
Sample records for solar wind energy
-
Limitation of solar energy and wind energy
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
White, R. S.
2008-01-01
Wind turbines, solar energy collectors and photovoltaic cells have been popular sources of electricity since the oil crisis in the late seventies, and they are increasingly favored by many scientists and much of the public as methods for reducing global warming. The older wind farms in California are outdated. New wind turbines have not followed, primarily because of competition from lower-cost natural gas. The Times urges increased federal and state subsidies for the wind and solar industries. The primary reason that wind and solar energies have not made inroads in the past, and will never supply more than a few percentage points of the world's electrical energy, is their unpredictable variations in time and their constant need for back-ups. The only non-carbon-dioxide-emitting generator capable of backing up wind and solar energy and replacing coal and gas generators is nuclear fission. Nuclear power may be the practical solution to global warming, after all.
-
Weather-power station. Solar energy, wind energy, water energy
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Schatta, M
1975-10-02
A combined power station is described, which enables one to convert solar energy and wind energy into other forms of energy. The plant consists of a water-filled boiler, in which solar energy heats the water by concentration, solar cells, and finally wind rotors, which transform wind energy into electrical energy. The transformed energy is partly available as steam heat, partly as mechanical or electrical energy. The plant can be used for supplying heating systems or electrolysis equipment. Finally, by incorporating suitable motors, a mobile version of the system can be produced.
-
Wind and solar energy incentives in Iran
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Taleghani, G.; Kazemi Karegar, H.
2006-01-01
Incentive have yet been viewed as a means of supporting technological developments until a new technology becomes cost competitive wind based electricity is not jet generally competitive with alternate sources of electricity such as fossil fuels. This paper presents the potential for wind and solar in Iran and shows how much electric energy is now produced by renewable power plants compared to steam and gas. The importance of renewable energy effects on Iran environment and economy is also discussed and the issue of the contribution of renewable energy for producing electricity in the future will be shown. Also this paper highlights the ability of Iran to manufacture the components of the wind turbine and solar system locally, and its effect on the price of wind turbine and solar energy
-
Solar energy system with wind vane
Grip, Robert E
2015-11-03
A solar energy system including a pedestal defining a longitudinal axis, a frame that is supported by the pedestal and that is rotateable relative to the pedestal about the longitudinal axis, the frame including at least one solar device, and a wind vane operatively connected to the frame to urge the frame relative to the pedestal about the longitudinal axis in response to wind acting on the wind vane.
-
ENERGY DISSIPATION PROCESSES IN SOLAR WIND TURBULENCE
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Wang, Y.; Wei, F. S.; Feng, X. S.; Sun, T. R.; Zuo, P. B. [SIGMA Weather Group, State Key Laboratory for Space Weather, National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190 (China); Xu, X. J. [Space Science Institute, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macao (China); Zhang, J., E-mail: yw@spaceweather.ac.cn [School of Physics, Astronomy and Computational Sciences, George Mason University, 4400 University Drive, MSN 3F3, Fairfax, Virginia 22030 (United States)
2015-12-15
Turbulence is a chaotic flow regime filled by irregular flows. The dissipation of turbulence is a fundamental problem in the realm of physics. Theoretically, dissipation ultimately cannot be achieved without collisions, and so how turbulent kinetic energy is dissipated in the nearly collisionless solar wind is a challenging problem. Wave particle interactions and magnetic reconnection (MR) are two possible dissipation mechanisms, but which mechanism dominates is still a controversial topic. Here we analyze the dissipation region scaling around a solar wind MR region. We find that the MR region shows unique multifractal scaling in the dissipation range, while the ambient solar wind turbulence reveals a monofractal dissipation process for most of the time. These results provide the first observational evidences for intermittent multifractal dissipation region scaling around a MR site, and they also have significant implications for the fundamental energy dissipation process.
-
Wind loads on solar energy roofs
Geurts, C.P.W.; Bentum, C.A. van
2007-01-01
This paper presents an overview of the wind loads on roofs, equipped with solar energy products, so called Active Roofs. Values given in this paper have been based on wind tunnel and full scale measurements, carried out at TNO, and on an interpretation of existing rules and guidelines. The results
-
Design of Hybrid Solar and Wind Energy Harvester for Fishing Boat
Banjarnahor, D. A.; Hanifan, M.; Budi, E. M.
2017-07-01
In southern beach of West Java, Indonesia, there are many villagers live as fishermen. They use small boats for fishing, in one to three days. Therefore, they need a fish preservation system. Fortunately, the area has high potential of solar and wind energy. This paper presents the design of a hybrid solar and wind energy harvester to power a refrigerator in the fishing boat. The refrigerator should keep the fish in 2 - 4 °C. The energy needed is 720 Wh daily. In the area, the daily average wind velocity is 4.27 m/s and the sun irradiation is 672 W/m2. The design combined two 100W solar panels and a 300W wind turbine. The testing showed that the solar panels can harvest 815 - 817 Wh of energy, while the wind turbine can harvest 43 - 62 Wh of energy daily. Therefore, the system can fulfil the energy requirement in fishing boat, although the solar panels were more dominant. To install the wind turbine on the fishing-boat, a computational design had been conducted. The boat hydrostatic dimension was measured to determine its stability condition. To reach a stable equilibrium condition, the wind turbine should be installed no more than 1.7 m of height.
-
Enhancing information for solar and wind energy technology deployment in Brazil
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ramos Martins, Fernando, E-mail: fernando.martins@inpe.br [Centro de Ciencia do Sistema Terrestre-Instituto Nacisonal de Pesquisas Espaciais (Earth System Center-National Institute for Space Research), P.O. Box 515, 12245-970, Sao Jose dos Campos (Brazil); Pereira, Enio Bueno, E-mail: enio.pereira@inpe.br [Centro de Ciencia do Sistema Terrestre-Instituto Nacisonal de Pesquisas Espaciais (Earth System Center-National Institute for Space Research), P.O. Box 515, 12245-970, Sao Jose dos Campos (Brazil)
2011-07-15
Brazil's primary energy matrix is based on more than 47% of renewables, and more than 85% of its electricity is generated by hydro power sources. Despite this large fraction of renewable energy resources, less than 0.3% of the national energy supply comes from solar or wind sources. This paper presents a diagnostic review on the penetration of the solar and wind energy technologies in Brazil. It also includes a survey of the latest government policies and incentives for renewable energies deployment by entrepreneurs, industry and commercial and residential consumers. In addition, the paper analyses how to best meet the requirements for policy support and information technology to boost the deployment of solar technology and wind energy in Brazil. This study was mostly based on results of a widely distributed survey covering key issues, and also by personal interviews carried out with key stakeholders in order to better understand the issues highlighted in the survey responses. The study pointed out some of the main obstacles to effectively promote and improve government policies and actions for investment in solar and wind energy market in Brazil. - Highlights: > Current status on the solar and wind energy deployment in Brazil is presented. > Policy framework required to support solar and wind energy was discussed. > Study was based on responses for consultations with key stakeholders. > Worthiness Index was established to rank the stakeholders outlooks. > Energy price, human resources and tax reductions were indicated as priority.
-
Enhancing information for solar and wind energy technology deployment in Brazil
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ramos Martins, Fernando; Pereira, Enio Bueno
2011-01-01
Brazil's primary energy matrix is based on more than 47% of renewables, and more than 85% of its electricity is generated by hydro power sources. Despite this large fraction of renewable energy resources, less than 0.3% of the national energy supply comes from solar or wind sources. This paper presents a diagnostic review on the penetration of the solar and wind energy technologies in Brazil. It also includes a survey of the latest government policies and incentives for renewable energies deployment by entrepreneurs, industry and commercial and residential consumers. In addition, the paper analyses how to best meet the requirements for policy support and information technology to boost the deployment of solar technology and wind energy in Brazil. This study was mostly based on results of a widely distributed survey covering key issues, and also by personal interviews carried out with key stakeholders in order to better understand the issues highlighted in the survey responses. The study pointed out some of the main obstacles to effectively promote and improve government policies and actions for investment in solar and wind energy market in Brazil. - Highlights: → Current status on the solar and wind energy deployment in Brazil is presented. → Policy framework required to support solar and wind energy was discussed. → Study was based on responses for consultations with key stakeholders. → Worthiness Index was established to rank the stakeholders outlooks. → Energy price, human resources and tax reductions were indicated as priority.
-
A hybrid reconfigurable solar and wind energy system
Gadkari, Sagar A.
We study the feasibility of a novel hybrid solar-wind hybrid system that shares most of its infrastructure and components. During periods of clear sunny days the system will generate electricity from the sun using a parabolic concentrator. The concentrator is formed by individual mirror elements and focuses the light onto high intensity vertical multi-junction (VMJ) cells. During periods of high wind speeds and at night, the same concentrator setup will be reconfigured to channel the wind into a wind turbine which will be used to harness wind energy. In this study we report on the feasibility of this type of solar/wind hybrid energy system. The key mechanisms; optics, cooling mechanism of VMJ cells and air flow through the system were investigated using simulation tools. The results from these simulations, along with a simple economic analysis giving the levelized cost of energy for such a system are presented. An iterative method of design refinement based on the simulation results was used to work towards a prototype design. The levelized cost of the system achieved in the economic analysis shows the system to be a good alternative for a grid isolated site and could be used as a standalone system in regions of lower demand. The new approach to solar wind hybrid system reported herein will pave way for newer generation of hybrid systems that share common infrastructure in addition to the storage and distribution of energy.
-
Wind tunnel and CFD modelling of wind pressures on solar energy systems on flat roofs
Bronkhorst, A.J.; Franke, J.; Geurts, C.P.W.; Bentum, van C.A.; Grepinet, F.
2010-01-01
Design of solar energy mounting systems requires more knowledge on the wind patterns around these systems. To obtain more insight in the flow patterns, which cause the pressure distributions on the solar energy systems, a wind tunnel test and Computational Fluid Dynamics analysis have been
-
Vestas Power Plant Solutions Integrating Wind, Solar PV and Energy Storage
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Petersen, Lennart; Hesselbæk, Bo; Martinez, Antonio
2018-01-01
This paper addresses a value proposition and feasible system topologies for hybrid power plant solutions integrating wind, solar PV and energy storage and moreover provides insights into Vestas hybrid power plant projects. Seen from the perspective of a wind power plant developer, these hybrid...... solutions provide a number of benefits that could potentially reduce the Levelized Cost of Energy and enable entrance to new markets for wind power and facilitate the transition to a more sustainable energy mix. First, various system topologies are described in order to distinguish the generic concepts...... for the electrical infrastructure of hybrid power plants. Subsequently, the benefits of combining wind and solar PV power as well as the advantages of combining variable renewable energy sources with energy storage are elaborated. Finally, the world’s first utility-scale hybrid power plant combining wind, solar PV...
-
A desalination plant with solar and wind energy
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen, H; Ye, Z; Gao, W
2013-01-01
The shortage of freshwater resources has become a worldwide problem. China has a water shortage, although the total amount of water resources is the sixth in the world, the per capita water capacity is the 121th (a quarter of the world's per capita water capacity), and the United Nations considers China one of the poorest 13 countries in the world in terms of water. In order to increase the supply of fresh water, a realistic way is to make full use of China's long and narrow coastline for seawater desalination. This paper discusses a sea water desalination device, the device adopts distillation, uses the greenhouse effect principle and wind power heating principle, and the two-type start is used to solve the problem of vertical axis wind turbine self-starting. Thrust bearings are used to ensure the stability of the device, and to ensure absorbtion of wind energy and solar energy, and to collect evaporation of water to achieve desalination. The device can absorb solar and wind energy instead of input energy, so it can be used in ship, island and many kinds of environment. Due to the comprehensive utilization of wind power and solar power, the efficiency of the device is more than other passive sea water desalting plants, the initial investment and maintenance cost is lower than active sea water desalting plant. The main part of the device cannot only be used in offshore work, but can also be used in deep sea floating work, so the device can utilise deep sea energy. In order to prove the practicability of the device, the author has carried out theory of water production calculations. According to the principle of conservation of energy, the device ais bsorbing solar and wind power, except loose lost part which is used for water temperature rise and phase transition. Assume the inflow water temperature is 20 °C, outflow water temperature is 70 °C, the energy utilization is 60%, we can know that the water production quantity is 8 kg/ m 2 per hour. Comparing
-
COMPLEX MAPPING OF ENERGY RESOURCES FOR ALLOCATION OF SOLAR AND WIND ENERGY OBJECTS
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. A. Novakovskiy
2016-01-01
Full Text Available The paper presents developed methodology of solar and wind energy resources complex mapping at the regional level, taking into account the environmental and socio-economic factors affecting the placement of renewable energy facilities. Methodology provides a reasonable search and allocation of areas, the most promising for the placement of wind and solar power plants.
-
Low-energy ion outflow modulated by the solar wind energy input
Li, Kun; Wei, Yong; Andre, Mats; Eriksson, Anders; Haaland, Stein; Kronberg, Elena; Nilsson, Hans; Maes, Lukas
2017-04-01
Due to the spacecraft charging issue, it has been difficult to measure low-energy ions of ionospheric origin in the magnetosphere. A recent study taking advantage of the spacecraft electric potential has found that the previously 'hidden' low-energy ions is dominant in the magnetosphere. This comprehensive dataset of low-energy ions allows us to study the relationship between the ionospheric outflow and energy input from the solar wind (ɛ). In this study, we discuss the ratios of the solar wind energy input to the energy of the ionospheric outflow. We show that the ɛ controls the ionospheric outflow when the ɛ is high, while the ionospheric outflow does not systematically change with the ɛ when the ɛ is low.
-
Sustainable business models for wind and solar energy in Romania
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Nichifor Maria Alexandra
2015-06-01
Full Text Available Renewable energy has become a crucial element for the business environment as the need for new energy resources and the degree of climate change are increasing. As developed economies strive towards greater progress, sustainable business models are of the essence in order to maintain a balance between the triple bottom line: people, planet and profit. In recent years, European Union countries have installed important capacities of renewable energy, especially wind and solar energy to achieve this purpose. The objective of this article is to make a comparative study between the current sustainable business models implemented in companies that are active in the wind and solar energy sector in Romania. Both sectors underwent tremendous changes in the last two years due to changing support schemes which have had a significant influence on the mechanism of the renewable energy market, as well as on its development. Using the classical Delphi method, based on questionnaires and interviews with experts in the fields of wind and solar energy, this paper offers an overview of the sustainable business models of wind and solar energy companies, both sectors opting for the alternative of selling electricity to trading companies as a main source of revenue until 2013 and as the main future trend until 2020. Furthermore, the participating wind energy companies noted a pessimistic outlook of future investments due to legal instability that made them to reduce their projects in comparison to PV investments, which are expected to continue. The subject of the article is of interest to scientific literature because sustainable business models in wind and photovoltaic energy have been scarcely researched in previous articles and are essential in understanding the activity of the companies in these two fields of renewable energy.
-
Thermodynamic characteristics of a novel wind-solar-liquid air energy storage system
Ji, W.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Pan, C. Z.; Wang, J. J.
2017-12-01
Due to the nature of fluctuation and intermittency, the utilization of wind and solar power will bring a huge impact to the power grid management. Therefore a novel hybrid wind-solar-liquid air energy storage (WS-LAES) system was proposed. In this system, wind and solar power are stored in the form of liquid air by cryogenic liquefaction technology and thermal energy by solar thermal collector, respectively. Owing to the high density of liquid air, the system has a large storage capacity and no geographic constraints. The WS-LAES system can store unstable wind and solar power for a stable output of electric energy and hot water. Moreover, a thermodynamic analysis was carried out to investigate the best system performance. The result shows that the increases of compressor adiabatic efficiency, turbine inlet pressure and inlet temperature all have a beneficial effect.
-
Economic Dispatch for Power System Included Wind and Solar Thermal Energy
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Saoussen BRINI
2009-07-01
Full Text Available With the fast development of technologies of alternative energy, the electric power network can be composed of several renewable energy resources. The energy resources have various characteristics in terms of operational costs and reliability. In this study, the problem is the Economic Environmental Dispatching (EED of hybrid power system including wind and solar thermal energies. Renewable energy resources depend on the data of the climate such as the wind speed for wind energy, solar radiation and the temperature for solar thermal energy. In this article it proposes a methodology to solve this problem. The resolution takes account of the fuel costs and reducing of the emissions of the polluting gases. The resolution is done by the Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm (SPEA method and the simulations have been made on an IEEE network test (30 nodes, 8 machines and 41 lines.
-
2012-10-10
... DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY Federal Energy Regulatory Commission [Docket No. EL12-109-000] Avalon Wind, LLC; Avalon Wind 2, LLC; Catalina Solar, LLC; Catalina Solar 2, LLC; Pacific Wind Lessee, LLC; Pacific Wind 2, LLC; Valentine Solar, LLC; EDF Renewable Development, Inc.; Notice of Petition for Declaratory...
-
Reliability and cost/worth evaluation of generating systems utilizing wind and solar energy
Bagen
The utilization of renewable energy resources such as wind and solar energy for electric power supply has received considerable attention in recent years due to adverse environmental impacts and fuel cost escalation associated with conventional generation. At the present time, wind and/or solar energy sources are utilized to generate electric power in many applications. Wind and solar energy will become important sources for power generation in the future because of their environmental, social and economic benefits, together with public support and government incentives. The wind and sunlight are, however, unstable and variable energy sources, and behave far differently than conventional sources. Energy storage systems are, therefore, often required to smooth the fluctuating nature of the energy conversion system especially in small isolated applications. The research work presented in this thesis is focused on the development and application of reliability and economic benefits assessment associated with incorporating wind energy, solar energy and energy storage in power generating systems. A probabilistic approach using sequential Monte Carlo simulation was employed in this research and a number of analyses were conducted with regards to the adequacy and economic assessment of generation systems containing wind energy, solar energy and energy storage. The evaluation models and techniques incorporate risk index distributions and different operating strategies associated with diesel generation in small isolated systems. Deterministic and probabilistic techniques are combined in this thesis using a system well-being approach to provide useful adequacy indices for small isolated systems that include renewable energy and energy storage. The concepts presented and examples illustrated in this thesis will help power system planners and utility managers to assess the reliability and economic benefits of utilizing wind energy conversion systems, solar energy conversion
-
Economic viability of wind and solar energy for industrial use
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lashkari, Z.F.
1994-01-01
Non conventional energy sources have begun to move from fringes of technological possibility towards commercial viability. Out of the four sources, i e. solar, wind, biogas and minimicro hydel the first two viz. wind and solar energy are of relevance for industries in western region of India. This has to be seen in the context of developments in technology and hence economics both worldwide and in India. (author)
-
Liu, Quanhua
2014-01-01
Energy and environmental issues are among the most important problems of public concern. Wind and solar energy may be one of the alternative solutions to overcome energy shortage and to reduce greenhouse gaseous emission. Using electric cars in cities can significantly improve the air quality there. Through our analyses and modeling on the basis of the National Centers for Environment Prediction data we confirm that the amount of usable solar and wind energy far exceeds the world's total energy demand, considering the feasibility of the technology being used. Storing the surplus solar and wind energy and then releasing this surplus on demand is an important approach to maintaining uninterrupted solar- and wind-generated electricity. This approach requires us to be aware of the available solar and wind energy in advance in order to manage their storage. Solar and wind energy depends on weather conditions and we know weather forecasting. This implies that solar and wind energy is predictable. In this article, we demonstrate how solar and wind energy can be forecasted. We provide a web tool that can be used by all to arrive at solar and wind energy amount at any location in the world. The tool is available at http://www.renewableenergyst.org. The website also provides additional information on renewable energy, which is useful to a wide range of audiences, including students, educators, and the general public.
-
The Feasibility of Wind and Solar Energy Application for Oil and Gas Offshore Platform
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tiong, Y K; Zahari, M A; Wong, S F; Dol, S S
2015-01-01
Renewable energy is an energy which is freely available in nature such as winds and solar energy. It plays a critical role in greening the energy sector as these sources of energy produce little or no pollution to environment. This paper will focus on capability of renewable energy (wind and solar) in generating power for offshore application. Data of wind speeds and solar irradiation that are available around SHELL Sabah Water Platform for every 10 minutes, 24 hours a day, for a period of one year are provided by SHELL Sarawak Sdn. Bhd. The suitable wind turbine and photovoltaic panel that are able to give a high output and higher reliability during operation period are selected by using the tabulated data. The highest power output generated using single wind energy application is equal to 492 kW while for solar energy application is equal to 20 kW. Using the calculated data, the feasibility of renewable energy is then determined based on the platform energy demand. (paper)
-
Wind and solar energy resources on the 'Roof of the World'
Zandler, Harald; Morche, Thomas; Samimi, Cyrus
2015-04-01
The Eastern Pamirs of Tajikistan, often referred to as 'Roof of the World', are an arid high mountain plateau characterized by severe energy poverty that may have great potential for renewable energy resources due to the prevailing natural conditions. The lack of energetic infrastructure makes the region a prime target for decentralized integration of wind and solar power. However, up to date no scientific attempt to assess the regional potential of these resources has been carried out. In this context, it is particularly important to evaluate if wind and solar energy are able to provide enough power to generate thermal energy, as other thermal energy carriers are scarce or unavailable and the existing alternative, local harvest of dwarf shrubs, is unsustainable due to the slow regeneration in this environment. Therefore, this study examines the feasibility of using wind and solar energy as thermal energy sources. Financial frame conditions were set on a maximum amount of five million Euros. This sum provides a realistic scenario as it is based on the current budget of the KfW development bank to finance the modernization of the local hydropower plant in the regions only city, Murghab, with about 1500 households. The basis for resource assessment is data of four climate stations, erected for this purpose in 2012, where wind speed, wind direction, global radiation and temperature are measured at a half hourly interval. These measurements confirm the expectation of a large photovoltaic potential and high panel efficiency with up to 84 percent of extraterrestrial radiation reaching the surface and only 16 hours of temperatures above 25°C were measured in two years at the village stations on average. As these observations are only point measurements, radiation data and the ASTER GDEM was used to train a GIS based solar radiation model to spatially extrapolate incoming radiation. With mean validation errors ranging from 5% in July (minimum) to 15% in December (maximum
-
Energy Primer: Solar, Water, Wind, and Biofuels.
Portola Inst., Inc., Menlo Park, CA.
This is a comprehensive, fairly technical book about renewable forms of energy--solar, water, wind, and biofuels. The biofuels section covers biomass energy, agriculture, aquaculture, alcohol, methane, and wood. The focus is on small-scale systems which can be applied to the needs of the individual, small group, or community. More than one-fourth…
-
Energy Cascade Rate in Compressible Fast and Slow Solar Wind Turbulence
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hadid, L. Z.; Sahraoui, F.; Galtier, S., E-mail: lina.hadid@lpp.polytechnique.fr [LPP, CNRS, Ecole Polytechnique, UPMC Univ Paris 06, Univ. Paris-Sud, Observatoire de Paris, Université Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne Universités, PSL Research University, F-91128 Palaiseau (France)
2017-03-20
Estimation of the energy cascade rate in the inertial range of solar wind turbulence has been done so far mostly within incompressible magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) theory. Here, we go beyond that approximation to include plasma compressibility using a reduced form of a recently derived exact law for compressible, isothermal MHD turbulence. Using in situ data from the THEMIS / ARTEMIS spacecraft in the fast and slow solar wind, we investigate in detail the role of the compressible fluctuations in modifying the energy cascade rate with respect to the prediction of the incompressible MHD model. In particular, we found that the energy cascade rate (1) is amplified particularly in the slow solar wind; (2) exhibits weaker fluctuations in spatial scales, which leads to a broader inertial range than the previous reported ones; (3) has a power-law scaling with the turbulent Mach number; (4) has a lower level of spatial anisotropy. Other features of solar wind turbulence are discussed along with their comparison with previous studies that used incompressible or heuristic (nonexact) compressible MHD models.
-
Energy Cascade Rate in Compressible Fast and Slow Solar Wind Turbulence
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hadid, L. Z.; Sahraoui, F.; Galtier, S.
2017-01-01
Estimation of the energy cascade rate in the inertial range of solar wind turbulence has been done so far mostly within incompressible magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) theory. Here, we go beyond that approximation to include plasma compressibility using a reduced form of a recently derived exact law for compressible, isothermal MHD turbulence. Using in situ data from the THEMIS / ARTEMIS spacecraft in the fast and slow solar wind, we investigate in detail the role of the compressible fluctuations in modifying the energy cascade rate with respect to the prediction of the incompressible MHD model. In particular, we found that the energy cascade rate (1) is amplified particularly in the slow solar wind; (2) exhibits weaker fluctuations in spatial scales, which leads to a broader inertial range than the previous reported ones; (3) has a power-law scaling with the turbulent Mach number; (4) has a lower level of spatial anisotropy. Other features of solar wind turbulence are discussed along with their comparison with previous studies that used incompressible or heuristic (nonexact) compressible MHD models.
-
The 1991 Japan Solar Energy Society. Japan Wind Energy Association Joint Conference
1991-09-01
Thie paper summarizes the lectures presented at the research presentation conference held by the Japan Solar Energy Society and the Japan Wind Energy Association. The contents include a lecture relating to photovoltaic cells intended for efficiency improvement; a lecture relating to a light power generation system including the field test reports, improvements on peripheral devices and output characteristics; a lecture relating to optical chemistry; a lecture relating to heat pumps utilizing solar heat and well water; a lecture relating air conditioning utilizing photovoltaic cells; a lecture relating to heat systems utilizing solar heat directly; a lecture relating to heat collection; a lecture relating to cold heat for cooling using earth tubes; a lecture relating to direct utilization of ground water heat and solar heat; a lecture relating to underground heat storage; a lecture relating to accumulation of cold heat and hot heat; a lecture relating to insolation on the amount of insolation and spectroscopy; a lecture relating to light collection intended of energy saving; a lecture relating to improving materials including light collecting plates and thin films; a lecture relating to development and characteristics of solar cars; and a lecture relating to wind energy.
-
Wind and Solar Energy Role in the Achievement of EU Climate Policy After 2020
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Knezevic, S.
2016-01-01
This paper grades the possible role of solar and wind energy in the generation of electricity after 2020. The development of those energy sources will be defined by the climate policy implemented based on the last year's Paris Climate Agreement, but also by the existing initiatives of the European Commission (2030 climate and energy framework and 2050 low-carbon economy). Additionally, electricity generation from RES is observed through the decrease of dependency on the import of fossil fuels outside of the EU. According to the report of the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the biggest share of RES power plants, after hydro power plants, in EU are wind and solar power plants. Both wind and sun are constantly available resources, but with variable specific power, which makes the maximal generation dependent on the time of day and/or weather (wind, clouds). Future increase of wind and solar energy has to be observed from various perspectives as to properly grade it for the next period, until 2020. Therefore, this paper considers the following, intertwined aspects: Maturity of wind and solar technologies and future trends, Price of electricity generation from wind and solar power plants, with an analysis of price decreasing trends; Possibilities of power energy system and measures for the acceptance of wind and solar power plants; Integrative approach to all forms and transformations of electricity; Market integration of RES - aspirations towards free trade(author).
-
Efficient Scavenging of Solar and Wind Energies in a Smart City.
Wang, Shuhua; Wang, Xue; Wang, Zhong Lin; Yang, Ya
2016-06-28
To realize the sustainable energy supply in a smart city, it is essential to maximize energy scavenging from the city environments for achieving the self-powered functions of some intelligent devices and sensors. Although the solar energy can be well harvested by using existing technologies, the large amounts of wasted wind energy in the city cannot be effectively utilized since conventional wind turbine generators can only be installed in remote areas due to their large volumes and safety issues. Here, we rationally design a hybridized nanogenerator, including a solar cell (SC) and a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), that can individually/simultaneously scavenge solar and wind energies, which can be extensively installed on the roofs of the city buildings. Under the same device area of about 120 mm × 22 mm, the SC can deliver a largest output power of about 8 mW, while the output power of the TENG can be up to 26 mW. Impedance matching between the SC and TENG has been achieved by using a transformer to decrease the impedance of the TENG. The hybridized nanogenerator has a larger output current and a better charging performance than that of the individual SC or TENG. This research presents a feasible approach to maximize solar and wind energies scavenging from the city environments with the aim to realize some self-powered functions in smart city.
-
Wind and solar resource data sets: Wind and solar resource data sets
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Clifton, Andrew [National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden CO USA; Hodge, Bri-Mathias [National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden CO USA; Power Systems Engineering Center, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden CO USA; Draxl, Caroline [National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden CO USA; National Wind Technology Center, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden CO USA; Badger, Jake [Department of Wind Energy, Danish Technical University, Copenhagen Denmark; Habte, Aron [National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden CO USA; Power Systems Engineering Center, National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden CO USA
2017-12-05
The range of resource data sets spans from static cartography showing the mean annual wind speed or solar irradiance across a region to high temporal and high spatial resolution products that provide detailed information at a potential wind or solar energy facility. These data sets are used to support continental-scale, national, or regional renewable energy development; facilitate prospecting by developers; and enable grid integration studies. This review first provides an introduction to the wind and solar resource data sets, then provides an overview of the common methods used for their creation and validation. A brief history of wind and solar resource data sets is then presented, followed by areas for future research.
-
Assessment of solar and wind energy potentials for three free economic and industrial zones of Iran
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mohammadi, Kasra; Mostafaeipour, Ali; Sabzpooshani, Majid
2014-01-01
This paper aims to evaluate the potential of renewable energy sources of solar and wind in three free economic and industrial zones of Chabahar, Kish and Salafchegan in Iran. Feasibility of harnessing solar energy was investigated by using key solar parameters like monthly mean global, beam and diffuse solar radiation as well as clearness index. It was found that all locations had great potentials for utilizing different solar energy systems. Additionally, the monthly, seasonal, semi-yearly and yearly optimum tilt angles of south-facing solar surfaces were determined. For all zones, adjusting the tilt angle twice a year or in other words, the semi-yearly tilt adjustment for two periods of warm (April–September) and cold (October–March) were highly recommended, since it offers almost the same level of annual solar energy gain (SEG) as those of monthly and seasonal adjustments. Weibull Distribution Function (WDF) was performed for analyzing the wind potentials at different heights. It was found that Chabahar was not suitable for wind energy development, but Kish and Salafchegan with yearly wind powers of 111.28 W/m 2 and 114.34 W/m 2 , respectively ranked in class 2 which are considered marginal for wind power development. Three different wind turbine models were proposed for Kish and Salafchegan. - Highlights: • Feasibility of solar and wind energy for three locations of Iran was investigated. • All locations were suitable for solar energy utilization. • The optimum tilt angles of solar surfaces were determined. • Chabahar was unsuitable, but Kish and Salafchegan were marginal for wind purpose
-
Optimal Scheduling of Biogas-Solar-Wind Renewable Portfolio for Multi-Carrier Energy Supplies
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Zhou, Bin; Xu, Da; Li, Canbing
2018-01-01
the mitigation of renewable intermittency and the efficient utilization of batteries, and a multi-carrier generation scheduling scheme is further presented to dynamically optimize dispatch factors in the coupling matrix for energy-efficient con-version and storage, while different energy demands of end......This paper proposes a multi-source multi-product framework for coupled multi-carrier energy supplies with a biogas-solar-wind hybrid renewable system. In this framework, the biogas-solar-wind complementarities are fully exploited based on digesting thermodynamic effects for the synergetic...... interactions of electricity, gas and heating energy flows, and a coupling matrix is formulated for the modeling of production, conversion, storage, and consumption of different energy carriers. The multi-energy complementarity of biogas-solar-wind renewable portfolio can be utilized to facilitate...
-
Thermodynamic analysis of a novel hybrid wind-solar-compressed air energy storage system
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ji, Wei; Zhou, Yuan; Sun, Yu; Zhang, Wu; An, Baolin; Wang, Junjie
2017-01-01
Highlights: • We present a novel hybrid wind-solar-compressed air energy storage system. • Wind and solar power are transformed into stable electric energy and hot water. • The system output electric power is 8053 kWh with an exergy efficiency of 65.4%. • Parametric sensitivity analysis is presented to optimize system performance. - Abstract: Wind and solar power have embraced a strong development in recent years due to the energy crisis in China. However, owing to their nature of fluctuation and intermittency, some power grid management problems can be caused. Therefore a novel hybrid wind-solar-compressed air energy storage (WS-CAES) system was proposed to solve the problems. The WS-CAES system can store unstable wind and solar power for a stable output of electric energy and hot water. Also, combined with organic Rankin cycle (ORC), the cascade utilization of energy with different qualities was achieved in the WS-CAES system. Aiming to obtain the optimum performance, the analysis of energy, exergy and parametric sensitivity were all conducted for this system. Furthermore, exergy destruction ratio of each component in the WS-CAES system was presented. The results show that the electric energy storage efficiency, round trip efficiency and exergy efficiency can reach 87.7%, 61.2% and 65.4%, respectively. Meanwhile, the parameters analysis demonstrates that the increase of ambient temperature has a negative effect on the system performance, while the increase of turbine inlet temperature has a positive effect. However, when the air turbine inlet pressure varies, there is a tradeoff between the system performance and the energy storage density.
-
Ehrke, Elizabeth
Nearly every aspect of human existence relies on energy in some way. Most of this energy is currently derived from fossil fuel resources. Increasing energy demands coupled with environmental and national security concerns have facilitated the move towards renewable energy sources. Biofuels like corn ethanol are one of the ways the U.S. has significantly reduced petroleum consumption. However, the large energy requirement of corn ethanol limits the net benefit of the fuel. Using renewable energy sources to produce ethanol can greatly improve its economic and environmental benefits. The main purpose of this study was to model the useful energy received from a solar thermal array and a wind turbine at various locations to determine the feasibility of applying these technologies at ethanol plants around the country. The model calculates thermal energy received from a solar collector array and electricity generated by a wind turbine utilizing various input data to characterize the equipment. Project cost and energy rate inputs are used to evaluate the profitability of the solar array or wind turbine. The current state of the wind and solar markets were examined to give an accurate representation of the economics of each industry. Eighteen ethanol plant locations were evaluated for the viability of a solar thermal array and/or wind turbine. All ethanol plant locations have long payback periods for solar thermal arrays, but high natural gas prices significantly reduce this timeframe. Government incentives will be necessary for the economic feasibility of solar thermal arrays. Wind turbines can be very profitable for ethanol plants in the Midwest due to large wind resources. The profitability of wind power is sensitive to regional energy prices. However, government incentives for wind power do not significantly change the economic feasibility of a wind turbine. This model can be used by current or future ethanol facilities to investigate or begin the planning process for a
-
Flux and transformation of the solar wind energy in the magnetosheath of the magnetosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pudovkin, M.I.; Semenov, V.S.
1986-01-01
Energy flux, incoming from the solar wind to the Earth magnetosphere is calculated. It is shown that Poynting vector flux, incoming to the reconnection area is generated mainly in the transitional area between the departed shock wave front and magnetopause in the result of the retardation of the solar wind and partial transformation of its kinetic energy into magnetic one. In this case the energy transformation coefficient depends on the interplanetary magnetic field intensity. Solar wind energy gets into the area of magnetic field reconnection at the magnetopause mainly in two forms: electromagnetic and thermal energy. In the course of reconnection process magnetic energy converts into kinetic energy of the accelerated plasma mass movement and subsequently turns (in a high-latitude boundary layer) into electromagnetic energy, incoming directly to magnetosphere tail
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jing Huang
2018-05-01
Full Text Available With ever increasing demand for electricity and the huge potential of renewable energy, an increasing number of renewable-energy sources are being used to generate electricity. However, due to the intermittency of renewable-energy generation, many researchers try to overcome the variable nature of renewable energy. A hybrid renewable-energy system is one possible way to introduce smoothing of the supply. Many hybrid renewable-energy studies focus on system optimization and management. This paper mainly researches the performance prediction accuracy of a hybrid solar and wind system. Through a mixed autoregressive and dynamical system model, we test the predictability of the hybrid system and compare it with individual solar and wind series forecasting. After error analysis, the predictability of the hybrid system shows a better performance than solar or wind for Adelaide global solar radiation and Starfish Hill wind farm data. The prediction errors were reduced by 13% to more than 30% according to various error analyses. This result indicates an advantage of the hybrid solar and wind system compared to solar and wind systems taken individually.
-
Optimization of hybrid system (wind-solar energy) for pumping water
African Journals Online (AJOL)
DR OKE
Keywords: Renewable energy; pumping water; technical optimization; ... The country already start on a mega-project of solar power production (2000 MW) ...... with a wind turbine in a standalone renewable energy system based on hydrogen.
-
Rostoker, G.; Akasofu, S. I.; Baumjohann, W.; Kamide, Y.; Mcpherron, R. L.
1987-01-01
The contributions to the substorm expansive phase of direct energy input from the solar wind and from energy stored in the magnetotail which is released in an unpredictable manner are considered. Two physical processes for the dispensation of the energy input from the solar wind are identified: (1) a driven process in which energy supplied from the solar wind is directly dissipated in the ionosphere; and (2) a loading-unloading process in which energy from the solar wind is first stored in the magnetotail and then is suddenly released to be deposited in the ionosphere. The pattern of substorm development in response to changes in the interplanetary medium has been elucidated for a canonical isolated substorm.
-
Reliability Assessment Considering the Coordination of Wind Power, Solar Energy and Energy Storage
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
WANG Haiying; BAI Xiaomin; XU Jing
2012-01-01
Large-scale integration of wind power and solar photovoltaic (PV) power in an electric grid can result in a high operating risk due to their randomness and intermi- ttency. Energy storage (ES) can be used to coordinate with them to reduce this risk by improving supply continuity. It is therefore important to evaluate the reliability benefits of systems consist of wind power, solar photovoltaic power and energy storage. The objective of this paper is to evaluate how the parameters such as the capacity and characteristics of ES and the configuration of a hybrid generation system (HGS) affect the system adequacy based on the sequential Monte Carlo approach.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ordóñez, G; Osma, G; Vergara, P; Rey, J
2014-01-01
Currently, the trend of micro-grids and small-scale renewable generation systems implementation in urban environments requires to have historical and detailed information about the energy potential resource in site. In Colombia, this information is limited and do not favor the design of these applications; for this reason, must be made detailed studies of the energy potential in their cities. In this paper is presented the wind and solar energy resource assessment for the city of Bucaramanga, based on the monitoring on four strategic points during the years 2010, 2011 and 2012. According to the analysis, is evidenced a significant solar resource throughout the year ascending on average to 1 734 kWh/m 2 , equivalent to 4.8 kWh/m 2 /day. Also, from a wind statistical study based on the Weibull probability distribution and Wind Power Density (WPD) was established the wind potential as Class 1 according to the scale of the Department of Energy of the United States (DOE), since the average speed is near 1.4 m/s. Due this, it is technically unfeasible the using of micro-turbines in the city, even so their potential for natural ventilation of building was analyzed. Finally, is presented a methodology to analyze solar harvesting by sectors in the city, according to the solar motion and shadowing caused by existing structures
-
Application of dimensional analysis to the problem of solar wind-magnetosphere energy coupling
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bargatze, L.F.; McPherron, R.L.; Baker, D.N.; Hones, E.W. Jr.
1984-01-01
The constraints imposed by dimensional analyses are used to find how the solar wind-magnetosphere energy transfer rate depends upon interplanetary parameters. The analyses reported here assume that only magnetohydrodynamic processes are important in controlling the rate of energy transfer. The study utilizes ISEE-3 solar wind observations, the AE index, and U/sub T/ from three 10-day intervals during the IMS: Simple linear regression and histogram techniques are used to find the value of the MHD coupling exponent, α, which is consistent with observations of magnetospheric response. Once α is estimated, the form of the solar wind energy transfer rate is obtained by substitution into an equation of the interplanetary variables whose exponents depend upon α. 7 references, 6 figures, 1 table
-
Quesada-Ruiz, S.; Pozo-Vazquez, D.; Santos-Alamillos, F. J.; Lara-Fanego, V.; Ruiz-Arias, J. A.; Tovar-Pescador, J.
2010-09-01
A drawback common to the solar and wind energy systems is their unpredictable nature and dependence on weather and climate on a wide range of time scales. In addition, the variation of the energy output may not match with the time distribution of the load demand. This can partially be solved by the use of batteries for energy storage in stand-alone systems. The problem caused by the variable nature of the solar and wind resources can be partially overcome by the use of energy systems that uses both renewable resources in a combined manner, that is, hybrid wind-solar systems. Since both resources can show complementary characteristics in certain location, the independent use of solar or wind systems results in considerable over sizing of the batteries system compared to the use of hybrid solar-wind systems. Nevertheless, to the day, there is no single recognized method for properly sizing these hybrid wind-solar systems. In this work, we present a method for sizing wind-solar hybrid systems in southern Spain. The method is based on the analysis of the wind and solar resources on daily scale, particularly, its temporal complementary characteristics. The method aims to minimize the size of the energy storage systems, trying to provide the most reliable supply.
-
Integrating wind and solar power into the energy systems of the 21st century
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Flavin, C [Worldwatch Inst., Washington, DC (United States)
1996-12-31
Although they have been pursued by scientists and entrepreneurs for two decades, solar and wind energy have not yet claimed the large share of the world energy market that proponents hoped they would. Yet the past two years brought a series of developments that suggest the time has come for solar and wind energy to compete directly with fossil fuels. Wind and solar power generators are likely to contribute significant power to the electricity systems of scores of countries within the next decade, with generating costs as low as 4-5 cents per kilowatt-hour. This will require adjustment in the operation of power transmission and distribution systems to accommodate intermittent resources, as well as new time-specific pricing of electricity. The transition to more open, competitive power systems, with liberal access by independent producers, is likely to speed introduction of the new technologies. Altogether, the energy that strikes the earth`s atmosphere in the form of sunlight each year, and the winds that flow from it, represent the equivalent of nearly 1,000 trillion barrels of oil-sufficient to fuel the global economy thousands of times over. By relying on a new generation of efficient, high-tech, and mass produced energy conversion devices such as advanced wind turbines and photovoltaics, the world can rapidly reduce its dependence on oil and coal in the twenty-first century. In the more distant future, solar and wind energy have the potential not only to supply much of the world`s electricity but to displace the direct use of oil and natural gas. Solar and wind energy can be used to split water via electrolysis, producing hydrogen gas that can be substituted for liquid and gaseous fuels. (46 refs.)
-
Integrating wind and solar power into the energy systems of the 21st century
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Flavin, C. [Worldwatch Inst., Washington, DC (United States)
1995-12-31
Although they have been pursued by scientists and entrepreneurs for two decades, solar and wind energy have not yet claimed the large share of the world energy market that proponents hoped they would. Yet the past two years brought a series of developments that suggest the time has come for solar and wind energy to compete directly with fossil fuels. Wind and solar power generators are likely to contribute significant power to the electricity systems of scores of countries within the next decade, with generating costs as low as 4-5 cents per kilowatt-hour. This will require adjustment in the operation of power transmission and distribution systems to accommodate intermittent resources, as well as new time-specific pricing of electricity. The transition to more open, competitive power systems, with liberal access by independent producers, is likely to speed introduction of the new technologies. Altogether, the energy that strikes the earth`s atmosphere in the form of sunlight each year, and the winds that flow from it, represent the equivalent of nearly 1,000 trillion barrels of oil-sufficient to fuel the global economy thousands of times over. By relying on a new generation of efficient, high-tech, and mass produced energy conversion devices such as advanced wind turbines and photovoltaics, the world can rapidly reduce its dependence on oil and coal in the twenty-first century. In the more distant future, solar and wind energy have the potential not only to supply much of the world`s electricity but to displace the direct use of oil and natural gas. Solar and wind energy can be used to split water via electrolysis, producing hydrogen gas that can be substituted for liquid and gaseous fuels. (46 refs.)
-
Solar and wind energy utilization at Sarawak Southern national parks
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Abdul Rahman, N.; Kolot, A.
2006-01-01
The intentions of renewable energy utilization in Sarawak national parks were to reduce the environmental impacts to the protected surrounding and to overcome fuel transportation problem, as most national parks in Sarawak are not viable for the state electricity grid connection. The study was conducted at three national parks in southern Sarawak; viz. Samusan, Tanjung Datu and Pulau Talang-Talang Besar National Park. The study focused on the effectiveness of the system implementation, energy load and associated problems. Both Samusan and Tanjung Datu National systems are hybrids, which consist of solar photovoltaic panels, wind turbine and diesel generators, whereas, Pulau Talang-Talang Besar National Park is a stand alone system of solar photovoltaic panels only. In addition, the inefficient energy usage was observed at Samusan National Park. The study have identified that lack of local expertise, spare parts availability, transportation and inefficient energy management as the major problems associated to the solar and wind energy system in all national parks studied. Albeit the problems mentioned, the study discovered that the systems were acceptably reliable and satisfactorily supply fraction of the energy requirements to the national parks communities
-
Wind and Solar Energy Resource Assessment for Navy Installations in the Midwestern US
Darmenova, K.; Apling, D.; Higgins, G. J.; Carnes, J.; Smith, C.
2012-12-01
A stable supply of energy is critical for sustainable economic development and the ever-increasing demand for energy resources drives the need for alternative weather-driven renewable energy solutions such as solar and wind-generated power. Recognizing the importance of energy as a strategic resource, the Department of the Navy has focused on energy efficient solutions aiming to increase tactical and shore energy security and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing alternative energy solutions will alleviate the Navy installations demands on the National power grid, however transitioning to renewable energy sources is a complex multi-stage process that involves initial investment in resource assessment and feasibility of building solar and wind power systems in Navy's facilities. This study focuses on the wind and solar energy resource assessment for Navy installations in the Midwestern US. We use the dynamically downscaled datasets at 12 km resolution over the Continental US generated with the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model to derive the wind climatology in terms of wind speed, direction, and wind power at 20 m above the surface for 65 Navy facilities. In addition, we derived the transmissivity of the atmosphere, diffuse radiation fraction, cloud cover and seasonal energy potential for a zenith facing surface with unobstructed horizon for each installation location based on the results of a broadband radiative transfer model and our cloud database based on 17-years of GOES data. Our analysis was incorporated in a GIS framework in combination with additional infrastructure data that enabled a synergistic resource assessment based on the combination of climatological and engineering factors.
-
Wind and solar energy curtailment: A review of international experience
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Bird, Lori; Lew, Debra; Milligan, Michael
2016-01-01
Greater penetrations of variable renewable generation on some electric grids have resulted in increased levels of curtailment in recent years. Studies of renewable energy grid integration have found that curtailment levels may grow as the penetration of wind and solar energy generation increases....
-
Solar wind energy transfer through the magnetopause of an open magnetosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lee, L.C.; Roederer, J.G.
1982-01-01
An expression for the total power P/sub T/ transferred from the solar wind to an ''open'' magnetopause with a nonzero normal component of the magnetic field, which is identified as a rotational discontinuity. The total power P/sub T/ consists of (1) the power P/sub EM/ representing the electromagnetic energy transfer and (2) the power P/sub KE/ representing the rate of kinetic energy carried by particles penetrating into the magnetosphere. It is found that P/sub EM/approx. =V/sub SW/ B/sub SW/psi, P/sub KE/approx. =(1/2 M/sub A/-1) P/sub EM/ and P/sub T/approx. =1/2M/sub A/P/sub EM/, where V/sub SW/, B/sub SW/, and M/sub A/ are the velocity, magnetic field, and the Alfven--Mach number in the solar wind, respectively, and Psi is the open magnetic flux in the magnetosphere. The Alfven--Mach number of flow at the magnetopause determines the nature of the local energy transfer; the power per unit area transferred from the solar wind to the magnetosphere consists mainly of kinetic energy. The electromagnetic energy rate P/sub EM/ controls the near-earth magnetospheric activity, whereas the kinetic energy rate P/sub KE/(approx. =3--4 P/sub EM/) should dominate the dynamics of the distant magnetotail
-
Kuznetsova, Tamara; Laptukhov, Alexej; Petrov, Valery
Causes of the geomagnetic activity (GA) in the report are divided into temporal changes of the solar wind parameters and the changes of the geomagnetic moment orientation relative directions of the solar wind electric and magnetic fields. Based on our previous study we concluded that a reconnection based on determining role of mutual orientation of the solar wind electric field and geomagnetic moment taking into account effects of the Earth's orbital and daily motions is the most effective compared with existing mechanisms. At present a reconnection as paradigma that has applications in broad fields of physics needs analysis of experimental facts to be developed. In terms of reconnection it is important not only mutual orientation of vectors describing physics of interaction region but and reconnection rate which depends from rate of energy flux to those regions where the reconnection is permitted. Applied to magnetosphere these regions first of all are dayside magnetopause and polar caps. Influence of rate of the energy flux to the lobe magnetopause (based on calculations of the Poyting electromagnetic flux component controlling the reconnection rate along the solar wind velocity Pv) on planetary GA (Dst, Kp indices) is investigated at different phases of geomagnetic storms. We study also the rate of energy flux to the polar caps during storms (based on calculations of the Poyting flux vector component along the geomagnetic moment Pm) and its influence on magnetic activity in the polar ionosphere: at the auroral zone (AU,AL indices). Results allow to evaluate contributions of high and low latitude sources of electromagnetic energy to the storm development and also to clear mechanism of the electromagnetic energy transmission from the solar wind to the magnetosphere. We evaluate too power of the solar wind electromagnetic energy during well-known large storms and compare result with power of the energy sources of other geophysical processes (atmosphere, ocean
-
Solar, wind and waves: Natural limits to renewable sources of energy within the Earth system
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kleidon, Axel [Max-Planck-Institute for Biogeochemistry, Jena (Germany)
2013-07-01
Renewable sources of energy, such as solar, wind, wave, or hydropower, utilize energy that is continuously generated by natural processes within the Earth system from the planetary forcing. Here we estimate the limits of these natural energy conversions and the extent to which these can be used as renewable energy sources using the laws of thermodynamics. At most, wind power in the order of 1 000 TW (1 TW = 1E12 W) can be derived from the total flux of incoming solar radiation of 175 000 TW, which is consistent with estimates based on observations. Other generation rates that are derived from the kinetic energy of wind are in the order of 10-100 TW. In comparison, the human primary energy demand of about 17 TW constitutes a considerable fraction of these rates. We provide some further analysis on the limits of wind power using a combination of conceptual models, observational data, and numerical simulation models. We find that many current estimates of wind power substantially overestimate the potential of wind power because the effect of kinetic energy extraction on the air flow is neglected. We conclude that the only form of renewable energy that is available in substantial amounts and that is associated with minor climatic impacts is solar power.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mohammed, K G; Ramli, A Q; Amirulddin, U A U
2013-01-01
This paper proposes the design of a new bi-directional DC-AC rotary converter machine to convert a d.c. voltage to three-phase voltage and vice-versa using a two-stage energy conversion machine. The rotary converter consists of two main stages which are combined into single frame. These two stages are constructed from three main electromagnetic components. The first inner electromagnetic component represents the input stage that enables the DC power generated by solar energy from photo-voltaic cells to be transformed by the second and third components electro-magnetically to produce multi-phase voltages at the output stage. At the same time, extra kinetic energy from wind, which is sufficiently available, can be added to existing torque on the second electromagnetic component. Both of these input energies will add up to the final energy generated at the output terminals. Therefore, the machine will be able to convert solar and wind energies to the output terminals simultaneously. If the solar energy is low, the available wind energy will be able to provide energy to the output terminals and at the same time charges the batteries which are connected as backup system. At this moment, the machine behaves as wind turbine. The energy output from the machine benefits from two energy sources which are solar and wind. At night when the solar energy is not available and also the load is low, the wind energy is able to charge the batteries and at the same time provides output electrical power to the remaining the load. Therefore, the proposed system will have high usage of available renewable energy as compared to separated wind or solar systems. MATLAB codes are used to calculate the required dimensions, the magnetic and electrical circuits parameters to design of the new bi-directional rotary converter machine.
-
A Review of Hybrid Solar PV and Wind Energy System
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Rashid Al Badwawi
2015-07-01
Full Text Available Due to the fact that solar and wind power is intermittent and unpredictable in nature, higher penetration of their types in existing power system could cause and create high technical challenges especially to weak grids or stand-alone systems without proper and enough storage capacity. By integrating the two renewable resources into an optimum combination, the impact of the variable nature of solar and wind resources can be partially resolved and the overall system becomes more reliable and economical to run. This paper provides a review of challenges and opportunities / solutions of hybrid solar PV and wind energy integration systems. Voltage and frequency fluctuation, and harmonics are major power quality issues for both grid-connected and stand-alone systems with bigger impact in case of weak grid. This can be resolved to a large extent by having proper design, advanced fast response control facilities, and good optimization of the hybrid systems. The paper gives a review of the main research work reported in the literature with regard to optimal sizing design, power electronics topologies and control. The paper presents a review of the state of the art of both grid-connected and stand-alone hybrid solar and wind systems.
-
Eaton, William W.
Presented is the utilization of solar radiation as an energy resource principally for the production of electricity. Included are discussions of solar thermal conversion, photovoltic conversion, wind energy, and energy from ocean temperature differences. Future solar energy plans, the role of solar energy in plant and fossil fuel production, and…
-
Electrifying Greece with solar and wind energy
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mentis Dimitris
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Ensuring energy security, reducing GHG emissions and boosting the competitiveness of a country’s economy by attracting investments and technical knowhow are of paramount importance considering the targets of “20-20-20” set by the European community. Being the cradle of civilization, Greece appears today as a country caught in a prolonged hard economic and social crisis, the way out of which its citizens are looking forward as well as the entire European Union. Establishment of the leading renewable energy sources like solar and wind in Greece will not only increase the independence of its own electrification but will also provide with a foundation for developing the market of international trade of “green” energy. This paper initially highlights the current status of photovoltaics and wind turbines in Greece. Furthermore, this study evaluates whether a higher penetration of the above mentioned green energy sources would have positive impact in the economy of the country or not and in what extent they could decline the CO2 emissions until 2020, comparing to the corresponding levels in 2010.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tarawneh, Sultan; Rireh, Mohmd; Al-Razzi, Met'eb
2015-01-01
This research aims to study the acceptance of real management of designing electrical generation plants that work using solar energy and wind energy, to explain the benefits for the decision makers of the use of the solar energy and wind energy, and to define the most important obstacles that hinder the use of solar energy in generating electricity in spite of fulfilling the environmental conditions as clean energy and renewing energy contribute to sustainability of natural resources. The descriptive methodology was used by going back to reference material including books, and scientific journals and periodicals as well as scientific researches to identify the real management and design of electrical plant generation using solar energy and wind energy. A questionnaire was distributed among the study sample that was composed of the engineers working in energy field and electrical generation plants, the general institute for environment, Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, and Kuwait Society of Engineers. 203 responses were received from the study sample. Results of the study showed the presence of obstacles and special problems related to the use of solar energy that face the decision makers with regard to the ability for acquiring important advanced technology and the huge financial support and the partnership of the private sector and training of unskilled human resources. And it was declared that there is a huge focus and attention in generation electrical energy from fossil fuel because of its presence and sustainability in investment in this field and the ability to fulfill the needs of the local market from energy.(author)
-
Wind and solar resource data sets
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Clifton, Andrew; Hodge, Bri-Mathias; Draxl, Caroline
2017-01-01
The range of resource data sets spans from static cartography showing the mean annual wind speed or solar irradiance across a region to high temporal and high spatial resolution products that provide detailed information at a potential wind or solar energy facility. These data sets are used...... to support continental-scale, national, or regional renewable energy development; facilitate prospecting by developers; and enable grid integration studies. This review first provides an introduction to the wind and solar resource data sets, then provides an overview of the common methods used...... for their creation and validation. A brief history of wind and solar resource data sets is then presented, followed by areas for future research. For further resources related to this article, please visit the WIREs website....
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cicia, Gianni; Cembalo, Luigi; Del Giudice, Teresa; Palladino, Andrea
2012-01-01
In Italy there has been considerable political debate around the new energy policy, which is specifically designed to contribute to climate change mitigation. While there is renewed interest in nuclear energy generation, there has been heated debate concerning wind farms that have rapidly expanded and are dramatically changing the landscape in many rural areas. Finally, interest has also increased in biomass as an energy source. However, in this case, a significant part of the population is worried about landscape change and primary crop reduction. In this study we report the results from a nation-wide survey (=504 households) in Italy undertaken during summer 2009. A Latent Class Choice Experiment was used to quantify household preferences over different energy sources. Our results show that Italian households can be split into three segments with homogeneous preferences. The first segment (35% of the population) shows strong preference for wind and solar energy and dislikes both biomass and nuclear. The second (33% of the population) shows moderate preference for solar and wind energy and, as with the first segment, dislikes both nuclear and biomass. The third (32% of the population) shows a strong preference for green energy (solar, wind and biomass) and is very much against nuclear energy. The three segments were also characterized in terms of household socio-economic characteristics. - Highlights: ► We quantify Italian household preferences over different energy sources. ► Results come from a nation-wide survey undertaken during summer 2009. ► Energy sources tested: fossil fuel, nuclear, wind, solar and agricultural biomass. ► A latent class choice experiment was used. ► Italians can be split into three segments with different energy source preferences.
-
Effects of large scale integration of wind and solar energy in Japan
Esteban, Miguel; Zhang, Qi; Utama, Agya; Tezuka, Tetsuo; Ishihara, Keiichi
2010-05-01
A number of different energy scenarios exist for the development of renewable energy technologies in a variety of countries. Each of these scenarios produces different composition mixes depending on the assumptions on which they are based and the motivation of the authors. These studies are often based on annual data, which make general assumptions about the maximum and minimum output of a range of renewable technologies that are not considered to produce electricity at a predictable rate. These include solar power (which generally varies with the intensity of sunlight) and wind power (depending on the strength of the wind). To take into account the variability in the production of these technologies, many authors assume that the energy production sector cannot whole rely on these technologies, and that enough conventional production capacity (thermo, nuclear or hydro) must exist to cover the essential part of the electricity production. In the present work, the authors used the historical records of wind and solar radiation to estimate the minimum amount of electricity that could be produced by a given composition of renewable energies in the year 2100. The methodology used starts by inputting the geographical location and power rating of each of the power plants in the system. It assumes that PV installations will be located in roof-tops in cities (hence each of the major cities would act as a solar power plant) and that the location of wind farms closely resembles those of today. Wind farms, however, are assumed to use much greater units than those presently used, with each one having a rated power of 20MW. The method then used the historical meteorological data obtained from the Japan Meteorological Agency to compute the power production at each location sequentially for each of the 8760 hours in the year. The results show how although on adverse climate days in certain parts of the country the electricity generation from renewables is greatly reduced, when the
-
Solar Wind Earth Exchange Project (SWEEP)
2016-10-28
highly charged ions of the solar wind. The main challenge in predicting the resultant photon flux in the X-ray energy bands is due to the...Newton, an X-ray astronomical observatory. We use OMNI solar wind conditions, heavy ion composition data from ACE, the Hodges neutral hydrogen model...of SWEEP was to compare theoretical models of X-ray emission in the terrestrial magnetosphere caused by the Solar Wind Charge Exchange
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Portilla S, L.A.
1995-01-01
The wind energy or eolic energy is a consequence of solar energy, the one which is absorbed by the atmosphere and is transformed into energy of movement of large bulks of air. In this process the atmosphere acts as the filter to the solar radiation and demotes the ultraviolet beams that result fatal to life in the Earth. The ionosphere is the most external cap and this is ionized by means of absorption process of ultraviolet radiation arising to the Sun. The atmosphere also acts as a trap to the infrared radiation, it that results from the continual process of energetic degradation. In this way, the interaction between Earth - Atmospheres, is behaved as a great greenhouse, maintaining the constant temperatures, including in the dark nights. Processes as the natural convection (that occur by the thermodynamic phenomenon), equatorial calmness, trade winds and against trade winds and global distribution of the air currents are described. The other hand, techniques as the transformation of the wind into energy and its parameters also are shown
-
2013-12-23
... Energy Association, First Solar, Inc. v. California Independent System Operator Corporation, Southern...), California Wind Energy Association and First Solar, Inc. (collectively, Complainants) filed a formal complaint against the California Independent System Operator Corporation (CAISO) and Southern California...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gosling, J.T.; Asbridge, J.R.; Bame, S.J.; Feldman, W.C.; Zwickl, R.D.; Paschmann, G.; Sckopke, N.; Hynds, R.J.
1981-01-01
Data from the Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory/Max-Planck-Institut fast plasma experiment on Isee 2 have been combined with data from the European Space Agency/Imperial College/Space Research Laboratory low-energy proton experiment on Isee 3 to obtain for the first time an ion velocity distribution function f(v) extending from solar wind energies (-1 keV) to 1.6 MeV during the postshock phase of an energetic storm particle (ESP) event. This study reveals that f(v) of the ESP population is roughly isotropic in the solar wind frame from solar wind thermal energies out to 1.6 MeV. Emerging smoothly out of the solar wind thermal distribution, the ESP f(v) initially falls with increasing energy as E/sup -2.4/ in the solar wind frame. Above about 40 keV no single power law exponent adequately describes the energy dependence of f(v) in the solar wind frame. Above approx.200 keV in both the spacecraft frame and the solar wind frame, f(v) can be described by an exponential in speed (f(v)proportionale/sup -v/v//sub o/) with v/sub o/ = 1.05 x 10 8 cm s -1 . The ESP event studied (August 27, 1978) was superposed upon a more energetic particle event which was predominantly field-aligned and which was probably of solar origin. Our observations suggest that the ESP population is accelerated directly out of the solar wind thermal population or its quiescent suprathermal tail by a stochastic process associated with the shock wave disturbance. The acceleration mechanism is sufficiently efficient that approx.1% of the solar wind population is accelerated to suprathermal energies. These suprathermal particles have an energy density of approx.290 eV cm -3
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
1997-01-01
An international Advisory Group Meeting on Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emission from the Full Energy Chain of Solar and Wind Power was convened by the IAEA at its Headquarters in Vienna, 21-24 October, 1996. The meeting was attended by 12 experts from 9 countries and two international organizations, and including one consultant to the Agency. The objectives of the workshop were: to define and to analyze the solar and wind power chains in terms of emissions of greenhouse gases from the whole energy chain, i.e., during a plant's operation, and from the construction of the plant to the plant's decommissioning and waste storage; to evaluate existing assessments of full-energy-chain emissions of greenhouse gases from the wind and solar power chains and, where possible, compare these results with such emissions from nuclear power and other energy chains
-
Cost-covering remuneration - wind and solar energy skinned
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Niederhaeusern, A.
