical feedback contribute to a negative direct solar radiative forcing, which in the CCM amounts to −0.007 W m−2 at the top of the atmosphere for the anthropogenic fraction, more than two times the direct warming forcing of COS. Considering that the lifetime of COS is twice that of stratospheric aerosols the warming and cooling tendencies approximately cancel.
-
Stratospheric Ozone Reactive Chemicals Generated by Space Launches Worldwide.
1994-11-01
I ODCs). Their carbon - chlorine bond is severed in the stratosphere by solar photolysis or reaction. Once the carbon-chlorine bond is broken, the...include the Russian Proton and Energia , and the Chinese Long March series. Roughly half (seven per year) of the Ariane 4 launches use two solid strap-ons
-
The boiling point of stratospheric aerosols.
Rosen, J. M.
1971-01-01
A photoelectric particle counter was used for the measurement of aerosol boiling points. The operational principle involves raising the temperature of the aerosol by vigorously heating a portion of the intake tube. At or above the boiling point, the particles disintegrate rather quickly, and a noticeable effect on the size distribution and concentration is observed. Stratospheric aerosols appear to have the same volatility as a solution of 75% sulfuric acid. Chemical analysis of the aerosols indicates that there are other substances present, but that the sulfate radical is apparently the major constituent.
-
Photochemistry of materials in the stratosphere
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Johnston, H.S. [Lawrence Berkeley Laboratories, CA (United States)
1993-12-01
This research is concerned with global change in the atmosphere, including photochemical modeling and, in the past, experimental gas-phase photochemistry involving molecular dynamics and laboratory study of atmospheric chemical reactions. The experimental work on this project concluded in August 1991, but there is a back-log of several journal articles to be written and submitted for publication. The theoretical work involves photochemical modeling in collaboration with Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and advising the Upper Atmosphere Research Program on Atmospheric Effects of Stratospheric Aircraft, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
-
Allin, S. J.; Laube, J. C.; Witrant, E.; Kaiser, J.; McKenna, E.; Dennis, P.; Mulvaney, R.; Capron, E.; Martinerie, P.; Roeckmann, Thomas; Blunier, T.; Schwander, J.; Fraser, P. J.; Langenfelds, R. L.; Sturges, W. T.
2015-01-01
The stratospheric degradation of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) releases chlorine, which is a major contributor to the destruction of stratospheric ozone (O-3). A recent study reported strong chlorine isotope fractionation during the breakdown of the most abundant CFC (CFC-12, CCl2F2, Laube et al.,
-
Tolbert, Margaret A.; Rossi, Michel J.; Malhotra, Ripudaman; Golden, David M.
1987-01-01
Laboratory studies of heterogeneous reactions important for ozone depletion over Antarctica are reported. The reaction of chlorine nitrate (ClONO2) with H2O and HCl on surfacers that simulate polar stratospheric clouds are studied at temperatures relevant to the Antarctic stratosphere. The gaseous products of the resulting reactions, HOCl, Cl2O, and Cl2, could readily photolyze in the Antarctic spring to produce active chlorine for ozone depletion. Furthermore, the additional formation of condensed-phase HNO3 could serve as a sink for odd nitrogen species that would otherwise scavenge the active chlorine.
