
Sample records for space solar dynamic
-
Solar dynamic power systems for space station
Irvine, Thomas B.; Nall, Marsha M.; Seidel, Robert C.
1986-01-01
The Parabolic Offset Linearly Actuated Reflector (POLAR) solar dynamic module was selected as the baseline design for a solar dynamic power system aboard the space station. The POLAR concept was chosen over other candidate designs after extensive trade studies. The primary advantages of the POLAR concept are the low mass moment of inertia of the module about the transverse boom and the compactness of the stowed module which enables packaging of two complete modules in the Shuttle orbiter payload bay. The fine pointing control system required for the solar dynamic module has been studied and initial results indicate that if disturbances from the station are allowed to back drive the rotary alpha joint, pointing errors caused by transient loads on the space station can be minimized. This would allow pointing controls to operate in bandwidths near system structural frequencies. The incorporation of the fine pointing control system into the solar dynamic module is fairly straightforward for the three strut concentrator support structure. However, results of structural analyses indicate that this three strut support is not optimum. Incorporation of a vernier pointing system into the proposed six strut support structure is being studied.
-
Radiator selection for Space Station Solar Dynamic Power Systems
Fleming, Mike; Hoehn, Frank
A study was conducted to define the best radiator for heat rejection of the Space Station Solar Dynamic Power System. Included in the study were radiators for both the Organic Rankine Cycle and Closed Brayton Cycle heat engines. A number of potential approaches were considered for the Organic Rankine Cycle and a constructable radiator was chosen. Detailed optimizations of this concept were conducted resulting in a baseline for inclusion into the ORC Preliminary Design. A number of approaches were also considered for the CBC radiator. For this application a deployed pumped liquid radiator was selected which was also refined resulting in a baseline for the CBC preliminary design. This paper reports the results and methodology of these studies and describes the preliminary designs of the Space Station Solar Dynamic Power System radiators for both of the candidate heat engine cycles.
-
Dynamical 3-Space Gravity Theory: Effects on Polytropic Solar Models
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
May R. D.
2011-01-01
Full Text Available Numerous experiments and observations have confirmed the existence of a dynamical 3-space, detectable directly by light-speed anisotropy experiments, and indirectly by means of novel gravitational effects, such as bore hole g anomalies, predictable black hole masses, flat spiral-galaxy rotation curves, and the expansion of the universe, all without dark matter and dark energy. The dynamics for this 3-space follows from a unique generalisation of Newtonian gravity, once that is cast into a velocity formalism. This new theory of gravity is applied to the solar model of the sun to compute new density, pressure and temperature profiles, using polytrope modelling of the equation of state for the matter. These results should be applied to a re-analysis of solar neutrino production, and to stellar evolution in general.
-
The ground testing of a 2 kWe solar dynamic space power system
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Calogeras, J.E.
1992-01-01
Over the past 25 years Space Solar Dynamic component development has advanced to the point where it is considered a leading candidate power source technology for the evolutionary phases of the Space Station Freedom (SSF) program. Selection of SD power was based on studies and analyses which indicated significant savings in life cycle costs, launch mass and EVA requirements were possible when the system is compared to more conventional photovoltaic/battery power systems. Issues associated with micro-gravity operation such as the behavior of the thermal energy storage materials are being addressed in other programs. This paper reports that a ground test of a 2 kWe solar dynamic system is being planned by the NASA Office of Aeronautics and Space Technology to address the integration issues. The test will be scalable up to 25 kWe, will be flight configured and will incorporate relevant features of the SSF Solar Dynamic Power Module design
-
Solar array flight dynamic experiment
Schock, Richard W.
1987-01-01
The purpose of the Solar Array Flight Dynamic Experiment (SAFDE) is to demonstrate the feasibility of on-orbit measurement and ground processing of large space structures' dynamic characteristics. Test definition or verification provides the dynamic characteristic accuracy required for control systems use. An illumination/measurement system was developed to fly on space shuttle flight STS-41D. The system was designed to dynamically evaluate a large solar array called the Solar Array Flight Experiment (SAFE) that had been scheduled for this flight. The SAFDE system consisted of a set of laser diode illuminators, retroreflective targets, an intelligent star tracker receiver and the associated equipment to power, condition, and record the results. In six tests on STS-41D, data was successfully acquired from 18 retroreflector targets and ground processed, post flight, to define the solar array's dynamic characteristic. The flight experiment proved the viability of on-orbit test definition of large space structures dynamic characteristics. Future large space structures controllability should be greatly enhanced by this capability.
-
A heat receiver design for solar dynamic space power systems
Baker, Karl W.; Dustin, Miles O.; Crane, Roger
1990-01-01
An advanced heat pipe receiver designed for a solar dynamic space power system is described. The power system consists of a solar concentrator, solar heat receiver, Stirling heat engine, linear alternator and waste heat radiator. The solar concentrator focuses the sun's energy into a heat receiver. The engine and alternator convert a portion of this energy to electric power and the remaining heat is rejected by a waste heat radiator. Primary liquid metal heat pipes transport heat energy to the Stirling engine. Thermal energy storage allows this power system to operate during the shade portion of an orbit. Lithium fluoride/calcium fluoride eutectic is the thermal energy storage material. Thermal energy storage canisters are attached to the midsection of each heat pipe. The primary heat pipes pass through a secondary vapor cavity heat pipe near the engine and receiver interface. The secondary vapor cavity heat pipe serves three important functions. First, it smooths out hot spots in the solar cavity and provides even distribution of heat to the engine. Second, the event of a heat pipe failure, the secondary heat pipe cavity can efficiently transfer heat from other operating primary heat pipes to the engine heat exchanger of the defunct heat pipe. Third, the secondary heat pipe vapor cavity reduces temperature drops caused by heat flow into the engine. This unique design provides a high level of reliability and performance.
-
Thermal energy storage for a space solar dynamic power system
Faget, N. M.; Fraser, W. M., Jr.; Simon, W. E.
1985-01-01
In the past, NASA has employed solar photovoltaic devices for long-duration missions. Thus, the Skylab system has operated with a silicon photovoltaic array and a nickel-cadmium electrochemical system energy storage system. Difficulties regarding the employment of such a system for the larger power requirements of the Space Station are related to a low orbit system efficiency and the large weight of the battery. For this reason the employment of a solar dynamic power system (SDPS) has been considered. The primary components of an SDPS include a concentrating mirror, a heat receiver, a thermal energy storage (TES) system, a thermodynamic heat engine, an alternator, and a heat rejection system. The heat-engine types under consideration are a Brayton cycle engine, an organic Rankine cycle engine, and a free-piston/linear-alternator Stirling cycle engine. Attention is given to a system description, TES integration concepts, and a TES technology assessment.
-
Dynamics and Control of a Flexible Solar Sail
Jiafu Liu; Siyuan Rong; Fan Shen; Naigang Cui
2014-01-01
Solar sail can merely make use of solar radiation pressure (SRP) force as the thrust for space missions. The attitude dynamics is obtained for the highly flexible solar sail with control vanes, sliding masses, and a gimbaled control boom. The vibration equations are derived considering the geometric nonlinearity of the sail structure subjected to the forces generated by the control vanes, solar radiation pressure (SRP), and sliding masses. Then the dynamic models for attitude/vibration contr...
-
Nonlinear dynamics of the magnetosphere and space weather
Sharma, A. Surjalal
1996-01-01
The solar wind-magnetosphere system exhibits coherence on the global scale and such behavior can arise from nonlinearity on the dynamics. The observational time series data were used together with phase space reconstruction techniques to analyze the magnetospheric dynamics. Analysis of the solar wind, auroral electrojet and Dst indices showed low dimensionality of the dynamics and accurate prediction can be made with an input/output model. The predictability of the magnetosphere in spite of the apparent complexity arises from its dynamical synchronism with the solar wind. The electrodynamic coupling between different regions of the magnetosphere yields its coherent, low dimensional behavior. The data from multiple satellites and ground stations can be used to develop a spatio-temporal model that identifies the coupling between different regions. These nonlinear dynamical models provide space weather forecasting capabilities.
-
Recent Progress in Heliogyro Solar Sail Structural Dynamics
Wilkie, William K.; Warren, Jerry E.; Horta, Lucas G.; Juang, Jer-Nan; Gibbs, Samuel C.; Dowell, E.; Guerrant, Daniel; Lawrence Dale
2014-01-01
Results from recent National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) research on the structural dynamics and control characteristics of heliogyro solar sails are summarized. Specific areas under investigation include coupled nonlinear finite element analysis of heliogyro membrane blade with solar radiation pressure effects, system identification of spinning membrane structures, solarelastic stability analysis of heliogyro solar sails, including stability during blade deployment, and results from small-scale in vacuo dynamics experiments with spinning high-aspect ratio membranes. A low-cost, rideshare payload heliogyro technology demonstration mission concept, used as a mission context for these heliogyro structural dynamics and solarelasticity investigations, is also described.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Cahill R. T.
2014-10-01
Full Text Available Space speed fluctuations, which have a 1 / f spectrum, are shown to be the cause of solar flares. The direction and magnitude of the space flow has been detected from numer- ous different experimental techniques, and is close to the normal to the plane of the ecliptic. Zener diode data shows that the fluctuations in the space speed closely match the Sun Solar Cycle 23 flare count, and reveal that major solar flares follow major space speed fluctuations by some 6 days. This implies that a warning period of some 5 days in predicting major solar flares is possible using such detectors. This has significant conse- quences in being able to protect various spacecraft and Earth located electrical systems from the subsequent arrival of ejected plasma from a solar flare. These space speed fluctuations are the actual gravitational waves, and have a significant magnitude. This discovery is a significant application of the dynamical space phenomenon and theory. We also show that space flow turbulence impacts on the Earth’s climate, as such tur- bulence can input energy into systems, which is the basis of the Zener Diode Quantum Detector. Large scale space fluctuations impact on both the sun and the Earth, and as well explain temperature correlations with solar activity, but that the Earth temperatures are not caused by such solar activity. This implies that the Earth climate debate has been missing a key physical process. Observed diminishing gravitational waves imply a cooling epoch for the Earth for the next 30 years.
-
Solar dynamic power system definition study
Wallin, Wayne E.; Friefeld, Jerry M.
1988-01-01
The solar dynamic power system design and analysis study compared Brayton, alkali-metal Rankine, and free-piston Stirling cycles with silicon planar and GaAs concentrator photovoltaic power systems for application to missions beyond the Phase 2 Space Station level of technology for all power systems. Conceptual designs for Brayton and Stirling power systems were developed for 35 kWe and 7 kWe power levels. All power systems were designed for 7-year end-of-life conditions in low Earth orbit. LiF was selected for thermal energy storage for the solar dynamic systems. Results indicate that the Stirling cycle systems have the highest performance (lowest weight and area) followed by the Brayton cycle, with photovoltaic systems considerably lower in performance. For example, based on the performance assumptions used, the planar silicon power system weight was 55 to 75 percent higher than for the Stirling system. A technology program was developed to address areas wherein significant performance improvements could be realized relative to the current state-of-the-art as represented by Space Station. In addition, a preliminary evaluation of hardenability potential found that solar dynamic systems can be hardened beyond the hardness inherent in the conceptual designs of this study.
-
Faget, N. M.
1986-01-01
Attention is given to results obtained to date in developmental investigations of a thermal energy storage (TES) system for the projected NASA Space Station's solar dynamic power system; these tests have concentrated on issues related to materials compatibility for phase change materials (PCMs) and their containment vessels' materials. The five PCMs tested have melting temperatures that correspond to the operating temperatures of either the Brayton or Rankine heat engines, which were independently chosen for their high energy densities.
-
On protection of freedom's solar dynamic radiator from the orbital debris environment. Part 2
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rhatigan, J.L.
1992-01-01
In this paper, recent progress to better understand the environmental threat of micrometeoroid and space debris to the solar dynamic radiator for the Space Station Freedom power system is reported. The objective was to define a design which would perform to survivability requirements over the expected lifetime of the radiator. A previous paper described the approach developed to assess on-orbit survivability of the solar dynamic radiator due to micrometeoroid and space debris impacts. Preliminary analyses were presented to quantify the solar dynamic radiator survivability. These included the type of particle and particle population expected to defeat the radiator bumpering. Results of preliminary hypervelocity impact (HVI) testing performed on radiator panel samples were also presented. This paper presents results of a more extensive test program undertaken to further define the response of the solar dynamic radiator to HVI. Tests were conducted on representative radiator panels (under ambient, nonoperating conditions) over a range of particle size, particle density, impact angle, and impact velocity. Target parameters were also varied. Data indicate that analytical penetration predictions are conservative (i.e., pessimistic) for the specific configuration of the solar dynamic radiator. Test results are used to define more rigorously the solar dynamic radiator reliability with respect to HVI. Test data, analyses, and survivability results are presented
-
Solar origins of space weather and space climate
Komm, Rudolf; Pevtsov, Alexei; Leibacher, John
2014-01-01
This topical issue is based on the presentations given at the 26th National Solar Observatory (NSO) Summer Workshop held at the National Solar Observatory/Sacramento Peak, New Mexico, USA from 30 April to 4 May 2012. This unique forum brought together experts in different areas of solar and space physics to help in developing a full picture of the origin of solar phenomena that affect Earth’s technological systems. The articles include theory, model, and observation research on the origin of the solar activity and its cycle, as well as a discussion on how to incorporate the research into space-weather forecasting tools. This volume is aimed at graduate students and researchers active in solar physics and space science. Previously published in Solar Physics, Vol. 289/2, 2014.
-
Space Solar Power Satellite Technology Development at the Glenn Research Center: An Overview
Dudenhoefer, James E.; George, Patrick J.
2000-01-01
NASA Glenn Research Center (GRC). is participating in the Space Solar Power Exploratory Research and Technology program (SERT) for the development of a solar power satellite concept. The aim of the program is to provide electrical power to Earth by converting the Sun's energy and beaming it to the surface. This paper will give an overall view of the technologies being pursued at GRC including thin film photovoltaics, solar dynamic power systems, space environmental effects, power management and distribution, and electric propulsion. The developmental path not only provides solutions to gigawatt sized space power systems for the future, but provides synergistic opportunities for contemporary space power architectures. More details of Space Solar Power can be found by reading the references sited in this paper and by connecting to the web site http://moonbase.msfc.nasa.gov/ and accessing the "Space Solar Power" section "Public Access" area.
-
The Origin and Dynamics of Solar Magnetism
Thompson, M. J; Culhane, J. L; Nordlund, Å; Solanki, S. K; Zahn, J.-P
2009-01-01
The articles collected in this volume present all aspects of solar magnetism: from its origin in the solar dynamo to its evolution and dynamics that create the variability of solar phenomena, its well-known 11-year activity cycle that leads to the ever-changing pattern of sunspots and active regions on the Sun. Several contributions deal with the solar dynamo, the driver of many solar phenomena. Other contributions treat the transport and emergence of the magnetic flux through the outer layers of the Sun. The coupling of magnetic fields from the surface to the solar corona and beyond is also described, together with current studies on the predictability of solar activity. This book is aimed at researchers and graduate students working in solar physics and space science. It provides a full review of our current understanding of solar magnetism by the foremost experts in the field.
-
Vortex, ULF wave and Aurora Observation after Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Change
Shi, Q.
2017-12-01
Here we will summarize our recent study and show some new results on the Magnetosphere and Ionosphere Response to Dynamic Pressure Change/disturbances in the Solar Wind and foreshock regions. We study the step function type solar wind dynamic pressure change (increase/decrease) interaction with the magnetosphere using THEMIS satellites at both dayside and nightside in different geocentric distances. Vortices generated by the dynamic pressure change passing along the magnetopause are found and compared with model predictions. ULF waves and vortices are excited in the dayside and nightside plasma sheet when dynamic pressure change hit the magnetotail. The related ionospheric responses, such as aurora and TCVs, are also investigated. We compare Global MHD simulations with the observations. We will also show some new results that dayside magnetospheric FLRs might be caused by foreshock structures.Shi, Q. Q. et al. (2013), THEMIS observations of ULF wave excitation in the nightside plasma sheet during sudden impulse events, J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics, 118, doi:10.1029/2012JA017984. Shi, Q. Q. et al. (2014), Solar wind pressure pulse-driven magnetospheric vortices and their global consequences, J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics, 119, doi:10.1002/2013JA019551. Tian, A.M. et al.(2016), Dayside magnetospheric and ionospheric responses to solar wind pressure increase: Multispacecraft and ground observations, J. Geophys. Res., 121, doi:10.1002/2016JA022459. Shen, X.C. et al.(2015), Magnetospheric ULF waves with increasing amplitude related to solar wind dynamic pressure changes: THEMIS observations, J. Geophys. Res., 120, doi:10.1002/2014JA020913Zhao, H. Y. et al. (2016), Magnetospheric vortices and their global effect after a solar wind dynamic pressure decrease, J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics, 121, doi:10.1002/2015JA021646. Shen, X. C., et al. (2017), Dayside magnetospheric ULF wave frequency modulated by a solar wind dynamic pressure negative impulse, J. Geophys. Res
-
Space weather: Why are magnetospheric physicists interested in solar explosive phenomena
Koskinen, H. E. J.; Pulkkinen, T. I.
That solar activity drives magnetospheric dynamics has for a long time been the basis of solar-terrestrial physics. Numerous statistical studies correlating sunspots, 10.7 cm radiation, solar flares, etc., with various magnetospheric and geomagnetic parameters have been performed. However, in studies of magnetospheric dynamics the role of the Sun has often remained in the background and only the actual solar wind impinging the magnetosphere has gained most of the attention. During the last few years a new applied field of solar-terrestrial physics, space weather, has emerged. The term refers to variable particle and field conditions in our space environment, which may be hazardous to space-borne or ground-based technological systems and can endanger human life and health. When the modern society is becoming increasingly dependent on space technology, the need for better modelling and also forecasting of space weather becomes urgent. While for post analysis of magnetospheric phenomena it is quite sufficient to include observations from the magnetospheric boundaries out to L1 where SOHO is located, these observations do not provide enough lead-time to run space weather forecasting models and to distribute the forecasts to potential customers. For such purposes we need improved physical understanding and models to predict which active processes on the Sun will impact the magnetosphere and what their expected consequences are. An important change of view on the role of the Sun as the origin of magnetospheric disturbances has taken place during last 10--20 years. For a long time, the solar flares were thought to be the most geoeffective solar phenomena. Now the attention has shifted much more towards coronal mass ejections and the SOHO coronal observations seem to have turned the epoch irreversibly. However, we are not yet ready to make reliable perdictions of the terrestrial environment based on CME observations. From the space weather viewpoint, the key questions are
-
Dynamics and Control of a Flexible Solar Sail
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jiafu Liu
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Solar sail can merely make use of solar radiation pressure (SRP force as the thrust for space missions. The attitude dynamics is obtained for the highly flexible solar sail with control vanes, sliding masses, and a gimbaled control boom. The vibration equations are derived considering the geometric nonlinearity of the sail structure subjected to the forces generated by the control vanes, solar radiation pressure (SRP, and sliding masses. Then the dynamic models for attitude/vibration controller design and dynamic simulation are obtained, respectively. The linear quadratic regulator (LQR based and optimal proportional-integral (PI based controllers are designed for the coupled attitude/vibration models with constant disturbance torques caused by the center-of-mass (cm/center-of-pressure (cp offset, respectively. It can be concluded from the theoretical analysis and simulation results that the optimal PI based controller performs better than the LQR based controller from the view of eliminating the steady-state errors. The responses with and without the geometrical nonlinearity are performed, and the differences are observed and analyzed. And some suggestions are also presented.
-
Analysis of shadowing effects on MIR photovoltaic and solar dynamic power systems
Fincannon, James
1995-01-01
The NASA Lewis Research Center is currently working with RSC-Energia, the Russian Space Agency, and Allied Signal in developing a flight demonstration solar dynamic power system. This type of power system is dependent upon solar flux that is reflected and concentrated into a thermal storage system to provide the thermal energy input to a closed-cycle Brayton heat engine. The solar dynamic unit will be flown on the Russian Mir space station in anticipation of use on the International Space Station Alpha. By the time the power system is launched, the Mir will be a spatially complex configuration which will have, in addition to the three-gimbaled solar dynamic unit, eleven solar array wings that are either fixed or track the Sun along one axis and a variety or repositionable habitation and experiment modules. The proximity of arrays to modules creates a situation which makes it highly probable that there will be varying solar flux due to shadowing on the solar dynamic unit and some of the arrays throughout the orbit. Shadowing causes fluctuations in the power output from the arrays and the solar dynamic power system, thus reducing the energy capabilities of the spacecraft. An assessment of the capabilities of the power system under these conditions is an important part in influencing the design and operations of the spacecraft and predicting its energy performance. This paper describes the results obtained from using the Orbiting Spacecraft Shadowing Analysis Station program that was integrated into the Station Power Analysis for Capability Evaluation (SPACE) electrical power system computer program. OSSA allows one to consider the numerous complex factors for analyzing the shadowing effects on the electrical power system including the variety of spacecraft hardware geometric configurations, yearly and daily orbital variations in the vehicle attitude and orbital maneuvers (for communications coverage, payload pointing requirements and rendezvous/docking with other
-
Solar dynamic power module design
Secunde, Richard R.; Labus, Thomas L.; Lovely, Ronald G.
1989-01-01
Studies have shown that the use of solar dynamic (SD) power for the growth areas of the Space Station Freedom program will result in life cycle cost savings when compared to power supplied by photovoltaic sources. In the SD power module, a concentrator collects and focuses solar energy into a heat receiver which has integral thermal energy storage. A Power Conversion Unit (PCU) based on the closed Brayton cycle removes thermal energy from the receiver and converts that energy to electrical energy. Since the closed Brayton cycle is a single phase gas cycle, the conversion hardware (heat exchangers, turbine, compressor, etc.) can be designed for operation in low earth orbit, and tested with confidence in test facilities on earth before launch into space. The concentrator subassemblies will be aligned and the receiver/PCU/radiator combination completely assembled and charged with gas and cooling liquid on earth before launch to, and assembly on, orbit.
-
Conceptual definition of a technology development mission for advanced solar dynamic power systems
Migra, R. P.
1986-01-01
An initial conceptual definition of a technology development mission for advanced solar dynamic power systems is provided, utilizing a space station to provide a dedicated test facility. The advanced power systems considered included Brayton, Stirling, and liquid metal Rankine systems operating in the temperature range of 1040 to 1400 K. The critical technologies for advanced systems were identified by reviewing the current state of the art of solar dynamic power systems. The experimental requirements were determined by planning a system test of a 20 kWe solar dynamic power system on the space station test facility. These requirements were documented via the Mission Requirements Working Group (MRWG) and Technology Development Advocacy Group (TDAG) forms. Various concepts or considerations of advanced concepts are discussed. A preliminary evolutionary plan for this technology development mission was prepared.
-
Kusano, K.
2016-12-01
Project for Solar-Terrestrial Environment Prediction (PSTEP) is a Japanese nation-wide research collaboration, which was recently launched. PSTEP aims to develop a synergistic interaction between predictive and scientific studies of the solar-terrestrial environment and to establish the basis for next-generation space weather forecasting using the state-of-the-art observation systems and the physics-based models. For this project, we coordinate the four research groups, which develop (1) the integration of space weather forecast system, (2) the physics-based solar storm prediction, (3) the predictive models of magnetosphere and ionosphere dynamics, and (4) the model of solar cycle activity and its impact on climate, respectively. In this project, we will build the coordinated physics-based model to answer the fundamental questions concerning the onset of solar eruptions and the mechanism for radiation belt dynamics in the Earth's magnetosphere. In this paper, we will show the strategy of PSTEP, and discuss about the role and prospect of the physics-based space weather forecasting system being developed by PSTEP.
-
An IBM PC-based math model for space station solar array simulation
Emanuel, E. M.
1986-01-01
This report discusses and documents the design, development, and verification of a microcomputer-based solar cell math model for simulating the Space Station's solar array Initial Operational Capability (IOC) reference configuration. The array model is developed utilizing a linear solar cell dc math model requiring only five input parameters: short circuit current, open circuit voltage, maximum power voltage, maximum power current, and orbit inclination. The accuracy of this model is investigated using actual solar array on orbit electrical data derived from the Solar Array Flight Experiment/Dynamic Augmentation Experiment (SAFE/DAE), conducted during the STS-41D mission. This simulator provides real-time simulated performance data during the steady state portion of the Space Station orbit (i.e., array fully exposed to sunlight). Eclipse to sunlight transients and shadowing effects are not included in the analysis, but are discussed briefly. Integrating the Solar Array Simulator (SAS) into the Power Management and Distribution (PMAD) subsystem is also discussed.
-
Lacy, Dovie E.; Coles-Hamilton, Carolyn; Juhasz, Albert
1987-01-01
Under the direction of NASA's Office of Aeronautics and Technology (OAST), the NASA Lewis Research Center has initiated an in-house thermal energy storage program to identify combinations of phase change thermal energy storage media for use with a Brayton and Stirling Advanced Solar Dynamic (ASD) space power system operating between 1070 and 1400 K. A study has been initiated to determine suitable combinations of thermal energy storage (TES) phase change materials (PCM) that result in the smallest and lightest weight ASD power system possible. To date the heats of fusion of several fluoride salt mixtures with melting points greater than 1025 K have been verified experimentally. The study has indicated that these salt systems produce large ASD systems because of their inherent low thermal conductivity and low density. It is desirable to have PCMs with high densities and high thermal conductivities. Therefore, alternate phase change materials based on metallic alloy systems are also being considered as possible TES candidates for future ASD space power systems.
-
Plasma physics and the 2013-2022 decadal survey in solar and space physics
Baker, Daniel N.
2016-11-01
The U.S. National Academies established in 2011 a steering committee to develop a comprehensive strategy for solar and space physics research. This updated and extended the first (2003) solar and space physics decadal survey. The latest decadal study implemented a 2008 Congressional directive to NASA for the fields of solar and space physics, but also addressed research in other federal agencies. The new survey broadly canvassed the fields of research to determine the current state of the discipline, identified the most important open scientific questions, and proposed the measurements and means to obtain them so as to advance the state of knowledge during the years 2013-2022. Research in this field has sought to understand: dynamical behaviour of the Sun and its heliosphere; properties of the space environments of the Earth and other solar system bodies; multiscale interaction between solar system plasmas and the interstellar medium; and energy transport throughout the solar system and its impact on the Earth and other solar system bodies. Research in solar and space plasma processes using observation, theory, laboratory studies, and numerical models has offered the prospect of understanding this interconnected system well enough to develop a predictive capability for operational support of civil and military space systems. We here describe the recommendations and strategic plans laid out in the 2013-2022 decadal survey as they relate to measurement capabilities and plasma physical research. We assess progress to date. We also identify further steps to achieve the Survey goals with an emphasis on plasma physical aspects of the program.
-
Weakest solar wind of the space age and the current 'MINI' solar maximum
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McComas, D. J.; Angold, N.; Elliott, H. A.; Livadiotis, G.; Schwadron, N. A.; Smith, C. W.; Skoug, R. M.
2013-01-01
The last solar minimum, which extended into 2009, was especially deep and prolonged. Since then, sunspot activity has gone through a very small peak while the heliospheric current sheet achieved large tilt angles similar to prior solar maxima. The solar wind fluid properties and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) have declined through the prolonged solar minimum and continued to be low through the current mini solar maximum. Compared to values typically observed from the mid-1970s through the mid-1990s, the following proton parameters are lower on average from 2009 through day 79 of 2013: solar wind speed and beta (∼11%), temperature (∼40%), thermal pressure (∼55%), mass flux (∼34%), momentum flux or dynamic pressure (∼41%), energy flux (∼48%), IMF magnitude (∼31%), and radial component of the IMF (∼38%). These results have important implications for the solar wind's interaction with planetary magnetospheres and the heliosphere's interaction with the local interstellar medium, with the proton dynamic pressure remaining near the lowest values observed in the space age: ∼1.4 nPa, compared to ∼2.4 nPa typically observed from the mid-1970s through the mid-1990s. The combination of lower magnetic flux emergence from the Sun (carried out in the solar wind as the IMF) and associated low power in the solar wind points to the causal relationship between them. Our results indicate that the low solar wind output is driven by an internal trend in the Sun that is longer than the ∼11 yr solar cycle, and they suggest that this current weak solar maximum is driven by the same trend.
-
Overview of Small and Large-Scale Space Solar Power Concepts
Potter, Seth; Henley, Mark; Howell, Joe; Carrington, Connie; Fikes, John
2006-01-01
An overview of space solar power studies performed at the Boeing Company under contract with NASA will be presented. The major concepts to be presented are: 1. Power Plug in Orbit: this is a spacecraft that collects solar energy and distributes it to users in space using directed radio frequency or optical energy. Our concept uses solar arrays having the same dimensions as ISS arrays, but are assumed to be more efficient. If radiofrequency wavelengths are used, it will necessitate that the receiving satellite be equipped with a rectifying antenna (rectenna). For optical wavelengths, the solar arrays on the receiving satellite will collect the power. 2. Mars Clipper I Power Explorer: this is a solar electric Mars transfer vehicle to support human missions. A near-term precursor could be a high-power radar mapping spacecraft with self-transport capability. Advanced solar electric power systems and electric propulsion technology constitute viable elements for conducting human Mars missions that are roughly comparable in performance to similar missions utilizing alternative high thrust systems, with the one exception being their inability to achieve short Earth-Mars trip times. 3. Alternative Architectures: this task involves investigating alternatives to the traditional solar power satellite (SPS) to supply commercial power from space for use on Earth. Four concepts were studied: two using photovoltaic power generation, and two using solar dynamic power generation, with microwave and laser power transmission alternatives considered for each. All four architectures use geostationary orbit. 4. Cryogenic Propellant Depot in Earth Orbit: this concept uses large solar arrays (producing perhaps 600 kW) to electrolyze water launched from Earth, liquefy the resulting hydrogen and oxygen gases, and store them until needed by spacecraft. 5. Beam-Powered Lunar Polar Rover: a lunar rover powered by a microwave or laser beam can explore permanently shadowed craters near the lunar
-
Voluble: a space-time diagram of the solar system
Aguilera, Julieta C.; SubbaRao, Mark U.
2008-02-01
Voluble is a dynamic space-time diagram of the solar system. Voluble is designed to help users understand the relationship between space and time in the motion of the planets around the sun. Voluble is set in virtual reality to relate these movements to our experience of immediate space. Beyond just the visual, understanding dynamic systems is naturally associated to the articulation of our bodies as we perform a number of complex calculations, albeit unconsciously, to deal with simple tasks. Such capabilities encompass spatial perception and memory. Voluble investigates the balance between the visually abstract and the spatially figurative in immersive development to help illuminate phenomena that are beyond the reach of human scale and time. While most diagrams, even computer-based interactive ones, are flat, three-dimensional real-time virtual reality representations are closer to our experience of space. The representation can be seen as if it was "really there," engaging a larger number of cues pertaining to our everyday spatial experience.
-
The applications of Complexity Theory and Tsallis Non-extensive Statistics at Solar Plasma Dynamics
Pavlos, George
2015-04-01
As the solar plasma lives far from equilibrium it is an excellent laboratory for testing complexity theory and non-equilibrium statistical mechanics. In this study, we present the highlights of complexity theory and Tsallis non extensive statistical mechanics as concerns their applications at solar plasma dynamics, especially at sunspot, solar flare and solar wind phenomena. Generally, when a physical system is driven far from equilibrium states some novel characteristics can be observed related to the nonlinear character of dynamics. Generally, the nonlinearity in space plasma dynamics can generate intermittent turbulence with the typical characteristics of the anomalous diffusion process and strange topologies of stochastic space plasma fields (velocity and magnetic fields) caused by the strange dynamics and strange kinetics (Zaslavsky, 2002). In addition, according to Zelenyi and Milovanov (2004) the complex character of the space plasma system includes the existence of non-equilibrium (quasi)-stationary states (NESS) having the topology of a percolating fractal set. The stabilization of a system near the NESS is perceived as a transition into a turbulent state determined by self-organization processes. The long-range correlation effects manifest themselves as a strange non-Gaussian behavior of kinetic processes near the NESS plasma state. The complex character of space plasma can also be described by the non-extensive statistical thermodynamics pioneered by Tsallis, which offers a consistent and effective theoretical framework, based on a generalization of Boltzmann - Gibbs (BG) entropy, to describe far from equilibrium nonlinear complex dynamics (Tsallis, 2009). In a series of recent papers, the hypothesis of Tsallis non-extensive statistics in magnetosphere, sunspot dynamics, solar flares, solar wind and space plasma in general, was tested and verified (Karakatsanis et al., 2013; Pavlos et al., 2014; 2015). Our study includes the analysis of solar plasma time
-
Space Solar Power: Satellite Concepts
Little, Frank E.
1999-01-01
Space Solar Power (SSP) applies broadly to the use of solar power for space related applications. The thrust of the NASA SSP initiative is to develop concepts and demonstrate technology for applying space solar power to NASA missions. Providing power from satellites in space via wireless transmission to a receiving station either on earth, another celestial body or a second satellite is one goal of the SSP initiative. The sandwich design is a satellite design in which the microwave transmitting array is the front face of a thin disk and the back of the disk is populated with solar cells, with the microwave electronics in between. The transmitter remains aimed at the earth in geostationary orbit while a system of mirrors directs sunlight to the photovoltaic cells, regardless of the satellite's orientation to the sun. The primary advantage of the sandwich design is it eliminates the need for a massive and complex electric power management and distribution system for the satellite. However, it requires a complex system for focusing sunlight onto the photovoltaic cells. In addition, positioning the photovoltaic array directly behind the transmitting array power conversion electronics will create a thermal management challenge. This project focused on developing designs and finding emerging technology to meet the challenges of solar tracking, a concentrating mirror system including materials and coatings, improved photovoltaic materials and thermal management.
-
Space Weather: The Solar Perspective
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Schwenn Rainer
2006-08-01
Full Text Available The term space weather refers to conditions on the Sun and in the solar wind, magnetosphere, ionosphere, and thermosphere that can influence the performance and reliability of space-borne and ground-based technological systems and that can affect human life and health. Our modern hi-tech society has become increasingly vulnerable to disturbances from outside the Earth system, in particular to those initiated by explosive events on the Sun: Flares release flashes of radiation that can heat up the terrestrial atmosphere such that satellites are slowed down and drop into lower orbits, solar energetic particles accelerated to near-relativistic energies may endanger astronauts traveling through interplanetary space, and coronal mass ejections are gigantic clouds of ionized gas ejected into interplanetary space that after a few hours or days may hit the Earth and cause geomagnetic storms. In this review, I describe the several chains of actions originating in our parent star, the Sun, that affect Earth, with particular attention to the solar phenomena and the subsequent effects in interplanetary space.
-
Space Weather: The Solar Perspective
Schwenn, Rainer
2006-08-01
The term space weather refers to conditions on the Sun and in the solar wind, magnetosphere, ionosphere, and thermosphere that can influence the performance and reliability of space-borne and ground-based technological systems and that can affect human life and health. Our modern hi-tech society has become increasingly vulnerable to disturbances from outside the Earth system, in particular to those initiated by explosive events on the Sun: Flares release flashes of radiation that can heat up the terrestrial atmosphere such that satellites are slowed down and drop into lower orbits, solar energetic particles accelerated to near-relativistic energies may endanger astronauts traveling through interplanetary space, and coronal mass ejections are gigantic clouds of ionized gas ejected into interplanetary space that after a few hours or days may hit the Earth and cause geomagnetic storms. In this review, I describe the several chains of actions originating in our parent star, the Sun, that affect Earth, with particular attention to the solar phenomena and the subsequent effects in interplanetary space.
-
Solar neutrinos, helioseismology and the solar internal dynamics
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Turck-Chieze, Sylvaine [Service d' Astrophysique/IRFU/DSM/CEA, 91191 Gif sur Yvette Cedex (France); Couvidat, Sebastien, E-mail: sylvaine.turck-chieze@cea.fr, E-mail: couvidat@stanford.edu [HEPL, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305 (United States)
2011-08-15
masses are still unknown, and the research on the solar interior focuses on the dynamical aspects and on the signature of dark matter. The magnetic moment of the neutrino begins to be an actor in stellar evolution. The third part of the review is dedicated to this prospect. The understanding of the crucial role of both rotation and magnetism in solar physics benefits from SoHO, SDO and PICARD space observations, and from a new prototype, GOLF-NG. The magnetohydrodynamical view of the solar interior is a new way of understanding the impact of the Sun on the Earth's environment and climate. For now, the particle and stellar challenges seem decoupled, but this is only a superficial appearance. The development of asteroseismology-with the COROT and KEPLER spacecraft-and of neutrino physics will both contribute to improvements in our understanding of, for instance, supernova explosions. This shows the far-reaching impact of neutrino and stellar astronomy.
-
Phase change energy storage for solar dynamic power systems
Chiaramonte, F. P.; Taylor, J. D.
1992-01-01
This paper presents the results of a transient computer simulation that was developed to study phase change energy storage techniques for Space Station Freedom (SSF) solar dynamic (SD) power systems. Such SD systems may be used in future growth SSF configurations. Two solar dynamic options are considered in this paper: Brayton and Rankine. Model elements consist of a single node receiver and concentrator, and takes into account overall heat engine efficiency and power distribution characteristics. The simulation not only computes the energy stored in the receiver phase change material (PCM), but also the amount of the PCM required for various combinations of load demands and power system mission constraints. For a solar dynamic power system in low earth orbit, the amount of stored PCM energy is calculated by balancing the solar energy input and the energy consumed by the loads corrected by an overall system efficiency. The model assumes an average 75 kW SD power system load profile which is connected to user loads via dedicated power distribution channels. The model then calculates the stored energy in the receiver and subsequently estimates the quantity of PCM necessary to meet peaking and contingency requirements. The model can also be used to conduct trade studies on the performance of SD power systems using different storage materials.
-
Space Station solar water heater
Horan, D. C.; Somers, Richard E.; Haynes, R. D.
1990-01-01
The feasibility of directly converting solar energy for crew water heating on the Space Station Freedom (SSF) and other human-tended missions such as a geosynchronous space station, lunar base, or Mars spacecraft was investigated. Computer codes were developed to model the systems, and a proof-of-concept thermal vacuum test was conducted to evaluate system performance in an environment simulating the SSF. The results indicate that a solar water heater is feasible. It could provide up to 100 percent of the design heating load without a significant configuration change to the SSF or other missions. The solar heater system requires only 15 percent of the electricity that an all-electric system on the SSF would require. This allows a reduction in the solar array or a surplus of electricity for onboard experiments.
-
Solar EUV irradiance for space weather applications
Viereck, R. A.
2015-12-01
Solar EUV irradiance is an important driver of space weather models. Large changes in EUV and x-ray irradiances create large variability in the ionosphere and thermosphere. Proxies such as the F10.7 cm radio flux, have provided reasonable estimates of the EUV flux but as the space weather models become more accurate and the demands of the customers become more stringent, proxies are no longer adequate. Furthermore, proxies are often provided only on a daily basis and shorter time scales are becoming important. Also, there is a growing need for multi-day forecasts of solar EUV irradiance to drive space weather forecast models. In this presentation we will describe the needs and requirements for solar EUV irradiance information from the space weather modeler's perspective. We will then translate these requirements into solar observational requirements such as spectral resolution and irradiance accuracy. We will also describe the activities at NOAA to provide long-term solar EUV irradiance observations and derived products that are needed for real-time space weather modeling.
-
Solar terrestrial coupling through space plasma processes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Birn, J.
2000-01-01
This is the final report of a three-year, Laboratory-Directed Research and Development (LDRD) project at the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). The project investigates plasma processes that govern the interaction between the solar wind, charged particles ejected from the sun, and the earth's magnetosphere, the region above the ionosphere governed by the terrestrial magnetic field. Primary regions of interest are the regions where different plasma populations interact with each other. These are regions of particularly dynamic plasma behavior, associated with magnetic flux and energy transfer and dynamic energy release. The investigations concerned charged particle transport and energization, and microscopic and macroscopic instabilities in the magnetosphere and adjacent regions. The approaches combined space data analysis with theory and computer simulations
-
Short-term solar irradiation forecasting based on Dynamic Harmonic Regression
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Trapero, Juan R.; Kourentzes, Nikolaos; Martin, A.
2015-01-01
Solar power generation is a crucial research area for countries that have high dependency on fossil energy sources and is gaining prominence with the current shift to renewable sources of energy. In order to integrate the electricity generated by solar energy into the grid, solar irradiation must be reasonably well forecasted, where deviations of the forecasted value from the actual measured value involve significant costs. The present paper proposes a univariate Dynamic Harmonic Regression model set up in a State Space framework for short-term (1–24 h) solar irradiation forecasting. Time series hourly aggregated as the Global Horizontal Irradiation and the Direct Normal Irradiation will be used to illustrate the proposed approach. This method provides a fast automatic identification and estimation procedure based on the frequency domain. Furthermore, the recursive algorithms applied offer adaptive predictions. The good forecasting performance is illustrated with solar irradiance measurements collected from ground-based weather stations located in Spain. The results show that the Dynamic Harmonic Regression achieves the lowest relative Root Mean Squared Error; about 30% and 47% for the Global and Direct irradiation components, respectively, for a forecast horizon of 24 h ahead. - Highlights: • Solar irradiation forecasts at short-term are required to operate solar power plants. • This paper assesses the Dynamic Harmonic Regression to forecast solar irradiation. • Models are evaluated using hourly GHI and DNI data collected in Spain. • The results show that forecasting accuracy is improved by using the model proposed
-
Effects of solar activity in the middle atmosphere dynamical regime over Eastern Siberia, USSR
Gaidukov, V. A.; Kazimirovsky, E. S.; Zhovty, E. I.; Chernigovskaya, M. A.
1989-01-01
Lower thermospheric (90 to 120 km) wind data was acquired by ground based spaced-receiver method (HF, LF) near Irkutsk (52 deg N, 104 deg E). There is interrelated solar and meteorological control of lower thermosphere dynamics. Some features of solar control effects on the wind parameters are discussed.
-
Space solar power - An energy alternative
Johnson, R. W.
1978-01-01
The space solar power concept is concerned with the use of a Space Power Satellite (SPS) which orbits the earth at geostationary altitude. Two large symmetrical solar collectors convert solar energy directly to electricity using photovoltaic cells woven into blankets. The dc electricity is directed to microwave generators incorporated in a transmitting antenna located between the solar collectors. The antenna directs the microwave beam to a receiving antenna on earth where the microwave energy is efficiently converted back to dc electricity. The SPS design promises 30-year and beyond lifetimes. The SPS is relatively pollution free as it promises earth-equivalence of 80-85% efficient ground-based thermal power plant.
-
New directions for space solar power
Mankins, John C.
2009-07-01
Several of the central issues associated with the eventual realization of the vision of solar power from space for terrestrial markets resolve around the expect costs associated with the assembly, inspection, maintenance and repair of future solar power satellite (SPS) stations. In past studies (for example, NASA's "Fresh Look Study", c. 1995-1997) efforts were made to reduce both the scale and mass of large, systems-level interfaces (e.g., the power management and distribution (PMAD) system) and on-orbit fixed infrastructures through the use of modular systems strategies. These efforts have had mixed success (as reflected in the projected on-orbit mass of various systems concepts. However, the author remains convinced of the importance of modular strategies for exceptionally large space systems in eventually realizing the vision of power from space. This paper will introduce some of the key issues associated with cost-competitive space solar power in terrestrial markets. It will examine some of the relevant SPS concepts and will assess the 'pros and cons' of each in terms of space assembly, maintenance and servicing (SAMS) requirements. The paper discusses at a high level some relevant concepts and technologies that may play r role in the eventual, successful resolution of these challenges. The paper concludes with an example of the kind of novel architectural approach for space solar power that is needed.
-
Key techniques for space-based solar pumped semiconductor lasers
He, Yang; Xiong, Sheng-jun; Liu, Xiao-long; Han, Wei-hua
2014-12-01
In space, the absence of atmospheric turbulence, absorption, dispersion and aerosol factors on laser transmission. Therefore, space-based laser has important values in satellite communication, satellite attitude controlling, space debris clearing, and long distance energy transmission, etc. On the other hand, solar energy is a kind of clean and renewable resources, the average intensity of solar irradiation on the earth is 1353W/m2, and it is even higher in space. Therefore, the space-based solar pumped lasers has attracted much research in recent years, most research focuses on solar pumped solid state lasers and solar pumped fiber lasers. The two lasing principle is based on stimulated emission of the rare earth ions such as Nd, Yb, Cr. The rare earth ions absorb light only in narrow bands. This leads to inefficient absorption of the broad-band solar spectrum, and increases the system heating load, which make the system solar to laser power conversion efficiency very low. As a solar pumped semiconductor lasers could absorb all photons with energy greater than the bandgap. Thus, solar pumped semiconductor lasers could have considerably higher efficiencies than other solar pumped lasers. Besides, solar pumped semiconductor lasers has smaller volume chip, simpler structure and better heat dissipation, it can be mounted on a small satellite platform, can compose satellite array, which can greatly improve the output power of the system, and have flexible character. This paper summarizes the research progress of space-based solar pumped semiconductor lasers, analyses of the key technologies based on several application areas, including the processing of semiconductor chip, the design of small and efficient solar condenser, and the cooling system of lasers, etc. We conclude that the solar pumped vertical cavity surface-emitting semiconductor lasers will have a wide application prospects in the space.
-
Space Solar Power Program. Final report
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Arif, Humayun; Barbosa, Hugo; Bardet, Christophe; Baroud, Michel; Behar, Alberto; Berrier, Keith; Berthe, Phillipe; Bertrand, Reinhold; Bibyk, Irene; Bisson, Joel; Bloch, Lawrence; Bobadilla, Gabriel; Bourque, Denis; Bush, Lawrence; Carandang, Romeo; Chiku, Takemi; Crosby, Norma; De Seixas, Manuel; De Vries, Joha; Doll, Susan; Dufour, Francois; Eckart, Peter; Fahey, Michael; Fenot, Frederic; Foeckersperger, Stefan; Fontaine, Jean-Emmanuel; Fowler, Robert; Frey, Harald; Fujio, Hironobu; Gasa, Jaume Munich; Gleave, Janet; Godoe, Jostein; Green, Iain; Haeberli, Roman; Hanada, Toshiya; Harris, Peter; Hucteau, Mario; Jacobs, Didier Fernand; Johnson, Richard; Kanno, Yoshitsugu; Koenig, Eva Maria; Kojima, Kazuo; Kondepudi, Phani; Kottbauer, Christian; Kulper, Doede; Kulagin, Konstantin; Kumara, Pekka; Kurz, Rainer; Laaksonen, Jyrki; Lang, Andrew Neill; Lathan, Corinna; Le Fur, Thierry; Lewis, David; Louis, Alain; Mori, Takeshi; Morlanes, Juan; Murbach, Marcus; Nagatomo, Hideo; O' brien, Ivan; Paines, Justin; Palaszewski, Bryan; Palmnaes, Ulf; Paraschivolu, Marius; Pathare, Asmin; Perov, Egor; Persson, Jan; Pessoa-Lopes, Isabel; Pinto, Michel; Porro, Irene; Reichert, Michael; Ritt-Fischer, Monika; Roberts, Margaret; Robertson II, Lawrence; Rogers, Keith; Sasaki, Tetsuo; Scire, Francesca; Shibatou, Katsuya; Shirai, Tatsuya; Shiraishi, Atsushi; Soucaille, Jean-Francois; Spivack, Nova; St. Pierre, Dany; Suleman, Afzal; Sullivan, Thomas; Theelen, Bas Johan; Thonstad, Hallvard; Tsuji, Masatoshi; Uchiumi, Masaharu; Vidqvist, Jouni; Warrell, David; Watanabe, Takafumi; Willis, Richard; Wolf, Frank; Yamakawa, Hiroshi; Zhao, Hong
1992-08-01
Information pertaining to the Space Solar Power Program is presented on energy analysis; markets; overall development plan; organizational plan; environmental and safety issues; power systems; space transportation; space manufacturing, construction, operations; design examples; and finance.
-
On the effects of solar storms to the decaying orbital space debris
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Herdiwijaya, Dhani; Rachman, Abdul
2014-01-01
Any man-made object in Earth's orbit that no longer serves a useful purpose is classified as orbital debris. Debris objects come from a variety of sources. The majority is related to satellite fragmentation. Other major sources of debris are propulsion systems, and fragmentation of spent upper stages, payload and mission related debris. Serious concern about orbital debris has been growing. Knowledge of the future debris environment is important to both satellite designers, and mission planners, who need to know what hazards a satellite might encounter during the course of its mission. Therefore, it is important to know how much debris is in orbit, where it is located, and when it will decay. The debris environment is complex and dynamically evolving. Objects of different shape and size behave differently in orbit. The geoeffectiveness space environments include solar flux at 10.7 cm, solar energetic particles flux or speed, solar wind flow pressure, electric field, and geomagnetic indices. We study the decaying orbital debris from Tracking and Impact Prediction (TIP) messages in conjuction with geoeffectiveness space environments through time epoch correlation. We found that the decaying and reentry orbital debris are triggered by space environment enhancement within at least one week before reentry. It is not necessary a transient or high energetic and severe solar storm events are needed in decaying processes. We propose that the gradual enhancement processes of space environment will cause satellite surface charging due to energetic electron and enhance drag force
-
On the effects of solar storms to the decaying orbital space debris
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Herdiwijaya, Dhani, E-mail: dhani@as.itb.ac.id [Astronomy Division and Bosscha Observatory, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Bandung Institute of Technology, Ganesha 10, Bandung 40132 (Indonesia); Rachman, Abdul [Space Science Center, National Institute of Aeronautics and Space, Junjunan 133, Bandung 40173 (Indonesia)
2014-03-24
Any man-made object in Earth's orbit that no longer serves a useful purpose is classified as orbital debris. Debris objects come from a variety of sources. The majority is related to satellite fragmentation. Other major sources of debris are propulsion systems, and fragmentation of spent upper stages, payload and mission related debris. Serious concern about orbital debris has been growing. Knowledge of the future debris environment is important to both satellite designers, and mission planners, who need to know what hazards a satellite might encounter during the course of its mission. Therefore, it is important to know how much debris is in orbit, where it is located, and when it will decay. The debris environment is complex and dynamically evolving. Objects of different shape and size behave differently in orbit. The geoeffectiveness space environments include solar flux at 10.7 cm, solar energetic particles flux or speed, solar wind flow pressure, electric field, and geomagnetic indices. We study the decaying orbital debris from Tracking and Impact Prediction (TIP) messages in conjuction with geoeffectiveness space environments through time epoch correlation. We found that the decaying and reentry orbital debris are triggered by space environment enhancement within at least one week before reentry. It is not necessary a transient or high energetic and severe solar storm events are needed in decaying processes. We propose that the gradual enhancement processes of space environment will cause satellite surface charging due to energetic electron and enhance drag force.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Calise, Francesco; Dentice d'Accadia, Massimo; Figaj, Rafal Damian; Vanoli, Laura
2016-01-01
This paper presents a dynamic simulation model and a thermo-economic analysis of a novel polygeneration system based on a solar-assisted heat pump and an adsorption chiller, both driven by PVT (photovoltaic/thermal) collectors. The aim of this work is to design and dynamically simulate a novel ultra-high efficient solar heating and cooling system. The overall plant layout is designed to supply electricity, space heating and cooling and domestic hot water for a small residential building. The system combines solar cooling, solar-assisted heat pump and photovoltaic/thermal collector technologies in a novel solar polygeneration system. In fact, the polygeneration system is based on a PVT solar field, coupled with a water-to-water electric heat pump or to an adsorption chiller. PVT collectors simultaneously produce electricity and thermal energy. During the winter, hot water produced by PVT collectors primarily supplies the evaporator of the heat pump, whereas in summer, solar energy supplies an adsorption chiller providing the required space cooling. All year long, solar thermal energy in excess is converted into DHW (domestic hot water). The system model was developed in TRNSYS environment. 1-year dynamic simulations are performed for different case studies in various weather conditions. The results are analysed on different time bases presenting energetic, environmental and economic performance data. Finally, a sensitivity analysis and a thermoeconomic optimization were performed, in order to determine the set of system design/control parameters that minimize the simple pay-back period. The results showed a total energy efficiency of the PVT of 49%, a heat pump yearly coefficient of performance for heating mode above 4 and a coefficient of performance of the adsorption chiller of 0.55. Finally, it is also concluded that system performance is highly sensitive to the PVT field area. The system is profitable when a capital investment subsidy of 50% is considered
-
Wisdom, Jack
2002-01-01
In these 18 years, the research has touched every major dynamical problem in the solar system, including: the effect of chaotic zones on the distribution of asteroids, the delivery of meteorites along chaotic pathways, the chaotic motion of Pluto, the chaotic motion of the outer planets and that of the whole solar system, the delivery of short period comets from the Kuiper belt, the tidal evolution of the Uranian arid Galilean satellites, the chaotic tumbling of Hyperion and other irregular satellites, the large chaotic variations of the obliquity of Mars, the evolution of the Earth-Moon system, and the resonant core- mantle dynamics of Earth and Venus. It has introduced new analytical and numerical tools that are in widespread use. Today, nearly every long-term integration of our solar system, its subsystems, and other solar systems uses algorithms that was invented. This research has all been primarily Supported by this sequence of PGG NASA grants. During this period published major investigations of tidal evolution of the Earth-Moon system and of the passage of the Earth and Venus through non-linear core-mantle resonances were completed. It has published a major innovation in symplectic algorithms: the symplectic corrector. A paper was completed on non-perturbative hydrostatic equilibrium.
-
Potential for solar space heating in Scotland
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Macgregor, A W.K.
1980-07-01
This paper investigates the relative effectiveness of passive-type solar-assisted space heating systems at various latitudes within the British Isles. A comparison is made of the useful solar gain of the same system linked to the same house at four different locations. Month-by-month energy balances indicate that the annual useful solar contribution at the highest latitude (Lerwick, 60 deg N) is about 35% higher than at the lowest latitude (Kew, 53 deg N). The main reason for this difference is the higher heating loads in the north, particularly outside the winter months. The estimated available irradiation on south-facing vertical surfaces was almost the same at all four locations. Previous work in the UK indicates that, contrary to the conclusions in this paper, more southerly latitudes were the most favorable for solar space heating. The reasons for the disparity are discussed. It is recommended that research and development of passive solar-assisted space heating systems should be most vigorously pursued in the more northerly latitudes of the British Isles, where both the potential benefit and the need are greatest.
-
Summerer, L.; Pipoli, T.; Galvez, A.; Ongaro, F.; Vasile, M.
The paper presents the prospective roles of SPS concepts for Europe, shows the outcome of recent studies undertaken by ESA's Advanced Concepts Team (ACT) together with European industry and research centres and gives insight into planned activities. The main focus is on the assessment of the principal validity and economic viability of solar power from space concepts in the light of advances in alternative sustainable, clean and potentially abundant solar-based terrestrial concepts. The paper takes into account expected changes in the European energy system (e.g. gradual introduction of hydrogen as energy vector). Special emphasis is given to the possibilities of integrating space and terrestrial solar plants. The relative geographic proximity of areas in North Africa with high average solar irradiation to the European energy consumer market puts Europe in a special position regarding the integration of space and terrestrial solar power concepts. The paper presents a method to optimise such an integration, taking into account different possible orbital constellations, terrestrial locations, plant number and sizes as well as consumer profiles and extends the scope from the European-only to a multi continental approach including the fast growing Chinese electricity market. The work intends to contribute to the discussion on long-term options for the European commitment to worldwide CO2 emission reduction. Cleaner electricity generation and environmentally neutral transport fuels (e.g. solar generated hydrogen) might be two major tools in reaching this goal.
-
Radiation hardened high efficiency silicon space solar cell
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Garboushian, V.; Yoon, S.; Turner, J.
1993-01-01
A silicon solar cell with AMO 19% Beginning of Life (BOL) efficiency is reported. The cell has demonstrated equal or better radiation resistance when compared to conventional silicon space solar cells. Conventional silicon space solar cell performance is generally ∼ 14% at BOL. The Radiation Hardened High Efficiency Silicon (RHHES) cell is thinned for high specific power (watts/kilogram). The RHHES space cell provides compatibility with automatic surface mounting technology. The cells can be easily combined to provide desired power levels and voltages. The RHHES space cell is more resistant to mechanical damage due to micrometeorites. Micro-meteorites which impinge upon conventional cells can crack the cell which, in turn, may cause string failure. The RHHES, operating in the same environment, can continue to function with a similar crack. The RHHES cell allows for very efficient thermal management which is essential for space cells generating higher specific power levels. The cell eliminates the need for electrical insulation layers which would otherwise increase the thermal resistance for conventional space panels. The RHHES cell can be applied to a space concentrator panel system without abandoning any of the attributes discussed. The power handling capability of the RHHES cell is approximately five times more than conventional space concentrator solar cells
-
Full-size solar dynamic heat receiver thermal-vacuum tests
Sedgwick, L. M.; Kaufmann, K. J.; Mclallin, K. L.; Kerslake, T. W.
1991-01-01
The testing of a full-size, 102 kW, solar dynamic heat receiver utilizing high-temperature thermal energy storage is described. The purpose of the test program was to quantify receiver thermodynamic performance, operating temperatures, and thermal response to changes in environmental and power module interface boundary conditions. The heat receiver was tested in a vacuum chamber with liquid nitrogen cold shrouds and an aperture cold plate to partly simulate a low-Earth-orbit environment. The cavity of the receiver was heated by an infrared quartz lamp heater with 30 independently controllable zones to allow axially and circumferentially varied flux distributions. A closed-Brayton cycle engine simulator conditioned a helium-xenon gas mixture to specific interface conditions to simulate the various operational modes of the solar dynamic power module on the Space Station Freedom. Inlet gas temperature, pressure, and flow rate were independently varied. A total of 58 simulated orbital cycles, each 94 minutes in duration, was completed during the test period.
-
Formation and dynamics of a solar eruptive flux tube
Inoue, Satoshi; Kusano, Kanya; Büchner, Jörg; Skála, Jan
2018-01-01
Solar eruptions are well-known drivers of extreme space weather, which can greatly disturb the Earth's magnetosphere and ionosphere. The triggering process and initial dynamics of these eruptions are still an area of intense study. Here we perform a magnetohydrodynamic simulation taking into account the observed photospheric magnetic field to reveal the dynamics of a solar eruption in a real magnetic environment. In our simulation, we confirmed that tether-cutting reconnection occurring locally above the polarity inversion line creates a twisted flux tube, which is lifted into a toroidal unstable area where it loses equilibrium, destroying the force-free state, and driving the eruption. Consequently, a more highly twisted flux tube is built up during this initial phase, which can be further accelerated even when it returns to a stable area. We suggest that a nonlinear positive feedback process between the flux tube evolution and reconnection is the key to ensure this extra acceleration.
-
Space Environmental Effects on Candidate Solar Sail Materials
Edwards, David L.; Nehls, Mary; Semmel, Charles; Hovater, Mary; Gray, Perry; Hubbs, Whitney; Wertz, George
2004-01-01
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) continues research into the utilization of photonic materials for spacecraft propulsion. Spacecraft propulsion, using photonic materials, will be achieved using a solar sail. A solar sail operates on the principle that photons, originating from the sun, impart pressure to the sail and therefore provide a source for spacecraft propulsion. The pressure imparted ot a solar sail can be increased, up to a factor of two, if the sun-facing surface is perfectly reflective. Therefore, these solar sails are generally composed of a highly reflective metallic sun-facing layer, a thin polymeric substrate and occasionally a highly emissive back surface. Near term solar sail propelled science missions are targeting the Lagrange point 1 (L1) as well as locations sunward of L1 as destinations. These near term missions include the Solar Polar Imager and the L1 Diamond. The Environmental Effects Group at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) continues to actively characterize solar sail material in preparation for these near term solar sail missions. Previous investigations indicated that space environmental effects on sail material thermo-optical properties were minimal and would not significantly affect the propulsion efficiency of the sail. These investigations also indicated that the sail material mechanical stability degrades with increasing radiation exposure. This paper will further quantify the effect of space environmental exposure on the mechanical properties of candidate sail materials. Candidate sail materials for these missions include Aluminum coated Mylar, Teonex, and CP1 (Colorless Polyimide). These materials were subjected to uniform radiation doses of electrons and protons in individual exposures sequences. Dose values ranged from 100 Mrads to over 5 Grads. The engineering performance property responses of thermo-optical and mechanical properties were characterized
-
Solar Pumped Solid State Lasers for Space Solar Power: Experimental Path
Fork, Richard L.; Carrington, Connie K.; Walker, Wesley W.; Cole, Spencer T.; Green, Jason J. A.; Laycock, Rustin L.
2003-01-01
We outline an experimentally based strategy designed to lead to solar pumped solid state laser oscillators useful for space solar power. Our method involves solar pumping a novel solid state gain element specifically designed to provide efficient conversion of sunlight in space to coherent laser light. Kilowatt and higher average power is sought from each gain element. Multiple such modular gain elements can be used to accumulate total average power of interest for power beaming in space, e.g., 100 kilowatts and more. Where desirable the high average power can also be produced as a train of pulses having high peak power (e.g., greater than 10(exp 10 watts). The modular nature of the basic gain element supports an experimental strategy in which the core technology can be validated by experiments on a single gain element. We propose to do this experimental validation both in terrestrial locations and also on a smaller scale in space. We describe a terrestrial experiment that includes diagnostics and the option of locating the laser beam path in vacuum environment. We describe a space based experiment designed to be compatible with the Japanese Experimental Module (JEM) on the International Space Station (ISS). We anticipate the gain elements will be based on low temperature (approx. 100 degrees Kelvin) operation of high thermal conductivity (k approx. 100 W/cm-K) diamond and sapphire (k approx. 4 W/cm-K). The basic gain element will be formed by sequences of thin alternating layers of diamond and Ti:sapphire with special attention given to the material interfaces. We anticipate this strategy will lead to a particularly simple, robust, and easily maintained low mass modelocked multi-element laser oscillator useful for space solar power.
-
Shekoyan, V.; Dehipawala, S.; Liu, Ernest; Tulsee, Vivek; Armendariz, R.; Tremberger, G.; Holden, T.; Marchese, P.; Cheung, T.
2012-10-01
Digital solar image data is available to users with access to standard, mass-market software. Many scientific projects utilize the Flexible Image Transport System (FITS) format, which requires specialized software typically used in astrophysical research. Data in the FITS format includes photometric and spatial calibration information, which may not be useful to researchers working with self-calibrated, comparative approaches. This project examines the advantages of using mass-market software with readily downloadable image data from the Solar Dynamics Observatory for comparative analysis over with the use of specialized software capable of reading data in the FITS format. Comparative analyses of brightness statistics that describe the solar disk in the study of magnetic energy using algorithms included in mass-market software have been shown to give results similar to analyses using FITS data. The entanglement of magnetic energy associated with solar eruptions, as well as the development of such eruptions, has been characterized successfully using mass-market software. The proposed algorithm would help to establish a publicly accessible, computing network that could assist in exploratory studies of all FITS data. The advances in computer, cell phone and tablet technology could incorporate such an approach readily for the enhancement of high school and first-year college space weather education on a global scale. Application to ground based data such as that contained in the Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey is discussed.