2008-01-01
In this article, the details of Switzerland's cost-covering remuneration scheme for electrical energy from renewable resources are discussed. Several experts from the renewable energies area express their opinions on the scheme's tariffs for the remuneration of electrical energy fed into the public mains. Wind energy is quoted as being 'skinned', with a lower tariff than before and solar energy is quoted as being promoted 'with the hand brake still on'. Geothermal energy and power from biomass power stations is quoted as being 'undamaged' by the new remuneration system. In general, the opinion is expressed that small investors and producers have, once more, been put at a disadvantage. The situation in Switzerland is briefly compared with that in Germany, France, Spain and Italy. An overview of the tariffs is presented in tabular form
-
Is nuclear energy power generation more dangerous than power generation by wind and solar energy
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ding, Y
1979-03-01
Since the occurrence of the petroleum crisis, many countries have devoted a great deal of effort to search for substitute energy sources. Aside from nuclear energy, forms of power generation with wind, solar energy, and geothermal energy have all been actually adopted in one place or another. Most recently, a research report was published by the Canadian Bureau of Nuclear Energy Management stating that the use of wind and solar energy to generate electricity is much more dangerous than power generation with nuclear energy. When mining, transportation, machine manufacturing, etc. are included in the process of producing unit power, i.e. kilowatt/year, the data of various risks of death, injury, and diseases are computed in terms of man/day losses by the bureau. They indicate that of the ten forms of power generation, the danger is the least with natural gas, only about a 6 man/day, and nuclear energy is the next least dangerous, about 10 man/day. The danger of using temperature differential of sea water to generate electricity is about 25 man/day, and the most dangerous form of power generation is coal, amounting to three thousand man/day.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
1998-12-31
An international Advisory Group Meeting on Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emission from the Full Energy Chain of Solar and Wind Power was convened by the IAEA at its Headquarters in Vienna, 21-24 October, 1996. The meeting was attended by 12 experts from 9 countries and two international organizations, and including one consultant to the Agency. The objectives of the workshop were: to define and to analyze the solar and wind power chains in terms of emissions of greenhouse gases from the whole energy chain, i.e., during a plant`s operation, and from the construction of the plant to the plant`s decommissioning and waste storage; to evaluate existing assessments of full-energy-chain emissions of greenhouse gases from the wind and solar power chains and, where possible, compare these results with such emissions from nuclear power and other energy chains. Refs, figs, tabs.
-
Solar Illumination Control of the Polar Wind
Maes, L.; Maggiolo, R.; De Keyser, J.; André, M.; Eriksson, A. I.; Haaland, S.; Li, K.; Poedts, S.
2017-11-01
Polar wind outflow is an important process through which the ionosphere supplies plasma to the magnetosphere. The main source of energy driving the polar wind is solar illumination of the ionosphere. As a result, many studies have found a relation between polar wind flux densities and solar EUV intensity, but less is known about their relation to the solar zenith angle at the ionospheric origin, certainly at higher altitudes. The low energy of the outflowing particles and spacecraft charging means it is very difficult to measure the polar wind at high altitudes. We take advantage of an alternative method that allows estimations of the polar wind flux densities far in the lobes. We analyze measurements made by the Cluster spacecraft at altitudes from 4 up to 20 RE. We observe a strong dependence on the solar zenith angle in the ion flux density and see that both the ion velocity and density exhibit a solar zenith angle dependence as well. We also find a seasonal variation of the flux density.
-
Turbulent Transport in a Three-dimensional Solar Wind
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Shiota, D. [Institute for Space-Earth Environmental Research, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Aichi 464-8601 (Japan); Zank, G. P.; Adhikari, L.; Hunana, P. [Center for Space Plasma and Aeronomic Research (CSPAR), Department of Space Science, University of Alabama in Huntsville, Huntsville, AL 35805 (United States); Telloni, D. [INAF—Astrophysical Observatory of Torino, Via Osservatorio 20, I-10025 Pino Torinese (Italy); Bruno, R., E-mail: shiota@isee.nagoya-u.ac.jp [INAF-IAPS Istituto di Astrofisica e Planetologia Spaziali, Via del Fosso del Cavaliere 100, I-00133 Roma (Italy)
2017-03-01
Turbulence in the solar wind can play essential roles in the heating of coronal and solar wind plasma and the acceleration of the solar wind and energetic particles. Turbulence sources are not well understood and thought to be partly enhanced by interaction with the large-scale inhomogeneity of the solar wind and the interplanetary magnetic field and/or transported from the solar corona. To investigate the interaction with background inhomogeneity and the turbulence sources, we have developed a new 3D MHD model that includes the transport and dissipation of turbulence using the theoretical model of Zank et al. We solve for the temporal and spatial evolution of three moments or variables, the energy in the forward and backward fluctuating modes and the residual energy and their three corresponding correlation lengths. The transport model is coupled to our 3D model of the inhomogeneous solar wind. We present results of the coupled solar wind-turbulence model assuming a simple tilted dipole magnetic configuration that mimics solar minimum conditions, together with several comparative intermediate cases. By considering eight possible solar wind and turbulence source configurations, we show that the large-scale solar wind and IMF inhomogeneity and the strength of the turbulence sources significantly affect the distribution of turbulence in the heliosphere within 6 au. We compare the predicted turbulence distribution results from a complete solar minimum model with in situ measurements made by the Helios and Ulysses spacecraft, finding that the synthetic profiles of the turbulence intensities show reasonable agreement with observations.
-
Effect of Alfvenic fluctuations on the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chien, T.H.
1974-01-01
The major source of microscale fluctuations in the interplanetary medium due to the outwardly propagating Alfven waves is considered. The effect of the Alfven waves on the supersonic expansion of the solar wind is studied under the assumption that the motion of the interplanetary medium can be resolved physically into a comparatively smooth and slowly varying mesoscale flow and field with very irregular disordered incompressible microscale Alfvenic fluctuations superposed on it. The important features of the solar wind such as heat conduction flux, spiral interplanetary magnetic field, and proton thermal anisotropy are included in the theory. For inviscid, steady state, spherically symmetrical model of the solar wind, the two-fluid formulation of the background mesoscale MHD equations is obtained. The results show that during the expansion process, fluctuation energy is converted into the kinetic energy of the solar wind. Due to the presence of the Alfvenic fluctuations, the velocity of the solar wind is about 5 percent higher than that without considering the fluctuations. (U.S.)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bekele, Getachew
2009-12-15
The tendency to use renewable energy resources has grown continuously over the past few decades, be it due to fear over warnings of global warming or because of the depletion and short life of fossil fuels or even as a result of the interest which has developed among researchers doing scientific research into it. This work can be considered as joining any of these groups with an objective of giving electric light to the poor population living in one of the poorest nations in the world. The aim of the work is to investigate supplying electric energy from solar-wind hybrid resources to remotely located communities detached from the main grid line in Ethiopia. The communities in mind are one of two types; the first is the majority of the poor population residing in the country-side; and the other is people relocated by the Government from the over-used and dry regions to relatively productive and fertile ones in line with the long-term poverty reduction plan. The work was begun by investigating wind energy and solar energy potentials at four geographically different locations in Ethiopia by compiling data from different sources and analyzing it using a software tool. The locations are Addis Ababa (09:02N, 038:42E), Mekele (13:33N,39:30E), Nazret (08:32N, 039:22E), and Debrezeit (8:44N, 39:02E). The results related to wind energy potential are given in terms of the monthly Average wind speed, the wind speed probability density function (PDF), the wind speed cumulative density function (CDF), the wind speed duration curve (DC), and power density plots for all four selected sites. According to the results obtained through the analysis, the wind energy potential, even if it is not exceptional, is irrefutably high enough to be exploited for generating electric energy. The solar energy potential, based on sunshine duration data collected over a period of 7 - 11 years and radiation data obtained from different sources, has been calculated using regression coefficients
-
The problem of intermittency of renewable energies: solar and wind energy
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Livet, Frederic
2011-01-01
As solar and wind energies are to be intensively developed but are intermittent, more or less regular and unpredictable, the author first discusses methods which are presently used to manage this intermittency in various European countries. He also discusses the various methods which are proposed to compensate this intermittency: hydraulic storage, hydrogen-based storage, batteries, and large scale interconnections. He gives and comments cost assessments of the various proposed methods and of capacities. He shows that various measures which are discussed at the European level to promote renewable energies and to promote electricity exchanges will in fact result in a three times higher price of electricity for individuals
-
Potential for Development of Solar and Wind Resource in Bhutan
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Gilman, P.; Cowlin, S.; Heimiller, D.
2009-09-01
With support from the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) produced maps and data of the wind and solar resources in Bhutan. The solar resource data show that Bhutan has an adequate resource for flat-plate collectors, with annual average values of global horizontal solar radiation ranging from 4.0 to 5.5 kWh/m2-day (4.0 to 5.5 peak sun hours per day). The information provided in this report may be of use to energy planners in Bhutan involved in developing energy policy or planning wind and solar projects, and to energy analysts around the world interested in gaining an understanding of Bhutan's wind and solar energy potential.
-
Analysis of the balancing of the wind and solar energy resources in Andalusia (Southern Spain)
Santos-Alamillos, F. J.; Pozo-Vazquez, D.; Lara-Fanego, V.; Ruiz-Arias, J. A.; Hernandez-Alvaro, J.; Tova-Pescador, J.
2010-09-01
A higher penetration of the renewable energy in the electric system in the future will be conditioned to a reduction of the uncertainty of the yield. A way to obtain this goal is to analyze the balancing between the productions of different sources of renewable energy, trying to combine these productions. In this work we analyze, from a meteorological point of view, the balancing between wind and solar energy resources in Andalusia (southern Iberian Peninsula). To this end, wind speed and global radiation data corresponding to an one year integration of the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) model were analyzed. Two method of analysis were used: a point correlation analysis and a Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA). Results from these analyses allow obtaining, eventually, areas of local and distributed balancing between the wind and solar energy resources. The analysis was carried out separately for the different seasons of the year. Results showed, overall, a considerable balancing effect between the wind and solar resources in the mountain areas of the interior of the region, along the coast of the central part of the region and, specially, in the coastal area near the Gibraltar strait. Nevertheless, considerable differences were found between the seasons of the year, which may lead to compensating effects. Autumn proved to be the season with the most significant results.
-
Solar and wind exergy potentials for Mars
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Delgado-Bonal, Alfonso; Martín-Torres, F. Javier; Vázquez-Martín, Sandra; Zorzano, María-Paz
2016-01-01
The energy requirements of the planetary exploration spacecrafts constrain the lifetime of the missions, their mobility and capabilities, and the number of instruments onboard. They are limiting factors in planetary exploration. Several missions to the surface of Mars have proven the feasibility and success of solar panels as energy source. The analysis of the exergy efficiency of the solar radiation has been carried out successfully on Earth, however, to date, there is not an extensive research regarding the thermodynamic exergy efficiency of in-situ renewable energy sources on Mars. In this paper, we analyse the obtainable energy (exergy) from solar radiation under Martian conditions. For this analysis we have used the surface environmental variables on Mars measured in-situ by the Rover Environmental Monitoring Station onboard the Curiosity rover and from satellite by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer instrument onboard the Mars Global Surveyor satellite mission. We evaluate the exergy efficiency from solar radiation on a global spatial scale using orbital data for a Martian year; and in a one single location in Mars (the Gale crater) but with an appreciable temporal resolution (1 h). Also, we analyse the wind energy as an alternative source of energy for Mars exploration and compare the results with those obtained on Earth. We study the viability of solar and wind energy station for the future exploration of Mars, showing that a small square solar cell of 0.30 m length could maintain a meteorological station on Mars. We conclude that the low density of the atmosphere of Mars is responsible of the low thermal exergy efficiency of solar panels. It also makes the use of wind energy uneffective. Finally, we provide insights for the development of new solar cells on Mars. - Highlights: • We analyse the exergy of solar radiation under Martian environment • Real data from in-situ instruments is used to determine the maximum efficiency of radiation • Wind
-
Agua Caliente Wind/Solar Project at Whitewater Ranch
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hooks, Todd [Agua Caliente Band of Cahuilla Indians, Palm Springs, CA (United States); Stewart, Royce [Red Mountain Energy Partners, Sante Fe, NM (United States)
2014-12-16
Agua Caliente Band of Cahuilla Indians (ACBCI) was awarded a grant by the Department of Energy (DOE) to study the feasibility of a wind and/or solar renewable energy project at the Whitewater Ranch (WWR) property of ACBCI. Red Mountain Energy Partners (RMEP) was engaged to conduct the study. The ACBCI tribal lands in the Coachella Valley have very rich renewable energy resources. The tribe has undertaken several studies to more fully understand the options available to them if they were to move forward with one or more renewable energy projects. With respect to the resources, the WWR property clearly has excellent wind and solar resources. The DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has continued to upgrade and refine their library of resource maps. The newer, more precise maps quantify the resources as among the best in the world. The wind and solar technology available for deployment is also being improved. Both are reducing their costs to the point of being at or below the costs of fossil fuels. Technologies for energy storage and microgrids are also improving quickly and present additional ways to increase the wind and/or solar energy retained for later use with the network management flexibility to provide power to the appropriate locations when needed. As a result, renewable resources continue to gain more market share. The transitioning to renewables as the major resources for power will take some time as the conversion is complex and can have negative impacts if not managed well. While the economics for wind and solar systems continue to improve, the robustness of the WWR site was validated by the repeated queries of developers to place wind and/or solar there. The robust resources and improving technologies portends toward WWR land as a renewable energy site. The business case, however, is not so clear, especially when the potential investment portfolio for ACBCI has several very beneficial and profitable alternatives.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Danielo, Olivier
2014-01-01
This article discusses the calculation of a new index created by Kepler-Chevreux experts: the energy return on invested capital, EROCI. This index reveals the benefit of solar-energy and wind-energy based electro-mobility compared to the oil-based thermo-mobility. This index only takes economic issues into account, but not the benefits in terms of public health, environment, climate or geopolitics. It also outlines that whenever oil prices increase or decrease, the oil sector has reached a dead end, and that photovoltaic and wind energy present a growing interest among not only ecologists but also finance experts
-
Gosling, J. T.; Asbridge, J. R.; Bame, S. J.; Feldman, W. C.; Zwickl, R. D.; Paschmann, G.; Sckopke, N.; Hynds, R. J.
1981-01-01
An ion velocity distribution function of the postshock phase of an energetic storm particle (ESP) event is obtained from data from the ISEE 2 and ISEE 3 experiments. The distribution function is roughly isotropic in the solar wind frame from solar wind thermal energies to 1.6 MeV. The ESP event studied (8/27/78) is superposed upon a more energetic particle event which was predominantly field-aligned and which was probably of solar origin. The observations suggest that the ESP population is accelerated directly out of the solar wind thermal population or its quiescent suprathermal tail by a stochastic process associated with shock wave disturbance. The acceleration mechanism is sufficiently efficient so that approximately 1% of the solar wind population is accelerated to suprathermal energies. These suprathermal particles have an energy density of approximately 290 eV cubic centimeters.
-
Alterman, B. L.; Klein, K. G.; Verscharen, D.; Stevens, M. L.; Kasper, J. C.
2017-12-01
Long duration, in situ data sets enable large-scale statistical analysis of free-energy-driven instabilities in the solar wind. The plasma beta and temperature anisotropy plane provides a well-defined parameter space in which a single-fluid plasma's stability can be represented. Because this reduced parameter space can only represent instability thresholds due to the free energy of one ion species - typically the bulk protons - the true impact of instabilities on the solar wind is under estimated. Nyquist's instability criterion allows us to systematically account for other sources of free energy including beams, drifts, and additional temperature anisotropies. Utilizing over 20 years of Wind Faraday cup and magnetic field observations, we have resolved the bulk parameters for three ion populations: the bulk protons, beam protons, and alpha particles. Applying Nyquist's criterion, we calculate the number of linearly growing modes supported by each spectrum and provide a more nuanced consideration of solar wind stability. Using collisional age measurements, we predict the stability of the solar wind close to the sun. Accounting for the free-energy from the three most common ion populations in the solar wind, our approach provides a more complete characterization of solar wind stability.
-
Distributed Wind Cost Reduction: Learning from Solar
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tegen, Suzanne
2016-02-23
The distributed wind energy industry can learn several lessons from the solar industry regarding reducing soft costs. Suzanne Tegen presented this overview at the 2016 Distributed Wind Energy Association Business Conference in Washington, D.C., on February 23, 2016.
-
Solar Wind Associated with Near Equatorial Coronal Hole M ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
2015-05-25
May 25, 2015 ... coronal hole and solar wind. For both the wavelength bands, we also com- pute coronal hole radiative energy near the earth and it is found to be of similar order as that of solar wind energy. However, for the wavelength. 193 Å, owing to almost similar magnitudes of energy emitted by coronal hole and ...
-
A Geospatial Database for Wind and Solar Energy Applications: The Kingdom of Bahrain Study Case
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Al-Joburi Khalil
2017-01-01
Full Text Available This research is aimed at designing, implementing, and testing a geospatial database for wind and solar energy applications in the Kingdom of Bahrain. All decision making needed to determine economic feasibility and establish site location for wind turbines or solar panels depends primarily on geospatial feature theme information and non-spatial (attribute data for wind, solar, rainfall, temperature and weather characteristics of a particular region. Spatial data includes, but is not limited to, digital elevation, slopes, land use, zonings, parks, population density, road utility maps, and other related information. Digital elevations for over 450,000 spot at 50 m spatial horizontal resolution plus field surveying and GPS (at selected locations was obtained from the Surveying and Land Registration Bureau (SLRB. Road, utilities, and population density are obtained from the Central Information Organization (CIO. Land use zoning, recreational parks, and other data are obtained from the Ministry of Municipalities and Agricultural Affairs. Wind, solar, humidity, rainfall, and temperature data are obtained from the Ministry of Transportation, Civil Aviation Section. LandSat Satellite and others images are obtained from NASA and online sources respectively. The collected geospatial data was geo-referenced to Ain el-Abd UTM Zone 39 North. 3D Digital Elevation Model (DEM-50 m spatial resolutions was created using SLRB spot elevations. Slope and aspect maps were generate based on the DEM. Supervised image classification to identify open spaces was performed utilizing satellite images. Other geospatial data was converted to raster format with the same cell resolution. Non-spatial data are entered as an attribute to spatial features. To eliminate ambiguous solution, multi-criteria GIS model is developed based on, vector (discrete point, line, and polygon representations as well as raster model (continuous representation. The model was tested at the Al
-
A Geospatial Database for Wind and Solar Energy Applications: The Kingdom of Bahrain Study Case
Al-Joburi, Khalil; Dahman, Nidal
2017-11-01
This research is aimed at designing, implementing, and testing a geospatial database for wind and solar energy applications in the Kingdom of Bahrain. All decision making needed to determine economic feasibility and establish site location for wind turbines or solar panels depends primarily on geospatial feature theme information and non-spatial (attribute) data for wind, solar, rainfall, temperature and weather characteristics of a particular region. Spatial data includes, but is not limited to, digital elevation, slopes, land use, zonings, parks, population density, road utility maps, and other related information. Digital elevations for over 450,000 spot at 50 m spatial horizontal resolution plus field surveying and GPS (at selected locations) was obtained from the Surveying and Land Registration Bureau (SLRB). Road, utilities, and population density are obtained from the Central Information Organization (CIO). Land use zoning, recreational parks, and other data are obtained from the Ministry of Municipalities and Agricultural Affairs. Wind, solar, humidity, rainfall, and temperature data are obtained from the Ministry of Transportation, Civil Aviation Section. LandSat Satellite and others images are obtained from NASA and online sources respectively. The collected geospatial data was geo-referenced to Ain el-Abd UTM Zone 39 North. 3D Digital Elevation Model (DEM)-50 m spatial resolutions was created using SLRB spot elevations. Slope and aspect maps were generate based on the DEM. Supervised image classification to identify open spaces was performed utilizing satellite images. Other geospatial data was converted to raster format with the same cell resolution. Non-spatial data are entered as an attribute to spatial features. To eliminate ambiguous solution, multi-criteria GIS model is developed based on, vector (discrete point, line, and polygon representations) as well as raster model (continuous representation). The model was tested at the Al-Areen proposed
-
Bibliography of Literature for Avian Issues in Solar and Wind Energy and Other Activities
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Walston, Leroy J. [Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States); White, Ellen M. [Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States); Meyers, Stephanie A. [Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States); Turchi, Craig [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States). National Center for Photovoltaics; Sinclair, Karin [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States). National Center for Photovoltaics
2015-04-01
Utility-scale solar energy has been a rapidly expanding energy sector in the United States in recent years and is expected to continue to grow. In 2014, concerns were raised over the risk of avian fatalities associated with utility-scale solar plants. With funding from the U.S. Department of Energy SunShot Program, Argonne National Laboratory and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory studied the issue and released A Review of Avian Monitoring and Mitigation Information at Existing Utility-Scale Solar Facilities (ANL/EVS-15/2, March 2015). A comprehensive literature review included peer-reviewed journal articles on avian fatalities from solar energy facilities and other sources (e.g., wind energy, building collisions, etc.), project-specific technical reports on avian monitoring and fatality at solar facilities, information on mitigation measures and best management practices, and literature pertaining to avian behavioral patterns and habitat use. The source citations are listed in this bibliography; they are current through December 2014.
-
The Character of the Solar Wind, Surface Interactions, and Water
Farrell, William M.
2011-01-01
We discuss the key characteristics of the proton-rich solar wind and describe how it may interact with the lunar surface. We suggest that solar wind can be both a source and loss of water/OH related volatiles, and review models showing both possibilities. Energy from the Sun in the form of radiation and solar wind plasma are in constant interaction with the lunar surface. As such, there is a solar-lunar energy connection, where solar energy and matter are continually bombarding the lunar surface, acting at the largest scale to erode the surface at 0.2 Angstroms per year via ion sputtering [1]. Figure 1 illustrates this dynamically Sun-Moon system.
-
Control of particle precipitation by energy transfer from solar wind
Bremer, J.; Gernandt, H.
1985-12-01
The energy transfer function (epsilon), introduced by Perreault and Akasofu (1978), appears to be well suited for the description of the long-term control of the particle precipitation by interplanetary parameters. An investigation was conducted with the objective to test this control in more detail. This investigation included the calculation of hourly epsilon values on the basis of satellite-measured solar wind and IMF (interplanetary magnetic field) data. The results were compared with corresponding geomagnetic and ionospheric data. The ionospheric data had been obtained by three GDR (German Democratic Republic) teams during the 21st, 22nd, and 23rd Soviet Antarctic Expeditions in the time period from 1976 to 1979. It was found that, in high latitudes, the properties of the solar wind exercise a pronounced degree of control on the precipitation of energetic particles into the atmosphere, taking into account a time delay of about one hour due to the occurrence of magnetospheric storage processes.
-
Smoothing out the volatility of South Africa’s wind and solar energy resources
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Mushwana, Crescent
2015-10-01
Full Text Available In the past, renewables were mainly driven by the US, Europe and China, but South Africa is slowly picking up. This presentation discusses South Africa's wind and solar resources as alternative energy resources....
-
Renewable Energy Systems: Development and Perspectives of a Hybrid Solar-Wind System
C. Shashidhar; K. Bhanupriya; P. Alluvada; Bandana; J. B. V. Subrahmanyam
2012-01-01
Considering the intermittent natural energy resources and the seasonal un-balance, a phtovoltaic-wind hybrid electrical power supply system was developed to accommodate remote locations where a conventional grid connection is inconvenient or expensive. However, the hybrid system can also be applied with grid connection and owners are allowed to sell excessive power back to the electric utility. The proposed set-up consists of a photo-voltaic solar-cell array, a mast mounted wind generator, le...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Van De Vate, J.F.
1997-01-01
Fair comparison of the climate impacts from different energy sources can be made only by accounting for the emissions of all relevant greenhouse gases (GHGs) from the full energy chain (FENCH) of the energy sources. The scanty FENCH-GHG literature is reviewed. The literature data on FENCH material and energy use for renewable, solar and wind power technologies are discussed. Some calculations of FENCH-GHG emission factors are presented using basic literature data on the major energy and materials fluxes associated with each link of the FENCH. GHGs considered are CO 2 , CH 4 , N 2 O, and CF 4 . The FENCH CO 2 -equivalent emission factors of wind and solar power systems are in the range of 10-50 and 100-400 g CO 2 /kWh, resp. This is low compared to those of fossil fuels: 500-1200 g CO 2 /kWh. Compared to the international-consensus emission factors of nuclear and hydropower (5-20 g CO 2 /kWh), those of modern wind power and solar-thermal power are somewhat higher: 10-50 and 20-200 g CO 2 /kWh, resp. Solar PV has a ca. 10 times higher FENCH-GHG emission factor; however, advanced solar PV systems are expected to have 5-10 times lower emission factors. Important inconsistencies exist between literature data on FENCH-GHG emission factors which require explanation. Land-use associated (negative CO 2 sink) contributions due to low photosynthesis under solar systems have been estimated, amounting to ca. 20 and 11 g CO 2 /kWh for solar PV and solar thermal, resp. No information is available about contributions associated with backup supply or storage systems. (author)
-
NEMO 2 - Be aware: Wind and solar are coming
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lund, P. [Helsinki Univ. of Technology, Otaniemi (Finland)
1996-12-31
Finnish research and development is well placed with respect to new renewable energy technologies in that there exists considerable expertise in specialized areas. For example, over 20 % of all power transmission equipment and generators used in wind energy systems world-wide are manufactured in Finland, while advanced instruments for monitoring wind speed are also highly regarded internationally. Moreover, unique wind technology for complex windy and freezing conditions have been developed. Finland has a 10 % share in the European photovoltaic market, and has competitive advantages in photovoltaic systems and applications, thin film solar cells, and automated electronic controlling systems. A unique solar energy storage system based on hydrogen technology demonstrates skills on overcoming the summer-winter syndrome of large-scale solar energy utilization. The annual turnover of the Finnish industries on solar and wind energy has increased from 5 million ECU in 1988 to almost 50 million ECU in 1996. The national R and D and D from 1988 onwards has played an important role in this context. Most of the research and development into new and renewable energy technologies in Finland has been carried out through the Advanced New Energy Systems and Technologies Research Programme (NEMO2) of Tekes
-
Energy coupling function and solar wind-magnetosphere dynamo
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kan, J.R.; Lee, L.C.
1979-01-01
The power delivered by the solar wind dynamo to the open magnetosphere is calculated based on the concept of field line reconnection, independent of the MHD steady reconnection theories. By recognizing a previously overlooked geometrical relationship between the reconnection electric field and the magnetic field, the calculated power is shown to be approximately proportional to the Akasofu-Perreault energy coupling function for the magnetospheric substorm. In addition to the polar cap potential, field line reconnection also gives rise to parallel electric fields on open field lines in the high-latitude cusp and the polar cap reions
-
Assessing temporal complementarity of solar, wind and hydrokinetic energy
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jurasz Jakub
2016-01-01
Full Text Available Renewable energy sources (RES exhibit various characteristics when it comes to their availability in time and space domain. Some are characterised by significant variability and limited predictability. This makes their integration to the power grid a complicated task. Temporal and spatial complementarity of RES is perceived as one of the possible ways to facilitate the process of integration. This paper investigates the concept of temporal complementarity of solar wind and hydrokinetic energy in case of two sites in Poland. Obtained results indicate existence of some beneficial complementarity on inter-annual and annual time scale. Combination of those three RES in one hybrid system makes power source more reliable.
-
Alfvénic fluctuations in "newborn"' polar solar wind
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. Bavassano
2005-06-01
Full Text Available The 3-D structure of the solar wind is strongly dependent upon the Sun's activity cycle. At low solar activity a bimodal structure is dominant, with a fast and uniform flow at the high latitudes, and slow and variable flows at low latitudes. Around solar maximum, in sharp contrast, variable flows are observed at all latitudes. This last kind of pattern, however, is a relatively short-lived feature, and quite soon after solar maximum the polar wind tends to regain its role. The plasma parameter distributions for these newborn polar flows appear very similar to those typically observed in polar wind at low solar activity. The point addressed here is about polar wind fluctuations. As is well known, the low-solar-activity polar wind is characterized by a strong flow of Alfvénic fluctuations. Does this hold for the new polar flows too? An answer to this question is given here through a comparative statistical analysis on parameters such as total energy, cross helicity, and residual energy, that are of general use to describe the Alfvénic character of fluctuations. Our results indicate that the main features of the Alfvénic fluctuations observed in low-solar-activity polar wind have been quickly recovered in the new polar flows developed shortly after solar maximum. Keywords. Interplanetary physics (MHD waves and turbulence; Sources of the solar wind – Space plasma physics (Turbulence
-
A novel off-grid hybrid power system comprised of solar photovoltaic, wind, and hydro energy sources
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bhandari, Binayak; Lee, Kyung-Tae; Lee, Caroline Sunyong; Song, Chul-Ki; Maskey, Ramesh K.; Ahn, Sung-Hoon
2014-01-01
Highlights: • We propose two hybridization methods for small off-grid power systems consisting solar (PV), wind, and micro-hydro sources. • One of the methods was implemented in a mini-grid connecting Thingan and Kolkhop villages in Makawanpur District, Nepal. • The results can be applied to help achieve Millennium Development Goal 7: Ensuring environmental sustainability. • This is the first implementation anywhere comprising of three renewable energy power, in a single off-grid power system. • This research may be applied as a practical guide for implementing similar systems in various locations. - Abstract: Several factors must be considered before adopting a full-phase power generation system based on renewable energy sources. Long-term necessary data (for one year if possible) should be collected before making any decisions concerning implementation of such a systems. To accurately assess the potential of available resources, we measured solar irradiation, wind speed, and ambient temperature at two high-altitude locations in Nepal: the Lama Hotel in Rasuwa District and Thingan in Makawanpur District. Here, we propose two practical, economical hybridization methods for small off-grid systems consisting entirely of renewable energy sources—specifically solar photovoltaic (PV), wind, and micro-hydro sources. One of the methods was tested experimentally, and the results can be applied to help achieve Millennium Development Goal 7: Ensuring environmental sustainability. Hydro, wind, and solar photovoltaic energy are the top renewable energy sources in terms of globally installed capacity. However, no reports have been published about off-grid hybrid systems comprised of all three sources, making this implementation the first of its kind anywhere. This research may be applied as a practical guide for implementing similar systems in various locations. Of the four off-grid PV systems installed by the authors for village electrification in Nepal, one was
-
Steinberg, J. L.; Caroubalos, C.
1976-01-01
The mechanism causing solar radio bursts (1 and 111) is examined. It is proposed that a nonthermal energy source is responsible for the bursts; nonthermal energy is converted into electromagnetic energy. The advantages are examined for an out-of-the-ecliptic solar probe mission, which is proposed as a means of stereoscopically viewing solar radio bursts, solar magnetic fields, coronal structure, and the solar wind.
-
Du, A. M.; Tsurutani, B. T.; Sun, W.
2012-04-01
Sudden energy release (ER) events in the midnight sector at auroral zone latitudes during intense (B > 10 nT), long-duration (T > 3 hr), northward (Bz > 0 nT = N) IMF magnetic clouds (MCs) during solar cycle 23 (SC23) have been examined in detail. The MCs with northward-then-southward (NS) IMFs were analyzed separately from MCs with southward-then-northward (SN) configurations. It is found that there is a lack of substorms during the N field intervals of NS clouds. In sharp contrast, ER events do occur during the N field portions of SN MCs. From the above two results it is reasonable to conclude that the latter ER events represent residual energy remaining from the preceding S portions of the SN MCs. We derive a new solar wind-magnetosphere coupling function during northward IMFs: ENIMF = α N-1/12V 7/3B1/2 + β V |Dstmin|. The first term on the right-hand side of the equation represents the energy input via "viscous interaction", and the second term indicates the residual energy stored in the magnetotail. It is empirically found that the magnetosphere/magnetotail can store energy for a maximum of ~ 4 hrs before it has dissipated away. This concept is defining one for ER/substorm energy storage. Our scenario indicates that the rate of solar wind energy injection into the magnetosphere/magnetotail determines the form of energy release into the magnetosphere/ionosphere. This may be more important than the dissipation mechanism itself (in understanding the form of the release). The concept of short-term energy storage is applied for the solar case. It is argued that it may be necessary to identify the rate of energy input into solar magnetic loop systems to be able to predict the occurrence of solar flares.
-
The Potential of hybrid solar-wind electricity generation in Ghana
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tibiru, Ayirewura Vitus
2013-07-01
In this work the potential of harnessing electricity from solar and wind sources in Ghana is evaluated both quantitatively and qualitatively. In this regard solar, wind and other relevant data were collected (over a period of one year) from various parts of Ghana. Detailed assessment of the capacity or potential of power production from hybrid solar-wind sources is done with the use of empirical mathematical formulae and the PRO VITUS model incorporated in the 'ENERGY X' software. The various characteristics of wind, solar and available energy resources for the five locations over a one year period have been studied too. The annual mean wind speed at a height of 10 m above ground level for five locations namely Accra, Kumasi, Takoradi, Sunyani and Tamale are 2.38 ms"-"1 ± 0.05, 2.39 ms"-"1 ± 0.05, 2.38 ms"-"1 ± 0.06, 2.18 ms"-"1 ± 0.05 and 2.47 ± ms"-"1 respectively and their corresponding annual mean solar radiations are 228.71 Wm"-"2 ± 9.81, 187.69 Wm"-"2 ± 9.60, 236.58 Wm"-"2 ± 10.39, 200.99 Wm"-"2 ± 9.88 and 231.63 Wm"-"2 . Thus, the five sites hold potential for hybrid solar-wind energy exploitation. (au)
-
Verification of high-speed solar wind stream forecasts using operational solar wind models
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Reiss, Martin A.; Temmer, Manuela; Veronig, Astrid M.
2016-01-01
and the background solar wind conditions. We found that both solar wind models are capable of predicting the large-scale features of the observed solar wind speed (root-mean-square error, RMSE ≈100 km/s) but tend to either overestimate (ESWF) or underestimate (WSA) the number of high-speed solar wind streams (threat......High-speed solar wind streams emanating from coronal holes are frequently impinging on the Earth's magnetosphere causing recurrent, medium-level geomagnetic storm activity. Modeling high-speed solar wind streams is thus an essential element of successful space weather forecasting. Here we evaluate...... high-speed stream forecasts made by the empirical solar wind forecast (ESWF) and the semiempirical Wang-Sheeley-Arge (WSA) model based on the in situ plasma measurements from the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft for the years 2011 to 2014. While the ESWF makes use of an empirical relation...
-
Integrated solar energy system optimization
Young, S. K.
1982-11-01
The computer program SYSOPT, intended as a tool for optimizing the subsystem sizing, performance, and economics of integrated wind and solar energy systems, is presented. The modular structure of the methodology additionally allows simulations when the solar subsystems are combined with conventional technologies, e.g., a utility grid. Hourly energy/mass flow balances are computed for interconnection points, yielding optimized sizing and time-dependent operation of various subsystems. The program requires meteorological data, such as insolation, diurnal and seasonal variations, and wind speed at the hub height of a wind turbine, all of which can be taken from simulations like the TRNSYS program. Examples are provided for optimization of a solar-powered (wind turbine and parabolic trough-Rankine generator) desalinization plant, and a design analysis for a solar powered greenhouse.
-
The Western Wind and Solar Integration Study Phase 2
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lew, Debra [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Brinkman, Greg [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Ibanez, E. [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Florita, A. [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Heaney, M. [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Hodge, B. -M. [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Hummon, M. [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Stark, G. [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); King, J. [RePPAE; Lefton, S. A. [Intertek-APTECH, Houston, TX (United States); Kumar, N. [Intertek-APTECH, Houston, TX (United States); Agan, D. [Intertek-APTECH, Houston, TX (United States); Jordan, G. [GE Energy, Fairfield, CT (United States); Venkataraman, S. [GE Energy, Fairfield, CT (United States)
2013-09-01
The electric grid is a highly complex, interconnected machine, and changing one part of the grid can have consequences elsewhere. Adding wind and solar affects the operation of the other power plants and adding high penetrations can induce cycling of fossil-fueled generators. Cycling leads to wear-and-tear costs and changes in emissions. Phase 2 of the Western Wind and Solar Integration Study (WWSIS-2) evaluated these costs and emissions and simulated grid operations for a year to investigate the detailed impact of wind and solar on the fossil-fueled fleet. This built on Phase 1, one of the largest wind and solar integration studies ever conducted, which examined operational impacts of high wind and solar penetrations in the West(GE Energy 2010).
-
ANALYSING SOLAR-WIND HYBRID POWER GENERATING SYSTEM
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mustafa ENGİN
2005-02-01
Full Text Available In this paper, a solar-wind hybrid power generating, system that will be used for security lighting was designed. Hybrid system was installed and solar cells, wind turbine, battery bank, charge regulators and inverter performance values were measured through the whole year. Using measured values of overall system efficiency, reliability, demanded energy cost per kWh were calculated, and percentage of generated energy according to resources were defined. We also include in the paper a discussion of new strategies to improve hybrid power generating system performance and demanded energy cost per kWh.
-
Combined wind and solar feed-in to the grid
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Mushwana, Crescent
2018-05-01
Full Text Available This presentation highlights South African wind and solar resources and presents a case study on wind and solar PV combination. It also distinguishes between traditional and new philosophies regarding energy system design and the changes...
-
GPP Webinar: Market Outlook and Innovations in Wind and Solar Power
Green Power Partnership webinar reviewing the state of the renewable energy industry as a whole, with a focus on wind and solar power and exploring recent marketplace innovations in wind and solar power and renewable energy purchases.
-
Renewable Energy Systems: Development and Perspectives of a Hybrid Solar-Wind System
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. Shashidhar
2012-02-01
Full Text Available Considering the intermittent natural energy resources and the seasonal un-balance, a phtovoltaic-wind hybrid electrical power supply system was developed to accommodate remote locations where a conventional grid connection is inconvenient or expensive. However, the hybrid system can also be applied with grid connection and owners are allowed to sell excessive power back to the electric utility. The proposed set-up consists of a photo-voltaic solar-cell array, a mast mounted wind generator, lead-acid storage batteries, an inverter unit to convert DC to AC, electrical lighting loads, electrical heating loads, several fuse and junction boxes and associated wiring, and test instruments for measuring voltages, currents, power factors, and harmonic contamination data throughout the system. The proposed hybrid solar-wind power generating system can be extensively used to illustrate electrical concepts in hands-on laboratories and also for demonstrations in the Industrial Technology curriculum. This paper describes an analysis of local PV-wind hybrid systems for supplying electricity to a private house, farmhouse or small company with electrical power depending on the site needs. The major system components, work principle and specific working condition are presented.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chong, W.T.; Naghavi, M.S.; Poh, S.C.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Pan, K.C.
2011-01-01
Graphical abstract: This wind-solar hybrid renewable energy system is a new concept of the utilization, integration and optimization of existing renewable energy and rain water harvesting technologies. It is compact and can be built on the top of high rise buildings to provide on-site green power to that building or feed into the grid line. This system utilizes the advantages of Malaysian climate, i.e. high solar radiation and rainfall for green energy generation and free water supply. It also overcomes the inferior aspect on the low wind speed by guiding and increasing the speed of the high altitude free-stream wind from all directions radially through power-augmentation-guide-vane (PAGV) before entering the wind turbine at center portion. The PAGV is an innovative design used to guide and create venturi effect to increase the wind speed before the wind-stream enters wind turbine. The system must also be designed to provide optimum surface area for solar panel (solar thermal or photovoltaic or solar PV/T)) installation and battery compartment for power storage. In addition; rain water collection feature must be built-into the system design. The system is recommended to be sited on the top of high rise buildings or structures with its appearance or outer design can be blended into the building architecture without negative visual impact. With this system, the size of wind turbine can be reduced for a given power output and the noise is also reduced since it is contained in the PAGV. The design is also safer and suitable to be used in populated area. Mesh can be mounted at the entrance of the PAGV to prevent the bird-strike. This system can eliminate or minimize the current problems concerning public acceptance of wind energy, i.e. poor starting behavior in low wind speed, noise, visual impact, electromagnetic interference, safety and environmental factors. Highlights: → This wind, solar and rain harvester integrates existing renewable energy and rain water
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pegels, Anna; Lütkenhorst, Wilfried
2014-01-01
In this paper, we address the challenge of Germany's energy transition (Energiewende) as the centrepiece of the country's green industrial policy. In addition to contributing to global climate change objectives, the Energiewende is intended to create a leading position for German industry in renewable energy technologies, boost innovative capabilities and create employment opportunities in future growth markets at the least possible cost. The success in reaching these aims, and indeed the future of the entire concept, is hotly debated. The paper aims to provide an up-to-date assessment of what has become a fierce controversy by comparing solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind energy along five policy objectives: (1) competitiveness, (2) innovation, (3) job creation, (4) climate change mitigation, and (5) cost. We find mixed evidence that Germany reaches its green industrial policy aims at reasonable costs. Wind energy seems to perform better against all policy objectives, while the solar PV sector has come under intense pressure from international competition. However, this is only a snapshot of current performance, and the long term and systemic perspective required for the energy sector transformation suggests a need for a balanced mix of a variety of clean energy sources. - Highlights: • We give an up-to-date assessment of costs and benefits of Germany's Energiewende. • We compare solar PV and wind to show key elements of policy success. • Considered policy objectives: competitiveness, innovation, jobs, emissions, costs. • Wind energy seems to perform better than solar PV against all policy objectives. • The results are a snapshot: a deep transformation requires energy diversification
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kost, Christoph; Pfluger, Benjamin; Eichhammer, Wolfgang; Ragwitz, Mario
2011-01-01
The idea of generating electricity in North Africa using concentrating solar thermal power (CSP) has been around for some time now but has recently gained momentum through the Mediterranean Solar Plan (MSP) and the formation of the Desertec Industrial Initiative. This paper argues that while the large-scale deployment of CSP in North Africa does not seem economically attractive for either European or African institutions or countries on their own at present, combining domestic use and electricity exports could be profitable for both parties. A detailed economic portfolio covering both solar and wind power plants can achieve competitive price levels, which would accelerate the diffusion of solar technology in North Africa. This portfolio could be financed partially by exporting electricity from solar thermal plants in North Africa via HVDC interconnections to European consumers. Sharing the costs in this way makes it possible to generate solar electricity for the domestic market at a reasonable cost. Some of the electricity produced from the solar power plants and wind parks in North Africa is sold on European energy markets in the form of a long-term contracted solar-wind portfolio, which would qualify for support from the financial incentive schemes of the European Member States (e.g. feed-in tariffs). This transfer of green electricity could help to meet the targets for energy from renewable energy sources (RES) in the EU Member States as the new EU Directive of 2009 opened the European electricity market to imports from third states. - Research highlights: → This paper describes a feasible approach to financing a larger deployment of CSP in North Africa. → The proposed portfolio includes local consumption and electricity export to Europe. → Bundling wind with solar power as a business model for exporting solar electricity. → Prices of the solar-wind mix are competitive with other renewable energy sources. → Scenario outlook for the North African CSP
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kost, Christoph, E-mail: christoph.kost@ise.fraunhofer.de [Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE, Heidenhofstrasse 2, 79110 Freiburg (Germany); Pfluger, Benjamin, E-mail: benjamin.pfluger@isi.fraunhofer.de [Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research ISI, Breslauer Strasse 48, 76139 Karlsruhe (Germany); Eichhammer, Wolfgang, E-mail: wolfgang.eichhammer@isi.fraunhofer.de [Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research ISI, Breslauer Strasse 48, 76139 Karlsruhe (Germany); Ragwitz, Mario, E-mail: mario.ragwitz@isi.fraunhofer.de [Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research ISI, Breslauer Strasse 48, 76139 Karlsruhe (Germany)
2011-11-15
The idea of generating electricity in North Africa using concentrating solar thermal power (CSP) has been around for some time now but has recently gained momentum through the Mediterranean Solar Plan (MSP) and the formation of the Desertec Industrial Initiative. This paper argues that while the large-scale deployment of CSP in North Africa does not seem economically attractive for either European or African institutions or countries on their own at present, combining domestic use and electricity exports could be profitable for both parties. A detailed economic portfolio covering both solar and wind power plants can achieve competitive price levels, which would accelerate the diffusion of solar technology in North Africa. This portfolio could be financed partially by exporting electricity from solar thermal plants in North Africa via HVDC interconnections to European consumers. Sharing the costs in this way makes it possible to generate solar electricity for the domestic market at a reasonable cost. Some of the electricity produced from the solar power plants and wind parks in North Africa is sold on European energy markets in the form of a long-term contracted solar-wind portfolio, which would qualify for support from the financial incentive schemes of the European Member States (e.g. feed-in tariffs). This transfer of green electricity could help to meet the targets for energy from renewable energy sources (RES) in the EU Member States as the new EU Directive of 2009 opened the European electricity market to imports from third states. - Research Highlights: > This paper describes a feasible approach to financing a larger deployment of CSP in North Africa. > The proposed portfolio includes local consumption and electricity export to Europe. > Bundling wind with solar power as a business model for exporting solar electricity. > Prices of the solar-wind mix are competitive with other renewable energy sources. > Scenario outlook for the North African CSP market in
-
Wind energy systems information user study
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Belew, W.W.; Wood, B.L.; Marle, T.L.; Reinhardt, C.L.
1981-01-01
This report describes the results of a series of telephone interviews with potential users of information on wind energy conversion. These interviews, part of a larger study covering nine different solar technologies, attempted to identify: the type of information each distinctive group of information users needed, and the best way of getting information to that group. Groups studied include: wind energy conversion system researchers; wind energy conversion system manufacturer representatives; wind energy conversion system distributors; wind turbine engineers; utility representatives; educators; county agents and extension service agents; and wind turbine owners.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ebert, R. W.; Dayeh, M. A.; Desai, M. I.; McComas, D. J. [Southwest Research Institute, P.O. Drawer 28510, San Antonio, TX 78228 (United States); Pogorelov, N. V. [Physics Department, University of Alabama in Huntsville, Huntsville, AL 35899 (United States)
2013-05-10
We examined solar wind plasma and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) observations from Ulysses' first and third orbits to study hemispheric differences in the properties of the solar wind and IMF originating from the Sun's large polar coronal holes (PCHs) during the declining and minimum phase of solar cycles 22 and 23. We identified hemispheric asymmetries in several parameters, most notably {approx}15%-30% south-to-north differences in averages for the solar wind density, mass flux, dynamic pressure, and energy flux and the radial and total IMF magnitudes. These differences were driven by relatively larger, more variable solar wind density and radial IMF between {approx}36 Degree-Sign S-60 Degree-Sign S during the declining phase of solar cycles 22 and 23. These observations indicate either a hemispheric asymmetry in the PCH output during the declining and minimum phase of solar cycles 22 and 23 with the southern hemisphere being more active than its northern counterpart, or a solar cycle effect where the PCH output in both hemispheres is enhanced during periods of higher solar activity. We also report a strong linear correlation between these solar wind and IMF parameters, including the periods of enhanced PCH output, that highlight the connection between the solar wind mass and energy output and the Sun's magnetic field. That these enhancements were not matched by similar sized variations in solar wind speed points to the mass and energy responsible for these increases being added to the solar wind while its flow was subsonic.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ebert, R. W.; Dayeh, M. A.; Desai, M. I.; McComas, D. J.; Pogorelov, N. V.
2013-01-01
We examined solar wind plasma and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) observations from Ulysses' first and third orbits to study hemispheric differences in the properties of the solar wind and IMF originating from the Sun's large polar coronal holes (PCHs) during the declining and minimum phase of solar cycles 22 and 23. We identified hemispheric asymmetries in several parameters, most notably ∼15%-30% south-to-north differences in averages for the solar wind density, mass flux, dynamic pressure, and energy flux and the radial and total IMF magnitudes. These differences were driven by relatively larger, more variable solar wind density and radial IMF between ∼36°S-60°S during the declining phase of solar cycles 22 and 23. These observations indicate either a hemispheric asymmetry in the PCH output during the declining and minimum phase of solar cycles 22 and 23 with the southern hemisphere being more active than its northern counterpart, or a solar cycle effect where the PCH output in both hemispheres is enhanced during periods of higher solar activity. We also report a strong linear correlation between these solar wind and IMF parameters, including the periods of enhanced PCH output, that highlight the connection between the solar wind mass and energy output and the Sun's magnetic field. That these enhancements were not matched by similar sized variations in solar wind speed points to the mass and energy responsible for these increases being added to the solar wind while its flow was subsonic.
-
Wind Energy for Sustainable Development
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Comsan, M.N.H.
2009-01-01
The growing demand in energy and concern about depleting natural resources and global warming has led states worldwide to consider alternatives to the use of fossil fuel for energy production. Several countries especially in Europe have already increased their renewable energy share 6-10%, expected to increase to 20% by the year 2020. For Egypt excellent resources of wind and solar energy exist. The article discusses perspectives of wind energy in Egypt with projections to generate ∼ 3.5 GWe by 2022, representing ∼ 9% of the total installed power at that time (40.2 GW). Total renewable (hydro + wind + solar) are expected to provide ∼ 7.4 GWe by 2022 representing ∼ 19% of the total installed power. Such a share would reduce dependence on depleting oil and gas resources, and hence improve country's sustainable development
-
2016-06-01
iii Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited MICROGRID CONTROL STRATEGY UTLIZING THERMAL ENERGY STORAGE WITH RENEWABLE SOLAR AND WIND... control tracks increasing power generation in the morning. The batteries require a large amount of electrical power to charge every morning, as charge ...is 37 lost throughout the night. This causes the solar panels to output their maximum power generation. The MPPT control records when power
-
The Yaglom law in the expanding solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gogoberidze, G.; Perri, S.; Carbone, V.
2013-01-01
We study the Yaglom law, which relates the mixed third-order structure function to the average dissipation rate of turbulence, in a uniformly expanding solar wind by using the two-scale expansion model of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) turbulence. We show that due to the expansion of the solar wind, two new terms appear in the Yaglom law. The first term is related to the decay of the turbulent energy by nonlinear interactions, whereas the second term is related to the non-zero cross-correlation of the Elsässer fields. Using magnetic field and plasma data from WIND and Helios 2 spacecrafts, we show that at lower frequencies in the inertial range of MHD turbulence the new terms become comparable to Yaglom's third-order mixed moment, and therefore they cannot be neglected in the evaluation of the energy cascade rate in the solar wind.
-
An analysis of wind and solar energy resources for the State of Kuwait
Alhusainan, Haya Nasser
Kuwait is an important producer of oil and gas. Its rapid socio-economic growth has been characterized by increasing population, high rates of urbanization, and substantial industrialization, which is transforming it into a large big energy consumer as well. In addition to urbanization, climatic conditions have played an important function in increasing demand for electricity in Kuwait. Electricity for thermal cooling has become essential in the hot desert climate, and its use has developed rapidly along with the economic development, urbanization, and population growth. This study examines the long-term wind and solar resources over the Kuwait to determine the feasibility of these resources as potential sustainable and renewable energy sources. The ultimate goal of this research is to help identify the potential role of renewable energy in Kuwait. This study will examine the drivers and requirements for the deployment of these energy sources and their possible integration into the electricity generation sector to illustrate how renewable energy can be a suitable resource for power production in Kuwait and to illustrate how they can also be used to provide electricity for the country. For this study, data from sixteen established stations monitored by the meteorological department were analyzed. A solar resource map was developed that identifies the most suitable locations for solar farm development. A range of different relevant variables, including, for example, electric networks, population zones, fuel networks, elevation, water wells, streets, and weather stations, were combined in a geospatial analysis to predict suitable locations for solar farm development and placement. An analysis of recommendations, future energy targets and strategies for renewable energy policy in Kuwait are then conducted. This study was put together to identify issues and opportunities related to renewable energy in the region, since renewable energy technologies are still limited in
-
Laboratory Facility for Simulating Solar Wind Sails
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Funaki, Ikkoh; Ueno, Kazuma; Oshio, Yuya; Ayabe, Tomohiro; Horisawa, Hideyuki; Yamakawa, Hiroshi
2008-01-01
Magnetic sail (MagSail) is a deep space propulsion system, in which an artificial magnetic cavity captures the energy of the solar wind to propel a spacecraft in the direction leaving the sun. For a scale-model experiment of the plasma flow of MagSail, we employed a magnetoplasmadynamic arcjet as a solar wind simulator. It is observed that a plasma flow from the solar wind simulator reaches a quasi-steady state of about 0.8 ms duration after a transient phase when initiating the discharge. During this initial phase of the discharge, a blast-wave was observed to develop radially in a vacuum chamber. When a solenoidal coil (MagSail scale model) is immersed into the quasi-steady flow where the velocity is 45 km/s, and the number density is 10 19 m-3, a bow shock as well as a magnetic cavity were formed in front of the coil. As a result of the interaction between the plasma flow and the magnetic cavity, the momentum of the simulated solar wind is decreased, and it is found from the thrust measurement that the solar wind momentum is transferred to the coil simulating MagSail.
-
Design and analysis of a hybrid renewable energy plant with solar and wind power
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kabalci, Ersan
2013-01-01
Highlights: • A distributed generation system is developed with separate solar plant and wind turbine. • The solar plant is controlled with MPPT infrastructure of Perturb and Observe algorithm. • Power generation of source sites are converted to DC with PI controlled buck converters and collected on a DC busbar. • Harvested DC power is converted to AC with a full bridge inverter and SPWM control is performed in inverter. • The total harmonic distortion (THD) ratio of the generated 3-phase line is obtained in the limit of standards. - Abstract: A hybrid renewable energy plant that is based on solar and wind energy conversion systems is designed and analysed in this paper. Each separate energy conversion system is controlled either using regular PI controller or extended PI controller with an auxiliary controller containing Perturb and Observe algorithm. The solar plant model is constituted by connecting 170 W photovoltaic (PV) panels serially and energy conversion is performed with maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithm that controls the modulator of buck converter. The MPPT algorithm utilized in the control step of converter is developed using Perturb and Observe (P and O) that is extended with PI controller. The wind energy plant is designed with a permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG), and the AC–DC conversion stage is constituted with an uncontrolled full-bridge rectifier. All the converter outputs are connected to a busbar over interphase transformers (IPTs). The DC bus-bar voltage is supplied to a full bridge inverter to generate three-phase AC voltages at the output of inverter. The three-phase inverter is controlled with sinusoidal pulse width modulation (SPWM) scheme, which is developed with phase shifted carrier signals. The total harmonic distortion (THD) ratios are obtained at proper values according to international standards such as IEC61000 and IEEE 519-1992. Measurement results and obtained three phase voltage are analysed
-
Wind and Solar Curtailment: International Experience and Practices
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Lew, Debra; Bird, Lori; Milligan, Michael
2013-01-01
High penetrations of wind and solar generation on power systems are resulting in increasing curtailment. Wind and solar integration studies predict increased curtailment as penetration levels grow. This paper examines experiences with curtailment on bulk power systems internationally. It discusses...... how much curtailment is occurring, how it is occurring, why it is occurring, and what is being done to reduce curtailment. This summary is produced as part of the International Energy Agency Wind Task 25 on Design and Operation of Power Systems with Large Amounts of Wind Power....
-
Kinetic Physics of the Solar Corona and Solar Wind
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Marsch Eckart
2006-07-01
Full Text Available Kinetic plasma physics of the solar corona and solar wind are reviewed with emphasis on the theoretical understanding of the in situ measurements of solar wind particles and waves, as well as on the remote-sensing observations of the solar corona made by means of ultraviolet spectroscopy and imaging. In order to explain coronal and interplanetary heating, the microphysics of the dissipation of various forms of mechanical, electric and magnetic energy at small scales (e.g., contained in plasma waves, turbulences or non-uniform flows must be addressed. We therefore scrutinise the basic assumptions underlying the classical transport theory and the related collisional heating rates, and also describe alternatives associated with wave-particle interactions. We elucidate the kinetic aspects of heating the solar corona and interplanetary plasma through Landau- and cyclotron-resonant damping of plasma waves, and analyse in detail wave absorption and micro instabilities. Important aspects (virtues and limitations of fluid models, either single- and multi-species or magnetohydrodynamic and multi-moment models, for coronal heating and solar wind acceleration are critically discussed. Also, kinetic model results which were recently obtained by numerically solving the Vlasov–Boltzmann equation in a coronal funnel and hole are presented. Promising areas and perspectives for future research are outlined finally.
-
Determinants of wind and solar energy system adoption by U.S. farms: A multilevel modeling approach
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Borchers, Allison M.; Xiarchos, Irene; Beckman, Jayson
2014-01-01
This article offers the first national examination of the determinants of adoption of wind and solar energy generation on U.S. farming operations. The inclusion of state policies and characteristics in a multilevel modeling approach distinguishes this study from past research utilizing logit models of technology adoption which focus only on the characteristics of the farm operation. Results suggest the propensity to adopt is higher for livestock operations, larger farms, operators with internet access, organic operations, and newer farmers. The results find state characteristics such as solar resources, per capita income levels, and predominantly democratic voting increasing the odds of farm adoption. This research suggests the relevance of state policy variables in explaining farm level outcomes is limited, although in combination best practice net metering and interconnection policies—policies designed to encourage the development of small scale distributed applications—are shown to increase the likelihood of farm solar and wind adoption. The prevalence of electric cooperatives—which are often not subject to state renewable energy policies and often service farms—is negatively related with the propensity to adopt and suggests that policy design may be a factor. - Highlights: • This is the first national examination of wind and solar energy adoption on U.S. farms. • Controlling for state policies distinguishes this study from past research of technology adoption. • We find net metering and interconnection policies increase the likelihood of farm adoption. • Results suggest that the design of renewable energy policies may limit their impact on farms
-
Save with Solar and Wind, Summer 2002 (Newsletter)
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
2002-07-01
This newsletter is published by the Department of Energy's Federal Energy Management Program. It is intended for facility managers, contracting officials, energy specialists, and others involved in helping Federal agencies increase their use of cost-effective solar and wind energy systems at their facilities. Renewable energy systems ultimately save agencies money by reducing utility costs; they also help to lower the emissions associated with the use of fossil fuels. This issue describes a new strategy to achieve the Federal goal for renewable energy, as well as some new solar and wind systems installed at facilities of the Department of Defense, the U.S. Geological Survey, the U.S. Postal Service, the National Park Service, and other agencies.
-
Geometry of solar corona expansion and solar wind parameters
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Krajnev, M.B.
1980-01-01
The character of the parameter chanqe of solar wind plasma in the region of the Earth orbit is studied. The main regularities in the parametep behaviour of solar wind (plasma velocity and density) are qualitatively explained in the framework of a model according to which solar corona expansion stronqly differs from radial expansion, that is: the solar wind current lines are focused towards helioequator during the period of low solar activity with gradual transfer to radial expansion during the years of high solar activity. It is shown that the geometry of the solar wind current tubes and its change with the solar activity cycle can not serve an explanation of the observed change of the solar wind parameters
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Usmanov, Arcadi V.; Matthaeus, William H. [Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, Newark, DE 19716 (United States); Goldstein, Melvyn L., E-mail: arcadi.usmanov@nasa.gov [Code 672, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771 (United States)
2014-06-10
We have developed a three-fluid, three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic solar wind model that incorporates turbulence transport, eddy viscosity, turbulent resistivity, and turbulent heating. The solar wind plasma is described as a system of co-moving solar wind protons, electrons, and interstellar pickup protons, with separate energy equations for each species. Numerical steady-state solutions of Reynolds-averaged solar wind equations coupled with turbulence transport equations for turbulence energy, cross helicity, and correlation length are obtained by the time relaxation method in the corotating with the Sun frame of reference in the region from 0.3 to 100 AU (but still inside the termination shock). The model equations include the effects of electron heat conduction, Coulomb collisions, photoionization of interstellar hydrogen atoms and their charge exchange with the solar wind protons, turbulence energy generation by pickup protons, and turbulent heating of solar wind protons and electrons. The turbulence transport model is based on the Reynolds decomposition and turbulence phenomenologies that describe the conversion of fluctuation energy into heat due to a turbulent cascade. In addition to using separate energy equations for the solar wind protons and electrons, a significant improvement over our previous work is that the turbulence model now uses an eddy viscosity approximation for the Reynolds stress tensor and the mean turbulent electric field. The approximation allows the turbulence model to account for driving of turbulence by large-scale velocity gradients. Using either a dipole approximation for the solar magnetic field or synoptic solar magnetograms from the Wilcox Solar Observatory for assigning boundary conditions at the coronal base, we apply the model to study the global structure of the solar wind and its three-dimensional properties, including embedded turbulence, heating, and acceleration throughout the heliosphere. The model results are
-
Variation of the solar wind velocity following solar flares
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Huang, Y.; Lee, Y.