-
Modelling stratospheric chemistry in a global three-dimensional chemical transport model
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rummukainen, M [Finnish Meteorological Inst., Sodankylae (Finland). Sodankylae Observatory
1996-12-31
Numerical modelling of atmospheric chemistry aims to increase the understanding of the characteristics, the behavior and the evolution of atmospheric composition. These topics are of utmost importance in the study of climate change. The multitude of gases and particulates making up the atmosphere and the complicated interactions between them affect radiation transfer, atmospheric dynamics, and the impacts of anthropogenic and natural emissions. Chemical processes are fundamental factors in global warming, ozone depletion and atmospheric pollution problems in general. Much of the prevailing work on modelling stratospheric chemistry has so far been done with 1- and 2-dimensional models. Carrying an extensive chemistry parameterisation in a model with high spatial and temporal resolution is computationally heavy. Today, computers are becoming powerful enough to allow going over to 3-dimensional models. In order to concentrate on the chemistry, many Chemical Transport Models (CTM) are still run off-line, i.e. with precalculated and archived meteorology and radiation. In chemistry simulations, the archived values drive the model forward in time, without interacting with the chemical evolution. This is an approach that has been adopted in stratospheric chemistry modelling studies at the Finnish Meteorological Institute. In collaboration with the University of Oslo, a development project was initiated in 1993 to prepare a stratospheric chemistry parameterisation, fit for global 3-dimensional modelling. This article presents the parameterisation approach. Selected results are shown from basic photochemical simulations
-
A model study of the plasma chemistry of stratospheric Blue Jets
Winkler, Holger; Notholt, Justus
2015-04-01
Stratospheric Blue Jets (BJs) are upward propagating discharges in the altitude range 15-40 km above thunderstorms. They appear as conical bodies of blue light originating at the top of thunderclouds and proceed upward with velocities of the order of 100 km/s. Electric discharges in the atmosphere are known to have chemical effects. Of particular interest is the liberation of atomic oxygen and the formation of reactive nitrogen radicals. We have used a numerical plasma chemistry model in order to simulate the chemical processes in stratospheric BJs. It was applied to BJ streamers in the altitude range 18-38 km. The model results show that there is a production of ozone from atomic oxygen liberated at the streamer tips. At the same time, significant amounts of nitric oxide are produced. Compared to earlier plasma chemistry simulations of BJ streamers, the production of NO and O3 is by orders of magnitude larger. Additionally, the chemical processes in the leader part of a BJ have been simulated for the first time. In the leader channel, driven by high-temperature reactions, the concentration of N2O and NO increases by several orders of magnitude, and there is a significant depletion of ozone. The model results might gain importance by the fact that the chemical perturbations in BJs are largest at altitudes of the stratospheric ozone layer.
-
Modelling stratospheric chemistry in a global three-dimensional chemical transport model
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rummukainen, M. [Finnish Meteorological Inst., Sodankylae (Finland). Sodankylae Observatory
1995-12-31
Numerical modelling of atmospheric chemistry aims to increase the understanding of the characteristics, the behavior and the evolution of atmospheric composition. These topics are of utmost importance in the study of climate change. The multitude of gases and particulates making up the atmosphere and the complicated interactions between them affect radiation transfer, atmospheric dynamics, and the impacts of anthropogenic and natural emissions. Chemical processes are fundamental factors in global warming, ozone depletion and atmospheric pollution problems in general. Much of the prevailing work on modelling stratospheric chemistry has so far been done with 1- and 2-dimensional models. Carrying an extensive chemistry parameterisation in a model with high spatial and temporal resolution is computationally heavy. Today, computers are becoming powerful enough to allow going over to 3-dimensional models. In order to concentrate on the chemistry, many Chemical Transport Models (CTM) are still run off-line, i.e. with precalculated and archived meteorology and radiation. In chemistry simulations, the archived values drive the model forward in time, without interacting with the chemical evolution. This is an approach that has been adopted in stratospheric chemistry modelling studies at the Finnish Meteorological Institute. In collaboration with the University of Oslo, a development project was initiated in 1993 to prepare a stratospheric chemistry parameterisation, fit for global 3-dimensional modelling. This article presents the parameterisation approach. Selected results are shown from basic photochemical simulations
-
Stratospheric aerosol geoengineering
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Robock, Alan [Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers University, 14 College Farm Road, New Brunswick, NJ 08901 (United States)
2015-03-30
The Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project, conducting climate model experiments with standard stratospheric aerosol injection scenarios, has found that insolation reduction could keep the global average temperature constant, but global average precipitation would reduce, particularly in summer monsoon regions around the world. Temperature changes would also not be uniform; the tropics would cool, but high latitudes would warm, with continuing, but reduced sea ice and ice sheet melting. Temperature extremes would still increase, but not as much as without geoengineering. If geoengineering were halted all at once, there would be rapid temperature and precipitation increases at 5–10 times the rates from gradual global warming. The prospect of geoengineering working may reduce the current drive toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and there are concerns about commercial or military control. Because geoengineering cannot safely address climate change, global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to adapt are crucial to address anthropogenic global warming.