-
Closed Cycle Engine Program Used in Solar Dynamic Power Testing Effort
Ensworth, Clint B., III; McKissock, David B.
1998-01-01
NASA Lewis Research Center is testing the world's first integrated solar dynamic power system in a simulated space environment. This system converts solar thermal energy into electrical energy by using a closed-cycle gas turbine and alternator. A NASA-developed analysis code called the Closed Cycle Engine Program (CCEP) has been used for both pretest predictions and post-test analysis of system performance. The solar dynamic power system has a reflective concentrator that focuses solar thermal energy into a cavity receiver. The receiver is a heat exchanger that transfers the thermal power to a working fluid, an inert gas mixture of helium and xenon. The receiver also uses a phase-change material to store the thermal energy so that the system can continue producing power when there is no solar input power, such as when an Earth-orbiting satellite is in eclipse. The system uses a recuperated closed Brayton cycle to convert thermal power to mechanical power. Heated gas from the receiver expands through a turbine that turns an alternator and a compressor. The system also includes a gas cooler and a radiator, which reject waste cycle heat, and a recuperator, a gas-to-gas heat exchanger that improves cycle efficiency by recovering thermal energy.
-
Space solar power satellite systems with a space elevator
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kellum, M. J. (Mervyn J.); Laubscher, B. E. (Bryan E.)
2004-01-01
The Space Elevator (SE) represents a major paradigm shift in mankind's access to outer space. If the SE's promise of low-cost access to space can be realized, the economics of space-based business endeavors becomes much more feasible. In this paper, we describe a Solar Power Satellite (SPS) system and estimate its costs within the context of an SE. We also offer technical as well as financial comparisons between SPS and terrestrial solar photovoltaic technologies. Even though SPS systems have been designed for over 35 years, technologies pertinent to SPS systems are continually evolving. One of the designs we present includes an evolving technology, optical rectennas. SPS systems could be a long-term energy source that is clean, technologically feasible, and virtually limitless. Moreover, electrical energy could be distributed inexpensively to remote areas where such power does not currently exist, thereby raising the quality of life of the people living in those areas. The energy 'playing field' will be leveled across the world and the resulting economic growth will improve the lot of humankind everywhere.
-
A Dedicated Space Observatory For Time-domain Solar System Science
Wong, Michael H.; Ádámkovics, M.; Benecchi, S.; Bjoraker, G.; Clarke, J. T.; de Pater, I.; Hendrix, A. R.; Marchis, F.; McGrath, M.; Noll, K.; Rages, K. A.; Retherford, K.; Smith, E. H.; Strange, N. J.
2009-09-01
Time-variable phenomena with scales ranging from minutes to decades have led to a large fraction of recent advances in many aspects of solar system science. We present the scientific motivation for a dedicated space observatory for solar system science. This facility will ideally conduct repeated imaging and spectroscopic observations over a period of 10 years or more. It will execute a selection of long-term projects with interleaved scheduling, resulting in the acquisition of data sets with consistent calibration, long baselines, and optimized sampling intervals. A sparse aperture telescope would be an ideal configuration for the mission, trading decreased sensitivity for reduced payload mass, while preserving spatial resolution. Ultraviolet capability is essential, especially once the Hubble Space Telescope retires. Specific investigations will include volcanism and cryovolcanism (on targets including Io, Titan, Venus, Mars, and Enceladus); zonal flow, vortices, and storm evolution on the giant planets; seasonal cycles in planetary atmospheres; mutual events and orbit determination of multiple small solar system bodies; auroral activity and solar wind interactions; and cometary evolution. The mission will produce a wealth of data products--such as multi-year time-lapse movies of planetary atmospheres--with significant education and public outreach potential. Existing and planned ground- and space-based facilities are not suitable for these time-domain optimized planetary dynamics studies for numerous reasons, including: oversubscription by astrophysical users, field-of-regard limitations, sensitive detector saturation limits that preclude bright planetary targets, and limited mission duration. The abstract author list is a preliminary group of scientists who have shown interest in prior presentations on this topic; interested parties may contact the lead author by 1 September to sign the associated Planetary Science Decadal Survey white paper or by 1 October to
-
Solar and Space Physics: A Science for a Technological Society
2013-01-01
From the interior of the Sun, to the upper atmosphere and near-space environment of Earth, and outward to a region far beyond Pluto where the Sun's influence wanes, advances during the past decade in space physics and solar physics the disciplines NASA refers to as heliophysics have yielded spectacular insights into the phenomena that affect our home in space. This report, from the National Research Council's (NRC's) Committee for a Decadal Strategy in Solar and Space Physics, is the second NRC decadal survey in heliophysics. Building on the research accomplishments realized over the past decade, the report presents a program of basic and applied research for the period 2013-2022 that will improve scientific understanding of the mechanisms that drive the Sun's activity and the fundamental physical processes underlying near-Earth plasma dynamics, determine the physical interactions of Earth's atmospheric layers in the context of the connected Sun-Earth system, and enhance greatly the capability to provide realistic and specific forecasts of Earth's space environment that will better serve the needs of society. Although the recommended program is directed primarily to NASA (Science Mission Directorate -- Heliophysics Division) and the National Science Foundation (NSF) (Directorate for Geosciences -- Atmospheric and Geospace Sciences) for action, the report also recommends actions by other federal agencies, especially the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) those parts of NOAA charged with the day-to-day (operational) forecast of space weather. In addition to the recommendations included in this summary, related recommendations are presented in the main text of the report.
-
Validated TRNSYS Model for Solar Assisted Space Heating System
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Abdalla, Nedal
2014-01-01
The present study involves a validated TRNSYS model for solar assisted space heating system as applied to a residential building in Jordan using new detailed radiation models of the TRNSYS 17.1 and geometric building model Trnsys3d for the Google SketchUp 3D drawing program. The annual heating load for a building (Solar House) which is located at the Royal ScientiFIc Society (RS5) in Jordan is estimated under climatological conditions of Amman. The aim of this Paper is to compare measured thermal performance of the Solar House with that modeled using TRNSYS. The results showed that the annual measured space heating load for the building was 6,188 kWh while the heati.ng load for the modeled building was 6,391 kWh. Moreover, the measured solar fraction for the solar system was 50% while the modeled solar fraction was 55%. A comparison of modeled and measured data resulted in percentage mean absolute errors for solar energy for space heating, auxiliary heating and solar fraction of 13%, 7% and 10%, respectively. The validated model will be useful for long-term performance simulation under different weather and operating conditions.(author)
-
Design of a gigawatt space solar power satellite using optical concentrator system
Dessanti, B.; Komerath, N.; Shah, S.
A 1-gigawatt space solar power satellite using a large array of individually pointable optical elements is identified as the key mass element of a large scale space solar power architecture using the Space Power Grid concept. The proposed satellite design enables a significant increase in specific power. Placed in sun-synchronous dynamic orbits near 2000km altitude, these satellites can maintain the constant solar view requirement of GEO-based architectures, while greatly reducing the beaming distance required, decreasing the required antenna size and in turn the overall system mass. The satellite uses an array of individually pointable optical elements (which we call a Mirasol Concentrator Array) to concentrate solar energy to an intensified feed target that feeds into the main heater of the spacecraft, similar conceptually to heliostat arrays. The spacecraft then utilizes Brayton cycle conversion to take advantage of non-linear power level scaling in order to generate high specific power values. Using phase array antennas, the power is then beamed at a millimeter wave frequency of 220GHz down to Earth. The design of the Mirasol concentrator system will be described and a detailed mass estimation of the system is developed. The technical challenges of pointing the elements and maintaining constant solar view is investigated. An end-to-end efficiency analysis is performed. Subsystem designs for the spacecraft are outlined. A detailed mass budget is refined to reflect reductions in uncertainty of the spacecraft mass, particularly in the Mirasol system. One of the key mass drivers of the spacecraft is the active thermal control system. The design of a lightweight thermal control system utilizing graphene sheets is also detailed.
-
Thermal energy storage for organic Rankine cycle solar dynamic space power systems
Heidenreich, G. R.; Parekh, M. B.
An organic Rankine cycle-solar dynamic power system (ORC-SDPS) comprises a concentrator, a radiator, a power conversion unit, and a receiver with a thermal energy storage (TES) subsystem which charges and discharges energy to meet power demands during orbital insolation and eclipse periods. Attention is presently given to the criteria used in designing and evaluating an ORC-SDPS TES, as well as the automated test facility employed. It is found that a substantial data base exists for the design of an ORC-SDPS TES subsystem.
-
Solar Power Beaming: From Space to Earth
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rubenchik, A M; Parker, J M; Beach, R J; Yamamoto, R M
2009-04-14
Harvesting solar energy in space and power beaming the collected energy to a receiver station on Earth is a very attractive way to help solve mankind's current energy and environmental problems. However, the colossal and expensive 'first step' required in achieving this goal has to-date stifled its initiation. In this paper, we will demonstrate that recent advance advances in laser and optical technology now make it possible to deploy a space-based system capable of delivering 1 MW of energy to a terrestrial receiver station, via a single unmanned commercial launch into Low Earth Orbit (LEO). Figure 1 depicts the overall concept of our solar power beaming system, showing a large solar collector in space, beaming a coherent laser beam to a receiving station on Earth. We will describe all major subsystems and provide technical and economic discussion to support our conclusions.
-
New solar irradiances for use in space research
Tobiska, W.; Bouwer, D.; Jones, A.
Space environment research applications require solar irradiances in a variety of time scales and spectral formats We describe the development of research grade modeled solar irradiances using four models and systems that are also used for space weather operations The four models systems include SOLAR2000 S2K SOLARFLARE SFLR APEX and IDAR which are used by Space Environment Technologies SET to provide solar irradiances from the soft X-rays through the visible spectrum SFLR uses the GOES 0 1--0 8 nm X-rays in combination with a Mewe model subroutine to provide 0 1--30 0 nm irradiances at 0 1 nm spectral resolution at 1 minute time resolution and in a 6-hour XUV--EUV spectral solar flare evolution forecast with a 7 minute latency and a 2 minute cadence These irradiances have been calibrated with the SORCE XPS observations and we report on the inclusion of these irradiances in the S2K model There are additional developments with S2K that we discuss particularly the method by which S2K is emerging as a hybrid model empirical plus physics-based and real-time data integration platform Numerous new solar indices have been recently developed for the operations community and we describe their inclusion in S2K The APEX system is a real-time data retrieval system developed under contract to the University of Southern California Space Sciences Center SSC to provide SOHO SEM data processing and distribution SSC provides the updated SEM data to the research community and SET provides the operational data to the space operations community We
-
Solar/Space Environment Data (Satellites)
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Department of Commerce — The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) monitors the geospace and solar environments using a variety of space weather sensors aboard its fleet of...
-
Cermet Coatings for Solar Stirling Space Power
Jaworske, Donald A.; Raack, Taylor
2004-01-01
Cermet coatings, molecular mixtures of metal and ceramic are being considered for the heat inlet surface of a solar Stirling space power converter. This paper will discuss the solar absorption characteristics of as-deposited cermet coatings as well as the solar absorption characteristics of the coatings after heating. The role of diffusion and island formation, during the deposition process and during heating will also be discussed.
-
Scattering Effects of Solar Panels on Space Station Antenna Performance
Panneton, Robert J.; Ngo, John C.; Hwu, Shian U.; Johnson, Larry A.; Elmore, James D.; Lu, Ba P.; Kelley, James S.
1994-01-01
Characterizing the scattering properties of the solar array panels is important in predicting Space Station antenna performance. A series of far-field, near-field, and radar cross section (RCS) scattering measurements were performed at S-Band and Ku-Band microwave frequencies on Space Station solar array panels. Based on investigation of the measured scattering patterns, the solar array panels exhibit similar scattering properties to that of the same size aluminum or copper panel mockup. As a first order approximation, and for worse case interference simulation, the solar array panels may be modeled using perfect reflecting plates. Numerical results obtained using the Geometrical Theory of Diffraction (GTD) modeling technique are presented for Space Station antenna pattern degradation due to solar panel interference. The computational and experimental techniques presented in this paper are applicable for antennas mounted on other platforms such as ship, aircraft, satellite, and space or land vehicle.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Baugher, J.F.
1988-01-01
This book is a description of the sun, planets, moons, asteroids, and comets in the solar system. Discussion is based heavily on results obtained from recent space probes to Mercury, Venus, Mars Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus. Offers detailed descriptions of the moons of Jupiter and Saturn, and the results of the recent probes of Halley's comet. A discussion of meteorites leads to a description of the current models of the solar system. Introductory chapters present theories of the solar system from the ancient Greeks to the present day. Other topics covered include the sun, its structure, and how it generates energy; the surfaces, internal structures, and histories of the planets, from innermost Mercury to farthest Pluto, and their moons
-
Structure and dynamics of the solar chromosphere
Krijger, Johannes Mattheus
2002-01-01
The thesis "Structure and dynamics of the solar chromosphere" of J.M. Krijger is a study on the behavior of the solar chromosphere, the thin layer just above the solar surface (photosphere) visible in purple red light during a total solar eclipse. The most important result of this thesis is that the
-
Characterization of Candidate Solar Sail Material Exposed to Space Environmental Effects
Edwards, David; Hovater, Mary; Hubbs, Whitney; Wertz, George; Hollerman, William; Gray, Perry
2003-01-01
Solar sailing is a unique form of propulsion where a spacecraft gains momentum from incident photons. Solar sails are not limited by reaction mass and provide continual acceleration, reduced only by the lifetime of the lightweight film in the space environment and the distance to the Sun. Once thought to be difficult or impossible, solar sailing has come out of science fiction and into the realm of possibility. Any spacecraft using this method would need to deploy a thin sail that could be as large as many kilometers in extent. The availability of strong, ultra lightweight, and radiation resistant materials will determine the future of solar sailing. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is concentrating research into the utilization of ultra lightweight materials for spacecraft propulsion. The Space Environmental Effects Team at MSFC is actively characterizing candidate solar sail material to evaluate the thermo-optical and mechanical properties after exposure to space environmental effects. This paper will describe the exposure of candidate solar sail materials to emulated space environmental effects including energetic electrons, combined electrons and Ultraviolet radiation, and hypervelocity impact of irradiated solar sail material. This paper will describe the testing procedure and the material characterization results of this investigation.
-
Solar system for domestic hot water and space heating
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Weiss, W. [Arbeitsgemeinschaf Erneubare Energie, Gleisdorf (Austria)
1997-12-31
The solar thermal markets, different types of solar systems for hot water and space heating, the dimensioning and the components of solar heating systems, the properties of the systems are reviewed in this presentation
-
Solar system for domestic hot water and space heating
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Weiss, W [Arbeitsgemeinschaf Erneubare Energie, Gleisdorf (Austria)
1998-12-31
The solar thermal markets, different types of solar systems for hot water and space heating, the dimensioning and the components of solar heating systems, the properties of the systems are reviewed in this presentation
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Corno, S.E.
1995-01-01
Analytical methods for Space Dynamics of fission reactors, are presented. It is shown how a few sample problems in space dynamics can be solved, within the one and two group diffusion model, by purely analytical tools, essentially based on Laplace transform and complex Green function techniques. A quite suggestive generalization of this approach, applicable to the fluid core reactors, whose fuel is undergoing a violent mixing, is reported and briefly discussed. (author)
-
A Novel Robot of Manufacturing Space Solar Cell Arrays
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wu Yuexin
2008-11-01
Full Text Available This paper presents a novel robot employed to manufacture space solar cell arrays. First of all including the mechanical configuration and control system, the architecture of the robot is described. Then the flow velocity field of adhesive in the dispensing needles is acquired based on hydrodynamics. The accurate section form model of adhesive dispensed on the solar cells is obtained, which is essential for the robot to control the uniformity of dispensing adhesive. Finally the experiment validates the feasibility and reliability of the robot system. The application of robots instead of manual work in manufacturing space solar cell arrays will enhance the development of space industry.
-
A Novel Robot of Manufacturing Space Solar Cell Arrays
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wu Yuexin
2007-03-01
Full Text Available This paper presents a novel robot employed to manufacture space solar cell arrays. First of all including the mechanical configuration and control system, the architecture of the robot is described. Then the flow velocity field of adhesive in the dispensing needles is acquired based on hydrodynamics. The accurate section form model of adhesive dispensed on the solar cells is obtained, which is essential for the robot to control the uniformity of dispensing adhesive. Finally the experiment validates the feasibility and reliability of the robot system. The application of robots instead of manual work in manufacturing space solar cell arrays will enhance the development of space industry.
-
Economic feasibility of solar water and space heating.
Bezdek, R H; Hirshberg, A S; Babcock, W H
1979-03-23
The economic feasibility in 1977 and 1978 of solar water and combined water and space heating is analyzed for single-family detached residences and multi-family apartment buildings in four representative U.S. cities: Boston, Massachusetts; Washington, D.C.; Grand Junction, Colorado; and Los Angeles, California. Three economic decision criteria are utilized: payback period, years to recovery of down payment, and years to net positive cash flow. The cost competitiveness of the solar systems compared to heating systems based on electricity, fuel oil, and natural gas is then discussed for each city, and the impact of the federal tax credit for solar energy systems is assessed. It is found that even without federal incentives some solar water and space heating systems are competitive. Enactment of the solar tax credit, however, greatly enhances their competitiveness. The implications of these findings for government tax and energy pricing policies are discussed.
-
Solar Stirling for deep space applications
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mason, Lee S.
2000-01-01
A study was performed to quantify the performance of solar thermal power systems for deep space planetary missions. The study incorporated projected advances in solar concentrator and energy conversion technologies. These technologies included inflatable structures, lightweight primary concentrators, high efficiency secondary concentrators, and high efficiency Stirling convertors. Analyses were performed to determine the mass and deployed area of multihundred watt solar thermal power systems for missions out to 40 astronomical units. Emphasis was given to system optimization, parametric sensitivity analyses, and concentrator configuration comparisons. The results indicated that solar thermal power systems are a competitive alternative to radioisotope systems out to 10 astronomical units without the cost or safety implications associated with nuclear sources
-
Chamberlin, P. C.
2011-01-01
The solar photon output, which was once thought to be constant, varies over all time scales from seconds during solar flares to years due to the solar cycle. These solar variations cause significant deviations in the Earth and space environments on similar time scales, such as affecting the atmospheric densities and composition of particular atoms, molecules, and ions in the atmospheres of the Earth and other planets. Presented and discussed will be examples of unprecedented observations from NASA's new solar observatory, the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Using three specialized instruments, SDO measures the origins of solar activity from inside the Sun, though its atmosphere, then accurately measuring the Sun's radiative output in X-ray and EUV wavelengths (0.1-121 nm). Along with the visually appealing observations will be discussions of what these measurements can tell us about how the plasma motions in all layers of the Sun modifies and strengthens the weak solar dipole magnetic field to drive large energy releases in solar eruptions. Also presented will be examples of how the release of the Sun's energy, in the form of photons and high energy particles, physically influence other bodies in the solar system such as Earth, Mars, and the Moon, and how these changes drive changes in the technology that we are becoming dependent upon. The presentation will continuously emphasize how SDO, the first satellite in NASA's Living with a Star program, improving our understanding of the variable Sun and its Heliospheric influence.
-
Solar water heater for NASA's Space Station
Somers, Richard E.; Haynes, R. Daniel
1988-01-01
The feasibility of using a solar water heater for NASA's Space Station is investigated using computer codes developed to model the Space Station configuration, orbit, and heating systems. Numerous orbit variations, system options, and geometries for the collector were analyzed. Results show that a solar water heater, which would provide 100 percent of the design heating load and would not impose a significant impact on the Space Station overall design is feasible. A heat pipe or pumped fluid radial plate collector of about 10-sq m, placed on top of the habitat module was found to be well suited for satisfying water demand of the Space Station. Due to the relatively small area required by a radial plate, a concentrator is unnecessary. The system would use only 7 to 10 percent as much electricity as an electric water-heating system.
-
Evaluation of thermal control coatings for use on solar dynamic radiators in low earth orbit
Dever, Joyce A.; Rodriguez, Elvin; Slemp, Wayne S.; Stoyack, Joseph E.
1991-01-01
Thermal control coatings with high thermal emittance and low solar absorptance are needed for Space Station Freedom (SSF) solar dynamic power module radiator (SDR) surfaces for efficient heat rejection. Additionally, these coatings must be durable to low earth orbital (LEO) environmental effects of atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation and deep thermal cycles which occur as a result of start-up and shut-down of the solar dynamic power system. Eleven candidate coatings were characterized for their solar absorptance and emittance before and after exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation (200 to 400 nm), vacuum UV (VUV) radiation (100 to 200 nm) and atomic oxygen. Results indicated that the most durable and best performing coatings were white paint thermal control coatings Z-93, zinc oxide pigment in potassium silicate binder, and YB-71, zinc orthotitanate pigment in potassium silicate binder. Optical micrographs of these materials exposed to the individual environmental effects of atomic oxygen and vacuum thermal cycling showed that no surface cracking occurred.
-
Solar atmosphere wave dynamics generated by solar global oscillating eigenmodes
Griffiths, M. K.; Fedun, V.; Erdélyi, R.; Zheng, R.
2018-01-01
The solar atmosphere exhibits a diverse range of wave phenomena, where one of the earliest discovered was the five-minute global acoustic oscillation, also referred to as the p-mode. The analysis of wave propagation in the solar atmosphere may be used as a diagnostic tool to estimate accurately the physical characteristics of the Sun's atmospheric layers. In this paper, we investigate the dynamics and upward propagation of waves which are generated by the solar global eigenmodes. We report on a series of hydrodynamic simulations of a realistically stratified model of the solar atmosphere representing its lower region from the photosphere to low corona. With the objective of modelling atmospheric perturbations, propagating from the photosphere into the chromosphere, transition region and low corona, generated by the photospheric global oscillations the simulations use photospheric drivers mimicking the solar p-modes. The drivers are spatially structured harmonics across the computational box parallel to the solar surface. The drivers perturb the atmosphere at 0.5 Mm above the bottom boundary of the model and are placed coincident with the location of the temperature minimum. A combination of the VALIIIC and McWhirter solar atmospheres are used as the background equilibrium model. We report how synthetic photospheric oscillations may manifest in a magnetic field free model of the quiet Sun. To carry out the simulations, we employed the magnetohydrodynamics code, SMAUG (Sheffield MHD Accelerated Using GPUs). Our results show that the amount of energy propagating into the solar atmosphere is consistent with a model of solar global oscillations described by Taroyan and Erdélyi (2008) using the Klein-Gordon equation. The computed results indicate a power law which is compared to observations reported by Ireland et al. (2015) using data from the Solar Dynamics Observatory/Atmospheric Imaging Assembly.
-
Building Space Heating with a Solar-Assisted Heat Pump Using Roof-Integrated Solar Collectors
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zhiyong Yang
2011-03-01
Full Text Available A solar assisted heat pump (SAHP system was designed by using a roof-integrated solar collector as the evaporator, and then it was demonstrated to provide space heating for a villa in Tianjin, China. A building energy simulation tool was used to predict the space heating load and a three dimensional theoretical model was established to analyze the heat collection performance of the solar roof collector. A floor radiant heating unit was used to decrease the energy demand. The measurement results during the winter test period show that the system can provide a comfortable living space in winter, when the room temperature averaged 18.9 °C. The average COP of the heat pump system is 2.97 and with a maximum around 4.16.
-
Optical design of visible emission line coronagraph on Indian space solar mission Aditya-L1
Raj Kumar, N.; Raghavendra Prasad, B.; Singh, Jagdev; Venkata, Suresh
2018-03-01
The ground based observations of the coronal emission lines using a coronagraph are affected by the short duration of clear sky and varying sky transparency. These conditions do not permit to study small amplitude variations in the coronal emission reliably necessary to investigate the process or processes involved in heating the coronal plasma and dynamics of solar corona. The proposed Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) over comes these limitations and will provide continuous observation 24 h a day needed for detailed studies of solar corona and drivers for space weather predictions. VELC payload onboard India's Aditya-L1 space mission is an internally occulted solar coronagraph for studying the temperature, velocity, density and heating of solar corona. To achieve the proposed science goals, an instrument which is capable of carrying out simultaneous imaging, spectroscopy and spectro-polarimetric observations of the solar corona close to the solar limb is required. VELC is designed with salient features of (a) Imaging solar corona at 500 nm with an angular resolution of 5 arcsec over a FOV of 1.05Ro to 3Ro (Ro:Solar radius) (b) Simultaneous multi-slit spectroscopy at 530.3 nm [Fe XIV],789.2 nm [Fe XI] and 1074.7 nm [Fe XIII] with spectral dispersion of 28mÅ, 31mÅ and 202mÅ per pixel respectively, over a FOV of 1.05Ro to 1.5Ro. (c) Multi-slit dual beam spectro-polarimetry at 1074.7 nm. All the components of instrument have been optimized in view of the scientific objectives and requirements of space payloads. In this paper we present the details of optical configuration and the expected performance of the payload.
-
Optical design of visible emission line coronagraph on Indian space solar mission Aditya-L1
Raj Kumar, N.; Raghavendra Prasad, B.; Singh, Jagdev; Venkata, Suresh
2018-04-01
The ground based observations of the coronal emission lines using a coronagraph are affected by the short duration of clear sky and varying sky transparency. These conditions do not permit to study small amplitude variations in the coronal emission reliably necessary to investigate the process or processes involved in heating the coronal plasma and dynamics of solar corona. The proposed Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) over comes these limitations and will provide continuous observation 24 h a day needed for detailed studies of solar corona and drivers for space weather predictions. VELC payload onboard India's Aditya-L1 space mission is an internally occulted solar coronagraph for studying the temperature, velocity, density and heating of solar corona. To achieve the proposed science goals, an instrument which is capable of carrying out simultaneous imaging, spectroscopy and spectro-polarimetric observations of the solar corona close to the solar limb is required. VELC is designed with salient features of (a) Imaging solar corona at 500 nm with an angular resolution of 5 arcsec over a FOV of 1.05Ro to 3Ro (Ro:Solar radius) (b) Simultaneous multi-slit spectroscopy at 530.3 nm [Fe XIV],789.2 nm [Fe XI] and 1074.7 nm [Fe XIII] with spectral dispersion of 28mÅ, 31mÅ and 202mÅ per pixel respectively, over a FOV of 1.05Ro to 1.5Ro. (c) Multi-slit dual beam spectro-polarimetry at 1074.7 nm. All the components of instrument have been optimized in view of the scientific objectives and requirements of space payloads. In this paper we present the details of optical configuration and the expected performance of the payload.
-
Solar proton events and their effect on space systems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tranquille, C.
1994-01-01
Solar protons present a major problem to space systems because of the ionisation and displacement effects which arise from their interaction with matter. This is likely to become a greater problem in the future due to the use of more sensitive electronic components and the proposed expansion of manned activities in space. An outline is provided of the physical processes associated with individual solar events, the solar activity cycle and the transport of solar particles between the Sun and the Earth. The problems of predicting solar event fluences, both over short- and long-term periods, are discussed. The currently available solar proton event models used for long-term forecasting are briefly reviewed, and the advantages and deficiencies of each model are investigated. Predictions using the models are compared to measurements made by the GOES-7 satellite during the rising phase of the current solar cycle. These measurements are also used to illustrate the sensitivity of the models to the choice of confidence level and to the spectral form used for extrapolation over the solar proton energy range. (author)
-
Solar Electric Propulsion Concepts for Human Space Exploration
Mercer, Carolyn R.; Mcguire, Melissa L.; Oleson, Steven R.; Barrett, Michael J.
2016-01-01
Advances in solar array and electric thruster technologies now offer the promise of new, very capable space transportation systems that will allow us to cost effectively explore the solar system. NASA has developed numerous solar electric propulsion spacecraft concepts with power levels ranging from tens to hundreds of kilowatts for robotic and piloted missions to asteroids and Mars. This paper describes nine electric and hybrid solar electric/chemical propulsion concepts developed over the last 5 years and discusses how they might be used for human exploration of the inner solar system.
-
Solar Energy for Space Heating & Hot Water.
Energy Research and Development Administration, Washington, DC. Div. of Solar Energy.
This pamphlet reviews the direct transfer of solar energy into heat, particularly for the purpose of providing space and hot water heating needs. Owners of buildings and homes are provided with a basic understanding of solar heating and hot water systems: what they are, how they perform, the energy savings possible, and the cost factors involved.…
-
Space solar array reliability: A study and recommendations
Brandhorst, Henry W., Jr.; Rodiek, Julie A.
2008-12-01
Providing reliable power over the anticipated mission life is critical to all satellites; therefore solar arrays are one of the most vital links to satellite mission success. Furthermore, solar arrays are exposed to the harshest environment of virtually any satellite component. In the past 10 years 117 satellite solar array anomalies have been recorded with 12 resulting in total satellite failure. Through an in-depth analysis of satellite anomalies listed in the Airclaim's Ascend SpaceTrak database, it is clear that solar array reliability is a serious, industry-wide issue. Solar array reliability directly affects the cost of future satellites through increased insurance premiums and a lack of confidence by investors. Recommendations for improving reliability through careful ground testing, standardization of testing procedures such as the emerging AIAA standards, and data sharing across the industry will be discussed. The benefits of creating a certified module and array testing facility that would certify in-space reliability will also be briefly examined. Solar array reliability is an issue that must be addressed to both reduce costs and ensure continued viability of the commercial and government assets on orbit.
-
Solar Sail Material Performance Property Response to Space Environmental Effects
Edwards, David L.; Semmel, Charles; Hovater, Mary; Nehls, Mary; Gray, Perry; Hubbs, Whitney; Wertz, George
2004-01-01
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) continues research into the utilization of photonic materials for spacecraft propulsion. Spacecraft propulsion, using photonic materials, will be achieved using a solar sail. A solar sail operates on the principle that photons, originating from the sun, impart pressure to the sail and therefore provide a source for spacecraft propulsion. The pressure imparted to a solar sail can be increased, up to a factor of two, if the sun-facing surface is perfectly reflective. Therefore, these solar sails are generally composed of a highly reflective metallic sun-facing layer, a thin polymeric substrate and occasionally a highly emissive back surface. Near term solar sail propelled science missions are targeting the Lagrange point 1 (Ll) as well as locations sunward of L1 as destinations. These near term missions include the Solar Polar Imager and the L1 Diamond. The Environmental Effects Group at NASA s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) continues to actively characterize solar sail material in preparation for these near term solar sail missions. Previous investigations indicated that space environmental effects on sail material thermo-optical properties were minimal and would not significantly affect the propulsion efficiency of the sail. These investigations also indicated that the sail material mechanical stability degrades with increasing radiation exposure. This paper will further quantify the effect of space environmental exposure on the mechanical properties of candidate sail materials. Candidate sail materials for these missions include Aluminum coated Mylar[TM], Teonex[TM], and CPl (Colorless Polyimide). These materials were subjected to uniform radiation doses of electrons and protons in individual exposures sequences. Dose values ranged from 100 Mrads to over 5 Grads. The engineering performance property responses of thermo-optical and mechanical properties were
-
Solar power from space: the worldwide grid of the future
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Anon.
2000-01-01
Recent interest in the feasibility and prospects for generating large amounts of electricity from space-based solar power systems is reviewed. The interest is generated by reports which suggest that sun-surfacing solar arrays in stationary earth orbit at an altitude 22,300 miles would not only be unaffected by the Earth's day-night cycle, cloud cover and atmospheric dust, but would also receive some eight times as much sunlight as solar collectors at the Earth's surface. The prediction is that relevant technology will be perfected to the point where by the middle of the 21. century a large share of the world's demand for electricity will be met by a series of very large space-based solar photovoltaic arrays. Several billion watts of power could be beamed to the Earth at microwave radio frequencies for collection by wide area rectifying ground antennas for conversion to electricity via transmitters connected to the photovoltaic arrays. A chronological account of development of this concept of beaming solar power from space shows that the idea has been around since the 1880s, gaining more and more credibility with each advance in space science . The moon, too, has been suggested as an ideal site for developing large-scale solar power systems that beam microwave energy to Earth. The lunar soil could supply silicon to build solar arrays, and metals such as iron and aluminum, for support structures and electric wiring. NASA is actively pursuing this line of inquiry, especially since all the problems involved with solar energy generation on earth, are absent on the moon.While a breakthrough is not imminent, the significant progress achieved to date in demonstrating the feasibility of wireless power transmission from space provides good reason for continuing to pursue this line of investigation
-
Solar dynamics influence on the atmospheric ozone
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gogosheva, T.; Grigorieva, V.; Mendeva, B.; Krastev, D.; Petkov, B.
2007-01-01
A response of the atmospheric ozone to the solar dynamics has been studied using the total ozone content data, taken from the satellite experiments GOME on ERS-2 and TOMS-EP together with data obtained from the ground-based spectrophotometer Photon operating in Stara Zagora, Bulgaria during the period 1999-2005. We also use data from surface ozone observations performed in Sofia, Bulgaria. The solar activity was characterized by the sunspot daily numbers W, the solar radio flux at 10.7 cm (F10.7) and the MgII wing-to-core ratio solar index. The impact of the solar activity on the total ozone has been investigated analysing the ozone response to sharp changes of these parameters. Some of the examined cases showed a positive correlation between the ozone and the solar parameters, however, a negative correlation in other cases was found. There were some cases when the sharp increases of the solar activity did not provoke any ozone changes. The solar radiation changes during an eclipse can be considered a particular case of the solar dynamics as this event causes a sharp change of irradiance within a comparatively short time interval. The results of both - the total and surface ozone measurements carried out during the eclipses on 11 August 1999, 31 May 2003 and 29 March 2006 are presented. It was found that the atmospheric ozone behavior shows strong response to the fast solar radiation changes which take place during solar eclipse. (authors)
-
High efficiency thin-film solar cells for space applications: challenges and opportunities
Leest, R.H. van
2017-01-01
In theory high efficiency thin-film III-V solar cells obtained by the epitaxial lift-off (ELO) technique offer excellent characteristics for application in space solar panels. The thesis describes several studies that investigate the space compatibility of the thin-film solar cell design developed
-
Solar-pumped lasers for space power transmission
Taussig, R.; Bruzzone, C.; Nelson, L.; Quimby, D.; Christiansen, W.
1979-01-01
Multi-Megawatt CW solar-pumped lasers appear to be technologically feasible for space power transmission in the 1990s time frame. A new concept for a solar-pumped laser is presented which utilizes an intermediate black body cavity to provide a uniform optical pumping environment for the lasant, either CO or CO2. Reradiation losses are minimized with resulting high efficiency operation. A 1 MW output laser may weigh as little as 8000 kg including solar collector, black body cavity, laser cavity and ducts, pumps, power systems and waste heat radiator. The efficiency of such a system will be on the order of 10 to 20%. Details of the new concept, laser design, comparison to competing solar-powered lasers and applications to a laser solar power satellite (SPS) concept are presented.
-
The JPL space photovoltaic program. [energy efficient so1 silicon solar cells for space applications
Scott-Monck, J. A.
1979-01-01
The development of energy efficient solar cells for space applications is discussed. The electrical performance of solar cells as a function of temperature and solar intensity and the influence of radiation and subsequent thermal annealing on the electrical behavior of cells are among the factors studied. Progress in GaAs solar cell development is reported with emphasis on improvement of output power and radiation resistance to demonstrate a solar cell array to meet the specific power and stability requirements of solar power satellites.
-
A Process for Comparing Dynamics of Distributed Space Systems Simulations
Cures, Edwin Z.; Jackson, Albert A.; Morris, Jeffery C.
2009-01-01
The paper describes a process that was developed for comparing the primary orbital dynamics behavior between space systems distributed simulations. This process is used to characterize and understand the fundamental fidelities and compatibilities of the modeling of orbital dynamics between spacecraft simulations. This is required for high-latency distributed simulations such as NASA s Integrated Mission Simulation and must be understood when reporting results from simulation executions. This paper presents 10 principal comparison tests along with their rationale and examples of the results. The Integrated Mission Simulation (IMSim) (formerly know as the Distributed Space Exploration Simulation (DSES)) is a NASA research and development project focusing on the technologies and processes that are related to the collaborative simulation of complex space systems involved in the exploration of our solar system. Currently, the NASA centers that are actively participating in the IMSim project are the Ames Research Center, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), the Johnson Space Center (JSC), the Kennedy Space Center, the Langley Research Center and the Marshall Space Flight Center. In concept, each center participating in IMSim has its own set of simulation models and environment(s). These simulation tools are used to build the various simulation products that are used for scientific investigation, engineering analysis, system design, training, planning, operations and more. Working individually, these production simulations provide important data to various NASA projects.
-
Alenia Spazio: Space Programs for Solar System Exploration .
Ferri, A.
Alenia Spazio is the major Italian space industry and one of the largest in Europe, with 2,400 highly skilled employees and 16,000 square meters of clean rooms and laboratories for advanced technological research that are among the most modern and well-equipped in Europe. The company has wide experience in the design, development, assembly, integration, verification and testing of complete space systems: satellites for telecommunications and navigation, remote sensing, meteorology and scientific applications; manned systems and space infrastructures; launch, transport and re-entry systems, and control centres. Alenia Spazio has contributed to the construction of over 200 satellites and taken part in the most important national and international space programmes, from the International Space Station to the new European global navigation system Galileo. Focusing on Solar System exploration, in the last 10 years the Company took part, with different roles, to the major European and also NASA missions in the field: Rosetta, Mars Express, Cassini; will soon take part in Venus Express, and is planning the future with Bepi Colombo, Solar Orbiter, GAIA and Exomars. In this paper, as in the presentation, a very important Earth Observation mission is also presented: GOCE. All in all, the Earth is by all means part of the Solar system as well and we like to see it as a planet to be explored.
-
In-Space Propulsion Technologies for Robotic Exploration of the Solar System
Johnson, Les; Meyer, Rae Ann; Frame, Kyle
2006-01-01
Supporting NASA's Science Mission Directorate, the In-Space Propulsion Technology Program is developing the next generation of space propulsion technologies for robotic, deep-space exploration. Recent technological advancements and demonstrations of key, high-payoff propulsion technologies have been achieved and will be described. Technologies under development and test include aerocapture, solar electric propulsion, solar sail propulsion, and advanced chemical propulsion.
-
Krietemeyer, Elizabeth A.; Smith, Shane I.; Dyson, Anna H.
2011-04-01
Human health and energy problems associated with the lack of control of sunlight in contemporary buildings have necessitated research into dynamic windows for energy efficient buildings. Existing window technologies have made moderate progress towards greater energy performance for facades but remain limited in their response to dynamic solar conditions, building energy requirements, and variable user preferences for visual comfort. Recent developments in electropolymeric display technology provide opportunities to transfer electroactive polymers to windows that can achieve high levels of geometric and spectral selectivity through the building envelope in order to meet the lighting, thermal and user requirements of occupied spaces. Experimental simulations that investigate daylight quality, energy performance, and architectural effects of electropolymeric glazing technology are presented.
-
Strategy for the Explorer program for solar and space physics
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
1984-01-01
Contents include: executive summary; the Explorer program - background and current status; strategy - level of activity; solar-terrestrial research (solar physics, space plasma physics, and upper atmospheric physics)
-
Space Moves: Adding Movement to Solar System Lessons
Jenkins, Deborah Bainer; Heidorn, Brent
2009-01-01
Earth and space science figure prominently in the National Science Education Standards for levels 5-8 (NRC 1996). The Earth in the Solar System standard focuses on students' ability to understand (1) the composition of the solar system (Earth, Moon, Sun, planets with their moons, and smaller objects like asteroids and comets) and (2) that…
-
The coronas-F space mission key results for solar terrestrial physics
2014-01-01
This volume is the updated and extended translation of the Russian original. It presents the results of observations of solar activity and its effects in the Earth space environment carried out from July 2001 to December 2005 on board the CORONAS-F space mission. The general characteristics of the CORONAS-F scientific payload are provided with a description of the principal experiments. The main results focus on the global oscillations of the Sun (p-modes), solar corona, solar flares, solar cosmic rays, Earth’s radiation belts, and upper atmosphere. The book will be welcomed by students, post-graduates, and scientists working in the field of solar and solar-terrestrial physics. This English edition is supplemented by sections presenting new results of the SPIRIT and TESIS experiments under the CORONAS solar program, as well as from the SONG experiment onboard the CORONAS-F satellite.
-
Numerical model of solar dynamic radiator for parametric analysis
Rhatigan, Jennifer L.
1989-01-01
Growth power requirements for Space Station Freedom will be met through addition of 25 kW solar dynamic (SD) power modules. Extensive thermal and power cycle modeling capabilities have been developed which are powerful tools in Station design and analysis, but which prove cumbersome and costly for simple component preliminary design studies. In order to aid in refining the SD radiator to the mature design stage, a simple and flexible numerical model was developed. The model simulates heat transfer and fluid flow performance of the radiator and calculates area mass and impact survivability for many combinations of flow tube and panel configurations, fluid and material properties, and environmental and cycle variations.
-
New space value of the solar oblateness obtained with PICARD
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Irbah, Abdanour; Meftah, Mustapha; Hauchecorne, Alain; Bocquier, Maxime; Cisse, E. Momar [Laboratoire Atmosphères, Milieux, Observations Spatiales (LATMOS), CNRS: UMR 8190-Université Paris VI-Pierre et Marie Curie-Université de Versailles Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines-INSU, F-78280, Guyancourt (France); Djafer, Djelloul [Unité de Recherche Appliquée en Energies Renouvelables, URAER, Centre de Développement des Energies Renouvelables, CDER, 47133, Ghardaïa (Algeria); Corbard, Thierry, E-mail: Abdenour.Irbah@latmos.ipsl.fr [Laboratoire Lagrange, UMR7293, Université de Nice Sophia-Antipolis, CNRS, Observatoire de la Côte d' Azur, Bd. de l' Observatoire, F-06304 Nice (France)
2014-04-20
The PICARD spacecraft was launched on 2010 June 15 with the scientific objective of studying the geometry of the Sun. It is difficult to measure solar oblateness because images are affected by optical distortion. Rolling the satellite, as done in previous space missions, determines the contribution of the telescope by assuming that the geometry of the Sun is constant during the observations. The optical response of the telescope is considered to be time-invariant during the roll operations. This is not the case for PICARD because an orbital signature is clearly observed in the solar radius computed from its images. We take this effect into account and provide the new space value of solar oblateness from PICARD images recorded in the solar continuum at 535.7 nm on 2011 July 4-5. The equator-pole radius difference is 8.4 ± 0.5 mas, which corresponds to an absolute radius difference of 6.1 km. This coincides with the mean value of all solar oblateness measurements obtained during the last two decades from the ground, balloons, and space. It is also consistent with values determined from models using helioseismology data.
-
Simulated Space Environment Effects on a Candidate Solar Sail Material
Kang, Jin Ho; Bryant, Robert G.; Wilkie, W. Keats; Wadsworth, Heather M.; Craven, Paul D.; Nehls, Mary K.; Vaughn, Jason A.
2017-01-01
For long duration missions of solar sails, the sail material needs to survive harsh space environments and the degradation of the sail material controls operational lifetime. Therefore, understanding the effects of the space environment on the sail membrane is essential for mission success. In this study, we investigated the effect of simulated space environment effects of ionizing radiation, thermal aging and simulated potential damage on mechanical, thermal and optical properties of a commercial off the shelf (COTS) polyester solar sail membrane to assess the degradation mechanisms on a feasible solar sail. The solar sail membrane was exposed to high energy electrons (about 70 keV and 10 nA/cm2), and the physical properties were characterized. After about 8.3 Grad dose, the tensile modulus, tensile strength and failure strain of the sail membrane decreased by about 20 95%. The aluminum reflective layer was damaged and partially delaminated but it did not show any significant change in solar absorbance or thermal emittance. The effect on mechanical properties of a pre-cracked sample, simulating potential impact damage of the sail membrane, as well as thermal aging effects on metallized PEN (polyethylene naphthalate) film will be discussed.
-
New astrophysical school of thermodynamics. Space dynamics and gravitism
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Gal-Or, B [Technion-Israel Inst. of Tech., Haifa. Dept. of Aeronautical Engineering
1978-07-01
Much verified information has been accumulated in recent years which shows that many fundamental concepts involving classical physics, thermodynamics, astrophysics and the general theory of relativity are strongly coupled together. This evidence is employed in this paper to explain principles of the astrophysical school of thermodynamics; a growing revolutionary school which deduces thermodynamics, energy dissipation, and time anisotropies from the Newtonian and Einsteinian theories of gravitation and from the dynamics of radiation in 'unsaturable' (intercluster) space. Accordingly, the density of radiation and the dynamics of ('unsaturable') outer space affect all processes in the galactic media, in the solar system, in the magnetosphere and on Earth. The origin of all observed irreversibilities in nature - of time, of all time anisotropics, of energy dissipation, of T-violations in 'elementary particles', of retarded potentials in electrodynamics, of the biological clocks, and of biological arrows of time - is one; it is the radiation unsaturability of space. But, since this unsaturability and gravitation are interconnected, the origin of asymmetries, structure, and thermodynamics is explained within the framework of the Newtonian and Einsteinian theories of gravitation. The theory presented here forms a part of a general approach called gravitism, which unifies some other disciplinary studies in the natural sciences with a unified approach to gravitation and the theory of time.
-
AUTOMATIC DETECTION ALGORITHM OF DYNAMIC PRESSURE PULSES IN THE SOLAR WIND
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zuo, Pingbing; Feng, Xueshang; Wang, Yi; Xie, Yanqiong; Li, Huijun; Xu, Xiaojun
2015-01-01
Dynamic pressure pulses (DPPs) in the solar wind are a significant phenomenon closely related to the solar-terrestrial connection and physical processes of solar wind dynamics. In order to automatically identify DPPs from solar wind measurements, we develop a procedure with a three-step detection algorithm that is able to rapidly select DPPs from the plasma data stream and simultaneously define the transition region where large dynamic pressure variations occur and demarcate the upstream and downstream region by selecting the relatively quiet status before and after the abrupt change in dynamic pressure. To demonstrate the usefulness, efficiency, and accuracy of this procedure, we have applied it to the Wind observations from 1996 to 2008 by successfully obtaining the DPPs. The procedure can also be applied to other solar wind spacecraft observation data sets with different time resolutions
-
Flight Plasma Diagnostics for High-Power, Solar-Electric Deep-Space Spacecraft
Johnson, Lee; De Soria-Santacruz Pich, Maria; Conroy, David; Lobbia, Robert; Huang, Wensheng; Choi, Maria; Sekerak, Michael J.
2018-01-01
NASA's Asteroid Redirect Robotic Mission (ARRM) project plans included a set of plasma and space environment instruments, the Plasma Diagnostic Package (PDP), to fulfill ARRM requirements for technology extensibility to future missions. The PDP objectives were divided into the classes of 1) Plasma thruster dynamics, 2) Solar array-specific environmental effects, 3) Plasma environmental spacecraft effects, and 4) Energetic particle spacecraft environment. A reference design approach and interface requirements for ARRM's PDP was generated by the PDP team at JPL and GRC. The reference design consisted of redundant single-string avionics located on the ARRM spacecraft bus as well as solar array, driving and processing signals from multiple copies of several types of plasma, effects, and environments sensors distributed over the spacecraft and array. The reference design sensor types were derived in part from sensors previously developed for USAF Research Laboratory (AFRL) plasma effects campaigns such as those aboard TacSat-2 in 2007 and AEHF-2 in 2012.
-
Potential high efficiency solar cells: Applications from space photovoltaic research
Flood, D. J.
1986-01-01
NASA involvement in photovoltaic energy conversion research development and applications spans over two decades of continuous progress. Solar cell research and development programs conducted by the Lewis Research Center's Photovoltaic Branch have produced a sound technology base not only for the space program, but for terrestrial applications as well. The fundamental goals which have guided the NASA photovoltaic program are to improve the efficiency and lifetime, and to reduce the mass and cost of photovoltaic energy conversion devices and arrays for use in space. The major efforts in the current Lewis program are on high efficiency, single crystal GaAs planar and concentrator cells, radiation hard InP cells, and superlattice solar cells. A brief historical perspective of accomplishments in high efficiency space solar cells will be given, and current work in all of the above categories will be described. The applicability of space cell research and technology to terrestrial photovoltaics will be discussed.
-
Simulated Space Environmental Effects on Thin Film Solar Array Components
Finckenor, Miria; Carr, John; SanSoucie, Michael; Boyd, Darren; Phillips, Brandon
2017-01-01
The Lightweight Integrated Solar Array and Transceiver (LISA-T) experiment consists of thin-film, low mass, low volume solar panels. Given the variety of thin solar cells and cover materials and the lack of environmental protection typically afforded by thick coverglasses, a series of tests were conducted in Marshall Space Flight Center's Space Environmental Effects Facility to evaluate the performance of these materials. Candidate thin polymeric films and nitinol wires used for deployment were also exposed. Simulated space environment exposures were selected based on SSP 30425 rev. B, "Space Station Program Natural Environment Definition for Design" or AIAA Standard S-111A-2014, "Qualification and Quality Requirements for Space Solar Cells." One set of candidate materials were exposed to 5 eV atomic oxygen and concurrent vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) radiation for low Earth orbit simulation. A second set of materials were exposed to 1 MeV electrons. A third set of samples were exposed to 50, 100, 500, and 700 keV energy protons, and a fourth set were exposed to >2,000 hours of near ultraviolet (NUV) radiation. A final set was rapidly thermal cycled between -55 and +125degC. This test series provides data on enhanced power generation, particularly for small satellites with reduced mass and volume resources. Performance versus mass and cost per Watt is discussed.
-
Heat receivers for solar dynamic space power systems
Perez-Davis, Marla Esther
A review of state-of-the-art technology is presented and discussed for phase change materials. Some of the advanced solar dynamic designs developed as part of the Advanced Heat Receiver Conceptual Design Study performed for LeRC are discussed. The heat receivers are analyzed and several recommendations are proposed, including two new concepts. The first concept evaluated the effect of tube geometries inside the heat receiver. It was found that a triangular configuration would provide better heat transfer to the working fluid, although not necessarily with a reduction in receiver size. A sensible heat receiver considered in this study uses vapor grown graphite fiber-carbon (VGCF/C) composite as the thermal storage media and was designed for a 7 kW Brayton engine. The proposed heat receiver stores the required energy to power the system during eclipse in the VGCF/C composite. The heat receiver analysis was conducted through the Systems Improved Numerical Differencing Analyzer and Fluid Integrator (SINDA) software package. The proposed heat receiver compares well with other latent and advanced sensible heat receivers while avoiding the problems associated with latent heat storage salts and liquid metal heat pipes. The weight and size of the system can be optimized by changes in geometry and technology advances for this new material. In addition to the new concepts, the effect of atomic oxygen on several materials is reviewed. A test was conducted for atomic oxygen attack on boron nitride, which experienced a negligible mass loss when exposed to an atomic oxygen fluence of 5 x 10 exp 21 atoms/sq cm. This material could be used to substitute the graphite aperture plate of the heat receiver.
-
Cermet coatings for solar Stirling space power
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jaworske, Donald A.; Raack, Taylor
2004-01-01
Cermet coatings, molecular mixtures of metal and ceramic, are being considered for the heat inlet surface of a solar Stirling space power convertor. The role of the cermet coating is to absorb as much of the incident solar energy as possible. The ability to mix metal and ceramic at the atomic level offers the opportunity to tailor the composition and the solar absorptance of these coatings. Several candidate cermet coatings were created and their solar absorptance was characterized as-manufactured and after exposure to elevated temperatures. Coating composition was purposely varied through the thickness of the coating. As a consequence of changing composition, islands of metal are thought to form in the ceramic matrix. Computer modeling indicated that diffusion of the metal atoms played an important role in island formation while the ceramic was important in locking the islands in place. Much of the solar spectrum is absorbed as it passes through this labyrinth
-
High Efficiency Quantum Dot III-V Multijunction Solar Cell for Space Power, Phase II
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — We are proposing to utilize quantum dots to develop a super high-efficiency multijunction III-V solar cell for space. In metamorphic triple junction space solar...
-
Future Market Share of Space Solar Electric Power Under Open Competition
Smith, S. J.; Mahasenan, N.; Clarke, J. F.; Edmonds, J. A.
2002-01-01
This paper assesses the value of Space Solar Power deployed under market competition with a full suite of alternative energy technologies over the 21st century. Our approach is to analyze the future energy system under a number of different scenarios that span a wide range of possible future demographic, socio-economic, and technological developments. Scenarios both with, and without, carbon dioxide concentration stabilization policies are considered. We use the comprehensive set of scenarios created for the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Special Report on Emissions Scenarios (Nakicenovic and Swart 2000). The focus of our analysis will be the cost of electric generation. Cost is particularly important when considering electric generation since the type of generation is, from a practical point of view, largely irrelevant to the end-user. This means that different electricity generation technologies must compete on the basis of price. It is important to note, however, that even a technology that is more expensive than average can contribute to the overall generation mix due to geographical and economic heterogeneity (Clarke and Edmonds 1993). This type of competition is a central assumption of the modeling approach used here. Our analysis suggests that, under conditions of full competition of all available technologies, Space Solar Power at 7 cents per kW-hr could comprise 5-10% of global electric generation by the end of the century, with a global total generation of 10,000 TW-hr. The generation share of Space Solar Power is limited due to competition with lower-cost nuclear, biomass, and terrestrial solar PV and wind. The imposition of a carbon constraint does not significantly increase the total amount of power generated by Space Solar Power in cases where a full range of advanced electric generation technologies are also available. Potential constraints on the availability of these other electric generation options can increase the amount of
-
Effects of Solar Activity and Space Environment in 2003 Oct.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kyung-Seok Cho
2004-12-01
Full Text Available In this paper, we present a good example of extreme solar and geomagnetic activities from October to November, 2003. These activities are characterized by very large sunspot groups, X-class solar flares, strong particle events, and huge geomagnetic storms. We discuss ground-based and space-based data in terms of space weather scales. Especially, we present several solar and geomagnetic disturbance data produced in Korea : sunspots, geo-magnetograms, aurora, Ionogram, and Total Electron Content (TEC map by GPS data. Finally, we introduce some examples of the satellite orbit and communication effects caused by these activities; e.g., the disturbances of the KOMPSAT-1 operational orbit and HF communication.
-
Ground test program for a full-size solar dynamic heat receiver
Sedgwick, L. M.; Kaufmann, K. J.; Mclallin, K. L.; Kerslake, T. W.
1991-01-01
Test hardware, facilities, and procedures were developed to conduct ground testing of a full-size, solar dynamic heat receiver in a partially simulated, low earth orbit environment. The heat receiver was designed to supply 102 kW of thermal energy to a helium and xenon gas mixture continuously over a 94 minute orbit, including up to 36 minutes of eclipse. The purpose of the test program was to quantify the receiver thermodynamic performance, its operating temperatures, and thermal response to changes in environmental and power module interface boundary conditions. The heat receiver was tested in a vacuum chamber using liquid nitrogen cold shrouds and an aperture cold plate. Special test equipment was designed to provide the required ranges in interface boundary conditions that typify those expected or required for operation as part of the solar dynamic power module on the Space Station Freedom. The support hardware includes an infrared quartz lamp heater with 30 independently controllable zones and a closed-Brayton cycle engine simulator to circulate and condition the helium-xenon gas mixture. The test article, test support hardware, facilities, and instrumentation developed to conduct the ground test program are all described.
-
Novel Space-based Solar Power Technologies and Architectures for Earth and Beyond
Howell, Joe T.; Fikes, John C.; O'Neill, Mark J.
2005-01-01
Research, development and studies of novel space-based solar power systems, technologies and architectures for Earth and beyond are needed to reduce the cost of clean electrical power for terrestrial use and to provide a stepping stone for providing an abundance of power in space, i.e., manufacturing facilities, tourist facilities, delivery of power between objects in space, and between space and surface sites. The architectures, technologies and systems needed for space to Earth applications may also be used for in-space applications. Advances in key technologies, i.e., power generation, power management and distribution, power beaming and conversion of beamed power are needed to achieve the objectives of both terrestrial and extraterrestrial applications. Power beaming or wireless power transmission (WPT) can involve lasers or microwaves along with the associated power interfaces. Microwave and laser transmission techniques have been studied with several promising approaches to safe and efficient WPT identified. These investigations have included microwave phased array transmitters, as well as laser transmission and associated optics. There is a need to produce "proof-of-concept" validation of critical WPT technologies for both the near-term, as well as far-term applications. Investments may be harvested in near-term beam safe demonstrations of commercial WPT applications. Receiving sites (users) include ground-based stations for terrestrial electrical power, orbital sites to provide power for satellites and other platforms, future space elevator systems, space vehicle propulsion, and space to surface sites. This paper briefly discusses achieving a promising approach to the solar power generation and beamed power conversion. The approach is based on a unique high-power solar concentrator array called Stretched Lens Array (SLA) for both solar power generation and beamed power conversion. Since both versions (solar and laser) of SLA use many identical components
-
Evolutionary growth for Space Station Freedom electrical power system
Marshall, Matthew Fisk; Mclallin, Kerry; Zernic, Mike
1989-01-01
Over an operational lifetime of at least 30 yr, Space Station Freedom will encounter increased Space Station user requirements and advancing technologies. The Space Station electrical power system is designed with the flexibility to accommodate these emerging technologies and expert systems and is being designed with the necessary software hooks and hardware scars to accommodate increased growth demand. The electrical power system is planned to grow from the initial 75 kW up to 300 kW. The Phase 1 station will utilize photovoltaic arrays to produce the electrical power; however, for growth to 300 kW, solar dynamic power modules will be utilized. Pairs of 25 kW solar dynamic power modules will be added to the station to reach the power growth level. The addition of solar dynamic power in the growth phase places constraints in the initial Space Station systems such as guidance, navigation, and control, external thermal, truss structural stiffness, computational capabilities and storage, which must be planned-in, in order to facilitate the addition of the solar dynamic modules.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yassine Charabi
2016-11-01
Full Text Available A bankable solar radiation database is required for the financial viability of solar energy project. Accurate estimation of solar energy resources in a country is very important for proper siting, sizing and life cycle cost analysis of solar energy systems. During the last decade an important progress has been made to develop multiple solar irradiance database (Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI and Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI, using satellite of different resolution and sophisticated models. This paper assesses the performance of High-resolution solar irradiance derived with dynamical downscaling Numerical Weather Prediction model with, GIS topographical solar radiation model, satellite data and ground measurements, for the production of bankable solar radiation datasets. For this investigation, NWP model namely Consortium for Small-scale Modeling (COSMO is used for the dynamical downscaling of solar radiation. The obtained results increase confidence in solar radiation data base obtained from dynamical downscaled NWP model. The mean bias of dynamical downscaled NWP model is small, on the order of a few percents for GHI, and it could be ranked as a bankable datasets. Fortunately, these data are usually archived in the meteorological department and gives a good idea of the hourly, monthly, and annual incident energy. Such short time-interval data are valuable in designing and operating the solar energy facility. The advantage of the NWP model is that it can be used for solar radiation forecast since it can estimate the weather condition within the next 72–120 hours. This gives a reasonable estimation of the solar radiation that in turns can be used to forecast the electric power generation by the solar power plant.
-
Fox, N. J.; Goldberg, R.; Barnes, R. J.; Sigwarth, J. B.; Beisser, K. B.; Moore, T. E.; Hoffman, R. A.; Russell, C. T.; Scudder, J.; Spann, J. F.; Newell, P. T.; Hobson, L. J.; Gribben, S. P.; Obrien, J. E.; Menietti, J. D.; Germany, G. G.; Mobilia, J.; Schulz, M.
2004-12-01
To showcase the on-going and wide-ranging scope of the Polar science discoveries, the Polar science team has created a one-stop shop for a thorough introduction to geospace physics, in the form of a DVD with supporting website. The DVD, Earth's Dynamic Space: Solar-Terrestrial Physics & NASA's Polar Mission, can be viewed as an end-to-end product or split into individual segments and tailored to lesson plans. Capitalizing on the Polar mission and its amazing science return, the Polar team created an exciting multi-use DVD intended for audiences ranging from a traditional classroom and after school clubs, to museums and science centers. The DVD tackles subjects such as the aurora, the magnetosphere and space weather, whilst highlighting the science discoveries of the Polar mission. This platform introduces the learner to key team members as well as the science principles. Dramatic visualizations are used to illustrate the complex principles that describe Earth’s dynamic space. In order to produce such a wide-ranging product on a shoe-string budget, the team poured through existing NASA resources to package them into the Polar story, and visualizations were created using Polar data to complement the NASA stock footage. Scientists donated their time to create and review scripts in order to make this a real team effort, working closely with the award winning audio-visual group at JHU/Applied Physics Laboratory. The team was excited to be invited to join NASA’s Sun-Earth Day 2005 E/PO program and the DVD will be distributed as part of the supporting educational packages.
-
Pavlos, G. P.; Malandraki, O.; Khabarova, O.; Livadiotis, G.; Pavlos, E.; Karakatsanis, L. P.; Iliopoulos, A. C.; Parisis, K.
2017-12-01
In this work we study the non-extensivity of Solar Wind space plasma by using electric-magnetic field data obtained by in situ spacecraft observations at different dynamical states of solar wind system especially in interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs), Interplanetary shocks, magnetic islands, or near the Earth Bow shock. Especially, we study the energetic particle non extensive fractional acceleration mechanism producing kappa distributions as well as the intermittent turbulence mechanism producing multifractal structures related with the Tsallis q-entropy principle. We present some new and significant results concerning the dynamics of ICMEs observed in the near Earth at L1 solar wind environment, as well as its effect in Earth's magnetosphere as well as magnetic islands. In-situ measurements of energetic particles at L1 are analyzed, in response to major solar eruptive events at the Sun (intense flares, fast CMEs). The statistical characteristics are obtained and compared for the Solar Energetic Particles (SEPs) originating at the Sun, the energetic particle enhancements associated with local acceleration during the CME-driven shock passage over the spacecraft (Energetic Particle Enhancements, ESPs) as well as the energetic particle signatures observed during the passage of the ICME. The results are referred to Tsallis non-extensive statistics and in particular to the estimation of Tsallis q-triplet, (qstat, qsen, qrel) of electric-magnetic field and the kappa distributions of solar energetic particles time series of the ICME, magnetic islands, resulting from the solar eruptive activity or the internal Solar Wind dynamics. Our results reveal significant differences in statistical and dynamical features, indicating important variations of the magnetic field dynamics both in time and space domains during the shock event, in terms of rate of entropy production, relaxation dynamics and non-equilibrium meta-stable stationary states.
-
Studies of Earth Space Environment and Sudden Disappearances of Solar Prominences
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Huang, Tian-Sen
2005-01-01
With the support from AFOSR's Minority University Program, we worked on research of Sun-Earth space environment, conducted daily solar observation programs, improved solar instruments, and established...