1975-01-01
By use of the superposed epoch method, changes in the solar wind velocity following solar flares have been investigated by using the solar wind velocity data obtained by Pioneer 6 and 7 and Vela 3, 4, and 5 satellites. A significant increase of the solar wind velocity has been found on the second day following importance 3 solar flares and on the third day following importance 2 solar flares. No significant increase of the solar wind velocity has been found for limb flares. (auth)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Akasofu, I.; Kamide, Y.
1987-01-01
The sun constantly emits an enormous amount of radiation into space. This energy emission consists of three modes. Almost all the energy is emitted in the form of familiar sunlight but sun also emits X-rays, extreme ultraviolet (EUV), and UV radiation, which is absorbed above the earth's stratosphere, as a second mode of solar energy. The sun has made another important mode of energy emission in which the energy is carried out by charged particles. These particles have a bery wide range of energies, from less than 1 keV to more than 1 GeV. Because of this wide range, it is convenient to group them into two components: particles, with energies greater than 10 keV and the lower-energy particles. The former are generally referred to as solar portions or solar cosmic rays; their emission is associated with active features on the sun. Low-energy particles constitute plasma which is called the solar wind
-
Harmonic analysis and suppression in hybrid wind & PV solar system
Gupta, Tripti; Namekar, Swapnil
2018-04-01
The growing demand of electricity has led to produce power through non-conventional source of energy such as solar energy, wind energy, hydro power, energy through biogas and biomass etc. Hybrid system is taken to complement the shortcoming of either sources of energy. The proposed system is grid connected hybrid wind and solar system. A 2.1 MW Doubly fed Induction Generator (DFIG) has been taken for analysis of wind farm whose rotor part is connected to two back-to-back converters. A 250 KW Photovoltaic (PV) array taken to analyze solar farm where inverter is required to convert power from DC to AC since electricity generated through solar PV is in the form of DC. Stability and reliability of the system is very important when the system is grid connected. Harmonics is the major Power quality issue which degrades the quality of power at load side. Harmonics in hybrid system arise through the use of power conversion unit. The other causes of harmonics are fluctuation in wind speed and solar irradiance. The power delivered to grid must be free from harmonics and within the limits specified by Indian grid codes. In proposed work, harmonic analysis of the hybrid system is performed in Electrical Transient Analysis program (ETAP) and single tuned harmonic filter is designed to maintain the utility grid harmonics within limits.
-
THE CONTRIBUTION OF CORONAL JETS TO THE SOLAR WIND
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lionello, R.; Török, T.; Titov, V. S.; Mikić, Z.; Linker, J. A. [Predictive Science Inc., 9990 Mesa Rim Road, Suite 170, San Diego, CA 92121 (United States); Leake, J. E.; Linton, M. G., E-mail: lionel@predsci.com [US Naval Research Laboratory 4555 Overlook Avenue, SW Washington, DC 20375 (United States)
2016-11-01
Transient collimated plasma eruptions in the solar corona, commonly known as coronal (or X-ray) jets, are among the most interesting manifestations of solar activity. It has been suggested that these events contribute to the mass and energy content of the corona and solar wind, but the extent of these contributions remains uncertain. We have recently modeled the formation and evolution of coronal jets using a three-dimensional (3D) magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) code with thermodynamics in a large spherical domain that includes the solar wind. Our model is coupled to 3D MHD flux-emergence simulations, i.e., we use boundary conditions provided by such simulations to drive a time-dependent coronal evolution. The model includes parametric coronal heating, radiative losses, and thermal conduction, which enables us to simulate the dynamics and plasma properties of coronal jets in a more realistic manner than done so far. Here, we employ these simulations to calculate the amount of mass and energy transported by coronal jets into the outer corona and inner heliosphere. Based on observed jet-occurrence rates, we then estimate the total contribution of coronal jets to the mass and energy content of the solar wind to (0.4–3.0)% and (0.3–1.0)%, respectively. Our results are largely consistent with the few previous rough estimates obtained from observations, supporting the conjecture that coronal jets provide only a small amount of mass and energy to the solar wind. We emphasize, however, that more advanced observations and simulations (including parametric studies) are needed to substantiate this conjecture.
-
Allton, J. H.; Gonzalez, C. P.; Allums, K. K.
2016-01-01
The Genesis mission collected solar wind for 27 months at Earth-Sun L1 on both passive and active collectors carried inside of a Science Canister, which was cleaned and assembled in an ISO Class 4 cleanroom prior to launch. The primary passive collectors, 271 individual hexagons and 30 half-hexagons of semiconductor materials, are described in. Since the hard landing reduced the 301 passive collectors to many thousand smaller fragments, characterization and posting in the online catalog remains a work in progress, with about 19% of the total area characterized to date. Other passive collectors, surfaces of opportunity, have been added to the online catalog. For species needing to be concentrated for precise measurement (e.g. oxygen and nitrogen isotopes) an energy-independent parabolic ion mirror focused ions onto a 6.2 cm diameter target. The target materials, as recovered after landing, are described in. The online catalog of these solar wind collectors, a work in progress, can be found at: http://curator.jsc.nasa.gov/gencatalog/index.cfm This paper describes the next step, the cataloging of pieces of the Science Canister, which were surfaces exposed to the solar wind or component materials adjacent to solar wind collectors which may have contributed contamination.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Taillant, Pierre
2005-01-01
The objective of this research thesis is to study the building up and the development of technologies for renewable energies considered as environmental radical innovations. In a first part, the author discusses the systemic aspects of innovation and the environmental challenges associated with energy technologies. He examines the main evolutions of energy systems over a long period. In a second part, he addresses innovation incentives in the case of environmental technologies and within the frame of the neo-classical economic theory. The next parts aim at presenting the theoretical framework of the evolutionary analysis of innovation and technical change, and at applying it to the case of technological innovations for renewable energies (photovoltaic and wind energy). World PV market trends are discussed and the technological competition context of this sector is analysed. The evolution of the solar PV technological system in Germany is discussed, as well as the specific case of development of the wind energy technological system in Denmark
-
Wind power statistics and an evaluation of wind energy density
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jamil, M.; Parsa, S.; Majidi, M. [Materials and Energy Research Centre, Tehran (Iran, Islamic Republic of)
1995-11-01
In this paper the statistical data of fifty days` wind speed measurements at the MERC- solar site are used to find out the wind energy density and other wind characteristics with the help of the Weibull probability distribution function. It is emphasized that the Weibull and Rayleigh probability functions are useful tools for wind energy density estimation but are not quite appropriate for properly fitting the actual wind data of low mean speed, short-time records. One has to use either the actual wind data (histogram) or look for a better fit by other models of the probability function. (Author)
-
Che, H.; Goldstein, M. L.; Vinas, A. F.
2014-01-01
The observed steep kinetic scale turbulence spectrum in the solar wind raises the question of how that turbulence originates. Observations of keV energetic electrons during solar quiet time suggest them as a possible source of free energy to drive kinetic turbulence. Using particle-in-cell simulations, we explore how the free energy released by an electron two-stream instability drives Weibel-like electromagnetic waves that excite wave-wave interactions. Consequently, both kinetic Alfvénic and whistler turbulence are excited that evolve through inverse and forward magnetic energy cascades.
-
Interaction of intersteller pick-up ions with the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mobius, E.; Klecker, B.; Hovestadt, D.; Scholer, M.
1988-01-01
The interaction of interstellar pick-up ions with the solar wind is studied by comparing a model for the velocity distribution function of pick-up ions with actual measurements of He + ions in the solar wind. The model includes the effects of pitch-angle diffusion due to interplanetary Alfven waves, adiabatic deceleration in the expanding solar wind and the radial variation of the source function. It is demonstrated that the scattering mean free path is in the range ≤0.1 AU and that energy diffusion can be neglected as compared with adiabatic deceleration. The effects of adiabatic focusing, of the radial variation of the neutral density and of an variation of the solar wind velocity with distance from the Sun are investigated. With the correct choice of these parameters the authors can model the measured energy spectra of the pick-up ions does not vary with the solar wind velocity and the direction of the interplanetary magnetic field for a given local neutral gas density and ionization rate. Therefore, the comparison of the model distributions with the measurements leads to a quantitative determination of the local interstellar gas density
-
Solar wind heating by an embedded quasi-isothermal pick-up ion fluid
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. J. Fahr
Full Text Available It is well known that the solar wind plasma consists of primary ions of solar coronal origin and secondary ions of interstellar origin. Interstellar H-atoms penetrate into the inner heliosphere and when ionized there are converted into secondary ions. These are implanted into the magnetized solar wind flow and are essentially enforced to co-move with this flow. By nonlinear interactions with wind-entrained Alfvén waves the latter are processed in the co-moving velocity space. This pick-up process, however, also causes actions back upon the original solar wind flow, leading to a deceleration, as well as a heating of the solar wind plasma. The resulting deceleration is not only due to the loading effect, but also due to the action of the pressure gradient. To calculate the latter, it is important to take into account the stochastic acceleration that suffers at their convection out of the inner heliosphere by the quasi-linear interactions with MHD turbulences. Only then can the presently reported VOYAGER observations of solar wind decelerations and heatings in the outer heliosphere be understood in terms of the current, most likely values of interstellar gas parameters. In a consistent view of the thermodynamics of the solar wind plasma, which is composed of secondary ions and solar wind protons, we also derive that the latter are globally heated at their motion to larger solar distances. The arising heat transfer is due to the action of suprathermal ions which drive MHD waves that are partially absorbed by solar wind protons and thereby establish their observed quasi-polytropy. We obtain a quantitative expression for the solar wind proton pressure as a function of solar distance. This expression clearly shows the change from an adiabatic to a quasi-polytropic behaviour with a decreasing polytropic index at increasing distances, as has been observed by the VOYAGERS. This also allows one to calculate the average percentage of the intitial energy
-
Solar wind heating by an embedded quasi-isothermal pick-up ion fluid
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. J. Fahr
2002-10-01
Full Text Available It is well known that the solar wind plasma consists of primary ions of solar coronal origin and secondary ions of interstellar origin. Interstellar H-atoms penetrate into the inner heliosphere and when ionized there are converted into secondary ions. These are implanted into the magnetized solar wind flow and are essentially enforced to co-move with this flow. By nonlinear interactions with wind-entrained Alfvén waves the latter are processed in the co-moving velocity space. This pick-up process, however, also causes actions back upon the original solar wind flow, leading to a deceleration, as well as a heating of the solar wind plasma. The resulting deceleration is not only due to the loading effect, but also due to the action of the pressure gradient. To calculate the latter, it is important to take into account the stochastic acceleration that suffers at their convection out of the inner heliosphere by the quasi-linear interactions with MHD turbulences. Only then can the presently reported VOYAGER observations of solar wind decelerations and heatings in the outer heliosphere be understood in terms of the current, most likely values of interstellar gas parameters. In a consistent view of the thermodynamics of the solar wind plasma, which is composed of secondary ions and solar wind protons, we also derive that the latter are globally heated at their motion to larger solar distances. The arising heat transfer is due to the action of suprathermal ions which drive MHD waves that are partially absorbed by solar wind protons and thereby establish their observed quasi-polytropy. We obtain a quantitative expression for the solar wind proton pressure as a function of solar distance. This expression clearly shows the change from an adiabatic to a quasi-polytropic behaviour with a decreasing polytropic index at increasing distances, as has been observed by the VOYAGERS. This also allows one to calculate the average percentage of the intitial energy
-
Solar and Wind Site Screening Decision Trees
EPA and NREL created a decision tree to guide state and local governments and other stakeholders through a process for screening sites for their suitability for future redevelopment with solar photovoltaic (PV) energy and wind energy.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Al-falahi, Monaaf D.A.; Jayasinghe, S.D.G.; Enshaei, H.
2017-01-01
Highlights: • Possible combinations and configurations for standalone PV-WT HES were discussed. • Most recently used assessment parameters for standalone PV-WT HES were explained. • Optimization algorithms and software tools were comprehensively reviewed. • The recent trend of using hybrid algorithms over single algorithms was discussed. • Optimization algorithms for sizing standalone PV-WT HES were critically compared. - Abstract: Electricity demand in remote and island areas are generally supplied by diesel or other fossil fuel based generation systems. Nevertheless, due to the increasing cost and harmful emissions of fossil fuels there is a growing trend to use standalone hybrid renewable energy systems (HRESs). Due to the complementary characteristics, matured technologies and availability in most areas, hybrid systems with solar and wind energy have become the popular choice in such applications. However, the intermittency and high net present cost are the challenges associated with solar and wind energy systems. In this context, optimal sizing is a key factor to attain a reliable supply at a low cost through these standalone systems. Therefore, there has been a growing interest to develop algorithms for size optimization in standalone HRESs. The optimal sizing methodologies reported so far can be broadly categorized as classical algorithms, modern techniques and software tools. Modern techniques, based on single artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, are becoming more popular than classical algorithms owing to their capabilities in solving complex optimization problems. Moreover, in recent years, there has been a clear trend to use hybrid algorithms over single algorithms mainly due to their ability to provide more promising optimization results. This paper aims to present a comprehensive review on recent developments in size optimization methodologies, as well as a critical comparison of single algorithms, hybrid algorithms, and software tools
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Shuvankar Podder
2015-01-01
Full Text Available The size optimization and economic evaluation of the solar-wind hybrid renewable energy system (RES to meet the electricity demand of 276 kWh/day with 40 kW peak load have been determined in this study. The load data has been collected from the motels situated in the coastal areas of Patenga, Chittagong. RES in standalone as well as grid connected mode have been considered. The optimal system configurations have been determined based on systems net present cost (NPC and cost of per unit energy (COE. A standalone solar-wind-battery hybrid system is feasible and economically comparable to the present cost of diesel based power plant if 8% annual capacity shortage is allowed. Grid tied solar-wind hybrid system, where more than 70% electricity contribution is from RES, is economically comparable to present grid electricity price. Moreover, grid tied RES results in more than 60% reduction in greenhouse gases emission compared to the conventional grid. Sensitivity analysis has been performed in this study to determine the effect of capital cost variation or renewable resources variation on the system economy. Simulation result of sensitivity analysis has showed that 20% reduction of installation cost results in nearly 9%–12% reductions in cost of per unit energy.
-
Different magnetospheric modes: solar wind driving and coupling efficiency
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
N. Partamies
2009-11-01
Full Text Available This study describes a systematic statistical comparison of isolated non-storm substorms, steady magnetospheric convection (SMC intervals and sawtooth events. The number of events is approximately the same in each group and the data are taken from about the same years to avoid biasing by different solar cycle phase. The very same superposed epoch analysis is performed for each event group to show the characteristics of ground-based indices (AL, PCN, PC potential, particle injection at the geostationary orbit and the solar wind and IMF parameters. We show that the monthly occurrence of sawtooth events and isolated non-stormtime substorms closely follows maxima of the geomagnetic activity at (or close to the equinoxes. The most strongly solar wind driven event type, sawtooth events, is the least efficient in coupling the solar wind energy to the auroral ionosphere, while SMC periods are associated with the highest coupling ratio (AL/EY. Furthermore, solar wind speed seems to play a key role in determining the type of activity in the magnetosphere. Slow solar wind is capable of maintaining steady convection. During fast solar wind streams the magnetosphere responds with loading–unloading cycles, represented by substorms during moderately active conditions and sawtooth events (or other storm-time activations during geomagnetically active conditions.
-
Solar wind radiation damage in lunar dust grains and the characteristics of the ancient solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Borg, J.; Chaumont, J.
1980-01-01
Current understanding of the exposure history of lunar dust grains to the ancient solar wind is reviewed, the work being based mostly on a Monte Carlo statistical code, describing the 'gardening' effects of the meteorite bombardment in the lunar regolith, and on analytical models, yielding the lifetimes of the grains against various types of destruction processes. Families of lunar dust grains are identified, and evidence is presented showing that lunar dust grains were not partially shielded from solar wind ions. Results of solar wind simulation experiments are used to interpret the thickness distribution of the amorphous coatings of solar wind radiation-damaged material observed on 1-micron lunar dust grains. It is argued that such distributions reflect the speed distribution of the ancient solar wind as averaged over periods of approximately 5000 years in duration, and that the ancient solar wind is less energetic than the present day solar wind
-
Solar wind classification from a machine learning perspective
Heidrich-Meisner, V.; Wimmer-Schweingruber, R. F.
2017-12-01
It is a very well known fact that the ubiquitous solar wind comes in at least two varieties, the slow solar wind and the coronal hole wind. The simplified view of two solar wind types has been frequently challenged. Existing solar wind categorization schemes rely mainly on different combinations of the solar wind proton speed, the O and C charge state ratios, the Alfvén speed, the expected proton temperature and the specific proton entropy. In available solar wind classification schemes, solar wind from stream interaction regimes is often considered either as coronal hole wind or slow solar wind, although their plasma properties are different compared to "pure" coronal hole or slow solar wind. As shown in Neugebauer et al. (2016), even if only two solar wind types are assumed, available solar wind categorization schemes differ considerably for intermediate solar wind speeds. Thus, the decision boundary between the coronal hole and the slow solar wind is so far not well defined.In this situation, a machine learning approach to solar wind classification can provide an additional perspective.We apply a well-known machine learning method, k-means, to the task of solar wind classification in order to answer the following questions: (1) How many solar wind types can reliably be identified in our data set comprised of ten years of solar wind observations from the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE)? (2) Which combinations of solar wind parameters are particularly useful for solar wind classification?Potential subtypes of slow solar wind are of particular interest because they can provide hints of respective different source regions or release mechanisms of slow solar wind.
-
Coskun, Aynur Aydin; Türker, Yavuz Özhan
2012-03-01
The global energy requirement for sustaining economic activities, meeting social needs and social development is increasing daily. Environmentally friendly, renewable energy resources are an alternative to the primary non-renewable energy resources, which devastate ecosystems in order to meet increasing demand. Among renewable energy sources such as hydropower, biopower, geothermal power and solar power, wind power offers distinct advantages to Turkey. There is an increasing tendency toward wind globally and the European Union adjusted its legal regulations in this regard. As a potential EU Member state, Turkey is going through a similar process. The number of institutional and legal regulations concerning wind power has increased in recent years; technical infrastructure studies were completed, and some important steps were taken in this regard. This study examines the way in which Turkey has developed support for wind power, presents a SWOT analysis of the wind power sector in Turkey and a projection was made for the concrete success expected to be accomplished in the future.
-
Shematovich, Valery I.
2017-04-01
One of the first surprises of the NASA MAVEN mission was the observation by the SWIA instrument of a tenuous population of protons with solar wind energies travelling anti-sunward near periapsis, at altitudes of 150-250 km (Halekas et al., 2015). While the penetration of solar wind protons to low altitude is not completely unexpected given previous Mars Express results, this population maintains exactly the same velocity as the solar wind observed. From previous studies it was known that some fraction of the solar wind can interact with the extended corona of Mars. By charge exchange with the neutral particles in this corona, some fraction of the incoming solar wind protons can gain an electron and become an energetic neutral hydrogen atom. Once neutral, these particles penetrate through the Martian induced magnetosphere with ease, with free access to the collisional atmosphere/ionosphere. The origin, kinetics and transport of the suprathermal O atoms in the transition region (from thermosphere to exosphere) of the Martian upper atmosphere due to the precipitation of the high-energy protons and hydrogen atoms are discussed. Kinetic energy distribution functions of suprathermal and superthermal (ENA) oxygen atoms formed in the Martian upper atmosphere were calculated using the kinetic Monte Carlo model (Shematovich et al., 2011, Shematovich, 2013) of the high-energy proton and hydrogen atom precipitation into the atmosphere. These functions allowed us: (a) to estimate the non-thermal escape rates of neutral oxygen from the Martian upper atmosphere, and (b) to compare with available MAVEN measurements of oxygen corona. Induced by precipitation the escape of hot oxygen atoms may become dominant under conditions of extreme solar events - solar flares and coronal mass ejections, - as it was shown by recent observations of the NASA MAVEN spacecraft (Jakosky et al., 2015). This work is supported by the RFBR project and by the Basic Research Program of the Praesidium of
-
Analysis of off-grid hybrid wind turbine/solar PV water pumping systems
While many remote water pumping systems exist (e.g. mechanical windmills, solar photovoltaic , wind-electric, diesel powered), very few combine both the wind and solar energy resources to possibly improve the reliability and the performance of the system. In this paper, off-grid wind turbine (WT) a...
-
Lue, C.; Halekas, J. S.
2017-12-01
Particle sensors on the MAVEN spacecraft (SWIA, SWEA, STATIC) observe precipitating solar wind ions during MAVEN's periapsis passes in the Martian atmosphere (at 120-250 km altitude). The signature is observed as positive and negative particles at the solar wind energy, traveling away from the Sun. The observations can be explained by the solar wind penetrating the Martian magnetic barrier in the form of energetic neutral atoms (ENAs) due to charge-exchange with the Martian hydrogen corona, and then being reionized in positive or negative form upon impact with the atmosphere (1). These findings have elucidated solar wind precipitation dynamics at Mars, and can also be used to monitor the solar wind even when MAVEN is at periapsis (2). In the present study, we focus on a SWIA instrument background signal that has been interpreted as spacecraft/instrument-scattered ions (2). We aim to model and subtract the scattered ion signal from the observations including those of reionized solar wind. We also aim to use the scattered ion signal to track hydrogen ENAs impacting the spacecraft above the reionization altitude. We characterize the energy spectrum and directional scattering function for solar wind scattering off the SWIA aperture structure, the radome and the spacecraft body. We find a broad scattered-ion energy spectrum up to the solar wind energy, displaying increased energy loss and reduced flux with increasing scattering angle, allowing correlations with the solar wind direction, energy, and flux. We develop models that can be used to predict the scattered signal based on the direct solar wind observations or to infer the solar wind properties based on the observed scattered signal. We then investigate deviations to the models when the spacecraft is in the Martian atmosphere and evaluate the plausibility of that these are caused by ENAs. We also perform SIMION modeling of the scattering process and the resulting signal detection by SWIA, to study the results from
-
Study on Pyroelectric Harvesters Integrating Solar Radiation with Wind Power
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Chun-Ching Hsiao
2015-07-01
Full Text Available Pyroelectric harvesters use temperature fluctuations to generate electrical outputs. Solar radiation and waste heat are rich energy sources that can be harvested. Pyroelectric energy converters offer a novel and direct energy-conversion technology by transforming time-dependent temperatures directly into electricity. Moreover, the great challenge for pyroelectric energy harvesting lies in finding promising temperature variations or an alternating thermal loading in real situations. Hence, in this article, a novel pyroelectric harvester integrating solar radiation with wind power by the pyroelectric effect is proposed. Solar radiation is a thermal source, and wind is a dynamic potential. A disk generator is used for harvesting wind power. A mechanism is considered to convert the rotary energy of the disk generator to drive a shutter for generating temperature variations in pyroelectric cells using a planetary gear system. The optimal period of the pyroelectric cells is 35 s to harvest the stored energy, about 70 μJ, while the rotary velocity of the disk generator is about 31 RPM and the wind speed is about 1 m/s. In this state, the stored energy acquired from the pyroelectric harvester is about 75% more than that from the disk generator. Although the generated energy of the proposed pyroelectric harvester is less than that of the disk generator, the pyroelectric harvester plays a complementary role when the disk generator is inactive in situations of low wind speed.
-
A study on evaluating the power generation of solar-wind hybrid systems in Izmir, Turkey
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ulgen, K. [Ege Univ., Solar Energy Inst., Izmir (Turkey); Hepbasli, A. [Ege Univ., Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Izmir (Turkey)
2003-03-15
Turkey is abundant in terms of renewable energy resources. Residential and industrial utilization of solar energy started in the 1980s, while the first Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) windmill park, located at Alacati, Izmir, was commissioned in 1998. Additionally, power generation through solar-wind hybrid systems has recently appeared on the Turkish market. This study investigates the wind and solar thermal power availability in Izmir, located in the western part of Turkey. Simple models were developed to determine wind, solar, and hybrid power resources per unit area. Experimental data, consisting of hourly records over a 5 yr period, 1995-1999, were measured in the Solar/Wind Meteorological Station of the Solar Energy Institute at Ege University. Correlations between solar and wind power data were carried out on an hourly, a daily, and a monthly basis. It can be concluded that possible applications of hybrid systems could be considered for the efficient utilization of these resources. (Author)
-
Solar Energy Education. Renewable energy: a background text. [Includes glossary
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
1985-01-01
Some of the most common forms of renewable energy are presented in this textbook for students. The topics include solar energy, wind power hydroelectric power, biomass ocean thermal energy, and tidal and geothermal energy. The main emphasis of the text is on the sun and the solar energy that it yields. Discussions on the sun's composition and the relationship between the earth, sun and atmosphere are provided. Insolation, active and passive solar systems, and solar collectors are the subtopics included under solar energy. (BCS)
-
The turbulent cascade and proton heating in the solar wind during solar minimum
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Coburn, Jesse T.; Smith, Charles W.; Vasquez, Bernard J.; Stawarz, Joshua E.; Forman, Miriam A.
2013-01-01
Solar wind measurements at 1 AU during the recent solar minimum and previous studies of solar maximum provide an opportunity to study the effects of the changing solar cycle on in situ heating. Our interest is to compare the levels of activity associated with turbulence and proton heating. Large-scale shears in the flow caused by transient activity are a source that drives turbulence that heats the solar wind, but as the solar cycle progresses the dynamics that drive the turbulence and heat the medium are likely to change. The application of third-moment theory to Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) data gives the turbulent energy cascade rate which is not seen to vary with the solar cycle. Likewise, an empirical heating rate shows no significan changes in proton heating over the cycle.
-
Solar wind structure out of the ecliptic plane over solar cycles
Sokol, J. M.; Bzowski, M.; Tokumaru, M.
2017-12-01
Sun constantly emits a stream of plasma known as solar wind. Ground-based observations of the solar wind speed through the interplanetary scintillations (IPS) of radio flux from distant point sources and in-situ measurements by Ulysses mission revealed that the solar wind flow has different characteristics depending on the latitude. This latitudinal structure evolves with the cycle of solar activity. The knowledge on the evolution of solar wind structure is important for understanding the interaction between the interstellar medium surrounding the Sun and the solar wind, which is responsible for creation of the heliosphere. The solar wind structure must be taken into account in interpretation of most of the observations of heliospheric energetic neutral atoms, interstellar neutral atoms, pickup ions, and heliospheric backscatter glow. The information on the solar wind structure is not any longer available from direct measurements after the termination of Ulysses mission and the only source of the solar wind out of the ecliptic plane is the IPS observations. However, the solar wind structure obtained from this method contains inevitable gaps in the time- and heliolatitude coverage. Sokół et al 2015 used the solar wind speed data out of the ecliptic plane retrieved from the IPS observations performed by Institute for Space-Earth Environmental Research (Nagoya University, Japan) and developed a methodology to construct a model of evolution of solar wind speed and density from 1985 to 2013 that fills the data gaps. In this paper we will present a refined model of the solar wind speed and density structure as a function of heliographic latitude updated by the most recent data from IPS observations. And we will discuss methods of extrapolation of the solar wind structure out of the ecliptic plane for the past solar cycles, when the data were not available, as well as forecasting for few years upward.
-
Assessing the lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions from solar PV and wind energy
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nugent, Daniel; Sovacool, Benjamin
2014-01-01
This paper critically screens 153 lifecycle studies covering a broad range of wind and solar photovoltaic (PV) electricity generation technologies to identify 41 of the most relevant, recent, rigorous, original, and complete assessments so that the dynamics of their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions...... profiles can be determined. When viewed in a holistic manner, including initial materials extraction, manufacturing, use and disposal/decommissioning, these 41 studies show that both wind and solar systems are directly tied to and responsible for GHG emissions. They are thus not actually emissions free......, this article uncovers best practices in wind and solar design and deployment that can better inform climate change mitigation efforts in the electricity sector...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Heber, Veronika S.; Baur, Heinrich; Wieler, Rainer; Bochsler, Peter; McKeegan, Kevin D.; Neugebauer, Marcia; Reisenfeld, Daniel B.; Wiens, Roger C.
2012-01-01
NASA's Genesis space mission returned samples of solar wind collected over ∼2.3 years. We present elemental and isotopic compositions of He, Ne, and Ar analyzed in diamond-like carbon targets from the slow and fast solar wind collectors to investigate isotopic fractionation processes during solar wind formation. The solar wind provides information on the isotopic composition for most volatile elements for the solar atmosphere, the bulk Sun and hence, on the solar nebula from which it formed 4.6 Ga ago. Our data reveal a heavy isotope depletion in the slow solar wind compared to the fast wind composition by 63.1 ± 2.1 per mille for He, 4.2 ± 0.5 per mille amu –1 for Ne and 2.6 ± 0.5 per mille amu –1 for Ar. The three Ne isotopes suggest that isotopic fractionation processes between fast and slow solar wind are mass dependent. The He/H ratios of the collected slow and fast solar wind samples are 0.0344 and 0.0406, respectively. The inefficient Coulomb drag model reproduces the measured isotopic fractionation between fast and slow wind. Therefore, we apply this model to infer the photospheric isotopic composition of He, Ne, and Ar from our solar wind data. We also compare the isotopic composition of oxygen and nitrogen measured in the solar wind with values of early solar system condensates, probably representing solar nebula composition. We interpret the differences between these samples as being due to isotopic fractionation during solar wind formation. For both elements, the magnitude and sign of the observed differences are in good agreement with the values predicted by the inefficient Coulomb drag model.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Heber, Veronika S.; Baur, Heinrich; Wieler, Rainer [Institute for Geochemistry and Petrology, ETH Zurich, Clausiusstrasse 25, CH-8092 Zurich (Switzerland); Bochsler, Peter [Physikalisches Institut, Universitaet Bern, Sidlerstasse 5, CH-3012 Bern (Switzerland); McKeegan, Kevin D. [Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California Los Angeles, 595 Charles Young Drive East, Box 951567, Los Angeles, CA 90095-1567 (United States); Neugebauer, Marcia [Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721-0092 (United States); Reisenfeld, Daniel B. [Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Montana, Missoula, MT 59812 (United States); Wiens, Roger C., E-mail: heber@ess.ucla.edu [Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM 87545 (United States)
2012-11-10
NASA's Genesis space mission returned samples of solar wind collected over {approx}2.3 years. We present elemental and isotopic compositions of He, Ne, and Ar analyzed in diamond-like carbon targets from the slow and fast solar wind collectors to investigate isotopic fractionation processes during solar wind formation. The solar wind provides information on the isotopic composition for most volatile elements for the solar atmosphere, the bulk Sun and hence, on the solar nebula from which it formed 4.6 Ga ago. Our data reveal a heavy isotope depletion in the slow solar wind compared to the fast wind composition by 63.1 {+-} 2.1 per mille for He, 4.2 {+-} 0.5 per mille amu{sup -1} for Ne and 2.6 {+-} 0.5 per mille amu{sup -1} for Ar. The three Ne isotopes suggest that isotopic fractionation processes between fast and slow solar wind are mass dependent. The He/H ratios of the collected slow and fast solar wind samples are 0.0344 and 0.0406, respectively. The inefficient Coulomb drag model reproduces the measured isotopic fractionation between fast and slow wind. Therefore, we apply this model to infer the photospheric isotopic composition of He, Ne, and Ar from our solar wind data. We also compare the isotopic composition of oxygen and nitrogen measured in the solar wind with values of early solar system condensates, probably representing solar nebula composition. We interpret the differences between these samples as being due to isotopic fractionation during solar wind formation. For both elements, the magnitude and sign of the observed differences are in good agreement with the values predicted by the inefficient Coulomb drag model.
-
Ogilvie, K. W.; Coplan, M. A.; Roberts, D. A.; Ipavich, F.
2007-08-01
We calculate the cross-spacecraft maximum lagged-cross-correlation coefficients for 2-hour intervals of solar wind speed and density measurements made by the plasma instruments on the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and Wind spacecraft over the period from 1996, the minimum of solar cycle 23, through the end of 2005. During this period, SOHO was located at L1, about 200 R E upstream from the Earth, while Wind spent most of the time in the interplanetary medium at distances of more than 100 R E from the Earth. Yearly histograms of the maximum, time-lagged correlation coefficients for both the speed and density are bimodal in shape, suggesting the existence of two distinct solar wind regimes. The larger correlation coefficients we suggest are due to structured solar wind, including discontinuities and shocks, while the smaller are likely due to Alfvénic turbulence. While further work will be required to firmly establish the physical nature of the two populations, the results of the analysis are consistent with a solar wind that consists of turbulence from quiet regions of the Sun interspersed with highly filamentary structures largely convected from regions in the inner solar corona. The bimodal appearance of the distributions is less evident in the solar wind speed than in the density correlations, consistent with the observation that the filamentary structures are convected with nearly constant speed by the time they reach 1 AU. We also find that at solar minimum the fits for the density correlations have smaller high-correlation components than at solar maximum. We interpret this as due to the presence of more relatively uniform Alfvénic regions at solar minimum than at solar maximum.
-
Western Wind and Solar Integration Study: Hydropower Analysis
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Acker, T.; Pete, C.
2012-03-01
The U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) study of 20% Wind Energy by 2030 was conducted to consider the benefits, challenges, and costs associated with sourcing 20% of U.S. energy consumption from wind power by 2030. This study found that with proactive measures, no insurmountable barriers were identified to meet the 20% goal. Following this study, DOE and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) conducted two more studies: the Eastern Wind Integration and Transmission Study (EWITS) covering the eastern portion of the U.S., and the Western Wind and Solar Integration Study (WWSIS) covering the western portion of the United States. The WWSIS was conducted by NREL and research partner General Electric (GE) in order to provide insight into the costs, technical or physical barriers, and operational impacts caused by the variability and uncertainty of wind, photovoltaic, and concentrated solar power when employed to serve up to 35% of the load energy in the WestConnect region (Arizona, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, and Wyoming). WestConnect is composed of several utility companies working collaboratively to assess stakeholder and market needs to and develop cost-effective improvements to the western wholesale electricity market. Participants include the Arizona Public Service, El Paso Electric Company, NV Energy, Public Service of New Mexico, Salt River Project, Tri-State Generation and Transmission Cooperative, Tucson Electric Power, Xcel Energy and the Western Area Power Administration.
-
Turbulence and Waves as Sources for the Solar Wind
Cranmer, S. R.
2008-05-01
Gene Parker's insights from 50 years ago provided the key causal link between energy deposition in the solar corona and the acceleration of solar wind streams. However, the community is still far from agreement concerning the actual physical processes that give rise to this energy. It is still unknown whether the solar wind is fed by flux tubes that remain open (and are energized by footpoint-driven wavelike fluctuations) or if mass and energy is input more intermittently from closed loops into the open-field regions. No matter the relative importance of reconnections and loop-openings, though, we do know that waves and turbulent motions are present everywhere from the photosphere to the heliosphere, and it is important to determine how they affect the mean state of the plasma. In this presentation, I will give a summary of wave/turbulence models that seem to succeed in explaining the time-steady properties of the corona (and the fast and slow solar wind). The coronal heating and solar wind acceleration in these models comes from anisotropic turbulent cascade, which is driven by the partial reflection of low-frequency Alfven waves propagating along the open magnetic flux tubes. Specifically, a 2D model of coronal holes and streamers at solar minimum reproduces the latitudinal bifurcation of slow and fast streams seen by Ulysses. The radial gradient of the Alfven speed affects where the waves are reflected and damped, and thus whether energy is deposited below or above Parker's critical point. As predicted by earlier studies, a larger coronal expansion factor gives rise to a slower and denser wind, higher temperature at the coronal base, less intense Alfven waves at 1 AU, and correlative trends for commonly measured ratios of ion charge states and FIP-sensitive abundances that are in general agreement with observations. Finally, I will outline the types of future observations that would be most able to test and refine these ideas.
-
Malaspina, David M.; Newman, David L.; Wilson, Lynn Bruce; Goetz, Keith; Kellogg, Paul J.; Kerstin, Kris
2013-01-01
A strong spatial association between bipolar electrostatic solitary waves (ESWs) and magnetic current sheets (CSs) in the solar wind is reported here for the first time. This association requires that the plasma instabilities (e.g., Buneman, electron two stream) which generate ESWs are preferentially localized to solar wind CSs. Distributions of CS properties (including shear angle, thickness, solar wind speed, and vector magnetic field change) are examined for differences between CSs associated with ESWs and randomly chosen CSs. Possible mechanisms for producing ESW-generating instabilities at solar wind CSs are considered, including magnetic reconnection.
-
Wind energy literature survey no. 34
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Pavese, Christian
2015-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawnfrom recent issues of Wind Energy itself and a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering andIndustrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy...... Research, Renewable Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of SolarEnergy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systemsalong with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list...... is limitedexclusively to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separatedinto broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the categorythought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion...
-
Charging electric cars from solar energy
Liang, Xusheng; Tanyi, Elvis; Zou, Xin
2016-01-01
Before vehicles were heavily relied on coal, fossil fuels and wind for power. Now, they are rapidly being replaced by electric vehicles and or plug-in hybrid electric cars. But these electric cars are still faced with the problem of energy availability because they rely on energy from biomass, hydro power and wind turbines for power generation. The abundance of solar radiation and its use as solar energy as a power source in driving these rapidly increasing electric cars is not only an impor...
-
Solar energy: Technology and applications
Williams, J. R.
1974-01-01
It is pointed out that in 1970 the total energy consumed in the U.S. was equal to the energy of sunlight received by only 0.15% of the land area of the continental U.S. The utilization of solar energy might, therefore, provide an approach for solving the energy crisis produced by the consumption of irreplaceable fossil fuels at a steadily increasing rate. Questions regarding the availability of solar energy are discussed along with the design of solar energy collectors and various approaches for heating houses and buildings by utilizing solar radiation. Other subjects considered are related to the heating of water partly or entirely with solar energy, the design of air conditioning systems based on the use of solar energy, electric power generation by a solar thermal and a photovoltaic approach, solar total energy systems, industrial and agricultural applications of solar energy, solar stills, the utilization of ocean thermal power, power systems based on the use of wind, and solar-energy power systems making use of geosynchronous power plants.
-
Dudem, Bhaskar; Ko, Yeong Hwan; Leem, Jung Woo; Lim, Joo Ho; Yu, Jae Su
2016-11-09
We report the creation of hybrid energy cells based on hierarchical nano/micro-architectured polydimethylsiloxane (HNMA-PDMS) films with multifunctionality to simultaneously harvest mechanical, solar, and wind energies. These films consist of nano/micro dual-scale architectures (i.e., nanonipples on inverted micropyramidal arrays) on the PDMS surface. The HNMA-PDMS is replicable by facile and cost-effective soft imprint lithography using a nanoporous anodic alumina oxide film formed on the micropyramidal-structured silicon substrate. The HNMA-PDMS film plays multifunctional roles as a triboelectric layer in nanogenerators and an antireflection layer for dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs), as well as a self-cleaning surface. This film is employed in triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) devices, fabricated by laminating it on indium-tin oxide-coated polyethylene terephthalate (ITO/PET) as a bottom electrode. The large effective contact area that emerged from the densely packed hierarchical nano/micro-architectures of the PDMS film leads to the enhancement of TENG device performance. Moreover, the HNMA-PDMS/ITO/PET, with a high transmittance of >90%, also results in highly transparent TENG devices. By placing the HNMA-PDMS/ITO/PET, where the ITO/PET is coated with zinc oxide nanowires, as the top glass substrate of DSSCs, the device is able to add the functionality of TENG devices, thus creating a hybrid energy cell. The hybrid energy cell can successfully convert mechanical, solar, and wind energies into electricity, simultaneously or independently. To specify the device performance, the effects of external pushing frequency and load resistance on the output of TENG devices are also analyzed, including the photovoltaic performance of the hybrid energy cells.
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 32
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2014-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of Wind Energy itself and a large number of periodicals including the following: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International...... Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, and so...... on. The list is limited exclusively to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 31
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2014-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of Wind Energy itself and a large number of periodicals including: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy...... Research, Renewable Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, and so on. The list...... is limited exclusively to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note...
-
Wind energy literature survey no. 33
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Pavese, Christian
2014-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of Wind Energy itself and a large number of periodicals, including the following: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International...... Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, and so...... on. The list is limited exclusively to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate...
-
Weakest solar wind of the space age and the current 'MINI' solar maximum
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McComas, D. J.; Angold, N.; Elliott, H. A.; Livadiotis, G.; Schwadron, N. A.; Smith, C. W.; Skoug, R. M.
2013-01-01
The last solar minimum, which extended into 2009, was especially deep and prolonged. Since then, sunspot activity has gone through a very small peak while the heliospheric current sheet achieved large tilt angles similar to prior solar maxima. The solar wind fluid properties and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) have declined through the prolonged solar minimum and continued to be low through the current mini solar maximum. Compared to values typically observed from the mid-1970s through the mid-1990s, the following proton parameters are lower on average from 2009 through day 79 of 2013: solar wind speed and beta (∼11%), temperature (∼40%), thermal pressure (∼55%), mass flux (∼34%), momentum flux or dynamic pressure (∼41%), energy flux (∼48%), IMF magnitude (∼31%), and radial component of the IMF (∼38%). These results have important implications for the solar wind's interaction with planetary magnetospheres and the heliosphere's interaction with the local interstellar medium, with the proton dynamic pressure remaining near the lowest values observed in the space age: ∼1.4 nPa, compared to ∼2.4 nPa typically observed from the mid-1970s through the mid-1990s. The combination of lower magnetic flux emergence from the Sun (carried out in the solar wind as the IMF) and associated low power in the solar wind points to the causal relationship between them. Our results indicate that the low solar wind output is driven by an internal trend in the Sun that is longer than the ∼11 yr solar cycle, and they suggest that this current weak solar maximum is driven by the same trend.
-
Contribution to the study of the wind and solar radiation over Guadeloupe
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bertin, A.; Frangi, J.P.
2013-01-01
Highlights: • We study wind and solar resource in Guadeloupe (FWI). • Weibull distributions reveal a nocturnal radiative layer blocking wind at airport. • We provide monthly and annual irradiations, horizontal and tilted, for four sites. • Five Linke turbidity coefficient calculation methods are reviewed and compared. - Abstract: Guadeloupean archipelago must reach energy autonomy in 2030 and include at least 50% of renewables in 2020, where wind and photovoltaics can play a significant role. Still, Guadeloupe gathers a lot of landscapes having great impact on wind and solar resource. Study of three 10-years database and one 5-year database locates a nocturnal radiative layer above the airport meteorological station, drastically limiting the wind potential there, and gives all the irradiation components (monthly sums) and therefore key parameters for photovoltaic energy yield. This paper also points out the underestimation of Linke turbidity coefficient in the airport station with Solar Radiation Database (SoDa), compared to ground-based determination, and calculates the value of this coefficient for three stations across Guadeloupe. All those parameters are discussed, as being of importance to make fair predictions of statistical relationships involving preliminary assessment and modeling of wind and solar energy systems. These results can then be used in neighboring countries, Guadeloupe having various meteorological conditions retrieved in Caribbean
-
Use of meteorological information in the risk analysis of a mixed wind farm and solar
Mengelkamp, H.-T.; Bendel, D.
2010-09-01
Use of meteorological information in the risk analysis of a mixed wind farm and solar power plant portfolio H.-T. Mengelkamp*,** , D. Bendel** *GKSS Research Center Geesthacht GmbH **anemos Gesellschaft für Umweltmeteorologie mbH The renewable energy industry has rapidly developed during the last two decades and so have the needs for high quality comprehensive meteorological services. It is, however, only recently that international financial institutions bundle wind farms and solar power plants and offer shares in these aggregate portfolios. The monetary value of a mixed wind farm and solar power plant portfolio is determined by legal and technical aspects, the expected annual energy production of each wind farm and solar power plant and the associated uncertainty of the energy yield estimation or the investment risk. Building an aggregate portfolio will reduce the overall uncertainty through diversification in contrast to the single wind farm/solar power plant energy yield uncertainty. This is similar to equity funds based on a variety of companies or products. Meteorological aspects contribute to the diversification in various ways. There is the uncertainty in the estimation of the expected long-term mean energy production of the wind and solar power plants. Different components of uncertainty have to be considered depending on whether the power plant is already in operation or in the planning phase. The uncertainty related to a wind farm in the planning phase comprises the methodology of the wind potential estimation and the uncertainty of the site specific wind turbine power curve as well as the uncertainty of the wind farm effect calculation. The uncertainty related to a solar power plant in the pre-operational phase comprises the uncertainty of the radiation data base and that of the performance curve. The long-term mean annual energy yield of operational wind farms and solar power plants is estimated on the basis of the actual energy production and it
-
Multicriteria GIS modeling of wind and solar farms in Colorado
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Janke, Jason R. [Metropolitan State College of Denver, Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, CB 22 P.O. Box 173362-22, Denver, CO 80217-3362 (United States)
2010-10-15
The majority of electricity and heat in Colorado comes from coal and natural gas; however, renewable energy sources will play an integral role in the state's energy future. Colorado is the 11th windiest state and has more than 250 sunny days per year. The objectives of this research are to: 1) determine which landcover classes are affiliated with high wind and solar potential; and 2) identify areas that are suitable for wind and solar farms using multicriteria GIS modelling techniques. Renewable potential (NREL wind speed measurements at 50 m above the ground and NREL annual insolation data), landcover, population density, federal lands, and distance to roads, transmission lines, and cities were reclassified according to their suitability. Each was assigned weights based on their relative importance to one another. Superb wind classes are located in high alpine areas. Unfortunately, these areas are not suitable for large-scale wind farm development due to their inaccessibility and location within a sensitive ecosystem. Federal lands have low wind potential. According to the GIS model, ideal areas for wind farm development are located in northeastern Colorado. About 41 850 km{sup 2} of the state has model scores that are in the 90-100% range. Although annual solar radiation varies slightly, inter-mountain areas receive the most insolation. As far as federal lands, Indian reservations have the greatest solar input. The GIS model indicates that ideal areas for solar development are located in northwestern Colorado and east of Denver. Only 191 km{sup 2} of the state had model scores that were in the 90-100% range. These results suggest that the variables used in this analysis have more of an effect at eliminating non-suitable areas for large-scale solar farms; a greater area exists for suitable wind farms. However, given the statewide high insolation values with minimal variance, solar projects may be better suited for small-scale residential or commercial
-
The Solar Wind as a Turbulence Laboratory
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Vincenzo Carbone
2013-05-01
Full Text Available In this review we will focus on a topic of fundamental importance for both astrophysics and plasma physics, namely the occurrence of large-amplitude low-frequency fluctuations of the fields that describe the plasma state. This subject will be treated within the context of the expanding solar wind and the most meaningful advances in this research field will be reported emphasizing the results obtained in the past decade or so. As a matter of fact, Helios inner heliosphere and Ulysses' high latitude observations, recent multi-spacecrafts measurements in the solar wind (Cluster four satellites and new numerical approaches to the problem, based on the dynamics of complex systems, brought new important insights which helped to better understand how turbulent fluctuations behave in the solar wind. In particular, numerical simulations within the realm of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD turbulence theory unraveled what kind of physical mechanisms are at the basis of turbulence generation and energy transfer across the spectral domain of the fluctuations. In other words, the advances reached in these past years in the investigation of solar wind turbulence now offer a rather complete picture of the phenomenological aspect of the problem to be tentatively presented in a rather organic way.
-
Wind energy, status and opportunities
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Van Wijk, A.
1994-01-01
Wind energy is diffuse but was widely used before the industrial revolution. The first oil crisis triggered renewed interest in wind energy technology in remote areas. Winds develop when solar radiation reaches the earth's highly varied surface unevenly, creating temperature density and pressure differences. The earth's atmosphere has to circulate to transport heat from the tropics towards the poles. On a global scale, these atmospheric currents work as an immense energy transfer medium. Three main applications can be distinguished: wind pumps, off-grid applications and grid-connected applications. The total generating costs for wind turbine systems are determined by total investments costs, the life time, the operating and maintenance costs, the wind regime (the wind energy potential is proportional to v 3 where v is the wind speed), the efficiency and availability of the wind turbine. The main gains are achieved as a result of improved reliability. The optimum size of a wind turbine depends on the wind speed, the wind turbine costs, the construction costs, the environmental impact and the social costs. The value of wind energy depends on the application that is made of the energy generated and on the costs of alternatives, it can be calculated by the avoided costs of damage to flora, fauna and mankind due to acid rain deposition, enhancement of the greenhouse effect. The environmental aspects are bird hindrance, noise, telecommunication interference and safety. 2 tabs., 1 fig
-
THREE-DIMENSIONAL EVOLUTION OF SOLAR WIND DURING SOLAR CYCLES 22–24
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Manoharan, P. K.
2012-01-01
This paper presents an analysis of three-dimensional evolution of solar wind density turbulence and speed at various levels of solar activity between solar cycles 22 and 24. The solar wind data used in this study have been obtained from the interplanetary scintillation (IPS) measurements made at the Ooty Radio Telescope, operating at 327 MHz. Results show that (1) on average, there was a downward trend in density turbulence from the maximum of cycle 22 to the deep minimum phase of cycle 23; (2) the scattering diameter of the corona around the Sun shrunk steadily toward the Sun, starting from 2003 to the smallest size at the deepest minimum, and it corresponded to a reduction of ∼50% in the density turbulence between the maximum and minimum phases of cycle 23; (3) the latitudinal distribution of the solar wind speed was significantly different between the minima of cycles 22 and 23. At the minimum phase of solar cycle 22, when the underlying solar magnetic field was simple and nearly dipole in nature, the high-speed streams were observed from the poles to ∼30° latitudes in both hemispheres. In contrast, in the long-decay phase of cycle 23, the sources of the high-speed wind at both poles, in accordance with the weak polar fields, occupied narrow latitude belts from poles to ∼60° latitudes. Moreover, in agreement with the large amplitude of the heliospheric current sheet, the low-speed wind prevailed in the low- and mid-latitude regions of the heliosphere. (4) At the transition phase between cycles 23 and 24, the high levels of density and density turbulence were observed close to the heliospheric equator and the low-speed solar wind extended from the equatorial-to-mid-latitude regions. The above results in comparison with Ulysses and other in situ measurements suggest that the source of the solar wind has changed globally, with the important implication that the supply of mass and energy from the Sun to the interplanetary space has been significantly reduced
-
Market to facilitate wind and solar energy integration in the bulk power supply
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Milligan, Michael [National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Soeder, Lennart [Royal Inst. of Tech., Stockholm (Sweden); Holttinen, Hannele [VTT Energy, Espoo (Finland); Clark, Charlton [U.S. Department of Energy Washington, DC (United States); Pineda, Ivan [European Wind Energy Association, Brussels (Belgium); Collaboration: IEA Task 25 collaboration
2012-07-01
Wind and solar power will give rise to challenges in electricity markets regarding flexibility, capacity adequacy, and the participation of wind and solar generators to markets. Large amounts of wind power will have impacts on bulk power system markets and electricity prices. If the markets respond to increased wind power by increasing investments in low-capital-cost/high-marginal-cost power, the average price may remain in the same range. However, the experiences so far from Denmark, Germany, Spain, and Ireland are that the average market prices decreased because of wind power. This reduction in price may result in additional revenue insufficiency, which may be corrected with a capacity market; however, capacity markets are difficult to design. Further, the flexibility attributes of the capacity need to be considered. Markets facilitating wind and solar integration will include possibilities for trading close to delivery (either by shorter gate closure times or intraday markets). Time steps chosen for markets can enable more flexibility to be assessed. Experience from 5- and 10-minute markets has been encouraging. (orig.)
-
Regional variations in the health, environmental, and climate benefits of wind and solar generation
Siler-Evans, Kyle; Azevedo, Inês Lima; Morgan, M. Granger; Apt, Jay
2013-01-01
When wind or solar energy displace conventional generation, the reduction in emissions varies dramatically across the United States. Although the Southwest has the greatest solar resource, a solar panel in New Jersey displaces significantly more sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter than a panel in Arizona, resulting in 15 times more health and environmental benefits. A wind turbine in West Virginia displaces twice as much carbon dioxide as the same turbine in California. Depending on location, we estimate that the combined health, environmental, and climate benefits from wind or solar range from $10/MWh to $100/MWh, and the sites with the highest energy output do not yield the greatest social benefits in many cases. We estimate that the social benefits from existing wind farms are roughly 60% higher than the cost of the Production Tax Credit, an important federal subsidy for wind energy. However, that same investment could achieve greater health, environmental, and climate benefits if it were differentiated by region. PMID:23798431
-
Regional variations in the health, environmental, and climate benefits of wind and solar generation.
Siler-Evans, Kyle; Azevedo, Inês Lima; Morgan, M Granger; Apt, Jay
2013-07-16
When wind or solar energy displace conventional generation, the reduction in emissions varies dramatically across the United States. Although the Southwest has the greatest solar resource, a solar panel in New Jersey displaces significantly more sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter than a panel in Arizona, resulting in 15 times more health and environmental benefits. A wind turbine in West Virginia displaces twice as much carbon dioxide as the same turbine in California. Depending on location, we estimate that the combined health, environmental, and climate benefits from wind or solar range from $10/MWh to $100/MWh, and the sites with the highest energy output do not yield the greatest social benefits in many cases. We estimate that the social benefits from existing wind farms are roughly 60% higher than the cost of the Production Tax Credit, an important federal subsidy for wind energy. However, that same investment could achieve greater health, environmental, and climate benefits if it were differentiated by region.
-
Johnson Space Center's Solar and Wind-Based Renewable Energy System
Vasquez, A.; Ewert, M.; Rowlands, J.; Post, K.
2009-01-01
The NASA Johnson Space Center (JSC) in Houston, Texas has a Sustainability Partnership team that seeks ways for earth-based sustainability practices to also benefit space exploration research. A renewable energy gathering system was installed in 2007 at the JSC Child Care Center (CCC) which also offers a potential test bed for space exploration power generation and remote monitoring and control concepts. The system comprises: 1) several different types of photovoltaic panels (29 kW), 2) two wind-turbines (3.6 kW total), and 3) one roof-mounted solar thermal water heater and tank. A tie to the JSC local electrical grid was provided to accommodate excess power. The total first year electrical energy production was 53 megawatt-hours. A web-based real-time metering system collects and reports system performance and weather data. Improvements in areas of the CCC that were detected during subsequent energy analyses and some concepts for future efforts are also presented.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Huiming Zhang
2015-12-01
Full Text Available The effectiveness of subsidies in improving the performance of renewable energy firms has aroused significant research attention in recent years. As subsidy modes may affect corporate financial performance,we have chosen companies specializing in wind and solar energy in the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock markets as samples.The relationships between the subsidy modes and financial performance of these two types of companies are investigated with a panel data model. Results of the total sample indicate that both indirect and non-innovative subsidy have significant effects on the financial performance of renewable energy companies. The regressive coefficient of the former,however, is a negative value, which illustrates that taxation, bonus, and other market-based mechanisms impair corporate profitability. Moreover, the influence of innovative subsidy is weak, which means that the subsidy used for research and development, technical demonstration, and other innovations of renewable energy enterprises have failed to effectively enhance corporate financial performance. In terms of sub-industries, the direct subsidy for wind energy companies has achieved a significant effect. Incomparison, the indirect subsidy and innovative subsidy acquired by solar energy companies have notably reduced corporate profitability. Thissuggests an urgent reform of subsidy policy for this industry is needed. The government should consider differences in the effects subsidies have for wind and solar energy companies when improving subsidy policy. In addition, market-based subsidy mechanisms should be perfected, and the structure of innovative subsidies should be ameliorated.
-
Solar Spots - Activities to Introduce Solar Energy into the K-8 Curricula.
Longe, Karen M.; McClelland, Michael J.
Following an introduction to solar technology which reviews solar heating and cooling, passive solar systems (direct gain systems, thermal storage walls, sun spaces, roof ponds, and convection loops), active solar systems, solar electricity (photovoltaic and solar thermal conversion systems), wind energy, and biomass, activities to introduce solar…
-
2012-08-13
... Ranch II, LLC; Bethel Wind Energy LLC; Rippey Wind Energy LLC; Pacific Wind, LLC; Colorado Highlands Wind, LLC; Shooting Star Wind Project, LLC; Notice of Effectiveness of Exempt Wholesale Generator or... DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY Federal Energy Regulatory Commission [Docket Nos. EG12-63-000; EG12-64-000...
-
Characteristics of Solar Wind Density Depletions During Solar Cycles 23 and 24
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Keunchan Park
2017-06-01
Full Text Available Solar wind density depletions are phenomena that solar wind density is rapidly decreased and keep the state. They are generally believed to be caused by the interplanetary (IP shocks. However, there are other cases that are hardly associated with IP shocks. We set up a hypothesis for this phenomenon and analyze this study. We have collected the solar wind parameters such as density, speed and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF data related to the solar wind density depletion events during the period from 1996 to 2013 that are obtained with the advanced composition explorer (ACE and the Wind satellite. We also calculate two pressures (magnetic, dynamic and analyze the relation with density depletion. As a result, we found total 53 events and the most these phenomena’s sources caused by IP shock are interplanetary coronal mass ejection (ICME. We also found that solar wind density depletions are scarcely related with IP shock’s parameters. The solar wind density is correlated with solar wind dynamic pressure within density depletion. However, the solar wind density has an little anti-correlation with IMF strength during all events of solar wind density depletion, regardless of the presence of IP shocks. Additionally, In 47 events of IP shocks, we find 6 events that show a feature of blast wave. The quantities of IP shocks are weaker than blast wave from the Sun, they are declined in a short time after increasing rapidly. We thus argue that IMF strength or dynamic pressure are an important factor in understanding the nature of solar wind density depletion. Since IMF strength and solar wind speed varies with solar cycle, we will also investigate the characteristics of solar wind density depletion events in different phases of solar cycle as an additional clue to their physical nature.
-
Western Wind and Solar Integration Study Phase 3 – Frequency Response and Transient Stability
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Miller, N. W. [GE Energy Management, Schenectady, NY (United States); Shao, M. [GE Energy Management, Schenectady, NY (United States); Pajic, S. [GE Energy Management, Schenectady, NY (United States); D' Aquila, R. [GE Energy Management, Schenectady, NY (United States)
2014-12-01
Power system operators and utilities worldwide have concerns about the impact of high-penetration wind and solar generation on electric grid reliability (EirGrid 2011b, Hydro-Quebec 2006, ERCOT 2010). The stability of North American grids under these conditions is a particular concern and possible impediment to reaching future renewable energy goals. Phase 3 of the Western Wind and Solar Integration Study (WWSIS-3) considers a 33% wind and solar annual energy penetration level that results in substantial changes to the characteristics of the bulk power system, including different power flow patterns, different commitment and dispatch of existing synchronous generation, and different dynamic behavior of wind and solar generation. WWSIS-3 evaluates two specific aspects of fundamental frequency system stability: frequency response and transient stability.
-
The AMPTE program's contribution to studies of the solar wind-magnetosphere-ionosphere interaction
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sibeck, D.G.
1990-01-01
The Active Magnetospheric Particle Tracer Explorers (AMPTE) program provided important information on the behavior of clouds of plasma artificially injected into the solar wind and the earth's magnetosphere. Now that the releases are over, data from the satellites are being analyzed to investigate the processes by which the ambient solar wind mass, momentum, and energy are transferred to the magnetosphere. Work in progress at APL indicates that the solar wind is much more inhomogeneous than previously believed, that the solar wind constantly buffets the magnetosphere, and that ground observers may remotely sense these interactions as geomagnetic pulsations. 8 refs
-
The role of solar and wind energy in sustainable development of the Adriatic Marco region in Croatia
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hrastnik, B.
1999-01-01
Aggregated energy demand in the Adriatic region, as well as the specific demand of individual sectors like industry, tourism, residential and commercial sector and agriculture has been assessed. Seasonal and daily load characteristics of the thermal and electric energy consumption in the Adriatic macro-region, as applied for heating, cooling and electrical appliances are discussed. Optimal mix of energy carrier (fossil and renewable) covering thermal and electric demand in the region is proposed. It has been shown that present regional energy mix, particularly for thermal applications based on electric energy, can be modified in favor of other energy carriers like LPG, LNG, hydropower, solar and wind energy, which are more appropriate for the sustainable development of the region. The expected market penetration of flat plate collectors, power plants with line focusing collectors, wind parks, photovoltaic power plants (off grid and grid connected) and passive use of solar radiation in commercial and residential buildings is given in the outlines. Based on the low energy consumption and seasonal/daily load characteristics, latest by the year 2050, it could be expected that renewables, at least for a number of Adriatic islands, could by nearly 100% substitute the present use of fossil sources, supplying electricity and thermal energy. (author)
-
Wind energy in Africa; L'energie eolienne en Afrique
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kone, A. [Moncton Univ., NB (Canada)
2008-04-15
This article discussed the opportunities that wind energy technology can bring to developing countries in Africa. Solar, hydro and wind energy along with biofuels are among the renewable energy sources being used in Africa, although wind energy is not being used to its potential due to a lack of financial means; constraints in regulatory legislation; lack of structure; lack of knowledge concerning wind energy; and the lack of competent human resources for the installation and management of wind turbines. Technical barriers also exist, such as the lack of interconnection networks and the already existing facilities for power generation. According to a 2004 Canadian study, the greatest potential for wind energy development lies in the northern part of Africa followed by regions in the east, west and south of the continent. Morocco and Tunisia have established regulations regarding wind energy development. Countries such as Algeria and Egypt, which have abundant fossil fuel, would turn to wind energy from an environmental standpoint. The countries of Djibouti, Lesotho, Tchad, Seychelles, Mauritius rely on other forms of renewable energy, including hydro, geothermal, photovoltaic and biofuels. It was concluded that the future of wind energy relies on regional cooperation, technology transfer and subsidies from industrialized nations. 1 fig.