-
Stratospheric aerosol geoengineering
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Robock, Alan
2015-01-01
The Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project, conducting climate model experiments with standard stratospheric aerosol injection scenarios, has found that insolation reduction could keep the global average temperature constant, but global average precipitation would reduce, particularly in summer monsoon regions around the world. Temperature changes would also not be uniform; the tropics would cool, but high latitudes would warm, with continuing, but reduced sea ice and ice sheet melting. Temperature extremes would still increase, but not as much as without geoengineering. If geoengineering were halted all at once, there would be rapid temperature and precipitation increases at 5–10 times the rates from gradual global warming. The prospect of geoengineering working may reduce the current drive toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and there are concerns about commercial or military control. Because geoengineering cannot safely address climate change, global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to adapt are crucial to address anthropogenic global warming
-
Li, Feng; Vikhliaev, Yury V.; Newman, Paul A.; Pawson, Steven; Perlwitz, Judith; Waugh, Darryn W.; Douglass, Anne R.
2016-01-01
Stratospheric ozone depletion plays a major role in driving climate change in the Southern Hemisphere. To date, many climate models prescribe the stratospheric ozone layer's evolution using monthly and zonally averaged ozone fields. However, the prescribed ozone underestimates Antarctic ozone depletion and lacks zonal asymmetries. In this study we investigate the impact of using interactive stratospheric chemistry instead of prescribed ozone on climate change simulations of the Antarctic and Southern Ocean. Two sets of 1960-2010 ensemble transient simulations are conducted with the coupled ocean version of the Goddard Earth Observing System Model, version 5: one with interactive stratospheric chemistry and the other with prescribed ozone derived from the same interactive simulations. The model's climatology is evaluated using observations and reanalysis. Comparison of the 1979-2010 climate trends between these two simulations reveals that interactive chemistry has important effects on climate change not only in the Antarctic stratosphere, troposphere, and surface, but also in the Southern Ocean and Antarctic sea ice. Interactive chemistry causes stronger Antarctic lower stratosphere cooling and circumpolar westerly acceleration during November-December-January. It enhances stratosphere-troposphere coupling and leads to significantly larger tropospheric and surface westerly changes. The significantly stronger surface wind stress trends cause larger increases of the Southern Ocean Meridional Overturning Circulation, leading to year-round stronger ocean warming near the surface and enhanced Antarctic sea ice decrease.
-
Regional seismic-wave propagation from the M5.8 23 August 2011, Mineral, Virginia, earthquake
Pollitz, Fred; Mooney, Walter D.
2015-01-01
The M5.8 23 August 2011 Mineral, Virginia, earthquake was felt over nearly the entire eastern United States and was recorded by a wide array of seismic broadband instruments. The earthquake occurred ~200 km southeast of the boundary between two distinct geologic belts, the Piedmont and Blue Ridge terranes to the southeast and the Valley and Ridge Province to the northwest. At a dominant period of 3 s, coherent postcritical P-wave (i.e., direct longitudinal waves trapped in the crustal waveguide) arrivals persist to a much greater distance for propagation paths toward the northwest quadrant than toward other directions; this is probably related to the relatively high crustal thickness beneath and west of the Appalachian Mountains. The seismic surface-wave arrivals comprise two distinct classes: those with weakly dispersed Rayleigh waves and those with strongly dispersed Rayleigh waves. We attribute the character of Rayleigh wave arrivals in the first class to wave propagation through a predominantly crystalline crust (Blue Ridge Mountains and Piedmont terranes) with a relatively thin veneer of sedimentary rock, whereas the temporal extent of the Rayleigh wave arrivals in the second class are well explained as the effect of the thick sedimentary cover of the Valley and Ridge Province and adjacent Appalachian Plateau province to its northwest. Broadband surface-wave ground velocity is amplified along both north-northwest and northeast azimuths from the Mineral, Virginia, source. The former may arise from lateral focusing effects arising from locally thick sedimentary cover in the Appalachian Basin, and the latter may result from directivity effects due to a northeast rupture propagation along the finite fault plane.