-
Opgenoorth, H. J.; Guhathakurta, M.; Liu, W.; Kosugi, T.; Zelenyi, L.
2003-04-01
International cooperation has long been a vital element in the scientific investigation of solar variability and its impact on Earth and its space environment. Recently a new international cooeperative program in solar terrestrial physics has been established by the major space agencies of the world, called the International Living With a Star (ILWS) program. ILWS is a follow on to the highly successful International Solar Terrestrial Physics (ISTP) program which involved international parterners. ISTP, with its steady flow of discoveries and new knowledge in solar Terrestrial physics, has laid the foundation for the coordinated study of the Sun-Earth sytem as a connected stellar-planetary system, system which is humanity's home. The first step in establishing ILWS was taken in the fall of 2000 when funding was approved for the NASA's Living With a Star (LWS) program whose goal is to develop the scientific understanding necessary to effectively address those aspects of the connected Sun-Earth system that directly affect life and society. The scientific goals of ILWS are defined in a broader sense, aiming to include future solar, heliospheric and solar terrestrial missions of both applied and fundamental scientific focus. The ultimate goal of ILWS wil be to increase our understanding of how solar variability affects the terrestrial and other planetary environments both in the short and long term, and in particular how man and society may be affected by solar variability and its consequences. The mission charter of ILWS is 'to stimulate, strengthen and coordinate space research in order to understand the governing processes of the connected Sun-Earth System as an integrated entity'. More detailed ILWS Objectives are to stimulate and facilitate: - The study of the Sun Earth connected system and the effects which influence life and society - Collaboration among all potential partners in solar-terrestrial space missions - Synergistic coordination of international
-
Review on the solar spectral variability in the EUV for space weather purposes
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Lilensten
2008-02-01
Full Text Available The solar XUV-EUV flux is the main energy source in the terrestrial diurnal thermosphere: it produces ionization, dissociation, excitation and heating. Accurate knowledge of this flux is of prime importance for space weather. We first list the space weather applications that require nowcasting and forecasting of the solar XUV-EUV flux. We then review present models and discuss how they account for the variability of the solar spectrum. We show why the measurement of the full spectrum is difficult, and why it is illusory to retrieve it from its atmospheric effects. We then address the problem of determining a set of observations that are adapted for space weather purposes, in the frame of ionospheric studies. Finally, we review the existing and future space experiments that are devoted to the observation of the solar XUV-EUV spectrum.
-
A 100 kW-Class Technology Demonstrator for Space Solar Power
Howell, J.; Carrington, C.; Day, G.
2004-12-01
A first step in the development of solar power from space is the flight demonstration of critical technologies. These fundamental technologies include efficient solar power collection and generation, power management and distribution, and thermal management. In addition, the integration and utilization of these technologies into a viable satellite bus could provide an energy-rich platform for a portfolio of payload experiments such as wireless power transmission (WPT). This paper presents the preliminary design of a concept for a 100 kW-class free-flying platform suitable for flight demonstration of Space Solar Power (SSP) technology experiments.
-
High Voltage Solar Concentrator Experiment with Implications for Future Space Missions
Mehdi, Ishaque S.; George, Patrick J.; O'Neill, Mark; Matson, Robert; Brockschmidt, Arthur
2004-01-01
This paper describes the design, development, fabrication, and test of a high performance, high voltage solar concentrator array. This assembly is believed to be the first ever terrestrial triple-junction-cell solar array rated at over 1 kW. The concentrator provides over 200 W/square meter power output at a nominal 600 Vdc while operating under terrestrial sunlight. Space-quality materials and fabrication techniques were used for the array, and the 3005 meter elevation installation below the Tropic of Cancer allowed testing as close as possible to space deployment without an actual launch. The array includes two concentrator modules, each with a 3 square meter aperture area. Each concentrator module uses a linear Fresnel lens to focus sunlight onto a photovoltaic receiver that uses 240 series-connected triple-junction solar cells. Operation of the two receivers in series can provide 1200 Vdc which would be adequate for the 'direct drive' of some ion engines or microwave transmitters in space. Lens aperture width is 84 cm and the cell active width is 3.2 cm, corresponding to a geometric concentration ratio of 26X. The evaluation includes the concentrator modules, the solar cells, and the materials and techniques used to attach the solar cells to the receiver heat sink. For terrestrial applications, a finned aluminum extrusion was used for the heat sink for the solar cells, maintaining a low cell temperature so that solar cell efficiency remains high.
-
Orbital Dynamics of a Simple Solar Photon Thruster
Guerman, Anna D.; Smirnov, Georgi V.; Pereira, Maria Cecilia
2009-01-01
We study orbital dynamics of a compound solar sail, namely, a Simple Solar Photon Thruster and compare its behavior to that of a common version of sailcraft. To perform this analysis, development of a mathematical model for force created by light reflection on all sailcraft elements is essential. We deduce the equations of sailcraft's motion and compare performance of two schemes of solar propulsion for two test time-optimal control problems of trajectory transfer.
-
Radiation resistance of solar cells for space application, 1
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mitsui, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Ryuichi; Sunaga, Hiromi
1989-07-01
A 50-μm thick ultrathin silicon solar cell and a 280-μm thick high performance AlGaAs/GaAs solar cell with high radiation resistance have been recently developed by National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). In order to study the radiation resistance of these cells, a joint research was carried out between Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and NASDA from 1984 through 1987. In this research, the irradiation method of electron beams, the effects of the irradiation conditions on the deterioration of solar cells by electron beams, and the annealing effects of the radiation damage in solar cells were investigated. This paper is the first one of a series of reports of the joint research. In this paper, the space radiation environment which artificial satellites will encounter, the solar cells used, and the experimental methods are described. In addition to these, the results of the study on the irradiation procedure of electron beams are reported. In the study of the irradiation method of electron beams, three methods, that is, the fixed irradiation method, the moving irradiation method, and the spot irradiation method were examined. In the fixed irradiation method and moving one, stationary solar cells and solar cells moving by conveyer were irradiated by scanning electron beams, respectively. On the other hand, in the spot irradiation method, stationary solar cells were irradiated by non-scanning steady electron beams. It was concluded that the fixed irradiation method was the most proper method. In addition to this, in this study, some pieces of information were obtained with respect to the changes in the electrical characteristics of solar cells caused by the irradiation of electron beams. (author) 52 refs
-
Chapman, S. C.; Dods, J.; Gjerloev, J. W.
2017-12-01
Observations of how the solar wind interacts with earth's magnetosphere, and its dynamical response, are increasingly becoming a data analytics challenge. Constellations of satellites observe the solar corona, the upstream solar wind and throughout earth's magnetosphere. These data are multipoint in space and extended in time, so in principle are ideal for study using dynamical networks to characterize the full time evolving spatial pattern. We focus here on analysis of data from the full set of 100+ auroral ground based magnetometer stations that have been collated by SuperMAG. Spatio-temporal patterns of correlation between the magnetometer time series can be used to form a dynamical network [1]. The properties of the network can then be captured by (time dependent) network parameters. This offers the possibility of characterizing detailed spatio-temporal pattern by a few parameters, so that many events can then be compared [2] with each other. Whilst networks are in widespread use in the data analytics of societal and commercial data, there are additional challenges in their application to physical timeseries. Determining whether two nodes (here, ground based magnetometer stations) are connected in a network (seeing the same dynamics) requires normalization w.r.t. the detailed sensitivities and dynamical responses of specific observing stations and seasonal conductivity variations and we have developed methods to achieve this dynamical normalization. The detailed properties of the network capture time dependent spatial correlation in the magnetometer responses and we will show how this can be used to infer a transient current system response to magnetospheric activity. [l] Dods et al, J. Geophys. Res 120, doi:10.1002/2015JA02 (2015). [2] Dods et al, J. Geophys. Res. 122, doi:10.1002/2016JA02 (2017).
-
Alternative power generation concepts for space
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brandhorst, H.W. Jr.; Juhasz, A.J.; Jones, B.I.
1994-01-01
With the advent of the NASA Space Station, there has emerged a general realization that large quantities of power in space are necessary and, in fact, enabling. This realization has led to the examination of alternative options to the ubiquitous solar array/battery power system. Several factors led to the consideration of solar dynamic and nuclear power systems. These include better scaling to high power levels, higher efficiency conversion and storage subsystems, and lower system specific mass. The objective of this paper is to present the results of trade and optimization studies that high-light the potential of solar and nuclear dynamic systems relative to photovoltaic power systems
-
Analysis of dynamic effects in solar thermal energy conversion systems
Hamilton, C. L.
1978-01-01
The paper examines a study the purpose of which is to assess the performance of solar thermal power systems insofar as it depends on the dynamic character of system components and the solar radiation which drives them. Using a dynamic model, the daily operation of two conceptual solar conversion systems was simulated under varying operating strategies and several different time-dependent radiation intensity functions. These curves ranged from smoothly varying input of several magnitudes to input of constant total energy whose intensity oscillated with periods from 1/4 hour to 6 hours.
-
A fresh look at space solar power
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mankins, J.C.
1996-01-01
Studies of systems to provide solar power from space for terrestrial use defined very large, geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) satellite concepts that--given massive initial government investments and extremely low cost space launch--might have led to power production at costs only somewhat higher than expected commercial prices. These studies of space solar power (SSP) succeeded in establishing technical feasibility. Shortly after the completion of the 1970s study, however, US funding came to an abrupt and seemingly permanent halt--in part because projected costs for the reference system were staggering: well in excess of $100B to achieve the first commercial kilowatt-hour of power. SSP has seen sporadic study and limited experimentation during the past decade (e.g., in Japan). Still, no existing SSP concept has engendered private development. New technologies now make possible concepts and approaches that suggest that SSP economic feasibility may be achievable early in the next century. In 1995, NASA's Advanced Concepts Office initiated a study taking a fresh look at innovative concepts for SSP that differ markedly from previously examined concepts, addressing innovative system architectures, markets and technologies that could radically reduce initial and operational costs. This paper will explore the issues associated with SSP and will summarize the results to date of NASA's recent fresh look at this important and increasingly timely field of space applications
-
High resolution solar observations in the context of space weather prediction
Yang, Guo
Space weather has a great impact on the Earth and human life. It is important to study and monitor active regions on the solar surface and ultimately to predict space weather based on the Sun's activity. In this study, a system that uses the full power of speckle masking imaging by parallel processing to obtain high-spatial resolution images of the solar surface in near real-time has been developed and built. The application of this system greatly improves the ability to monitor the evolution of solar active regions and to predict the adverse effects of space weather. The data obtained by this system have also been used to study fine structures on the solar surface and their effects on the upper solar atmosphere. A solar active region has been studied using high resolution data obtained by speckle masking imaging. Evolution of a pore in an active region presented. Formation of a rudimentary penumbra is studied. The effects of the change of the magnetic fields on the upper level atmosphere is discussed. Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) have a great impact on space weather. To study the relationship between CMEs and filament disappearance, a list of 431 filament and prominence disappearance events has been compiled. Comparison of this list with CME data obtained by satellite has shown that most filament disappearances seem to have no corresponding CME events. Even for the limb events, only thirty percent of filament disappearances are associated with CMEs. A CME event that was observed on March 20, 2000 has been studied in detail. This event did not show the three-parts structure of typical CMEs. The kinematical and morphological properties of this event were examined.
-
Solar pumped laser technology options for space power transmission
Conway, E. J.
1986-01-01
An overview of long-range options for in-space laser power transmission is presented. The focus is on the new technology and research status of solar-pumped lasers and their solar concentration needs. The laser options include gas photodissociation lasers, optically-pumped solid-state lasers, and blackbody-pumped transfer lasers. The paper concludes with a summary of current research thrusts.
-
Design of annual storage solar space heating systems
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hooper, F C; Cook, J D
1979-11-01
Design considerations for annual storage solar space heating systems are discussed. A simulation model for the performance of suh systems is described, and a method of classifying system configurations is proposed. It is shown that annual systems sized for unconstrained performance, with no unused collector or storage capacity, and no rejected heat, minimize solar acquisition costs. The optimal performance corresponds to the condition where the marginal storage-to-collector sizing ratio is equal to the corresponding marginal cost ratio.
-
Orbital Dynamics of a Simple Solar Photon Thruster
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Anna D. Guerman
2009-01-01
Full Text Available We study orbital dynamics of a compound solar sail, namely, a Simple Solar Photon Thruster and compare its behavior to that of a common version of sailcraft. To perform this analysis, development of a mathematical model for force created by light reflection on all sailcraft elements is essential. We deduce the equations of sailcraft's motion and compare performance of two schemes of solar propulsion for two test time-optimal control problems of trajectory transfer.
-
A new concept of space solar power satellite
Li, Xun; Duan, Baoyan; Song, Liwei; Yang, Yang; Zhang, Yiqun; Wang, Dongxu
2017-07-01
Space solar power satellite (SSPS) is a tremendous energy system that collects and converts solar power to electric power in space, and then transmits the electric power to earth wirelessly. In this paper, a novel SSPS concept based on ε-near-zero (ENZ) metamaterial is proposed. A spherical condenser made of ENZ metamaterial is developed, by using the refractive property of the ENZ metamaterial sunlight can be captured and redirected to its center. To make the geometric concentration ratio of the PV array reasonable, a hemispherical one located at the center is used to collect and convert the normal-incidence sunlight to DC power, then through a phased array transmitting antenna the DC power is beamed down to the rectenna on the ground. Detailed design of the proposed concept is presented.
-
The Solar Umbrella: A Low-cost Demonstration of Scalable Space Based Solar Power
Contreras, Michael T.; Trease, Brian P.; Sherwood, Brent
2013-01-01
Within the past decade, the Space Solar Power (SSP) community has seen an influx of stakeholders willing to entertain the SSP prospect of potentially boundless, base-load solar energy. Interested parties affiliated with the Department of Defense (DoD), the private sector, and various international entities have all agreed that while the benefits of SSP are tremendous and potentially profitable, the risk associated with developing an efficient end to end SSP harvesting system is still very high. In an effort to reduce the implementation risk for future SSP architectures, this study proposes a system level design that is both low-cost and seeks to demonstrate the furthest transmission of wireless power to date. The overall concept is presented and each subsystem is explained in detail with best estimates of current implementable technologies. Basic cost models were constructed based on input from JPL subject matter experts and assume that the technology demonstration would be carried out by a federally funded entity. The main thrust of the architecture is to demonstrate that a usable amount of solar power can be safely and reliably transmitted from space to the Earth's surface; however, maximum power scalability limits and their cost implications are discussed.
-
Distributed solar radiation fast dynamic measurement for PV cells
Wan, Xuefen; Yang, Yi; Cui, Jian; Du, Xingjing; Zheng, Tao; Sardar, Muhammad Sohail
2017-10-01
To study the operating characteristics about PV cells, attention must be given to the dynamic behavior of the solar radiation. The dynamic behaviors of annual, monthly, daily and hourly averages of solar radiation have been studied in detail. But faster dynamic behaviors of solar radiation need more researches. The solar radiation random fluctuations in minute-long or second-long range, which lead to alternating radiation and cool down/warm up PV cell frequently, decrease conversion efficiency. Fast dynamic processes of solar radiation are mainly relevant to stochastic moving of clouds. Even in clear sky condition, the solar irradiations show a certain degree of fast variation. To evaluate operating characteristics of PV cells under fast dynamic irradiation, a solar radiation measuring array (SRMA) based on large active area photodiode, LoRa spread spectrum communication and nanoWatt MCU is proposed. This cross photodiodes structure tracks fast stochastic moving of clouds. To compensate response time of pyranometer and reduce system cost, the terminal nodes with low-cost fast-responded large active area photodiode are placed besides positions of tested PV cells. A central node, consists with pyranometer, large active area photodiode, wind detector and host computer, is placed in the center of the central topologies coordinate to scale temporal envelope of solar irradiation and get calibration information between pyranometer and large active area photodiodes. In our SRMA system, the terminal nodes are designed based on Microchip's nanoWatt XLP PIC16F1947. FDS-100 is adopted for large active area photodiode in terminal nodes and host computer. The output current and voltage of each PV cell are monitored by I/V measurement. AS62-T27/SX1278 LoRa communication modules are used for communicating between terminal nodes and host computer. Because the LoRa LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) specification provides seamless interoperability among Smart Things without the
-
Radiation resistance of thin-film solar cells for space photovoltaic power
Woodyard, James R.; Landis, Geoffrey A.
1991-01-01
Copper indium diselenide, cadmium telluride, and amorphous silicon alloy solar cells have achieved noteworthy performance and are currently being studied for space power applications. Cadmium sulfide cells had been the subject of much effort but are no longer considered for space applications. A review is presented of what is known about the radiation degradation of thin film solar cells in space. Experimental cadmium telluride and amorphous silicon alloy cells are reviewed. Damage mechanisms and radiation induced defect generation and passivation in the amorphous silicon alloy cell are discussed in detail due to the greater amount of experimental data available.
-
Ultrafast Electron Dynamics in Solar Energy Conversion.
Ponseca, Carlito S; Chábera, Pavel; Uhlig, Jens; Persson, Petter; Sundström, Villy
2017-08-23
Electrons are the workhorses of solar energy conversion. Conversion of the energy of light to electricity in photovoltaics, or to energy-rich molecules (solar fuel) through photocatalytic processes, invariably starts with photoinduced generation of energy-rich electrons. The harvesting of these electrons in practical devices rests on a series of electron transfer processes whose dynamics and efficiencies determine the function of materials and devices. To capture the energy of a photogenerated electron-hole pair in a solar cell material, charges of opposite sign have to be separated against electrostatic attractions, prevented from recombining and being transported through the active material to electrodes where they can be extracted. In photocatalytic solar fuel production, these electron processes are coupled to chemical reactions leading to storage of the energy of light in chemical bonds. With the focus on the ultrafast time scale, we here discuss the light-induced electron processes underlying the function of several molecular and hybrid materials currently under development for solar energy applications in dye or quantum dot-sensitized solar cells, polymer-fullerene polymer solar cells, organometal halide perovskite solar cells, and finally some photocatalytic systems.
-
Space Solar Power Technical Interchange Meeting 2: SSP TIM 2
Sanders, Jim; Hawk, Clark W.
1998-01-01
The 2nd Space Solar Power Technical Interchange Meeting (SSP TIM 2) was conducted September 21st through 24th with the first part consisting of a Plenary session. The summary results of this Plenary session are contained in part one of this report. The attendees were then organized into Working Breakout Sessions and Integrated Product Team (IPT) Sessions for the purpose of conducting in-depth discussions in specific topic areas and developing a consensus as to appropriate study plans and actions to be taken. The Second part covers the Plenary Summary Session, which contains the summary results of the Working Breakout Sessions and IPT Sessions. The appendix contains the list of attendees. The ob'jective was to provide an update for the study teams and develop plans for subsequent study activities. This SSP TIM 2 was initiated and the results reported electronically over the Internet. The International Space Station (ISS) could provide the following opportunities for conducting research and technology (R&T) which are applicable to SSP: (1) Automation and Robotics, (2) Advanced Power Generation, (3) Advanced Power Management & Distribution (PMAD), (4) Communications Systems and Networks, (5) Energy Storage, (6) In Space Propulsion (ISP), (7) Structural Dynamics and Control, and Assembly and (8) Wireless Power Transmission.
-
Solar wind dynamic pressure variations and transient magnetospheric signatures
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sibeck, D.G.; Baumjohann, W.
1989-01-01
Contrary to the prevailing popular view, we find some transient ground events with bipolar north-south signatures are related to variations in solar wind dynamic pressure and not necessarily to magnetic merging. We present simultaneous solar wind plasma observations for two previously reported transient ground events observed at dayside auroral latitudes. During the first event, originally reported by Lanzerotti et al. [1987], conjugate ground magnetometers recorded north-south magetic field deflections in the east-west and vertical directions. The second event was reported by Todd et al. [1986], we noted ground rader observations indicating strong northward then southward ionospheric flows. The events were associated with the postulated signatures of patchy, sporadic, merging of magnetosheath and magnetospheric magnetic field lines at the dayside magnetospause, known as flux transfer events. Conversely, we demonstrate that the event reported by Lanzerotti et al. was accompanied by a sharp increase in solar wind dynamic pressure, a magnetospheric compression, and a consequent ringing of the magnetospheric magnetic field. The event reported by Todd et al. was associated with a brief but sharp increase in the solar wind dynamic pressure. copyright American Geophysical Union 1989
-
Frequency agile solar radiotelescope
Bastian, Tim S.
2003-02-01
The Frequency Agile Solar Radiotelescope (FASR) is a solar-dedicated, ground based, interferometric array optimized to perform broadband imaging spectroscopy from ~ 0.1-30+ GHz. It will do so with the angular, spectral, and temporal resolution required to exploit radio emission from the Sun as a diagnostic of the wide variety of astrophysical processes that occur there. FASR represents a major advance over existing radioheliographs, and is expected to remain the world's premier solar radio instrument for two decades or more after completion. FASR will be a versatile and powerful instrument, providing unique data to a broad users community. Solar, solar-terrestrial, and space physicists will exploit FASR to attack a broad science program, including problems of fundamental interest: coronal magnetography, solar flares and particle acceleration, drivers of space weather, and the thermal structure and dynamics of the solar atmosphere. A design study and implementation planning are underway. Recent progress is reviewed here.
-
Design and Development of the Space Technology 5 (ST5) Solar Arrays
Lyons, John; Fatemi, Navid; Gamica, Robert; Sharma, Surya; Senft, Donna; Maybery, Clay
2005-01-01
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA's) Space Technology 5 (ST5) is designed to flight-test the concept of miniaturized 'small size" satellites and innovative technologies in Earth's magnetosphere. Three satellites will map the intensity and direction of the magnetic fields within the inner magnetosphere. Due to the small area available for the solar arrays, and to meet the mission power requirements, very high-efficiency multijunction solar cells were selected to power the spacecraft built by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC). This was done in partnership with the Air Force Research Lab (AFRL) through the Dual-Use Science and Technology (DUS&T) program. Emcore's InGaP/lnGaAs/Ge Advanced triple-junction (ATJ) solar cells, exhibiting an average air mass zero (AMO) efficiency of 28.0% (one-sun, 28 C), were used to populate the arrays. Each spacecraft employs 8 identical solar panels (total area of about 0.3 square meters), with 15 large-area solar cells per panel. The requirement for power is to support on-orbit average load of 13.5 W at 8.4 V, with plus or minus 5% off pointing. The details of the solar array design, development and qualification considerations, as well as ground electrical performance & shadowing analysis results are presented.
-
Nonlinear techniques for forecasting solar activity directly from its time series
Ashrafi, S.; Roszman, L.; Cooley, J.
1993-01-01
This paper presents numerical techniques for constructing nonlinear predictive models to forecast solar flux directly from its time series. This approach makes it possible to extract dynamical in variants of our system without reference to any underlying solar physics. We consider the dynamical evolution of solar activity in a reconstructed phase space that captures the attractor (strange), give a procedure for constructing a predictor of future solar activity, and discuss extraction of dynamical invariants such as Lyapunov exponents and attractor dimension.
-
Wireless Power Transmission Options for Space Solar Power
Potter, Seth; Davis, Dean; Born, Martin; Bayer, Martin; Howell, Joe; Mankins, John
2008-01-01
Space Solar Power (SSP), combined with Wireless Power Transmission (WPT), offers the far-term potential to solve major energy problems on Earth. In the long term, we aspire to beam energy to Earth from geostationary Earth orbit (GEO), or even further distances in space. In the near term, we can beam power over more moderate distances, but still stretch the limits of today s technology. In recent studies, a 100 kWe-class "Power Plug" Satellite and a 10 kWe-class Lunar Polar Solar Power outpost have been considered as the first steps in using these WPT options for SSP. Our current assessments include consideration of orbits, wavelengths, and structural designs to meet commercial, civilian government, and military needs. Notional transmitter and receiver sizes are considered for use in supplying 5 to 40 MW of power. In the longer term, lunar or asteroidal material can be used. By using SSP and WPT technology for near-term missions, we gain experience needed for sound decisions in designing and developing larger systems to send power from space to Earth.
-
Solar Energetic Particles Events and Human Exploration: Measurements in a Space Habitat
Narici, L.; Berrilli, F.; Casolino, M.; Del Moro, D.; Forte, R.; Giovannelli, L.; Martucci, M.; Mergè, M.; Picozza, P.; Rizzo, A.; Scardigli, S.; Sparvoli, R.; Zeitlin, C.
2016-12-01
Solar activity is the source of Space Weather disturbances. Flares, CME and coronal holes modulate physical conditions of circumterrestrial and interplanetary space and ultimately the fluxes of high-energy ionized particles, i.e., solar energetic particle (SEP) and galactic cosmic ray (GCR) background. This ionizing radiation affects spacecrafts and biological systems, therefore it is an important issue for human exploration of space. During a deep space travel (for example the trip to Mars) radiation risk thresholds may well be exceeded by the crew, so mitigation countermeasures must be employed. Solar particle events (SPE) constitute high risks due to their impulsive high rate dose. Forecasting SPE appears to be needed and also specifically tailored to the human exploration needs. Understanding the parameters of the SPE that produce events leading to higher health risks for the astronauts in deep space is therefore a first priority issue. Measurements of SPE effects with active devices in LEO inside the ISS can produce important information for the specific SEP measured, relative to the specific detector location in the ISS (in a human habitat with a shield typical of manned space-crafts). Active detectors can select data from specific geo-magnetic regions along the orbits, allowing geo-magnetic selections that best mimic deep space radiation. We present results from data acquired in 2010 - 2012 by the detector system ALTEA inside the ISS (18 SPEs detected). We compare this data with data from the detector Pamela on a LEO satellite, with the RAD data during the Curiosity Journey to Mars, with GOES data and with several Solar physical parameters. While several features of the radiation modulation are easily understood by the effect of the geomagnetic field, as an example we report a proportionality of the flux in the ISS with the energetic proton flux measured by GOES, some features appear more difficult to interpret. The final goal of this work is to find the
-
Solar System Observations with the James Webb Space Telescope
Norwood, James; Hammel, Heidi; Milam, Stefanie; Stansberry, John; Lunine, Jonathan; Chanover, Nancy; Hines, Dean; Sonneborn, George; Tiscareno, Matthew; Brown, Michael; Ferruit, Pierre
2014-01-01
The James Webb Space Telescope will enable a wealth of new scientific investigations in the near- and mid-infrared, with sensitivity and spatial/spectral resolution greatly surpassing its predecessors. In this paper, we focus upon Solar System science facilitated by JWST, discussing the most current information available concerning JWST instrument properties and observing techniques relevant to planetary science. We also present numerous example observing scenarios for a wide variety of Solar...
-
Solar cells for space applications (part 2)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gomez, T.J.
1992-01-01
This lecture focusses on qualification and verification tests and procedures on solar cells designed for space applications. The series of tests should produce orbital performance under determined illumination, temperature and irradiance. Tests are divided in outdoor and laboratory experiments. Environmental tests include durability, qualification (mechanical and electrical), I-V curves, Spectral response
-
Dynamic performance of a novel solar photovoltaic/loop-heat-pipe heat pump system
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zhang, Xingxing; Zhao, Xudong; Shen, Jingchun; Xu, Jihuan; Yu, Xiaotong
2014-01-01
Highlights: • A transient model was developed to predict dynamic performance of new PV/LHP system. • The model accuracy was validated by experiment giving less than 9% in error. • The new system had basic and advanced performance coefficients of 5.51 and 8.71. • The new system had a COP 1.5–4 times that for conventional heat pump systems. • The new system had higher exergetic efficiency than PV and solar collector systems. - Abstract: Objective of the paper is to present an investigation into the dynamic performance of a novel solar photovoltaic/loop-heat-pipe (PV/LHP) heat pump system for potential use in space heating or hot water generation. The methods used include theoretical computer simulation, experimental verification, analysis and comparison. The fundamental equations governing the transient processes of solar transmission, heat transfer, fluid flow and photovoltaic (PV) power generation were appropriately integrated to address the energy balances occurring in different parts of the system, e.g., glazing cover, PV cells, fin sheet, loop heat pipe, heat pump cycle and water tank. A dedicated computer model was developed to resolve the above grouping equations and consequently predict the system’s dynamic performance. An experimental rig was constructed and operated under the real weather conditions for over one week in Shanghai to evaluate the system living performance, which was undertaken by measurement of various operational parameters, e.g., solar radiation, photovoltaic power generation, temperatures and heat pump compressor consumption. On the basis of the first- (energetic) and second- (exergetic) thermodynamic laws, an overall evaluation approach was proposed and applied to conduct both quantitative and qualitative analysis of the PV/LHP module’s efficiency, which involved use of the basic thermal performance coefficient (COP th ) and the advanced performance coefficient (COP PV/T ) of such a system. Moreover, a simple comparison
-
Computer Vision for the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO)
Martens, P. C. H.; Attrill, G. D. R.; Davey, A. R.; Engell, A.; Farid, S.; Grigis, P. C.; Kasper, J.; Korreck, K.; Saar, S. H.; Savcheva, A.; Su, Y.; Testa, P.; Wills-Davey, M.; Bernasconi, P. N.; Raouafi, N.-E.; Delouille, V. A.; Hochedez, J. F.; Cirtain, J. W.; Deforest, C. E.; Angryk, R. A.; de Moortel, I.; Wiegelmann, T.; Georgoulis, M. K.; McAteer, R. T. J.; Timmons, R. P.
2012-01-01
In Fall 2008 NASA selected a large international consortium to produce a comprehensive automated feature-recognition system for the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). The SDO data that we consider are all of the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) images plus surface magnetic-field images from the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI). We produce robust, very efficient, professionally coded software modules that can keep up with the SDO data stream and detect, trace, and analyze numerous phenomena, including flares, sigmoids, filaments, coronal dimmings, polarity inversion lines, sunspots, X-ray bright points, active regions, coronal holes, EIT waves, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), coronal oscillations, and jets. We also track the emergence and evolution of magnetic elements down to the smallest detectable features and will provide at least four full-disk, nonlinear, force-free magnetic field extrapolations per day. The detection of CMEs and filaments is accomplished with Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)/ Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph (LASCO) and ground-based Hα data, respectively. A completely new software element is a trainable feature-detection module based on a generalized image-classification algorithm. Such a trainable module can be used to find features that have not yet been discovered (as, for example, sigmoids were in the pre- Yohkoh era). Our codes will produce entries in the Heliophysics Events Knowledgebase (HEK) as well as produce complete catalogs for results that are too numerous for inclusion in the HEK, such as the X-ray bright-point metadata. This will permit users to locate data on individual events as well as carry out statistical studies on large numbers of events, using the interface provided by the Virtual Solar Observatory. The operations concept for our computer vision system is that the data will be analyzed in near real time as soon as they arrive at the SDO Joint Science Operations Center and have undergone basic
-
Negative space charge effects in photon-enhanced thermionic emission solar converters
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Segev, G.; Weisman, D.; Rosenwaks, Y.; Kribus, A.
2015-01-01
In thermionic energy converters, electrons in the gap between electrodes form a negative space charge and inhibit the emission of additional electrons, causing a significant reduction in conversion efficiency. However, in Photon Enhanced Thermionic Emission (PETE) solar energy converters, electrons that are reflected by the electric field in the gap return to the cathode with energy above the conduction band minimum. These electrons first occupy the conduction band from which they can be reemitted. This form of electron recycling makes PETE converters less susceptible to negative space charge loss. While the negative space charge effect was studied extensively in thermionic converters, modeling its effect in PETE converters does not account for important issues such as this form of electron recycling, nor the cathode thermal energy balance. Here, we investigate the space charge effect in PETE solar converters accounting for electron recycling, with full coupling of the cathode and gap models, and addressing conservation of both electric and thermal energy. The analysis shows that the negative space charge loss is lower than previously reported, allowing somewhat larger gaps compared to previous predictions. For a converter with a specific gap, there is an optimal solar flux concentration. The optimal solar flux concentration, the cathode temperature, and the efficiency all increase with smaller gaps. For example, for a gap of 3 μm the maximum efficiency is 38% and the optimal flux concentration is 628, while for a gap of 5 μm the maximum efficiency is 31% and optimal flux concentration is 163
-
Solar Flare Dynamic Microwave Imaging with EOVSA
Gary, D. E.; Chen, B.; Nita, G. M.; Fleishman, G. D.; Yu, S.; White, S. M.; Hurford, G. J.; McTiernan, J. M.
2017-12-01
The Expanded Owens Valley Solar Array (EOVSA) is both an expansion of our existing solar array and serves as a prototype for a much larger future project, the Frequency Agile Solar Radiotelescope (FASR). EOVSA is now complete, and is producing daily imaging of the full solar disk, including active regions and solar radio bursts at hundreds of frequencies in the range 2.8-18 GHz. We present highlights of the 1-s-cadence dynamic imaging spectroscropy of radio bursts we have obtained to date, along with deeper analysis of multi-wavelength observations and modeling of a well-observed burst. These observations are revealing the full life-cycle of the trapped population of high-energy electrons, from their initial acceleration and subsequent energy-evolution to their eventual decay through escape and thermalization. All of our data are being made available for download in both quick-look image form and in the form of the community-standard CASA measurement sets for subsequent imaging and analysis.
-
Testing relativity with solar system dynamics
Hellings, R. W.
1984-01-01
A major breakthrough is described in the accuracy of Solar System dynamical tests of relativistic gravity. The breakthrough was achieved by factoring in ranging data from Viking Landers 1 and 2 from the surface of Mars. Other key data sources included optical transit circle observations, lunar laser ranging, planetary radar, and spacecraft (Mariner 9 to Mars and Mariner 10 to Mercury). The Solar System model which is used to fit the data and the process by which such fits are performed are explained and results are discussed. The results are fully consistent with the predictions of General Relativity.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Couvidat, Sebastien
2002-01-01
This dissertation focuses on the solar interior dynamics and the neutrino puzzle, using helioseismology and more specifically the SoHO/GOLF data as a tool to probe the radiative interior of the Sun. We show how helioseismology gives us a direct access to the deep-layer dynamics through the solar rotation profile. Our data favor a decrease of the rotation velocity near the nuclear core. This can be used to constrain the angular momentum distribution processes, and to set an upper bound on the intensity of the magnetic field in this part of the Sun. The search for gravity modes with an original method is another topic of this dissertation. Several candidates are detected that need now to be confirmed. Gravity modes will give us a precious insight into the solar core structure and dynamics. We also use the stellar evolution code CESAM. By combining seismic data and solar modelling, we produce solar seismic models. The neutrino flux predictions from these models are partly derived on an observational basis. The comparison of these fluxes with the SNO results gives the solution to the solar neutrino puzzle: neutrinos have masses and they oscillate between different lepton flavors. This explains the deficit of detections observed since the sixties. We also work on the internal magnetic fields that take part to the dynamic processes. In particular, we start to study the impact of these fields on the neutrino production and transport. Finally, we reach the limits of the 1D stellar codes: they cannot take into account the dynamic processes efficiently. This justifies the current development of 2D or 3D codes. (author) [fr
-
Colagrossi, Andrea; Lavagna, Michèle
2018-03-01
A space station in the vicinity of the Moon can be exploited as a gateway for future human and robotic exploration of the solar system. The natural location for a space system of this kind is about one of the Earth-Moon libration points. The study addresses the dynamics during rendezvous and docking operations with a very large space infrastructure in an EML2 Halo orbit. The model takes into account the coupling effects between the orbital and the attitude motion in a circular restricted three-body problem environment. The flexibility of the system is included, and the interaction between the modes of the structure and those related with the orbital motion is investigated. A lumped parameter technique is used to represents the flexible dynamics. The parameters of the space station are maintained as generic as possible, in a way to delineate a global scenario of the mission. However, the developed model can be tuned and updated according to the information that will be available in the future, when the whole system will be defined with a higher level of precision.
-
Solar Dynamics and Its Effects on the Heliosphere and Earth
Baker, D. N; Schwartz, S. J; Schwenn, R; Steiger, R
2007-01-01
The SOHO and Cluster missions form a single ESA cornerstone. Yet they observe very different regions in our solar system: the solar atmosphere on one hand and the Earth’s magnetosphere on the other. At the same time the Ulysses mission provides observations in the third dimension of the heliosphere, and many others add to the picture from the Lagrangian point L1 to the edge of the heliosphere. It is the aim of this ISSI volume to tie these observations together in addressing the topic of Solar Dynamics and its Effects on the Heliosphere and Earth, thus contributing to the International Living With a Star (ILWS) program. The volume starts out with an assessment and description of the reasons for solar dynamics and how it couples into the heliosphere. The three subsequent sections are each devoted to following one chain of events from the Sun all the way to the Earth’s magnetosphere and ionosphere: The normal solar wind chain, the chain associated with coronal mass ejections, and the solar energetic particl...
-
Geometry of the solar wind transition region during the 11-year solar cycle
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lotova, N.A.; Blums, D.F.
1986-01-01
Geometry of the solar wind transition region and its dynamics during the 11-year solar cycle is investigated. It is shown that the space geometry of the transition region suffers considerable changes. In the years of minimum of solar activity (1975-1977) the transition region has a form close to elliptical, shifts nearer to the Sun, while its width decreases. During the years of maximum of Solar activity (1979-1981) the form of the transition region becomes close to spherically symmetric, is located further from the Sun and its width is increased
-
Wolford, David S.; Myers, Matthew G.; Prokop, Norman F.; Krasowski, Michael J.; Parker, David S.; Cassidy, Justin C.; Davies, William E.; Vorreiter, Janelle O.; Piszczor, Michael F.; McNatt, Jeremiah S.
2015-01-01
Measurement is essential for the evaluation of new photovoltaic (PV) technology for space solar cells. NASA Glenn Research Center (GRC) is in the process of measuring several solar cells in a supplemental experiment on NASA Goddard Space Flight Center's (GSFC) Robotic Refueling Mission's (RRM) Task Board 4 (TB4). Four industry and government partners have provided advanced PV devices for measurement and orbital environment testing. The experiment will be on-orbit for approximately 18 months. It is completely self-contained and will provide its own power and internal data storage. Several new cell technologies including four- junction (4J) Inverted Metamorphic Multijunction (IMM) cells will be evaluated and the results compared to ground-based measurements.
-
New techniques for the characterisation of dynamical phenomena in solar coronal images
Robbrecht, E.
2007-02-01
^23-10^25 J. They are often observed n association with low coronal activity, such as flares and filament eruptions. During the first years of CME observation, it was believed that a flare was a necessary condition for CME occurrence. The widely accepted picture today is that flares and CMEs are both different manifestations of magnetic field restructuring through reconnection (flare) and the expulsion of mass (CME). Up till now, the SOHO mission has been the best mission for CME studies because of the increased resolution, cadence, sensitivity and dynamic range of the LASCO instruments, but also because of the large array of ground-based instruments (Howard 2006). The complexity of the CME-picture grew likewise. The next mission with a coronagraph is the NASA STEREO mission (Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory), launched on 26 Oct. 2006. In chapter 4 we test the possibility of automatically detecting CMEs in LASCO data. We describe the algorithm CACTus (Computer Aided CME Tracking) and test its validity on a short period of 6 days. In chapter 5 we present our newly constructed CME catalog based on our automated detection scheme. It is the first automatically generated catalog which runs over a complete solar cycle (cycle 23). It required no human interaction, which implies it is totally objective. It includes all transients obeying the observational definition of CME as a "new, discrete, bright, white-light feature in the coronagraph field-of-view moving radially outward" (Hundhausen et al. 1984). As a result, our catalog contains much more events, mostly narrow, than are included in the classical CDAW CME catalog (Yashiro et al. 2004) which is assembled manually. We discuss the CME rate over the solar cycle and present important new statistics on the CACTus CME parameters (size, latitude, speed). CME research has gained an increased interest due to their strong space weather impact. Space weather is defined by the European Space Agency (ESA) 1 as the "conditions on the
-
Radiation hardening of InP solar cells for space applications
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Vilela, M. F.; Freundlich, A.; Monier, C.; Newman, F.; Aguilar, L.
1998-01-01
The aim of this work is to develop a radiation resistant thin InP-based solar cells for space applications on more mechanically resistant, lighter, and cheaper substrates. In this paper, we present the development of a p + /nn + InP-based solar cell structures with very thin emitter and base layers. A thin emitter helps to increase the collection of carriers generated by high energy incident photons from the solar spectrum. The use of a thin n base structure should improve the radiation resistance of this already radiation resistant technology. A remarkable improvement of high energy photons response is shown for InP solar cells with emitters 400 A thick
-
Application of the idea of morphism in solar-terrestrial physics and space weather
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mateev, Lachezar; Tassev, Yordan; Velinov, Peter
2016-01-01
The actual problems of solar-terrestrial physics, in particular of space weather are related to the prediction of the space environment state and are solved by means of different analyses and models. In the present work we introduce a new mathematical approach to the study of physical processes in the system Sun-Earth. For example, in the ionization of the ionosphere and atmosphere under the influence of cosmic rays a model is used that applies the principle of homomorphism. When calculating the parameters of space weather such as solar wind, interplanetary magnetic fields, Earth’s magnetosphere, geomagnetic storms and others, the introduction and application of mathematical objects is appropriate: morphisms, groups, categories, monads, functors, natural transformations and others. Such an approach takes into account the general laws of physical processes in the system Sun – Earth and helps in their testing and calculation. It is useful for such complex systems and processes as these in the solar-terrestrial physics and space weather. Some methods for algebraic structures can be introduced. These methods give the possibility for axiomatization of the physical data reality and the application of algebraic methods for their processing. Here we give the base for the transformation from the algebraic theory of categories and morphisms to the physical structure of concepts and data. Such problems are principally considered in the proposed work. Key words: pace weather, space radiation environment, solar effects, forecasting, energetic solar particles, cosmic rays
-
Development of Space Qualified Microlens Arrays for Solar Cells Used on Satellite Power Systems
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ömer Faruk Keser
2017-08-01
Full Text Available The power system, one of the main systems of satellite, provides energy required for the satellite. Solar cells are also the most used energy source in the power system. The third generation multi-junction solar cells are known as the ones with highest performance. One of the methods to increase the performance of the solar cells is anti-reflective surface coatings with the Micro Lens Array-MLA. It's expected that satellite technologies has high power efficiency and low mass. The space environment has many effects like atomic oxygen, radiation and thermal cycles. Researches for increasing the solar cells performance shows that MLA coated solar cell has increased light absorption performance and less cell heating with very low additional mass. However, it is established that few studies on MLA coatings of solar cells are not applicable on space platforms. In this study, the process of development of MLA which is convenient to space power systems is investigated in a methodological way. In this context, a method which is developed based on MLA coatings of multi-junction solar cells for satellite power systems is presented.
-
Solar System Observations with the James Webb Space Telescope
Norwood, James; Hammel, Heidi; Milam, Stefanie; Stansberry, John; Lunine, Jonathan; Chanover, Nancy; Hines, Dean; Sonneborn, George; Tiscareno, Matthew; Brown, Michael;

2016-01-01
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will enable a wealth of new scientific investigations in the near- and mid-infrared, with sensitivity and spatial/spectral resolution greatly surpassing its predecessors. In this paper, we focus upon Solar System science facilitated by JWST, discussing the most current information available concerning JWST instrument properties and observing techniques relevant to planetary science. We also present numerous example observing scenarios for a wide variety of Solar System targets to illustrate the potential of JWST science to the Solar System community. This paper updates and supersedes the Solar System white paper published by the JWST Project in 2010. It is based both on that paper and on a workshop held at the annual meeting of the Division for Planetary Sciences in Reno, NV, in 2012.
-
A dynamic model of an innovative high-temperature solar heating and cooling system
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Buonomano Annamaria
2016-01-01
Full Text Available In this paper a new simulation model of a novel solar heating and cooling system based on innovative high temperature flat plate evacuated solar thermal collector is presented. The system configuration includes: flat-plate evacuated solar collectors, a double-stage LiBr-H2O absorption chiller, gas-fired auxiliary heater, a closed loop cooling tower, pumps, heat exchangers, storage tanks, valves, mixers and controllers. The novelty of this study lies in the utilization of flat-plate stationary solar collectors, manufactured by TVP Solar, rather than concentrating ones (typically adopted for driving double-stage absorption chillers. Such devices show ultra-high thermal efficiencies, even at very high (about 200°C operating temperatures, thanks to the high vacuum insulation. Aim of the paper is to analyse the energy and economic feasibility of such novel technology, by including it in a prototypal solar heating and cooling system. For this purpose, the solar heating and cooling system design and performance were analysed by means of a purposely developed dynamic simulation model, implemented in TRNSYS. A suitable case study is also presented. Here, the simulated plant is conceived for the space heating and cooling and the domestic hot water production of a small building, whose energy needs are fulfilled through a real installation (settled also for experimental purposes built up close to Naples (South Italy. Simulation results show that the investigated system is able to reach high thermal efficiencies and very good energy performance. Finally, the economic analysis shows results comparable to those achieved through similar renewable energy systems.
-
A New Approach to Observing Coronal Dynamics: MUSE, the Multi-Slit Solar Explorer
Tarbell, T. D.
2017-12-01
The Multi-Slit Solar Explorer is a Small Explorer mission recently selected for a Phase A study, which could lead to a launch in 2022. It will provide unprecendented observations of the dynamics of the corona and transition region using both conventional and novel spectral imaging techniques. The physical processes that heat the multi-million degree solar corona, accelerate the solar wind and drive solar activity (CMEs and flares) remain poorly known. A breakthrough in these areas can only come from radically innovative instrumentation and state-of-the-art numerical modeling and will lead to better understanding of space weather origins. MUSE's multi-slit coronal spectroscopy will exploit a 100x improvement in spectral raster cadence to fill a crucial gap in our knowledge of Sun-Earth connections; it will reveal temperatures, velocities and non-thermal processes over a wide temperature range to diagnose physical processes that remain invisible to current or planned instruments. MUSE will contain two instruments: an EUV spectrograph (SG) and EUV context imager (CI). Both have similar spatial resolution and leverage extensive heritage from previous high-resolution instruments such as IRIS and the HiC rocket payload. The MUSE investigation will build on the success of IRIS by combining numerical modeling with a uniquely capable observatory: MUSE will obtain EUV spectra and images with the highest resolution in space (1/3 arcsec) and time (1-4 s) ever achieved for the transition region and corona, along 35 slits and a large context FOV simultaneously. The MUSE consortium includes LMSAL, SAO, Stanford, ARC, HAO, GSFC, MSFC, MSU, ITA Oslo and other institutions.
-
Dynamic model of an autonomous solar absorption refrigerator
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ali Fellah; Tahar Khir; Ammar Ben Brahim
2009-01-01
The performance analysis of a solar absorption refrigerator operating in an autonomous way is investigated. The water/LiBr machine satisfies the air-conditioning needs along the day. The refrigerator performances were simulated regarding a dynamic model. For the solar driven absorption machines, two applications could be distinguished. The sun provides the thermal part of the useful energy. In this case, it is necessary to use additional energy as the electric one to activate the pumps, the fans and the control system. On the other hand, the sun provides all the necessary energy. Here, both photovoltaic cells and thermal concentrators should be used. The simulation in dynamic regime of the cycle requires the knowledge of the geometric characteristics of every component as the exchange areas and the internal volumes. Real characteristics of a refrigerator available at the applied thermodynamic research unit (ATRU) at the engineers' national school of Gabes are notified. The development of the thermal and matter balances in every component of the cycle has permitted to simulate in dynamic regime the performances of a solar absorption refrigerator operating with the water/LiBr couple for air-conditioning needs. The developed model could be used to perform intermittent refrigeration cycle autonomously driven. (author)
-
Space solar power for powering a space elevator
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Laubscher, B. E. (Bryan E.); Kellum, M. J. (Mervyn J.)
2004-01-01
The Space Elevator (SE) represents a major paradigm shift in space access. If the SE's promise of low cost access can be realized, everything becomes economically more feasible to accomplish in space. In this paper we describe a Space Solar Power (SSP) system capable of powering the climbers of an SE. The initial SE will use laser power beaming from floating platforms near the SE platform. This study outlines an SSP system, based near the SE at geosynchronous altitude (GEO), which powers the climbers traversing the elevator. Such a system would reduce the SE system's dependence on fuel supply from land for its power beaming facilities. Moreover, since deploying SSP systems is anticipated to be a major use for SE's, SSP's could represent an elegant solution to the problem of SE energy consumption. SSP systems for sending usable power to Earth have been designed for well over 30 years. Technologies pertinent to SSP systems are continually evolving. This slightly different application carries the added requirements of aiming the beamed power at a moving target and sending the power in a form the climbers can use. Systems considered include beaming power to the climbers directly from a traditional SSP and reflecting sunlight onto the climbers. One of our designs includes a very new technology, optical rectennas. Mars SEs are conceived as having space-based power systems. Therefore, it is important to consider the problems that will be encountered in these types of applications.
-
Solar air heating system: design and dynamic simulation
Bououd, M.; Hachchadi, O.; Janusevicius, K.; Martinaitis, V.; Mechaqrane, A.
2018-05-01
The building sector is one of the big energy consumers in Morocco, accounting for about 23% of the country’s total energy consumption. Regarding the population growth, the modern lifestyle requiring more comfort and the increase of the use rate of electronic devices, the energy consumption will continue to increase in the future. In this context, the introduction of renewable energy systems, along with energy efficiency, is becoming a key factor in reducing the energy bill of buildings. This study focuses on the design and dynamic simulation of an air heating system for the mean categories of the tertiary sector where the area exceeds 750 m3. Heating system has been designed via a dynamic simulation environment (TRNSYS) to estimate the produced temperature and airflow rate by one system consisting of three essential components: vacuum tube solar collector, storage tank and water-to-air finned heat exchanger. The performances estimation of this system allows us to evaluate its capacity to meet the heating requirements in Ifrane city based on the prescriptive approach according to the Moroccan Thermal Regulation. The simulation results show that in order to maintain a comfort temperature of 20°C in a building of 750m3, the places requires a thermal powers of approximately 21 kW, 29 kW and 32 kW, respectively, for hotels, hospitals, administrative and public-school. The heat generation is ensured by a solar collector areas of 5 m², 7 m² and 10 m², respectively, for hotels, hospitals, administrative and public-school spaces, a storage tank of 2 m3 and a finned heat exchanger with 24 tubes. The finned tube bundles have been modelled and integrated into the system design via a Matlab code. The heating temperature is adjusted via two controllers to ensure a constant air temperature of 20°C during the heating periods.
-
Materials on the International Space Station - Forward Technology Solar Cell Experiment
Walters, R. J.; Garner, J. C.; Lam, S. N.; Vazquez, J. A.; Braun, W. R.; Ruth, R. E.; Lorentzen, J. R.; Bruninga, R.; Jenkins, P. P.; Flatico, J. M.
2005-01-01
This paper describes a space solar cell experiment currently being built by the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) in collaboration with NASA Glenn Research Center (GRC), and the US Naval Academy (USNA). The experiment has been named the Forward Technology Solar Cell Experiment (FTSCE), and the purpose is to rapidly put current and future generation space solar cells on orbit and provide validation data for these technologies. The FTSCE is being fielded in response to recent on-orbit and ground test anomalies associated with space solar arrays that have raised concern over the survivability of new solar technologies in the space environment and the validity of present ground test protocols. The FTSCE is being built as part of the Fifth Materials on the International Space Station (MISSE) Experiment (MISSE-5), which is a NASA program to characterize the performance of new prospective spacecraft materials when subjected to the synergistic effects of the space environment. Telemetry, command, control, and communication (TNC) for the FTSCE will be achieved through the Amateur Satellite Service using the PCSat2 system, which is an Amateur Radio system designed and built by the USNA. In addition to providing an off-the-shelf solution for FTSCE TNC, PCSat2 will provide a communications node for the Amateur Radio satellite system. The FTSCE and PCSat2 will be housed within the passive experiment container (PEC), which is an approximately 2ft x2ft x 4in metal container built by NASA Langley Research Center (NASA LaRC) as part of the MISSE-5 program. NASA LaRC has also supplied a thin film materials experiment that will fly on the exterior of the thermal blanket covering the PCSat2. The PEC is planned to be transported to the ISS on a Shuttle flight. The PEC will be mounted on the exterior of the ISS by an astronaut during an extravehicular activity (EVA). After nominally one year, the PEC will be retrieved and returned to Earth. At the time of writing this paper, the
-
Solar chimney: A sustainable approach for ventilation and building space conditioning
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Lal, S.,
2013-03-01
Full Text Available The residential and commercial buildings demand increase with rapidly growing population. It leads to the vertical growth of the buildings and needs proper ventilation and day-lighting. The natural air ventilation system is not significantly works in conventional structure, so fans and air conditioners are mandatory to meet the proper ventilation and space conditioning. Globally building sector consumed largest energy and utmost consumed in heating, ventilation and space conditioning. This load can be reduced by application of solar chimney and integrated approaches in buildings for heating, ventilation and space conditioning. It is a sustainable approach for these applications in buildings. The authors are reviewed the concept, various method of evaluation, modelings and performance of solar chimney variables, applications and integrated approaches.
-
Nonlinear transport of dynamic system phase space
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Xie Xi; Xia Jiawen
1993-01-01
The inverse transform of any order solution of the differential equation of general nonlinear dynamic systems is derived, realizing theoretically the nonlinear transport for the phase space of nonlinear dynamic systems. The result is applicable to general nonlinear dynamic systems, with the transport of accelerator beam phase space as a typical example
-
Solar panels for the International Space Station are uncrated and moved in the SSPF
1998-01-01
In the Space Station Processing Facility, a worker (left) guides the lifting of solar panels for the International Space Station (ISS). The panels are the first set of U.S.-provided solar arrays and batteries for ISS, scheduled to be part of mission STS-97 in December 1999. The mission, fifth in the U.S. flights for construction of ISS, will build and enhance the capabilities of the Space Station. It will deliver the solar panels as well as radiators to provide cooling. The Shuttle will spend 5 days docked to the station, which at that time will be staffed by the first station crew. Two space walks will be conducted to complete assembly operations while the arrays are attached and unfurled. A communications system for voice and telemetry also will be installed.
-
Commercialization of solar space power
Pant, Alok; Sera, Gary
1995-01-01
The objective of this research is to help U.S. companies commercialize renewable energy in India, with a special focus on solar energy. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Mid-Continent Technology Transfer Center (MCTTC) is working with ENTECH, Inc., a solar photovoltaic (SPV) systems manufacturer to form partnerships with Indian companies. MCTTC has conducted both secondary and primary market research and obtained travel funding to meet potential Indian partners face to face. MCTTC and ENTECH traveled to India during June 2-20, 1994, and visited New Delhi, Bombay, Pune and Calcutta. Meetings were held with several key government officials and premier Indian business houses and entrepreneurs in the area of solar energy. A firsthand knowledge of India's renewable energy industry was gained, and companies were qualified in terms of capabilities and commitment to the SPV business. The World Bank has awarded India with 280 million to commercialize renewable energies, including 55 million for SPV. There is a market in India for both small-scale (kW) and large SPV (MW) applications. Each U.S. company needs to form a joint venture with an Indian firm and let the latter identify the states and projects with the greatest business potential. Several big Indian companies and entrepreneurs are planning to enter the SPV business, and they currently are seeking foreign technology partners. Since the lager companies have adopted a more conservative approach, however, partnerships with entrepreneurs might offer the quickest route to market entry in India.
-
Adaptive control of solar energy collector systems
Lemos, João M; Igreja, José M
2014-01-01
This book describes methods for adaptive control of distributed-collector solar fields: plants that collect solar energy and deliver it in thermal form. Controller design methods are presented that can overcome difficulties found in these type of plants:they are distributed-parameter systems, i.e., systems with dynamics that depend on space as well as time;their dynamics is nonlinear, with a bilinear structure;there is a significant level of uncertainty in plant knowledge.Adaptive methods form the focus of the text because of the degree of uncertainty in the knowledge of plant dynamics. Parts
-
Structural assessment of a space station solar dynamic heat receiver thermal energy storage canister
Thompson, R. L.; Kerslake, T. W.; Tong, M. T.
1988-01-01
The structural performance of a space station thermal energy storage (TES) canister subject to orbital solar flux variation and engine cold start up operating conditions was assessed. The impact of working fluid temperature and salt-void distribution on the canister structure are assessed. Both analytical and experimental studies were conducted to determine the temperature distribution of the canister. Subsequent finite element structural analyses of the canister were performed using both analytically and experimentally obtained temperatures. The Arrhenius creep law was incorporated into the procedure, using secondary creep data for the canister material, Haynes 188 alloy. The predicted cyclic creep strain accumulations at the hot spot were used to assess the structural performance of the canister. In addition, the structural performance of the canister based on the analytically determined temperature was compared with that based on the experimentally measured temperature data.
-
Solar Space and Water Heating for School -- Dallas, Texas
1982-01-01
90 page report gives overview of retrofitted solar space-heating and hot-water system installation for 61-year-old high school. Description, specifications, modifications, plan drawings for roof, three floors, basement, correspondence, and documents are part of report.
-
Full space device optimization for solar cells.
Baloch, Ahmer A B; Aly, Shahzada P; Hossain, Mohammad I; El-Mellouhi, Fedwa; Tabet, Nouar; Alharbi, Fahhad H
2017-09-20
Advances in computational materials have paved a way to design efficient solar cells by identifying the optimal properties of the device layers. Conventionally, the device optimization has been governed by single or double descriptors for an individual layer; mostly the absorbing layer. However, the performance of the device depends collectively on all the properties of the material and the geometry of each layer in the cell. To address this issue of multi-property optimization and to avoid the paradigm of reoccurring materials in the solar cell field, a full space material-independent optimization approach is developed and presented in this paper. The method is employed to obtain an optimized material data set for maximum efficiency and for targeted functionality for each layer. To ensure the robustness of the method, two cases are studied; namely perovskite solar cells device optimization and cadmium-free CIGS solar cell. The implementation determines the desirable optoelectronic properties of transport mediums and contacts that can maximize the efficiency for both cases. The resulted data sets of material properties can be matched with those in materials databases or by further microscopic material design. Moreover, the presented multi-property optimization framework can be extended to design any solid-state device.
-
3D Visualization of Solar Data: Preparing for Solar Orbiter and Parker Solar Probe
Mueller, D.; Nicula, B.; Felix, S.; Verstringe, F.; Bourgoignie, B.; Csillaghy, A.; Berghmans, D.; Jiggens, P.; Ireland, J.; Fleck, B.
2017-12-01
Solar Orbiter and Parker Solar Probe will focus on exploring the linkage between the Sun and the heliosphere. These new missions will collect unique data that will allow us to study, e.g., the coupling between macroscopic physical processes to those on kinetic scales, the generation of solar energetic particles and their propagation into the heliosphere and the origin and acceleration of solar wind plasma. Combined with the several petabytes of data from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, the scientific community will soon have access to multidimensional remote-sensing and complex in-situ observations from different vantage points, complemented by petabytes of simulation data. Answering overarching science questions like "How do solar transients drive heliospheric variability and space weather?" will only be possible if the community has the necessary tools at hand. In this contribution, we will present recent progress in visualizing the Sun and its magnetic field in 3D using the open-source JHelioviewer framework, which is part of the ESA/NASA Helioviewer Project.
-
A 100 kW-Class Technology Demonstrator for Space Solar Power
Carrington, Connie; Howell, Joe; Day, Greg
2004-01-01
A first step in the development of solar power from space is the flight demonstration of critical technologies. These fundamental technologies include efficient solar power collection and generation, power management and distribution, and thermal management. In addition, the integration and utilization of these technologies into a viable satellite bus could provide an energy-rich platform for a portfolio of payload experiments such as wireless power transmission (WPT). This paper presents the preliminary design of a concept for a 100 kW-class fiee-flying platform suitable for flight demonstration of technology experiments. Recent space solar power (SSP) studies by NASA have taken a stepping stones approach that lead to the gigawatt systems necessary to cost-effectively deliver power from space. These steps start with a 100 kW-class satellite, leading to a 500 kW and then a 1 MW-class platform. Later steps develop a 100 M W bus that could eventually lead to a 1-2 GW pilot plant for SSP. Our studies have shown that a modular approach is cost effective. Modular designs include individual laser-power-beaming satellites that fly in constellations or that are autonomously assembled into larger structures at geosynchronous orbit (GEO). Microwave power-beamed approaches are also modularized into large numbers of identical units of solar arrays, power converters, or supporting structures for arrays and microwave transmitting antennas. A cost-effective approach to launching these modular units is to use existing Earth-to-orbit (ETO) launch systems, in which the modules are dropped into low Earth orbit (LEO) and then the modules perform their own orbit transfer to GEO using expendable solar arrays to power solar electric thrusters. At GEO, the modules either rendezvous and are assembled robotically into larger platforms, or are deployed into constellations of identical laser power-beaming satellites. Since solar electric propulsion by the modules is cost-effective for both
-
Radiative hazard of solar flares in the nearterrestrial cosmic space
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kolomenskij, A.V.; Petrov, V.M.; Zil', M.V.; Eremkina, T.M.
1978-01-01
Simulation of radiation enviroment due to solar cosmic rays was carried out in the near-terrestrial space. Systematized are the data on cosmic ray flux and spectra detected during 19-th and 20-th cycles of solar activity. 127 flares are considered with proton fluxes of more than 10 proton/cm 2 at energies higher than 30 MeV. Obtained are distribution functions of intervals between flares, flux distribution of flares and characteristic rigidity, and also distribution of magnetic disturbances over Dsub(st)-variation amplitude. The totality of these distributions presents the statistic model of radiation enviroment caused by solar flare protons for the period of maximum solar .activity. This model is intended for estimation of radiation hazard at manned cosmic flights
-
Solar Radio Bursts and Space Weather
Gopalswamy, Natchimuthuk,
2012-01-01
Radio bursts from the Sun are produced by electron accelerated to relativistic energies by physical processes on the Sun such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). The radio bursts are thus good indicators of solar eruptions. Three types of nonthermal radio bursts are generally associated with CMEs. Type III bursts due to accelerated electrons propagating along open magnetic field lines. The electrons are thought to be accelerated at the reconnection region beneath the erupting CME, although there is another view that the electrons may be accelerated at the CME-driven shock. Type II bursts are due to electrons accelerated at the shock front. Type II bursts are also excellent indicators of solar energetic particle (SEP) events because the same shock is supposed accelerate electrons and ions. There is a hierarchical relationship between the wavelength range of type /I bursts and the CME kinetic energy. Finally, Type IV bursts are due to electrons trapped in moving or stationary structures. The low frequency stationary type IV bursts are observed occasionally in association with very fast CMEs. These bursts originate from flare loops behind the erupting CME and hence indicate tall loops. This paper presents a summary of radio bursts and their relation to CMEs and how they can be useful for space weather predictions.