-
Estimates of the price of hydrogen as a medium for wind and solar sources
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bockris, John O'M.; Veziroglu, T. Nejat
2007-01-01
The rejection of hydrogen as a solution to global warming by becoming the medium of wind and solar was made when gasoline was priced at $1/gallon. From wind, H 2 would now cost (by electrolysis of water and steam) less than $3 for an amount equivalent in energy to that in a gallon of gasoline ('equivalent'). From solar photovoltaics (pv), H 2 would be sinking in price between $8 toward $5 equivalent as the efficiency of solar pv increases toward 20%. Solar thermal's present prices offer about one-half the solar pv prices. Prediction of the maximum of the delivery rate of world oil is [Laherre's Oil Production Forecast, 1950-2150. Reprinted with permission from correspondence with William Horvath, U.S. Department of Energy, March 29, 2001] 2010. Future energy sources will develop inexhaustible energies from wind, solar, geothermal, tidal, and wave sources. The common media will be hydrogen and electricity. These sources yield energy at around one-half the cost of nuclear fission. Growing corn to make alcohol involves a net loss of energy and need for a heating mechanism. It may increase the Greenhouse. (author)
-
Estimating the Quantity of Wind and Solar Required To Displace Storage-Induced Emissions.
Hittinger, Eric; Azevedo, Inês M L
2017-11-07
The variable and nondispatchable nature of wind and solar generation has been driving interest in energy storage as an enabling low-carbon technology that can help spur large-scale adoption of renewables. However, prior work has shown that adding energy storage alone for energy arbitrage in electricity systems across the U.S. routinely increases system emissions. While adding wind or solar reduces electricity system emissions, the emissions effect of both renewable generation and energy storage varies by location. In this work, we apply a marginal emissions approach to determine the net system CO 2 emissions of colocated or electrically proximate wind/storage and solar/storage facilities across the U.S. and determine the amount of renewable energy required to offset the CO 2 emissions resulting from operation of new energy storage. We find that it takes between 0.03 MW (Montana) and 4 MW (Michigan) of wind and between 0.25 MW (Alabama) and 17 MW (Michigan) of solar to offset the emissions from a 25 MW/100 MWh storage device, depending on location and operational mode. Systems with a realistic combination of renewables and storage will result in net emissions reductions compared with a grid without those systems, but the anticipated reductions are lower than a renewable-only addition.
-
Dependence of Substorm Evolution on Solar Wind Condition: Simulation Study
Kamiyoshikawa, N.; Ebihara, Y.; Tanaka, T.
2017-12-01
A substorm is one of the remarkable disturbances occurring in the magnetosphere. It is known that the substorm occurs frequently when IMF is southward and solar wind speed is high. However, the physical process to determine substorm scale is not well understood. We reproduced substorms by using global MHD simulation, calculated auroral electrojet (ionospheric Hall current) flowing in the ionosphere to investigate the dependence of substorm evolution on solar wind condition. Solar wind speed of 372.4 km/s and IMF Bz of 5.0 nT were imposed to, obtain the quasi-stationary state of the magnetosphere. Then the solar wind parameters were changed as a step function. For the solar wind speed, we assumed 300 km/s, 500 km/s and 700 km/s. For IMF, we assumed -1.0 nT, -3.0 nT, -5.0 nT, -7.0 nT and -9.0 nT. In total, 15 simulation runs were performed. In order to objectively evaluate the substorm, the onset was identified with the method based on the one proposed by Newell et al. (2011). This method uses the SME index that is an extension of the AE index. In this study, the geomagnetic variation induced by the ionospheric Hall current was obtained every 1 degree from the magnetic latitude 40 degrees to 80 degrees and in every 0.5 hours in the magnetic region direction. The upper and the lower envelopes of the geomagnetic variation are regarded as SMU index and SML index, respectively. The larger the solar wind speed, the larger the southward IMF, the more the onset tends to be faster. This tendency is consistent with the onset occurrence probability indicated by Newell et al. (2016). Moreover, the minimum value of the SML index within 30 minutes from the beginning of the onset tends to decrease with the solar wind speed and the magnitude of the southward IMF. A rapid decrease of the SML index can be explained by a rapid increase in the field-aligned currents flowing in and out of the nightside ionosphere. This means that electromagnetic energies flowing into the ionosphere
-
Solar wind stagnation near comets
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Galeev, A.A.; Cravens, T.E.; Gombosi, T.I.
1983-03-01
The nature of the solar wind flow near comets is examined analytically. In particular, the typical values for the stagnation pressure and magnetic barrier strength are estimated, taking into account the magnetic field line tension and the charge exchange cooling of the mass loaded solar wind. Knowledge of the strength of the magnetic barrier is required in order to determine the location of the contact discontinuity which separates the contaminated solar wind plasma and the outflowing plasma of the cometary ionosphere. (author)
-
Jolitz, Rebecca; Dong, Chuanfei; Lee, Christina; Lillis, Rob; Brain, David; Curry, Shannon; Halekas, Jasper; Bougher, Stephen W.; Jakosky, Bruce
2017-10-01
Precipitating energetic particles ionize and excite planetary atmospheres, increasing electron content and producing aurora. At Mars, the solar wind and solar energetic particles (SEPs) can precipitate directly into the atmosphere because solar wind protons can charge exchange to become neutral and pass the magnetosheath, and SEPs are sufficiently energetic to cross the magnetosheath unchanged. We will compare ionization and Lyman alpha emission rates for solar wind and SEP protons during nominal solar activity and a CME shock front impact event on May 16 2016. We will use the Atmospheric Scattering of Protons and Energetic Neutrals (ASPEN) model to compare excitation and ionization rates by SEPs and solar wind protons currently measured by the SWIA (Solar Wind Ion Analyzer) and SEP instruments aboard the MAVEN spacecraft. Results will help quantify how SEP and solar wind protons influence atmospheric energy deposition during solar minimum.
-
The solar wind-magentosphere energy coupling and magnetospheric disturbances
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Akasofu, S.I.
1980-01-01
The recent finding of the solar wind-magnetosphere energy coupling function epsilon has advanced significantly our understanding of magnetosphere disturbances. It is shown that the magnetosphere-ionosphere coupling system responds somewhat differently to three different input energy flux levels of epsilon. As epsilon increases from 17 erg s -1 to >10 19 erg s -1 , typical responses of the magnetosphere-ionosphere coupling system are: (1) epsilon 17 erg s -1 : an enhancement of the Ssub(q)sup(p), etc. (2) epsilon approximately 10 18 erg s -1 : substorm onset. (3) 10 18 erg s -1 19 erg s -1 : a typical substorm. (4) epsilon >10 19 erg s -1 : an abnormal growth of the ring current belt, resulting in a magnetospheric storm. It is stressed that the magnetospheric substorm results as a direct response of the magnetosphere to a rise and fall of epsilon above approximately 10 18 erg s -1 , so that it is not caused by a sudden conversion of magnetic energy accumulated prior to substorm onset. The variety of the development of the main phase of geomagnetic storms is also primarily controlled by epsilon. (author)
-
Astrospheres and Solar-like Stellar Winds
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wood Brian E.
2004-07-01
Full Text Available Stellar analogs for the solar wind have proven to be frustratingly difficult to detect directly. However, these stellar winds can be studied indirectly by observing the interaction regions carved out by the collisions between these winds and the interstellar medium (ISM. These interaction regions are called "astrospheres", analogous to the "heliosphere" surrounding the Sun. The heliosphere and astrospheres contain a population of hydrogen heated by charge exchange processes that can produce enough H I Ly alpha absorption to be detectable in UV spectra of nearby stars from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST. The amount of astrospheric absorption is a diagnostic for the strength of the stellar wind, so these observations have provided the first measurements of solar-like stellar winds. Results from these stellar wind studies and their implications for our understanding of the solar wind are reviewed here. Of particular interest are results concerning the past history of the solar wind and its impact on planetary atmospheres.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ifaei, Pouya; Karbassi, Abdolreza; Jacome, Gabriel; Yoo, ChangKyoo
2017-01-01
Highlights: • Proposing DaSOSaCa flowchart as a novel hybrid solar/wind assessment approach. • Calculating four key parameters to generate synthetic wind hourly data for Iran. • Proposing technical and economic hybrid solar/wind GIS maps of Iran. • Revising renewable energies management plans of Iran by macroeconomic evaluation. - Abstract: In the current study, an algorithm-based data processing, sizing, optimization, sensitivity analysis and clustering approach (DaSOSaCa) is proposed as an efficient simultaneous solar/wind assessment methodology. Accordingly, data processing is performed to obtain reliable high quality meteorological data among various datasets, which are used for hybrid photovoltaic/wind turbine/storage/converter system optimal design for consequent sites in a large region. The optimal hybrid systems are consequently simulated to meet hourly power demand in various sites. The solar/wind fraction and net present cost of the systems are then used as the technical and economic clustering variables, respectively. The clustering results are finally used as input to obtain novel hybrid solar/wind GIS maps. Iran is selected as the case study to validate the proposed methodology and detail its applicability. Ten minute annual global horizontal radiation, wind speed, and temperature data are analyzed, and the optimal, robust hybrid systems are simulated for various sites in order to classify the country. The generated GIS maps show that Iran can be efficiently clustered into four technical and five economic clusters under optimal conditions. The clustering results prove that Iran is mainly a solar country with approximately 74% solar power fraction under optimum conditions. A macroeconomic evaluation using DaSOSaCa also reveals that the nominal discount rate is recommended to be greater than 20% considering the current economic situation for the renewable energy sector in Iran. An environmental analysis results show that an average 106.68 tonCO 2
-
Heating of Solar Wind Ions via Cyclotron Resonance
Navarro, R.; Moya, P. S.; Figueroa-Vinas, A.; Munoz, V.; Valdivia, J. A.
2017-12-01
Remote and in situ observations in the solar wind show that ion and electron velocity distributions persistently deviate from thermal equilibrium in the form of relative streaming between species components, temperature anisotropy, etc. These non-thermal features represent a source of free energy for the excitation of kinetic instabilities and fluctuations in the plasma. In this regard, it is believed that plasma particles can be heated, through a second order Fermi acceleration process, by multiple resonances with unstable counter-propagating field-aligned Ion-cyclotron waves. For multi-species plasmas, several collective wave modes participate in this process. In this work, we test this model by studying the percentage of ions that resonate with the waves modes described by the proper kinetic multi-species dispersion relation in a solar-wind-like plasma composed of electrons, protons, and alpha particles. Numerical results are compared with WIND spacecraft data to test its relevance for the existence of thresholds for the preferential perpendicular heating of He+2 ions as observed in the solar wind fast streams.
-
Feasibility study for a standalone solar-wind-based hybrid energy system for application in Ethiopia
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bekele, Getachew; Palm, Bjoern
2010-01-01
The aim of this paper is to investigate the possibility of supplying electricity from a solar-wind hybrid system to a remotely located model community detached from the main electricity grid in Ethiopia. The wind energy potential of four typical locations has been assessed in a previous article. The solar potential has also been investigated and the results are presented in detail in an accompanying article awaiting publication. For one of the sites, Addis Ababa, the results of the investigation are given here in detail. For the other sites, the results are given as sensitivity diagrams only. Based on the findings of the studies into energy potential, a feasibility study has been carried out on how to supply electricity to a model community of 200 families, which comprises 1000 people in total. The community is equipped with a community school and a health post. The electric load consists of both primary and deferrable types and comprises lighting, water pumps, radio receivers, and some clinical equipment. A software tool, Hybrid Optimization Model for Electric Renewables (HOMER) is used for the analysis. The result of the analysis is a list of feasible power supply systems, sorted according to their net present cost. Furthermore, sensitivity diagrams, showing the influence of wind speeds, PV costs, and diesel prices on the optimum solutions are also provided. (author)
-
Feasibility study for a standalone solar-wind-based hybrid energy system for application in Ethiopia
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bekele, Getachew; Palm, Bjoern [Department of Energy Technology, KTH, Stockholm (Sweden)
2010-02-15
The aim of this paper is to investigate the possibility of supplying electricity from a solar-wind hybrid system to a remotely located model community detached from the main electricity grid in Ethiopia. The wind energy potential of four typical locations has been assessed in a previous article. The solar potential has also been investigated and the results are presented in detail in an accompanying article awaiting publication. For one of the sites, Addis Ababa, the results of the investigation are given here in detail. For the other sites, the results are given as sensitivity diagrams only. Based on the findings of the studies into energy potential, a feasibility study has been carried out on how to supply electricity to a model community of 200 families, which comprises 1000 people in total. The community is equipped with a community school and a health post. The electric load consists of both primary and deferrable types and comprises lighting, water pumps, radio receivers, and some clinical equipment. A software tool, Hybrid Optimization Model for Electric Renewables (HOMER) is used for the analysis. The result of the analysis is a list of feasible power supply systems, sorted according to their net present cost. Furthermore, sensitivity diagrams, showing the influence of wind speeds, PV costs, and diesel prices on the optimum solutions are also provided. (author)
-
Bruno, Roberto
2016-01-01
This book provides an overview of solar wind turbulence from both the theoretical and observational perspective. It argues that the interplanetary medium offers the best opportunity to directly study turbulent fluctuations in collisionless plasmas. In fact, during expansion, the solar wind evolves towards a state characterized by large-amplitude fluctuations in all observed parameters, which resembles, at least at large scales, the well-known hydrodynamic turbulence. This text starts with historical references to past observations and experiments on turbulent flows. It then introduces the Navier-Stokes equations for a magnetized plasma whose low-frequency turbulence evolution is described within the framework of the MHD approximation. It also considers the scaling of plasma and magnetic field fluctuations and the study of nonlinear energy cascades within the same framework. It reports observations of turbulence in the ecliptic and at high latitude, treating Alfvénic and compressive fluctuations separately in...
-
Control Strategy: Wind Energy Powered Variable Chiller with Thermal Ice Storage
2014-12-01
of the DOD facilities. A. RENEWABLE ENERGY The United States Department of Energy (DOE) defines renewable energy as being obtained from...include arrays of solar PV cells, solar thermal cells, wind turbines, or biogas digestors. Energy storage devices could consist of one or more of the...At Hachinohe, Japan, the Aomori Project obtains up to 100 kW of power from PV cells and wind turbines (WTs). The New Energy and Industrial Technology
-
Solar-wind system powers mountain clean-up
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2001-03-01
By using a hybrid solar-wind system, the Japanese have tackled the problem of human excrement left by tourists in mountain lodges and in natural parks by installing flush toilets and wastewater treatment plants. The solar array (4.9 kW{sub p}) consists of 76 panels of single-crystal photovoltaic cells each with an output of 64 Wp. The wind turbines (total capacity 2.1 kW) operate whatever the wind strength or direction. Storage batteries prevent any dip in power which would result from low ambient temperatures. The system can still function at temperatures as low as minus 25{sup o}C. Between November and April when the lodge is closed, the waste is decomposed biologically. A block diagram shows the elements of the system, and details of cost are given. The system won the 1999 New Energy Award.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
2014-04-01
After a general presentation of the framework of support to renewable energies and co-generation (purchasing obligation, tendering, support funding), of the missions of the CRE (Commission for Energy Regulation) within the frame of the purchasing obligation, and of the methodology adopted for this analysis, this document reports an analysis of production costs for three different renewable energy sectors: ground-based wind energy, biomass energy, and solar photovoltaic energy. For each of them, the report recalls the context (conditions of purchasing obligation, winning bid installations, installed fleet in France at the end of 2012), indicates the installations taken into consideration in this study, analyses the installation costs and funding (investment costs, exploitation and maintenance costs, project funding, production costs), and assesses the profitability in terms of capital and for stakeholders
-
Jou, H. L.; Wu, J. C.; Lin, J. H.; Su, W. N.; Wu, T. S.; Lin, Y. T.
2017-11-01
The operation strategy for a small-capacity grid-tied DC-coupling power converter interface (GDPCI) integrating wind energy, solar energy and battery energy storage is proposed. The GDPCI is composed of a wind generator, a solar module set a battery bank, a boost DC-DC power converter (DDPC), a bidirectional DDPC power converter, an AC-DC power converter (ADPC) and a five-level DC-AC inverter (DAI). A solar module set, a wind generator and a battery bank are coupled to the common DC bus through the boost DDPC, the ADPC and the bidirectional DDPC, respectively. For verifying the performance of the GDPCI under different operation modes, computer simulation is carried out by PSIM.
-
Solar energy – new photovoltaic technologies
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Sommer-Larsen, Peter
2009-01-01
Solar energy technologies directly convert sunlight into electricity and heat, or power chemical reactions that convert simple molecules into synthetic chemicals and fuels. The sun is by far the most abundant source of energy, and a sustainable society will need to rely on solar energy as one...... of its major energy sources. Solar energy is a focus point in many strategies for a sustainable energy supply. The European Commission’s Strategic Energy Plan (SET-plan) envisages a Solar Europe Initiative, where photovoltaics and concentrated solar power (CSP) supply as much power as wind mills...... in the future. Much focus is directed towards photovoltaics presently. Installation of solar cell occurs at an unprecedented pace and the expectations of the photovoltaics industry are high: a total PV capacity of 40 GW by 2012 as reported by a recent study. The talk progresses from general solar energy topics...
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hallerberg, Sarah [Chemnitz University of Technology (Germany); Ruzmaikin, Alexander; Feynman, Joan [Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology (United States)
2011-07-01
Shock waves in the solar wind associated with solar coronal mass ejections produce fluxes of high-energy protons and ions with energies larger than 10 MeV. These fluxes present a danger to humans and electronic equipment in space, and also endanger passengers of over-pole air flights. The approaches that have been exploited for the prediction of high-energy particle events so far consist in training artificial neural networks on catalogues of events. Our approach towards this task is based on the identification of precursory structures in the fluxes of particles. In contrast to artificial neural networks that function as a ''black box'' transforming data into predictions, this classification approach can additionally provide information on relevant precursory events and thus might help to improve the understanding of underlying mechanisms of particle acceleration.
-
Western Wind and Solar Integration Study Phase 3A: Low Levels of Synchronous Generation
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Miller, Nicholas W. [GE Energy Management, Atlanta, GA (United States); Leonardi, Bruno [GE Energy Management, Atlanta, GA (United States); D' Aquila, Robert [GE Energy Management, Atlanta, GA (United States); Clark, Kara [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
2015-11-17
The stability of the North American electric power grids under conditions of high penetrations of wind and solar is a significant concern and possible impediment to reaching renewable energy goals. The 33% wind and solar annual energy penetration considered in this study results in substantial changes to the characteristics of the bulk power system. This includes different power flow patterns, different commitment and dispatch of existing synchronous generation, and different dynamic behavior from wind and solar generation. The Western Wind and Solar Integration Study (WWSIS), sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy, is one of the largest regional solar and wind integration studies to date. In multiple phases, it has explored different aspects of the question: Can we integrate large amounts of wind and solar energy into the electric power system of the West? The work reported here focused on the impact of low levels of synchronous generation on the transient stability performance in one part of the region in which wind generation has displaced synchronous thermal generation under highly stressed, weak system conditions. It is essentially an extension of WWSIS-3. Transient stability, the ability of the power system to maintain synchronism among all elements following disturbances, is a major constraint on operations in many grids, including the western U.S. and Texas systems. These constraints primarily concern the performance of the large-scale bulk power system. But grid-wide stability concerns with high penetrations of wind and solar are still not thoroughly understood. This work focuses on 'traditional' fundamental frequency stability issues, such as maintaining synchronism, frequency, and voltage. The objectives of this study are to better understand the implications of low levels of synchronous generation and a weak grid on overall system performance by: 1) Investigating the Western Interconnection under conditions of both high renewable
-
On the solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere coupling: AMPTE/CCE particle data and the AE indices
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Daglis, I.A.; Wilken, B.; Sarris, E.T.; Kremser, G.
1992-01-01
We present a statistical study of the substorm particle energization in terms of the energy density of the major magnetospheric ions (H + , O + , He ++ , He + ). The correlation between energy density during substorm expansion phase and the auroral indices (AE, AU, Al) is examined and interpreted. Most distinct result is that the ionospheric origin O + energy density correlate remarkable well with the AE index, while the solar wind origin He ++ energy density does not correlate at all with AE. Mixed origin H + and He + ions exhibit an intermediate behavior. Furthermore, the O + energy density correlates very well with the pre-onset AU index level, while there is no correlation with the pre-onset AL index. The results are interpreted as a result of solar wind. The results are interpreted as a result of solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere coupling through the internal magnetospheric dynamo: the ionosphere responds to the increased activity of the internal dynamo (which is due to the high solar wind input) and influences substorm dynamics by feeding the near-Earth magnetotail with energetic ionospheric ions during late growth phase and expansion phase
-
Shezan, S. K. A.; Saidur, R.; Hossain, A.; Chong, W. T.; Kibria, M. A.
2015-09-01
A large number of populations of the world live in rural or remote areas those are geographically isolated. Power supply and uninterrupted fuel transportation to produce electrical power for these remote areas poses a great challenge. Using renewable energy in hybrid energy system might be a pathway to solve this problem. Malaysia is a large hilly land with the gift of renewable energy resources. There is a good chance to utilize these renewable resources to produce electrical power and to limit the dependency on the fossil fuel as well as reduce the carbon emissions. In this perspective, a research is carried out to analyze the performance of a solar-wind-diesel-battery hybrid energy system for a remote area named “KLIA Sepang station” in the state of Selangor, Malaysia. In this study, a 56 kW hybrid energy system has been proposed that is capable to support more than 50 households and 6 shops in that area. Real time field data of solar radiation and wind speed is used for the simulation and optimization of operations using “Homer” renewable energy software. The proposed system can reduce CO2 emission by about 16 tons per year compared to diesel generator only. In the same time the Cost of energy (COE) of the optimized system is USD 5.126/kWh.The proposed hybrid energy system might be applicable for other parts of the world where the climate conditions are similar.
-
WIND SPEED AND ENERGY POTENTIAL ANALYSES
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. TOKGÖZLÜ
2013-01-01
Full Text Available This paper provides a case study on application of wavelet techniques to analyze wind speed and energy (renewable and environmental friendly energy. Solar and wind are main sources of energy that allows farmers to have the potential for transferring kinetic energy captured by the wind mill for pumping water, drying crops, heating systems of green houses, rural electrification's or cooking. Larger wind turbines (over 1 MW can pump enough water for small-scale irrigation. This study tried to initiate data gathering process for wavelet analyses, different scale effects and their role on wind speed and direction variations. The wind data gathering system is mounted at latitudes: 37° 50" N; longitude 30° 33" E and height: 1200 m above mean sea level at a hill near Süleyman Demirel University campus. 10 minutes average values of two levels wind speed and direction (10m and 30m above ground level have been recorded by a data logger between July 2001 and February 2002. Wind speed values changed between the range of 0 m/s and 54 m/s. Annual mean speed value is 4.5 m/s at 10 m ground level. Prevalent wind
-
Photovoltaic Solar Energy : From Fundamentals to Applications
Reinders, Angelina H.M.E.; Verlinden, P.J.; van Sark, W.G.J.H.M.; Freundlich, A.
2016-01-01
Solar PV is now the third most important renewable energy source, after hydro and wind power, in terms of global installed capacity. Bringing together the expertise of international PV specialists Photovoltaic Solar Energy: From Fundamentals to Applications provides a comprehensive and up-to-date
-
A.B. Dorsman (Andre); A. Khoshrou (Abdolrahman); E.J. Pauwels (Eric)
2016-01-01
textabstractGermany is actively pursuing a switch from fossil fuel to renewables, the so-called Energiewende (energy transition). Due to the fact that the supply of wind and solar energy is less predictable than the supply of fossil fuel, stabilizing the grid has become more challenging. On sunny
-
Surface meteorology and Solar Energy
Stackhouse, Paul W. (Principal Investigator)
The Release 5.1 Surface meteorology and Solar Energy (SSE) data contains parameters formulated for assessing and designing renewable energy systems. Parameters fall under 11 categories including: Solar cooking, solar thermal applications, solar geometry, tilted solar panels, energy storage systems, surplus product storage systems, cloud information, temperature, wind, other meteorological factors, and supporting information. This latest release contains new parameters based on recommendations by the renewable energy industry and it is more accurate than previous releases. On-line plotting capabilities allow quick evaluation of potential renewable energy projects for any region of the world. The SSE data set is formulated from NASA satellite- and reanalysis-derived insolation and meteorological data for the 10-year period July 1983 through June 1993. Results are provided for 1 degree latitude by 1 degree longitude grid cells over the globe. Average daily and monthly measurements for 1195 World Radiation Data Centre ground sites are also available. [Mission Objectives] The SSE project contains insolation and meteorology data intended to aid in the development of renewable energy systems. Collaboration between SSE and technology industries such as the Hybrid Optimization Model for Electric Renewables ( HOMER ) may aid in designing electric power systems that employ some combination of wind turbines, photovoltaic panels, or diesel generators to produce electricity. [Temporal_Coverage: Start_Date=1983-07-01; Stop_Date=1993-06-30] [Spatial_Coverage: Southernmost_Latitude=-90; Northernmost_Latitude=90; Westernmost_Longitude=-180; Easternmost_Longitude=180].
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 20
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2011-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including the following: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research......, Renewable Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal and Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifi cally devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fi t several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind Energy Literature Survey No. 16
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2010-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers etc. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 24
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2012-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including the Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, and Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, and so on. The list is limited...... exclusively to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. For the reader to be assisted, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note...
-
Wind energy literature survey no. 10
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2008-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers etc. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 19
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2011-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy......, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively to journals...... not specifi cally devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fi t several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind Energy Literature Survey No. 14
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2009-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers etc. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind Energy Literature Survey No. 13
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2009-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including: Journal of Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy......, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems, along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively to journals...... not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list is not an endorsement...
-
Wind energy literature survey no. 8
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2008-01-01
To keep readers up-to-date in the field, each issue of Wind Energy will contain a list of relevant published articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Also note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind energy literature survey no. 18
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2010-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind energy literature survey no. 17
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2010-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers etc. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind energy literature survey no. 11
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2009-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 21
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2012-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including the following: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research......, Renewable Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers and others. The list is limited...... exclusively to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 22
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2012-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including the following: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research......, Renewable Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers and others. The list is limited...... exclusively to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion...
-
Wind Energy Literature Survey No. 15
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2010-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers etc. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 30
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2013-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy......, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively to journals...... not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list is not an endorsement...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 29
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2013-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including the following: Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research......, Renewable Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal and Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited...... exclusively to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 23
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2012-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including the Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, and Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, and so on. The list is limited...... exclusively to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. For the reader to be assisted, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 25
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2012-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy......, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers and so on. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 28
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2013-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant papers drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy......, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal and Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively to journals...... not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list is not an endorsement...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 27
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2013-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant papers drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy......, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal and Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively to journals...... not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list is not an endorsement...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 12
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2009-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant papers drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy......, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal and Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively to journals...... not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list is not an endorsement...
-
Wind Energy literature survey no. 26
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2012-01-01
As a service to readers, Wind Energy regularly conducts literature surveys and publishes lists of relevant papers drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable Energy......, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal and Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, etc. The list is limited exclusively to journals...... not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Please note that the inclusion in the list is not an endorsement...
-
Comparison of Solar and Wind Power Output and Correlation with Real-Time Pricing
Hoepfl, Kathryn E.; Compaan, Alvin D.; Solocha, Andrew
2011-03-01
This study presents a method that can be used to determine the least volatile power output of a wind and solar hybrid energy system in which wind and solar systems have the same peak power. Hourly data for wind and PV systems in Northwest Ohio are used to show that a combination of both types of sustainable energy sources produces a more stable power output and would be more valuable to the grid than either individually. This method could be used to determine the ideal ratio in any part of the country and should help convince electric utility companies to bring more renewable generation online. This study also looks at real-time market pricing and how each system (solar, wind, and hybrid) correlates with 2009 hourly pricing from the Midwest Interconnect. KEH acknowledges support from the NSF-REU grant PHY-1004649 to the Univ. of Toledo and Garland Energy Systems/Ohio Department of Development.
-
Solar Energy: Its Technologies and Applications
Auh, P. C.
1978-06-01
Solar heat, as a potential source of clean energy, is available to all of us. Extensive R and D efforts are being made to effectively utilize this renewable energy source. A variety of different technologies for utilizing solar energy have been proven to be technically feasible. Here, some of the most promising technologies and their applications are briefly described. These are: Solar Heating and Cooling of Buildings (SHACOB), Solar Thermal Energy Conversion (STC), Wind Energy Conversion (WECS), Bioconversion to Fuels (BCF), Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC), and Photovoltaic Electric Power Systems (PEPS). Special emphasis is placed on the discussion of the SHACOB technologies, since the technologies are being expeditiously developed for the near commercialization.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jacobson, Mark Z., E-mail: jacobson@stanford.ed [Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-4020 (United States); Delucchi, Mark A., E-mail: madelucchi@ucdavis.ed [Institute of Transportation Studies, University of California at Davis, Davis, CA 95616 (United States)
2011-03-15
Climate change, pollution, and energy insecurity are among the greatest problems of our time. Addressing them requires major changes in our energy infrastructure. Here, we analyze the feasibility of providing worldwide energy for all purposes (electric power, transportation, heating/cooling, etc.) from wind, water, and sunlight (WWS). In Part I, we discuss WWS energy system characteristics, current and future energy demand, availability of WWS resources, numbers of WWS devices, and area and material requirements. In Part II, we address variability, economics, and policy of WWS energy. We estimate that {approx}3,800,000 5 MW wind turbines, {approx}49,000 300 MW concentrated solar plants, {approx}40,000 300 MW solar PV power plants, {approx}1.7 billion 3 kW rooftop PV systems, {approx}5350 100 MW geothermal power plants, {approx}270 new 1300 MW hydroelectric power plants, {approx}720,000 0.75 MW wave devices, and {approx}490,000 1 MW tidal turbines can power a 2030 WWS world that uses electricity and electrolytic hydrogen for all purposes. Such a WWS infrastructure reduces world power demand by 30% and requires only {approx}0.41% and {approx}0.59% more of the world's land for footprint and spacing, respectively. We suggest producing all new energy with WWS by 2030 and replacing the pre-existing energy by 2050. Barriers to the plan are primarily social and political, not technological or economic. The energy cost in a WWS world should be similar to that today. - Research highlights: {yields} Replacing world energy with wind, water, and sun (WWS) reduces world power demand 30%. {yields} WWS for world requires only 0.41% and 0.51% more world land for footprint and spacing, respectively. {yields} Practical to provide 100% new energy with WWS by 2030 and replace existing energy by 2050.
-
PHOTOIONIZATION IN THE SOLAR WIND
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Landi, E.; Lepri, S. T., E-mail: elandi@umich.edu [Department of Climate and Space Sciences and Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (United States)
2015-10-20
In this work we investigate the effects of photoionization on the charge state composition of the solar wind. Using measured solar EUV and X-ray irradiance, the Michigan Ionization Code and a model for the fast and slow solar wind, we calculate the evolution of the charge state distribution of He, C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe with and without including photoionization for both types of wind. We find that the solar radiation has significant effects on the charge state distribution of C, N, and O, causing the ionization levels of these elements to be higher than without photoionization; differences are largest for oxygen. The ions commonly observed for elements heavier than O are much less affected, except in ICMEs where Fe ions more ionized than 16+ can also be affected by the solar radiation. We also show that the commonly used O{sup 7+}/O{sup 6+} density ratio is the most sensitive to photoionization; this sensitivity also causes the value of this ratio to depend on the phase of the solar cycle. We show that the O{sup 7+}/O{sup 6+} ratio needs to be used with caution for solar wind classification and coronal temperature estimates, and recommend the C{sup 6+}/C{sup 4+} ratio for these purposes.
-
Solar wind-magnetosphere coupling during intense magnetic storms (1978-1979)
Gonzalez, Walter D.; Gonzalez, Alicia L. C.; Tsurutani, Bruce T.; Smith, Edward J.; Tang, Frances
1989-01-01
The solar wind-magnetosphere coupling problem during intense magnetic storms was investigated for ten intense magnetic storm events occurring between August 16, 1978 to December 28, 1979. Particular attention was given to the dependence of the ring current energization on the ISEE-measured solar-wind parameters and the evolution of the ring current during the main phase of the intense storms. Several coupling functions were tested as energy input, and several sets of the ring current decay time-constant were searched for the best correlation with the Dst response. Results indicate that a large-scale magnetopause reconnection operates during an intense storm event and that the solar wind ram pressure plays an important role in the energization of the ring current.
-
The solar wind plasma density control of night-time auroral particle precipitation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. G. Vorobjev
2004-03-01
Full Text Available DMSP F6 and F7 spacecraft observations of the average electron and ion energy, and energy fluxes in different night-time precipitation regions for the whole of 1986 were used to examine the precipitation features associated with solar wind density changes. It was found that during magnetic quietness |AL|<100nT, the enhancement of average ion fluxes was observed at least two times, along with the solar wind plasma density increase from 2 to 24cm–3. More pronounced was the ion flux enhancement that occurred in the b2i–b4s and b4s–b5 regions, which are approximately corresponding to the statistical auroral oval and map to the magnetospheric plasma sheet tailward of the isotropy boundary. The average ion energy decrease of about 2–4kev was registered simultaneously with this ion flux enhancement. The results verify the occurrence of effective penetration of the solar wind plasma into the magnetospheric tail plasma sheet. Key words. Ionosphere (auroral ionosphere, particle precipitation – Magnetospheric physics (solar windmagnetosphere interaction
-
Heliospheric pick-up ions influencing thermodynamics and dynamics of the distant solar wind
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
H. J. Fahr
2002-01-01
Full Text Available Neutral interstellar H-atoms penetrate into the inner heliosphere and upon the event of ionization are converted into pick-up ions (PUIs. The magnetized solar wind flow incorporates these ions into the plasma bulk and enforces their co-motion. By nonlinear interactions with wind-entrained Alfvén waves, these ions are then processed in the comoving velocity space. The complete pick-up process is connected with forces acting back to the original solar wind ion flow, thereby decelerating and heating the solar wind plasma. As we show here, the resulting deceleration cannot be treated as a pure loading effect, but requires adequate consideration of the action of the pressure of PUI-scattered waves operating by the PUI pressure gradient. Hereby, it is important to take into proper account the stochastic acceleration which PUIs suffer from at their convection out of the inner heliosphere by quasi-linear interactions with MHD turbulences. Only then can the presently reported VOYAGER observations of solar wind decelerations and heatings in the outer heliosphere be understood in view of the most likely values of interstellar gas parameters, such as an H-atom density of 0.12 cm-3 . Solar wind protons (SWPs appear to be globally heated in their motion to larger solar distances. Ascribing the needed heat transfer to the action of suprathermal PUIs, which drive MHD waves that are partly absorbed by SWPs, in order to establish the observed SWP polytropy, we can obtain a quantitative expression for the solar wind proton pressure as a function of solar distance. This expression clearly shows the change from an adiabatic to a quasi-polytropic SWP behaviour with a decreasing polytropic index at increasing distances. This also allows one to calculate the average percentage of initial pick-up energy fed into the thermal proton energy. In a first order evaluation of this expression, we can estimate that about 10% of the initial PUI injection energy is eventually
-
Implementation Strategy for a Global Solar and Wind Atlas
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2012-01-15
In July 2009, Major Economies Forum leaders met to prepare for the COP 15 Copenhagen Conference that took place later that year. At this occasion the Major Economies Forum Global Partnership f or low carbon and climate-friendly technology was founded and Technology Action Plans (TAPs) for ten key low-carbon technologies were drafted. At that juncture Denmark, Germany and Spain took on the responsibility for drafting TAPs for Solar and Wind Energy Technologies. The TAPs were then consolidated and presented at COP 15 that would later take place in December in Copenhagen. Since then, countries that led the development of the Action Plans have started their implementation. During a first Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) in July 2010 in Washington on the invitation of Steven Chu, US Secretary of Energy, several initiatives were launched. Denmark, Germany and Spain took the lead in the implementation of the TAPs for Solar and Wind Technologies and initiated the Multilateral Working Group on Solar and Wind Energy Technologies (MWGSW). Several countries joined the working group in Washington and afterwards. In two international workshops in Bonn (June 2010) and Madrid (November 2010) and in meetings during the first CEM in Washington (July 2010) and the second CEM in Abu Dhabi (April 2011) the Multilateral Working Group made substantial progress in the two initial fields of action: (1) the Development of a Global Solar and Wind Atlas; and (2) the Development of a Long-term Strategy on Joint Capacity Building. Discussion papers on the respective topics were elaborated involving the Working Group's member countries as well as various international institutions. This led to concrete proposals for several pilot activities in both fields of action. After further specifying key elements of the suggested projects in two expert workshops in spring 2011, the Multilateral Working Group convened for a third international workshop in Copenhagen, Denmark, to discuss the project
-
Assessment of wind energy potential in China
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
Zhu Rong; Zhang De; Wang Yuedong; Xing Xuhuang; Li Zechun
2009-01-01
China wind atlas was made by numerical simulation and the wind energy potential in China was calculated. The model system for wind energy resource assessment was set up based on Canadian Wind Energy Simulating Toolkit (WEST) and the simulating method was as follows. First, the weather classes were obtained depend on meteorological data of 30 years. Then, driven by the initial meteorological field produced by each weather class, the meso-scale model ran for the distribution of wind energy resources according each weather class condition one by one. Finally, averaging all the modeling output weighted by the occurrence frequency of each weather class, the annual mean distribution of wind energy resources was worked out. Compared the simulated wind energy potential with other results from several ac-tivities and studies for wind energy resource assessment, it is found that the simulated wind energy potential in mainland of China is 3 times that from the second and the third investigations for wind energy resources by CMA, and is similar to the wind energy potential obtained by NREL in Solar and Wind Energy Resource Assessment (SWERA) project. The simulated offshore wind energy potential of China seems smaller than the true value. According to the simulated results of CMA and considering lots of limited factors to wind energy development, the final conclusion can be obtained that the wind energy availability in China is 700~1 200 GW, in which 600~1 000 GW is in mainland and 100~200 GW is on offshore, and wind power will become the important part of energy composition in future.
-
Réville, V.; Velli, M.; Brun, S.
2017-12-01
The dynamics of the solar wind depends intrinsically on the structure of the global solar magnetic field, which undergoes fundamental changes over the 11yr solar cycle. For instance, the wind terminal velocity is thought to be anti-correlated with the expansion factor, a measure of how the magnetic field varies with height in the solar corona, usually computed at a fixed height (≈ 2.5 Rȯ, the source surface radius which approximates the distance at which all magnetic field lines become open). However, the magnetic field expansion affects the solar wind in a more detailed way, its influence on the solar wind properties remaining significant well beyond the source surface: we demonstrate this using 3D global MHD simulations of the solar corona, constrained by surface magnetograms over half a solar cycle (1989-2001). For models to comply with the constraints provided by observed characteristics of the solar wind, namely, that the radial magnetic field intensity becomes latitude independent at some distance from the Sun (Ulysses observations beyond 1 AU), and that the terminal wind speed is anti-correlated with the mass flux, they must accurately describe expansion beyond the solar wind critical point (even up to 10Rȯ and higher in our model). We also show that near activity minimum, expansion in the higher corona beyond 2.5 Rȯ is actually the dominant process affecting the wind speed. We discuss the consequences of this result on the necessary acceleration profile of the solar wind, the location of the sonic point and of the energy deposition by Alfvén waves.
-
Techno-Economic Assessment of Concentrating Solar Power and Wind Hybridization in Jordan
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Osama Ayadi
2018-03-01
A strong complementarity between wind and direct normal solar radiation was observed in the selected location in Jordan, which emphasizes the attractiveness of the selected hybrid system. The optimal configuration of the CSP-wind hybrid system was obtained with a solar field of a 2.6 solar multiple and a 5 hours energy storage. The achieved capacity factor was 94%, and the LCOE is lower than those resulted for standalone CSP plants.
-
Solar power. [comparison of costs to wind, nuclear, coal, oil and gas
Walton, A. L.; Hall, Darwin C.
1990-01-01
This paper describes categories of solar technologies and identifies those that are economic. It compares the private costs of power from solar, wind, nuclear, coal, oil, and gas generators. In the southern United States, the private costs of building and generating electricity from new solar and wind power plants are less than the private cost of electricity from a new nuclear power plant. Solar power is more valuable than nuclear power since all solar power is available during peak and midpeak periods. Half of the power from nuclear generators is off-peak power and therefore is less valuable. Reliability is important in determining the value of wind and nuclear power. Damage from air pollution, when factored into the cost of power from fossil fuels, alters the cost comparison in favor of solar and wind power. Some policies are more effective at encouraging alternative energy technologies that pollute less and improve national security.
-
Worldwide potential of wind energy
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Flavin, C
1982-01-01
A well-documented discussion is presented dealing with the worldwide potential of wind energy as a source of electrical and mechanical power. It is pointed out that 2% of the solar insolation is converted to wind kinetic energy; it is constantly renewed and nondepletable. Efficiency of windmills are discussed (20 to 40%) and payback periods of less than 5 years are cited. Effects of wind velocity and site location are described. Wind pumps are reviewed and the need for wind pumps, particularly in the developing countries is stressed. The generation of electricity by windmills using small turbines is reviewed and appears promising in areas with wind velocities greater than 12 mi/hr. The development of large windmills and groups of windmills (windfarms) for large scale electrical power is discussed, illustrated, and reviewed (offshore sites included). Environmental and safety problems are considered as well as the role of electrical utilities, government support and research activities. It is concluded that the potential contribution of wind energy is immense and that mechanical windmills may become one of the most important renewable technologies. Electrical generating potential is estimated at 20 to 30% of electrical needs. International programs are discussed briefly. 57 references. (MJJ)
-
Sputtering of Lunar Regolith Simulant by Protons and Multicharged Heavy Ions at Solar Wind Energies
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Meyer, Fred W.; Harris, Peter R.; Taylor, C.N.; Meyer, Harry M. III; Barghouty, N.; Adams, J. Jr.
2011-01-01
We report preliminary results on sputtering of a lunar regolith simulant at room temperature by singly and multiply charged solar wind ions using quadrupole and time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometry approaches. Sputtering of the lunar regolith by solar-wind heavy ions may be an important particle source that contributes to the composition of the lunar exosphere, and is a possible mechanism for lunar surface ageing and compositional modification. The measurements were performed in order to assess the relative sputtering efficiency of protons, which are the dominant constituent of the solar wind, and less abundant heavier multicharged solar wind constituents, which have higher physical sputtering yields than same-velocity protons, and whose sputtering yields may be further enhanced due to potential sputtering. Two different target preparation approaches using JSC-1A AGGL lunar regolith simulant are described and compared using SEM and XPS surface analysis.
-
A consistent thermodynamics of the MHD wave-heated two-fluid solar wind
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
I. V. Chashei
Full Text Available We start our considerations from two more recent findings in heliospheric physics: One is the fact that the primary solar wind protons do not cool off adiabatically with distance, but appear to be heated. The other one is that secondary protons, embedded in the solar wind as pick-up ions, behave quasi-isothermal at their motion to the outer heliosphere. These two phenomena must be physically closely connected with each other. To demonstrate this we solve a coupled set of enthalpy flow conservation equations for the two-fluid solar wind system consisting of primary and secondary protons. The coupling of these equations comes by the heat sources that are relevant, namely the dissipation of MHD turbulence power to the respective protons at the relevant dissipation scales. Hereby we consider both the dissipation of convected turbulences and the dissipation of turbulences locally driven by the injection of new pick-up ions into an unstable mode of the ion distribution function. Conversion of free kinetic energy of freshly injected secondary ions into turbulence power is finally followed by partial reabsorption of this energy both by primary and secondary ions. We show solutions of simultaneous integrations of the coupled set of differential thermodynamic two-fluid equations and can draw interesting conclusions from the solutions obtained. We can show that the secondary proton temperature with increasing radial distance asymptotically attains a constant value with a magnitude essentially determined by the actual solar wind velocity. Furthermore, we study the primary proton temperature within this two-fluid context and find a polytropic behaviour with radially and latitudinally variable polytropic indices determined by the local heat sources due to dissipated turbulent wave energy. Considering latitudinally variable solar wind conditions, as published by McComas et al. (2000, we also predict latitudinal variations of primary proton temperatures at
-
A consistent thermodynamics of the MHD wave-heated two-fluid solar wind
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
I. V. Chashei
2003-07-01
Full Text Available We start our considerations from two more recent findings in heliospheric physics: One is the fact that the primary solar wind protons do not cool off adiabatically with distance, but appear to be heated. The other one is that secondary protons, embedded in the solar wind as pick-up ions, behave quasi-isothermal at their motion to the outer heliosphere. These two phenomena must be physically closely connected with each other. To demonstrate this we solve a coupled set of enthalpy flow conservation equations for the two-fluid solar wind system consisting of primary and secondary protons. The coupling of these equations comes by the heat sources that are relevant, namely the dissipation of MHD turbulence power to the respective protons at the relevant dissipation scales. Hereby we consider both the dissipation of convected turbulences and the dissipation of turbulences locally driven by the injection of new pick-up ions into an unstable mode of the ion distribution function. Conversion of free kinetic energy of freshly injected secondary ions into turbulence power is finally followed by partial reabsorption of this energy both by primary and secondary ions. We show solutions of simultaneous integrations of the coupled set of differential thermodynamic two-fluid equations and can draw interesting conclusions from the solutions obtained. We can show that the secondary proton temperature with increasing radial distance asymptotically attains a constant value with a magnitude essentially determined by the actual solar wind velocity. Furthermore, we study the primary proton temperature within this two-fluid context and find a polytropic behaviour with radially and latitudinally variable polytropic indices determined by the local heat sources due to dissipated turbulent wave energy. Considering latitudinally variable solar wind conditions, as published by McComas et al. (2000, we also predict latitudinal variations of primary proton temperatures at
-
Solar wind energy transfer regions inside the dayside magnetopause
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lundin, R.; Dubinin, E.
1984-01-01
PROGNOZ-7 high temporal resolution measurements of the ion composition and hot plasma distribution in the dayside high latitude boundary layer near noon have revealed that magnetosheath plasma may penetrate the dayside magnetopause and form high density, high β, magnetosheath-like regions inside the magnetopause. From these measurements it is demonstrated that the magnetosheath injection regions most probably play an important role in transferring solar wind energy into the magnetosphere. The transfer regions are characterized by a strong perpendicular flow towards dawn or dusk (depending on local time) but are also observed to expand rapidly along the boundary field lines. This increased flow component transverse to the local magnetic field corresponds to a predominantly radial electric field of up to several mV m -1 , which indicates that the injected magnetosheath plasma causes an enhanced polarization of the boundary layer. Polarization of the boundary layer can therefore be considered a result of a local MHD-process where magnetosheath plasma excess momentum is converted into electromagnetic energy (electric field), i.e. there is an MHD-generator. It was observed that the boundary layer is charged up to tens of kilovolts, a potential which may be highly variable on e.g. the presence of a momentum exchange by the energy transfer regions. (author)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Colak, Ilhami; Sagiroglu, Seref; Demirtas, Mehmet; Yesilbudak, Mehmet
2013-01-01
Highlights: ► Wind speed and insolation period data were analyzed using a data mining approach. ► Most of the studies in the literature were based on Weibull and Rayleigh models. ► Nearest and farest neighbor algorithms were used with different distance metrics. ► Many inferences were achieved in efficient limits for wind and solar farm analyses. - Abstract: Wind and solar power plant installations have been recently increased rapidly with respect to the depletion of fossil-based fuels all over the world. Due to stochastic nature of meteorological conditions, wind and solar energies have a non-schedulable nature and they require several installation analyses to determine the location and the capacities of wind and solar power to be produced. This paper focuses on the similarity, feasibility and numerical analyses of 75 cities in Turkey based on the monthly average wind speed and insolation period data. The nearest and the farest neighbor algorithms are used as agglomerative hierarchical clustering methods with Euclidean, Manhattan and Minkowski distance metrics in the stage of making the similarity and feasibility analyses. The maximum cophenetic correlation coefficient is achieved by the nearest neighbor algorithm with the Minkowski distance metric in the similarity and feasibility analyses. On the other hand, graphical representations of the monthly average wind speed and insolation period data are utilized for making the numerical analysis. The highest annual average wind speed and insolation period are obtained as 3.88 m/s and 8.45 h/day, respectively. Overall, many inferences were achieved in acceptable and efficient limits for wind and solar energy.
-
Solar wind flows associated with hot heavy ions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fenimore, E.E.
1980-05-01
Solar wind heavy ion spectra measured with the Vela instrumentation have been studied with the goal of determining the solar origins of various solar wind structures which contain anomalously high ionization states. Since the ionization states freeze-in close to the sun they are good indicators of the plasma conditions in the low and intermediate corona. Heavy ion spectra from three different periods throughout the solar cycle have been analyzed. These data are consistent with freezing-in temperatures ranging from approx. 1.5 x 10 6 K to higher than 9 x 10 6 . The spectra indicating hot coronal conditions occur in roughly 1/7 of all measurements and almost exclusively in postshock flows (PSFs), nonshock related helium abundance enhancements (HAEs), or noncompressive density enhancements (NCDEs). The PSFs and HAEs are both probably interplanetary manifestations of solar flares. The observation of several flare-related HAEs which were not preceded by an interplanetary shock suggests that the flare-heated plasma can evolve into the solar wind without producing a noticeable shock at 1 AU. The NCDEs with hot heavy ions differ from the PSF-HAEs in several ways implying that they evolve from events or places with lower temperatures and less energy than those associated with the flares, but with higher temperatures and densities than the quiet corona. Active regions, coronal mass ejections, and equatorial streamers are possible sources for the NCDEs with spectra indicating hot coronal conditions. These events owe their enhanced densities to coronal processes as opposed to interplanetary dynamical processes. Models of the solar wind expansion demonstrate how some NCDEs can have extreme, nonequilibrium ionization distributions
-
Modelling and Optimising the Value of a Hybrid Solar-Wind System
Nair, Arjun; Murali, Kartik; Anbuudayasankar, S. P.; Arjunan, C. V.
2017-05-01
In this paper, a net present value (NPV) approach for a solar hybrid system has been presented. The system, in question aims at supporting an investor by assessing an investment in solar-wind hybrid system in a given area. The approach follow a combined process of modelling the system, with optimization of major investment-related variables to maximize the financial yield of the investment. The consideration of solar wind hybrid supply presents significant potential for cost reduction. The investment variables concern the location of solar wind plant, and its sizing. The system demand driven, meaning that its primary aim is to fully satisfy the energy demand of the customers. Therefore, the model is a practical tool in the hands of investor to assess and optimize in financial terms an investment aiming at covering real energy demand. Optimization is performed by taking various technical, logical constraints. The relation between the maximum power obtained between individual system and the hybrid system as a whole in par with the net present value of the system has been highlighted.
-
Troshichev, Oleg; Sormakov, Dmitry
The PC index has been approved by the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (Merida, Mexico, 2013) as a new international index of magnetic activity. Application of the PC index as a proxy of a solar wind energy that entered into the magnetosphere determines a principal distinction of the PC index from AL and Dst indices, which are regarded as characteristics of the energy that realized in magnetosphere in form of substorms and magnetic storms. This conclusion is based on results of analysis of relationships between the polar cap magnetic activity (PC-index) and parameters of the solar wind, on the one hand, relationships between changes of PC and development of magnetospheric substorms (AL-index) and magnetic storms (Dst-index), on the other hand. In this study the relationships between the PC and Dst indices in course of more than 200 magnetic storms observed in epoch of solar maximum (1998-2004) have been examined for different classes of storms separated by their kind and intensity. Results of statistical analysis demonstrate that depression of geomagnetic field starts to develop as soon as PC index steadily excess the threshold level ~1.5 mV/m; the storm intensity (DstMIN) follows, with delay ~ 1 hour, the maximum of PC in course of the storm. Main features of magnetic storms are determined, irrespective of their class and intensity, by the accumulated-mean PC value (PCAM): storm is developed as long as PCAM increases, comes to maximal intensity when PCAM attains the maximum, and starts to decay as soon as PCAM value displays decline. The run of “anomalous” magnetic storm on January 21-22, 2005, lasting many hours (with intensity of ≈ -100 nT) under conditions of northward or close to zero BZ component, is perfectly governed by behavior of the accumulated-mean PCAM index and, therefore, this storm should be regarded as an ordinary phenomenon. The conclusion is made that the PC index provides the unique on-line information on solar wind
-
SOLAR WIND HEAVY IONS OVER SOLAR CYCLE 23: ACE/SWICS MEASUREMENTS
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lepri, S. T.; Landi, E.; Zurbuchen, T. H.
2013-01-01
Solar wind plasma and compositional properties reflect the physical properties of the corona and its evolution over time. Studies comparing the previous solar minimum with the most recent, unusual solar minimum indicate that significant environmental changes are occurring globally on the Sun. For example, the magnetic field decreased 30% between the last two solar minima, and the ionic charge states of O have been reported to change toward lower values in the fast wind. In this work, we systematically and comprehensively analyze the compositional changes of the solar wind during cycle 23 from 2000 to 2010 while the Sun moved from solar maximum to solar minimum. We find a systematic change of C, O, Si, and Fe ionic charge states toward lower ionization distributions. We also discuss long-term changes in elemental abundances and show that there is a ∼50% decrease of heavy ion abundances (He, C, O, Si, and Fe) relative to H as the Sun went from solar maximum to solar minimum. During this time, the relative abundances in the slow wind remain organized by their first ionization potential. We discuss these results and their implications for models of the evolution of the solar atmosphere, and for the identification of the fast and slow wind themselves.
-
Troshichev, O. A.; Podorozhkina, N. A.; Sormakov, D. A.; Janzhura, A. S.
2014-08-01
The Polar Cap (PC) index has been approved by the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA XXII Assembly, Merida, Mexico, 2013) as a new index of magnetic activity. The PC index can be considered to be a proxy of the solar wind energy that enters the magnetosphere. This distinguishes PC from AL and Dst indices that are more related to the dissipation of energy through auroral currents or storage of energy in the ring current during magnetic substorms or storms. The association of the PC index with the direct coupling of the solar wind energy into the magnetosphere is based upon analysis of the relationship of PC with parameters in the solar wind, on the one hand, and correlation between the time series of PC and the AL index (substorm development), on the other hand. This paper (the first of a series) provides the results of statistical investigations that demonstrate a strong correlation between the behavior of PC and the development of magnetic substorms. Substorms are classified as isolated and expanded. We found that (1) substorms are preceded by growth in the RS index, (2) sudden substorm expansion onsets are related to "leap" or "reverse" signatures in the PC index which are indicative of a sharp increase in the PC growth rate, (3) substorms start to develop when PC exceeds a threshold level 1.5 ± 0.5 mV/m irrespective of the length of the substorm growth phase, and (4) there is a linear relation between the intensity of substorms and PC for all substorm events.
-
Ten questions to Gilbert Ruelle: the wind energy, an energy for the 21. century
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
2009-01-01
The author gives explanations and answers and comments data on issues related to wind energy. He discusses why this energy which is one of the oldest, emerges in the 21. century again, what is its share in electricity production and what it may become, how to compare KWh costs (wind and other sources), what are the other consequences of wind intermittence, whether wind energy is actually a promising way to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, where this energy is growing the fastest, what are the best wind sites, what is the potential of offshore wind facilities, what are the other limits of the wind energy development, whether wind energy has a different behaviour than other generators with respect to network disturbances, what are the selling condition, what is the role of the European Union in the development of solar energy in France
-
The Solar Wind Environment in Time
Pognan, Quentin; Garraffo, Cecilia; Cohen, Ofer; Drake, Jeremy J.
2018-03-01
We use magnetograms of eight solar analogs of ages 30 Myr–3.6 Gyr obtained from Zeeman Doppler Imaging and taken from the literature, together with two solar magnetograms, to drive magnetohydrodynamical wind simulations and construct an evolutionary scenario of the solar wind environment and its angular momentum loss rate. With observed magnetograms of the radial field strength as the only variant in the wind model, we find that a power-law model fitted to the derived angular momentum loss rate against time, t, results in a spin-down relation Ω ∝ t ‑0.51, for angular speed Ω, which is remarkably consistent with the well-established Skumanich law Ω ∝ t ‑0.5. We use the model wind conditions to estimate the magnetospheric standoff distances for an Earth-like test planet situated at 1 au for each of the stellar cases, and to obtain trends of minimum and maximum wind ram pressure and average ram pressure in the solar system through time. The wind ram pressure declines with time as \\overline{{P}ram}}\\propto {t}2/3, amounting to a factor of 50 or so over the present lifetime of the solar system.
-
Venzmer, M. S.; Bothmer, V.
2018-03-01
Context. The Parker Solar Probe (PSP; formerly Solar Probe Plus) mission will be humanitys first in situ exploration of the solar corona with closest perihelia at 9.86 solar radii (R⊙) distance to the Sun. It will help answer hitherto unresolved questions on the heating of the solar corona and the source and acceleration of the solar wind and solar energetic particles. The scope of this study is to model the solar-wind environment for PSPs unprecedented distances in its prime mission phase during the years 2018 to 2025. The study is performed within the Coronagraphic German And US SolarProbePlus Survey (CGAUSS) which is the German contribution to the PSP mission as part of the Wide-field Imager for Solar PRobe. Aim. We present an empirical solar-wind model for the inner heliosphere which is derived from OMNI and Helios data. The German-US space probes Helios 1 and Helios 2 flew in the 1970s and observed solar wind in the ecliptic within heliocentric distances of 0.29 au to 0.98 au. The OMNI database consists of multi-spacecraft intercalibrated in situ data obtained near 1 au over more than five solar cycles. The international sunspot number (SSN) and its predictions are used to derive dependencies of the major solar-wind parameters on solar activity and to forecast their properties for the PSP mission. Methods: The frequency distributions for the solar-wind key parameters, magnetic field strength, proton velocity, density, and temperature, are represented by lognormal functions. In addition, we consider the velocity distributions bi-componental shape, consisting of a slower and a faster part. Functional relations to solar activity are compiled with use of the OMNI data by correlating and fitting the frequency distributions with the SSN. Further, based on the combined data set from both Helios probes, the parameters frequency distributions are fitted with respect to solar distance to obtain power law dependencies. Thus an empirical solar-wind model for the inner
-
Numerical simulation of wind loads on solar panels
Su, Kao-Chun; Chung, Kung-Ming; Hsu, Shu-Tsung
2018-05-01
Solar panels mounted on the roof of a building or ground are often vulnerable to strong wind loads. This study aims to investigate wind loads on solar panels using computational fluid dynamic (CFD). The results show good agreement with wind tunnel data, e.g. the streamwise distribution of mean surface pressure coefficient of a solar panel. Wind uplift for solar panels with four aspect ratios is evaluated. The effect of inclined angle and clearance (or height) of a solar panel is addressed. It is found that wind uplift of a solar panel increases when there is an increase in inclined angle and the clearance above ground shows an opposite effect.
-
Wind energy literature survey no. 9
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Henriksen, Lars Christian
2008-01-01
To keep readers up-to-date in the field, each issue of Wind Energy will contain a list of relevant published articles drawn from recent issues of a large number of periodicals including Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, International Journal of Energy Research, Renewable...... Energy, Energy Sources, Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics Journal, Electric Power Components and Systems along with a number of periodicals published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), etc. The list is limited exclusively...... to journals not specifically devoted to wind energy and its applications. To assist the reader, the list is separated into broad categories. Although many papers fit several categories, each paper is listed only once under the category thought most appropriate. Also note that the inclusion in the list...
-
GLOBAL IMPACT OF SOLAR ENERGY, CASE STUDY - GERMANY
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gheorghe Caralicea Marculescu
2014-02-01
Full Text Available Renewable energy is a socially and politically defined category of energy sources. Renewable energy is generally defined as energy that comes from resources which are continually replenished on a human timescale such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves and geothermal heat. About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewable resources, with 10% of all energy from traditional biomass, mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from hydroelectricity. New renewables (small hydro, modern biomass, wind, solar, geothermal, and biofuels accounted for another 3% and are growing rapidly. This paper seeks is aimed at presenting the impact solar energy could have on a world level given the finitude, reachability and ever increasing prices of fossil fuels. As a case study we will present the solar energy industry in Germany emphasizing the advantages and disadvantages this form of energy has in this country and worldwide.
-
Deceleration of the solar wind in the earth's foreshock region - Isee 2 and Imp 8 observations
Bonifazi, C.; Moreno, G.; Lazarus, A. J.; Sullivan, J. D.
1980-01-01
The deceleration of the solar wind in the region of the interplanetary space filled by ions backstreaming from the earth's bow shock and associated waves is studied using a two-spacecraft technique. This deceleration depends on the solar wind bulk velocity; at low velocities (below 300 km/s) the velocity decrease is about 5 km/s, while at higher velocities (above 400 km/s) the decrease may be as large as 30 km/s. The energy balance shows that the kinetic energy loss far exceeds the thermal energy which is possibly gained by the solar wind; therefore at least part of this energy must go into waves and/or into the backstreaming ions.
-
The Solar Wind as a Turbulence Laboratory
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Bruno Roberto
2005-09-01
Full Text Available In this review we will focus on a topic of fundamental importance for both plasma physics and astrophysics, namely the occurrence of large-amplitude low-frequency fluctuations of the fields that describe the plasma state. This subject will be treated within the context of the expanding solar wind and the most meaningful advances in this research field will be reported emphasizing the results obtained in the past decade or so. As a matter of fact, Ulysses’ high latitude observations and new numerical approaches to the problem, based on the dynamics of complex systems, brought new important insights which helped to better understand how turbulent fluctuations behave in the solar wind. In particular, numerical simulations within the realm of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD turbulence theory unraveled what kind of physical mechanisms are at the basis of turbulence generation and energy transfer across the spectral domain of the fluctuations. In other words, the advances reached in these past years in the investigation of solar wind turbulence now offer a rather complete picture of the phenomenological aspect of the problem to be tentatively presented in a rather organic way.