-
Snow hydrology in Mediterranean mountain regions: A review
Fayad, Abbas; Gascoin, Simon; Faour, Ghaleb; López-Moreno, Juan Ignacio; Drapeau, Laurent; Page, Michel Le; Escadafal, Richard
2017-08-01
Water resources in Mediterranean regions are under increasing pressure due to climate change, economic development, and population growth. Many Mediterranean rivers have their headwaters in mountainous regions where hydrological processes are driven by snowpack dynamics and the specific variability of the Mediterranean climate. A good knowledge of the snow processes in the Mediterranean mountains is therefore a key element of water management strategies in such regions. The objective of this paper is to review the literature on snow hydrology in Mediterranean mountains to identify the existing knowledge, key research questions, and promising technologies. We collected 620 peer-reviewed papers, published between 1913 and 2016, that deal with the Mediterranean-like mountain regions in the western United States, the central Chilean Andes, and the Mediterranean basin. A large amount of studies in the western United States form a strong scientific basis for other Mediterranean mountain regions. We found that: (1) the persistence of snow cover is highly variable in space and time but mainly controlled by elevation and precipitation; (2) the snowmelt is driven by radiative fluxes, but the contribution of heat fluxes is stronger at the end of the snow season and during heat waves and rain-on-snow events; (3) the snow densification rates are higher in these regions when compared to other climate regions; and (4) the snow sublimation is an important component of snow ablation, especially in high-elevation regions. Among the pressing issues is the lack of continuous ground observation in high-elevation regions. However, a few years of snow depth (HS) and snow water equivalent (SWE) data can provide realistic information on snowpack variability. A better spatial characterization of snow cover can be achieved by combining ground observations with remotely sensed snow data. SWE reconstruction using satellite snow cover area and a melt model provides reasonable information that
-
Chlorine activation and ozone destruction in the northern lowermost stratosphere
Lelieveld, J; Bregman, A; Scheeren, HA; Strom, J; Carslaw, KS; Fischer, H; Siegmund, PC; Arnold, F
1999-01-01
We report aircraft measurements from the Stratosphere-Troposphere Experiments by Aircraft Measurements (STREAM) II campaign, performed during February 1995 from Kiruna, northern Sweden, near 67 degrees N latitude. We have measured trace species, e.g., O-3, nitrogen compounds, HCl, hydrocarbons, CO,
-
A stratospheric NO2 climatology from Odin/OSIRIS limb-scatter measurements
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brohede, S.; Murtagh, D.; Berthet, G.; Haley, C.S.