-
Charge transport and recombination dynamics in organic bulk heterojunction solar cells
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Baumann, Andreas
2011-08-02
The charge transport in disordered organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ) solar cells is a crucial process affecting the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the solar cell. With the need of synthesizing new materials for improving the power conversion efficiency of those cells it is important to study not only the photophysical but also the electrical properties of the new material classes. Thereby, the experimental techniques need to be applicable to operating solar cells. In this work, the conventional methods of transient photoconductivity (also known as ''Time-of-Flight'' (TOF)), as well as the transient charge extraction technique of ''Charge Carrier Extraction by Linearly Increasing Voltage'' (CELIV) are performed on different organic blend compositions. Especially with the latter it is feasible to study the dynamics - i.e. charge transport and charge carrier recombination - in bulk heterojunction (BHJ) solar cells with active layer thicknesses of 100-200 nm. For a well performing organic BHJ solar cells the morphology is the most crucial parameter finding a trade-off between an efficient photogeneration of charge carriers and the transport of the latter to the electrodes. Besides the morphology, the nature of energetic disorder of the active material blend and its influence on the dynamics are discussed extensively in this work. Thereby, the material system of poly(3-hexylthiophene-2,5-diyl) (P3HT) and [6,6]-phenyl-C{sub 61}butyric acid methyl ester (PC{sub 61}BM) serves mainly as a reference material system. New promising donor or acceptor materials and their potential for application in organic photovoltaics are studied in view of charge dynamics and compared with the reference system. With the need for commercialization of organic solar cells the question of the impact of environmental conditions on the PCE of the solar cells raises. In this work, organic BHJ solar cells exposed to synthetic air for finite duration are
-
Dilute Nitrides For 4-And 6- Junction Space Solar Cells
Essig, S.; Stammler, E.; Ronsch, S.; Oliva, E.; Schachtner, M.; Siefer, G.; Bett, A. W.; Dimroth, F.
2011-10-01
According to simulations the efficiency of conventional, lattice-matched GaInP/GaInAs/Ge triple-junction space solar cells can be strongly increased by the incorporation of additional junctions. In this way the existing excess current of the Germanium bottom cell can be reduced and the voltage of the stack can be increased. In particular, the use of 1.0 eV materials like GaInNAs opens the door for solar cells with significantly improved conversion efficiency. We have investigated the material properties of GaInNAs grown by metal organic vapour phase epitaxy (MOVPE) and its impact on the quantum efficiency of solar cells. Furthermore we have developed a GaInNAs subcell with a bandgap energy of 1.0 eV and integrated it into a GaInP/GaInAs/GaInNAs/Ge 4-junction and a AlGaInP/GaInP/AlGaInAs/GaInAs/GaInNAs/Ge 6- junction space solar cell. The material quality of the dilute nitride junction limits the current density of these devices to 9.3 mA/cm2 (AM0). This is not sufficient for a 4-junction cell but may lead to current matched 6- junction devices in the future.
-
Prospects to solar energy power generation in space. Uchu taiyo hatsuden eno tenbo
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kudo, I. (Electrotechnical Laboratory, Tsukuba (Japan))
1993-05-01
Solar energy power generation in space uses large arrays of solar cells developed on a geosynchronous orbit to obtain electric energy, which is transmitted to the earth using microwaves. The idea had already been advocated in 1968, which was followed a decade later by joint discussions done by NASA and DOE. The concept intended to take care of the U.S. power demand by using 60 power plant satellites, each having an output of 5 GW. This expanse of the scale, regarded reasonable even today, calls for the solar cell arrays in space spreading over an area of 10 km [times] 5 km if silicon solar cells with a conversion efficiency of 15% are used, and rectenna on the ground (a received wave converting facility) forming an ellipse of 10 km [times] 13 km (assuming a location at the north latitude of 36[degree]). Although there are a number of problems in the idea such as transportation means to lift construction materials into the space and effect of microwaves on the ionosphere and the ecosystems, the Agency of Industrial Science and Technology organized a 'committee for investigating and studying the space power generation systems' in the fiscal year 1991, and has been moving discussions forward since then. 7 refs., 5 figs.
-
Chart links solar, geophysical events with impacts on space technologies
Davenport, George R.
While developing a Space Weather Training Program for Air Force Space Command and the 50th Weather Squadron, both based in Colorado, ARINC Incorporated produced a flowchart that correlates solar and geophysical events with their impacts on Air Force systems.Personnel from both organizations collaborated in the development of the flowchart and provided many comments and suggestions. The model became the centerpiece of the Space Environment Impacts Reference Pamphlet, as well as the formal Space Weather Training Program. Although it is not a numerical or computer model, the flowchart became known as the “Space Environmental Impacts Model.”
-
A new Laplace transformation method for dynamic testing of solar collectors
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Kong, Weiqiang; Perers, Bengt; Fan, Jianhua
2015-01-01
A new dynamic method for solar collector testing is developed. It is characterized by using the Laplace transformation technique to solve the differential governing equation. The new method was inspired by the so called New Dynamic Method (NDM) (Amer E. et al (1999) [1]) but totally different....... By integration of the Laplace transformation technique with the Quasi Dynamic Test (QDT) model (Fischer S. et al (2004) [2]), the Laplace – QDT (L-QDT) model is derived. Two experimental methods are then introduced. One is the shielding method which needs to shield and un-shield solar collector continuously...
-
Recent Advances in Heliogyro Solar Sail Structural Dynamics, Stability, and Control Research
Wilkie, W. Keats; Warren, Jerry E.; Horta, Lucas G.; Lyle, Karen H.; Juang, Jer-Nan; Gibbs, S. Chad; Dowell, Earl H.; Guerrant, Daniel V.; Lawrence, Dale
2015-01-01
Results from recent NASA sponsored research on the structural dynamics, stability, and control characteristics of heliogyro solar sails are summarized. Specific areas under investigation include coupled nonlinear finite element analysis of heliogyro membrane blade with solar radiation pressure effects, system identification of spinning membrane structures, and solarelastic stability analysis of heliogyro solar sails, including stability during blade deployment. Recent results from terrestrial 1-g blade dynamics and control experiments on "rope ladder" membrane blade analogs, and small-scale in vacuo system identification experiments with hanging and spinning high-aspect ratio membranes will also be presented. A low-cost, rideshare payload heliogyro technology demonstration mission concept is used as a mission context for these heliogyro structural dynamics and solarelasticity investigations, and is also described. Blade torsional dynamic response and control are also shown to be significantly improved through the use of edge stiffening structural features or inclusion of modest tip masses to increase centrifugal stiffening of the blade structure. An output-only system identification procedure suitable for on-orbit blade dynamics investigations is also developed and validated using ground tests of spinning sub-scale heliogyro blade models. Overall, analytical and experimental investigations to date indicate no intractable stability or control issues for the heliogyro solar sail concept.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
ZERBO Issa
2010-01-01
A bibliographic study on the techniques of characterization of silicon solar cell, diodes, massifs and silicon wafer are presented. The influence of the modulation frequency and recombination in volume and in surface phenomena of on the profiles of carriers' densities, photocurrent and photovoltage has been put in evidence. The study of surface recombination velocities permitted to show that the bi facial silicon solar cell of Back Surface Field type behaves like an ohmic contacts solar cell for modulation frequencies above 40 khz. pplicability in frequency dynamic regime in the frequency range [0 - 40 khz] of three techniques of steady state recombination parameters determination is shown. A technique of diffusion length determination, in the range of (200 Hz - 40 khz] is proposed. It rests on the measurement of the short circuit current phase that is compared with the theoretical curve of short circuit current phase. The intersection of the experimental short circuit current phase and the theoretical curve of short circuit current phase permits to get the minority carriers effective diffusion length. An equivalent electric model of a solar cell in frequency dynamic regime is proposed. A study in modelling of the bi facial solar cell shunt resistance and space charge zone capacity is led from a determination method of these parameters proposed in steady state. (Author [fr
-
THE KEY ROLE OF SOLAR DYNAMICS IN THE CHROMOSPHERIC HANLE POLARIZATION
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Carlin, E. S.; Bianda, M., E-mail: escarlin@irsol.ch [Istituto Ricerche Solari Locarno, 6600 Locarno (Switzerland)
2016-11-01
The quantum theory of polarized light allows one to model scattering in the solar atmosphere for inferring its properties. This powerful approach has revealed two key long-standing problems in solar physics: the puzzling dilemmas between theory and observations in several anomalously polarized spectral lines and the need for inferring the ubiquitous weak chromospheric magnetic fields, which requires discriminating the Hanle effect in dynamic optically thick plasmas. However, the ever-present dynamics, i.e., the temporal evolution of heatings and macroscopic motions, has been widely disregarded when modeling and interpreting the scattering polarization. This has hindered a consistent theoretical solution to the puzzle while falsifying the Hanle diagnosis. Here, we show that the dynamical evolution is a keystone for solving both problems because its systematic impact allows an explanation of the observations from “anomalous” instantaneous polarization signals. Evolution accounted for, we reproduce amplitudes and (spectral and spatial) shapes of the Ca i 4227 Å polarization at solar disk center, identifying a restrictive arrangement of magnetic fields, kinematics, heatings, and spatio-temporal resolution. We find that the joint action of dynamics, Hanle effect, and low temporal resolutions mimics Zeeman linear polarization profiles, the true weak-field Zeeman signals being negligible. Our results allow reinterpretation of many polarization signals of the solar spectra and support time-dependent scattering polarization as a powerful tool for deciphering the spatio-temporal distribution of chromospheric heatings and fields. This approach may be a key aid in developing the Hanle diagnosis for the solar atmosphere.
-
Dynamics and design of space nets for orbital capture
Yang, Leping; Zhen, Ming; Liu, Haitao
2017-01-01
This book covers the topics of theoretical principles, dynamics model and algorithm, mission analysis, system design and experimental studies of space nets system, aiming to provide an initial framework in this field and serve as a ready reference for those interested. Space nets system represents a forefront field in future development of aerospace technologies. However, it involves new challenges and problems such as nonlinear and distorted nets structure, complex rigid flexible coupling dynamics, orbital transfer of space flexible composite and dynamics control. Currently, no comprehensive books on space nets dynamics and design are available, so potential readers can get to know the working mechanism, dynamics elements, and mission design of the space nets system from a Chinese perspective.
-
Solar radio bursts as a tool for space weather forecasting
Klein, Karl-Ludwig; Matamoros, Carolina Salas; Zucca, Pietro
2018-01-01
The solar corona and its activity induce disturbances that may affect the space environment of the Earth. Noticeable disturbances come from coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which are large-scale ejections of plasma and magnetic fields from the solar corona, and solar energetic particles (SEPs). These particles are accelerated during the explosive variation of the coronal magnetic field or at the shock wave driven by a fast CME. In this contribution, it is illustrated how full Sun microwave observations can lead to (1) an estimate of CME speeds and of the arrival time of the CME at the Earth, (2) the prediction of SEP events attaining the Earth. xml:lang="fr"
-
deGroh, Kim, K.; Dever, Joyce A.; Snyder, Aaron; Kaminski, Sharon; McCarthy, Catherine E.; Rapoport, Alison L.; Rucker, Rochelle N.
2006-01-01
A section of the retrieved Hubble Space Telescope (HST) solar array drive arm (SADA) multilayer insulation (MLI), which experienced 8.25 years of space exposure, was analyzed for environmental durability of the top layer of silver-Teflon (DuPont) fluorinated ethylene propylene (Ag-FEP). Because the SADA MLI had solar and anti-solar facing surfaces and was exposed to the space environment for a long duration, it provided a unique opportunity to study solar effects on the environmental degradation of Ag-FEP, a commonly used spacecraft thermal control material. Data obtained included tensile properties, solar absorptance, surface morphology and chemistry. The solar facing surface was found to be extremely embrittled and contained numerous through-thickness cracks. Tensile testing indicated that the solar facing surface lost 60% of its mechanical strength and 90% of its elasticity while the anti-solar facing surface had ductility similar to pristine FEP. The solar absorptance of both the solar facing surface (0.155 plus or minus 0.032) and the anti-solar facing surface (0.208 plus or minus 0.012) were found to be greater than pristine Ag-FEP (0.074). Solar facing and anti-solar facing surfaces were microscopically textured, and locations of isolated contamination were present on the anti-solar surface resulting in increased localized texturing. Yet, the overall texture was significantly more pronounced on the solar facing surface indicating a synergistic effect of combined solar exposure and increased heating with atomic oxygen erosion. The results indicate a very strong dependence of degradation, particularly embrittlement, upon solar exposure with orbital thermal cycling having a significant effect.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Andersen, Elsa
2007-01-01
The focus in the present Ph.D. thesis is on the active use of solar energy for domestic hot water and space heating in so-called solar combi systems. Most efforts have been put into detailed investigations on the design of solar combi systems and on devices used for building up thermal...... the thermal behaviour of different components, and the theoretical investigations are used to study the influence of the thermal behaviour on the yearly thermal performance of solar combi systems. The experimental investigations imply detailed temperature measurements and flow visualization with the Particle...... Image Velocimetry measurement method. The theoretical investigations are based on the transient simulation program TrnSys and Computational Fluid Dynamics. The Ph.D. thesis demonstrates the influence on the thermal performance of solar combi systems of a number of different parameters...
-
Phase space density representations in fluid dynamics
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ramshaw, J.D.
1989-01-01
Phase space density representations of inviscid fluid dynamics were recently discussed by Abarbanel and Rouhi. Here it is shown that such representations may be simply derived and interpreted by means of the Liouville equation corresponding to the dynamical system of ordinary differential equations that describes fluid particle trajectories. The Hamiltonian and Poisson bracket for the phase space density then emerge as immediate consequences of the corresponding structure of the dynamics. For barotropic fluids, this approach leads by direct construction to the formulation presented by Abarbanel and Rouhi. Extensions of this formulation to inhomogeneous incompressible fluids and to fluids in which the state equation involves an additional transported scalar variable are constructed by augmenting the single-particle dynamics and phase space to include the relevant additional variable
-
MULTISCALE DYNAMICS OF SOLAR MAGNETIC STRUCTURES
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Uritsky, Vadim M.; Davila, Joseph M.
2012-01-01
Multiscale topological complexity of the solar magnetic field is among the primary factors controlling energy release in the corona, including associated processes in the photospheric and chromospheric boundaries. We present a new approach for analyzing multiscale behavior of the photospheric magnetic flux underlying these dynamics as depicted by a sequence of high-resolution solar magnetograms. The approach involves two basic processing steps: (1) identification of timing and location of magnetic flux origin and demise events (as defined by DeForest et al.) by tracking spatiotemporal evolution of unipolar and bipolar photospheric regions, and (2) analysis of collective behavior of the detected magnetic events using a generalized version of the Grassberger-Procaccia correlation integral algorithm. The scale-free nature of the developed algorithms makes it possible to characterize the dynamics of the photospheric network across a wide range of distances and relaxation times. Three types of photospheric conditions are considered to test the method: a quiet photosphere, a solar active region (NOAA 10365) in a quiescent non-flaring state, and the same active region during a period of M-class flares. The results obtained show (1) the presence of a topologically complex asymmetrically fragmented magnetic network in the quiet photosphere driven by meso- and supergranulation, (2) the formation of non-potential magnetic structures with complex polarity separation lines inside the active region, and (3) statistical signatures of canceling bipolar magnetic structures coinciding with flaring activity in the active region. Each of these effects can represent an unstable magnetic configuration acting as an energy source for coronal dissipation and heating.
-
Preliminary results on the dynamics of large and flexible space structures in Halo orbits
Colagrossi, Andrea; Lavagna, Michèle
2017-05-01
The global exploration roadmap suggests, among other ambitious future space programmes, a possible manned outpost in lunar vicinity, to support surface operations and further astronaut training for longer and deeper space missions and transfers. In particular, a Lagrangian point orbit location - in the Earth- Moon system - is suggested for a manned cis-lunar infrastructure; proposal which opens an interesting field of study from the astrodynamics perspective. Literature offers a wide set of scientific research done on orbital dynamics under the Three-Body Problem modelling approach, while less of it includes the attitude dynamics modelling as well. However, whenever a large space structure (ISS-like) is considered, not only the coupled orbit-attitude dynamics should be modelled to run more accurate analyses, but the structural flexibility should be included too. The paper, starting from the well-known Circular Restricted Three-Body Problem formulation, presents some preliminary results obtained by adding a coupled orbit-attitude dynamical model and the effects due to the large structure flexibility. In addition, the most relevant perturbing phenomena, such as the Solar Radiation Pressure (SRP) and the fourth-body (Sun) gravity, are included in the model as well. A multi-body approach has been preferred to represent possible configurations of the large cis-lunar infrastructure: interconnected simple structural elements - such as beams, rods or lumped masses linked by springs - build up the space segment. To better investigate the relevance of the flexibility effects, the lumped parameters approach is compared with a distributed parameters semi-analytical technique. A sensitivity analysis of system dynamics, with respect to different configurations and mechanical properties of the extended structure, is also presented, in order to highlight drivers for the lunar outpost design. Furthermore, a case study for a large and flexible space structure in Halo orbits around
-
Solar Pumped High Power Solid State Laser for Space Applications
Fork, Richard L.; Laycock, Rustin L.; Green, Jason J. A.; Walker, Wesley W.; Cole, Spencer T.; Frederick, Kevin B.; Phillips, Dane J.
2004-01-01
Highly coherent laser light provides a nearly optimal means of transmitting power in space. The simplest most direct means of converting sunlight to coherent laser light is a solar pumped laser oscillator. A key need for broadly useful space solar power is a robust solid state laser oscillator capable of operating efficiently in near Earth space at output powers in the multi hundred kilowatt range. The principal challenges in realizing such solar pumped laser oscillators are: (1) the need to remove heat from the solid state laser material without introducing unacceptable thermal shock, thermal lensing, or thermal stress induced birefringence to a degree that improves on current removal rates by several orders of magnitude and (2) to introduce sunlight at an effective concentration (kW/sq cm of laser cross sectional area) that is several orders of magnitude higher than currently available while tolerating a pointing error of the spacecraft of several degrees. We discuss strategies for addressing these challenges. The need to remove the high densities of heat, e.g., 30 kW/cu cm, while keeping the thermal shock, thermal lensing and thermal stress induced birefringence loss sufficiently low is addressed in terms of a novel use of diamond integrated with the laser material, such as Ti:sapphire in a manner such that the waste heat is removed from the laser medium in an axial direction and in the diamond in a radial direction. We discuss means for concentrating sunlight to an effective areal density of the order of 30 kW/sq cm. The method integrates conventional imaging optics, non-imaging optics and nonlinear optics. In effect we use a method that combines some of the methods of optical pumping solid state materials and optical fiber, but also address laser media having areas sufficiently large, e.g., 1 cm diameter to handle the multi-hundred kilowatt level powers needed for space solar power.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Deng, Jie; Tian, Zhiyong; Fan, Jianhua
2016-01-01
A pilot project of the solar water heating system combined with a low temperature air source heat pump (ASHP) unit was established in 2014 in a detached residential house in the rural region of Beijing, in order to investigate the system application prospect for single family houses via system...... optimization design and economic analysis. The established system was comprised of the glass heat-pipe based evacuated tube solar collectors with a gross area of 18.8 m2 and an ASHP with a stated heating power of 8 kW for the space heating of a single family rural house of 81.4 m2. The dynamic thermal...... with good building insulation were undertaken to figure out the system economical efficiency in the rural regions of Beijing. The results show that the payback periods of the solar space heating system combined with the ASHP with the collector areas 15.04-22.56 m2 are 17.3-22.4 years for the established...
-
Analysis of Energy Efficiency in Dynamic Optical Networks Employing Solar Energy Sources
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Wang, Jiayuan; Fagertun, Anna Manolova; Ruepp, Sarah Renée
2013-01-01
The paper presents energy efficient routing in dynamic optical networks, where solar energy sources are employed for the network nodes. Different parameters are evaluated, including the number of nodes that have access to solar energy sources, the different maximum solar output power, traffic type...... and the locations of solar powered nodes. Results show a maximum 39% savings in energy consumption with different increases in connection blocking probability....
-
Ho, D.; Sobon, L. E.
1979-01-01
A conceptual design is presented for fiberglass production systems in both lunar and space environments. The raw material, of lunar origin, will be plagioclase concentrate, high silica content slag, and calcium oxide. Glass will be melted by solar energy. The multifurnace in the lunar plant and the spinning cylinder in the space plant are unique design features. Furnace design appears to be the most critical element in optimizing system performance. A conservative estimate of the total power generated by solar concentrators is 1880 kW; the mass of both plants is 120 tons. The systems will reproduce about 90 times their total mass in fiberglass in 1 year. A new design concept would be necessary if glass rods were produced in space.
-
Dynamic Characterization of an Inflatable Concentrator for Solar Thermal Propulsion
Leigh, Larry; Hamidzadeh, Hamid; Tinker, Michael L.; Rodriguez, Pedro I. (Technical Monitor)
2001-01-01
An inflatable structural system that is a technology demonstrator for solar thermal propulsion and other applications is characterized for structural dynamic behavior both experimentally and computationally. The inflatable structure is a pressurized assembly developed for use in orbit to support a Fresnel lens or inflatable lenticular element for focusing sunlight into a solar thermal rocket engine. When the engine temperature reaches a pre-set level, the propellant is injected into the engine, absorbs heat from an exchanger, and is expanded through the nozzle to produce thrust. The inflatable structure is a passively adaptive system in that a regulator and relief valve are utilized to maintain pressure within design limits during the full range of orbital conditions. Modeling and test activities are complicated by the fact that the polyimide film material used for construction of the inflatable is nonlinear, with modulus varying as a function of frequency, temperature, and level of excitation. Modal vibration testing and finite element modeling are described in detail in this paper. The test database is used for validation and modification of the model. This work is highly significant because of the current interest in inflatable structures for space application, and because of the difficulty in accurately modeling such systems.
-
Henley, M. W.; Fikes, J. C.; Howell, J.; Mankins, J. C.; Howell, Joe T. (Technical Monitor)
2002-01-01
Space Solar Power technology offers unique benefits for near-term NASA space science missions, which can mature this technology for other future applications. "Laser-Photo-Voltaic Wireless Power Transmission" (Laser-PV WPT) is a technology that uses a laser to beam power to a photovoltaic receiver, which converts the laser's light into electricity. Future Laser-PV WPT systems may beam power from Earth to satellites or large Space Solar Power satellites may beam power to Earth, perhaps supplementing terrestrial solar photo-voltaic receivers. In a near-term scientific mission to the moon, Laser-PV WPT can enable robotic operations in permanently shadowed lunar polar craters, which may contain ice. Ground-based technology demonstrations are proceeding, to mature the technology for this initial application, in the moon's polar regions.
-
Solar Dynamic Power System Stability Analysis and Control
Momoh, James A.; Wang, Yanchun
1996-01-01
The objective of this research is to conduct dynamic analysis, control design, and control performance test of solar power system. Solar power system consists of generation system and distribution network system. A bench mark system is used in this research, which includes a generator with excitation system and governor, an ac/dc converter, six DDCU's and forty-eight loads. A detailed model is used for modeling generator. Excitation system is represented by a third order model. DDCU is represented by a seventh order system. The load is modeled by the combination of constant power and constant impedance. Eigen-analysis and eigen-sensitivity analysis are used for system dynamic analysis. The effects of excitation system, governor, ac/dc converter control, and the type of load on system stability are discussed. In order to improve system transient stability, nonlinear ac/dc converter control is introduced. The direct linearization method is used for control design. The dynamic analysis results show that these controls affect system stability in different ways. The parameter coordination of controllers are recommended based on the dynamic analysis. It is concluded from the present studies that system stability is improved by the coordination of control parameters and the nonlinear ac/dc converter control stabilize system oscillation caused by the load change and system fault efficiently.
-
Prey-predator dynamics driven by the solar radiation - Part 1
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sertorio, L.
2000-01-01
In this paper is studied a model ecosystem represented by two components: prey and predator. The predator feeds only on the prey, the prey, in turn, feeds on the solar radiation. In this scheme the two-species dynamics is no longer independent of the external physical conditions. Such independence was instead postulated in the Lotka-Volterra scheme. In this paper is considered the growth of the prey not unbounded (exponential), but logistic, where the saturation factor is governed by the available solar flux, more precisely by the percent of the solar flux that contains the photon frequencies which can drive the photosynthesis. In this way the solar flux represents the driving term of the dynamics, as it is expected in general for a realistic ecosystem. The system is asymptotically stable. The equilibrium values of the prey and predator numbers depend on several parameters. The system contains two nonlinear coupling terms and two coupling parameters. The dependence of the equilibrium point on the coupling parameters is studied in detail. According to this model, it can be defined a predator efficiency and a global solar efficiency. It is discussed the relationship between these two functions of the coupling parameters and the maximum value that the predator population can reach
-
Chaos of discrete dynamical systems in complete metric spaces
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shi Yuming; Chen Guanrong
2004-01-01
This paper is concerned with chaos of discrete dynamical systems in complete metric spaces. Discrete dynamical systems governed by continuous maps in general complete metric spaces are first discussed, and two criteria of chaos are then established. As a special case, two corresponding criteria of chaos for discrete dynamical systems in compact subsets of metric spaces are obtained. These results have extended and improved the existing relevant results of chaos in finite-dimensional Euclidean spaces
-
Correlation tracking study for meter-class solar telescope on space shuttle. [solar granulation
Smithson, R. C.; Tarbell, T. D.
1977-01-01
The theory and expected performance level of correlation trackers used to control the pointing of a solar telescope in space using white light granulation as a target were studied. Three specific trackers were modeled and their performance levels predicted for telescopes of various apertures. The performance of the computer model trackers on computer enhanced granulation photographs was evaluated. Parametric equations for predicting tracker performance are presented.
-
Real-time dynamic analysis for complete loop of direct steam generation solar trough collector
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Guo, Su; Liu, Deyou; Chu, Yinghao; Chen, Xingying; Shen, Bingbing; Xu, Chang; Zhou, Ling; Wang, Pei
2016-01-01
Highlights: • A nonlinear distribution parameter dynamic model has been developed. • Real-time local heat transfer coefficient and friction coefficient are adopted. • The dynamic behavior of the solar trough collector loop are simulated. • High-frequency chattering of outlet fluid flow are analyzed and modeled. • Irradiance disturbance at subcooled water region generates larger influence. - Abstract: Direct steam generation is a potential approach to further reduce the levelized electricity cost of solar trough. Dynamic modeling of the collector loop is essential for operation and control of direct steam generation solar trough. However, the dynamic behavior of fluid based on direct steam generation is complex because of the two-phase flow in the pipeline. In this work, a nonlinear distribution parameter model has been developed to model the dynamic behaviors of direct steam generation parabolic trough collector loops under either full or partial solar irradiance disturbance. Compared with available dynamic model, the proposed model possesses two advantages: (1) real-time local values of heat transfer coefficient and friction resistance coefficient, and (2) considering of the complete loop of collectors, including subcooled water region, two-phase flow region and superheated steam region. The proposed model has shown superior performance, particularly in case of sensitivity study of fluid parameters when the pipe is partially shaded. The proposed model has been validated using experimental data from Solar Thermal Energy Laboratory of University of New South Wales, with an outlet fluid temperature relative error of only 1.91%. The validation results show that: (1) The proposed model successfully outperforms two reference models in predicting the behavior of direct steam generation solar trough. (2) The model theoretically predicts that, during solar irradiance disturbance, the discontinuities of fluid physical property parameters and the moving back and
-
EUV imager and spectrometer for LYOT and solar orbiter space missions
Millard, Anne; Lemaire, Philippe; Vial, Jean-Claude
2017-11-01
In the 2010 horizon, solar space missions such as LYOT and Solar Orbiter will allow high cadence UV observations of the Sun at spatial and spectral resolution never obtained before. To reach these goals, the two missions could take advantage of spectro-imagers. A reflective only optical solution for such an instrument is described in this paper and the first results of the mock-up being built at IAS are shown.
-
A parametric study of a solar calcinator using computational fluid dynamics
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fidaros, D.K.; Baxevanou, C.A.; Vlachos, N.S.
2007-01-01
In this work a horizontal rotating solar calcinator is studied numerically using computational fluid dynamics. The specific solar reactor is a 10 kW model designed and used for efficiency studies. The numerical model is based on the solution of the Navier-Stokes equations for the gas flow, and on Lagrangean dynamics for the discrete particles. All necessary mathematical models were developed and incorporated into a computational fluid dynamics model with the influence of turbulence simulated by a two-equation (RNG k-ε) model. The efficiency of the reactor was calculated for different thermal inputs, feed rates, rotational speeds and particle diameters. The numerically computed degrees of calcination compared well with equivalent experimental results
-
Evolutionary dynamics on infinite strategy spaces
Oechssler, Jörg; Riedel, Frank
1998-01-01
The study of evolutionary dynamics was so far mainly restricted to finite strategy spaces. In this paper we show that this unsatisfying restriction is unnecessary. We specify a simple condition under which the continuous time replicator dynamics are well defined for the case of infinite strategy spaces. Furthermore, we provide new conditions for the stability of rest points and show that even strict equilibria may be unstable. Finally, we apply this general theory to a number of applications ...
-
Dynamics and control of a solar collector system for near Earth object deflection
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gong Shenping; Li Junfeng; Gao Yunfeng
2011-01-01
A solar collector system is a possible method using solar energy to deflect Earth-threatening near-Earth objects. We investigate the dynamics and control of a solar collector system including a main collector (MC) and secondary collector (SC). The MC is used to collect the sunlight to its focal point, where the SC is placed and directs the collected light to an asteroid. Both the relative position and attitude of the two collectors should be accurately controlled to achieve the desired optical path. First, the dynamical equation of the relative motion of the two collectors in the vicinity of the asteroid is modeled. Secondly, the nonlinear sliding-mode method is employed to design a control law to achieve the desired configuration of the two collectors. Finally, the deflection capability of this solar collector system is compared with those of the gravitational tractor and solar sail gravitational tractor. The results show that the solar collector is much more efficient with respect to deflection capability.
-
Landis, Geoffrey A.; Bailey, Sheila G.; Jenkins, Phillip; Sexton, J. Andrew; Scheiman, David; Christie, Robert; Charpie, James; Gerber, Scott S.; Johnson, D. Bruce
2001-01-01
The Photovoltaic Engineering Testbed ("PET") is a facility to be flown on the International Space Station to perform calibration, measurement, and qualification of solar cells in the space environment and then returning the cells to Earth for laboratory use. PET will allow rapid turnaround testing of new photovoltaic technology under AM0 conditions.
-
CORONAL DYNAMIC ACTIVITIES IN THE DECLINING PHASE OF A SOLAR CYCLE
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jang, Minhwan; Choe, G. S. [Department of Astronomy and Space Science, Kyung Hee University, Yongin 17104 (Korea, Republic of); Woods, T. N. [Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80303 (United States); Hong, Sunhak, E-mail: gchoe@khu.ac.kr [School of Space Research, Kyung Hee University, Yongin 17104 (Korea, Republic of)
2016-12-10
It has been known that some solar activity indicators show a double-peak feature in their evolution through a solar cycle, which is not conspicuous in sunspot number. In this Letter, we investigate the high solar dynamic activity in the declining phase of the sunspot cycle by examining the evolution of polar and low-latitude coronal hole (CH) areas, splitting and merging events of CHs, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) detected by SOHO /LASCO C3 in solar cycle 23. Although the total CH area is at its maximum near the sunspot minimum, in which polar CHs prevail, it shows a comparable second maximum in the declining phase of the cycle, in which low-latitude CHs are dominant. The events of CH splitting or merging, which are attributed to surface motions of magnetic fluxes, are also mostly populated in the declining phase of the cycle. The far-reaching C3 CMEs are also overpopulated in the declining phase of the cycle. From these results we suggest that solar dynamic activities due to the horizontal surface motions of magnetic fluxes extend far in the declining phase of the sunspot cycle.
-
CORONAL DYNAMIC ACTIVITIES IN THE DECLINING PHASE OF A SOLAR CYCLE
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jang, Minhwan; Choe, G. S.; Woods, T. N.; Hong, Sunhak
2016-01-01
It has been known that some solar activity indicators show a double-peak feature in their evolution through a solar cycle, which is not conspicuous in sunspot number. In this Letter, we investigate the high solar dynamic activity in the declining phase of the sunspot cycle by examining the evolution of polar and low-latitude coronal hole (CH) areas, splitting and merging events of CHs, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) detected by SOHO /LASCO C3 in solar cycle 23. Although the total CH area is at its maximum near the sunspot minimum, in which polar CHs prevail, it shows a comparable second maximum in the declining phase of the cycle, in which low-latitude CHs are dominant. The events of CH splitting or merging, which are attributed to surface motions of magnetic fluxes, are also mostly populated in the declining phase of the cycle. The far-reaching C3 CMEs are also overpopulated in the declining phase of the cycle. From these results we suggest that solar dynamic activities due to the horizontal surface motions of magnetic fluxes extend far in the declining phase of the sunspot cycle.
-
The Effects of Solar Maximum on the Earth's Satellite Population and Space Situational Awareness
Johnson, Nicholas L.
2012-01-01
The rapidly approaching maximum of Solar Cycle 24 will have wide-ranging effects not only on the number and distribution of resident space objects, but also on vital aspects of space situational awareness, including conjunction assessment processes. The best known consequence of high solar activity is an increase in the density of the thermosphere, which, in turn, increases drag on the vast majority of objects in low Earth orbit. The most prominent evidence of this is seen in a dramatic increase in space object reentries. Due to the massive amounts of new debris created by the fragmentations of Fengyun-1C, Cosmos 2251 and Iridium 33 during the recent period of Solar Minimum, this effect might reach epic levels. However, space surveillance systems are also affected, both directly and indirectly, historically leading to an increase in the number of lost satellites and in the routine accuracy of the calculation of their orbits. Thus, at a time when more objects are drifting through regions containing exceptionally high-value assets, such as the International Space Station and remote sensing satellites, their position uncertainties increase. In other words, as the possibility of damaging and catastrophic collisions increases, our ability to protect space systems is degraded. Potential countermeasures include adjustments to space surveillance techniques and the resetting of collision avoidance maneuver thresholds.
-
Effect of solar wind plasma parameters on space weather
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rathore, Balveer S.; Gupta, Dinesh C.; Kaushik, Subhash C.
2015-01-01
Today's challenge for space weather research is to quantitatively predict the dynamics of the magnetosphere from measured solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) conditions. Correlative studies between geomagnetic storms (GMSs) and the various interplanetary (IP) field/plasma parameters have been performed to search for the causes of geomagnetic activity and develop models for predicting the occurrence of GMSs, which are important for space weather predictions. We find a possible relation between GMSs and solar wind and IMF parameters in three different situations and also derived the linear relation for all parameters in three situations. On the basis of the present statistical study, we develop an empirical model. With the help of this model, we can predict all categories of GMSs. This model is based on the following fact: the total IMF B total can be used to trigger an alarm for GMSs, when sudden changes in total magnetic field B total occur. This is the first alarm condition for a storm's arrival. It is observed in the present study that the southward B z component of the IMF is an important factor for describing GMSs. A result of the paper is that the magnitude of B z is maximum neither during the initial phase (at the instant of the IP shock) nor during the main phase (at the instant of Disturbance storm time (Dst) minimum). It is seen in this study that there is a time delay between the maximum value of southward B z and the Dst minimum, and this time delay can be used in the prediction of the intensity of a magnetic storm two-three hours before the main phase of a GMS. A linear relation has been derived between the maximum value of the southward component of B z and the Dst, which is Dst = (−0.06) + (7.65) B z +t. Some auxiliary conditions should be fulfilled with this, for example the speed of the solar wind should, on average, be 350 km s −1 to 750 km s −1 , plasma β should be low and, most importantly, plasma temperature
-
Theory and Simulations of Solar System Plasmas
Goldstein, Melvyn L.
2011-01-01
"Theory and simulations of solar system plasmas" aims to highlight results from microscopic to global scales, achieved by theoretical investigations and numerical simulations of the plasma dynamics in the solar system. The theoretical approach must allow evidencing the universality of the phenomena being considered, whatever the region is where their role is studied; at the Sun, in the solar corona, in the interplanetary space or in planetary magnetospheres. All possible theoretical issues concerning plasma dynamics are welcome, especially those using numerical models and simulations, since these tools are mandatory whenever analytical treatments fail, in particular when complex nonlinear phenomena are at work. Comparative studies for ongoing missions like Cassini, Cluster, Demeter, Stereo, Wind, SDO, Hinode, as well as those preparing future missions and proposals, like, e.g., MMS and Solar Orbiter, are especially encouraged.
-
NASA Glenn Research Center Solar Cell Experiment Onboard the International Space Station
Myers, Matthew G.; Wolford, David S.; Prokop, Norman F.; Krasowski, Michael J.; Parker, David S.; Cassidy, Justin C.; Davies , William E.; Vorreiter, Janelle O.; Piszczor, Michael F.; Mcnatt, Jeremiah S.;

2016-01-01
Accurate air mass zero (AM0) measurement is essential for the evaluation of new photovoltaic (PV) technology for space solar cells. The NASA Glenn Research Center (GRC) has flown an experiment designed to measure the electrical performance of several solar cells onboard NASA Goddard Space Flight Center's (GSFC) Robotic Refueling Missions (RRM) Task Board 4 (TB4) on the exterior of the International Space Station (ISS). Four industry and government partners provided advanced PV devices for measurement and orbital environment testing. The experiment was positioned on the exterior of the station for approximately eight months, and was completely self-contained, providing its own power and internal data storage. Several new cell technologies including four-junction (4J) Inverted Metamorphic Multi-junction (IMM) cells were evaluated and the results will be compared to ground-based measurement methods.
-
Smirnova, Olga A; Cucinotta, Francis A
2018-02-01
A recently developed biologically motivated dynamical model of the assessment of the excess relative risk (ERR) for radiogenic leukemia among acutely/continuously irradiated humans (Smirnova, 2015, 2017) is applied to estimate the ERR for radiogenic leukemia among astronauts engaged in long-term interplanetary space missions. Numerous scenarios of space radiation exposure during space missions are used in the modeling studies. The dependence of the ERR for leukemia among astronauts on several mission parameters including the dose equivalent rates of galactic cosmic rays (GCR) and large solar particle events (SPEs), the number of large SPEs, the time interval between SPEs, mission duration, the degree of astronaut's additional shielding during SPEs, the degree of their additional 12-hour's daily shielding, as well as the total mission dose equivalent, is examined. The results of the estimation of ERR for radiogenic leukemia among astronauts, which are obtained in the framework of the developed dynamical model for various scenarios of space radiation exposure, are compared with the corresponding results, computed by the commonly used linear model. It is revealed that the developed dynamical model along with the linear model can be applied to estimate ERR for radiogenic leukemia among astronauts engaged in long-term interplanetary space missions in the range of applicability of the latter. In turn, the developed dynamical model is capable of predicting the ERR for leukemia among astronauts for the irradiation regimes beyond the applicability range of the linear model in emergency cases. As a supplement to the estimations of cancer incidence and death (REIC and REID) (Cucinotta et al., 2013, 2017), the developed dynamical model for the assessment of the ERR for leukemia can be employed on the pre-mission design phase for, e.g., the optimization of the regimes of astronaut's additional shielding in the course of interplanetary space missions. The developed model can
-
Monitoring of the solar activity and solar energetic particles
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Akioka, Maki; Kubo, Yuki; Nagatsuma, Tsutomu; Ohtaka, Kazuhiro
2009-01-01
Solar activity is the source of various space weather phenomena in geospace and deep space. Solar X-ray radiation in flare, energetic particles, coronal mass ejection (CME) can cause various kind of disturbance near earth space. Therefore, detailed monitoring of the solar activity and its propagation in the interplanetary space is essential task for space weather. For example, solar energetic particle which sometimes affect spacecraft operation and manned space flight, is considered to be produced by solar flares and travelling shockwave caused by flares and CME. The research and development of monitoring technique and system for various solar activity has been an important topic of space weather forecast program in NICT. In this article, we will introduce the real time data acquisitions of STEREO and optical and radio observations of the Sun at Hiraiso Solar Observatory. (author)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Thomas R. Rimmele
2011-06-01
Full Text Available Adaptive optics (AO has become an indispensable tool at ground-based solar telescopes. AO enables the ground-based observer to overcome the adverse effects of atmospheric seeing and obtain diffraction limited observations. Over the last decade adaptive optics systems have been deployed at major ground-based solar telescopes and revitalized ground-based solar astronomy. The relatively small aperture of solar telescopes and the bright source make solar AO possible for visible wavelengths where the majority of solar observations are still performed. Solar AO systems enable diffraction limited observations of the Sun for a significant fraction of the available observing time at ground-based solar telescopes, which often have a larger aperture than equivalent space based observatories, such as HINODE. New ground breaking scientific results have been achieved with solar adaptive optics and this trend continues. New large aperture telescopes are currently being deployed or are under construction. With the aid of solar AO these telescopes will obtain observations of the highly structured and dynamic solar atmosphere with unprecedented resolution. This paper reviews solar adaptive optics techniques and summarizes the recent progress in the field of solar adaptive optics. An outlook to future solar AO developments, including a discussion of Multi-Conjugate AO (MCAO and Ground-Layer AO (GLAO will be given.
-
200W Deep Space CubeSat Composite Beam Roll-Up Solar Array (COBRA), Phase II
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — Solar arrays that have very high specific power (W/kg) and compact stowed volume (W/m3), while still providing shielding to the solar cell, are an enabling...
-
200W Deep Space CubeSat Composite Beam Roll-Up Solar Array (COBRA), Phase I
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — Solar arrays that have very high specific power (W/kg) and compact stowed volume (W/m3), while still providing shielding to the solar cell, are an enabling...
-
Dynamic modeling and sensitivity analysis of solar thermal energy conversion systems
Hamilton, C. L.
1977-01-01
Since the energy input to solar thermal conversion systems is both time variant and probabilistic, it is unlikely that simple steady-state methods for estimating lifetime performance will provide satisfactory results. The work described here uses dynamic modeling to begin identifying what must be known about input radiation and system dynamic characteristics to estimate performance reliably. Daily operation of two conceptual solar energy systems was simulated under varying operating strategies with time-dependent radiation intensity ranging from smooth input of several magnitudes to input of constant total energy whose intensity oscillated with periods from 1/4 hour to 6 hours. Integrated daily system output and efficiency were functions of both level and dynamic characteristics of insolation. Sensitivity of output to changes in total input was greater than one.
-
Dynamics of Intense Currents in the Solar Wind
Artemyev, Anton V.; Angelopoulos, Vassilis; Halekas, Jasper S.; Vinogradov, Alexander A.; Vasko, Ivan Y.; Zelenyi, Lev M.
2018-06-01
Transient currents in the solar wind are carried by various magnetic field discontinuities that contribute significantly to the magnetic field fluctuation spectrum. Internal instabilities and dynamics of these discontinuities are believed to be responsible for magnetic field energy dissipation and corresponding charged particle acceleration and heating. Accurate modeling of these phenomena requires detailed investigation of transient current formation and evolution. By examining such evolution using a unique data set compiled from observations of the same solar wind flow by two spacecraft at Earth’s and Mars’s orbits, we show that it consists of several processes: discontinuity thinning (decrease in thickness normalized by the ion inertial length), intensification of currents normalized to the proton thermal current (i.e., the product of proton charge, density, and thermal velocity), and increase in the compressional component of magnetic field variations across discontinuities. The significant proton temperature variation around most observed discontinuities indicates possible proton heating. Plasma velocity jumps across the discontinuities are well correlated with Alfvén velocity changes. We discuss possible explanations of the observed discontinuity evolution. We also compare the observed evolution with predictions of models describing discontinuity formation due to Alfvén wave steepening. Our results show that discontinuity modeling likely requires taking into account both the effects of nonlinear Alfvén wave dynamics and solar wind expansion.
-
Study of the Most Harmful Solar Energetic Particle for Shielding next Human Space Flights
Komei Yamashiro, Bryan
2015-04-01
Solar energetic particles (SEPs) accelerated by solar events such as flares and coronal mass ejections are radiation risks for humans in space on board the International Space Station (ISS), and will be significant obstacles for future long-duration manned space flight missions. This research supported efforts to improve predictions of large solar storms and aimed for a better understanding of Heliophysics. The main objective was to generate a dated catalog of the highest energy range SEPs measured by the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS-02). Using online graphical user interfaces from the satellites, Solar and Heliospeheric Observatory (SOHO) and Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-13, 15), the generated data files from the mounted particle detectors were plotted along a specified energy range. The resulting histograms illustrated the low energy range data from SOHO (4 MeV to 53 MeV) and the low-mid energy range from GOES (0.8 MeV to 500 MeV), which collectively provided a low- to mid-energy range spectrum of the specific event energy ranges versus the SEP proton flux. The high energy range results of the AMS-02 (125 MeV to a few TeV) will eventually be incorporated with the two alternative space satellites of lower energy ranges for a complete analysis across a full SEP energy range. X-ray flux from GOES-15 were then obtained and plotted with the corresponding time to portray initial phenomena of the solar events. This procedure was reproduced for 5 different events determined energetic enough to be measured by AMS-02. The generated plots showed correlation between the different satellite detectors.
-
Johnson, Les
2009-01-01
Solar sailing is a topic of growing technical and popular interest. Solar sail propulsion will make space exploration more affordable and offer access to destinations within (and beyond) the solar system that are currently beyond our technical reach. The lecture will describe solar sails, how they work, and what they will be used for in the exploration of space. It will include a discussion of current plans for solar sails and how advanced technology, such as nanotechnology, might enhance their performance. Much has been accomplished recently to make solar sail technology very close to becoming an engineering reality and it will soon be used by the world s space agencies in the exploration of the solar system and beyond. The first part of the lecture will summarize state-of-the-art space propulsion systems and technologies. Though these other technologies are the key to any deep space exploration by humans, robots, or both, solar-sail propulsion will make space exploration more affordable and offer access to distant and difficult destinations. The second part of the lecture will describe the fundamentals of space solar sail propulsion and will describe the near-, mid- and far-term missions that might use solar sails as a propulsion system. The third part of the lecture will describe solar sail technology and the construction of current and future sailcraft, including the work of both government and private space organizations.
-
Hardage, Donna (Technical Monitor); Walters, R. J.; Morton, T. L.; Messenger, S. R.
2004-01-01
The objective is to develop an improved space solar cell radiation response analysis capability and to produce a computer modeling tool which implements the analysis. This was accomplished through analysis of solar cell flight data taken on the Microelectronics and Photonics Test Bed experiment. This effort specifically addresses issues related to rapid technological change in the area of solar cells for space applications in order to enhance system performance, decrease risk, and reduce cost for future missions.
-
Overview of NASA's Space Solar Power Technology Advanced Research and Development Program
Howell, Joe; Mankins, John C.; Davis, N. Jan (Technical Monitor)
2001-01-01
Large solar power satellite (SPS) systems that might provide base load power into terrestrial markets were examined extensively in the 1970s by the US Department of Energy (DOE) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Following a hiatus of about 15 years, the subject of space solar power (SSP) was reexamined by NASA from 1995-1997 in the 'fresh look' study, and during 1998 in an SSP 'concept definition study', and during 1999-2000 in the SSP Exploratory Research and Technology (SERT) program. As a result of these efforts, during 2001, NASA has initiated the SSP Technology Advanced Research and Development (STAR-Dev) program based on informed decisions. The goal of the STAR-Dev program is to conduct preliminary strategic technology research and development to enable large, multi-megawatt to gigawatt-class space solar power (SSP) systems and wireless power transmission (WPT) for government missions and commercial markets (in-space and terrestrial). Specific objectives include: (1) Release a NASA Research Announcement (NRA) for SSP Projects; (2) Conduct systems studies; (3) Develop Component Technologies; (4) Develop Ground and Flight demonstration systems; and (5) Assess and/or Initiate Partnerships. Accomplishing these objectives will allow informed future decisions regarding further SSP and related research and development investments by both NASA management and prospective external partners. In particular, accomplishing these objectives will also guide further definition of SSP and related technology roadmaps including performance objectives, resources and schedules; including 'multi-purpose' applications (commercial, science, and other government).
-
Simulating Nonlinear Dynamics of Deployable Space Structures, Phase I
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — To support NASA's vital interest in developing much larger solar array structures over the next 20 years, MotionPort LLC's Phase I SBIR project will strengthen...
-
Early, Derrick A.; Haile, William B.; Turczyn, Mark T.; Griffin, Thomas J. (Technical Monitor)
2001-01-01
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) conducted a disturbance verification test on a flight Solar Array 3 (SA3) for the Hubble Space Telescope using the ESA Large Space Simulator (LSS) in Noordwijk, the Netherlands. The LSS cyclically illuminated the SA3 to simulate orbital temperature changes in a vacuum environment. Data acquisition systems measured signals from force transducers and accelerometers resulting from thermally induced vibrations of the SAI The LSS with its seismic mass boundary provided an excellent background environment for this test. This paper discusses the analysis performed on the measured transient SA3 responses and provides a summary of the results.
-
Space-Based Solar Power: A Technical, Economic, and Operational Assessment
2015-04-01
design concept for SBSP systems. Results from the research and develop- ment of individual components and subsystems could fill libraries , but from this...Solar Power System: A Business Plan to Make Space So- lar Power a Reality,” A Multicultural Team Project for Master of Business Administration in
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Khrennikov, A.
2005-01-01
We constructed the representation of contextual probabilistic dynamics in the complex Hilbert space. Thus dynamics of the wave function can be considered as Hilbert space projection of realistic dynamics in a pre space. The basic condition for representing the pre space-dynamics is the law of statistical conservation of energy-conservation of probabilities. The construction of the dynamical representation is an important step in the development of contextual statistical viewpoint of quantum processes. But the contextual statistical model is essentially more general than the quantum one. Therefore in general the Hilbert space projection of the pre space dynamics can be nonlinear and even irreversible (but it is always unitary). There were found conditions of linearity and reversibility of the Hilbert space dynamical projection. We also found conditions for the conventional Schrodinger dynamics (including time-dependent Hamiltonians). We remark that in general even the Schrodinger dynamics is based just on the statistical conservation of energy; for individual systems the law of conservation of energy can be violated (at least in our theoretical model)
-
Smull, Neil A.; Armstrong, Gerald L.
1979-01-01
Amity Elementary School in Boise, Idaho, features a solar space heating and domestic hot water system along with an earth covering to accommodate the passive aspects of energy conservation. (Author/MLF)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zhao Dawei
2016-01-01
Full Text Available In recent years, a significant number of large-scale solar photovoltaic (PV plants have been put into operation or been under planning around the world. The model accuracy of solar PV plant is the key factor to investigate the mutual influences between solar PV plants and a power grid. However, this problem has not been well solved, especially in how to apply the real measurements to validate the models of the solar PV plants. Taking fast-responding generator method as an example, this paper presents a model validation methodology for solar PV plant via the hybrid data dynamic simulation. First, the implementation scheme of hybrid data dynamic simulation suitable for DIgSILENT PowerFactory software is proposed, and then an analysis model of solar PV plant integration based on IEEE 9 system is established. At last, model validation of solar PV plant is achieved by employing hybrid data dynamic simulation. The results illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in solar PV plant model validation.
-
ICARUS Mission, Next Step of Coronal Exploration after Solar Orbiter and Solar Probe Plus
Krasnoselskikh, V.; Tsurutani, B.; Velli, M.; Maksimovic, M.; Balikhin, M. A.; Dudok de Wit, T.; Kretzschmar, M.
2017-12-01
The primary scientific goal of ICARUS, a mother-daughter satellite mission, will be to determine how the magnetic field and plasma dynamics in the outer solar atmosphere give rise to the corona, the solar wind and the heliosphere. Reaching this goal will be a Rosetta-stone step, with results broadly applicable in the fields of space plasma and astrophysics. Within ESA's Cosmic Vision roadmap, these goals address Theme 2: How does the solar system work ?" Investigating basic processes occurring from the Sun to the edge of the Solar System". ICARUS will not only advance our understanding of the plasma environment around the Sun, but also of the numerous magnetically active stars with hot plasma coronae. ICARUS I will perform the firstever direct in situ measurements of electromagnetic fields, particle acceleration, wave activity, energy distribution and flows directly in the regions where the solar wind emerges from the coronal plasma. ICARUS I will have a perihelion at 1 Solar radius from its surface, it will cross the region where the major energy deposition occurs. The polar orbit of ICARUS I will enable crossing the regions where both the fast and slow wind are generated. It will probe local characteristics of the plasma and provide unique information about the processes involved in the creation of the solar wind. ICARUS II will observe this region using remote-sensing instruments, providing simultaneous information about regions crossed by ICARUS I and the solar atmosphere below as observed by solar telescopes. It will provide bridges for understanding the magnetic links between heliosphere and solar atmosphere. Such information is crucial to understanding of the physics and electrodynamics of the solar atmosphere. ICARUS II will also play an important relay role, enabling the radio-link with ICARUS I. It will receive, collect and store information transmitted from ICARUS I during its closest approach to the Sun. It will perform preliminary data processing and
-
Orientation of Space Station Freedom electrical power system in environmental effects assessment
Lu, Cheng-Yi
1990-01-01
The orientation effects of six Space Station Freedom Electrical Power System (EPS) components are evaluated for three environmental interactions: aerodynamic drag, atomic oxygen erosion, and orbital debris impact. Designers can directly apply these orientation factors to estimate the magnitude of the examined environment and the environmental effects for the EPS component of interest. The six EPS components are the solar array, photovoltaic module radiator, integrated equipment assembly, solar dynamic concentrator, solar dynamic radiator, and beta gimbal.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Benghin, V.V.; Petrov, V.M.; Chernykh, I.V.; Teltsov, M.V.; Shumshurov, V.I.
1992-01-01
A set of dosimetric units for the control of radiation doses to cosmonauts on board the MIR space station contains an active dosimeter R-16 and a personal display dosimeter IPD-2. During the powerful solar proton events (SPE) in September-October 1989, the readings of these devices were used for the control of the crew's radiation damage. Results of the dose measurements and analysis of the dynamics caused by some heliogeophysical factors are given. It is shown that the total doses from SPE registered by the dosimeters R-16 and IPD-2 were 3.6 x 10 -2 and 0.9 x 10 -2 Gy, respectively. (author)
-
Advanced Solar Cell and Array Technology for NASA Deep Space Missions
Piszczor, Michael; Benson, Scott; Scheiman, David; Finacannon, Homer; Oleson, Steve; Landis, Geoffrey
2008-01-01
A recent study by the NASA Glenn Research Center assessed the feasibility of using photovoltaics (PV) to power spacecraft for outer planetary, deep space missions. While the majority of spacecraft have relied on photovoltaics for primary power, the drastic reduction in solar intensity as the spacecraft moves farther from the sun has either limited the power available (severely curtailing scientific operations) or necessitated the use of nuclear systems. A desire by NASA and the scientific community to explore various bodies in the outer solar system and conduct "long-term" operations using using smaller, "lower-cost" spacecraft has renewed interest in exploring the feasibility of using photovoltaics for to Jupiter, Saturn and beyond. With recent advances in solar cell performance and continuing development in lightweight, high power solar array technology, the study determined that photovoltaics is indeed a viable option for many of these missions.
-
Space Solar Power Satellite Systems, Modern Small Satellites, and Space Rectenna
Bergsrud, Corey Alexis Marvin
Space solar power satellite (SSPS) systems is the concept of placing large satellite into geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) to harvest and convert massive amounts of solar energy into microwave energy, and to transmit the microwaves to a rectifying antenna (rectenna) array on Earth. The rectenna array captures and converts the microwave power into usable power that is injected into the terrestrial electric grid for use. This work approached the microwave power beam as an additional source of power (with solar) for lower orbiting satellites. Assuming the concept of retrodirectivity, a GEO-SSPS antenna array system tracks and delivers microwave power to lower orbiting satellites. The lower orbiting satellites are equipped with a stacked photovoltaic (PV)/rectenna array hybrid power generation unit (HPGU) in order to harvest solar and/or microwave energy for on-board use during orbit. The area, and mass of the PV array part of the HPGU was reduced at about 32% beginning-of-life power in order to achieve the spacecraft power requirements. The HPGU proved to offer a mass decrease in the PGU, and an increase in mission life due to longer living component life of the rectenna array. Moreover, greater mission flexibility is achieved through a track and power delivery concept. To validate the potential advantages offered by a HPGU, a mission concept was presented that utilizes modern small satellites as technology demonstrators. During launch, a smaller power receiving "daughter" satellite sits inside a larger power transmitting "mother" satellite. Once separated from the launch vehicle the daughter satellite is ejected away from the mother satellite, and each satellite deploys its respective power transmitting or power receiving hardware's for experimentation. The concept of close proximity mission operations between the satellites is considered. To validate the technology of the space rectenna array part of the HPGU, six milestones were completed in the design. The first
-
Denker, C.; Wang, H.; Conod, K. D.; Wintemberg, T.; Calderon, I.
2005-05-01
Astronomers at The Newark Museum's Alice and Leonard Dreyfuss Planetarium teamed up with the New Jersey Institute of Technology's (NJIT) Center for Solar-Terrestrial Research (CSTR) and the Big Bear Solar Observatory in presenting Solar Fireworks. The exhibit opened on May 15, 2004 and features two exhibition kiosks with interactive touch screen displays, where students and other visitors can take "virtual tours" in the fields of solar physics, solar activity, Sun-Earth connection, and geo-sciences. Planetarium and museum visits are an integral part of the introductory physics and astronomy classes at NJIT and the exhibition has been integrated in the astronomy curriculum. For example, NJIT students of the Astronomy Club and regular astronomy courses were closely involved in the design and development of the exhibit. The exhibit is the latest addition to the long-running natural science exhibit "Dynamic Earth: Revealing Nature's Secrets" at the museum. More than 30,000 people per year attend various programs offered by the planetarium including public shows, more than a dozen programs for school groups, after school activities, portable planetarium outreach, outdoor sky watches, solar observing and other family events. More than 1,000 high school students visited the planetarium in 2004. The exhibit is accompanied by a yearly teacher workshop (the first one was held on October 18-20, 2004) to enhance the learning experience of classes visiting the Newark Museum. The planetarium and museum staff has been working with teachers of Newark high schools and has presented many workshops for educators on a wide range of topics from astronomy to zoology. At the conclusion of the exhibit in December 2005, the exhibit will go "on the road" and will be made available to schools or other museums. Finally, the exhibit will find its permanent home at the new office complex of CSTR at NJIT. Acknowledgements: Solar Fireworks was organized by The Newark Museum and the New Jersey
-
Effect of Space Vehicle Structure Vibration on Control Moment Gyroscope Dynamics
Dobrinskaya, Tatiana
2008-01-01
Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs) are used for non-propulsive attitude control of satellites and space stations, including the International Space Station (ISS). CMGs could be essential for future long duration space missions due to the fact that they help to save propellant. CMGs were successfully tested on the ground for many years, and have been successfully used on satellites. However, operations have shown that the CMG service life on the ISS is significantly shorter than predicted. Since the dynamic environment of the ISS differs greatly from the nominal environment of satellites, it was important to analyze how operations specific to the station (dockings and undockings, huge solar array motion, crew exercising, robotic operations, etc) can affect the CMG performance. This task became even more important since the first CMG failure onboard the ISS. The CMG failure resulted in the limitation of the attitude control capabilities, more propellant consumption, and additional operational issues. Therefore, the goal of this work was to find out how the vibrations of a space vehicle structure, caused by a variety of onboard operations, can affect the CMG dynamics and performance. The equations of CMG motion were derived and analyzed for the case when the gyro foundation can vibrate in any direction. The analysis was performed for unbalanced CMG gimbals to match the CMG configuration on ISS. The analysis showed that vehicle structure vibrations can amplify and significantly change the CMG motion if the gyro gimbals are unbalanced in flight. The resonance frequencies were found. It was shown that the resonance effect depends on the magnitude of gimbal imbalance, on the direction of a structure vibration, and on gimbal bearing friction. Computer modeling results of CMG dynamics affected by the external vibration are presented. The results can explain some of the CMG vibration telemetry observed on ISS. This work shows that balancing the CMG gimbals decreases the effect
-
SEP solar array Shuttle flight experiment
Elms, R. V., Jr.; Young, L. E.; Hill, H. C.
1981-01-01
An experiment to verify the operational performance of a full-scale Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) solar array is described. Scheduled to fly on the Shuttle in 1983, the array will be deployed from the bay for ten orbits, with dynamic excitation to test the structural integrity being furnished by the Orbiter verniers; thermal, electrical, and sun orientation characteristics will be monitored, in addition to safety, reliability, and cost effective performance. The blanket, with aluminum and glass as solar cell mass simulators, is 4 by 32 m, with panels (each 0.38 by 4 m) hinged together; two live Si cell panels will be included. The panels are bonded to stiffened graphite-epoxy ribs and are storable in a box in the bay. The wing support structure is detailed, noting the option of releasing the wing into space by use of the Remote Manipulator System if the wing cannot be refolded. Procedures and equipment for monitoring the array behavior are outlined, and comprise both analog data and TV recording for later playback and analysis. The array wing experiment will also aid in developing measurement techniques for large structure dynamics in space.
-
Space tether dynamics: an introduction
Denny, Mark
2018-05-01
The dynamics of orbiting tethers (space elevators and skyhooks) is developed from an unusual direction: Lagrangian rather than Newtonian mechanics. These basic results are derived among others: space elevator required length with and without counterweight, location and magnitude of maximum tether tension, skyhook orbital parameters and tether tension. These conceptual devices are being increasingly discussed as technologically feasible; here they make an interesting pedagogical application of Lagrangian mechanics suitable for undergraduate physics students.
-
Rimmele, Thomas R; Marino, Jose
Adaptive optics (AO) has become an indispensable tool at ground-based solar telescopes. AO enables the ground-based observer to overcome the adverse effects of atmospheric seeing and obtain diffraction limited observations. Over the last decade adaptive optics systems have been deployed at major ground-based solar telescopes and revitalized ground-based solar astronomy. The relatively small aperture of solar telescopes and the bright source make solar AO possible for visible wavelengths where the majority of solar observations are still performed. Solar AO systems enable diffraction limited observations of the Sun for a significant fraction of the available observing time at ground-based solar telescopes, which often have a larger aperture than equivalent space based observatories, such as HINODE. New ground breaking scientific results have been achieved with solar adaptive optics and this trend continues. New large aperture telescopes are currently being deployed or are under construction. With the aid of solar AO these telescopes will obtain observations of the highly structured and dynamic solar atmosphere with unprecedented resolution. This paper reviews solar adaptive optics techniques and summarizes the recent progress in the field of solar adaptive optics. An outlook to future solar AO developments, including a discussion of Multi-Conjugate AO (MCAO) and Ground-Layer AO (GLAO) will be given. Supplementary material is available for this article at 10.12942/lrsp-2011-2.