-
Costs of solar and wind power variability for reducing CO2 emissions.
Lueken, Colleen; Cohen, Gilbert E; Apt, Jay
2012-09-04
We compare the power output from a year of electricity generation data from one solar thermal plant, two solar photovoltaic (PV) arrays, and twenty Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) wind farms. The analysis shows that solar PV electricity generation is approximately one hundred times more variable at frequencies on the order of 10(-3) Hz than solar thermal electricity generation, and the variability of wind generation lies between that of solar PV and solar thermal. We calculate the cost of variability of the different solar power sources and wind by using the costs of ancillary services and the energy required to compensate for its variability and intermittency, and the cost of variability per unit of displaced CO(2) emissions. We show the costs of variability are highly dependent on both technology type and capacity factor. California emissions data were used to calculate the cost of variability per unit of displaced CO(2) emissions. Variability cost is greatest for solar PV generation at $8-11 per MWh. The cost of variability for solar thermal generation is $5 per MWh, while that of wind generation in ERCOT was found to be on average $4 per MWh. Variability adds ~$15/tonne CO(2) to the cost of abatement for solar thermal power, $25 for wind, and $33-$40 for PV.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zhang, J.; Hodge, B. M.; Florita, A.
2013-05-01
Wind and solar power generations differ from conventional energy generation because of the variable and uncertain nature of their power output. This variability and uncertainty can have significant impacts on grid operations. Thus, short-term forecasting of wind and solar generation is uniquely helpful for power system operations to balance supply and demand in an electricity system. This paper investigates the correlation between wind and solar power forecasting errors.
-
Technology Teacher, 1991
1991-01-01
These three learning activities are on measuring accessible distances, designing a wind powered generator, and designing a hot dog heater using solar energy. Each activity includes description of context, objectives, list of materials and equipment, challenge to students, and evaluation questions. (SK)
-
Quiet-time Suprathermal (~0.1-1.5 keV) Electrons in the Solar Wind
Tao, Jiawei; Wang, Linghua; Zong, Qiugang; Li, Gang; Salem, Chadi S.; Wimmer-Schweingruber, Robert F.; He, Jiansen; Tu, Chuanyi; Bale, Stuart D.
2016-03-01
We present a statistical survey of the energy spectrum of solar wind suprathermal (˜0.1-1.5 keV) electrons measured by the WIND 3DP instrument at 1 AU during quiet times at the minimum and maximum of solar cycles 23 and 24. After separating (beaming) strahl electrons from (isotropic) halo electrons according to their different behaviors in the angular distribution, we fit the observed energy spectrum of both strahl and halo electrons at ˜0.1-1.5 keV to a Kappa distribution function with an index κ and effective temperature Teff. We also calculate the number density n and average energy Eavg of strahl and halo electrons by integrating the electron measurements between ˜0.1 and 1.5 keV. We find a strong positive correlation between κ and Teff for both strahl and halo electrons, and a strong positive correlation between the strahl n and halo n, likely reflecting the nature of the generation of these suprathermal electrons. In both solar cycles, κ is larger at solar minimum than at solar maximum for both strahl and halo electrons. The halo κ is generally smaller than the strahl κ (except during the solar minimum of cycle 23). The strahl n is larger at solar maximum, but the halo n shows no difference between solar minimum and maximum. Both the strahl n and halo n have no clear association with the solar wind core population, but the density ratio between the strahl and halo roughly anti-correlates (correlates) with the solar wind density (velocity).
-
Smoothing out the volatility of South Africa's wind and PV energy resources
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Bofinger, S
2015-10-01
Full Text Available Solar PV & wind are the cheapest new-build options per kWh in South Africa. By 2020, a mix of PV, wind and flexible gas (LNG-based) costs the same as new coal, even without any value given to excess wind/PV energy. South Africa has abundant solar...
-
What is the Relationship between the Solar Wind and Storms/Substorms?
Fairfield, D. H.; Burlaga, L. F.
1999-01-01
The interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) carried past the Earth by the solar wind has long been known to be the principal quantity that controls geomagnetic storms and substorms. Intervals of strong southward IMF with durations of at least a significant fraction of a day produce storms, while more typical, shorter intervals of less-intense southward fields produce substorms. The strong, long-duration southward fields are generally associated with coronal mass ejections and magnetic clouds or else they are produced by interplanetary dynamics initiated by fast solar wind flows that compress preexisting southward fields. Smaller, short-duration southward fields that occur on most days are related to long period waves, turbulence, or random variations in the IMF. Southward IMF enhances dayside reconnection between the IMF and the Earth's dipole with the reconnected field lines supplementing open field lines of the geomagnetic tail and producing an expanded polar cap and increased tail energy. Although the frequent storage of solar wind energy and its release during substorms is the most common mode of solar wind/magnetosphere interaction, under certain circumstances, steady southward IMF seems to produce intervals of relatively steady magnetosphere convection without substorms. During these latter times, the inner magnetosphere remains in a stressed tail-like state while the more distant magnetotail has larger northward field and more dipolar-like field lines. Recent evidence suggests that enhanced magnetosphere particle densities associated with enhanced solar wind densities allow more particles to be accelerated for the ring current, thus creating larger storms.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Scheer, H.; Alt, F.
2007-07-01
All renewable energy potentials (water power, bioenergy, wave power, geothermal energy) clearly are widespread as oil, natural gas, coal or uranium. For these potentials there are natural, spatial restrictions. In contrast to this, there exist any spatial restrictions for solar power and wind force. Under this aspect, the author of the contribution under consideration reports on wind force as a pacesetter and guide to a fast turn to renewable energy. Solar energy and wind energy have two crucial advantages of realizations: (a) The solar power plants and wind power plants can be installed faster than all other plants for generation of electrical power; (b) Solar power plants and wind power plants enable a radical shortening and simplification for the power supply. The generation and supply of electricity from solar power and wind power are also economically undefeatable. It is not a utopia to increase the contribution of the wind energy at the German power generation on basis of the renewable energy law in few years on over 40 %. The thesis, a further development of the wind power only is possible with offshore installations, because no suitable locations are present in the inland, is not correct. The emphasis of the use of wind power must remain with onshore plants. A broad dispersion of wind power plants should have priority, because the grid entrance is more easily realizable. The political attention must be directed toward the overcoming of the permission obstacles. Wind energy enables the passing of electricity from the shade of atomic and fossil power supply.
-
Developing a hybrid solar/wind powered irrigation system for crops in the Great Plains
Some small scale irrigation systems (powered by wind or solar do not require subsidies, but this paper discusses ways to achieve an economical renewable energy powered center pivot irrigation system for crops in the Great Plains. By adding a solar-photovoltaic (PV) array together with a wind...
-
A New Energy Management Technique for PV/Wind/Grid Renewable Energy System
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Onur Ozdal Mengi
2015-01-01
Full Text Available An intelligent energy management system (IEMS for maintaining the energy sustainability in renewable energy systems (RES is introduced here. It consists of wind and photovoltaic (PV solar panels are established and used to test the proposed IEMS. Since the wind and solar sources are not reliable in terms of sustainability and power quality, a management system is required for supplying the load power demand. The power generated by RES is collected on a common DC bus as a renewable green power pool to be used for supplying power to loads. The renewable DC power bus is operated in a way that there is always a base power available for permanent loads. Then the additional power requirement is supplied from either wind or PV or both depending upon the availability of these power sources. The decision about operating these systems is given by an IEMS with fuzzy logic decision maker proposed in this study. Using the generated and required power information from the wind/PV and load sides, the fuzzy reasoning based IEMS determines the amount of power to be supplied from each or both sources. Besides, the IEMS tracks the maximum power operating point of the wind energy system.
-
Review of wind energy use in Algeria
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Himri, Y.; Boudghene Stambouli, A.; Draoui, B.; Himri, S.
2009-01-01
Most scientists now agree that human-induced global climate change poses a serious threat to both society and the Earth's ecosystems. Renewable energy holds the key to future prosperity and a healthy global environment and is considered as a promising way to solve the problem of environmental pollution such as major environmental accidents, water pollution, maritime pollution, land use and sitting impact, radiation and radioactivity, solid waste disposal, hazardous air pollutants, ambient air quality (CO, CO 2 , SO x , NO x effluent gas emissions), acid rain, stratospheric ozone depletion, and global warming (GHG). Solar, wind and hydrogen power can be considered as potential renewable energy sources in Algeria. The share of renewable energy sources in Algeria primary energy supply is relatively low compared with European countries, though the trends of development are positive. One of the main strategic priorities of New Energy Algeria (NEAL) which is Algeria's renewable energy agency (government, Sonelgaz and Sonatrach), is striving to achieve a share of renewable energy sources in primary energy supply of 10-12% by 2010. IEA projects that the fastest growing sources of energy will be supplied by renewables. Much of this capacity will be installed in developing nations where solar and wind electric power is already competitive. Clearly, the nation that can capture a leadership position has potential for substantial economic returns. The article presents a review of the present wind energy situation and assessed potential of wind energy sources in Algeria in particular the southwest region of Algeria (Adrar, Timimoun and Tindouf). (author)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kimura, Y; Sakuma, H; Ushiyama, I [Ashikaga Institute of Technology, Tochigi (Japan)
1996-10-27
In order to verify the complementary relationship between wind and solar energy, the long-term field test of the hybrid power system was conducted at the natural energy square of Ashikaga Institute of Technology. The solar cell blade windmill composed of a Savonius windmill and flexible solar cells applied to swept buckets was also prepared. As a result, the wind power generation was promising mainly in the winter period including the late fall and early spring, while solar one was stable all the year through although it was slightly poor in winter. Stable power generation was thus achieved by combining wind energy with solar energy. As the whole data of other wind and solar power generation systems at the square were analyzed for every month, the same conclusion as the solar cell blade windmill was obtained as follows: the wind power generation in Ashikaga area is promising in Nov.-March from the field test result for 16 months, solar power generation is stable all the year through, the hybrid power system is effective in Nov.-April, and the solar cell blade windmill is equivalent to the hybrid power system. 3 refs., 5 figs.
-
Dubinin, E.; Fraenz, M.; Pätzold, M.; McFadden, J.; Halekas, J. S.; DiBraccio, G. A.; Connerney, J. E. P.; Eparvier, F.; Brain, D.; Jakosky, B. M.; Vaisberg, O.; Zelenyi, L.
2017-11-01
We present multi-instrument observations of the effects of solar wind on ion escape fluxes on Mars based on the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) data from 1 November 2014 to 15 May 2016. Losses of oxygen ions through different channels (plasma sheet, magnetic lobes, boundary layer, and ion plume) as a function of the solar wind and the interplanetary magnetic field variations were studied. We have utilized the modified Mars Solar Electric (MSE) coordinate system for separation of the different escape routes. Fluxes of the low-energy (≤30 eV) and high-energy (≥30 eV) ions reveal different trends with changes in the solar wind dynamic pressure, the solar wind flux, and the motional electric field. Major oxygen fluxes occur through the tail of the induced magnetosphere. The solar wind motional electric field produces an asymmetry in the ion fluxes and leads to different relations between ion fluxes supplying the tail from the different hemispheres and the solar wind dynamic pressure (or flux) and the motional electric field. The main driver for escape of the high-energy oxygen ions is the solar wind flux (or dynamic pressure). On the other hand, the low-energy ion component shows the opposite trend: ion flux decreases with increasing solar wind flux. As a result, the averaged total oxygen ion fluxes reveal a low variability with the solar wind strength. The large standard deviations from the averages values of the escape fluxes indicate the existence of mechanisms which can enhance or suppress the efficiency of the ion escape. It is shown that the Martian magnetosphere possesses the properties of a combined magnetosphere which contains different classes of field lines. The existence of the closed magnetic field lines in the near-Mars tail might be responsible for suppression of the ion escape fluxes.
-
Dynamic Biogas Upgrading for Integration of Renewable Energy from Wind, Biomass and Solar
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Jurgensen, Lars
The Sabatier process is investigated as a storage scheme for renewable energy. Hydrogen derived from fluctuating renewable energy sources like wind and solar is converted to methane by the hydrogenation/methanation of carbon oxides. Biogas from anaerobic digestion is considered in this study...... as a sustainable process for electricity storage and system integration in Northern Germany, i. e. the state of Schleswig-Holstein. A feasibility study was conducted to analyze the energy system in this region and the potential for this process. Process simulation tools were used to prove the product gas...... properties and the degree of efficiency of the system. Lab-scale and bench-scale experiments where further applied to demonstrate the utilization of industrial waste water for biogas production and the general applicability of biogas in the Sabatier process....
-
Manifestation of solar activity in solar wind particle flux density
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kovalenko, V.A.
1988-01-01
An analysis has been made of the origin of long-term variations in flux density of solar wind particles (nv) for different velocity regimes. The study revealed a relationship of these variations to the area of the polar coronal holes (CH). It is shown that within the framework of the model under development, the main longterm variations of nv are a result of the latitude redistribution of the solar wind mass flux in the heliosphere and are due to changes in the large-scale geometry of the solar plasma flow in the corona. A study has been made of the variations of nv for high speed solar wind streams. It is found that nv in high speed streams which are formed in CH, decreases from minimum to maximum solar activity. The analysis indicates that this decrease is attributable to the magnetic field strength increase in coronal holes. It has been found that periods of rapid global changes of background magnetic fields on the Sun are accompanied by a reconfiguration of coronal magnetic fields, rapid changes in the length of quiescent filaments, and by an increase in the density of the particle flux of a high speed solar wind. It has been established that these periods precede the formation of CH, corresponding to the increase in solar wind velocity near the Earth and to enhancement of the level of geomagnetic disturbance. (author)
-
Solar energy legal bibliography. Final report. [160 references
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Seeley, D.; Euser, B.; Joyce, C.; Morgan, G. H.; Laitos, J. G.; Adams, A.
1979-03-01
The Solar Energy Legal Bibliography is a compilation of approximately 160 solar publications abstracted for their legal and policy content (through October 1978). Emphasis is on legal barriers and incentives to solar energy development. Abstracts are arranged under the following categories: Antitrust, Biomass, Building Codes, Consumer Protection, Environmental Aspects, Federal Legislation and Programs, Financing/Insurance, International Law, Labor, Land Use (Covenants, Easements, Nuisance, Zoning), Local Legislation and Programs, Ocean Energy, Patents and Licenses, Photovoltaics, Solar Access Rights, Solar Heating and Cooling, Solar Thermal Power Systems, Standards, State Legislation and Programs, Tax Law, Tort Liability, Utilities, Warranties, Wind Resources, and General Solar Law.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ebert, Robert W. [Space Science and Engineering Division, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, TX (United States); Bagenal, Fran [Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO (United States); McComas, David J. [Space Science and Engineering Division, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, TX (United States); Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio, TX (United States); Fowler, Christopher M., E-mail: rebert@swri.edu [Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO (United States)
2014-09-19
We examine Ulysses solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) observations at 5 AU for two ~13 month intervals during the rising and declining phases of solar cycle 23 and the predicted response of the Jovian magnetosphere during these times. The declining phase solar wind, composed primarily of corotating interaction regions and high-speed streams, was, on average, faster, hotter, less dense, and more Alfvénic relative to the rising phase solar wind, composed mainly of slow wind and interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Interestingly, none of solar wind and IMF distributions reported here were bimodal, a feature used to explain the bimodal distribution of bow shock and magnetopause standoff distances observed at Jupiter. Instead, many of these distributions had extended, non-Gaussian tails that resulted in large standard deviations and much larger mean over median values. The distribution of predicted Jupiter bow shock and magnetopause standoff distances during these intervals were also not bimodal, the mean/median values being larger during the declining phase by ~1–4%. These results provide data-derived solar wind and IMF boundary conditions at 5 AU for models aimed at studying solar wind-magnetosphere interactions at Jupiter and can support the science investigations of upcoming Jupiter system missions. Here, we provide expectations for Juno, which is scheduled to arrive at Jupiter in July 2016. Accounting for the long-term decline in solar wind dynamic pressure reported by McComas et al. (2013a), Jupiter's bow shock and magnetopause is expected to be at least 8–12% further from Jupiter, if these trends continue.
-
Were chondrites magnetized by the early solar wind?
Oran, Rona; Weiss, Benjamin P.; Cohen, Ofer
2018-06-01
Chondritic meteorites have been traditionally thought to be samples of undifferentiated bodies that never experienced large-scale melting. This view has been challenged by the existence of post-accretional, unidirectional natural remanent magnetization (NRM) in CV carbonaceous chondrites. The relatively young inferred NRM age [∼10 million years (My) after solar system formation] and long duration of NRM acquisition (1-106 y) have been interpreted as evidence that the magnetizing field was that of a core dynamo within the CV parent body. This would imply that CV chondrites represent the primitive crust of a partially differentiated body. However, an alternative hypothesis is that the NRM was imparted by the early solar wind. Here we demonstrate that the solar wind scenario is unlikely due to three main factors: 1) the magnitude of the early solar wind magnetic field is estimated to be limits field amplification due to pile-up of the solar wind to less than a factor of 3.5 times that of the instantaneous solar wind field, and 3) the solar wind field likely changed over timescales orders of magnitude shorter than the timescale of NRM acquisition. Using analytical arguments, numerical simulations and astronomical observations of the present-day solar wind and magnetic fields of young stars, we show that the maximum mean field the ancient solar wind could have imparted on an undifferentiated CV parent body is <3.5 nT, which is 3-4 and 3 orders of magnitude weaker than the paleointensities recorded by the CV chondrites Allende and Kaba, respectively. Therefore, the solar wind is highly unlikely to be the source of the NRM in CV chondrites. Nevertheless, future high sensitivity paleomagnetic studies of rapidly-cooled meteorites with high magnetic recording fidelity could potentially trace the evolution of the solar wind field in time.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
2011-01-01
This study first proposes an analysis of data related to the renewable energy market context. It aims at identifying the current and future impact of environmental factors on actors. It focuses on structural evolutions as opposed to cyclical factors. It also gives an overview of the evolution of World demand in the fields of conventional and renewable energies, and proposes a detailed analysis of three main segments: solar, wind, and hydraulic energy. The second part reports an analysis of the structure of the sector of electric equipment manufacturing for the production of energy by using clean or renewable sources, with a focus on solar, wind and hydraulic energies. Strategies are discussed, notably for the main operators (First Solar, Goldwind, Q-Cells, Suntech Power, Suzlon, and Vestas). The next part presents financial and economic data (and their evolution) for the world main equipment manufacturers (the above-mentioned ones and Alstom, Dongfang, General Electric, Siemens)
-
Correlation of wind and solar power in high-latitude arctic areas in Northern Norway and Svalbard
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Solbakken Kine
2016-01-01
Full Text Available This paper assesses the possibilities for combining wind and solar power in a household-scale hybrid renewable energy system in arctic high-latitude areas in the North of Norway. By combining two complementary renewable energy sources, the efficiency and reliability of the power output can be improved compared to a system utilizing wind or solar power independently. This paper assesses the correlation between wind and solar power on different timescales in four different locations in Northern Norway and Svalbard. For all locations complementary characteristics of wind and solar power are found, however, the strength of the correlation is highly variable for each location and for the different timescales. The best correlation for all places is found on a monthly timescale. HOMER is used to run simulations on hybrid renewable energy systems (HRES for each location. For three of the four locations the HRES produces more power than what is consumed in the household.
-
Analysis of Correlation Tendency between Wind and Solar from Various Spatio-temporal Perspectives
Wang, X.; Weihua, X.; Mei, Y.
2017-12-01
Analysis of correlation between wind resources and solar resources could explore their complementary features, enhance the utilization efficiency of renewable energy and further alleviate the carbon emission issues caused by the fossil energy. In this paper, we discuss the correlation between wind and solar from various spatio-temporal perspectives (from east to west, in terms of plain, plateau, hill, and mountain, from hourly to daily, ten days and monthly) with observed data and modeled data from NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) and NERL (National Renewable Energy Laboratory). With investigation of wind speed time series and solar radiation time series (period: 10 years, resolution: 1h) of 72 stations located in various landform and distributed dispersedly in USA, the results show that the correlation coefficient, Kendall's rank correlation coefficient, changes negative to positive value from east coast to west coast of USA, and this phenomena become more obvious when the time scale of resolution increases from daily to ten days and monthly. Furthermore, considering the differences of landforms which influence the local meteorology the Kendall coefficients of diverse topographies are compared and it is found that the coefficients descend from mountain to hill, plateau and plain. However, no such evident tendencies could be found in daily scale. According to this research, it is proposed that the complementary feature of wind resources and solar resources in the east or in the mountain area of USA is conspicuous. Subsequent study would try to further verify this analysis by investigating the operation status of wind power station and solar power station.
-
On the Origins of the Intercorrelations Between Solar Wind Variables
Borovsky, Joseph E.
2018-01-01
It is well known that the time variations of the diverse solar wind variables at 1 AU (e.g., solar wind speed, density, proton temperature, electron temperature, magnetic field strength, specific entropy, heavy-ion charge-state densities, and electron strahl intensity) are highly intercorrelated with each other. In correlation studies of the driving of the Earth's magnetosphere-ionosphere-thermosphere system by the solar wind, these solar wind intercorrelations make determining cause and effect very difficult. In this report analyses of solar wind spacecraft measurements and compressible-fluid computer simulations are used to study the origins of the solar wind intercorrelations. Two causes are found: (1) synchronized changes in the values of the solar wind variables as the plasma types of the solar wind are switched by solar rotation and (2) dynamic interactions (compressions and rarefactions) in the solar wind between the Sun and the Earth. These findings provide an incremental increase in the understanding of how the Sun-Earth system operates.
-
Design Of Single-Axis And Dual-Axis Solar Tracking Systems Protected Against High Wind Speeds
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mai Salaheldin Elsherbiny
2017-09-01
Full Text Available Solar energy is rapidly gaining ground as an important mean of expanding renewable energy use. Solar tracking is employed in order to maximize collected solar radiation by a photovoltaic panel. In this paper we present a prototype for Automatic solar tracker that is designed using Arduino UNO with Wind sensor to Cease Wind effect on panels if wind speed exceeds certain threshold. The Proposed solar tracker tracks the location of the sun anywhere in any time by calculating the position of the sun. For producing the maximum amount of solar energy a solar panel must always be perpendicular to the source of light. Because the sun motion plane varies daily and during the day it moves from east to west one needs two axis tracking to follow the suns position. Maximum possible power is collected when two axis tracking is done. However two axis tracking is relatively costly and complex. A compromise between maximum power collection and system simplicity is obtained by single axis tracking where the plane North south axis is fixed while the east west motion is accomplished. This work deals with the design of both single and two axis tracking systems. Automatic trackers is also compared to Fixed one in terms of Energy generated Efficiency Cost and System reliability.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Robert Wilkes Ebert
2014-09-01
Full Text Available We examine Ulysses solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF observations at 5 AU for two ~13 month intervals during the rising and declining phases of solar cycle 23 and the predicted response of the Jovian magnetosphere during these times. The declining phase solar wind, composed primarily of corotating interaction regions and high-speed streams, was, on average, faster, hotter, less dense, and more Alfvénic relative to the rising phase solar wind, composed mainly of slow wind and interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Interestingly, none of solar wind and IMF distributions reported here were bimodal, a feature used to explain the bimodal distribution of bow shock and magnetopause standoff distances observed at Jupiter. Instead, many of these distributions had extended, non-Gaussian tails that resulted in large standard deviations and much larger mean over median values. The distribution of predicted Jupiter bow shock and magnetopause standoff distances during these intervals were also not bimodal, the mean/median values being larger during the declining phase by ~1 – 4%. These results provide data-derived solar wind and IMF boundary conditions at 5 AU for models aimed at studying solar wind-magnetosphere interactions at Jupiter and can support the science investigations of upcoming Jupiter system missions. Here, we provide expectations for Juno, which is scheduled to arrive at Jupiter in July 2016. Accounting for the long-term decline in solar wind dynamic pressure reported by McComas et al. (2013, Jupiter’s bow shock and magnetopause is expected to be at least 8 – 12% further from Jupiter, if these trends continue.
-
Simulation study of solar wind push on a charged wire: basis of solar wind electric sail propulsion
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Janhunen
2007-03-01
Full Text Available One possibility for propellantless propulsion in space is to use the momentum flux of the solar wind. A way to set up a solar wind sail is to have a set of thin long wires which are kept at high positive potential by an onboard electron gun so that the wires repel and deflect incident solar wind protons. The efficiency of this so-called electric sail depends on how large force a given solar wind exerts on a wire segment and how large electron current the wire segment draws from the solar wind plasma when kept at a given potential. We use 1-D and 2-D electrostatic plasma simulations to calculate the force and present a semitheoretical formula which captures the simulation results. We find that under average solar wind conditions at 1 AU the force per unit length is (5±1×10−8 N/m for 15 kV potential and that the electron current is accurately given by the well-known orbital motion limited (OML theory cylindrical Langmuir probe formula. Although the force may appear small, an analysis shows that because of the very low weight of a thin wire per unit length, quite high final speeds (over 50 km/s could be achieved by an electric sailing spacecraft using today's flight-proved components. It is possible that artificial electron heating of the plasma in the interaction region could increase the propulsive effect even further.
-
2010-12-08
... DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY Federal Energy Regulatory Commission [Docket Nos. EG10-65-000; EG10-66-000; EG10-67-000; EG10-68-000; EG10- 69-000; EG10-70-000; EG10-71-000] Top of the World Wind Energy, LLC; Kit Carson Windpower, LLC; Chestnut Flats Wind, LLC; Minco Wind, LLC; Arizona Solar One LLC; Criterion...
-
Optimization of hybrid system (wind-solar energy) for pumping water ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
This paper presents an optimization method for a hybrid (wind-solar) autonomous system designed for pumping water. This method is based on mathematical models demonstrated for the analysis and control of the performance of the various components of the hybrid system. These models provide an estimate of ...
-
Development of wind energy in Morocco
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Enzili, M.
2008-01-01
Morocco's national energy policy includes the use of renewable energy sources to lessen its reliance on fossil fuels such as coal and oil. Legislation was recently passed to increase the threshold of electrical power from 10 MW to 50 MW. Solar and wind energy are the most abundant renewable energy resources in the country and are recommended for exploitation on a large scale. Feasibility studies conducted by the Centre de Developpement des Energies Renouvelables have shown that Morocco has enough wind energy to produce electricity on a large scale and interconnect it with the national power grid. Wind energy in the country could also be used for on-site power generation in remote villages or for desalination of seawater, particularly in the southern regions of Morocco which are most affected by drought. Essaouira, Tangier, Tetouan, Tarfaya, Dakhla, Laayoune and Taza were among the regions identified with significant wind resources. The total wind energy potential for Morocco is estimated to be 2,650 GW, while the technical wind energy potential is estimated to be 1,600 GW. Several projects have been realized in the areas of electricity production, interconnection to the national power grid, decentralized rural electrification and eventually the introduction of water pumping. It was concluded that exporting green energy to Europe, via the Morocco-Spain route after the restructuring of Morocco's electricity sector will create a viable market for the medium and long-term. 3 figs
-
Offshore wind energy. Innovators talking; Wind op zee. Innovators aan het woord
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2013-02-15
Qualitative studies have been conducted of the results of completed projects focused on energy innovation, spread over the seven themes of the top sector Energy: Energy saving in industry, Energy conservation in the built environment, Gas, Bio-energy, Smart grids, Offshore Wind, Solar PV. This provides insight into the follow-up activities and lessons of some EOS (Energy Research Subsidy) completed projects with the aim to inspire, connect and strengthen the TKIs (Topconsortia for Knowledge and Innovation) and individual companies and researchers working on energy innovation. This report concerns the research on offshore wind energy [Dutch] Er is een kwalitatief onderzoek uitgevoerd naar de resultaten van afgeronde projecten gericht op energie-innovatie, verdeeld over de zeven thema's van de topsector Energie: Energiebesparing in de industrie; Energiebesparing in de gebouwde omgeving; Gas; Bio-energie; Smart grids; Wind op zee; Zon-pv. Daarmee wordt inzicht gegeven in de vervolgactiviteiten en lessen van een aantal afgesloten EOS-projecten (Energie Onderzoek Subsidie) met het oog op het inspireren, verbinden en versterken van de TKI's (Topconsortia voor Kennis en Innovatie) en individuele bedrijven en onderzoekers die werken aan energie-innovatie. Dit rapport betreft het onderzoek naar wind op zee.
-
Offshore wind energy. Innovators talking; Wind op zee. Innovators aan het woord
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2013-02-15
Qualitative studies have been conducted of the results of completed projects focused on energy innovation, spread over the seven themes of the top sector Energy: Energy saving in industry, Energy conservation in the built environment, Gas, Bio-energy, Smart grids, Offshore Wind, Solar PV. This provides insight into the follow-up activities and lessons of some EOS (Energy Research Subsidy) completed projects with the aim to inspire, connect and strengthen the TKIs (Topconsortia for Knowledge and Innovation) and individual companies and researchers working on energy innovation. This report concerns the research on offshore wind energy [Dutch] Er is een kwalitatief onderzoek uitgevoerd naar de resultaten van afgeronde projecten gericht op energie-innovatie, verdeeld over de zeven thema's van de topsector Energie: Energiebesparing in de industrie; Energiebesparing in de gebouwde omgeving; Gas; Bio-energie; Smart grids; Wind op zee; Zon-pv. Daarmee wordt inzicht gegeven in de vervolgactiviteiten en lessen van een aantal afgesloten EOS-projecten (Energie Onderzoek Subsidie) met het oog op het inspireren, verbinden en versterken van de TKI's (Topconsortia voor Kennis en Innovatie) en individuele bedrijven en onderzoekers die werken aan energie-innovatie. Dit rapport betreft het onderzoek naar wind op zee.
-
Study on optimal configuration of the grid-connected wind-solar-battery hybrid power system
Ma, Gang; Xu, Guchao; Ju, Rong; Wu, Tiantian
2017-08-01
The capacity allocation of each energy unit in the grid-connected wind-solar-battery hybrid power system is a significant segment in system design. In this paper, taking power grid dispatching into account, the research priorities are as follows: (1) We establish the mathematic models of each energy unit in the hybrid power system. (2) Based on dispatching of the power grid, energy surplus rate, system energy volatility and total cost, we establish the evaluation system for the wind-solar-battery power system and use a number of different devices as the constraint condition. (3) Based on an improved Genetic algorithm, we put forward a multi-objective optimisation algorithm to solve the optimal configuration problem in the hybrid power system, so we can achieve the high efficiency and economy of the grid-connected hybrid power system. The simulation result shows that the grid-connected wind-solar-battery hybrid power system has a higher comprehensive performance; the method of optimal configuration in this paper is useful and reasonable.
-
Seasonal optimal mix of wind and solar power in a future, highly renewable Europe
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Heide, Dominik [Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies (FIAS) and Frankfurt International Graduate School for Science, Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universitaet, Ruth-Moufang-Strasse 1, D-60438 Frankfurt am Main (Germany); von Bremen, Lueder [ForWind - Center for Wind Energy Research, University of Oldenburg, Marie-Curie-Str. 1, D-26129 Oldenburg (Germany); Greiner, Martin [Corporate Research and Technology, Siemens AG, D-81730 Muenchen (Germany); Aarhus School of Engineering and Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Aarhus University, Ny Munkegade 118, 8000 Aarhus C (Denmark); Hoffmann, Clemens [Corporate Research and Technology, Siemens AG, D-81730 Muenchen (Germany); Speckmann, Markus; Bofinger, Stefan [Fraunhofer Institut fuer Windenergie und Energiesystemtechnik (IWES), Koenigstor 59, D-34119 Kassel (Germany)
2010-11-15
The renewable power generation aggregated across Europe exhibits strong seasonal behaviors. Wind power generation is much stronger in winter than in summer. The opposite is true for solar power generation. In a future Europe with a very high share of renewable power generation those two opposite behaviors are able to counterbalance each other to a certain extent to follow the seasonal load curve. The best point of counterbalancing represents the seasonal optimal mix between wind and solar power generation. It leads to a pronounced minimum in required stored energy. For a 100% renewable Europe the seasonal optimal mix becomes 55% wind and 45% solar power generation. For less than 100% renewable scenarios the fraction of wind power generation increases and that of solar power generation decreases. (author)
-
Solar energy research and development: program balance. Annex, Volume I
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
None
1978-02-01
An evaluation of federal research, development, and demonstration options on solar energy is presented. This assessment treats seven groups of solar energy technologies: solar heating and cooling of buildings, agricultural and industrial process heat, biomass, photovoltaics, thermal power, wind, and ocean thermal energy conversion. The evaluation methodology is presented in detail. (MHR)
-
Solar wind fluctuations at large scale: A comparison between low and high solar activity conditions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bavassano, B.; Bruno, R.
1991-01-01
The influence of the Sun's activity cycle on the solar wind fluctuations at time scales from 1 hour to 3 days in the inner heliosphere (0.3 to 1 AU) is investigated. Hourly averages of plasma and magnetic field data by Helios spacecraft are used. Since fluctuations behave quite differently with changing scale, the analysis is performed separately for two different ranges in time scale. Between 1 and 6 hours Alfvenic fluctuations and pressure-balanced structures are extensively observed. At low solar activity and close to 0.3 AU, Alfvenic fluctuations are more frequent than pressure-balanced structures. This predominance, however, weakens for rising solar activity and radial distance, to the point that a role exchange, in terms of occurrence rate, is found at the maximum of the cycle close to 1 AU. On the other hand, in all cases Alfvenic fluctuations have a larger amplitude than pressure-balanced structures. On the whole, the Alfvenic contribution to the solar wind energy spectrum comes out to be dominant at all solar activity conditions. At scales from 0.5 to 3 days the most important feature is the growth, as the solar wind expansion develops, of strong positive correlations between magnetic and thermal pressures. These structures are progressively built up by the interaction between different wind flows. This effect is more pronounced at low than at high activity. Our findings support the conclusion that the solar cycle evolution of the large-scale velocity pattern is the factor governing the observed variations
-
Halekas, J. S.; Poppe, A. R.; Lue, C.; Farrell, W. M.; McFadden, J. P.
2017-06-01
A statistical investigation of 5 years of observations from the two-probe Acceleration, Reconnection, Turbulence, and Electrodynamics of Moon's Interaction with the Sun (ARTEMIS) mission reveals that strong compressional interactions occur infrequently at high altitudes near the ecliptic but can form in a wide range of solar wind conditions and can occur up to two lunar radii downstream from the lunar limb. The compressional events, some of which may represent small-scale collisionless shocks ("limb shocks"), occur in both steady and variable interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) conditions, with those forming in steady IMF well organized by the location of lunar remanent crustal magnetization. The events observed by ARTEMIS have similarities to ion foreshock phenomena, and those observed in variable IMF conditions may result from either local lunar interactions or distant terrestrial foreshock interactions. Observed velocity deflections associated with compressional events are always outward from the lunar wake, regardless of location and solar wind conditions. However, events for which the observed velocity deflection is parallel to the upstream motional electric field form in distinctly different solar wind conditions and locations than events with antiparallel deflections. Consideration of the momentum transfer between incoming and reflected solar wind populations helps explain the observed characteristics of the different groups of events.Plain Language SummaryWe survey the environment around the Moon to determine when and where strong amplifications in the charged particle density and magnetic field strength occur. These structures may be some of the smallest shock waves in the solar system, and learning about their formation informs us about the interaction of charged particles with small-scale magnetic fields throughout the solar system and beyond. We find that these compressions occur in an extended region downstream from the lunar dawn and dusk regions and
-
Ring current energy injection rate and solar wind-magnetosphere energy coupling
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lee, L.C.; Kan, J.R.; Akasofu, S.-I.
1982-01-01
The purpose of this paper is to (i) formulate the ring current injection rate Usub(R) in terms of phisub(CT) (cross-tail potential drop) by assuming that the ring current formation is a direct consequence of an enhanced convection, (ii) examine the relationship between the injection rate Usub(R) and the power transferred from the solar wind to the magnetosphere and (iii) demonstrate that an enhanced convection indeed leads to the formation of the ring current. (author)
-
Statistical analysis of dispersion relations in turbulent solar wind fluctuations using Cluster data
Perschke, C.; Narita, Y.
2012-12-01
Multi-spacecraft measurements enable us to resolve three-dimensional spatial structures without assuming Taylor's frozen-in-flow hypothesis. This is very useful to study frequency-wave vector diagram in solar wind turbulence through direct determination of three-dimensional wave vectors. The existence and evolution of dispersion relation and its role in fully-developed plasma turbulence have been drawing attention of physicists, in particular, if solar wind turbulence represents kinetic Alfvén or whistler mode as the carrier of spectral energy among different scales through wave-wave interactions. We investigate solar wind intervals of Cluster data for various flow velocities with a high-resolution wave vector analysis method, Multi-point Signal Resonator technique, at the tetrahedral separation about 100 km. Magnetic field data and ion data are used to determine the frequency- wave vector diagrams in the co-moving frame of the solar wind. We find primarily perpendicular wave vectors in solar wind turbulence which justify the earlier discussions about kinetic Alfvén or whistler wave. The frequency- wave vector diagrams confirm (a) wave vector anisotropy and (b) scattering in frequencies.
-
Solar energy activities in the Arab countries
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sayigh, A.A.M.
1991-01-01
The Arab countries, 22 in total, are divided into three groups. Group one consists of all countries of the Middle East. The second group is the Arabian Peninsula, and the third group consists of all Arab countries in Africa. The paper outlines the solar density and sunshine hours, as well as wind data in the region and compares them with some industrialized countries. Brief surveys of various solar energy projects are tabulated: that is solar, wind and biomass. Several specific major projects in various parts of the Arab World will be discussed. More specifically, the cooling of the solar energy research building in Baghdad (120 tons of solar absorption chillers, 80 tons of heat pumps), the heating of King Abdu-Asis Airborne and Physical Training School near Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, the 350 kW PV. field of the solar energy village near Riyadh and the 100 kW solar thermal plant in Kuwait are discussed. It is worth noting that the present photovoltaic capacity in the Arab world is more than 3.0 MW and the yearly installation potential per year is 2.0 MW. There are at least five photovoltaic production facilities in the Arab countries. Two of them in Saudi Arabia with capacity of 400 kW, one in Iraq with a capacity of 200 kW, one in Tunisia with a capacity of 100 kW and on in Algeria with capacity of 100 kW. The Arab countries can absorb 5MW per year and more countries like Egypt, Sudan, Morocco, Jordan and Libya are thinking of having their own production capabilities. Five desalination plants are also mentioned, plus the Yanbu plant of 240m/day, which is one of the largest in the world. The potential of wind energy utilisation is considered. Obstacles hindering the process of solar energy in the region are also outlined. (author). 11 refs, 1 fig., 4 tabs
-
Beam tracking strategies for studies of kinetic scales in the solar wind with THOR-CSW
De Keyser, Johan; Lavraud, Benoit; Neefs, Eddy; Berkenbosch, Sophie; Anciaux, Michel; Maggiolo, Romain
2016-04-01
Modern plasma spectrometers for monitoring the solar wind attempt to intelligently track the energy and direction of the solar wind beam in order to obtain solar wind velocity distributions more efficiently. Such beam tracking strategies offer some benefits, but also have their limitations and drawbacks. Benefits include an improved resolution and/or a faster velocity distribution function acquisition time. Limitations are due to instrument characteristics that tend to be optimized for a particular range of particle energies and arrival directions. A drawback is the risk to miss an important part of the velocity distribution or to lose track of the beam altogether. A comparison is presented of different beam tracking strategies under consideration for the THOR-CSW instrument in order to highlight a number of design decisions and their impact on the acquired velocity distributions. The gain offered by beam tracking in terms of increased time resolution turns out to be essential for studies of solar wind physics at kinetic scales.
-
Solar Wind 0.1-1 keV Electrons in the Corotating Interaction Regions
Wang, L.; Tao, J.; Li, G.; Wimmer-Schweingruber, R. F.; Jian, L. K.; He, J.; Tu, C.; Tian, H.; Bale, S. D.
2017-12-01
Here we present a statistical study of the 0.1-1 keV suprathermal electrons in the undisturbed and compressed slow/fast solar wind, for the 71 corotating interaction regions (CIRs) with good measurements from the WIND 3DP and MFI instruments from 1995 to 1997. For each of these CIRs, we separate the strahl and halo electrons based on their different behaviors in pitch angle distributions in the undisturbed and compressed solar wind. We fit both the strahl and halo energy spectra to a kappa function with an index κ index and effective temperature Teff, and calculate the pitch-angle width at half-maximum (PAHM) of the strahl population. We also integrate the electron measurements between 0.1 and 1.0 keV to obtain the number density n and average energy Eavg for the strahl and halo populations. We find that for both the strahl and halo populations within and around these CIRs, the fitted κ index strongly correlates with Teff, similar to the quiet-time solar wind (Tao et al., ApJ, 2016). The number density of both the strahl and halo shows a strong positive correlation with the electron core temperature. The strahl number density ns is correlated with the magnitude of interplanetary magnetic field, and the strahl PAHM width is anti-correlated with the solar wind speed. These results suggest that the origin of strahl electrons from the solar corona is likely related to the electron core temperature and magnetic field strength, while the production of halo electrons in the interplanetary medium could depend on the solar wind velocity.
-
Wind energy's role in a deregulated environment
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gallagher, F.M.
1998-01-01
The current status of wind energy in Canada was the focus of this presentation. Wind energy is the fastest growing source of new electrical power in the world. In 1997 the world-wide capacity was 1495 MW, with Germany (535 MW), Spain (263 MW) and Denmark (259 MW) leading the way. It is clear that Canadian markets lag behind the world in recognizing the value of wind energy. The rationale for this is economic downturn, cheap hydrocarbon energy, a closed electricity market, minimal commitment to greenhouse gas reduction, and a significant oversupply of installed capacity. Nevertheless, there are many potential benefits for Canadian grids by wind generated electricity, not the least of which are tangible reductions in carbon emissions per kWh. It was noted that significant risk reductions have resulted from size and technological improvements. Besides being environmentally benign, wind energy also provides unequaled opportunities for load matching, distributed generation, and low operating and ongoing fuel costs. Aggressive marketers such as Enron and Vision Quest have predicted that because of these advantages, and the willingness of many potential customers to pay more for 'green' energy, renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, will capture a significant share of the world energy market over the next 20 years. tabs., figs
-
Wind's share in global energy markets
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Madsen, B.T.
1997-01-01
The question of how great of a contribution wind power can really make to the world's energy needs is discussed. Emphasis up until recently has been mainly on improving wind turbine technology and siting practices as it is these that will provide an answer. The International Energy Agency predicts that world energy demand will increase by 30-50% by 2010. More countries than ever are either using wind power now or are preparing for its use. Wind power continues to improve its price competitiveness. There is enough wind to cover our energy needs many times over, according to some reports twice the world's electricity supply could be met by utilizing just 5-10% of areas identified as having average wind speeds of 5 m/s or greater - ignoring population centers, forests and specially protected areas. But a major limiting factor to utilizing the available wind resource is the established grid systems, which can only base 20% of supply on wind power. It is concluded that wind can contribute significantly to the world's energy needs in the next century and beyond. If wind, which has taken giant leaps in improving its competitiveness over the past 20 hears, can be a major energy contributor by early next century, other renewables such as solar and biomass might also evolve to become major contributors too. If so, renewables, including hydro, could conceivably cover 50% of our energy needs by the middle of the next century. Much will depend on decision-makers at the centers of power. For Europe and certain other areas of the world, policies governing cross-border trade of electricity as well as the framework for environmental protection related to energy production will determine the final outcome
-
Sørensen, B
1975-07-25
Two possible futures for the industrial world may be distinguished: (i) Large amounts of low-cost energy become available and the more energy-intensive methods for extracting resources from lowergrade deposits continue to sustain industrial expansion until either the environmental impact becomes unacceptable or ultimate limits, such as climate disruptions, put an end to such growth. (ii) The cost of nonrenewable energy resources continue to rise, but a fixed amount of energy from continuous sources may be utilized at constant cost. In this case a lower production level may be set by the amount of energy that is available from renewable sources, and society may thus have to be reshaped with energy economization in focus. If it is possible to choose between these two alternatives, the choice should be based on a discussion of the pros and cons of each one, and in particular on the desirability of having to process an increasing fraction of the earth's crust in search of raw materials in order to maintain growth as long as possible. However, the availability, of the first option is far from certain and it thus seems reasonable to plan for the second alternative. I have tried to propose such a plan for a small, homogeneous geographical region, namely Denmark. The ceiling on the consumption of energy from continuous sources is chosen in accordance with the criterion of not having to convert a major part of the land area to energy-collecting systems. The proposed annual average energy consumption of 19 gigawatts by the year 2050 corresponds to solar energy collecting panels (in use only 50 percent of the time) with an area of roughly 180 square kilometers and a windmill swept area of about 150 square kilometers. These (vertical) areas constitute less than 1 percent of the total land area. The selection of solar or wind energy for different applications has been based on known technology and may be subject to adjustments. The project has been shown to be economically
-
Recent Successes of Wave/Turbulence Driven Models of Solar Wind Acceleration
Cranmer, S. R.; Hollweg, J. V.; Chandran, B. D.; van Ballegooijen, A. A.
2010-12-01
A key obstacle in the way of producing realistic simulations of the Sun-heliosphere system is the lack of a first-principles understanding of coronal heating. Also, it is still unknown whether the solar wind is "fed" through flux tubes that remain open (and are energized by footpoint-driven wavelike fluctuations) or if mass and energy are input intermittently from closed loops into the open-field regions. In this presentation, we discuss self-consistent models that assume the energy comes from solar Alfven waves that are partially reflected, and then dissipated, by magnetohydrodynamic turbulence. These models have been found to reproduce many of the observed features of the fast and slow solar wind without the need for artificial "coronal heating functions" used by earlier models. For example, the models predict a variation with wind speed in commonly measured ratios of charge states and elemental abundances that agrees with observed trends. This contradicts a commonly held assertion that these ratios can only be produced by the injection of plasma from closed-field regions on the Sun. This presentation also reviews two recent comparisons between the models and empirical measurements: (1) The models successfully predict the amplitude and radial dependence of Faraday rotation fluctuations (FRFs) measured by the Helios probes for heliocentric distances between 2 and 15 solar radii. The FRFs are a particularly sensitive test of turbulence models because they depend not only on the plasma density and Alfven wave amplitude in the corona, but also on the turbulent correlation length. (2) The models predict the correct sense and magnitude of changes seen in the polar high-speed solar wind by Ulysses from the previous solar minimum (1996-1997) to the more recent peculiar minimum (2008-2009). By changing only the magnetic field along the polar magnetic flux tube, consistent with solar and heliospheric observations at the two epochs, the model correctly predicts that the
-
Simulation study of solar wind push on a charged wire: basis of solar wind electric sail propulsion
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Janhunen
2007-03-01
Full Text Available One possibility for propellantless propulsion in space is to use the momentum flux of the solar wind. A way to set up a solar wind sail is to have a set of thin long wires which are kept at high positive potential by an onboard electron gun so that the wires repel and deflect incident solar wind protons. The efficiency of this so-called electric sail depends on how large force a given solar wind exerts on a wire segment and how large electron current the wire segment draws from the solar wind plasma when kept at a given potential. We use 1-D and 2-D electrostatic plasma simulations to calculate the force and present a semitheoretical formula which captures the simulation results. We find that under average solar wind conditions at 1 AU the force per unit length is (5±1×10−8 N/m for 15 kV potential and that the electron current is accurately given by the well-known orbital motion limited (OML theory cylindrical Langmuir probe formula. Although the force may appear small, an analysis shows that because of the very low weight of a thin wire per unit length, quite high final speeds (over 50 km/s could be achieved by an electric sailing spacecraft using today's flight-proved components. It is possible that artificial electron heating of the plasma in the interaction region could increase the propulsive effect even further.
-
The genesis solar-wind sample return mission
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wiens, Roger C.
2009-01-01
The compositions of the Earth's crust and mantle, and those of the Moon and Mars, are relatively well known both isotopically and elementally. The same is true of our knowledge of the asteroid belt composition, based on meteorite analyses. Remote measurements of Venus, the Jovian atmosphere, and the outer planet moons, have provided some estimates of their compositions. The Sun constitutes a large majority, > 99%, of all the matter in the solar system. The elemental composition of the photosphere, the visible 'surface' of the Sun, is constrained by absorption lines produced by particles above the surface. Abundances for many elements are reported to the ±10 or 20% accuracy level. However, the abundances of other important elements, such as neon, cannot be determined in this way due to a relative lack of atomic states at low excitation energies. Additionally and most importantly, the isotopic composition of the Sun cannot be determined astronomically except for a few species which form molecules above sunspots, and estimates derived from these sources lack the accuracy desired for comparison with meteoritic and planetary surface samples measured on the Earth. The solar wind spreads a sample of solar particles throughout the heliosphere, though the sample is very rarified: collecting a nanogram of oxygen, the third most abundant element, in a square centimeter cross section at the Earth's distance from the Sun takes five years. Nevertheless, foil collectors exposed to the solar wind for periods of hours on the surface of the Moon during the Apollo missions were used to determine the helium and neon solar-wind compositions sufficiently to show that the Earth's atmospheric neon was significantly evolved relative to the Sun. Spacecraft instruments developed subsequently have provided many insights into the composition of the solar wind, mostly in terms of elemental composition. These instruments have the advantage of observing a number of parameters simultaneously
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Anon.
1992-01-01
This chapter discusses the role wind energy may have in the energy future of the US. The topics discussed in the chapter include historical aspects of wind energy use, the wind energy resource, wind energy technology including intermediate-size and small wind turbines and intermittency of wind power, public attitudes toward wind power, and environmental, siting and land use issues
-
Potency of Solar Energy Applications in Indonesia
Handayani, Noer Abyor; Ariyanti, Dessy
2012-01-01
Currently, 80% of conventional energy is used to fulfill general public's needs andindustries. The depletion of oil and gas reserves and rapid growth in conventional energyconsumption have continuously forced us to discover renewable energy sources, like solar, wind,biomass, and hydropower, to support economic development in the future. Solar energy travels at aspeed of 186,000 miles per second. Only a small part of the radiant energy that the sun emits intospace ever reaches the Earth, but t...
-
Solar and wind potentialities in Mauritania. Presentation of pumping
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Adell, A.; Fagel, L.
1996-01-01
The programs of rural hydraulics based upon the use of renewable energies, either solar or wind, have gained in importance in Africa during the last decade; particularly in Mauritania, a Sahelian country, which is extending widely beyond the western edge of Sahara. This country has been hardly affected by the prolonged droughts which have recently struck this region. Water is a major problem here. Important projects appeared concerning the pumping of water with the help of solar photovoltaic systems and wind mechanical pumps; other processes are being studied: pumping with aero-generators, sea water desalinating... Today Mauritania is at the top of countries of the subregion concerning the number of installations of wind mechanical pumps. The meteorological conditions are in fact favourable to such realizations. A technical and economic comparative study of the results of functioning obtained on the field with a photovoltaic pumping installation and a wind pumping installation, is presented: better technical performances and greater reliability for the photovoltaic pump, lower cost and technological mastery for the wind pump. (author). 9 refs., 8 figs
-
Regional variations in the health, environmental, and climate benefits of wind and solar generation
Siler-Evans, Kyle; Azevedo, Inês Lima; Morgan, M. Granger; Apt, Jay
2013-01-01
When wind or solar energy displace conventional generation, the reduction in emissions varies dramatically across the United States. Although the Southwest has the greatest solar resource, a solar panel in New Jersey displaces significantly more sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter than a panel in Arizona, resulting in 15 times more health and environmental benefits. A wind turbine in West Virginia displaces twice as much carbon dioxide as the same turbine in California. De...
-
Solar farms grow out of town renewable energy goals | State, Local, and
Tribal Governments | NREL Solar farms grow out of town renewable energy goals Solar farms grow ) - With enough solar energy generated within its borders to power 3,250[1] homes, Dartmouth leads the . Dartmouth's solar leadership began with the pursuit of wind energy. In 2009, seeking to fulfill their Master
-
THE NEW HORIZONS SOLAR WIND AROUND PLUTO (SWAP) OBSERVATIONS OF THE SOLAR WIND FROM 11–33 au
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Elliott, H. A.; McComas, D. J.; Valek, P.; Weidner, S.; Livadiotis, G. [Southwest Research Institute, 6220 Culebra Road, San Antonio, TX 78238 (United States); Nicolaou, G., E-mail: helliott@swri.edu [Swedish Institute of Space Physics, Box 812, SE-98128, Kiruna (Sweden)
2016-04-15
The Solar Wind Around Pluto (SWAP) instrument on National Aeronautics and Space Administration's New Horizons Pluto mission has collected solar wind observations en route from Earth to Pluto, and these observations continue beyond Pluto. Few missions have explored the solar wind in the outer heliosphere making this dataset a critical addition to the field. We created a forward model of SWAP count rates, which includes a comprehensive instrument response function based on laboratory and flight calibrations. By fitting the count rates with this model, the proton density (n), speed (V), and temperature (T) parameters are determined. Comparisons between SWAP parameters and both propagated 1 au observations and prior Voyager 2 observations indicate consistency in both the range and mean wind values. These comparisons as well as our additional findings confirm that small and midsized solar wind structures are worn down with increasing distance due to dynamic interaction of parcels of wind with different speed. For instance, the T–V relationship steepens, as the range in V is limited more than the range in T with distance. At times the T–V correlation clearly breaks down beyond 20 au, which may indicate wind currently expanding and cooling may have an elevated T reflecting prior heating and compression in the inner heliosphere. The power of wind parameters at shorter periodicities decreases with distance as the longer periodicities strengthen. The solar rotation periodicity is present in temperature beyond 20 au indicating the observed parcel temperature may reflect not only current heating or cooling, but also heating occurring closer to the Sun.
-
THE NEW HORIZONS SOLAR WIND AROUND PLUTO (SWAP) OBSERVATIONS OF THE SOLAR WIND FROM 11–33 au
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Elliott, H. A.; McComas, D. J.; Valek, P.; Weidner, S.; Livadiotis, G.; Nicolaou, G.
2016-01-01
The Solar Wind Around Pluto (SWAP) instrument on National Aeronautics and Space Administration's New Horizons Pluto mission has collected solar wind observations en route from Earth to Pluto, and these observations continue beyond Pluto. Few missions have explored the solar wind in the outer heliosphere making this dataset a critical addition to the field. We created a forward model of SWAP count rates, which includes a comprehensive instrument response function based on laboratory and flight calibrations. By fitting the count rates with this model, the proton density (n), speed (V), and temperature (T) parameters are determined. Comparisons between SWAP parameters and both propagated 1 au observations and prior Voyager 2 observations indicate consistency in both the range and mean wind values. These comparisons as well as our additional findings confirm that small and midsized solar wind structures are worn down with increasing distance due to dynamic interaction of parcels of wind with different speed. For instance, the T–V relationship steepens, as the range in V is limited more than the range in T with distance. At times the T–V correlation clearly breaks down beyond 20 au, which may indicate wind currently expanding and cooling may have an elevated T reflecting prior heating and compression in the inner heliosphere. The power of wind parameters at shorter periodicities decreases with distance as the longer periodicities strengthen. The solar rotation periodicity is present in temperature beyond 20 au indicating the observed parcel temperature may reflect not only current heating or cooling, but also heating occurring closer to the Sun
-
Janus: Graphical Software for Analyzing In-Situ Measurements of Solar-Wind Ions
Maruca, B.; Stevens, M. L.; Kasper, J. C.; Korreck, K. E.
2016-12-01
In-situ observations of solar-wind ions provide tremendous insights into the physics of space plasmas. Instrument on spacecraft measure distributions of ion energies, which can be processed into scientifically useful data (e.g., values for ion densities and temperatures). This analysis requires a strong, technical understanding of the instrument, so it has traditionally been carried out by the instrument teams using automated software that they had developed for that purpose. The automated routines are optimized for typical solar-wind conditions, so they can fail to capture the complex (and scientifically interesting) microphysics of transient solar-wind - such as coronal mass ejections (CME's) and co-rotating interaction regions (CIR's) - which are often better analyzed manually.This presentation reports on the ongoing development of Janus, a new software package for processing in-situ measurement of solar-wind ions. Janus will provide user with an easy-to-use graphical user interface (GUI) for carrying out highly customized analyses. Transparent to the user, Janus will automatically handle the most technical tasks (e.g., the retrieval and calibration of measurements). For the first time, users with only limited knowledge about the instruments (e.g., non-instrumentalists and students) will be able to easily process measurements of solar-wind ions. Version 1 of Janus focuses specifically on such measurements from the Wind spacecraft's Faraday Cups and is slated for public release in time for this presentation.
-
Estimation of monthly solar radiation distribution for solar energy system analysis
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Coskun, C.; Oktay, Z.; Dincer, I.
2011-01-01
The concept of probability density frequency, which is successfully used for analyses of wind speed and outdoor temperature distributions, is now modified and proposed for estimating solar radiation distributions for design and analysis of solar energy systems. In this study, global solar radiation distribution is comprehensively analyzed for photovoltaic (PV) panel and thermal collector systems. In this regard, a case study is conducted with actual global solar irradiation data of the last 15 years recorded by the Turkish State Meteorological Service. It is found that intensity of global solar irradiance greatly affects energy and exergy efficiencies and hence the performance of collectors. -- Research highlights: → The first study to apply global solar radiation distribution in solar system analyzes. → The first study showing global solar radiation distribution as a parameter of the solar irradiance intensity. → Time probability intensity frequency and probability power distribution do not have similar distribution patterns for each month. → There is no relation between the distribution of annual time lapse and solar energy with the intensity of solar irradiance.
-
WIND observations of coherent electrostatic waves in the solar wind
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Mangeney
1999-03-01
Full Text Available The time domain sampler (TDS experiment on WIND measures electric and magnetic wave forms with a sampling rate which reaches 120 000 points per second. We analyse here observations made in the solar wind near the Lagrange point L1. In the range of frequencies above the proton plasma frequency fpi and smaller than or of the order of the electron plasma frequency fpe, TDS observed three kinds of electrostatic (e.s. waves: coherent wave packets of Langmuir waves with frequencies f ~ fpe, coherent wave packets with frequencies in the ion acoustic range fpi < f < fpe, and more or less isolated non-sinusoidal spikes lasting less than 1 ms. We confirm that the observed frequency of the low frequency (LF ion acoustic wave packets is dominated by the Doppler effect: the wavelengths are short, 10 to 50 electron Debye lengths λD. The electric field in the isolated electrostatic structures (IES and in the LF wave packets is more or less aligned with the solar wind magnetic field. Across the IES, which have a spatial width of the order of ~ 25λD, there is a small but finite electric potential drop, implying an average electric field generally directed away from the Sun. The IES wave forms, which have not been previously reported in the solar wind, are similar, although with a smaller amplitude, to the weak double layers observed in the auroral regions, and to the electrostatic solitary waves observed in other regions in the magnetosphere. We have also studied the solar wind conditions which favour the occurrence of the three kinds of waves: all these e.s. waves are observed more or less continuously in the whole solar wind (except in the densest regions where a parasite prevents the TDS observations. The type (wave packet or IES of the observed LF waves is mainly determined by the proton temperature and by the direction of the magnetic field, which themselves depend on the latitude of WIND with respect to the heliospheric current sheet.Key words
-
Wind versus Biofuels for Addressing Climate, Health, and Energy
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jacobson, Mark Z.
2007-01-01
The favored approach today for addressing global warming is to promote a variety of options: biofuels, wind, solar thermal, solar photovoltaic, geothermal, hydroelectric, and nuclear energy and to improve efficiency. However, by far, most emphasis has been on biofuels. It is shown here, though, that current-technology biofuels cannot address global warming and may slightly increase death and illness due to ozone-related air pollution. Future biofuels may theoretically slow global warming, but only temporarily and with the cost of increased air pollution mortality. In both cases, the land required renders biofuels an impractical solution. Recent measurements and statistical analyses of U.S. and world wind power carried out at Stanford University suggest that wind combined with other options can substantially address global warming, air pollution mortality, and energy needs simultaneously.
-
Some problems of solar-terrestrial energy relations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kovalevskij, I.V.
1982-01-01
Energy aspects of relations of phenomena occurring on the Sun, in the interplanetary space, magnetosphere, ionosphere and on the Earth's surface are discussed. Particular attention is given to the energy radiated by the Sun (flares, coronal holes). The problems are considered of the energy transfer and transformation in high-velocity and flare flows of solar wind. Estimates are performed: of densities of various types of energy of the interplanetary space at the Earth's orbit level; energy fluxes incident on the magnetosphere; energy accumulated inside the magnetosphere; a series of energy parameters of magnetic storms. It is pointed out that nowadays one of the main problems of the magnetosphere physics is studying ways of the interplanatary space energy transfer into the magnetosphere. In this connection some problems are investigated: plasma penetration through the dayside magnetopause, solar wind plasma entry into the magnetotail, the electric field effect on transition region plasma penetration into the distant magnetotail
-
Solar wind-magnetosphere coupling during intense magnetic storms (1978--1979)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gonzalez, W.D.; Tsurutani, B.T.; Gonzalez, A.L.C.; Smith, E.J.; Tang, F.; Akasofu, S.
1989-01-01
The solar wind-magnetosphere coupling problem is investigated for the ten intense magnetic storms (Dst <-100 nT) that occurred during the 500 days (August 16, 1978 to December 28, 1979) studied by Gonzalez and Tsurutani [1987]. This investigation concentrates on the ring current energization in terms of solar wind parameters, in order to explain the | -Dst | growth observed during these storms. Thus several coupling functions are tested as energy input and several sets of the ring current decay time-constant τ are searched to find best correlations with the Dst response. From the fairly large correlation coefficients found in this study, there is strong evidence that large scale magnetopause reconnection operates during such intense storm events and that the solar wind ram pressure plays an important role in the ring current energization. Thus a ram pressure correction factor is suggested for expressions concerning the reconnection power during time intervals with large ram pressure variations
-
Solar-wind minor ions: recent observations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bame, S.J.
1982-01-01
During the years following the Solar Wind Four Conference at Burghausen our knowledge of the solar wind ion composition and dynamics has grown. There have been some surprises, and our understanding of the evolution of the solar wind has been improved. Systematic studies have shown that the minor ions generally travel with a common bulk speed and have temperatures roughly proportional to their masses. It has been determined that the 3 He ++ content varies greatly; 3 He ++ / 4 He ++ ranges from as high as 10 2 values to below 2 x 10 - 4 . In some solar wind flows which can be related to energetic coronal events, the minor ions are found in unusual ionization states containing Fe 16 + as a prominent ion, showing that the states were formed at unusually high temperatures. Unexpectedly, in a few flows substantial quantities of 4 He + have been detected, sometimes with ions identifiable as O 2 + and O 3 + . Surprisingly, in some of these examples the ionization state is mixed showing that part of the plasma escaped the corona without attaining the usual million-degree temperatures while other parts were heated more nearly in the normal manner. Additionally, detailed studies of the minor ions have increased our understanding of the coronal expansion. For example, such studies have contributed to identifying near equatorial coronal streamers as the source of solar wind flows between high speed streams
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Daren Watson
2017-11-01
Full Text Available Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems (HRES use multiple renewable resources such as hydro, solar and wind collaboratively to produce energy that can meet a defined load demand continuously. Their combination can lead to the improvement in the systems efficiency and overall reliability. However, the level of penetration of HRES in the Caribbean region is less than its expected potential. The constraints generated by their complexity and the costly access to useful energy planning tools is a limitation to their implementation. Therefore, in collaboration with the Alternative Energy Research Group, UWI Mona, we develop a free Linear Optimization software, Photurgen, for the design and analysis of hybrid solar-wind systems within the Caribbean region. Solar-wind hybrid systems are simulated based on historic climatological resources and instantaneous load consumption data, providing the user with graphics and advice for their optimal configuration. This paper introduces the first version of Photurgen and its associated development policies. This tool is one simple solution to be applied to increase the rate of autonomous and grid-tied households within the region, with Jamaica being its experimental location.
-
Solar wind ion trends and signatures: STEREO PLASTIC observations approaching solar minimum
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. B. Galvin
2009-10-01
Full Text Available STEREO has now completed the first two years of its mission, moving from close proximity to Earth in 2006/2007 to more than 50 degrees longitudinal separation from Earth in 2009. During this time, several large-scale structures have been observed in situ. Given the prevailing solar minimum conditions, these structures have been predominantly coronal hole-associated solar wind, slow solar wind, their interfaces, and the occasional transient event. In this paper, we extend earlier solar wind composition studies into the current solar minimum using high-resolution (1-h sampling times for the charge state analysis. We examine 2-year trends for iron charge states and solar wind proton speeds, and present a case study of Carrington Rotation 2064 (December 2007 which includes minor ion (He, Fe, O kinetic and Fe composition parameters in comparison with proton and magnetic field signatures at large-scale structures observed during this interval.
-
An illustrative note on the system price effect of wind and solar power. The German case
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jaegemann, Cosima
2014-07-15
Exposing wind and solar power to the market price signal allows for cost-efficient investment decisions, as it incentivizes investors to account for the marginal value (MV{sup el}) of renewable energy technologies. As shown by Lamont (2008), the MV{sup el} of wind and solar power units depends on their penetration level. More specifically, the MV el of wind and solar power units is a function of the respective unit's capacity factor and the covariance between its generation profile and the system marginal costs. The latter component of the MV{sup el} (i.e., the covariance) is found to decline as the wind and solar power penetration increases, displacing dispatchable power plants with higher short-run marginal costs of power production and thus reducing the system marginal costs in all generation hours. This so called 'system price effect' is analyzed in more detail in this paper. The analysis complements the work Lamont (2008) in two regards. First of all, an alternative expression for the MV{sup el} of wind and solar power units is derived, which shows that the MV{sup el} of fluctuating renewable energy technologies depends not only on their own penetration level but also on a variety of other parameters that are specific to the electricity system. Second, based on historical wholesale prices and wind and solar power generation data for Germany, a numerical 'ceteris paribus' example for Germany is presented which illustrates that the system price effect is already highly relevant for both wind and solar power generation in Germany.
-
An illustrative note on the system price effect of wind and solar power. The German case
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jaegemann, Cosima
2014-01-01
Exposing wind and solar power to the market price signal allows for cost-efficient investment decisions, as it incentivizes investors to account for the marginal value (MV el ) of renewable energy technologies. As shown by Lamont (2008), the MV el of wind and solar power units depends on their penetration level. More specifically, the MV el of wind and solar power units is a function of the respective unit's capacity factor and the covariance between its generation profile and the system marginal costs. The latter component of the MV el (i.e., the covariance) is found to decline as the wind and solar power penetration increases, displacing dispatchable power plants with higher short-run marginal costs of power production and thus reducing the system marginal costs in all generation hours. This so called 'system price effect' is analyzed in more detail in this paper. The analysis complements the work Lamont (2008) in two regards. First of all, an alternative expression for the MV el of wind and solar power units is derived, which shows that the MV el of fluctuating renewable energy technologies depends not only on their own penetration level but also on a variety of other parameters that are specific to the electricity system. Second, based on historical wholesale prices and wind and solar power generation data for Germany, a numerical 'ceteris paribus' example for Germany is presented which illustrates that the system price effect is already highly relevant for both wind and solar power generation in Germany.
-
Potency of Solar Energy Applications in Indonesia
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Noer Abyor Handayani
2012-07-01
Full Text Available Currently, 80% of conventional energy is used to fulfill general public's needs andindustries. The depletion of oil and gas reserves and rapid growth in conventional energyconsumption have continuously forced us to discover renewable energy sources, like solar, wind,biomass, and hydropower, to support economic development in the future. Solar energy travels at aspeed of 186,000 miles per second. Only a small part of the radiant energy that the sun emits intospace ever reaches the Earth, but that is more than enough to supply all our energy demand.Indonesia is a tropical country and located in the equator line, so it has an abundant potential ofsolar energy. Most of Indonesian area get enough intensity of solar radiation with the average dailyradiation around 4 kWh/m2. Basically, the solar systems use solar collectors and concentrators forcollecting, storing, and using solar radiation to be applied for the benefit of domestics, commercials,and industrials. Common applications for solar thermal energy used in industry are the SWHs, solardryers, space heating, cooling systems and water desalination.
-
On the optimal mix of wind and solar generation in the future Chinese power system
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Huber, Matthias; Weissbart, Christoph
2015-01-01
China is one of the largest and fastest growing economies in the world. Until now, the corresponding growth of electricity consumption has been mainly provided by coal. However, as national reserves are limited and since burning coal leads to severe environmental problems, the employment of alternative sources of energy supply has become an important part of the Chinese energy policy. Recent studies show that wind energy alone could meet all of China's electricity demand. While our results validate these findings with regard to annual production, we look at the hour-by-hour resolution and uncover a major limitation: wind generation will not match the demand at every given point in time. This results in significant periods with over- and undersupply. Our study shows that combining wind and solar generation in the power system reduces overproduction significantly and increases the capacity credit of the combined VRE (variable renewable energy sources). The article demonstrates that up to 70% of VRE comprising 20–30% solar generation in the form of photovoltaics (PV) can be integrated into China's electricity system with moderate storage requirements. We encourage planners to consider those findings in their long-term planning in order to set up a sustainable power system for China at low costs. - Highlights: • Analyzing the potentials for wind and solar generation in China. • Capacity credit of variable renewable energy sources. • Future storage demand for a renewable based Chinese power system. • Defining the optimal mix of wind and solar generation.
-
Solar wind acceleration in a prescribed flow geometry
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Biernat, H.; Koemle, N.; Lichtenegger, H.
1985-01-01
It is known that the flow tubes above coronal holes diverge stronger than radial and that the magnetic field lines may be considerably curved near the border of the holes. The authors investigate the consequences of such a magnetic field geometry on the flow of the solar wind plasma in the vicinity of the Sun. For this purpose the one-dimensional conservation equations are solved along prescribed flow tubes. A temperature profile based on observational data (EUV rocket-observations) is used in the calculations. In an alternative approach the temperature is determined by a polytropic index, which is assumed to be variable. The authors study how both curvature and non-radial divergence of the flow tubes modify the velocity, the density, and the energy balance of the solar wind plasma. (Auth.)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bobrov, M.S.
1977-01-01
Solar wind effect on the magnetospheric ring-current region has been considered. The correlations with solar wind parameters of the magnitude qsub(o) proportional to the total energy of particles being injected into the magnetospheric ring-current region per one hour are studied statistically and by comparison of time variations. The data on 8 sporadic geomagnetic storms of various intensity, from moderate to very severe one, are used. It is found that qsub(o) correlates not only with the magnitude and the direction of the solar-wind magnetic field component normal to the ecliptic plane, Bsub(z), but also with the variability, sigmasub(B), of the total magnetic-field strength vector. The solar-wind flux velocity ν influences the average storm intensity but the time variations of ν during any individual storm do not correlate with those of qsub(o)
-
Production, consumption and research on solar energy
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Sanz-Casado, Elias; Lascurain-Sánchez, Maria Luisa; Serrano-Lopez, Antonio Eleazar
2014-01-01
An analysis of scientific publications on solar energy was conducted to determine whether public interest in the subject is mirrored by more intense research in the area. To this end, the research published by Spain and Germany, the two EU countries with the highest installed photovoltaic capacity......, was analyzed based on Web of Science data. The results show that: solar output has risen substantially; solar research has a greater impact (measured in terms of citations) than publications on other renewables such as wind power; scientific production on solar energy is high in Germany and Spain, which...... intense. The main conclusion is the divergence in Germany and Spain between solar energy demand/output growth, being exponential, and the growth of research papers on the subject, which is linear...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Samuel Asumadu-Sarkodie
2016-12-01
Full Text Available This paper presents an energy demand model by designing a hybrid solar-wind-thermal power generation system of the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, a promising substitute for the expensive battery banks. The study models the future energy demand of Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus based on the IPCC emissions scenario A1B and A2 by designing a new hybrid solar-wind-thermal power system that satisfies the current and future requirements of firm capacity during peak periods. The study suggests an improvement in a hybrid solar-wind-thermal power system performance by predicting reliable outputs that can integrate renewable energy technologies to conventional power generation. The energy consumption prediction model emphasizes the energy requirement that has a growing demand from 300 to 400 GWh in scenario A1B and 150–450 GWh in scenario A2 from 2010 to 2050. The proposed design can meet 400 GWh of electricity demand in TRNC based on IPCC scenario A1B and 450 GWh of electricity demand in TRNC based on IPCC scenario A2. The percentage contribution of solar, wind and thermal energy for 2010, 2020, 2030, 2040 and 2050 are presented along with CO2 emissions and water consumption for each of the years.
-
Elemental composition and ionization state of the solar atmosphere and solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Joselyn, J.A.C.
1978-01-01
Abundance measurements have always proved useful in generating and refining astrophysical theories. Some of the classical problems of astrophysics involve determining the relative abundances of elements in the atmosphere of a star from observations of its line spectrum, and then synthesizing the physical processes which would produce such abundances. Theories of the formation of the solar system are critically tested by their ability to explain observed abundances, and, elemental abundances can serve as tracers, helping to determine the origin and transport of ions. Since the solar wind originates at the sun, it can act as a diagnostic probe of solar conditions. In particular, measurements of the composition of the solar wind should be related to the solar composition. And, assuming ionization equilibrium, measurements of the relative abundances of the ionization states in the solar wind should infer coronal temperatures and temperature gradients. However, most spherically symmetric models of the solar wind are unable to explain the relationship between the composition estimated from solar observations and as measured at 1 AU; and, recent observations of significant flow speeds in the transition region raise doubts about the validity of the assumption of ionization equilibrium
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Derrouazin, A., E-mail: derrsid@gmail.com [University Hassiba BenBouali of Chlef, LGEER,Chlef (Algeria); Université de Lorraine, LMOPS, EA 4423, 57070 Metz (France); CentraleSupélec, LMOPS, 57070 Metz (France); Aillerie, M., E-mail: aillerie@metz.supelec.fr; Charles, J. P. [Université de Lorraine, LMOPS, EA 4423, 57070 Metz (France); CentraleSupélec, LMOPS, 57070 Metz (France); Mekkakia-Maaza, N. [Université des sciences et de la Technologie d’Oran, Mohamed Boudiaf-USTO MB,LMSE, Oran Algérie (Algeria)
2016-07-25
Several researches for management of diverse hybrid energy systems and many techniques have been proposed for robustness, savings and environmental purpose. In this work we aim to make a comparative study between two supervision and control techniques: fuzzy and classic logics to manage the hybrid energy system applied for typical housing fed by solar and wind power, with rack of batteries for storage. The system is assisted by the electric grid during energy drop moments. A hydrogen production device is integrated into the system to retrieve surplus energy production from renewable sources for the household purposes, intending the maximum exploitation of these sources over years. The models have been achieved and generated signals for electronic switches command of proposed both techniques are presented and discussed in this paper.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Derrouazin, A.; Aillerie, M.; Charles, J. P.; Mekkakia-Maaza, N.
2016-01-01
Several researches for management of diverse hybrid energy systems and many techniques have been proposed for robustness, savings and environmental purpose. In this work we aim to make a comparative study between two supervision and control techniques: fuzzy and classic logics to manage the hybrid energy system applied for typical housing fed by solar and wind power, with rack of batteries for storage. The system is assisted by the electric grid during energy drop moments. A hydrogen production device is integrated into the system to retrieve surplus energy production from renewable sources for the household purposes, intending the maximum exploitation of these sources over years. The models have been achieved and generated signals for electronic switches command of proposed both techniques are presented and discussed in this paper.
-
Estimates of Sputter Yields of Solar-Wind Heavy Ions of Lunar Regolith Materials
Barghouty, Abdulmasser F.; Adams, James H., Jr.
2008-01-01
At energies of approximately 1 keV/amu, solar-wind protons and heavy ions interact with the lunar surface materials via a number of microscopic interactions that include sputtering. Solar-wind induced sputtering is a main mechanism by which the composition of the topmost layers of the lunar surface can change, dynamically and preferentially. This work concentrates on sputtering induced by solar-wind heavy ions. Sputtering associated with slow (speeds the electrons speed in its first Bohr orbit) and highly charged ions are known to include both kinetic and potential sputtering. Potential sputtering enjoys some unique characteristics that makes it of special interest to lunar science and exploration. Unlike the yield from kinetic sputtering where simulation and approximation schemes exist, the yield from potential sputtering is not as easy to estimate. This work will present a preliminary numerical scheme designed to estimate potential sputtering yields from reactions relevant to this aspect of solar-wind lunar-surface coupling.
-
The solar energy in Colombia, Atlas of solar radiation of Colombia
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rodriguez P, F.
1995-01-01
This study was made by means of the Agreement inter-institutional subscribed between Mines Ministry and Energy, HIMAT and INEA and was published by CARBOCOL. In the evaluation of solar energy potential, the information of the radiometric net of the HIMAT taken in 203 stations distributed throughout all Country from 1980 until 1990, it was had in account. A meteorological station is an observation point where are located different instruments and equipment that serve to measure and study meteorological parameter as solar radiation (radiometer actinograph), Solar sheen (Campbell Stoke), Temperature (Thermograph), Moisture (hydrographer), Wind (Anemograph Anemometer) and Precipitation (Pluviograph)
-
Solar-wind interactions with the Moon: role of oxygen ions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mukherjee, N.R.
1979-01-01
The solar-wind interacts directly with the lunar surface due to tenuous atmosphere and magnetic field. The interaction results in an almost complete absorption of the solar-wind corpuscles producing no upstream bowshock but a cavity downstream. The solar-wind oxygen ionic species induce and undergo a complex set of reactions with the elements of the lunar minerals and the solar-wind derived trapped gases. In this paper, the long-term concentration and the role of oxygen derived from the solar-wind is discussed. (Auth.)
-
Ion acoustic waves in the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gurnett, D.A.; Frank, L.A.
1978-01-01
Plasma wave measurements on the Helios I and 2 spacecraft have revealed the occurrence of electric field turbulence in the solar wind at frequencies between the electron and ion plasma frequencies. Wavelength measurements with the Imp 6 spacecraft now provide strong evidence that these waves are short-wavelength ion acoustic waves which are Doppler-shifted upward in frequency by the motion of the solar wind. Comparison of the Helios results with measurements from the earth-orbiting Imp 6 and 8 spacecraft shows that the ion acoustic turbulence detected in interplanetary space has characteristics essentially identical to those of bursts of electrostatic turbulence generated by protons streaming into the solar wind from the earth's bow shock. In a few cases, enhanced ion acoustic wave intensities have been observed in direct association with abrupt increases in the anisotropy of the solar wind electron distribution. This relationship strongly suggests that the ion acoustic waves detected by Helios far from the earth are produced by an electron heat flux instability, as was suggested by Forslund. Possible related mechanisms which could explain the generation of ion acoustic waves by protons streaming into the solar wind from the earth's bow shock are also considered
-
Solar wind temperature observations in the outer heliosphere
Gazis, P. R.; Barnes, A.; Mihalov, J. D.; Lazarus, A. J.
1992-01-01
The Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11, and Voyager 2 spacecraft are now at heliocentric distances of 50, 32 and 33 AU, and heliographic latitudes of 3.5 deg N, 17 deg N, and 0 deg N, respectively. Pioneer 11 and Voyager 2 are at similar celestial longitudes, while Pioneer l0 is on the opposite side of the sun. The baselines defined by these spacecraft make it possible to resolve radial, longitudinal, and latitudinal variations of solar wind parameters. The solar wind temperature decreases with increasing heliocentric distance out to a distance of 10-15 AU. At larger heliocentric distances, this gradient disappears. These high solar wind temperatures in the outer heliosphere have persisted for at least 10 years, which suggests that they are not a solar cycle effect. The solar wind temperature varied with heliographic latitude during the most recent solar minimum. The solar wind temperature at Pioneer 11 and Voyager 2 was higher than that seen at Pioneer 10 for an extended period of time, which suggests the existence of a large-scale variation of temperature with celestial longitude, but the contribution of transient phenomena is yet to be clarified.
-
The Western Wind and Solar Integration Study Phase 2
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lew, D.; Brinkman, G.; Ibanez, E.; Hodge, B. M.; Hummon, M.; Florita, A.; Heaney, M.
2013-09-01
The electric grid is a highly complex, interconnected machine, and changing one part of the grid can have consequences elsewhere. Adding wind and solar affects the operation of the other power plants and adding high penetrations can induce cycling of fossil-fueled generators. Cycling leads to wear-and-tear costs and changes in emissions. Phase 2 of the Western Wind and Solar Integration Study (WWSIS-2) evaluated these costs and emissions and simulated grid operations for a year to investigate the detailed impact of wind and solar on the fossil-fueled fleet. This built on Phase 1, one of the largest wind and solar integration studies ever conducted, which examined operational impacts of high wind and solar penetrations in the West.
-
Dawn-dusk asymmetry in particles of solar wind origin within the magnetosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
T. J. Stubbs
2001-01-01
Full Text Available Solar wind/magnetosheath plasma in the magnetosphere can be identified using a component that has a higher charge state, lower density and, at least soon after their entry into the magnetosphere, lower energy than plasma from a terrestrial source. We survey here observations taken over 3 years of He2+ ions made by the Magnetospheric Ion Composition Sensor (MICS of the Charge and Mass Magnetospheric Ion Composition Experiment (CAMMICE instrument aboard POLAR. The occurrence probability of these solar wind ions is then plotted as a function of Magnetic Local Time (MLT and invariant latitude (7 for various energy ranges. For all energies observed by MICS (1.8–21.4 keV and all solar wind conditions, the occurrence probabilities peaked around the cusp region and along the dawn flank. The solar wind conditions were filtered to see if this dawnward asymmetry is controlled by the Svalgaard-Mansurov effect (and so depends on the BY component of the interplanetary magnetic field, IMF or by Fermi acceleration of He2+ at the bow shock (and so depends on the IMF ratio BX /BY . It is shown that the asymmetry remained persistently on the dawn flank, suggesting it was not due to effects associated with direct entry into the magnetosphere. This asymmetry, with enhanced fluxes on the dawn flank, persisted for lower energy ions (below a "cross-over" energy of about 23 keV but reversed sense to give higher fluxes on the dusk flank at higher energies. This can be explained by the competing effects of gradient/curvature drifts and the convection electric field on ions that are convecting sunward on re-closed field lines. The lower-energy He2+ ions E × B drift dawnwards as they move earthward, whereas the higher energy ions curvature/ gradient drift towards dusk. The convection electric field in the tail is weaker for northward IMF. Ions then need less energy to drift to the dusk flank, so that the cross-over energy, at which the asymmetry changes sense, is reduced
-
WIND observations of coherent electrostatic waves in the solar wind
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Mangeney
Full Text Available The time domain sampler (TDS experiment on WIND measures electric and magnetic wave forms with a sampling rate which reaches 120 000 points per second. We analyse here observations made in the solar wind near the Lagrange point L1. In the range of frequencies above the proton plasma frequency fpi and smaller than or of the order of the electron plasma frequency fpe, TDS observed three kinds of electrostatic (e.s. waves: coherent wave packets of Langmuir waves with frequencies f ~ fpe, coherent wave packets with frequencies in the ion acoustic range fpi < f < fpe, and more or less isolated non-sinusoidal spikes lasting less than 1 ms. We confirm that the observed frequency of the low frequency (LF ion acoustic wave packets is dominated by the Doppler effect: the wavelengths are short, 10 to 50 electron Debye lengths λD. The electric field in the isolated electrostatic structures (IES and in the LF wave packets is more or less aligned with the solar wind magnetic field. Across the IES, which have a spatial width of the order of ~ 25λD, there is a small but finite electric potential drop, implying an average electric field generally directed away from the Sun. The IES wave forms, which have not been previously reported in the solar wind, are similar, although with a smaller amplitude, to the weak double layers observed in the auroral regions, and to the electrostatic solitary waves observed in other regions in the magnetosphere. We have also studied the solar wind conditions which favour the occurrence of the three kinds of waves: all these e.s. waves are observed more or less continuously in the whole solar wind (except in the densest regions where a parasite prevents the TDS observations. The type (wave packet or IES of the observed LF waves is mainly determined
-
The solar wind at solar maximum: comparisons of EISCAT IPS and in situ observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. R. Breen
Full Text Available The solar maximum solar wind is highly structured in latitude, longitude and in time. Coronal measurements show a very high degree of variability, with large variations that are less apparent within in situ spacecraft measurements. Interplanetary scintillation (IPS observations from EISCAT, covering distances from 20 to 100 solar radii (RS, are an ideal source of information on the inner solar wind and can be used, therefore, to cast light on its evolution with distance from the Sun. Earlier comparisons of in situ and IPS measurements under solar minimum conditions showed good large-scale agreement, particularly in the fast wind. In this study we attempt a quantitative comparison of measurements made over solar maximum by EISCAT (20–100 RS and the Wind and Ulysses spacecraft (at 215 RS and 300–1000 RS, respectively. The intervals studied were August–September 1999, May 2000, September 2000 and May 2001, the last-named being the period of the second Ulysses fast latitude scan. Both ballistic and – when possible – MHD/ballistic hybrid models were used to relate the data sets, and we compare the results obtained from these two mapping methods. The results of this study suggest that solar wind velocities measured in situ were less variable than those estimated from IPS measurements closer to the Sun, with the greatest divergence between IPS velocities and in situ measurements occurring in regions where steep longitudinal velocity gradients were seen in situ. We suggest that the interaction between streams of solar wind with different velocities leads to "smoothing" of solar wind velocities between 30–60 RS and 1 AU, and that this process continues at greater distances from the Sun.
Key words. Interplanetary physics (solar wind plasma; sources of the solar wind; instruments and techniques -
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Caneppele, Fernando de Lima [Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP), Itapeva, SP (Brazil). Campus Experimental], E-mail: fernando@itapeva.unesp.br; Seraphim, Odivaldo Jose [Universidade Estadual Paulista (FCA/UNESP), Botucatu, SP (Brazil). Fac. de Ciencias Agronomicas. Dept. de Engenharia Rural; Gabriel Filho, Luis Roberto de Almeida [Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP), Tupa, SP (Brazil). Campus Experimental
2010-07-01
The work developed a methodology fuzzy and simulated its use in control of a hybrid system of electric power generation, using solar-photovoltaic and wind energy. Using this control system, we get the point of maximum energy generation and transfer all the energy generated from alternative sources, solar-photovoltaic and wind energy to charge and / or batteries. The model uses three input variables, which are: wind (wind speed), sun (solar radiation) and batteries (charge the battery bank). With these variables, the fuzzy system will play, according to the rules to be described, what is the source of power supply system, which will have priority and how the batteries are loaded. For the simulations regarding the use of fuzzy theory to control, we used the scientific computing environment MATLAB. In this environment have been analyzed and simulated all mathematical modeling, rules and other variables described in the fuzzy system. This model can be applied to implement a control system of hybrid power generation, providing the best use of renewable energy, solar and wind, so that we can extract the maximum possible energy of these alternative sources without compromising the environment. (author)
-
Evolution of turbulence in the expanding solar wind, a numerical study
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dong, Yue; Grappin, Roland; Verdini, Andrea
2014-01-01
We study the evolution of turbulence in the solar wind by solving numerically the full three-dimensional (3D) magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) equations embedded in a radial mean wind. The corresponding equations (expanding box model or EBM) have been considered earlier but never integrated in 3D simulations. Here, we follow the development of turbulence from 0.2 AU up to about 1.5 AU. Starting with isotropic spectra scaling as k –1 , we observe a steepening toward a k –5/3 scaling in the middle of the wave number range and formation of spectral anisotropies. The advection of a plasma volume by the expanding solar wind causes a non-trivial stretching of the volume in directions transverse to radial and the selective decay of the components of velocity and magnetic fluctuations. These two effects combine to yield the following results. (1) Spectral anisotropy: gyrotropy is broken, and the radial wave vectors have most of the power. (2) Coherent structures: radial streams emerge that resemble the observed microjets. (3) Energy spectra per component: they show an ordering in good agreement with the one observed in the solar wind at 1 AU. The latter point includes a global dominance of the magnetic energy over kinetic energy in the inertial and f –1 range and a dominance of the perpendicular-to-the-radial components over the radial components in the inertial range. We conclude that many of the above properties are the result of evolution during transport in the heliosphere, and not just the remnant of the initial turbulence close to the Sun.
-
CONDITIONED ANALYSIS OF HIGH-LATITUDE SOLAR WIND INTERMITTENCY
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
D'Amicis, R.; Consolini, G.; Bavassano, B.; Bruno, R.
2012-01-01
The solar wind is a turbulent medium displaying intermittency. Its intermittent features have been widely documented and studied, showing how the intermittent character is different in fast and slow wind. In this paper, a statistical conditioned analysis of the solar wind intermittency for a period of high-latitude fast solar wind is presented. In particular, the intermittent features are investigated as a function of the Alfvénic degree of fluctuations at a given scale. The results show that the main contribution to solar wind intermittency is due to non-Alfvénic structures, while Alfvénic increments are found to be characterized by a smaller level of intermittency than the previous ones. Furthermore, the lifetime statistics of Alfvénic periods are discussed in terms of a multiscale texture of randomly oriented flux tubes.
-
The energetic implications of curtailing versus storing wind- and solar-generated electricity
Barnhart, C. J.; Dale, M.; Brandt, A. R.; Benson, S. M.
2013-12-01
Rapid deployment of power generation technologies harnessing wind and solar resources continues to reduce the carbon intensity of the power grid. But as these technologies comprise a larger fraction of power supply, their variable, weather-dependent nature poses challenges to power grid operation. Today, during times of power oversupply or unfavorable market conditions, power grid operators curtail these resources. Rates of curtailment are expected to increase with increased renewable electricity production. That is unless technologies are implemented that can provide grid flexibility to balance power supply with power demand. Curtailment is an obvious forfeiture of energy and it decreases the profitability of electricity from curtailed generators. What are less obvious are the energetic costs for technologies that provide grid flexibility. We present a theoretical framework to calculate how storage affects the energy return on energy investment (EROI) ratios of wind and solar resources. Our methods identify conditions under which it is more energetically favorable to store energy than it is to simply curtail electricity production. Electrochemically based storage technologies result in much smaller EROI ratios than large-scale geologically based storage technologies like compressed air energy storage (CAES) and pumped hydroelectric storage (PHS). All storage technologies paired with solar photovoltaic (PV) generation yield EROI ratios that are greater than curtailment. Due to their low energy stored on electrical energy invested (ESOIe) ratios, conventional battery technologies reduce the EROI ratios of wind generation below curtailment EROI ratios. To yield a greater net energy return than curtailment, battery storage technologies paired with wind generation need an ESOIe>80. We identify improvements in cycle life as the most feasible way to increase battery ESOIe. Depending upon the battery's embodied energy requirement, an increase of cycle life to 10
-
Solar wind fluctuations at large scale - A comparison between low and high solar activity conditions
Bavassano, B.; Bruno, R.
1991-02-01
The influence of the sun's activity cycle on the solar wind fluctuations at time scales from 1 hour to 3 days in the inner heliosphere (0.3 to 1 AU) is investigated. Hourly averages of plasma and magnetic field data by Helios spacecraft are used. Since fluctuations behave quite differently with changing scale, the analysis is performed separately for two different ranges in time scale. Between 1 and 6 hours Alfvenic fluctuations and pressure-balanced structures are extensively observed. At low solar activity and close to 0.3 AU Alfvenic fluctuations are more frequent than pressure-balanced structures. This predominance, however, weakens for rising solar activity and radial distance, to the point that a role-exchange, in terms of occurrence rate, is found at the maximum of the cycle close to 1 AU. On the other hand, in all cases Alfvenic fluctuations have a larger amplitude than pressure-balanced structures. The Alfvenic contribution to the solar wind energy spectrum comes out to be dominant at all solar activity conditions. These findings support the conclusion that the solar cycle evolution of the large-scale velocity pattern is the factor governing the observed variations.
-
The influence of solar wind variability on magnetospheric ULF wave power
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pokhotelov, D.; Rae, I.J.; Mann, I.R.
2015-01-01
Magnetospheric ultra-low frequency (ULF) oscillations in the Pc 4-5 frequency range play an important role in the dynamics of Earth's radiation belts, both by enhancing the radial diffusion through incoherent interactions and through the coherent drift-resonant interactions with trapped radiation belt electrons. The statistical distributions of magnetospheric ULF wave power are known to be strongly dependent on solar wind parameters such as solar wind speed and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) orientation. Statistical characterisation of ULF wave power in the magnetosphere traditionally relies on average solar wind-IMF conditions over a specific time period. In this brief report, we perform an alternative characterisation of the solar wind influence on magnetospheric ULF wave activity through the characterisation of the solar wind driver by its variability using the standard deviation of solar wind parameters rather than a simple time average. We present a statistical study of nearly one solar cycle (1996-2004) of geosynchronous observations of magnetic ULF wave power and find that there is significant variation in ULF wave powers as a function of the dynamic properties of the solar wind. In particular, we find that the variability in IMF vector, rather than variabilities in other parameters (solar wind density, bulk velocity and ion temperature), plays the strongest role in controlling geosynchronous ULF power. We conclude that, although time-averaged bulk properties of the solar wind are a key factor in driving ULF powers in the magnetosphere, the solar wind variability can be an important contributor as well. This highlights the potential importance of including solar wind variability especially in studies of ULF wave dynamics in order to assess the efficiency of solar wind-magnetosphere coupling.
-
Wave-trains in the solar wind. III
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Richter, A.K.
1975-01-01
Applying an Alfven-Wave-Extended-QRH-approximation and the method of characteristics, the equations of motion for outwardly propagating Alfven waves are solved analytically for three different cases of an azimuthal dependence of the background solar wind, (a) for a pure fast-slow stream configuration, (b) for the situation where the high-speed stream originates from a diverging magnetic field, and (c) for the case of (b) and an initially decreasing density configuration ('coronal hole'). The reaction of these waves on the background state as well as mode-mode coupling effects are neglected. These three solar wind models are discussed shortly. For the superimposed Alfven waves it is found, on an average, that there is a strong azimuthal dependence of all relevant parameters which, correlated with the azimuthal distributions of the solar wind variables, leads to good agreements with observations. The signature of high-speed streams and these correlations could clearly indicate solar wind streams originating from 'coronal holes'. Contrary to the purely radial solar wind, where outwardly propagating Alfven waves are exclusively refracted towards the radial direction, a refraction nearly perpendicular to the direction of the interplanetary magnetic field in the compression region and closely towards the magnetic field direction down the trailing edge and in the low-speed regime is found. (Auth.)
-
Maneva, Y. G.; Poedts, S.
2017-12-01
Non-thermal kinetic components such as deformed velocity distributions, temperature anisotropies and relative drifts between the multiple ion populations are frequently observed features in the collisionless fast solar wind streams near the Earth whose origin is still to be better understood. Some of the traditional models consider the formation of the temperature anisotropies through the effect of the solar wind expansion, while others assume in situ heating and particle acceleration by local fluctuations, such as plasma waves, or by spacial structures, such as advected or locally generated current sheets. In this study we consider the evolution of initial ion temperature anisotropies and relative drifts in the presence of plasma oscillations, such as ion-cyclotron and kinetic Alfven waves. We perform 2.5D hybrid simulations to study the evolution of observed fast solar wind plasma parcels, including the development of the plasma micro-instabilities, the field-particle correlations and the energy transfer between the multiple ion species. We consider two distinct cases of highly anisotropic and quickly drifting protons which excite ion-cyclotron waves and of moderately anisotropic slower protons, which co-exist with kinetic Alfven waves. The alpha particles for both cases are slightly anisotropic in the beginning and remain anisotropic throughout the simulation time. Both the imposed magnetic fluctuations and the initial differential streaming decrease in time for both cases, while the minor ions are getting heated. Finally we study the effects of the solar wind expansion and discuss its implications for the nonlinear evolution of the system.
-
Why fast solar wind originates from slowly expanding coronal flux tubes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wang, Y.M.; Sheeley, N.R. Jr.
1991-01-01
Empirical studies indicate that the solar wind speed at earth is inversely correlated with the divergence rate of the coronal magnetic field. It is shown that this result is consistent with simple wind acceleration models involving Alfven waves, provided that the wave energy flux at the coronal base is taken to be roughly constant within open field regions. 9 refs
-
High-speed solar wind flow parameters at 1 AU
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Feldman, W.C.; Asbridge, J.R.; Bame, S.J.; Gosling, J.T.
1976-01-01
To develop a set of constraints for theories of solar wind high-speed streams, a detailed study was made of the fastest streams observed at 1 AU during the time period spanning March 1971 through July 1974. Streams were accepted for study only if (1) the maximum speed exceeded 650 km s -1 ; (2) effects of stream-stream dynamical interaction on the flow parameters could be safely separated from the intrinsic characteristics of the high-speed regions; (3) the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the stream when mapped back to 20 solar radii by using a constant speed approximation was greater than 45degree in Carrington longitude; and (4) there were no obvious solar-activity-induced contaminating effects. Nineteen streams during this time interval satisfied these criteria. Average parameters at 1 AU for those portions of these streams above V=650 km s -1 are given.Not only is it not presently known why electrons are significantly cooler than the protons within high-speed regions, but also observed particle fluxes and convected energy fluxes for speed greater than 650 km s -1 are substantially larger than those values predicted by any of the existing theories of solar wind high-speed streams. More work is therefore needed in refining present solar wind models to see whether suitable modifications and/or combinations of existing theories based on reasonable coronal conditions can accommodate the above high-speed flow parameters
-
Kinetic Properties of the Neutral Solar Wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Florinski, V.; Heerikhuisen, J.
2017-01-01
Charge-exchange collisions between the solar wind protons and interstellar hydrogen produce a distinctive population of neutral hydrogen streaming radially at nearly the solar-wind speed. This tenuous population, known as the neutral solar wind (NSW) is thought to play a key role in the appearance of the Interplanetary Boundary EXplorer ribbon, a bright circular band in the sky that is the source of neutral hydrogen with energies near 1 keV. According to the leading model of the ribbon, the velocity distribution of NSW hydrogen is imparted on the pickup ions (PUIs) generated via charge exchange with the interstellar protons beyond the heliopause, and in this way controls the stability of the resulting ring distribution of PUIs against hydromagnetic wave generation. In this paper, we examine the velocity distributions of the NSW atoms in the heliosphere and the outer heliosheath regions by following the phase-space trajectories of the Boltzmann equation. It is demonstrated that these distributions are highly anisotropic, with the parallel (radial) temperature greatly exceeding the perpendicular temperature. Ions picked up near 90° from the anisotropic NSW would form a stable ring distribution capable of generating the ribbon flux. We also discuss a second population of neutrals born in charge transfer collisions with interstellar PUIs, the so-called neutralized pickup ion (NPI) component. Their high thermal velocities translate into large parallel velocity spread of the daughter ribbon PUIs, which would adversely affect plasma stability in local interstellar space.
-
Kinetic Properties of the Neutral Solar Wind
Florinski, V.; Heerikhuisen, J.
2017-03-01
Charge-exchange collisions between the solar wind protons and interstellar hydrogen produce a distinctive population of neutral hydrogen streaming radially at nearly the solar-wind speed. This tenuous population, known as the neutral solar wind (NSW) is thought to play a key role in the appearance of the Interplanetary Boundary EXplorer ribbon, a bright circular band in the sky that is the source of neutral hydrogen with energies near 1 keV. According to the leading model of the ribbon, the velocity distribution of NSW hydrogen is imparted on the pickup ions (PUIs) generated via charge exchange with the interstellar protons beyond the heliopause, and in this way controls the stability of the resulting ring distribution of PUIs against hydromagnetic wave generation. In this paper, we examine the velocity distributions of the NSW atoms in the heliosphere and the outer heliosheath regions by following the phase-space trajectories of the Boltzmann equation. It is demonstrated that these distributions are highly anisotropic, with the parallel (radial) temperature greatly exceeding the perpendicular temperature. Ions picked up near 90° from the anisotropic NSW would form a stable ring distribution capable of generating the ribbon flux. We also discuss a second population of neutrals born in charge transfer collisions with interstellar PUIs, the so-called neutralized pickup ion (NPI) component. Their high thermal velocities translate into large parallel velocity spread of the daughter ribbon PUIs, which would adversely affect plasma stability in local interstellar space.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Graichen, Patrick; Grotewold, Lars [Agora Energiewende, Berlin (Germany); Kordowski, Klaus; Wesemann, Philipp [Stiftung Mercator, Essen (Germany)
2015-01-15
The global market for renewable energy technologies has experienced strong growth since the year 2000. In 2013 newly installed electricity production plants based on renewable energy for the first time outnumbered the aggregate of newly installed plants based on coal, gas or nuclear energy. In more and more parts of the world, wind and solar energy plants are becoming the most cost-effective means of electricity production. As renewable energy resources begin to claim significant shares in the energy mix they also become more system-relevant, resulting in a need for more investment as well as regulatory changes. Due to their specific features (high capital intensity, low incremental costs, fluctuating electricity production), and in spite of the marked decline in costs, wind and solar energy are still dependent on proactive policies in support of renewable energy.
-
The climate and air-quality benefits of wind and solar power in the United States
Millstein, Dev; Wiser, Ryan; Bolinger, Mark; Barbose, Galen
2017-09-01
Wind and solar energy reduce combustion-based electricity generation and provide air-quality and greenhouse gas emission benefits. These benefits vary dramatically by region and over time. From 2007 to 2015, solar and wind power deployment increased rapidly while regulatory changes and fossil fuel price changes led to steep cuts in overall power-sector emissions. Here we evaluate how wind and solar climate and air-quality benefits evolved during this time period. We find cumulative wind and solar air-quality benefits of 2015 US$29.7-112.8 billion mostly from 3,000 to 12,700 avoided premature mortalities, and cumulative climate benefits of 2015 US$5.3-106.8 billion. The ranges span results across a suite of air-quality and health impact models and social cost of carbon estimates. We find that binding cap-and-trade pollutant markets may reduce these cumulative benefits by up to 16%. In 2015, based on central estimates, combined marginal benefits equal 7.3 ¢ kWh-1 (wind) and 4.0 ¢ kWh-1 (solar).
-
Observation of solar wind with radio-star scintillation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Watanabe, Takashi
1974-01-01
Large solar flares occurred in groups in early August 1972, and many interesting phenomena were observed. The solar wind condition during this period, obtained by scintillation observation, is reviewed. The velocity of solar wind has been determined from the observation of interplanetary space scintillation at Toyokawa, Fujigamine and Sugadaira. Four to ten radio wave sources were observed for ten minutes at each southing every day. Strong earth magnetic storm and the Forbush decrease of cosmic ray were observed during the period from August 3rd to 7th. Pioneer 9 observed a solar wind having the maximum velocity as high as 1,100 km/sec, and HEOS-II observed a solar wind having the velocity close to 2,000 km/sec. On the other hand, according to the scintillation of 3C-48 and 3C-144, the velocity of solar wind passing in the interplanetary space on the westside of the earth was only 300 to 400 km/sec. Therefore it is considered that the condition of solar wind on the east side of the earth differs from that on the west side of the earth. Pioneer 9 observed the pass of a shock wave on August 9th. With all radio wave sources, high velocity solar wind was observed and Pioneer 6 positioned on the west side of the earth also observed it. The thickness of this shock wave is at least 0.3 AU. Discussion is made on the cause for the difference between the asymmetric shock wave in the direction of south-west and symmetrical shock wave. The former may be blast wave, and the latter may be piston driven shock wave and the like. (Iwakiri, K.)
-
Applying Nyquist's method for stability determination to solar wind observations
Klein, Kristopher G.; Kasper, Justin C.; Korreck, K. E.; Stevens, Michael L.
2017-10-01
The role instabilities play in governing the evolution of solar and astrophysical plasmas is a matter of considerable scientific interest. The large number of sources of free energy accessible to such nearly collisionless plasmas makes general modeling of unstable behavior, accounting for the temperatures, densities, anisotropies, and relative drifts of a large number of populations, analytically difficult. We therefore seek a general method of stability determination that may be automated for future analysis of solar wind observations. This work describes an efficient application of the Nyquist instability method to the Vlasov dispersion relation appropriate for hot, collisionless, magnetized plasmas, including the solar wind. The algorithm recovers the familiar proton temperature anisotropy instabilities, as well as instabilities that had been previously identified using fits extracted from in situ observations in Gary et al. (2016). Future proposed applications of this method are discussed.
-
Simulation experiments and solar wind sputtering
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Griffith, J.E.; Papanastassiou, D.A.; Russell, W.A.; Tombrello, T.A.; Weller, R.A.
1978-01-01
In order to isolate the role played by solar wind sputtering from other lunar surface phenomena a number of simulation experiments were performed, including isotope abundance measurements of Ca sputtered from terrestrial fluorite and plagioclase by 50-keV and 130-keV 14 N beams, measurement of the energy distribution of U atoms sputtered with 80-keV 40 Ar, and measurement of the fraction of sputtered U atoms which stick on the surfaces used to collect these atoms. 10 references
-
Solar wind controlled pulsations: A review
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Odera, T.J.
1986-01-01
Studies of the solar wind controlled Pc 3, 4 pulsations by early and recent researchers are highlighted. The review focuses on the recent observations, which cover the time during the International Magnetospheric Study (IMS). Results from early and recent observations agree on one point, that is, that the Pc 3, 4 pulsations are influenced by three main solar wind parameters, namely, the solar wind velocity V/sub 5w/, the IMF orientation theta/sub x/B, and magnitude B. The results can be interpreted, preferably, in terms of an external origin for Pc 3, 4 pulsations. This implies, essentially, the signal model, which means that the pulsations originate in the upstream waves (in the interplanetary medium) and are transported by convection to the magnetopause, where they couple to oscillations of the magnetospheric field lines
-
Does renewable energy in Spain still have wind in its sails?
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Vial, Th.; Molenat, G.
2009-01-01
Spain is apparently contradictory. It figures among the European countries farthest from the Kyoto Protocol's objectives but is often cited as an example, even by President Obama, for its success in speeding up developments in renewable energy. Successes in solar and wind power have proven that Spanish industry can, with support from the state and within a decade, develop to become competitive internationally at the very time when climate change will be having repercussions on economic models and opening new markets. From this vantage point, big projects (like the Mediterranean Solar Plan or future European Union initiatives related to the Energy-Climate package) should stimulate the Spanish, who will probably soon be looking for European partners. Given its advantages in wind and solar energy, the country should be able to consolidate an efficient energy solution with a promising future, while reinforcing its particularly innovative industry. (authors)
-
Heronemus, W.
1973-01-01
An offshore wind power system is described that consists of wind driven electrical dc generators mounted on floating towers in offshore waters. The output from the generators supplies underwater electrolyzer stations in which water is converted into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen is piped to shore for conversion to electricity in fuel cell stations. It is estimated that this system can produce 159 x 10 to the ninth power kilowatt-hours per year. It is concluded that solar energy - and that includes wind energy - is the only way out of the US energy dilemma in the not too distant future.
-
Wind, Sun and Water: Complexities of Alternative Energy Development in Rural Northern Peru
Love, Thomas; Garwood, Anna
2011-01-01
Drawing on recent research with NGO-driven projects in rural Cajamarca, Peru, we examine the paradoxes of relying on wind, solar and micro-hydro generation of electricity for rural community development. In spite of cost, vagaries of these energy resources and limited material benefits, especially with wind and solar systems, villagers are eagerly…
-
Solar wind velocity and temperature in the outer heliosphere
Gazis, P. R.; Barnes, A.; Mihalov, J. D.; Lazarus, A. J.
1994-01-01
At the end of 1992, the Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11, and Voyager 2 spacecraft were at heliocentric distances of 56.0, 37.3, and 39.0 AU and heliographic latitudes of 3.3 deg N, 17.4 deg N, and 8.6 deg S, respectively. Pioneer 11 and Voyager 2 are at similar celestial longitudes, while Pioneer 10 is on the opposite side of the Sun. All three spacecraft have working plasma analyzers, so intercomparison of data from these spacecraft provides important information about the global character of the solar wind in the outer heliosphere. The averaged solar wind speed continued to exhibit its well-known variation with solar cycle: Even at heliocentric distances greater than 50 AU, the average speed is highest during the declining phase of the solar cycle and lowest near solar minimum. There was a strong latitudinal gradient in solar wind speed between 3 deg and 17 deg N during the last solar minimum, but this gradient has since disappeared. The solar wind temperature declined with increasing heliocentric distance out to a heliocentric distance of at least 20 AU; this decline appeared to continue at larger heliocentric distances, but temperatures in the outer heliosphere were suprisingly high. While Pioneer 10 and Voyager 2 observed comparable solar wind temperatures, the temperature at Pioneer 11 was significantly higher, which suggests the existence of a large-scale variation of temperature with heliographic longitude. There was also some suggestion that solar wind temperatures were higher near solar minimum.
-
Huiming Zhang; Yu Zheng; Dequn Zhou; Peifeng Zhu
2015-01-01
The effectiveness of subsidies in improving the performance of renewable energy firms has aroused significant research attention in recent years. As subsidy modes may affect corporate financial performance,we have chosen companies specializing in wind and solar energy in the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock markets as samples.The relationships between the subsidy modes and financial performance of these two types of companies are investigated with a panel data model. Results of the total sample in...
-
Interaction of suprathermal solar wind electron fluxes with sheared whistler waves: fan instability
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. Krafft
Full Text Available Several in situ measurements performed in the solar wind evidenced that solar type III radio bursts were some-times associated with locally excited Langmuir waves, high-energy electron fluxes and low-frequency electrostatic and electromagnetic waves; moreover, in some cases, the simultaneous identification of energetic electron fluxes, Langmuir and whistler waves was performed. This paper shows how whistlers can be excited in the disturbed solar wind through the so-called "fan instability" by interacting with energetic electrons at the anomalous Doppler resonance. This instability process, which is driven by the anisotropy in the energetic electron velocity distribution along the ambient magnetic field, does not require any positive slope in the suprathermal electron tail and thus can account for physical situations where plateaued reduced electron velocity distributions were observed in solar wind plasmas in association with Langmuir and whistler waves. Owing to linear calculations of growth rates, we show that for disturbed solar wind conditions (that is, when suprathermal particle fluxes propagate along the ambient magnetic field, the fan instability can excite VLF waves (whistlers and lower hybrid waves with characteristics close to those observed in space experiments.
Key words. Space plasma physics (waves and instabilities – Radio Science (waves in plasma – Solar physics, astrophysics and astronomy (radio emissions -
Interaction of suprathermal solar wind electron fluxes with sheared whistler waves: fan instability
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. Krafft
2003-07-01
Full Text Available Several in situ measurements performed in the solar wind evidenced that solar type III radio bursts were some-times associated with locally excited Langmuir waves, high-energy electron fluxes and low-frequency electrostatic and electromagnetic waves; moreover, in some cases, the simultaneous identification of energetic electron fluxes, Langmuir and whistler waves was performed. This paper shows how whistlers can be excited in the disturbed solar wind through the so-called "fan instability" by interacting with energetic electrons at the anomalous Doppler resonance. This instability process, which is driven by the anisotropy in the energetic electron velocity distribution along the ambient magnetic field, does not require any positive slope in the suprathermal electron tail and thus can account for physical situations where plateaued reduced electron velocity distributions were observed in solar wind plasmas in association with Langmuir and whistler waves. Owing to linear calculations of growth rates, we show that for disturbed solar wind conditions (that is, when suprathermal particle fluxes propagate along the ambient magnetic field, the fan instability can excite VLF waves (whistlers and lower hybrid waves with characteristics close to those observed in space experiments.Key words. Space plasma physics (waves and instabilities – Radio Science (waves in plasma – Solar physics, astrophysics and astronomy (radio emissions
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Alfredo G M Gámez López
2011-02-01
Full Text Available En el artículo se realiza un análisis de dos sensores que se aplican en energías renovables (eólica y solar,obteniéndose una ley de control óptima. Para las fuentes energéticas elegidas se proponen técnicas de altafrecuencia de conmutación y eficiencia. Para la validación de los resultados se emplean técnicas desimulación digital In this article we make an analysis of two sensors applied in renewable energies (wind and solar,obtaining an ideal law of control. For the chosen energetic sources there appear technologies of highfrequency of commutation and of high efficiency. Technologies of digital simulation validate the results.
-
Clouds blown by the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Voiculescu, M; Condurache-Bota, S; Usoskin, I
2013-01-01
In this letter we investigate possible relationships between the cloud cover (CC) and the interplanetary electric field (IEF), which is modulated by the solar wind speed and the interplanetary magnetic field. We show that CC at mid–high latitudes systematically correlates with positive IEF, which has a clear energetic input into the atmosphere, but not with negative IEF, in general agreement with predictions of the global electric circuit (GEC)-related mechanism. Thus, our results suggest that mid–high latitude clouds might be affected by the solar wind via the GEC. Since IEF responds differently to solar activity than, for instance, cosmic ray flux or solar irradiance, we also show that such a study allows distinguishing one solar-driven mechanism of cloud evolution, via the GEC, from others. (letter)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Salamov, O. M.; Aliev, F. F.
2013-01-01
This paper analyzes the discovery of the potential for jointly using solar and wind energy for heat supply (HS) and hot water supply (HWS) to a one-family private house located in the Apsheron Peninsula. (authors)
-
Magnetosheath waves under very low solar wind dynamic pressure: Wind/Geotail observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. J. Farrugia
2005-06-01
Full Text Available The expanded bow shock on and around "the day the solar wind almost disappeared" (11 May 1999 allowed the Geotail spacecraft to make a practically uninterrupted 54-h-long magnetosheath pass near dusk (16:30-21:11 magnetic local time at a radial distance of 24 to 30 RE (Earth radii. During most of this period, interplanetary parameters varied gradually and in such a way as to give rise to two extreme magnetosheath structures, one dominated by magnetohydrodynamic (MHD effects and the other by gas dynamic effects. We focus attention on unusual features of electromagnetic ion wave activity in the former magnetosheath state, and compare these features with those in the latter. Magnetic fluctuations in the gas dynamic magnetosheath were dominated by compressional mirror mode waves, and left- and right-hand polarized electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EIC waves transverse to the background field. In contrast, the MHD magnetosheath, lasting for over one day, was devoid of mirror oscillations and permeated instead by EIC waves of weak intensity. The weak wave intensity is related to the prevailing low solar wind dynamic pressures. Left-hand polarized EIC waves were replaced by bursts of right-hand polarized waves, which remained for many hours the only ion wave activity present. This activity occurred when the magnetosheath proton temperature anisotropy (= became negative. This was because the weakened bow shock exposed the magnetosheath directly to the (negative temperature anisotropy of the solar wind. Unlike the normal case studied in the literature, these right-hand waves were not by-products of left-hand polarized waves but derived their energy source directly from the magnetosheath temperature anisotropy. Brief entries into the low latitude boundary layer (LLBL and duskside magnetosphere occurred under such inflated conditions that the magnetospheric magnetic pressure was insufficient to maintain pressure balance. In these crossings, the inner edge of
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Barrows, Clayton P. [National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Katz, Jessica R. [National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Cochran, Jaquelin M. [National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Maclaurin, Galen J. [National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Marollano, Mark C. [Dept. of Energy of the Philippines, Taguig (Philippines); Gabis, Mary G. [Dept. of Energy of the Philippines, Taguig (Philippines); Reyes, Noriel C. [Dept. of Energy of the Philippines, Taguig (Philippines); Munoz, Kenneth J. [Dept. of Energy of the Philippines, Taguig (Philippines); Jesus, Clarita D. [Dept. of Energy of the Philippines, Taguig (Philippines); Asedillo, Nielson [Grid Management Committee (GMC), Inc., Pasig City (Philipines); Binayug, Jake [Grid Management Committee (GMC), Inc., Pasig City (Philipines); Cubangbang, Hanzel [National Grid Corporation of the Philippines, Metro Manila (Philippines); Reyes, Rommel [National Grid Corporation of the Philippines, Metro Manila (Philippines); de la Vina, Jonathan [Philippine Electricity Market Corporation, Pasig City (Phillipines); Olmedo, Edward [Philippine Electricity Market Corporation, Pasig City (Phillipines); Leisch, Jennifer [United States Agency for International Development, Washington DC (United States)
2018-01-24
The Republic of the Philippines is home to abundant solar, wind, and other renewable energy (RE) resources that contribute to the national government's vision to ensure sustainable, secure, sufficient, accessible, and affordable energy. Because solar and wind resources are variable and uncertain, significant generation from these resources necessitates an evolution in power system planning and operation. To support Philippine power sector planners in evaluating the impacts and opportunities associated with achieving high levels of variable RE penetration, the Department of Energy of the Philippines (DOE) and the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) have spearheaded this study along with a group of modeling representatives from across the Philippine electricity industry, which seeks to characterize the operational impacts of reaching high solar and wind targets in the Philippine power system, with a specific focus on the integrated Luzon-Visayas grids.
-
Our prodigal sun. [solar energy technology
1974-01-01
Characteristics of the sun are reported indicating it as a source of energy. Data from several space missions are discussed, and the solar activity cycle is presented. The corona, flares, prominences, spots, and wind of the sun are also discussed.
-
Relationship between velocity gradients and magnetic turbulence in the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Garrett, H.B.
1974-01-01
The correlations among the time derivative of the solar-wind velocity, the magnitude of the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF), and the IMF turbulence level are examined to test the idea that interaction between two colliding solar-wind streams can generate turbulence in the solar wind and the IMF. Data obtained by Explorer 33 on the solar wind and IMF are described, and the analysis techniques are outlined. The results indicate that the IMF turbulence level, as measured by the variance, is correlated with the existence of positive velocity gradients in the solar wind. It is noted that while the variance is an increasing function of the field magnitude, it is also independently correlated with the solar-wind velocity gradient
-
Wind energy potential assessment at four typical locations in Ethiopia
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bekele, Getachew; Palm, Bjoern [Department of Energy Technology, KTH, 10044 Stockholm (Sweden)
2009-03-15
The wind energy potential at four different sites in Ethiopia - Addis Ababa (09:02N, 38:42E), Mekele (13:33N, 39:30E), Nazret (08:32N, 39:22E), and Debrezeit (8:44N, 39:02E) - has been investigated by compiling data from different sources and analyzing it using a software tool. The results relating to wind energy potential are given in terms of the monthly average wind speed, wind speed probability density function (PDF), wind speed cumulative density function (CDF), and wind speed duration curve (DC) for all four selected sites. In brief, for measurements taken at a height of 10 m, the results show that for three of the four locations the wind energy potential is reasonable, with average wind speeds of approximately 4 m/s. For the fourth site, the mean wind speed is less than 3 m/s. This study is the first stage in a longer project and will be followed by an analysis of solar energy potential and finally the design of a hybrid standalone electric energy supply system that includes a wind turbine, PV, diesel generator and battery. (author)
-
Spectroscopic Measurements of the Ion Velocity Distribution at the Base of the Fast Solar Wind
Jeffrey, Natasha L. S.; Hahn, Michael; Savin, Daniel W.; Fletcher, Lyndsay
2018-03-01
In situ measurements of the fast solar wind reveal non-thermal distributions of electrons, protons, and minor ions extending from 0.3 au to the heliopause. The physical mechanisms responsible for these non-thermal properties and the location where these properties originate remain open questions. Here, we present spectroscopic evidence, from extreme ultraviolet spectroscopy, that the velocity distribution functions (VDFs) of minor ions are already non-Gaussian at the base of the fast solar wind in a coronal hole, at altitudes of thermal equilibrium, (b) fluid motions such as non-Gaussian turbulent fluctuations or non-uniform wave motions, or (c) some combination of both. These observations provide important empirical constraints for the source region of the fast solar wind and for the theoretical models of the different acceleration, heating, and energy deposition processes therein. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that the ion VDF in the fast solar wind has been probed so close to its source region. The findings are also a timely precursor to the upcoming 2018 launch of the Parker Solar Probe, which will provide the closest in situ measurements of the solar wind at approximately 0.04 au (8.5 solar radii).
-
Local Equation of State for Protons, and Implications for Proton Heating in the Solar Wind.
Zaslavsky, A.; Maksimovic, M.; Kasper, J. C.
2017-12-01
The solar wind protons temperature is observed to decrease with distance to the Sun at a slower rate than expected from an adiabatic expansion law: the protons are therefore said to be heated. This observation raises the question of the evaluation of the heating rate, and the question of the heat source.These questions have been investigated by previous authors by gathering proton data on various distances to the Sun, using spacecraft as Helios or Ulysses, and then computing the radial derivative of the proton temperature in order to obtain a heating rate from the internal energy equation. The problem of such an approach is the computation of the radial derivative of the temperature profile, for which uncertainties are very large, given the dispersion of the temperatures measured at a given distance.An alternative approach, that we develop in this paper, consists in looking for an equation of state that links locally the pressure (or temperature) to the mass density. If such a relation exists then one can evaluate the proton heating rate on a local basis, without having any space derivative to compute.Here we use several years of STEREO and WIND proton data to search for polytropic equation of state. We show that such relationships are indeed a good approximation in given solar wind's velocity intervals and deduce the associated protons heating rates as a function of solar wind's speed. The obtained heating rates are shown to scale from around 1 kW/kg in the slow wind to around 10 kW/kg in the fast wind, in remarkable agreement with the rate of energy observed by previous authors to cascade in solar wind's MHD turbulence at 1 AU. These results therefore support the idea of proton turbulent heating in the solar wind.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rio, Pablo del [Department of Spanish and International Economics, Econometrics and History and Economic Institutions, Facultad de Ciencias Juridicas y Sociales de Toledo, C/Cobertizo de S. Pedro Martir s/n, Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha, Toledo-45071 (Spain); Unruh, Gregory [Alumni Association Chair for Corporate Sustainability, Center for Eco-Intelligent Management, Instituto de Empresa, Serrano, 105 Madrid-28006 (Spain)
2007-09-15
This paper applies an evolutionary economics framework to analyse the factors leading to lock-out of renewable energy technologies (RETs). The cases of wind and solar photovoltaics (PV) in Spain are empirically analysed. The paper shows that a wide array of interrelated factors (technoeconomic characteristics of technology components, system-level infrastructure and institutional factors) can create both barriers to the wide diffusion of RETs and can also be drivers that foster an escape from a lock-in situation. Based on this analysis, the paper suggests several policy measures which may help to overcome the lock-out of promising renewable energy technologies. (author)
-
Intermittency Statistics in the Expanding Solar Wind
Cuesta, M. E.; Parashar, T. N.; Matthaeus, W. H.
2017-12-01
The solar wind is observed to be turbulent. One of the open questions in solar wind research is how the turbulence evolves as the solar wind expands to great distances. Some studies have focused on evolution of the outer scale but not much has been done to understand how intermittency evolves in the expanding wind beyond 1 AU (see [1,2]). We use magnetic field data from Voyager I spacecraft from 1 to 10AU to study the evolution of statistics of magnetic discontinuities. We perform various statistical tests on these discontinuities and make connections to the physical processes occurring in the expanding wind.[1] Tsurutani, Bruce T., and Edward J. Smith. "Interplanetary discontinuities: Temporal variations and the radial gradient from 1 to 8.5 AU." Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics 84.A6 (1979): 2773-2787.[2] Greco, A., et al. "Evidence for nonlinear development of magnetohydrodynamic scale intermittency in the inner heliosphere." The Astrophysical Journal 749.2 (2012): 105.
-
Coherent structures at ion scales in fast and slow solar wind: Cluster observations
Perrone, D.; Alexandrova, O.; Zouganelis, Y.; Roberts, O.; Lion, S.; Escoubet, C. P.; Walsh, A. P.; Maksimovic, M.; Lacombe, C.
2017-12-01
Spacecraft measurements generally reveal that solar wind electromagnetic fluctuations are in a state of fully-developed turbulence. Turbulence represents a very complex problem in plasmas since cross-scale coupling and kinetic effects are present. Moreover, the intermittency phenomenon, i.e. the manifestation of the non-uniform and inhomogeneous energy transfer and dissipation in a turbulent system, represents a very important aspect of the solar wind turbulent cascade. Here, we study coherent structures responsible for solar wind intermittency around ion characteristic scales. We find that, in fast solar wind, intermittency is due to Alfvén vortex-like structures and current sheets. In slow solar wind, we observe as well compressive structures like magnetic solitons, holes and shocks. By using high-time resolution magnetic field data of multi-point measurements of Cluster spacecraft, we characterize the observed coherent structures in terms of topology and propagation speed. We show that all structures around ion characteristic scales, both in fast and slow solar wind, are characterized by a strong wave-vector anisotropy in the perpendicular direction with respect to the local magnetic field. Moreover, some of them propagate in the plasma rest frame in the direction perpendicular to the local field. Finally, a further analysis on the electron and ion velocity distributions shows a high variability; in particular, close to coherent structures the electron and ion distribution functions appear strongly deformed and far from the thermodynamic equilibrium. Possible interpretations of the observed structures and their role in the heating process of the plasma are also discussed.
-
Dynamics of Intense Currents in the Solar Wind
Artemyev, Anton V.; Angelopoulos, Vassilis; Halekas, Jasper S.; Vinogradov, Alexander A.; Vasko, Ivan Y.; Zelenyi, Lev M.
2018-06-01
Transient currents in the solar wind are carried by various magnetic field discontinuities that contribute significantly to the magnetic field fluctuation spectrum. Internal instabilities and dynamics of these discontinuities are believed to be responsible for magnetic field energy dissipation and corresponding charged particle acceleration and heating. Accurate modeling of these phenomena requires detailed investigation of transient current formation and evolution. By examining such evolution using a unique data set compiled from observations of the same solar wind flow by two spacecraft at Earth’s and Mars’s orbits, we show that it consists of several processes: discontinuity thinning (decrease in thickness normalized by the ion inertial length), intensification of currents normalized to the proton thermal current (i.e., the product of proton charge, density, and thermal velocity), and increase in the compressional component of magnetic field variations across discontinuities. The significant proton temperature variation around most observed discontinuities indicates possible proton heating. Plasma velocity jumps across the discontinuities are well correlated with Alfvén velocity changes. We discuss possible explanations of the observed discontinuity evolution. We also compare the observed evolution with predictions of models describing discontinuity formation due to Alfvén wave steepening. Our results show that discontinuity modeling likely requires taking into account both the effects of nonlinear Alfvén wave dynamics and solar wind expansion.
-
Meteoric ions in the corona and solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lemaire, J.
1990-01-01
The total mass of refractory material of interplanetary origin penetrating and evaporated in the meltosphere surrounding the sun has been inferred from observations of meteoroids and fireballs falling in earth's atmosphere. The amount of iron atoms deposited this way in the solar corona is of the order of 3000 t/s or larger. The measured flux of outflowing solar wind iron ions is equal to 2200 t/s. The close agreement of both fluxes is evidence that a significant fraction of iron ions observed in the solar wind and in the corona must be of meteoric origin. A similar accord is also obtained for silicon ions. The mean velocity of meteoroid ions formed in the solar corona is equal to the free-fall velocity: i.e., independent of their atomic mass as the thermal speed of heavy ion measured in low-density solar wind streams at 1 AU. Furthermore, the heavy ions of meteoric origin escape out of the corona with a larger bulk velocity than the protons which are mainly of solar origin. These differences of heavy ion and proton bulk velocities are also observed in the solar wind. 52 refs
-
Greening the Grid - Advancing Solar, Wind, and Smart Grid Technologies (Spanish Version)
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
2016-04-01
This is the Spanish version of 'Greening the Grid - Advancing Solar, Wind, and Smart Grid Technologies'. Greening the Grid provides technical assistance to energy system planners, regulators, and grid operators to overcome challenges associated with integrating variable renewable energy into the grid.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Haixiang Zang
2016-12-01
Full Text Available In this paper, a novel method is proposed and applied to quickly calculate the capacity of energy storage for stand-alone and grid-connected wind energy systems, according to the discrete Fourier transform theory. Based on practical wind resource data and power data, which are derived from the American Wind Energy Technology Center and HOMER software separately, the energy storage capacity of a stand-alone wind energy system is investigated and calculated. Moreover, by applying the practical wind power data from a wind farm in Fujian Province, the energy storage capacity for a grid-connected wind system is discussed in this paper. This method can also be applied to determine the storage capacity of a stand-alone solar energy system with practical photovoltaic power data.
-
Three Dimensional Explicit Model for Cometary Tail Ions Interactions with Solar Wind
Al Bermani, M. J. F.; Alhamed, S. A.; Khalaf, S. Z.; Ali, H. Sh.; Selman, A. A.
2009-06-01
The different interactions between cometary tail and solar wind ions are studied in the present paper based on three-dimensional Lax explicit method. The model used in this research is based on the continuity equations describing the cometary tail-solar wind interactions. Three dimensional system was considered in this paper. Simulation of the physical system was achieved using computer code written using Matlab 7.0. The parameters studied here assumed Halley comet type and include the particle density rho, the particles velocity v, the magnetic field strength B, dynamic pressure p and internal energy E. The results of the present research showed that the interaction near the cometary nucleus is mainly affected by the new ions added to the plasma of the solar wind, which increases the average molecular weight and result in many unique characteristics of the cometary tail. These characteristics were explained in the presence of the IMF.
-
Physical Limits of Solar Energy Conversion in the Earth System.
Kleidon, Axel; Miller, Lee; Gans, Fabian
2016-01-01
Solar energy provides by far the greatest potential for energy generation among all forms of renewable energy. Yet, just as for any form of energy conversion, it is subject to physical limits. Here we review the physical limits that determine how much energy can potentially be generated out of sunlight using a combination of thermodynamics and observed climatic variables. We first explain how the first and second law of thermodynamics constrain energy conversions and thereby the generation of renewable energy, and how this applies to the conversions of solar radiation within the Earth system. These limits are applied to the conversion of direct and diffuse solar radiation - which relates to concentrated solar power (CSP) and photovoltaic (PV) technologies as well as biomass production or any other photochemical conversion - as well as solar radiative heating, which generates atmospheric motion and thus relates to wind power technologies. When these conversion limits are applied to observed data sets of solar radiation at the land surface, it is estimated that direct concentrated solar power has a potential on land of up to 11.6 PW (1 PW=10(15) W), whereas photovoltaic power has a potential of up to 16.3 PW. Both biomass and wind power operate at much lower efficiencies, so their potentials of about 0.3 and 0.1 PW are much lower. These estimates are considerably lower than the incoming flux of solar radiation of 175 PW. When compared to a 2012 primary energy demand of 17 TW, the most direct uses of solar radiation, e.g., by CSP or PV, have thus by far the greatest potential to yield renewable energy requiring the least space to satisfy the human energy demand. Further conversions into solar-based fuels would be reduced by further losses which would lower these potentials. The substantially greater potential of solar-based renewable energy compared to other forms of renewable energy simply reflects much fewer and lower unavoidable conversion losses when solar
-
Ramping Performance Analysis of the Kahuku Wind-Energy Battery Storage System
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Gevorgian, V. [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Corbus, D. [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
2013-11-01
High penetrations of wind power on the electrical grid can introduce technical challenges caused by resource variability. Such variability can have undesirable effects on the frequency, voltage, and transient stability of the grid. Energy storage devices can be an effective tool in reducing variability impacts on the power grid in the form of power smoothing and ramp control. Integrating anenergy storage system with a wind power plant can help smooth the variable power produced from wind. This paper explores the fast-response, megawatt-scale, wind-energy battery storage systems that were recently deployed throughout the Hawaiian islands to support wind and solar projects.
-
Electric solar wind sail mass budget model
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Janhunen
2013-02-01
Full Text Available The electric solar wind sail (E-sail is a new type of propellantless propulsion system for Solar System transportation, which uses the natural solar wind to produce spacecraft propulsion. The E-sail consists of thin centrifugally stretched tethers that are kept charged by an onboard electron gun and, as such, experience Coulomb drag through the high-speed solar wind plasma stream. This paper discusses a mass breakdown and a performance model for an E-sail spacecraft that hosts a mission-specific payload of prescribed mass. In particular, the model is able to estimate the total spacecraft mass and its propulsive acceleration as a function of various design parameters such as the number of tethers and their length. A number of subsystem masses are calculated assuming existing or near-term E-sail technology. In light of the obtained performance estimates, an E-sail represents a promising propulsion system for a variety of transportation needs in the Solar System.
-
Magnetic fields in the solar system planets, moons and solar wind interactions
Wicht, Johannes; Gilder, Stuart; Holschneider, Matthias
2018-01-01
This book addresses and reviews many of the still little understood questions related to the processes underlying planetary magnetic fields and their interaction with the solar wind. With focus on research carried out within the German Priority Program ”PlanetMag”, it also provides an overview of the most recent research in the field. Magnetic fields play an important role in making a planet habitable by protecting the environment from the solar wind. Without the geomagnetic field, for example, life on Earth as we know it would not be possible. And results from recent space missions to Mars and Venus strongly indicate that planetary magnetic fields play a vital role in preventing atmospheric erosion by the solar wind. However, very little is known about the underlying interaction between the solar wind and a planet’s magnetic field. The book takes a synergistic interdisciplinary approach that combines newly developed tools for data acquisition and analysis, computer simulations of planetary interiors an...
-
Temporal and radial variation of the solar wind temperature-speed relationship
Elliott, H. A.; Henney, C. J.; McComas, D. J.; Smith, C. W.; Vasquez, B. J.
2012-09-01
The solar wind temperature (T) and speed (V) are generally well correlated at ˜1 AU, except in Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejections where this correlation breaks down. We perform a comprehensive analysis of both the temporal and radial variation in the temperature-speed (T-V) relationship of the non-transient wind, and our analysis provides insight into both the causes of the T-V relationship and the sources of the temperature variability. Often at 1 AU the speed-temperature relationship is well represented by a single linear fit over a speed range spanning both the slow and fast wind. However, at times the fast wind from coronal holes can have a different T-V relationship than the slow wind. A good example of this was in 2003 when there was a very large and long-lived outward magnetic polarity coronal hole at low latitudes that emitted wind with speeds as fast as a polar coronal hole. The long-lived nature of the hole made it possible to clearly distinguish that some holes can have a different T-V relationship. In an earlier ACE study, we found that both the compressions and rarefactions T-V curves are linear, but the compression curve is shifted to higher temperatures. By separating compressions and rarefactions prior to determining the radial profiles of the solar wind parameters, the importance of dynamic interactions on the radial evolution of the solar wind parameters is revealed. Although the T-V relationship at 1 AU is often well described by a single linear curve, we find that the T-V relationship continually evolves with distance. Beyond ˜2.5 AU the differences between the compressions and rarefactions are quite significant and affect the shape of the overall T-V distribution to the point that a simple linear fit no longer describes the distribution well. Since additional heating of the ambient solar wind outside of interaction regions can be associated with Alfvénic fluctuations and the turbulent energy cascade, we also estimate the heating rate
-
Construction of research wind-solar monitoring station 'North-East Bulgaria'
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mateeva, Z.; Filipov, A.; Filipov, V.
2008-01-01
The rising energy prices, the lack of conventional energy sources, as well as the growing ecological problems, imposing the development of a new energy strategy of Bulgaria, are the prerequisites for the thorough researches in the field of wind-solar resources and the construction of experimental bases with modern equipment for the detailed investigations on the specificities of these resources with the view of their optimal utilization. The lack of homogenous covering of the territory of the country with meteorological stations, as well as the rather specific microclimatic conditions in the diverse physical-geographic localities in the country make the necessity of building experimental stations for meteo-monitoring under specific local conditions still more indispensable. This work presents the monitoring parameters of wind-solar resources in a real physical-geographic environment, for carrying out scientific-research, applied-practical and educational-training activity. A broad spectrum of scientific methods and approaches - instrumental, topographic, terrain, mathematical-statistical, numerical modeling, cartographic, educational and team-working, are envisaged for attaining the set objective. (author)
-
Weaving the history of the solar wind with magnetic field lines
Alvarado Gomez, Julian
2017-08-01
Despite its fundamental role for the evolution of the solar system, our observational knowledge of the wind properties of the young Sun comes from a single stellar observation. This unexpected fact for a field such as astrophysics arises from the difficulty of detecting Sun-like stellar winds. Their detection relies on the appearance of an astrospheric signature (from the stellar wind-ISM interaction region), visible only with the aid of high-resolution HST Lyman-alpha spectra. However, observations and modelling of the present day Sun have revealed that magnetic fields constitute the main driver of the solar wind, providing guidance on how such winds would look like back in time. In this context we propose observations of four young Sun-like stars in order to detect their astrospheres and characterise their stellar winds. For all these objects we have recovered surface magnetic field maps using the technique of Zeeman Doppler Imaging, and developed detailed wind models based on these observed field distributions. Even a single detection would represent a major step forward for our understanding of the history of the solar wind, and the outflows in more active stars. Mass loss rate estimates from HST will be confronted with predictions from realistic models of the corona/stellar wind. In one of our objects the comparison would allow us to quantify the wind variability induced by the magnetic cycle of a star, other than the Sun, for the first time. Three of our targets are planet hosts, thus the HST spectra would also provide key information on the high-energy environment of these systems, guaranteeing their legacy value for the growing field of exoplanet characterisation.
-
Synoptic maps of solar wind parameters from in situ spacecraft observations
Gazis, P. R.
1995-01-01
Solar wind observations from the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform-8 (IMP-8) and Pioneer Venus Orbiter (PVO) spacecraft from 1982 until 1988 are combined to construct synoptic maps of solar wind parameters near 1 AU. Each map consists of 6 months of hourly averaged solar wind data, binned by heliographic latitude and Carrington longitude and projected back to the Sun. These maps show the structure and time evolution of solar wind streams near 1 AU in the heliographic latitudes of +/- 7.25 deg and provide and explicit picture of several phenomena, such as gradients, changes in the inclination of the heliospheric current sheet, and the relative positions of various structures in the inner heliosphere, that is difficult to obtain from single-spacecraft observations. The stream structure varied significantly during the last solar cycle. Between 1982 and early 1985, solar wind parameters did not depend strongly on heliographic latitude. During the last solar minimum, the solar wind developed significant latitudinal structure, and high-speed streams were excluded from the vicinity of the solar equator. The interplanetary magnetic field was strongly correlated with the coronal field, and the current sheet tended to coincide with the coronal neutral line. The solar wind speed showed the expected correlations with temperature, interplanetary magnetic field, and distance from the current sheet. The solar wind speed was anticorrelated with density, but the regions of highest density occurred east of the heliospheric current sheet and the regions of lowest solar wind speed. This is consistent with compression at the leading edge of high-speed streams.
-
On the exergetic capacity factor of a wind – Solar power generation system
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Xydis, George
2013-01-01
production. In this paper, a detailed exergetic analysis aiming to identify the overall Exergetic Capacity Factor (ExCF) for a wind – solar power generation system was done. ExCF, as a new parameter, can be used for better classification and evaluation of renewable energy sources (RES). All the energy...... and exergy characteristics of wind and solar energy were examined in order to identify the variables that affect the power output of the hybrid system. A validated open source PV optimization tool was also included in the analysis, It was shown that parameters as e.g. air density or tracking losses, low......In the recent years, exergy analysis has become a very important tool in the evaluation of systems’ efficiency. It aims on minimizing the energy related-system losses and therefore maximizing energy savings and helps society substantially to move towards sustainable development and cleaner...
-
The influence of solar wind variability on magnetospheric ULF wave power
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
D. Pokhotelov
2015-06-01
Full Text Available Magnetospheric ultra-low frequency (ULF oscillations in the Pc 4–5 frequency range play an important role in the dynamics of Earth's radiation belts, both by enhancing the radial diffusion through incoherent interactions and through the coherent drift-resonant interactions with trapped radiation belt electrons. The statistical distributions of magnetospheric ULF wave power are known to be strongly dependent on solar wind parameters such as solar wind speed and interplanetary magnetic field (IMF orientation. Statistical characterisation of ULF wave power in the magnetosphere traditionally relies on average solar wind–IMF conditions over a specific time period. In this brief report, we perform an alternative characterisation of the solar wind influence on magnetospheric ULF wave activity through the characterisation of the solar wind driver by its variability using the standard deviation of solar wind parameters rather than a simple time average. We present a statistical study of nearly one solar cycle (1996–2004 of geosynchronous observations of magnetic ULF wave power and find that there is significant variation in ULF wave powers as a function of the dynamic properties of the solar wind. In particular, we find that the variability in IMF vector, rather than variabilities in other parameters (solar wind density, bulk velocity and ion temperature, plays the strongest role in controlling geosynchronous ULF power. We conclude that, although time-averaged bulk properties of the solar wind are a key factor in driving ULF powers in the magnetosphere, the solar wind variability can be an important contributor as well. This highlights the potential importance of including solar wind variability especially in studies of ULF wave dynamics in order to assess the efficiency of solar wind–magnetosphere coupling.
-
Progress in passive solar energy systems. Volume 8. Part 1
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hayes, J.; Andrejko, D.A.
1983-01-01
This book presents the papers given at a conference sponsored by the US DOE, the Solar Energy Research Institute, SolarVision, Inc., and the Southern California Solar Energy Society. The topics considered at the conference included sizing solar energy systems for agricultural applications, a farm scale ethanol production plant, the EEC wind energy RandD program, the passive solar performance assessment of an earth-sheltered house, the ARCO 1 MW photovoltaic power plant, the performance of a dendritic web photovoltaic module, second generation point focused concentrators, linear fresnel lens concentrating photovoltaic collectors, photovoltaic conversion efficiency, amorphous silicon thin film solar cells, a photovoltaic system for a shopping center, photovoltaic power generation for the utility industry, spectral solar radiation, and the analysis of insolation data.
-
Dawn-dusk asymmetry in particles of solar wind origin within the magnetosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
T. J. Stubbs
Full Text Available Solar wind/magnetosheath plasma in the magnetosphere can be identified using a component that has a higher charge state, lower density and, at least soon after their entry into the magnetosphere, lower energy than plasma from a terrestrial source. We survey here observations taken over 3 years of He2+ ions made by the Magnetospheric Ion Composition Sensor (MICS of the Charge and Mass Magnetospheric Ion Composition Experiment (CAMMICE instrument aboard POLAR. The occurrence probability of these solar wind ions is then plotted as a function of Magnetic Local Time (MLT and invariant latitude (7 for various energy ranges. For all energies observed by MICS (1.8–21.4 keV and all solar wind conditions, the occurrence probabilities peaked around the cusp region and along the dawn flank. The solar wind conditions were filtered to see if this dawnward asymmetry is controlled by the Svalgaard-Mansurov effect (and so depends on the BY component of the interplanetary magnetic field, IMF or by Fermi acceleration of He2+ at the bow shock (and so depends on the IMF ratio BX /BY . It is shown that the asymmetry remained persistently on the dawn flank, suggesting it was not due to effects associated with direct entry into the magnetosphere. This asymmetry, with enhanced fluxes on the dawn flank, persisted for lower energy ions (below a "cross-over" energy of about 23 keV but reversed sense to give higher fluxes on the dusk flank at higher energies. This can be explained by the competing effects of gradient/curvature drifts and the convection electric field on ions that are convecting sunward on re-closed field lines. The lower-energy He2+ ions E × B drift dawnwards as they move earthward, whereas the higher energy ions curvature/ gradient drift towards dusk. The convection electric field in the tail is weaker for
-
Solar winds along curved magnetic field lines
Li, Bo; Xia, Li-Dong; Chen, Yao
2011-01-01
Both remote-sensing measurements using the interplanetary scintillation (IPS) technique and in situ measurements by the Ulysses spacecraft show a bimodal structure for the solar wind at solar minimum conditions. At present what makes the fast wind fast and the slow wind slow still remains to be answered. While a robust empirical correlation exists between the coronal expansion rate $f_c$ of the flow tubes and the speeds $v$ measured in situ, further data analysis suggests that $v$ depends on ...
-
Nagai, F.
1984-01-01
Transient behavior of flare-associated solar wind in the nonradial open field region is numerically investigated, taking into account the thermal and dynamical coupling between the chromosphere and the corona. A realistic steady solar wind is constructed which passes through the inner X-type critical point in the rapidly diverging region. The wind speed shows a local maximum at the middle, O-type, critical point. The wind's density and pressure distributions decrease abruptly in the rapidly diverging region of the flow tube. The transient behavior of the wind following flare energy deposition includes ascending and descending conduction fronts. Thermal instability occurs in the lower corona, and ascending material flows out through the throat after the flare energy input ceases. A local density distribution peak is generated at the shock front due to the pressure deficit just behind the shock front.
-
Solar wind and its interaction with the Earth magnetosphere
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Grib, S.A.
1978-01-01
A critical review is given regarding the research of the stationary and non-stationary interaction of the solar wind with the Earth magnetosphere. Highlighted is the significance of the interplanetary magnetic field in the non-stationary movement of the solar wind flux. The problem of the solar wind shock waves interaction with the ''bow wave-Earth's magnetosphere'' system is being solved. Considered are the secondary phenomena, as a result of which the depression-type wave occurs, that lowers the pressure on the Earth's maanetosphere. The law, governing the movement of the magnetosphere subsolar point during the abrupt start of a geomagnetic storm has been discovered. Stationary circumvention of the magnetosphere by the solar wind flux is well described by the gas dynamic theory of the hypersonic flux. Non-stationary interaction of the solar wind shock waves with the magnetosphere is magnetohydrodynamic. It is pointed out, that the problems under consideration are important for the forecasting of strong geomagnetic perturbations on the basis of cosmic observations
-
Korreck, K. E.; Klein, K. G.; Maruca, B.; Alterman, B. L.
2017-12-01
The evolution of the solar wind from the corona to the Earth and throughout the heliosphere is a complex interplay between local micro kinetics and large scale expansion effects. These processes in the solar wind need to be separated in order to understand and distinguish the dominant mechanism for heating and acceleration of the solar wind. With the upcoming launch in 2018 of Parker Solar Probe and the launch of Solar Orbiter after, addressing the local and global phenomena will be enabled with in situ measurements. Parker Solar Probe will go closer to the Sun than any previous mission enabling the ability to examine the solar wind at an early expansion age. This work examines the predictions for what will be seen inside of the 0.25 AU (54 solar radii) where Parker Solar Probe will take measurements and lays the groundwork for disentangling the expansion and collisional effects. In addition, methods of thermal plasma data analysis to determine the stability of the plasma in the Parker Solar Probe measurements will be discussed.
-
Innovations in Wind and Solar PV Financing
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cory, K.; Coughlin, J.; Jenkin, T.; Pater, J.; Swezey, B.
2008-02-01
There is growing national interest in renewable energy development based on the economic, environmental, and security benefits that these resources provide. Historically, greater development of our domestic renewable energy resources has faced a number of hurdles, primarily related to cost, regulation, and financing. With the recent sustained increase in the costs and associated volatility of fossil fuels, the economics of renewable energy technologies have become increasingly attractive to investors, both large and small. As a result, new entrants are investing in renewable energy and new business models are emerging. This study surveys some of the current issues related to wind and solar photovoltaic (PV) energy project financing in the electric power industry, and identifies both barriers to and opportunities for increased investment.
-
A study of the solar wind deceleration in the Earth's foreshock region
Zhang, T.-L.; Schwingenschuh, K.; Russell, C. T.
1995-01-01
Previous observations have shown that the solar wind is decelerated and deflected in the earth's upstream region populated by long-period waves. This deceleration is corelated with the 'diffuse' but not with the 'reflected' ion population. The speed of the solar wind may decrease tens of km/s in the foreshock region. The solar wind dynamic pressure exerted on the magnetopause may vary due to the fluctuation of the solar wind speed and density in the foreshock region. In this study, we examine this solar wind deceleration and determine how the solar wind deceleration varies in the foreshock region.
-
Transient flows of the solar wind associated with small-scale solar activity in solar minimum
Slemzin, Vladimir; Veselovsky, Igor; Kuzin, Sergey; Gburek, Szymon; Ulyanov, Artyom; Kirichenko, Alexey; Shugay, Yulia; Goryaev, Farid
The data obtained by the modern high sensitive EUV-XUV telescopes and photometers such as CORONAS-Photon/TESIS and SPHINX, STEREO/EUVI, PROBA2/SWAP, SDO/AIA provide good possibilities for studying small-scale solar activity (SSA), which is supposed to play an important role in heating of the corona and producing transient flows of the solar wind. During the recent unusually weak solar minimum, a large number of SSA events, such as week solar flares, small CMEs and CME-like flows were observed and recorded in the databases of flares (STEREO, SWAP, SPHINX) and CMEs (LASCO, CACTUS). On the other hand, the solar wind data obtained in this period by ACE, Wind, STEREO contain signatures of transient ICME-like structures which have shorter duration (<10h), weaker magnetic field strength (<10 nT) and lower proton temperature than usual ICMEs. To verify the assumption that ICME-like transients may be associated with the SSA events we investigated the number of weak flares of C-class and lower detected by SPHINX in 2009 and STEREO/EUVI in 2010. The flares were classified on temperature and emission measure using the diagnostic means of SPHINX and Hinode/EIS and were confronted with the parameters of the solar wind (velocity, density, ion composition and temperature, magnetic field, pitch angle distribution of the suprathermal electrons). The outflows of plasma associated with the flares were identified by their coronal signatures - CMEs (only in few cases) and dimmings. It was found that the mean parameters of the solar wind projected to the source surface for the times of the studied flares were typical for the ICME-like transients. The results support the suggestion that weak flares can be indicators of sources of transient plasma flows contributing to the slow solar wind at solar minimum, although these flows may be too weak to be considered as separate CMEs and ICMEs. The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union’s Seventh Programme
-
The model of unshocked deceleration of the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gidalevich, E.Ya.
1977-01-01
The motion of the Sun relative to the interstellar gas is considered as an hydrodynamic flow in a point-source field. Interstellar gas has been found to undergo considerable compaction as it is braked in the solar gravitational field. Solar-wind braking due to ion charge exchange processes on interstellar hydrogen atoms is discussed. It is shown that tangible solar-wind braking occurs at a distance of about 3x1O 14 cm from the Sun in the apex direction. In the opposite direction solar wind propagates freely
-
Wide Field-of-View Soft X-Ray Imaging for Solar Wind-Magnetosphere Interactions
Walsh, B. M.; Collier, M. R.; Kuntz, K. D.; Porter, F. S.; Sibeck, D. G.; Snowden, S. L.; Carter, J. A.; Collado-Vega, Y.; Connor, H. K.; Cravens, T. E.;

2016-01-01
Soft X-ray imagers can be used to study the mesoscale and macroscale density structures that occur whenever and wherever the solar wind encounters neutral atoms at comets, the Moon, and both magnetized and unmagnetized planets. Charge exchange between high charge state solar wind ions and exospheric neutrals results in the isotropic emission of soft X-ray photons with energies from 0.1 to 2.0 keV. At Earth, this process occurs primarily within the magnetosheath and cusps. Through providing a global view, wide field-of-view imaging can determine the significance of the various proposed solar wind-magnetosphere interaction mechanisms by evaluating their global extent and occurrence patterns. A summary of wide field-of-view (several to tens of degrees) soft X-ray imaging is provided including slumped micropore microchannel reflectors, simulated images, and recent flight results.
-
Solar Energy Education. Social studies: activities and teacher's guide. Field test edition
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
1982-01-01
Solar energy information is made available to students through classroom instruction by way of the Solar Energy Education teaching manuals. In this manual solar energy, as well as other energy sources like wind power, is introduced by performing school activities in the area of social studies. A glossary of energy related terms is included. (BCS)
-
Tropospheric weather influenced by solar wind through atmospheric vertical coupling downward control
Prikryl, Paul; Bruntz, Robert; Tsukijihara, Takumi; Iwao, Koki; Muldrew, Donald B.; Rušin, Vojto; Rybanský, Milan; Turňa, Maroš; Šťastný, Pavel
2018-06-01
Occurrence of severe weather in the context of solar wind coupling to the magnetosphere-ionosphere-atmosphere (MIA) system is investigated. It is observed that significant snowfall, wind and heavy rain, particularly if caused by low pressure systems in winter, tend to follow arrivals of high-speed solar wind. Previously published statistical evidence that explosive extratropical cyclones in the northern hemisphere tend to occur within a few days after arrivals of high-speed solar wind streams from coronal holes (Prikryl et al., 2009, 2016) is corroborated for the southern hemisphere. Cases of severe weather events are examined in the context of the magnetosphere-ionosphere-atmosphere (MIA) coupling. Physical mechanism to explain these observations is proposed. The leading edge of high-speed solar wind streams is a locus of large-amplitude magneto-hydrodynamic waves that modulate Joule heating and/or Lorentz forcing of the high-latitude lower thermosphere generating medium-scale atmospheric gravity waves that propagate upward and downward through the atmosphere. Simulations of gravity wave propagation in a model atmosphere using the Transfer Function Model (Mayr et al., 1990) reveal that propagating waves originating in the lower thermosphere can excite a spectrum of gravity waves in the lower atmosphere. In spite of significantly reduced amplitudes but subject to amplification upon reflection in the upper troposphere, these gravity waves can provide a lift of unstable air to release instabilities in the troposphere and initiate convection to form cloud/precipitation bands. It is primarily the energy provided by release of latent heat that leads to intensification of storms. These results indicate that vertical coupling in the atmosphere exerts downward control from solar wind to the lower atmospheric levels influencing tropospheric weather development.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Holttinen, H.; Tammelin, B.; Hyvoenen, R.
1997-01-01
The recording, analyzing and publishing of statistics of wind energy production has been reorganized in cooperation of VTT Energy, Finnish Meteorological (FMI Energy) and Finnish Wind Energy Association (STY) and supported by the Ministry of Trade and Industry (KTM). VTT Energy has developed a database that contains both monthly data and information on the wind turbines, sites and operators involved. The monthly production figures together with component failure statistics are collected from the operators by VTT Energy, who produces the final wind energy statistics to be published in Tuulensilmae and reported to energy statistics in Finland and abroad (Statistics Finland, Eurostat, IEA). To be able to verify the annual and monthly wind energy potential with average wind energy climate a production index in adopted. The index gives the expected wind energy production at various areas in Finland calculated using real wind speed observations, air density and a power curve for a typical 500 kW-wind turbine. FMI Energy has produced the average figures for four weather stations using the data from 1985-1996, and produces the monthly figures. (orig.)
-
Climate information for the application of solar energy
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Robles-Gil, S.
1997-01-01
In view of population growth, industrialization and urbanization which provoked increasing energy demand there has been an increasing interest in developing new technologies that use various renewable energy sources and have less environmental impact, such as solar, wind, tidal and biomass. Solar energy is one of the energy resources with a wide geographical distribution. Nowadays, its contribution to the world's energy supply is very small, but it is considered an important long term option which will satisfy, together with conventional energy sources, the future energy needs of the world. The main objective of this work is to report the actual uses of the principal types of solar energy systems, based on their climatic, technological and economical context. This is to improve the dissemination of information on the application of climate knowledge and data, especially by national meteorological services, with the purpose to improve the planning, design and operation of solar energy systems, as well as facilitate their more widespread use
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lehner, Franz; Vuille, Francois; Ziem, Sabine [E4tech UK Ltd, London (United Kingdom); Rastogi, Ankur; Sengupta, Subhabrata [Avalon Consulting, Mumbai (India)
2012-11-15
The RE-SUPPLY project aimed to provide insight into the elements of the supply chains which are presently or can in the future evolve as critical constraints in further large-scale deployment of on- and offshore wind and solar photovoltaic energy. The objectives of the study were twofold: Risk assessment: identify potential bottlenecks in the supply chains of wind and PV and assess their criticality and timeline for occurrence; and, Risk management: identify suitable mitigation strategies and recommend specific actions at policy and industry level.
-
Experience on Wind Energy and other renewable energies in Guatemala
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Azurdia, Ivan; Arriaza, Hugo
2000-01-01
In this paper a description of the eco-regions in Central America with high potential for development of renewable energies is described. Also the applications more usual and/or in terms of effective-cost. Aspects on energy demand and supply are presented in Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua Costa Rica y Panama. Also options in terms of cost-effective for each renewable source like geothermal, solar, hydroelectric and wind power are discussed
-
Ensemble downscaling in coupled solar wind-magnetosphere modeling for space weather forecasting.
Owens, M J; Horbury, T S; Wicks, R T; McGregor, S L; Savani, N P; Xiong, M
2014-06-01
Advanced forecasting of space weather requires simulation of the whole Sun-to-Earth system, which necessitates driving magnetospheric models with the outputs from solar wind models. This presents a fundamental difficulty, as the magnetosphere is sensitive to both large-scale solar wind structures, which can be captured by solar wind models, and small-scale solar wind "noise," which is far below typical solar wind model resolution and results primarily from stochastic processes. Following similar approaches in terrestrial climate modeling, we propose statistical "downscaling" of solar wind model results prior to their use as input to a magnetospheric model. As magnetospheric response can be highly nonlinear, this is preferable to downscaling the results of magnetospheric modeling. To demonstrate the benefit of this approach, we first approximate solar wind model output by smoothing solar wind observations with an 8 h filter, then add small-scale structure back in through the addition of random noise with the observed spectral characteristics. Here we use a very simple parameterization of noise based upon the observed probability distribution functions of solar wind parameters, but more sophisticated methods will be developed in the future. An ensemble of results from the simple downscaling scheme are tested using a model-independent method and shown to add value to the magnetospheric forecast, both improving the best estimate and quantifying the uncertainty. We suggest a number of features desirable in an operational solar wind downscaling scheme. Solar wind models must be downscaled in order to drive magnetospheric models Ensemble downscaling is more effective than deterministic downscaling The magnetosphere responds nonlinearly to small-scale solar wind fluctuations.
-
Conductive solar wind models in rapidly diverging flow geometries
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Holzer, T.E.; Leer, E.
1980-01-01
A detailed parameter study of conductive models of the solar wind has been carried out, extending the previous similar studies of Durney (1972) and Durney and Hundhausen (1974) by considering collisionless inhibition of thermal conduction, rapidly diverging flow geometries, and the structure of solutions for the entire n 0 -T 0 plane (n 0 and T 0 are the coronal base density and temperature). Primary emphasis is placed on understanding the complex effects of the physical processes operative in conductive solar wind models. There are five points of particular interest that have arisen from the study: (1) neither collisionless inhibition of thermal conduction nor rapidly diverging flow geometries can significantly increase the solar wind speed at 1 AU; (2) there exists a firm upper limit on the coronal base temperature consistent with observed values of the coronal base pressure and solar wind mass flux density; (3) the principal effect of rapidly diverging flow geometries is a decrease in the solar wind mass flux density at 1 AU and an increase in the mass flux density at the coronal base; (4) collisionless inhibition of thermal conduction can lead to a solar wind flow speed that either increases or decreases with increasing coronal base density (n 0 ) and temperature (T 0 , depending on the region of the n 0 -T 0 plane considered; (5) there is a region of the n 0 -T/sub o/ plane at high coronal base densities where low-speed, high-mass-flux, transonic solar wind flows exist: a region not previously considered
-
Three Sides Billboard Wind-Solar Hybrid System Design
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Bai Xuefeng
2015-01-01
Full Text Available With the high development of world economy, the demand of energy is increasing all the time, As energy shortage and environment problem are increasing outstanding, Renewable energy has been attracting more and more attention. A kind of three sides billboard supply by wind-Solar hybrid system has been designed in this paper, the overall structure of the system, components, working principle and control strategy has been analyzed from the system perspective. The software and hardware of the system are debugged together and the result is acquired. System function is better and has achieved the expected results.
-
Charge States of Krypton and Xenon in the Solar Wind
Bochsler, Peter; Fludra, Andrzej; Giunta, Alessandra
2017-09-01
We calculate charge state distributions of Kr and Xe in a model for two different types of solar wind using the effective ionization and recombination rates provided from the OPEN_ADAS data base. The charge states of heavy elements in the solar wind are essential for estimating the efficiency of Coulomb drag in the inner corona. We find that xenon ions experience particularly low Coulomb drag from protons in the inner corona, comparable to the notoriously weak drag of protons on helium ions. It has been found long ago that helium in the solar wind can be strongly depleted near interplanetary current sheets, whereas coronal mass ejecta are sometimes strongly enriched in helium. We argue that if the extraordinary variability of the helium abundance in the solar wind is due to inefficient Coulomb drag, the xenon abundance must vary strongly. In fact, a secular decrease of the solar wind xenon abundance relative to the other heavier noble gases (Ne, Ar, Kr) has been postulated based on a comparison of noble gases in recently irradiated and ancient samples of ilmenite in the lunar regolith. We conclude that decreasing solar activity and decreasing frequency of coronal mass ejections over the solar lifetime might be responsible for a secularly decreasing abundance of xenon in the solar wind.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Maged A. Abu Adma
2017-12-01
Full Text Available This study explains a design of a fully independent -off grid- hybrid solar and wind road lighting system according to geography and weather conditions recorded from the Egyptian National Research Institute of Astronomy and Geophysics.Presenting here the virtual simulation by using Matlab/Simulink & real-time implementation of road lighting system consists of 150 W photovoltaic cell, 420 W wind generator, 100 Ah acid gel battery and LED lighting luminar 30 W -12 VDC . Over three different stages; 1.Operating the system with PV only as power source, 2. Switching to Wind generator only configuration and 3. Running the hybrid design with both PV & Wind power sources ; load characteristics and output real-time data will be recorded, evaluated ,compared and validated against the virtual simulation generated by Matlab/Simulink model.The results of this research will be used to investigate the advantages of using a hybrid system to counteract the limitations of solar and wind as solo renewable energy sources due to adverse weather conditions ,the efficiency of the proposed system as an alternative for the current conventional road lighting poles as well as the accuracy of the virtual model data in order to be used for future adaptation of the model for different geographical locations.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Komatsubara, Kazuyo [Embassy of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Tokyo (Japan)
2012-06-15
An overview is given of wind energy in Japan: Background; Wind Energy in Japan; Japanese Wind Energy Industry; Government Supports; Useful Links; Major Japanese Companies; Profiles of Major Japanese Companies; Major Wind Energy Projects in Japan.
-
Spectral analysis of turbulence propagation mechanisms in solar wind and tokamaks plasmas
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dong, Yue
2014-01-01
This thesis takes part in the study of spectral transfers in the turbulence of magnetized plasmas. We will be interested in turbulence in solar wind and tokamaks. Spacecraft measures, first principle simulations and simple dynamical systems will be used to understand the mechanisms behind spectral anisotropy and spectral transfers in these plasmas. The first part of this manuscript will introduce the common context of solar wind and tokamaks, what is specific to each of them and present some notions needed to understand the work presented here. The second part deals with turbulence in the solar wind. We will present first an observational study on the spectral variability of solar wind turbulence. Starting from the study of Grappin et al. (1990, 1991) on Helios mission data, we bring a new analysis taking into account a correct evaluation of large scale spectral break, provided by the higher frequency data of the Wind mission. This considerably modifies the result on the spectral index distribution of the magnetic and kinetic energy. A second observational study is presented on solar wind turbulence anisotropy using autocorrelation functions. Following the work of Matthaeus et al. (1990); Dasso et al. (2005), we bring a new insight on this statistical, in particular the question of normalisation choices used to build the autocorrelation function, and its consequence on the measured anisotropy. This allows us to bring a new element in the debate on the measured anisotropy depending on the choice of the referential either based on local or global mean magnetic field. Finally, we study for the first time in 3D the effects of the transverse expansion of solar wind on its turbulence. This work is based on a theoretical and numerical scheme developed by Grappin et al. (1993); Grappin and Velli (1996), but never used in 3D. Our main results deal with the evolution of spectral and polarization anisotropy due to the competition between non-linear and linear (Alfven coupling
-
Diagnostics of the solar wind transition region
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lotova, N.A.; Nagelis, Ya.V.; Rudnitskij, G.M.; Smirnova, T.V.; AN Latvijskoj SSR, Riga. Radioastrofizicheskaya Observatoriya; Moskovskij Gosudarstvennyj Univ.; AN SSSR, Moscow. Fizicheskij Inst.)
1988-01-01
Possibilities are discussed of a more complete study of hardly observable regions of the interplanetary medium, in the zone of the solar wind formation, where transition from subsonic to supersonic flow occurs at R sun . It is shown that an investigation of fine structure of the extended transonic region of the solar wind and of the sequence of changes in the parameters of the interplanetary plasma in the region of the solar wind formation with the changing distance from the Sun can be effectuated by using jointly different modifications of the occupation method. Combination of two or more modifications of this method supposes using compact radio sources of different classes and observations in two different wavelength ranges, namely at short centimeter and at meter waves
-
Stewart, H. J.
1978-01-01
A discussion on wind energy systems involved with the DOE wind energy program is presented. Some of the problems associated with wind energy systems are discussed. The cost, efficiency, and structural design of wind energy systems are analyzed.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nicol, R. M.; Chapman, S. C.; Dendy, R. O.
2009-01-01
The power spectrum of the evolving solar wind shows evidence of a spectral break between an inertial range (IR) of turbulent fluctuations at higher frequencies and a '1/f' like region at lower frequencies. In the ecliptic plane at ∼1 AU, this break occurs approximately at timescales of a few hours and is observed in the power spectra of components of velocity and magnetic field. The '1/f' energy range is of more direct coronal origin than the IR, and carries signatures of the complex magnetic field structure of the solar corona, and of footpoint stirring in the solar photosphere. To quantify the scaling properties we use generic statistical methods such as generalized structure functions and probability density functions (PDFs), focusing on solar cycle dependence and on anisotropy with respect to the background magnetic field. We present structure function analysis of magnetic and velocity field fluctuations, using a novel technique to decompose the fluctuations into directions parallel and perpendicular to the mean local background magnetic field. Whilst the magnetic field is close to '1/f', we show that the velocity field is '1/f α ' with α ≠ 1. For the velocity, the value of α varies between parallel and perpendicular fluctuations and with the solar cycle. There is also variation in α with solar wind speed. We have examined the PDFs in the fast, quiet solar wind and intriguingly, whilst parallel and perpendicular are distinct, both the B field and velocity show the same PDF of their perpendicular fluctuations, which is close to gamma or inverse Gumbel. These results point to distinct physical processes in the corona and to their mapping out into the solar wind. The scaling exponents obtained constrain the models for these processes.
-
A comparison of solar wind streams and coronal structure near solar minimum
Nolte, J. T.; Davis, J. M.; Gerassimenko, M.; Lazarus, A. J.; Sullivan, J. D.
1977-01-01
Solar wind data from the MIT detectors on the IMP 7 and 8 satellites and the SOLRAD 11B satellite for the solar-minimum period September-December, 1976, were compared with X-ray images of the solar corona taken by rocket-borne telescopes on September 16 and November 17, 1976. There was no compelling evidence that a coronal hole was the source of any high speed stream. Thus it is possible that either coronal holes were not the sources of all recurrent high-speed solar wind streams during the declining phase of the solar cycle, as might be inferred from the Skylab period, or there was a change in the appearance of some magnetic field regions near the time of solar minimum.
-
QUIET-TIME SUPRATHERMAL (∼0.1–1.5 keV) ELECTRONS IN THE SOLAR WIND
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tao, Jiawei; Wang, Linghua; Zong, Qiugang; He, Jiansen; Tu, Chuanyi [School of Earth and Space Science, Peking University, Beijing 100871 (China); Li, Gang [Department of Physics and CSPAR, University of Alabama in Huntsville, Alabama 35899 (United States); Salem, Chadi S.; Bale, Stuart D. [Space Sciences Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 (United States); Wimmer-Schweingruber, Robert F., E-mail: wanglhwang@gmail.com [Institute for Experimental and Applied Physics, University of Kiel, Leibnizstrasse 11, D-24118 Kiel (Germany)
2016-03-20
We present a statistical survey of the energy spectrum of solar wind suprathermal (∼0.1–1.5 keV) electrons measured by the WIND 3DP instrument at 1 AU during quiet times at the minimum and maximum of solar cycles 23 and 24. After separating (beaming) strahl electrons from (isotropic) halo electrons according to their different behaviors in the angular distribution, we fit the observed energy spectrum of both strahl and halo electrons at ∼0.1–1.5 keV to a Kappa distribution function with an index κ and effective temperature T{sub eff}. We also calculate the number density n and average energy E{sub avg} of strahl and halo electrons by integrating the electron measurements between ∼0.1 and 1.5 keV. We find a strong positive correlation between κ and T{sub eff} for both strahl and halo electrons, and a strong positive correlation between the strahl n and halo n, likely reflecting the nature of the generation of these suprathermal electrons. In both solar cycles, κ is larger at solar minimum than at solar maximum for both strahl and halo electrons. The halo κ is generally smaller than the strahl κ (except during the solar minimum of cycle 23). The strahl n is larger at solar maximum, but the halo n shows no difference between solar minimum and maximum. Both the strahl n and halo n have no clear association with the solar wind core population, but the density ratio between the strahl and halo roughly anti-correlates (correlates) with the solar wind density (velocity)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kirby, B.; King, J.; Milligan, M.
2012-06-01
The anticipated increase in variable generation in the Western Interconnection over the next several years has raised concerns about how to maintain system balance, especially in smaller Balancing Authority Areas (BAAs). Given renewable portfolio standards in the West, it is possible that more than 50 gigawatts of wind capacity will be installed by 2020. Significant quantities of solar generation are likely to be added as well. The consequent increase in variability and uncertainty that must be managed by the conventional generation fleet and responsive loads has resulted in a proposal for an Energy Imbalance Market (EIM). This paper extends prior work to estimate the reserve requirements for regulation, spinning, and non-spinning reserves with and without the EIM. We also discuss alternative approaches to allocating reserve requirements and show that some apparently attractive allocation methods have undesired consequences.
-
The solar wind control of electron fluxes in geostationary orbit during magnetic storms
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Popov, G.V.; Degtyarev, V.I.; Sheshukov, S.S.; Chudnenko, S.E.
1999-01-01
The dynamics of electron fluxes (with energies from 30 to 1360 keV) in geostationary orbit during magnetic storms was investigated on the basis of LANL spacecraft 1976-059 and 1977-007 data. Thirty-seven magnetic storms with distinct onsets from the time interval July 1976-December 1978 were used in the analysis. A treatment of experimental data involved the moving averaging and the overlapping epoch method. The smoothed component of electron fluxes represents mainly trapped electrons and shows their strong dependence on the solar wind velocity. The time lag between a smoothed electron flux and the solar wind velocity increases with electron energy reflecting dynamics of the inner magnetosphere filling with trapped energetic electrons originating from substorm injection regions located not far outside geostationary orbit
-
Effect of wind energy system performance on optimal renewable energy model - an analysis
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Iniyan, S.; Jagadeesan, T.R.
1998-01-01
The Optimal Renewable Energy Model (OREM) has been developed to determine the optimum level of renewable energy sources utilisation in India for the year 2020-21. The model aims at minimising cost/efficiency ratio and determines the optimum allocation of different renewable energy sources for various end-uses. The extent of social acceptance level, potential limit, demand and reliability will decide the renewable energy distribution pattern and are hence used as constraints in the model. In this paper, the performance and reliability of wind energy system and its effects on OREM model has been analysed. The demonstration windfarm (4 MW) which is situated in Muppandal, a village in the southern part of India, has been selected for the study. The windfarm has 20 wind turbine machines of 200 KW capacity . The average technical availability, real availability and capacity factor have been analysed from 1991 to 1995 and they are found to be 94.1%, 76.4% and 25.5% respectively. The reliability factor of wind energy systems is found to be 0.5 at 10,000 hours. The OREM model is analysed considering the above said factors for wind energy system, solar energy system and biomass energy systems. The model selects wind energy for pumping end-use to an extent of 0.3153 x10 15 KJ. (Author)
-
风能、光伏发电与储能%Wind energy,photovoltaic generation and energy-storage
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
王金良
2009-01-01
发展可再生能源对满足能源需求、减少环境污染和促进经济可持续发展具有重大意义.总结了全球风能、太阳能发电产业的发展:详细分析了中国风能和光伏发电的现状、市场分布和发展目标.储能是风能、光伏发电系统的重要组成部分,阐述了储能电源的技术要求,蓄电池储能仍是目前最成熟、最可靠的储能技术;风能、太阳能发电产业的高速发展将为储能电池和储能技术的发展带来新的市场和机会:开发新型储能电源和技术将成为今后电池业界的研究热点.%It's significant that developing the renewable energy to meet the energy demands, reducing environmental pollution and accelerating the sustainable economic development. The global progresses of power generation industry with wind energy and solar energy were summarized in this paper. The status market distribution and development goal of wind energy and solar energy in China were analyzed in detail. Energy-storage is an important part of power generation systems in wind energy and solar energy. The technical demands of energy-storage power sources were represented. At present, energy-storage with secondary batteries was the most mature and credible ways. The rapid development of power generation industry with wind energy and solar energy would bring new markets and opportunities for energy-storage batteries and technique. The development of new type of storage power sources and techniques would be the research hotspots in the field of battery industries in the future.
-
From the Solar Wind to the Magnetospheric Substorm
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
E.A. Ponomarev; P.A. Sedykh; O.V. Mager
2005-01-01
This paper gives a brief outline of the progression from the first substorm model developed in Ref.[4] and [8] based on Kennel's ideas[3], to the present views about the mechanism by which solar wind kinetic energy is converted to electromagnetic energy at the Bow Shock and by which this energy is transferred to the magnetosphere in the form of current; about the transformation of the energy of this current to gas kinetic energy of convecting plasma tubes, and, finally, the back transformation of gas kinetic energy to electromagnetic energy in secondary magnetospheric MHD generators. The questions of the formation of the magnetospheric convection system, the nature of substorm break-up, and of the matching of currents in the magnetosphere-ionosphere system are discussed.
-
McIntosh, Gordon
2010-01-01
As an astronomy instructor I am always looking for commonly experienced Earthly phenomena to help my students and me understand and appreciate similar occurrences elsewhere in the solar system. Recently I wrote short "TPT" articles on frost and precipitation. The present article is on winds in the solar system. A windy day or storm might…
-
Hybrid power system (hydro, solar and wind) for rural electricity generation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mahinda Kurukulasuriya
2000-01-01
Generation of affordable cheap electric energy for rural development by a hybrid power system (10-50 kW) of hydropower, solar and wind energies on self determining basis and computer application to determine its performance. In this paper the following topics were discussed, design of hybrid power system, its justification and economic analysis, manufacturing and installation of the system. (Author)
-
Magnetosheath waves under very low solar wind dynamic pressure: Wind/Geotail observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. J. Farrugia
2005-06-01
Full Text Available The expanded bow shock on and around "the day the solar wind almost disappeared" (11 May 1999 allowed the Geotail spacecraft to make a practically uninterrupted 54-h-long magnetosheath pass near dusk (16:30-21:11 magnetic local time at a radial distance of 24 to 30 RE (Earth radii. During most of this period, interplanetary parameters varied gradually and in such a way as to give rise to two extreme magnetosheath structures, one dominated by magnetohydrodynamic (MHD effects and the other by gas dynamic effects. We focus attention on unusual features of electromagnetic ion wave activity in the former magnetosheath state, and compare these features with those in the latter. Magnetic fluctuations in the gas dynamic magnetosheath were dominated by compressional mirror mode waves, and left- and right-hand polarized electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EIC waves transverse to the background field. In contrast, the MHD magnetosheath, lasting for over one day, was devoid of mirror oscillations and permeated instead by EIC waves of weak intensity. The weak wave intensity is related to the prevailing low solar wind dynamic pressures. Left-hand polarized EIC waves were replaced by bursts of right-hand polarized waves, which remained for many hours the only ion wave activity present. This activity occurred when the magnetosheath proton temperature anisotropy (=
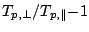 became negative. This was because the weakened bow shock exposed the magnetosheath directly to the (negative temperature anisotropy of the solar wind. Unlike the normal case studied in the literature, these right-hand waves were not by-products of left-hand polarized waves but derived their energy source directly from the magnetosheath temperature anisotropy. Brief entries into the
became negative. This was because the weakened bow shock exposed the magnetosheath directly to the (negative temperature anisotropy of the solar wind. Unlike the normal case studied in the literature, these right-hand waves were not by-products of left-hand polarized waves but derived their energy source directly from the magnetosheath temperature anisotropy. Brief entries into the -
The Solar Wind Source Cycle: Relationship to Dynamo Behavior
Luhmann, J. G.; Li, Y.; Lee, C. O.; Jian, L. K.; Petrie, G. J. D.; Arge, C. N.
2017-12-01
Solar cycle trends of interest include the evolving properties of the solar wind, the heliospheric medium through which the Sun's plasmas and fields interact with Earth and the planets -including the evolution of CME/ICMEs enroute. Solar wind sources include the coronal holes-the open field regions that constantly evolve with solar magnetic fields as the cycle progresses, and the streamers between them. The recent cycle has been notably important in demonstrating that not all solar cycles are alike when it comes to contributions from these sources, including in the case of ecliptic solar wind. In particular, it has modified our appreciation of the low latitude coronal hole and streamer sources because of their relative prevalence. One way to understand the basic relationship between these source differences and what is happening inside the Sun and on its surface is to use observation-based models like the PFSS model to evaluate the evolution of the coronal field geometry. Although the accuracy of these models is compromised around solar maximum by lack of global surface field information and the sometimes non-potential evolution of the field related to more frequent and widespread emergence of active regions, they still approximate the character of the coronal field state. We use these models to compare the inferred recent cycle coronal holes and streamer belt sources of solar wind with past cycle counterparts. The results illustrate how (still) hemispherically asymmetric weak polar fields maintain a complex mix of low-to-mid latitude solar wind sources throughout the latest cycle, with a related marked asymmetry in the hemispheric distribution of the ecliptic wind sources. This is likely to be repeated until the polar field strength significantly increases relative to the fields at low latitudes, and the latter symmetrize.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Breus, T.K.; Krymskij, A.M.; Mitnitskij, V.Ya.
1987-01-01
Numeric modelling of the Venus flow-around by the solar wind with regard to stream loading by heavy ions, produced under photoionization of the Venus neutral oxygen corona, is conducted. It is shown, that this effect can account for a whole number of peculiarities related to the solar wind interaction with the planet which have not been clearly explained yet, namely, shock wave position, solar wind stream and magnetic field characteristics behind the front
-
Computational techniques for assessing power grids with wind energy and storage
Bhaumik, D.
2018-01-01
The electricity sector is going through a rapid transition in the energy landscape. The global share of distributed renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind power for energy generation is on the rise. Even though this transition to renewable energy sources is beneficial for reducing global
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kasper, J. C.; Stevens, M. L.; Korreck, K. E.; Maruca, B. A.; Kiefer, K. K.; Schwadron, N. A.; Lepri, S. T.
2012-01-01
The changing relationships between solar wind speed, helium abundance, and minor ion charge state are examined over solar cycle 23. Observations of the abundance of helium relative to hydrogen (A He ≡ 100 × n He /n H ) by the Wind spacecraft are used to examine the dependence of A He on solar wind speed and solar activity between 1994 and 2010. This work updates an earlier study of A He from 1994 to 2004 to include the recent extreme solar minimum and broadly confirms our previous result that A He in slow wind is strongly correlated with sunspot number, reaching its lowest values in each solar minima. During the last minimum, as sunspot numbers reached their lowest levels in recent history, A He continued to decrease, falling to half the levels observed in slow wind during the previous minimum and, for the first time observed, decreasing even in the fastest solar wind. We have also extended our previous analysis by adding measurements of the mean carbon and oxygen charge states observed with the Advanced Composition Explorer spacecraft since 1998. We find that as solar activity decreased, the mean charge states of oxygen and carbon for solar wind of a given speed also fell, implying that the wind was formed in cooler regions in the corona during the recent solar minimum. The physical processes in the coronal responsible for establishing the mean charge state and speed of the solar wind have evolved with solar activity and time.
-
Leithead, W E
2007-04-15
From its rebirth in the early 1980s, the rate of development of wind energy has been dramatic. Today, other than hydropower, it is the most important of the renewable sources of power. The UK Government and the EU Commission have adopted targets for renewable energy generation of 10 and 12% of consumption, respectively. Much of this, by necessity, must be met by wind energy. The US Department of Energy has set a goal of 6% of electricity supply from wind energy by 2020. For this potential to be fully realized, several aspects, related to public acceptance, and technical issues, related to the expected increase in penetration on the electricity network and the current drive towards larger wind turbines, need to be resolved. Nevertheless, these challenges will be met and wind energy will, very likely, become increasingly important over the next two decades. An overview of the technology is presented.
-
Solar wind plasma structure near a 'HELIOS-Perihelion'
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kikuchi, H.
1979-01-01
The purpose of this paper is to introduce a couple of preliminary but important results obtained from HELIOS observation concerning solar wind plasma structure near a ''HELIOS-Perihelion'' among the data analyses in progress, partly in relation to laboratory plasma. Idealized profiles of the bulk velocity, density and temperature of solar wind near 0.3 AU as deduced from HELIOS A data and correlated K-coronal contours were obtained. During 1974 - 1976, the sun was in the period of declining cycle, and the coronal holes expanded to lower latitudes from northern and southern holes. There is general tendency that the northern coronal hole is somewhat larger than the southern coronal hole. In regards to solar wind velocity, there are two fast stream regions with velocity as high as 800 Km/sec. An electron spectrum measured near a HELIOS-Perihelion (0.3 AU) approximately in the solar direction is shown. Three regions can be distinguished in velocity distribution. The density contours of solar wind electrons in velocity space exhibit a narrow beam of electrons in the magnetic field direction close to the plane of observation. (Kato, T.)
-
Theoretical models for MHD turbulence in the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Veltri, P.; Malara, F.
1997-01-01
The in situ measurements of velocity, magnetic field, density and temperature fluctuations performed in the solar wind have greatly improved our knowledge of MDH turbulence not only from the point of view of space physics but also from the more general point of view of plasma physics. These fluctuations which extend over a wide range of frequencies (about 5 decades), a fact which seems to be the signature of turbulent nonlinear energy cascade, display, mainly in the trailing edge of high-speed streams, a number of features characteristic of a self-organized situation: i) a high degree of correlation between magnetic and velocity field fluctuations, ii) a very low level of fluctuations in mass density and magnetic-field intensity, iii) a considerable anisotropy revealed by minimum variance analysis of the magnetic-field correlation tensor. Many fundamental processes in plasma physics, which were largely unknown or not understood before their observations in the solar wind, have been explained, by building up analytical models or performing numerical simulations. We discuss the most recent analytical theories and numerical simulations and outline the limits implicit in any analysis which consider the low-frequency solar-wind fluctuations as a superposition of linear modes. The characterization of low-frequency fluctuations during Alfvenic periods, which results from the models discussed, is finally presented
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Milligan, M.; Holttinen, H.; Soder, L.; Clark, C.; Pineda, I.
2012-09-01
Wind and solar power will give rise to challenges in electricity markets regarding flexibility, capacity adequacy, and the participation of wind and solar generators to markets. Large amounts of wind power will have impacts on bulk power system markets and electricity prices. If the markets respond to increased wind power by increasing investments in low-capital, high-cost or marginal-cost power, the average price may remain in the same range. However, experiences so far from Denmark, Germany, Spain, and Ireland are such that the average market prices have decreased because of wind power. This reduction may result in additional revenue insufficiency, which may be corrected with a capacity market, yet capacity markets are difficult to design. However, the flexibility attributes of the capacity also need to be considered. Markets facilitating wind and solar integration will include possibilities for trading close to delivery (either by shorter gate closure times or intraday markets). Time steps chosen for markets can enable more flexibility to be assessed. Experience from 5- and 10-minute markets has been encouraging.
-
Scale Dependence of Magnetic Helicity in the Solar Wind
Brandenburg, Axel; Subramanian, Kandaswamy; Balogh, Andre; Goldstein, Melvyn L.
2011-01-01
We determine the magnetic helicity, along with the magnetic energy, at high latitudes using data from the Ulysses mission. The data set spans the time period from 1993 to 1996. The basic assumption of the analysis is that the solar wind is homogeneous. Because the solar wind speed is high, we follow the approach first pioneered by Matthaeus et al. by which, under the assumption of spatial homogeneity, one can use Fourier transforms of the magnetic field time series to construct one-dimensional spectra of the magnetic energy and magnetic helicity under the assumption that the Taylor frozen-in-flow hypothesis is valid. That is a well-satisfied assumption for the data used in this study. The magnetic helicity derives from the skew-symmetric terms of the three-dimensional magnetic correlation tensor, while the symmetric terms of the tensor are used to determine the magnetic energy spectrum. Our results show a sign change of magnetic helicity at wavenumber k approximately equal to 2AU(sup -1) (or frequency nu approximately equal to 2 microHz) at distances below 2.8AU and at k approximately equal to 30AU(sup -1) (or nu approximately equal to 25 microHz) at larger distances. At small scales the magnetic helicity is positive at northern heliographic latitudes and negative at southern latitudes. The positive magnetic helicity at small scales is argued to be the result of turbulent diffusion reversing the sign relative to what is seen at small scales at the solar surface. Furthermore, the magnetic helicity declines toward solar minimum in 1996. The magnetic helicity flux integrated separately over one hemisphere amounts to about 10(sup 45) Mx(sup 2) cycle(sup -1) at large scales and to a three times lower value at smaller scales.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nelson, V.; Starcher, K.; Gaines, H. [West Texas A& M Univ., Canyon, TX (United States)
1997-12-31
Data are being collected at 17 sites to delineate a baseline for the wind and solar resource across Texas. Wind data are being collected at 10, 25, and 40 m (in some cases at 50 m) to determine wind shear and power at hub heights of large turbines. Many of the sites are located in areas of predicted terrain enhancement. The typical day in a month for power and wind turbine output was calculated for selected sites and combination of sites; distributed systems. Major result to date is that there is the possibility of load matching in South Texas during the summer months, even though the average values by month indicate a low wind potential.
-
RECONSTRUCTING THE SOLAR WIND FROM ITS EARLY HISTORY TO CURRENT EPOCH
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Airapetian, Vladimir S.; Usmanov, Arcadi V., E-mail: vladimir.airapetian@nasa.gov, E-mail: avusmanov@gmail.com [NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD (United States)
2016-02-01
Stellar winds from active solar-type stars can play a crucial role in removal of stellar angular momentum and erosion of planetary atmospheres. However, major wind properties except for mass-loss rates cannot be directly derived from observations. We employed a three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic Alfvén wave driven solar wind model, ALF3D, to reconstruct the solar wind parameters including the mass-loss rate, terminal velocity, and wind temperature at 0.7, 2, and 4.65 Gyr. Our model treats the wind thermal electrons, protons, and pickup protons as separate fluids and incorporates turbulence transport, eddy viscosity, turbulent resistivity, and turbulent heating to properly describe proton and electron temperatures of the solar wind. To study the evolution of the solar wind, we specified three input model parameters, the plasma density, Alfvén wave amplitude, and the strength of the dipole magnetic field at the wind base for each of three solar wind evolution models that are consistent with observational constrains. Our model results show that the velocity of the paleo solar wind was twice as fast, ∼50 times denser and 2 times hotter at 1 AU in the Sun's early history at 0.7 Gyr. The theoretical calculations of mass-loss rate appear to be in agreement with the empirically derived values for stars of various ages. These results can provide realistic constraints for wind dynamic pressures on magnetospheres of (exo)planets around the young Sun and other active stars, which is crucial in realistic assessment of the Joule heating of their ionospheres and corresponding effects of atmospheric erosion.
-
RECONSTRUCTING THE SOLAR WIND FROM ITS EARLY HISTORY TO CURRENT EPOCH
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Airapetian, Vladimir S.; Usmanov, Arcadi V.
2016-01-01
Stellar winds from active solar-type stars can play a crucial role in removal of stellar angular momentum and erosion of planetary atmospheres. However, major wind properties except for mass-loss rates cannot be directly derived from observations. We employed a three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic Alfvén wave driven solar wind model, ALF3D, to reconstruct the solar wind parameters including the mass-loss rate, terminal velocity, and wind temperature at 0.7, 2, and 4.65 Gyr. Our model treats the wind thermal electrons, protons, and pickup protons as separate fluids and incorporates turbulence transport, eddy viscosity, turbulent resistivity, and turbulent heating to properly describe proton and electron temperatures of the solar wind. To study the evolution of the solar wind, we specified three input model parameters, the plasma density, Alfvén wave amplitude, and the strength of the dipole magnetic field at the wind base for each of three solar wind evolution models that are consistent with observational constrains. Our model results show that the velocity of the paleo solar wind was twice as fast, ∼50 times denser and 2 times hotter at 1 AU in the Sun's early history at 0.7 Gyr. The theoretical calculations of mass-loss rate appear to be in agreement with the empirically derived values for stars of various ages. These results can provide realistic constraints for wind dynamic pressures on magnetospheres of (exo)planets around the young Sun and other active stars, which is crucial in realistic assessment of the Joule heating of their ionospheres and corresponding effects of atmospheric erosion
-
Evaluation of beam tracking strategies for the THOR-CSW solar wind instrument
De Keyser, Johan; Lavraud, Benoit; Prech, Lubomir; Neefs, Eddy; Berkenbosch, Sophie; Beeckman, Bram; Maggiolo, Romain; Fedorov, Andrei; Baruah, Rituparna; Wong, King-Wah; Amoros, Carine; Mathon, Romain; Génot, Vincent
2017-04-01
We compare different beam tracking strategies for the Cold Solar Wind (CSW) plasma spectrometer on the ESA M4 THOR mission candidate. The goal is to intelligently select the energy and angular windows the instrument is sampling and to adapt these windows as the solar wind properties evolve, with the aim to maximize the velocity distribution acquisition rate while maintaining excellent energy and angular resolution. Using synthetic data constructed using high-cadence measurements by the Faraday cup instrument on the Spektr-R mission (30 ms resolution), we test the performance of energy beam tracking with or without angular beam tracking. The algorithm can be fed both by data acquired by the plasma spectrometer during the previous measurement cycle, or by data from another instrument, in casu the Faraday Cup (FAR) instrument foreseen on THOR. We verify how these beam tracking algorithms behave for different sizes of the energy and angular windows, and for different data integration times, in order to assess the limitations of the algorithm and to avoid situations in which the algorithm loses track of the beam.
-
Wind energy-hydrogen storage hybrid power generation
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Wenjei Yang; Orhan Aydin [University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI (United States). Dept. of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics
2001-07-01
In this theoretical investigation, a hybrid power generation system utilizing wind energy and hydrogen storage is presented. Firstly, the available wind energy is determined, which is followed by evaluating the efficiency of the wind energy conversion system. A revised model of windmill is proposed from which wind power density and electric power output are determined. When the load demand is less than the output of the generation, the excess electric power is relayed to the electrolytic cell where it is used to electrolyse the de-ionized water. Hydrogen thus produced can be stored as hydrogen compressed gas or liquid. Once the hydrogen is stored in an appropriate high-pressure vessel, it can be used in a combustion engine, fuel cell, or burned in a water-cooled burner to produce a very high-quality steam for space heating, or to drive a turbine to generate electric power. It can also be combined with organic materials to produce synthetic fuels. The conclusion is that the system produces no harmful waste and depletes no resources. Note that this system also works well with a solar collector instead of a windmill. (author)
-
Solar-wind krypton and solid/gas fractionation in the early solar nebula
Wiens, Roger C.; Burnett, D. S.; Neugebauer, M.; Pepin, R. O.
1991-01-01
The solar-system Kr abundance is calculated from solar-wind noble-gas ratios, determined previously by low-temperature oxidations of lunar ilmenite grains, normalized to Si by spacecraft solar-wind measurements. The estimated Kr-83 abundance of 4.1 + or - 1.5 per million Si atoms is within uncertainty of estimates assuming no fractionation, determined from CI-chondrite abundances of surrounding elements. This is significant because it is the first such constraint on solid/gas fractionation, though the large uncertainty only confines it to somewhat less than a factor of two.
-
Identifying Wind and Solar Ramping Events: Preprint
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Florita, A.; Hodge, B. M.; Orwig, K.
2013-01-01
Wind and solar power are playing an increasing role in the electrical grid, but their inherent power variability can augment uncertainties in power system operations. One solution to help mitigate the impacts and provide more flexibility is enhanced wind and solar power forecasting; however, its relative utility is also uncertain. Within the variability of solar and wind power, repercussions from large ramping events are of primary concern. At the same time, there is no clear definition of what constitutes a ramping event, with various criteria used in different operational areas. Here the Swinging Door Algorithm, originally used for data compression in trend logging, is applied to identify variable generation ramping events from historic operational data. The identification of ramps in a simple and automated fashion is a critical task that feeds into a larger work of 1) defining novel metrics for wind and solar power forecasting that attempt to capture the true impact of forecast errors on system operations and economics, and 2) informing various power system models in a data-driven manner for superior exploratory simulation research. Both allow inference on sensitivities and meaningful correlations, as well as the ability to quantify the value of probabilistic approaches for future use in practice.
-
The solar wind in time: a change in the behaviour of older winds?
O'Fionnagáin, D.; Vidotto, A. A.
2018-05-01
In this paper, we model the wind of solar analogues at different ages to investigate the evolution of the solar wind. Recently, it has been suggested that winds of solar type stars might undergo a change in properties at old ages, whereby stars older than the Sun would be less efficient in carrying away angular momentum than what was traditionally believed. Adding to this, recent observations suggest that old solar-type stars show a break in coronal properties, with a steeper decay in X-ray luminosities and temperatures at older ages. We use these X-ray observations to constrain the thermal acceleration of winds of solar analogues. Our sample is based on the stars from the `Sun in Time' project with ages between 120 and 7000 Myr. The break in X-ray properties leads to a break in wind mass-loss rates (\\dot{M}) at roughly 2 Gyr, with \\dot{M} (t 2 Gyr) ∝ t-3.9. This steep decay in \\dot{M} at older ages could be the reason why older stars are less efficient at carrying away angular momentum, which would explain the anomalously rapid rotation observed in older stars. We also show that none of the stars in our sample would have winds dense enough to produce thermal emission above 1-2 GHz, explaining why their radio emissions have not yet been detected. Combining our models with dynamo evolution models for the magnetic field of the Earth, we find that, at early ages (≈100 Myr), our Earth had a magnetosphere that was three or more times smaller than its current size.
-
Podder, Shuvankar; Khan, Raihan Sayeed; Alam Mohon, Shah Md Ashraful
2015-01-01
The size optimization and economic evaluation of the solar-wind hybrid renewable energy system (RES) to meet the electricity demand of 276 kWh/day with 40 kW peak load have been determined in this study. The load data has been collected from the motels situated in the coastal areas of Patenga, Chittagong. RES in standalone as well as grid connected mode have been considered. The optimal system configurations have been determined based on systems net present cost (NPC) and cost of per unit ene...
-
Chang, Ouliang
The objective of this dissertation is to study the physics of whistler turbulence evolution and its role in energy transport and dissipation in the solar wind plasmas through computational and theoretical investigations. This dissertation presents the first fully three-dimensional (3D) particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations of whistler turbulence forward cascade in a homogeneous, collisionless plasma with a uniform background magnetic field B o, and the first 3D PIC simulation of whistler turbulence with both forward and inverse cascades. Such computationally demanding research is made possible through the use of massively parallel, high performance electromagnetic PIC simulations on state-of-the-art supercomputers. Simulations are carried out to study characteristic properties of whistler turbulence under variable solar wind fluctuation amplitude (epsilon e) and electron beta (betae), relative contributions to energy dissipation and electron heating in whistler turbulence from the quasilinear scenario and the intermittency scenario, and whistler turbulence preferential cascading direction and wavevector anisotropy. The 3D simulations of whistler turbulence exhibit a forward cascade of fluctuations into broadband, anisotropic, turbulent spectrum at shorter wavelengths with wavevectors preferentially quasi-perpendicular to B o. The overall electron heating yields T ∥ > T⊥ for all epsilone and betae values, indicating the primary linear wave-particle interaction is Landau damping. But linear wave-particle interactions play a minor role in shaping the wavevector spectrum, whereas nonlinear wave-wave interactions are overall stronger and faster processes, and ultimately determine the wavevector anisotropy. Simulated magnetic energy spectra as function of wavenumber show a spectral break to steeper slopes, which scales as k⊥lambda e ≃ 1 independent of betae values, where lambdae is electron inertial length, qualitatively similar to solar wind observations. Specific
-
Magnetosheath Propagation Time of Solar Wind Directional Discontinuities
Samsonov, A. A.; Sibeck, D. G.; Dmitrieva, N. P.; Semenov, V. S.; Slivka, K. Yu.; Å afránkova, J.; Němeček, Z.
2018-05-01
Observed delays in the ground response to solar wind directional discontinuities have been explained as the result of larger than expected magnetosheath propagation times. Recently, Samsonov et al. (2017, https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL075020) showed that the typical time for a southward interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) turning to propagate across the magnetosheath is 14 min. Here by using a combination of magnetohydrodynamic simulations, spacecraft observations, and analytic calculations, we study the dependence of the propagation time on solar wind parameters and near-magnetopause cutoff speed. Increases in the solar wind speed result in greater magnetosheath plasma flow velocities, decreases in the magnetosheath thickness and, as a result, decreases in the propagation time. Increases in the IMF strength result in increases in the magnetosheath thickness and increases in the propagation time. Both magnetohydrodynamic simulations and observations suggest that propagation times are slightly smaller for northward IMF turnings. Magnetosheath flow deceleration must be taken into account when predicting the arrival times of solar wind structures at the dayside magnetopause.
-
Theoretical contributions to solar wind research - a review
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cuperman, S.
1977-01-01
The theoretical work on the solar wind phenomena done since 1958 can be divided into two main parts: Part I - development and refinement of Parker's initial macroscopic model, the emphasis being placed upon steady state, spherically symmetric flow and the identification of the structure-less background solar wind plasma with the low speed flow. It is in this part that much progress in understanding the solar wind phenomenon has been achieved; Part II - generalization of Parker's initial model such as to include microscopic (kinetic) aspects, temporal variations, deviations from spherically symmetric conditions, complex local magnetic configurations, etc. The last two aspects, in particular, have received considerable attention with the discovery of the coronal holes, their association with high-speed flows and the tentative identification of these flows with the structure-less background solar wind plasma. This review is confined to Part I, as defined above. However, for completeness, several important aspects connected with the subjects enumerated under Part II and which represent the objects of the most recent investigation are also briefly reviewed. (Auth.)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ibanez, Eduardo; Brinkman, Gregory; Hummon, Marissa [National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Lew, Debra
2012-07-01
Increasing penetration of wind and solar energy are raising concerns among electric system operators because of the variability and uncertainty associated with the power sources. Previous work focused on the quantification of reserves for systems with wind power. This paper presents a new methodology that allows the determination of necessary reserves for high penetrations of photovoltaic power and compares it to the wind-based methodology. The solar reserve methodology was applied to Phase 2 of the Western Wind and Solar Integration Study. A summary of the results is included. (orig.)
-
Transient behavior of a flare-associated solar wind. I - Gas dynamics in a radial open field region
Nagai, F.
1984-01-01
A numerical investigation is conducted into the way in which a solar wind model initially satisfying both steady state and energy balance conditions is disturbed and deformed, under the assumption of heating that correspoonds to the energy release of solar flares of an importance value of approximately 1 which occur in radial open field regions. Flare-associated solar wind transient behavior is modeled for 1-8 solar radii. The coronal temperature around the heat source region rises, and a large thermal conductive flux flows inward to the chromosphere and outward to interplanetary space along field lines. The speed of the front of expanding chromospheric material generated by the impingement of the conduction front on the upper chromosphere exceeds the local sound velocity in a few minutes and eventually exceeds 100 million cm/sec.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. Lacombe
Full Text Available The solar wind properties depend on λ, the heliomagnetic latitude with respect to the heliospheric current sheet (HCS, more than on the heliographic latitude. We analyse the wind properties observed by Wind at 1 AU during about 2.5 solar rotations in 1995, a period close to the last minimum of solar activity. To determine λ, we use a model of the HCS which we fit to the magnetic sector boundary crossings observed by Wind. We find that the solar wind properties mainly depend on the modulus |λ|. But they also depend on a local parameter, the total pressure (magnetic pressure plus electron and proton thermal pressure. Furthermore, whatever the total pressure, we observe that the plasma properties also depend on the time: the latitudinal gradients of the wind speed and of the proton temperature are not the same before and after the closest HCS crossing. This is a consequence of the dynamical stream interactions. In the low pressure wind, at low |λ|, we find a clear maximum of the density, a clear minimum of the wind speed and of the proton temperature, a weak minimum of the average magnetic field strength, a weak maximum of the average thermal pressure, and a weak maximum of the average β factor. This overdense sheet is embedded in a density halo. The latitudinal thickness is about 5° for the overdense sheet, and 20° for the density halo. The HCS is thus wrapped in an overdense sheet surrounded by a halo, even in the non-compressed solar wind. In the high-pressure wind, the plasma properties are less well ordered as functions of the latitude than in the low-pressure wind; the minimum of the average speed is seen before the HCS crossing. The latitudinal thickness of the high-pressure region is about 20°. Our observations are qualitatively consistent with the numerical model of Pizzo for the deformation of the heliospheric current sheet and plasma sheet.
Key words: Interplanetary physics (solar wind -
The distribution of waves in the inner magnetosphere as a function of solar wind parameters
Aryan, Homayon; Balikhin, Michael A.; Agapitov, Oleksiy; Krasnoselskikh, Vladimir; Yearby, Keith
Energetic electrons within the Earth’s radiation belts represent a serious hazard to geostationary satellites. The interactions of electrons with chorus waves play an important role in both the acceleration and loss of radiation belt electrons. Studies of the evolution of energetic electron fluxes rely heavily on numerical codes in order to model energy and pitch angle diffusion due to electron interaction with plasma waves in the frame of quasilinear approximation. Application of these codes requires knowledge of statistical wave models to present wave distributions in the magnetosphere. A number of such models are based on CRESS, Cluster, THEMIS and other mission data. These models present wave distributions as a function of L-shell, magnetic local time, magnetic latitude and geomagnetic activity expressed by geomagnetic indices (Kp or Ae). However, it has been shown by G. Reeves and co-authors that only 50% of geomagnetic storms increase flux of relativistic electrons at GEO while 20% cause a decrease. This emphasizes the importance of including solar wind parameters in addition to geomagnetic indices. The present study examines almost four years (01, January, 2004 to 29, September, 2007) of STAFF (Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Field Fluctuation) data from Double Star TC1 combined with geomagnetic indices and solar wind parameters from OMNI database in order to present a comprehensive model of chorus wave intensities as a function of L-shell, magnetic local time, magnetic latitude, geomagnetic indices and solar wind parameters. The results show that chorus emission is not only sub-storm dependent but also dependent upon solar wind parameters with solar wind velocity evidently the most influential solar wind parameter. The largest peak intensities are observed for lower band chorus during active conditions, high solar wind velocity, low density and high pressure.
-
Velocity fluctuations in polar solar wind: a comparison between different solar cycles
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. Bavassano
2009-02-01
Full Text Available The polar solar wind is a fast, tenuous and steady flow that, with the exception of a relatively short phase around the Sun's activity maximum, fills the high-latitude heliosphere. The polar wind properties have been extensively investigated by Ulysses, the first spacecraft able to perform in-situ measurements in the high-latitude heliosphere. The out-of-ecliptic phases of Ulysses cover about seventeen years. This makes possible to study heliospheric properties at high latitudes in different solar cycles. In the present investigation we focus on hourly- to daily-scale fluctuations of the polar wind velocity. Though the polar wind is a quite uniform flow, fluctuations in its velocity do not appear negligible. A simple way to characterize wind velocity variations is that of performing a multi-scale statistical analysis of the wind velocity differences. Our analysis is based on the computation of velocity differences at different time lags and the evaluation of statistical quantities (mean, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis for the different ensembles. The results clearly show that, though differences exist in the three-dimensional structure of the heliosphere between the investigated solar cycles, the velocity fluctuations in the core of polar coronal holes exhibit essentially unchanged statistical properties.
-
Velocity fluctuations in polar solar wind: a comparison between different solar cycles
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
B. Bavassano
2009-02-01
Full Text Available The polar solar wind is a fast, tenuous and steady flow that, with the exception of a relatively short phase around the Sun's activity maximum, fills the high-latitude heliosphere. The polar wind properties have been extensively investigated by Ulysses, the first spacecraft able to perform in-situ measurements in the high-latitude heliosphere. The out-of-ecliptic phases of Ulysses cover about seventeen years. This makes possible to study heliospheric properties at high latitudes in different solar cycles. In the present investigation we focus on hourly- to daily-scale fluctuations of the polar wind velocity. Though the polar wind is a quite uniform flow, fluctuations in its velocity do not appear negligible. A simple way to characterize wind velocity variations is that of performing a multi-scale statistical analysis of the wind velocity differences. Our analysis is based on the computation of velocity differences at different time lags and the evaluation of statistical quantities (mean, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis for the different ensembles. The results clearly show that, though differences exist in the three-dimensional structure of the heliosphere between the investigated solar cycles, the velocity fluctuations in the core of polar coronal holes exhibit essentially unchanged statistical properties.
-
Development of wind energy in Morocco; Developpement de l'energie eolienne au Maroc
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Enzili, M. [Centre de Developpement des Energies Renouvelables de Maroc, Rabat (Morocco)
2008-04-15
Morocco's national energy policy includes the use of renewable energy sources to lessen its reliance on fossil fuels such as coal and oil. Legislation was recently passed to increase the threshold of electrical power from 10 MW to 50 MW. Solar and wind energy are the most abundant renewable energy resources in the country and are recommended for exploitation on a large scale. Feasibility studies conducted by the Centre de Developpement des Energies Renouvelables have shown that Morocco has enough wind energy to produce electricity on a large scale and interconnect it with the national power grid. Wind energy in the country could also be used for on-site power generation in remote villages or for desalination of seawater, particularly in the southern regions of Morocco which are most affected by drought. Essaouira, Tangier, Tetouan, Tarfaya, Dakhla, Laayoune and Taza were among the regions identified with significant wind resources. The total wind energy potential for Morocco is estimated to be 2,650 GW, while the technical wind energy potential is estimated to be 1,600 GW. Several projects have been realized in the areas of electricity production, interconnection to the national power grid, decentralized rural electrification and eventually the introduction of water pumping. It was concluded that exporting green energy to Europe, via the Morocco-Spain route after the restructuring of Morocco's electricity sector will create a viable market for the medium and long-term. 3 figs.
-
Wind power today: 1999 Wind Energy program highlights
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Weis-Taylor, Pat
2000-04-06
Wind Power Today is an annual publication that provides an overview for the Department of Energy's Wind Energy Program. The purpose of Wind Power Today is to show how DOE's Wind Energy Program supports wind turbine research and deployment in hopes of furthering the advancement of wind technologies that produce clean, low-cost, reliable energy for the 21st century. Content objectives include: Educate readers about the advantages and potential for widespread deployment of wind energy; explain DOE wind energy program objectives and goals; describe program accomplishments in research and application; examine the barriers to widespread deployment; describe benefits of continued research and development; facilitate technology transfer; attract cooperative wind energy projects with industry.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Beurskens, H.J.M. [SET Analysis, Kievitlaan 26, 1742 AD Schagen (Netherlands); Brand, A.J. [Energy research Centre of the Netherlands ECN, Unit Wind Energy, P.O. Box 1, 1755 ZG Petten (Netherlands)
2013-02-15
Over the years, wind energy has become a major source of renewable energy worldwide. The present chapter addresses the wind resource, which is available for exploitation for large-scale electricity production, and its specific physical properties. Furthermore, the technical options available to convert the energy of the air flow into mechanical energy and electricity are described. Specific problems of large-scale integration of wind energy into the grid as well as the present and future market developments are described in this chapter. Finally, environmental aspects are discussed briefly.
-
Decay of Solar Wind Turbulence behind Interplanetary Shocks
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Pitňa, Alexander; Šafránková, Jana; Němeček, Zdeněk [Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, V Holesovickach 2, Prague, CZ-18000 (Czech Republic); Franci, Luca, E-mail: offelius@gmail.com [Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia, Universita degli Studi di Firenze, I-50125 Firenze (Italy)
2017-07-20
We investigate the decay of magnetic and kinetic energies behind IP shocks with motivation to find a relaxation time when downstream turbulence reaches a usual solar wind value. We start with a case study that introduces computation techniques and quantifies a contribution of kinetic fluctuations to the general energy balance. This part of the study is based on high-time (31 ms) resolution plasma data provided by the Spektr-R spacecraft. On the other hand, a statistical part is based on 92 s Wind plasma and magnetic data and its results confirm theoretically established decay laws for kinetic and magnetic energies. We observe the power-law behavior of the energy decay profiles and we estimated the power-law exponents of both kinetic and magnetic energy decay rates as −1.2. We found that the decay of MHD turbulence does not start immediately after the IP shock ramp and we suggest that the proper decay of turbulence begins when a contribution of the kinetic processes becomes negligible. We support this suggestion with a detailed analysis of the decay of turbulence at the kinetic scale.
-
Decay of Solar Wind Turbulence behind Interplanetary Shocks
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pitňa, Alexander; Šafránková, Jana; Němeček, Zdeněk; Franci, Luca
2017-01-01
We investigate the decay of magnetic and kinetic energies behind IP shocks with motivation to find a relaxation time when downstream turbulence reaches a usual solar wind value. We start with a case study that introduces computation techniques and quantifies a contribution of kinetic fluctuations to the general energy balance. This part of the study is based on high-time (31 ms) resolution plasma data provided by the Spektr-R spacecraft. On the other hand, a statistical part is based on 92 s Wind plasma and magnetic data and its results confirm theoretically established decay laws for kinetic and magnetic energies. We observe the power-law behavior of the energy decay profiles and we estimated the power-law exponents of both kinetic and magnetic energy decay rates as −1.2. We found that the decay of MHD turbulence does not start immediately after the IP shock ramp and we suggest that the proper decay of turbulence begins when a contribution of the kinetic processes becomes negligible. We support this suggestion with a detailed analysis of the decay of turbulence at the kinetic scale.
-
SOLAR WIND STRAHL BROADENING BY SELF-GENERATED PLASMA WAVES
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Pavan, J.; Gaelzer, R. [UFPEL, Pelotas (Brazil); Vinas, A. F. [NASA GSFC, Greenbelt, MD 20771 (United States); Yoon, P. H. [IPST, UMD, College Park, MD (United States); Ziebell, L. F., E-mail: joel.pavan@ufpel.edu.br, E-mail: rudi@ufpel.edu.br, E-mail: adolfo.vinas@nasa.gov, E-mail: yoonp@umd.edu, E-mail: luiz.ziebell@ufrgs.br [UFRGS, Porto Alegre (Brazil)
2013-06-01
This Letter reports on the results of numerical simulations which may provide a possible explanation for the strahl broadening during quiet solar conditions. The relevant processes involved in the broadening are due to kinetic quasi-linear wave-particle interaction. Making use of static analytical electron distribution in an inhomogeneous field, it is found that self-generated electrostatic waves at the plasma frequency, i.e., Langmuir waves, are capable of scattering the strahl component, resulting in energy and pitch-angle diffusion that broadens its velocity distribution significantly. The present theoretical results provide an alternative or complementary explanation to the usual whistler diffusion scenario, suggesting that self-induced electrostatic waves at the plasma frequency might play a key role in broadening the solar wind strahl during quiet solar conditions.
-
The solar wind neon abundance observed with ACE/SWICS and ULYSSES/SWICS
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shearer, Paul; Raines, Jim M.; Lepri, Susan T.; Thomas, Jonathan W.; Gilbert, Jason A.; Landi, Enrico; Zurbuchen, Thomas H.; Von Steiger, Rudolf
2014-01-01
Using in situ ion spectrometry data from ACE/SWICS, we determine the solar wind Ne/O elemental abundance ratio and examine its dependence on wind speed and evolution with the solar cycle. We find that Ne/O is inversely correlated with wind speed, is nearly constant in the fast wind, and correlates strongly with solar activity in the slow wind. In fast wind streams with speeds above 600 km s –1 , we find Ne/O = 0.10 ± 0.02, in good agreement with the extensive polar observations by Ulysses/SWICS. In slow wind streams with speeds below 400 km s –1 , Ne/O ranges from a low of 0.12 ± 0.02 at solar maximum to a high of 0.17 ± 0.03 at solar minimum. These measurements place new and significant empirical constraints on the fractionation mechanisms governing solar wind composition and have implications for the coronal and photospheric abundances of neon and oxygen. The results are made possible by a new data analysis method that robustly identifies rare elements in the measured ion spectra. The method is also applied to Ulysses/SWICS data, which confirms the ACE observations and extends our view of solar wind neon into the three-dimensional heliosphere.
-
The solar wind neon abundance observed with ACE/SWICS and ULYSSES/SWICS
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Shearer, Paul; Raines, Jim M.; Lepri, Susan T.; Thomas, Jonathan W.; Gilbert, Jason A.; Landi, Enrico; Zurbuchen, Thomas H. [Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic, and Space Sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109 (United States); Von Steiger, Rudolf [International Space Science Institute, Hallerstrasse 6, CH-3012 Bern (Switzerland)
2014-07-01
Using in situ ion spectrometry data from ACE/SWICS, we determine the solar wind Ne/O elemental abundance ratio and examine its dependence on wind speed and evolution with the solar cycle. We find that Ne/O is inversely correlated with wind speed, is nearly constant in the fast wind, and correlates strongly with solar activity in the slow wind. In fast wind streams with speeds above 600 km s{sup –1}, we find Ne/O = 0.10 ± 0.02, in good agreement with the extensive polar observations by Ulysses/SWICS. In slow wind streams with speeds below 400 km s{sup –1}, Ne/O ranges from a low of 0.12 ± 0.02 at solar maximum to a high of 0.17 ± 0.03 at solar minimum. These measurements place new and significant empirical constraints on the fractionation mechanisms governing solar wind composition and have implications for the coronal and photospheric abundances of neon and oxygen. The results are made possible by a new data analysis method that robustly identifies rare elements in the measured ion spectra. The method is also applied to Ulysses/SWICS data, which confirms the ACE observations and extends our view of solar wind neon into the three-dimensional heliosphere.
-
The renewable energies have the wind aft; Les energies renouvelables ont le vent en poupe
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2001-02-20
This document brings together four papers on the future of the renewable energies. It shows the market development hopeful the enterprises demand and the enjoy of the economy for these green energies, way of greenhouse gases control. A special interest is given to the solar and wind energies and to the fuel cells. (A.L.B.)
-
Solar energy demonstration zones in the Dalmatian region
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hrastnik, B. [Energy Institute, Zagreb (Croatia); Frankovic, B. [University of Rijeka (Croatia). Faculty of Engineering
2001-11-01
The energy consumption in the Dalmatian region was estimated for residential and public sector, tourism, commercial sector and industry. The national energy program for the use of solar energy, SUNEN, assessed solar energy potential in Croatia. Energy from fossil fuels and electricity consumption in the region, which is mostly used in households for preparing hot water and space heating, could be economically substituted by renewable energy. The situation is most promising for the islands of the Adriatic, where solar thermal collectors, PV modules and wind generators could substitute conventional energy sources in satisfying the present thermal and electric demand. The Dalmatian Islands, characterised by a small density of energy consumption, are proposed as unique candidates in Europe for renewable zones, which could demonstrate the full potential of the renewable energy option. As a practical demonstration, the island of Lastovo and the planned tourist village and yacht marina in the Bay of Jurjeva Luka are proposed as a first solar demonstration project on the islands. Technical, economic, legal and institutional barriers, as well as shortages of financing the project identification process produced hereto an adverse environment for solar applications in Croatia. This paper is an initiative for eliminating the barriers and intensify the solar energy use in Croatia providing the clean environment and activation of indigenous energy resources in the region. (author)
-
Conservation and solar energy program: congressional budget request, FY 1982
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
None
1981-01-01
Funding summaries are presented for the Conservation and Solar Energy Program funding information and program overview on energy conservation (Volume 7 of 7, DOE/CR-0011/2) are included for the Buildings and Community Systems, Industrial, Transportation; State and Local, Multi-Sector, Energy Impact Assistance, and Residential/Commercial retrofit programs. Funding information and program overviews on solar technology (Volume 2 of 7, DOE/CR-011/2) are included for Active and Passive Solar Heating and Cooling, Photovoltaics Energy Systems, Solar Thermal Power Systems, Biomass Energy Systems, Wind Energy Conversion Systems, Ocean Systems, Solar International Activities, Solar Information Systems, SERI Facility, MX-RES, Program Direction, and Alcohol Fuels programs. Information and overviews on energy production, demonstration, and distribution (Volume 6 of 7, DOE/CR-0011/2) are given for the solar program. A funding summary and a program overview are included for electrochemical and physical and chemical storage systems as appearing in DOE/CR-0011/2, Volume 3 of 7. Relevant tabulated data from the FY 1981. Request to the Congress are presented for Supplementals, Rescissions, and Deferrals. (MCW)
-
Collecting Solar Energy. Solar Energy Education Project.
O'Brien, Alexander
This solar energy learning module for use with junior high school students offers a list of activities, a pre-post test, job titles, basic solar energy vocabulary, and diagrams of solar energy collectors and installations. The purpose is to familiarize students with applications of solar energy and titles of jobs where this knowledge could be…
-
Collier, Michael R.; Snowden, S. L.; Sarantos, M.; Benna, M.; Carter, J. A.; Cravens, T. E.; Farrell, W. M.; Fatemi, S.; Hills, H. Kent; Hodges, R. R.;

2014-01-01
We analyze the Rontgen satellite (ROSAT) position sensitive proportional counter soft X-ray image of the Moon taken on 29 June 1990 by examining the radial profile of the surface brightness in three wedges: two 19 deg wedges (one north and one south) 13-32 deg off the terminator toward the dark side and one wedge 38 deg wide centered on the antisolar direction. The radial profiles of both the north and the south wedges show significant limb brightening that is absent in the 38 deg wide antisolar wedge. An analysis of the soft X-ray intensity increase associated with the limb brightening shows that its magnitude is consistent with that expected due to solar wind charge exchange (SWCX) with the tenuous lunar atmosphere based on lunar exospheric models and hybrid simulation results of solar wind access beyond the terminator. Soft X-ray imaging thus can independently infer the total lunar limb column density including all species, a property that before now has not been measured, and provide a large-scale picture of the solar wind-lunar interaction. Because the SWCX signal appears to be dominated by exospheric species arising from solar wind implantation, this technique can also determine how the exosphere varies with solar wind conditions. Now, along with Mars, Venus, and Earth, the Moon represents another solar system body at which SWCX has been observed.
-
Response of Earth and Venus ionospheres to corotating solar wind stream of 3 July 1979
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Taylor, H.A. Jr.
1985-01-01
Corotating solar wind streams emanating from stable coronal structures provide an unique opportunity to compare the response of planetary ionospheres to the energy conveyed in the streams. For recurrent solar conditions the 'signal' propagating outward along spiral paths in interplanetary space can at times exhibit rather similar content at quite different downstream locations in the ecliptic plane. Using solar wind measurements from plasma detectors on ISEE-3, Pioneer Venus Orbiter (PVO) and Helios-A, as well as in-situ ion composition measurements from Bennett Ion Mass Spectrometers on the Atmosphere Explorer-E and PVO spacecraft, corotating stream interactions are examined at Earth and Venus. (Auth.)
-
Additional acceleration of solar-wind particles in current sheets of the heliosphere
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. Zharkova
2015-04-01
Full Text Available Particles of fast solar wind in the vicinity of the heliospheric current sheet (HCS or in a front of interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs often reveal very peculiar energy or velocity profiles, density distributions with double or triple peaks, and well-defined streams of electrons occurring around or far away from these events. In order to interpret the parameters of energetic particles (both ions and electrons measured by the WIND spacecraft during the HCS crossings, a comparison of the data was carried out with 3-D particle-in-cell (PIC simulations for the relevant magnetic topology (Zharkova and Khabarova, 2012. The simulations showed that all the observed particle-energy distributions, densities, ion peak velocities, electron pitch angles and directivities can be fitted with the same model if the heliospheric current sheet is in a status of continuous magnetic reconnection. In this paper we present further observations of the solar-wind particles being accelerated to rather higher energies while passing through the HCS and the evidence that this acceleration happens well before the appearance of the corotating interacting region (CIR, which passes through the spacecraft position hours later. We show that the measured particle characteristics (ion velocity, electron pitch angles and the distance at which electrons are turned from the HCS are in agreement with the simulations of additional particle acceleration in a reconnecting HCS with a strong guiding field as measured by WIND. A few examples are also presented showing additional acceleration of solar-wind particles during their passage through current sheets formed in a front of ICMEs. This additional acceleration at the ICME current sheets can explain the anticorrelation of ion and electron fluxes frequently observed around the ICME's leading front. Furthermore, it may provide a plausible explanation of the appearance of bidirectional "strahls" (field-aligned most energetic
-
Wind Energy Basics Wind Energy Basics We have been harnessing the wind's energy for hundreds of grinding grain. Today, the windmill's modern equivalent-a wind turbine can use the wind's energy to most energy. At 100 feet (30 meters) or more aboveground, they can take advantage of the faster and
-
AUTOMATIC DETECTION ALGORITHM OF DYNAMIC PRESSURE PULSES IN THE SOLAR WIND
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zuo, Pingbing; Feng, Xueshang; Wang, Yi; Xie, Yanqiong; Li, Huijun; Xu, Xiaojun
2015-01-01
Dynamic pressure pulses (DPPs) in the solar wind are a significant phenomenon closely related to the solar-terrestrial connection and physical processes of solar wind dynamics. In order to automatically identify DPPs from solar wind measurements, we develop a procedure with a three-step detection algorithm that is able to rapidly select DPPs from the plasma data stream and simultaneously define the transition region where large dynamic pressure variations occur and demarcate the upstream and downstream region by selecting the relatively quiet status before and after the abrupt change in dynamic pressure. To demonstrate the usefulness, efficiency, and accuracy of this procedure, we have applied it to the Wind observations from 1996 to 2008 by successfully obtaining the DPPs. The procedure can also be applied to other solar wind spacecraft observation data sets with different time resolutions
-
Solar wind power electric plant on Vis (Croatia)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
1998-01-01
A project of a solar photovoltaic electric power plant presented by the Republic of Croatia at the meeting of the E.P.I.A. Mission for photovoltaic technology of the Mediterranean countries, aroused a great interest of the representatives of the invited countries. However, the interest within Croatia in the project has disappeared although E.P.I.A. offered a financing of two thirds of costs. There are attempts to construct 1800 kw wind-driven generators at the same location not taking into consideration a possibility of building a hybrid solar-wind-power electric plant. The chance that the solar part is completely of domestic origin is not accepted but the preference is given to the building of imported wind-driven generators. (orig.)
-
INERTIAL RANGE TURBULENCE OF FAST AND SLOW SOLAR WIND AT 0.72 AU AND SOLAR MINIMUM
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Teodorescu, Eliza; Echim, Marius; Munteanu, Costel [Institute for Space Sciences, Măgurele (Romania); Zhang, Tielong [Space Research Institute, Graz (Austria); Bruno, Roberto [INAF-IAPS, Istituto di Astrofizica e Planetologia Spaziali, Rome (Italy); Kovacs, Peter, E-mail: eliteo@spacescience.ro [Geological and Geophysical Institute of Hungary, Budapest (Hungary)
2015-05-10
We investigate Venus Express observations of magnetic field fluctuations performed systematically in the solar wind at 0.72 Astronomical Units (AU), between 2007 and 2009, during the deep minimum of solar cycle 24. The power spectral densities (PSDs) of the magnetic field components have been computed for time intervals that satisfy the data integrity criteria and have been grouped according to the type of wind, fast and slow, defined for speeds larger and smaller, respectively, than 450 km s{sup −1}. The PSDs show higher levels of power for the fast wind than for the slow. The spectral slopes estimated for all PSDs in the frequency range 0.005–0.1 Hz exhibit a normal distribution. The average value of the trace of the spectral matrix is −1.60 for fast solar wind and −1.65 for slow wind. Compared to the corresponding average slopes at 1 AU, the PSDs are shallower at 0.72 AU for slow wind conditions suggesting a steepening of the solar wind spectra between Venus and Earth. No significant time variation trend is observed for the spectral behavior of both the slow and fast wind.
-
Performance Analysis of a Savonius Wind Turbine in the Solar Integrated Rotor House
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
ABDUL LATIFMANGANHAR
2017-07-01
Full Text Available Rooftop, building integrated and building augmented micro wind systems have the potential for small scale power generation in the built environment. Nevertheless, the expansion of micro wind technology is very slow and its market is strongly affected by the low efficiency of conventional wind generators. WAG-RH (Wind Accelerating and Guiding Rotor House which is a new technique introduced to enhance the efficiency of vertical axis rotor. The present study utilizes other green energy element by integrating the WAG-RH with a solar heating system. In this effort roof of the WAG-RH has been utilized to heat air through micro solar chimney for creating buoyancy effect in the air flow channel at rotor zone in the WAG-RH. The integration is capable of improving the performance of rotor setup in the WAG-RH as well as providing hot air with sufficient air mass flow rate for space heating. The WAG-RH had brought about 138% increase in the performance coefficient(Cp of conventional three bladed Savonius rotor, whereas solar integrated WAG-RH has contributed 162% increase in the Cp of the same rotor.
-
Performance analysis of a savonius wind turbine in the solar integrated rotor house
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Manganhar, A.L.
2017-01-01
Rooftop, building integrated and building augmented micro wind systems have the potential for small scale power generation in the built environment. Nevertheless, the expansion of micro wind technology is very slow and its market is strongly affected by the low efficiency of conventional wind generators. WAG-RH (Wind Accelerating and Guiding Rotor House) which is a new technique introduced to enhance the efficiency of vertical axis rotor. The present study utilizes other green energy element by integrating the WAG-RH with a solar heating system. In this effort roof of the WAG-RH has been utilized to heat air through micro solar chimney for creating buoyancy effect in the air flow channel at rotor zone in the WAG-RH. The integration is capable of improving the performance of rotor setup in the WAG-RH as well as providing hot air with sufficient air mass flow rate for space heating. The WAG-RH had brought about 138% increase in the performance coefficient(Cp) of conventional three bladed Savonius rotor, whereas solar integrated WAG-RH has contributed 162% increase in the Cp of the same rotor. (author)
-
Wind energy renewable energy and the environment
Nelson, Vaughn
2013-01-01
As the demand for energy increases, and fossil fuels continue to decrease, Wind Energy: Renewable Energy and the Environment, Second Edition considers the viability of wind as an alternative renewable energy source. This book examines the wind industry from its start in the 1970s until now, and introduces all aspects of wind energy. The phenomenal growth of wind power for utilities is covered along with applications such as wind-diesel, village power, telecommunications, and street lighting.. It covers the characteristics of wind, such as shear, power potential, turbulence, wind resource, wind
-
Wind energy. To produce electricity with the wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bareau, Helene
2015-11-01
This guide addresses the different aspects of wind-based power generation. It outlines the role of wind energy to meet objectives related to the share of renewable energies in the French energy mix, that wind energy is actually replacing fossil energies, that it is based on local resources within higher safety and less wastage, that current advances are made to integrate wind energy production into the grid, and that it is a solution to diversify energy production. Some figures are presented and commented, regarding onshore wind energy production in France, the location of wind farms, and wind energy production in comparison with other renewable sources. The operation of a wind turbine is described and the different types of wind turbines are evoked. The issue of wind farm planning with citizen participation is addressed: regional planning, studies of pre-feasibility for location selection, procedure, and content of the impact study (radars, fauna and flora, landscapes, safety, health). Other features are outlined: a planned dismantling, and a globally favourable perception. The next part addresses offshore wind energy: the interesting potential of stronger and more reliable wind at sea (European situation, French opportunities, elements comprised in an offshore wind farm), impacts (on marine ecosystems, on neighbouring localities, and interests for visitors). Economic aspects are then addressed: cost and profitability, economic spin-offs, and perspectives. The last part concerns individuals and the possibilities to participate to wind farm projects or to invest in small wind turbines with some prerequisites (constant and steady winds, installation assessment, required expertise, indispensable preliminary steps, costs, aids and profitability)
-
LONG-TERM TRENDS IN THE SOLAR WIND PROTON MEASUREMENTS
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Elliott, Heather A.; McComas, David J. [Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, TX (United States); DeForest, Craig E. [Southwest Research Institute, Boulder, CO (United States)
2016-11-20
We examine the long-term time evolution (1965–2015) of the relationships between solar wind proton temperature ( T {sub p}) and speed ( V {sub p}) and between the proton density ( n {sub p}) and speed using OMNI solar wind observations taken near Earth. We find a long-term decrease in the proton temperature–speed ( T {sub p}– V {sub p}) slope that lasted from 1972 to 2010, but has been trending upward since 2010. Since the solar wind proton density–speed ( n {sub p}– V {sub p}) relationship is not linear like the T {sub p}– V {sub p} relationship, we perform power-law fits for n {sub p}– V {sub p}. The exponent (steepness in the n {sub p}– V {sub p} relationship) is correlated with the solar cycle. This exponent has a stronger correlation with current sheet tilt angle than with sunspot number because the sunspot number maxima vary considerably from cycle to cycle and the tilt angle maxima do not. To understand this finding, we examined the average n {sub p} for different speed ranges, and found that for the slow wind n {sub p} is highly correlated with the sunspot number, with a lag of approximately four years. The fast wind n {sub p} variation was less, but in phase with the cycle. This phase difference may contribute to the n {sub p}– V {sub p} exponent correlation with the solar cycle. These long-term trends are important since empirical formulas based on fits to T {sub p} and V {sub p} data are commonly used to identify interplanetary coronal mass ejections, but these formulas do not include any time dependence. Changes in the solar wind density over a solar cycle will create corresponding changes in the near-Earth space environment and the overall extent of the heliosphere.
-
Current status of wind energy and wind energy policy in Turkey
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yaniktepe, B.; Savrun, M.M.; Koroglu, T.
2013-01-01
Highlights: • Present installations of wind power in the world. • Focus on the current state, potential, and development of Turkey’s wind energy. • Explain the institutional framework and support/incentive mechanisms in Turkey. • Investigate and give information about the new Turkish Renewable Energy Law. - Abstract: Over the past decades, the importance of renewable and sustainable energy resources has increased in the world due to both the rapid increase in energy demand and disadvantages of the fossil fuels. Many countries, such as Turkey, aim to increase the use of renewable and sustainable energy sources with different incentive mechanisms. In parallel with these incentive methods being implemented, wind energy capacity in Turkey has a remarkable increase in the growing rates of renewable energy sources according to installed wind power. Up to now, several wind power projects have been developed at different regions of Turkey. This paper aims to analyze the potential and development of wind energy systems in Turkey. Besides, the current usage and development of wind power installations have been explored for the World and Turkey in detail at the end of the 2011. Furthermore, this study also presents tax exemption, support, and incentive mechanisms to develop new wind energy investments in Turkey
-
Solar Pond Potential as A New Renewable Energy in South Sulawesi
Fadliah Baso, Nur; Chaerah Gunadin, Indar; Yusran
2018-03-01
Renewable energy sources need to be developed to maintain the electric energy availability by utilizing oceanic energy, namely solar pond energy. This energy is highly influenced by several factors including salinity, air temperature and solar radiation. This study was focused on finding the potential of solar pond in South Sulawesi, a region with fairly high solar radiation and abundant salt water raw materials availability. The method used in this study was analyzing the values from the mathematic models of daily horizontal solar radiation, air temperature, wind speed, relative humidity and atmospheric pressure for the last 22 years which were finalized using MATLAB. The findings of this study will show the areas with good potentials to apply solar pond in South Sulawesi that can be utilized in various fields including power generator, industrial heating process, desalination and heating for biomass conversion.
-
Nuclear energy of the future, solar energy of the future: some convergencies
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Flamant, G.
2006-01-01
Most medium- and long-term energy scenarios foresee the joint development of renewable and nuclear energies. In other words, the energy sources must be as various as possible. Among the renewable energy sources, the solar energy presents the highest development potential, even if today the biomass and wind energies are quantitatively more developed. In France, the solar power generation is ensured by photovoltaic systems. However, the thermodynamical conversion of solar energy (using concentrating systems) represents an enormous potential at the world scale and several projects of solar plants are in progress in Spain and in the USA. The advantages of this solution are numerous: high efficiency of thermodynamic cycles, possibility of heat storage and hybridization (solar/fuels), strong potential of innovation. Moreover, the solar concentrators allow to reach temperatures higher than 1000 deg. C and thus allow to foresee efficient thermochemical cycles for hydrogen generation. The future solar plants will have to be efficient, reliable and will have to be able to meet the energy demand. In order to reach high thermodynamic cycle efficiencies, it is necessary to increase the temperature of the hot source and to design combined cycles. These considerations are common to the communities of researchers and engineers of both the solar thermal and nuclear industries. Therefore, the future development of generation 4 nuclear power plants and of generation 3 solar plants are conditioned by the resolution of similar problems, like the coolants (molten salts and gases), the materials (metals and ceramics), the heat transfers (hydrogen generation), and the qualification of systems (how solar concentrators can help to perform qualification tests of nuclear materials). Short communication. (J.S.)
-
Solar-wind interactions with the Moon: nature and composition of nitrogen compounds
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mukherjee, N.R.
1981-01-01
The lunar atmosphere and magnetic field are very tenuous. The solar wind, therefore, interacts directly with the lunar surface material and the dominant nature of interaction is essentially complete absorption of solar-wind particles by the surface material resulting in no upstream bowshock, but a cavity downstream. The solar-wind nitrogen ion species induce and undergo a complex set of reactions with the elements of lunar material and the solar-wind-derived trapped elements. The nitrogen concentration indigeneous to the lunar surface material is practically nil. Therefore any nitrogen and nitrogen compounds found in the lunar surface material are due to the solar-wind implantation of nitrogen ions. The flux of the solar-wind nitrogen ion species is about 6 X 10 3 cm -2 s -1 . Since there is no evidence for accumulation of nitrogen species in the lunar surface material, the outflux of nitrogen species from the lunar material to the atmosphere is the same as the solar-wind nitrogen ion flux. The species of the outflux are primarily NO and NH 3 , and their respective concentrations in the near surface lunar atmosphere are found to be 327 and 295 cm -3 . (Auth.)
-
Wind Power Today: Wind Energy Program Highlights 2001
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
2002-05-01
Wind Power Today is an annual publication that provides an overview of the U.S. Department of Energy's Wind Energy Program accomplishments for the previous year. The purpose of Wind Power Today is to show how DOE's Wind Energy Program supports wind turbine research and deployment in hopes of furthering the advancement of wind technologies that produce clean, low-cost, reliable energy. Content objectives include: educate readers about the advantages and potential for widespread deployment of wind energy; explain the program's objectives and goals; describe the program's accomplishments in research and application; examine the barriers to widespread deployment; describe the benefits of continued research and development; facilitate technology transfer; and attract cooperative wind energy projects with industry. This 2001 edition of Wind Power Today also includes discussions about wind industry growth in 2001, how DOE is taking advantage of low wind speed regions through advancing technology, and distributed applications for small wind turbines.
-
Cometary X-rays : solar wind charge exchange in cometary atmospheres
Bodewits, Dennis
2007-01-01
The interaction of the solar wind with the planets and the interstellar medium is of key importance for the evolution of our solar system. The interaction with Earth's atmosphere is best known for the northern light. In case of Mars, the interaction with the solar wind might have lead to the erosion
-
Ecological and economical aspects of solar energy use
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sobczyk Wiktoria
2017-01-01
Full Text Available The natural environment is devastated by the industry and by households, which use fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas for heating water and buildings as well as for generating electricity. One of the ways to limit the degradation of the environment and the usage of natural resources is to use unconventional and renewable resources and to implement energy-saving technologies in construction, industry and households. A dynamic development of systems based on renewable energy sources such as biomass, water, wind, heat from inside the Earth and sunbeams has recently occurred in the whole world. This thesis is related to the purest and the least onerous for environment source of energy which is undoubtedly the energy that comes directly from the solar radiation. In this article the solar energy application is presented, taking into account its impact on the environment and financial costs of developing solar techniques. The installation of alternative energy sources are entitled to grants and credits, which reduces the investment costs. Ecological effects, although immeasurable, are significant and definitely testify in favor of the solar system.
-
Air emissions due to wind and solar power.
Katzenstein, Warren; Apt, Jay
2009-01-15
Renewables portfolio standards (RPS) encourage large-scale deployment of wind and solar electric power. Their power output varies rapidly, even when several sites are added together. In many locations, natural gas generators are the lowest cost resource available to compensate for this variability, and must ramp up and down quickly to keep the grid stable, affecting their emissions of NOx and CO2. We model a wind or solar photovoltaic plus gas system using measured 1-min time-resolved emissions and heat rate data from two types of natural gas generators, and power data from four wind plants and one solar plant. Over a wide range of renewable penetration, we find CO2 emissions achieve approximately 80% of the emissions reductions expected if the power fluctuations caused no additional emissions. Using steam injection, gas generators achieve only 30-50% of expected NOx emissions reductions, and with dry control NOx emissions increase substantially. We quantify the interaction between state RPSs and NOx constraints, finding that states with substantial RPSs could see significant upward pressure on NOx permit prices, if the gas turbines we modeled are representative of the plants used to mitigate wind and solar power variability.
-
Improvement of Wind Energy Production through HVDC Systems
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Morris Brenna
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Variable and non-programmable resources, such as solar and wind, have undergone a stunning growth in recent years and are likely to gain even more importance in the future. Their strong presence in the national electricity mix has created issues in many countries regarding the secure operation of the power system. In order to guarantee the stability of the system, several TSOs have resorted to wind energy curtailment, which represents a waste of clean energy and an economic loss. In order to analyze this issue, a model of the Italian power system was developed, a program able to simulate the electricity dispatching mechanism. The model was, then, used to evaluate possible solutions to reduce wind curtailment. In particular, a proposal for the construction of an HVDC line linking Southern and Northern Italy was studied.
-
Jacobson, M. Z.; Delucchi, M. A.; Cameron, M. A.; Frew, B. A.
2016-12-01
The greatest concern facing the large-scale integration of wind, water, and solar (WWS) into a power grid is the high cost of avoiding load loss caused by WWS variability and uncertainty. This talk discusses the recent development of a new grid integration model to address this issue. The model finds low-cost, no-load-loss, non-unique solutions to this problem upon electrification of all U.S. energy sectors (electricity, transportation, heating/cooling, and industry) while accounting for wind and solar time-series data from a 3-D global weather model that simulates extreme events and competition among wind turbines for available kinetic energy. Solutions are obtained by prioritizing storage for heat (in soil and water); cold (in ice and water); and electricity (in phase-change materials, pumped hydro, hydropower, and hydrogen); and using demand response. No natural gas, biofuels, or stationary batteries are needed. The resulting 2050-2055 U.S. electricity social cost for a full system is much less than for fossil fuels. These results hold for many conditions, suggesting that low-cost, stable 100% WWS systems should work many places worldwide. The paper this talk is based on was published in PNAS, 112, 15,060-15,065, 2015, doi:10.1073/pnas.1510028112.
-
Luhmann, Janet G.; Petrie, Gordon; Riley, Pete
2012-01-01
The solar wind was originally envisioned using a simple dipolar corona/polar coronal hole sources picture, but modern observations and models, together with the recent unusual solar cycle minimum, have demonstrated the limitations of this picture. The solar surface fields in both polar and low-to-mid-latitude active region zones routinely produce coronal magnetic fields and related solar wind sources much more complex than a dipole. This makes low-to-mid latitude coronal holes and their associated streamer boundaries major contributors to what is observed in the ecliptic and affects the Earth. In this paper we use magnetogram-based coronal field models to describe the conditions that prevailed in the corona from the decline of cycle 23 into the rising phase of cycle 24. The results emphasize the need for adopting new views of what is ‘typical’ solar wind, even when the Sun is relatively inactive. PMID:25685422
-
A Combined Energy Management Algorithm for Wind Turbine/Battery Hybrid System
Altin, Necmi; Eyimaya, Süleyman Emre
2018-03-01
From an energy management standpoint, natural phenomena such as solar irradiation and wind speed are uncontrolled variables, so the correlation between the energy generated by renewable energy sources and energy demand cannot always be predicted. For this reason, energy storage systems are used to provide more efficient renewable energy systems. In these systems, energy management systems are used to control the energy storage system and establish a balance between the generated power and the power demand. In addition, especially in wind turbines, rapidly varying wind speeds cause wind power fluctuations, which threaten the power system stability, especially at high power levels. Energy storage systems are also used to mitigate the power fluctuations and sustain the power system's stability. In these systems, another controller which controls the energy storage system power to mitigate power fluctuations is required. These two controllers are different from each other. In this study, a combined energy management algorithm is proposed which can perform both as an energy control system and a power fluctuation mitigation system. The proposed controller is tested with wind energy conversion system modeled in MATLAB/Simulink. Simulation results show that the proposed controller acts as an energy management system while, at the same time, mitigating power fluctuations.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zvolun, Yona.
1990-11-01
Independent alternative energy systems, such as wind and solar, need batteries to store produced energy in order to supply a reliable source of electricity when needed. Increasing reliability of these sources automatically influence the quality and availability of this type of power supply. Every solar and wind energy system includes a certain number of principle components : Photovoltaic arrays or wind generator, regulator/control unit to control charge/ discharge of the batteries and power supply to consumers, converters from AC to DC and DC to AC, batteries and load. The mode of system operation for both the independent or combined system is influenced by many complicated factors some of which are stochastic variables, time and location variables or constant. From the above complicated data one must choose the optimal system which answers the following criteria: a. Minimum cost which determines the inter relative array sizes for combined systems (photovoltaic cells wind generator and batteries). b. Reliability of power supply in general. c. Full consumption of power installation by obtaining maximum possible output under existing conditions at any time. This paper deals with the connected problems caused in a combined system of solar/photovoltaic cells, wind generator and batteries and will offer alternative economic and technical alternatives for power supply from fuel operated generators . Inverter components: photovoltaic cells and wind generators, which are the principle components without which solar and/or wind systems cannot exist, are discussed from the theoretical and physical aspects. Also, operation of the attached components, such as batteries, inverters, generators, regulators etc, is discussed. The last part of this paper discusses the choosing of the optimal system in a Techno-economic sense as opposed to energy supplied from generator, The work exhibited on these pages will contribute to better understanding of the different systems while
-
Temporal and spatial complementarity of wind and solar resources in Lower Silesia (Poland)
Jurasz, Jakub; Wdowikowski, Marcin; Kaźmierczak, Bartosz; Dąbek, Paweł
2017-11-01
This paper investigates the concept of temporal and spatial complementarity of wind and solar resources in Lower Silesia (south-wester Poland). For the purpose of our research we have used hourly load and energy yield from photovoltaics and wind turbines covering period 2010-2014. In order to assess the spatial complementarity we have divided the considered voivodeship into 74 squared regions with maximal area of 400 km2. The obtained results indicate an existence of temporal complementarity on a monthly time scale and a positive correlation between load and wind generation patterns (also on a monthly time scale). The temporal complementarity for hourly time series in relatively low but has potential to smooth the energy generation curves.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Strickland, J.K. Jr. [Texas Univ., Austin, TX (United States)
1998-06-01
The arguments in favour of using solar power satellites for primary base-load electrical supply are presented and compared with the advantages and drawbacks of other renewable energy sources, especially ground solar and wind systems. Popular misconceptions about energy use and the importation of space solar energy to the Earth`s surface are examined and discounted. Finally an optimal mix of space solar (focusing on geosynchronous solar power satellites), ground solar, and other energy sources is described which, it is argued, would be capable to meet future global energy demand. (UK)
-
Solar Wind Charge Exchange During Geomagnetic Storms
Robertson, Ina P.; Cravens, Thomas E.; Sibeck, David G.; Collier, Michael R.; Kuntz, K. D.
2012-01-01
On March 31st. 2001, a coronal mass ejection pushed the subsolar magnetopause to the vicinity of geosynchronous orbit at 6.6 RE. The NASA/GSFC Community Coordinated Modeling Center (CCMe) employed a global magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) model to simulate the solar wind-magnetosphere interaction during the peak of this geomagnetic storm. Robertson et aL then modeled the expected 50ft X-ray emission due to solar wind charge exchange with geocoronal neutrals in the dayside cusp and magnetosheath. The locations of the bow shock, magnetopause and cusps were clearly evident in their simulations. Another geomagnetic storm took place on July 14, 2000 (Bastille Day). We again modeled X-ray emission due to solar wind charge exchange, but this time as observed from a moving spacecraft. This paper discusses the impact of spacecraft location on observed X-ray emission and the degree to which the locations of the bow shock and magnetopause can be detected in images.
-
Wind Power Today: 1998 Wind Energy Program Highlights
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tromly, K.
1999-06-17
The US Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy manages the Federal Wind Energy Program. The mission of the program is to help the US wind industry to complete the research, testing, and field verification needed to fully develop advanced wind technologies that will lead the world in cost-effectiveness and reliability. This publication, printed annually, provides a summary of significant achievements in wind energy made during the previous calendar year. Articles include wind energy in the Midwest, an Alaskan wind energy project, the US certification program, structural testing, and the federal program in review.
-
Analysis of ISEE-3/ICE solar wind data
Coplan, Michael A.
1989-01-01
Under the grant that ended November 11, 1988 work was accomplished in a number of areas, as follows: (1) Analysis of solar wind data; (2) Analysis of Giacobini/Zinner encounter data; (3) Investigation of solar wind and magnetospheric electron velocity distributions; and (4) Experimental investigation of the electronic structure of clusters. Reprints and preprints of publications resulting from this work are included in the appendices.