2007-01-01
Since the late 1960s, it has been known that stratospheric nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) and ozone are closely coupled. However, stratospheric nitrogen chemistry is not yet fully understood, given the lack of observing systems that can provide both high vertical and temporal resolution measurements of NO 2 . Limb-scattering data from the optical spectrograph and infrared imager system (OSIRIS) aboard the Odin satellite was used in this study along with a photochemical box model to investigate stratospheric NO 2 climatology in terms of mean and standard deviation as a function of latitude, altitude, month and local solar time. The Odin orbit provided near global coverage around the equinoxes and hemispheric coverage elsewhere, due to lack of sunlight. The mean NO 2 field at a specific local solar time involved high concentrations in the polar summer, peaking at about 25 km, with a negative equatorward gradient. High levels between 40 to 50 degrees latitude at 30 km in the winter/spring hemisphere were also found, and were associated with the Noxon-cliff. The diurnal cycle revealed the lowest NO 2 concentrations just after sunrise and steep gradients at twilight. The 1σ standard deviation was around 20 per cent, except for winter and spring high latitudes, where values were above 50 per cent and stretched through the entire stratosphere. NO 2 concentrations were found to be log-normally distributed. Comparisons with the REPROBUS chemical transport model for climatology showed that the relative differences for the mean values were below 20 per cent and comparable to the estimated OSIRIS systematic uncertainty. The polar regions in winter/spring throughout the atmosphere and equatorial regions below 25 km were exceptions, where OSIRIS was higher by 40 per cent and more. It was concluded that further study is needed to determine if these discrepancies are due to limitations of the model. 47 refs., 10 figs., 1 appendix
-
Hayashida, S.; Iikura, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Sasano, Y.; Nakane, H.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsui, I.; Takeuchi, N.
1986-01-01
The results of the observation for stratospheric aerosols which were carried out since the autumn of 1982 by using the NIES large lidar are described. Specifications of the lidar system are shown. The lidar has two wavelenghts of 1.06 and 0.53 micrometers. The 0.53 micrometer is mainly used for the stratospheric aerosols, because the PMT for 0.53 micrometers has higher sensitivity that that for 1.06 micrometers and the total efficiency is higher in the former. A switching circuit is used to control the PMT gain for avoiding signal induced noise in PMT. For the last four years, the stratospheric aerosol layer which was significantly perturbed by the El Chichon volcanic eruption was observed. The scattering ratio profiles observed from 1982 through 1983 are given.
-
Towards Mars — Stratospheric Balloons as Test-Beds for Mars Exploration
Dannenberg, K.
2018-04-01
The abstract deals with the possibilities to use stratospheric balloons for Mars science and technology needs, especially with the opportunities offered by the new European infrastructure project HEMERA, recently selected by the European Commission.
-
In-situ observation of Asian pollution transported into the Arctic lowermost stratosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Roiger
2011-11-01
Full Text Available On a research flight on 10 July 2008, the German research aircraft Falcon sampled an air mass with unusually high carbon monoxide (CO, peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN and water vapour (H2O mixing ratios in the Arctic lowermost stratosphere. The air mass was encountered twice at an altitude of 11.3 km, ~800 m above the dynamical tropopause. In-situ measurements of ozone, NO, and NOy indicate that this layer was a mixed air mass containing both air from the troposphere and stratosphere. Backward trajectory and Lagrangian particle dispersion model analysis suggest that the Falcon sampled the top of a polluted air mass originating from the coastal regions of East Asia. The anthropogenic pollution plume experienced strong up-lift in a warm conveyor belt (WCB located over the Russian east-coast. Subsequently the Asian air mass was transported across the North Pole into the sampling area, elevating the local tropopause by up to ~3 km. Mixing with surrounding Arctic stratospheric air most likely took place during the horizontal transport when the tropospheric streamer was stretched into long and narrow filaments. The mechanism illustrated in this study possibly presents an important pathway to transport pollution into the polar tropopause region.
-
Change rules of a stratospheric airship’s envelope shape during ascent process
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Shuai Zhao
2017-04-01
Full Text Available Stratospheric airship is a special near-space air vehicle, and has more advantages than other air vehicles, such as long endurance, strong survival ability, excellent resolution, low cost, and so on, which make it an ideal stratospheric platform. It is of great significance to choose a reasonable and effective way to launch a stratospheric airship to the space for both academic research and engineering applications. In this paper, the non-forming launch way is studied and the method of differential pressure gradient is used to study the change rules of the airship’s envelope shape during the ascent process. Numerical simulation results show that the head of the envelope will maintain the inflatable shape and the envelope under the zero-pressure level will be compressed into a wide range of wrinkles during the ascent process. The airship’s envelope will expand with the ascent of the airship and the position of the zero-pressure level will move downward constantly. At the same time, the envelope will gradually form a certain degree of stiffness under the action of the inner and external differential pressure. The experimental results agree well with the analytical results, which shows that the non-forming launch way is effective and reliable, and the analytical method has exactness and feasibility.