-
Attitude Dynamics and Stability of a Simple Solar Photon Thruster
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Anna D. Guerman
2013-01-01
Full Text Available This paper is dedicated to the development of a model of the attitude dynamics for a nonideal Simple Solar Photon Thruster (SSPT and to the analysis of sailcraft motions with respect to their centre of mass. Derivation of the expressions for force and torque due to solar radiation that is valid for the case, when there is a misalignment of the SSPT axis with the sun direction, is followed by study of sailcraft dynamics and stability properties. Analysis of stability shows that an ideally reflecting sail is unstable, while for a sailcraft with nonideal collector, the symmetry axis is stable with respect to the Sun direction for large variety of system parameters. The motion around symmetry axis is always unstable and requires an active stabilizer.
-
Near Earth Asteroid Solar Sail Engineering Development Unit Test Program
Lockett, Tiffany Russell; Few, Alexander; Wilson, Richard
2017-01-01
The Near Earth Asteroid (NEA) Scout project is a 30x20x10cm (6U) cubesat reconnaissance mission to investigate a near Earth asteroid utilizing an 86m2 solar sail as the primary propulsion system. This will be the largest solar sail NASA will launch to date. NEA Scout is a secondary payload currently manifested on the maiden voyage of the Space Launch System in 2018. In development of the solar sail subsystem, design challenges were identified and investigated for packaging within a 6U form factor and deployment in cis-lunar space. Analysis furthered understanding of thermal, stress, and dynamics of the stowed system and matured an integrated sail membrane model for deployed flight dynamics. This paper will address design, fabrication, and lessons learned from the NEA Scout solar sail subsystem engineering development unit. From optical properties of the sail material to folding and spooling the single 86m2 sail, the team has developed a robust deployment system for the solar sail. This paper will also address expected and received test results from ascent vent, random vibration, and deployment tests.
-
Solar Activity Across the Scales: From Small-Scale Quiet-Sun Dynamics to Magnetic Activity Cycles
Kitiashvili, Irina N.; Collins, Nancy N.; Kosovichev, Alexander G.; Mansour, Nagi N.; Wray, Alan A.
2017-01-01
Observations as well as numerical and theoretical models show that solar dynamics is characterized by complicated interactions and energy exchanges among different temporal and spatial scales. It reveals magnetic self-organization processes from the smallest scale magnetized vortex tubes to the global activity variation known as the solar cycle. To understand these multiscale processes and their relationships, we use a two-fold approach: 1) realistic 3D radiative MHD simulations of local dynamics together with high resolution observations by IRIS, Hinode, and SDO; and 2) modeling of solar activity cycles by using simplified MHD dynamo models and mathematical data assimilation techniques. We present recent results of this approach, including the interpretation of observational results from NASA heliophysics missions and predictive capabilities. In particular, we discuss the links between small-scale dynamo processes in the convection zone and atmospheric dynamics, as well as an early prediction of Solar Cycle 25.
-
Yanqing solar field: Dynamic optical model and operational safety analysis
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zhao, Dongming; Wang, Zhifeng; Xu, Ershu; Zhu, Lingzhi; Lei, Dongqiang; Xu, Li; Yuan, Guofeng
2017-01-01
Highlights: • A dynamic optical model of the Yanqing solar field was built. • Tracking angle characteristics were studied with different SCA layouts and time. • The average energy flux was simulated across four clear days. • Influences of defocus angles for energy flux were analyzed. - Abstract: A dynamic optical model was established for the Yanqing solar field at the parabolic trough solar thermal power plant and a simulation was conducted on four separate days of clear weather (March 3rd, June 2nd, September 25th, December 17th). The solar collector assembly (SCA) was comprised of a North-South and East-West layout. The model consisted of the following modules: DNI, SCA operational, and SCA optical. The tracking angle characteristics were analyzed and the results showed that the East-West layout of the tracking system was the most viable. The average energy flux was simulated for a given time period and different SCA layouts, yielding an average flux of 6 kW/m 2 , which was then used as the design and operational standards of the Yanqing parabolic trough plant. The mass flow of North-South layout was relatively stable. The influences of the defocus angles on both the average energy flux and the circumferential flux distribution were also studied. The results provided a theoretical basis for the following components: solar field design, mass flow control of the heat transfer fluid, design and operation of the tracking system, operational safety of SCAs, and power production prediction in the Yanqing 1 MW parabolic trough plant.
-
A 1 cm space debris impact onto the Sentinel-1A solar array
Krag, H.; Serrano, M.; Braun, V.; Kuchynka, P.; Catania, M.; Siminski, J.; Schimmerohn, M.; Marc, X.; Kuijper, D.; Shurmer, I.; O'Connell, A.; Otten, M.; Muñoz, Isidro; Morales, J.; Wermuth, M.; McKissock, D.
2017-08-01
Sentinel-1A is a 2-ton spacecraft of the Copernicus Earth observation program operated by ESA's Space Operations Centre in Darmstadt, Germany. Sentinel-1A and its sister spacecraft Sentinel-1B operate in a sun-synchronous orbit at about 700 km altitude. On 2016/08/23 17:07:37 UTC, Sentinel-1A suffered from an anomaly resulting in a sudden permanent partial power loss and significant impulsive orbit and attitude changes. A deeper investigation identified that an impulsive orbit change against flight direction of 0.7 mm/s, estimated at the time of the event, gave the best results in terms of GPS residuals. At the same time, a peak attitude off-pointing of 0.7° (around the spacecraft yaw axis) and peak attitude rate increase of 0.04°/s (around the same axis) were observed. The simultaneous occurrence of these anomalies, starting from a sudden attitude change and ending with a permanent partial power loss, made an MMOD (Micro-Meteoroid and Orbital Debris) impact onto a solar array a possible explanation for this event. While the spacecraft is able to continue its mission nominally, a detailed investigation involving ESA's Space Debris and Flight Dynamics experts was conducted. An MMOD impact as an explanation gained further credibility, due to the pictures of the solar array taken by the on-board camera displaying a significant damage area. On September 7th, JSpOC (US Joint Space Operations Centre) informed SDO on 8 tracked fragments that are considered to be released by Sentinel-1A after the impact. This paper addresses the analysis that was performed on the data characterising the attitude and orbit change, the on-board camera image, and the tracked fragments. The data helped to identify the linear momentum vector while a flux analysis helped to identify the origin of the impactor and allowed to understand its mass and size characteristics.
-
Experimental studies on a ground coupled heat pump with solar thermal collectors for space heating
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Xi, Chen; Hongxing, Yang; Lin, Lu; Jinggang, Wang; Wei, Liu
2011-01-01
This paper presents experimental studies on a solar-assisted ground coupled heat pump (SAGCHP) system for space heating. The system was installed at the Hebei Academy of Sciences in Shijiazhuang (lat. N38 o 03', long. E114 o 26'), China. Solar collectors are in series connection with the borehole array through plate heat exchangers. Four operation modes of the system were investigated throughout the coldest period in winter (Dec 5th to Dec 27th). The heat pump performance, borehole temperature distributions and solar colleting characteristics of the SAGCHP system are analyzed and compared when the system worked in continuous or intermittent modes with or without solar-assisted heating. The SAGCHP system is proved to perform space heating with high energy efficiency and satisfactory solar fraction, which is a promising substitute for the conventional heating systems. It is also recommended to use the collected solar thermal energy as an alternative source for the heat pump instead of recharging boreholes for heat storage because of the enormous heat capacity of the earth. -- Highlights: → We study four working modes of a solar-assisted ground coupled heat pump. → The heating performance is in direct relation with the borehole temperature. → Solar-assisted heating elevates borehole temperature and system performance. → The system shows higher efficiency over traditional heating systems in cold areas. → Solar heat is not suggested for high temperature seasonal storage.
-
Dynamical structure of space and time
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sannikov-Proskuryakov, S.S.
2000-01-01
A mathematically correct solution of the problem of ultraviolet divergences requires a radical change of our ideas on space and matter. We show that the space is a discontinuum in small which is the carrier of a new dynamical structure. Taking into account this structure, a new theory of elementary particles can be suggested
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Dan CONSTANTINESCU
2010-01-01
Full Text Available The INCERC Bucharest experimental house is equipped on the Southern façade with a ventilated solar space. The solar space ensures the ventilation of the entire building at a constant rate of 0.60 exchanges / h during the cold season, by inletting the pre-heated space in the greenhouse space. In the hot season the system ensures the building reversible ventilation by providing the fresh air rate by air suction in the building Northern zone, a consequence of the natural draught effect ensured by the solar space. This report presents the experiments performed in the season 2008-2009 and the experimental validation of the mathematical model used in assessing the solar space energy performance in the heating season.
-
The geometry of empty space is the key to arresting dynamics
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lawlor, Aonghus; De Gregorio, Paolo; Dawson, K A [Department of Chemistry, University College Dublin, Irish Centre for Colloid Science and Biomaterials, Belfield, Dublin 4 (Ireland)
2004-10-27
We present the concept of dynamically available volume as a suitable order parameter for dynamical arrest. We show that dynamical arrest can be understood as a de-percolation transition of a vacancy network or available space. Beyond the arrest transition we find that droplets of available space are disconnected and the dynamics is frozen. This connection of the dynamics to the underlying geometrical structure of empty space provides us with a rich framework for studying the arrest transition.
-
Indium phosphide space solar cell research: Where we are and where we are going
Jain, R. K.; Flood, D. J.; Weinberg, Irving
1995-01-01
Indium phosphide is considered to be a strong contender for many photovoltaic space applications because of its radiation resistance and its potential for high efficiency. An overview of recent progress is presented, and possible future research directions for indium phosphide space solar cells are discussed. The topics considered include radiation damage studies and space flight experiments.
-
A Space Based Solar Power Satellite System
Engel, J. M.; Polling, D.; Ustamujic, F.; Yaldiz, R.; et al.
2002-01-01
(SPoTS) supplying other satellites with energy. SPoTS is due to be commercially viable and operative in 2020. of Technology designed the SPoTS during a full-time design period of six weeks as a third year final project. The team, organized according to the principles of systems engineering, first conducted a literature study on space wireless energy transfer to select the most suitable candidates for use on the SPoTS. After that, several different system concepts have been generated and evaluated, the most promising concept being worked out in greater detail. km altitude. Each SPoTS satellite has a 50m diameter inflatable solar collector that focuses all received sunlight. Then, the received sunlight is further redirected by means of four pointing mirrors toward four individual customer satellites. A market-analysis study showed, that providing power to geo-stationary communication satellites during their eclipse would be most beneficial. At arrival at geo-stationary orbit, the focused beam has expended to such an extent that its density equals one solar flux. This means that customer satellites can continue to use their regular solar arrays during their eclipse for power generation, resulting in a satellite battery mass reduction. the customer satellites in geo-stationary orbit, the transmitted energy beams needs to be pointed with very high accuracy. Computations showed that for this degree of accuracy, sensors are needed, which are not mainstream nowadays. Therefore further research must be conducted in this area in order to make these high-accuracy-pointing systems commercially attractive for use on the SPoTS satellites around 2020. Total 20-year system lifetime cost for 18 SPoT satellites are estimated at approximately USD 6 billion [FY2001]. In order to compete with traditional battery-based satellite power systems or possible ground based wireless power transfer systems the price per kWh for the customer must be significantly lower than the present one
-
Development, Qualification and Production of Space Solar Cells with 30% EOL Efficiency
Guter, Wolfgang; Ebel, Lars; Fuhrmann, Daniel; Kostler, Wolfgang; Meusel, Matthias
2014-08-01
AZUR SPACE's latest qualified solar cell product 3G30-advanced provides a high end-of-life (EOL) efficiency of 27.8% for 5E14 (1 MeV e-/cm2) at low production costs. In order to further reduce the mass, the 3G30-advanced was thinned down to as thin as 20 μm and tested in space. Next generation solar cells must exceed the EOL efficiency of the 3G30-advanced and therefore will utilize the excess current of the Ge subcell. This can be achieved by a metamorphic cell concept. While average beginning-of-life efficiencies above 31% have already been demonstrated with upright metamorphic triple-junction cells, AZUR's next generation product will comprise a metamorphic 4- junction device targeting 30% EOL.
-
A Space Weather mission concept: Observatories of the Solar Corona and Active Regions (OSCAR)
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Strugarek, Antoine; Janitzek, Nils; Lee, Arrow
2015-01-01
advancements in the field of solar physics, improvements of the current CME prediction models, and provide data for reliable space weather forecasting. These objectives are achieved by utilising two spacecraft with identical instrumentation, located at a heliocentric orbital distance of 1 AU from the Sun......Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) and Corotating Interaction Regions (CIRs) are major sources of magnetic storms on Earth and are therefore considered to be the most dangerous space weather events. The Observatories of Solar Corona and Active Regions (OSCAR) mission is designed to identify the 3D...... structure of coronal loops and to study the trigger mechanisms of CMEs in solar Active Regions (ARs) as well as their evolution and propagation processes in the inner heliosphere. It also aims to provide monitoring and forecasting of geo-effective CMEs and CIRs. OSCAR would contribute to significant...
-
Mechanical design of a low concentration ratio solar array for a space station application
Biss, M. S.; Hsu, L.
1983-01-01
This paper describes a preliminary study and conceptual design of a low concentration ratio solar array for a space station application with approximately a 100 kW power requirement. The baseline design calls for a multiple series of inverted, truncated, pyramidal optical elements with a geometric concentration ratio (GCR) of 6. It also calls for low life cycle cost, simple on-orbit maintainability, 1984 technology readiness date, and gallium arsenide (GaAs) of silicon (Si) solar cell interchangeability. Due to the large area needed to produce the amount of power required for the baseline space station, a symmetrical wing design, making maximum use of the commonality of parts approach, was taken. This paper will describe the mechanical and structural design of a mass-producible solar array that is very easy to tailor to the needs of the individual user requirement.
-
SOLAR-LIKE OSCILLATIONS IN A METAL-POOR GLOBULAR CLUSTER WITH THE HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Stello, Dennis; Gilliland, Ronald L.
2009-01-01
We present analyses of variability in the red giant stars in the metal-poor globular cluster NGC 6397, based on data obtained with the Hubble Space Telescope. We use a nonstandard data reduction approach to turn a 23 day observing run originally aimed at imaging the white dwarf population, into time-series photometry of the cluster's highly saturated red giant stars. With this technique we obtain noise levels in the final power spectra down to 50 parts per million, which allows us to search for low-amplitude solar-like oscillations. We compare the observed excess power seen in the power spectra with estimates of the typical frequency range, frequency spacing, and amplitude from scaling the solar oscillations. We see evidence that the detected variability is consistent with solar-like oscillations in at least one and perhaps up to four stars. With metallicities 2 orders of magnitude lower than those of the Sun, these stars present so far the best evidence of solar-like oscillations in such a low-metallicity environment.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Adam, Mario; Lohmann, Sandra [Fachhochschule Duesseldorf (Germany). E2 - Erneuerbare Energien und Energieeffizienz
2011-05-15
The research project 'Solar cooling in the Hardware-in-the-Loop-Test' is funded by the BMBF and deals with the modeling of a pilot plant for solar cooling with the 17.5 kW absorption chiller of Yazaki in the simulation environment of MATLAB/ Simulink with the toolboxes Stateflow and CARNOT. Dynamic simulations and parameter variations according to the work-efficient methodology of design of experiments are used to select meaningful system configurations, control strategies and dimensioning of the components. The results of these simulations will be presented and a view of the use of acquired knowledge for the planned laboratory field tests on a hardware-in-the-loop test stand will be given. (orig.)
-
Dynamics and control of robot for capturing objects in space
Huang, Panfeng
Space robots are expected to perform intricate tasks in future space services, such as satellite maintenance, refueling, and replacing the orbital replacement unit (ORU). To realize these missions, the capturing operation may not be avoided. Such operations will encounter some challenges because space robots have some unique characteristics unfound on ground-based robots, such as, dynamic singularities, dynamic coupling between manipulator and space base, limited energy supply and working without a fixed base, and so on. In addition, since contacts and impacts may not be avoided during capturing operation. Therefore, dynamics and control problems of space robot for capturing objects are significant research topics if the robots are to be deployed for the space services. A typical servicing operation mainly includes three phases: capturing the object, berthing and docking the object, then repairing the target. Therefore, this thesis will focus on resolving some challenging problems during capturing the object, berthing and docking, and so on. In this thesis, I study and analyze the dynamics and control problems of space robot for capturing objects. This work has potential impact in space robotic applications. I first study the contact and impact dynamics of space robot and objects. I specifically focus on analyzing the impact dynamics and mapping the relationship of influence and speed. Then, I develop the fundamental theory for planning the minimum-collision based trajectory of space robot and designing the configuration of space robot at the moment of capture. To compensate for the attitude of the space base during the capturing approach operation, a new balance control concept which can effectively balance the attitude of the space base using the dynamic couplings is developed. The developed balance control concept helps to understand of the nature of space dynamic coupling, and can be readily applied to compensate or minimize the disturbance to the space base
-
Chen, Zhengwei; Wang, Yueshe; Hao, Yun; Wang, Qizhi
2013-07-01
The solar cavity receiver is an important light-energy to thermal-energy convector in the tower solar thermal power plant system. The heat flux in the inner surface of the cavity will show the characteristics of non-continuous step change especially in non-normal and transient weather conditions, which may result in a continuous dynamic variation of the characteristic parameters. Therefore, the research of dynamic characteristics of the receiver plays a very important role in the operation and the control safely in solar cavity receiver system. In this paper, based on the non-continuous step change of radiation flux, a non-linear dynamic model is put forward to obtain the effects of the non-continuous step change radiation flux and step change feed water flow on the receiver performance by sequential modular approach. The subject investigated in our study is a 1MW solar power station constructed in Yanqing County, Beijing. This study has obtained the dynamic responses of the characteristic parameters in the cavity receiver, such as drum pressure, drum water level, main steam flow and main steam enthalpy under step change radiation flux. And the influence law of step-change feed water flow to the dynamic characteristics in the receiver also has been analyzed. The results have a reference value for the safe operation and the control in solar cavity receiver system.
-
Effect of solar chimney inclination angle on space flow pattern and ventilation rate
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bassiouny, Ramadan; Korah, Nader S.A. [Department of Mechanical Power Engineering and Energy, Minia University, Minia 61111 (Egypt)
2009-02-15
The solar chimney is a simple and practical idea that is applied to enhance space natural ventilation. The chimney could be vertical or inclined. The chimney inclination angle is an important parameter that greatly affects space flow pattern and ventilation rate. In the present study, the effect of chimney inclination angle on air change per hour and indoor flow pattern was numerically and analytically investigated. A numerical simulation using Ansys, a FEM-based code, was used to predict flow pattern. Then the results were compared with published experimental measurements. A FORTRAN program was developed to iteratively solve the mathematical model that was obtained through an overall energy balance on the solar chimney. The analytical results showed that an optimum air flow rate value was achieved when the chimney inclination is between 45 and 70 for latitude of 28.4 . The numerically predicted flow pattern inside the space supports this finding. Moreover, in the present study a correlation to predict the air change per hour was developed. The correlation was tested within a solar intensity greater than or equal to 500 W/m{sup 2}, and chimney width from 0.1 m to 0.35 m for different inclination angles with acceptable values. (author)
-
Breathing of heliospheric structures triggered by the solar-cycle activity
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
K. Scherer
Full Text Available Solar wind ram pressure variations occuring within the solar activity cycle are communicated to the outer heliosphere as complicated time-variabilities, but repeating its typical form with the activity period of about 11 years. At outer heliospheric regions, the main surviving solar cycle feature is a periodic variation of the solar wind dynamical pressure or momentum flow, as clearly recognized by observations of the VOYAGER-1/2 space probes. This long-periodic variation of the solar wind dynamical pressure is modeled here through application of appropriately time-dependent inner boundary conditions within our multifluid code to describe the solar wind – interstellar medium interaction. As we can show, it takes several solar cycles until the heliospheric structures adapt to an average location about which they carry out a periodic breathing, however, lagged in phase with respect to the solar cycle. The dynamically active heliosphere behaves differently from a static heliosphere and especially shows a historic hysteresis in the sense that the shock structures move out to larger distances than explained by the average ram pressure. Obviously, additional energies are pumped into the heliosheath by means of density and pressure waves which are excited. These waves travel outwards through the interface from the termination shock towards the bow shock. Depending on longitude, the heliospheric sheath region memorizes 2–3 (upwind and up to 6–7 (downwind preceding solar activity cycles, i.e. the cycle-induced waves need corresponding travel times for the passage over the heliosheath. Within our multifluid code we also adequately describe the solar cycle variations in the energy distributions of anomalous and galactic cosmic rays, respectively. According to these results the distribution of these high energetic species cannot be correctly described on the basis of the actually prevailing solar wind conditions.
Key words. Interplanetary -
Photoluminescence in large fluence radiation irradiated space silicon solar cells
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hisamatsu, Tadashi; Kawasaki, Osamu; Matsuda, Sumio [National Space Development Agency of Japan, Tsukuba, Ibaraki (Japan). Tsukuba Space Center; Tsukamoto, Kazuyoshi
1997-03-01
Photoluminescence spectroscopy measurements were carried out for silicon 50{mu}m BSFR space solar cells irradiated with 1MeV electrons with a fluence exceeding 1 x 10{sup 16} e/cm{sup 2} and 10MeV protons with a fluence exceeding 1 x 10{sup 13} p/cm{sup 2}. The results were compared with the previous result performed in a relative low fluence region, and the radiation-induced defects which cause anomalous degradation of the cell performance in such large fluence regions were discussed. As far as we know, this is the first report which presents the PL measurement results at 4.2K of the large fluence radiation irradiated silicon solar cells. (author)
-
Photoexcitation dynamics in organic solar cell donor/acceptor system
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Aarnio, H.
2012-07-01
In this work, photoinduced absorption techniques have been used in a number of ways to clarify the charge generation and recombination processes in two polymers used in organic solar cells, namely APFO3 and P3HT. Emphasis has been on identifying photoexcitations, modeling their dynamics and determining their lifetimes.
-
Stevens, N. J.
1974-01-01
The Space Plasma, High Voltage Interaction Experiment (SPHINX) is the name given to an auxiliary payload satellite scheduled to be launched in January 1974. The principal experiments carried on this satellite are specifically designed to obtain the engineering data on the interaction of high voltage systems with the space plasma. The classes of experiments are solar array segments, insulators, insulators with pin holes and conductors. The satellite is also carrying experiments to obtain flight data on three new solar array configurations: the edge illuminated-multijunction cells, the teflon encased cells, and the violet cells.
-
FFT analysis of sensible-heat solar-dynamic receivers
Lund, Kurt O.
The use of solar dynamic receivers with sensible energy storage in single-phase materials is considered. The feasibility of single-phase designs with weight and thermal performance comparable to existing two-phase designs is addressed. Linearized heat transfer equations are formulated for the receiver heat storage, representing the periodic input solar flux as the sum of steady and oscillating distributions. The steady component is solved analytically to produce the desired receiver steady outlet gas temperature, and the FFT algorithm is applied to the oscillating components to obtain the amplitudes and mode shapes of the oscillating solid and gas temperatures. The results indicate that sensible-heat receiver designs with performance comparable to state-of-the-art two-phase receivers are available.
-
What can the annual 10Be solar activity reconstructions tell us about historic space weather?
Barnard, Luke; McCracken, Ken G.; Owens, Mat J.; Lockwood, Mike
2018-04-01
Context: Cosmogenic isotopes provide useful estimates of past solar magnetic activity, constraining past space climate with reasonable uncertainty. Much less is known about past space weather conditions. Recent advances in the analysis of 10Be by McCracken & Beer (2015, Sol Phys 290: 305-3069) (MB15) suggest that annually resolved 10Be can be significantly affected by solar energetic particle (SEP) fluxes. This poses a problem, and presents an opportunity, as the accurate quantification of past solar magnetic activity requires the SEP effects to be determined and isolated, whilst doing so might provide a valuable record of past SEP fluxes. Aims: We compare the MB15 reconstruction of the heliospheric magnetic field (HMF), with two independent estimates of the HMF derived from sunspot records and geomagnetic variability. We aim to quantify the differences between the HMF reconstructions, and speculate on the origin of these differences. We test whether the differences between the reconstructions appear to depend on known significant space weather events. Methods: We analyse the distributions of the differences between the HMF reconstructions. We consider how the differences vary as a function of solar cycle phase, and, using a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, we compare the distributions under the two conditions of whether or not large space weather events were known to have occurred. Results: We find that the MB15 reconstructions are generally marginally smaller in magnitude than the sunspot and geomagnetic HMF reconstructions. This bias varies as a function of solar cycle phase, and is largest in the declining phase of the solar cycle. We find that MB15's excision of the years with very large ground level enhancement (GLE) improves the agreement of the 10Be HMF estimate with the sunspot and geomagnetic reconstructions. We find no statistical evidence that GLEs, in general, affect the MB15 reconstruction, but this analysis is limited by having too few samples. We do find
-
Multi-scale Dynamical Processes in Space and Astrophysical Plasmas
Vörös, Zoltán; IAFA 2011 - International Astrophysics Forum 2011 : Frontiers in Space Environment Research
2012-01-01
Magnetized plasmas in the universe exhibit complex dynamical behavior over a huge range of scales. The fundamental mechanisms of energy transport, redistribution and conversion occur at multiple scales. The driving mechanisms often include energy accumulation, free-energy-excited relaxation processes, dissipation and self-organization. The plasma processes associated with energy conversion, transport and self-organization, such as magnetic reconnection, instabilities, linear and nonlinear waves, wave-particle interactions, dynamo processes, turbulence, heating, diffusion and convection represent fundamental physical effects. They demonstrate similar dynamical behavior in near-Earth space, on the Sun, in the heliosphere and in astrophysical environments. 'Multi-scale Dynamical Processes in Space and Astrophysical Plasmas' presents the proceedings of the International Astrophysics Forum Alpbach 2011. The contributions discuss the latest advances in the exploration of dynamical behavior in space plasmas environm...
-
Dynamics of ozone layer under Serbia and solar activity: Previous statement
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ducić Vladan
2008-01-01
Full Text Available The aim of this paper is to identify ozone layer dynamics under Serbian area, as well as possible relations of change in stratospheric ozone concentration with some parameters of solar activity. During the period 1979-2005, the statistical decrease of ozone concentration was noticed under Serbian territory cumulatively for 24.5 DU (7.2%, apropos 9.4 DU (2.8% by decade. These changes are consistent with the changes in surrounding countries. From absolute minimum 1993, flexible trend of ozone layer pentad values validate hypotheses of its recovery. Correspondence of ozone thickness extreme period with Wolf's number and with the greatest volcanic eruptions shows that interannual variations of stratospheric ozone concentration are still in the function of natural factors above all, as are solar and volcanic activities. Investigation of larger number solar activity parameters shows statistically important antiphase synchronous between the number of polar faculae on the Sun and stratospheric ozone dynamics under Serbia. Respecting that relation between these two features until now isn't depicted, some possible causal mechanisms are proposed.
-
Radiation Belt Transport Driven by Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Fluctuations
Kress, B. T.; Hudson, M. K.; Ukhorskiy, A. Y.; Mueller, H.
2012-12-01
The creation of the Earth's outer zone radiation belts is attributed to earthward transport and adiabatic acceleration of electrons by drift-resonant interactions with electromagnetic fluctuations in the magnetosphere. Three types of radial transport driven by solar wind dynamic pressure fluctuations that have been identified are: (1) radial diffusion [Falthammer, 1965], (2) significant changes in the phase space density radial profile due to a single or few ULF drift-resonant interactions [Ukhorskiy et al., 2006; Degeling et al., 2008], and (3) shock associated injections of radiation belt electrons occurring in less than a drift period [Li et al., 1993]. A progress report will be given on work to fully characterize different forms of radial transport and their effect on the Earth's radiation belts. The work is being carried out by computing test-particle trajectories in electric and magnetic fields from a simple analytic ULF field model and from global MHD simulations of the magnetosphere. Degeling, A. W., L. G. Ozeke, R. Rankin, I. R. Mann, and K. Kabin (2008), Drift resonant generation of peaked relativistic electron distributions by Pc 5 ULF waves, textit{J. Geophys. Res., 113}, A02208, doi:10.1029/2007JA012411. Fälthammar, C.-G. (1965), Effects of Time-Dependent Electric Fields on Geomagnetically Trapped Radiation, J. Geophys. Res., 70(11), 2503-2516, doi:10.1029/JZ070i011p02503. Li, X., I. Roth, M. Temerin, J. R. Wygant, M. K. Hudson, and J. B. Blake (1993), Simulation of the prompt energization and transport of radiation belt particles during the March 24, 1991 SSC, textit{Geophys. Res. Lett., 20}(22), 2423-2426, doi:10.1029/93GL02701. Ukhorskiy, A. Y., B. J. Anderson, K. Takahashi, and N. A. Tsyganenko (2006), Impact of ULF oscillations in solar wind dynamic pressure on the outer radiation belt electrons, textit{Geophys. Res. Lett., 33}(6), L06111, doi:10.1029/2005GL024380.
-
Lightweight Phase-Change Material For Solar Power
Stark, Philip
1993-01-01
Lightweight panels containing phase-change materials developed for use as heat-storage elements of compact, lightweight, advanced solar dynamic power system. During high insolation, heat stored in panels via latent heat of fusion of phase-change material; during low insolation, heat withdrawn from panels. Storage elements consist mainly of porous carbon-fiber structures imbued with germanium. Developed for use aboard space station in orbit around Earth, also adapted to lightweight, compact, portable solar-power systems for use on Earth.
-
Solar Plant Growth System for Food Production in Space Exploration Missions, Phase I
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — Physical Sciences Inc. (PSI), in collaboration with Vencore Services and Solutions, Inc. (Vencore) and Utah State University (USU), proposes to develop a Solar Plant...
-
Solar flares as harbinger of new physics
Zioutas, K; Semertzidis, Y.; Papaevangelou, T.; Georgiopoulou, E.; Gardikiotis, A.; Dafni, T.; Tsagri, M.; Semertzidis, Y.; Papaevangelou, T.; Dafni, T.
2011-01-01
This work provides additional evidence on the involvement of exotic particles like axions and/or other WISPs, following recent measurements during the quietest Sun and flaring Sun. Thus, SPHINX mission observed a minimum basal soft X-rays emission in the extreme solar minimum in 2009. The same scenario (with ~17 meV axions) fits also the dynamical behaviour of white-light solar flares, like the measured spectral components in the visible and in soft X-rays, and, the timing between them. Solar chameleons remain a viable candidate, since they may preferentially convert to photons in outer space.
-
Activities of NICT space weather project
Murata, Ken T.; Nagatsuma, Tsutomu; Watari, Shinichi; Shinagawa, Hiroyuki; Ishii, Mamoru
NICT (National Institute of Information and Communications Technology) has been in charge of space weather forecast service in Japan for more than 20 years. The main target region of the space weather is the geo-space in the vicinity of the Earth where human activities are dominant. In the geo-space, serious damages of satellites, international space stations and astronauts take place caused by energetic particles or electromagnetic disturbances: the origin of the causes is dynamically changing of solar activities. Positioning systems via GPS satellites are also im-portant recently. Since the most significant effect of positioning error comes from disturbances of the ionosphere, it is crucial to estimate time-dependent modulation of the electron density profiles in the ionosphere. NICT is one of the 13 members of the ISES (International Space Environment Service), which is an international assembly of space weather forecast centers under the UNESCO. With help of geo-space environment data exchanging among the member nations, NICT operates daily space weather forecast service every day to provide informa-tion on forecasts of solar flare, geomagnetic disturbances, solar proton event, and radio-wave propagation conditions in the ionosphere. The space weather forecast at NICT is conducted based on the three methodologies: observations, simulations and informatics (OSI model). For real-time or quasi real-time reporting of space weather, we conduct our original observations: Hiraiso solar observatory to monitor the solar activity (solar flare, coronal mass ejection, and so on), domestic ionosonde network, magnetometer HF radar observations in far-east Siberia, and south-east Asia low-latitude ionosonde network (SEALION). Real-time observation data to monitor solar and solar-wind activities are obtained through antennae at NICT from ACE and STEREO satellites. We have a middle-class super-computer (NEC SX-8R) to maintain real-time computer simulations for solar and solar
-
Ensemble downscaling in coupled solar wind-magnetosphere modeling for space weather forecasting.
Owens, M J; Horbury, T S; Wicks, R T; McGregor, S L; Savani, N P; Xiong, M
2014-06-01
Advanced forecasting of space weather requires simulation of the whole Sun-to-Earth system, which necessitates driving magnetospheric models with the outputs from solar wind models. This presents a fundamental difficulty, as the magnetosphere is sensitive to both large-scale solar wind structures, which can be captured by solar wind models, and small-scale solar wind "noise," which is far below typical solar wind model resolution and results primarily from stochastic processes. Following similar approaches in terrestrial climate modeling, we propose statistical "downscaling" of solar wind model results prior to their use as input to a magnetospheric model. As magnetospheric response can be highly nonlinear, this is preferable to downscaling the results of magnetospheric modeling. To demonstrate the benefit of this approach, we first approximate solar wind model output by smoothing solar wind observations with an 8 h filter, then add small-scale structure back in through the addition of random noise with the observed spectral characteristics. Here we use a very simple parameterization of noise based upon the observed probability distribution functions of solar wind parameters, but more sophisticated methods will be developed in the future. An ensemble of results from the simple downscaling scheme are tested using a model-independent method and shown to add value to the magnetospheric forecast, both improving the best estimate and quantifying the uncertainty. We suggest a number of features desirable in an operational solar wind downscaling scheme. Solar wind models must be downscaled in order to drive magnetospheric models Ensemble downscaling is more effective than deterministic downscaling The magnetosphere responds nonlinearly to small-scale solar wind fluctuations.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Shi, Liping; Brehm, Robert
2016-01-01
The overall energy conversion efficiency of solar cell arrays is highly effected by partial shading effects. Especially for solar panel arrays installed in environments which are exposed to inhomogeneous dynamic changing illuminations such as on roof tops of electrical vehicles the overall system...... efficiency is drastically reduced. Dynamic real-time reconfiguration of the solar panel array can reduce effects on the output efficiency due to partial shading. This results in a maximized power output of the panel array when exposed to dynamic changing illuminations. The optimal array configuration...... with respect to shading patterns can be stated as a combinatorial optimization problem and this paper proposes a dynamic programming (DP) based algorithm which finds the optimal feasible solution to reconfigure the solar panel array for maximum efficiency in real-time with linear time complexity. It is shown...
-
Theoretical energy and exergy analyses of solar assisted heat pump space heating system
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Atmaca Ibrahim
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Due to use of alternative energy sources and energy efficient operation, heat pumps come into prominence in recent years. Especially in solar-assisted heat pumps, sizing the required system is difficult and arduous task in order to provide optimum working conditions. Therefore, in this study solar assisted indirect expanded heat pump space heating system is simulated and the results of the simulation are compared with available experimental data in the literature in order to present reliability of the model. Solar radiation values in the selected region are estimated with the simulation. The case study is applied and simulation results are given for Antalya, Turkey. Collector type and storage tank capacity effects on the consumed power of the compressor, COP of the heat pump and the overall system are estimated with the simulation, depending on the radiation data, collector surface area and the heating capacity of the space. Exergy analysis is also performed with the simulation and irreversibility, improvement potentials and exergy efficiencies of the heat pump and system components are estimated.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Vejen, Niels Kristian
1999-01-01
A solar storage tank for space heating and domestic hot water supply was designed and testet in af laboratory test facility.......A solar storage tank for space heating and domestic hot water supply was designed and testet in af laboratory test facility....
-
Dynamic Modeling of Natural Convection Solar Energy Flat Plate ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
The analytical solutions to the dynamic model of an air-heating flat plate solar energy thermal collector were validated by direct measurement from a physical model constructed for that purpose, of the temperatures of the cover and absorber plates, the inlet and outlet fluids, and the ambient air from morning to evening for ...
-
Flexible Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin-film solar cells for space application
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Otte, Karsten; Makhova, Liudmila; Braun, Alexander; Konovalov, Igor
2006-01-01
Thin film solar cells (TFSC) with Cu(In,Ga)Se 2 (CIGS) as absorber layer have been produced on rigid glass substrates for the terrestrial market. There exist, however, different investigations for manufacturing of TFSC on flexible substrates in order to achieve very thin and highly flexible (rollable) solar cells. Besides their capability to open new terrestrial market segments, they are considered as competitive candidates for future flexible thin film space power generators compared to traditional crystalline solar cells. This paper explains the advantages of flexible TFSC for usage in space, including:-low mass and storage volume, -high power/mass ratio [>100 W/kg at array level], -high radiation resistance against proton and electron radiation and, -lower production costs. These cells can be produced on flexible conductive and insulating substrate materials and have efficiency potentials of up to 15%. We report on the current development steps to adopt the TFSC technology to space requirements as well as the first European industrial approach to the roll-to-roll production of flexible CIGS-TFSC on polyimide as substrate material. Stability issues in space environment concern not only the TFSC itself, but all system components such as interconnects, cell assembly and flexible blankets. The adhesion of the back-contact to the substrate, the emissivity control in the infrared wavelength range, the electrical contacting and interconnection as well as flexible encapsulation are currently under investigation and are discussed in the paper. The production costs for TFSC for space application can be further reduced by sharing resources for the production of flexible TFSC for the terrestrial market; namely by using both, the existing terrestrial investment in production facilities as well as the synergies in R and D
-
Sun, Jingya; Adhikari, Aniruddha; Shaheen, Basamat; Yang, Haoze; Mohammed, Omar F.
2016-01-01
Selectively capturing the ultrafast dynamics of charge carriers on materials surfaces and at interfaces is crucial to the design of solar cells and optoelectronic devices. Despite extensive research efforts over the past few decades, information and understanding about surface-dynamical processes, including carrier trapping and recombination remains extremely limited. A key challenge is to selectively map such dynamic processes, a capability that is hitherto impractical by time-resolved laser techniques, which are limited by the laser’s relatively large penetration depth and consequently they record mainly bulk information. Such surface dynamics can only be mapped in real space and time by applying four-dimensional (4D) scanning ultrafast electron microscopy (S-UEM), which records snapshots of materials surfaces with nanometer spatial and sub-picosecond temporal resolutions. In this method, the secondary electron (SE) signal emitted from the sample’s surface is extremely sensitive to the surface dynamics and is detected in real time. In several unique applications, we spatially and temporally visualize the SE energy gain and loss, the charge carrier dynamics on the surface of InGaN nanowires and CdSe single crystals and its powder film. We also provide the mechanisms for the observed dynamics, which will be the foundation for future potential applications of S-UEM to a wide range of studies on material surfaces and device interfaces.
-
Sun, Jingya
2016-02-25
Selectively capturing the ultrafast dynamics of charge carriers on materials surfaces and at interfaces is crucial to the design of solar cells and optoelectronic devices. Despite extensive research efforts over the past few decades, information and understanding about surface-dynamical processes, including carrier trapping and recombination remains extremely limited. A key challenge is to selectively map such dynamic processes, a capability that is hitherto impractical by time-resolved laser techniques, which are limited by the laser’s relatively large penetration depth and consequently they record mainly bulk information. Such surface dynamics can only be mapped in real space and time by applying four-dimensional (4D) scanning ultrafast electron microscopy (S-UEM), which records snapshots of materials surfaces with nanometer spatial and sub-picosecond temporal resolutions. In this method, the secondary electron (SE) signal emitted from the sample’s surface is extremely sensitive to the surface dynamics and is detected in real time. In several unique applications, we spatially and temporally visualize the SE energy gain and loss, the charge carrier dynamics on the surface of InGaN nanowires and CdSe single crystals and its powder film. We also provide the mechanisms for the observed dynamics, which will be the foundation for future potential applications of S-UEM to a wide range of studies on material surfaces and device interfaces.
-
Harnessing solar pressure to slew and point large infrared space telescopes
Errico, Simona; Angel, Roger P.; Calvert, Paul D.; Woof, Neville
2003-03-01
Large astronomical Gossamer telescopes in space will need to employ large solar shields to safeguard the optics from solar radiation. These types of telescopes demand accurate controls to maintain telescope pointing over long integration periods. We propose an active solar shield system that harnesses radiation pressure to accurately slew and acquire new targets without the need for reaction wheels or thrusters. To provide the required torques, the solar shield is configured as an inverted, 4-sided pyramidal roof. The sloped roof interior surfaces are covered with hinged “tiles” made from piezoelectric film bimorphs with specular metallized surfaces. Nominally, the tiles lie flat against the roof and the sunlight is reflected outward equally from all sloped surfaces. However, when the tiles on one roof pitch are raised, the pressure balance is upset and the sunshade is pushed to one side. By judicious selection of the tiles and control of their lift angle, the solar pressure can be harvested to stabilize the spacecraft orientation or to change its angular momentum. A first order conceptual design performance analysis and the results from the experimental design, fabrication and testing of piezoelectric bimorph hinge elements will be presented. Next phase challenges in engineering design, materials technology, and systems testing will be discussed.
-
Dynamic auroral storms on Saturn as observed by the Hubble Space Telescope.
Nichols, J D; Badman, S V; Baines, K H; Brown, R H; Bunce, E J; Clarke, J T; Cowley, S W H; Crary, F J; Dougherty, M K; Gérard, J-C; Grocott, A; Grodent, D; Kurth, W S; Melin, H; Mitchell, D G; Pryor, W R; Stallard, T S
2014-05-28
We present observations of significant dynamics within two UV auroral storms observed on Saturn using the Hubble Space Telescope in April/May 2013. Specifically, we discuss bursts of auroral emission observed at the poleward boundary of a solar wind-induced auroral storm, propagating at ∼330% rigid corotation from near ∼01 h LT toward ∼08 h LT. We suggest that these are indicative of ongoing, bursty reconnection of lobe flux in the magnetotail, providing strong evidence that Saturn's auroral storms are caused by large-scale flux closure. We also discuss the later evolution of a similar storm and show that the emission maps to the trailing region of an energetic neutral atom enhancement. We thus identify the auroral form with the upward field-aligned continuity currents flowing into the associated partial ring current.
-
Invited article: Electric solar wind sail: toward test missions.
Janhunen, P; Toivanen, P K; Polkko, J; Merikallio, S; Salminen, P; Haeggström, E; Seppänen, H; Kurppa, R; Ukkonen, J; Kiprich, S; Thornell, G; Kratz, H; Richter, L; Krömer, O; Rosta, R; Noorma, M; Envall, J; Lätt, S; Mengali, G; Quarta, A A; Koivisto, H; Tarvainen, O; Kalvas, T; Kauppinen, J; Nuottajärvi, A; Obraztsov, A
2010-11-01
The electric solar wind sail (E-sail) is a space propulsion concept that uses the natural solar wind dynamic pressure for producing spacecraft thrust. In its baseline form, the E-sail consists of a number of long, thin, conducting, and centrifugally stretched tethers, which are kept in a high positive potential by an onboard electron gun. The concept gains its efficiency from the fact that the effective sail area, i.e., the potential structure of the tethers, can be millions of times larger than the physical area of the thin tethers wires, which offsets the fact that the dynamic pressure of the solar wind is very weak. Indeed, according to the most recent published estimates, an E-sail of 1 N thrust and 100 kg mass could be built in the rather near future, providing a revolutionary level of propulsive performance (specific acceleration) for travel in the solar system. Here we give a review of the ongoing technical development work of the E-sail, covering tether construction, overall mechanical design alternatives, guidance and navigation strategies, and dynamical and orbital simulations.
-
Quantum Dynamics of Test Particle in Curved Space-Time
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Piechocki, W.
2002-01-01
To reveal the nature of space-time singularities of removable type we examine classical and quantum dynamics of a free particle in the Sitter type spacetimes. Consider space-times have different topologies otherwise are isometric. Our systems are integrable and we present analytic solutions of the classical dynamics. We quantize the systems by making use of the group theoretical method: we find an essentially self-adjoint representation of the algebra of observables integrable to the irreducible unitarity representation of the symmetry group of each consider gravitational system. The massless particle dynamics is obtained in the zero-mass limit of the massive case. Global properties of considered gravitational systems are of primary importance for the quantization procedure. Systems of a particle in space-times with removable singularities appear to be quantizable. We give specific proposal for extension of our analysis to space-times with essential type singularities. (author)
-
Dynamical 3-Space: Black Holes in an Expanding Universe
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Rothall D. P.
2013-10-01
Full Text Available Black holes are usually studied without including effects of the expanding universe. However in some recent studies black holes have been embedded in an expanding universe, in order to determine the interplay, if any, of these two dynamical processes. Dynamical 3-space theory contains time independent solutions for black holes, which are spatial in-flows, and separately the time dependent Hubble expansion. This theory has explained numerous puzzles in observational astrophysics and contains 3 constants; G, - which from experimental data turns out to be the fine structure constant, and - which is a small but nonzero distance, possibly a Planck-type length. The Hubble expansion in the dynamical 3-space theory cannot be “switched o”, forcing the study, first, of isolated black holes coexisting with the expanding universe. It is shown that a time dependent black hole and expanding universe solution exists. The nature and implications of these solutions are discussed as they evolve over time. A dynamical network of black holes and induced linking cosmic filaments forming bubble structures is discussed, as a consequence of dynamical 3-space undergoing a dynamical breakdown of homogeneity and isotropy, even in the absence of baryonic matter.
-
Modeling of a solar-pumped iodine laser
Wilson, J. W.; Lee, J. H.
1980-01-01
The direct conversion in space of solar radiation into laser radiation for power transmission to earth, satellites, or deep space probes shows promise as a reasonably simple technology and may have cost advantage in deployment and greater reliability compared to other methods of space power generation and transmission. The main candidates for solar pumping are the gas dynamic, photochemical, and direct photoexcited lasers. Here consideration is given to the photochemical reaction of alkyliodides which predominantly excite the I(2P1/2) state which then lases at 1.315 microns. The iodine ground state is eventually lost to reconstituting the gas or in the formation of molecular iodine. The rates at which the gas is required to be recycled through the laser system are modest. The side exposure at 100-fold solar concentration of a 100-m long tube with a 1 sq m cross section is estimated to provide 20 kW of continuous laser output. Scaling laws and optimum operating conditions of this system are discussed.
-
Space weather monitoring by groundbased means
Troshichev, Oleg
2012-01-01
This book demonstrates that the method, based on the ground polar cap magnetic observations is a reliable diagnosis of the solar wind energy coming into the magnetosphere Method for the uninterruptive monitoring of the magnetosphere state (i.e. space weather). It shows that the solar wind energy pumping power, can be described by the PC growth rate, thus, the magnetospheric substorms features are predetermined by the PC dynamics. Furthermore, it goes on to show that the beginning and ending of magnetic storms is predictable. The magnetic storm start only if the solar energy input into the magn
-
Shape control of slack space reflectors using modulated solar pressure.
Borggräfe, Andreas; Heiligers, Jeannette; Ceriotti, Matteo; McInnes, Colin R
2015-07-08
The static deflection profile of a large spin-stabilized space reflector because of solar radiation pressure acting on its surface is investigated. Such a spacecraft consists of a thin reflective circular film, which is deployed from a supporting hoop structure in an untensioned, slack manner. This paper investigates the use of a variable reflectivity distribution across the surface to control the solar pressure force and hence the deflected shape. In this first analysis, the film material is modelled as one-dimensional slack radial strings with no resistance to bending or transverse shear, which enables a semi-analytic derivation of the nominal deflection profile. An inverse method is then used to find the reflectivity distribution that generates a specific, for example, parabolic deflection shape of the strings. Applying these results to a parabolic reflector, short focal distances can be obtained when large slack lengths of the film are employed. The development of such optically controlled reflector films enables future key mission applications such as solar power collection, radio-frequency antennae and optical telescopes.
-
Effect of the Space between Two Glasses on the Solar Sensor ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
The work presented in this paper is a contribution to the theoretical study of the impact of space between the protective glass and the glass through the performance of a solar plan double glazing. Under the climatic conditions in the region of Ouargla Algeria. The study was carried out using a mathematical model obtained ...
-
Third International Symposium on Solar Sailing
2014-01-01
Hosted by the Advanced Space Concepts Laboratory within the department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering of the University of Strathclyde, the third International Symposium on Solar Sailing was held in McCance Building at 16 Richmond Street, Glasgow, between 11 and 13 June 2013. The symposium attracted over 90 delegates from19 different counties, bringing together international experts from across the globe to discuss funded solar sail flight programs alongside on-going technology development and testing programs. The symposium also provided a forum for the discussion of enabling technologies, new application concepts, materials and structural concepts, space environmental effects, dynamics, navigation, control, and much more. This volume contains the unabridged symposium proceedings, in the gathered experts own words. As symposium chair, I thank our partners at Scottish Enterprise and L’Garde, Inc., the symposium’s gold sponsor, for their support in realising this symposium.
-
Quantum mechanics and dynamics in phase space
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zlatev, I.S.
1979-01-01
Attention is paid to formal similarity of quantum mechanics and classical statistical physics. It is supposed that quantum mechanics can be reformulated by means of the quasiprobabilistic distributions (QPD). The procedure of finding a possible dynamics of representative points in a phase space is described. This procedure would lead to an equation of the Liouville type for the given QPD. It is shown that there is always a dynamics for which the phase volume is preserved and there is another dynamics for which the equations of motion are ''canonical''. It follows from the paper that in terms of the QPD the quantum mechanics is analogous to the classical statistical mechanics and it can be interpreted as statistics of phase points, their motion obeying the canonical equations. The difference consists in the fact that in the classical statistical physics constructed is statistics of points in a phase space which depict real, existing, observable states of the system under consideration. In the quantum mechanics constructed is statistics of points in a phase space which correspond to the ''substrate'' of quantum-mechanical objects which have no any physical sense and cannot be observed separately
-
Edwards, D. L.; Hubbs, W. S.; Wertz, G. E.; Alstatt, R.; Munafo, Paul (Technical Monitor)
2001-01-01
The usage of solar sails as a propellantless propulsion system has been proposed for many years. The technical challenges associated with solar sails are fabrication of ultralightweight films, deploying the sails and controlling the spacecraft. Integral to all these challenges is the mechanical property integrity of the sail while exposed to the harsh environment of space. This paper describes testing and characterization of a candidate solar sail material, Aluminized Mylar. This material was exposed to a simulated Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) and evaluated by measuring thermooptical and mechanical property changes. Testing procedures and results are presented.
-
Design package for a complete residential solar space heating and hot water system
1978-01-01
Information necessary to evaluate the design of a solar space heating and hot water system is reported. System performance specifications, the design data brochure, the system description, and other information pertaining to the design are included.
-
Efficient Neural Network Modeling for Flight and Space Dynamics Simulation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ayman Hamdy Kassem
2011-01-01
Full Text Available This paper represents an efficient technique for neural network modeling of flight and space dynamics simulation. The technique will free the neural network designer from guessing the size and structure for the required neural network model and will help to minimize the number of neurons. For linear flight/space dynamics systems, the technique can find the network weights and biases directly by solving a system of linear equations without the need for training. Nonlinear flight dynamic systems can be easily modeled by training its linearized models keeping the same network structure. The training is fast, as it uses the linear system knowledge to speed up the training process. The technique is tested on different flight/space dynamic models and showed promising results.
-
Solar concentrator panel and gore testing in the JPL 25-foot space simulator
Dennison, E. W.; Argoud, M. J.
1981-01-01
The optical imaging characteristics of parabolic solar concentrator panels (or gores) have been measured using the optical beam of the JPL 25-foot space simulator. The simulator optical beam has been characterized, and the virtual source position and size have been determined. These data were used to define the optical test geometry. The point source image size and focal length have been determined for several panels. A flux distribution of a typical solar concentrator has been estimated from these data. Aperture photographs of the panels were used to determine the magnitude and characteristics of the reflecting surface errors. This measurement technique has proven to be highly successful at determining the optical characteristics of solar concentrator panels.
-
Global-scale equatorial Rossby waves as an essential component of solar internal dynamics
Löptien, Björn; Gizon, Laurent; Birch, Aaron C.; Schou, Jesper; Proxauf, Bastian; Duvall, Thomas L.; Bogart, Richard S.; Christensen, Ulrich R.
2018-05-01
The Sun’s complex dynamics is controlled by buoyancy and rotation in the convection zone. Large-scale flows are dominated by vortical motions1 and appear to be weaker than expected in the solar interior2. One possibility is that waves of vorticity due to the Coriolis force, known as Rossby waves3 or r modes4, remove energy from convection at the largest scales5. However, the presence of these waves in the Sun is still debated. Here, we unambiguously discover and characterize retrograde-propagating vorticity waves in the shallow subsurface layers of the Sun at azimuthal wavenumbers below 15, with the dispersion relation of textbook sectoral Rossby waves. The waves have lifetimes of several months, well-defined mode frequencies below twice the solar rotational frequency, and eigenfunctions of vorticity that peak at the equator. Rossby waves have nearly as much vorticity as the convection at the same scales, thus they are an essential component of solar dynamics. We observe a transition from turbulence-like to wave-like dynamics around the Rhines scale6 of angular wavenumber of approximately 20. This transition might provide an explanation for the puzzling deficit of kinetic energy at the largest spatial scales.
-
Space Solar Power Technology Demonstration for Lunar Polar Applications
Henley, M. W.; Fikes, J. C.; Howell, J.; Mankins, J. C.; Howell, J.
2002-01-01
A solar power generation station on a mountaintop near the moon's North or South pole can receive sunlight 708 hours per lunar day, for continuous power generation. Power can be beamed from this station over long distances using a laser-based wireless power transmission system and a photo-voltaic receiver. This beamed energy can provide warmth, electricity, and illumination for a robotic rover to perform scientific experiments in cold, dark craters where no other power source is practical. Radio-frequency power transmission may also be demonstrated in lunar polar applications to locate and recover sub-surface deposits of volatile material, such as water ice. High circular polarization ratios observed in data from Clementine spacecraft and Arecibo radar reflections from the moon's South pole suggest that water ice is indeed present in certain lunar polar craters. Data from the Lunar Prospector spacecraft's epi-thermal neutron spectrometer also indicate that hydrogen is present at the moon's poles. Space Solar Power technology enables investigation of these craters, which may contain a billion-year-old stratigraphic record of tremendous scientific value. Layers of ice, preserved at the moon's poles, could help us determine the sequence and composition of comet impacts on the moon. Such ice deposits may even include distinct strata deposited by secondary ejecta following significant Earth (ocean) impacts, linked to major extinctions of life on Earth. Ice resources at the moon's poles could provide water and air for human exploration and development of space as well as rocket propellant for future space transportation. Technologies demonstrated and matured via lunar polar applications can also be used in other NASA science missions (Valles Marineris. Phobos, Deimos, Mercury's poles, asteroids, etc.) and in future large-scale SSP systems to beam energy from space to Earth. Ground-based technology demonstrations are proceeding to mature the technology for such a near
-
Dynamic tuning of optical absorbers for accelerated solar-thermal energy storage.
Wang, Zhongyong; Tong, Zhen; Ye, Qinxian; Hu, Hang; Nie, Xiao; Yan, Chen; Shang, Wen; Song, Chengyi; Wu, Jianbo; Wang, Jun; Bao, Hua; Tao, Peng; Deng, Tao
2017-11-14
Currently, solar-thermal energy storage within phase-change materials relies on adding high thermal-conductivity fillers to improve the thermal-diffusion-based charging rate, which often leads to limited enhancement of charging speed and sacrificed energy storage capacity. Here we report the exploration of a magnetically enhanced photon-transport-based charging approach, which enables the dynamic tuning of the distribution of optical absorbers dispersed within phase-change materials, to simultaneously achieve fast charging rates, large phase-change enthalpy, and high solar-thermal energy conversion efficiency. Compared with conventional thermal charging, the optical charging strategy improves the charging rate by more than 270% and triples the amount of overall stored thermal energy. This superior performance results from the distinct step-by-step photon-transport charging mechanism and the increased latent heat storage through magnetic manipulation of the dynamic distribution of optical absorbers.
-
Quantum dynamics in dual spaces
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sudarshan, E.C.G.
1993-01-01
Quantum mechanics gives us information about spectra of dynamical variables and transition rates including scattering cross sections. They can be exhibited as spectral information in analytically continued spaces and their duals. Quantum mechanics formulated in these generalized spaces is used to study scattering and time evolution. It is shown that the usual asymptotic condition is inadequate to deal with scattering of composite or unstable particles. Scattering theory needs amendment when the interacting system is not isospectral with the free Hamiltonian, and the amendment is formulated. Perturbation theory in generalized spaces is developed and used to study the deletion and augmentation of the spectrum of the Hamiltonian. A complete set of algebraically independent constants for an interacting system is obtained. The question of the breaking of time symmetry is discussed
-
Rapp, D.
1981-01-01
The book opens with a review of the patterns of energy use and resources in the United States, and an exploration of the potential of solar energy to supply some of this energy in the future. This is followed by background material on solar geometry, solar intensities, flat plate collectors, and economics. Detailed attention is then given to a variety of solar units and systems, including domestic hot water systems, space heating systems, solar-assisted heat pumps, intermediate temperature collectors, space heating/cooling systems, concentrating collectors for high temperatures, storage systems, and solar total energy systems. Finally, rights to solar access are discussed.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Carvalho, M.J.; Neves, Ana [INETI/DER, Lisboa (Portugal)
2006-07-01
The system concept evaluation performed focused on systems that can provide hot water, space heating and swimming-pool heating, and are designed for application in southern climates specifically for single-family houses. Due to the climate characteristics of southern Europe, space heating is required only for a few months in the year. In this evaluation it was considered a six month period for space heating and, on the other six months, swimming pool heating was considered. This type of systems are applicable to a niche market of people who are building their houses as single-family houses and want also to take profit of the good climate conditions for the use of solar energy. It is common that the construction of a swimming pool is also planned and constructed. The evaluation is made considering as reference system a factory made with 4m{sup 2} collector area and 300 l storage tank. The system in evaluation offers extra service - space heating and swimming pool heating and is formed by a collector field and a combistore providing solar hot water preparation and space heating in the winter period and providing also swimming pool heating in the summer period. The evaluation made shows that in southern Europe climates this system will give extra service in comparison to the traditional solar systems used and can be economically interesting.
-
The dynamic relation between activities in the Northern and Southern solar hemispheres
Volobuev, D. M.; Makarenko, N. G.
2016-12-01
The north-south (N/S) asymmetry of solar activity is the most pronounced phenomenon during 11-year cycle minimums. The goal of this work is to try to interpret the asymmetry as a result of the generalized synchronization of two dynamic systems. It is assumed that these systems are localized in two solar hemispheres. The evolution of these systems is considered in the topological embeddings of a sunspot area time series obtained with the use of the Takens algorithm. We determine the coupling measure and estimate it on the time series of daily sunspot areas. The measurement made it possible to interpret the asymmetry as an exchangeable dynamic equation, in which the roles of the driver-slave components change in time for two hemispheres.
-
Little Eyes on Large Solar Motions
Kohler, Susanna
2017-10-01
Images taken during the solar eclipse in 2012. The central color composite of the eclipsed solar surface was captured by SDO, the white-light view of the solar corona around it was taken by the authors, and the background, wide-field black-and-white view is from LASCO. The white arrows mark the atypical structure. [Alzate et al. 2017]It seems like science is increasingly being done with advanced detectors on enormous ground- and space-based telescopes. One might wonder: is there anything left to learn from observations made with digital cameras mounted on 10-cm telescopes?The answer is yes plenty! Illustrating this point, a new study using such equipment recently reports on the structure and dynamics of the Suns corona during two solar eclipses.A Full View of the CoronaThe solar corona is the upper part of the Suns atmosphere, extending millions of kilometers into space. This plasma is dynamic, with changing structures that arise in response to activity on the Suns surface such as enormous ejections of energy known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs). Studying the corona is therefore important for understanding what drives its structure and how energy is released from the Sun.Though there exist a number of space-based telescopes that observe the Suns corona, they often have limited fields of view. The Solar Dynamics Observatory AIA, for instance, has spectacular resolution but only images out to 1/3 of a solar radius above the Suns limb. The space-based coronagraph LASCO C2, on the other hand, provides a broad view of the outer regions of the corona, but it only images down to 2.2 solar radii above the Suns limb. Piecing together observations from these telescopes therefore leaves a gap that prevents a full picture of the large-scale corona and how it connects to activity at the solar surface.Same as the previous figure, but for the eclipse in 2013. [Alzate et al. 2017]To provide this broad, continuous picture, a team of scientists used digital cameras mounted on 10
-
Nuclear dynamics in phase space
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Di Toro, M.
1984-07-01
We present a unified semiclassical picture of nuclear dynamics, from collective states to heavy ion physics, based on a study of the time evolution of the Wigner distribution function. We discuss in particular the mean field dynamics, in this ''quantal'' phase space, which is ruled by the nuclear Vlasov equation. Simple approximate solutions are worked out for rotational and vibrational collective motions. Giant resonances are shown to be quite well described as scaling modes, which are equivalent to a lowest multipole (up to 1sub(max)=2) distortions of the momentum distribution. Applications are shown to heavy ion physics to study giant resonances on high spin states and dynamical collective effects in subthreshold π-production. Several possible extensions and in particular the inclusion of two-body collision terms are finally discussed
-
Long-term influence of asteroids on planet longitudes and chaotic dynamics of the solar system
Woillez, E.; Bouchet, F.
2017-11-01
Over timescales much longer than an orbital period, the solar system exhibits large-scale chaotic behavior and can thus be viewed as a stochastic dynamical system. The aim of the present paper is to compare different sources of stochasticity in the solar system. More precisely we studied the importance of the long term influence of asteroids on the chaotic dynamics of the solar system. We show that the effects of asteroids on planets is similar to a white noise process, when those effects are considered on a timescale much larger than the correlation time τϕ ≃ 104 yr of asteroid trajectories. We computed the timescale τe after which the effects of the stochastic evolution of the asteroids lead to a loss of information for the initial conditions of the perturbed Laplace-Lagrange secular dynamics. The order of magnitude of this timescale is precisely determined by theoretical argument, and we find that τe ≃ 104 Myr. Although comparable to the full main-sequence lifetime of the sun, this timescale is considerably longer than the Lyapunov time τI ≃ 10 Myr of the solar system without asteroids. This shows that the external sources of chaos arise as a small perturbation in the stochastic secular behavior of the solar system, rather due to intrinsic chaos.
-
Wright, Kenneth H.; Schneider, Todd; Vaughn, Jason; Hoang, Bao; Funderburk, Victor V.; Wong, Frankie; Gardiner, George
2010-01-01
A set of multi-junction GaAs/Ge solar array test coupons were subjected to a sequence of 5-year increments of combined environmental exposure tests. The test coupons capture an integrated design intended for use in a geosynchronous (GEO) space environment. A key component of this test campaign is conducting electrostatic discharge (ESD) tests in the inverted gradient mode. The protocol of the ESD tests is based on the ISO/CD 11221, the ISO standard for ESD testing on solar array panels. This standard is currently in its final review with expected approval in 2010. The test schematic in the ISO reference has been modified with Space System/Loral designed circuitry to better simulate the on-orbit operational conditions of its solar array design. Part of the modified circuitry is to simulate a solar array panel coverglass flashover discharge. All solar array coupons used in the test campaign consist of 4 cells. The ESD tests are performed at the beginning of life (BOL) and at each 5-year environment exposure point. The environmental exposure sequence consists of UV radiation, electron/proton particle radiation, thermal cycling, and ion thruster plume. This paper discusses the coverglass flashover simulation, ESD test setup, and the importance of the electrical test design in simulating the on-orbit operational conditions. Results from 5th-year testing are compared to the baseline ESD characteristics determined at the BOL condition.
-
Anspaugh, B. E.; Beckert, D. M.; Downing, R. G.; Weiss, R. S.
1980-01-01
Parametric characterization data on Spectrolab 2 by 4 cm, 2 ohm/cm, 228 micron thick wraparound cell, a candidate for the Solar Electric Propulsion Mission, are presented. These data consist of the electrical characteristics of the solar cell under a wide range of temperature and illumination intensity combinations of the type encountered in space applications.
-
Teaching solar physics in an informal educational space
Aroca, S. C.
2009-02-01
Observatories and planetariums offer the possibility of developing contextualized astronomy teaching by fostering educational activities that provide access to a more authentic school science. Thus, this research consisted in developing, applying and evaluating courses about the Sun for middle, junior high school students and solar physics for high school students in an informal educational space, the CDCC/USP Astronomical Observatory. Topics of chemical composition, temperature and stellar evolution were taught in a room totally dedicated to the study of the Sun, a Solar Room, designed with simple and inexpensive equipment. The course strongly emphasized practical, observational and inquirybased activities, such as estimation of the solar surface temperature, observation of the visible solar spectrum, identication of solar absorption lines, understanding how they are produced, and what kind of information can be extracted from the observed spectral lines. Some of the course goals were to foster the comprehension of the key role played by spectroscopy in astrophysics, to contextualize contents with practical activities, and to allow interdisciplinary approaches including modern physics and chemistry in physics teaching. The research methodology consisted of a qualitative approach by fillming the whole course and performing written questionnaires and semi-structured interviews. Before the courses were applied most students conceived the Sun as a hot sphere composed of fire, sunspots as holes in the Sun and solar prominences as magma expelled by volcanoes. After the courses students presented ideas about the Sun and solar physics more closely related to the ones accepted by contemporary science. This research was not restricted to students' cognitive gains after concluding the courses, since it considered the interaction of different contexts responsible for learning in science museums. This was possible due to the theoretical framework adopted: The Contextual Model
-
Curreri, Peter A.; Detweiler, Michael K.
2011-01-01
In 1975 Gerard O Neill published in the journal Science a model for the construction of solar power satellites. He found that the solar power satellites suggested by Peter Glaser would be too massive to launch economically from Earth, but could be financially viable if the workforce was permanently located in free space habitats and if lunar and asteroid materials were used for construction. All new worldwide electrical generating capacity could be then achieved by solar power satellites. The project would financially break even in about 20 years after which it would generate substantial income selling power below fossil fuel prices. Two NASA / Stanford University led studies at Ames Research center during the summers of 1974 and 1976 found the concept technically sound and developed a detailed financial parametric model. Although the project was not undertaken when suggested in the 1970s, several contemporary issues make pursuing the O Neill -- Glaser concept more compelling today. First, our analysis suggests that if in the first ten years of construction that small habitats (compared to the large vista habitats envisioned by O Neill) supporting approximately 300 people were utilized, development costs of the program and the time for financial break even could be substantially improved. Second, the contemporary consensus is developing that carbon free energy is required to mitigate global climate change. It is estimated that 300 GW of new carbon free energy would be necessary per year to stabilize global atmospheric carbon. This is about 4 times greater energy demand than was considered by the O Neill Glaser model. Our analysis suggests that after the initial investments in lunar mining and space manufacturing and transportation, that the profit margin for producing space solar power is very high (even when selling power below fossil fuel prices). We have investigated the financial scaling of ground launched versus space derived space solar power satellites. We
-
Dynamical Networks Characterization of Space Weather Events
Orr, L.; Chapman, S. C.; Dods, J.; Gjerloev, J. W.
2017-12-01
Space weather can cause disturbances to satellite systems, impacting navigation technology and telecommunications; it can cause power loss and aviation disruption. A central aspect of the earth's magnetospheric response to space weather events are large scale and rapid changes in ionospheric current patterns. Space weather is highly dynamic and there are still many controversies about how the current system evolves in time. The recent SuperMAG initiative, collates ground-based vector magnetic field time series from over 200 magnetometers with 1-minute temporal resolution. In principle this combined dataset is an ideal candidate for quantification using dynamical networks. Network properties and parameters allow us to characterize the time dynamics of the full spatiotemporal pattern of the ionospheric current system. However, applying network methodologies to physical data presents new challenges. We establish whether a given pair of magnetometers are connected in the network by calculating their canonical cross correlation. The magnetometers are connected if their cross correlation exceeds a threshold. In our physical time series this threshold needs to be both station specific, as it varies with (non-linear) individual station sensitivity and location, and able to vary with season, which affects ground conductivity. Additionally, the earth rotates and therefore the ground stations move significantly on the timescales of geomagnetic disturbances. The magnetometers are non-uniformly spatially distributed. We will present new methodology which addresses these problems and in particular achieves dynamic normalization of the physical time series in order to form the network. Correlated disturbances across the magnetometers capture transient currents. Once the dynamical network has been obtained [1][2] from the full magnetometer data set it can be used to directly identify detailed inferred transient ionospheric current patterns and track their dynamics. We will show
-
Opportunities for Space Science Education Using Current and Future Solar System Missions
Matiella Novak, M.; Beisser, K.; Butler, L.; Turney, D.
2010-12-01
The Education and Public Outreach (E/PO) office in The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) Space Department strives to excite and inspire the next generation of explorers by creating interactive education experiences. Since 1959, APL engineers and scientists have designed, built, and launched 61 spacecraft and over 150 instruments involved in space science. With the vast array of current and future Solar System exploration missions available, endless opportunities exist for education programs to incorporate the real-world science of these missions. APL currently has numerous education and outreach programs tailored for K-12 formal and informal education, higher education, and general outreach communities. Current programs focus on Solar System exploration missions such as the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM), Miniature Radio Frequency (Mini-RF) Moon explorer, the Radiation Belt Storm Probes (RBSP), New Horizons mission to Pluto, and the Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics (TIMED) Satellite, to name a few. Education and outreach programs focusing on K-12 formal education include visits to classrooms, summer programs for middle school students, and teacher workshops. APL hosts a Girl Power event and a STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) Day each year. Education and outreach specialists hold teacher workshops throughout the year to train educators in using NASA spacecraft science in their lesson plans. High school students from around the U.S. are able to engage in NASA spacecraft science directly by participating in the Mars Exploration Student Data Teams (MESDT) and the Student Principal Investigator Programs. An effort is also made to generate excitement for future missions by focusing on what mysteries will be solved. Higher education programs are used to recruit and train the next generation of scientists and engineers. The NASA/APL Summer Internship Program offers a
-
Free-piston Stirling engine system considerations for various space power applications
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dochat, G.R.; Dhar, M.
1991-01-01
The U.S. Government is evaluating power requirements for future space applications. As power requirements increase solar or nuclear dynamic systems become increasingly attractive. Free-Piston Stirling Engines (FPSE) have the potential to provide high reliability, long life, and efficient operation. Therefore, they are excellent candidates for the dynamic power conversion module of a space-based, power-generating system. FPSE can be coupled with many potential heat sources (radioisotope, solar, or nuclear reactor), various heat input systems (pumped loop, heat pipe), heat rejection (pumped loop or heat pipe), and various power management and distribution systems (AC, DC, high or low voltage, and fixed or variable load). This paper will review potential space missions that can be met using free-piston Stirling engines and discusses options of various system integration approaches. Currently free-piston Stirling engine technology for space power applications is being developed under contract with NASA-Lewis Research Center. This paper will also briefly outline the program and recent progress
-
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — Solar cells are the critical power source for the majority of space missions. The advancement from single junction silicon cells to current, state-of-the-art, triple...
-
Development of micro-mirror slicer integral field unit for space-borne solar spectrographs
Suematsu, Yoshinori; Saito, Kosuke; Koyama, Masatsugu; Enokida, Yukiya; Okura, Yukinobu; Nakayasu, Tomoyasu; Sukegawa, Takashi
2017-12-01
We present an innovative optical design for image slicer integral field unit (IFU) and a manufacturing method that overcomes optical limitations of metallic mirrors. Our IFU consists of a micro-mirror slicer of 45 arrayed, highly narrow, flat metallic mirrors and a pseudo-pupil-mirror array of off-axis conic aspheres forming three pseudo slits of re-arranged slicer images. A prototype IFU demonstrates that the final optical quality is sufficiently high for a visible light spectrograph. Each slicer micro-mirror is 1.58 mm long and 30 μm wide with surface roughness ≤1 nm rms, and edge sharpness ≤ 0.1 μm, etc. This IFU is small size and can be implemented in a multi-slit spectrograph without any moving mechanism and fore optics, in which one slit is real and the others are pseudo slits from the IFU. The IFU mirrors were deposited by a space-qualified, protected silver coating for high reflectivity in visible and near IR wavelength regions. These properties are well suitable for space-borne spectrograph such as the future Japanese solar space mission SOLAR-C. We present the optical design, performance of prototype IFU, and space qualification tests of the silver coating.
-
Dynamics of Structures in Configuration Space and Phase Space: An Introductory Tutorial
Diamond, P. H.; Kosuga, Y.; Lesur, M.
2015-12-01
Some basic ideas relevant to the dynamics of phase space and real space structures are presented in a pedagogical fashion. We focus on three paradigmatic examples, namely; G. I. Taylor's structure based re-formulation of Rayleigh's stability criterion and its implications for zonal flow momentum balance relations; Dupree's mechanism for nonlinear current driven ion acoustic instability and its implication for anomalous resistivity; and the dynamics of structures in drift and gyrokinetic turbulence and their relation to zonal flow physics. We briefly survey the extension of mean field theory to calculate evolution in the presence of localized structures for regimes where Kubo number K ≃ 1 rather than K ≪ 1, as is usual for quasilinear theory.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Benseman, R.
1977-10-15
The potential for solar space heating and solar water heating in New Zealand is discussed. Available solar energy in New Zealand is indicated, and the economics of solar space and water heating is considered. (WHK)
-
Reliability models for Space Station power system
Singh, C.; Patton, A. D.; Kim, Y.; Wagner, H.
1987-01-01
This paper presents a methodology for the reliability evaluation of Space Station power system. The two options considered are the photovoltaic system and the solar dynamic system. Reliability models for both of these options are described along with the methodology for calculating the reliability indices.
-
Magnetosheath waves under very low solar wind dynamic pressure: Wind/Geotail observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. J. Farrugia
2005-06-01
Full Text Available The expanded bow shock on and around "the day the solar wind almost disappeared" (11 May 1999 allowed the Geotail spacecraft to make a practically uninterrupted 54-h-long magnetosheath pass near dusk (16:30-21:11 magnetic local time at a radial distance of 24 to 30 RE (Earth radii. During most of this period, interplanetary parameters varied gradually and in such a way as to give rise to two extreme magnetosheath structures, one dominated by magnetohydrodynamic (MHD effects and the other by gas dynamic effects. We focus attention on unusual features of electromagnetic ion wave activity in the former magnetosheath state, and compare these features with those in the latter. Magnetic fluctuations in the gas dynamic magnetosheath were dominated by compressional mirror mode waves, and left- and right-hand polarized electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EIC waves transverse to the background field. In contrast, the MHD magnetosheath, lasting for over one day, was devoid of mirror oscillations and permeated instead by EIC waves of weak intensity. The weak wave intensity is related to the prevailing low solar wind dynamic pressures. Left-hand polarized EIC waves were replaced by bursts of right-hand polarized waves, which remained for many hours the only ion wave activity present. This activity occurred when the magnetosheath proton temperature anisotropy (= became negative. This was because the weakened bow shock exposed the magnetosheath directly to the (negative temperature anisotropy of the solar wind. Unlike the normal case studied in the literature, these right-hand waves were not by-products of left-hand polarized waves but derived their energy source directly from the magnetosheath temperature anisotropy. Brief entries into the low latitude boundary layer (LLBL and duskside magnetosphere occurred under such inflated conditions that the magnetospheric magnetic pressure was insufficient to maintain pressure balance. In these crossings, the inner edge of
-
MUSE, the Multi-Slit Solar Explorer
Lemen, J. R.; Tarbell, T. D.; De Pontieu, B.; Wuelser, J. P.
2017-12-01
The Multi-Slit Solar Explorer (MUSE) has been selected for a Phase A study for the NASA Heliophysics Small Explorer program. The science objective of MUSE is to make high spatial and temporal resolution imaging and spectral observations of the solar corona and transition region in order to probe the mechanisms responsible for energy release in the corona and understand the dynamics of the solar atmosphere. The physical processes are responsible for heating the corona, accelerating the solar wind, and the rapid release of energy in CMEs and flares. The observations will be tightly coupled to state-of-the-art numerical modeling to provide significantly improved estimates for understanding and anticipating space weather. MUSE contains two instruments: an EUV spectrograph and an EUV context imager. Both have similar spatial resolutions and leverage extensive heritage from previous high-resolution instruments such as IRIS and the HiC rocket payload. The MUSE spectrograph employs a novel multi-slit design that enables a 100x improvement in spectral scanning rates, which will reveal crucial information about the dynamics (e.g., temperature, velocities) of the physical processes that are not observable with current instruments. The MUSE investigation builds on the success of IRIS by combining numerical modeling with a uniquely capable observatory: MUSE will obtain EUV spectra and images with the highest resolution in space (1/3 arcsec) and time (1-4 s) ever achieved for the transition region and corona, along 35 slits and a large context FOV simultaneously. The MUSE consortium includes LMSAL, SAO, Stanford, ARC, HAO, GSFC, MSFC, MSU, and ITA Oslo.
-
2005-01-01
This is a Roadmap to understanding the environment of our Earth, from its life-sustaining Sun out past the frontiers of the solar system. A collection of spacecraft now patrols this space, revealing not a placid star and isolated planets, but an immense, dynamic, interconnected system within which our home planet is embedded and through which space explorers must journey. These spacecraft already form a great observatory with which the Heliophysics program can study the Sun, the heliosphere, the Earth, and other planetary environments as elements of a system--one that contains dynamic space weather and evolves in response to solar, planetary, and interstellar variability. NASA continually evolves the Heliophysics Great Observatory by adding new missions and instruments in order to answer the challenging questions confronting us now and in the future as humans explore the solar system. The three heliophysics science objectives: opening the frontier to space environment prediction; understanding the nature of our home in space, and safeguarding the journey of exploration, require sustained research programs that depend on combining new data, theory, analysis, simulation, and modeling. Our program pursues a deeper understanding of the fundamental physical processes that underlie the exotic phenomena of space.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Vincent, Frederic E.; Ben-Jaffel, Lotfi; Harris, Walter M.
2011-01-01
The interplanetary hydrogen (IPH), a population of neutrals that fill the space between planets inside the heliosphere, carries the signature of the interstellar medium (ISM) and the heliospheric interface. As the incoming ISM-ionized component deflects at the heliopause, charge exchange reactions decelerate the bulk motion of the neutrals that penetrate the heliosphere. Inside the heliosphere, the IPH bulk velocity is further affected by solar gravity, radiation pressure, and ionization processes, with the latter two processes dependent on solar activity. Solar cycle 23 provided the first partial temporal map of the IPH velocity, including measurements from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) spectrometers (Goddard High Resolution Spectrograph (GHRS) and Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS)) and the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory/Solar Wind ANisotropies (SWAN) instrument. We present an updated analysis of IPH velocity measurements from GHRS and STIS and compare these results with those of SWAN and two different time-dependent models. Our reanalysis of STIS data reveals a significant change in IPH velocity relative to earlier reports, because of the contamination by geocoronal oxygen that was not accounted for. While current models of the heliospheric interface predict the observed IPH velocity for solar maximum, they are not consistent with data covering solar minimum. With updates to the HST data points, we now find that all data can be fit by the existing models to within 1σ, with the exception of SWAN observations taken at solar minimum (1997/1998). We conclude that the current data lack the temporal coverage and/or precision necessary to determine the detailed characteristics of the solar cycle dependence. Hence, new observations are merited.
-
Status of the organic Rankine cycle for space applications
Bland, T. J.; Lacey, P. D.; Sorensen, G. L.
The Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) has been under continuous development and evaluation since the 1960s for both terrestrial and space power applications. Recent activities (Bland et al, 1987) have focused primarily on the Space Station's solar dynamic power system and Dynamic Isotope Power Systems (DIPS) applications. This paper addresses ORC-DIPS system level trade studies conducted during the past year and a half. Two companion papers (Bland and Pearson) present more detailed data on specific ORC-DIPS technology issues and testing conducted during the same period.
-
Fusion, space and solar plasmas as complex systems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dendy, R O; Chapman, S C; Paczuski, M
2007-01-01
Complex systems science seeks to identify simple universal models that capture the key physics of extended macroscopic systems, whose behaviour is governed by multiple nonlinear coupled processes that operate across a wide range of spatiotemporal scales. In such systems, it is often the case that energy release occurs intermittently, in bursty events, and the phenomenology can exhibit scaling, that is a significant degree of self-similarity. Within plasma physics, such systems include Earth's magnetosphere, the solar corona and toroidal magnetic confinement experiments. Guided by broad understanding of the dominant plasma processes-for example, turbulent transport in tokamaks or reconnection in some space and solar contexts-one may construct minimalist complex systems models that yield relevant global behaviour. Examples considered here include the sandpile approach to tokamaks and the magnetosphere and a multiple loops model for the solar coronal magnetic carpet. Such models can address questions that are inaccessible to analytical treatment and are too demanding for contemporary computational resources; thus they potentially yield new insights, but risk being simplistic. Central to the utility of these models is their capacity to replicate distinctive aspects of observed global phenomenology, often strongly nonlinear, or of event statistics, for which no explanation can be obtained from first principles considerations such as the underlying equations. For example, a sandpile model, which embodies critical-gradient-triggered avalanching transport associated with nearest-neighbour mode coupling and simple boundary conditions (and little else), can be used to generate some of the distinctive observed elements of tokamak confinement phenomenology such as ELMing and edge pedestals. The same sandpile model can also generate distributions of energy-release events whose distinctive statistics resemble those observed in the auroral zone. Similarly, a multiple loops model
-
Thermal design, analysis and comparison on three concepts of space solar power satellite
Yang, Chen; Hou, Xinbin; Wang, Li
2017-08-01
Space solar power satellites (SSPS) have been widely studied as systems for collecting solar energy in space and transmitting it wirelessly to earth. A previously designed planar SSPS concept collects solar power in two huge arrays and then transmits it through one side of the power-conduction joint to the antenna. However, the system's one group of power-conduction joints may induce a single point of failure. As an SSPS concept, the module symmetrical concentrator (MSC) architecture has many advantages. This architecture can help avoid the need for a large, potentially failure-prone conductive rotating joint and limit wiring mass. However, the thermal control system has severely restricted the rapid development of MSC, especially in the sandwich module. Because of the synchronous existence of five suns concentration and solar external heat flux, the sandwich module will have a very high temperature, which will surpass the permissible temperature of the solar cells. Recently, an alternate multi-rotary joints (MR) SSPS concept was designed by the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST). This system has multiple joints to avoid the problem of a single point of failure. Meanwhile, this concept has another advantage for reducing the high power and heat removal in joints. It is well known to us that, because of the huge external flux in SSPS, the thermal management sub-system is an important component that cannot be neglected. Based on the three SSPS concepts, this study investigated the thermal design and analysis of a 1-km, gigawatt-level transmitting antenna in SSPS. This study compares the thermal management sub-systems of power-conduction joints in planar and MR SSPS. Moreover, the study considers three classic thermal control architectures of the MSC's sandwich module: tile, step, and separation. The study also presents an elaborate parameter design, analysis and discussion of step architecture. Finally, the results show the thermal characteristics of each SSPS
-
Phase space approach to quantum dynamics
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Leboeuf, P.
1991-03-01
The Schroedinger equation for the time propagation of states of a quantised two-dimensional spherical phase space is replaced by the dynamics of a system of N particles lying in phase space. This is done through factorization formulae of analytic function theory arising in coherent-state representation, the 'particles' being the zeros of the quantum state. For linear Hamiltonians, like a spin in a uniform magnetic field, the motion of the particles is classical. However, non-linear terms induce interactions between the particles. Their time propagation is studied and it is shown that, contrary to integrable systems, for chaotic maps they tend to fill, as their classical counterpart, the whole phase space. (author) 13 refs., 3 figs
-
The SOLAR-C Mission: Science Objectives and Current Status
Suematsu, Y.; Solar-C Working Group
2016-04-01
The SOLAR-C is a Japan-led international solar mission for mid-2020s designed to investigate the magnetic activities of the Sun, focusing on the study in heating and dynamical phenomena of the chromosphere and corona, and to advance algorithms for predicting short and long term solar magnetic activities. For these purposes, SOLAR-C will carry three dedicated instruments; the Solar UV-Vis-IR Telescope (SUVIT), the EUV Spectroscopic Telescope (EUVST) and the High Resolution Coronal Imager (HCI), to jointly observe the entire visible solar atmosphere with essentially the same high spatial resolution (0.1"-0.3"), performing high resolution spectroscopic measurements over all atmospheric regions and spectro-polarimetric measurements from the photosphere through the upper chromosphere. SOLAR-C will also contribute to understand the solar influence on the Sun-Earth environments with synergetic wide-field observations from ground-based and other space missions.
-
Suematsu, Y.
2015-12-01
The Solar-C is a Japan-led international solar mission planned to be launched in mid2020. It is designed to investigate the magnetic activities of the Sun, focusing on the study in heating and dynamical phenomena of the chromosphere and corona, and also to develop an algorithm for predicting short and long term solar evolution. Since it has been revealed that the different parts of the magnetized solar atmosphere are essentially coupled, the SOLAR-C should tackle the spatial scales and temperature regimes that need to be observed in order to achieve a comprehensive physical understanding of this coupling. The science of Solar-C will greatly advance our understanding of the Sun, of basic physical processes operating throughout the universe. To dramatically improve the situation, SOLAR-C will carry three dedicated instruments; the Solar UV-Vis-IR Telescope (SUVIT), the EUV Spectroscopic Telescope (EUVST) and the High Resolution Coronal Imager (HCI), to jointly observe the entire visible solar atmosphere with essentially the same high spatial resolution (0.1-0.3 arcsec), performing high resolution spectroscopic measurements over all atmospheric regions and spectro-polarimetric measurements from the photosphere through the upper chromosphere. In addition, Solar-C will contribute to our understanding on the influence of the Sun-Earth environments with synergetic wide-field observations from ground-based and other space missions. Some leading science objectives and the mission concept, including designs of the three instruments aboard SOLAR-C will be presented.
-
Powering an in-space 3D printer using solar light energy
Leake, Skye; McGuire, Thomas; Parsons, Michael; Hirsch, Michael P.; Straub, Jeremy
2016-05-01
This paper describes how a solar power source can enable in-space 3D printing without requiring conversion to electric power and back. A design for an in-space 3D printer is presented, with a particular focus on the power generation system. Then, key benefits are presented and evaluated. Specifically, the approach facilitates the design of a spacecraft that can be built, launched, and operated at very low cost levels. The proposed approach also facilitates easy configuration of the amount of energy that is supplied. Finally, it facilitates easier disposal by removing the heavy metals and radioactive materials required for a nuclear-power solution.
-
Johnson Space Center's Solar and Wind-Based Renewable Energy System
Vasquez, A.; Ewert, M.; Rowlands, J.; Post, K.
2009-01-01
The NASA Johnson Space Center (JSC) in Houston, Texas has a Sustainability Partnership team that seeks ways for earth-based sustainability practices to also benefit space exploration research. A renewable energy gathering system was installed in 2007 at the JSC Child Care Center (CCC) which also offers a potential test bed for space exploration power generation and remote monitoring and control concepts. The system comprises: 1) several different types of photovoltaic panels (29 kW), 2) two wind-turbines (3.6 kW total), and 3) one roof-mounted solar thermal water heater and tank. A tie to the JSC local electrical grid was provided to accommodate excess power. The total first year electrical energy production was 53 megawatt-hours. A web-based real-time metering system collects and reports system performance and weather data. Improvements in areas of the CCC that were detected during subsequent energy analyses and some concepts for future efforts are also presented.
-
Experimental analysis and dynamic simulation of a novel high-temperature solar cooling system
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Buonomano, Annamaria; Calise, Francesco; D’Accadia, Massimo Dentice; Ferruzzi, Gabriele; Frascogna, Sabrina; Palombo, Adolfo; Russo, Roberto; Scarpellino, Marco
2016-01-01
Highlights: • The paper presents an innovative high temperature solar cooling system. • The system is based on novel flat-plate evacuated solar thermal collectors. • Results of an experimental campaign in Saudi Arabia are reported. • A dynamic simulation model and a detailed economic analyses are developed. • Results show that the collector and the system as a whole exhibit excellent performance. - Abstract: This paper presents experimental and numerical analyses of a novel high-temperature solar cooling system based on innovative flat-plate evacuated solar thermal collectors (SC). This is the first solar cooling system, including a double-effect absorption chiller, which is based on non-concentrating solar thermal collectors. The aim of the paper is prove the technical and economic feasibility of the system, also presenting a comparison with a conventional technology, based on concentrating solar thermal collectors. To this scope, an experimental setup has been installed in Saudi Arabia. Here, several measurement devices are installed in order to monitor and control all the thermodynamic parameters of the system. The paper presents some of the main results of this experimental campaign, showing temperatures, powers, energies and efficiencies for a selected period. Experimental results showed that collector peak efficiency is higher than 60%, whereas daily average efficiency is around 40%. This prototypal solar cooling system has been numerically analysed, developing a dynamic simulation model aiming at predicting system performance. For a representative operating period, numerical data were compared with the experimental one, showing an excellent accuracy of the model. A similar system, equipped with Parabolic Trough solar thermal collectors (PTC) was also simulated in order to compare the novel solar collectors with such reference technology. For both systems a detailed thermo-economic model has been implemented in order to perform such comparison also
-
The Origin of the "Seasons" in Space Weather
Dikpati, Mausumi; Cally, Paul S.; McIntosh, Scott W.; Heifetz, Eyal
2017-11-01
Powerful `space weather' events caused by solar activity pose serious risks to human health, safety, economic activity and national security. Spikes in deaths due to heart attacks, strokes and other diseases occurred during prolonged power outages. Currently it is hard to prepare for and mitigate the impact of space weather because it is impossible to forecast the solar eruptions that can cause these terrestrial events until they are seen on the Sun. However, as recently reported in Nature, eruptive events like coronal mass ejections and solar flares, are organized into quasi-periodic "seasons", which include enhanced bursts of eruptions for several months, followed by quiet periods. We explored the dynamics of sunspot-producing magnetic fields and discovered for the first time that bursty and quiet seasons, manifested in surface magnetic structures, can be caused by quasi-periodic energy-exchange among magnetic fields, Rossby waves and differential rotation of the solar interior shear-layer (called tachocline). Our results for the first time provide a quantitative physical mechanism for forecasting the strength and duration of bursty seasons several months in advance, which can greatly enhance our ability to warn humans about dangerous solar bursts and prevent damage to satellites and power stations from space weather events.
-
Fe IX CALCULATIONS FOR THE SOLAR DYNAMICS OBSERVATORY
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Foster, Adam R.; Testa, Paola
2011-01-01
New calculations of the energy levels, radiative transition rates, and collisional excitation rates of Fe IX have been carried out using the Flexible Atomic Code, paying close attention to experimentally identified levels and extending existing calculations to higher energy levels. For lower levels, R-matrix collisional excitation rates from earlier work have been used. Significant emission is predicted by these calculations in the 5f-3d transitions, which will impact analysis of Solar Dynamics Observatory Atmospheric Imaging Assembly observations using the 94 A filter.
-
Population Pressure, Global Living Standards, and the Promise of Space Solar Power
Strickland, John K., Jr.
2002-01-01
uses of electricity and fuels currently covered by fossil fuels. This is a global replacement load of about 9000 gigawatts. Green theorists are divided on this issue. Some claim that ground based solar, wind, and other renewable sources will supply all the energy we need, ignoring economic costs that severely limit their use. Others would (unrealistically) require the developed countries to reduce their energy consumption per capita to a level closer to that of the developing world, thereby admitting the limitations of the "appropriate" systems they espouse. Both sides in the past have rejected as "non-appropriate" and/or "dangerous" all the chemically clean energy sources of high capacity that have been previously proposed, such as safer nuclear fission, fusion power, and space solar power. If ground based "appropriate" energy sources are not sufficient, the economic and social effects of sudden forced curtailments of fossil energy use could be drastic. This paper supports the thesis that Space Solar Power does have the potential to provide such a clean, abundant, and economical energy source. It will cover both the limitations and promise of ground based energy sources, including the difficulties of using intermittent energy sources. It will discuss whether specified levels of energy cost increases would be damaging to the world economy and whether economical ground based sources alone would have sufficient capacity. It will show how the one major problem of launch costs, (currently preventing economical implementation of Space Solar Power), has a number of quite reasonable solutions. Finally, it will consider whether Space Solar Power, along with the other major space goals of Science &Exploration, Mars Colonization, Non- terrestrial Materials Recovery and Space Tourism, could be another space "killer app" which, by creating a high demand for launch services, could force large reductions in launch costs.
-
Solar heating systems for houses. A design handbook for solar combisystems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Weiss, W.
2003-11-01
A handbook giving guidance on systems for providing combined solar space heating and solar water heating for houses has been produced by an international team. The guidance focuses on selection of the optimum combi-system for groups of single-family houses and multi-family houses. Standard classification and evaluation procedures are described. The book should be a valuable tool for building engineers, architects, solar manufacturers and installers of solar solar energy systems, and anyone interested in optimizing combined water and space heating solar systems
-
Dynamical Changes Induced by the Solar Proton Events in October-November 2003
Jackman, C. H.; Roble, R. G.; Fleming, E. L.
2006-05-01
The very large solar storms in October-November 2003 caused solar proton events (SPEs) at the Earth and impacted the upper atmospheric polar cap regions. The Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Electrodynamic General Circulation Mode (TIME-GCM) was used to study the atmospheric dynamical influence of the solar protons that occurred in Oct-Nov 2003, the fourth largest period of SPEs measured in the past 40 years. The highly energetic solar protons caused ionization and changes in the electric field, which led to Joule heating of the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. This heating led to temperature increases up to 4K in the upper mesosphere. The solar proton-induced ionization, as well as dissociation processes, led to the production of odd hydrogen (HOx) and odd nitrogen (NOy). Substantial (>40%) short-lived ozone decreases followed these enhancements of HOx and NOy and led to a cooling of the mesosphere and upper stratosphere. This cooling led to temperature decreases up to 2.5K. The solar proton-caused temperature changes led to maximum meridional and zonal wind variations of +/- 2 m/s on background winds up to +/- 30 m/s. The solar proton-induced wind perturbations were computed to taper off over a period of several days past the SPEs. Solar cycle 23 was accompanied by ten very large SPEs between 1998 and 2005, along with numerous smaller events. These solar proton-driven atmospheric variations need to be carefully considered when examining other polar changes.
-
Mechanism on radiation degradation of Si space solar cells
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yamaguchi, Masafumi; Taylor, S.J.; Hisamatsu, Tadashi; Matsuda, Sumio
1998-01-01
Radiation testing of Si n + -p-p + structure space solar cells has revealed an anomalous increase in short-circuit current Isc, followed by an abrupt decrease and cell failure, induced by high fluence electron and proton irradiations. A model to explain these phenomena by expressing the change in carrier concentration p of the base region is proposed in addition to the well-known model where Isc is decreased by minority-carrier lifetime reduction with irradiation. Change in carrier concentration causes broadening the depletion layer to contribute increase in the generated photocurrent and increase in recombination-generation current in the depletion layer, and increase in the resistivity of the base layer to result in the abrupt decrease of Isc and failure of the solar cell. Type conversion from p-type to n-type in base layer has been confirmed by EBIC (electron-beam induced current) and spectral response measurements. Moreover, origins of radiation-induced defects in heavily irradiated Si and generation of deep donor defects have also been examined by using DLTS (deep level transient spectroscopy) analysis. (author)
-
Comparison of candidate solar array maximum power utilization approaches. [for spacecraft propulsion
Costogue, E. N.; Lindena, S.
1976-01-01
A study was made of five potential approaches that can be utilized to detect the maximum power point of a solar array while sustaining operations at or near maximum power and without endangering stability or causing array voltage collapse. The approaches studied included: (1) dynamic impedance comparator, (2) reference array measurement, (3) onset of solar array voltage collapse detection, (4) parallel tracker, and (5) direct measurement. The study analyzed the feasibility and adaptability of these approaches to a future solar electric propulsion (SEP) mission, and, specifically, to a comet rendezvous mission. Such missions presented the most challenging requirements to a spacecraft power subsystem in terms of power management over large solar intensity ranges of 1.0 to 3.5 AU. The dynamic impedance approach was found to have the highest figure of merit, and the reference array approach followed closely behind. The results are applicable to terrestrial solar power systems as well as to other than SEP space missions.
-
Ceriotti, Matteo
The idea of exploiting solar radiation pressure for space travel, or solar sailing, is more than a 100 years old, and yet most of the research thus far has considered only a limited number of sail configurations. However solar sails do not have to be inertially-pointing squares, spin-stabilised discs or heliogyros: there is a range of different configurations and concepts that present some advantageous features. This chapter will show and discuss three non-conventional solar sail configurations and their applications. In the first, the sail is complemented by an electric thruster, resulting in a hybrid-propulsion spacecraft which is capable to hover above the Earth's Poles in a stationary position (pole-sitter). The second concept makes use of a variable-geometry pyramidal sail, naturally pointing towards the sun, to increase or decrease the orbit altitude without the need of propellant or attitude manoeuvres. Finally, the third concept shows that the orbit altitude can also be changed, without active manoeuvres or geometry change, if the sail naturally oscillates synchronously with the orbital motion. The main motivation behind these novel configurations is to overcome some of the engineering limitations of solar sailing; the resulting concepts pose some intriguing orbital and attitude dynamics problems, which will be discussed.
-
On Non-Universality of Solar-Terrestrial Connections
Pustilnik, Lev; Yom Din, Gregory
The discussion on the principal possibility of a causal chain from solar activity and space weather to the earth weather and agriculture price dynamics continues over 200 years from the first publication of Herschel (1801) up to the current time. We analyze main arguments of the two sides and show that the root of the critics of this possibility lies in the wide accepted conception of the universality of the solar-terrestrial connection (that can appear, for example, in daily and seasonal variations) what suggest that the effect can be observed in any historical period and in any region. We show that this expectation is not correct because of the solar-terrestrial connections generated by different sides of solar activity with different agents of solar magnetic dynamo process that have different and non-stable phase patterns. We remind that the realization of the causal chain “solar activity/space weather” - “earth weather” - “crops” -“market reaction” may have a place only in specific historical periods and in specific zones where and when the three necessary conditions hold true. This limitation leads to one of four possible scenarios of the market reaction. We show that the critical arguments used for rejecting a principal possibility of the causal connection “solar activity” - Earth agriculture markets” are based on neglecting the three necessary conditions for realization of this connection, and on analyzing periods and regions when and where the necessary conditions are not hold.
-
The Sustainable Development of Space: Astro-environmental and dynamical considerations
Boley, Aaron; Byers, Michael; Russell, Sara
2018-04-01
The sustainable development of space is a global (and exo-global) challenge that is not limited by borders or research disciplines. Sustainable development is "development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs". While the development of space brings new economic and scientific possibilities, it also carries significant political, legal, and technical uncertainties. For example, the rapidly increasing accessibility of space is motivating states to unilaterally adopt legislation for the new era of space use, which may have significant unintended consequences, such as increased risks to space assets, disputes among state as well as non-state actors, and changes to unique astro-environments. Any policy or legal position must be informed by the dynamical and astrophysical realities of space use, creating complex and interwoven challenges. Here, we explore several of these potential challenges related to astro-environmentalism, space minining operations, and the associated dynamics.
-
Solar energetic particles and space weather
Reames, Donald V.; Tylka, Allan J.; Ng, Chee K.
2001-02-01
The solar energetic particles (SEPs) of consequence to space weather are accelerated at shock waves driven out from the Sun by fast coronal mass ejections (CMEs). In the large events, these great shocks fill half of the heliosphere. SEP intensity profiles change appearance with longitude. Events with significant intensities of >10 MeV protons occur at an average rate of ~13 yr-1 near solar maximum and several events with high intensities of >100 MeV protons occur each decade. As particles stream out along magnetic field lines from a shock near the Sun, they generate waves that scatter subsequent particles. At high intensities, wave growth throttles the flow below the ``streaming limit.'' However, if the shock maintains its strength, particle intensities can rise above this limit to a peak when the shock itself passes over the observer creating a `delayed' radiation hazard, even for protons with energies up to ~1 GeV. The streaming limit makes us blind to the intensities at the oncoming shock, however, heavier elements such as He, O, and Fe probe the shape of the wave spectrum, and variation in abundances of these elements allow us to evade the limit and probe conditions at the shock, with the aid of detailed modeling. At high energies, spectra steepen to form a spectral `knee.' The location of the proton spectral knee can vary from ~10 MeV to ~1 GeV, depending on shock conditions, greatly affecting the radiation hazard. Hard spectra are a serious threat to astronauts, placing challenging requirements for shielding, especially on long-duration missions to the moon or Mars. .
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Su, Di; Jia, Yuting; Alva, Guruprasad; Liu, Lingkun; Fang, Guiyin
2017-01-01
Highlights: • The dynamic model of photovoltaic–thermal collector with phase change material was developed. • The performances of photovoltaic–thermal collector are performed comparative analyses. • The performances of photovoltaic–thermal collector with phase change material were evaluated. • Upper phase change material mode can improve performances of photovoltaic–thermal collector. - Abstract: The operating conditions (especially temperature) of photovoltaic–thermal solar collectors have significant influence on dynamic performance of the hybrid photovoltaic–thermal solar collectors. Only a small percentage of incoming solar radiation can be converted into electricity, and the rest is converted into heat. This heat leads to a decrease in efficiency of the photovoltaic module. In order to improve the performance of the hybrid photovoltaic–thermal solar collector, we performed comparative analyses on a hybrid photovoltaic–thermal solar collector integrated with phase change material. Electrical and thermal parameters like solar cell temperature, outlet temperature of air, electrical power, thermal power, electrical efficiency, thermal efficiency and overall efficiency are simulated and analyzed to evaluate the dynamic performance of the hybrid photovoltaic–thermal collector. It is found that the position of phase change material layer in the photovoltaic–thermal collector has a significant effect on the performance of the photovoltaic–thermal collector. The results indicate that upper phase change material mode in the photovoltaic–thermal collector can significantly improve the thermal and electrical performance of photovoltaic–thermal collector. It is found that overall efficiency of photovoltaic–thermal collector in ‘upper phase change material’ mode is 10.7% higher than that in ‘no phase change material’ mode. Further, for a photovoltaic–thermal collector with upper phase change material, it is verified that 3 cm
-
Colliding worlds: A journey in time and space through the solar system (Farinella Prize Lecture)
Marchi, S.
2017-09-01
The evolution of the interiors, surfaces, and atmospheres of solid bodies in the solar system is affected by interplanetary collisions. From Mercury to the outskirts of the solar system, collisions with leftover planetesimals -asteroids, comets and their debris- provide a primary evolutionary process. Impact craters mark this evolution and provide a diagnostic tool, which coupled with modeling and, when possible, sample analysis, allow us to unravel the ancient history of the solar system. In this prize talk, I will present a few selected cutting-edge research topics at the frontier between modeling and space exploration that without any doubt would have deeply interested the curious mind of Paolo Farinella.
-
Wong, Sun; Del Genio, Anthony; Wang, Tao; Kahn, Brian; Fetzer, Eric J.; L'Ecuyer, Tristan S.
2015-01-01
Goals: Water budget-related dynamical phase space; Connect large-scale dynamical conditions to atmospheric water budget (including precipitation); Connect atmospheric water budget to cloud type distributions.
-
Adjustment, error analysis and modular strategy for Space Solar Power Station
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Meng, Xian-Long; Xia, Xin-Lin; Sun, Chuang; Hou, Xin-Bin
2014-01-01
Highlights: • The optimal adjustment method for SSPS when it travels on orbit is determined. • Two solutions for the arrangement of transverse truss are proposed. • The effect and regulating method for the tracking error are investigated. • The mathematical partition model of a flat hexagon module concept is built. • The flux distributions on solar panel based on different number of modules are simulated. - Abstract: Space Solar Power Station (SSPS) is a very potential candidate for supplying abundant electrical energy. Symmetrical two-stage flat reflected concentrator (STFC) has many advantages when used in SSPS. However the steady performance and control method on orbit has become a big problem which will be discussed in this paper. The actual posture of entire station is analyzed in detail due to the requirements of good flux uniformity, circular concentrated spot and controlled concentration ratio. Here two regulating directions are studied. And the most optimal method in multidimensional space of adjusting parameters is developed. In order to verify the correctness and reliability, the concentrating characteristics in different cases are simulated by Monte-Carlo ray tracing method (MCRTM). Based on the optimal adjusting parameters, solutions for the arrangement of transverse truss are proposed. After that the effect and regulating method for tracking error is investigated to improve the tolerance performance as highly as possible. Finally the construction of concentrators is much important to the realizability, cost and working performance. A flat hexagon module concept and the regular pattern are investigated to build the optical model. The flux distribution on solar panel based on different big number of modules is simulated, which provides certain reference for the build of SSPS
-
Space Resource Utilization and Extending Human Presence Across the Solar System
Curreri, Peter A.
2005-01-01
investment enables commercial and private viability beyond Earth orbit. For example, analysis has shown the lunar oxygen production for propellant becomes commercially viable after the exploration program completes the R&D, and power from lunar derived photovoltaics could, according to past NASA sponsored studies, pay for themselves while supplying most of Earth's electrical energy after about 17 years. Besides the Moon and Mars the resources of the near Earth asteroids enable the building of large space structures and science payloads. Analysis has shown that one of the thousands of these objects (some as easily accessible in space as the Moon and Mars), 2 km dia, the size of a typical open pit mine, would cost the total global financial product of Earth for 30,000 years if we were to launch it from Earth. Beyond Mars, the belt asteroids have been calculated to contain enough materials for habitat and life to support 10 quadrillion people. Thus, the development and use of space resources enables the extension of human life through the solar system allowing humanity to move from a planetary to a solar system society.
-
On the track of gravity modes: study of the dynamics of the solar core
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mathur, Savita
2007-01-01
This thesis is dedicated to the study of the dynamics of the solar radiative zone through gravity modes. Though the core represents more than 50% of the solar mass, we still do not have an accurate vision of the rotation profile in the very inner part of the Sun. To understand the evolution of stars, we try to put constraints on dynamic processes. Several paths have been followed in this thesis to tackle this issue: solar modeling, the study of a new instrument, observations and inversions of the rotation. The necessity of the detection of gravity modes is driven by the will for a better comprehension of the solar dynamics. With a technological prototype built at the CEA (GOLF-NG), we want to validate a few technical points and prepare the scientific mission which aim will be to detect these gravity modes. We studied first the photodetector and then the whole instrument response. We show the feasibility of the instrument. The observation of the resonance in all the channels proves that it works the way we expected. However, before this mission takes place, the analysis of GOLF data enabled us to detect one gravity-mode candidate as well as the signature of dipole gravity modes. This work benefited from a more theoretical approach on the prediction of gravity-mode frequencies. We show the influence of several physical processes and quantities. Finally, as the dynamical processes in the Sun are not well constrained, we tried to understand the impact of the introduction of one and several gravity modes on the inferred rotation profiles. We also tried to give constraints on the observations so that we could obtain some information on the rotation profile in the core. (author) [fr
-
Investigations of Solar Prominence Dynamics Using Laboratory Simulations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bellan, Paul M.
2008-01-01
Laboratory experiments simulating many of the dynamical features of solar coronal loops have been carried out. These experiments manifest collimation, kinking, jet flows, and S-shapes. Diagnostics include high-speed photography and x-ray detectors. Two loops having opposite or the same magnetic helicity polarities have been merged and it is found that counter-helicity merging provides much greater x-ray emission. A non-MHD particle orbit instability has been discovered whereby ions going in the opposite direction of the current flow direction can be ejected from a magnetic flux tube.
-
Phase-space dynamics of Bianchi IX cosmological models
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Soares, I.D.
1985-01-01
The complex phase-space dynamical behaviour of a class of Biachi IX cosmological models is discussed, as the chaotic gravitational collapse due Poincare's homoclinic phenomena, and the n-furcation of periodic orbits and tori in the phase space of the models. Poincare maps which show this behaviour are constructed merically and applications are discussed. (Author) [pt
-
Magnetosheath waves under very low solar wind dynamic pressure: Wind/Geotail observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. J. Farrugia
2005-06-01
Full Text Available The expanded bow shock on and around "the day the solar wind almost disappeared" (11 May 1999 allowed the Geotail spacecraft to make a practically uninterrupted 54-h-long magnetosheath pass near dusk (16:30-21:11 magnetic local time at a radial distance of 24 to 30 RE (Earth radii. During most of this period, interplanetary parameters varied gradually and in such a way as to give rise to two extreme magnetosheath structures, one dominated by magnetohydrodynamic (MHD effects and the other by gas dynamic effects. We focus attention on unusual features of electromagnetic ion wave activity in the former magnetosheath state, and compare these features with those in the latter. Magnetic fluctuations in the gas dynamic magnetosheath were dominated by compressional mirror mode waves, and left- and right-hand polarized electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EIC waves transverse to the background field. In contrast, the MHD magnetosheath, lasting for over one day, was devoid of mirror oscillations and permeated instead by EIC waves of weak intensity. The weak wave intensity is related to the prevailing low solar wind dynamic pressures. Left-hand polarized EIC waves were replaced by bursts of right-hand polarized waves, which remained for many hours the only ion wave activity present. This activity occurred when the magnetosheath proton temperature anisotropy (=
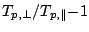 became negative. This was because the weakened bow shock exposed the magnetosheath directly to the (negative temperature anisotropy of the solar wind. Unlike the normal case studied in the literature, these right-hand waves were not by-products of left-hand polarized waves but derived their energy source directly from the magnetosheath temperature anisotropy. Brief entries into the
became negative. This was because the weakened bow shock exposed the magnetosheath directly to the (negative temperature anisotropy of the solar wind. Unlike the normal case studied in the literature, these right-hand waves were not by-products of left-hand polarized waves but derived their energy source directly from the magnetosheath temperature anisotropy. Brief entries into the -
Structure and Dynamics of the Quiet Solar Chromosphere
Kalkofen, Wolfgang
2002-04-01
The grant supported research on the structure of the quiet, nonmagnetic chromosphere and on wave excitation and propagation in both the nonmagnetic chromosphere and the magnetic network. The work on the structure of the chromosphere culminated in the recognition that between two competing views of the solar chromosphere, older models by Avrett and collaborators (referred to as VAL) and the newer, dynamical model by Carlsson & Stein (referred to as CS), the clear decision is in favor of the older models, and this in spite of the evident lack of physics, which does not include wave motion and oscillations. The contrast between the static VAL models and the dynamical CS model can be stated most succinctly by comparing the temperature variation implied by the VAL models and the temperature fluctuations of the CS model, which are, respectively, of the order of 10% for the VAL model (at heights where hydrogen is 50% ionized) and a factor of 10 (at the upper boundary of their chromospheric model). The huge fluctuations of the CS model have never been observed, whereas the smaller temperature variations of the VAL models are consistent with ground-based and space-based observations. While it should be obvious which model describes the Sun and which one fails, the case is far from settled in the minds of solar physicists. Thus, much educational work remains to be done and, of course, more research to develop arguments that make the case more convincing. The research on waves and oscillations has been based on a unified theory of excitation of acoustic waves in the field-free atmosphere and of transverse and longitudinal waves in magnetic flux tubes located in the magnetic network by noting, first, that impulsive excitation of all these waves in gravitationally stratified media leads to oscillations at the respective cutoff frequencies and, second, that the observed oscillation frequencies in the nonmagnetic and magnetic parts of the chromosphere match corresponding cutoff
-
Solar thermal - the new dynamics
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
2017-01-01
This booklet is intended to engineering consultants and construction professionals and aims at showing them the real interest of solar thermal energy. It notably highlights the very high efficiency which can be reached, the high performance value compared to gas, the high rank of solar thermal energy in terms of profitability over a 20-year period, the fact that solar thermal energy is almost always the most economic solution for buildings and the less expensive in comparison with non renewable energies. It outlines that, as far as purchase is concerned, solar thermal energy is more than competitive, is also a leader as far as financing issues are concerned. It finally briefly describes how the SOCOL initiative can be a support at any step of a solar thermal project
-
Hawkins, I.; Higdon, R.; Cline, T.
2006-12-01
Over the past seven years, NASA's Sun-Earth Connection Education Forum has sponsored and coordinated education and public outreach events to highlight NASA's heliophysics research and discoveries. Our strategy involves using celestial events, such as total solar eclipses and the Transit of Venus, as well as Sun-Earth Day during the March Equinox, to engage K-12 schools and the general public in space science activities, demonstrations, and interactions with space scientists. In collaboration with partners that include the Exploratorium and other museums, Ideum, NASA TV, NASA heliophysics missions, and others, we produce webcasts, other multi-media, and print resources for use by school and informal educators nation-wide and internationally. We provide training and professional development to K-12 educators, museum personnel, amateur astronomers, Girl Scout leaders, etc., so they can implement their own outreach programs taking advantage of our resources. A coordinated approach promotes multiple programs occurring each year under a common theme. As part of an Ancient Observatories theme in 2005, we have successfully featured solar alignments with ancient structures made by indigenous cultures that mark the equinoxes and/or solstices in cultural and historical parks in the Americas. In partnership with the Exploratorium, we produced broadcast-quality and webcast programming during the March equinox that shared heliophysics within a broad cultural context with formal and informal education audiences internationally. The program: "Descent of the Serpent" featured the light and shadow effect at sunset that takes place during the spring equinox at the Pyramid of El Castillo, in Chichén Itzá (México). This program made unique and authentic cultural connections to the knowledge of solar astronomy of the Maya, the living Mayan culture of today, and the importance of the Sun across the ages. We involved Sun-Earth Connection scientists, their missions, and research
-
Dynamic screening in solar and stellar nuclear reactions
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Daeppen, W. [Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA (United States); Mussack, K. [Los Alamos National Laboratory, XTD-2, Los Alamos, NM (United States)
2012-02-15
In the hot, dense plasma of solar and stellar interiors, Coulomb potentials are screened, resulting in increased nuclear reaction rates. Although Salpeter's approximation for static screening is widely accepted and used in stellar modeling, the question of screening in nuclear reactions was revisited in the 1990s. In particular the issue of dynamic effects was raised by Shaviv and Shaviv, who applied the techniques of molecular dynamics to the conditions in the Sun's core in order to numerically determine the effect of screening. By directly calculating the motion of ions and electrons due to Coulomb interactions, the simulations are used to compute the effect of screening without the mean-field assumption inherent in Salpeter's approximation. In the last few years, the USC group has first reproduced Shaviv and Shaviv's numerical analysis of the screening energy, showing an effect of dynamic screening. When the consequence for the reaction-rate was computed, a rather surprising resulted, which is contrary to that from static screening theory. Our calculations showed that dynamic screening does not significantly change the reaction rate from that of the bare Coulomb potential. If this can be independently confirmed, then the effects of dynamic screening are highly relevant and should be included in stellar nuclear reaction rates (copyright 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, Weinheim) (orig.)
-
Space Solar Patrol data and changes in weather and climate, including global warming
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Avakyan, S V; Leonov, N B; Voronin, N A; Baranova, L A; Savinov, E P
2010-01-01
In this paper, the results obtained during the execution of several ISTC projects are presented. The general aim of these projects has been the study of global changes in the environment, connected with solar activity. A brief description of the optical apparatus of the Space Solar Patrol (SSP) developed and built in the framework of the ISTC projects 385, 385.2, 1523 and 2500 is given. The SSP is intended for permanent monitoring of spectra and absolute fluxes of soft x-ray and extreme ultraviolet (x-ray/EUV) radiation from the full disk of the Sun which ionizes the upper atmosphere of the Earth. Permanent solar monitoring in the main part of the ionizing radiation spectra 0.8–115 (119) nm does not exist. The apparatus of the SSP was developed in the years 1996–2005 with multiyear experience of developing such apparatus in S I Vavilov State Optical Institute. The basis of this apparatus is the use of unique detectors of ionizing radiation—open secondary electron multipliers, which are 'solar blind' to near UV, visible and IR radiation from the Sun, and new methodology of these solar spectroradiometric absolute measurements. The prospects are discussed of using the SSP data for the investigation and forecast of the influence of solar variability on the weather and climate including global warming and also on the biosphere including human beings (proposal 3878)
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Vejen, Niels Kristian
1997-01-01
A low flow solar heating system for space heating and domestic hot water supply from Aidt Miljø A/Swas tested in a laboratory test facility.......A low flow solar heating system for space heating and domestic hot water supply from Aidt Miljø A/Swas tested in a laboratory test facility....
-
Gamut mapping in a high-dynamic-range color space
Preiss, Jens; Fairchild, Mark D.; Ferwerda, James A.; Urban, Philipp
2014-01-01
In this paper, we present a novel approach of tone mapping as gamut mapping in a high-dynamic-range (HDR) color space. High- and low-dynamic-range (LDR) images as well as device gamut boundaries can simultaneously be represented within such a color space. This enables a unified transformation of the HDR image into the gamut of an output device (in this paper called HDR gamut mapping). An additional aim of this paper is to investigate the suitability of a specific HDR color space to serve as a working color space for the proposed HDR gamut mapping. For the HDR gamut mapping, we use a recent approach that iteratively minimizes an image-difference metric subject to in-gamut images. A psychophysical experiment on an HDR display shows that the standard reproduction workflow of two subsequent transformations - tone mapping and then gamut mapping - may be improved by HDR gamut mapping.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Raphaldini, Breno; Raupp, Carlos F. M., E-mail: brenorfs@gmail.com, E-mail: carlos.raupp@iag.usp.br [Instituto de Astronomia, Geofísica e Ciências Atmosféricas, Departamento de Geofísica, Rua do Matão, 1226-Cidade Universitária São Paulo-SP 05508-090 (Brazil)
2015-01-20
The solar dynamo is known to be associated with several periodicities, with the nearly 11/22 yr cycle being the most pronounced one. Even though these quasiperiodic variations of solar activity have been attributed to the underlying dynamo action in the Sun's interior, a fundamental theoretical description of these cycles is still elusive. Here, we present a new possible direction in understanding the Sun's cycles based on resonant nonlinear interactions among magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) Rossby waves. The WKB theory for dispersive waves is applied to magnetohydrodynamic shallow-water equations describing the dynamics of the solar tachocline, and the reduced dynamics of a resonant triad composed of MHD Rossby waves embedded in constant toroidal magnetic field is analyzed. In the conservative case, the wave amplitudes evolve periodically in time, with periods on the order of the dominant solar activity timescale (∼11 yr). In addition, the presence of linear forcings representative of either convection or instabilities of meridionally varying background states appears to be crucial in balancing dissipation and thus sustaining the periodic oscillations of wave amplitudes associated with resonant triad interactions. Examination of the linear theory of MHD Rossby waves embedded in a latitudinally varying mean flow demonstrates that MHD Rossby waves propagate toward the equator in a waveguide from –35° to 35° in latitude, showing a remarkable resemblance to the structure of the butterfly diagram of the solar activity. Therefore, we argue that resonant nonlinear magnetohydrodynamic Rossby wave interactions might significantly contribute to the observed cycles of magnetic solar activity.
-
Seeing real-space dynamics of liquid water through inelastic x-ray scattering.
Iwashita, Takuya; Wu, Bin; Chen, Wei-Ren; Tsutsui, Satoshi; Baron, Alfred Q R; Egami, Takeshi
2017-12-01
Water is ubiquitous on earth, but we know little about the real-space motion of molecules in liquid water. We demonstrate that high-resolution inelastic x-ray scattering measurement over a wide range of momentum and energy transfer makes it possible to probe real-space, real-time dynamics of water molecules through the so-called Van Hove function. Water molecules are found to be strongly correlated in space and time with coupling between the first and second nearest-neighbor molecules. The local dynamic correlation of molecules observed here is crucial to a fundamental understanding of the origin of the physical properties of water, including viscosity. The results also suggest that the quantum-mechanical nature of hydrogen bonds could influence its dynamics. The approach used here offers a powerful experimental method for investigating real-space dynamics of liquids.
-
Silva, H G; Lopes, I
Heliospheric modulation of galactic cosmic rays links solar cycle activity with neutron monitor count rate on earth. A less direct relation holds between neutron monitor count rate and atmospheric electric field because different atmospheric processes, including fluctuations in the ionosphere, are involved. Although a full quantitative model is still lacking, this link is supported by solid statistical evidence. Thus, a connection between the solar cycle activity and atmospheric electric field is expected. To gain a deeper insight into these relations, sunspot area (NOAA, USA), neutron monitor count rate (Climax, Colorado, USA), and atmospheric electric field (Lisbon, Portugal) are presented here in a phase space representation. The period considered covers two solar cycles (21, 22) and extends from 1978 to 1990. Two solar maxima were observed in this dataset, one in 1979 and another in 1989, as well as one solar minimum in 1986. Two main observations of the present study were: (1) similar short-term topological features of the phase space representations of the three variables, (2) a long-term phase space radius synchronization between the solar cycle activity, neutron monitor count rate, and potential gradient (confirmed by absolute correlation values above ~0.8). Finally, the methodology proposed here can be used for obtaining the relations between other atmospheric parameters (e.g., solar radiation) and solar cycle activity.
-
Hybrid photovoltaic–thermal solar collectors dynamic modeling
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Amrizal, N.; Chemisana, D.; Rosell, J.I.
2013-01-01
Highlights: ► A hybrid photovoltaic/thermal dynamic model is presented. ► The model, once calibrated, can predict the power output for any set of climate data. ► The physical electrical model includes explicitly thermal and irradiance dependences. ► The results agree with those obtained through steady-state characterization. ► The model approaches the junction cell temperature through the system energy balance. -- Abstract: A hybrid photovoltaic/thermal transient model has been developed and validated experimentally. The methodology extends the quasi-dynamic thermal model stated in the EN 12975 in order to involve the electrical performance and consider the dynamic behavior minimizing constraints when characterizing the collector. A backward moving average filtering procedure has been applied to improve the model response for variable working conditions. Concerning the electrical part, the model includes the thermal and radiation dependences in its variables. The results revealed that the characteristic parameters included in the model agree reasonably well with the experimental values obtained from the standard steady-state and IV characteristic curve measurements. After a calibration process, the model is a suitable tool to predict the thermal and electrical performance of a hybrid solar collector, for a specific weather data set.
-
Magnetohydrodynamic Modeling of Solar Coronal Dynamics with an Initial Non-force-free Magnetic Field
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Prasad, A.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Kumar, Sanjay [Udaipur Solar Observatory, Physical Research Laboratory, Dewali, Bari Road, Udaipur-313001 (India)
2017-05-01
The magnetic fields in the solar corona are generally neither force-free nor axisymmetric and have complex dynamics that are difficult to characterize. Here we simulate the topological evolution of solar coronal magnetic field lines (MFLs) using a magnetohydrodynamic model. The simulation is initialized with a non-axisymmetric non-force-free magnetic field that best correlates with the observed vector magnetograms of solar active regions (ARs). To focus on these ideas, simulations are performed for the flaring AR 11283 noted for its complexity and well-documented dynamics. The simulated dynamics develops as the initial Lorentz force pushes the plasma and facilitates successive magnetic reconnections at the two X-type null lines present in the initial field. Importantly, the simulation allows for the spontaneous development of mass flow, unique among contemporary works, that preferentially reconnects field lines at one of the X-type null lines. Consequently, a flux rope consisting of low-lying twisted MFLs, which approximately traces the major polarity inversion line, undergoes an asymmetric monotonic rise. The rise is attributed to a reduction in the magnetic tension force at the region overlying the rope, resulting from the reconnection. A monotonic rise of the rope is in conformity with the standard scenario of flares. Importantly, the simulated dynamics leads to bifurcations of the flux rope, which, being akin to the observed filament bifurcation in AR 11283, establishes the appropriateness of the initial field in describing ARs.
-
Going 'green': trade specialisation dynamics in the solar photovoltaic sector
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Algieri, Bernardina; Aquino, Antonio; Succurro, Marianna
2011-01-01
The present study aims at providing a comprehensive analysis of trade flows and the domestic value creation of the major solar photovoltaic industry at the world level. Solar technologies convert light and heat from the sun into useful energy. The use of the sun's energy can not only reduce the consumption of conventional fuels, thus reducing the emission of detrimental greenhouse gases, but it can also enable a gain in enhanced fuel and energy security along with lessening costs. In addition, green technologies and industries can promote economic growth and international competitiveness, and can offer new business and employment opportunities. It becomes, therefore, extremely important to deeply explore the dynamics of the solar photovoltaic sector. Specifically, the present work analyses the main global trends of this sector and sketches the key players on the world market, including producers, installers, and top traders. Based on an analysis of trade flows at the 6-digit level, the international specialisation patterns are investigated, and the role of various market and trade drivers, including subsidies in the uptake of solar technologies, is identified and examined. - Highlights: → Trade specialisation in solar photovoltaics is examined using an index analysis. → Trade of the US, UK and Germany has an intra-industry nature. → Trade of Italy, Greece and Japan is more inter-industry oriented. → There is a long-run relationship between PV exports, foreign income and prices.
-
Gene expression from polynomial dynamics in the 2-adic information space
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Khrennikov, Andrei Yu.
2009-01-01
We perform geometrization of genetics by representing genetic information by points of the 4-adic information space. By well known theorem of number theory this space can also be represented as the 2-adic space. The process of DNA-reproduction is described by the action of a 4-adic (or equivalently 2-adic) dynamical system. As we know, the genes contain information for production of proteins. The genetic code is a degenerate map of codons to proteins. We model this map as functioning of a polynomial dynamical system. The purely mathematical problem under consideration is to find a dynamical system reproducing the degenerate structure of the genetic code. We present one of possible solutions of this problem.