-
Effects of Volcanic Eruptions on Stratospheric Ozone Recovery
Rosenfield, Joan E.
2002-01-01
The effects of the stratospheric sulfate aerosol layer associated with the Mt. Pinatubo volcano and future volcanic eruptions on the recovery of the ozone layer is studied with an interactive two-dimensional photochemical model. The time varying chlorine loading and the stratospheric cooling due to increasing carbon dioxide have been taken into account. The computed ozone and temperature changes associated with the Mt. Pinatubo eruption in 1991 agree well with observations. Long model runs out to the year 2050 have been carried out, in which volcanoes having the characteristics of the Mount Pinatubo volcano were erupted in the model at 10-year intervals starting in the year 2010. Compared to a non-volcanic run using background aerosol loading, transient reductions of globally averaged column ozone of 2-3 percent were computed as a result of each of these eruptions, with the ozone recovering to that computed for the non-volcanic case in about 5 years after the eruption. Computed springtime Arctic column ozone losses of from 10 to 18 percent also recovered to the non-volcanic case within 5 years. These results suggest that the long-term recovery of ozone would not be strongly affected by infrequent volcanic eruptions with a sulfur loading approximating Mt. Pinatubo. Sensitivity studies in which the Arctic lower stratosphere was forced to be 4 K and 10 K colder resulted in transient ozone losses of which also recovered to the non-volcanic case in 5 years. A case in which a volcano five times Mt. Pinatubo was erupted in the year 2010 led to maximum springtime column ozone losses of 45 percent which took 10 years to recover to the background case. Finally, in order to simulate a situation in which frequent smaller volcanic eruptions result in increasing the background sulfate loading, a simulation was made in which the background aerosol was increased by 10 percent per year. This resulted in a delay of the recovery of column ozone to 1980 values of more than 10 years.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. Funke
2016-07-01
Full Text Available The MIPAS Fourier transform spectrometer on board Envisat has measured global distributions of the six principal reactive nitrogen (NOy compounds (HNO3, NO2, NO, N2O5, ClONO2, and HNO4 during 2002–2012. These observations were used previously to detect regular polar winter descent of reactive nitrogen produced by energetic particle precipitation (EPP down to the lower stratosphere, often called the EPP indirect effect. It has further been shown that the observed fraction of NOy produced by EPP (EPP-NOy has a nearly linear relationship with the geomagnetic Ap index when taking into account the time lag introduced by transport. Here we exploit these results in a semi-empirical model for computation of EPP-modulated NOy densities and wintertime downward fluxes through stratospheric and mesospheric pressure levels. Since the Ap dependence of EPP-NOy is distorted during episodes of strong descent in Arctic winters associated with elevated stratopause events, a specific parameterization has been developed for these episodes. This model accurately reproduces the observations from MIPAS and is also consistent with estimates from other satellite instruments. Since stratospheric EPP-NOy depositions lead to changes in stratospheric ozone with possible implications for climate, the model presented here can be utilized in climate simulations without the need to incorporate many thermospheric and upper mesospheric processes. By employing historical geomagnetic indices, the model also allows for reconstruction of the EPP indirect effect since 1850. We found secular variations of solar cycle-averaged stratospheric EPP-NOy depositions on the order of 1 GM. In particular, we model a reduction of the EPP-NOy deposition rate during the last 3 decades, related to the coincident decline of geomagnetic activity that corresponds to 1.8 % of the NOy production rate by N2O oxidation. As the decline of the geomagnetic activity level is expected to continue in the
-
Ziemke, J.R.; Chandra, S.; Labow, G.; Bhartia, P. K.; Froidevaux, L.; Witte, J. C.