-
Lavraud, B.; Liu, Y.; Segura, K.; He, J.; Qin, G.; Temmer, M.; Vial, J.-C.; Xiong, M.; Davies, J. A.; Rouillard, A. P.;

2016-01-01
We present a concept for a small mission to the Sun-Earth Lagrangian L5 point for innovative solar, heliospheric and space weather science. The proposed INvestigation of Solar-Terrestrial Activity aNd Transients (INSTANT) mission is designed to identify how solar coronal magnetic fields drive eruptions, mass transport and particle acceleration that impact the Earth and the heliosphere. INSTANT is the first mission designed to (1) obtain measurements of coronal magnetic fields from space and (2) determine coronal mass ejection (CME) kinematics with unparalleled accuracy. Thanks to innovative instrumentation at a vantage point that provides the most suitable perspective view of the Sun-Earth system, INSTANT would uniquely track the whole chain of fundamental processes driving space weather at Earth. We present the science requirements, payload and mission profile that fulfill ambitious science objectives within small mission programmatic boundary conditions.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Vejen, Niels Kristian
1999-01-01
A solar heating system for space heating and domestic hot water supply from "Sol&Træ A.m.b.a." was tested in a laboratory test facility.......A solar heating system for space heating and domestic hot water supply from "Sol&Træ A.m.b.a." was tested in a laboratory test facility....
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Saim Memon
2017-06-01
Full Text Available A considerable effort is devoted to devising retrofit solutions for reducing space-heating energy in the domestic sector. Existing UK solid-wall dwellings, which have both heritage values and historic fabric, are being improved but they tend to have meagre thermal performance, partly, due to the heat-loss through glazings. This paper takes comparative analyses approach to envisage space-heating supply required in order to maintain thermal comfort temperatures and attainable solar energy gains to households with the retrofit of an experimentally achievable thermal performance of the fabricated sample of triple vacuum glazing to a UK solid-wall dwelling. 3D dynamic thermal models (timely regimes of heating, occupancy, ventilation and internal heat gains of an externally-insulated solid-wall detached dwelling with a range of existing glazing types along with triple vacuum glazings are modelled. A dramatic decrease of space-heating load and moderate increase of solar gains are resulted with the dwelling of newly achievable triple vacuum glazings (having centre-of-pane U-value of 0.33 Wm-2K-1 compared to conventional glazing types. The space-heating annual cost of single glazed dwellings was minimised to 15.31% (≈USD 90.7 with the retrofit of triple-vacuum glazings. An influence of total heat-loss through the fabric of solid-wall dwelling was analysed with steady-state calculations which indicates a fall of 10.23 % with triple vacuum glazings compared to single glazings.
-
Efficient placement of structural dynamics sensors on the space station
Lepanto, Janet A.; Shepard, G. Dudley
1987-01-01
System identification of the space station dynamic model will require flight data from a finite number of judiciously placed sensors on it. The placement of structural dynamics sensors on the space station is a particularly challenging problem because the station will not be deployed in a single mission. Given that the build-up sequence and the final configuration for the space station are currently undetermined, a procedure for sensor placement was developed using the assembly flights 1 to 7 of the rephased dual keel space station as an example. The procedure presented approaches the problem of placing the sensors from an engineering, as opposed to a mathematical, point of view. In addition to locating a finite number of sensors, the procedure addresses the issues of unobserved structural modes, dominant structural modes, and the trade-offs involved in sensor placement for space station. This procedure for sensor placement will be applied to revised, and potentially more detailed, finite element models of the space station configuration and assembly sequence.
-
The Second Annual International Space University Alumni Conference
Johnson, Les (Compiler); Robinson, Paul A. (Compiler)
1994-01-01
The papers presented at the conference reflect the multidisciplinary nature of the International Space University (ISU) and its alumni. The first papers presented hold special relevance to the design projects, and cover such topics as lunar-based astronomical instrumentation, solar lunar power generation, habitation on the moon, and the legal issues governing multinational astronauts conducting research in space. The next set of papers cover various technical issues such as project success assessment, satellite networks and space station dynamics, thus reflecting the diverse backgrounds of the ISU alumni.
-
Asymptotic matching of the solar-system gravitational yields
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kopejkin, S.M.
1989-01-01
In the framework of the general relativity, the structure of the Solar-system gravitational fields is investigated and the relativistic formulae of transformation between nonrotating in the dynamical sense harmonic reference systems - barycentric, planetocentric and topocentric (satelite) ones - are derived by the method of the asymptotic mathing of components of the metric tensor. The derived formulae generalize the linear Poincare transformation in the case of curved space-time. With the help of the asymptotic matching formulae, the relationships between relativistic time scales inside the Solar system have been established, the equations of relativistic precession of the space axis of one reference system with respect to another one have been derived, the equations of translational motion of the center-of-mass of planets (the Sun) and their satellites have been obtained
-
A Study of the Solar Wind-Magnetosphere Coupling Using Neural Networks
Wu, Jian-Guo; Lundstedt, Henrik
1996-12-01
The interaction between solar wind plasma and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) and Earth's magnetosphere induces geomagnetic activity. Geomagnetic storms can cause many adverse effects on technical systems in space and on the Earth. It is therefore of great significance to accurately predict geomagnetic activity so as to minimize the amount of disruption to these operational systems and to allow them to work as efficiently as possible. Dynamic neural networks are powerful in modeling the dynamics encoded in time series of data. In this study, we use partially recurrent neural networks to study the solar wind-magnetosphere coupling by predicting geomagnetic storms (as measured by the Dstindex) from solar wind measurements. The solar wind, the IMF and the geomagnetic index Dst data are hourly averaged and read from the National Space Science Data Center's OMNI database. We selected these data from the period 1963 to 1992, which cover 10552h and contain storm time periods 9552h and quiet time periods 1000h. The data are then categorized into three data sets: a training set (6634h), across-validation set (1962h), and a test set (1956h). The validation set is used to determine where the training should be stopped whereas the test set is used for neural networks to get the generalization capability (the out-of-sample performance). Based on the correlation analysis between the Dst index and various solar wind parameters (including various combinations of solar wind parameters), the best coupling functions can be found from the out-of-sample performance of trained neural networks. The coupling functions found are then used to forecast geomagnetic storms one to several hours in advance. The comparisons are made on iterating the single-step prediction several times and on making a non iterated, direct prediction. Thus, we will present the best solar wind-magnetosphere coupling functions and the corresponding prediction results. Interesting Links: Lund Space Weather and AI
-
Microparticle impacts in space: Results from Solar Max and shuttle witness plate inspections
Mckay, David S.
1989-01-01
The Solar Maximum Satellite developed electronic problems after operating successfully in space for several years. Astronauts on Space Shuttle mission STS-41C retrieved the satellite into the orbiter cargo bay, replaced defective components, and re-deployed the repaired satellite into orbit. The defective components were returned to Earth for study. The space-exposed surfaces were examined. The approach and objectives were to: document morphology of impact; find and analyze projectile residue; classify impact by origin; determine flux distribution; and determine implications for space exposure. The purpose of the shuttle witness plate experiment was to detect impacts from PAM D2 solid rocket motor; determine flux and size distribution of particles; and determine abrasion effects on various conditions. Results are given for aluminum surfaces, copper surfaces, stainless steel surfaces, Inconel surfaces, and quartz glass surfaces.
-
Solar Array Sails: Possible Space Plasma Environmental Effects
Mackey, Willie R.
2005-01-01
An examination of the interactions between proposed "solar sail" propulsion systems with photovoltaic energy generation capabilities and the space plasma environments. Major areas of interactions ere: Acting from high voltage arrays, ram and wake effects, V and B current loops and EMI. Preliminary analysis indicates that arcing will be a major risk factor for voltages greater than 300V. Electron temperature enhancement in the wake will be produce noise that can be transmitted via the wake echo process. In addition, V and B induced potential will generate sheath voltages with potential tether like breakage effects in the thin film sails. Advocacy of further attention to these processes is emphasized so that plasma environmental mitigation will be instituted in photovoltaic sail design.
-
Solar India - 82: national solar energy convention
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
1982-01-01
This document is the proceedings of the Solar India - 82 conference, which was held 17-19 December 1982. The papers are organized into functional groupings which include: (1) solar radiation, (2) flat plate solar collectors and solar water heaters, (3) solar concentrators, (4) solar air heaters and dryers, (5) solar ponds and energy storage, (6) solar cookers, (7) solar stills, (8) selective coatings, (9) photovoltaics, (10) space heating and cooling, (11) bio-energy, and (12) miscellaneous papers. The vast majority of the papers describe work carried out in India, the vast majority of the papers also contain relatively readable abstracts.
-
Dye-sensitized solar cells: Atomic scale investigation of interface structure and dynamics
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ma Wei; Zhang Fan; Meng Sheng
2014-01-01
Recent progress in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSC) research is reviewed, focusing on atomic-scale investigations of the interface electronic structures and dynamical processes, including the structure of dye adsorption onto TiO 2 , ultrafast electron injection, hot-electron injection, multiple-exciton generation, and electron—hole recombination. Advanced experimental techniques and theoretical approaches are briefly summarized, and then progressive achievements in photovoltaic device optimization based on insights from atomic scale investigations are introduced. Finally, some challenges and opportunities for further improvement of dye solar cells are presented. (invited review — international conference on nanoscience and technology, china 2013)
-
Trembach, Vera
2014-01-01
Space is an introduction to the mysteries of the Universe. Included are Task Cards for independent learning, Journal Word Cards for creative writing, and Hands-On Activities for reinforcing skills in Math and Language Arts. Space is a perfect introduction to further research of the Solar System.
-
Solar system maps from antiquity to the space age
Kanas, Nick
2013-01-01
In recent years, there has been increased interest in our Solar System. This has been prompted by the launching of giant orbiting telescopes and space probes, the discovery of new planetary moons and heavenly bodies that orbit the Sun, and the demotion of Pluto as a planet. In one generation, our place in the heavens has been challenged, but this is not unusual. Throughout history, there have been a number of such world views. Initially, Earth was seen as the center of the universe and surrounded by orbiting planets and stars. Then the Sun became the center of the cosmos. Finally, there was no
-
Predicting Solar Activity Using Machine-Learning Methods
Bobra, M.
2017-12-01
Of all the activity observed on the Sun, two of the most energetic events are flares and coronal mass ejections. However, we do not, as of yet, fully understand the physical mechanism that triggers solar eruptions. A machine-learning algorithm, which is favorable in cases where the amount of data is large, is one way to [1] empirically determine the signatures of this mechanism in solar image data and [2] use them to predict solar activity. In this talk, we discuss the application of various machine learning algorithms - specifically, a Support Vector Machine, a sparse linear regression (Lasso), and Convolutional Neural Network - to image data from the photosphere, chromosphere, transition region, and corona taken by instruments aboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory in order to predict solar activity on a variety of time scales. Such an approach may be useful since, at the present time, there are no physical models of flares available for real-time prediction. We discuss our results (Bobra and Couvidat, 2015; Bobra and Ilonidis, 2016; Jonas et al., 2017) as well as other attempts to predict flares using machine-learning (e.g. Ahmed et al., 2013; Nishizuka et al. 2017) and compare these results with the more traditional techniques used by the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center (Crown, 2012). We also discuss some of the challenges in using machine-learning algorithms for space science applications.
-
Charge carrier recombination dynamics in perovskite and polymer solar cells
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Paulke, Andreas; Kniepert, Juliane; Kurpiers, Jona; Wolff, Christian M.; Schön, Natalie; Brenner, Thomas J. K.; Neher, Dieter [Institute of Physics and Astronomy, University of Potsdam, Karl-Liebknecht-Str. 24–25, 14476, Potsdam (Germany); Stranks, Samuel D. [Clarendon Laboratory, Department of Physics, University of Oxford, Parks Road, Oxford OX1 3PU (United Kingdom); Research Laboratory of Electronics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139 (United States); Cavendish Laboratory, JJ Thomson Avenue, Cambridge CB3 0HE (United Kingdom); Snaith, Henry J. [Clarendon Laboratory, Department of Physics, University of Oxford, Parks Road, Oxford OX1 3PU (United Kingdom)
2016-03-14
Time-delayed collection field experiments are applied to planar organometal halide perovskite (CH{sub 3}NH{sub 3}PbI{sub 3}) based solar cells to investigate charge carrier recombination in a fully working solar cell at the nanosecond to microsecond time scale. Recombination of mobile (extractable) charges is shown to follow second-order recombination dynamics for all fluences and time scales tested. Most importantly, the bimolecular recombination coefficient is found to be time-dependent, with an initial value of ca. 10{sup −9} cm{sup 3}/s and a progressive reduction within the first tens of nanoseconds. Comparison to the prototypical organic bulk heterojunction device PTB7:PC{sub 71}BM yields important differences with regard to the mechanism and time scale of free carrier recombination.
-
A novel small dynamic solar thermal desalination plant with a fluid piston converter
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mahkamov, Khamid; Orda, Eugene; Belgasim, Basim; Makhkamova, Irina
2015-01-01
Highlights: • A dynamic solar desalination plant was developed which works cyclically. • It integrates an evacuated tube solar collector and fluid piston converter. • Pressure during desalination process varies with frequency of 2–4 Hz. • The system has a small increase in fresh water yield and provides pumping capacity. • Mathematical modelling provides accurate description of experimental performance. - Abstract: An innovative small dynamic water desalination plant was developed and tested under laboratory conditions. The system is a combination of a heat pipe evacuated tube solar collector, conventional condenser and novel fluid piston converter. Saline water is boiled and turned into vapour in the manifold of the solar collector. A small fraction of the solar energy supplied to the plant is used to drive the fluid piston converter. Oscillations of the fluid piston periodically change the volume and pressure in the plant. For the duration of approximately half of the periodic cycle the pressure in the plant drops below the atmospheric level causing flash boiling of saline water in the manifold of the solar collector. Generated vapour is turned into fresh water in the condenser which is surrounded by a cooling jacket with saline water. The flash boiling effect improves the fresh water production capacity of the plant. Additionally, the fluid piston converter drives a pump which provides lifting of saline water from a well and pumps this through the cooling jacket of the condenser to a saline water storage tank. This tank replenishes saline water in the manifold of the solar collector. Experimental investigations demonstrated the saline water self-circulation capability of the plant and increase in the fresh water production compared to the static mode of operation. Experimental data was also used to calibrate the mathematical model of the plant. Comparison of theoretical and experimental information demonstrates that the model accurately predicts the
-
Technology for Bayton-cycle powerplants using solar and nuclear energy
English, R. E.
1986-01-01
Brayton cycle gas turbines have the potential to use either solar heat or nuclear reactors for generating from tens of kilowatts to tens of megawatts of power in space, all this from a single technology for the power generating system. Their development for solar energy dynamic power generation for the space station could be the first step in an evolution of such powerplants for a very wide range of applications. At the low power level of only 10 kWe, a power generating system has already demonstrated overall efficiency of 0.29 and operated 38 000 hr. Tests of improved components show that these components would raise that efficiency to 0.32, a value twice that demonstrated by any alternate concept. Because of this high efficiency, solar Brayton cycle power generators offer the potential to increase power per unit of solar collector area to levels exceeding four times that from photovoltaic powerplants using present technology for silicon solar cells. The technologies for solar mirrors and heat receivers are reviewed and assessed. This Brayton technology for solar powerplants is equally suitable for use with the nuclear reactors. The available long time creep data on the tantalum alloy ASTAR-811C show that such Brayton cycles can evolve to cycle peak temperatures of 1500 K (2240 F). And this same technology can be extended to generate 10 to 100 MW in space by exploiting existing technology for terrestrial gas turbines in the fields of both aircraft propulsion and stationary power generation.
-
Optimization of a solar driven absorption refrigerator in the transient regime
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hamed, Mouna; Fellah, Ali; Ben Brahim, Ammar
2012-01-01
Highlights: ► Dynamic behavior of a solar absorption refrigerator endoreversible model. ► Using the principles of classical thermodynamics, mass and heat transfers. ► Minimizing heat exchange time to reach maximum performances. ► Major influence of the collector temperature on the model’s characteristics. ► Analogous effects of both the thermal load and the thermal conductance. -- Abstract: This contribution deals with the theoretical study in dynamic mode of an absorption refrigerator endoreversible model. The system is a cold generating station driven by solar energy. The main elements of the cycle are a refrigerated space, an absorption refrigerator and a solar collector form. A mathematical model is developed. It combines the classical thermodynamics and mass and heat transfers principles. The numerical simulation is made for different operating and conceptual conditions. A global minimizing time optimization is performed in view to reach maximum performances. Appropriate dimensionless groups are defined. The results are presented in normalized charts for general applications. The collector temperature presents major influence on the conceptual and functional characteristics compared to the stagnation temperature influence. On the other hand the thermal load in the refrigerated space and the thermal conductance of the walls has analogous effects, therefore important to be considered in actual design. As a result, the model is expected to be a useful tool for simulation, design, and optimization of solar collector based energy systems.
-
Dynamic Space - uus köögistandard
2005-01-01
Furnituuritootja Blum'i - ainuesindaja Eestis Hahle Eesti OÜ - poolt välja töötatud köögistandardi Dynamic Space põhimõtetest (piisav kasulik paigutusruum, viis köögitsooni, alumiste kappide asemel lõpuni lahtitõmmatavate ORGA-LINE sisejaotustega sahtlite eelistamine)
-
1973-01-01
The astronomy and space physics investigations conducted in the Skylab program include over 20 experiments in four categories to explore space phenomena that cannot be observed from earth. The categories of space research are as follows: (1) phenomena within the solar system, such as the effect of solar energy on Earth's atmosphere, the composition of interplanetary space, the possibility of an inner planet, and the X-ray radiation from Jupiter, (2) analysis of energetic particles such as cosmic rays and neutrons in the near-earth space, (3) stellar and galactic astronomy, and (4) self-induced environment surrounding the Skylab spacecraft.
-
A model for the origin of solar wind stream interfaces
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hundhausen, A.J.; Burlaga, L.F.
1975-01-01
The basic variations in solar wind properties that have been observed at 'stream interfaces' near 1 AU are explained by a gas dynamic model in which a radially propagating stream, produced by a temperature variation in the solar envelope, steepens nonlinearly while moving through interplanetary space. The region thus identified with the stream interface separates the ambient solar wind from the fresh hot material originally in the stream. However, the interface regions given by the present model are thicker than most stream interfaces observed in the solar wind, a fact suggesting that some additional physical process may be important in determining that thickness. Variations in the density, speed, or Alfven pressure alone appear not to produce streams with such an interface
-
Long-term dynamics of OH * temperatures over central Europe: trends and solar correlations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. Kalicinsky
2016-12-01
Full Text Available We present the analysis of annual average OH* temperatures in the mesopause region derived from measurements of the Ground-based Infrared P-branch Spectrometer (GRIPS at Wuppertal (51° N, 7° E in the time interval 1988 to 2015. The new study uses a temperature time series which is 7 years longer than that used for the latest analysis regarding the long-term dynamics. This additional observation time leads to a change in characterisation of the observed long-term dynamics. We perform a multiple linear regression using the solar radio flux F10.7 cm (11-year cycle of solar activity and time to describe the temperature evolution. The analysis leads to a linear trend of (−0.089 ± 0.055 K year−1 and a sensitivity to the solar activity of (4.2 ± 0.9 K (100 SFU−1 (r2 of fit 0.6. However, one linear trend in combination with the 11-year solar cycle is not sufficient to explain all observed long-term dynamics. In fact, we find a clear trend break in the temperature time series in the middle of 2008. Before this break point there is an explicit negative linear trend of (−0.24 ± 0.07 K year−1, and after 2008 the linear trend turns positive with a value of (0.64 ± 0.33 K year−1. This apparent trend break can also be described using a long periodic oscillation. One possibility is to use the 22-year solar cycle that describes the reversal of the solar magnetic field (Hale cycle. A multiple linear regression using the solar radio flux and the solar polar magnetic field as parameters leads to the regression coefficients Csolar = (5.0 ± 0.7 K (100 SFU−1 and Chale = (1.8 ± 0.5 K (100 µT−1 (r2 = 0.71. The second way of describing the OH* temperature time series is to use the solar radio flux and an oscillation. A least-square fit leads to a sensitivity to the solar activity of (4.1 ± 0.8 K (100 SFU−1, a period P = (24.8 ± 3.3 years, and
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Calise, Francesco; Figaj, Rafal Damian; Vanoli, Laura
2017-01-01
Highlights: • Space heating/cooling, domestic hot water and electrical energy are provided by the system. • Two different users are investigated: fitness center and office. • The influence of the battery system on system economic performance is scarce. • Net metering contract is more profitable compared to simplified purchase/resale arrangement one. - Abstract: In this paper a dynamic simulation model and a thermo-economic analysis of a novel polygeneration system are presented. The system includes photovoltaic/thermal collectors coupled with a solar-assisted heat pump, an adsorption chiller and an electrical energy storage. The modelled plant supplies electrical energy, space heating and cooling and domestic hot water. The produced solar thermal energy is used during the winter to supply the heat pump evaporator, providing the required space heating. In summer, solar thermal energy is used to drive an adsorption chiller providing the required space cooling. All year long, solar thermal energy in excess, with respect to the space heating and cooling demand, is used to produce domestic hot water. The produced electrical energy is self-consumed by both user and system auxiliary equipment and/or supplied to the grid. The system model includes a detailed electrical energy model for user storage and exchange with the grid along with a detailed building model. This study is a continuation of previous works recently presented by the authors. In particular, the present paper focuses on the real electrical demands of several types of users and on the analysis of the comfort of building users. Differently from the works previously published by the authors, the present work bases the calculations on measured electrical demands of real users (fitness center and offices). The system performance is analyzed with two different electricity supply contracts: net metering and simplified purchase/resale arrangement. Daily, weekly and yearly results are presented. Finally, a
-
Zhou, Dazhuang; Gaza, R.; Roed, Y.; Semones, E.; Lee, K.; Steenburgh, R.; Johnson, S.; Flanders, J.; Zapp, N.
2010-01-01
Radiation field of particles in low Earth orbit (LEO) is mainly composed of galactic cosmic rays (GCR), solar energetic particles and particles in SAA (South Atlantic Anomaly). GCR are modulated by solar activity, at the period of solar minimum activity, GCR intensity is at maximum and the main contributor for space radiation is GCR. At present for space radiation measurements conducted by JSC (Johnson Space Center) SRAG (Space Radiation Analysis Group), the preferred active dosimeter sensitive to all LET (Linear Energy Transfer) is the tissue equivalent proportional counter (TEPC); the preferred passive dosimeters are thermoluminescence dosimeters (TLDs) and optically stimulated luminescence dosimeters (OSLDs) sensitive to low LET as well as CR-39 plastic nuclear track detectors (PNTDs) sensitive to high LET. For the method using passive dosimeters, radiation quantities for all LET can be obtained by combining radiation results measured with TLDs/OSLDs and CR-39 PNTDs. TEPC, TLDs/OSLDs and CR-39 detectors were used to measure the radiation field for the ISS (International Space Station) - Expedition 18-19/ULF2 space mission which was conducted from 15 November 2008 to 31 July 2009 - near the period of the recent solar minimum activity. LET spectra (differential and integral fluence, absorbed dose and dose equivalent) and radiation quantities were measured for positions TEPC, TESS (Temporary Sleeping Station, inside the polyethylene lined sleep station), SM-P 327 and 442 (Service Module - Panel 327 and 442). This paper presents radiation LET spectra measured with TEPC and CR-39 PNTDs and radiation dose measured with TLDs/OSLDs as well as the radiation quantities combined from results measured with passive dosimeters.
-
Lower thermosphere (80-100 km) dynamics response to solar and geomagnetic activity: Overview
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kazimirovsky, E.S.
1989-01-01
The variations of solar and geomagnetic activity may affect the thermosphere circulation via plasma heating and electric fields, especially at high latitudes. The possibility exists that the energy involved in auroral and magnetic storms can produce significant changes of mesosphere and lower thermosphere wind systems. A study of global radar measurements of winds at 80 to 100 km region revealed the short term effects (correlation between wind field and geomagnetic storms) and long term variations over a solar cycle. It seems likely that the correlation results from a modification of planetary waves and tides propagated from below, thus altering the dynamical regime of the thermosphere. Sometimes the long term behavior points rather to a climatic variation with the internal atmospheric cause than to a direct solar control
-
YOUNG SOLAR SYSTEM's FIFTH GIANT PLANET?
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nesvorný, David
2011-01-01
Studies of solar system formation suggest that the solar system's giant planets formed and migrated in the protoplanetary disk to reach the resonant orbits with all planets inside ∼15 AU from the Sun. After the gas disk's dispersal, Uranus and Neptune were likely scattered by the gas giants, and approached their current orbits while dispersing the transplanetary disk of planetesimals, whose remains survived to this time in the region known as the Kuiper Belt. Here we performed N-body integrations of the scattering phase between giant planets in an attempt to determine which initial states are plausible. We found that the dynamical simulations starting with a resonant system of four giant planets have a low success rate in matching the present orbits of giant planets and various other constraints (e.g., survival of the terrestrial planets). The dynamical evolution is typically too violent, if Jupiter and Saturn start in the 3:2 resonance, and leads to final systems with fewer than four planets. Several initial states stand out in that they show a relatively large likelihood of success in matching the constraints. Some of the statistically best results were obtained when assuming that the solar system initially had five giant planets and one ice giant, with the mass comparable to that of Uranus and Neptune, and which was ejected to interstellar space by Jupiter. This possibility appears to be conceivable in view of the recent discovery of a large number of free-floating planets in interstellar space, which indicates that planet ejection should be common.
-
Young Solar System's Fifth Giant Planet?
Nesvorný, David
2011-12-01
Studies of solar system formation suggest that the solar system's giant planets formed and migrated in the protoplanetary disk to reach the resonant orbits with all planets inside ~15 AU from the Sun. After the gas disk's dispersal, Uranus and Neptune were likely scattered by the gas giants, and approached their current orbits while dispersing the transplanetary disk of planetesimals, whose remains survived to this time in the region known as the Kuiper Belt. Here we performed N-body integrations of the scattering phase between giant planets in an attempt to determine which initial states are plausible. We found that the dynamical simulations starting with a resonant system of four giant planets have a low success rate in matching the present orbits of giant planets and various other constraints (e.g., survival of the terrestrial planets). The dynamical evolution is typically too violent, if Jupiter and Saturn start in the 3:2 resonance, and leads to final systems with fewer than four planets. Several initial states stand out in that they show a relatively large likelihood of success in matching the constraints. Some of the statistically best results were obtained when assuming that the solar system initially had five giant planets and one ice giant, with the mass comparable to that of Uranus and Neptune, and which was ejected to interstellar space by Jupiter. This possibility appears to be conceivable in view of the recent discovery of a large number of free-floating planets in interstellar space, which indicates that planet ejection should be common.
-
The Mechanism for Energy Buildup in the Solar Corona
Antiochos, Spiro; Knizhnik, Kalman; DeVore, Richard
2017-10-01
Magnetic reconnection and helicity conservation are two of the most important basic processes determining the structure and dynamics of laboratory and space plasmas. The most energetic dynamics in the solar system are the giant CMEs/flares that produce the most dangerous space weather at Earth, yet may also have been essential for the origin of life. The origin of these explosions is that the lowest-lying magnetic flux in the Sun's corona undergoes the continual buildup of stress and free energy that can be released only through explosive ejection. We perform MHD simulations of a coronal volume driven by quasi-random boundary flows designed to model the processes by which the solar interior drives the corona. Our simulations are uniquely accurate in preserving magnetic helicity. We show that even though small-scale stress is injected randomly throughout the corona, the net result of magnetic reconnection is a coherent stressing of the lowest-lying field lines. This highly counter-intuitive result - magnetic stress builds up locally rather than spreading out to a minimum energy state - is the fundamental mechanism responsible for the Sun's magnetic explosions. It is likely to be a mechanism that is ubiquitous throughout laboratory and space plasmas. This work was supported by the NASA LWS and SR Programs.
-
Solar radiation interception of various planting space patterns of maize and its relation to yields
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Akhir, N.
2003-01-01
A research was carried out to study solar radiation interception and its relation to yield of maize in various plant spacing patterns at high elevation. The goal of this research was to contribute the development of crop science, especially the plant ecophysiology. A field experiment was executed from March to August 1998 at Assessment Institute of Agricultural Technology, Sukarami, West Sumatra. The experiment was arranged in Randomized Block Design and each treatment was replicated three times. The experiment data was analyzed by ANOVA and path analysis. The results of experiment indicated that the percentage of solar radiation interception gave high contribution to the dry grain yield for Pioneer-7 cultivar, and the solar radiation interception was depend on LAI and leaf angle
-
The USGS Geomagnetism Program and its role in Space-Weather Monitoring
Love, Jeffrey J.; Finn, Carol A.
2011-01-01
Magnetic storms result from the dynamic interaction of the solar wind with the coupled magnetospheric-ionospheric system. Large storms represent a potential hazard for the activities and infrastructure of a modern, technologically based society [Baker et al., 2008]; they can cause the loss of radio communications, reduce the accuracy of global positioning systems, damage satellite electronics and affect satellite operations, increase pipeline corrosion, and induce voltage surges in electric power grids, causing blackouts. So while space weather starts with the Sun and is driven by the solar wind, it is on, or just above, the surface of the Earth that the practical effects of space weather are realized. Therefore, ground-based sensor networks, including magnetic observatories [Love, 2008], play an important role in space weather monitoring.
-
Komendera, Erik E.; Dorsey, John T.
2017-01-01
Developing a capability for the assembly of large space structures has the potential to increase the capabilities and performance of future space missions and spacecraft while reducing their cost. One such application is a megawatt-class solar electric propulsion (SEP) tug, representing a critical transportation ability for the NASA lunar, Mars, and solar system exploration missions. A series of robotic assembly experiments were recently completed at Langley Research Center (LaRC) that demonstrate most of the assembly steps for the SEP tug concept. The assembly experiments used a core set of robotic capabilities: long-reach manipulation and dexterous manipulation. This paper describes cross-cutting capabilities and technologies for in-space assembly (ISA), applies the ISA approach to a SEP tug, describes the design and development of two assembly demonstration concepts, and summarizes results of two sets of assembly experiments that validate the SEP tug assembly steps.
-
Organizing for Spaces and Dynamics of Multipolar Learning in Multinational Corporations
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hull Kristensen, Peer; Lotz, Maja
Limited research has been conducted on how MNCs organize conditions and spaces for recursive learning to facilitate the practice of innovation across dispersed units as well as how organizational members at all levels may become involved in innovations through the engagement in ongoing multipolar...... learning dynamics. Based on longitudinal case studies in two MNCs this paper contributes with insights into how spaces and dynamics of multipolar learning are organized and governed across dispersed MNC units at the micro level of everyday work practices. The paper shows that it is possible to organize...... spaces and dynamics that can organize recursiveness and continuity in multipolar learning by way of experimentation with new coordination components and governance architectures. Against the previous literature, however, it becomes evident that these are not the outcome of spontaneous interactions...
-
Charge Carrier Dynamics of Methylammonium Lead-Iodide Perovskite Solar Cells
Neukom, Martin Thomas
2016-01-01
Transient opto-electrical measurements of methylammonium lead iodide (MALI) perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are performed and analyzed in order to elucidate the operating mechanisms. The current response to a light pulse or voltage pulse shows an extraordinarily broad dynamic range covering 9 orders of magnitude in time - from microseconds to minutes - until steady-state is reached. Evidence of a slowly changing charge density at the perovskite layer boundaries is found, which is most probably ...
-
Vuitton, Véronique; Briois, Christelle; Makarov, Alexander
Over the past decade, it has become apparent that organic molecules are widespread in our Solar System and beyond. The better understand of the prebiotic chemistry leading to their formation is a primary objective of many ongoing space missions. Cassini-Huygens revealed the existence of very large molecular structures in Titan's atmosphere as well as on its surface, in the form of dune deposits, but their exact nature remains elusive. One key science goal of the Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover is to assess the presence of organics on the red planet. Rosetta will characterize the elemental and isotopic composition of the gas and dust ejected from comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, while amino acids have been detected in meteorites. This search for complex organics relies heavily on mass spectrometry, which has the remarkable ability to analyze and quantify species from almost any type of sample (provided that the appropriate sampling and ionizing method is used). Because of the harsh constraints of the spatial environment, the mass resolution of the spectrometers onboard current space probes is quite limited compared to laboratory instruments, leading to significant limitations in the scientific return of the data collected. Therefore, future in situ solar system exploration missions would significantly benefit from instruments relying on High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS). Since 2009, 5 French laboratories (LPC2E, IPAG, LATMOS, LISA, CSNSM) involved in the chemical investigation of solar system bodies form a Consortium to develop HRMS for future space exploration, based on the use of the Orbitrap technology (C. Briois et al., 2014, to be submitted). The work is undertaken in close collaboration with the Thermo Fisher Scientific Company, which commercializes Orbitrap based laboratory instruments. The Orbitrap is an electrostatic mass analyzer, it is compact, lightweight, and can reach a good sensitivity and dynamic range. A prototype is under development at
-
Charge carrier dynamics in thin film solar cells
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Strothkaemper, Christian
2013-06-24
This work investigates the charge carrier dynamics in three different technological approaches within the class of thin film solar cells: radial heterojunctions, the dye solar cell, and microcrystalline CuInSe{sub 2}, focusing on charge transport and separation at the electrode, and the relaxation of photogenerated charge carriers due to recombination and energy dissipation to the phonon system. This work relies mostly on optical-pump terahertz-probe (OPTP) spectroscopy, followed by transient absorption (TA) and two-photon photoemission (2PPE). The charge separation in ZnO-electrode/In{sub 2}S{sub 3}-absorber core/shell nanorods, which represent a model system of a radial heterojunction, is analyzed by OPTP. It is concluded, that the dynamics in the absorber are determined by multiple trapping, which leads to a dispersive charge transport to the electrode that lasts over hundreds of picoseconds. The high trap density on the order of 10{sup 19}/cm{sup 3} is detrimental for the injection yield, which exhibits a decrease with increasing shell thickness. The heterogeneous electron transfer from a series of model dyes into ZnO proceeds on a time-scale of 200 fs. However, the photoconductivity builds up just on a 2-10 ps timescale, and 2PPE reveals that injected electrons are meanwhile localized spatially and energetically at the interface. It is concluded that the injection proceeds through adsorbate induced interface states. This is an important result because the back reaction from long lived interface states can be expected to be much faster than from bulk states. While the charge transport in stoichiometric CuInSe{sub 2} thin films is indicative of free charge carriers, CuInSe{sub 2} with a solar cell grade composition (Cu-poor) exhibits signs of carrier localization. This detrimental effect is attributed to a high density of charged defects and a high degree of compensation, which together create a spatially fluctuating potential that inhibits charge transport. On
-
Radar time delays in the dynamic theory of gravity
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Haranas I.I.
2004-01-01
Full Text Available There is a new theory gravity called the dynamic theory, which is derived from thermodynamic principles in a five dimensional space, radar signals traveling times and delays are calculated for the major planets in the solar system, and compared to those of general relativity. This is done by using the usual four dimensional spherically symmetric space-time element of classical general relativistic gravity which has now been slightly modified by a negative inverse radial exponential term due to the dynamic theory of gravity potential.
-
Electron beam interaction with space plasmas.
Krafft, C.; Bolokitin, A. S.
1999-12-01
Active space experiments involving the controlled injection of electron beams and the formation of artificially generated currents can provide in many cases a calibration of natural phenomena connected with the dynamic interaction of charged particles with fields. They have a long history beginning from the launches of small rockets with electron guns in order to map magnetic fields lines in the Earth's magnetosphere or to excite artificial auroras. Moreover, natural beams of charged particles exist in many space and astrophysical plasmas and were identified in situ by several satellites; a few examples are beams connected with solar bursts, planetary foreshocks or suprathermal fluxes traveling in planetary magnetospheres. Many experimental and theoretical works have been performed in order to interpret or plan space experiments involving beam injection as well as to understand the physics of wave-particle interaction, as wave radiation, beam dynamics and background plasma modification.
-
Kearsley, A. T.; Drolshagen, G.; McDonnell, J. A. M.; Mandeville, J.-C.; Moussi, A.
A Post-Flight Investigation was initiated by the European Space Agency to analyze impact fluxes on solar arrays of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), exposed to space for 8.25 years at approximately 600 km altitude. The solar cells were deployed during servicing mission SM-1 (December 1993), and retrieved by shuttle orbiter Columbia in March 2002 (SM-3B). A sub-panel of 2 m2 was cut from the --V2 wing and cells were selected for in-depth analysis. Twelve cells (9.6x10-3 m2) were surveyed for flux of all craters of sizes greater than 5 microns Dco; six at the NHM, and six at ONERA. Cumulative flux plots reveal slightly greater abundance of very small craters than in a comparable survey of SM-1 cells. Analytical scanning electron microscopy was used to locate impact features and to analyse residues at the NHM. 103 features of 3 -- 4000 micron conchoidal detachment diameter (Dco) were located on a total of 17 solar cells. 78 features show identifiable residue: 36 are Space Debris impacts and 42 Micrometeoroid impacts. Of the remaining 25: 4 contain residue of ambiguous origin, 1 is a minor manufacturing flaw, 1 is obscured by contamination, and 19 are unresolved, lacking recognizable residue. Space debris impacts on the SM-3B cells are all less than 80 microns Dco, dominated by Al- rich residue, probably of solid rocket motor origin, some may be unburnt fuel. Three craters may be sodium metal droplet impacts. No residues from paint pigment, aluminium or ferrous alloys, or copper- and tin-bearing metal were found. All craters larger than 100 microns are of micrometeoroid origin, or unresolved. Most residues are magnesium-iron silicate or iron sulfide. A few craters show vesicular Mg, S, Fe and Ni residue. A single Fe Ni metal residue was found, as well as enigmatic Mg- and S-bearing residues, all considered of micrometeoroid origin. A few Fe-, O- and C-bearing residues were classified as of ambiguous origin. The quality and quantity of residue is clearly linked to the
-
Advanced controls for stability assessment of solar dynamics space power generation
Momoh, James A.; Anwah, Nnamdi A.
1995-01-01
In support of the power requirements for the Space Station Alpha (SSA), a joint program by the U.S. and Russia for a permanently manned space station to be launched into orbit by 1998, a robust control scheme is needed to assure the stability of the rotating machines that will be integrated into the power subsystem. A framework design and systems studies for modeling and analysis is presented. It employs classical d-q axes machine model with voltage/frequency dependent loads. To guarantee that design requirements and necessary trade studies are done, a functional analysis tool CORE is used for the study. This provides us with different control options for stability assessment. Initial studies and recommendations using advanced simulation tools are also presented. The benefits of the stability/control scheme for evaluating future designs and power management are discussed.
-
Integrability and nonintegrability of quantum systems. II. Dynamics in quantum phase space
Zhang, Wei-Min; Feng, Da Hsuan; Yuan, Jian-Min
1990-12-01
Based on the concepts of integrability and nonintegrability of a quantum system presented in a previous paper [Zhang, Feng, Yuan, and Wang, Phys. Rev. A 40, 438 (1989)], a realization of the dynamics in the quantum phase space is now presented. For a quantum system with dynamical group scrG and in one of its unitary irreducible-representation carrier spaces gerhΛ, the quantum phase space is a 2MΛ-dimensional topological space, where MΛ is the quantum-dynamical degrees of freedom. This quantum phase space is isomorphic to a coset space scrG/scrH via the unitary exponential mapping of the elementary excitation operator subspace of scrg (algebra of scrG), where scrH (⊂scrG) is the maximal stability subgroup of a fixed state in gerhΛ. The phase-space representation of the system is realized on scrG/scrH, and its classical analogy can be obtained naturally. It is also shown that there is consistency between quantum and classical integrability. Finally, a general algorithm for seeking the manifestation of ``quantum chaos'' via the classical analogy is provided. Illustrations of this formulation in several important quantum systems are presented.
-
Thin film coatings for space electrical power system applications
Gulino, Daniel A.
1988-01-01
This paper examines some of the ways in which thin film coatings can play a role in aerospace applications. Space systems discussed include photovoltaic and solar dynamic electric power generation systems, including applications in environmental protection, thermal energy storage, and radiator emittance enhancement. Potential applications of diamondlike films to both atmospheric and space based systems are examined. Also, potential uses of thin films of the recently discovered high-temperature superconductive materials are discussed.
-
Recent results from advanced research on space solar cells at NASA
Flood, Dennis J.
1990-01-01
The NASA program in space photovoltaic research and development encompasses a wide range of emerging options for future space power systems, and includes both cell and array technology development. The long range goals are to develop technology capable of achieving 300 W/kg for planar arrays, and 300 W/sq m for concentrator arrays. InP and GaAs planar and concentrator cell technologies are under investigation for their potential high efficiency and good radiation resistance. The Advanced Photovoltaic Solar Array (APSA) program is a near term effort aimed at demonstrating 130 W/kg beginning of life specific power using thin (62 pm) silicon cells. It is intended to be technology transparent to future high efficiency cells and provides the baseline for development of the 300 W/kg array.
-
Application of dynamic model to predict some inside environment variables in a semi-solar greenhouse
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Behzad Mohammadi
2018-06-01
Full Text Available Greenhouses are one of the most effective cultivation methods with a yield per cultivated area up to 10 times more than free land cultivation but the use of fossil fuels in this production field is very high. The greenhouse environment is an uncertain nonlinear system which classical modeling methods have some problems to solve it. There are many control methods, such as adaptive, feedback and intelligent control and they require a precise model. Therefore, many modeling methods have been proposed for this purpose; including physical, transfer function and black-box modeling. The objective of this paper is to modeling and experimental validation of some inside environment variables in an innovative greenhouse structure (semi-solar greenhouse. For this propose, a semi-solar greenhouse was designed and constructed at the North-West of Iran in Azerbaijan Province (38°10′N and 46°18′E with elevation of 1364 m above the sea level. The main inside environment factors include inside air temperature (Ta and inside soil temperature (Ts were collected as the experimental data samples. The dynamic heat transfer model used to estimate the temperature in two different points of semi-solar greenhouse with initial values. The results showed that dynamic model can predict the inside temperatures in two different points (Ta and Ts with RMSE, MAPE and EF about 5.3 °C, 10.2% and 0.78% and 3.45 °C, 7.7% and 0.86%, respectively. Keywords: Semi-solar greenhouse, Dynamic model, Commercial greenhouse
-
Space Solar Patrol data and changes in weather and climate, including global warming
Avakyan, S. V.; Baranova, L. A.; Leonov, N. B.; Savinov, E. P.; Voronin, N. A.
2010-08-01
In this paper, the results obtained during the execution of several ISTC projects are presented. The general aim of these projects has been the study of global changes in the environment, connected with solar activity. A brief description of the optical apparatus of the Space Solar Patrol (SSP) developed and built in the framework of the ISTC projects 385, 385.2, 1523 and 2500 is given. The SSP is intended for permanent monitoring of spectra and absolute fluxes of soft x-ray and extreme ultraviolet (x-ray/EUV) radiation from the full disk of the Sun which ionizes the upper atmosphere of the Earth. Permanent solar monitoring in the main part of the ionizing radiation spectra 0.8-115 (119) nm does not exist. The apparatus of the SSP was developed in the years 1996-2005 with multiyear experience of developing such apparatus in S I Vavilov State Optical Institute. The basis of this apparatus is the use of unique detectors of ionizing radiation—open secondary electron multipliers, which are 'solar blind' to near UV, visible and IR radiation from the Sun, and new methodology of these solar spectroradiometric absolute measurements. The prospects are discussed of using the SSP data for the investigation and forecast of the influence of solar variability on the weather and climate including global warming and also on the biosphere including human beings (proposal 3878). This article was originally submitted for inclusion with the papers from the 9th International Symposium on Measurement Science and Intelligent Instruments (ISMTII-2009), published in the May 2010 issue.
-
Leitgab, M.
2018-02-01
A charged particle measurement experiment mounted externally to the Deep Space Gateway is proposed, contributing to improving astronaut radiation exposure management during Solar Particle Events and Extra Vehicular Activities.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sidlichovsky, M.
1987-01-01
The conference proceedings contains a total of 31 papers of which 7 have not been incorporated in INIS. The papers mainly discuss the mathematical methods of calculating the movement of planets, their satellites and asteroids in the solar system and the mathematical modelling of the past development of the solar system. Great attention is also devoted to resonance in the solar system and to the study of many celestial bodies. Four papers are devoted to planetary rings and three to modern astrometry. (M.D.). 63 figs., 10 tabs., 520 refs
-
Cooperative research in space geodesy and crustal dynamics
1994-01-01
This research grant, which covered the period of July 1991 to August 1994, was concerned with a variety of topics within the geodesy and crustal dynamics fields. The specific topics of this grant included satellite tracking and gravity field determinations and crustal dynamics (this concentrated of space geodetic site stability for VLBI sites). Summaries of the specific research projects are included along with a list of publications and presentations supported by this research grant.
-
Solar Spots - Activities to Introduce Solar Energy into the K-8 Curricula.
Longe, Karen M.; McClelland, Michael J.
Following an introduction to solar technology which reviews solar heating and cooling, passive solar systems (direct gain systems, thermal storage walls, sun spaces, roof ponds, and convection loops), active solar systems, solar electricity (photovoltaic and solar thermal conversion systems), wind energy, and biomass, activities to introduce solar…
-
Dynamic trapping of electrons in space plasmas
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brenning, N.; Bohm, M.; Faelthammar, C.G.
1989-12-01
The neutralization of positive space charge is studied in a case where heavy positive ions are added to a limited region of length L in a collisionfree magnetized plasma. It is found that electrons which become accelerated towards the positive space charge can only achieve a partial neutralization: they overshoot, and the positive region becomes surrounded by negative space charges which screen the electric field from the surroundings. The process is studied both analytically and by computer simulations with consistent results: large positive potentials (U>>kT e /e) can be built up with respect to the surrounding plasma. In the process of growth, the potential maximum traps electrons in transit so that quasineutrality is maintained. The potential U is proportional to the ambient electron temperature and the square of the plasma density increase, but independent of both the ion injection rate and the length L. The process explains several features of the Porcupinge xenon beam injection experiment. It could also have importance for the electrodynamic coupling between plasmas of different densities, e.g. the injection of neutral clouds in the ionosphere of species that becomes rapidly photoionized, or penetration of dense plasma clouds from the solar wind into the magnetosphere. (31 refs.) (authors)
-
Thermally-Induced Structural Disturbances of Rigid Panel Solar Arrays
Johnston, John D.; Thornton, Earl A.
1997-01-01
The performance of a significant number of spacecraft has been impacted negatively by attitude disturbances resulting from thermally-induced motions of flexible structures. Recent examples of spacecraft affected by these disturbances include the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS). Thermally-induced structural disturbances occur as the result of rapid changes in thermal loading typically initiated as a satellite exits or enters the Earth's shadow. Temperature differences in flexible appendages give rise to structural deformations, which in turn result in disturbance torques reacting back on the spacecraft. Structures which have proven susceptible to these disturbances include deployable booms and solar arrays. This paper investigates disturbances resulting from thermally-induced deformations of rigid panel solar arrays. An analytical model for the thermal-structural response of the solar array and the corresponding disturbance torque are presented. The effect of these disturbances on the attitude dynamics of a simple spacecraft is then investigated using a coupled system of governing equations which includes the effects of thermally-induced deformations. Numerical results demonstrate the effect of varying solar array geometry on the dynamic response of the system.
-
Thin film CdTe solar cells by close spaced sublimation: Recent results from pilot line
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Siepchen, B.; Drost, C.; Späth, B.; Krishnakumar, V.; Richter, H.; Harr, M.; Bossert, S.; Grimm, M.; Häfner, K.; Modes, T.; Zywitzki, O.; Morgner, H.
2013-01-01
CdTe is an attractive material to produce high efficient and low cost thin film solar cells. The semiconducting layers of this kind of solar cell can be deposited by the Close Spaced Sublimation (CSS) process. The advantages of this technique are high deposition rates and an excellent utilization of the raw material, leading to low production costs and competitive module prices. CTF Solar GmbH is offering equipment and process knowhow for the production of CdTe solar modules. For further improvement of the technology, research is done at a pilot line, which covers all relevant process steps for manufacture of CdTe solar cells. Herein, we present the latest results from the process development and our research activities on single functional layers as well as for complete solar cell devices. Efficiencies above 13% have already been obtained with Cu-free back contacts. An additional focus is set on different transparent conducting oxide materials for the front contact and a Sb 2 Te 3 based back contact. - Highlights: ► Laboratory established on industrial level for CdTe solar cell research ► 13.0% cell efficiency with our standard front contact and Cu-free back contact ► Research on ZnO-based transparent conducting oxide and Sb 2 Te 3 back contacts ► High resolution scanning electron microscopy analysis of ion polished cross section
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J.-F. Hochedez
2005-11-01
Full Text Available Space Weather nowcasting and forecasting require solar observations because geoeffective disturbances can arise from three types of solar phenomena: coronal mass ejections (CMEs, flares and coronal holes. For each, we discuss their definition and review their precursors in terms of remote sensing and in-situ observations. The objectives of Space Weather require some specific instrumental features, which we list using the experience gained from the daily operations of the Solar Influences Data analysis Centre (SIDC at the Royal Observatory of Belgium. Nowcasting requires real-time monitoring to assess quickly and reliably the severity of any potentially geoeffective solar event. Both research and forecasting could incorporate more observations in order to feed case studies and data assimilation respectively. Numerical models will result in better predictions of geomagnetic storms and solar energetic particle (SEP events. We review the data types available to monitor solar activity and interplanetary conditions. They come from space missions and ground observatories and range from sequences of dopplergrams, magnetograms, white-light, chromospheric, coronal, coronagraphic and radio images, to irradiance and in-situ time-series. Their role is summarized together with indications about current and future solar monitoring instruments.
-
In-Space Propulsion Technology Program Solar Electric Propulsion Technologies
Dankanich, John W.
2006-01-01
NASA's In-space Propulsion (ISP) Technology Project is developing new propulsion technologies that can enable or enhance near and mid-term NASA science missions. The Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) technology area has been investing in NASA s Evolutionary Xenon Thruster (NEXT), the High Voltage Hall Accelerator (HiVHAC), lightweight reliable feed systems, wear testing, and thruster modeling. These investments are specifically targeted to increase planetary science payload capability, expand the envelope of planetary science destinations, and significantly reduce the travel times, risk, and cost of NASA planetary science missions. Status and expected capabilities of the SEP technologies are reviewed in this presentation. The SEP technology area supports numerous mission studies and architecture analyses to determine which investments will give the greatest benefit to science missions. Both the NEXT and HiVHAC thrusters have modified their nominal throttle tables to better utilize diminished solar array power on outbound missions. A new life extension mechanism has been implemented on HiVHAC to increase the throughput capability on low-power systems to meet the needs of cost-capped missions. Lower complexity, more reliable feed system components common to all electric propulsion (EP) systems are being developed. ISP has also leveraged commercial investments to further validate new ion and hall thruster technologies and to potentially lower EP mission costs.
-
Damé, L.; Meftah, M.; Irbah, A.; Hauchecorne, A.; Bekki, S.; Bolsée, D.; Pereira, N.; Sluse, D.; Cessateur, G.
2017-12-01
Since April 5, 2008 and until February 15, 2017, the SOLSPEC (SOLar SPECtrometer) spectro-radiometer of the SOLAR facility on the International Space Station performed accurate measurements of Solar Spectral Irradiance (SSI) from the far ultraviolet to the infrared (165 nm to 3088 nm). These measurements, unique by their large spectral coverage and long time range, are of primary importance for a better understanding of solar physics and of the impact of solar variability on climate (via Earth's atmospheric photochemistry), noticeably through the "top-down" mechanism amplifying ultraviolet (UV) solar forcing effects on the climate (UV affects stratospheric dynamics and temperatures, altering interplanetary waves and weather patterns both poleward and downward to the lower stratosphere and troposphere regions). SOLAR/SOLSPEC, with almost 9 years of observations covering the essential of the unusual solar cycle 24 from minimum in 2008 to maximum, allowed to establish new reference solar spectra from UV to IR (165 to 3088 nm) at minimum (beginning of mission) and maximum of activity. The complete reanalysis was possible thanks to revised engineering corrections, improved calibrations and advanced procedures to account for thermal, aging and pointing corrections. The high quality and sensitivity of SOLSPEC data allow to follow temporal variability in UV but also in visible along the cycle. Uncertainties on these measurements are evaluated and results, absolute reference spectra and variability, are compared with other measurements (WHI, ATLAS-3, SCIAMACHY, SORCE/SOLSTICE, SORCE/SIM) and models (SATIRE-S, NRLSSI, NESSY)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hazra, Soumitra; Nandy, Dibyendu [Department of Physical Sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Kolkata (India)
2016-11-20
At present, the Babcock–Leighton flux transport solar dynamo models appear to be the most promising models for explaining diverse observational aspects of the sunspot cycle. The success of these flux transport dynamo models is largely dependent upon a single-cell meridional circulation with a deep equatorward component at the base of the Sun’s convection zone. However, recent observations suggest that the meridional flow may in fact be very shallow (confined to the top 10% of the Sun) and more complex than previously thought. Taken together, these observations raise serious concerns on the validity of the flux transport paradigm. By accounting for the turbulent pumping of magnetic flux, as evidenced in magnetohydrodynamic simulations of solar convection, we demonstrate that flux transport dynamo models can generate solar-like magnetic cycles even if the meridional flow is shallow. Solar-like periodic reversals are recovered even when meridional circulation is altogether absent. However, in this case, the solar surface magnetic field dynamics does not extend all the way to the polar regions. Very importantly, our results demonstrate that the Parker–Yoshimura sign rule for dynamo wave propagation can be circumvented in Babcock–Leighton dynamo models by the latitudinal component of turbulent pumping, which can generate equatorward propagating sunspot belts in the absence of a deep, equatorward meridional flow. We also show that variations in turbulent pumping coefficients can modulate the solar cycle amplitude and periodicity. Our results suggest the viability of an alternate magnetic flux transport paradigm—mediated via turbulent pumping—for sustaining solar-stellar dynamo action.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hazra, Soumitra; Nandy, Dibyendu
2016-01-01
At present, the Babcock–Leighton flux transport solar dynamo models appear to be the most promising models for explaining diverse observational aspects of the sunspot cycle. The success of these flux transport dynamo models is largely dependent upon a single-cell meridional circulation with a deep equatorward component at the base of the Sun’s convection zone. However, recent observations suggest that the meridional flow may in fact be very shallow (confined to the top 10% of the Sun) and more complex than previously thought. Taken together, these observations raise serious concerns on the validity of the flux transport paradigm. By accounting for the turbulent pumping of magnetic flux, as evidenced in magnetohydrodynamic simulations of solar convection, we demonstrate that flux transport dynamo models can generate solar-like magnetic cycles even if the meridional flow is shallow. Solar-like periodic reversals are recovered even when meridional circulation is altogether absent. However, in this case, the solar surface magnetic field dynamics does not extend all the way to the polar regions. Very importantly, our results demonstrate that the Parker–Yoshimura sign rule for dynamo wave propagation can be circumvented in Babcock–Leighton dynamo models by the latitudinal component of turbulent pumping, which can generate equatorward propagating sunspot belts in the absence of a deep, equatorward meridional flow. We also show that variations in turbulent pumping coefficients can modulate the solar cycle amplitude and periodicity. Our results suggest the viability of an alternate magnetic flux transport paradigm—mediated via turbulent pumping—for sustaining solar-stellar dynamo action.
-
Fault Detection and Correction for the Solar Dynamics Observatory Attitude Control System
Starin, Scott R.; Vess, Melissa F.; Kenney, Thomas M.; Maldonado, Manuel D.; Morgenstern, Wendy M.
2007-01-01
The Solar Dynamics Observatory is an Explorer-class mission that will launch in early 2009. The spacecraft will operate in a geosynchronous orbit, sending data 24 hours a day to a devoted ground station in White Sands, New Mexico. It will carry a suite of instruments designed to observe the Sun in multiple wavelengths at unprecedented resolution. The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly includes four telescopes with focal plane CCDs that can image the full solar disk in four different visible wavelengths. The Extreme-ultraviolet Variability Experiment will collect time-correlated data on the activity of the Sun's corona. The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager will enable study of pressure waves moving through the body of the Sun. The attitude control system on Solar Dynamics Observatory is responsible for four main phases of activity. The physical safety of the spacecraft after separation must be guaranteed. Fine attitude determination and control must be sufficient for instrument calibration maneuvers. The mission science mode requires 2-arcsecond control according to error signals provided by guide telescopes on the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly, one of the three instruments to be carried. Lastly, accurate execution of linear and angular momentum changes to the spacecraft must be provided for momentum management and orbit maintenance. In thsp aper, single-fault tolerant fault detection and correction of the Solar Dynamics Observatory attitude control system is described. The attitude control hardware suite for the mission is catalogued, with special attention to redundancy at the hardware level. Four reaction wheels are used where any three are satisfactory. Four pairs of redundant thrusters are employed for orbit change maneuvers and momentum management. Three two-axis gyroscopes provide full redundancy for rate sensing. A digital Sun sensor and two autonomous star trackers provide two-out-of-three redundancy for fine attitude determination. The use of software to maximize
-
Construction of a century solar chromosphere data set for solar activity related research
Lin, Ganghua; Wang, Xiao Fan; Yang, Xiao; Liu, Suo; Zhang, Mei; Wang, Haimin; Liu, Chang; Xu, Yan; Tlatov, Andrey; Demidov, Mihail; Borovik, Aleksandr; Golovko, Aleksey
2017-06-01
This article introduces our ongoing project "Construction of a Century Solar Chromosphere Data Set for Solar Activity Related Research". Solar activities are the major sources of space weather that affects human lives. Some of the serious space weather consequences, for instance, include interruption of space communication and navigation, compromising the safety of astronauts and satellites, and damaging power grids. Therefore, the solar activity research has both scientific and social impacts. The major database is built up from digitized and standardized film data obtained by several observatories around the world and covers a time span of more than 100 years. After careful calibration, we will develop feature extraction and data mining tools and provide them together with the comprehensive database for the astronomical community. Our final goal is to address several physical issues: filament behavior in solar cycles, abnormal behavior of solar cycle 24, large-scale solar eruptions, and sympathetic remote brightenings. Significant signs of progress are expected in data mining algorithms and software development, which will benefit the scientific analysis and eventually advance our understanding of solar cycles.
-
Construction of a century solar chromosphere data set for solar activity related research
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ganghua Lin
2017-06-01
Full Text Available This article introduces our ongoing project “Construction of a Century Solar Chromosphere Data Set for Solar Activity Related Research”. Solar activities are the major sources of space weather that affects human lives. Some of the serious space weather consequences, for instance, include interruption of space communication and navigation, compromising the safety of astronauts and satellites, and damaging power grids. Therefore, the solar activity research has both scientific and social impacts. The major database is built up from digitized and standardized film data obtained by several observatories around the world and covers a timespan more than 100 years. After careful calibration, we will develop feature extraction and data mining tools and provide them together with the comprehensive database for the astronomical community. Our final goal is to address several physical issues: filament behavior in solar cycles, abnormal behavior of solar cycle 24, large-scale solar eruptions, and sympathetic remote brightenings. Significant progresses are expected in data mining algorithms and software development, which will benefit the scientific analysis and eventually advance our understanding of solar cycles.
-
Development of an integrated heat pipe-thermal storage system for a solar receiver
Keddy, E. S.; Sena, J. T.; Merrigan, M. A.; Heidenreich, G.; Johnson, S.
1987-01-01
The Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) Solar Dynamic Power System (SDPS) is one of the candidates for Space Station prime power application. In the low Earth orbit of the Space Station approximately 34 minutes of the 94-minute orbital period is spent in eclipse with no solar energy input to the power system. For this period the SDPS will use thermal energy storage (TES) material to provide a constant power output. An integrated heat-pipe thermal storage receiver system is being developed as part of the ORC-SDPS solar receiver. This system incorporates potassium heat pipe elements to absorb and transfer the solar energy within the receiver cavity. The heat pipes contain the TES canisters within the potassium vapor space with the toluene heater tube used as the condenser region of the heat pipe. During the insolation period of the Earth orbit, solar energy is delivered to the heat pipe in the ORC-SDPS receiver cavity. The heat pipe transforms the non-uniform solar flux incident in the heat pipe surface within the receiver cavity to an essentially uniform flux at the potassium vapor condensation interface in the heat pipe. During solar insolation, part of the thermal energy is delivered to the heater tube and the balance is stored in the TES units. During the eclipse period of the orbit, the balance stored in the TES units is transferred by the potassium vapor to the toluene heater tube.
-
Development of an integrated heat pipe-thermal storage system for a solar receiver
Keddy, E. S.; Sena, J. T.; Merrigan, M. A.; Heidenreich, G.; Johnson, S.
1987-07-01
The Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) Solar Dynamic Power System (SDPS) is one of the candidates for Space Station prime power application. In the low Earth orbit of the Space Station approximately 34 minutes of the 94-minute orbital period is spent in eclipse with no solar energy input to the power system. For this period the SDPS will use thermal energy storage (TES) material to provide a constant power output. An integrated heat-pipe thermal storage receiver system is being developed as part of the ORC-SDPS solar receiver. This system incorporates potassium heat pipe elements to absorb and transfer the solar energy within the receiver cavity. The heat pipes contain the TES canisters within the potassium vapor space with the toluene heater tube used as the condenser region of the heat pipe. During the insolation period of the Earth orbit, solar energy is delivered to the heat pipe in the ORC-SDPS receiver cavity. The heat pipe transforms the non-uniform solar flux incident in the heat pipe surface within the receiver cavity to an essentially uniform flux at the potassium vapor condensation interface in the heat pipe. During solar insolation, part of the thermal energy is delivered to the heater tube and the balance is stored in the TES units. During the eclipse period of the orbit, the balance stored in the TES units is transferred by the potassium vapor to the toluene heater tube.
-
WILL THE LARGE SYNOPTIC SURVEY TELESCOPE DETECT EXTRA-SOLAR PLANETESIMALS ENTERING THE SOLAR SYSTEM?
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Moro-Martin, Amaya; Turner, Edwin L.; Loeb, Abraham
2009-01-01
Planetesimal formation is a common by-product of the star formation process. Taking the dynamical history of the solar system as a guideline-in which the planetesimal belts were heavily depleted due to gravitational perturbation with the giant planets-and assuming similar processes have taken place in other planetary systems, one would expect the interstellar space to be filled with extra-solar planetesimals. However, not a single one of these objects has been detected so far entering the solar system, even though it would clearly be distinguishable from a solar system comet due to its highly hyperbolic orbit. The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) will provide wide coverage maps of the sky to a very high sensitivity, ideal to detect moving objects like comets, both active and inactive. In anticipation of these observations, we estimate how many inactive 'interstellar comets' might be detected during the duration of the survey. The calculation takes into account estimates (from observations and models) of the number density of stars, the amount of solids available to form planetesimals, the frequency of planet and planetesimal formation, the efficiency of planetesimal ejection, and the possible size distribution of these small bodies.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Faninger, G.
1991-11-01
Solar and heat pump systems have been proved in many applications on the market. To achieve an efficient energy output it is necessary to consider the special conditions of these technologies. The energetical and ecological criteria of solar and heat pump systems for hot water preparation and space heating are analysed on the basis of experimental data. (author)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cheung, Mark C. M.; Boerner, P.; Schrijver, C. J.; Malanushenko, A. [Lockheed Martin Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory, 3251 Hanover Street Bldg. 252, Palo Alto, CA 94304 (United States); Testa, P. [Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge, MA 02138 (United States); Chen, F.; Peter, H., E-mail: cheung@lmsal.com [Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research, Justus-von-Liebig-Weg 3, D-37077 Göttingen (Germany)
2015-07-10
We present a new method for performing differential emission measure (DEM) inversions on narrow-band EUV images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) on board the Solar Dynamics Observatory. The method yields positive definite DEM solutions by solving a linear program. This method has been validated against a diverse set of thermal models of varying complexity and realism. These include (1) idealized Gaussian DEM distributions, (2) 3D models of NOAA Active Region 11158 comprising quasi-steady loop atmospheres in a nonlinear force-free field, and (3) thermodynamic models from a fully compressible, 3D MHD simulation of active region (AR) corona formation following magnetic flux emergence. We then present results from the application of the method to AIA observations of Active Region 11158, comparing the region's thermal structure on two successive solar rotations. Additionally, we show how the DEM inversion method can be adapted to simultaneously invert AIA and Hinode X-ray Telescope data, and how supplementing AIA data with the latter improves the inversion result. The speed of the method allows for routine production of DEM maps, thus facilitating science studies that require tracking of the thermal structure of the solar corona in time and space.
-
Comparison of phase space dynamics of Kopenhagen and causal interpretations of quantum mechanics
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tempel, Christoph; Schleich, Wolfgang P. [Institut fuer Quantenphysik, Universitaet Ulm, D-89069 Ulm (Germany)
2013-07-01
Recent publications pursue the attempt to reconstruct Bohm trajectories experimentally utilizing the technique of weak measurements. We study the phase space dynamics of a specific double slit setup in terms of the Bohm de-Broglie formulation of quantum mechanics. We want to compare the results of those Bohmian phase space dynamics to the usual quantum mechanical phase space formulation with the Wigner function as a quasi probability density.
-
Kelecy, Tom; Payne, Tim; Thurston, Robin; Stansbery, Gene
2007-01-01
A population of deep space objects is thought to be high area-to-mass ratio (AMR) debris having origins from sources in the geosynchronous orbit (GEO) belt. The typical AMR values have been observed to range anywhere from 1's to 10's of m(sup 2)/kg, and hence, higher than average solar radiation pressure effects result in long-term migration of eccentricity (0.1-0.6) and inclination over time. However, the nature of the debris orientation-dependent dynamics also results time-varying solar radiation forces about the average which complicate the short-term orbit determination processing. The orbit determination results are presented for several of these debris objects, and highlight their unique and varied dynamic attributes. Estimation or the solar pressure dynamics over time scales suitable for resolving the shorter term dynamics improves the orbit estimation, and hence, the orbit predictions needed to conduct follow-up observations.
-
Dynamical Changes Induced by the Very Large Solar Proton Events in October-November 2003
Jackman, Charles H.; Roble, Raymond G.
2006-01-01
The very large solar storms in October-November 2003 caused solar proton events (SPEs) at the Earth and impacted the upper atmospheric polar cap regions. The Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Electrodynamic General Circulation Mode (TIME-GCM) was used to study the atmospheric dynamical influence of the solar protons that occurred in Oct-Nov 2003, the fourth largest period of SPEs measured in the past 40 years. The highly energetic solar protons caused ionization and changes in the electric field, which led to Joule heating of the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. This heating led to temperature increases up to 4K in the upper mesosphere. The solar proton-induced ionization, as well as dissociation processes, led to the production of odd hydrogen (HO(x)) and odd nitrogen (NO(y)). Substantial (>40%) short-lived ozone decreases followed these enhancements of HO(x) and NO(y) and led to a cooling of the mesosphere and upper stratosphere. This cooling led to temperature decreases up to 2.5K. The solar proton-caused temperature changes led to maximum meridional and zonal wind variations of +/- 2 m/s on background winds up to +/- 30 m/s. The solar proton-induced wind perturbations were computed to taper off over a period of several days past the SPEs. Solar cycle 23 was accompanied by ten very large SPEs between 1998 and 2005, along with numerous smaller events. These solar proton-driven atmospheric variations need to be carefully considered when examining other polar changes.
-
Energetic and financial evaluation of solar assisted heat pump space heating systems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bellos, Evangelos; Tzivanidis, Christos; Moschos, Konstantinos; Antonopoulos, Kimon A.
2016-01-01
Highlights: • Four solar heating systems are presented in this work. • Various combinations between solar collectors and heat pumps are presented. • The systems are compared energetically and financially. • The use of PV and an air source heat pump is the best choice financially. • The use of PVT with a water source heat pump is the best solution energetically. - Abstract: Using solar energy for space heating purposes consists an alternative way for substituting fossil fuel and grid electricity consumption. In this study, four solar assisted heat pump heating systems are designed, simulated and evaluated energetically and financially in order to determine the most attractive solution. The use of PV collectors with air source heat pump is compared to the use of FPC, PVT and FPC with PV coupled with a water source heat pump. A sensitivity analysis for the electricity cost is conducted because of the great variety of this parameter over the last years. The final results proved that for electricity cost up to 0.23 €/kW h the use of PV coupled with an air source heat pump is the most sustainable solution financially, while for higher electricity prices the coupling of PVT with an water source heat pump is the best choice. For the present electricity price of 0.2 €/kW h, 20 m"2 of PV is able to drive the air source heat pump with a yearly solar coverage of 67% leading to the most sustainable solution. Taking into account energetic aspects, the use of PVT leads to extremely low grid electricity consumption, fact that makes this technology the most environmental friendly.
-
Welling, D. T.; Manchester, W.; Savani, N.; Sokolov, I.; van der Holst, B.; Jin, M.; Toth, G.; Liemohn, M. W.; Gombosi, T. I.
2017-12-01
The future of space weather prediction depends on the community's ability to predict L1 values from observations of the solar atmosphere, which can yield hours of lead time. While both empirical and physics-based L1 forecast methods exist, it is not yet known if this nascent capability can translate to skilled dB/dt forecasts at the Earth's surface. This paper shows results for the first forecast-quality, solar-atmosphere-to-Earth's-surface dB/dt predictions. Two methods are used to predict solar wind and IMF conditions at L1 for several real-world coronal mass ejection events. The first method is an empirical and observationally based system to estimate the plasma characteristics. The magnetic field predictions are based on the Bz4Cast system which assumes that the CME has a cylindrical flux rope geometry locally around Earth's trajectory. The remaining plasma parameters of density, temperature and velocity are estimated from white-light coronagraphs via a variety of triangulation methods and forward based modelling. The second is a first-principles-based approach that combines the Eruptive Event Generator using Gibson-Low configuration (EEGGL) model with the Alfven Wave Solar Model (AWSoM). EEGGL specifies parameters for the Gibson-Low flux rope such that it erupts, driving a CME in the coronal model that reproduces coronagraph observations and propagates to 1AU. The resulting solar wind predictions are used to drive the operational Space Weather Modeling Framework (SWMF) for geospace. Following the configuration used by NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center, this setup couples the BATS-R-US global magnetohydromagnetic model to the Rice Convection Model (RCM) ring current model and a height-integrated ionosphere electrodynamics model. The long lead time predictions of dB/dt are compared to model results that are driven by L1 solar wind observations. Both are compared to real-world observations from surface magnetometers at a variety of geomagnetic latitudes
-
Dynamic multibody modeling for tethered space elevators
Williams, Paul
2009-08-01
This paper presents a fundamental modeling strategy for dealing with powered and propelled bodies moving along space tethers. The tether is divided into a large number of discrete masses, which are connected by viscoelastic springs. The tether is subject to the full range of forces expected in Earth orbit in a relatively simple manner. Two different models of the elevator dynamics are presented. In order to capture the effect of the elevator moving along the tether, the elevator dynamics are included as a separate body in both models. One model treats the elevator's motion dynamically, where propulsive and friction forces are applied to the elevator body. The second model treats the elevator's motion kinematically, where the distance along the tether is determined by adjusting the lengths of tether on either side of the elevator. The tether model is used to determine optimal configurations for the space elevator. A modal analysis of two different configurations is presented which show that the fundamental mode of oscillation is a pendular one around the anchor point with a period on the order of 160 h for the in-plane motion, and 24 h for the out-of-plane motion. Numerical simulation results of the effects of the elevator moving along the cable are presented for different travel velocities and different elevator masses.
-
Moldwin, M.; Morrow, C. A.; White, S. C.; Ivie, R.
2014-12-01
Members of the Education & Workforce Working Group and the American Institute of Physics (AIP) conducted the first ever National Demographic Survey of working professionals for the 2012 National Academy of Sciences Solar and Space Physics Decadal Survey to learn about the demographics of this sub-field of space science. The instrument contained questions for participants on: the type of workplace; basic demographic information regarding gender and minority status, educational pathways (discipline of undergrad degree, field of their PhD), how their undergraduate and graduate student researchers are funded, participation in NSF and NASA funded spaceflight missions and suborbital programs, and barriers to career advancement. Using contact data bases from AGU, the American Astronomical Society's Solar Physics Division (AAS-SPD), attendees of NOAA's Space Weather Week and proposal submissions to NSF's Atmospheric, Geospace Science Division, the AIP's Statistical Research Center cross correlated and culled these data bases resulting in 2776 unique email addresses of US based working professionals. The survey received 1305 responses (51%) and generated 125 pages of single space answers to a number of open-ended questions. This talk will summarize the highlights of this first-ever demographic survey including findings extracted from the open-ended responses regarding barriers to career advancement which showed significant gender differences.
-
Configuration of and Motions in the Solar Corona at the 2017 Total Solar Eclipse
Pasachoff, Jay M.; Rusin, Vojtech; Vanur, Roman; Economou, Thanasis; Voulgaris, Aristeidis; Seiradakis, John H.; Seaton, Daniel; Dantowitz, Ronald; Lockwood, Christian A.; Nagle-McNaughton, Timothy; Perez, Cielo; Meadors, Erin N.; Marti, Connor J.; Yu, Ross; Rosseau, Brendan; Ide, Charles A.; Daly, Declan M.; Davis, Allen Bradford; Lu, Muzhou; Steele, Amy; Lee, Duane; Freeman, Marcus J.; Sliski, David; Rousseva, Ana; Greek Salem (Oregon) Team; Voulgaris, Aristeidis; Seiradakis, John Hugh; Koukioglou, Stavros; Kyriakou, Nikos; Vasileiadou, Anna; Greek Carbondale (Illinois) Team; Economou, Thanasis; Kanouras, Spyros; Irakleous, Christina; Golemis, Adrianos; Tsioumpanika, Nikoleta; Plexidas, Nikos; Tzimkas, Nikos; Kokkinidou, Ourania
2018-06-01
We report on high-contrast data reduction of white-light images from the August 21, 2017, total solar eclipse. We show the configuration of the solar corona at this declining phase of the solar-activity cycle, with the projection onto the plane of the sky of the three-dimensional coronal streamers plus extensive polar plumes. We discuss the relation of the white-light coronal loops visible in our observations with extreme-ultraviolet observations from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) and NOAA’s GOES-16 Solar Ultraviolet Imager (SUVI). We show differences and motions over a 65-minute interval between observations from our main site at Willamette University in Salem, Oregon, and a subsidiary site in Carbondale, Illinois. We discuss, in particular, a giant demarcation about 1 solar radius outward in the southwest that crosses the radial streamers.Our observations of the eclipse were sponsored in large part by the Committee for Research and Exploration of the National Geographic Society and by the Solar Terrestrial Program of the National Geographic Society. Additional support was received from the NASA Massachusetts Space Grant Consortium, the Sigma Xi honorary scientific society, the University of Pennsylvania (for DS), the Slovak Academy of Sciences VEGA project 2/0003/16, and the Freeman Foote Expeditionary and Brandi funds at Williams College. We thank Stephen Thorsett, Rick Watkins, and Honey Wilson of Willamette University for their hospitality. See http://totalsolareclipse.org or http://sites.williams.edu/eclipse/2017-usa/.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Kong, Weiqiang; Wang, Zhifeng; Fan, Jianhua
2012-01-01
obtain fluid thermal capacitance in data processing. Then theoretical analysis and experimental verification are carried out to investigate influencing factors of obtaining accurate and stable second order term. A flat plate and ETC solar collector are compared using both the new dynamic method......A new dynamic test method is introduced. This so called improved transfer function method features on two new collector parameters. One is time term which can indicate solar collector's inner heat transfer ability and the other is a second order term of collector mean fluid temperature which can...... and a standard method. The results show that the improved function method can accurately and robustly estimate these two kinds of solar collectors....
-
Lobb, Dan
2017-11-01
One of the most significant problems for space-based spectro-radiometer systems, observing Earth from space in the solar spectral band (UV through short-wave IR), is in achievement of the required absolute radiometric accuracy. Classical methods, for example using one or more sun-illuminated diffusers as reflectance standards, do not generally provide methods for monitoring degradation of the in-flight reference after pre-flight characterisation. Ratioing methods have been proposed that provide monitoring of degradation of solar attenuators in flight, thus in principle allowing much higher confidence in absolute response calibration. Two example methods are described. It is shown that systems can be designed for relatively low size and without significant additions to the complexity of flight hardware.
-
Numerical investigation on thermal and fluid dynamic behaviors of solar chimney building systems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Manca, O.; Nardini, S.; Romano, P.; Mihailov, E.
2013-01-01
Full text: Buildings as big energy-consuming systems require large amount of energy to operate. Globally, buildings are responsible for approximately 40% of total world annual energy consumption. Sustainable buildings with renewable energy systems are trying to operate independently without consumption of conventional resources. Renewable energy is a significant approach to reduce resource consumption in sustainable building. A solar chimney is essentially divided into two parts, one - the solar air heater (collector) and second - the chimney. Two configurations of solar chimney are usually used: vertical solar chimney with vertical absorber geometry, and roof solar chimney. For vertical solar chimney, vertical glass is used to gain solar heat. Designing a solar chimney includes height, width and depth of cavity, type of glazing, type of absorber, and inclusion of insulation or thermal mass. Besides these system parameters, other factors such as the location, climate, and orientation can also affect its performance. In this paper a numerical investigation on a prototypal solar chimney system integrated in a south facade of a building is presented. The analysis is carried out on a three-dimensional model in air flow and the governing equations are given in terms of k-s turbulence model. Two geometrical configurations are investigated: 1) a channel with vertical parallel walls and 2) a channel with principal walls one vertical and the other inclined. The problem is solved by means of the commercial code Ansys-Fluent and the results are performed for a uniform wall heat flux on the vertical wall is equal to 300 and 600 W/m2. Results are given in terms of wall temperature distributions, air velocity and temperature fields and transversal profiles in order to evaluate the differences between the two base configurations and thermal and fluid dynamic behaviors. Further, the ground effect on thermal performances is examined. key words: mathematical modeling, solar chimney
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Arsen'ev, A.A.
1979-01-01
Example of a classical dynamical system with the infinite-dimensional phase space, satisfying the analogue of the Kubo-Martin-Schwinger conditions for classical dynamics, is constructed explicitly. Connection between the system constructed and the Fock space dynamics is pointed out
-
Space Nuclear Power and Propulsion - a basic Tool for the manned Exploration of the Solar System
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Frischauf, Norbert; Hamilton, Booz Allen
2004-01-01
Humanity has started to explore space more than 40 years ago. Numerous spacecraft have left the Earth in this endeavour, but while unmanned spacecraft were already sent out on missions, where they would eventually reach the outer limits of the Solar System, manned exploration has always been confined to the tiny bubble of the Earth's gravitational well, stretching out at maximum to our closest celestial companion - the Moon - during the era of the Apollo programme in the late 60's and early 70's. When mankind made its giant leap, the exploration of our cosmic neighbour was seen as the initial step for the manned exploration of the whole Solar System. Consequently ambitious research and development programmes were undertaken at that time to enable what seemed to be the next logical steps: the establishment of a permanent settled base on the Moon and the first manned mission to Mars in the 80's. Nuclear space power and propulsion played an important role in these entire future scenarios, hence ambitious development programmes were undertaken to make these technologies available. Unfortunately the 70's-paradigm shift in space policies did not only bring an end to the Apollo programme, but it also brought a complete halt to all of these technology programmes and confined the human presence in space to a tiny bubble including nothing more than the Earth's sphere and a mere shell of a few hundred kilometres of altitude, too small to even include the Moon. Today, after more than three decades, manned exploration of the Solar System has become an issue again and so are missions to Moon and Mars. However, studies and analyses show that all of these future plans are hampered by today's available propulsion systems and by the problematic of solar power generation at distances at and beyond of Mars, a problem, however, that can readily be solved by the utilisation of space nuclear reactors and propulsion systems. This paper intends to provide an overview on the various fission
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Calise, Francesco; D’Accadia, Massimo Dentice; Vanoli, Laura
2012-01-01
Highlights: ► Sheet and tube photovoltaic/thermal (PVT) solar collector are investigated. ► PVT is integrated in a novel solar trigeneration system. ► The trigeneration system is dynamically investigated for a mediterranean climate. ► PVT performance is excellent during the summer. ► During the winter PVT thermal energy significantly decreases. - Abstract: In this paper, a Solar Heating and Cooling (SHC) system including photovoltaic/thermal (PVT) collectors is considered, implementing a novel polygeneration system producing electricity, space heating and cooling and domestic hot water. In particular, PVT collectors operating up to 80 °C are considered. A case study for a university building located in Naples (Italy) is developed and discussed. The system is mainly composed by: PVT collectors, a single-stage LiBr–H 2 O absorption chiller, storage tanks and auxiliary heaters. The system also includes additional balance-of-plant devices: heat exchangers, pumps, controllers, cooling tower, etc. The PVT produces electricity which is utilized in part by the building lights and equipments and in part by the system parasitic loads; the rest is eventually sold to the grid. Simultaneously, the PVT system provides the heat required to drive the absorption chiller. The system performance is analyzed from both energetic and economic points of view by means of a zero-dimensional transient simulation model, developed with TRNSYS. The economic results show that the system under investigation can be profitable, provided that an appropriate funding policy is available. In addition, the overall energetic and economic results are comparable to those reported in literature for similar systems.
-
Dynamical tunneling in systems with a mixed phase space
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Loeck, Steffen
2010-01-01
Tunneling is one of the most prominent features of quantum mechanics. While the tunneling process in one-dimensional integrable systems is well understood, its quantitative prediction for systems with a mixed phase space is a long-standing open challenge. In such systems regions of regular and chaotic dynamics coexist in phase space, which are classically separated but quantum mechanically coupled by the process of dynamical tunneling. We derive a prediction of dynamical tunneling rates which describe the decay of states localized inside the regular region towards the so-called chaotic sea. This approach uses a fictitious integrable system which mimics the dynamics inside the regular domain and extends it into the chaotic region. Excellent agreement with numerical data is found for kicked systems, billiards, and optical microcavities, if nonlinear resonances are negligible. Semiclassically, however, such nonlinear resonance chains dominate the tunneling process. Hence, we combine our approach with an improved resonance-assisted tunneling theory and derive a unified prediction which is valid from the quantum to the semiclassical regime. We obtain results which show a drastically improved accuracy of several orders of magnitude compared to previous studies. (orig.)
-
Dynamical tunneling in systems with a mixed phase space
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Loeck, Steffen
2010-04-22
Tunneling is one of the most prominent features of quantum mechanics. While the tunneling process in one-dimensional integrable systems is well understood, its quantitative prediction for systems with a mixed phase space is a long-standing open challenge. In such systems regions of regular and chaotic dynamics coexist in phase space, which are classically separated but quantum mechanically coupled by the process of dynamical tunneling. We derive a prediction of dynamical tunneling rates which describe the decay of states localized inside the regular region towards the so-called chaotic sea. This approach uses a fictitious integrable system which mimics the dynamics inside the regular domain and extends it into the chaotic region. Excellent agreement with numerical data is found for kicked systems, billiards, and optical microcavities, if nonlinear resonances are negligible. Semiclassically, however, such nonlinear resonance chains dominate the tunneling process. Hence, we combine our approach with an improved resonance-assisted tunneling theory and derive a unified prediction which is valid from the quantum to the semiclassical regime. We obtain results which show a drastically improved accuracy of several orders of magnitude compared to previous studies. (orig.)
-
Tada, H. Y.; Carter, J. R., Jr.; Anspaugh, B. E.; Downing, R. G.
1982-01-01
The handbook to predict the degradation of solar cell electrical performance in any given space radiation environment is presented. Solar cell theory, cell manufacturing and how they are modeled mathematically are described. The interaction of energetic charged particles radiation with solar cells is discussed and the concept of 1 MeV equivalent electron fluence is introduced. The space radiation environment is described and methods of calculating equivalent fluences for the space environment are developed. A computer program was written to perform the equivalent fluence calculations and a FORTRAN listing of the program is included. Data detailing the degradation of solar cell electrical parameters as a function of 1 MeV electron fluence are presented.
-
Formation of a strong southward IMF near the solar maximum of cycle 23
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. Watari
2004-01-01
Full Text Available We analyzed observations of the solar activities and the solar wind parameters associated with large geomagnetic storms near the maximum of solar cycle 23. This analysis showed that strong southward interplanetary magnetic fields (IMFs, formed through interaction between an interplanetary disturbance, and background solar wind or between interplanetary disturbances are an important factor in the occurrence of intense geomagnetic storms. Based on our analysis, we seek to improve our understanding of the physical processes in which large negative Bz's are created which will lead to improving predictions of space weather.
Key words. Interplanetary physics (Flare and stream dynamics; Interplanetary magnetic fields; Interplanetary shocks -
Mercury sodium exospheric emission as a proxy for solar perturbations transit
Orsini, S.; Mangano, V.; Milillo, A.; Plainaki, C.; Mura, A.; Raines, J. M.; Laurenza, M.; De Angelis, E.; Rispoli, R.; Lazzarotto, F.; Aronica, A.
2017-12-01
The first evidence at Mercury of direct relation between ICME transit and Na exosphere dynamics is presented, suggesting that Na emission, observed from ground, could be a proxy of planetary space weather at Mercury. The link existing between the dayside exosphere Na patterns and the solar wind-magnetosphere-surface interactions is investigated. This goal is pursued by analyzing the Na intensity hourly images, as observed by the ground-based THEMIS solar telescope (Mangano et al., 2015*) during 10 selected periods between 2012 and 2013 (with seeing, σ 10.1016/j.pss.2015.04.001, 2015.
-
Dynamic Hybrid Simulation of the Lunar Wake During ARTEMIS Crossing
Wiehle, S.; Plaschke, F.; Angelopoulos, V.; Auster, H.; Glassmeier, K.; Kriegel, H.; Motschmann, U. M.; Mueller, J.
2010-12-01
The interaction of the highly dynamic solar wind with the Moon is simulated with the A.I.K.E.F. (Adaptive Ion Kinetic Electron Fluid) code for the ARTEMIS P1 flyby on February 13, 2010. The A.I.K.E.F. hybrid plasma simulation code is the improved version of the Braunschweig code. It is able to automatically increase simulation grid resolution in areas of interest during runtime, which greatly increases resolution as well as performance. As the Moon has no intrinsic magnetic field and no ionosphere, the solar wind particles are absorbed at its surface, resulting in the formation of the lunar wake at the nightside. The solar wind magnetic field is basically convected through the Moon and the wake is slowly filled up with solar wind particles. However, this interaction is strongly influenced by the highly dynamic solar wind during the flyby. This is considered by a dynamic variation of the upstream conditions in the simulation using OMNI solar wind measurement data. By this method, a very good agreement between simulation and observations is achieved. The simulations show that the stationary structure of the lunar wake constitutes a tableau vivant in space representing the well-known Friedrichs diagram for MHD waves.
-
Non-thermal Power-Law Distributions in Solar and Space Plasmas
Oka, M.; Battaglia, M.; Birn, J.; Chaston, C. C.; Effenberger, F.; Eriksson, E.; Fletcher, L.; Hatch, S.; Imada, S.; Khotyaintsev, Y. V.; Kuhar, M.; Livadiotis, G.; Miyoshi, Y.; Retino, A.
2017-12-01
Particles are accelerated to very high, non-thermal energies in solar and space plasma environments. While energy spectra of accelerated particles often exhibit a power-law and are characterized by the power-law index δ, it remains unclear how particles are accelerated to high energies and how δ is determined. Here, we review previous observations of the power-law index δ in a variety of different plasma environments with a particular focus on sub-relativistic electrons. It appears that in regions more closely related to magnetic reconnection (such as the "above-the-looptop" solar hard X-ray source and the plasma sheet in Earth's magnetotail), the spectra are typically soft (δ> 4). This is in contrast to the typically hard spectra (δuniform in the plasma sheet, while power-law distributions still exist even in quiet times. The role of magnetotail reconnection in the electron power-law formation could therefore be confounded with these background conditions. Because different regions have been studied with different instrumentations and methodologies, we point out a need for more systematic and coordinated studies of power-law distributions for a better understanding of possible scaling laws in particle acceleration as well as their universality.
-
Gautam, Bhoj R; Lee, Changyeon; Younts, Robert; Lee, Wonho; Danilov, Evgeny; Kim, Bumjoon J; Gundogdu, Kenan
2015-12-23
All-polymer solar cells exhibit rapid progress in power conversion efficiency (PCE) from 2 to 7.7% over the past few years. While this improvement is primarily attributed to efficient charge transport and balanced mobility between the carriers, not much is known about the charge generation dynamics in these systems. Here we measured exciton relaxation and charge separation dynamics using ultrafast spectroscopy in polymer/polymer blends with different molecular packing and morphology. These measurements indicate that preferential face-on configuration with intermixed nanomorphology increases the charge generation efficiency. In fact, there is a direct quantitative correlation between the free charge population in the ultrafast time scales and the external quantum efficiency, suggesting not only the transport but also charge generation is key for the design of high performance all polymer solar cells.
-
Solar g-modes? Comparison of detected asymptotic g-mode frequencies with solar model predictions
Wood, Suzannah Rebecca; Guzik, Joyce Ann; Mussack, Katie; Bradley, Paul A.
2018-06-01
After many years of searching for solar gravity modes, Fossat et al. (2017) reported detection of the nearly equally spaced high-order g-modes periods using a 15-year time series of GOLF data from the SOHO spacecraft. Here we report progress towards and challenges associated with calculating and comparing g-mode period predictions for several previously published standard solar models using various abundance mixtures and opacities, as well as the predictions for some non-standard models incorporating early mass loss, and compare with the periods reported by Fossat et al (2017). Additionally, we have a side-by-side comparison of results of different stellar pulsation codes for calculating g-mode predictions. These comparisons will allow for testing of nonstandard physics input that affect the core, including an early more massive Sun and dynamic electron screening.
-
Dynamics of continuous medium in space with torsion
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Krechet, V.G.
1985-01-01
In frames of Einstein-Cartan gravitation theory general properties of continuous media dynamics using description formalism of continuous medium steam-line congruence geometry are investigated. Raichaudhuri type equations in space with torsion applied to study the problem of singularities in gravitation theory are derived. It is shown that space-time torsion tensor trace may immediately affect volumetric autoparallel divergence and torsion pseudo trace - rotation of continuous medium steam-line congruences. Using formalism considered metrics of homogeneous rotation nonstationary cosmological model is determined and investigated
-
A study of dynamical behavior of space environment
Wu, S. T.
1974-01-01
Studies have covered a wide range of problems in the space environment, such as the problems of the dynamical behavior of the thermosphere, hydromagnetic wave propagation in the ionosphere, and interplanetary space environment. The theories used to analyze these problems range from a continuum theory of magnetohydrodynamics to the kinetic theory of free molecular flow. This is because the problems encountered covered the entire range of the Knudsen number (i.e., the ratio of mean free path to the characteristic length). Significant results are summarized.
-
Dynamic Model Averaging in Large Model Spaces Using Dynamic Occam's Window.
Onorante, Luca; Raftery, Adrian E
2016-01-01
Bayesian model averaging has become a widely used approach to accounting for uncertainty about the structural form of the model generating the data. When data arrive sequentially and the generating model can change over time, Dynamic Model Averaging (DMA) extends model averaging to deal with this situation. Often in macroeconomics, however, many candidate explanatory variables are available and the number of possible models becomes too large for DMA to be applied in its original form. We propose a new method for this situation which allows us to perform DMA without considering the whole model space, but using a subset of models and dynamically optimizing the choice of models at each point in time. This yields a dynamic form of Occam's window. We evaluate the method in the context of the problem of nowcasting GDP in the Euro area. We find that its forecasting performance compares well with that of other methods.
-
Myers, Matthew G.; Prokop, Norman F.; Krasowski, Michael J.; Piszczor, Michael F.; McNatt, Jeremiah S.
2016-01-01
Accurate air mass zero (AM0) measurement is essential for the evaluation of new photovoltaic (PV) technology for space solar cells. The NASA Glenn Research Center (GRC) has flown an experiment designed to measure the electrical performance of several solar cells onboard NASA Goddard Space Flight Center's (GSFC) Robotic Refueling Mission's (RRM) Task Board 4 (TB4) on the exterior of the International Space Station (ISS). Four industry and government partners provided advanced PV devices for measurement and orbital environment testing. The experiment was positioned on the exterior of the station for approximately eight months, and was completely self-contained, providing its own power and internal data storage. Several new cell technologies including four-junction (4J) Inverted Metamorphic Multi-Junction (IMM) cells were evaluated and the results will be compared to ground-based measurement methods.
-
Space Weather Research at the National Science Foundation
Moretto, T.
2015-12-01
There is growing recognition that the space environment can have substantial, deleterious, impacts on society. Consequently, research enabling specification and forecasting of hazardous space effects has become of great importance and urgency. This research requires studying the entire Sun-Earth system to understand the coupling of regions all the way from the source of disturbances in the solar atmosphere to the Earth's upper atmosphere. The traditional, region-based structure of research programs in Solar and Space physics is ill suited to fully support the change in research directions that the problem of space weather dictates. On the observational side, dense, distributed networks of observations are required to capture the full large-scale dynamics of the space environment. However, the cost of implementing these is typically prohibitive, especially for measurements in space. Thus, by necessity, the implementation of such new capabilities needs to build on creative and unconventional solutions. A particularly powerful idea is the utilization of new developments in data engineering and informatics research (big data). These new technologies make it possible to build systems that can collect and process huge amounts of noisy and inaccurate data and extract from them useful information. The shift in emphasis towards system level science for geospace also necessitates the development of large-scale and multi-scale models. The development of large-scale models capable of capturing the global dynamics of the Earth's space environment requires investment in research team efforts that go beyond what can typically be funded under the traditional grants programs. This calls for effective interdisciplinary collaboration and efficient leveraging of resources both nationally and internationally. This presentation will provide an overview of current and planned initiatives, programs, and activities at the National Science Foundation pertaining to space weathe research.
-
Space Solar Cell Characterization Laboratory
Federal Laboratory Consortium — FUNCTION: Measures, characterizes, and analyzes photovoltaic materials and devices. The primary focus is the measurement and characterization of solar cell response...
-
Lee, Jung Gil; Kim, Woo-Seung; Choi, June-Seok; Ghaffour, NorEddine; Kim, Young-Deuk
2017-01-01
This paper presents a theoretical analysis of the monthly average daily and hourly performances of a solar-powered multi-stage direct contact membrane distillation (SMDCMD) system with an energy recovery scheme and dynamic operating system. Mid
-
Charania, A.
2002-01-01
At the end of the first decade of the 21st century, the International Space Station (ISS) will stand as a testament of the engineering capabilities of the international community. The choices for the next logical step for this community remain vast and conflicting: a Mars mission, moon colonization, Space Solar Power (SSP), etc. This examination focuses on positioning SSP as one such candidate for consideration. A marketing roadmap is presented that reveals the potential benefits of SSP to both the space community and the global populace at large. Recognizing that scientific efficiency itself has no constituency large enough to persuade entities to outlay funds for such projects, a holistic approach is taken to positioning SSP. This includes the scientific, engineering, exploratory, economic, political, and development capabilities of the system. SSP can be seen as both space exploration related and a resource project for undeveloped nations. Coupling these two non-traditional areas yields a broader constituency for the project that each one alone could generate. Space exploration is many times seen as irrelevant to the condition of the populace of the planet from which the money comes for such projects. When in this new century, billions of people on the planet still have never made a phone call or even have access to clean water, the origins of this skepticism can be understandable. An area of concern is the problem of not living up to the claims of overeager program marketers. Just as the ISS may never live up to the claims of its advocates in terms of space research, any SSP program must be careful in not promising utopian global solutions to any future energy starved world. Technically, SSP is a very difficult problem, even harder than creating the ISS, yet the promise it can hold for both space exploration and Earth development can lead to a renaissance of the relevance of space to the lives of the citizens of the world.
-
The Solar Connections Observatory for Planetary Environments
Oliversen, Ronald J.; Harris, Walter M.; Oegerle, William R. (Technical Monitor)
2002-01-01
The NASA Sun-Earth Connection theme roadmap calls for comparative study of how the planets, comets, and local interstellar medium (LISM) interact with the Sun and respond to solar variability. Through such a study we advance our understanding of basic physical plasma and gas dynamic processes, thus increasing our predictive capabilities for the terrestrial, planetary, and interplanetary environments where future remote and human exploration will occur. Because the other planets have lacked study initiatives comparable to the terrestrial ITM, LWS, and EOS programs, our understanding of the upper atmospheres and near space environments on these worlds is far less detailed than our knowledge of the Earth. To close this gap we propose a mission to study {\\it all) of the solar interacting bodies in our planetary system out to the heliopause with a single remote sensing space observatory, the Solar Connections Observatory for Planetary Environments (SCOPE). SCOPE consists of a binocular EUV/FUV telescope operating from a remote, driftaway orbit that provides sub-arcsecond imaging and broadband medium resolution spectro-imaging over the 55-290 nm bandpass, and high (R>10$^{5}$ resolution H Ly-$\\alpha$ emission line profile measurements of small scale planetary and wide field diffuse solar system structures. A key to the SCOPE approach is to include Earth as a primary science target. From its remote vantage point SCOPE will be able to observe auroral emission to and beyond the rotational pole. The other planets and comets will be monitored in long duration campaigns centered when possible on solar opposition when interleaved terrestrial-planet observations can be used to directly compare the response of both worlds to the same solar wind stream and UV radiation field. Using a combination of observations and MHD models, SCOPE will isolate the different controlling parameters in each planet system and gain insight into the underlying physical processes that define the
-
Dropouts, spreading, and squeezing of solar particle distributions and space weather variability
Matthaeus, W. H.; Ruffolo, D. J.; Seripienlert, A.; Tooprakai, P.; Chuychai, P.
2015-12-01
In the past 15 years, observations and theories concerning dropouts of solar energetic particles have made it clear that the lateral spread of field lines and particles from a given location near the Sun is not a purely diffusive process. Particles of low energy from impulsive solar events exhibit abrupt changes in flux (dropouts) due to filamentation of magnetic connection from the Sun, indicating that magnetic flux tube-like structures at least partially persist to Earth orbit. Our simulations based on a corresponding spherical two-component model of Alfvénic (slab) and 2D magnetic fluctuations indicate that such particles mostly follow field lines, which spread over ˜25° at Earth orbit, and exhibit dropout features. On the other hand, gradual solar events are of practical interest because they can produce greatly enhanced high-energy ion fluxes, which can cause radiation damage to satellites, spacecraft, and astronauts. While gradual events do not exhibit dropouts in the above sense, we show that the distribution of high-energy (E≥1 GeV) protons is squeezed toward magnetic flux tube-like structures with a specific polarity due to the structures' conical shape. Since it is difficult to observationally determine what polarity of flux structure the Earth is in at a given time, this transport phenomenon contributes to event-to-event variability in ground level enhancements of GeV-range ions from solar storms, presenting a fundamental uncertainty in space weather prediction. Partially supported by the Thailand Research Fund (Grant BRG5880009), a Postdoctoral Fellowship from the Thailand Center of Excellence in Physics, a Research Fellowship from the Faculty of Science at Mahidol University, the U.S. NSF (AGS-1063439 and SHINE AGS-1156094), NASA (Heliophysics Theory NNX14AI63G, and LWS NNX15AB88G), and the Solar Probe Plus/ISIS project (D99031L).
-
Solar and interplanetary disturbances
Alurkar, S K
1997-01-01
Over the last three decades, a spate of solar wind observations have been made with sophisticated ground-based and space-borne instruments. Two highly successful space missions of the Skylab and the twin spacecraft Helios 1 and 2 have amassed an invaluable wealth of information on the large scale structure of the inner heliosphere, the solar and interplanetary magnetic field, coronal holes, interplanetary dust, solar windflows, etc.Solar and interplanetary propagating phenomena have been extensively studied during the last two decades. Very recently, a new simple model based on results from a
-
Wainerdi, Richard E
1970-01-01
Analytical Chemistry in Space presents an analysis of the chemical constitution of space, particularly the particles in the solar wind, of the planetary atmospheres, and the surfaces of the moon and planets. Topics range from space engineering considerations to solar system atmospheres and recovered extraterrestrial materials. Mass spectroscopy in space exploration is also discussed, along with lunar and planetary surface analysis using neutron inelastic scattering. This book is comprised of seven chapters and opens with a discussion on the possibilities for exploration of the solar system by
-
Stochastic Modelling, Analysis, and Simulations of the Solar Cycle Dynamic Process
Turner, Douglas C.; Ladde, Gangaram S.
2018-03-01
Analytical solutions, discretization schemes and simulation results are presented for the time delay deterministic differential equation model of the solar dynamo presented by Wilmot-Smith et al. In addition, this model is extended under stochastic Gaussian white noise parametric fluctuations. The introduction of stochastic fluctuations incorporates variables affecting the dynamo process in the solar interior, estimation error of parameters, and uncertainty of the α-effect mechanism. Simulation results are presented and analyzed to exhibit the effects of stochastic parametric volatility-dependent perturbations. The results generalize and extend the work of Hazra et al. In fact, some of these results exhibit the oscillatory dynamic behavior generated by the stochastic parametric additative perturbations in the absence of time delay. In addition, the simulation results of the modified stochastic models influence the change in behavior of the very recently developed stochastic model of Hazra et al.
-
Mejia-Ambriz, J.; Gonzalez-Esparza, A.; De la Luz, V.; Villanueva-Hernandez, P.; Andrade, E.; Aguilar-Rodriguez, E.; Chang, O.; Romero Hernandez, E.; Sergeeva, M. A.; Perez Alanis, C. A.; Reyes-Marin, P. A.
2017-12-01
The National Space Weather Laboratory - Laboratorio Nacional de Clima Espacial (LANCE) - of Mexico has different ground based instruments to study and monitor the space weather. One of these instruments is the Mexican Array Radio Telescope (MEXART) which is principally dedicated to remote sensing the solar wind and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) at 140 MHz, the instrument can detect solar wind densities and speeds from about 0.4 to 1 AU by modeling observations of interplanetary scintillation (IPS). MEXART is also able to detect ionospheric disturbances associated with transient space weather events by the analysis of ionospheric scintillation (IONS) . Additionally, MEXART has followed the Sun since the beginning of the current Solar Cycle 24 with records of 8 minutes per day, and occasionally, has partially detected the process of strong solar flares. Here we show the contributions of MEXART to the LANCE by reporting recent detections of CMEs by IPS, the arrive of transient events at Earth by IONS, the influence of active regions in the flux of the Sun at 140 MHz and the detection of a M6.5 class flare. Furthermore we report the status of a near real time analysis of IPS data for forecast purposes and the potential contribution to the Worldwide IPS Stations network (WIPSS), which is an effort to achieve a better coverage of the solar wind observations in the inner heliosphere.
-
Henley, E. M.; Pope, E. C. D.
2017-12-01
This commentary concerns recent work on solar wind forecasting by Owens and Riley (2017). The approach taken makes effective use of tools commonly used in terrestrial weather—notably, via use of a simple model—generation of an "ensemble" forecast, and application of a "cost-loss" analysis to the resulting probabilistic information, to explore the benefit of this forecast to users with different risk appetites. This commentary aims to highlight these useful techniques to the wider space weather audience and to briefly discuss the general context of application of terrestrial weather approaches to space weather.
-
Dynamic space charge behaviour in polymeric DC cables
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Rasmussen, Claus Nygaard; Holbøll, Joachim; Henriksen, Mogens
2002-01-01
The use of extruded insulation for DC cables involves a risk of local electric field enhancement, caused by a space charge build-up within the dielectric. In this work, the theory of charge generation and transport in polymers is applied in a numerical computer model in order to predict...... the formation and transport of space charges in a polymeric dielectric. The model incorporates the processes of field assisted electron-hole pair generation from impurity atoms, trapping and charge injection at the electrodes. Its aim has been to study the field- and temperature dependent dynamic behaviour...
-
NASA Solar Sail Propulsion Technology Development
Johnson, Les; Montgomery, Edward E.; Young, Roy; Adams, Charles
2007-01-01
NASA's In-Space Propulsion Technology Program has developed the first generation of solar sail propulsion systems sufficient to accomplish inner solar system science and exploration missions. These first generation solar sails, when operational, will range in size from 40 meters to well over 100 meters in diameter and have an areal density of less than 13 grams per square meter. A rigorous, multi-year technology development effort culminated in 2005 with the testing of two different 20-m solar sail systems under thermal vacuum conditions. The first system, developed by ATK Space Systems of Goleta, California, uses rigid booms to deploy and stabilize the sail. In the second approach, L'Garde, Inc. of Tustin, California uses inflatable booms that rigidize in the coldness of space to accomplish sail deployment. This effort provided a number of significant insights into the optimal design and expected performance of solar sails as well as an understanding of the methods and costs of building and using them. In a separate effort, solar sail orbital analysis tools for mission design were developed and tested. Laboratory simulations of the effects of long-term space radiation exposure were also conducted on two candidate solar sail materials. Detailed radiation and charging environments were defined for mission trajectories outside the protection of the earth's magnetosphere, in the solar wind environment. These were used in other analytical tools to prove the adequacy of sail design features for accommodating the harsh space environment. Preceding and in conjunction with these technology efforts, NASA sponsored several mission application studies for solar sails. Potential missions include those that would be flown in the near term to study the sun and be used in space weather prediction to one that would use an evolved sail capability to support humanity's first mission into nearby interstellar space. This paper will describe the status of solar sail propulsion within
-
Graphene for thermoelectronic solar energy conversion
De, Dilip K.; Olukunle, Olawole C.
2017-08-01
Graphene is a high temperature material which can stand temperature as high as 4600 K in vacuum. Even though its work function is high (4.6 eV) the thermionic emission current density at such temperature is very high. Graphene is a wonderful material whose work function can be engineered as desired. Kwon et al41 reported a chemical approach to reduce work function of graphene using K2CO3, Li2CO3, Rb2CO3, Cs2CO3. The work functions are reported to be 3.7 eV, 3.8 eV, 3.5 eV and 3.4 eV. Even though they did not report the high temperature tolerance of such alkali metal carbonate doped graphene, their works open a great promise for use of pure graphene and doped graphene as emitter (cathode) and collector (anode) in a solar thermionic energy converter. This paper discusses the dynamics of solar energy conversion to electrical energy using thermionic energy converter with graphene as emitter and collector. We have considered parabolic mirror concentrator to focus solar energy onto the emitter to achieve temperature around 4300 K. Our theoretical calculations and the modelling show that efficiency as high as 55% can easily be achieved if space-charge problem can be reduced and the collector can be cooled to certain proper temperature. We have discussed methods of controlling the associated space-charge problems. Richardson-Dushman equation modified by the authors have been used in this modelling. Such solar energy conversion would reduce the dependence on silicon solar panel and has great potential for future applications.
-
Individual dynamic lighting control in a daylit space
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Logadóttir, Asta; Christoffersen, Jens
2008-01-01
in combination with daylight. Subjects performed office work for one day in a simulated office environment. Every 30 minutes the subjects were invited to use the dimmer controls to change the lighting conditions to their preferred level. Measurements were made of illuminance, luminance, CCT and energy use......The objectives of the study are to observe individual preferences for dynamic lighting, individual control and possibly achieve energy savings in a daylit space. The dynamics in this study are modifications of light level and correlated colour temperature (CCT) from the electric lighting system...
-
Utilization of space technology for terrestrial solar power applications
Yasui, R. K.; Patterson, R. E.
1974-01-01
A description is given of the evolution of photovoltaic power systems designed and built for terrestrial applications, giving attention to problem areas which are currently impeding the further development of such systems. The rooftop testing of surplus solar panels is considered along with solar powered seismic observatories, solar powered portable radio sets, and design considerations identified from past experience. Present activities discussed are related to a solar powered on-shore beacon flasher system, a solar powered buoy, and a solar powered beacon flasher buoy.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tomova, Dimitrinka; Velinov, Peter; Tassev, Yordan; Tomova, Dimitrinka
2018-01-01
Some of the most powerful Earth’s directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs) from the current 24 solar cycle have been investigated. These are CMEs on March 15, 2015 and on September 4 and 6, 2017. As a result of these impacts of Sun on Earth, the highest intensity of the geomagnetic storms for the 24th solar cycle is observed. These G4 – Severe geomagnetic storms are in the periods March 17÷19, 2015 and September 7÷10, 2017. We use the solar wind parameters (velocity V, density or concentration N , temperature T p and intensity of the magnetic field B) from measurements by WIND, ACE and SOHO space crafts in the Lagrange equilibrium point L1 between Sun and Earth. We make calculations for the kinetic (dynamic) energy density E k , thermal energy density E t and magnetic energy density E m during the investigated periods May 10÷24, 2015 and September 2÷16, 2017. Both the energy densities for the individual events and the cumulative energy for each of them are evaluated. The quantitative analysis shows that not always the size of the geomagnetic reaction is commensurate with the density of the energy flux reaching the magnetosphere. In both studied periods, the energy densities have different behaviour over time. But for both periods, we can talk about the prognostic effect – with varying degrees of increase of the dynamic and thermal energies. Such an effect is not observed in the density of magnetic energy. An inverse relationship between the magnitude of the density of energies and the effect of Forbush decrease of the galactic cosmic rays is established. Key words: solar activity, flares, coronal mass ejection (CME), G4 –Severe geomagnetic storms, energy density of the solar wind, space weather
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Rajendra Karwa
2013-01-01
Full Text Available The paper presents results of thermal performance analysis of a solar air heater with v-down discrete rib roughness on the air flow side of the absorber plate, which supplies heated air for space heating applications. The air heater operates in a closed loop mode with inlet air at a fixed temperature of 295 K from the conditional space. The ambient temperature varied from 278 K to 288 K corresponding to the winter season of Western Rajasthan, India. The results of the analysis are presented in the form of performance plots, which can be utilized by a designer for calculating desired air flow rate at different ambient temperature and solar insolation values.
-
Space-charge dynamics of polymethylmethacrylate under electron beam irradiation
Gong, H; Ong, C K
1997-01-01
Space-charge dynamics of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) under electron beam irradiation has been investigated employing a scanning electron microscope. Assuming a Gaussian space-charge distribution, the distribution range (sigma) has been determined using a time-resolved current method in conjunction with a mirror image method. sigma is found to increase with irradiation time and eventually attain a stationary value. These observations have been discussed by taking into account radiation-induced conductivity and charge mobility. (author)
-
Dudnic, A. V.; Zaljubovski, I. I.; Kartashev, V. M.; Shmatko, E. S.
1985-01-01
Sporadic radio emission of near Earth space at the frequency of 38 MHz is shown to appear in the event of a rapid development of instabilities in the ionospheric plasma. The instabilities are generated due to primary ionospheric disturbances occurring under the influence of solar chromospheric flares.
-
Static and Dynamic Verification of Critical Software for Space Applications
Moreira, F.; Maia, R.; Costa, D.; Duro, N.; Rodríguez-Dapena, P.; Hjortnaes, K.
Space technology is no longer used only for much specialised research activities or for sophisticated manned space missions. Modern society relies more and more on space technology and applications for every day activities. Worldwide telecommunications, Earth observation, navigation and remote sensing are only a few examples of space applications on which we rely daily. The European driven global navigation system Galileo and its associated applications, e.g. air traffic management, vessel and car navigation, will significantly expand the already stringent safety requirements for space based applications Apart from their usefulness and practical applications, every single piece of onboard software deployed into the space represents an enormous investment. With a long lifetime operation and being extremely difficult to maintain and upgrade, at least when comparing with "mainstream" software development, the importance of ensuring their correctness before deployment is immense. Verification &Validation techniques and technologies have a key role in ensuring that the onboard software is correct and error free, or at least free from errors that can potentially lead to catastrophic failures. Many RAMS techniques including both static criticality analysis and dynamic verification techniques have been used as a means to verify and validate critical software and to ensure its correctness. But, traditionally, these have been isolated applied. One of the main reasons is the immaturity of this field in what concerns to its application to the increasing software product(s) within space systems. This paper presents an innovative way of combining both static and dynamic techniques exploiting their synergy and complementarity for software fault removal. The methodology proposed is based on the combination of Software FMEA and FTA with Fault-injection techniques. The case study herein described is implemented with support from two tools: The SoftCare tool for the SFMEA and SFTA
-
Wilkinson, John
2016-01-01
In response to the new information gained about the Solar System from recent space probes and space telescopes, the experienced science author Dr. John Wilkinson presents the state-of-the art knowledge on the Sun, solar system planets and small solar system objects like comets and asteroids. He also describes space missions like the New Horizon’s space probe that provided never seen before pictures of the Pluto system; the Dawn space probe, having just visited the asteroid Vesta, and the dwarf planet Ceres; and the Rosetta probe inorbit around comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko that has sent extraordinary and most exciting pictures. Those and a number of other probes are also changing our understanding of the solar system and providing a wealth of new up close photos. This book will cover all these missions and discuss observed surface features of planets and moons like their compositions, geisers, aurorae, lightning phenomena etc. Presenting the fascinating aspects of solar system astronomy this book is a c...
-
A phase-space approach to atmospheric dynamics based on observational data. Theory and applications
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wang Risheng.
1994-01-01
This thesis is an attempt to develop systematically a phase-space approach to the atmospheric dynamics based on the theoretical achievement and application experiences in nonlinear time-series analysis. In particular, it is concerned with the derivation of quantities for describing the geometrical structure of the observed dynamics in phase-space (dimension estimation) and the examination of the observed atmospheric fluctuations in the light of phase-space representation. The thesis is, therefore composed of three major parts, i.e. an general survey of the theory of statistical approaches to dynamic systems, the methodology designed for the present study and specific applications with respect to dimension estimation and to a phase-space analysis of the tropical stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation. (orig./KW)
-
ANGULAR SPACE – TIME RELATIONS IN SOLAR RADIATION
African Journals Online (AJOL)
ES Obe
1979-03-01
Mar 1, 1979 ... The analyses are educational adaptations of engineering mechanics to this growing field of heliotechnoloy. NOTATION [1] α = solar altitude angle β = surface tilt angle, towards Equator +β, away from Equator -β γ = solar azimuth angle, clockwise from. North δ. = solar declination angle θ, i = incidence angle ...
-
Prediction of temperature variation in a rotating spacecraft in space environment
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gadalla, Mohamed A.
2005-01-01
This paper presents a closed-form prediction model for the temperature distribution of a thick-walled cylindrical space vehicle subjected to solar heating in deep space. The model is based on the coupling between dynamics and solar radiation. Since solar radiation is, in general, incident from a fixed direction, one side of the space vehicle will be shone bright, and the other side dark. Thus the space astronauts, instruments, and cryogenic-fuel tanks are gaining heat on the bright side and losing heat from the dark side. This radiative heat gain and loss become equally significant as the conductive heat transfer through the interior of the space vehicle. Thermal analysis is carried out to predict the effect of the spinning speed and angular position on the temperature variation and gradients attained by speed vehicles outside the Earth's atmosphere. This analysis is based on the non-linearity of the radiative heat dissipation, the significant conductive heat transfer role, and combined boundary conditions that involve the temperature and angular position of the vehicle. An exact analytical solution is obtained inspite of the non-linearity and non-homogeneity in the boundary conditions. The results indicate that the temperature distribution on the outer surface of the space vehicle is nearly independent of the angular position; at sub-cylindrical surface, this independence is achieved at low angular velocity
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dyer, C.S.; Truscott, P.R.; Peerless, C.L.; Watson, C.J.; Evans, H.E.; Knight, P.; Cosby, M.; Underwood, C.; Cousins, T.; Noulty, R.; Maag, C.
1999-01-01
Flight data obtained between 1990 and 1997 from the Cosmic Radiation Environment Monitors CREAM and CREDO carried on UoSAT-3, Space Shuttle, STRV-1a (Space Technology Research Vehicle) and APEX (Advanced Photovoltaic and Electronics Experiment Spacecraft) provide coverage over half a solar cycle. The modulation of cosmic rays and evolution of the South Atlantic Anomaly are observed, the former comprising a factor of three increase at high latitudes and the latter a general increase accompanied by a north-westward drift. Comparison of particle fluxes and linear energy transfer (LET) spectra is made with improved environment and radiation transport calculations which account for shield distributions and secondary particles. While there is an encouraging convergence between predictions and observations, significant improvements are still required, particularly in the treatment of locally produced secondary particles. Solar-particle events during this time period have LET spectra significantly below the October 1989 event which has been proposed as a worst case model
-
The space as a natural laboratory of Electrotechnics
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. K. Marhavilas
2008-01-01
Full Text Available Electricity is a general term for a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of charge, and “Electro-technics” is the study or the science of practical and industrial applications of electricity. On the other side, the space is mainly characterized by the interaction of energetic charged particles with electric and magnetic fields, which justifies the claim «the space composes a natural laboratory of electrotechnics». This paper reviews present understanding of the dy-namics of the solar-terrestrial environment, and its impacts on the human activity, and explain processes, which establish the space as a natural laboratory of electrotechnics.
-
Discussion on Application of Space Materials and Technological Innovation in Dynamic Fashion Show
Huo, Meilin; Kim, Chul Soo; Zhao, Wenhan
2018-03-01
In modern dynamic fashion show, designers often use the latest ideas and technology, and spend their energy in stage effect and overall environment to make audience’s watching a fashion show like an audio-visual feast. With rapid development of China’s science and technology, it has become a design trend to strengthen the relationship between new ideas, new trends and technology in modern art. With emergence of new technology, new methods and new materials, designers for dynamic fashion show stage art can choose the materials with an increasingly large scope. Generation of new technology has also made designers constantly innovate the stage space design means, and made the stage space design innovated constantly on the original basis of experiences. The dynamic clothing display space is on design of clothing display space, layout, platform decoration style, platform models, performing colors, light arrangement, platform background, etc.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ellehauge, K.
2002-12-01
The most common Danish solar combi-system is theoretically investigated in the report. The principle in the system is that in a normal solar hot water system a heat exchanger is added to deliver solar energy from the collector loop directly to the space heating loop. In this way solar energy for space heating is not stored which is expected to decrease the performance. On the other hand the system is relatively inexpensive, which can compensate for a reduced performance. A TRNSYS model of the system is developed and sensitivity analyses of parameters are performed by simulation. The analyses show no major improvements of the system. Special emphasis has been put on investigating the control strategy and to investigate if the thermal mass of radiators of floor could act as buffer for the solar energy delivered to space heating and in this way improve the performance. The analyses show that this is possible and has advantages at larger collector areas. However the improvements are not as large as expected. An economic optimisation gives and optimum solar collector area of approximately 10 m 2 . However the optimum curve is quite flat for areas above 7 m 2 , and collector areas up to 15 m 2 are also feasible. The calculated performacnes have been the basis for comparisons with the other systems modelled in the task 26. The comparison shows that the performance is not among the best, but however probably not as bad as expected. Furthermore the inexpensive design compensates to some extent for the lower performance. Furthermore the material use of the system and the energy used to produce the materials has been estimated. The energy demand is in a range that gives energy pay back times of 1.9-2.5 years. (au)
-
Bright Idea: Solar Energy Primer.
Missouri State Dept. of Natural Resources, Jefferson City.
This booklet is intended to address questions most frequently asked about solar energy. It provides basic information and a starting point for prospective solar energy users. Information includes discussion of solar space heating, solar water heating, and solar greenhouses. (Author/RE)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. Núñez
2005-11-01
Full Text Available Predicting the occurrence of solar flares is a challenge of great importance for many space weather scientists and users. We introduce a data mining approach, called Behavior Pattern Learning (BPL, for automatically discovering correlations between solar flares and active region data, in order to predict the former. The goal of BPL is to predict the interval of time to the next solar flare and provide a confidence value for the associated prediction. The discovered correlations are described in terms of easy-to-read rules. The results indicate that active region dynamics is essential for predicting solar flares.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. Shi
2009-02-01
Full Text Available Determination of the radial profile of phase space density of relativistic electrons at constant adiabatic invariants is crucial for identifying the source for them within the outer radiation belt. The commonly used method is to convert flux observed at fixed energy to phase space density at constant first, second and third adiabatic invariants, which requires an empirical global magnetic field model and thus might produce some uncertainties in the final results. From a different perspective, in this paper we indirectly infer the shape of the radial profile of phase space density of relativistic electrons near the geosynchronous region by statistically examining the geosynchronous energetic flux response to 128 solar wind dynamic pressure enhancements during the years 2000 to 2003. We thus avoid the disadvantage of using empirical magnetic field models. Our results show that the flux response is species and energy dependent. For protons and low-energy electrons, the primary response to magnetospheric compression is an increase in flux at geosynchronous orbit. For relativistic electrons, the dominant response is a decrease in flux, which implies that the phase space density decreases toward increasing radial distance at geosynchronous orbit and leads to a local peak inside of geosynchronous orbit. The flux response of protons and non-relativistic electrons could result from a phase density that increases toward increasing radial distance, but this cannot be determined for sure due to the particle energization associated with pressure enhancements. Our results for relativistic electrons are consistent with previous results obtained using magnetic field models, thus providing additional confirmation that these results are correct and indicating that they are not the result of errors in their selected magnetic field model.
-
Lee, Jung Gil
2017-04-26
This paper presents a theoretical analysis of the monthly average daily and hourly performances of a solar-powered multi-stage direct contact membrane distillation (SMDCMD) system with an energy recovery scheme and dynamic operating system. Mid-latitude meteorological data from Busan, Korea is employed, featuring large climate variation over the course of one year. The number of module stages used by the dynamic operating scheme changes dynamically based on the inlet feed temperature of the successive modules, which results in an improvement of the water production and thermal efficiency. The simulations of the SMDCMD system are carried out to investigate the spatial and temporal variations in the feed and permeate temperatures and permeate flux. The monthly average daily water production increases from 0.37m3/day to 0.4m3/day and thermal efficiency increases from 31% to 45% when comparing systems both without and with dynamic operation in December. The water production with respect to collector area ranged from 350m2 to 550m2 and the seawater storage tank volume ranged from 16m3 to 28.8m3, and the solar fraction at various desired feed temperatures from 50°C to 80°C have been investigated in October and December.
-
An Economic Analysis of Solar Water & Space Heating.
Energy Research and Development Administration, Washington, DC. Div. of Solar Energy.
Solar system designs for 13 cities were optimized so as to minimize the life cycle cost over the assumed 20-year lifetime of the solar energy systems. A number of major assumptions were made regarding the solar system, type and use of building, financial considerations, and economic environment used in the design optimization. Seven optimum…
-
Solar Dynamics Observatory Guidance, Navigation, and Control System Overview
Morgenstern, Wendy M.; Bourkland, Kristin L.; Hsu, Oscar C.; Liu, Kuo-Chia; Mason, Paul A. C.; O'Donnell, James R., Jr.; Russo, Angela M.; Starin, Scott R.; Vess, Melissa F.
2011-01-01
The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) was designed and built at the Goddard Space Flight Center, launched from Cape Canaveral on February 11, 2010, and reached its final geosynchronous science orbit on March 16, 2010. The purpose of SDO is to observe the Sun and continuously relay data to a dedicated ground station. SDO remains Sun-pointing throughout most of its mission for the instruments to take measurements of the Sun. The SDO attitude control system (ACS) is a single-fault tolerant design. Its fully redundant attitude sensor complement includes sixteen coarse Sun sensors (CSSs), a digital Sun sensor (DSS), three two-axis inertial reference units (IRUs), and two star trackers (STs). The ACS also makes use of the four guide telescopes included as a part of one of the science instruments. Attitude actuation is performed using four reaction wheels assemblies (RWAs) and eight thrusters, with a single main engine used to provide velocity-change thrust for orbit raising. The attitude control software has five nominal control modes, three wheel-based modes and two thruster-based modes. A wheel-based Safehold running in the attitude control electronics box improves the robustness of the system as a whole. All six modes are designed on the same basic proportional-integral-derivative attitude error structure, with more robust modes setting their integral gains to zero. This paper details the final overall design of the SDO guidance, navigation, and control (GN&C) system and how it was used in practice during SDO launch, commissioning, and nominal operations. This overview will include the ACS control modes, attitude determination and sensor calibration, the high gain antenna (HGA) calibration, and jitter mitigation operation. The Solar Dynamics Observatory mission is part of the NASA Living With a Star program, which seeks to understand the changing Sun and its effects on the Solar System, life, and society. To this end, the SDO spacecraft carries three Sun
-
A dynamical topology for the space of states
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dittrich, J.
1979-01-01
A new topology is introduced for the space of states of a physical system. This topology is given by dynamics, every state has a neighbourhood consisting of states connected by the time evolution only. With respect to the new topology, all conservation laws can be treated as topological laws. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Calise, Francesco; Palombo, Adolfo; Vanoli, Laura
2012-01-01
Highlights: ► A novel polygeneration system based on engines (RE) fed by rapeseed oil is investigated. ► RE are integrated with high temperature solar heating and cooling systems. ► The polygeneration system is dynamically investigated for a Mediterranean Climate. ► System performance is excellent from the energetic point of view. ► The system is economically profitable only in case of feed-in tariffs. - Abstract: In this paper the integration of vegetable oil-fed reciprocating engines with solar thermal collector is investigated, seeking to design a novel polygeneration system producing: electricity, space heating and cooling and domestic hot water, for a university building located in Naples (Italy), assumed as case study. The polygeneration system is based on the following main components: concentrating parabolic trough solar collector, double-stage LiBr–H 2 O absorption chiller and a reciprocating engine fed by vegetable oil. The engine operates at full load producing electrical energy which is in part consumed by the building lights and equipments, in part used by the system passive loads and the rest is eventually sold to the grid. In fact, the engine is grid connected in order to perform a convenient net metering. The system was designed and then simulated by means of a zero-dimensional transient simulation model, developed using the TRNSYS software. The simulation tool developed by the authors allows one to analyze the results for different time basis (minutes, days, weeks, months and years), from both energetic and economic points of view. The economic results show that the system under investigation is profitable, especially if properly funded.