2011-01-01
A global climatology of tropospheric and stratospheric column ozone is derived by combining six years of Aura Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) and Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) ozone measurements for the period October 2004 through December 2010. The OMI/MLS tropospheric ozone climatology exhibits large temporal and spatial variability which includes ozone accumulation zones in the tropical south Atlantic year-round and in the subtropical Mediterranean! Asia region in summer months. High levels of tropospheric ozone in the northern hemisphere also persist in mid-latitudes over the eastern North American and Asian continents extending eastward over the Pacific Ocean. For stratospheric ozone climatology from MLS, largest ozone abundance lies in the northern hemisphere in the latitude range 70degN-80degN in February-April and in the southern hemisphere around 40degS-50degS during months August-October. The largest stratospheric ozone abundances in the northern hemisphere lie over North America and eastern Asia extending eastward across the Pacific Ocean and in the southern hemisphere south of Australia extending eastward across the dateline. With the advent of many newly developing 3D chemistry and transport models it is advantageous to have such a dataset for evaluating the performance of the models in relation to dynamical and photochemical processes controlling the ozone distributions in the troposphere and stratosphere.
-
Classification of hemispheric monthly mean stratospheric potential vorticity fields
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. Huth
Full Text Available Monthly mean NCEP reanalysis potential vorticity fields at the 650 K isentropic level over the Northern and Southern Hemispheres between 1979 and 1997 were studied using multivariate analysis tools. Principal component analysis in the T-mode was applied to demonstrate the validity of such statistical techniques for the study of stratospheric dynamics and climatology. The method, complementarily applied to both the raw and anomaly fields, was useful in determining and classifying the characteristics of winter and summer PV fields on both hemispheres, in particular, the well-known differences in the behaviour and persistence of the polar vortices. It was possible to identify such features as sudden warming events in the Northern Hemisphere and final warming dates in both hemispheres. The stratospheric impact of other atmospheric processes, such as volcanic eruptions, also identified though the results, must be viewed at this stage as tentative. An interesting change in behaviour around 1990 was detected over both hemispheres.
Key words. Meteorology and atmospheric dynamics (middle atmosphere dynamics; general circulation; climatology -
Upper atmospheric gravity wave details revealed in nightglow satellite imagery
Miller, Steven D.; Straka, William C.; Yue, Jia; Smith, Steven M.; Alexander, M. Joan; Hoffmann, Lars; Setvák, Martin; Partain, Philip T.
2015-01-01
Gravity waves (disturbances to the density structure of the atmosphere whose restoring forces are gravity and buoyancy) comprise the principal form of energy exchange between the lower and upper atmosphere. Wave breaking drives the mean upper atmospheric circulation, determining boundary conditions to stratospheric processes, which in turn influence tropospheric weather and climate patterns on various spatial and temporal scales. Despite their recognized importance, very little is known about upper-level gravity wave characteristics. The knowledge gap is mainly due to lack of global, high-resolution observations from currently available satellite observing systems. Consequently, representations of wave-related processes in global models are crude, highly parameterized, and poorly constrained, limiting the description of various processes influenced by them. Here we highlight, through a series of examples, the unanticipated ability of the Day/Night Band (DNB) on the NOAA/NASA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership environmental satellite to resolve gravity structures near the mesopause via nightglow emissions at unprecedented subkilometric detail. On moonless nights, the Day/Night Band observations provide all-weather viewing of waves as they modulate the nightglow layer located near the mesopause (∼90 km above mean sea level). These waves are launched by a variety of physical mechanisms, ranging from orography to convection, intensifying fronts, and even seismic and volcanic events. Cross-referencing the Day/Night Band imagery with conventional thermal infrared imagery also available helps to discern nightglow structures and in some cases to attribute their sources. The capability stands to advance our basic understanding of a critical yet poorly constrained driver of the atmospheric circulation. PMID:26630004
-
YUCCA MOUNTAIN SITE DESCRIPTION
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Simmons, A.M.
2004-01-01
The ''Yucca Mountain Site Description'' summarizes, in a single document, the current state of knowledge and understanding of the natural system at Yucca Mountain. It describes the geology; geochemistry; past, present, and projected future climate; regional hydrologic system; and flow and transport within the unsaturated and saturated zones at the site. In addition, it discusses factors affecting radionuclide transport, the effect of thermal loading on the natural system, and tectonic hazards. The ''Yucca Mountain Site Description'' is broad in nature. It summarizes investigations carried out as part of the Yucca Mountain Project since 1988, but it also includes work done at the site in earlier years, as well as studies performed by others. The document has been prepared under the Office of Civilian Radioactive Waste Management quality assurance program for the Yucca Mountain Project. Yucca Mountain is located in Nye County in southern Nevada. The site lies in the north-central part of the Basin and Range physiographic province, within the northernmost subprovince commonly referred to as the Great Basin. The basin and range physiography reflects the extensional tectonic regime that has affected the region during the middle and late Cenozoic Era. Yucca Mountain was initially selected for characterization, in part, because of its thick unsaturated zone, its arid to semiarid climate, and the existence of a rock type that would support excavation of stable openings. In 1987, the United States Congress directed that Yucca Mountain be the only site characterized to evaluate its suitability for development of a geologic repository for high-level radioactive waste and spent nuclear fuel
-
Solar research with stratospheric balloons
Vázquez, Manuel; Wittmann, Axel D.
Balloons, driven by hot air or some gas lighter than air, were the first artificial machines able to lift payloads (including humans) from the ground. After some pioneering flights the study of the physical properties of the terrestrial atmosphere constituted the first scientific target. A bit later astronomers realized that the turbulence of the atmospheric layers above their ground-based telescopes deteriorated the image quality, and that balloons were an appropriate means to overcome, total or partially, this problem. Some of the most highly-resolved photographs and spectrograms of the sun during the 20th century were actually obtained by balloon-borne telescopes from the stratosphere. Some more recent projects of solar balloon astronomy will also be described.
-
UARS Improved Stratospheric and Mesospheric Sounder (ISAMS) Level 3AL V001
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — The Improved Stratospheric and Mesospheric Sounder (ISAMS) Level 3AL data product consists of daily, 4 degree increment latitude-ordered vertical profiles of...
-
Herman, R. L.; Ray, E. A.; Rosenlof, K. H.; Bedka, K. M.; Schwartz, M. J.; Read, W. G.; Troy, R. F.
2016-12-01
The NASA ER-2 aircraft sampled the UTLS region over North America during the NASA Studies of Emissions and Atmospheric Composition, Clouds and Climate Coupling by Regional Surveys (SEAC4RS) field mission. On four flights targeting convectively-influenced air parcels, in situ measurements of enhanced water vapor in the lower stratosphere over the summertime continental United States were made using the JPL Laser Hygrometer (JLH Mark2). Water vapor mixing ratios greater than 10 ppmv, twice the stratospheric background levels, were measured at pressure levels between 80 and 160 hPa. Through satellite observations and analysis, we make the connection between these in situ water measurements and overshooting cloud tops. The overshooting tops (OT) are identified from a SEAC4RS OT detection product based on satellite infrared window channel brightness temperature gradients. Back-trajectory analysis ties enhanced water to OT one to seven days prior to the intercept by the aircraft. The trajectory paths are dominated by the North American Monsoon (NAM) anticyclonic circulation. This connection suggests that ice is convectively transported to the overworld stratosphere in OT events and subsequently sublimated; such events may irreversibly enhance stratospheric water vapor in the summer over Mexico and the United States. Regional context is provided by water observations from the Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS).