
Sample records for reflectivity phase conjugation
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mukherjee, Nandini
2010-01-01
A comprehensive theoretical analysis is developed for the vectorial phase conjugation using resonant four-wave mixing (FWM) in a highly degenerate rotational vibrational molecular system. The dynamic Stark shifts, saturation, and Doppler broadening are included for a realistic analysis. It is shown that the electromagnetically induced multilevel coherence controls the nonlinear wave mixing yielding interesting results for the phase conjugate (PC) reflectivity. It turns out that the efficiency of the PC reflectivity is decided by the relative phase of the Zeeman coherence and the population grating. When these two contributions are aligned in phase by a small detuning of the pump frequency, a large PC reflectivity (∼20%) is obtained with moderate pump intensity (∼500 mW/cm 2 ).
-
Optical phase conjugation for time-domain undoing of dispersive self-phase-modulation effects
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fisher, R.A.; Suydam, B.R.; Yevick, D.
1983-01-01
We show that the temporal distortion and spectral broadening of a pulse generated by the combined effects of group-velocity dispersion and self-phase modulation is removed by reflection of a cw-pumped, broadband, unity-reflecting Kerr-like optical phase conjugator followed by retraversal of the nonlinear medium. We also examine numerically the effects of finite linear loss in the material, of nonunity conjugate reflectivity, and of finite conjugator thickness
-
Four-wave mixing and phase conjugation in plasmas
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Federici, J.F.
1989-01-01
Nonlinear optical effects such as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering, Stimulated Raman Scattering, self-focusing, wave-mixing, parametric mixing, etc., have a long history in plasma physics. Recently, four-wave mixing in plasmas and its applications to phase conjugation has been extensively studied. Although four-wave mixing (FWM), using various nonlinear mediums, has many practical applications in the visible regime, no successful attempt has been made to study or demonstrate FWM for wavelengths longer than 10μm. Plasmas as phase conjugate mirrors have received considerable attention since they become more efficient at longer wavelengths (far-infrared to microwave). The purpose of this thesis is to study various fundamental issues which concern the suitability of plasmas for four-wave mixing and phase conjugation. The major contributions of this thesis are the identification and study of thermal and ionization nonlinearities as potential four-wave mixing and phase conjugation mechanisms and the study of the affect of density inhomogeneities on the FWM process. Using a fluid description for the plasma, this thesis demonstrates that collisional heating generates a thermal force which substantially enhances the phase conjugate reflectivity. The prospect of using a novel ionization nonlinearity in weakly ionized plasmas for wave-mixing and phase conjugation is discussed. The ionization nonlinearity arises from localized heating of the plasma by the beat-wave. Wherever, the local temperature is increased, a plasma density grating is produced due to increased electron-impact ionization. Numerical estimates of the phase conjugate reflectivity indicate reflectivities in the range of 10 -4 -10 -3 are possible in a weakly ionized steady-state gas discharge plasma
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cronin-Golomb; Yariv
1986-07-01
A GaA1As semiconductor laser with feedback from a barium titanate photorefractive ring passive phase-conjugate mirror can be made to perform repeating or nonrepeating frequency scans over a 10-nm range toward either the blue or the red. The direction of scanning and whether the scans repeat may be controlled by adjusting the overlap of the interaction beams in the crystal. This overlap region may be adjusted so that the diode frequency spectrum, originally occupying about 10 longitudinal modes, scans and narrows as the conjugate signal builds up, coming to rest often in one, but sometimes two or three, longitudinal modes as a result of self-generated distributed-feedback effects. Also reported similar effects caused by feedback from the total-internal-reflection passive phase-conjugate mirror. The alignment-control mechanism of the ring mirror is, however, not available in this case.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cronin-Golomb, M.; Yariv, A.
1986-07-01
A GaAlAs semiconductor laser with feedback from a barium titanate photorefractive ring passive phase-conjugate mirror can be made to perform repeating or nonrepeating frequency scans over a 10-nm range toward either the blue or the red. The direction of scanning and whether the scans repeat may be controlled by adjusting the overlap of the interaction beams in the crystal. This overlap region may be adjusted so that the diode frequency spectrum, originally occupying about 10 longitudinal modes, scans and narrows as the conjugate signal builds up, coming to rest often in one, but sometimes two or three, longitudinal modes as a result of self-generated distributed-feedback effects. We also report similar effects caused by feedback from the total-internal-reflection passive phase-conjugate mirror. The alignment-control mechanism of the ring mirror is, however, not available in this case.
-
Cronin-Golomb, Mark; Yariv, Amnon
1986-07-01
A GaAlAs semiconductor laser with feedback from a barium titanate photorefractive ring passive phase-conjugate mirror can be made to perform repeating or nonrepeating frequency scans over a 10-nm range toward either the blue or the red. The direction of scanning and whether the scans repeat may be controlled by adjusting the overlap of the interaction beams in the crystal. This overlap region may be adjusted so that the diode frequency spectrum, originally occupying about 10 longitudinal modes, scans and narrows as the conjugate signal builds up, coming to rest often in one, but sometimes two or three, longitudinal modes as a result of self-generated distributed-feedback effects. We also report similar effects caused by feedback from the total-internal-reflection passive phase-conjugate mirror. The alignment-control mechanism of the ring mirror is, however, not available in this case.
-
Self-pumped optical phase conjugation and light oscillation in Fe doped KNbO 3
Medrano, C.; Ingold, M.; Günter, P.
1990-07-01
We report different experiments on self-pumped phase conjugation in iron doped KNbO 3 crystals at room temperature. Self-pumped phase conjugate reflectivities of a linear cavity, an external ring mirror and a configuration where no external optical elements are required have been measured. Using the passive ring resonator a reflectivity of 30% of a self-pumped phase conjugate mirror has been measured at room temperature. In the configuration requiring no external optical elements besides the KNbO 3 crystal a reflectivity of 12% has been measured. In degenerate four-wave mixing phase conjugate reflectivities of up to 270% have been observed in the diffusion recording mode.
-
Pump induced normal mode splittings in phase conjugation in a Kerr ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
Abstract. Phase conjugation in a Kerr nonlinear waveguide is studied with counter-propagating normally incident pumps and a probe beam at an arbitrary angle of incidence. Detailed numerical results for the specular and phase conjugated reflectivities are obtained with full account of pump depletion. For sufficient ...
-
Fisher, Robert A
1983-01-01
This book appears at a time of intense activity in optical phase conjugation. We chose not to await the maturation of the field, but instead to provide this material in time to be useful in its development. We have tried very hard to elucidate and interrelate the various nonlinear phenomena which can be used for optical phase conjugation.
-
Degenerate four-wave mixing and phase conjugation in a collisional plasma
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Federici, J.F.; Mansfield, D.K.
1986-06-01
Although degenerate four-wave mixing (DFWM) has many practical applications in the visible regime, no successful attempt has been made to study or demonstrate DFWM for wavelengths longer than 10μm. Recently, Steel and Lam established plasma as a viable DFWM and phase conjugation (PC) medium for infrared, far-infrared, and microwaves. However, their analysis is incomplete since collisional effects were not included. Using a fluid description, our results demonstrate that when collisional absorption is small and the collisional mean-free path is shorter than the nonlinear density grating scale length, collisional heating generates a thermal force which substantially enhances the phase conjugate reflectivity. When the collisional attenuation length becomes comparable to the length of the plasma, the dominant effect is collisional absorption of the pump waves. Numerical estimates of the phase conjugate reflectivity indicate that for modest power levels, gains greater than or equal to1 are possible in the submillimeter to centimeter wavelength range. This suggests that a plasma is a viable PC medium at those long wavelengths. In addition, doubly DFWM is discussed
-
All solid-state SBS phase conjugate mirror
Dane, C.B.; Hackel, L.A.
1999-03-09
A stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) phase conjugate laser mirror uses a solid-state nonlinear gain medium instead of the conventional liquid or high pressure gas medium. The concept has been effectively demonstrated using common optical-grade fused silica. An energy threshold of 2.5 mJ and a slope efficiency of over 90% were achieved, resulting in an overall energy reflectivity of >80% for 15 ns, 1 um laser pulses. The use of solid-state materials is enabled by a multi-pass resonant architecture which suppresses transient fluctuations that would otherwise result in damage to the SBS medium. This all solid state phase conjugator is safer, more reliable, and more easily manufactured than prior art designs. It allows nonlinear wavefront correction to be implemented in industrial and defense laser systems whose operating environments would preclude the introduction of potentially hazardous liquids or high pressure gases. 8 figs.
-
Application of optical phase conjugation to plasma diagnostics (invited)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jahoda, F.C.; Anderson, B.T.; Forman, P.R.; Weber, P.G.
1985-01-01
Several possibilities for plasma diagnostics provided by optical phase conjugation and, in particular, self-pumped phase conjugation in barium titanate (BaTiO 3 ) are discussed. These include placing a plasma within a dye laser cavity equipped with a phase conjugate mirror for intracavity absorption measurements, time differential refractometry with high spatial resolution, and simplified real-time holographic interferometry. The principles of phase conjugation with particular reference to photorefractive media and the special advantages of self-pumped phase conjugation are reviewed prior to the discussion of the applications. Distinctions are made in the applications between those for which photorefractive conjugators are essential and those for which they only offer experimental simplification relative to other types of phase conjugators
-
Phase-conjugate optical coherence tomography
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Erkmen, Baris I.; Shapiro, Jeffrey H.
2006-01-01
Quantum optical coherence tomography (Q-OCT) offers a factor-of-2 improvement in axial resolution and the advantage of even-order dispersion cancellation when it is compared to conventional OCT (C-OCT). These features have been ascribed to the nonclassical nature of the biphoton state employed in the former, as opposed to the classical state used in the latter. Phase-conjugate OCT (PC-OCT) shows that nonclassical light is not necessary to reap Q-OCT's advantages. PC-OCT uses classical-state signal and reference beams, which have a phase-sensitive cross correlation, together with phase conjugation to achieve the axial resolution and even-order dispersion cancellation of Q-OCT with a signal-to-noise ratio that can be comparable to that of C-OCT
-
Perfect lensing with phase-conjugating surfaces: toward practical realization
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Maslovski, Stanislav; Tretyakov, Sergei
2012-01-01
It is theoretically known that a pair of phase-conjugating surfaces can function as a perfect lens, focusing propagating waves and enhancing evanescent waves. However, the known experimental approaches based on thin sheets of nonlinear materials cannot fully realize the required phase conjugation boundary condition. In this paper, we show that the ideal phase-conjugating surface is, in principle, physically realizable and investigate the necessary properties of nonlinear and nonreciprocal particles which can be used to build a perfect lens system. The physical principle of the lens operation is discussed in detail and directions of possible experimental realizations are outlined. (paper)
-
Two novel plasma diagnostic tools: fiber sensors and phase conjugation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jahoda, F.C.
1985-01-01
A rapidly developing technology (single-mode optical fiber sensors) and recent fundamental research in nonlinear optics (phase conjugation) both offer opportunities for novel plasma diagnostics. Single-mode fiber sensors can replace electrical wire probes for current and magnetic field measurements with advantages in voltage insulation requirements, electromagnetic noise immunity, much greater bandwidth, and some configuration flexibility. Faraday rotation measurements through fibers wound on the ZT-40M RFP have demonstrated quantitative results, but competing linear birefringence effects still hinder independent interpretation. Twisted fiber may solve this problem. Optical phase conjugation (in which a phase reversed copy of a laser beam is generated) allows real time distortion corrections in laser diagnostics. Self-pumped phase conjugation in BaTiO 3 improves the quality of phase conjugation imagery and greatly simplifies experimentation directed toward plasma diagnostics. Our initial applications are a) time-differential refractometry with high spatial resolution and b) intracavity absorption Zeeman spectroscopy
-
Applications of phase conjugate mirror to Thomson scattering diagnostics (invited)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hatae, T.; Naito, O.; Nakatsuka, M.; Yoshida, H.
2006-01-01
A high performance phase conjugate mirror based on stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS-PCM) has been applied to the Thomson scattering system in the JT-60U tokamak for the first time in order to improve the measurement performance. A SBS-PCM realized a high reflectivity of 95% at a high input power of 145 W (2.9 J, 50 Hz). Using the SBS-PCM, two methods have been developed to increase the intensity of scattered light. For the first method, we have developed a new optical design to provide a double-pass scattering method with the SBS-PCM. A laser beam passing through the plasma is reflected by the SBS-PCM. The reflected beam passes the plasma again along the same path by means of the phase conjugation of the optically nonlinear stimulated Brillouin scattering process. The double-pass Thomson scattering method using the SBS-PCM has demonstrated an increase of the scattered light by a factor of 1.6 compared with the single-pass scattering method in JT-60U. A multipass Thomson scattering method in which the laser beam can be confined between a couple of SBS-PCMs is also proposed. It is estimated that the multipass scattering method generates the scattered light more than several times as large as that of the single-pass scattering method. For the second method, a high-average-power yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) laser system has been developed using the SBS-PCM. The SBS-PCM effectively compensated thermal degradation at two amplifier lines, and the average power was increased by a factor of >8 from 45 W (1.5 J, 30 Hz) to 373 W (7.46 J, 50 Hz). A Nd:YAG laser (5 J, 100 Hz) for the edge Thomson scattering in International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) has been designed based on the result
-
Nonlinear piezoelectricity in PZT ceramics for generating ultrasonic phase conjugate waves
Yamamoto; Kokubo; Sakai; Takagi
2000-03-01
We have succeeded in the generation of acoustic phase conjugate waves with nonlinear PZT piezoelectric ceramics and applied them to ultrasonic imaging systems. Our aim is to make a phase conjugator with 100% efficiency. For this purpose, it is important to clarify the mechanism of acoustic phase conjugation through nonlinear piezoelectricity. The process is explained by the parametric interaction via the third-order nonlinear piezoelectricity between the incident acoustic wave at angular frequency omega and the pump electric field at 2 omega. We solved the coupling equations including the third-ordered nonlinear piezoelectricity and theoretically derived the amplitude efficiency of the acoustic phase conjugation. We compared the efficiencies between the theoretical and experimental values for PZT ceramics with eight different compositions. Pb[(Zn1/3Nb2/3)(1 - x)Tix]O3 (X = 0.09, PZNT91/9) piezoelectric single crystals have been investigated for high-performance ultrasonic transducer application, because these have large piezoelectric constants, high electrical-mechanical coupling factors and high dielectric constants. We found that they have third-order nonlinear piezoelectric constants much larger than PZT and are hopeful that the material as a phase conjugator has over 100% efficiency.
-
Phase conjugation with random fields and with deterministic and random scatterers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gbur, G.; Wolf, E.
1999-01-01
The theory of distortion correction by phase conjugation, developed since the discovery of this phenomenon many years ago, applies to situations when the field that is conjugated is monochromatic and the medium with which it interacts is deterministic. In this Letter a generalization of the theory is presented that applies to phase conjugation of partially coherent waves interacting with either deterministic or random weakly scattering nonabsorbing media. copyright 1999 Optical Society of America
-
Stimulated Brillouin scattering continuous wave phase conjugation in step-index fiber optics.
Massey, Steven M; Spring, Justin B; Russell, Timothy H
2008-07-21
Continuous wave (CW) stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) phase conjugation in step-index optical fibers was studied experimentally and modeled as a function of fiber length. A phase conjugate fidelity over 80% was measured from SBS in a 40 m fiber using a pinhole technique. Fidelity decreases with fiber length, and a fiber with a numerical aperture (NA) of 0.06 was found to generate good phase conjugation fidelity over longer lengths than a fiber with 0.13 NA. Modeling and experiment support previous work showing the maximum interaction length which yields a high fidelity phase conjugate beam is inversely proportional to the fiber NA(2), but find that fidelity remains high over much longer fiber lengths than previous models calculated. Conditions for SBS beam cleanup in step-index fibers are discussed.
-
Experimental demonstration of continuous variable cloning with phase-conjugate inputs
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Sabuncu, Metin; Andersen, Ulrik Lund; Leuchs, G.
2007-01-01
We report the first experimental demonstration of continuous variable cloning of phase-conjugate coherent states as proposed by Cerf and Iblisdir [Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 247903 (2001)]. In contrast to this proposal, the cloning transformation is accomplished using only linear optical components......, homodyne detection, and feedforward. As a result of combining phase conjugation with a joint measurement strategy, superior cloning is demonstrated with cloning fidelities reaching 89%....
-
A Scanning Hologram Recorded by Phase Conjugate Property of Nonlinear Crystals
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Zi-Liang, Ping; Dalsgaard, Erik
1996-01-01
A methode of recording a scanning hologram with phase conjugate property of nonlinear crystal is provided. The principle of recording, setup and experiments are given.......A methode of recording a scanning hologram with phase conjugate property of nonlinear crystal is provided. The principle of recording, setup and experiments are given....
-
Threshold couplings of phase-conjugate mirrors with two interaction regions.
Beli, M; Petrovi, M; Sandfuchs, O; Kaiser, F
1998-03-01
Using the grating-action method, we determine the threshold coupling strengths of three generic examples of phase-conjugate mirrors with two interaction regions: the cat conjugator, the mutually incoherent beam coupler, and the interconnected ring mirror.
-
Nonlinear propagation of phase-conjugate focused sound beams in water
Brysev, A. P.; Krutyansky, L. M.; Preobrazhensky, V. L.; Pyl'nov, Yu. V.; Cunningham, K. B.; Hamilton, M. F.
2000-07-01
Nonlinear propagation of phase-conjugate, focused, ultrasound beams is studied. Measurements are presented of harmonic amplitudes along the axis and in the focal plane of the conjugate beam, and of the waveform and spectrum at the focus. A maximum peak pressure of 3.9 MPa was recorded in the conjugate beam. The measurements are compared with simulations based on the KZK equation, and satisfactory agreement is obtained.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen, Haixia; Zhang, Jing
2007-01-01
We propose a scheme for continuous-variable quantum cloning of coherent states with phase-conjugate input modes using linear optics. The quantum cloning machine yields M identical optimal clones from N replicas of a coherent state and N replicas of its phase conjugate. This scheme can be straightforwardly implemented with the setups accessible at present since its optical implementation only employs simple linear optical elements and homodyne detection. Compared with the original scheme for continuous-variable quantum cloning with phase-conjugate input modes proposed by Cerf and Iblisdir [Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 247903 (2001)], which utilized a nondegenerate optical parametric amplifier, our scheme loses the output of phase-conjugate clones and is regarded as irreversible quantum cloning
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Houen, G.; Olsen, D.T.; Hansen, P.R.
2003-01-01
A solid-phase conjugation method utilizing carrier protein bound to an ion exchange matrix was developed. Ovalbumin was adsorbed to an anion exchange matrix using a batch procedure, and the immobilized protein was then derivatized with iodoacetic acid N-hydroxysuccinimid ester. The activated......, and immunization experiments with the eluted conjugates showed that the more substituted conjugates gave rise to the highest titers of glutathione antibodies. Direct immunization with the conjugates adsorbed to the ion exchange matrix was possible and gave rise to high titers of glutathione antibodies. Conjugates...... of ovalbumin and various peptides were prepared in a similar manner and used for production of peptide antisera by direct immunization with the conjugates bound to the ion exchanger. Advantages of the method are its solid-phase nature, allowing fast and efficient reactions and intermediate washings...
-
Phase conjugation of gap solitons: A numerical study
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
We study the effect of a nearby phase-conjugate mirror (PCM) on the gap soliton of a. Kerr non-linear ... They are characterized by a sech field distribution corresponding to the ... It is a generalization of the earlier model proposed by Jose et.
-
Picosecond phase conjugation in two-photon absorption in poly-di-acetylenes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nunzi, Dominique Jean-Michel
1990-01-01
Poly-di-acetylenes exhibit a large two-photon absorption at 1064 nm wavelength. Its different effects on phase-conjugate nonlinearity are described in the framework of picosecond experiments. In solutions, gels, and films (optically thin media), third-order susceptibility appears as an increasing intensity dependent function. Phase measurements by nonlinear interferometry with the substrate or with the solvent are compared with predictions of a resonantly driven three level system. Phase-conjugate response exhibits a multi-exponential decay. Polarization symmetries analysis shows a one-dimensional effect. Study under strong static electric field action reveals that we face charged species bound to photoconductive polymer chains. In PTS single crystals (optically thick media), response saturates and cancels at high light intensity. This is well accounted for by propagation equations solved in large two-photon absorption conditions. The effect is exploited in a phase conjugation experiment under external optical pump excitation. We thus demonstrate that enhanced nonlinearity is a two-photon absorption relayed and amplified by mid-gap absorbing species which have been created by this two-photon absorption. We formally face a four-photon absorption described by a positive imaginary seventh-order non-linearity. (author) [fr
-
Laser cavities with self-pumped phase conjugation by mixing of four waves in an amplifier
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sillard, Pierre
1998-01-01
The purpose of this research thesis is to characterise a new type of cavities with self-pumped phase conjugation which uses a mixing of four waves degenerated in a solid amplifier. After a definition of phase conjugation and a brief overview of the history of this technique, the author describes and compares the different laser architectures with phase conjugation. He explains benefits and perspectives related to cavities with self-pumped phase conjugation using a mixing of four waves in an amplifier. He develops the necessary formalism for the resolution of the coupled equations of four wave mixing in transient regime for a resonant and saturated non-linearity. He shows how these results can be applied to solid amplifiers, in particularly to the Nd:YAG amplifier which is used in all experiments. In the next part, the author describes the principle and characteristics of cavity with self-pumped phase conjugation injected by another laser. An experiment is performed with two conventional Nd:YAG amplifiers pumped by flash lamps. The excellent performance of the cavity allows the study of cavity without this injection, but self-oscillating is to be envisaged, and a modelling of self-oscillating cavities is proposed and studied. Results are compared with those obtained with two N:YAG amplifiers pumped by flash lamps. Polarisation properties of the self-oscillating cavity are also studied. Finally, the author reports an experimental validation of a cavity with self-pumped phase conjugation all in solid state, pumped by laser diodes (a more efficient pumping) [fr
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hu, Hao; Jopson, R. M.; Dinu, M.
2013-01-01
We demonstrate compensation of fiber nonlinearities using optical phase conjugation of an 8-chamiel WDM 32-Gbaud PDM QPSK signal. Conjugating phase every 600 km in a fiber loop enabled a 6000 km transmission over True Wave fiber. © 2013 Optical Society of America....
-
Information properties of a hologram of mutually conjugate waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rubanov, A.S.; Serebryakova, L.M.
1995-01-01
A theoretical study of information properties of a correlation response to a fragment of an image of a thin referenceless hologram of mutually conjugate waves that is recorded with a phase-conjugating (PC) mirror is reported. It is shown that this hologram reconstructs a full image in reflected light and can be used as an associative storage device and as a selective PC mirror. 7 refs., 1 fig
-
Coherent chirped pulse laser network with Mickelson phase conjugator.
Okulov, A Yu
2014-04-10
The mechanisms of nonlinear phase-locking of a large fiber amplifier array are analyzed. The preference is given to the most suitable configuration for a coherent coupling of thousands of fundamental spatial mode fiber beams into a single smooth beam ready for chirped pulse compression. It is shown that a Michelson phase-conjugating configuration with double passage through an array of fiber amplifiers has the definite advantage compared to a one-way fiber array coupled in a Mach-Zehnder configuration. Regardless of the amount of synchronized fiber amplifiers, the Michelson phase-conjugating interferometer is expected to do a perfect compensation of the phase-piston errors and collimation of backwardly amplified fiber beams on an entrance/output beam splitter. In both configurations, the nonlinear transformation of the stretched pulse envelope, due to gain saturation, is capable of randomizing the position of chirp inside an envelope; thus it may reduce the visibility of the interference pattern at an output beam splitter. Certain advantages are inherent to the sech-form temporal envelope because of the exponential precursor and self-similar propagation in gain medium. The Gaussian envelope is significantly compressed in a deep gain saturation regime, and the frequency chirp position inside pulse envelope is more deformed.
-
Modeling of SBS Phase Conjugation in Multimode Step Index Fibers
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Spring, Justin B
2008-01-01
... limited, double-pass high-power amplifiers or coherent beam combination. Little modeling of such a fiber-based phase-conjugator has been done, making it difficult to make decisions about the right fiber to use...
-
KrF laser amplifier with phase-conjugate Brillouin retroreflectors.
Gower, M C
1982-09-01
We have demonstrated the use of phase-conjugate stimulated Brillouin scattering mirrors to produce high-quality, short-pulse KrF laser beams from angular multiplexed and regenerative amplifiers. The mirror was also shown to isolate systems optically from amplifier spontaneous emission. Automatic alignment of targets using this mirror as a retroreflector was also demonstrated.
-
Millerd, James E.; Garmire, Elsa M.; Klein, Marvin B.
1992-01-01
Data showing nonlinear resonantly enhanced photorefractive response at high modulation depths in InP:Fe are presented. A simple empirical model is used to describe the behavior. Next the impact of these large-signal effects, as well as linear absorption, on the self-pumped phase-conjugate mirror is examined. Predicted performance is compared to actual measurements of a ring self-pumped phase-conjugate mirror using InP. The performance of the double-pumped phase-conjugate mirror is also examined experimentally and compared with the performance of the ring mirror.
-
Sun, P C; Fainman, Y
1990-09-01
An optical processor for real-time generation of the Wigner distribution of complex amplitude functions is introduced. The phase conjugation of the input signal is accomplished by a highly efficient self-pumped phase conjugator based on a 45 degrees -cut barium titanate photorefractive crystal. Experimental results on the real-time generation of Wigner distribution slices for complex amplitude two-dimensional optical functions are presented and discussed.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shapiro, Elena G; Fedoruk, Mikhail P
2011-01-01
Analytical formulas are derived to approximate the probability density functions of 'zero' and 'one' bits in a linear communication channel with a binary format of optical signal phase modulation. Direct numerical simulation of the propagation of optical pulses in a communication line with optical phase conjugation is performed. The results of the numerical simulation are in good agreement with the analytical approximation. (fibreoptic communication lines)
-
Preliminary training of a self-pumped loop phase-conjugate mirror based on a photorefractive crystal
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mogaddam, Mehran Wahdani; Shuvalov, Vladimir V
2006-01-01
It is shown by the example of a loop self-pumped phase-conjugate (SPPC) mirror based on a photorefractive crystal (PRC) BaTiO 3 that formation of a phase-conjugate (PC) wave in a SPPC mirror can be considerably accelerated by using a preliminary training of the mirror. For this purpose, it is necessary to direct preliminary an auxiliary (training) optical field on the SPPC mirror, which contains some information on the properties of the input signal whose wave front will be conjugated later. This procedure provides the writing of static refractive-index gratings in the PRC already at the training stage. The presence of these gratings ensures a much more rapid (by 6-20 times) production of volume refractive-index gratings required for the efficient conjugation of the signal radiation. Several variants of static and dynamic SPPC mirror training procedures are simulated and their efficiencies are compared. (nonlinear optical phenomena)
-
Kobayashi, Hiroyuki; Tsuchiya, Kousuke; Ogino, Kenji; Vacha, Martin
2012-01-01
Single-molecule study of phenylenevinylene oligomers revealed distinct spectral forms due to different conjugation lengths which are determined by torsional defects. Large spectral jumps between different spectral forms were ascribed to torsional flips of a single phenylene ring. These spectral changes reflect the dynamic nature of electron delocalization in oligophenylenevinylenes and enable estimation of the phenylene torsional barriers. © 2012 The Owner Societies.
-
The Gas-Phase Photophysics of Eosin Y and its Maleimide Conjugate.
Daly, Steven; Kulesza, Alexander; Knight, Geoffrey; MacAleese, Luke; Antoine, Rodolphe; Dugourd, Philippe
2016-05-26
The use of the xanthene family of dyes as fluorescent probes in a wide range of applications has provided impetus for the studying of their photophysical properties. In particular, recent advances in gas-phase techniques such as FRET that utilize such chromophores have placed a greater importance on the characterization of these properties in the gas phase. Additionally, the use of synthetic linker chains to graft the chromophores in a site-specific manner to their target system is ubiquitous. There is, however, often limited information on how the addition of such a linker chain may affect the photophysical properties of the chromophores, which is of fundamental importance for interpretation of experimental data reliant on grafted chromophores. Here, we present data on the optical spectroscopy of different protonation states of Eosin Y, a fluorescein derivative. We compare the photophysics of Eosin Y to its maleimide conjugate, and to the thioether product of the reaction of this conjugate with cysteamine. Comparison of the mass spectra following laser irradiation shows that very different relaxation takes place upon addition of the maleimide moiety but that the photophysics of the bare chromophore are restored upon addition of cysteamine. This radical change in the photophysics is interpreted in terms of charge-transfer states, whose energy relative to the S1 ← S0 transition of the chromophore is dependent on the conjugation of the maleimide moiety. We also show that the shape of the absorption band is unchanged in the gas-phase as compared to the solution-phase, showing a maximum with a shoulder toward the blue, and examination of isotope distributions of the isolated ions show that this shoulder cannot be due to the presence of dimers. Consideration of the fluorescence emission spectrum allows a tentative assignment of the shoulder to be due to a vibrational progression with a high Franck-Condon factor.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Pastrana-Sanchez, R.; Rodriguez-Zurita, G.; Vazquez-Castillo, J. F. [Benemerita Universidad Autonoma de Puebla, Puebla (Mexico)
2001-04-01
A technique to estimate the refractive index and thickness of homogeneous plane parallel dielectric plates is proposed using a phase-conjugate interferometer, in which counting of interference fringes is employed. The light beam impinges a tilted plate before it enters a phase-conjugate interferometer, and a count of the fringes passing through a given reference at the observing plane gives the phase changes as a function of tilting angle. The obtained data is fitted to a mathematical model, which leads to the determination of both refractive index and thickness simultaneously. In this letter, experimental data from two interferometers are also discussed for comparison. One with an externally-pumped phase-conjugate mirror achieved with a BSO photorefractive crystal and another one with conventional mirrors. Results show that the phase sensitivity of the phase-conjugate interferometer is not simply twice the corresponding sensitivity of the conventional version. [Spanish] Se propone una tecnica para medir indices de refraccion y espesores de placas dielectricas plano paralelas homogeneas empleando un interferometro con fase conjugada, en el cual se usa el conteo de franjas. El haz luminoso incide en una placa inclinada bajo inspeccion antes de entrar en un interferometro equipado con un espejo conjugador de fase, y se realiza un conteo de las franjas que pasan por determinada referencia en el plano de observacion, proporcionando los cambios de fase en funcion del angulo de inclinacion. Los datos obtenidos se ajustan a un modelo, el cual conduce a la determinacion, tanto del indice de refraccion como del espesor, simultaneamente. En este trabajo se discuten datos experimentales provenientes de dos interferometros para su comparacion. Uno de ellos tiene un espejo conjugador basado en un cristal BSO fotorrefractivo, mientras que el otro es una variante con espejos convencionales. Se muestra que la sensibilidad de fase del interferometro con conjugador de fase no
-
Barashkov, M. S.; Iskanderov, N. A.
1987-08-01
An analysis is made of the reduction of the fluctuations introduced in the intensity of the phase conjugate wave and of the reduction in the time for establishment of quasisteady conjugation conditions and in the relaxation time of the intensity of the conjugate wave after switching on of the pump fields in the case of stochastic excitation of a transition. It is shown that, in principle, it is possible to generate a narrow-band pump-induced component of the conjugate wave spectrum.
-
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Litvin, IA
2007-01-01
Full Text Available The authors investigate the phase conjugating element of a two element Fourier transform beam shaping scheme and the impact this element has on the resulting propagation. It is shown that there are stricter limitations placed on the system when...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Jia, W.
1997-01-01
We investigated some novel geometries of self-pumped phase conjugation (SPPC) and mutually pumped phase conjugation (MPPC), relying on total internal reflection both from the a face and from corners, with beams entering the negative c face of doped (K 0.5 Na 0.5 ) 0.2 (Sr 0.75 Ba 0.25 ) 0.9 Nb 2 O 6 crystals. The different situations for internal light paths and their direct transformation at the same incident wavelength were observed. Similarities and differences between SPPC and MPPC are discussed. The dynamic features of SPPC and MPPC in different situations were also observed. Three or more four-wave-mixing interaction regions were clearly observed inside the phase conjugators. The multistep interaction and its influence on the response rate and conjugation fidelity are analyzed. The large size of the samples seems necessary to ensure an optical path that is long enough for multistep bifurcation. The stability of the light channels is discussed based on the fanning effect. copyright 1997 Optical Society of America
-
Ma, Chaojie; Di, Jianglei; Li, Ying; Xiao, Fajun; Zhang, Jiwei; Liu, Kaihui; Bai, Xuedong; Zhao, Jianlin
2018-06-01
We demonstrate, for the first time, the rotational memory effect of a multimode fiber (MMF) based on digital optical phase conjugation (DOPC) to achieve multiple-spot focusing. An implementation interferometer is used to address the challenging alignments in DOPC. By rotating the acquired phase conjugate pattern, rotational scanning through a MMF could be achieved by recording a single off-axis hologram. The generation of two focal spots through a MMF is also demonstrated by combining the rotational memory effect with the superposition principle. The results may be useful for ultrafast scanning imaging and optical manipulation of multiple objects through a MMF.
-
Zhang, Lu; Ming, Yi; Li, Jin
2017-11-01
Due to the unique phase noise (PN) characteristics in direct-detection optical OFDM (DDO-OFDM) systems, the design of PN compensator is considered as a difficult task. In this paper, a laser PN suppression scheme with low complexity for DDO-OFDM based on coherent superposition of data carrying subcarriers and their phase conjugates is proposed. Through theoretical derivation, the obvious PN suppression is observed. The effectiveness of this technique is demonstrated by simulation of a 4-QAM DDO-OFDM system over 1000 km transmission length at different laser line-width and subcarrier frequency spacing. The results show that the proposed scheme can significantly suppress both varied phase rotation term (PTR) and inter-carrier interference (ICI), and the laser line-width can be relaxed with up to 9 dB OSNR saving or even breakthrough of performance floor.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tzannis, A P; Beaud, P; Frey, H M; Gerber, T; Mischler, B; Radi, P P [Paul Scherrer Inst. (PSI), Villigen (Switzerland)
1997-06-01
Resonant Holographic Interferometry is a method based on the anomalous dispersion of light having a frequency close to an electronic transition of a molecule. We propose a novel single-laser, two-colour setup for recording resonant holograms and apply it to 2D species concentration measurements. The second colour is generated by optical phase-conjugation from Stimulated Brillouin scattering in a cell. Phase-Conjugate Resonant Holographic Interferometry (PCRHI) is demonstrated in a 2D NH{sub 3}/O{sub 2} flame yielding interferograms that contain information on the NH radical distribution in the flame. Experimental results are quantified by applying a numerical computation of the Voigt profiles. (author) 1 fig., 3 refs.
-
Effects of phase change on reflection in phase-measuring interference microscopy
Dubois , Arnaud
2004-01-01
International audience; We show by analytical and numerical calculations that the phase change on reflection that occurs in interference microscopy is almost independent of the numerical aperture of the objective. The shift of the microscope interferogram response due to the phase change on reflection, however, increases with the numerical aperture. Measurements of the interferogram shift are made with a Linnik interference microscope equipped with various numerical-aperture objectives and ar...
-
Conjugate gradient method for phase retrieval based on the Wirtinger derivative.
Wei, Zhun; Chen, Wen; Qiu, Cheng-Wei; Chen, Xudong
2017-05-01
A conjugate gradient Wirtinger flow (CG-WF) algorithm for phase retrieval is proposed in this paper. It is shown that, compared with recently reported Wirtinger flow and its modified methods, the proposed CG-WF algorithm is able to dramatically accelerate the convergence rate while keeping the dominant computational cost of each iteration unchanged. We numerically illustrate the effectiveness of our method in recovering 1D Gaussian signals and 2D natural color images under both Gaussian and coded diffraction pattern models.
-
Cretaceous to Recent Asymetrical Subsidence of South American and West African Conjugate Margins
Kenning, J.; Mann, P.
2017-12-01
Two divergent interpretations have been proposed for South American rifted-passive margins: the "mirror hypothesis" proposes that the rifted margins form symmetrically from pure shear of the lithosphere while upper-plate-lower plate models propose that the rifted margins form asymmetrically by simple shear. Models based on seismic reflection and refraction imaging and comparison of conjugate, rifted margins generally invoke a hybrid stretching process involving elements of both end member processes along with the effects of mantle plumes active during the rift and passive margin phases. We use subsidence histories of 14, 1-7 km-deep exploration wells located on South American and West African conjugate pairs now separated by the South Atlantic Ocean, applying long-term subsidence to reveal the symmetry or asymmetry of the underlying, conjugate, rift processes. Conjugate pairs characterize the rifted margin over a distance of 3500 km and include: Colorado-South Orange, Punta Del Este-North Orange, South Pelotas-Lüderitz and the North Pelotas-Walvis Basins. Of the four conjugate pairs, more rapid subsidence on the South American plate is consistently observed with greater initial rift and syn-rift subsidence rates of >60m/Ma (compared to 100 m/Ma are observed offshore South Africa between approximately 120-80 Ma, compatible with onset of the post-rift thermal sag phase. During this period the majority of burial is completed and rates remain low at Argentina/Uruguay displays more gradual subsidence throughout the Cretaceous, consistently averaging a moderate 15-30m/Ma. By the end of this stage there is a subsequent increase to 25-60 m/Ma within the last 20 Ma, interpreted to reflect lithospheric loading due to increased sedimentation rates during the Cenozoic. This increase in subsidence rate is not seen in the African conjugate section where the majority of sediments bypassed the highly aggraded Cretaceous shelf. Initially greater on the Brazilian margin compared to
-
Park, Sangwoo; Cha, Seongwoo; Oh, Jungsuk; Lee, Hwihyeong; Ahn, Heekyung; Churn, Kil Sung; Kong, Hong Jin
2016-04-18
The self-phase locking of a stimulated Brillouin scattering-phase conjugate mirror (SBS-PCM) allows a simple and scalable coherent beam combination of existing lasers. We propose a simple optical system composed of a rotating wedge and a concave mirror to overcome the power limit of the SBS-PCM. Its phase locking ability and the usefulness on the beam-combination laser are demonstrated experimentally. A four-beam combination is demonstrated using this SBS-PCM scheme. The relative phases between the beams were measured to be less than λ/24.7.
-
Bowman, D; Harte, T L; Chardonnet, V; De Groot, C; Denny, S J; Le Goc, G; Anderson, M; Ireland, P; Cassettari, D; Bruce, G D
2017-05-15
We demonstrate simultaneous control of both the phase and amplitude of light using a conjugate gradient minimisation-based hologram calculation technique and a single phase-only spatial light modulator (SLM). A cost function, which incorporates the inner product of the light field with a chosen target field within a defined measure region, is efficiently minimised to create high fidelity patterns in the Fourier plane of the SLM. A fidelity of F = 0.999997 is achieved for a pattern resembling an LG10 mode with a calculated light-usage efficiency of 41.5%. Possible applications of our method in optical trapping and ultracold atoms are presented and we show uncorrected experimental realisation of our patterns with F = 0.97 and 7.8% light efficiency.
-
Electrically Tunable Reflective Terahertz Phase Shifter Based on Liquid Crystal
Yang, Jun; Xia, Tianyu; Jing, Shuaicheng; Deng, Guangsheng; Lu, Hongbo; Fang, Yong; Yin, Zhiping
2018-02-01
We present a reflective spatial phase shifter which operates at terahertz regime above 325 GHz. The controllable permittivity of the nematic liquid crystals was utilized to realize a tunable terahertz (THz) reflective phase shifter. The reflective characteristics of the terahertz electromagnetic waves and the liquid crystal parameters were calculated and analyzed. We provide the simulation results for the effect of the incident angle of the plane wave on the reflection. The experiment was carried out considering an array consisting of 30 × 30 patch elements, printed on a 20 × 20 mm quartz substrate with 1-mm thickness. The phase shifter provides a tunable phase range of 300° over the frequency range of 325 to 337.6 GHz. The maximum phase shift of 331° is achieved at 330 GHz. The proposed phase shifter is a potential candidate for THz applications, particularly for reconfigurable reflectarrays.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hu, Hao; Jopson, R. M.; Gnauck, A. H.
2015-01-01
We demonstrate polarization-independent parametric amplification of a 2.048-Tbit/s 8-WDM PDM 16-QAM signal and simultaneous wavelength conversion and phase conjugation in a highly nonlinear fiber. Two high-power continuous-wave pumps with orthogonal polarizations and counter-phase modulation are ...
-
All solid-state diode pumped Nd:YAG MOPA with stimulated Brillouin phase conjugate mirror
Offerhaus, Herman L.; Godfried, Herman; Godfried, H.P; Witteman, W.J.
1996-01-01
At the Nederlands Centrum voor Laser Research (NCLR) a 1 kHz diode-pumped Nd:YAG Master Oscillator Power Amplifier (MOPA) chain with a Stimulated Brillouin Scattering (SBS) Phase Conjugate mirror is designed and operated. A small Brewster angle Nd:YAG slab (2 by 2 by 20 mm) is side pumped with 200
-
Anh Van Nguyen; Victor Deineka; Lumila Deineka; Anh Vu Thi Ngoc
2017-01-01
Relative retention analysis and increment approach were applied for the comparison of triglycerides (TGs) retention of a broad set of plant seed oils with isomeric conjugated octadecatrienoic acids (CLnA) by reversed-phase HPLC for “propanol-2-acetonitrile” mobile phases and Kromasil 100-5C18 stationary phase with diode array detection (DAD) and mass spectrometric (MS) detection. The subjects of investigation were TGs of seed oils: Calendula officinalis, Catalpa ovata, Jacaranda mimosifolia, ...
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Løbel, M.; Petersen, P.M.; Johansen, P.M.
1998-01-01
Experimental results show that angular dispersion strongly influences the self-induced frequency scanning of a multimode broad-area diode laser array coupled to a photorefractive self-pumped phase conjugate mirror. Prisms or a dispersive grating placed in the external cavity opposing the material...
-
Lee, Yi-Huan; Chen, Wei-Chih; Yang, Yi-Lung; Chiang, Chi-Ju; Yokozawa, Tsutomu; Dai, Chi-An
2014-05-21
Driven by molecular affinity and balance in the crystallization kinetics, the ability to co-crystallize dissimilar yet self-crystallizable blocks of a block copolymer (BCP) into a uniform domain may strongly affect its phase diagram. In this study, we synthesize a new series of crystalline and monodisperse all-π-conjugated poly(2,5-dihexyloxy-p-phenylene)-b-poly(3-(2-ethylhexyl)thiophene) (PPP-P3EHT) BCPs and investigate this multi-crystallization effect. Despite vastly different side-chain and main-chain structures, PPP and P3EHT blocks are able to co-crystallize into a single uniform domain comprising PPP and P3EHT main-chains with mutually interdigitated side-chains spaced in-between. With increasing P3EHT fraction, PPP-P3EHTs undergo sequential phase transitions and form hierarchical superstructures including predominately PPP nanofibrils, co-crystalline nanofibrils, a bilayer co-crystalline/pure P3EHT lamellar structure, a microphase-separated bilayer PPP-P3EHT lamellar structure, and finally P3EHT nanofibrils. In particular, the presence of the new co-crystalline lamellar structure is the manifestation of the interaction balance between self-crystallization and co-crystallization of the dissimilar polymers on the resulting nanostructure of the BCP. The current study demonstrates the co-crystallization nature of all-conjugated BCPs with different main-chain moieties and may provide new guidelines for the organization of π-conjugated BCPs for future optoelectronic applications.
-
Long-distance transmission over standard fiber by use of mid-way phase conjugation
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Zhang, Xiupu; Ebskamp, Frank; Jørgensen, Bo Foged
1995-01-01
In this letter, we predict transmission over more than 6000 km using standard fiber with the application of mid-way phase-conjugation in a 1.55-μm, 10-Gb/s IM/DD system with in-line amplifiers for the power penalty at BER=10-9, which is less than 6 dB; the system must operate with an average powe...... into the fiber within the range of -5 to 5 dBm...
-
Condon, Joshua; Martin, Tyler; Jayaraman, Arthi
We use atomistic (AA) and coarse-grained (CG) molecular dynamics simulations to elucidate the thermodynamic driving forces governing lower critical solution temperature (LCST)-like phase transition exhibited by elastin-like peptides (ELPs) and conjugates of ELP with other macromolecules. In the AA simulations, we study ELP oligomers in explicit water, and mark the transition as the temperature at which they undergo a change in ``hydration'' state. While AA simulations are restricted to small systems of short ELPs and do not capture the chain aggregation observed in experiments of ELPs, they guide the phenomenological CG model development by highlighting the solvent induced polymer-polymer effective interactions with changing temperature. In the CG simulations, we capture the LCST polymer aggregation by increasing polymer-polymer effective attractive interactions in an implicit solvent. We examine the impact of conjugating a block of LCST polymer to another rigid unresponsive macromolecular block on the LCST-like transition. We find that when multiple LCST polymers are conjugated to a rigid polymer block, increased crowding of the LCST polymers shifts the onset of chain aggregation to smaller effective polymer-polymer attraction compared to the free LCST polymers. These simulation results provide guidance on the design of conjugated bio-mimetic thermoresponsive materials, and shape the fundamental understanding of the impact of polymer crowding on phase behavior in thermoresponsive LCST polymer systems.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kir'yanov, Yu F; Kochemasov, G G; Maslov, N V; Shestakova, I V
1999-01-01
The influence of the strictive self-interaction on the threshold and quality of phase conjugation in the course of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) was investigated numerically in the linear approximation for steady-state linearly polarised pumping. The calculations were carried out for the three-dimensional case of a Gaussian pump beam and a beam representing a superposition of 10 x 10 Hermitian - Gaussian modes with random phases. It was found that in the case of a Gaussian beam the growth of the strictive aberrations leads to a significant reduction of the SBS threshold but has little influence on the conjugation quality. In the case of a pump beam with a divergence exceeding the diffraction limit such growth of the strictive aberrations results (on the average) in lowering the SBS threshold and in deterioration of the conjugation quality. The calculated results depend strongly on the specific phase combination of the superposed modes. (nonlinear optical phenomena)
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Gajda, A.; Da Ros, Francesco; Porto da Silva, Edson
2018-01-01
A 1-dB Q-factor improvement through optical phase conjugation in a silicon waveguide with a lateral p-i-n diode enables BER
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yarovoi, V V; Kirsanov, A V
2002-01-01
A model of the so-called short hologram, which does not exhibit in-depth diffraction deformation of the fine speckle pattern of the recording fields, is studied. The investigation is performed by the example of a thermal hologram recorded by two speckle waves, which is the output mirror of a ring laser produced as a result of this recording. It is shown that the ability of this short hologram to select a wave conjugated to a speckle signal in the mode of the holographic laser depends both on the degree of mutual mixing of the speckles of recording beams in the hologram volume and on the effects of its saturation by the beams. The maximum accuracy of phase conjugation of speckle radiation in the holographic Nd:YAG laser achieved upon the best selection of the conjugate wave by the short thermal hologram was 93%. (nonlinear optical phenomena)
-
Modern methods for the synthesis of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zubin, Evgenii M; Oretskaya, Tat'yana S; Romanova, Elena A
2002-01-01
The published data on the methods of chemical solution and solid-phase synthesis of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates are reviewed. The known methods are systematised and their advantages and disadvantages are considered. The approaches to the solution synthesis of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates are systematised according to the type of chemical bonds between the fragments, whereas those to the solid-phase synthesis are classified according to the procedure used for the preparation of conjugates, viz., stepwise elongation of oligonucleotide and peptide chains on the same polymeric support or solid-phase condensation of two presynthesised fragments. The bibliography includes 141 references.
-
Improving experimental phases for strong reflections prior to density modification
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Uervirojnangkoorn, Monarin; Hilgenfeld, Rolf; Terwilliger, Thomas C.; Read, Randy J.
2013-01-01
A genetic algorithm has been developed to optimize the phases of the strongest reflections in SIR/SAD data. This is shown to facilitate density modification and model building in several test cases. Experimental phasing of diffraction data from macromolecular crystals involves deriving phase probability distributions. These distributions are often bimodal, making their weighted average, the centroid phase, improbable, so that electron-density maps computed using centroid phases are often non-interpretable. Density modification brings in information about the characteristics of electron density in protein crystals. In successful cases, this allows a choice between the modes in the phase probability distributions, and the maps can cross the borderline between non-interpretable and interpretable. Based on the suggestions by Vekhter [Vekhter (2005 ▶), Acta Cryst. D61, 899–902], the impact of identifying optimized phases for a small number of strong reflections prior to the density-modification process was investigated while using the centroid phase as a starting point for the remaining reflections. A genetic algorithm was developed that optimizes the quality of such phases using the skewness of the density map as a target function. Phases optimized in this way are then used in density modification. In most of the tests, the resulting maps were of higher quality than maps generated from the original centroid phases. In one of the test cases, the new method sufficiently improved a marginal set of experimental SAD phases to enable successful map interpretation. A computer program, SISA, has been developed to apply this method for phase improvement in macromolecular crystallography
-
Voinovich, Peter; Merlen, Alain
2005-12-01
The effect of parametric wave phase conjugation (WPC) in application to ultrasound or acoustic waves in magnetostrictive solids has been addressed numerically by Ben Khelil et al. [J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 109, 75-83 (2001)] using 1-D unsteady formulation. Here the numerical method presented by Voinovich et al. [Shock waves 13(3), 221-230 (2003)] extends the analysis to the 2-D effects. The employed model describes universally elastic solids and liquids. A source term similar to Ben Khelil et al.'s accounts for the coupling between deformation and magnetostriction due to external periodic magnetic field. The compatibility between the isotropic constitutive law of the medium and the model of magnetostriction has been considered. Supplementary to the 1-D simulations, the present model involves longitudinal/transversal mode conversion at the sample boundaries and separate magnetic field coupling with dilatation and shear stress. The influence of those factors in a 2-D geometry on the potential output of a magneto-elastic wave phase conjugator is analyzed in this paper. The process under study includes propagation of a wave burst of a given frequency from a point source in a liquid into the active solid, amplification of the waves due to parametric resonance, and formation of time-reversed waves, their radiation into liquid, and focusing. The considered subject is particularly important for ultrasonic applications in acoustic imaging, nondestructive testing, or medical diagnostics and therapy.
-
Kaplan, Michael; Muraca, Maurizio; Hammerman, Cathy; Rubaltelli, Firmino F; Vilei, Maria T; Vreman, Hendrik J; Stevenson, David K
2002-10-01
The objective of this study was to evaluate the roles of production and conjugation of bilirubin, individually and in combination, in the mechanism of neonatal jaundice. A cohort of healthy, term male newborns was sampled on the third day of life, coincident with routine metabolic screening, for blood carboxyhemoglobin determination, a reflection of heme catabolism, and for serum unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin fractions, reflecting bilirubin conjugation. The former was determined by gas chromatography, corrected for inspired CO (COHbc), and expressed as percentage of total hemoglobin. Serum bilirubin fractions were quantified by alkaline methanolysis and reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography. The sum of all bilirubin fractions comprised serum total bilirubin (STB). Total conjugated bilirubin (TCB) was comprised of the sum of the conjugated fractions and was expressed as percentage of STB (TCB[%]). A "bilirubin production/conjugation index" (COHbc/[TCB(%)] represented the combined roles of these modalities in the mechanism of bilirubinemia. Relationships between STB concentrations on the one hand, and COHbc values, TCB(%) proportions, and the production/conjugation index on the other, were determined by applying a best-fit regression analysis methodology. Mean (+/- standard deviation) STB concentration at the time of sampling was 114 +/- 48 micro mol/L (range: 8-263 micro mol/L). Mean COHbc value was 0.77 +/- 0.19%, and median (interquartile range) TCB(%) was 0.737 (0.465-1.260)%. COHbc values correlated directly with STB concentrations (r = 0.38; s = 46.1), and TCB(%) correlated inversely with STB (r = 0.40; s = 45.8). The production/conjugation index correlated positively with STB values (r = 0.61; s = 45.8), the r value for the index being higher than that of either COHbc or TCB(%), individually. The bilirubin production/conjugation index seemed to have a biphasic relationship to STB: STB values rose steeply in concert with increasing index
-
Class, Kinship Density, and Conjugal Role Segregation.
Hill, Malcolm D.
1988-01-01
Studied conjugal role segregation in 150 married women from intact families in working-class community. Found that, although involvement in dense kinship networks was associated with conjugal role segregation, respondents' attitudes toward marital roles and phase of family cycle when young children were present were more powerful predictors of…
-
Concept for phase-to-intensity conversion in SOAs by facet reflections
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Blaaberg, Søren; Mørk, Jesper
2010-01-01
All-optical conversion from phase-modulated signals to intensity-modulated signals is theoretically demonstrated in semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs). Large-signal and small-signal calculations show significant conversion responses appearing as a result of even minute reflections at the end...... mirrors of the SOA. It is discussed how reflected phase-modulated signals can lead to interference resulting in intensity fluctuations that are amplified by the gain in a SOA. The effect can be utilized for deliberate conversion between optical modulation formats.......All-optical conversion from phase-modulated signals to intensity-modulated signals is theoretically demonstrated in semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs). Large-signal and small-signal calculations show significant conversion responses appearing as a result of even minute reflections at the end...
-
Phase retrieval from reflective fringe patterns of double-sided transparent objects
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Huang, Lei; Asundi, Anand Krishna
2012-01-01
‘Ghosted’ fringe patterns simultaneously reflected from both the upper and lower sides of a transparent target in the fringe reflection technique are captured for transparent surface 3D shape measurement, but the phase retrieval from the captured ‘ghosted’ fringe patterns is still not solved. A novel method is proposed to solve this issue by using two sets of phase-shifted fringe patterns with slightly different frequencies. The nonlinear least-squares method is used to estimate the fringe phase and modulation from both front and rear interfaces. Several simulations are done to show the feasibility of the proposed method. The influence of fringe noise on the algorithm is studied as well, which indicates that the proposed method is able to retrieve the phase from double-sided reflective fringe patterns with fringe noise equivalent to that in practical measurements. The merits and limitations of the method are discussed and recommendations for future studies are made. (paper)
-
Application of heat-balance integral method to conjugate thermal explosion
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Novozhilov Vasily
2009-01-01
Full Text Available Conjugate thermal explosion is an extension of the classical theory, proposed and studied recently by the author. The paper reports application of heat-balance integral method for developing phase portraits for systems undergoing conjugate thermal explosion. The heat-balance integral method is used as an averaging method reducing partical differential equation problem to the set of first-order ordinary differential equations. The latter reduced problem allows natural interpretation in appropriately chosen phase space. It is shown that, with the help of heat-balance integral technique, conjugate thermal explosion problem can be described with a good accuracy by the set of non-linear first-order differential equations involving complex error function. Phase trajectories are presented for typical regimes emerging in conjugate thermal explosion. Use of heat-balance integral as a spatial averaging method allows efficient description of system evolution to be developed.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Anh Van Nguyen
2017-12-01
Full Text Available Relative retention analysis and increment approach were applied for the comparison of triglycerides (TGs retention of a broad set of plant seed oils with isomeric conjugated octadecatrienoic acids (CLnA by reversed-phase HPLC for “propanol-2-acetonitrile” mobile phases and Kromasil 100-5C18 stationary phase with diode array detection (DAD and mass spectrometric (MS detection. The subjects of investigation were TGs of seed oils: Calendula officinalis, Catalpa ovata, Jacaranda mimosifolia, Centranthus ruber, Momordica charantia, Trichosanthes anguina, Punica granatum, Thladiantha dubia, Valeriana officinalis, and Vernicia montana. It was found that a sequence of elution of TGs of the same types is the same without any inversions for full range of mobile phase compositions: punicic (C18:39Z11E13Z < jacaric (C18:38Z10E12Z < catalpic (C18:39E11E13Z < α-eleostearic (C18:39Z11E13E < calendic (C18:38E10E12Z < β-eleostearic (C18:39E11E13E < all-E calendic (C18:38E10E12E acids. TGs and fatty acid compositions were calculated for all oil samples. Regularities of solute retentions as a function of isomeric conjugated octadecatrienoic acid moiety structure are discussed. Thus, it was proven that it is possible to differentiate TGs of complex composition with moieties of all natural CLnA by retention control accomplished by electronic spectra comparison, even though there are only three types of electronic-vibration spectra for seven isomeric CLnA.
-
Background velocity inversion by phase along reflection wave paths
Yu, Han; Guo, Bowen; Schuster, Gerard T.
2014-01-01
A background velocity model containing the correct lowwavenumber information is desired for both the quality of the migration image and the success of waveform inversion. We propose to invert for the low-wavenumber part of the velocity model by minimizing the phase difference between predicted and observed reflections. The velocity update is exclusively along the reflection wavepaths and, unlike conventional FWI, not along the reflection ellipses. This allows for reconstructing the smoothly varying parts of the background velocity model. Tests with synthetic data show both the benefits and limitations of this method.
-
Background velocity inversion by phase along reflection wave paths
Yu, Han
2014-08-05
A background velocity model containing the correct lowwavenumber information is desired for both the quality of the migration image and the success of waveform inversion. We propose to invert for the low-wavenumber part of the velocity model by minimizing the phase difference between predicted and observed reflections. The velocity update is exclusively along the reflection wavepaths and, unlike conventional FWI, not along the reflection ellipses. This allows for reconstructing the smoothly varying parts of the background velocity model. Tests with synthetic data show both the benefits and limitations of this method.
-
Esayan, A. A.; Zozulya, A. A.; Tikhonchuk, Vladimir T.
1991-10-01
An analysis is made of stimulated scattering in a ring resonator formed by a self-intersecting beam with simultaneous rotation and contraction of the beam due to feedback. Conditions for the excitation of lasing are obtained and the phase conjugation quality is determined near the lasing threshold.
-
Plasmonic metasurfaces for efficient phase control in reflection
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Pors, Anders Lambertus; Bozhevolnyi, Sergey I.
2013-01-01
nanobrick and nanocross elements allows one to fully control the phase of reflected light for two orthogonal polarizations simultaneously. The approach is exemplified by the design of a gradient birefringent metasurface that reflects two orthogonal polarization states into +2 and −3 diffraction order......We numerically study the optical properties of metal-insulator-metal resonators and metasurfaces, emphasizing the presence of gap-surface plasmon (GSP) resonances and their connection to the optical response. In relation to birefringent metal-backed metasurfaces, we show how a combination of metal......, respectively, with a reflectivity up to ∼ 80% and in a broad wavelength range around the design wavelength of 800 nm. Finally, we introduce the concept of metascatterers, which are wavelength-sized polarization-sensitive scatterers....
-
Multiple wall-reflection effect in adaptive-array differential-phase reflectometry on QUEST
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Idei, H.; Fujisawa, A.; Nagashima, Y.; Onchi, T.; Hanada, K.; Zushi, H.; Mishra, K.; Hamasaki, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.K.
2016-01-01
A phased array antenna and Software-Defined Radio (SDR) heterodyne-detection systems have been developed for adaptive array approaches in reflectometry on the QUEST. In the QUEST device considered as a large oversized cavity, standing wave (multiple wall-reflection) effect was significantly observed with distorted amplitude and phase evolution even if the adaptive array analyses were applied. The distorted fields were analyzed by Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) in wavenumber domain to treat separately the components with and without wall reflections. The differential phase evolution was properly obtained from the distorted field evolution by the FFT procedures. A frequency derivative method has been proposed to overcome the multiple-wall reflection effect, and SDR super-heterodyned components with small frequency difference for the derivative method were correctly obtained using the FFT analysis
-
Phase locking in backward-wave oscillators with strong end reflections
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nusinovich, G. S.; Sinitsyn, O. V.; Rodgers, J.; Shkvarunets, A. G.; Carmel, Y.
2007-01-01
The theory of phase-locked oscillations in a backward-wave oscillator with strong end reflections is developed. Numerical results demonstrate that the locking bandwidth of such a device phase-locked by a prebunched electron beam can be twice the bandwidth of a resonator formed by a waveguide with strong end reflections. It is also shown that the device can operate with the efficiency exceeding 50% and that, in some cases, it can exhibit a hysteresis in the process of tuning the signal frequency. The applicability of the results obtained to the experiments with the plasma-assisted backward-wave oscillator currently underway at the University of Maryland is discussed
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Xin Mi Yang
2015-01-01
Full Text Available We make preliminary investigations on a new approach to reducing radar cross section (RCS of conducting objects. This approach employs novel planar metasurfaces characterizing nonuniform distribution of reflection phase. The operation principle of this approach and the design rule of the associated metasurfaces are explained using a simplified theoretical model. We then present a design example of such metasurfaces, in which three-layer stacked square patches with variable sizes are utilized as the reflecting elements. The proposed RCS-reduction approach is verified by both numerical simulations and measurements on the example, under the assumption of normal plane wave incidence. It is observed that, in a fairly wide frequency band (from 3.6 to 5.5 GHz, the presented example is capable of suppressing the specular reflections of conducting plates significantly (by more than 7 dB for two orthogonal incident polarizations.
-
Frequency-wavenumber domain phase inversion along reflection wavepaths
Yu, Han
2014-12-01
A background velocity model containing the correct low-wavenumber information is desired for both the quality of the migration image and the success of waveform inversion. To achieve this goal, the velocity is updated along the reflection wavepaths, rather than along both the reflection ellipses and transmission wavepaths as in conventional FWI. This method allows for reconstructing the low-wavenumber part of the background velocity model, even in the absence of long offsets and low-frequency component of the data. Moreover, in gradient-based iterative updates, instead of forming the data error conventionally, we propose to exploit the phase mismatch between the observed and the calculated data. The phase mismatch emphasizes a kinematic error and varies quasi-linearly with respect to the velocity error. The phase mismatch is computed (1) in the frequency-wavenumber (f-k) domain replacing the magnitudes of the calculated common shot gather by those of the observed one, and (2) in the temporal-spatial domain to form the difference between the transformed calculated common-shot gather and the observed one. The background velocity model inverted according to the proposed methods can serve as an improved initial velocity model for conventional waveform inversion. Tests with synthetic and field data show both the benefits and limitations of this method.
-
Diclofenac in Arabidopsis cells: Rapid formation of conjugates.
Fu, Qiuguo; Ye, Qingfu; Zhang, Jianbo; Richards, Jaben; Borchardt, Dan; Gan, Jay
2017-03-01
Pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) are continuously introduced into the soil-plant system, through practices such as agronomic use of reclaimed water and biosolids containing these trace contaminants. Plants may accumulate PPCPs from soil, serving as a conduit for human exposure. Metabolism likely controls the final accumulation of PPCPs in plants, but is in general poorly understood for emerging contaminants. In this study, we used diclofenac as a model compound, and employed 14 C tracing, and time-of-flight (TOF) and triple quadruple (QqQ) mass spectrometers to unravel its metabolism pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana cells. We further validated the primary metabolites in Arabidopsis seedlings. Diclofenac was quickly taken up into A. thaliana cells. Phase I metabolism involved hydroxylation and successive oxidation and cyclization reactions. However, Phase I metabolites did not accumulate appreciably; they were instead rapidly conjugated with sulfate, glucose, and glutamic acid through Phase II metabolism. In particular, diclofenac parent was directly conjugated with glutamic acid, with acyl-glutamatyl-diclofenac accounting for >70% of the extractable metabolites after 120-h incubation. In addition, at the end of incubation, >40% of the spiked diclofenac was in the non-extractable form, suggesting extensive sequestration into cell matter. The rapid formation of non-extractable residue and dominance of diclofenac-glutamate conjugate uncover previously unknown metabolism pathways for diclofenac. In particular, the rapid conjugation of parent highlights the need to consider conjugates of emerging contaminants in higher plants, and their biological activity and human health implications. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Quantum dot-polymer conjugates for stable luminescent displays.
Ghimire, Sushant; Sivadas, Anjaly; Yuyama, Ken-Ichi; Takano, Yuta; Francis, Raju; Biju, Vasudevanpillai
2018-05-23
The broad absorption of light in the UV-Vis-NIR region and the size-based tunable photoluminescence color of semiconductor quantum dots make these tiny crystals one of the most attractive antennae in solar cells and phosphors in electrooptical devices. One of the primary requirements for such real-world applications of quantum dots is their stable and uniform distribution in optically transparent matrices. In this work, we prepare transparent thin films of polymer-quantum dot conjugates, where CdSe/ZnS quantum dots are uniformly distributed at high densities in a chitosan-polystyrene copolymer (CS-g-PS) matrix. Here, quantum dots in an aqueous solution are conjugated to the copolymer by a phase transfer reaction. With the stable conjugation of quantum dots to the copolymer, we prevent undesired phase separation between the two and aggregation of quantum dots. Furthermore, the conjugate allows us to prepare transparent thin films in which quantum dots are uniformly distributed at high densities. The CS-g-PS copolymer helps us in not only preserving the photoluminescence properties of quantum dots in the film but also rendering excellent photostability to quantum dots at the ensemble and single particle levels, making the conjugate a promising material for photoluminescence-based devices.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mogaddam, Mehran Wahdani; Shuvalov, Vladimir V
2005-01-01
The dynamics of formation of a nonlinear response of a double phase-conjugate (PC) BaTiO 3 mirror is calculated. It is shown that because of competition between processes of different types (related to the presence of several PC channels, the local and nonlocal components of the photorefractive nonlinearity), the transient and dynamic lasing regimes for this mirror can be substantially different. It is found that the development of lasing begins with the successive formation and phasing of dynamic holograms of two different types (two PC channels). It is shown that even under optimal conditions, the lasing regime is not stationary due to competition between processes of different types, and the parameters of output fields fluctuate in time in a nontrivial way (due to the presence of the in-phase and out-of-phase components). Several scenarios of transition to the dynamic chaos are described. (nonlinear optical phenomena)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Matern, S.; Gerok, W.
1977-01-01
Specific radioimmunoassays for separate determinations of serum unconjugated cholic, conjugated cholic and conjugated deoxycholic acids have been developed. Prior to the radioimmunoassay, extraction of serum bile acids was performed with Amberlite XAD-2. Unconjugated cholic acid was separated from glyco- and taurocholic acids by thin-layer chromatography. At 50% displacement of bound labeled glyco[ 3 H]cholic acid using antiserum obtained after immunization with cholic acid-bovine serum albumin-conjugate the cross-reactivity of taurocholic acid was 100%, cholic acid 80%, glycochenodeoxycholic acid 10%, chenodeoxycholic acid 7%, conjugated deoxycholic acid 3%, and conjugated lithocholic acid 3 H]cholic acid was linear on a logit-log plot from 5 to 80 pmol of unlabeled glycocholic acid. Fasting serum conjugated cholic acid in healthy subjects was 0.68 +- 0.34 μmol/l. Unconjugated cholic acid was determined by a solid phase radioimmunoassay using the cholic acid antibody chemically bound to Sepharose. The displacement curve of [ 3 H]cholic acid in the solid phase radioimmunoassay was linear on a logit-log plot from 5 to 200 pmol of unlabeled cholic acid. The coefficient of variation between samples was 5%. Fasting serum conjugated deoxycholic acid concentrations in 10 healthy subjects ranged from 0.18 to 0.92 μmol/l determined by a radioimmunoassay using antiserum obtained after immunization with deoxycholic acid-bovine serum albumin-conjugate. The clinical application of these bile acid radioimmunoassays is shown by an 'oral cholate tolerance test' as a sensitive indicator of liver function and by an 'oral cholyglycine tolerance test' as a useful test for bile acid absorption. (orig.) [de
-
Analytical characterization of polymer-drug conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rizzo, V.; Gigli, M.; Pinciroli, V.
1998-01-01
A few polymeric conjugates of antitumor drugs have been recently developed in view of possible therapeutic advantages: solubilization of sparingly soluble drugs in water, improvement of therapeutic index, organ targeting through a second chemical species bound to the same polymeric chain. In this article it's described the analytical approach used in the characterization of the conjugates for chemical identity, purity and strength of the contained active ingredient. The techniques are: high field NMR and size exclusion chromatography with non-aqueous mobile phase for identity; selective hydrolysis and HPLC for strength and purity. A complete and reliable picture is thus obtained both for qualitative and for quantitative aspects. This is an important step forward in the direction of further development and marketing of polymer-drug conjugates [it
-
Synthesis of Mikto-Arm Star Peptide Conjugates.
Koo, Jin Mo; Su, Hao; Lin, Yi-An; Cui, Honggang
2018-01-01
Mikto-arm star peptide conjugates are an emerging class of self-assembling peptide-based structural units that contain three or more auxiliary segments of different chemical compositions and/or functionalities. This group of molecules exhibit interesting self-assembly behavior in solution due to their chemically asymmetric topology. Here we describe the detailed procedure for synthesis of an ABC Mikto-arm star peptide conjugate in which two immiscible entities (a saturated hydrocarbon and a hydrophobic and lipophobic fluorocarbon) are conjugated onto a short β-sheet forming peptide sequence, GNNQQNY, derived from the Sup35 prion, through a lysine junction. Automated and manual Fmoc-solid phase synthesis techniques are used to synthesize the Mikto-arm star peptide conjugates, followed by HPLC purification. We envision that this set of protocols can afford a versatile platform to synthesize a new class of peptidic building units for diverse applications.
-
Ledoux, L.A.F.; Berkhoff, Arthur P.; Thijssen, J.M.
The Conjugate Gradient Rayleigh method for the calculation of acoustic reflection and transmission at a rough interface between two media was experimentally verified. The method is based on a continuous version of the conjugate gradient technique and plane-wave expansions. We measured the beam
-
Spatiotemporal behavior and nonlinear dynamics in a phase conjugate resonator
Liu, Siuying Raymond
1993-01-01
The work described can be divided into two parts. The first part is an investigation of the transient behavior and stability property of a phase conjugate resonator (PCR) below threshold. The second part is an experimental and theoretical study of the PCR's spatiotemporal dynamics above threshold. The time-dependent coupled wave equations for four-wave mixing (FWM) in a photorefractive crystal, with two distinct interaction regions caused by feedback from an ordinary mirror, was used to model the transient dynamics of a PCR below threshold. The conditions for self-oscillation were determined and the solutions were used to define the PCR's transfer function and analyze its stability. Experimental results for the buildup and decay times confirmed qualitatively the predicted behavior. Experiments were carried out above threshold to study the spatiotemporal dynamics of the PCR as a function of Pragg detuning and the resonator's Fresnel number. The existence of optical vortices in the wavefront were identified by optical interferometry. It was possible to describe the transverse dynamics and the spatiotemporal instabilities by modeling the three-dimensional-coupled wave equations in photorefractive FWM using a truncated modal expansion approach.
-
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Aderibigbe, BA
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Polyamidoamine conjugates containing curcumin and bisphosphonate were synthesized via a one-pot aqueous phase Michael addition reaction. In the design of the conjugate, bisphosphonate formed an integral part of the polymer carrier backbone. Curcumin...
-
Li, Yi; Gu, Christine; Gruenhagen, Jason; Zhang, Kelly; Yehl, Peter; Chetwyn, Nik P; Medley, Colin D
2015-05-08
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are complex therapeutic agents combining the specific targeting properties of antibodies and highly potent cytotoxic small molecule drugs to selectively eliminate tumor cells while limiting the toxicity to normal healthy tissues. One unique critical quality attribute of ADCs is the content of unconjugated small molecule drug present from either incomplete conjugation or degradation of the ADC. In this work, size exclusion chromatography (SEC) was coupled with reversed-phase (RP) HPLC in an online 2-dimensional chromatography format for identification and quantitation of unconjugated small molecule drugs and related small molecule impurities in ADC samples directly without sample preparation. The SEC method in the 1st dimension not only separated the small molecule impurities from the intact ADC, but also provided information about the size variants (monomer, dimer, aggregates, etc.) of the ADC. The small molecule peak from the SEC was trapped and sent to a RP-HPLC in the 2nd dimension to further separate and quantify the different small molecule impurities present in the ADC sample. This SEC-RP 2D-LC method demonstrated excellent precision (%RSDmolecule degradation products and aggregation of the conjugate were observed in the stability samples and the degradation pathways of the ADC were investigated. This 2D-LC method offers a powerful tool for ADC characterization and provides valuable information for conjugation and formulation development. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction.
Yu, Nanfang; Genevet, Patrice; Kats, Mikhail A; Aieta, Francesco; Tetienne, Jean-Philippe; Capasso, Federico; Gaburro, Zeno
2011-10-21
Conventional optical components rely on gradual phase shifts accumulated during light propagation to shape light beams. New degrees of freedom are attained by introducing abrupt phase changes over the scale of the wavelength. A two-dimensional array of optical resonators with spatially varying phase response and subwavelength separation can imprint such phase discontinuities on propagating light as it traverses the interface between two media. Anomalous reflection and refraction phenomena are observed in this regime in optically thin arrays of metallic antennas on silicon with a linear phase variation along the interface, which are in excellent agreement with generalized laws derived from Fermat's principle. Phase discontinuities provide great flexibility in the design of light beams, as illustrated by the generation of optical vortices through use of planar designer metallic interfaces.
-
Occurrence of Conjugated Linolenic Acids in Purified Soybean Oil
Kinami, Tomohisa; Horii, Naoto; Narayan, Bhaskar; Arato, Shingo; Hosokawa, Masashi; Miyashita, Kazuo; Negishi, Hironori; Ikuina, Junichi; Noda, Ryuji; Shirasawa, Seiichi
2007-01-01
A high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method is described for the determination of conjugated linoleic acids (CLA) and conjugated linolenic acids (CLN). Methyl esters prepared from purified lipid fractions of soybean oil were analyzed using an HPLC system equipped with photodiode-array detector to detect peaks having maximum absorption around 233 and 275 nm. These peaks were concentrated by AgNO3-silicic acid column chromatography and reversed-phase HPLC. The structural analysis, o...
-
Zuo, Shu-Yu; Tian, Ye; Wei, Qi; Cheng, Ying; Liu, Xiao-Jun
2018-03-01
The use of metasurfaces has allowed the provision of a variety of functionalities by ultrathin structures, paving the way toward novel highly compact analog computing devices. Here, we conceptually realize analog computing using an acoustic reflective computational metasurface (RCM) that can independently manipulate the reflection phase and amplitude of an incident acoustic signal. This RCM is composed of coating unit cells and perforated panels, where the first can tune the transmission phase within the full range of 2π and the second can adjust the reflection amplitude in the range of 0-1. We show that this RCM can achieve arbitrary reflection phase and amplitude and can be used to realize a unique linear spatially invariant transfer function. Using the spatial Fourier transform (FT), an acoustic analog computing (AAC) system is proposed based on the RCM together with a focusing lens. Based on numerical simulations, we demonstrate that this AAC system can perform mathematical operations such as spatial differentiation, integration, and convolution on an incident acoustic signal. The proposed system has low complexity and reduced size because the RCM is able to individually adjust the reflection phase and amplitude and because only one block is involved in performing the spatial FT. Our work may offer a practical, efficient, and flexible approach to the design of compact devices for acoustic computing applications, signal processing, equation solving, and acoustic wave manipulations.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Liu, Xiang; Hu, Hao; Chandrasekhar, S.
2014-01-01
We experimentally demonstrate the generation of 1.024-Tb/s Nyquist-WDM phase-conjugated vector twin waves (PCTWs), consisting of eight 128-Gb/s polarization-division-multiplexed QPSK signals and their idlers, by a broadband polarization-insensitive fiber optic parametric amplifier. This novel all...
-
Highly Reflecting, Broadband Deformable Membrane Mirror for Wavefront Control Applications, Phase I
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — This Phase I STTR project will develop a highly reflecting, broadband, radiation resistant, low-stress and lightweight, membrane integrated into an electrostatically...
-
Development of 360-W LD pumped Nd:YAG amplifier with a phase conjugation mirror
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Nagai, Toru; Yamakawa, Koichi; Kageyama, Nobuto; Miyajima, Hirofumi; Kan, Hirofumi; Yoshida, Hidetsugu; Nakatsuka, Masahiro
2004-01-01
We report on a high-average-power laser-diode (LD) pumped Nd:YAG master-oscillator-power-amplifier (MOPA) system with a minimum number of element for the single multi-pass zigzag-slab amplifier-stage for pumping of a high-peak and high-average power Ti:sapphire laser system. This phase conjugated system produces an average-power of 362 W at 1 kHz in a 30 ns pulse with an optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 14%. With an external KTP doubler, this system generates 132 W of green average-output-power at 1 kHz with a conversion efficiency of 60% when pumped at a power level of 222 W. To the best of our knowledge, these results represent the highest average-output-power at both infrared and green wavelengths achieved in a single-amplifier-stage. (author)
-
Purification of SUMO conjugating enzymes and kinetic analysis of substrate conjugation
Yunus, Ali A.; Lima, Christopher D.
2009-01-01
SUMO conjugation to protein substrates requires the concerted action of a dedicated E2 ubiquitin conjugation enzyme (Ubc9) and associated E3 ligases. Although Ubc9 can directly recognize and modify substrate lysine residues that occur within a consensus site for SUMO modification, E3 ligases can redirect specificity and enhance conjugation rates during SUMO conjugation in vitro and in vivo. In this chapter, we will describe methods utilized to purify SUMO conjugating enzymes and model substrates which can be used for analysis of SUMO conjugation in vitro. We will also describe methods to extract kinetic parameters during E3-dependent or E3-independent substrate conjugation. PMID:19107417
-
Solid-phase based synthesis of ureidopyrimidinone-peptide conjugates for supramolecular biomaterials
Feijter, de I.; Goor, O.J.G.M.; Hendrikse, S.I.S.; Comellas Aragones, M.; Sontjens, S.H.M.; Zaccaria, S.; Fransen, P.P.K.H.; Peeters, J.W.; Milroy, L.G.; Dankers, P.Y.W.
2015-01-01
Supramolecular polymers have shown to be powerful scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Supramolecular biomaterials functionalized with ureidopyrimidinone (UPy) moieties, which dimerize via quadruple hydrogen-bond formation, are eminently suitable for this purpose. The conjugation of the
-
Effect of TiO2 on conjugative transfer of RP4 plasmid
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Qian Di; Zhang Buchang; Yang Dong; Chen Zhaoli; Jin Min; Qiu Zhigang; Li Junwen
2013-01-01
Objective: To explore the effect and law of nano-titanium dioxide on the conjugative transfer of RP4 plasmid. Methods: Mating was conducted between Escherichia coli HB101 (RP4) and E. coli K12Rif in saline without stirring under certain conditions and the donor per recipient ratio was 1:1 constantly. The selective LB agar medium plates containing appropriate antibiotics were used to count the number of transconjugants and the conjugative transfer frequency. Results: Nano-titanium dioxide could promote the conjugative transfer of RP4. The nano-titanium dioxide concentration, bacterial concentration, mating temperature and mating time could affect the conjugative transfer of RP4. Conclusion: Nano-titanium dioxide can promote plasmid conjugal transfer in the liquid phase under certain conditions, which may pose a potential hazard to environmental and human health. (authors)
-
Dotres, Carlos P; Puga, Rinaldo; Ricardo, Yariset; Broño, Carmen R; Paredes, Beatriz; Echemendía, Vladimir; Rosell, Sandra; González, Nadezhda; García-Rivera, Dagmar; Valdés, Yury; Goldblatt, David; Vérez-Bencomo, Vicente
2014-09-15
A new heptavalent conjugate vaccine (PCV7-TT) is under development in Cuba. PCV7-TT contains 2 μg of serotypes 1, 5, 14, 18C, 19F, 23F and 4 μg of 6B, each one conjugated to tetanus toxoid (TT). This vaccine was designed with the serotypes that cause most invasive pneumococcal diseases (IPD) worldwide. In the present study, we investigated the safety and explored the immunogenicity of PCV7-TT during a controlled, randomized and double blind clinical trial phase I in 4-5-year-old children. PCV7-TT was well tolerated and as safe as Synflorix used as control vaccine. Following a single-dose vaccination, all individual serotypes included in PCV7-TT induced statistically significant increase of IgG GMC and OPA GMT. These are the first clinical results of PCV7-TT in children and they pave the way toward next clinical trials in children and infants. This clinical trial was published in the Cuban Public Register of Clinical Trials with code RPCEC00000173. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Adamo, Michael; Sun, Guoyong; Qiu, Difei; Valente, Joseph; Lan, Wenkui; Song, Hangtian; Bolgar, Mark; Katiyar, Amit; Krishnamurthy, Girija
2017-01-20
Antibody drug conjugates or ADCs are currently being evaluated for their effectiveness as targeted chemotherapeutic agents across the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the complexity arising from the choice of antibody, drug and linker; analytical methods for release and stability testing are required to provide a detailed understanding of both the antibody and the drug during manufacturing and storage. The ADC analyzed in this work consists of a tubulysin drug analogue that is randomly conjugated to lysine residues in a human IgG1 antibody. The drug is attached to the lysine residue through a peptidic, hydrolytically stable, cathepsin B cleavable linker. The random lysine conjugation produces a heterogeneous mixture of conjugated species with a variable drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR), therefore, the average amount of drug attached to the antibody is a critical parameter that needs to be monitored. In this work we have developed a universal method for determining DAR in ADCs that employ a cathepsin B cleavable linker. The ADC is first cleaved at the hinge region and then mildly reduced prior to treatment with the cathepsin B enzyme to release the drug from the antibody fragments. This pre-treatment allows the cathepsin B enzyme unrestricted access to the cleavage sites and ensures optimal conditions for the cathepsin B to cleave all the drug from the ADC molecule. The cleaved drug is then separated from the protein components by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) and quantitated using UV absorbance. This method affords superior cleavage efficiency to other methods that only employ a cathepsin digestion step as confirmed by mass spectrometry analysis. This method was shown to be accurate and precise for the quantitation of the DAR for two different random lysine conjugated ADC molecules. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Preparation of Conjugates of Cytotoxic Lupane Triterpenes with Biotin.
Soural, Miroslav; Hodon, Jiri; Dickinson, Niall J; Sidova, Veronika; Gurska, Sona; Dzubak, Petr; Hajduch, Marian; Sarek, Jan; Urban, Milan
2015-12-16
To better understand the mechanism of action of antitumor triterpenes, we are developing methods to identify their molecular targets. A promising method is based on combination of quantitative proteomics with SILAC and uses active compounds anchored to magnetic beads via biotin-streptavidin interaction. We developed a simple and fast solid-phase synthetic technique to connect terpenes to biotin through a linker. Betulinic acid was biotinylated from three different conjugation sites for use as a standard validation tool since many molecular targets of this triterpene are already known. Then, a set of four other cytotoxic triterpenoids was biotinylated. Biotinylated terpenes were similarly cytotoxic to their nonbiotinylated parents, which suggests that the target identification should not be influenced by linker or biotin. The developed solid-phase synthetic approach is the first attempt to use solid-phase synthesis to connect active triterpenes to biotin and is applicable as a general procedure for routine conjugation of triterpenes with other molecules of choice.
-
Fourier domain preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm for atmospheric tomography.
Yang, Qiang; Vogel, Curtis R; Ellerbroek, Brent L
2006-07-20
By 'atmospheric tomography' we mean the estimation of a layered atmospheric turbulence profile from measurements of the pupil-plane phase (or phase gradients) corresponding to several different guide star directions. We introduce what we believe to be a new Fourier domain preconditioned conjugate gradient (FD-PCG) algorithm for atmospheric tomography, and we compare its performance against an existing multigrid preconditioned conjugate gradient (MG-PCG) approach. Numerical results indicate that on conventional serial computers, FD-PCG is as accurate and robust as MG-PCG, but it is from one to two orders of magnitude faster for atmospheric tomography on 30 m class telescopes. Simulations are carried out for both natural guide stars and for a combination of finite-altitude laser guide stars and natural guide stars to resolve tip-tilt uncertainty.
-
Conjugate Etalon Spectral Imager (CESI) & Scanning Etalon Methane Mapper (SEMM), Phase I
National Aeronautics and Space Administration — The Conjugate Etalon Spectral Imaging (CESI) concept enables the development of miniature instruments with high spectral resolution, suitable for LEO missions aboard...
-
Broadband reflected wavefronts manipulation using structured phase gradient metasurfaces
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Xiao-Peng Wang
2016-06-01
Full Text Available Acoustic metasurface (AMS is a good candidate to manipulate acoustic waves due to special acoustic performs that cannot be realized by traditional materials. In this paper, we design the AMS by using circular-holed cubic arrays. The advantages of our AMS are easy assemble, subwavelength thickness, and low energy loss for manipulating acoustic waves. According to the generalized Snell’s law, acoustic waves can be manipulated arbitrarily by using AMS with different phase gradients. By selecting suitable hole diameter of circular-holed cube (CHC, some interesting phenomena are demonstrated by our simulations based on finite element method, such as the conversion of incoming waves into surface waves, anomalous reflections (including negative reflection, acoustic focusing lens, and acoustic carpet cloak. Our results can provide a simple approach to design AMSes and use them in wavefront manipulation and manufacturing of acoustic devices.
-
Židková, Monika; Linhart, Igor; Balíková, Marie; Himl, Michal; Dvořáčková, Veronika; Lhotková, Eva; Páleníček, Tomáš
2018-06-01
1. Methylone (3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylcathinone, MDMC), which appeared on the illicit drug market in 2004, is a frequently abused synthetic cathinone derivative. Known metabolic pathways of MDMC include N-demethylation to normethylone (3,4-methylenedioxycathinone, MDC), aliphatic chain hydroxylation and oxidative demethylenation followed by monomethylation and conjugation with glucuronic acid and/or sulphate. 2. Three new phase II metabolites, amidic conjugates of MDC with succinic, glutaric and adipic acid, were identified in the urine of rats dosed subcutaneously with MDMC.HCl (20 mg/kg body weight) by LC-ESI-HRMS using synthetic reference standards to support identification. 3. The main portion of administered MDMC was excreted unchanged. Normethylone, was a major urinary metabolite, of which a minor part was conjugated with dicarboxylic acids. 4. Previously identified ring-opened metabolites 4-hydroxy-3-methoxymethcathinone (4-OH-3-MeO-MC), 3-hydroxy-4-methoxymeth-cathinone (3-OH-4-MeO-MC) and 3,4-dihydroxymethcathinone (3,4-di-OH-MC) mostly in conjugated form with glucuronic and/or sulphuric acids were also detected. 5. Also, ring-opened metabolites derived from MDC, namely, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycathinone (4-OH-3-MeO-C), 3-hydroxy-4-methoxycathinone (3-OH-4-MeO-C) and 3,4-dihydroxycathinone (3,4-di-OH-C) were identified for the first time in vivo.
-
Conjugation of colloidal clusters and chains by capillary condensation.
Li, Fan; Stein, Andreas
2009-07-29
Capillary condensation was used to establish connections in colloidal clusters and 1D colloidal chains with high regional selectivity. This vapor-phase process produced conjugated clusters and chains with anisotropic functionality. The capillary condensation method is simple and can be applied to a wide range of materials. It can tolerate geometric variations and even permits conjugation of spatially separated particles. The selective deposition was also used to modulate the functionality on the colloid surfaces, producing tip-tethered nanosized building blocks that may be suitable for further assembly via directional interactions.
-
Antibody conjugate radioimmunotherapy of superficial bladder cancer
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Perkins, Alan; Hopper, Melanie; Murray, Andrea; Frier, Malcolm; Bishop, Mike
2002-01-01
The administration of antibody conjugates for cancer therapy is now proving to be of clinical value. We are currently undertaking a programme of clinical studies using the monoclonal antibody C 595 (gG3) which reacts with the MUC1 glycoprotein antigen that is aberrantly expressed in a high proportion of bladder tumours. Radio immuno conjugates of the C 595 antibody have been produced with high radiolabelling efficiency and immuno reactivity using Tc-99 m and In-111 for diagnostic imaging, and disease staging and the cytotoxic radionuclides Cu-67 and Re-188 for therapy of superficial bladder cancer. A Phase I/II therapeutic trail involving the intravesical administration of antibody directly into the bladder has now begun. (author)
-
Emulsifying properties of maillard conjugates produced from sodium caseinate and locust bean gum
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
F. A. Perrechil
2014-06-01
Full Text Available Emulsifying properties of sodium caseinate -locust bean gum Maillard conjugates produced at different temperatures (54 - 96 ºC, protein/polysaccharide ratios (0.3 - 1.0 and reaction times (1 - 24 hours were evaluated. Conjugate formation was confirmed by formation of color and high molecular weight fractions and the decrease of the αs- and β-casein bands. The emulsions stabilized by Maillard conjugates showed good stability. The mean droplet diameter (d32 tended to decrease with the increase of incubation time and temperature, except at extreme conditions (24 hours and 90 ºC or 96 ºC when the partial degradation of the conjugates was probably favored, resulting in phase separation of emulsions. The emulsion viscosity decreased with the increase in the protein/polysaccharide ratio and with the degradation of the conjugates. The conditions used in the experimental design made the optimization of the conjugate production viable, which showed greater emulsifier properties than the pure protein under acid conditions.
-
Rzeppa, S; Heinrich, G; Hemmersbach, P
2015-01-01
Improvements in doping analysis can be effected by speeding up analysis time and extending the detection time. Therefore, direct detection of phase II conjugates of doping agents, especially anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS), is proposed. Besides direct detection of conjugates with glucuronic acid, the analysis of sulfate conjugates, which are usually not part of the routine doping control analysis, can be of high interest. Sulfate conjugates of methandienone and methyltestosterone metabolites have already been identified as long-term metabolites. This study presents the synthesis of sulfate conjugates of six commonly used AAS and their metabolites: trenbolone, nandrolone, boldenone, methenolone, mesterolone, and drostanolone. In the following these sulfate conjugates were used for development of a fast and easy analysis method based on sample preparation using solid phase extraction with a mixed-mode sorbent and detection by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). Validation demonstrated the suitability of the method with regard to the criteria given by the technical documents of the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). In addition, suitability has been proven by successful detection of the synthesized sulfate conjugates in excretion urines and routine doping control samples. Copyright © 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Liu, Xiang; Hu, Hao; Chandrasekhar, S.
2013-01-01
We experimentally demonstrate the first Tb/s Nyquist-WDM phase-conjugated twin waves, consisting of eight 128-Gb/s PDM-QPSK signals and their idlers, by a broadband polarization-insensitive fiber optical parametric amplifier, enabling more than doubled reach in dispersion-managed transmission. © ...
-
Quantitative phase imaging with scanning holographic microscopy: an experimental assesment
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tada Yoshitaka
2006-11-01
Full Text Available Abstract This paper demonstrates experimentally how quantitative phase information can be obtained in scanning holographic microscopy. Scanning holography can operate in both coherent and incoherent modes, simultaneously if desired, with different detector geometries. A spatially integrating detector provides an incoherent hologram of the object's intensity distribution (absorption and/or fluorescence, for example, while a point detector in a conjugate plane of the pupil provides a coherent hologram of the object's complex amplitude, from which a quantitative measure of its phase distribution can be extracted. The possibility of capturing simultaneously holograms of three-dimensional specimens, leading to three-dimensional reconstructions with absorption contrast, reflectance contrast, fluorescence contrast, as was previously demonstrated, and quantitative phase contrast, as shown here for the first time, opens up new avenues for multimodal imaging in biological studies.
-
On image pre-processing for PIV of sinlge- and two-phase flows over reflecting objects
Deen, N.G.; Willems, P.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Kuipers, J.A.M.; Lammertink, Rob G.H.; Kemperman, Antonius J.B.; Wessling, Matthias; van der Meer, Walterus Gijsbertus Joseph
2010-01-01
A novel image pre-processing scheme for PIV of single- and two-phase flows over reflecting objects which does not require the use of additional hardware is discussed. The approach for single-phase flow consists of image normalization and intensity stretching followed by background subtraction. For
-
Women experiencing the intergenerationality of conjugal violence
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gilvânia Patrícia do Nascimento Paixão
2015-10-01
Full Text Available Objective: to analyze the family relationship, in childhood and adolescence, of women who experience conjugal violence.Method: qualitative study. Interviews were held with 19 women, who were experiencing conjugal violence, and who were resident in a community in Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. The project was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (N. 42/2011.Results: the data was organized using the Discourse of the Collective Subject, identifying the summary central ideas: they witnessed violence between their parents; they suffered repercussions from the violence between their parents: they were angry about the mother's submission to her partner; and they reproduced the conjugal violence. The discourse showed that the women witnessed, in childhood and adolescence, violence between their parents, and were injured both physically and psychologically. As a result of the mother's submission, feelings of anger arose in the children. However, in the adult phase of their own lives, they noticed that their conjugal life resembled that of their parents, reproducing the violence.Conclusion: investment is necessary in strategies designed to break inter-generational violence, and the health professionals are important in this process, as it is a phenomenon with repercussions in health. Because they work in the Family Health Strategy, which focuses on the prevention of harm and illness, health promotion and interdepartmentality, the nurses are essential in the process of preventing and confronting this phenomenon.
-
Ti-Catalyzed Hydroamination for the Synthesis of Amine-Containing π-Conjugated Materials.
Hao, Han; Thompson, Kyle A; Hudson, Zachary M; Schafer, Laurel L
2018-04-11
A series of conjugated enamines were prepared by Ti catalyzed anti-Markovnikov hydroamination. The synthetic route is efficient with yields of up to 94 % and the 100 % atom efficiency of the reaction means that these products are easily isolated and purified. Due to the extended conjugated system, the enamine tautomers were observed exclusively in both solid and solution phases, as determined by X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. These new conjugated molecules, with N incorporated into the backbone, show interesting photophysical properties including photo-luminescent quantum yields of up to 0.26. Notably, through the incorporation of B to give a donor-acceptor π-conjugated system, a redshift of approximately 100 nm is observed for the emission maximum along with the anticipated solvatochromic shifts. © 2018 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Phase transitions and reflection positivity for a class of quantum lattice systems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Perez, J.F.; Wreszinski, W.F.
1980-08-01
A form reflection positivity in planes containing sites is proved for a class of quantum lattice systems. Two apllications to typical models are given: a proof of phase transition of ferromagnetic type by the method of infrared bounds for hhe Fisher-stabilized Ising antiferromagnet in an external magnetic field with parallel and tranverse components, and a proof of a phase transition of antiferromagnetic type for the same model with no stabilization by a suitable version of the Peierls argument. The spherical model is also discussed in an appendix. (Author) [pt
-
Rapid, facile synthesis of conjugated polymer zwitterions in ionic liquids
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Page, Zachariah A. [Polymer Science & Engineering Department; Conte Center for Polymer Research; University of Massachusetts; Amherst, USA; Liu, Feng [Polymer Science & Engineering Department; Conte Center for Polymer Research; University of Massachusetts; Amherst, USA; Russell, Thomas P. [Polymer Science & Engineering Department; Conte Center for Polymer Research; University of Massachusetts; Amherst, USA; Emrick, Todd [Polymer Science & Engineering Department; Conte Center for Polymer Research; University of Massachusetts; Amherst, USA
2014-01-01
Ionic liquids (ILs) were utilized for the rapid air-stable Suzuki polymerization of polar zwitterionic thiophene monomers, precluding the need for volatile organic solvents, phosphine ligands and phase transfer catalysts typically used in conjugated polymer synthesis.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Marciano Junior, E.; Cunha Munhoz, F.A. da; Splettstoser Junior, J.; Placido, W.F.
1989-01-01
The identification and quantitative determination of phases in calcium aluminate clinker is of great importance to the producer, as it enables a better understanding of the cement and concrete properties, specially those concerning setting time and compressive strenght. Polished sections of three electrofused clinkers, one experimental and two industrial, were used to select the most suitable etchings in order to identify by microscopy the main phases (Ca, CA 2 , C 2 AS, C 12 A 7 , α-Al 2 O 3 ). Quantitative phases determinations by reflected light microscopy showed good results when compared to X-ray diffractometry measurements [pt
-
Optimized phase mask to realize retro-reflection reduction for optical systems
He, Sifeng; Gong, Mali
2017-10-01
Aiming at the threats to the active laser detection systems of electro-optical devices due to the cat-eye effect, a novel solution is put forward to realize retro-reflection reduction in this paper. According to the demands of both cat-eye effect reduction and the image quality maintenance of electro-optical devices, a symmetric phase mask is achieved from a stationary phase method and a fast Fourier transform algorithm. Then, based on a comparison of peak normalized cross-correlation (PNCC) between the different defocus parameters, the optimal imaging position can be obtained. After modification with the designed phase mask, the cat-eye effect peak intensity can be reduced by two orders of magnitude while maintaining good image quality and high modulation transfer function (MTF). Furthermore, a practical design example is introduced to demonstrate the feasibility of our proposed approach.
-
99mTc(CO)3-DTMA bombesin conjugates having high affinity for the GRP receptor
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lane, Stephanie R.; Veerendra, Bhadrasetty; Rold, Tammy L.; Sieckman, Gary L.; Hoffman, Timothy J.; Jurisson, Silvia S.; Smith, Charles J.
2008-01-01
Introduction: Targeted diagnosis of specific human cancer types continues to be of significant interest in nuclear medicine. 99m Tc is ideally suited as a diagnostic radiometal for in vivo tumor targeting due to its ideal physical characteristics and diverse labeling chemistries in numerous oxidation states. Methods: In this study, we report a synthetic approach toward design of a new tridentate amine ligand for the organometallic aqua-ion [ 99m Tc(H 2 O) 3 (CO) 3 ] + . The new chelating ligand framework, 2-(N,N'-Bis(tert-butoxycarbonyl)diethylenetriamine) acetic acid (DTMA), was synthesized from a diethylenetriamine precursor and fully characterized by mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy ( 1 H and 13 C). DTMA was conjugated to H 2 N-(X)-BBN(7-14)NH 2 , where X=an amino acid or aliphatic pharmacokinetic modifier and BBN=bombesin peptide, by means of solid phase peptide synthesis. DTMA-(X)-BBN(7-14)NH 2 conjugates were purified by reversed-phase high-performance chromatography and characterized by electrospray-ionization mass spectrometry. Results: The new conjugates were radiolabeled with [ 99m Tc(H 2 O) 3 (CO) 3 ] + produced via Isolink radiolabeling kits to produce [ 99m Tc(CO) 3 -DTMA-(X)-BBN(7-14)NH 2 ]. Radiolabeled conjugates were purified by reversed-phase high-performance chromatography. Effective receptor binding behavior was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. Conclusions: [ 99m Tc(CO) 3 -DTMA-(X)-BBN(7-14)NH 2 ] conjugates displayed very high affinity for the gastrin releasing peptide receptor in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, these conjugates hold some propensity to be investigated as molecular imaging agents that specifically target human cancers uniquely expressing the gastrin releasing peptide receptor subtypes
-
Osuch, Tomasz; Jaroszewicz, Zbigniew
2017-01-01
An apodized fiber Bragg grating formation using a phase mask with variable duty cycle is numerically analyzed. In particular, an impact of position of an optical fiber behind the phase mask with Gaussian apodization profile on Bragg grating reflection efficiencies at Bragg wavelength and its harmonics is extensively studied. It is shown that reflection efficiency of each harmonic strongly depends on the optical fiber location with respect to the adjacent Talbot planes during the grating inscription. An analytical formula for calculation such periodical changes of reflection strength is proposed. It is also proved, that the smaller optical fiber diameter the higher fluctuations of reflectivity for particular harmonic occur. Results presented for such general case (i.e. phase mask with variable duty cycle with all non-zero diffraction orders) directly correspond to less complex structures, such as uniform phase masks and those with variable groove depth. They are also useful in optimization of Bragg wavelength and harmonic reflection efficiencies as well as in deep understanding of apodized FBG formation using aforementioned phase masks.
-
Sensitive singular-phase optical detection without phase measurements with Tamm plasmons
Boriskina, Svetlana V.; Tsurimaki, Yoichiro
2018-06-01
Spectrally-tailored interactions of light with material interfaces offer many exciting applications in sensing, photo-detection, and optical energy conversion. In particular, complete suppression of light reflectance at select frequencies accompanied by sharp phase variations in the reflected signal forms the basis for the development of ultra-sensitive singular-phase optical detection schemes such as Brewster and surface plasmon interferometry. However, both the Brewster effect and surface-plasmon-mediated absorption on planar interfaces are limited to one polarization of the incident light and oblique excitation angles, and may have limited bandwidth dictated by the material dielectric index and plasma frequency. To alleviate these limitations, we design narrow-band super-absorbers composed of plasmonic materials embedded into dielectric photonic nanostructures with topologically-protected interfacial Tamm plasmon states. These structures have planar geometry and do not require nanopatterning to achieve perfect absorption of both polarizations of the incident light in a wide range of incident angles, including the normal incidence. Their absorption lines are tunable across a very broad spectral range via engineering of the photon bandstructure of the dielectric photonic nanostructures to achieve reversal of the geometrical phase across the interface with the plasmonic absorber. We outline the design strategy to achieve perfect absorptance in Tamm structures with dissipative losses via conjugate impedance matching. We further demonstrate via modeling how these structures can be engineered to support sharp asymmetric amplitude resonances, which can be used to improve the sensitivity of optical sensors in the amplitude-only detection scheme that does not require use of bulky and expensive ellipsometry equipment.
-
Yuan, Wenjia; Shen, Weidong; Zhang, Yueguang; Liu, Xu
2014-05-05
Dielectric multilayer beam splitter with differential phase shift on transmission and reflection for division-of-amplitude photopolarimeter (DOAP) was presented for the first time to our knowledge. The optimal parameters for the beam splitter are Tp = 78.9%, Ts = 21.1% and Δr - Δt = π/2 at 532nm at an angle of incidence of 45°. Multilayer anti-reflection coating with low phase shift was applied to reduce the backside reflection. Different design strategies that can achieve all optimal targets at the wavelength were tested. Two design methods were presented to optimize the differential phase shift. The samples were prepared by ion beam sputtering (IBS). The experimental results show good agreement with those of the design. The ellipsometric parameters of samples were measured in reflection (ψr, Δr) = (26.5°, 135.1°) and (28.2°, 133.5°), as well as in transmission (ψt, Δt) = (62.5°, 46.1°) and (63.5°, 46°) at 532.6nm. The normalized determinant of instrument matrix to evaluate the performance of samples is respectively 0.998 and 0.991 at 532.6nm.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hadley, S.W.; Wilbur, D.S.
1990-01-01
The preparations and conjugations of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorophenyl 5-[125I/131I]iodo-4-pentenoate (7a) and 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorophenyl 3,3-dimethyl-5-[125I/131I]iodo-4-pentenoate (7b) to monoclonal antibodies are reported. Reagents 7a and 7b were prepared in high radiochemical yield by iododestannylation of their corresponding 5-tri-n-butylstannyl precursors. Radioiodinated antibody conjugates were prepared by reaction of 7a or 7b with the protein at basic pH. Evaluation of these conjugates by several in vitro procedures demonstrated that the radiolabel was attached to the antibody in a stable manner and that the conjugates maintained immunoreactivity. Comparative dual-isotope biodistribution studies of a monoclonal antibody Fab fragment conjugate of 7a and 7b with the same Fab fragment labeled with N-succinimidyl p-[131I]iodobenzoate (PIB, p-iodobenzoate, 2) or directly radioiodinated have been carried out in tumor-bearing nude mice. Coinjection of the Fab conjugate of 7a with the Fab conjugate of 2 demonstrated that the biodistributions were similar in most organs, except the neck tissue (thyroid-containing) and the stomach, which contained substantially increased levels of the 7a label. Coinjection of the Fab conjugate of 7a with the Fab fragment radioiodinated by using the chloramine-T method demonstrated that the biodistributions were remarkably similar, suggesting roughly equivalent in vivo deiodination of these labeled antibody fragments. Coinjection of the Fab conjugate of 7a with the Fab conjugate of 7b indicated that there was ∼ a 2-fold reduction in the amount of in vivo deiodination of the 7b conjugate as compared to the 7a conjugate
-
Birajdar, Mallinath S.; Cho, Hyunjoo; Seo, Youngmin; Choi, Jonghoon; Park, Hansoo
2018-04-01
Poly (dimethyl siloxane) (PDMS) is widely used in various biomedical applications. However, the PDMS surface is known to cause bacterial adhesion and protein absorption issues due to its high hydrophobicity. Therefore, the development of antibacterial and anti-protein products is necessary to prevent these problems. In this study, to improve its antibacterial property and prevent protein adsorption, PDMS surfaces were conjugated with itaconic acid (IA) and poly (itaconic acid) (PIA) via a chemical method. Additionally, IA and PIA were physically blended with PDMS to compare the antibacterial properties of these materials with those of the chemically conjugated PDMS surfaces. The successful synthesis of the PIA polymer structure was confirmed by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) spectroscopy. The successful conjugation of IA and PIA on PDMS was confirmed by attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), water contact angle measurements, and microbicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay analyses. The PDMS surfaces functionalized with IA and PIA by the conjugation method better prevented protein adsorption than the bare PDMS. Therefore, these surface-conjugated PDMS can be used in various biomedical applications.
-
Phase Coherence and Andreev Reflection in Topological Insulator Devices
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. D. K. Finck
2014-11-01
Full Text Available Topological insulators (TIs have attracted immense interest because they host helical surface states. Protected by time-reversal symmetry, they are robust to nonmagnetic disorder. When superconductivity is induced in these helical states, they are predicted to emulate p-wave pairing symmetry, with Majorana states bound to vortices. Majorana bound states possess non-Abelian exchange statistics that can be probed through interferometry. Here, we take a significant step towards Majorana interferometry by observing pronounced Fabry-Pérot oscillations in a TI sandwiched between a superconducting and a normal lead. For energies below the superconducting gap, we observe a doubling in the frequency of the oscillations, arising from an additional phase from Andreev reflection. When a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the TI surface, a number of very sharp and gate-tunable conductance peaks appear at or near zero energy, which has consequences for interpreting spectroscopic probes of Majorana fermions. Our results demonstrate that TIs are a promising platform for exploring phase-coherent transport in a solid-state system.
-
Reflection Patterns Generated by Condensed-Phase Oblique Detonation Interaction with a Rigid Wall
Short, Mark; Chiquete, Carlos; Bdzil, John; Meyer, Chad
2017-11-01
We examine numerically the wave reflection patterns generated by a detonation in a condensed phase explosive inclined obliquely but traveling parallel to a rigid wall as a function of incident angle. The problem is motivated by the characterization of detonation-material confiner interactions. We compare the reflection patterns for two detonation models, one where the reaction zone is spatially distributed, and the other where the reaction is instantaneous (a Chapman-Jouguet detonation). For the Chapman-Jouguet model, we compare the results of the computations with an asymptotic study recently conducted by Bdzil and Short for small detonation incident angles. We show that the ability of a spatially distributed reaction energy release to turn flow streamlines has a significant impact on the nature of the observed reflection patterns. The computational approach uses a shock-fit methodology.
-
Jadhav, Swati B; Singhal, Rekha S
2013-10-15
Two enzymes, α-amylase and glucoamylase have been individually and co-conjugated to pectin by covalent binding. Both the enzyme systems showed better thermal and pH stability over the free enzyme system with the complete retention of original activities. Mixture of individually conjugated enzymes showed lower inactivation rate constant with longer half life than the co-conjugated enzyme system. Individually conjugated enzymes showed an increase of 56.48 kJ/mole and 38.22 kJ/mole in activation energy for denaturation than the free enzymes and co-conjugated enzymes, respectively. Km as well as Vmax of individually and co-conjugated enzymes was found to be higher than the free enzymes. SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis confirmed the formation of conjugate and co-conjugate as evident by increased molecular weight. Both the enzyme systems were used for starch hydrolysis where individually conjugated enzymes showed highest release of glucose at 60 °C and pH 5.0 as compared to free and co-conjugated enzyme. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Characterization of biliary conjugates of 4,4'-methylenedianiline in male versus female rats
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen, Kan; Cole, Richard B.; Santa Cruz, Vicente; Blakeney, Ernest W.; Kanz, Mary F.; Dugas, Tammy R.
2008-01-01
4,4'-Methylenedianiline (4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane; DAPM) is an aromatic diamine used in the production of numerous polyurethane foams and epoxy resins. Previous studies in rats revealed that DAPM initially injures biliary epithelial cells of the liver, that the toxicity is greater in female than in male rats, and that the toxic metabolites of DAPM are excreted into bile. Since male and female rats exhibit differences in the expression of both phase I and phase II enzymes, our hypothesis was that female rats either metabolize DAPM to more toxic metabolites or have a decreased capacity to conjugate metabolites to less toxic intermediates. Our objective was thus to isolate, characterize, and quantify DAPM metabolites excreted into bile in both male and female bile duct-cannulated Sprague Dawley rats. The rats were gavaged with [ 14 C]-DAPM, and the collected bile was subjected to reversed-phase HPLC with radioisotope detection. Peaks eluting from HPLC were collected and analyzed using electrospray MS and NMR spectroscopy. HPLC analysis indicated numerous metabolites in both sexes, but male rats excreted greater amounts of glutathione and glucuronide conjugates than females. Electrospray MS and NMR spectra of HPLC fractions revealed that the most prominent metabolite found in bile of both sexes was a glutathione conjugate of an imine metabolite of a 4'-nitroso-DAPM. Seven other metabolites were identified, including acetylated, cysteinyl-glycine, glutamyl-cysteine, glycine, and glucuronide conjugates. While our prior studies demonstrated increased covalent binding of DAPM in the liver and bile of female compared to male rats, in these studies, SDS-PAGE with autoradiography revealed 4-5 radiolabeled protein bands in the bile of rats treated with [ 14 C]-DAPM. In addition, these bands were much more prominent in female than in male rats. These studies thus suggest that a plausible mechanism for the increased sensitivity of female rats to DAPM toxicity may be decreased
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Yao, X.S.
1992-01-01
In Part I, the author presents a theory to describe the interaction between short optical pulses in a photorefractive crystal. This theory provides an analytical framework for pulse coherence length measurements using a photorefractive crystal. The theory also predicts how a pulse changes its temporal shape due to its coupling with another pulse in a photorefractive crystal. The author describes experiments to demonstrate how photorefractive coupling alters the temporal shape and the frequency spectrum of an optical pulse. The author describes a compact optical field correlator. Using this correlator, the author measured the field cross-correlation function of optical pulses using a photorefractive crystal. The author presents a more sophisticated theory to describe the photorefractive coupling of optical pulses that are too short for the previous theory to be valid. In Part II of this dissertation, the author analyzes how the group-velocity dispersion and the optical nonlinearity of an optical fiber ruin an fiberoptic code-division multiple-access (CDMA) communication system. The author treats the optical fiber's nonlinear response with a novel approach and derives the pulse propagation equation. Through analysis and numerically simulations, the author obtains the maximum and the maximum allowed peak pulse power, as well as the minimum and the maximum allowed pulse width for the communication system to function properly. The author simulates how the relative misalignment between the encoding and the decoding masks affects the system's performance. In Part III the author demonstrates a novel optical interconnection device based on a mutually pumped phase conjugator. This device automatically routes light from selected information-sending channels to selected information-receiving channels, and vice versa. The phase conjugator eliminates the need for critical alignment. It is shown that a large number of optical channels can be interconnected using this
-
Partition calculation for zero-order and conjugate image removal in digital in-line holography.
Ma, Lihong; Wang, Hui; Li, Yong; Jin, Hongzhen
2012-01-16
Conventional digital in-line holography requires at least two phase-shifting holograms to reconstruct an original object without zero-order and conjugate image noise. We present a novel approach in which only one in-line hologram and two intensity values (namely the object wave intensity and the reference wave intensity) are required. First, by subtracting the two intensity values the zero-order diffraction can be completely eliminated. Then, an algorithm, called partition calculation, is proposed to numerically remove the conjugate image. A preliminary experimental result is given to confirm the proposed method. The method can simplify the procedure of phase-shifting digital holography and improve the practical feasibility for digital in-line holography.
-
PEG conjugates in clinical development or use as anticancer agents: an overview.
Pasut, Gianfranco; Veronese, Francesco M
2009-11-12
During the almost forty years of PEGylation, several antitumour agents, either proteins, peptides or low molecular weight drugs, have been considered for polymer conjugation but only few entered clinical phase studies. The results from the first clinical trials have shared and improved the knowledge on biodistribution, clearance, mechanism of action and stability of a polymer conjugate in vivo. This has helped to design conjugates with improved features. So far, most of the PEG conjugates comprise of a protein, which in the native form has serious shortcomings that limit the full exploitation of its therapeutic action. The main issues can be short in vivo half-life, instability towards degrading enzymes or immunogenicity. PEGylation proved to be effective in shielding sensitive sites at the protein surface, such as antigenic epitopes and enzymatic degradable sequences, as well as in prolonging the drug half-life by decreasing the kidney clearance. In this review PEG conjugates of proteins or low molecular weight drugs, in clinical development or use as anticancer agents, will be taken into consideration. In the case of PEG-protein derivatives the most represented are depleting enzymes, which act by degrading amino acids essential for cancer cells. Interestingly, PEGylated conjugates have been also considered as adjuvant therapy in many standard anticancer protocols, in this regard the case of PEG-G-CSF and PEG-interferons will be presented.
-
Willis, George
2013-01-01
A family of equivalent submultiplicative weights on the to- tally disconnected, locally compact group $G$ is defined in terms of the conjugation action of $G$ on itself. These weights therefore reflect the structure of $G$, and the corresponding weighted convolution algebra is intrinsic to $G$ in the same way that $L^1(G) is.
-
An Integrated Solution for Performing Thermo-fluid Conjugate Analysis
Kornberg, Oren
2009-01-01
A method has been developed which integrates a fluid flow analyzer and a thermal analyzer to produce both steady state and transient results of 1-D, 2-D, and 3-D analysis models. The Generalized Fluid System Simulation Program (GFSSP) is a one dimensional, general purpose fluid analysis code which computes pressures and flow distributions in complex fluid networks. The MSC Systems Improved Numerical Differencing Analyzer (MSC.SINDA) is a one dimensional general purpose thermal analyzer that solves network representations of thermal systems. Both GFSSP and MSC.SINDA have graphical user interfaces which are used to build the respective model and prepare it for analysis. The SINDA/GFSSP Conjugate Integrator (SGCI) is a formbase graphical integration program used to set input parameters for the conjugate analyses and run the models. The contents of this paper describes SGCI and its thermo-fluids conjugate analysis techniques and capabilities by presenting results from some example models including the cryogenic chill down of a copper pipe, a bar between two walls in a fluid stream, and a solid plate creating a phase change in a flowing fluid.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tatyana V. Abramova
2013-12-01
Full Text Available Conjugates of 2’-deoxyguanosine, L-tryptophan and benzophenone designed to study pathways of fast radical reactions by the photo Chemically Induced Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (photo-CIDNP method were obtained by the phosphotriester block liquid phase synthesis. The phosphotriester approach to the oligonucleotide synthesis was shown to be a versatile and economic strategy for preparing the required amount of high quality samples of nucleotide–amino acid conjugates.
-
Optimised deconjugation of androgenic steroid conjugates in bovine urine
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Pedersen, Mikael; Frandsen, Henrik Lauritz; Andersen, Jens Hinge
2017-01-01
and glucuronidase resulting in free steroids in the extract. It is well known that some sulphates are not deconjugated using aryl sulphatase; instead, for example, solvolysis can be used for deconjugation of these aliphatic sulphates. The effectiveness of solvolysis on androgenic steroid sulphates was tested......After administration of steroids to animals the steroids are partially metabolised in the liver and kidney to phase 2 metabolites, i.e., glucuronic acid or sulphate conjugates. During analysis these conjugated metabolites are normally deconjugated enzymatically with aryl sulphatase...... with selected aliphatic steroid sulphates (boldenone sulphate, nortestosteron sulphate and testosterone sulphate), and the method was validated for analysis of androgenic steroids in bovine urine using free steroids, steroid sulphates and steroid glucuronides as standards. Glucuronidase and sulphuric acid...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Ehrlich
2008-12-01
Full Text Available Arctic boundary-layer clouds were investigated with remote sensing and in situ instruments during the Arctic Study of Tropospheric Aerosol, Clouds and Radiation (ASTAR campaign in March and April 2007. The clouds formed in a cold air outbreak over the open Greenland Sea. Beside the predominant mixed-phase clouds pure liquid water and ice clouds were observed. Utilizing measurements of solar radiation reflected by the clouds three methods to retrieve the thermodynamic phase of the cloud are introduced and compared. Two ice indices IS and IP were obtained by analyzing the spectral pattern of the cloud top reflectance in the near infrared (1500–1800 nm wavelength spectral range which is characterized by ice and water absorption. While IS analyzes the spectral slope of the reflectance in this wavelength range, IS utilizes a principle component analysis (PCA of the spectral reflectance. A third ice index IA is based on the different side scattering of spherical liquid water particles and nonspherical ice crystals which was recorded in simultaneous measurements of spectral cloud albedo and reflectance.
Radiative transfer simulations show that IS, IP and IA range between 5 to 80, 0 to 8 and 1 to 1.25 respectively with lowest values indicating pure liquid water clouds and highest values pure ice clouds. The spectral slope ice index IS and the PCA ice index IP are found to be strongly sensitive to the effective diameter of the ice crystals present in the cloud. Therefore, the identification of mixed-phase clouds requires a priori knowledge of the ice crystal dimension. The reflectance-albedo ice index IA is mainly dominated by the uppermost cloud layer (τ<1.5. Therefore, typical boundary-layer mixed-phase clouds with a liquid cloud top layer will -
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tina Sabel
2014-02-01
Full Text Available Volume phase gratings, recorded in a photosensitive polymer by two-beam interference exposure, are studied by means of optical microscopy. Transmission gratings and reflection gratings, with periods in the order of 10 μm down to 130 nm, were investigated. Mapping of holograms by means of imaging in sectional view is introduced to study reflection-type gratings, evading the resolution limit of classical optical microscopy. In addition, this technique is applied to examine so-called parasitic gratings, arising from interference from the incident reference beam and the reflected signal beam. The appearance and possible avoidance of such unintentionally recorded secondary structures is discussed.
-
An adaptive phase space method with application to reflection traveltime tomography
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chung, Eric; Qian, Jianliang; Uhlmann, Gunther; Zhao, Hongkai
2011-01-01
In this work, an adaptive strategy for the phase space method for traveltime tomography (Chung et al 2007 Inverse Problems 23 309–29) is developed. The method first uses those geodesics/rays that produce smaller mismatch with the measurements and continues on in the spirit of layer stripping without defining the layers explicitly. The adaptive approach improves stability, efficiency and accuracy. We then extend our method to reflection traveltime tomography by incorporating broken geodesics/rays for which a jump condition has to be imposed at the broken point for the geodesic flow. In particular, we show that our method can distinguish non-broken and broken geodesics in the measurement and utilize them accordingly in reflection traveltime tomography. We demonstrate that our method can recover the convex hull (with respect to the underlying metric) of unknown obstacles as well as the metric outside the convex hull. (paper)
-
Conjugate gradient optimization programs for shuttle reentry
Powers, W. F.; Jacobson, R. A.; Leonard, D. A.
1972-01-01
Two computer programs for shuttle reentry trajectory optimization are listed and described. Both programs use the conjugate gradient method as the optimization procedure. The Phase 1 Program is developed in cartesian coordinates for a rotating spherical earth, and crossrange, downrange, maximum deceleration, total heating, and terminal speed, altitude, and flight path angle are included in the performance index. The programs make extensive use of subroutines so that they may be easily adapted to other atmospheric trajectory optimization problems.
-
Bacteriophytochromes control conjugation in Agrobacterium fabrum.
Bai, Yingnan; Rottwinkel, Gregor; Feng, Juan; Liu, Yiyao; Lamparter, Tilman
2016-08-01
Bacterial conjugation, the transfer of single stranded plasmid DNA from donor to recipient cell, is mediated through the type IV secretion system. We performed conjugation assays using a transmissible artificial plasmid as reporter. With this assay, conjugation in Agrobacterium fabrum was modulated by the phytochromes Agp1 and Agp2, photoreceptors that are most sensitive in the red region of visible light. In conjugation studies with wild-type donor cells carrying a pBIN-GUSINT plasmid as reporter that lacked the Ti (tumor inducing) plasmid, no conjugation was observed. When either agp1(-) or agp2(-) knockout donor strains were used, plasmid DNA was delivered to the recipient, indicating that both phytochromes suppress conjugation in the wild type donor. In the recipient strains, the loss of Agp1 or Agp2 led to diminished conjugation. When wild type cells with Ti plasmid and pBIN-GUS reporter plasmid were used as donor, a high rate of conjugation was observed. The DNA transfer was down regulated by red or far-red light by a factor of 3.5. With agp1(-) or agp2(-) knockout donor cells, conjugation in the dark was about 10 times lower than with the wild type donor, and with the double knockout donor no conjugation was observed. These results imply that the phytochrome system has evolved to inhibit conjugation in the light. The decrease of conjugation under different temperature correlated with the decrease of phytochrome autophosphorylation. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Effects of transferrin conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes in lung cancer delivery
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Singh, Rahul Pratap [Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Sharma, Gunjan [Genotoxicology and Cancer Biology Lab, Department of Zoology, Institute of Science, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Sonali [Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Singh, Sanjay [Department of Pharmaceutics, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi 221005 (India); Patne, Shashikant C.U. [Department of Pathology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Pandey, Bajarangprasad L. [Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Koch, Biplob, E-mail: kochbiplob@gmail.com [Genotoxicology and Cancer Biology Lab, Department of Zoology, Institute of Science, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India); Muthu, Madaswamy S., E-mail: muthubits@rediffmail.com [Department of Pharmaceutics, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi 221005 (India); Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi 221005 (India)
2016-10-01
The aim of this study was to develop multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) which were covalently conjugated with transferrin by carbodiimide chemistry and loaded with docetaxel as a model drug for effective treatment of lung cancer in comparison with the commercial docetaxel injection (Docel™). D-Alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was used as amphiphilic surfactant to improve the aqueous dispersity and biocompatibility of MWCNT. Human lung cancer cells (A549 cells) were employed as an in-vitro model to access cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle analysis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) of the docetaxel/coumarin-6 loaded MWCNT. The cellular uptake results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT showed higher efficiency in comparison with free C6. The IC{sub 50} values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more efficient than Docel™ after 24 h treatment with the A549 cells. Flow cytometry analysis confirmed that cancerous cells appeared significantly (P < 0.05) in the sub-G1 phase for transferrin conjugated MWCNT in comparison with Docel™. Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™. - Highlights: • It shows the development of transferrin conjugated MWCNT formulation of DTX for the effective treatment of lung cancer. • Evaluated the cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle, and ROS level of the DTX/C6 loaded MWCNT. • The IC{sub 50} values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more effective than Docel™. • Safety of the DTX formulations were studied by the measurements of ALP, LDH and total protein count levels in BAL fluid. • Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™ in lung cancer delivery.
-
Effects of transferrin conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes in lung cancer delivery
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Singh, Rahul Pratap; Sharma, Gunjan; Sonali; Singh, Sanjay; Patne, Shashikant C.U.; Pandey, Bajarangprasad L.; Koch, Biplob; Muthu, Madaswamy S.
2016-01-01
The aim of this study was to develop multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) which were covalently conjugated with transferrin by carbodiimide chemistry and loaded with docetaxel as a model drug for effective treatment of lung cancer in comparison with the commercial docetaxel injection (Docel™). D-Alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was used as amphiphilic surfactant to improve the aqueous dispersity and biocompatibility of MWCNT. Human lung cancer cells (A549 cells) were employed as an in-vitro model to access cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle analysis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) of the docetaxel/coumarin-6 loaded MWCNT. The cellular uptake results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT showed higher efficiency in comparison with free C6. The IC_5_0 values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more efficient than Docel™ after 24 h treatment with the A549 cells. Flow cytometry analysis confirmed that cancerous cells appeared significantly (P < 0.05) in the sub-G1 phase for transferrin conjugated MWCNT in comparison with Docel™. Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™. - Highlights: • It shows the development of transferrin conjugated MWCNT formulation of DTX for the effective treatment of lung cancer. • Evaluated the cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, cellular apoptosis, cell cycle, and ROS level of the DTX/C6 loaded MWCNT. • The IC_5_0 values demonstrated that the transferrin conjugated MWCNT could be 136-fold more effective than Docel™. • Safety of the DTX formulations were studied by the measurements of ALP, LDH and total protein count levels in BAL fluid. • Results of transferrin conjugated MWCNT have showed better efficacy with safety than Docel™ in lung cancer delivery.
-
Polymers for Protein Conjugation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gianfranco Pasut
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Polyethylene glycol (PEG at the moment is considered the leading polymer for protein conjugation in view of its unique properties, as well as to its low toxicity in humans, qualities which have been confirmed by its extensive use in clinical practice. Other polymers that are safe, biodegradable and custom-designed have, nevertheless, also been investigated as potential candidates for protein conjugation. This review will focus on natural polymers and synthetic linear polymers that have been used for protein delivery and the results associated with their use. Genetic fusion approaches for the preparation of protein-polypeptide conjugates will be also reviewed and compared with the best known chemical conjugation ones.
-
Chen, Weitian; Sica, Christopher T; Meyer, Craig H
2008-11-01
Off-resonance effects can cause image blurring in spiral scanning and various forms of image degradation in other MRI methods. Off-resonance effects can be caused by both B0 inhomogeneity and concomitant gradient fields. Previously developed off-resonance correction methods focus on the correction of a single source of off-resonance. This work introduces a computationally efficient method of correcting for B0 inhomogeneity and concomitant gradients simultaneously. The method is a fast alternative to conjugate phase reconstruction, with the off-resonance phase term approximated by Chebyshev polynomials. The proposed algorithm is well suited for semiautomatic off-resonance correction, which works well even with an inaccurate or low-resolution field map. The proposed algorithm is demonstrated using phantom and in vivo data sets acquired by spiral scanning. Semiautomatic off-resonance correction alone is shown to provide a moderate amount of correction for concomitant gradient field effects, in addition to B0 imhomogeneity effects. However, better correction is provided by the proposed combined method. The best results were produced using the semiautomatic version of the proposed combined method.
-
Numerical Simulation of Solid Combustion with a Robust Conjugate-Gradient Solution for Pressure
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Wang, Yi-Zun
2002-01-01
A Bi-Conjugate Gradient method (Bi-CGSTAB) is studied and tested for solid combustion in which the gas and solid phases are coupled by a set of conditions describing mass, momentum and heat transport across the interface...
-
Eremin, A N; Metelitsa, D I
1997-01-01
Stable microemulsions in heptane retaining considerable amounts of the polar phase were obtained by using Aerosol OT (AOT), Triton X-45, and catalase. Conjugates of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase with aldehyde dextrans (AD) were synthesized in surfactant microemulsions in heptane. Effects of the reaction duration, the microemulsion polar phase volume, and concentrations of enzymes and modifiers on the properties of these conjugates were studied. The catalytic properties of conjugates depended on the nature of the surfactants used to stabilize the microemulsions, the initial concentration of protein in the reaction mixture, and the enzyme: modifier ratio. The degree of modification of the enzymes and the stabilities of their conjugates during isolation from microemulsions by a water-acetone solution depended on the concentration of the AD used. The catalytic properties of the conjugates synthesized were compared, and their stabilities in the presence of H2O2 were described. We suggested a simple method of transformation of whole kinetic curves of H2O2 conversion in coordinates 1/ln([H2O2]0/[H2O2]t - 1/t for simultaneous measurement of the constant of the catalase inactivation rate by H2O2 (Cin, S-1) and the rate constant of the catalase complex 1 interaction with the second H2O2 molecule (C2, M-1 S-1). This method was tested experimentally. Values C2 and Cin for catalase and its conjugates with ADs were compared, and these results were discussed.
-
Perioperative self-reflection among surgical residents.
Peshkepija, Andi N; Basson, Marc D; Davis, Alan T; Ali, Muhammad; Haan, Pam S; Gupta, Rama N; Hardaway, John C; Nebeker, Cody A; McLeod, Michael K; Osmer, Robert L; Anderson, Cheryl I
2017-09-01
We studied prevalence and predictors of meaningful self-reflection among surgical residents and with prompting/structured interventions, sought to improve/sustain resident skills. Residents from six programs recorded 1032 narrative self-reflective comments (120 residents), using a web-based platform. If residents identified something learned or to be improved, self-reflection was deemed meaningful. Independent variables PGY level, resident/surgeon gender, study site/Phase1: July2014-August2015 vs. Phase2: September2015-September2016) were analyzed. Meaningful self-reflection was documented in 40.6% (419/1032) of entries. PGY5's meaningfully self-reflected less than PGY1-4's, 26.1% vs. 49.6% (p = 0.002). In multivariate analysis, resident narratives during Phase 2 were 4.7 times more likely to engage in meaningful self-reflection compared to Phase1 entries (p self-reflection, compared to Phase1. Surgical residents uncommonly practice meaningful self-reflection, even when prompted, and PGY5/chief residents reflect less than more junior residents. Substantial/sustained improvements in resident self-reflection can occur with both training and interventions. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Fiber Nonlinearity Post-Compensation by Optical Phase Conjugation for 40Gb/s CO-OFDM Systems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Qiao Yao-Jun; Liu Xue-Jun; Ji Yue-Feng
2011-01-01
Fiber nonlinearity impairments in a 40-Gb/s coherent optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (COOFDM) system are post-compensated for by a new method of fiber nonlinearity post-compensation (FNPC). The FNPC located before the CO-OFDM receiver includes an optical phase conjugation (OPC) unit and a subsequent 80-km-high nonlinear fiber (HNLF) as a fiber nonlinearity compensator. The OPC unit is based on a four wave mixing effect in a semiconductor optical amplifier. The fiber nonlinearity impairments in the transmission link are post-compensated for after OPC by transmission through the HNLF with a large nonlinearity coefficient. Simulation results show that the nonlinear threshold (NLT) (for Q > 10 dB) can be increased by about 2.5 dB and the maximum Q factor is increased by about 1.2 dB for the single-channel 40-Gb/s CO-OFDM system with periodic dispersion maps. In the 50-GHz channel spacing wavelength-division-multiplexing system, the NLT increases by 1.1 dB, equating to a 0.7 dB improvement for the maximum Q factor. (fundamental areas of phenomenology(including applications))
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Michael G. Waddell; William J. Domoracki; Tom J. Temples; Jerome Eyer
2001-01-01
The Earth Sciences and Resources Institute, University of South Carolina is conducting a 14 month proof of concept study to determine the location and distribution of subsurface Dense Nonaqueous Phase Liquid (DNAPL) carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4 ) contamination at the 216-Z-9 crib, 200 West area, Department of Energy (DOE) Hanford Site, Washington by use of two-dimensional high resolution seismic reflection surveys and borehole geophysical data. The study makes use of recent advances in seismic reflection amplitude versus offset (AVO) technology to directly detect the presence of subsurface DNAPL. The techniques proposed are a noninvasive means towards site characterization and direct free-phase DNAPL detection. This report covers the results of Task 3 and change of scope of Tasks 4-6. Task 1 contains site evaluation and seismic modeling studies. The site evaluation consists of identifying and collecting preexisting geological and geophysical information regarding subsurface structure and the presence and quantity of DNAPL. The seismic modeling studies were undertaken to determine the likelihood that an AVO response exists and its probable manifestation. Task 2 is the design and acquisition of 2-D seismic reflection data designed to image areas of probable high concentration of DNAPL. Task 3 is the processing and interpretation of the 2-D data. Task 4, 5, and 6 were designing, acquiring, processing, and interpretation of a three dimensional seismic survey (3D) at the Z-9 crib area at 200 west area, Hanford
-
Nonn, Chloé; Leroy, Sylvie; Khanbari, Khaled; Ahmed, Abdulhakim
2017-11-01
Here, we focus on the yet unexplored eastern Gulf of Aden, on Socotra Island (Yemen), Southeastern Oman and offshore conjugate passive margins between the Socotra-Hadbeen (SHFZ) and the eastern Gulf of Aden fracture zones. Our interpretation leads to onshore-offshore stratigraphic correlation between the passive margins. We present a new map reflecting the boundaries between the crustal domains (proximal, necking, hyper-extended, exhumed mantle, proto-oceanic and oceanic domains) and structures using bathymetry, magnetic surveys and seismic reflection data. The most striking result is that the magma-poor conjugate margins exhibit asymmetrical architecture since the thinning phase (Upper Rupelian-Burdigalian). Their necking domains are sharp ( 40-10 km wide) and their hyper-extended domains are narrow and asymmetric ( 10-40 km wide on the Socotra margin and 50-80 km wide on the Omani margin). We suggest that this asymmetry is related to the migration of the rift center producing significant lower crustal flow and sequential faulting in the hyper-extended domain. Throughout the Oligo-Miocene rifting, far-field forces dominate and the deformation is accommodated along EW to N110°E northward-dipping low angle normal faults. Convection in the mantle near the SHFZ may be responsible of change in fault dip polarity in the Omani hyper-extended domain. We show the existence of a northward-dipping detachment fault formed at the beginning of the exhumation phase (Burdigalien). It separates the northern upper plate (Oman) from southern lower plate (Socotra Island) and may have generated rift-induced decompression melting and volcanism affecting the upper plate. We highlight multiple generations of detachment faults exhuming serpentinized subcontinental mantle in the ocean-continent transition. Associated to significant decompression melting, final detachment fault may have triggered the formation of a proto-oceanic crust at 17.6 Ma and induced late volcanism up to 10 Ma
-
Theory of fidelity measure in degenerate four-wave mixing
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bochove, E.J.
1983-01-01
Phase-conjugate beam fidelity is studied in degenerate four-wave mixing with spatially varying pump beams. The analysis includes the effects of probe depletion, diffracting non-linear phase variation focussing, and finally that of losses. Relatively simple algebraic expressions are found for the phase conjugate reflectivity for the cases of collinear and near-collinear beam gemetries. It is found that by focussing the probe beam into the mixing medium, the fraction of energy in the phase conjugate beam which was transferred to other modes, may typically be reduced by one order of magnitude. (Author) [pt
-
Absence of phase-dependent noise in time-domain reflectivity studies of impulsively excited phonons
Hussain, A.
2010-06-17
There have been several reports of phase-dependent noise in time-domain reflectivity studies of optical phonons excited by femtosecond laser pulses in semiconductors, semimetals, and superconductors. It was suggested that such behavior is associated with the creation of squeezed phonon states although there is no theoretical model that directly supports such a proposal. We have experimentally re-examined the studies of phonons in bismuth and gallium arsenide, and find no evidence of any phase-dependent noise signature associated with the phonons. We place an upper limit on any such noise at least 40–50 dB lower than previously reported.
-
Absence of phase-dependent noise in time-domain reflectivity studies of impulsively excited phonons
Hussain, A.; Andrews, S. R.
2010-01-01
There have been several reports of phase-dependent noise in time-domain reflectivity studies of optical phonons excited by femtosecond laser pulses in semiconductors, semimetals, and superconductors. It was suggested that such behavior is associated with the creation of squeezed phonon states although there is no theoretical model that directly supports such a proposal. We have experimentally re-examined the studies of phonons in bismuth and gallium arsenide, and find no evidence of any phase-dependent noise signature associated with the phonons. We place an upper limit on any such noise at least 40–50 dB lower than previously reported.
-
Anti-CD163-dexamethasone conjugate inhibits the acute phase response to lipopolysaccharide in rats
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Thomsen, Karen Louise; Møller, Holger Jon; Graversen, Jonas Heilskov
2016-01-01
± 4036 pg/mL, P = 0.03) compared to the low dose dexamethasone. The high dose dexamethasone dose decreased the spleen weight (421 ± 11 mg vs 465 ± 12 mg, P any other group. CONCLUSION: Low-dose anti-CD163-dexamethasone conjugate effectively decreased...
-
Qualidade conjugal: mapeando conceitos
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Clarisse Mosmann
2006-12-01
Full Text Available Apesar da ampla utilização do conceito de qualidade conjugal, identifica-se falta de clareza conceitual acerca das variáveis que o compõem. Esse artigo apresenta revisão da literatura na área com o objetivo de mapear o conceito de qualidade conjugal. Foram analisadas sete principais teorias sobre o tema: Troca Social, Comportamental, Apego, Teoria da Crise, Interacionismo Simbólico. Pelos postulados propostos nas diferentes teorias, podem-se identificar três grupos de variáveis fundamentais na definição da qualidade conjugal: recursos pessoais dos cônjuges, contexto de inserção do casal e processos adaptativos. Neste sentido, a qualidade conjugal é resultado do processo dinâmico e interativo do casal, razão deste caráter multidimensional.
-
Self-Assembly and Crystallization of Conjugated Block Copolymers
Davidson, Emily Catherine
This dissertation demonstrates the utility of molecular design in conjugated polymers to create diblock copolymers that robustly self-assemble in the melt and confine crystallization upon cooling. This work leverages the model conjugated polymer poly(3-(2'-ethyl)hexylthiophene) (P3EHT), which features a branched side chain, resulting in a dramatically reduced melting temperature (Tm 80°C) relative to the widely-studied poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT) (Tm 200°C). This reduced melting temperature permits an accessible melt phase, without requiring that the segregation strength (chiN) be dramatically increased. Thus, diblock copolymers containing P3EHT demonstrate robust diblock copolymer self-assembly in the melt over a range of compositions and morphologies. Furthermore, confined crystallization in the case of both glassy (polystyrene (PS) matrix block) and soft (polymethylacrylate (PMA) matrix block) confinement is studied, with the finding that even in soft confinement, crystallization is constrained within the diblock microdomains. This success demonstrates the strategy of leveraging molecular design to decrease the driving force for crystallization as a means to achieving robust self-assembly and confined crystallization in conjugated block copolymers. Importantly, despite the relatively flexible nature of P3EHT in the melt, the diblock copolymer phase behavior appears to be significantly impacted by the stiffness (persistence length of 3 nm) of the P3EHT chain compared to the coupled amorphous blocks (persistence length 0.7 nm). In particular, it is shown that the synthesized morphologies are dominated by a very large composition window for lamellar geometries (favored at high P3EHT volume fractions); cylindrical geometries are favored when P3EHT is the minority fraction. This asymmetry of the composition window is attributed to impact of conformational asymmetry (the difference in chain stiffness, as opposed to shape) between conjugated and amorphous blocks
-
Ball, Christopher P; Levick, Andrew P; Woolliams, Emma R; Green, Paul D; Dury, Martin R; Winkler, Rainer; Deadman, Andrew J; Fox, Nigel P; King, Martin D
2013-07-10
Sintered polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is highly reflective and is widely used as a reference standard in remote sensing, radiometry, and spectroscopy. The relative change in output flux from a PTFE integrating sphere over the room temperature phase transition at 19°C has been measured at a monochromatic wavelength of 633 nm as 1.82±0.21%. The change in output flux was attributed to a small change of 0.09±0.02% in the total hemispherical reflectance of PTFE, caused by a change in its material density as a result of the phase transition. For the majority of users, this small change measured in total hemispherical reflectance is unlikely to impact significantly the accuracy of PTFE flat panel reflectors used as reference standards. However, owing to the multiple reflections that occur inside an integrating sphere cavity, the effect is multiplied and remedial action should be applied, either via a mathematical correction or through temperature stabilization of the integrating sphere when high accuracy (PTFE-based integrating spheres at temperatures close to the phase transition at 19°C.
-
Cross-Conjugated n-Dopable Aromatic Polyketone
Voortman, Thomas P.; Bartesaghi, Davide; Koster, L. Jan Anton; Chiechi, Ryan C.
2015-01-01
This paper describes the synthesis and characterization of a high molecular weight cross-conjugated polyketone synthesized via scalable Friedel Crafts chemistry. Cross-conjugated polyketones are precursors to conjugated polyions; they become orders of magnitude more conductive after a two-electron
-
Dong, Lifeng; Witkowski, Colette M.; Craig, Michael M.; Greenwade, Molly M.; Joseph, Katherine L.
2009-12-01
Phase contrast and epifluorescence microscopy were utilized to monitor morphological changes in human astrocytoma cells during a time-course exposure to single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) conjugates with different surfactants and to investigate sub-cellular distribution of the nanotube conjugates, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that cytotoxicity of the nanotube/surfactant conjugates is related to the toxicity of surfactant molecules attached on the nanotube surfaces. Both sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS) are toxic to cells. Exposure to CNT/SDS conjugates (0.5 mg/mL) for less than 5 min caused changes in cell morphology resulting in a distinctly spherical shape compared to untreated cells. In contrast, sodium cholate (SC) and CNT/SC did not affect cell morphology, proliferation, or growth. These data indicate that SC is an environmentally friendly surfactant for the purification and dispersion of SWCNTs. Epifluorescence microscopy analysis of CNT/DNA conjugates revealed distribution in the cytoplasm of cells and did not show adverse effects on cell morphology, proliferation, or viability during a 72-h incubation. These observations suggest that the SWCNTs could be used as non-viral vectors for diagnostic and therapeutic molecules across the blood-brain barrier to the brain and the central nervous system.
-
Strozyk, Frank; Back, Stefan; Kukla, Peter A.
2017-10-01
This study presents a regional comparison between selected 2D seismic transects from large, conjugated salt and salt-free basins offshore southern Brazil (Campos Basin, Santos Basin, Pelotas Basin) and southwest Africa (Kwanza Basin, northern and southern Namibe Basin, Walvis Basin). Tectonic-stratigraphic interpretation of the main rift and post-rift units, free-air gravity data and flexural isostatic backstripping were used for a comprehensive basin-to-basin documentation of key mechanisms controlling the present-day differences in conjugated and neighbouring South Atlantic basins. A significant variation in the tectonic-sedimentary architecture along-strike at each margin and between the conjugated basins across the South Atlantic reflects major differences in (1) the structural configuration of each margin segment at transitional phase between rifting and breakup, as emphasized in the highly asymmetric settings of the large Santos salt basin and the conjugated, salt-free southern Namibe Basin, (2) the post-breakup subsidence and uplift history of the respective margin segment, which caused major differences for example between the Campos and Espirito Santo basins and the conjugated northern Namibe and Kwanza basins, (3) variations in the quantity and distribution of post-breakup margin sediments, which led to major differences in the subsidence history and the related present-day basin architecture, for example in the initially rather symmetric, siliciclastic Pelotas and Walvis basins, and (4) the deposition of Aptian evaporites in the large rift and sag basin provinces north of the Rio Grande Rise and Walvis Ridge, highly contrasting the siliciclastic basins along the margin segments south of the ridges. The resulting present-day architecture of the basins can be generally classified as (i) moderately symmetric, salt-free, and magma-rich in the northern part of the southern segment, (i) highly asymmetric, salt-bearing and magma-poor vs. salt-free and magma
-
Block-conjugate-gradient method
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McCarthy, J.F.
1989-01-01
It is shown that by using the block-conjugate-gradient method several, say s, columns of the inverse Kogut-Susskind fermion matrix can be found simultaneously, in less time than it would take to run the standard conjugate-gradient algorithm s times. The method improves in efficiency relative to the standard conjugate-gradient algorithm as the fermion mass is decreased and as the value of the coupling is pushed to its limit before the finite-size effects become important. Thus it is potentially useful for measuring propagators in large lattice-gauge-theory calculations of the particle spectrum
-
Protein carriers of conjugate vaccines
Pichichero, Michael E
2013-01-01
The immunogenicity of polysaccharides as human vaccines was enhanced by coupling to protein carriers. Conjugation transformed the T cell-independent polysaccharide vaccines of the past to T cell-dependent antigenic vaccines that were much more immunogenic and launched a renaissance in vaccinology. This review discusses the conjugate vaccines for prevention of infections caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Specifically, the characteristics of the proteins used in the construction of the vaccines including CRM, tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane complex, and Hemophilus influenzae protein D are discussed. The studies that established differences among and key features of conjugate vaccines including immunologic memory induction, reduction of nasopharyngeal colonization and herd immunity, and antibody avidity and avidity maturation are presented. Studies of dose, schedule, response to boosters, of single protein carriers with single and multiple polysaccharides, of multiple protein carriers with multiple polysaccharides and conjugate vaccines administered concurrently with other vaccines are discussed along with undesirable consequences of conjugate vaccines. The clear benefits of conjugate vaccines in improving the protective responses of the immature immune systems of young infants and the senescent immune systems of the elderly have been made clear and opened the way to development of additional vaccines using this technology for future vaccine products. PMID:23955057
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yoav Atsmon-Raz
Full Text Available We study the effect that conjugation-mediated Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT has on the mutation-selection balance of a population in a static environment. We consider a model whereby a population of unicellular organisms, capable of conjugation, comes to mutation-selection balance in the presence of an antibiotic, which induces a first-order death rate constant [Formula: see text] for genomes that are not resistant. We explicitly take into consideration the repression/de-repression dynamics of the conjugative plasmid, and assume that a de-repressed plasmid remains temporarily de-repressed after copying itself into another cell. We assume that both repression and de-repression are characterized by first-order rate constants [Formula: see text]and [Formula: see text], respectively. We find that conjugation has a deleterious effect on the mean fitness of the population, suggesting that HGT does not provide a selective advantage in a static environment, but is rather only useful for adapting to new environments. This effect can be ameliorated by repression, suggesting that while HGT is not necessarily advantageous for a population in a static environment, its deleterious effect on the mean fitness can be negated via repression. Therefore, it is likely that HGT is much more advantageous in a dynamic landscape. Furthermore, in the limiting case of a vanishing spontaneous de-repression rate constant, we find that the fraction of conjugators in the population undergoes a phase transition as a function of population density. Below a critical population density, the fraction of conjugators is zero, while above this critical population density the fraction of conjugators rises continuously to one. Our model for conjugation-mediated HGT is related to models of infectious disease dynamics, where the conjugators play the role of the infected (I class, and the non-conjugators play the role of the susceptible (S class.
-
Conjugated polymer zwitterions and solar cells comprising conjugated polymer zwitterions
Emrick, Todd; Russell, Thomas; Page, Zachariah; Liu, Yao
2018-06-05
A conjugated polymer zwitterion includes repeating units having structure (I), (II), or a combination thereof ##STR00001## wherein Ar is independently at each occurrence a divalent substituted or unsubstituted C3-30 arylene or heteroarylene group; L is independently at each occurrence a divalent C1-16 alkylene group, C6-30arylene or heteroarylene group, or alkylene oxide group; and R1 is independently at each occurrence a zwitterion. A polymer solar cell including the conjugated polymer zwitterion is also disclosed.
-
Research study of conjugate materials; Conjugate material no chosa kenkyu
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
1998-03-01
The paper reported an introductory research on possibilities of new glass `conjugate materials.` The report took up the structure and synthetic process of conjugate materials to be researched/developed, classified them according to structural elements on molecular, nanometer and cluster levels, and introduced the structures and functions. Further, as glasses with new functions to be proposed, the paper introduced transparent and high-strength glass used for houses and vehicles, light modulation glass which realizes energy saving and optical data processing, and environmentally functional glass which realizes environmental cleaning or high performance biosensor. An initial survey was also conducted on rights of intellectual property to be taken notice of in Japan and abroad in the present situation. Reports were summed up and introduced of Osaka National Research Institute, Electrotechnical Laboratory, and National Industrial Research Institute of Nagoya which are all carrying out leading studies of conjugate materials. 235 refs., 135 figs., 6 tabs.
-
C/NOFS Remote Sensing of Ionospheric Reflectance
Burke, W. J.; Pfaff, Robert F.; Martinis, C. R.; Gentile, L. C.
2016-01-01
Alfvn waves play critical roles in the electrodynamic coupling of plasmas at magnetically conjugate regions in near-Earth space. Associated electric (E*) and magnetic (dec B*) field perturbations sampled by sensors on satellites in low-Earth orbits are generally super positions of incident and reflected waves. However, lack of knowledge about ionospheric reflection coefficients (alpha) hinders understanding of generator outputs and load absorption of Alfvn wave energies. Here we demonstrate a new method for estimating using satellite measurements of ambient E* and dec B* then apply it to a case in which the Communication Navigation Outage Forecasting System (CNOFS) satellite flew conjugate to the field of view of a 630.0 nm all-sky imager at El Leoncito, Argentina, while medium-scale traveling ionosphere disturbances were detected in its field of view. In regions of relatively large amplitudes of E* and B*,calculated values ranged between 0.67 and 0.88. This implies that due to impedance mismatches, the generator ionosphere puts out significantly more electromagnetic energy than the load can absorb. Our analysis also uncovered caveats concerning the methods range of applicability in regions of low E* and B*. The method can be validated in future satellite-based auroral studies where energetic particle precipitation fluxes can be used to make independent estimates of alpha.
-
Shin, Sunghwan; Kang, Hani; Kim, Jun Soo; Kang, Heon
2014-11-26
We investigated the phase transformations of amorphous solid acetone under confined geometry by preparing acetone films trapped in amorphous solid water (ASW) or CCl4. Reflection absorption infrared spectroscopy (RAIRS) and temperature-programmed desorption (TPD) were used to monitor the phase changes of the acetone sample with increasing temperature. An acetone film trapped in ASW shows an abrupt change in the RAIRS features of the acetone vibrational bands during heating from 80 to 100 K, which indicates the transformation of amorphous solid acetone to a molecularly aligned crystalline phase. Further heating of the sample to 140 K produces an isotropic solid phase, and eventually a fluid phase near 157 K, at which the acetone sample is probably trapped in a pressurized, superheated condition inside the ASW matrix. Inside a CCl4 matrix, amorphous solid acetone crystallizes into a different, isotropic structure at ca. 90 K. We propose that the molecularly aligned crystalline phase formed in ASW is created by heterogeneous nucleation at the acetone-water interface, with resultant crystal growth, whereas the isotropic crystalline phase in CCl4 is formed by homogeneous crystal growth starting from the bulk region of the acetone sample.
-
Entanglements in Conjugated Polymers
Xie, Renxuan; Lee, Youngmin; Aplan, Melissa; Caggiano, Nick; Gomez, Enrique; Colby, Ralph
Conjugated polymers, such as poly(3-hexylthiophene-2,5-diyl) (P3HT) and poly-((9,9-dioctylfluorene)-2,7-diyl-alt-[4,7-bis(thiophen-5-yl)-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole]-2',2''-diyl) (PFTBT), are widely used as hole and electron transport materials in a variety of electronic devices. However, fundamental knowledge regarding chain entanglements and nematic-to-isotropic transition is still lacking and are crucial to maximize charge transport properties. A systematic melt rheology study on P3HT with various molecular weights and regio regularities was performed. We find that the entanglement molecular weight Me is 5.0 kg/mol for regiorandom P3HT, but the apparent Me for regioregular P3HT is significantly higher. The difference is postulated to arise from the presence of a nematic phase only in regioregular P3HT. Analogously, PFTBT shows a clear rheological signature of the nematic-to-isotropic transition as a reversible sharp transition at 278 C. Shearing of this nematic phase leads to anisotropic crystalline order in PFTBT. We postulate that aligning the microstructure will impact charge transport and thereby advance the field of conducting polymers. National Science Foundation.
-
Misonidazole-glutathione conjugates in CHO cells
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Varghese, A.J.; Whitmore, G.F.
1984-01-01
Misonidazole, after reduction to the hydroxylamine derivative, reacts with glutathione (GSH) under physiological conditions. The reaction product has been identified as a mixture of two isomeric conjugates. When water soluble extracts of CHO cells exposed to misonidazole under hypoxic conditions are subjected to HPLC analysis, misonidazole derivatives, having the same chromatographic properties as the GSH-MISO conjugates, were detected. When CHO cells were incubated with misonidazole in the presence of added GSH, a substantial increase in the amount of the conjugate was detected. When extracts of CHO cells exposed to misonidazole under hypoxia were subsequently exposed to GSH, an increased formation of the conjugate was observed. A rearrangement product of the hydroxylamine derivative of misonidazole is postulated as the reactive intermediate responsible for the formation of the conjugate
-
Modelling conjugation with stochastic differential equations
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Philipsen, Kirsten Riber; Christiansen, Lasse Engbo; Hasman, Henrik
2010-01-01
Enterococcus faecium strains in a rich exhaustible media. The model contains a new expression for a substrate dependent conjugation rate. A maximum likelihood based method is used to estimate the model parameters. Different models including different noise structure for the system and observations are compared......Conjugation is an important mechanism involved in the transfer of resistance between bacteria. In this article a stochastic differential equation based model consisting of a continuous time state equation and a discrete time measurement equation is introduced to model growth and conjugation of two...... using a likelihood-ratio test and Akaike's information criterion. Experiments indicating conjugation on the agar plates selecting for transconjugants motivates the introduction of an extended model, for which conjugation on the agar plate is described in the measurement equation. This model is compared...
-
Photoluminescence properties of a novel conjugate of water-soluble CdTe quantum dots to guanine
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Feng Xuejiao [North-East Normal University, Changchun 130024 (China); Shang, Qingkun, E-mail: shangqk995@nenu.edu.c [North-East Normal University, Changchun 130024 (China); Liu Hongjian [Relia Diagnostic Systems, Burlingame, CA 94010 (United States); Wang Wenlan; Wang Zhidan; Liu Junyu [North-East Normal University, Changchun 130024 (China)
2010-04-15
A novel conjugate of water-soluble CdTe quantum dots to a small biomolecule guanine has been obtained in aqueous phase. The photoluminescence property and the stability of the conjugate increased comparing to CdTe QDs. The interaction between CdTe QDs and guanine was studied by TEM, fluorescence microscope and photoluminescence (PL), IR, UV-Vis spectra. The effects of reflux time, pH value, ionic strength, and the ratio of CdTe QDs to guanine on the photoluminescence properties of conjugate were investigated in detail. The results show that guanine has a great influence on both the photoluminescence property and stability of thioglycolic acid-stabilized CdTe QDs. The formation of coordination and hydrogen bond between guanine molecules and CdTe including thioglycolic acid on its surface may effectively enhance the PL intensity and stability of CdTe QDs. The maximum PL intensity of the conjugate was obtained on the condition with lower ionic strength, less than 30 min reflux time, neutral pH value and 6/1 as molar ratio of guanine to CdTe.
-
Koskela, Katja A; Mattinen, Laura; Kalin-Mänttäri, Laura; Vergnaud, Gilles; Gorgé, Olivier; Nikkari, Simo; Skurnik, Mikael
2015-11-01
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat - CRISPR-associated genes (CRISPR-Cas) system is used by bacteria and archaea against invading conjugative plasmids or bacteriophages. Central to this immunity system are genomic CRISPR loci that contain fragments of invading DNA. These are maintained as spacers in the CRISPR loci between direct repeats and the spacer composition in any bacterium reflects its evolutionary history. We analysed the CRISPR locus sequences of 335 Yersinia pseudotuberculosis complex strains. Altogether 1902 different spacer sequences were identified and these were used to generate a database for the spacer sequences. Only ∼10% of the spacer sequences found matching sequences. In addition, surprisingly few spacers were shared by Yersinia pestis and Y. pseudotuberculosis strains. Interestingly, 32 different protospacers were present in the conjugative plasmid pYptb32953. The corresponding spacers were identified from 35 different Y. pseudotuberculosis strains indicating that these strains had encountered pYptb32953 earlier. In conjugation experiments, pYptb32953-specific spacers generally prevented conjugation with spacer-positive and spacer-free strains. However, some strains with one to four spacers were invaded by pYptb32953 and some spacer-free strains were fully resistant. Also some spacer-positive strains were intermediate resistant to conjugation. This suggests that one or more other defence systems are determining conjugation efficiency independent of the CRISPR-Cas system. © 2015 Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
-
Poly(2-oxazoline)-Antibiotic Conjugates with Penicillins.
Schmidt, Martin; Bast, Livia K; Lanfer, Franziska; Richter, Lena; Hennes, Elisabeth; Seymen, Rana; Krumm, Christian; Tiller, Joerg C
2017-09-20
The conjugation of antibiotics with polymers is rarely done, but it might be a promising alternative to low-molecular-weight derivatization. The two penicillins penicillin G (PenG) and penicillin V (PenV) were attached to the end groups of different water-soluble poly(2-oxazoline)s (POx) via their carboxylic acid function. This ester group was shown to be more stable against hydrolysis than the β-lactam ring of the penicillins. The conjugates are still antimicrobially active and up to 20 times more stable against penicillinase catalyzed hydrolysis. The antibiotic activity of the conjugates against Staphylococcus aureus in the presence of penicillinase is up to 350 times higher compared with the free antibiotics. Conjugates with a second antimicrobial function, a dodecyltrimethylammonium group (DDA-X), at the starting end of the PenG and PenV POx conjugates are more antimicrobially active than the conjugates without DDA-X and show high activity in the presence of penicillinase. For example, the conjugates DDA-X-PEtOx-PenG and DDA-X-PEtOx-PenV are 200 to 350 times more active against S. aureus in the presence of penicillinase and almost as effective as the penicillinase stable cloxacollin (Clox) under these conditions. These conjugates show even greater activity compared to cloxacollin without this enzyme present. Further, both conjugates kill Escherichia coli more effectively than PenG and Clox.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Filippo Romanato
2012-09-01
Full Text Available Peptide Nucleic Acids (PNAs linked to high molecular weight (MW poly(ethylene oxide (PEO derivatives could be useful conjugates for the direct functionalisation of gold surfaces dedicated to Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR-based DNA sensing. However their use is hampered by the difficulty to obtain them through a convenient and economical route. In this work we compared three synthetic strategies to obtain PNA-high MW PEO conjugates composed of (a a 15-mer PNA sequence as the probe complementary to genomic DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, (b a PEO moiety (2 or 5 KDa MW and (c a terminal trityl-protected thiol necessary (after acidic deprotection for grafting to gold surfaces. The 15-mer PNA was obtained by solid-phase synthesis. Its amino terminal group was later condensed to bi-functional PEO derivatives (2 and 5 KDa MW carrying a Trt-cysteine at one end and a carboxyl group at the other end. The reaction was carried out either in solution, using HATU or PyOxim as coupling agents, or through the solid-phase approach, with 49.6%, 100% and 5.2% yield, respectively. A differential solvent extraction strategy for product purification without the need for chromatography is described. The ability of the 5 KDa PEO conjugate to function as a probe for complementary DNA detection was demonstrated using a Grating-Coupling Surface Plasmon Resonance (GC-SPR system. The optimized PEO conjugation and purification protocols are economical and simple enough to be reproduced also within laboratories that are not highly equipped for chemical synthesis.
-
Amphotericin B-conjugated polypeptide hydrogels as a novel innovative strategy for fungal infections
Shu, Chang; Li, Tengfei; Yang, Wen; Li, Duo; Ji, Shunli; Ding, Li
2018-03-01
The present work is focused on the design and development of novel amphotericin B (AmB)-conjugated biocompatible and biodegradable polypeptide hydrogels to improve the antifungal activity. Using three kinds of promoting self-assembly groups (2-naphthalene acetic acid (Nap), naproxen (Npx) and dexamethasone (Dex)) and polypeptide sequence (Phe-Phe-Asp-Lys-Tyr, FFDKY), we successfully synthesized the Nap-FFDK(AmB)Y gels, Npx-FFDK(AmB)Y gels and Dex-FFDK(AmB)Y gels. The AmB-conjugated hydrogelators are highly soluble in different aqueous solutions. The cryo-transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy micrographs of hydrogels afford nanofibres with a width of 20-50 nm. Powder X-ray diffraction analyses demonstrate that the crystalline structures of the AmB and Dex are changed into amorphous structures after the formation of hydrogels. Circular dichroism spectra of the solution of blank carriers and the corresponding drug deliveries further help elucidate the molecular arrangement in gel phase, indicating the existence of turn features. The in vitro drug releases suggest that the AmB-conjugated hydrogels are suitable as drug-controlled release vehicles for hydrophobic drugs. The antifungal effect of AmB-conjugated hydrogels significantly exhibits the antifungal activity against Candida albicans. The results of the present study indicated that the AmB-conjugated hydrogels are suitable carriers for poorly water soluble drugs and for enhancement of therapeutic efficacy of antifungal drugs.
-
Approximate error conjugation gradient minimization methods
Kallman, Jeffrey S
2013-05-21
In one embodiment, a method includes selecting a subset of rays from a set of all rays to use in an error calculation for a constrained conjugate gradient minimization problem, calculating an approximate error using the subset of rays, and calculating a minimum in a conjugate gradient direction based on the approximate error. In another embodiment, a system includes a processor for executing logic, logic for selecting a subset of rays from a set of all rays to use in an error calculation for a constrained conjugate gradient minimization problem, logic for calculating an approximate error using the subset of rays, and logic for calculating a minimum in a conjugate gradient direction based on the approximate error. In other embodiments, computer program products, methods, and systems are described capable of using approximate error in constrained conjugate gradient minimization problems.
-
Klingelhoefer, F.; Biari, Y.; Sahabi, M.; Aslanian, D.; Philippe, S.; Schnabel, M.; Moulin, M.; Louden, K. E.; Funck, T.; Reichert, C. J.
2014-12-01
The structure of conjugate passive margins provides information about rifting styles, opening of an ocean and formation of it's associated sedimentary basins. In order to distinguish between tectonic inheritance and structures directly related to rifting of passive margins conjugate profiles have to be acquired on margins on diverse locations and different ages. In this study we use new and existing reflection and wide-angle seismic data from two margin pairs, the 200 Ma year old Nova-Scotia - Morocco margin pair and the only 20 Ma Gulf of Lions - Sardinia margin pair. On both margin pairs wide-angle seismic data combined with reflection seismic data were acquired on conjugate profiles on sea and extended on land. Forward modelling of the deep crustal structure along the four transects indicates that a high velocity zone (HVZ) (> 7.2 km/s) is present at the base of the lower crust on all four margins along the ocean-continental transition zone (OCT). This may represent either exhumed upper mantle material or injection of upper mantle material into proto-oceanic crust at the onset of sea-floor spreading. However the width of the HVZ might strongly differ between conjugates, which may be the result of tectonic inheritance, for example the presence of ancient subduction zones or orogens. Both margin pairs show a similar unthinned continental crustal thickness. Crustal thinning and upper-to-lower crustal thickness vary between margin pairs, but remain nearly symmetric on conjugate profiles and might therefore depend on the structure and mechanical properties of the original continental crust. For the Mediterranean margin pair, the oceanic crust is similar on both sides, with a thickness of only 4-5 km. For the Atlantic margin pair, oceanic crustal thickness is higher on the Moroccan Margin, a fact that can be explained by either asymmetric spreading or by the volcanic underplating, possibly originating from the Canary Hot Spot.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hu, Hao; Jopson, Robert M.; Gnauck, Alan H.
2017-01-01
We demonstrate fiber nonlinearity mitigation by using multiple optical phase conjugations (OPCs) in the WDM transmission systems of both 8 x 32-Gbaud PDM QPSK channels and 8 x 32-Gbaud PDM 16-QAM channels, showing improved performance over a single mid-span OPC and no OPC in terms of nonlinear...... threshold and a best achievable Q(2) factor after transmission. In addition, after an even number of OPCs, the signal wavelength can be preserved after transmission. The performance of multiple OPCs for fiber nonlinearity mitigation was evaluated independently for WDM PDM QPSK signals and WDM PDM 16QAM...... to 1 dB compared to the case of mid-span OPC. The improvements in the best achievable Q(2) factors were more modest, ranging from 0.2 dB to 1.1 dB for the results presented. (C) 2017 Optical Society of America...
-
Material Selection for Microchannel Heatsink: Conjugate Heat Transfer Simulation
Uday Kumar, A.; Javed, Arshad; Dubey, Satish K.
2018-04-01
Heat dissipation during the operation of electronic devices causes rise in temperature, which demands an effective thermal management for their performance, life and reliability. Single phase liquid cooling in microchannels is an effective and proven technology for electronics cooling. However, due to the ongoing trends of miniaturization and developments in the microelectronics technology, the future needs of heat flux dissipation rate are expected to rise to 1 kW/cm2. Air cooled systems are unable to meet this demand. Hence, liquid cooled heatsinks are preferred. This paper presents conjugate heat transfer simulation of single phase flow in microchannels with application to electronic cooling. The numerical model is simulated for different materials: copper, aluminium and silicon as solid and water as liquid coolant. The performances of microchannel heatsink are analysed for mass flow rate range of 20-40 ml/min. The investigation has been carried out on same size of electronic chip and heat flux in order to have comparative study of different materials. This paper is divided into two sections: fabrication techniques and numerical simulation for different materials. In the first part, a brief discussion of fabrication techniques of microchannel heatsink have been presented. The second section presents conjugate heat transfer simulation and parametric investigation for different material microchannel heatsink. The presented study and findings are useful for selection of materials for microchannel heatsink.
-
Li, Chunju; Lin, Qixun; Wang, Jun; Shen, Lijuan; Ma, Guanghui; Su, Zhiguo; Hu, Tao
2012-12-31
Ribonuclease A (RNase A) is a therapeutic enzyme with cytotoxic action against tumor cells. Its clinical application is limited by the short half-life and insufficient stability. Conjugation of albumin can overcome the limitation, whereas dramatically decrease the enzymatic activity of RNase A. Here, three strategies were proposed to prepare the RNase A-bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugates. R-SMCC-B (a conjugate of four RNase A attached with one BSA) and R-PEG-B (a mono-conjugate) were prepared using Sulfo-SMCC (a short bifunctional linker) and mal-PEG-NHS (a bifunctional PEG), respectively. Mal-PEG-NHS and hexadecylamine (HDA) were used to prepare the mono-conjugate, R-HDA-B, where HDA was adopted to bind BSA. The PEG linker can elongate the proximity between RNase A and BSA. In contrast, four RNase A were closely located on BSA in R-SMCC-B. R-SMCC-B showed the lowest K(m) and the highest relative enzymatic activity and k(cat)/K(m) in the three conjugates. Presumably, the tetravalent interaction of RNase A in R-SMCC-B can increase the binding affinity to its substrate. In addition, the slow release of BSA from R-HDA-B may increase the enzymatic activity of R-HDA-B. Our study is expected to provide strategies to develop protein-albumin conjugate with high therapeutic potential. Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Chen, Tao; Su, Dian; Gruenhagen, Jason; Gu, Christine; Li, Yi; Yehl, Peter; Chetwyn, Nik P; Medley, Colin D
2016-01-05
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) offer new therapeutic options for advanced cancer patients through precision killing with fewer side effects. The stability and efficacy of ADCs are closely related, emphasizing the urgency and importance of gaining a comprehensive understanding of ADC stability. In this work, a chemical de-conjugation approach was developed to investigate the in-situ stability of the small molecule drug while it is conjugated to the antibody. This method involves chemical-mediated release of the small molecule drug from the ADC and subsequent characterization of the released small molecule drug by HPLC. The feasibility of this technique was demonstrated utilizing a model ADC containing a disulfide linker that is sensitive to the reducing environment within cancer cells. Five reducing agents were screened for use in de-conjugation; tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine (TCEP) was selected for further optimization due to its high efficiency and clean impurity profile. The optimized de-conjugation assay was shown to have excellent specificity and precision. More importantly, it was shown to be stability indicating, enabling the identification and quantification of the small molecule drug and its degradation products under different formulation pHs and storage temperatures. In summary, the chemical de-conjugation strategy demonstrated here offers a powerful tool to assess the in-situ stability of small molecule drugs on ADCs and the resulting information will shed light on ADC formulation/process development and storage condition selection. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Cai, Bingqing; Saito, Anna; Ikeda, Shinya
2018-01-24
Whey protein adsorbed to an interface forms a viscoelastic interfacial film but is displaced competitively from the interface by a small-molecule surfactant added afterward. The present study evaluated the impact of the covalent conjugation of high- or low-molecular-weight sodium alginate (HA or LA) to whey protein isolate (WPI) via the Maillard reaction on the ability of whey protein to resist surfactant-induced competitive displacement from the air-water interface. Surfactant added after the pre-adsorption of conjugate to the interface increased surface pressure. At a given surface pressure, the WPI-LA conjugate showed a significantly higher interfacial area coverage and lower interfacial film thickness compared to those of the WPI-HA conjugate or unconjugated WPI. The addition of LA to the aqueous phase had little effect on the interfacial area and thickness of pre-adsorbed WPI. These results suggest the importance of the molecular weight of the polysaccharide moiety in determining interfacial properties of whey protein-alginate conjugates.
-
Taylor, Rhys Dylan; Asamitsu, Sefan; Takenaka, Tomohiro; Yamamoto, Makoto; Hashiya, Kaori; Kawamoto, Yusuke; Bando, Toshikazu; Nagase, Hiroki; Sugiyama, Hiroshi
2014-01-27
Hairpin N-methylpyrrole-N-methylimidazole polyamide seco-CBI conjugates 2-6 were designed for synthesis by Fmoc solid-phase synthesis, and their DNA-alkylating activities against the Kras codon 13 mutation were compared by high-resolution denaturing gel electrophoresis with 225 base pair (bp) DNA fragments. Conjugate 5 had high reactivity towards the Kras codon 13 mutation site, with alkylation occurring at the A of the sequence 5'-ACGTCACCA-3' (site 2), including minor 1 bp-mismatch alkylation against wild type 5'-ACGCCACCA-3' (site 3). Conjugate 6, which differs from conjugate 5 by exchanging one Py unit with a β unit, showed high selectivity but only weakly alkylated the A of 5'-ACGTCACCA-3' (site 2). The hairpin polyamide seco-CBI conjugate 5 thus alkylates according to Dervan's pairing rule with the pairing recognition which β/β pair targets T-A and A-T pairs. SPR and a computer-minimized model suggest that 5 binds to the target sequence with high affinity in a hairpin conformation, allowing for efficient DNA alkylation. Copyright © 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Phase alteration compensation in reflection digital holography
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rincon, O; Amezquita, R; Monroy, F
2011-01-01
The phase maps obtained from digital holographic microscopy techniques carry information about the axial lengths of the object under study. Additionally, these phase maps have information of tilt and curvatures with origin in the off-axis geometry and the magnification lenses system, respectively. Only a complete compensation of these extra phases allows a correct interpretation of the phase information. In this article a numerical strategy to compensate for these alterations is designed, using a phase mask located in different planes. This strategy is applied in the measurement of a phase steps plate using a digital holography setup.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fukunishi, H.; Lanzerotti, L.J.; MaClennan, C.G.
1975-01-01
By using magnetic data measured at a network of stations extending from L approx. 3.2 to L approx. 4.4 and at a station in the conjugate area, ellipticities in the three orthogonal planes (H-D, H-Z, and D-Z) for the frequency range 2-5 mHz were computed continuously by the cross-spectral matrix method over 10 days with various levels of magnetic activity. The ellipticity diagrams in the H-D plane show that, except for the time interval during the main phase of a major magnetic storm, the sense of polarization reverses every day across local noon, with a left-hand polarization observed during local morning hours and a right-hand polarization observed during local evening hours, regardless of the level of magnetic activity. The second reversal of the sense of polarization occurs generally around approx. 2000 LT. The ellipticity diagrams in the H-Z plane show a predominantly clockwise polarization throughout the day, while the diurnal variation of the ellipticity in the D-Z plane tends to be confused. As to the latitude dependence of the wave phase, it is found that the D component oscillations are almost in phase at all latitudes, while the H component oscillations have advanced phase shifts at the lower-latitude stations. As to the conjugate dependence of wave phase, it is found that the D component oscillations are almost out of phase, while the H component oscillations are almost in phase atthe conjugate pair stations. These polarization characteristics are discussed in terms of external driving sources coupling to the shear Alfven waves of the local resonant field lines. Possible energy sources of Pc 5 waves are also discussed on the basis of the local time dependence of the sense of polarization
-
Photoluminescence in conjugated polymers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Furst, J.E.; Laugesen, R.; Dastoor, P.; McNeill, C.
2002-01-01
Full text: Conjugated polymers combine the electronic and optical properties of semiconductors with the processability of polymers. They contain a sequence of alternate single and double carbon bonds so that the overlap of unhybridised p z orbitals creates a delocalised ρ system which gives semiconducting properties with p-bonding (valence) and p* -antibonding (conduction) bands. Photoluminesence (PL) in conjugated polymers results from the radiative decay of singlet excitons confined to a single chain. The present work is the first in a series of studies in our laboratory that will characterize the optical properties of conjugated polymers. The experiment involves the illumination of thin films of conjugated polymer with UV light (I=360 nm) and observing the subsequent fluorescence using a custom-built, fluorescence spectrometer. Photoluminesence spectra provide basic information about the structure of the polymer film. A typical spectrum is shown in the accompanying figure. The position of the first peak is related to the polymer chain length and resolved multiple vibronic peaks are an indication of film structure and morphology. We will also present results related to the optical degradation of these materials when exposed to air and UV light
-
Bio-Conjugates for Nanoscale Applications
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Villadsen, Klaus
Bio-conjugates for Nanoscale Applications is the title of this thesis, which covers three different projects in chemical bio-conjugation research, namely synthesis and applications of: Lipidated fluorescent peptides, carbohydrate oxime-azide linkers and N-aryl O-R2 oxyamine derivatives. Lipidated...
-
Lima, Igo T.; Risko, Chad; Aziz, Saadullah Gary; Da Silva Filho, Demé trio A Da Silva; Bredas, Jean-Luc
2014-01-01
Donor-acceptor π-conjugated copolymers are of interest for a wide range of electronic applications, including field-effect transistors and solar cells. Here, we present a density functional theory (DFT) study of the impact of varying the conjugation pathway on the geometric, electronic, and optical properties of donor-acceptor systems. We consider both linear ("in series"), traditional conjugation among the donor-acceptor moieties versus structures where the acceptor units are appended orthogonally to the linear, donor-only conjugated backbone. Long-range-corrected hybrid functionals are used in the investigation with the values of the tuned long-range separation parameters providing an estimate of the extent of conjugation as a function of the oligomer architecture. Considerable differences in the electronic and optical properties are determined as a function of the nature of the conjugation pathway, features that should be taken into account in the design of donor-acceptor copolymers.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McCallum, J.C.; Simpson, T.W.; Mitchell, I.V.
1994-01-01
Time resolved optical reflectivity (TRR) has been used to measure the growth kinetics associated with the amorphous-to-gamma and gamma-to-alpha phase transitions in ion-beam amorphised c-axis oriented α-Al 2 O 3 . The optical reflectivity technique allows the recrystallisation behaviour to be monitored dynamically during regrowth so that the growth kinetics associated with the two phase transitions can be measured simply and accurately from a relatively small number of samples. The amorphous-to-gamma and gamma-to-alpha phase transitions were studied over the temperature ranges of 670-770 C and 900-1070 C, respectively. The growth kinetics obtained for the two transitions are compared to previous work. ((orig.))
-
Du, Ju; Bandara, H M H N; Du, Ping; Huang, Hui; Hoang, Khang; Nguyen, Dang; Mogarala, Sri Vasudha; Smyth, Hugh D C
2015-05-04
The objective of this study was to develop a functionally enhanced antibiotic that would improve the therapeutic activity against bacterial biofilms. Tobramycin was chemically conjugated with polyethylene glycol (PEG) via site-specific conjugation to form PEGylated-tobramycin (Tob-PEG). The antibacterial efficacy of Tob-PEG, as compared to tobramycin, was assessed on the planktonic phase and biofilms phase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC80) of Tob-PEG was higher (13.9 μmol/L) than that of tobramycin (1.4 μmol/L) in the planktonic phases. In contrast, the Tob-PEG was approximately 3.2-fold more effective in eliminating bacterial biofilms than tobramycin. Specifically, Tob-PEG had a MIC80 lower than those exhibited by tobramycin (27.8 μmol/L vs 89.8 μmol/L). Both confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy further confirmed these data. Thus, modification of antimicrobials by PEGylation appears to be a promising approach for overcoming the bacterial resistance in the established biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
-
Phase mixing of Alfvén waves in axisymmetric non-reflective magnetic plasma configurations
Petrukhin, N. S.; Ruderman, M. S.; Shurgalina, E. G.
2018-02-01
We study damping of phase-mixed Alfvén waves propagating in non-reflective axisymmetric magnetic plasma configurations. We derive the general equation describing the attenuation of the Alfvén wave amplitude. Then we applied the general theory to a particular case with the exponentially divergent magnetic field lines. The condition that the configuration is non-reflective determines the variation of the plasma density along the magnetic field lines. The density profiles exponentially decreasing with the height are not among non-reflective density profiles. However, we managed to find non-reflective profiles that fairly well approximate exponentially decreasing density. We calculate the variation of the total wave energy flux with the height for various values of shear viscosity. We found that to have a substantial amount of wave energy dissipated at the lower corona, one needs to increase shear viscosity by seven orders of magnitude in comparison with the value given by the classical plasma theory. An important result that we obtained is that the efficiency of the wave damping strongly depends on the density variation with the height. The stronger the density decrease, the weaker the wave damping is. On the basis of this result, we suggested a physical explanation of the phenomenon of the enhanced wave damping in equilibrium configurations with exponentially diverging magnetic field lines.
-
Hyaluronan-conjugated liposomes encapsulating gemcitabine for breast cancer stem cells
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Han NK
2016-04-01
Full Text Available Na-Kyung Han,1,* Dae Hwan Shin,1,* Jung Seok Kim,1 Kwon Yeon Weon,2 Chang-Young Jang,1 Jin-Seok Kim1 1Research Center for Cell Fate Control (RCCFC and College of Pharmacy, Sookmyung Women’s University, Seoul, 2College of Pharmacy, Catholic University of Daegu, Gyeongbuk, Korea *These authors contributed equally to this work Abstract: Investigation of potential therapeutics for targeting breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs is important because these cells are regarded as culprit of breast cancer relapse. Accomplishing this kind of strategy requires a specific drug-delivery system using the distinct features of liposomes. Studies on targeted liposomal delivery systems have indicated the conjugation of hyaluronan (HA, a primary ligand for CD44 surface markers, as an appropriate method for targeting BCSCs. For this study, enriched BCSCs were obtained by culturing MCF-7 breast cancer cells in nonadherent conditions. The enriched BCSCs were challenged with HA-conjugated liposomes encapsulating gemcitabine (2, 2-difluoro-2-deoxycytidine, GEM. In vitro study showed that the HA-conjugated liposomes significantly enhanced the cytotoxicity, anti-migration, and anti-colony formation abilities of GEM through targeting of CD44 expressed on BCSCs. In pharmacokinetic study, area under the drug concentration vs time curve (AUC of the immunoliposomal GEM was 3.5 times higher than that of free GEM, indicating that the HA-conjugated liposomes enhanced the stability of GEM in the bloodstream and therefore prolonged its half-life time. The antitumor effect of the immunoliposomal GEM was 3.3 times higher than that of free GEM in a xenograft mouse model, probably reflecting the unique targeting of the CD44 receptor by HA and the increased cytotoxicity and stability through the liposomal formulation. Furthermore, marginal change in body weight demonstrated that the use of liposomes considerably reduced the systemic toxicity of GEM on normal healthy cells. Taken together
-
Doğaç, Yasemin Ispirli; Teke, Mustafa
2016-04-01
We reported natural polymer-conjugated magnetic featured urease systems for removal of urea effectively. The optimum temperature (20-60 °C), optimum pH (3.0-10.0), kinetic parameters, thermal stability (4-70 °C), pH stability (4.0-9.0), operational stability (0-250 min), reusability (18 times) and storage stability (24 weeks) were studied for characterisation of the urease-encapsulated biocompatible polymer-conjugated magnetic beads. Also, the surface groups and chemical structure of the magnetic beads were determined by using attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR). The all urease-encapsulated magnetic beads protected their stability of 30-45 % relative activity at 70 °C. A significant increase was observed at their pH stability compared with the free urease for both acidic and alkaline medium. Besides this, their repeatability activity were approximately 100 % during 4(th) run. They showed residual activity of 50 % after 16 weeks. The importance of this work is enhancement stability of immobilised urease by biocompatible polymer-conjugated magnetic beads for the industrial application based on removal of urea.
-
Decker, A. J.
1982-01-01
The use of a Nd:YAG laser to record holographic motion pictures of time-varying reflecting objects and time-varying phase objects is discussed. Sample frames from both types of holographic motion pictures are presented. The holographic system discussed is intended for three-dimensional flow visualization of the time-varying flows that occur in jet-engine components.
-
Organometallic B12-DNA conjugate
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hunger, Miriam; Mutti, Elena; Rieder, Alexander
2014-01-01
Design, synthesis, and structural characterization of a B12-octadecanucleotide are presented herein, a new organometallic B12-DNA conjugate. In such covalent conjugates, the natural B12 moiety may be a versatile vector for controlled in vivo delivery of oligonucleotides to cellular targets in hum...
-
The Conjugate Acid-Base Chart.
Treptow, Richard S.
1986-01-01
Discusses the difficulties that beginning chemistry students have in understanding acid-base chemistry. Describes the use of conjugate acid-base charts in helping students visualize the conjugate relationship. Addresses chart construction, metal ions, buffers and pH titrations, and the organic functional groups and nonaqueous solvents. (TW)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Takuya Anzai
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Due to their macromolecular nature, conjugated polymers can be relatively easily aligned by applying a variety of processes resulting in either elongation or ordering of their conjugated backbones. Processes that induce chain alignment include electrospinning, mechanical rubbing, epitaxial growth, and nanoconfinement and unidirectional deposition techniques such as off-center spin-coating. In this study, we compare these deposition techniques by applying them to a green-emitting conjugated polymer material that exhibits liquid crystalline phase behavior. Our study reveals that while methods such as electrospinning and mechanical rubbing can be useful to locally generate polymer chain alignment, the combination of epitaxial growth using 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene as crystallizing agent with off-center spin-coating results in the formation of anisotropic nanofiber-like structures with enhanced crystallinity degree and polarized light-emission properties. The unidirectional epitaxial growth was also applied to a red-emitting polymer that exhibits polarization ratios up to 4.1. Our results emphasize that this simple solution formulation and process can be used for the fabrication of polarized thin films of a variety of conjugated polymers with potential applications in the advanced display technologies or analytical equipment fields.
-
REVIEW ARTICLE Conjugated Hyperbilirubinaemia in Early Infancy ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
REVIEW ARTICLE Conjugated Hyperbilirubinaemia in Early Infancy. AOK Johnson. Abstract. Conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia exists when the conjugated serum bilirubin level is more than 2 mg/dl or more than 20 per cent of the total serum bilirubin. It is always pathological in early infancy. The causes are many and diverse ...
-
Marvania, Bhavin; Kakadiya, Rajesh; Christian, Wilson; Chen, Tai-Lin; Wu, Ming-Hsi; Suman, Sharda; Tala, Kiran; Lee, Te-Chang; Shah, Anamik; Su, Tsann-Long
2014-08-18
We synthesized a series of phenyl N-mustard-4-anilinoquinoline conjugates to study their antitumorigenic effects. These agents were prepared by the condensation of 4-[N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenyl isocyanate with 6-amino-4-methylamino or 4-anilinoquinolines. The structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies revealed that the C2-methylquinoline derivatives (18a-o) were generally more cytotoxic than the C2-phenylquinoline conjugates (23a-d) in inhibiting the cell growth of various human tumor cell lines in vitro. However, the methylamino or aniline substituents at C4 of quinoline did not influence the cytotoxic effects. The title conjugates were capable of inducing DNA cross-linking and promoting cell-cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. This study demonstrates that phenyl N-mustard-4-anilinoquinoline conjugates are generally more potent than phenyl N-mustard-4-anilinoquinazoline conjugates against the cell growth of various tumor cell-lines. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
-
Self/anti-self charge conjugate states in the helicity basis
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dvoeglazov, Valeriy V.
2013-01-01
We construct self/anti-self charge conjugate (Majorana-like) states for the (1/2,0)⊕(0,1/2) representation of the Lorentz group, and their analogs for higher spins within the quantum field theory. The problem of the basis rotations and that of the selection of phases in the Dirac-like and Majorana-like field operators are considered. The discrete symmetries properties (P, C, T) are studied. Particular attention has been paid to the question of (anti)commutation of the Charge conjugation operator and the Parity in the helicity basis. Dynamical equations have also been presented. In the (1/2,0)⊕(0,1/2) representation they obey the Dirac-like equation with eight components, which has been first introduced by Markov. Thus, the Fock space for corresponding quantum fields is doubled (as shown by Ziino). The chirality and the helicity (two concepts which are frequently confused in the literature) for Dirac and Majorana states have been discussed
-
Smith, J. A.; Cooper, K.; Randolph, M.
1984-01-01
A classical description of the one dimensional radiative transfer treatment of vegetation canopies was completed and the results were tested against measured prairie (blue grama) and agricultural canopies (soybean). Phase functions are calculated in terms of directly measurable biophysical characteristics of the canopy medium. While the phase functions tend to exhibit backscattering anisotropy, their exact behavior is somewhat more complex and wavelength dependent. A Monte Carlo model was developed that treats soil surfaces with large periodic variations in three dimensions. A photon-ray tracing technology is used. Currently, the rough soil surface is described by analytic functions and appropriate geometric calculations performed. A bidirectional reflectance distribution function is calculated and, hence, available for other atmospheric or canopy reflectance models as a lower boundary condition. This technique is used together with an adding model to calculate several cases where Lambertian leaves possessing anisotropic leaf angle distributions yield non-Lambertian reflectance; similar behavior is exhibited for simulated soil surfaces.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ye, Haijun; Jiang, Fangqing; Li, Hongqin; Xu, Zheng; Yin, Jiao; Zhu, Hui
2017-01-01
Graphical abstract: Polymeric Schiff base (PSB) exhibits a stable cyclability as an organic Li-ion battery anode Display Omitted -- Highlights: •A conjugated Schiff base polymer has been synthesized by a solid-phase reaction. •The polymer suppresses the dissolution of organic monomer into the organic electrolyte. •The polymer demonstrates high reversible capacity and excellent cyclic performance. -- Abstract: The redox-active organic compounds show great potentials as anodes for high energy density Li-ion batteries (LIBs), comparing with the traditional transition metal-based inorganic compounds. However, the inevitable dissolution behaviors of these organics in organic electrolyte will arouse the recession in their cycling stabilities. To circumvent this problem, we successfully applied an electrochemically active imine group to connect the carbonyl compound to form conjugated polymer, where the occurrence of multi-electron reactions suppressed the dissolution of anthraquinone in the organic electrolyte with improved cycling stability and high capacity for LIBs. In detail, by virtue of a facile solid-phase reaction between 1, 4-diaminoanthraquinone (14DAAQ) and p-phthalaldehyde (PPD), a highly conjugated polymeric Schiff base (PSB) was synthesized. The obtained PSB exhibited a reversible specific capacity of 175 mAh g −1 at a current density of 10 mA g −1 . In addition, after 100 cycles, a cycling stability with 90% capacity retention can be maintained, manifesting a promising application of the organic material in high performance anodes for LIBs.
-
Canonically conjugate pairs and phase operators
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Schoenhammer, K.
2002-01-01
For quantum mechanics on a lattice the position ('particle number') operator and the quasimomentum ('phase') operator obey canonical commutation relations (CCRs) only on a dense set of the Hilbert space. We compare exact numerical results for a particle in a linear and a quadratic potential on the lattice with the expectations, when the CCRs are assumed to be strictly obeyed. Only for sufficiently smooth eigenfunctions does this lead to reasonable results. In the long time limit the use of the CCRs can lead to a qualitatively wrong dynamics even if the initial state is in the dense set
-
Hamidi, Ahd; Verdijk, Pauline; Kreeftenberg, Hans
2014-01-01
Introduction of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine in low- and middle-income countries has been limited by cost and availability of Hib conjugate vaccines for a long time. It was previously recognized by the Institute for Translational Vaccinology (Intravacc, originating from the former Vaccinology Unit of the National Institute of Public Health [RIVM] and the Netherlands Vaccine Institute [NVI]) that local production of a Hib conjugate vaccine would increase the affordability and sustainability of the vaccine and thereby help to speed up Hib introduction in these countries. A new affordable and a non-infringing production process for a Hib conjugate vaccine was developed, including relevant quality control tests, and the technology was transferred to a number of vaccine manufacturers in India, Indonesia, and China. As part of the Hib technology transfer project managed by Intravacc, a preclinical toxicity study was conducted in the Netherlands to test the safety and immunogenicity of this new Hib conjugate vaccine. The data generated by this study were used by the technology transfer partners to accelerate the clinical development of the new Hib conjugate vaccine. A repeated dose toxicity and local tolerance study in rats was performed to assess the reactogenicity and immunogenicity of a new Hib conjugate vaccine compared to a licensed vaccine. The results showed that the vaccine was well tolerated and immunogenic in rats, no major differences in both safety and immunogenicity in rats were found between the vaccine produced according to the production process developed by Intravacc and the licensed one. Rats may be useful to verify the immunogenicity of Hib conjugate vaccines and for preclinical evaluation. In general, nonclinical evaluation of the new Hib conjugate vaccine, including this proof of concept (safety and immunogenicity study in rats), made it possible for technology transfer partners, having implemented the original process with no changes
-
Microfluidic Fabrication of Conjugated Polymer Sensor Fibers
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Yoo, Imsung; Song, Simon [Hanyang University, Seoul (Korea, Republic of)
2014-10-15
We propose a fabrication method for polydiacetylene (PDA)-embedded hydrogel microfibers on a microfluidic chip. These fibers can be applied to the detection of cyclodextrines (CDs), which are a family of sugar and aluminum ions. PDA, a family of conjugated polymers, has unique characteristics when used for a sensor, because it undergoes a blue-to-red color transition and nonfluorescence-to-fluorescence transition in response to environmental stimulation. PDAs have different sensing characteristics depending on the head group of PCDA. By taking advantage of ionic crosslinking-induced hydrogel formation and the 3D hydrodynamic focusing effect on a microfluidic chip, PCDA-EDEA-derived diacetylene (DA) monomer-embedded microfibers were successfully fabricated. UV irradiation of the fibers afforded blue-colored PDA, and the resulting blue PDA fibers underwent a phase transition to red and emitted red fluorescence upon exposure to CDs and aluminum ions. Their fluorescence intensity varied depending on the CDs and aluminum ion concentrations. This phase transition was also observed when the fibers were dried.
-
Methotrexate and epirubicin conjugates as potential antitumor drugs
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Szymon Wojciech Kmiecik
2017-07-01
Full Text Available Introduction: The use of hybrid molecules has become one of the most significant approaches in new cytotoxic drug design. This study describes synthesis and characterization of conjugates consisting of two well-known and characterized chemotherapeutic agents: methotrexate (MTX and epirubicin (EPR. The synthesized conjugates combine two significant anticancer strategies: combinatory therapy and targeted therapy. These two drugs were chosen because they have different mechanisms of action, which can increase the anticancer effect of the obtained conjugates. MTX, which is a folic acid analog, has high cytotoxic properties and can serve as a targeting moiety that can reach folate receptors (FRs overexpresing tumor cells. Combination of nonselective drugs such as EPR with MTX can increase the selectivity of the obtained conjugates, while maintaining the high cytotoxic properties.Materials and methods: Conjugates were purified by RP-HPLC and the structure was investigated by MS and MS/MS methods. The effect of the conjugates on proliferation of LoVo, LoVo/Dx, MCF-7 and MV-4-11 human cancer cell lines was determined by SRB or MTT assay.Results: The conjugation reaction results in the formation of monosubstituted (α, γ and disubstituted MTX derivatives. In vitro proliferation data demonstrate that the conjugates synthesized in our study show lower cytotoxic properties than both chemotherapeutics used alone.Discussion: Epirubicin cytotoxicity was not observed in obtained conjugates. Effective drugs release after internalization needs further investigation.
-
Yamauchi, Toyohiko; Fukami, Tadashi; Iwai, Hidenao; Yamashita, Yutaka
2012-03-01
Embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells, which are cell lines derived from teratocarcinomas, have characteristics in common with stem cells and differentiate into many kinds of functional cells. Similar to embryonic stem (ES) cells, undifferentiated EC cells form multi-layered spheroids. In order to visualize the three-dimensional structure of multilayered EC cells without labeling, we employed full-field interference microscopy with the aid of a low-coherence quantitative phase microscope, which is a reflection-type interference microscope employing the digital holographic technique with a low-coherent light source. Owing to the low-coherency of the light-source (halogen lamp), only the light reflected from reflective surface at a specific sectioning height generates an interference image on the CCD camera. P19CL6 EC cells, derived from mouse teratocarcinomas, formed spheroids that are about 50 to 200 micrometers in diameter. Since the height of each cell is around 10 micrometers, it is assumed that each spheroid has 5 to 20 cell layers. The P19CL6 spheroids were imaged in an upright configuration and the horizontally sectioned reflection images of the sample were obtained by sequentially and vertically scanning the zero-path-length height. Our results show the threedimensional structure of the spheroids, in which plasma and nuclear membranes were distinguishably imaged. The results imply that our technique is further capable of imaging induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells for the assessment of cell properties including their pluripotency.
-
Reflections on the development of a pre-service language curriculum for the BEd (Foundation Phase
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zubeida Desai
2014-12-01
Full Text Available The initiative of the Department of Higher Education and Training (DHET in South Africa to strengthen foundation phase teaching has resulted in the development of new foundation phase (Grades R–3 programmes at institutions that did not previously offer them. In this article we reflect on the conceptualisation and development of a pre-service language curriculum for one such programme. We base our discussion on principles that underpin teacher education programme development for early childhood education and on issues and insights about appropriate language curriculum content for a foundation phase teacher. Whilst awaiting the outcome of our accreditation, the authors, as two of the persons who assisted in the design of the language curriculum, thought it appropriate to subject the curriculum to an internal scrutiny whilst we prepare to offer the programme. This internal dialogue is informed by the literature on early language development, particularly in multilingual contexts such as in South Africa.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Helena Gonzalez
2008-01-01
Full Text Available Background Benzophenone-3 (BZ-3 is a common ultraviolet (UV absorbing compound in sunscreens. It is the most bioavailable species of all UV-absorbing compounds after topical application and can be found in plasma and urine. Objectives The aim of this study was to develop a reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC method for determining the amounts BZ-3 and its metabolite 2,4-dihydroxybenzophenone (DHB in human urine. The method had to be suitable for handling a large number of samples. It also had to be rapid and simple, but still sensitive, accurate and reproducible. The assay was applied to study the urinary excretion pattern after repeated whole-body applications of a commercial sunscreen, containing 4% BZ-3, to 25 healthy volunteers. Methods Each sample was analyzed with regard to both conjugated/non-conjugated BZ-3 and conjugated/non-conjugated DHB, since both BZ-3 and DHB are extensively conjugated in the body. Solid-phase extraction (SPE with C8 columns was followed by reverse-phase HPLC. For separation a Genesis C18 column was used with an acethonitrile-water mobile phase and the UV-detector was set at 287 nm. Results The assay was linear r 2 > 0.99, with detection limits for BZ-3 and DHB of 0.01 µmol L -1 and 0.16 µmol L -1 respectively. Relative standard deviation (RSD was less than 10% for BZ-3 and less than 13% for DHB. The excretion pattern varied among the human volunteers; we discerned different patterns among the individuals. Conclusions The reverse-phase HPLC assay and extraction procedures developed are suitable for use when a large number of samples need to be analyzed and the method fulfilled our objectives. The differences in excretion pattern may be due to differences in enzyme activity but further studies, especially about genetic polymorphism, need to be performed to verify this finding.
-
A conjugate thermo-electric model for a composite medium.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Oscar Chávez
Full Text Available Electrical transmission signals have been used for decades to characterize the internal structure of composite materials. We theoretically analyze the transmission of an electrical signal through a composite material which consists of two phases with different chemical compositions. We assume that the temperature of the biphasic system increases as a result of Joule heating and its electrical resistivity varies linearly with temperature; this last consideration leads to simultaneously study the electrical and thermal effects. We propose a nonlinear conjugate thermo-electric model, which is solved numerically to obtain the current density and temperature profiles for each phase. We study the effect of frequency, resistivities and thermal conductivities on the current density and temperature. We validate the prediction of the model with comparisons with experimental data obtained from rock characterization tests.
-
Coherent beam combination via microparticle plasma modes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rogovin, D.; Shen, T.P.
1988-01-01
Recently, there have been interesting observations and calculations on phase conjugation via degenerate four-wave mixing in gold colloids. The generation of phase conjugate radiation in these media arises from and reflects the creation of static index grating imposed on the electronic wave functions within the microparticles. These encouraging findings motivate us to consider the possibility of generating moving index gratings in these media with possible applications to coherent beam combination
-
Sexton, E. A.; Snelson, C. M.; Chipman, V.; Emer, D. F.; White, R. L.; Emmitt, R.; Wright, A. A.; Drellack, S.; Huckins-Gang, H.; Mercadante, J.; Floyd, M.; McGowin, C.; Cothrun, C.; Bonal, N.
2013-12-01
An objective of the Source Physics Experiment (SPE) is to identify low-yield nuclear explosions from a regional distance. Low-yield nuclear explosions can often be difficult to discriminate among the clutter of natural and man-made explosive events (e.g., earthquakes and mine blasts). The SPE is broken into three phases. Phase I has provided the first of the physics-based data to test the empirical models that have been used to discriminate nuclear events. The Phase I series of tests were placed within a highly fractured granite body. The evolution of the project has led to development of Phase II, to be placed within the opposite end member of geology, an alluvium environment, thereby increasing the database of waveforms to build upon in the discrimination models. Both the granite and alluvium sites have hosted nearby nuclear tests, which provide comparisons for the chemical test data. Phase III of the SPE is yet to be determined. For Phase II of the experiment, characterization of the location is required to develop the geologic/geophysical models for the execution of the experiment. Criteria for the location are alluvium thickness of approximately 170 m and a water table below 170 m; minimal fracturing would be ideal. A P-wave mini-vibroseis survey was conducted at a potential site in alluvium to map out the subsurface geology. The seismic reflection profile consisted of 168 geophone stations, spaced 5 m apart. The mini-vibe was a 7,000-lb peak-force source, starting 57.5 m off the north end of the profile and ending 57.5 m past the southern-most geophone. The length of the profile was 835 m. The source points were placed every 5 m, equally spaced between geophones to reduce clipping. The vibroseis sweep was from 20 Hz down to 180 Hz over 8 seconds, and four sweeps were stacked at each shot location. The shot gathers show high signal-to-noise ratios with clear first arrivals across the entire spread and the suggestion of some shallow reflectors. The data were
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sugahara, M.; Ando, N.; Kaneda, H.; Nagai, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Yoshikawa, N.
1985-01-01
Theoretical and Experimental study on granular superconductors shows that they are classified into two groups; fixed-phase superconductor (theta-superconductor) and fixed-pair-number superconductor (N-superconductor) and that a new macroscopic quantum device with conjugate property to Josephson effect can be made by use of N-superconductors
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sujiet Puthenveetil
Full Text Available Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs are no longer an unknown entity in the field of cancer therapy with the success of marketed ADCs like ADCETRIS and KADCYLA and numerous others advancing through clinical trials. The pursuit of novel cytotoxic payloads beyond the mictotubule inhibitors and DNA damaging agents has led us to the recent discovery of an mRNA splicing inhibitor, thailanstatin, as a potent ADC payload. In our previous work, we observed that the potency of this payload was uniquely tied to the method of conjugation, with lysine conjugates showing much superior potency as compared to cysteine conjugates. However, the ADC field is rapidly shifting towards site-specific ADCs due to their advantages in manufacturability, characterization and safety. In this work we report the identification of a highly efficacious site-specific thailanstatin ADC. The site of conjugation played a critical role on both the in vitro and in vivo potency of these ADCs. During the course of this study, we developed a novel methodology of loading a single site with multiple payloads using an in situ generated multi-drug carrying peptidic linker that allowed us to rapidly screen for optimal conjugation sites. Using this methodology, we were able to identify a double-cysteine mutant ADC delivering four-loaded thailanstatin that was very efficacious in a gastric cancer xenograft model at 3mg/kg and was also shown to be efficacious against T-DM1 resistant and MDR1 overexpressing tumor cell lines.
-
Puthenveetil, Sujiet; He, Haiyin; Loganzo, Frank; Musto, Sylvia; Teske, Jesse; Green, Michael; Tan, Xingzhi; Hosselet, Christine; Lucas, Judy; Tumey, L Nathan; Sapra, Puja; Subramanyam, Chakrapani; O'Donnell, Christopher J; Graziani, Edmund I
2017-01-01
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are no longer an unknown entity in the field of cancer therapy with the success of marketed ADCs like ADCETRIS and KADCYLA and numerous others advancing through clinical trials. The pursuit of novel cytotoxic payloads beyond the mictotubule inhibitors and DNA damaging agents has led us to the recent discovery of an mRNA splicing inhibitor, thailanstatin, as a potent ADC payload. In our previous work, we observed that the potency of this payload was uniquely tied to the method of conjugation, with lysine conjugates showing much superior potency as compared to cysteine conjugates. However, the ADC field is rapidly shifting towards site-specific ADCs due to their advantages in manufacturability, characterization and safety. In this work we report the identification of a highly efficacious site-specific thailanstatin ADC. The site of conjugation played a critical role on both the in vitro and in vivo potency of these ADCs. During the course of this study, we developed a novel methodology of loading a single site with multiple payloads using an in situ generated multi-drug carrying peptidic linker that allowed us to rapidly screen for optimal conjugation sites. Using this methodology, we were able to identify a double-cysteine mutant ADC delivering four-loaded thailanstatin that was very efficacious in a gastric cancer xenograft model at 3mg/kg and was also shown to be efficacious against T-DM1 resistant and MDR1 overexpressing tumor cell lines.
-
Live Cell Refractometry Using Hilbert Phase Microscopy and Confocal Reflectance Microscopy†
Lue, Niyom; Choi, Wonshik; Popescu, Gabriel; Yaqoob, Zahid; Badizadegan, Kamran; Dasari, Ramachandra R.; Feld, Michael S.
2010-01-01
Quantitative chemical analysis has served as a useful tool for understanding cellular metabolisms in biology. Among many physical properties used in chemical analysis, refractive index in particular has provided molecular concentration that is an important indicator for biological activities. In this report, we present a method of extracting full-field refractive index maps of live cells in their native states. We first record full-field optical thickness maps of living cells by Hilbert phase microscopy and then acquire physical thickness maps of the same cells using a custom-built confocal reflectance microscope. Full-field and axially averaged refractive index maps are acquired from the ratio of optical thickness to physical thickness. The accuracy of the axially averaged index measurement is 0.002. This approach can provide novel biological assays of label-free living cells in situ. PMID:19803506
-
Live cell refractometry using Hilbert phase microscopy and confocal reflectance microscopy.
Lue, Niyom; Choi, Wonshik; Popescu, Gabriel; Yaqoob, Zahid; Badizadegan, Kamran; Dasari, Ramachandra R; Feld, Michael S
2009-11-26
Quantitative chemical analysis has served as a useful tool for understanding cellular metabolisms in biology. Among many physical properties used in chemical analysis, refractive index in particular has provided molecular concentration that is an important indicator for biological activities. In this report, we present a method of extracting full-field refractive index maps of live cells in their native states. We first record full-field optical thickness maps of living cells by Hilbert phase microscopy and then acquire physical thickness maps of the same cells using a custom-built confocal reflectance microscope. Full-field and axially averaged refractive index maps are acquired from the ratio of optical thickness to physical thickness. The accuracy of the axially averaged index measurement is 0.002. This approach can provide novel biological assays of label-free living cells in situ.
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Third Generation PAMAM Dendrimer Conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Mohammad Najlah
2017-10-01
Full Text Available The present study compares the use of high generation G3 and low generation G0 Polyamidoamine (PAMAM dendrimers as drug carriers of naproxen (NAP, a poorly water soluble drug. Naproxen was conjugated to G3 in different ratios and to G0 in a 1:1 ratio via a diethylene glycol linker. A lauroyl chain (L, a lipophilic permeability enhancer, was attached to G3 and G0 prodrugs. The G3 and G0 conjugates were more hydrophilic than naproxen as evaluated by the measurement of partitioning between 1-octanol and a phosphate buffer at pH 7.4 and pH 1.2. The unmodified surface PAMAM-NAP conjugates showed significant solubility enhancements of NAP at pH 1.2; however, with the number of NAP conjugated to G3, this was limited to 10 molecules. The lactate dehydrogenase (LDH assay indicated that the G3 dendrimer conjugates had a concentration dependent toxicity towards Caco-2 cells. Attaching naproxen to the surface of the dendrimer increased the IC50 of the resulting prodrugs towards Caco-2 cells. The lauroyl G3 conjugates showed the highest toxicity amongst the PAMAM dendrimer conjugates investigated and were significantly more toxic than the lauroyl-G0-naproxen conjugates. The permeability of naproxen across monolayers of Caco-2 cells was significantly increased by its conjugation to either G3 or G0 PAMAM dendrimers. Lauroyl-G0 conjugates displayed considerably lower cytotoxicity than G3 conjugates and may be preferable for use as a drug carrier for low soluble drugs such as naproxen.
-
Numerical Modeling of Conjugate Heat Transfer in Fluid Network
Majumdar, Alok
2004-01-01
Fluid network modeling with conjugate heat transfer has many applications in Aerospace engineering. In modeling unsteady flow with heat transfer, it is important to know the variation of wall temperature in time and space to calculate heat transfer between solid to fluid. Since wall temperature is a function of flow, a coupled analysis of temperature of solid and fluid is necessary. In cryogenic applications, modeling of conjugate heat transfer is of great importance to correctly predict boil-off rate in propellant tanks and chill down of transfer lines. In TFAWS 2003, the present author delivered a paper to describe a general-purpose computer program, GFSSP (Generalized Fluid System Simulation Program). GFSSP calculates flow distribution in complex flow circuit for compressible/incompressible, with or without heat transfer or phase change in all real fluids or mixtures. The flow circuit constitutes of fluid nodes and branches. The mass, energy and specie conservation equations are solved at the nodes where as momentum conservation equations are solved at the branches. The proposed paper describes the extension of GFSSP to model conjugate heat transfer. The network also includes solid nodes and conductors in addition to fluid nodes and branches. The energy conservation equations for solid nodes solves to determine the temperatures of the solid nodes simultaneously with all conservation equations governing fluid flow. The numerical scheme accounts for conduction, convection and radiation heat transfer. The paper will also describe the applications of the code to predict chill down of cryogenic transfer line and boil-off rate of cryogenic propellant storage tank.
-
CONJUGATED BLOCK-COPOLYMERS FOR ELECTROLUMINESCENT DIODES
Hilberer, A; Gill, R.E; Herrema, J.K; Malliaras, G.G; Wildeman, J.; Hadziioannou, G
In this article we review results obtained in our laboratory on the design and study of new light-emitting polymers. We are interested in the synthesis and characterisation of block copolymers with regularly alternating conjugated and non conjugated sequences. The blocks giving rise to luminescence
-
Tetrafullerene conjugates for all-organic photovoltaics
Fernández, G.; Sánchez, L.; Veldman, D.; Wienk, M.M.; Atienza, C.M.; Guldi, D.M.; Janssen, R.A.J.; Martin, N.
2008-01-01
The synthesis of two new tetrafullerene nanoconjugates in which four C60 units are covalently connected through different -conjugated oligomers (oligo(p-phenylene ethynylene) and oligo(p-phenylene vinylene)) is described. The photovoltaic (PV) response of these C60-based conjugates was evaluated by
-
Novel Aflatoxin Derivatives and Protein Conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Reinhard Niessner
2007-03-01
Full Text Available Aflatoxins, a group of structurally related mycotoxins, are well known for their toxic and carcinogenic effects in humans and animals. Aflatoxin derivatives and protein conjugates are needed for diverse analytical applications. This work describes a reliable and fast synthesis of novel aflatoxin derivatives, purification by preparative HPLC and characterisation by ESI-MS and one- and two-dimensional NMR. Novel aflatoxin bovine serum albumin conjugates were prepared and characterised by UV absorption and MALDI-MS. These aflatoxin protein conjugates are potentially interesting as immunogens for the generation of aflatoxin selective antibodies with novel specificities.
-
Structure Property Relationships in Organic Conjugated Systems
O'Neill, Luke
2008-01-01
A series of pi(п) conjugated oligomers containing 1 to 6 monomer units were studied by absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopies. The results are discussed and examined with regard to the variation of the optical properties with the increase of effective conjugation length. It was found that there was a linear relationship between the positioning of the absorption and photoluminescence maxima plotted against inverse conjugation length. The relationships are in good agreement with the si...
-
Reisinger, Keith S; Baxter, Roger; Block, Stanley L; Shah, Jina; Bedell, Lisa; Dull, Peter M
2009-12-01
Neisseria meningitidis is a leading cause of bacterial meningitis in the United States, with the highest case fatality rates reported for individuals > or = 15 years of age. This study compares the safety and immunogenicity of the Novartis Vaccines investigational quadrivalent meningococcal CRM(197) conjugate vaccine, MenACWY-CRM, to those of the licensed meningococcal conjugate vaccine, Menactra, when administered to healthy adults. In this phase III multicenter study, 1,359 adults 19 to 55 years of age were randomly assigned to one of four groups (1:1:1:1 ratio) to receive a single dose of one of three lots of MenACWY-CRM or a single dose of Menactra. Serum samples obtained at baseline and 1 month postvaccination were tested for serogroup-specific serum bactericidal activity using human complement (hSBA). The hSBA titers following vaccination with MenACWY-CRM and Menactra were compared in noninferiority and prespecified superiority analyses. Reactogenicity was similar in the MenACWY-CRM and Menactra groups, and neither vaccine was associated with a serious adverse event. When compared with Menactra, MenACWY-CRM met the superiority criteria for the proportions of recipients achieving a seroresponse against serogroups C, W-135, and Y and the proportion of subjects achieving postvaccination titers of > or = 1:8 for serogroups C and Y. MenACWY-CRM's immunogenicity was statistically noninferior (the lower limit of the two-sided 95% confidence interval was more than -10%) to that of Menactra for all four serogroups, with the postvaccination hSBA geometric mean titers being consistently higher for MenACWY-CRM than for Menactra. MenACWY-CRM is well tolerated in adults 19 to 55 years of age, with immune responses to each of the serogroups noninferior and, in some cases, statistically superior to those to Menactra.
-
Sources and Bioactive Properties of Conjugated Dietary Fatty Acids.
Hennessy, Alan A; Ross, Paul R; Fitzgerald, Gerald F; Stanton, Catherine
2016-04-01
The group of conjugated fatty acids known as conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) isomers have been extensively studied with regard to their bioactive potential in treating some of the most prominent human health malignancies. However, CLA isomers are not the only group of potentially bioactive conjugated fatty acids currently undergoing study. In this regard, isomers of conjugated α-linolenic acid, conjugated nonadecadienoic acid and conjugated eicosapentaenoic acid, to name but a few, have undergone experimental assessment. These studies have indicated many of these conjugated fatty acid isomers commonly possess anti-carcinogenic, anti-adipogenic, anti-inflammatory and immune modulating properties, a number of which will be discussed in this review. The mechanisms through which these bioactivities are mediated have not yet been fully elucidated. However, existing evidence indicates that these fatty acids may play a role in modulating the expression of several oncogenes, cell cycle regulators, and genes associated with energy metabolism. Despite such bioactive potential, interest in these conjugated fatty acids has remained low relative to the CLA isomers. This may be partly attributed to the relatively recent emergence of these fatty acids as bioactives, but also due to a lack of awareness regarding sources from which they can be produced. In this review, we will also highlight the common sources of these conjugated fatty acids, including plants, algae, microbes and chemosynthesis.
-
Preparation and immunological properties of procaine-protein conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Liakopoulou, A.
1981-01-01
Procaine was conjugated to BSA and rat and rabbit Gf using the carbodiimide method and 14 C-procaine as tracer. The composition of the conjugates could be varied depending on the time of incubation and the concentration of procaine in the reaction mixtures. Procaine-BSA conjugates were soluble in water or saline. However, procaine conjugates to rat or rabbit Gf were not readily soluble in saline. These conjugates were good for immunization purposes, but it was cumbersome to work with them when clear solutions were needed, as in the immunochemical procedures used in this study. The immunological properties of the conjugates were studied in rats and rabbits. Rats responded with production of IgGa and precipitating antibodies to the procaine group, but IgE antibodies to the immunogen could not be detected. Furthermore, precipitating antibodies towards the procaine group were raised in rabbits. When BSA was the protein carrier, antibodies to the carrier molecule were also detected in both rats and rabbits. The conjugates of procaine to rat or rabbit Gf did not elicit antibody response to the carrier molecule when used in the homologous species. Hapten inhibition studies suggested that, in the rabbit, antibodies were also produced with specificity directed towards the molecular configuration of the hapten-carrier bond. (author)
-
IRDye78 Conjugates for Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Atif Zaheer
2002-10-01
Full Text Available The detection of human malignancies by near-infrared (NIR fluorescence will require the conjugation of cancer-specific ligands to NIR fluorophores that have optimal photoproperties and pharmacokinetics. IRDye78, a tetra-sulfonated heptamethine indocyanine NIR fluorophore, meets most of the criteria for an in vivo imaging agent, and is available as an N-hydroxysuccinimide ester for conjugation to low-molecular-weight ligands. However, IRDye78 has a high charge-to-mass ratio, complicating purification of conjugates. It also has a potentially labile linkage between fluorophore and ligand. We have developed an ion-pairing purification strategy for IRDye78 that can be performed with a standard C18 column under neutral conditions, thus preserving the stability of fluorophore, ligand, and conjugate. By employing parallel evaporative light scatter and absorbance detectors, all reactants and products are identified, and conjugate purity is maximized. We describe reversible and irreversible conversions of IRDye78 that can occur during sample purification, and describe methods for preserving conjugate stability. Using seven ligands, spanning several classes of small molecules and peptides (neutral, charged, and/or hydrophobic, we illustrate the robustness of these methods, and confirm that IRDye78 conjugates so purified retain bioactivity and permit NIR fluorescence imaging of specific targets.
-
Preconditioning the modified conjugate gradient method ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
In this paper, the convergence analysis of the conventional conjugate Gradient method was reviewed. And the convergence analysis of the modified conjugate Gradient method was analysed with our extension on preconditioning the algorithm. Convergence of the algorithm is a function of the condition number of M-1A.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Yu, Wenjian; Donohoo-Vallett, Paul J.; Zhou, Jiawang; Bragg, Arthur E., E-mail: artbragg@jhu.edu [Department of Chemistry, Johns Hopkins University, 3400 N. Charles St., Baltimore, Maryland 21218 (United States)
2014-07-28
A combination of transient absorption (TAS) and femtosecond stimulated Raman (FSRS) spectroscopies were used to interrogate the photo-induced nuclear relaxation dynamics of poly(3-cyclohexyl,4-methylthiophene) (PCMT). The large difference in inter-ring dihedral angles of ground and excited-state PCMT make it an ideal candidate for studying large-amplitude vibrational relaxation associated with exciton trapping. Spectral shifting in the S{sub 1} TA spectra on sub-ps timescales (110 ± 20 and 800 ± 100 fs) is similar to spectroscopic signatures of excited-state relaxation observed with related photoexcited conjugated polymers and which have been attributed to exciton localization and a combination of resonant energy transfer and torsional relaxation, respectively. Measurements made with both techniques reveal fast PCMT S{sub 1} decay and triplet formation (τ{sub S1} = 25–32 ps), which is similar to the excited-state dynamics of short oligothiophenes and highly twisted polyconjugated molecules. On ultrafast timescales FSRS of S{sub 1} PCMT offers a new perspective on the nuclear dynamics that underlie localization of excitons in photoexcited conjugated polymers: Spectral dynamics in the C=C stretching region (1400–1600 cm{sup −1}) include a red-shift of the in-phase C=C stretching frequency, as well as a change in the relative intensity of in-phase and out-of-phase stretch intensities on a timescale of ∼100 fs. Both changes indicate an ultrafast vibrational distortion that increases the conjugation length in the region of the localized excitation and are consistent with exciton self-localization or trapping. Wavelength-dependent excited-state FSRS measurements further demonstrate that the C=C stretching frequency provides a useful spectroscopic handle for interrogating the degree of delocalization in excited conjugated polymers given the selectivity achieved via resonance enhancement.
-
Conjugate pair of non-extensive statistics in quantum scattering
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ion, D.B.; Ion, M.L.D.
1999-01-01
In this paper, by defining the Fourier transform of the scattering amplitudes as a bounded linear mapping from the space L 2p to the space L 2q when 1/(2p)+1/(2q)=1, we introduced a new concept in quantum physics in terms of Tsallis-like entropies S J (p) and S θ (q), namely, that of conjugate pair of non-extensive statistics. This new concept is experimentally illustrated by using 88 + 49 sets of pion-nucleon and pion-nucleus phase shifts. From the experimental determination of the (p,q) - non-extensivity indices by choosing the pairs for which the [χ L 2 (p) + χ θ 2 (q min )] - optimal - test function is minimum we get the conjugate pair of [(p min ,J),(q min , θ)]- non-extensive statistics with 0.50 ≤ p min ≤ 0.60. This new non-extensive statistical effect is experimentally evidenced with high degree of accuracy (CL≥ 99%). Moreover, it is worth to mention that the modification of the statistics has been more efficient than the modification of the PMD-SQS-optimum principle in obtaining the best overall fitting to the experimental data. (authors)
-
A four-phase strategy for the implementation of reflectance confocal microscopy in dermatology.
Hoogedoorn, L; Gerritsen, M J P; Wolberink, E A W; Peppelman, M; van de Kerkhof, P C M; van Erp, P E J
2016-08-01
Reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) is gradually implemented in dermatology. Strategies for further implementation and practical 'hands on' guidelines are lacking. The primary outcome was to conduct a general strategy for further implementation of RCM. The secondary outcome was the diagnosis of psoriasis and differentiation of stable from unstable psoriatic plaques by means of the 'hands on' protocol, derived from the strategy. We used a four-phased model; an exploring phase, a systematic literature search, a clinical approach and, finally, an integration phase to develop a clinical guideline for RCM in psoriasis. Receiver operating characteristic curve statistics was applied to define the accuracy for the diagnosis of unstable psoriasis. A general strategy for further implementation of RCM and practical approach was developed to examine psoriasis by RCM and to distinguish stable from unstable psoriasis. Unstable psoriasis was diagnosed by epidermal inflammatory cell counts with a sensitivity and specificity of 91.7% and 98.3%, respectively, and with an accuracy of 0.92 (area under the curve). In addition, a monitoring model was proposed. This is the first study that shows a method for implementation of RCM in dermatology. The strategy and hands on protocol for psoriasis may serve as a model for other dermatological entities and additionally may lead to specialized ready-to-use RCM protocols for clinical dermatological practice. © 2016 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
-
Numerical investigation of multichannel laser beam phase locking in turbulent atmosphere
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Volkov, V A; Volkov, M V; Garanin, S G; Starikov, F A [Russian Federal Nuclear Center ' All-Russian Research Institute of Experimental Physics' , Sarov, Nizhnii Novgorod region (Russian Federation)
2015-12-31
The efficiency of coherent multichannel beam combining under focusing through a turbulent medium on a target in the cases of phase conjugation and target irradiation in the feedback loop is investigated numerically in various approximations. The conditions of efficient focusing of multichannel radiation on the target are found. It is shown that the coherent beam combining with target irradiation in the feedback loop, which does not require a reference beam and wavefront measurements, is as good as the phase conjugation approach in the efficiency of focusing. It is found that the main effect of focusing is provided by properly chosen phase shifts in the channels, whereas taking into account local wavefront tip tilts weakly affects the result. (control of laser radiation parameters)
-
Cao, Na; Feng, Si-Shen
2008-10-01
To develop a polymer-anticancer drug conjugate, D-alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was employed as a carrier of doxorubicin (DOX) to enhance its therapeutic effects and reduce its side effects. Doxorubicin was chemically conjugated to TPGS. The molecular structure, drug loading efficiency, drug release kinetics and stability of the conjugate were characterized. The cellular uptake, intracellular distribution, and cytotoxicity were accessed by using MCF-7 breast cancer cells and C6 glioma cells as in vitro cell model. The conjugate showed higher cellular uptake efficiency and broader distribution within the cells. Judged by IC(50), the conjugate was found 31.8, 69.6, 84.1% more effective with MCF-7 cells and 43.9, 87.7, 42.2% more effective with C6 cells than the parent drug after 24, 48, 72 h culture, respectively. The in vivo pharmacokinetics and biodistribution were investigated after an i.v. administration at 5 mg DOX/kg body weight in rats. Promisingly, 4.5-fold increase in the half-life and 24-fold increase in the area-under-the-curve (AUC) of DOX were achieved for the TPGS-DOX conjugate compared with the free DOX. The drug level in heart, gastric and intestine was significantly reduced, which is an indication of reduced side effects. Our TPGS-DOX conjugate showed great potential to be a prodrug of higher therapeutic effects and fewer side effects than DOX itself.
-
Sabir, Aneela; Shafiq, Muhammad; Islam, Atif; Jabeen, Faiza; Shafeeq, Amir; Ahmad, Adnan; Zahid Butt, Muhammad Taqi; Jacob, Karl I; Jamil, Tahir
2016-01-20
Thermally-induced phase separation (TIPS) method was used to synthesize polymer matrix (PM) membranes for reverse osmosis from cellulose acetate/polyethylene glycol (CA/PEG300) conjugated with silica nanoparticles (SNPs). Experimental data showed that the conjugation of SNPs changed the surface properties as dense and asymmetric composite structure. The results were explicitly determined by the permeability flux and salt rejection efficiency of the PM-SNPs membranes. The effect of SNPs conjugation on MgSO4 salt rejection was more significant in magnitude than on permeation flux i.e. 2.38 L/m(2)h. FTIR verified that SNPs were successfully conjugated on the surface of PM membrane. DSC of PM-SNPs shows an improved Tg from 76.2 to 101.8 °C for PM and PM-S4 respectively. Thermal stability of the PM-SNPs membranes was observed by TGA which was significantly enhanced with the conjugation of SNPs. The micrographs of SEM and AFM showed the morphological changes and increase in the valley and ridges on membrane surface. Experimental data showed that the PM-S4 (0.4 wt% SNPs) membrane has maximum salt rejection capacity and was selected as an optimal membrane. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Phase noise reduction by self-phase locking in semiconductor lasers using phase conjugate feedback
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Petersen, Lykke; Gliese, Ulrik Bo; Nielsen, Torben Nørskov
1994-01-01
noise takes a finite-low value corresponding to a state of first-order self-phase locking of the laser. As a result, the spectral shape of the laser signal does not remain Lorentzian but collapses around the carrier to a delta function with a close to carrier noise level of less than -137 d...
-
Bis-polymer lipid-peptide conjugates and nanoparticles thereof
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Xu, Ting; Dong, He; Shu, Jessica; Dube, Nikhil
2018-04-24
The present invention provides bis-polymer lipid-peptide conjugates containing a hydrophobic block and headgroup containing a helical peptide and two polymer blocks. The conjugates can self-assemble to form helix bundle subunits, which in turn assemble to provide micellar nanocarriers for drug cargos and other agents. Particles containing the conjugates and methods for forming the particles are also disclosed.
-
Influence of fluctuating strain on exciton reflection spectra
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Skettrup, Torben
1982-01-01
The influence of an internal distribution of strain on the exciton reflection spectra is investigated. The resulting fluctuating optical constants give rise to a fluctuating phase of reflectivity. The standard deviation σ of these phase fluctuations is the quantity which can be observed...... to derive the dependence of the phase of reflectivity on the direction of the fluctuating optical axis. The results obtained for σ are compared with the experimental depolarization spectra of ZnO. The only fitting parameter is the common standard deviation of the strain components. It is found......, for example, between crossed polarizers or from ellipsometric measurements. Assuming the phase fluctuations to obey a Gaussian distribution, σ can be expressed in a simple way in terms of the degree of polarization or the depolarization of the reflected light. σ is then derived in terms of the standard...
-
Diffuse x-ray scattering study of interfacial structure of self-assembled conjugated polymers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wang Jun; Park, Y.J.; Lee, K.-B.; Hong, H.; Davidov, D.
2002-01-01
The interfacial structures of self-assembled heterostructures through alternate deposition of conjugated and nonconjugated polymers were studied by x-ray reflectivity and nonspecular scattering. We found that the interfacial width including the effects of both interdiffusion and interfacial roughness (correlated) was mainly contributed by the latter one. The self-assembled deposition induced very small interdiffusion between layers. The lateral correlation length ξ parallel grew as a function of deposition time (or film thickness) described by a power law ξ parallel ∝t β/H and was also observed from the off-specular scattering
-
Compact quantum dot-antibody conjugates for FRET immunoassays with subnanomolar detection limits
Mattera, Lucia; Bhuckory, Shashi; Wegner, K. David; Qiu, Xue; Agnese, Fabio; Lincheneau, Christophe; Senden, Tim; Djurado, David; Charbonnière, Loïc J.; Hildebrandt, Niko; Reiss, Peter
2016-05-01
A novel two-step approach for quantum dot (QD) functionalization and bioconjugation is presented, which yields ultra-compact, stable, and highly luminescent antibody-QD conjugates suitable for use in FRET immunoassays. Hydrophobic InPZnS/ZnSe/ZnS (emission wavelength: 530 nm), CdSe/ZnS (605 nm), and CdSeTe/ZnS (705 nm) QDs were surface functionalized with zwitterionic penicillamine, enabling aqueous phase transfer under conservation of the photoluminescence properties. Post-functionalization with a heterobifunctional crosslinker, containing a lipoic acid group and a maleimide function, enabled the subsequent coupling to sulfhydryl groups of proteins. This was demonstrated by QD conjugation with fragmented antibodies (F(ab)). The obtained F(ab)-QD conjugates range among the smallest antibody-functionalized nanoprobes ever reported, with a hydrodynamic diameter coating for FRET could be demonstrated by an 6.2 and 2.5 fold improvement of the limit of detection (LOD) for PSA compared to commercially available hydrophilic QDs emitting at 605 and 705 nm, respectively. While the commercial QDs contain identical inorganic cores responsible for their fluorescence, they are coated with a comparably thick amphiphilic polymer layer leading to much larger hydrodynamic diameters (>26 nm without biomolecules). The LODs of 0.8 and 3.7 ng mL-1 obtained in 50 μL serum samples are below the clinical cut-off level of PSA (4 ng mL-1) and demonstrate their direct applicability in clinical diagnostics.A novel two-step approach for quantum dot (QD) functionalization and bioconjugation is presented, which yields ultra-compact, stable, and highly luminescent antibody-QD conjugates suitable for use in FRET immunoassays. Hydrophobic InPZnS/ZnSe/ZnS (emission wavelength: 530 nm), CdSe/ZnS (605 nm), and CdSeTe/ZnS (705 nm) QDs were surface functionalized with zwitterionic penicillamine, enabling aqueous phase transfer under conservation of the photoluminescence properties. Post
-
Schacht, Anna Christina; Sørensen, Michael; Munk, Ole Lajord; Frisch, Kim
2016-04-01
During cholestasis, accumulation of conjugated bile acids may occur in the liver and lead to hepatocellular damage. Inspired by our recent development of N-(11)C-methyl-glycocholic acid-that is, (11)C-cholylsarcosine-a tracer for PET of the endogenous glycine conjugate of cholic acid, we report here a radiosynthesis of N-(11)C-methyl-taurine-conjugated bile acids and biodistribution studies in pigs by PET/CT. A radiosynthesis of N-(11)C-methyl-taurine-conjugated bile acids was developed and used to prepare N-(11)C-methyl-taurine conjugates derived from cholic, chenodeoxycholic, deoxycholic, ursodeoxycholic, and lithocholic acid. The lipophilicity of these new tracers was determined by reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography. The effect of lipophilicity and structure on the biodistribution was investigated in pigs by PET/CT using the tracers derived from cholic acid (3α-OH, 7α-OH, 12α-OH), ursodeoxycholic acid (3α-OH, 7β-OH), and lithocholic acid (3α-OH). The radiosyntheses of the N-(11)C-methyl-taurine-conjugated bile acids proceeded with radiochemical yields of 61% (decay-corrected) or greater and radiochemical purities greater than 99%. PET/CT in pigs revealed that the tracers were rapidly taken up by the liver and secreted into bile. There was no detectable radioactivity in urine. Significant reflux of N-(11)C-methyl-taurolithocholic acid into the stomach was observed. We have successfully developed a radiosynthesis of N-(11)C-methyl-taurine-conjugated bile acids. These tracers behave in a manner similar to endogenous taurine-conjugated bile acids in vivo and are thus promising for functional PET of patients with cholestatic diseases. © 2016 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Inc.
-
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles, methods of using, and methods of making
Habuchi, Satoshi; Piwonski, Hubert Marek; Michinobu, Tsuyoshi
2017-01-01
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide for conjugated polymer nanoparticle, method of making conjugated polymer nanoparticles, method of using conjugated polymer nanoparticle, polymers, and the like.
-
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles, methods of using, and methods of making
Habuchi, Satoshi
2017-03-16
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide for conjugated polymer nanoparticle, method of making conjugated polymer nanoparticles, method of using conjugated polymer nanoparticle, polymers, and the like.
-
Laser projection using generalized phase contrast
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Glückstad, Jesper; Palima, Darwin; Rodrigo, Peter John
2007-01-01
is introduced. An arbitrary phase shift filter eliminates the need for high-frequency modulation and conjugate phase encoding. This lowers device performance requirements and allows practical implementation with currently available dynamic spatial light modulators. (c) 2007 Optical Society of America.......We demonstrate experimental laser projection of a gray-level photographic image with 74% light efficiency using the generalized phase contrast (GPC) method. In contrast with a previously proposed technique [Alonzo et al., New J. Phys. 9, 132 (2007)], a new approach to image construction via GPC...
-
Nonlinear conjugate gradient methods in micromagnetics
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. Fischbacher
2017-04-01
Full Text Available Conjugate gradient methods for energy minimization in micromagnetics are compared. The comparison of analytic results with numerical simulation shows that standard conjugate gradient method may fail to produce correct results. A method that restricts the step length in the line search is introduced, in order to avoid this problem. When the step length in the line search is controlled, conjugate gradient techniques are a fast and reliable way to compute the hysteresis properties of permanent magnets. The method is applied to investigate demagnetizing effects in NdFe12 based permanent magnets. The reduction of the coercive field by demagnetizing effects is μ0ΔH = 1.4 T at 450 K.
-
A general relationship between disorder, aggregation and charge transport in conjugated polymers
Noriega, Rodrigo; Rivnay, Jonathan; Vandewal, Koen; Koch, Felix P. V.; Stingelin, Natalie; Smith, Paul; Toney, Michael F.; Salleo, Alberto
2013-01-01
Conjugated polymer chains have many degrees of conformational freedom and interact weakly with each other, resulting in complex microstructures in the solid state. Understanding charge transport in such systems, which have amorphous and ordered phases exhibiting varying degrees of order, has proved difficult owing to the contribution of electronic processes at various length scales. The growing technological appeal of these semiconductors makes such fundamental knowledge extremely important for materials and process design. We propose a unified model of how charge carriers travel in conjugated polymer films. We show that in high-molecular-weight semiconducting polymers the limiting charge transport step is trapping caused by lattice disorder, and that short-range intermolecular aggregation is sufficient for efficient long-range charge transport. This generalization explains the seemingly contradicting high performance of recently reported, poorly ordered polymers and suggests molecular design strategies to further improve the performance of future generations of organic electronic materials. © 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
-
A general relationship between disorder, aggregation and charge transport in conjugated polymers
Noriega, Rodrigo
2013-08-04
Conjugated polymer chains have many degrees of conformational freedom and interact weakly with each other, resulting in complex microstructures in the solid state. Understanding charge transport in such systems, which have amorphous and ordered phases exhibiting varying degrees of order, has proved difficult owing to the contribution of electronic processes at various length scales. The growing technological appeal of these semiconductors makes such fundamental knowledge extremely important for materials and process design. We propose a unified model of how charge carriers travel in conjugated polymer films. We show that in high-molecular-weight semiconducting polymers the limiting charge transport step is trapping caused by lattice disorder, and that short-range intermolecular aggregation is sufficient for efficient long-range charge transport. This generalization explains the seemingly contradicting high performance of recently reported, poorly ordered polymers and suggests molecular design strategies to further improve the performance of future generations of organic electronic materials. © 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
-
Usta, M.; Wortelboer, H.M.; Vervoort, J.J.M.; Boersma, M.G.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Bladeren, van P.J.; Cnubben, N.H.P.
2007-01-01
Curcumin, an alpha,beta-unsaturated carbonyl compound, reacts with glutathione, leading to the formation of two monoglutathionyl curcumin conjugates. In the present study, the structures of both glutathione conjugates of curcumin were identified by LC-MS and one- and two-dimensional H-1 NMR
-
Selective Covalent Conjugation of Phosphorothioate DNA Oligonucleotides with Streptavidin
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Christof M. Niemeyer
2011-08-01
Full Text Available Protein-DNA conjugates have found numerous applications in the field of diagnostics and nanobiotechnology, however, their intrinsic susceptibility to DNA degradation by nucleases represents a major obstacle for many applications. We here report the selective covalent conjugation of the protein streptavidin (STV with phosphorothioate oligonucleotides (psDNA containing a terminal alkylthiolgroup as the chemically addressable linking unit, using a heterobifunctional NHS-/maleimide crosslinker. The psDNA-STV conjugates were synthesized in about 10% isolated yields. We demonstrate that the terminal alkylthiol group selectively reacts with the maleimide while the backbone sulfur atoms are not engaged in chemical conjugation. The novel psDNA-STV conjugates retain their binding capabilities for both biotinylated macromolecules and the complementary nucleic acid. Moreover, the psDNA-STV conjugate retained its binding capacity for complementary oligomers even after a nuclease digestion step, which effectively degrades deoxyribonucleotide oligomers and thus the binding capability of regular DNA-STV conjugates. The psDNA-STV therefore hold particular promise for applications e.g. in proteome research and novel biosensing devices, where interfering endogenous nucleic acids need to be removed from analytes by nuclease digestion.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, K.T.; Spanggaard, H.; Krebs, Frederik C
2004-01-01
. Electroluminescent devices of the homopolymer itself and of the zinc-porphyrin containing polymer were prepared and the nature of the electroluminescence was characterized. The homopolymer segments were found to optically pump the emission of the zinc-porphyrin dye moities. The homopolymer exhibits blue......Zinc-porphyrin dye molecules were incorporated into the backbone of a conjugated polymer material by a method, which allowed for the incorporation of only one zinc-porphyrin dye molecule into the backbone of each conjugated polymer molecule. The electronic properties of the homopolymer were...
-
Lipid-peptide-polymer conjugates and nanoparticles thereof
Xu, Ting; Dong, He; Shu, Jessica
2015-06-02
The present invention provides a conjugate having a peptide with from about 10 to about 100 amino acids, wherein the peptide adopts a helical structure. The conjugate also includes a first polymer covalently linked to the peptide, and a hydrophobic moiety covalently linked to the N-terminus of the peptide, wherein the hydrophobic moiety comprises a second polymer or a lipid moiety. The present invention also provides helix bundles form by self-assembling the conjugates, and particles formed by self-assembling the helix bundles. Methods of preparing the helix bundles and particles are also provided.
-
Novel β-cyclodextrin-eosin conjugates.
Benkovics, Gábor; Afonso, Damien; Darcsi, András; Béni, Szabolcs; Conoci, Sabrina; Fenyvesi, Éva; Szente, Lajos; Malanga, Milo; Sortino, Salvatore
2017-01-01
Eosin B (EoB) and eosin Y (EoY), two xanthene dye derivatives with photosensitizing ability were prepared in high purity through an improved synthetic route. The dyes were grafted to a 6-monoamino-β-cyclodextrin scaffold under mild reaction conditions through a stable amide linkage using the coupling agent 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium chloride. The molecular conjugates, well soluble in aqueous medium, were extensively characterized by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Preliminary spectroscopic investigations showed that the β-cyclodextrin-EoY conjugate retains both the fluorescence properties and the capability to photogenerate singlet oxygen of the unbound chromophore. In contrast, the corresponding β-cyclodextrin-EoB conjugate did not show either relevant emission or photosensitizing activity probably due to aggregation in aqueous medium, which precludes any response to light excitation.
-
Novel β-cyclodextrin–eosin conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gábor Benkovics
2017-03-01
Full Text Available Eosin B (EoB and eosin Y (EoY, two xanthene dye derivatives with photosensitizing ability were prepared in high purity through an improved synthetic route. The dyes were grafted to a 6-monoamino-β-cyclodextrin scaffold under mild reaction conditions through a stable amide linkage using the coupling agent 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl-4-methylmorpholinium chloride. The molecular conjugates, well soluble in aqueous medium, were extensively characterized by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. Preliminary spectroscopic investigations showed that the β-cyclodextrin–EoY conjugate retains both the fluorescence properties and the capability to photogenerate singlet oxygen of the unbound chromophore. In contrast, the corresponding β-cyclodextrin–EoB conjugate did not show either relevant emission or photosensitizing activity probably due to aggregation in aqueous medium, which precludes any response to light excitation.
-
Photodynamic tissue adhesion with chlorin(e6) protein conjugates.
Khadem, J; Veloso, A A; Tolentino, F; Hasan, T; Hamblin, M R
1999-12-01
To test the hypothesis that a photodynamic laser-activated tissue solder would perform better in sealing scleral incisions when the photosensitizer was covalently linked to the protein than when it was noncovalently mixed. Conjugates and mixtures were prepared between the photosensitizer chlorin(e6) and various proteins (albumin, fibrinogen, and gelatin) in different ratios and used to weld penetrating scleral incisions made in human cadaveric eyes. A blue-green (488-514 nm) argon laser activated the adhesive, and the strength of the closure was measured by increasing the intraocular pressure until the wound showed leakage. Both covalent conjugates and noncovalent mixtures showed a light dose-dependent increase in leaking pressure. A preparation of albumin chlorin(e6) conjugate with additional albumin added (2.5 protein to chlorin(e6) molar ratio) showed significantly higher weld strength than other protein conjugates and mixtures. This is the first report of dye-protein conjugates as tissue solders. These conjugates may have applications in ophthalmology.
-
Tian, Baomin; Wong, Wah Yau; Hegmann, Elda; Gaspar, Kim; Kumar, Praveen; Chao, Heman
2015-06-17
A novel immunoconjugate (L-DOS47) was developed and characterized as a therapeutic agent for tumors expressing CEACAM6. The single domain antibody AFAIKL2, which targets CEACAM6, was expressed in the Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) pT7-7 system. High purity urease (HPU) was extracted and purified from Jack bean meal. AFAIKL2 was activated using N-succinimidyl [4-iodoacetyl] aminobenzoate (SIAB) as the cross-linker and then conjugated to urease. The activation and conjugation reactions were controlled by altering pH. Under these conditions, the material ratio achieved conjugation ratios of 8-11 antibodies per urease molecule, the residual free urease content was practically negligible (95%) L-DOS47 conjugate was produced using only ultradiafiltration to remove unreacted antibody and hydrolyzed cross-linker. L-DOS47 was characterized by a panel of analytical techniques including SEC, IEC, Western blot, ELISA, and LC-MS(E) peptide mapping. As the antibody-urease conjugate ratio increased, a higher binding signal was observed. The specificity and cytotoxicity of L-DOS47 was confirmed by screening in four cell lines (BxPC-3, A549, MCF7, and CEACAM6-transfected H23). BxPC-3, a CEACAM6-expressing cell line was found to be most susceptible to L-DOS47. L-DOS47 is being investigated as a potential therapeutic agent in human phase I clinical studies for nonsmall cell lung cancer.
-
Usta, M.; Wortelboer, H.M.; Vervoort, J.; Boersma, M.G.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Bladeren, P.J. van; Cnubben, N.H.P.
2007-01-01
Curcumin, an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound, reacts with glutathione, leading to the formation of two monoglutathionyl curcumin conjugates. In the present study, the structures of both glutathione conjugates of curcumin were identified by LC-MS and one- and two-dimensional 1H NMR analysis, and
-
DENDRIMER CONJUGATES FOR SELECTIVE OF PROTEIN AGGREGATES
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
2004-01-01
Dendrimer conjugates are presented, which are formed between a dendrimer and a protein solubilising substance. Such dendrimer conjugates are effective in the treatment of protein aggregate-related diseases (e.g. prion-related diseases). The protein solubilising substance and the dendrimer together...
-
Phase retrieval for X-ray in-line phase contrast imaging
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Scattarella, F.; Bellotti, R.; Tangaro, S.; Gargano, G.; Giannini, C.
2011-01-01
A review article about phase retrieval problem in X-ray phase contrast imaging is presented. A simple theoretical framework of Fresnel diffraction imaging by X-rays is introduced. A review of the most important methods for phase retrieval in free-propagation-based X-ray imaging and a new method developed by our collaboration are shown. The proposed algorithm, Combined Mixed Approach (CMA) is based on a mixed transfer function and transport of intensity approach, and it requires at most an initial approximate estimate of the average phase shift introduced by the object as prior knowledge. The accuracy with which this initial estimate is known determines the convenience speed of algorithm. The new proposed algorithm is based on the retrieval of both the object phase and its complex conjugate. The results obtained by the algorithm on simulated data have shown that the obtained reconstructed phase maps are characterized by particularly low normalized mean square errors. The algorithm was also tested on noisy experimental phase contrast data, showing a good efficiency in recovering phase information and enhancing the visibility of details inside soft tissues.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jacob Thomas
Full Text Available Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs are agents of horizontal gene transfer and have major roles in evolution and acquisition of new traits, including antibiotic resistances. ICEs are found integrated in a host chromosome and can excise and transfer to recipient bacteria via conjugation. Conjugation involves nicking of the ICE origin of transfer (oriT by the ICE-encoded relaxase and transfer of the nicked single strand of ICE DNA. For ICEBs1 of Bacillus subtilis, nicking of oriT by the ICEBs1 relaxase NicK also initiates rolling circle replication. This autonomous replication of ICEBs1 is critical for stability of the excised element in growing cells. We found a conserved and previously uncharacterized ICE gene that is required for conjugation and replication of ICEBs1. Our results indicate that this gene, helP (formerly ydcP, encodes a helicase processivity factor that enables the host-encoded helicase PcrA to unwind the double-stranded ICEBs1 DNA. HelP was required for both conjugation and replication of ICEBs1, and HelP and NicK were the only ICEBs1 proteins needed for replication from ICEBs1 oriT. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we measured association of HelP, NicK, PcrA, and the host-encoded single-strand DNA binding protein Ssb with ICEBs1. We found that NicK was required for association of HelP and PcrA with ICEBs1 DNA. HelP was required for association of PcrA and Ssb with ICEBs1 regions distal, but not proximal, to oriT, indicating that PcrA needs HelP to progress beyond nicked oriT and unwind ICEBs1. In vitro, HelP directly stimulated the helicase activity of the PcrA homologue UvrD. Our findings demonstrate that HelP is a helicase processivity factor needed for efficient unwinding of ICEBs1 for conjugation and replication. Homologues of HelP and PcrA-type helicases are encoded on many known and putative ICEs. We propose that these factors are essential for ICE conjugation, replication, and genetic stability.
-
Mohajerin-Ariaei, Amirhossein; Ziyadi, Morteza; Chitgarha, Mohammad Reza; Almaiman, Ahmed; Cao, Yinwen; Shamee, Bishara; Yang, Jeng-Yuan; Akasaka, Youichi; Sekiya, Motoyoshi; Takasaka, Shigehiro; Sugizaki, Ryuichi; Touch, Joseph D; Tur, Moshe; Langrock, Carsten; Fejer, Martin M; Willner, Alan E
2015-07-15
We demonstrate an all-optical phase noise mitigation scheme based on the generation, delay, and coherent summation of higher order signal harmonics. The signal, its third-order harmonic, and their corresponding delayed variant conjugates create a staircase phase-transfer function that quantizes the phase of quadrature-phase-shift-keying (QPSK) signal to mitigate phase noise. The signal and the harmonics are automatically phase-locked multiplexed, avoiding the need for phase-based feedback loop and injection locking to maintain coherency. The residual phase noise converts to amplitude noise in the quantizer stage, which is suppressed by parametric amplification in the saturation regime. Phase noise reduction of ∼40% and OSNR-gain of ∼3 dB at BER 10(-3) are experimentally demonstrated for 20- and 30-Gbaud QPSK input signals.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Carraro Nicolas
2011-10-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background Two closely related ICEs, ICESt1 and ICESt3, have been identified in the lactic acid bacterium Streptococcus thermophilus. While their conjugation and recombination modules are almost identical (95% nucleotide identity and their regulation modules related, previous work has demonstrated that transconjugants carrying ICESt3 were generated at rate exceeding by a 1000 factor that of ICESt1. Results The functional regulation of ICESt1 and ICESt3 transcription, excision and replication were investigated under different conditions (exponential growth or stationary phase, DNA damage by exposition to mitomycin C. Analysis revealed an identical transcriptional organization of their recombination and conjugation modules (long unique transcript whereas the transcriptional organization of their regulation modules were found to be different (two operons in ICESt1 but only one in ICESt3 and to depend on the conditions (promoter specific of stationary phase in ICESt3. For both elements, stationary phase and DNA damage lead to the rise of transcript levels of the conjugation-recombination and regulation modules. Whatever the growth culture conditions, excision of ICESt1 was found to be lower than that of ICESt3, which is consistent with weaker transfer frequencies. Furthermore, for both elements, excision increases in stationary phase (8.9-fold for ICESt1 and 1.31-fold for ICESt3 and is strongly enhanced by DNA damage (38-fold for ICESt1 and 18-fold for ICESt3. Although ICEs are generally not described as replicative elements, the copy number of ICESt3 exhibited a sharp increase (9.6-fold after mitomycin C exposure of its harboring strain CNRZ385. This result was not observed when ICESt3 was introduced in a strain deriving ICESt1 host strain CNRZ368, deleted for this element. This finding suggests an impact of the host cell on ICE behavior. Conclusions All together, these results suggest a novel mechanism of regulation shared by ICESt1
-
... version Home Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerve Disorders Cranial Nerve Disorders Conjugate Gaze Palsies Horizontal gaze palsy Vertical ... Version. DOCTORS: Click here for the Professional Version Cranial Nerve Disorders Overview of the Cranial Nerves Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia ...
-
Rapid determination of ions by combined solid-phase extraction--diffuse reflectance spectroscopy
Fritz, James S.; Arena, Matteo P.; Steiner, Steven A.; Porter, Marc D.
2003-01-01
We introduce colorimetric solid-phase extraction (C-SPE) for the rapid determination of selected ions. This new technique links the exhaustive concentration of an analyte by SPE onto a membrane disk surface for quantitative measurement with a hand-held diffuse reflectance spectrometer. The concentration/measurement procedure is complete in approximately 1 min and can be performed almost anywhere. This method has been used to monitor iodine and iodide in spacecraft water in the 0.1-5.0 ppm range and silver(I) in the range of 5.0-1000 microg/l. Applications to the trace analysis of copper(II), nickel(II), iron(III) and chromium(VI) are described. Studies on the mechanism of extraction showed that impregnation of the disk with a surfactant as well as a complexing reagent results in uptake of additional water, which markedly improves the extraction efficiency.
-
Buecheler, Jakob W; Winzer, Matthias; Weber, Christian; Gieseler, Henning
2018-05-01
Oxidation of protein therapeutics is a major chemical degradation pathway which may impact bioactivity, serum half-life and stability. Therefore, oxidation is a relevant parameter which has to be monitored throughout formulation development. Methods such as HIC, RPLC and LC/MS achieve a separation of oxidized and non-oxidized species by differences in hydrophobicity. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) although are highly more complex due to the heterogeneity in linker, drug, drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) and conjugation site. The analytical protein A chromatography can provide a simple and fast alternative to these common methods. A miniature analytical protein A chromatography method in combination with an IdeS digest was developed to analyse ADCs. The IdeS digest efficiency of an IgG1 was monitored using SEC-HPLC and non-reducing SDS-PAGE. An antibody-fluorescent dye conjugate was conjugated at different dye-to-antibody ratios as model construct to mimic an ADC. With IdeS, an almost complete digest of a model IgG1 can be achieved (digested protein amount >98%). This enables subsequent analytical protein A chromatography, which consequently eliminates any interference of payload with the stationary phase. A novel high-throughput method for an interchain cysteine-linked ADC oxidation screens during formulation development was developed. © 2018 Royal Pharmaceutical Society.
-
Fullerene-biomolecule conjugates and their biomedicinal applications.
Yang, Xinlin; Ebrahimi, Ali; Li, Jie; Cui, Quanjun
2014-01-01
Fullerenes are among the strongest antioxidants and are characterized as "radical sponges." The research on biomedicinal applications of fullerenes has achieved significant progress since the landmark publication by Friedman et al in 1993. Fullerene-biomolecule conjugates have become an important area of research during the past 2 decades. By a thorough literature search, we attempt to update the information about the synthesis of different types of fullerene-biomolecule conjugates, including fullerene-containing amino acids and peptides, oligonucleotides, sugars, and esters. Moreover, we also discuss in this review recently reported data on the biological and pharmaceutical utilities of these compounds and some other fullerene derivatives of biomedical importance. While within the fullerene-biomolecule conjugates, in which fullerene may act as both an antioxidant and a carrier, specific targeting biomolecules conjugated to fullerene will undoubtedly strengthen the delivery of functional fullerenes to sites of clinical interest.
-
Retroreflective Phase Retardation Prisms.
1981-06-01
resonant cavity of a 1.064 Mm laser. This report shows that it is possible to coat the reflecting surfaces of a porro prism so that incident plane...with controlled phase retardation can be made by coating each reflecting surface of a porro prism with a single dielectric film. The amount of phase...of angle of incidence (n, < n2) S. Phase change on reflection as a function of angle of incidence (n" n ) [RL-0202-’R 6. Porro prism 7. Phase change
-
Gold Nanoparticle Conjugation Enhances the Antiacanthamoebic Effects of Chlorhexidine
Aqeel, Yousuf; Siddiqui, Ruqaiyyah; Anwar, Ayaz; Shah, Muhammad Raza
2015-01-01
Acanthamoeba keratitis is a serious infection with blinding consequences and often associated with contact lens wear. Early diagnosis, followed by aggressive topical application of drugs, is a prerequisite in successful treatment, but even then prognosis remains poor. Several drugs have shown promise, including chlorhexidine gluconate; however, host cell toxicity at physiologically relevant concentrations remains a challenge. Nanoparticles, subcolloidal structures ranging in size from 10 to 100 nm, are effective drug carriers for enhancing drug potency. The overall aim of the present study was to determine whether conjugation with gold nanoparticles enhances the antiacanthamoebic potential of chlorhexidine. Gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles were synthesized. Briefly, gold solution was mixed with chlorhexidine and reduced by adding sodium borohydride, resulting in an intense deep red color, indicative of colloidal gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles. The synthesis was confirmed using UV-visible spectrophotometry that shows a plasmon resonance peak of 500 to 550 nm, indicative of gold nanoparticles. Further characterization using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-mass spectrometry showed a gold-conjugated chlorhexidine complex at m/z 699 ranging in size from 20 to 100 nm, as determined using atomic force microscopy. To determine the amoebicidal and amoebistatic effects, amoebae were incubated with gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles. For controls, amoebae also were incubated with gold and silver nanoparticles alone, chlorhexidine alone, neomycin-conjugated nanoparticles, and neomycin alone. The findings showed that gold-conjugated chlorhexidine nanoparticles exhibited significant amoebicidal and amoebistatic effects at 5 μM. Amoebicidal effects were observed by parasite viability testing using a Trypan blue exclusion assay and flow-cytometric analysis using propidium iodide, while amoebistatic effects were observed using growth
-
Conjugate gradient algorithms using multiple recursions
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Barth, T.; Manteuffel, T.
1996-12-31
Much is already known about when a conjugate gradient method can be implemented with short recursions for the direction vectors. The work done in 1984 by Faber and Manteuffel gave necessary and sufficient conditions on the iteration matrix A, in order for a conjugate gradient method to be implemented with a single recursion of a certain form. However, this form does not take into account all possible recursions. This became evident when Jagels and Reichel used an algorithm of Gragg for unitary matrices to demonstrate that the class of matrices for which a practical conjugate gradient algorithm exists can be extended to include unitary and shifted unitary matrices. The implementation uses short double recursions for the direction vectors. This motivates the study of multiple recursion algorithms.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ângela Maria Rubel Fanini
2017-05-01
Full Text Available http://dx.doi.org/10.5007/1807-1384.2017v14n2p132 This paper analysis virtual posts from women visiting the Blog, which focuses on conjugal problems. Violence between couples is analyzed through the relational perspective based on Santos and Izumino (2005. About machismo, it is adopted Castañeda’s (2006 point of view that emphasizes machismo as a behavior and a not male exclusive discourse. The passion-love ideology (Rougemont (1988 also enforces the culture of violence. The article is based on Foucault’s (1982, 1984, 1995, 2012 theoretical background in which violence and power are perceived as relational dimensions, and sexuality is also viewed as an important source of violence. The research desires to contribute on the violence against women discussion and their conjugal relations, aiming to reflect about the essentiality of changing cultural paradigms to then transform the scenery described.
-
Hu, Shun; Yu, Weili; Hu, Chunyang; Wei, Dong; Shen, Lijuan; Hu, Tao; Yi, Youjin
2017-11-01
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is a serious fatal pathogen that causes tuberculosis (TB). Effective vaccination is urgently needed to deal with the serious threat from TB. Mtb-secreted protein antigens are important virulence determinants of Mtb with poor immunogenicity. Adjuvants and antigen delivery systems are thus highly desired to improve the immunogenicity of protein antigens. Inulin is a biocompatible polysaccharide (PS) adjuvant that can stimulate a strong cellular and humoral immunity. Bacterial capsular PS and haptens have been conjugated with cross-reacting material 197 (CRM 197 ) to improve their immunogenicity. CFP10 and TB10.4 were two Mtb-secreted immunodominant protein antigens. A CFP10-TB10.4 fusion protein (CT) was used as the antigen for covalent conjugation with the CRM 197 -inulin conjugate (CRM-inu). The resultant conjugate (CT-CRM-inu) elicited high CT-specific IgG titers, stimulated splenocyte proliferation and provoked the secretion of Th1-type and Th2-type cytokines. Conjugation with CRM-inu significantly prolonged the systemic circulation of CT and exposure to the immune system. Moreover, CT-CRM-inu showed no apparent toxicity to cardiac, hepatic and renal functions. Thus, conjugation of CT with CRM-inu provided an effective strategy for development of protein-based vaccines against Mtb infection. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Direct observation of ballistic Andreev reflection
Klapwijk, T. M.; Ryabchun, S. A.
2014-12-01
An overview is presented of experiments on ballistic electrical transport in inhomogeneous superconducting systems which are controlled by the process of Andreev reflection. The initial experiments based on the coexistence of a normal phase and a superconducting phase in the intermediate state led to the concept itself. It was followed by a focus on geometrically inhomogeneous systems like point contacts, which provided a very clear manifestation of the energy and direction dependence of the Andreev reflection process. The point contacts have recently evolved towards the atomic scale owing to the use of mechanical break-junctions, revealing a very detailed dependence of Andreev reflection on the macroscopic phase of the superconducting state. In present-day research, the superconducting in homogeneity is constructed by clean room technology and combines superconducting materials, for example, with low-dimensional materials and topological insulators. Alternatively, the superconductor is combined with nano-objects, such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, or semiconducting nanowires. Each of these "inhomogeneous systems" provides a very interesting range of properties, all rooted in some manifestation of Andreev reflection.
-
Gomes, Nadirlene Pereira; Erdmann, Alacoque Lorenzini
2014-01-01
to construct a theoretical matrix based on the meanings of the interactions and actions experienced by the professionals regarding the nursing care practices and the health of women in situations of conjugal violence in the ambit of the Family Health Strategy. research based in Grounded Theory. Following approval by the Research Ethics Committee, 52 professionals were interviewed in Santa Catarina, Brazil. The analysis was based on open, axial and selective codifications. the theoretical model was delimited based on the phenomenon "Recognizing conjugal violence as a public health problem, and the need for management of the care for the woman", which reflects the experience of the professionals in relation to care for the woman, as well as the meanings attributed to this care. the phenomenon allows one to understand the movement of action and interaction regarding the care for the woman in a situation of conjugal violence.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kiyko, V V; Kislov, V I; Ofitserov, E N
2015-01-01
In the framework of a statistical model of an adaptive optics system (AOS) of phase conjugation, three algorithms based on an integrated mathematical approach are considered, each of them intended for minimisation of one of the following characteristics: the sensor error (in the case of an ideal corrector), the corrector error (in the case of ideal measurements) and the compensation error (with regard to discreteness and measurement noises and to incompleteness of a system of response functions of the corrector actuators). Functional and statistical relationships between the algorithms are studied and a relation is derived to ensure calculation of the mean-square compensation error as a function of the errors of the sensor and corrector with an accuracy better than 10%. Because in adjusting the AOS parameters, it is reasonable to proceed from the equality of the sensor and corrector errors, in the case the Hartmann sensor is used as a wavefront sensor, the required number of actuators in the absence of the noise component in the sensor error turns out 1.5 – 2.5 times less than the number of counts, and that difference grows with increasing measurement noise. (adaptive optics)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kiyko, V V; Kislov, V I; Ofitserov, E N [A M Prokhorov General Physics Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow (Russian Federation)
2015-08-31
In the framework of a statistical model of an adaptive optics system (AOS) of phase conjugation, three algorithms based on an integrated mathematical approach are considered, each of them intended for minimisation of one of the following characteristics: the sensor error (in the case of an ideal corrector), the corrector error (in the case of ideal measurements) and the compensation error (with regard to discreteness and measurement noises and to incompleteness of a system of response functions of the corrector actuators). Functional and statistical relationships between the algorithms are studied and a relation is derived to ensure calculation of the mean-square compensation error as a function of the errors of the sensor and corrector with an accuracy better than 10%. Because in adjusting the AOS parameters, it is reasonable to proceed from the equality of the sensor and corrector errors, in the case the Hartmann sensor is used as a wavefront sensor, the required number of actuators in the absence of the noise component in the sensor error turns out 1.5 – 2.5 times less than the number of counts, and that difference grows with increasing measurement noise. (adaptive optics)
-
Phase-space spinor amplitudes for spin-1/2 systems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Watson, P.; Bracken, A. J.
2011-01-01
The concept of phase-space amplitudes for systems with continuous degrees of freedom is generalized to finite-dimensional spin systems. Complex amplitudes are obtained on both a sphere and a finite lattice, in each case enabling a more fundamental description of pure spin states than that previously given by Wigner functions. In each case the Wigner function can be expressed as the star product of the amplitude and its conjugate, so providing a generalized Born interpretation of amplitudes that emphasizes their more fundamental status. The ordinary product of the amplitude and its conjugate produces a (generalized) spin Husimi function. The case of spin-(1/2) is treated in detail, and it is shown that phase-space amplitudes on the sphere transform correctly as spinors under rotations, despite their expression in terms of spherical harmonics. Spin amplitudes on a lattice are also found to transform as spinors. Applications are given to the phase space description of state superposition, and to the evolution in phase space of the state of a spin-(1/2) magnetic dipole in a time-dependent magnetic field.
-
He, Jiao; Zhang, Yongmin; Ito, Yoichiro; Sun, Wenji
2011-01-01
Coupled with evaporative light scattering detection, a high-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) method was applied to the separation and purification of three tauro-conjugated cholic acids of taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA), taurohyodeoxycholic acid (THDCA) and taurohyocholic acid (THCA) from Pulvis Fellis Suis (Pig gallbladder bile) for the first time. The two-phase solvent system composed of chloroform-methanol-water-acetic acid (4:4:2:0.3, v/v/v/v) was selected for the one-step separation where the lower phase was used as the mobile phase in the head to tail elution mode. The revolution speed of the separation column, flow rate of the mobile phase and separation temperature were 800 rpm, 1.5 ml/min and 25°C respectively. From 100 mg of the crude extract, 10.2 mg of TCDCA, 11.8 mg of THDCA and 5.3 mg of THCA were obtained with the purity of 94.6%, 96.5% and 95.4%, respectively. in one step separation The HSCCC fractions were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and the structures of the three tauro-conjugated cholic acids were identified by ESI-MS, (1)H NMR and (13)C NMR.
-
Shinkai, Yasuhiro; Kashihara, Shinichi; Minematsu, Go; Fujii, Hirofumi; Naemura, Madoka; Kotake, Yojiro; Morita, Yasutaka; Ohnuki, Koichiro; Fokina, Alesya A; Stetsenko, Dmitry A; Filichev, Vyacheslav V; Fujii, Masayuki
2017-06-01
Herein we described the synthesis of siRNA-NES (nuclear export signal) peptide conjugates by solid phase fragment coupling and the application of them to silencing of bcr/abl chimeric gene in human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K562. Two types of siRNA-NES conjugates were prepared, and both sense strands at 5' ends were covalently linked to a NES peptide derived from TFIIIA and HIV-1 REV, respectively. Significant enhancement of silencing efficiency was observed for both of them. siRNA-TFIIIA NES conjugate suppressed the expression of BCR/ABL gene to 8.3% at 200 nM and 11.6% at 50 nM, and siRNA-HIV-1REV NES conjugate suppressed to 4.0% at 200 nM and 6.3% at 50 nM, whereas native siRNA suppressed to 36.3% at 200 nM and 30.2% at 50 nM. We could also show complex of siRNA-NES conjugate and designed amphiphilic peptide peptideβ7 could be taken up into cells with no cytotoxicity and showed excellent silencing efficiency. We believe that the complex siRNA-NES conjugate and peptideβ7 is a promising candidate for in vivo use and therapeutic applications.
-
O:2-CRM(197) conjugates against Salmonella Paratyphi A.
Micoli, Francesca; Rondini, Simona; Gavini, Massimiliano; Lanzilao, Luisa; Medaglini, Donata; Saul, Allan; Martin, Laura B
2012-01-01
Enteric fevers remain a common and serious disease, affecting mainly children and adolescents in developing countries. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi was believed to cause most enteric fever episodes, but several recent reports have shown an increasing incidence of S. Paratyphi A, encouraging the development of a bivalent vaccine to protect against both serovars, especially considering that at present there is no vaccine against S. Paratyphi A. The O-specific polysaccharide (O:2) of S. Paratyphi A is a protective antigen and clinical data have previously demonstrated the potential of using O:2 conjugate vaccines. Here we describe a new conjugation chemistry to link O:2 and the carrier protein CRM(197), using the terminus 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO), thus leaving the O:2 chain unmodified. The new conjugates were tested in mice and compared with other O:2-antigen conjugates, synthesized adopting previously described methods that use CRM(197) as carrier protein. The newly developed conjugation chemistry yielded immunogenic conjugates with strong serum bactericidal activity against S. Paratyphi A.
-
O:2-CRM(197 conjugates against Salmonella Paratyphi A.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Francesca Micoli
Full Text Available Enteric fevers remain a common and serious disease, affecting mainly children and adolescents in developing countries. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi was believed to cause most enteric fever episodes, but several recent reports have shown an increasing incidence of S. Paratyphi A, encouraging the development of a bivalent vaccine to protect against both serovars, especially considering that at present there is no vaccine against S. Paratyphi A. The O-specific polysaccharide (O:2 of S. Paratyphi A is a protective antigen and clinical data have previously demonstrated the potential of using O:2 conjugate vaccines. Here we describe a new conjugation chemistry to link O:2 and the carrier protein CRM(197, using the terminus 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO, thus leaving the O:2 chain unmodified. The new conjugates were tested in mice and compared with other O:2-antigen conjugates, synthesized adopting previously described methods that use CRM(197 as carrier protein. The newly developed conjugation chemistry yielded immunogenic conjugates with strong serum bactericidal activity against S. Paratyphi A.
-
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Etrych, Tomáš; Tsukigawa, K.; Nakamura, H.; Chytil, Petr; Fang, J.; Ulbrich, Karel; Otagiri, M.; Maeda, H.
2017-01-01
Roč. 106, 30 August (2017), s. 10-19 ISSN 0928-0987 R&D Projects: GA ČR(CZ) GA15-02986S; GA MŠk(CZ) LQ1604; GA MŠk(CZ) ED1.1.00/02.0109 Grant - others:AV ČR,Japan Society for the Promotion of Science(CZ) JSPS-16-05 Program:Bilaterální spolupráce Institutional support: RVO:61389013 Keywords : pirarubicin * PHPMA conjugate * tandem-diblock PHPMA conjugate Subject RIV: FR - Pharmacology ; Medidal Chemistry OBOR OECD: Pharmacology and pharmacy Impact factor: 3.756, year: 2016
-
Integrated circuits based on conjugated polymer monolayer.
Li, Mengmeng; Mangalore, Deepthi Kamath; Zhao, Jingbo; Carpenter, Joshua H; Yan, Hongping; Ade, Harald; Yan, He; Müllen, Klaus; Blom, Paul W M; Pisula, Wojciech; de Leeuw, Dago M; Asadi, Kamal
2018-01-31
It is still a great challenge to fabricate conjugated polymer monolayer field-effect transistors (PoM-FETs) due to intricate crystallization and film formation of conjugated polymers. Here we demonstrate PoM-FETs based on a single monolayer of a conjugated polymer. The resulting PoM-FETs are highly reproducible and exhibit charge carrier mobilities reaching 3 cm 2 V -1 s -1 . The high performance is attributed to the strong interactions of the polymer chains present already in solution leading to pronounced edge-on packing and well-defined microstructure in the monolayer. The high reproducibility enables the integration of discrete unipolar PoM-FETs into inverters and ring oscillators. Real logic functionality has been demonstrated by constructing a 15-bit code generator in which hundreds of self-assembled PoM-FETs are addressed simultaneously. Our results provide the state-of-the-art example of integrated circuits based on a conjugated polymer monolayer, opening prospective pathways for bottom-up organic electronics.
-
Jang, Mooseok; Ruan, Haowen; Vellekoop, Ivo M.; Judkewitz, Benjamin; Chung, Euiheon; Yang, Changhuei
2014-01-01
Light scattering in biological tissue significantly limits the accessible depth for localized optical interrogation and deep-tissue optical imaging. This challenge can be overcome by exploiting the time-reversal property of optical phase conjugation (OPC) to reverse multiple scattering events or suppress turbidity. However, in living tissue, scatterers are highly movable and the movement can disrupt time-reversal symmetry when there is a latency in the OPC playback. In this paper, we show that the motion-induced degradation of the OPC turbidity-suppression effect through a dynamic scattering medium shares the same decorrelation time constant as that determined from speckle intensity autocorrelation – a popular conventional measure of scatterer movement. We investigated this decorrelation characteristic time through a 1.5-mm-thick dorsal skin flap of a living mouse and found that it ranges from 50 ms to 2.5 s depending on the level of immobilization. This study provides information on relevant time scales for applying OPC to living tissues. PMID:25657876
-
METHOD OF CONJUGATED CIRCULAR ARCS TRACING
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
N. Ageyev Vladimir
2017-01-01
Full Text Available The geometric properties of conjugated circular arcs connecting two points on the plane with set directions of tan- gent vectors are studied in the work. It is shown that pairs of conjugated circular arcs with the same conditions in frontier points create one-parameter set of smooth curves tightly filling all the plane. One of the basic properties of this set is the fact that all coupling points of circular arcs are on the circular curve going through the initially given points. The circle radius depends on the direction of tangent vectors. Any point of the circle curve, named auxiliary in this work, determines a pair of conjugated arcs with given boundary conditions. One more condition of the auxiliary circle curve is that it divides the plane into two parts. The arcs going from the initial point are out of the circle limited by this circle curve and the arcs coming to the final point are inside it. These properties are the basis for the method of conjugated circular arcs tracing pro- posed in this article. The algorithm is rather simple and allows to fulfill all the needed plottings using only the divider and ruler. Two concrete examples are considered. The first one is related to the problem of tracing of a pair of conjugated arcs with the minimal curve jump when going through the coupling point. The second one demonstrates the possibility of trac- ing of the smooth curve going through any three points on the plane under condition that in the initial and final points the directions of tangent vectors are given. The proposed methods of conjugated circular arcs tracing can be applied in solving of a wide variety of problems connected with the tracing of cam contours, for example pattern curves in textile industry or in computer-aided-design systems when programming of looms with numeric control.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hansen, Paul Robert
2015-01-01
To produce antibodies against synthetic peptides it is necessary to couple them to a protein carrier. This chapter provides a nonspecialist overview of peptide-carrier conjugation. Furthermore, a protocol for coupling cysteine-containing peptides to bovine serum albumin is outlined....
-
Hein, Jason E; Zimmerman, Jake; Sibi, Mukund P; Hultin, Philip G
2005-06-23
[reaction: see text] A series of asymmetric free-radical-mediated intermolecular conjugate additions using a fluorous oxazolidinone chiral auxiliary has been completed. The fluorous auxiliary facilitated product isolation using fluorous solid phase extractions (FSPE), effectively removing excess organic and organometallic reagents. Parallel reactions carried out with a similar but nonfluorous norephedrine-derived oxazolidinone demonstrated the superior stereoselectivity and purification obtainable with the fluorous chiral auxiliary.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Collignon, A.; German, A.; Scherrmann, J.M.; Bourdon, R.
1983-01-01
Antidigitoxin antibodies prepared by immunizing rabbits with a digitoxin-bovine serum albumin conjugate have been studied by radioimmunoassay in the native serum (homogeneous phase antibodies) and after coupling on glass beads (heterogeneous phase antibodies). Homogeneous phase antibodies present a satisfactory titer and affinity constant and react very specifically with digitoxin. Fixation of antibodies on a solid phase induce a loss of their immunoreactivity as it is showed by modification of the inhibition curves, by a greater sensitivity to the chemical structure of the tracer and by a decrease of the affinity constant. Reactionnal kinetic and sensitivity to the incubation temperature are not modified. Heterogeneous phase antibodies present a greater stability. Both antibodies types can be used for a digitoxin radioimmunoassay [fr
-
Solar multi-conjugate adaptive optics performance improvement
Zhang, Zhicheng; Zhang, Xiaofang; Song, Jie
2015-08-01
In order to overcome the effect of the atmospheric anisoplanatism, Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics (MCAO), which was developed based on turbulence correction by means of several deformable mirrors (DMs) conjugated to different altitude and by which the limit of a small corrected FOV that is achievable with AO is overcome and a wider FOV is able to be corrected, has been widely used to widen the field-of-view (FOV) of a solar telescope. With the assistance of the multi-threaded Adaptive Optics Simulator (MAOS), we can make a 3D reconstruction of the distorted wavefront. The correction is applied by one or more DMs. This technique benefits from information about atmospheric turbulence at different layers, which can be used to reconstruct the wavefront extremely well. In MAOS, the sensors are either simulated as idealized wavefront gradient sensors, tip-tilt sensors based on the best Zernike fit, or a WFS using physical optics and incorporating user specified pixel characteristics and a matched filter pixel processing algorithm. Only considering the atmospheric anisoplanatism, we focus on how the performance of a solar MCAO system is related to the numbers of DMs and their conjugate heights. We theoretically quantify the performance of the tomographic solar MCAO system. The results indicate that the tomographic AO system can improve the average Strehl ratio of a solar telescope by only employing one or two DMs conjugated to the optimum altitude. And the S.R. has a significant increase when more deformable mirrors are used. Furthermore, we discuss the effects of DM conjugate altitude on the correction achievable by the MCAO system, and present the optimum DM conjugate altitudes.
-
Phase-change related epigenetic and physiological changes in Pinus radiata D. Don.
Fraga, Mario F; Cañal, Maria Jesús; Rodríguez, Roberto
2002-08-01
DNA methylation and polyamine levels were analysed before and after Pinus radiata D. Don. phase change in order to identify possible molecular and physiological phase markers. Juvenile individuals (without reproductive ability) were characterised by a degree of DNA methylation of 30-35% and a ratio of free polyamines to perchloric acid-soluble polyamine conjugates greater than 1, while mature trees (with reproductive ability) had 60% 5-methylcytosine and a ratio of free polyamines to perchloric acid-soluble polyamine conjugates of less than 1. Results obtained with trees that attained reproductive capacity during the experimental period confirmed that changes in the degree of DNA methylation and polyamine concentrations found among juvenile and mature states come about immediately after the phase change. We suggest that both indicators may be associated with the loss of morphogenic ability during ageing, particularly after phase change, through a number of molecular interactions, which are subsequently discussed.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Kirketerp, Maj-Britt Suhr; Ryhding, Torben; Støchkel, Kristian
2011-01-01
Oligo(p-phenyleneethynylene)s (OPEs) are conjugated oligomers of great interest within materials science and molecular electronics on account of their highly applicable electronic and optical properties. Here we use gas-phase action spectroscopy to elucidate how the intrinsic electronic properties...
-
Cai, B; Ikeda, S
2016-08-01
Whey proteins can be used to stabilize foams and emulsions against coalescence because of their ability to form viscoelastic films at the interface that resist film rupture on collision between colloidal particles. However, whey proteins are competitively displaced from the interface if small-molecule surfactants are added, leading to destabilization of the entire system. This is because surfactants are more effective in molecular packing at the interface, and they lower interfacial tension to a greater degree than whey proteins do, but their interfacial films are poor in viscoelasticity. We hypothesized that whey proteins would become more resistant to surfactant-induced competitive displacement if they were conjugated with network-forming polysaccharides. The protein moiety of the conjugate would be expected to enable its adsorption to the interface, and the polysaccharide moiety would be expected to form self-assembled networks, strengthening the interfacial film as a whole. In this study, whey proteins were conjugated with gellan polysaccharides using the Maillard reaction. Atomic force microscopy images of interfacial films formed by the whey protein-gellan conjugate at the air-water interface and transferred onto mica sheets using the Langmuir-Blodgett method revealed that gellan did form self-assembled networks at the interface and that interfacial films also contained a large number of unconjugated whey protein molecules. Following the addition of a small-molecule surfactant (Tween 20) to the sub-phase, surface pressure increased, indicating spontaneous adsorption of surfactants to the interface. Atomic force microscopy images showed decreases in interfacial area coverage by whey proteins as surface pressure increased. At a given surface pressure, the interfacial area coverage by whey protein-gellan conjugates was greater than coverage by unconjugated whey proteins, confirming that whey proteins became more resistant to surfactant-induced displacement after
-
Site-Selective Conjugation of Native Proteins with DNA
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Trads, Julie Brender; Tørring, Thomas; Gothelf, Kurt Vesterager
2017-01-01
Conjugation of DNA to proteins is increasingly used in academia and industry to provide proteins with tags for identification or handles for hybridization to other DNA strands. Assay technologies such as immuno-PCR and proximity ligation and the imaging technology DNA-PAINT require DNA-protein....... The introduction of a bioorthogonal handle at a specific position of a protein by recombinant techniques provides an excellent approach to site-specific conjugation, but for many laboratories and for applications where several proteins are to be labeled, the expression of recombinant proteins may be cumbersome...... conjugates. In DNA nanotechnology, the DNA handle is exploited to precisely position proteins by self-assembly. For these applications, site-selective conjugation is almost always desired because fully functional proteins are required to maintain the specificity of antibodies and the activity of enzymes...
-
Conjugated Polymers for Flexible Energy Harvesting and Storage.
Zhang, Zhitao; Liao, Meng; Lou, Huiqing; Hu, Yajie; Sun, Xuemei; Peng, Huisheng
2018-03-01
Since the discovery of conjugated polymers in the 1970s, they have attracted considerable interest in light of their advantages of having a tunable bandgap, high electroactivity, high flexibility, and good processability compared to inorganic conducting materials. The above combined advantages make them promising for effective energy harvesting and storage, which have been widely studied in recent decades. Herein, the key advancements in the use of conjugated polymers for flexible energy harvesting and storage are reviewed. The synthesis, structure, and properties of conjugated polymers are first summarized. Then, their applications in flexible polymer solar cells, thermoelectric generators, supercapacitors, and lithium-ion batteries are described. The remaining challenges are then discussed to highlight the future direction in the development of conjugated polymers. © 2018 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Kulkarni, Prasad S.; Socquet, Muriel; Jadhav, Suresh S.; Kapre, Subhash V.; LaForce, F. Marc; Poonawalla, Cyrus S.
2015-01-01
Background. In 2002, the Meningitis Vaccine Project (MVP) chose the Serum Institute of India, Ltd (SIIL), as its manufacturing partner to establish a product development partnership (PDP) with the Meningitis Vaccine Project (MVP). MVP was a collaboration between PATH and the World Health Organization (WHO) to develop meningococcal conjugate vaccines for sub-Saharan Africa. Method. From the outset, SIIL recognized that a partnership with MVP carried some risk but also offered important opportunities for accessing new conjugate vaccine technology and know-how. Over 3 years, SIIL successfully accepted technology transfer for the group A meningococcal polysaccharide from SynCo Bio Partners and a conjugation method from the US Food and Drug Administration. Results. SIIL successfully scaled up production of a group A meningococcal conjugate vaccine that used SIIL tetanus toxoid as the carrier protein. Phase 1 studies began in India in 2005, followed by phase 2/3 studies in Africa and India. A regulatory dossier was submitted to the Indian authorities in April 2009 and WHO in September 2009. Export license was granted in December 2009, and WHO prequalification was obtained in June 2010. Vaccine was introduced at public scale in Burkina Faso that December. The group A meningococcal conjugate vaccine was named MenAfriVac, and is the first internationally qualified vaccine developed outside of big pharma. Conclusions. The project proved to be a sound investment for SIIL and is a concrete example of the potential for PDPs to provide needed products for resource-poor countries. PMID:26553678
-
Lipke, Elisabeth; Michalik, Peter
2012-11-01
Sperm conjugation, where two or more sperm are physically united, is a rare but widespread pheno-menon across the animal kingdom. One group well known for its different types of sperm conjugation are spiders. Particularly, haplogyne spiders show a high diversity of sperm traits. Besides individual cleistospermia, primary (synspermia) and secondary (coenospermia, "spermatophore") sperm conjugation occurs. However, the evolution of sperm conjugates and sperm is not understood in this group. Here, we look at how sperm are transferred in Caponiidae (Haplogynae) in pursuit of additional information about the evolution of sperm transfer forms in spiders. Additionally, we investigated the male reproductive system and spermatozoa using light- and transmission electron-microscopy and provide a 3D reconstruction of individual as of well as conjugated spermatozoa. Mature spermatozoa are characterized by an extremely elongated, helical nucleus resulting in the longest spider sperm known to date. At the end of spermiogenesis, synspermia are formed by complete fusion of four spermatids. Thus, synspermia might have evolved early within ecribellate Haplogynae. The fused sperm cells are surrounded by a prominent vesicular area. The function of the vesicular area remains still unknown but might be correlated with the capacitation process inside the female. Further phylogenetic and functional implications of the spermatozoa and sperm conjugation are discussed. Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Design and biological activity of β-sheet breaker peptide conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rocha, Sandra; Cardoso, Isabel; Boerner, Hans; Pereira, Maria Carmo; Saraiva, Maria Joao; Coelho, Manuel
2009-01-01
The sequence LPFFD (iAβ 5 ) prevents amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) fibrillogenesis and neurotoxicity, hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD), as previously demonstrated. In this study iAβ 5 was covalently linked to poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and the activity of conjugates was assessed and compared to the activity of the peptide alone by in vitro studies. The conjugates were characterized by MALDI-TOF. Competition binding assays established that conjugates retained the ability to bind Aβ with similar strength as iAβ 5 . Transmission electron microscopy analysis showed that iAβ 5 conjugates inhibited amyloid fibril formation, which is in agreement with binding properties observed for the conjugates towards Aβ. The conjugates were also able to prevent amyloid-induced cell death, as evaluated by activation of caspase 3. These results demonstrated that the biological activity of iAβ 5 is not affected by the pegylation process.
-
Poulin-Laprade, Dominic; Carraro, Nicolas; Burrus, Vincent
2015-01-01
Nowadays, healthcare systems are challenged by a major worldwide drug resistance crisis caused by the massive and rapid dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and associated emergence of multidrug resistant pathogenic bacteria, in both clinical and environmental settings. Conjugation is the main driving force of gene transfer among microorganisms. This mechanism of horizontal gene transfer mediates the translocation of large DNA fragments between two bacterial cells in direct contact. Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) of the SXT/R391 family (SRIs) and IncA/C conjugative plasmids (ACPs) are responsible for the dissemination of a broad spectrum of antibiotic resistance genes among diverse species of Enterobacteriaceae and Vibrionaceae. The biology, diversity, prevalence and distribution of these two families of conjugative elements have been the subject of extensive studies for the past 15 years. Recently, the transcriptional regulators that govern their dissemination through the expression of ICE- or plasmid-encoded transfer genes have been described. Unrelated repressors control the activation of conjugation by preventing the expression of two related master activator complexes in both types of elements, i.e., SetCD in SXT/R391 ICEs and AcaCD in IncA/C plasmids. Finally, in addition to activating ICE- or plasmid-borne genes, these master activators have been shown to specifically activate phylogenetically unrelated mobilizable genomic islands (MGIs) that also disseminate antibiotic resistance genes and other adaptive traits among a plethora of pathogens such as Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella enterica.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Dominic ePoulin-Laprade
2015-08-01
Full Text Available Nowadays, healthcare systems are challenged by a major worldwide drug resistance crisis caused by the massive and rapid dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and associated emergence of multidrug resistant pathogenic bacteria, in both clinical and environmental settings. Conjugation is the main driving force of gene transfer among microorganisms. This mechanism of horizontal gene transfer mediates the translocation of large DNA fragments between two bacterial cells in direct contact. Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs of the SXT/R391 family (SRIs and IncA/C conjugative plasmids (ACPs are responsible for the dissemination of a broad spectrum of antibiotic resistance genes among diverse species of Enterobacteriaceae and Vibrionaceae. The biology, diversity, prevalence and distribution of these two families of conjugative elements have been the subject of extensive studies for the past 15 years. Recently, the transcriptional regulators that govern their dissemination through the expression of ICE- or plasmid-encoded transfer genes have been described. Unrelated repressors control the activation of conjugation by preventing the expression of two related master activator complexes in both types of elements, i.e. SetCD in SXT/R391 ICEs and AcaCD in IncA/C plasmids. Finally, in addition to activating ICE- or plasmid-borne genes, these master activators have been shown to specifically activate phylogenetically unrelated mobilizable genomic islands (MGIs that also disseminate antibiotic resistance genes and other adaptive traits among a plethora of pathogens such as Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella enterica.
-
Khazanov, G. V.; Merkin, V. G.; Zesta, E.; Sibeck, D. G.; Grubbs, G. A., II; Chu, M.; Wiltberger, M. J.
2017-12-01
The magnetosphere and ionosphere are strongly coupled by precipitating electrons during storm times. Therefore, first principle simulations of precipitating electron fluxes are required to understand storm time variations of ionospheric conductances and related electric fields. As has been discussed by Khazanov et al. [2015 - 2017], the first step in such simulations is initiation of electron precipitation from the Earth's plasma sheet via wave particle interaction processes into both magnetically conjugate points, and the step 2 is the follow up of multiple atmospheric reflections of electron fluxes formed at the boundary between the ionosphere and magnetosphere of two magnetically conjugate points. To demonstrate this effect on the global magnetospheric response the Lyon-Fedder-Mobarry global magnetosphere model coupled with the Rice Convection Model of the inner magnetosphere has been used and run for the geomagnetic storm of 17 March 2013.
-
Superconvergent sum rules for the normal reflectivity
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Furuya, K.; Zimerman, A.H.; Villani, A.
1976-05-01
Families of superconvergent relations for the normal reflectivity function are written. Sum rules connecting the difference of phases of the reflectivities of two materials are also considered. Finally superconvergence relations and sum rules for magneto-reflectivity in the Faraday and Voigt regimes are also studied
-
Comparison of phase-constrained parallel MRI approaches: Analogies and differences.
Blaimer, Martin; Heim, Marius; Neumann, Daniel; Jakob, Peter M; Kannengiesser, Stephan; Breuer, Felix A
2016-03-01
Phase-constrained parallel MRI approaches have the potential for significantly improving the image quality of accelerated MRI scans. The purpose of this study was to investigate the properties of two different phase-constrained parallel MRI formulations, namely the standard phase-constrained approach and the virtual conjugate coil (VCC) concept utilizing conjugate k-space symmetry. Both formulations were combined with image-domain algorithms (SENSE) and a mathematical analysis was performed. Furthermore, the VCC concept was combined with k-space algorithms (GRAPPA and ESPIRiT) for image reconstruction. In vivo experiments were conducted to illustrate analogies and differences between the individual methods. Furthermore, a simple method of improving the signal-to-noise ratio by modifying the sampling scheme was implemented. For SENSE, the VCC concept was mathematically equivalent to the standard phase-constrained formulation and therefore yielded identical results. In conjunction with k-space algorithms, the VCC concept provided more robust results when only a limited amount of calibration data were available. Additionally, VCC-GRAPPA reconstructed images provided spatial phase information with full resolution. Although both phase-constrained parallel MRI formulations are very similar conceptually, there exist important differences between image-domain and k-space domain reconstructions regarding the calibration robustness and the availability of high-resolution phase information. © 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Veselovskii Igor
2018-01-01
Full Text Available Lidar sounding is used for the analysis of possible contribution of the corner reflection (CR effect to the total backscattering in case of ice crystals. Our study is based on observations of mixed phase clouds performed during the SHADOW campaign in Senegal. Mie-Raman lidar allows measurements at 355 nm and 532 nm at 43 dg. off-zenith angle, so the extinction and backscattering Ångström exponents can be evaluated. In some measurements we observed the positive values of backscattering Ångström exponent, which can be attributed to the corner reflection by horizontally oriented ice plates.
-
Graphene based terahertz phase modulators
Kakenov, N.; Ergoktas, M. S.; Balci, O.; Kocabas, C.
2018-07-01
Electrical control of amplitude and phase of terahertz radiation (THz) is the key technological challenge for high resolution and noninvasive THz imaging. The lack of active materials and devices hinders the realization of these imaging systems. Here, we demonstrate an efficient terahertz phase and amplitude modulation using electrically tunable graphene devices. Our device structure consists of electrolyte-gated graphene placed at quarter wavelength distance from a reflecting metallic surface. In this geometry, graphene operates as a tunable impedance surface which yields electrically controlled reflection phase. Terahertz time domain reflection spectroscopy reveals the voltage controlled phase modulation of π and the reflection modulation of 50 dB. To show the promises of our approach, we demonstrate a multipixel phase modulator array which operates as a gradient impedance surface.
-
Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of gold nanoparticle conjugates with cefotaxime
Titanova, Elena O.; Burygin, Gennady L.
2016-04-01
Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) have attracted significant interest as a novel platform for various applications to nanobiotechnology and biomedicine. The conjugates of GNPs with antibiotics and antibodies were also used for selective photothermal killing of protozoa and bacteria. Also the conjugates of some antibiotics with GNPs decreased the number of bacterial growing cells. In this work was made the procedure optimization for conjugation of cefotaxime (a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic) with GNPs (15 nm) and we examined the antimicrobial properties of this conjugate to bacteria culture of E. coli K-12. Addition of cefotaxime solution to colloidal gold does not change their color and extinction spectrum. For physiologically active concentration of cefotaxime (3 μg/mL), it was shown that the optimum pH for the conjugation was more than 9.5. A partial aggregation of the GNPs in saline medium was observed at pH 6.5-7.5. The optimum concentration of K2CO3 for conjugation cefotaxime with GNPs-15 was 5 mM. The optimum concentration of cefotaxime was at 0.36 μg/mL. We found the inhibition of the growth of E. coli K12 upon application cefotaxime-GNP conjugates.
-
Conjugated Polymer Solar Cells
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Paraschuk, Dmitry Y
2006-01-01
This report results from a contract tasking Moscow State University as follows: Conjugated polymers are promising materials for many photonics applications, in particular, for photovoltaic and solar cell devices...
-
Gomes, Nadirlene Pereira; Erdmann, Alacoque Lorenzini
2014-01-01
Objective to construct a theoretical matrix based on the meanings of the interactions and actions experienced by the professionals regarding the nursing care practices and the health of women in situations of conjugal violence in the ambit of the Family Health Strategy. Methods research based in Grounded Theory. Following approval by the Research Ethics Committee, 52 professionals were interviewed in Santa Catarina, Brazil. The analysis was based on open, axial and selective codifications. Results the theoretical model was delimited based on the phenomenon "Recognizing conjugal violence as a public health problem, and the need for management of the care for the woman", which reflects the experience of the professionals in relation to care for the woman, as well as the meanings attributed to this care. Conclusions the phenomenon allows one to understand the movement of action and interaction regarding the care for the woman in a situation of conjugal violence. PMID:24553706
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Nadirlene Pereira Gomes
2014-01-01
Full Text Available OBJECTIVE: to construct a theoretical matrix based on the meanings of the interactions and actions experienced by the professionals regarding the nursing care practices and the health of women in situations of conjugal violence in the ambit of the Family Health Strategy. METHODS: research based in Grounded Theory. Following approval by the Research Ethics Committee, 52 professionals were interviewed in Santa Catarina, Brazil. The analysis was based on open, axial and selective codifications. RESULTS: the theoretical model was delimited based on the phenomenon "Recognizing conjugal violence as a public health problem, and the need for management of the care for the woman", which reflects the experience of the professionals in relation to care for the woman, as well as the meanings attributed to this care. CONCLUSIONS: the phenomenon allows one to understand the movement of action and interaction regarding the care for the woman in a situation of conjugal violence.
-
Kadamne, Jeta V; Jain, Vishal P; Saleh, Mohammed; Proctor, Andrew
2009-11-25
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) isomers in oils are currently measured as fatty acid methyl esters by a gas chromatography-flame ionization detector (GC-FID) technique, which requires approximately 2 h to complete the analysis. Hence, we aim to develop a method to rapidly determine CLA isomers in CLA-rich soy oil. Soy oil with 0.38-25.11% total CLA was obtained by photo-isomerization of 96 soy oil samples for 24 h. A sample was withdrawn at 30 min intervals with repeated processing using a second batch of oil. Six replicates of GC-FID fatty acid analysis were conducted for each oil sample. The oil samples were scanned using attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), and the spectrum was collected. Calibration models were developed using partial least-squares (PLS-1) regression using Unscrambler software. Models were validated using a full cross-validation technique and tested using samples that were not included in the calibration sample set. Measured and predicted total CLA, trans,trans CLA isomers, total mono trans CLA isomers, trans-10,cis-12 CLA, trans-9,cis-11 CLA and cis-10,trans-12 CLA, and cis-9,trans-11 CLA had cross-validated coefficients of determinations (R2v) of 0.97, 0.98, 0.97, 0.98, 0.97, and 0.99 and corresponding root-mean-square error of validation (RMSEV) of 1.14, 0.69, 0.27, 0.07, 0.14, and 0.07% CLA, respectively. The ATR-FTIR technique is a rapid and less expensive method for determining CLA isomers in linoleic acid photo-isomerized soy oil than GC-FID.
-
Soluble polymer conjugates for drug delivery.
Minko, Tamara
2005-01-01
The use of water-soluble polymeric conjugates as drug carriers offers several possible advantages. These advantages include: (1) improved drug pharmacokinetics; (2) decreased toxicity to healthy organs; (3) possible facilitation of accumulation and preferential uptake by targeted cells; (4) programmed profile of drug release. In this review, we will consider the main types of useful polymeric conjugates and their role and effectiveness as carriers in drug delivery systems.: © 2005 Elsevier Ltd . All rights reserved.
-
Diffeomorphisms Holder conjugate to Anosov diffeomorphisms
Gogolev, Andrey
2008-01-01
We show by means of a counterexample that a $C^{1+Lip}$ diffeomorphism Holder conjugate to an Anosov diffeomorphism is not necessarily Anosov. The counterexample can bear higher smoothness up to $C^3$. Also we include a result from the 2006 Ph.D. thesis of T. Fisher: a $C^{1+Lip}$ diffeomorphism Holder conjugate to an Anosov diffeomorphism is Anosov itself provided that Holder exponents of the conjugacy and its inverse are sufficiently large.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Waddell, Michael G.; Domoracki, William J.; Eyer, Jerome
2003-01-01
The Earth Sciences and Resources Institute, University of South Carolina is conducting a proof of concept study to determine the location and distribution of subsurface DNAPL carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4 ) contamination at the 216-Z-9 crib, 200 West area, DOE Hanford Site, Washington by use of two-dimensional high-resolution seismic reflection surveys and borehole geophysical data. The study makes use of recent advances in seismic reflection amplitude versus offset (AVO) technology to directly detect the presence of subsurface DNAPL. The techniques proposed are noninvasive means of site characterization and direct free-phase DNAPL detection. This final report covers the results of Tasks 1, 2, and 3. Task (1) contains site evaluation and seismic modeling studies. The site evaluation consists of identifying and collecting preexisting geological and geophysical information regarding subsurface structure and the presence and quantity of DNAPL. The seismic modeling studies were undertaken to determine the likelihood that an AVO response exists and its probable manifestation. Task (2) is the design and acquisition of 2-D seismic reflection data to image areas of probable high concentration of DNAPL. Task (3) is the processing and interpretation of the 2-D data. During the commission of these tasks four seismic reflection profiles were collected. Subsurface velocity information was obtained by vertical seismic profile surveys in three wells. The interpretation of these data is in two parts. Part one is the construction and interpretation of structural contour maps of the contact between the Hanford Fine unit and the underlying Plio/Pleistocene unit and of the contact between the Plio/Pleistocene unit and the underlying caliche layer. These two contacts were determined to be the most likely surfaces to contain the highest concentration CCl 4 . Part two of the interpretation uses the results of the AVO modeling to locate any seismic amplitude anomalies that might be
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Michael G. Waddell; William J. Domoracki; Jerome Eyer
2003-01-01
The Earth Sciences and Resources Institute, University of South Carolina is conducting a proof of concept study to determine the location and distribution of subsurface DNAPL carbon tetrachloride (CCl{sub 4}) contamination at the 216-Z-9 crib, 200 West area, DOE Hanford Site, Washington by use of two-dimensional high-resolution seismic reflection surveys and borehole geophysical data. The study makes use of recent advances in seismic reflection amplitude versus offset (AVO) technology to directly detect the presence of subsurface DNAPL. The techniques proposed are noninvasive means of site characterization and direct free-phase DNAPL detection. This final report covers the results of Tasks 1, 2, and 3. Task (1) contains site evaluation and seismic modeling studies. The site evaluation consists of identifying and collecting preexisting geological and geophysical information regarding subsurface structure and the presence and quantity of DNAPL. The seismic modeling studies were undertaken to determine the likelihood that an AVO response exists and its probable manifestation. Task (2) is the design and acquisition of 2-D seismic reflection data to image areas of probable high concentration of DNAPL. Task (3) is the processing and interpretation of the 2-D data. During the commission of these tasks four seismic reflection profiles were collected. Subsurface velocity information was obtained by vertical seismic profile surveys in three wells. The interpretation of these data is in two parts. Part one is the construction and interpretation of structural contour maps of the contact between the Hanford Fine unit and the underlying Plio/Pleistocene unit and of the contact between the Plio/Pleistocene unit and the underlying caliche layer. These two contacts were determined to be the most likely surfaces to contain the highest concentration CCl{sub 4}. Part two of the interpretation uses the results of the AVO modeling to locate any seismic amplitude anomalies that might be
-
Conjugate Problems in Convective Heat Transfer: Review
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Abram Dorfman
2009-01-01
Full Text Available A review of conjugate convective heat transfer problems solved during the early and current time of development of this modern approach is presented. The discussion is based on analytical solutions of selected typical relatively simple conjugate problems including steady-state and transient processes, thermal material treatment, and heat and mass transfer in drying. This brief survey is accompanied by the list of almost two hundred publications considering application of different more and less complex analytical and numerical conjugate models for simulating technology processes and industrial devices from aerospace systems to food production. The references are combined in the groups of works studying similar problems so that each of the groups corresponds to one of selected analytical solutions considered in detail. Such structure of review gives the reader the understanding of early and current situation in conjugate convective heat transfer modeling and makes possible to use the information presented as an introduction to this area on the one hand, and to find more complicated publications of interest on the other hand.
-
Improvement of Emulsifying Properties of Wheat Gluten Hydrolysate λ-Carrageenan Conjugates
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jin-Shui Wang
2006-01-01
Full Text Available Gluten hydrolysate was prepared through limited enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat gluten resulting from the byproducts of wheat starch. The enzyme applied in the present study was Protamex. Response surface methodology was used to investigate the effects of pH, gluten hydrolysate (GHPλ-carrageenan (C ratio and reaction time on emulsifying properties of the GHP-C conjugate. The regression model for emulsion activity index (EAI was significant at p=0.001, while reaction time had a significant effect on EAI of the conjugate with regression coefficient of 4.25. The interactions of pH and GHP/ C ratio, and GHP/C ratio and reaction time significantly affected the EAI of the conjugate. Both the emulsifying property and nitrogen solubility index (NSI of GHP-C conjugate prepared under the optimal conditions increased more remarkably, compared to the control. The denaturation temperature of GHP-C conjugate obviously increased compared to wheat gluten. The addition of GHP-C conjugate had different effects on dough characteristics. Moreover, this conjugate can delay the increase in the bread crumb firmness during storage. It demonstrated that this conjugate couldimprove the dough characteristics and had anti-staling properties of bread.
-
Vogel, Curtis R; Yang, Qiang
2006-08-21
We present two different implementations of the Fourier domain preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm (FD-PCG) to efficiently solve the large structured linear systems that arise in optimal volume turbulence estimation, or tomography, for multi-conjugate adaptive optics (MCAO). We describe how to deal with several critical technical issues, including the cone coordinate transformation problem and sensor subaperture grid spacing. We also extend the FD-PCG approach to handle the deformable mirror fitting problem for MCAO.
-
Preparation and biodistribution study of 99Tcm labelled dextran conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yang Chunhui; Li Hongyu; Liang Jixin; Lu Jia; Luo Hongyi; Zheng Deqiang; Sun Guiquan
2012-01-01
99 Tc m Mannosylated dextran conjugates were prepared through [ 99 Tc m (CO) 3 ] + precursor synthesized by carbonyl Isolink kit. The labelled conjugates were injected sub-dermally into the rear foots of the mice, and the patent blue solution was injected at the same site 10 min before sacrifice. The mice were killed at 1 h and 4 h postinjection, and the samples of different tissues including SLN, 2LN, injection site, liver, spleen, blood were dissected and counted. The uptake in terms was calculated. The results of biodistribution demonstrated that the SLN uptakes of radiopharmaceutical (without mannose in the molecules) were rather low and in vivo excretion of these conjugates were comparatively faster, and the uptake of injection site was also low; on the other hand, the SLN uptakes of radio pharmaceutical (with mannose in their molecules) were much higher than those of their corresponding dextran conjugates without mannose, but the retention in the injection site of these conjugates increased too. The results indicated that the affinity of mannosyl-dextran conjugates to the receptors on the surface of macrophages in the lymph node. In addition, the different relative molecular mass of dextran conjugates also cause different biodistribution results, the major one had higher SLN uptake, the difference was significant (P 99 Tc m (CO) 3 ] + labelled mannosylated dextran conjugates showed promising properties as SLN imaging agent and worth further investigation. (authors)
-
Swept source optical coherence tomography of objects with arbitrary reflectivity profiles
Mezgebo, Biniyam; Nagib, Karim; Fernando, Namal; Kordi, Behzad; Sherif, Sherif
2018-03-01
Swept Source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) has become a well established imaging modality for both medical and industrial diagnostic applications. A cross-sectional SS-OCT image is obtained by applying an inverse discrete Fourier transform (DFT) to axial interferogram measured in the frequency domain (k-space). Fourier inversion of the obtained interferogram typically produces a potentially overlapping conjugate mirror image, whose overlap could be avoided by restricting the object to have its highest reflectivity at its surface. However, this restriction may not be fulfilled when imaging a very thin object that is placed on a highly reflective surface, or imaging an object containing a contrast agent with high reflectivity. In this paper, we show that oversampling of the SS-OCT signal in k-space would overcome the need for such restriction on the object. Our result is demonstrated using SS-OCT images of Axolotl salamander eggs.
-
Dutta, Rishabh; Wang, Teng; Feng, Guangcai; Harrington, Jonathan; Vasyura-Bathke, Hannes; Jónsson, Sigurjón
2017-04-01
Strain localizations in compliant fault zones (with elastic moduli lower than the surrounding rocks) induced by nearby earthquakes have been detected using geodetic observations in a few cases in the past. Here we observe small-scale changes in interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) measurements along multiple conjugate faults near the rupture of the 2013 Mw7.7 Baluchistan (Pakistan) earthquake. After removing the main coseismic deformation signal in the interferograms and correcting them for topography-related phase, we observe 2-3 cm signal along several conjugate faults that are 15-30 km from the mainshock fault rupture. These conjugate compliant faults have strikes of N30°E and N45°W. The sense of motion indicates left-lateral deformation across the N30°E faults and right-lateral deformation across the N45°W faults, which suggests the conjugate faults were subjected to extensional coseismic stresses along the WSW-ENE direction. The spacing between the different sets of faults is around 5 to 8 km. We explain the observed strain localizations as an elastic response of the compliant conjugate faults induced by the Baluchistan earthquake. Using 3D Finite Element models (FEM), we impose coseismic static displacements due to the earthquake along the boundaries of the FEM domain to reproduce the coseismic stress changes acting across the compliant faults. The InSAR measurements are used to constrain the geometry and rigidity variations of the compliant faults with respect to the surrounding rocks. The best fitting models show the compliant fault zones to have a width of 0.5 km to 2 km and a reduction of the shear modulus by a factor of 3 to 4. Our study yields similar values as were found for compliant fault zones near the 1992 Landers and the 1999 Hector Mine earthquakes in California, although here the strain localization is occurring on more complex conjugate sets of faults.
-
Functional properties of nisin–carbohydrate conjugates formed by radiation induced Maillard reaction
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Muppalla, Shobita R.; Sonavale, Rahul; Chawla, Surinder P.; Sharma, Arun
2012-01-01
Nisin–carbohydrate conjugates were prepared by irradiating nisin either with glucose or dextran. Increase in browning and formation of intermediate products was observed with a concomitant decrease in free amino and reducing sugar groups indicating occurrence of the Maillard reaction catalyzed by irradiation. Nisin–carbohydrate conjugates showed a broad spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fluorescence) as well as Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus). Results of antioxidant assays, including that of DPPH radical-scavenging activity and reducing power, showed that the nisin–dextran conjugates possessed better antioxidant potential than nisin–glucose conjugate. These results suggested that it was possible to enhance the functional properties of nisin by preparing radiation induced conjugates suitable for application in food industry. - Highlights: ► Nisin–carbohydrate conjugates were prepared using radiation induced Maillard reaction. ► Conjugation of nisin with dextran/glucose resulted in improvement of antibacterial spectrum. ► Conjugates of nisin with dextran/glucose had significant radical scavenging activity.
-
Yang, Long; Yu, Yuyan; Zhang, Jianling; Chen, Fu; Meng, Xiao; Qiu, Yong; Dan, Yi; Jiang, Long
2018-03-01
Aiming at developing highly efficient photocatalysts by broadening the light-harvesting region and suppressing photo-generated electron-hole recombination simultaneously, this work reports rational design and fabrication of donor-acceptor (D-A) conjugated polymer/TiO2 heterojunction catalyst with strong interfacial interactions by a facile in-situ thermal treatment. To expand the light-harvesting window, soluable conjugated copolymers with D-A architecture are prepared by Pd-mediated polycondensation of diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) and t-butoxycarbonyl (t-Boc) modified carbazole (Car), and used as visible-light-harvesting antenna to couple with TiO2 nanocrystals. The DPP-Car/TiO2 composites show wide range absorption in 300-1000 nm. To improve the interfacial binding at the interface, a facile in-situ thermal treatment is carried out to cleave the pendant t-Boc groups in carbazole units and liberate the polar amino groups (-NH-) which strongly bind to the surface of TiO2 through dipole-dipole interactions, forming a heterojunction interface. This in-situ thermal treatment changes the surface elemental distribution of TiO2, reinforces the interface bonding at the boundary of conjugated polymers/TiO2 and finally improves the photocatalytic efficiency of DPP-Car/TiO2 under visible-light irradiation. The interface changes are characterized and verified through Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), photo images, UV/Vis (solution state and powder diffuse reflection spectroscopy), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), fluorescence, scanning electron microscopy(SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques. This study provides a new strategy to avoid the low solubility of D-A conjugated polymers and construct highly-efficient conjugated polymer/TiO2 heterojunction by enforcing the interface contact and facilitating charge or energy transfer for the applications in photocatalysis.
-
Cross-conjugation and quantum interference: a general correlation?
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Valkenier, Hennie; Guedon, Constant M.; Markussen, Troels
2014-01-01
We discuss the relationship between the pi-conjugation pattern, molecular length, and charge transport properties of molecular wires, both from an experimental and a theoretical viewpoint. Specifically, we focus on the role of quantum interference in the conductance properties of cross-conjugated...
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Baran, Erkan T., E-mail: erkantur@metu.edu.tr; Tuzlakoglu, Kadriye, E-mail: kadriye@dep.uminho.pt; Mano, Joao F., E-mail: jmano@dep.uminho.pt; Reis, Rui L., E-mail: rgreis@dep.uminho.pt
2012-08-01
The objective of this study was to investigate the influence of silk fibroin and oxidized starch conjugation on the enzymatic degradation behavior and the cytocompatability of chitosan based biomaterials. The tensile stress of conjugate membranes, which was at 50 Megapascal (MPa) for the lowest fibroin and starch composition (10 weight percent (wt.%)), was decreased significantly with the increased content of fibroin and starch. The weight loss of conjugates in {alpha}-amylase was more notable when the starch concentration was the highest at 30 wt.%. The conjugates were resistant to the degradation by protease and lysozyme except for the conjugates with the lowest starch concentration. After 10 days of cell culture, the proliferation of osteoblast-like cells (SaOS-2) was stimulated significantly by higher fibroin compositions and the DNA synthesis on the conjugate with the highest fibroin (30 wt.%) was about two times more compared to the native chitosan. The light microscopy and the image analysis results showed that the cell area and the lengths were decreased significantly with higher fibroin/chitosan ratio. The study proved that the conjugation of fibroin and starch with the chitosan based biomaterials by the use of non-toxic reductive alkylation crosslinking significantly improved the cytocompatibility and modulated the biodegradation, respectively. - Highlights: Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Silk fibroin, starch and chitosan conjugates were prepared by reductive alkylation. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer The enzymatic biodegradation and the cytocompatibility of conjugates were tested. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer The conjugate with 30% starch composition was degraded by {alpha}-amylase significantly. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Higher starch composition in conjugates prevented protease and lysozyme degradation. Black-Right-Pointing-Pointer Fibroin incorporation effectively increased the cell proliferation of conjugates.
-
Recent Advances in Conjugated Polymers for Light Emitting Devices
AlSalhi, Mohamad Saleh; Alam, Javed; Dass, Lawrence Arockiasamy; Raja, Mohan
2011-01-01
A recent advance in the field of light emitting polymers has been the discovery of electroluminescent conjugated polymers, that is, kind of fluorescent polymers that emit light when excited by the flow of an electric current. These new generation fluorescent materials may now challenge the domination by inorganic semiconductor materials of the commercial market in light-emitting devices such as light-emitting diodes (LED) and polymer laser devices. This review provides information on unique properties of conjugated polymers and how they have been optimized to generate these properties. The review is organized in three sections focusing on the major advances in light emitting materials, recent literature survey and understanding the desirable properties as well as modern solid state lighting and displays. Recently, developed conjugated polymers are also functioning as roll-up displays for computers and mobile phones, flexible solar panels for power portable equipment as well as organic light emitting diodes in displays, in which television screens, luminous traffic, information signs, and light-emitting wallpaper in homes are also expected to broaden the use of conjugated polymers as light emitting polymers. The purpose of this review paper is to examine conjugated polymers in light emitting diodes (LEDs) in addition to organic solid state laser. Furthermore, since conjugated polymers have been approved as light-emitting organic materials similar to inorganic semiconductors, it is clear to motivate these organic light-emitting devices (OLEDs) and organic lasers for modern lighting in terms of energy saving ability. In addition, future aspects of conjugated polymers in LEDs were also highlighted in this review. PMID:21673938
-
Haemmerli, G; Sträuli, P
1981-05-15
The motile behavior of six cell lines derived from human squamous carcinomas (two from the larynx, four from the tongue) was studied by cinematography under phase- and reflection-contrast illumination. The recorded cell activities consist in spreading, stationary and translocation motility, and aggregate formation. Within this common pattern, quantitative modifications ("sub-pattern") are stable properties of the individual cells lines. Such modifications are particularly evident with regard to the dynamic texture of the aggregates which ranges from loose, netlike structures to compact islands with smooth borders. Accordingly, the intensity of cell traffic within and around the aggregates varies considerably. It is discussed to what extent the in vitro motility of the carcinoma cell populations reflects their behavior in the organism and thus the significance of cell movements for invasion.
-
Degenerate four-wave mixing with the phase diffusion field
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Anderson, M.H.; Chen, CE.; Elliott, D.S.; Cooper, J.; Smith, S.J.
1993-01-01
We report measurements of the effect of laser fluctuations on a strong-field degenerate four-wave mixing interaction, carried out in a nearly Doppler-free, two-level system using a single laser with statistically well-defined phase fluctuations. The counterpropagating pump beams and the probe beam, each split from this phase-noise-modulated source, were fully correlated. The nonlinear medium was an optically-pumped diffuse beam of atomic sodium. By time-delaying the probe with respect to the pump beams, the composite field becomes non-Markovian. Four-wave mixing results in the generation of a phase-conjugate beam anti-parallel to the probe beam. With the laser field spectrum nearly Lorentzian in shape, and with a field linewidth greater (and, for comparison, much narrower) than the natural linewidth of the sodium, we measured the intensity of the phase-conjugate beam as the pump and probe beams were tuned through the D2 resonance, as a function of intensity of die pump beam (up to intensities several times the saturation intensity), and for varying delay between the pump and probe fields. This experiment provides a cleaner measurement of this interaction than any previously available
-
Some aspects of geomagnetically conjugate phenomena
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rycroft, M.J.
1987-12-01
Both charged particles and waves convey information about the thermosphere, ionosphere and magnetosphere from the Northern to the Southern Hemisphere and vice versa, along geomagnetic flux tubes.The interhemispheric travel time of electrons or ions, being dependent upon L-value , pitch angle and energy (which may lie between less than or equal to 1 eV and greater than or equal to 1 MeV) may be many hours, ranging down to less than or equal to 1 s. However, the one-hop propagation time for magnetohydrodynamic or whistler mode waves generally lies between 10/sup 2/s and 1 s. Such times, therefore, give the time scales of transient phenomena that are geomagnetically conjugate and of changes in steady-state plasma processes occurring in geomagnetically conjugate regions. Contrasting examples are presented of conjugate physical phenomena, obtained using satellite, rocket, aircraft and ground-based observations; the latter capitalise upon the rather rare disposition of land - rather than ocean - at each end of a geophysically interesting flux tube. Particular attention is paid to the interactions between whistler mode waves and energetic electrons. Geomagnetic, radio, optical and plasma observations, taken together with model computations, provide a wealth of knowledge on conjugate phenomena and their dependence on conditions in the solar wind, substorms, L-value, etc... Finally, some suggestions are made for future lines of research.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nikhil, Kumar; Sharan, Shruti; Chakraborty, Ajanta [Molecular Endocrinology Laboratory, Department of Biotechnology, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee 247 667, Uttarakhand (India); Bodipati, Naganjaneyulu; Krishna Peddinti, Rama [Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee 247 667, Uttarakhand (India); Roy, Partha, E-mail: paroyfbs@iitr.ernet.in [Molecular Endocrinology Laboratory, Department of Biotechnology, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee 247 667, Uttarakhand (India)
2014-01-15
Naturally occurring pterostilbene (PTER) and isothiocyanate (ITC) attract great attention due to their wide range of biological properties, including anti-cancer, anti-leukemic, anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory activities. A novel class of hybrid compound synthesized by introducing an ITC moiety on PTER backbone was evaluated for its anti-cancer efficacy in hormone-dependent breast cancer cell line (MCF-7) in vitro and Ehrlich ascitic tumor bearing mice model in vivo. The novel hybrid molecule showed significant in vitro anti-cancer activity (IC{sub 50}=25±0.38) when compared to reference compound PTER (IC{sub 50}=65±0.42). The conjugate molecule induced both S and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest as indicated by flow cytometry analysis. In addition, the conjugate induced cell death was characterized by changes in cell morphology, DNA fragmentation, activation of caspase-9, release of cytochrome-c into cytosol and increased Bax: Bcl-2 ratio. The conjugate also suppressed the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK. The conjugate induced cell death was significantly increased in presence of A6730 (a potent Akt1/2 kinase inhibitor) and PD98059 (a specific ERK inhibitor). Moreover, the conjugated PTER inhibited tumor growth in Ehrlich ascitic cell induced tumor bearing mice as observed by reduction in tumor volume compared to untreated animals. Collectively, the pro-apoptotic effect of conjugate is mediated through the activation of caspases, and is correlated with the blockade of the Akt and ERK signaling pathways in MCF-7 cells. - Highlights: • Conjugate was prepared by appending isothiocyanate moiety on pterostilbene backbone. • Conjugate showed anticancer effects at comparatively lower dose than pterostilbene. • Conjugate caused blockage of the Akt and ERK signaling pathways in MCF-7 cells. • Conjugate significantly reduced solid tumor volume as compared to pterostilbene.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nikhil, Kumar; Sharan, Shruti; Chakraborty, Ajanta; Bodipati, Naganjaneyulu; Krishna Peddinti, Rama; Roy, Partha
2014-01-01
Naturally occurring pterostilbene (PTER) and isothiocyanate (ITC) attract great attention due to their wide range of biological properties, including anti-cancer, anti-leukemic, anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory activities. A novel class of hybrid compound synthesized by introducing an ITC moiety on PTER backbone was evaluated for its anti-cancer efficacy in hormone-dependent breast cancer cell line (MCF-7) in vitro and Ehrlich ascitic tumor bearing mice model in vivo. The novel hybrid molecule showed significant in vitro anti-cancer activity (IC 50 =25±0.38) when compared to reference compound PTER (IC 50 =65±0.42). The conjugate molecule induced both S and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest as indicated by flow cytometry analysis. In addition, the conjugate induced cell death was characterized by changes in cell morphology, DNA fragmentation, activation of caspase-9, release of cytochrome-c into cytosol and increased Bax: Bcl-2 ratio. The conjugate also suppressed the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK. The conjugate induced cell death was significantly increased in presence of A6730 (a potent Akt1/2 kinase inhibitor) and PD98059 (a specific ERK inhibitor). Moreover, the conjugated PTER inhibited tumor growth in Ehrlich ascitic cell induced tumor bearing mice as observed by reduction in tumor volume compared to untreated animals. Collectively, the pro-apoptotic effect of conjugate is mediated through the activation of caspases, and is correlated with the blockade of the Akt and ERK signaling pathways in MCF-7 cells. - Highlights: • Conjugate was prepared by appending isothiocyanate moiety on pterostilbene backbone. • Conjugate showed anticancer effects at comparatively lower dose than pterostilbene. • Conjugate caused blockage of the Akt and ERK signaling pathways in MCF-7 cells. • Conjugate significantly reduced solid tumor volume as compared to pterostilbene
-
Comparative cytotoxicity of gold-doxorubicin and InP-doxorubicin conjugates.
Zhang, Xuan; Chibli, Hicham; Kong, Dekun; Nadeau, Jay
2012-07-11
Direct comparisons of different types of nanoparticles for drug delivery have seldom been performed. In this study we compare the physical properties and cellular activity of doxorubicin (Dox) conjugates to gold nanoparticles (Au) and InP quantum dots of comparable diameter. Although the Au particles alone are non-toxic and InP is moderately toxic, Au-Dox is more effective than InP-Dox against the Dox-resistant B16 melanoma cell line. Light exposure does not augment the efficacy of InP-Dox, suggesting that conjugates are breaking down. Electron and confocal microscopy and atomic absorption spectroscopy reveal that over 60% of the Au-Dox conjugates reach the cell nucleus. In contrast, InP-Dox enters cell nuclei to a very limited extent, although liberated Dox from the conjugates does eventually reach the nucleus. These observations are attributed to faster Dox release from Au conjugates under endosomal conditions, greater aggregation of InP-Dox with cytoplasmic proteins, and adherence of InP to membranes. These findings have important implications for design of active drug-nanoparticle conjugates.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of the antioxidative potential of minoxidil-polyamine conjugates.
Hadjipavlou-Litina, Dimitra; Magoulas, George E; Bariamis, Stavros E; Tsimali, Zinovia; Avgoustakis, Konstantinos; Kontogiorgis, Christos A; Athanassopoulos, Constantinos M; Papaioannou, Dionissios
2013-07-01
A series of conjugates (MNX-CO-PA) of minoxidil (MNX) with the polyamines (PAs) putrescine (PUT), spermidine (SPD) and spermine (SPM) as well as dopamine were produced through activation of MNX with N,N'-carbonyldiimidazole, followed by reaction with dopamine or selectively protected PAs and acid-mediated deprotection. These conjugates together with conjugates of the general type MNX-PA or PA-MNX-PA, readily produced using literature protocols, were tested as antioxidants. The most potent inhibitors of lipid peroxidation were the conjugates MNX-SPM (2, 94%), SPM-MNX-SPM (4, 94%) and MNX-N(4)-SPD (7, 91%) and MNX (91%). The most powerful lipoxygenase (LOX) inhibitors were MNX (IC50 = 20 μM) and the conjugates MNX-N(8)-SPD (9, IC50 = 22.1 μM), MNX-CO-dopamine (11, IC50 = 28 μM) and MNX-N(1)-SPD (8, IC50 = 30 μM). The most interesting conjugates 2, MNX-CO-PUT (5), 8 and 11 as well as MNX were generally found to exhibit weaker (22-36.5%) or no (conjugate 8) anti-inflammatory activity than indomethacin (47%) with the exception of MNX which showed almost equal potency (49%) to indomethacin. The cytocompatibility of conjugates and MNX at the highest concentration of 100 μM showed a survival percentage of 87-107%, with the exception of conjugates with SPM (compound 2) and MNX-CO-SPM (6), which showed considerable cytotoxicity (survival percentage 8-14%). Molecular docking studies were carried on conjugate 9 and the parent compound MNX and were found to be in accordance with our experimental biological results. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
-
Anticancer activity of drug conjugates in head and neck cancer cells.
Majumdar, Debatosh; Rahman, Mohammad Aminur; Chen, Zhuo Georgia; Shin, Dong M
2016-06-01
Sexually transmitted oral cancer/head and neck cancer is increasing rapidly. Human papilloma virus (HPV) is playing a role in the pathogenesis of a subset of squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck (SCCHN). Paclitaxel is a widely used anticancer drug for breast, ovarian, testicular, cervical, non-small cell lung, head and neck cancer. However, it is water insoluble and orally inactive. We report the synthesis of water soluble nanosize conjugates of paclitaxel, branched PEG, and EGFR-targeting peptide by employing native chemical ligation. We performed a native chemical ligation between the N-hydroxy succinimide (NHS) ester of paclitaxel succinate and cysteine at pH 6.5 to give the cysteine-conjugated paclitaxel derivative. The thiol functionality of cysteine was activated and subsequently conjugated to multiarm thiol-PEG to obtain the paclitaxel branched PEG conjugate. Finally, we conjugated an EGFR-targeting peptide to obtain conjugates of paclitaxel, branched PEG, and EGFR-targeting peptide. These conjugates show anticancer activity against squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck cells (SCCHN, Tu212).
-
A glutathione conjugate of hepoxilin A3: Formation and action in the rat central nervous system
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pace-Asciak, C.R.; Laneuville, O.; Su, W.G.; Corey, E.J.; Gurevich, N.; Wu, P.; Carlen, P.L.
1990-01-01
Incubation of (8R)- and (8S)-[1-14C]hepoxilin A3 [where hepoxilin A3 is 8-hydroxy-11,12-epoxyeicosa-(5Z,9E,14Z)-trienoic acid] and glutathione with homogenates of rat brain hippocampus resulted in a product that was identified as the (8R) and (8S) diastereomers of 11-glutathionyl hepoxilin A3 by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatographic comparison with the authentic standard made by total synthesis. Identity was further confirmed by cleavage of the isolated product with gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase to yield the corresponding cysteinylglycinyl conjugate that was identical by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatographic analysis with the enzymic cleavage product derived from the synthetic glutathionyl conjugate. The glutathionyl and cysteinylglycinyl conjugate are referred to as hepoxilin A3-C and hepoxilin A3-D, respectively, by analogy with the established leukotriene nomenclature. Formation of hepoxilin A3-C was greatly enhanced with a concomitant decrease in formation of the epoxide hydrolase product, trioxilin A3, when the epoxide hydrolase inhibitor trichloropropene oxide was added to the incubation mixture demonstrating the presence of a dual metabolic pathway in this tissue involving hepoxilin epoxide hydrolase and glutathione S-transferase processes. Hepoxilin A3-C was tested using intracellular electrophysiological techniques on hippocampal CA1 neurons and found to be active at concentrations as low as 16 nM in causing membrane hyperpolarization, enhanced amplitude and duration of the post-spike train afterhyperpolarization, a marked increase in the inhibitory postsynaptic potential, and a decrease in the spike threshold. These findings suggest that these products in the hepoxilin pathway of arachidonic acid metabolism formed by the rat brain may function as neuromodulators
-
Small angle scattering from protein/sugar conjugates
Jackson, Andrew; White, John
2006-11-01
The Maillard reaction between free amine groups on proteins and sugars is well known. We have examined the effect of the reaction of the casein group of milk proteins with sugars on their nanoscale structure and aggregation. The small angle neutron scattering from beta casein and sodium caseinate and their sugar conjugates have been studied as a function of solution concentration. At high conjugate concentration (greater than ca. 5 mg/ml) the addition of sugar reduces supra-micellar aggregation of the protein whilst at lower concentration, where the protein is expected to be deaggregated already, little effect is seen. Guinier analysis of the scattering data show a radius of gyration of around 75 A˚ for beta casein in solution and around 80 A˚ for the sucrose conjugate.
-
Zhao, Yifan; Du, Jing; Zhang, Jinrun; Shen, Li; Wang, Jian
2018-04-01
Mid-infrared (2-20 μm) light has been attracting great attention in many areas of science and technology. Beyond the extended wavelength range from visible and near-infrared to mid-infrared, shaping spatial structures may add opportunities to grooming applications of mid-infrared photonics. Here, we design and fabricate a reflection-enhanced plasmonic metasurface and demonstrate efficient generation of structured light with the phase helix and intensity helix at 2 μm. This work includes two distinct aspects. First, structured light (phase helix, intensity helix) generation at 2 μm, which is far beyond the ability of conventional spatial light modulators, is enabled by the metasurface with sub-wavelength engineered structures. Second, the self-referenced intensity helix against environmental noise is generated without using a spatially separated light. The demonstrations may open up advanced perspectives to structured light applications at 2 μm, such as phase helix for communications and non-communications (imaging, sensing) and intensity helix for enhanced microscopy and advanced metrology.
-
Free and conjugated dopamine in human ventricular fluid
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sharpless, N.S.; Thal, L.J.; Wolfson, L.I.; Tabaddor, K.; Tyce, G.M.; Waltz, J.M.
1981-01-01
Free dopamine and an acid hydrolyzable conjugate of dopamine were measured in human ventricular fluid specimens with a radioenzymatic assay and by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection. Only trace amounts of free norepinephrine and dopamine were detected in ventricular fluid from patients with movement disorders. When the ventricular fluid was hydrolyzed by heating in HClO 4 or by lyophilization in dilute HClO 4 , however, a substantial amount of free dopamine was released. Values for free plus conjugated dopamine in ventricular fluid from patients who had never taken L-DOPA ranged from 139 to 340 pg/ml when determined by HPLC and from 223 to 428 pg/ml when measured radioenzymatically. The correlation coefficient for values obtained by the two methods in the same sample of CSF was 0.94 (P<0.001). Patients who had been treated with L-DOPA had higher levels of conjugated dopamine in their ventricular CSF which correlated inversely with the time between the last dose of L-DOPA and withdrawal of the ventricular fluid. Additionally, one patient with acute cerebral trauma had elevated levels of free norepinephrine and both free and conjugated dopamine in his ventricular fluid. Conjugation may be an important inactivation pathway for released dopamine in man. (Auth.)
-
Antibody-radioisotope conjugates for tumor localization and treatment
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Larson, S.M.; Carrasquillo, J.A.
1985-01-01
In principle, anti-tumor antibodies can be used to carry radioactivity to tumors for in-vivo diagnosis and treatment of cancer. First, for diagnostic purposes, an antibody that targets a specific antigen (for example, the p97 antigen of human melanoma tumor), is labeled with a tracer amount of radioactivity. When this antibody-radioisotope conjugate is injected into the blood stream, the antibody carries the radioactivity throughout the body and in time, percolates through all the tissues of the body. Because the tumor has specific antigens to which the antibody can bind, the antibody conjugate progressively accumulates in the tumor. Using conventional nuclear medicine imaging equipment, the body of the patient is scanned for radioactivity content, and a map of the distribution of the radioactivity is displayed on photographic film. The tumor shows up as a dense area of radio-activity. These same antibody-radioisotope conjugates may be used for therapy of tumors, except that in this case large amounts of radioactivity are loaded on the antibody. After localization of the conjugate there is sufficient radiation deposited in the tumor of radiotherapy. The success of this approach in the clinic is determined in large measure by the concentration gradient that can be achieved between tissue antibody conjugate in tumor versus normal tissue
-
Conjugal conflict and violence: a review and theoretical paradigm.
Smilkstein, G; Aspy, C B; Quiggins, P A
1994-02-01
Conjugal violence has been described as having multiple etiologies. The variables are so numerous that intervention and research protocols are difficult to effect. This paper proposes a paradigm that establishes conjugal conflict and violence as separate entities. According to the paradigm, conjugal conflict is viewed as "an inevitable part of human association," whereas conjugal violence is determined to be a learned behavioral tactic that is employed as a coping strategy when an individual's conflict threshold potential is exceeded. Evidence will be offered that violence is learned from family of origin and from observing what is common or accepted practice in the community. Use of this paradigm would give primacy to community education programs that advance the concept of conflict resolution through rational discourse.
-
Bending of conjugated molecular wires and its effect on electron conduction properties
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Das, Bidisa
2010-01-01
The electronic structure and electron transport properties of simple conjugated molecular wires like oligophenylene ethynylene (OPE) and oligophenylene vinylene (OPV) are studied under compression. If artificially confined to a given shorter length, the oligomers tend to bend and bending causes a loss in the overlap of the conjugated molecular orbitals. Theoretical modeling of electronic transport has been carried out for all undistorted and compressed OPE/OPV oligomers. OPV exists in step-like or V-like conformations and they have the same stability with very similar frontier molecular orbitals. The conductances of these molecular wires are calculated when inserted between two gold probes and the conductances for OPV are found to be comparable to OPE when the interfaces are same. The conductance decreases with bending due to the gradual loss in overlap of the molecular orbitals. It is also found that the conductances of the molecular wires decrease very strongly if the terminal sulfur atom is simultaneously bonded to hydrogen and a gold surface, thus reflecting the importance of the interface in determining the conductance in two-probe systems. From the conductance studies it may be concluded that if one or more benzene rings of OPE are rotated from coplanar conditions, the orthogonal molecular orbitals may completely block the electronic transport, rendering the molecule insulating.
-
Hsiao, Shih-Chia; Francis, Matthew B.; Bertozzi, Carolyn; Mathies, Richard; Chandra, Ravi; Douglas, Erik; Twite, Amy; Toriello, Nicholas; Onoe, Hiroaki
2016-05-03
The present invention provides conjugates of DNA and cells by linking the DNA to a native functional group on the cell surface. The cells can be without cell walls or can have cell walls. The modified cells can be linked to a substrate surface and used in assay or bioreactors.
-
Hsiao, Shih-Chia; Francis, Matthew B.; Bertozzi, Carolyn; Mathies, Richard; Chandra, Ravi; Douglas, Erik; Twite, Amy; Toriello, Nicholas; Onoe, Hiroaki
2018-05-15
The present invention provides conjugates of DNA and cells by linking the DNA to a native functional group on the cell surface. The cells can be without cell walls or can have cell walls. The modified cells can be linked to a substrate surface and used in assay or bioreactors.
-
Transmission of electric fields and photoelectron fluxes between conjugate ionospheric F2-regions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Petelski, E.F.
1975-01-01
The dynamic behaviour of the ionospheric F2-layer requires considerable vertical transport of ionization. Possible causes of such transport are ambipolar diffusion, neutral air winds and electric fields. Here mid-latitude electric fields are investigated. Real height variations of the F2-layer indicate that the phases and amplitudes of these fields are similar at well conjugate points and that the field strengths can become unexpectedly high. It is further shown that photoelectrons can migrate between the two hemispheres along the geomagnetic field lines. (orig.) [de
-
Structure and function of nanoparticle-protein conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Aubin-Tam, M-E; Hamad-Schifferli, K
2008-01-01
Conjugation of proteins to nanoparticles has numerous applications in sensing, imaging, delivery, catalysis, therapy and control of protein structure and activity. Therefore, characterizing the nanoparticle-protein interface is of great importance. A variety of covalent and non-covalent linking chemistries have been reported for nanoparticle attachment. Site-specific labeling is desirable in order to control the protein orientation on the nanoparticle, which is crucial in many applications such as fluorescence resonance energy transfer. We evaluate methods for successful site-specific attachment. Typically, a specific protein residue is linked directly to the nanoparticle core or to the ligand. As conjugation often affects the protein structure and function, techniques to probe structure and activity are assessed. We also examine how molecular dynamics simulations of conjugates would complete those experimental techniques in order to provide atomistic details on the effect of nanoparticle attachment. Characterization studies of nanoparticle-protein complexes show that the structure and function are influenced by the chemistry of the nanoparticle ligand, the nanoparticle size, the nanoparticle material, the stoichiometry of the conjugates, the labeling site on the protein and the nature of the linkage (covalent versus non-covalent)
-
Fullerene–biomolecule conjugates and their biomedicinal applications
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yang X
2013-12-01
Full Text Available Xinlin Yang,1 Ali Ebrahimi,1 Jie Li,1,2 Quanjun Cui11Orthopaedic Research Laboratory, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA, USA; 2School of Materials Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, People's Republic of ChinaAbstract: Fullerenes are among the strongest antioxidants and are characterized as "radical sponges." The research on biomedicinal applications of fullerenes has achieved significant progress since the landmark publication by Friedman et al in 1993. Fullerene–biomolecule conjugates have become an important area of research during the past 2 decades. By a thorough literature search, we attempt to update the information about the synthesis of different types of fullerene–biomolecule conjugates, including fullerene-containing amino acids and peptides, oligonucleotides, sugars, and esters. Moreover, we also discuss in this review recently reported data on the biological and pharmaceutical utilities of these compounds and some other fullerene derivatives of biomedical importance. While within the fullerene–biomolecule conjugates, in which fullerene may act as both an antioxidant and a carrier, specific targeting biomolecules conjugated to fullerene will undoubtedly strengthen the delivery of functional fullerenes to sites of clinical interest.Keywords: fullerene, amino acid, peptide, oligonucleotide, sugar, ester
-
Fine-tuning of electronic properties in donor-acceptor conjugated polymers based on oligothiophenes
Imae, Ichiro; Sagawa, Hitoshi; Harima, Yutaka
2018-03-01
A novel series of donor-acceptor conjugated polymers having oligothiophenes with well-defined structures were synthesized and their optical, electrochemical, and photovoltaic properties were investigated. It was found that the absorption bands of polymers were red-shifted with increasing number of ethylenedioxy groups added to each oligothiophene unit and that their band edges reached over 1000 nm. The systematical fine-tuning of the electronic properties was achieved using the chemical structures of oligothiophene units. Photovoltaic cells based on polymer/(6,6)-phenyl C61 butyric acid methyl ester (PC61BM) exhibited power conversion efficiencies in the range from 0.004 to 1.10%, reflecting the electronic properties of the polymers.
-
The Synthesis of Substituted Piperazine-cholesterol Conjugates for ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
A small library of cholesterol-piperazine conjugates were synthesized by the reaction of cholesteryl chloroformate with a set of substituted piperazines in dichloromethane at room temperature. The conjugates, all obtained in good to excellent yields, were synthesized to be key components of nucleic acid transfection ...
-
Wu, Bo; Lu, Peijuan; Cloer, Caryn; Shaban, Mona; Grewal, Snimar; Milazi, Stephanie; Shah, Sapana N; Moulton, Hong M; Lu, Qi Long
2012-08-01
Exon skipping is capable of correcting frameshift and nonsense mutations in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Phase 2 clinical trials in the United Kingdom and the Netherlands have reported induction of dystrophin expression in muscle of Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients by systemic administration of both phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers (PMO) and 2'-O-methyl phosphorothioate. Peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino offers significantly higher efficiency than phosphorodiamidate morpholino, with the ability to induce near-normal levels of dystrophin, and restores function in both skeletal and cardiac muscle. We examined 1-year systemic efficacy of peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino targeting exon 23 in dystrophic mdx mice. The LD(50) of peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino was determined to be approximately 85 mg/kg. The half-life of dystrophin expression was approximately 2 months in skeletal muscle, but shorter in cardiac muscle. Biweekly injection of 6 mg/kg peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino produced >20% dystrophin expression in all skeletal muscles and ≤5% in cardiac muscle, with improvement in muscle function and pathology and reduction in levels of serum creatine kinase. Monthly injections of 30 mg/kg peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino restored dystrophin to >50% normal levels in skeletal muscle, and 15% in cardiac muscle. This was associated with greatly reduced serum creatine kinase levels, near-normal histology, and functional improvement of skeletal muscle. Our results demonstrate for the first time that regular 1-year administration of peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino can be safely applied to achieve significant therapeutic effects in an animal model. Copyright © 2012 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kellar, Joshua A.; Lin, Jui-Ching; Kim, Jun-Hyun; Yoder, Nathan L.; Bevan, Kirk H.; Stokes, Grace Y.; Geiger, Franz M.; Nguyen, SonBinh T.; Bedzyk, Michael J.; Hersam, Mark C.
2009-01-01
Highly conjugated molecules bound to silicon are promising candidates for organosilicon electronic devices and sensors. In this study, 1-bromo-4-ethynylbenzene was synthesized and reacted with a hydrogen-passivated Si(111) surface via ultraviolet irradiation. Through an array of characterization and modeling tools, the binding configuration and morphology of the reacted molecule were thoroughly analyzed. Atomic force microscopy confirmed an atomically flat surface morphology following reaction, while X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy verified reaction to the surface via the terminal alkyne moiety. In addition, synchrotron X-ray characterization, including X-ray reflectivity, X-ray fluorescence, and X-ray standing wave measurements, enabled sub-angstrom determination of the position of the bromine atom with respect to the silicon lattice. This structural characterization was quantitatively compared with density functional theory (DFT) calculations, thus enabling the π-conjugation of the terminal carbon atoms to be deduced. The X-ray and DFT results were additionally corroborated with the vibrational spectrum of the organic adlayer, which was measured with sum frequency generation. Overall, these results illustrate that the terminal carbon atoms in 1-bromo-4-ethynylbenzene adlayers on Si(111) retain π-conjugation, thus revealing alkyne molecules as promising candidates for organosilicon electronics and sensing.
-
Nanostructured conjugated polymers in chemical sensors: synthesis, properties and applications.
Correa, D S; Medeiros, E S; Oliveira, J E; Paterno, L G; Mattoso, Luiz C
2014-09-01
Conjugated polymers are organic materials endowed with a π-electron conjugation along the polymer backbone that present appealing electrical and optical properties for technological applications. By using conjugated polymeric materials in the nanoscale, such properties can be further enhanced. In addition, the use of nanostructured materials makes possible miniaturize devices at the micro/nano scale. The applications of conjugated nanostructured polymers include sensors, actuators, flexible displays, discrete electronic devices, and smart fabric, to name a few. In particular, the use of conjugated polymers in chemical and biological sensors is made feasible owning to their sensitivity to the physicochemical conditions of its surrounding environment, such as chemical composition, pH, dielectric constant, humidity or even temperature. Subtle changes in these conditions bring about variations on the electrical (resistivity and capacitance), optical (absorptivity, luminescence, etc.), and mechanical properties of the conjugated polymer, which can be precisely measured by different experimental methods and ultimately associated with a specific analyte and its concentration. The present review article highlights the main features of conjugated polymers that make them suitable for chemical sensors. An especial emphasis is given to nanostructured sensors systems, which present high sensitivity and selectivity, and find application in beverage and food quality control, pharmaceutical industries, medical diagnosis, environmental monitoring, and homeland security, and other applications as discussed throughout this review.
-
Intense correlation between brain infarction and protein-conjugated acrolein.
Saiki, Ryotaro; Nishimura, Kazuhiro; Ishii, Itsuko; Omura, Tomohiro; Okuyama, Shigeru; Kashiwagi, Keiko; Igarashi, Kazuei
2009-10-01
We recently found that increases in plasma levels of protein-conjugated acrolein and polyamine oxidases, enzymes that produce acrolein, are good markers for stroke. The aim of this study was to determine whether the level of protein-conjugated acrolein is increased and levels of spermine and spermidine, the substrates of acrolein production, are decreased at the locus of infarction. A unilateral infarction was induced in mouse brain by photoinduction after injection of Rose Bengal. The volume of the infarction was analyzed using the public domain National Institutes of Health image program. The level of protein-conjugated acrolein at the locus of infarction and in plasma was measured by Western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively. The levels of polyamines at the locus of infarction and in plasma were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. The level of protein-conjugated acrolein was greatly increased, and levels of spermine and spermidine were decreased at the locus of infarction at 24 hours after the induction of stroke. The size of infarction was significantly decreased by N-acetylcysteine, a scavenger of acrolein. It was also found that the increases in the protein-conjugated acrolein, polyamines, and polyamine oxidases in plasma were observed after the induction of stroke. The results indicate that the induction of infarction is well correlated with the increase in protein-conjugated acrolein at the locus of infarction and in plasma.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Wu, Taotao, E-mail: wutaotao@nint.ac.cn; Wang, Lijun; Wei, Chenghua; Zhou, Menglian; He, Minbo; Wu, Lixiong
2016-11-30
Highlights: • Firstly, iron samples with different color features were obtained by continuous wave laser irradiation depending on progressive durations. The real-time reflectivity and temperature of samples were measured. The color and the reflectivity evolution were related. They were both caused by the forming oxide films. • Secondly, laser-induced oxidation process of iron was studied by microscope, X-ray diffraction and Raman spectrum. The first formed magnetite made the surface reflectivity decline rapidly and caused the “positive feedback” effect because of molecular absorption. The later formed hematite oscillated the reflectivity by interference effect. • Lastly, the laser-induced oxide films were thin, orientated and badly crystallized. The Wagner oxidation theory was incapable of describing the non-isothermal and early stage oxidation process. So we emphasized that a precise oxidation model depending on the experiment and the optical constants of the laser-induced oxides must be studied. - Abstract: Laser-induced oxidation will change the laser reflectivity and color features of metal surface. Both changes can be theoretically calculated based on the oxidation kinetics and the optical constants of oxides. For the purpose of calculation, the laser-induced oxidation process of pure polycrystalline iron was studied. Samples with various color features were obtained by continuous wave Nd:YAG fiber laser (1.06 μm) irradiation depending on progressive durations in the intensity of 1.90 W/cm{sup 2}. The real-time reflectivity and temperature were measured with integral sphere and thermocouples. The irradiated surface morphology and phase structures were characterized by microscope, X-ray diffraction and Raman spectrum. It was found that the first formed magnetite made the surface reflectivity decline rapidly and caused the “positive feedback” effect because of molecular absorption. The later formed hematite oscillated the reflectivity by
-
Optical observations geomagnetically conjugate to sprite-producing lightning discharges
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. A. Marshall
2005-09-01
Full Text Available Theoretical studies have predicted that large positive cloud-to-ground discharges can trigger a runaway avalanche process of relativistic electrons, forming a geomagnetically trapped electron beam. The beam may undergo pitch angle and energy scattering during its traverse of the Earth's magnetosphere, with a small percentage of electrons remaining in the loss cone and precipitating in the magnetically conjugate atmosphere. In particular, N2 1P and N2+1N optical emissions are expected to be observable. In July and August 2003, an attempt was made to detect these optical emissions, called "conjugate sprites", in correlation with sprite observations in Europe near . Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam. Keywords. Ionosphere (Ionsophere-magnetosphere interactions; Ionospheric disturbances; Instruments and techniques
-
Pump depletion effects in thermal degenerate four-wave mixing
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Guha, S.; Chen, W.
1987-01-01
Characteristics such as a large magnitude of nonlinearity, fast response, broadband operation, and easy availability make absorbing liquids attractive candidates for performing phase conjugation of optical beams by degenerate four-wave mixing. The coupled-wave equations describing the interaction of four optical fields in an absorbing medium have been solved previously for the case of no pump depletion and no self-action of any of the beams. When studying phase conjugation oscillation, however, the effect of depletion of the pump beams on the phase conjugate reflectivity must be considered. Moreover, in absorbing media the self-action effects are always present. The coupled-wave equations, including the self-action terms for all four waves involved, are derived here for the first time to the authors' knowledge. For the case of small absorption, these equations are solved analytically, and the effect of pump depletion on phase conjugate reflectivity R is determined. In the absence of the pump depletion, R is proportional to tan 2 (Ql), where Ql is a dimensionless gain parameter characterizing the nonlinear medium and the input pump power. When pump depletion and self-action are included, R does not go to infinity when Ql equals odd multiples of π2. Instead R takes on values dependent on the probe ratio q 1 , which is the ratio of the input probe irradiance to the input pump irradiance. The authors find that the maximum value for R is 1q 1 . They also find that for Ql close to odd multiples of π2, the reflectivity is significantly reduced from the value obtained by ignoring pump depletion, even for probe ratios as small as one-tenth of 1%. Experimental confirmation of this theory, using an argon-ion laser as the pump and carbon tetrachloride mixed with a dye as the absorbing medium, is in progress and is reported
-
Minimizing inner product data dependencies in conjugate gradient iteration
Vanrosendale, J.
1983-01-01
The amount of concurrency available in conjugate gradient iteration is limited by the summations required in the inner product computations. The inner product of two vectors of length N requires time c log(N), if N or more processors are available. This paper describes an algebraic restructuring of the conjugate gradient algorithm which minimizes data dependencies due to inner product calculations. After an initial start up, the new algorithm can perform a conjugate gradient iteration in time c*log(log(N)).
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sallam, Kh.M.; El-Bayoumy, A.S.A.; Ebeid, N.H.; Michael, E.; Zein, N.; Elfarargy, Ah.F.
2017-01-01
The main objective of the present study was the preparation of the primary reagents of cortisol radioimmunoassay (RIA) using liquid phase double antibody technique. Three basic components were prepared and characterized to obtain valid and accurate system. These components were polyclonal anti-cortisol antibody, "1"2"5I-cortisol RIA tracer and cortisol standards. Cortisol requires conjugation step to be real antigen. Therefore, in this study this mandatory conjugation step was performed & characterized. Then formulation, optimization and validation of this liquid phase RIA technique were carried out. This assay is precise, specific and sensitive enough for using as a diagnostic tool for the adrenal cortex status. (author)
-
Site-specific conjugation and labelling of prostate antibody 7E11C5.3 (CYT-351) with technetium-99m
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Stalteri, M.A.; Mather, S.J.; Belinka, B.A.; Coughlin, D.J.; Chengazi, V.U.; Britton, K.E.
1997-01-01
Attachment of chelating agents to the sugar residues of antibodies for subsequent radiolabelling is an attractive approach since it may have less effect on the immunoreactivity than attachment through lysine residues, which are distributed throughout the antibody and may be present near the antigen binding site. We have attached a new hydrazide-linked chelator CYT-395 (Cytogen Corp., Princeton, N.J.) to the sugar residues of the anti-prostate monoclonal antibody 7E11C5.3 and optimised the conditions for labelling the conjugate with technetium-99m in order to compare the conjugate to 7E11C5.3 antibody labelled directly with technetium using a mercaptoethanol reduction technique. Labelling yields of 70%-90% were obtained at specific activities up to 2000 MBq/mg antibody. The stability of the technetium-labelled conjugate in plasma or to a challenge with 0.1 or 1.0 mM cysteine was similar to that of direct-labelled antibody. In nine patients with prostate cancer, the plasma clearance of the labelled conjugate followed a two-compartment model, with an average β-phase half-life of 31.4±3.9 h. The average urinary clearance at 24 h was 15.3±5.0% of the injected dose. In this group of patients there was no significant difference between the blood and urine clearance of the labelled conjugate, and the clearances of the direct-labelled antibody. (orig.). With 5 figs
-
Covalently bound conjugates of albumin and heparin: Synthesis, fractionation and characterization
Hennink, Wim E.; Feijen, Jan; Ebert, Charles D.; Kim, Sung Wan
1983-01-01
Covalently bound conjugates of human serum albumin and heparin were prepared as compounds which could improve the blood-compatibility of polymer surfaces either by preadsorption or by covalent coupling of the conjugates onto blood contacting surfaces. The conjugates (10–16 weight % of heparin) were
-
Small angle scattering from protein/sugar conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jackson, Andrew; White, John
2006-01-01
The Maillard reaction between free amine groups on proteins and sugars is well known. We have examined the effect of the reaction of the casein group of milk proteins with sugars on their nanoscale structure and aggregation. The small angle neutron scattering from beta casein and sodium caseinate and their sugar conjugates have been studied as a function of solution concentration. At high conjugate concentration (greater than ca. 5mg/ml) the addition of sugar reduces supra-micellar aggregation of the protein whilst at lower concentration, where the protein is expected to be deaggregated already, little effect is seen. Guinier analysis of the scattering data show a radius of gyration of around 75A-bar for beta casein in solution and around 80A-bar for the sucrose conjugate
-
Small angle scattering from protein/sugar conjugates
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jackson, Andrew [Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200 (Australia)]. E-mail: ajj@nist.gov; White, John [Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200 (Australia)
2006-11-15
The Maillard reaction between free amine groups on proteins and sugars is well known. We have examined the effect of the reaction of the casein group of milk proteins with sugars on their nanoscale structure and aggregation. The small angle neutron scattering from beta casein and sodium caseinate and their sugar conjugates have been studied as a function of solution concentration. At high conjugate concentration (greater than ca. 5mg/ml) the addition of sugar reduces supra-micellar aggregation of the protein whilst at lower concentration, where the protein is expected to be deaggregated already, little effect is seen. Guinier analysis of the scattering data show a radius of gyration of around 75A-bar for beta casein in solution and around 80A-bar for the sucrose conjugate.
-
Deciphering conjugative plasmid permissiveness in wastewater microbiomes
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Jacquiod, Samuel Jehan Auguste; Brejnrod, Asker Daniel; Milani, Stefan Morberg
2017-01-01
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are designed to robustly treat polluted water. They are characterized by ceaseless flows of organic, chemical and microbial matter, followed by treatment steps before environmental release. WWTPs are hotspots of horizontal gene transfer between bacteria via...... still remains largely uncharted. Furthermore, current in vitro methods used to assess conjugation in complex microbiomes do not include in situ behaviours of recipient cells, resulting in partial understanding of transfers. We investigated the in vitro conjugation capacities of WWTP microbiomes from...... inlet sewage and outlet treated water using the broad-host range IncP-1 conjugative plasmid, pKJK5. A thorough molecular approach coupling metagenomes to 16S rRNA DNA/cDNA amplicon sequencing was established to characterize microbiomes using the ecological concept of functional response groups. A broad...
-
Analysis of Peptides and Conjugates by Amino Acid Analysis
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Højrup, Peter
2015-01-01
Amino acid analysis is a highly accurate method for characterization of the composition of synthetic peptides. Together with mass spectrometry, it gives a reliable control of peptide quality and quantity before conjugation and immunization.Peptides are hydrolyzed, preferably in gas phase, with 6 M...... HCl at 110 °C for 20-24 h and the resulting amino acids analyzed by ion-exchange chromatography with post-column ninhydrin derivatization. Depending on the hydrolysis conditions, tryptophan is destroyed, and cysteine also, unless derivatized, and the amides, glutamine and asparagine, are deamidated...... to glutamic acid and aspartic acid, respectively. Three different ways of calculating results are suggested, and taking the above limitations into account, a quantitation better than 5 % can usually be obtained....
-
Cheewatanakornkool, Kamonrak; Niratisai, Sathit; Manchun, Somkamol; Dass, Crispin R; Sriamornsak, Pornsak
2017-10-15
In this paper, pectin was cross-linked by a coupling reaction with either thioglycolic acid or cystamine dihydrochloride to form thiolated pectins. The thiolated pectins were then coupled with doxorubicin (DOX) derivative to obtain thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates by two different methods, disulfide bond formation and disulfide bond exchange. The disulfide bond exchange method provided a simple, fast, and efficient approach for synthesis of thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates, compared to the disulfide bond formation. Characteristics, physicochemical properties, and morphology of thiolated pectins and thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates were determined. DOX content in thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates using low methoxy pectin was found to be higher than that using high methoxy pectin. The in vitro anticancer activity of thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates was significantly higher than that of free DOX, in mouse colon carcinoma and human bone osteosarcoma cells, but insignificantly different from that of free DOX, in human prostate cancer cells. Due to their promising anticancer activity in mouse colon carcinoma cells, the thiolated pectin-DOX conjugates might be suitable for building drug platform for colorectal cancer-targeted delivery of DOX. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Less is More: A Comparison of Antibody-Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates of Different Ratios.
Byzova, Nadezhda A; Safenkova, Irina V; Slutskaya, Elvira S; Zherdev, Anatoly V; Dzantiev, Boris B
2017-11-15
This comprehensive study is related to gold nanoparticles (GNPs) conjugated with antibodies. The goal of the study is to determine the minimal concentration of antibodies for conjugate synthesis when the conjugates have high antigen-capturing activity. Two systems were studied: gold nanoparticles conjugated with monoclonal antibodies (mAb-GNP) specific to Helicobacter pylori and gold nanoparticles conjugated with polyclonal antibodies (pAb-GNP) specific to mouse immunoglobulins. Several conjugates were synthesized with different GNP-to-antibody molar ratios (from 1:1 to 1:245) through nondirectional and noncovalent immobilization on a surface of GNPs with a diameter of 25.3 ± 4.6 nm. The maximal antigen-capturing activities and equilibrium constants of the conjugates correlate with the formation of a constant hydrodynamic radius of the conjugates for mAb-GNP (GNP to antibody molar ratio 1:58) and with the stabilizing concentration by flocculation curves for pAb-GNP (GNP to antibody molar ratio 1:116). The application of the conjugates to the lateral flow immunoassay shows that the antibody concentrations used for the conjugation can be reduced (below the stabilizing concentration) without losing activity for the mAb-GNP conjugates. The findings highlight that the optimal concentration of antibodies immobilized on the surface of GNPs is not always equal to the stabilizing concentration determined by the flocculation curve.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Yu, Xianbin; Gibbon, Timothy Braidwood; Tafur Monroy, Idelfonso
2008-01-01
We propose and demonstrate a bidirectional radio-over-fiber (RoF) system based on a reflective semiconductor optical amplifier (RSOA). In this system, phase-modulated 5.25-GHz radio frequency (RF) carrying 850 Mb/s is used for the downstream signal. Optical envelope detection of 10-GHz RF carryin......-effective. The experimental results indicate that after simultaneous transmission of downstream and upstream signals over 25-km fiber, the receiver sensitivities are -22 and -14.5 dBm, respectively....
-
Conjugation vs hyperconjugation in molecular structure of acrolein
Shishkina, Svitlana V.; Slabko, Anzhelika I.; Shishkin, Oleg V.
2013-01-01
Analysis of geometric parameters of butadiene and acrolein reveals the contradiction between the Csp2-Csp2 bond length in acrolein and classical concept of conjugation degree in the polarized molecules. In this Letter the reasons of this contradiction have been investigated. It is concluded that the Csp2-Csp2 bond length in acrolein is determined by influence of the bonding for it π-π conjugation and antibonding n → σ∗ hyperconjugation between the oxygen lone pair and the antibonding orbital of the single bond. It was shown also this bond length depends on the difference in energy of conjugative and hyperconjugative interactions.
-
Enhanced photodynamic efficacy of zinc phthalocyanine by conjugating to heptalysine.
Li, Linsen; Luo, Zhipu; Chen, Zhuo; Chen, Jincan; Zhou, Shanyong; Xu, Peng; Hu, Ping; Wang, Jundong; Chen, Naisheng; Huang, Jinling; Huang, Mingdong
2012-11-21
Zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc) is a promising photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy, but faces some challenges: ZnPc is insoluble in water and thus requires either special formulation of ZnPc by, e.g., liposome or Cremophor EL, or chemical modification of Pc ring to enhance its bioavailability and photodynamic efficacy. Here, we conjugated monosubstituted ZnPc-COOH with a series of oligolysine moieties with different numbers of lysine residues (ZnPc-(Lys)(n) (n = 1, 3, 5, 7, 9) to improve the water solubility of the ZnPc conjugates. We measured the photosensitizing efficacies and the cellular uptakes of this series of conjugates on a normal and a cancerous cell line. In addition, we developed a sensitive in situ method to distinguish the difference in photodynamic efficacy among conjugates. Our results showed that ZnPc-(Lys)(7) has the highest photodynamic efficacy compared to the other conjugates investigated.
-
Tutticci, Naomi; Lewis, Peter A; Coyer, Fiona
2016-05-01
Critical reflection underpins critical thinking, a highly desirable generic nursing graduate capability. To improve the likelihood of critical thinking transferring to clinical practice, reflective thinking needs to be measured within the learning space of simulation. This study was divided into two phases to address the reliability and validity measures of previously untested surveys. Phase One data was collected from individuals (n = 6) using a 'think aloud' approach and an expert panel to review content validity, and verbatim comment analysis was undertaken. The Reflective Thinking Instrument and Critical Reflection Self-Efficacy Visual Analogue Scale items were contextualised to simulation. The expert review confirmed these instruments exhibited content validity. Phase Two data was collected through an online survey (n = 58). Cronbach's alpha measured internal consistency and was demonstrated by all subscales and the Instrument as a whole (.849). There was a small to medium positive correlation between critical reflection self-efficacy and general self-efficacy (r = .324, n = 56, p = .048). Participant responses were positive regarding the simulation experience. The research findings demonstrated that the Reflective Thinking and Simulation Satisfaction survey is reliable. Further development of this survey to establish validity is recommended to make it viable. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Application of the conjugate-gradient method to ground-water models
Manteuffel, T.A.; Grove, D.B.; Konikow, Leonard F.
1984-01-01
The conjugate-gradient method can solve efficiently and accurately finite-difference approximations to the ground-water flow equation. An aquifer-simulation model using the conjugate-gradient method was applied to a problem of ground-water flow in an alluvial aquifer at the Rocky Mountain Arsenal, Denver, Colorado. For this application, the accuracy and efficiency of the conjugate-gradient method compared favorably with other available methods for steady-state flow. However, its efficiency relative to other available methods depends on the nature of the specific problem. The main advantage of the conjugate-gradient method is that it does not require the use of iteration parameters, thereby eliminating this partly subjective procedure. (USGS)
-
The fate and transport of reproductive hormones and their conjugates in the environment (Invited)
Casey, F. X.; Shrestha, S. L.; Hakk, H.; Smith, D. J.; Larsen, G. L.; Padmanabhan, G.
2009-12-01
Reproductive steroid hormones can disrupt the endocrine system of some species at ng/L concentrations. Sources of steroid hormones to the environment include human waste water effluents or manure produced at animal feeding operations (AFOs). Steroid hormones, such as 17β-estradiol (E2) and estrone (E1), undergo various fate and transport processes, and laboratory studies have shown that they do not persist long (hours to few days), and have very little if any mobility in soil. Nonetheless, steroid hormones are detected at frequencies and concentrations of concern in the natural environment that would suggest their moderate persistence and mobility. One theory that may partially explain the disparity between field and laboratory studies is that conjugated forms of hormones are more mobile than their deconjugated counterparts. Glucuronide and sulfate conjugates are found in abundance in animal waste and are more soluble than their deconjugated forms. Laboratory studies were conducted to study the fate of a major urinary E2 conjugate, 17β-estradiol glucuronide (E2G), in a Hamar soil (Sandy, mixed, frigid typic Endoaquolls) from the surface and subsurface horizons. Speciation studies using batch sorption indicated that E2G degraded to E2 and E1 within 24 hours in the upper horizon soil with organic carbon content (OC) of 1.35%; whereas it persisted more in the lower horizon soil containing 0.32% OC. For initial concentrations of 2.8-28 mg/L, more than 15% of the applied dose concentration was still intact in the conjugate form in the aqueous phase for 3 - 14 days, in the lower horizon soil. The decline of E2G in the aqueous phase in the upper horizon soil was approximated with a first-order rate constant (k), which ranged from -0.208 to -0.279/h. The k values ranged from -0.006 to -0.016/h for the lower soil horizon. The differences in k values between the two horizons could be attributed to differences in bacterial activity and/or differences in sorption capacities
-
Jung, Youngkyoo; Samsonov, Alexey A; Bydder, Mark; Block, Walter F
2011-04-01
To remove phase inconsistencies between multiple echoes, an algorithm using a radial acquisition to provide inherent phase and magnitude information for self correction was developed. The information also allows simultaneous support for parallel imaging for multiple coil acquisitions. Without a separate field map acquisition, a phase estimate from each echo in multiple echo train was generated. When using a multiple channel coil, magnitude and phase estimates from each echo provide in vivo coil sensitivities. An algorithm based on the conjugate gradient method uses these estimates to simultaneously remove phase inconsistencies between echoes, and in the case of multiple coil acquisition, simultaneously provides parallel imaging benefits. The algorithm is demonstrated on single channel, multiple channel, and undersampled data. Substantial image quality improvements were demonstrated. Signal dropouts were completely removed and undersampling artifacts were well suppressed. The suggested algorithm is able to remove phase cancellation and undersampling artifacts simultaneously and to improve image quality of multiecho radial imaging, the important technique for fast three-dimensional MRI data acquisition. Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
-
Gas-Phase IR Spectroscopy of Deprotonated Amino Acids
Oomens, J.; Steill, J. D.; Redlich, B.
2009-01-01
Gas-phase infrared multiple photon dissociation (IRMPD) spectra have been recorded for the conjugate bases of a series of amino acids (Asp, Cys, Glu, Phe, Set, Trp, Tyr). The spectra are dominated by strong symmetric and antisymmetric carboxylate stretching modes around 1300 and 1600 cm(-1),
-
Repenko, Tatjana; Rix, Anne; Ludwanowski, Simon; Go, Dennis; Kiessling, Fabian; Lederle, Wiltrud; Kuehne, Alexander J C
2017-09-07
Conjugated polymer nanoparticles exhibit strong fluorescence and have been applied for biological fluorescence imaging in cell culture and in small animals. However, conjugated polymer particles are hydrophobic and often chemically inert materials with diameters ranging from below 50 nm to several microns. As such, conjugated polymer nanoparticles cannot be excreted through the renal system. This drawback has prevented their application for clinical bio-medical imaging. Here, we present fully conjugated polymer nanoparticles based on imidazole units. These nanoparticles can be bio-degraded by activated macrophages. Reactive oxygen species induce scission of the conjugated polymer backbone at the imidazole unit, leading to complete decomposition of the particles into soluble low molecular weight fragments. Furthermore, the nanoparticles can be surface functionalized for directed targeting. The approach opens a wide range of opportunities for conjugated polymer particles in the fields of medical imaging, drug-delivery, and theranostics.Conjugated polymer nanoparticles have been applied for biological fluorescence imaging in cell culture and in small animals, but cannot readily be excreted through the renal system. Here the authors show fully conjugated polymer nanoparticles based on imidazole units that can be bio-degraded by activated macrophages.
-
Pentanidium-catalyzed enantioselective phase-transfer conjugate addition reactions
Ma, Ting
2011-03-09
A new chiral entity, pentanidium, has been shown to be an excellent chiral phase-transfer catalyst. The enantioselective Michael addition reactions of tert-butyl glycinate-benzophenone Schiff base with various α,β- unsaturated acceptors provide adducts with high enantioselectivities. A successful gram-scale experiment at a low catalyst loading of 0.05 mol % indicates the potential for practical applications of this methodology. Phosphoglycine ester analogues can also be utilized as the Michael donor, affording enantioenriched α-aminophosphonic acid derivatives and phosphonic analogues of (S)-proline. © 2011 American Chemical Society.
-
Optical observations geomagnetically conjugate to sprite-producing lightning discharges
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. A. Marshall
2005-09-01
Full Text Available Theoretical studies have predicted that large positive cloud-to-ground discharges can trigger a runaway avalanche process of relativistic electrons, forming a geomagnetically trapped electron beam. The beam may undergo pitch angle and energy scattering during its traverse of the Earth's magnetosphere, with a small percentage of electrons remaining in the loss cone and precipitating in the magnetically conjugate atmosphere. In particular, N2 1P and N2+1N optical emissions are expected to be observable. In July and August 2003, an attempt was made to detect these optical emissions, called "conjugate sprites", in correlation with sprite observations in Europe near
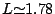 . Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam.
. Sprite observations were made from the Observatoire du Pic du Midi (OMP in the French Pyrenées, and VLF receivers were installed in Europe to detect causative sferics and ionospheric disturbances associated with sprites. In the Southern Hemisphere conjugate region, the Wide-angle Array for Sprite Photometry (WASP was deployed at the South African Astronomical Observatory (SAAO, near Sutherland, South Africa, to observe optical emissions with a field-of-view magnetically conjugate to the Northern Hemisphere observing region. Observations at OMP revealed over 130 documented sprites, with WASP observations covering the conjugate region successfully for 30 of these events. However, no incidences of optical emissions in the conjugate hemisphere were found. Analysis of the conjugate optical data from SAAO, along with ELF energy measurements from Palmer Station, Antarctica, and charge-moment analysis, show that the lightning events during the course of this experiment likely had insufficient intensity to create a relativistic beam.
Keywords. Ionosphere (Ionsophere-magnetosphere interactions; Ionospheric disturbances; Instruments and techniques -
Kim, Hwi; Min, Sung-Wook; Lee, Byoungho
2008-12-01
Geometrical optics analysis of the structural imperfection of retroreflection corner cubes is described. In the analysis, a geometrical optics model of six-beam reflection patterns generated by an imperfect retroreflection corner cube is developed, and its structural error extraction is formulated as a nonlinear optimization problem. The nonlinear conjugate gradient method is employed for solving the nonlinear optimization problem, and its detailed implementation is described. The proposed method of analysis is a mathematical basis for the nondestructive optical inspection of imperfectly fabricated retroreflection corner cubes.
-
Theoretical and computational studies of excitons in conjugated polymers
Barford, William; Bursill, Robert J.; Smith, Richard W.
2002-09-01
We present a theoretical and computational analysis of excitons in conjugated polymers. We use a tight-binding model of π-conjugated electrons, with 1/r interactions for large r. In both the weak-coupling limit (defined by W>>U) and the strong-coupling limit (defined by Wparticle models. We compare these to density matrix renormalization group (DMRG) calculations, and find good agreement in the extreme limits. We use these analytical results to interpret the DMRG calculations in the intermediate-coupling regime (defined by W~U), most applicable to conjugated polymers. We make the following conclusions. (1) In the weak-coupling limit the bound states are Mott-Wannier excitons, i.e., conduction-band electrons bound to valence-band holes. Singlet and triplet excitons whose relative wave functions are odd under a reflection of the relative coordinate are degenerate. Thus, the 2 1A+g and 1 3A-g states are degenerate in this limit. (2) In the strong-coupling limit the bound states are Mott-Hubbard excitons, i.e., particles in the upper Hubbard band bound to holes in the lower Hubbard band. These bound states occur in doublets of even and odd parity excitons. Triplet excitons are magnons bound to the singlet excitons, and hence are degenerate with their singlet counterparts. (3) In the intermediate-coupling regime Mott-Wannier excitons are the more appropriate description for large dimerization, while for the undimerized chain Mott-Hubbard excitons are the correct description. For dimerizations relevant to polyacetylene and polydiacetylene both Mott-Hubbard and Mott-Wannier excitons are present. (4) For all coupling strengths an infinite number of bound states exist for 1/r interactions for an infinite polymer. As a result of the discreteness of the lattice and the restrictions on the exciton wave functions in one dimension, the progression of states does not follow the Rydberg series. In practice, excitons whose particle-hole separation exceeds the length of the polymer
-
Retnakumari, Archana; Jayasimhan, Jasusri; Chandran, Parwathy; Menon, Deepthy; Nair, Shantikumar; Mony, Ullas; Koyakutty, Manzoor
2011-07-01
Protein stabilized gold nanoclusters (Au-NCs) are biocompatible, near-infrared (NIR) emitting nanosystems having a wide range of biomedical applications. Here, we report the development of a Au-NC based targeted fluorescent nano-bioprobe for the flow-cytometric detection of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) cells. Au-NCs with ~ 25-28 atoms showing bright red-NIR fluorescence (600-750 nm) and average size of ~ 0.8 nm were prepared by bovine serum albumin assisted reduction-cum-stabilization in aqueous phase. The protein protected clusters were conjugated with monoclonal antibody against CD33 myeloid antigen, which is overexpressed in ~ 99.2% of the primitive population of AML cells, as confirmed by immunophenotyping using flow cytometry. Au-NC-CD33 conjugates having average size of ~ 12 nm retained bright fluorescence over an extended duration of ~ a year, as the albumin protein protects Au-NCs against degradation. Nanotoxicity studies revealed excellent biocompatibility of Au-NC conjugates, as they showed no adverse effect on the cell viability and inflammatory response. Target specificity of the conjugates for detecting CD33 expressing AML cells (KG1a) in flow cytometry showed specific staining of ~ 95.4% of leukaemia cells within 1-2 h compared to a non-specific uptake of ~ 8.2% in human peripheral blood cells (PBMCs) which are CD33low. The confocal imaging also demonstrated the targeted uptake of CD33 conjugated Au-NCs by leukaemia cells, thus confirming the flow cytometry results. This study demonstrates that novel nano-bioprobes can be developed using protein protected fluorescent nanoclusters of Au for the molecular receptor targeted flow cytometry based detection and imaging of cancer cells.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Retnakumari, Archana; Jayasimhan, Jasusri; Chandran, Parwathy; Menon, Deepthy; Nair, Shantikumar; Mony, Ullas; Koyakutty, Manzoor
2011-01-01
Protein stabilized gold nanoclusters (Au-NCs) are biocompatible, near-infrared (NIR) emitting nanosystems having a wide range of biomedical applications. Here, we report the development of a Au-NC based targeted fluorescent nano-bioprobe for the flow-cytometric detection of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) cells. Au-NCs with ∼ 25-28 atoms showing bright red-NIR fluorescence (600-750 nm) and average size of ∼ 0.8 nm were prepared by bovine serum albumin assisted reduction-cum-stabilization in aqueous phase. The protein protected clusters were conjugated with monoclonal antibody against CD33 myeloid antigen, which is overexpressed in ∼ 99.2% of the primitive population of AML cells, as confirmed by immunophenotyping using flow cytometry. Au-NC-CD33 conjugates having average size of ∼ 12 nm retained bright fluorescence over an extended duration of ∼ a year, as the albumin protein protects Au-NCs against degradation. Nanotoxicity studies revealed excellent biocompatibility of Au-NC conjugates, as they showed no adverse effect on the cell viability and inflammatory response. Target specificity of the conjugates for detecting CD33 expressing AML cells (KG1a) in flow cytometry showed specific staining of ∼ 95.4% of leukaemia cells within 1-2 h compared to a non-specific uptake of ∼ 8.2% in human peripheral blood cells (PBMCs) which are CD33 low . The confocal imaging also demonstrated the targeted uptake of CD33 conjugated Au-NCs by leukaemia cells, thus confirming the flow cytometry results. This study demonstrates that novel nano-bioprobes can be developed using protein protected fluorescent nanoclusters of Au for the molecular receptor targeted flow cytometry based detection and imaging of cancer cells.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Retnakumari, Archana; Jayasimhan, Jasusri; Chandran, Parwathy; Menon, Deepthy; Nair, Shantikumar; Mony, Ullas; Koyakutty, Manzoor, E-mail: manzoork@aims.amrita.edu, E-mail: ullasmony@aims.amrita.edu [Amrita Centre for Nanoscience and Molecular Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Science, Cochin 682 041 (India)
2011-07-15
Protein stabilized gold nanoclusters (Au-NCs) are biocompatible, near-infrared (NIR) emitting nanosystems having a wide range of biomedical applications. Here, we report the development of a Au-NC based targeted fluorescent nano-bioprobe for the flow-cytometric detection of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) cells. Au-NCs with {approx} 25-28 atoms showing bright red-NIR fluorescence (600-750 nm) and average size of {approx} 0.8 nm were prepared by bovine serum albumin assisted reduction-cum-stabilization in aqueous phase. The protein protected clusters were conjugated with monoclonal antibody against CD33 myeloid antigen, which is overexpressed in {approx} 99.2% of the primitive population of AML cells, as confirmed by immunophenotyping using flow cytometry. Au-NC-CD33 conjugates having average size of {approx} 12 nm retained bright fluorescence over an extended duration of {approx} a year, as the albumin protein protects Au-NCs against degradation. Nanotoxicity studies revealed excellent biocompatibility of Au-NC conjugates, as they showed no adverse effect on the cell viability and inflammatory response. Target specificity of the conjugates for detecting CD33 expressing AML cells (KG1a) in flow cytometry showed specific staining of {approx} 95.4% of leukaemia cells within 1-2 h compared to a non-specific uptake of {approx} 8.2% in human peripheral blood cells (PBMCs) which are CD33{sup low}. The confocal imaging also demonstrated the targeted uptake of CD33 conjugated Au-NCs by leukaemia cells, thus confirming the flow cytometry results. This study demonstrates that novel nano-bioprobes can be developed using protein protected fluorescent nanoclusters of Au for the molecular receptor targeted flow cytometry based detection and imaging of cancer cells.
-
Bromberg, Lev; Raduyk, Svetlana; Hatton, T Alan; Concheiro, Angel; Rodriguez-Valencia, Cosme; Silva, Maite; Alvarez-Lorenzo, Carmen
2009-05-20
Conjugates of linear and branched polyethyleneimine (PEI) and monoamine polyether Jeffamine M-2070 (PO/EO mol ratio 10/31, 2000 Da) were synthesized through polyether activation by cyanuric chloride followed by attachment to PEI and guanidinylation by 1H-pyrazole-carboxamidine hydrochloride. The resulting guanidinylated PEI-polyether conjugates (termed gPEI-Jeffamine) efficiently complexed plasmid DNA, and their polyplexes possessed enhanced colloidal stability in the presence of serum proteins. In vitro studies with mammalian CHO-1, 3T3, and Cos-7 cell lines demonstrated improved transfection efficiency of the pCMVbeta-gal plasmid/gPEI-Jeffamine polyplexes. The guanidinylation of the amino groups of PEI and the conjugation of PEI with the Jeffamine polyether enhanced the conjugates' interaction with genetic material and reduced the cytotoxicity of the polyplexes in experiments with the L929 cell line.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
R. Lehmann
2005-10-01
Full Text Available Many studies have been done over the years to assess the effectiveness of Echinacea as an immunomodulator. We have assessed the potential bioavailability of alkyl- amides and caffeic acid conjugates using Caco-2 monolayers and compared it to their actual bioavailability in a Phase I clinical trial. The caffeic acid conjugates permeated poorly through the Caco-2 monolayers. Alkylamides were found to diffuse rapidly through Caco-2 monolayers. Differences in diffusion rates for each alkylamide correlated to structural variations, with saturation and N-terminal methylation contributing to decreases in diffusion rates. Alkylamide diffusion is not affected by the presence of other constituents and the results for a synthetic alkylamide were in line with those for alkylamides found in an ethanolic Echinacea preparation. We examined plasma from healthy volunteers for 12 hours after ingestion of Echinacea tablets manufactured from an ethanolic liquid extract. Caffeic acid conjugates could not be identified in any plasma sample at any time after tablet ingestion. Alkylamides were detected in plasma 20 minutes after tablet ingestion and for each alkylamide, pharmacokinetic profiles were devised. The data are consistent with the dosing regimen of one tablet three times daily and supports their usage as the primary markers for quality Echinacea preparations.
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Møller, Thea S B; Liu, Gang; Boysen, Anders
2017-01-01
research suggests that the effect of antibiotic treatment on plasmid conjugation frequencies, and hence the spread of resistance plasmids, may have been overestimated. We addressed the question by quantifying transfer proteins and conjugation frequencies of a blaCTX-M-1 encoding IncI1 resistance plasmid....... The frequency of plasmid conjugation, measured in an antibiotic free environment, increased significantly when the donor was pre-grown in broth containing CTX compared to growth without this drug, regardless of whether blaCTX-M-1 was located on the plasmid or in trans on the chromosome. The results shows...
-
125I Radioimmunoassay of serum ursodeoxycholyl conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hill, A.; Ross, P.E.; Bouchier, I.A.D.
1983-01-01
A radioimmunoassay for serum ursodeoxycholic conjugates using an iodine-125 ligand has been developed. The bile acid was present in normal fasting serum (0.19 +- SD 0.19 μmol/l, n=24) and 2-hour post-prandial serum (0.8 +- SD 0.8 μmol/l, n=16). Gallstone patients undergoing oral ursodeoxycholic acid therapy had significantly higher post-prandial serum levels (21.5 +- SD 14.0 μmol/l, n=15) by radioimmunoassay. Gas liquid chromatography analysis indicated that in normal serum ursodeoxycholic acid was totally conjugated, whereas sera from gallstone patients contained a proportion as the free bile acid (10.2 +- SD 8.1 μmol/l, n=15). Following an oral dose of ursodeoxycholic acid, both unconjugated and conjugated forms of the bile acid appeared in the serum of healthy individuals. (Auth.)
-
Scintillation Reduction using Conjugate-Plane Imaging (Abstract)
Vander Haagen, G. A.
2017-12-01
(Abstract only) All observatories are plagued by atmospheric turbulence exhibited as star scintillation or "twinkle" whether a high altitude adaptive optics research or a 30-cm amateur telescope. It is well known that these disturbances are caused by wind and temperature-driven refractive gradients in the atmosphere and limit the ultimate photometric resolution of land-based facilities. One approach identified by Fuchs (1998) for scintillation noise reduction was to create a conjugate image space at the telescope and focus on the dominant conjugate turbulent layer within that space. When focused on the turbulent layer little or no scintillation exists. This technique is described whereby noise reductions of 6 to 11/1 have been experienced with mathematical and optical bench simulations. Discussed is a proof-of-principle conjugate optical train design for an 80-mm, f7 telescope.
-
Transport synthetic acceleration with opposing reflecting boundary conditions
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zika, M R; Adams, M L
2000-02-01
The transport synthetic acceleration (TSA) scheme is extended to problems with opposing reflecting boundary conditions. This synthetic method employs a simplified transport operator as its low-order approximation. A procedure is developed that allows the use of the conjugate gradient (CG) method to solve the resulting low-order system of equations. Several well-known transport iteration algorithms are cast in a linear algebraic form to show their equivalence to standard iterative techniques. Source iteration in the presence of opposing reflecting boundary conditions is shown to be equivalent to a (poorly) preconditioned stationary Richardson iteration, with the preconditioner defined by the method of iterating on the incident fluxes on the reflecting boundaries. The TSA method (and any synthetic method) amounts to a further preconditioning of the Richardson iteration. The presence of opposing reflecting boundary conditions requires special consideration when developing a procedure to realize the CG method for the proposed system of equations. The CG iteration may be applied only to symmetric positive definite matrices; this condition requires the algebraic elimination of the boundary angular corrections from the low-order equations. As a consequence of this elimination, evaluating the action of the resulting matrix on an arbitrary vector involves two transport sweeps and a transmission iteration. Results of applying the acceleration scheme to a simple test problem are presented.
-
Bispecific small molecule-antibody conjugate targeting prostate cancer.
Kim, Chan Hyuk; Axup, Jun Y; Lawson, Brian R; Yun, Hwayoung; Tardif, Virginie; Choi, Sei Hyun; Zhou, Quan; Dubrovska, Anna; Biroc, Sandra L; Marsden, Robin; Pinstaff, Jason; Smider, Vaughn V; Schultz, Peter G
2013-10-29
Bispecific antibodies, which simultaneously target CD3 on T cells and tumor-associated antigens to recruit cytotoxic T cells to cancer cells, are a promising new approach to the treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Here we report a site-specific, semisynthetic method for the production of bispecific antibody-like therapeutics in which a derivative of the prostate-specific membrane antigen-binding small molecule DUPA was selectively conjugated to a mutant αCD3 Fab containing the unnatural amino acid, p-acetylphenylalanine, at a defined site. Homogeneous conjugates were generated in excellent yields and had good solubility. The efficacy of the conjugate was optimized by modifying the linker structure, relative binding orientation, and stoichiometry of the ligand. The optimized conjugate showed potent and selective in vitro activity (EC50 ~ 100 pM), good serum half-life, and potent in vivo activity in prophylactic and treatment xenograft mouse models. This semisynthetic approach is likely to be applicable to the generation of additional bispecific agents using drug-like ligands selective for other cell-surface receptors.
-
Bispecific small molecule–antibody conjugate targeting prostate cancer
Kim, Chan Hyuk; Axup, Jun Y.; Lawson, Brian R.; Yun, Hwayoung; Tardif, Virginie; Choi, Sei Hyun; Zhou, Quan; Dubrovska, Anna; Biroc, Sandra L.; Marsden, Robin; Pinstaff, Jason; Smider, Vaughn V.; Schultz, Peter G.
2013-01-01
Bispecific antibodies, which simultaneously target CD3 on T cells and tumor-associated antigens to recruit cytotoxic T cells to cancer cells, are a promising new approach to the treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Here we report a site-specific, semisynthetic method for the production of bispecific antibody-like therapeutics in which a derivative of the prostate-specific membrane antigen-binding small molecule DUPA was selectively conjugated to a mutant αCD3 Fab containing the unnatural amino acid, p-acetylphenylalanine, at a defined site. Homogeneous conjugates were generated in excellent yields and had good solubility. The efficacy of the conjugate was optimized by modifying the linker structure, relative binding orientation, and stoichiometry of the ligand. The optimized conjugate showed potent and selective in vitro activity (EC50 ∼100 pM), good serum half-life, and potent in vivo activity in prophylactic and treatment xenograft mouse models. This semisynthetic approach is likely to be applicable to the generation of additional bispecific agents using drug-like ligands selective for other cell-surface receptors. PMID:24127589
-
Synthesis and characterization of nido-carborane-cobalamin conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hogenkamp, Harry P.C.; Collins, Douglas A.; Live, David; Benson, Linda M.; Naylor, Stephen
2000-01-01
Three vitamin B 12 (cyanocobalamin) conjugates bearing one nido-carborane molecule or two nido-carborane molecules linked to the propionamide side chains via a four carbon linker have been synthesized. Reaction of o-carboranoylchloride with 1,4-diaminobutane in pyridine produced nido-carboranoyl(4-amidobutyl)amine, which was linked to the b- and d-monocarboxylic acids and the b,d-dicarboxylic acid of cyanocobalamin. Mass spectrometry analysis as well as 11 B nuclear magnetic resonance demonstrated that during the reaction of o-carboranonylchloride with diaminobutane one of the boron atoms was eliminated. In vitro biological activity of the cyanocobalamin-nido-carborane conjugates was assessed by the unsaturated vitamin B 12 binding capacity assay. When compared with 57 Co cyanocobalamin, the biological activity of cyanocobalamin-b-nido-carborane, cyanocobalamin-d-nido-carborane, and cyanocobalamin-b-d-bis-nido-carborane conjugates were 92.93%, 35.75%, and 37.02%, respectively. These findings suggest that the 10 B cobalamin conjugates might be useful agents in treating malignant tumors via neutron capture therapy
-
Shahnaz, G; Perera, G; Sakloetsakun, D; Rahmat, D; Bernkop-Schnürch, A
2010-05-21
This study was aimed at improving the mucoadhesive properties of carboxymethyl dextran by the covalent attachment of cysteine. Mediated by a carbodiimide, l-cysteine was covalently attached to the polymer. The resulting CMD-cysteine conjugate (CMD-(273) conjugate) displayed 273+/-20 micromol thiol groups per gram of polymer (mean+/-S.D.; n=3). Within 2h the viscosity of an aqueous mucus/CMD-(273) conjugate mixture pH 7.4 increased at 37 degrees C by more than 85% compared to a mucus/carboxymethyl dextran mixture indicating enlarged interactions between the mucus and the thiolated polymer. Due to the immobilization of cysteine, the swelling velocity of the polymer was significantly accelerated (ppolymer disintegrated within 15 min, whereas tablets of the CMD-(273) conjugate remained stable for 160 min (means+/-S.D.; n=3). Results from LDH and MTT assays on Caco-2 cells revealed 4.96+/-0.98% cytotoxicity and 94.1+/-0.9% cell viability for the CMD-(273) conjugate, respectively. Controlled release of model compound from CMD-(273) conjugate tablets was observed over 6h. These findings suggest that CMD-(273) conjugate is a promising novel polymer for drug delivery systems providing improved mucoadhesive and cohesive properties, greater stability and biocompatibility. Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Solid-phase synthesis of 3-amino-2-pyrazolines
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Nielsen, John
1998-01-01
The development of a solid-phase synthesis of 3-amino-2-pyrazolines is described. Conjugate addition of hydrazines to alpha,beta-unsaturated nitriles followed by cyclization yields 3-amino-2-pyrazolines. Acylation or sulfonation of the free amino-group yields a 24 member library of 3-amino-2...
-
Structure Property Relationships in Organic Conjugated Systems
O'Neill, Luke; Lynch, Patrick; McNamara, Mary
2005-01-01
A series of π conjugated oligomers were studied by absorption and photoluminescence spectroscopy. A linear relationship between the positioning of the absorption and photoluminescence maxima plotted against inverse conjugation length is observed. The relationships are in good agreement with the simple particle in a box method, one of the earliest descriptions of the properties of one-dimensional organic molecules. In addition to the electronic transition energies, it was observed that the Sto...
-
Protein carriers of conjugate vaccines: characteristics, development, and clinical trials.
Pichichero, Michael E
2013-12-01
The immunogenicity of polysaccharides as human vaccines was enhanced by coupling to protein carriers. Conjugation transformed the T cell-independent polysaccharide vaccines of the past to T cell-dependent antigenic vaccines that were much more immunogenic and launched a renaissance in vaccinology. This review discusses the conjugate vaccines for prevention of infections caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Specifically, the characteristics of the proteins used in the construction of the vaccines including CRM, tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, Neisseria meningitidis outer membrane complex, and Hemophilus influenzae protein D are discussed. The studies that established differences among and key features of conjugate vaccines including immunologic memory induction, reduction of nasopharyngeal colonization and herd immunity, and antibody avidity and avidity maturation are presented. Studies of dose, schedule, response to boosters, of single protein carriers with single and multiple polysaccharides, of multiple protein carriers with multiple polysaccharides and conjugate vaccines administered concurrently with other vaccines are discussed along with undesirable consequences of conjugate vaccines. The clear benefits of conjugate vaccines in improving the protective responses of the immature immune systems of young infants and the senescent immune systems of the elderly have been made clear and opened the way to development of additional vaccines using this technology for future vaccine products.
-
Detection of human spermatozoal peptides after conjugation to 125I-labelled human serum albumin
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Metler, L.; Skrabei, H.; Czuppon, A.B.
1981-01-01
Human spermatozoal peptides, liberated during autolysis of the cells, were fractionated by gel-filtration chromatography and thin-layer chromatography. After conjugation to 125 I-labelled human serum albumin, all fractions were assayed with rabbit antihuman spermatozoa antiserum. In earlier publications, human sperm-immobilizing and sperm-agglutinating sera were used for the detection of solubilized spermatozoal antigen. The low sensitivity of these tests necessitated a more sensitive test. The purpose of this work is to describe a solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the detection of antigenic peptides
-
In Vivo Exposure of Kaempferol Is Driven by Phase II Metabolic Enzymes and Efflux Transporters.
Zheng, Liang; Zhu, Lijun; Zhao, Min; Shi, Jian; Li, Yuhuan; Yu, Jia; Jiang, Huangyu; Wu, Jinjun; Tong, Yunli; Liu, Yuting; Hu, Ming; Lu, Linlin; Liu, Zhongqiu
2016-09-01
Kaempferol is a well-known flavonoid; however, it lacks extensive pharmacokinetic studies. Phase II metabolic enzymes and efflux transporters play an important role in the disposition of flavonoids. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism by which phase II metabolic enzymes and efflux transporters determine the in vivo exposure of kaempferol. Pharmacokinetic analysis in Sprague-Dawley rats revealed that kaempferol was mostly biotransformed to conjugates, namely, kaempferol-3-glucuronide (K-3-G), kaempferol-7-glucuronide (K-7-G), and kaempferol-7-sulfate, in plasma. K-3-G represented the major metabolite. Compared with that in wild-type mice, pharmacokinetics in knockout FVB mice demonstrated that the absence of multidrug resistance protein 2 (MRP2) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) significantly increased the area under the curve (AUC) of the conjugates. The lack of MRP1 resulted in a much lower AUC of the conjugates. Intestinal perfusion in rats revealed that the glucuronide conjugates were mainly excreted in the small intestine, but 7-sulfate was mainly excreted in the colon. In Caco-2 monolayers, K-7-G efflux toward the apical (AP) side was significantly higher than K-3-G efflux. In contrast, K-3-G efflux toward the basolateral (BL) side was significantly higher than K-7-G efflux. The BL-to-AP efflux was significantly reduced in the presence of the MRP2 inhibitor LTC4. The AP-to-BL efflux was significantly decreased in the presence of the BL-side MRPs inhibitor MK571. The BCRP inhibitor Ko143 decreased the glucuronide conjugate efflux. Therefore, kaempferol is mainly exposed as K-3-G in vivo, which is driven by phase II metabolic enzymes and efflux transporters (i.e., BCRP and MRPs).
-
Demonstration of conjugated dopamine in monkey CSF by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Elchisak, M A; Powers, K H; Ebert, M H
1982-09-01
A method for measuring unconjugated and conjugated dopamine in body tissues and fluids is described. Conjugated dopamine was hydrolyzed in acid to unconjugated dopamine, separated from the sample matrix by alumina chromatography, and assayed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Conjugated dopamine was detected in greater concentrations than unconjugated dopamine in CSF taken from lateral ventricle or thecal sac of the Rhesus monkey. Haloperidol administration did not increase the levels of conjugated dopamine in lumbar CSF.
-
DiFilippo, Erica L; Brusseau, Mark L
2011-11-01
A simple, noninvasive imaging technique was used to obtain in situ measurements of organic-liquid saturation in a two-phase system under dynamic conditions. Efficacy of the light reflection visualization (LRV) imaging method was tested through comparison of measured and known volumes of organic liquid for experiments conducted with a two-dimensional flow cell. Two sets of experiments were conducted, with source-zone configurations representing two archetypical residual-and-pool architectures. LRV measurements were collected during the injection of organic liquid and during a dissolution phase induced by water flushing. There was a strong correlation between measured and known organic-liquid volumes, with the LRV-measured values generally somewhat lower than the known volumes. Errors were greater for the system wherein organic liquid was present in multiple zones comprised of porous media of different permeabilities, and for conditions of multiphase flow. This method proved effective at determining organic-liquid distribution in a two-phase system using minimal specialized equipment.
-
Social behaviour and decision making in bacterial conjugation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Günther eKoraimann
2014-04-01
Full Text Available Bacteria frequently acquire novel genes by HGT (horizontal gene transfer. HGT through the process of bacterial conjugation is highly efficient and depends on the presence of conjugative plasmids (CPs or integrated conjugative elements (ICEs that provide the necessary genes for DNA transmission. This review focuses on recent advancements in our understanding of ssDNA transfer systems and regulatory networks ensuring timely and spatially controlled DNA transfer (tra gene expression. As will become obvious by comparing different systems, by default, tra genes are shut off in cells in which conjugative elements are present. Only when conditions are optimal, donor cells – through epigenetic alleviation of negatively acting roadblocks and direct stimulation of DNA transfer genes – become transfer competent. These transfer competent cells have developmentally transformed into specialized cells capable of secreting ssDNA via a T4S (type IV secretion complex directly into recipient cells. Intriguingly, even under optimal conditions, only a fraction of the population undergoes this transition, a finding that indicates specialization and cooperative, social behavior. Thereby, at the population level, the metabolic burden and other negative consequences of tra gene expression are greatly reduced without compromising the ability to horizontally transfer genes to novel bacterial hosts. This undoubtedly intelligent strategy may explain why conjugative elements – CPs and ICEs – have been successfully kept in and evolved with bacteria to constitute a major driving force of bacterial evolution.
-
Factors contributing to the immunogenicity of meningococcal conjugate vaccines
Bröker, Michael; Berti, Francesco; Costantino, Paolo
2016-01-01
ABSTRACT Various glycoprotein conjugate vaccines have been developed for the prevention of invasive meningococcal disease, having significant advantages over pure polysaccharide vaccines. One of the most important features of the conjugate vaccines is the induction of a T-cell dependent immune response, which enables both the induction of immune memory and a booster response after repeated immunization. The nature of the carrier protein to which the polysaccharides are chemically linked, is often regarded as the main component of the vaccine in determining its immunogenicity. However, other factors can have a significant impact on the vaccine's profile. In this review, we explore the physico-chemical properties of meningococcal conjugate vaccines, which can significantly contribute to the vaccine's immunogenicity. We demonstrate that the carrier is not the sole determining factor of the vaccine's profile, but, moreover, that the conjugate vaccine's immunogenicity is the result of multiple physico-chemical structures and characteristics. PMID:26934310
-
Gufford, Brandon T; Robarge, Jason D; Eadon, Michael T; Gao, Hongyu; Lin, Hai; Liu, Yunlong; Desta, Zeruesenay; Skaar, Todd C
2018-04-01
Rifampin is a pleiotropic inducer of multiple drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters. This work utilized a global approach to evaluate rifampin effects on conjugating enzyme gene expression with relevance to human xeno- and endo-biotic metabolism. Primary human hepatocytes from 7 subjects were treated with rifampin (10 μmol/L, 24 hours). Standard methods for RNA-seq library construction, EZBead preparation, and NextGen sequencing were used to measure UDP-glucuronosyl transferase UGT, sulfonyltransferase SULT, N acetyltransferase NAT, and glutathione-S-transferase GST mRNA expression compared to vehicle control (0.01% MeOH). Rifampin-induced (>1.25-fold) mRNA expression of 13 clinically important phase II drug metabolizing genes and repressed (>1.25-fold) the expression of 3 genes ( P accounting for simultaneous induction of both CYP3A4 and UGT1A4 predicted a ~10-fold decrease in parent midazolam exposure with only a ~2-fold decrease in midazolam N-glucuronide metabolite exposure. These data reveal differential effects of rifampin on the human conjugating enzyme transcriptome and potential associations with miRNAs that form the basis for future mechanistic studies to elucidate the interplay of conjugating enzyme regulatory elements.
-
Blaich, Olav A.; Tsikalas, Filippos; Faleide, Jan Inge
2008-10-01
Integration of regional seismic reflection and potential field data along the northeastern Brazilian margin, complemented by crustal-scale gravity modelling, is used to reveal and illustrate onshore-offshore crustal structure correlation, the character of the continent-ocean boundary, and the relationship of crustal structure to regional variation of potential field anomalies. The study reveals distinct along-margin structural and magmatic changes that are spatially related to a number of conjugate Brazil-West Africa transfer systems, governing the margin segmentation and evolution. Several conceptual tectonic models are invoked to explain the structural evolution of the different margin segments in a conjugate margin context. Furthermore, the constructed transects, the observed and modelled Moho relief, and the potential field anomalies indicate that the Recôncavo, Tucano and Jatobá rift system may reflect a polyphase deformation rifting-mode associated with a complex time-dependent thermal structure of the lithosphere. The constructed transects and available seismic reflection profiles, indicate that the northern part of the study area lacks major breakup-related magmatic activity, suggesting a rifted non-volcanic margin affinity. In contrast, the southern part of the study area is characterized by abrupt crustal thinning and evidence for breakup magmatic activity, suggesting that this region evolved, partially, with a rifted volcanic margin affinity and character.
-
Phase Diversity Wavefront Sensing for Control of Space Based Adaptive Optics Systems
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Schgallis, Richard J
2007-01-01
Phase Diversity Wavefront Sensing (PD WFS) is a wavefront reconstruction technique used in adaptive optics, which takes advantage of the curvature conjugating analog physical properties of a deformable mirror (MMDM or Bi-morph...
-
Efficient conjugate gradient algorithms for computation of the manipulator forward dynamics
Fijany, Amir; Scheid, Robert E.
1989-01-01
The applicability of conjugate gradient algorithms for computation of the manipulator forward dynamics is investigated. The redundancies in the previously proposed conjugate gradient algorithm are analyzed. A new version is developed which, by avoiding these redundancies, achieves a significantly greater efficiency. A preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm is also presented. A diagonal matrix whose elements are the diagonal elements of the inertia matrix is proposed as the preconditioner. In order to increase the computational efficiency, an algorithm is developed which exploits the synergism between the computation of the diagonal elements of the inertia matrix and that required by the conjugate gradient algorithm.
-
Functional Hybrid Biomaterials based on Peptide-Polymer Conjugates for Nanomedicine
Shu, Jessica Yo
The focus of this dissertation is the design, synthesis and characterization of hybrid functional biomaterials based on peptide-polymer conjugates for nanomedicine. Generating synthetic materials with properties comparable to or superior than those found in nature has been a "holy grail" for the materials community. Man-made materials are still rather simplistic when compared to the chemical and structural complexity of a cell. Peptide-polymer conjugates have the potential to combine the advantages of the biological and synthetic worlds---that is they can combine the precise chemical structure and diverse functionality of biomolecules with the stability and processibility of synthetic polymers. As a new family of soft matter, they may lead to materials with novel properties that have yet to be realized with either of the components alone. In order for peptide-polymer conjugates to reach their full potential as useful materials, the structure and function of the peptide should be maintained upon polymer conjugation. The success in achieving desirable, functional assemblies relies on fundamentally understanding the interactions between each building block and delicately balancing and manipulating these interactions to achieve targeted assemblies without interfering with designed structures and functionalities. Such fundamental studies of peptide-polymer interactions were investigated as the nature of the polymer (hydrophilic vs. hydrophobic) and the site of its conjugation (end-conjugation vs. side-conjugation) were varied. The fundamental knowledge gained was then applied to the design of amphiphiles that self-assemble to form stable functional micelles. The micelles exhibited exceptional monodispersity and long-term stability, which is atypical of self-assembled systems. Thus such micelles based on amphiphilic peptide-polymer conjugates may meet many current demands in nanomedicine, in particular for drug delivery of hydrophobic anti-cancer therapeutics. Lastly
-
Preparation and characterization of microspheres of albumin-heparin conjugates
Kwon, Glen S.; Bae, You Han; Kim, Sung Wan; Cremers, Harry; Cremers, H.F.M.; Feijen, Jan
1991-01-01
Albumin-heparin microspheres have been prepared as a new drug carrier. A soluble albumin-heparin conjugate was synthesized by forming amide bonds between human serum albumin and heparin. After purification the albumin-heparin conjugate was crosslinked in a water-in-oil emulsion to form
-
[Role of proton-motive force in the conjugative DNA transport in Staphylococci].
Gavriliuk, V G; Vinnikov, A I
1997-01-01
Sensitivity of the conjugative process in staphylococci to the action of uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation and inhibitors of electron transport systems have been proved, that testifies to the energy-dependent character of conjugative transport of DNA. Proceeding of the conjugation process depends upon the generation of delta microH+ on the membrane of both the donor and recipient cells. contribution of protonmotive forces to providing for the transfer of plasmids during conjugation to staphylococci has been defined.
-
PREPARATION OF CHEMICALLY WELL-DEFINED CARBOHYDRATE DENDRIMER CONJUGATES
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
2004-01-01
A method for the synthesis of dendrimer conjugates having a well-defined chemical structure, comprising one or more carbohydrate moieties and one or more immunomodulating substances coupled to a dendrimer, is presented. First, the carbohydrate is bound to the dendrimer in a chemoselective manner...... conjugates and their use in vaccination, production of antibodies, high throughput screening, diagnostic assays and libraries....
-
Thermal Stability of siRNA Modulates Aptamer- conjugated siRNA Inhibition
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Alexey Berezhnoy
2012-01-01
Full Text Available Oligonucleotide aptamer-mediated in vivo cell targeting of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs is emerging as a useful approach to enhance the efficacy and reduce the adverse effects resulting from siRNA-mediated genetic interference. A current main impediment in aptamer-mediated siRNA targeting is that the activity of the siRNA is often compromised when conjugated to an aptamer, often requiring labor intensive and time consuming design and testing of multiple configurations to identify a conjugate in which the siRNA activity has not been significantly reduced. Here, we show that the thermal stability of the siRNA is an important parameter of siRNA activity in its conjugated form, and that siRNAs with lower melting temperature (Tm are not or are minimally affected when conjugated to the 3′ end of 2′F-pyrimidine-modified aptamers. In addition, the configuration of the aptamer-siRNA conjugate retains activity comparable with the free siRNA duplex when the passenger strand is co-transcribed with the aptamer and 3′ overhangs on the passenger strand are removed. The approach described in this paper significantly reduces the time and effort necessary to screening siRNA sequences that retain biological activity upon aptamer conjugation, facilitating the process of identifying candidate aptamer-siRNA conjugates suitable for in vivo testing.
-
Dual peptide conjugation strategy for improved cellular uptake and mitochondria targeting.
Lin, Ran; Zhang, Pengcheng; Cheetham, Andrew G; Walston, Jeremy; Abadir, Peter; Cui, Honggang
2015-01-21
Mitochondria are critical regulators of cellular function and survival. Delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic agents into mitochondria is a challenging task in modern pharmacology because the molecule to be delivered needs to first overcome the cell membrane barrier and then be able to actively target the intracellular organelle. Current strategy of conjugating either a cell penetrating peptide (CPP) or a subcellular targeting sequence to the molecule of interest only has limited success. We report here a dual peptide conjugation strategy to achieve effective delivery of a non-membrane-penetrating dye 5-carboxyfluorescein (5-FAM) into mitochondria through the incorporation of both a mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) and a CPP into one conjugated molecule. Notably, circular dichroism studies reveal that the combined use of α-helix and PPII-like secondary structures has an unexpected, synergistic contribution to the internalization of the conjugate. Our results suggest that although the use of positively charged MTS peptide allows for improved targeting of mitochondria, with MTS alone it showed poor cellular uptake. With further covalent linkage of the MTS-5-FAM conjugate to a CPP sequence (R8), the dually conjugated molecule was found to show both improved cellular uptake and effective mitochondria targeting. We believe these results offer important insight into the rational design of peptide conjugates for intracellular delivery.
-
Theory of even-parity states and two-photon spectra of conjugated polymers
McWilliams, P. C. M.; Hayden, G. W.; Soos, Z. G.
1991-04-01
The two-photon absorption (TPA) spectrum of interacting π electrons in conjugated polymers is shown to be qualitatively different from any single-particle description, including the Hartree-Fock limit. Alternating transfer integrals t(1+/-δ) along the backbone lead to a weak TPA below the one-photon gap Eg for arbitrarily weak correlations at δ=0, for intermediate correlations at δ=0.07 in polyenes, and for strong correlations at any δtheory to Eg in the limit of strong correlations in Hubbard models and is around 1.5Eg for Pariser-Parr-Pople (PPP) parameters. The PPP model, which accounts for one- and two-photon excitations of finite polyenes, is extended to even-parity states in polydiacetylenes (PDA's), polyacetylene (PA), and polysilanes (PS's). Previous experimental data for PDA and PS support both the strong TPA above Eg and weak TPA slightly below Eg for δ=0.15 in PDA and above Eg for δ~0.3 in PS. The strong TPA expected around 1.5Eg in isolated PA strands shifts to ~Eg due to interchain π-electron dispersion forces. TPA intensities in correlated states are shown to reflect both ionicity and mean-square charge separation. The even-parity states of conjugated polymers, like those of polyenes, show qualitatively different features associated with electron-electron correlations.
-
Delocalization Drives Free Charge Generation in Conjugated Polymer Films
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Rumbles, Garry [National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Reid, Obadiah G [National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Pace, Natalie A [National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
2018-02-19
We demonstrate that the product of photoinduced electron transfer between a conjugated polymer host and a dilute molecular sensitizer is controlled by the structural state of the polymer. Ordered semicrystalline solids exhibit free charge generation, while disordered polymers in the melt phase do not. We use photoluminescence (PL) and time-resolved microwave conductivity (TRMC) measurements to sweep through polymer melt transitions in situ. Free charge generation measured by TRMC turns off upon melting, whereas PL quenching of the molecular sensitizers remains constant, implying unchanged electron transfer efficiency. The key difference is the intermolecular order of the polymer host in the solid state compared to the melt. We propose that this order-disorder transition modulates the localization length of the initial charge-transfer state, which controls the probability of free charge formation.
-
Peptide-conjugated micelles as a targeting nanocarrier for gene delivery
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lin, Wen Jen, E-mail: wjlin@ntu.edu.tw; Chien, Wei Hsuan [National Taiwan University, School of Pharmacy, Graduate Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences (China)
2015-09-15
The aim of this study was to develop peptide-conjugated micelles possessing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) targeting ability for gene delivery. A sequence-modified dodecylpeptide, GE11(2R), with enhancing EGF receptor binding affinity, was applied in this study as a targeting ligand. The active targeting micelles were composed of poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)-poly(ethylene glycol) (PLGA-PEG) copolymer conjugated with GE11(2R)-peptide. The particle sizes of peptide-free and peptide-conjugated micelles were 277.0 ± 5.1 and 308.7 ± 14.5 nm, respectively. The peptide-conjugated micelles demonstrated the cellular uptake significantly higher than peptide-free micelles in EGFR high-expressed MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 cells due to GE11(2R)-peptide specificity. Furthermore, the peptide-conjugated micelles were able to encapsulate plasmid DNA and expressed cellular transfection higher than peptide-free micelles in EGFR high-expressed cells. The EGFR-targeting delivery micelles enhanced DNA internalized into cells and achieved higher cellular transfection in EGFR high-expressed cells.
-
Nanostructured Conjugated Polymers for Energy-Related Applications beyond Solar Cells.
Xie, Jian; Zhao, Cui-E; Lin, Zong-Qiong; Gu, Pei-Yang; Zhang, Qichun
2016-05-20
To meet the ever-increasing requirements for the next generation of sustainable and versatile energy-related devices, conjugated polymers, which have potential advantages over small molecules and inorganic materials, are among the most promising types of green candidates. The properties of conjugated polymers can be tuned through modification of the structure and incorporation of different functional moieties. In addition, superior performances can be achieved as a result of the advantages of nanostructures, such as their large surface areas and the shortened pathways for charge transfer. Therefore, nanostructured conjugated polymers with different properties can be obtained to be applied in different energy-related organic devices. This review focuses on the application and performance of the recently reported nanostructured conjugated polymers for high-performance devices, including rechargeable lithium batteries, microbial fuel cells (MFCs), thermoelectric generators, and photocatalytic systems. The design strategies, reaction mechanisms, advantages, and limitations of nanostructured conjugated polymers are further discussed in each section. Finally, possible routes to improve the performances of the current systems are also included in the conclusion. © 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
A nanodiamond-fluorescein conjugate for cell studies
Pedroso-Santana, Seidy; Fleitas-Salazar, Noralvis; Sarabia-Sainz, Andrei; Silva-Campa, Erika; Burgara-Estrella, Alexel; Angulo-Molina, Aracely; Melendrez, Rodrigo; Pedroza-Montero, Martin; Riera, Raul
2018-03-01
The use of nanodiamonds in studies with living systems generally involves the modification of their surfaces with functional groups. Fluorescent molecules can be attached to these groups, so that one can know the exact position of the particles in each moment of the interaction with the cells. Here we modify the surface of detonation nanodiamonds and nitrogen-vacancy center nanodiamonds using carboxylation and hydroxylation procedures. Subsequent reactions with silicates and cysteine, before addition of fluorescein allow to obtain fluorescent nano-conjugates. We used confocal microscopy to observe the position of nanodiamonds interacting with HeLa cells. At 3 h post-incubation the green fluorescence is localized in extracellular rounded like-vesicles assemblies while at 24 h the conjugates can be observed inside the cells. The measurement of the fluorescence emitted by both conjugates allowed to find an enhanced emission of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) when the nitrogen-vacancy center is present. We propose the existence of a fluorescence enhancement by electron transference process. The procedure described in this work allows the functionalization of nanodiamonds with FITC and other molecules using functional surface groups and small size mediators. Also, as was proved in our work, the nanodiamond-fluorescein conjugates can be used to track nanoparticles position within the cell. Localization studies are particularly important for drug delivery applications of nanodiamonds.
-
21 CFR 862.1115 - Urinary bilirubin and its conjugates (nonquantitative) test system.
2010-04-01
... 21 Food and Drugs 8 2010-04-01 2010-04-01 false Urinary bilirubin and its conjugates... Clinical Chemistry Test Systems § 862.1115 Urinary bilirubin and its conjugates (nonquantitative) test system. (a) Identification. A urinary bilirubin and its conjugates (nonquantitative) test system is a...
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kim, Eun-Kyung; Shrestha, Nabeen K. [Department of Chemistry, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791 (Korea, Republic of); Lee, Wonjoo [Department of Chemistry, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791 (Korea, Republic of); Department of Defense Ammunitions, Daeduk College, Daejeon 305-715 (Korea, Republic of); Cai, Gangri, E-mail: caigangri@naver.com [Department of Applied Chemistry, TianJin University of Technology, Tianjin 300384 (China); Department of Chemistry, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791 (Korea, Republic of); Han, Sung-Hwan, E-mail: shhan@hanyang.ac.kr [Department of Chemistry, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-791 (Korea, Republic of)
2015-04-01
Manganese dioxide (MnO{sub 2}) thin films are deposited electrochemically on an indium–tin-oxide (ITO) electrode using aqueous bath in presence of conjugated water soluble sulfonated polyaniline (SPAN) or a non-conjugated polyacrylic acid (PAA) polyelectrolyte surfactant. The surface morphology and nature of the electrodeposited MnO{sub 2} films are found to be influenced strongly by the amount and type of polyelectrolyte in the deposition bath. Increasing the SPAN concentration, a porous structure resulting from the reduction of voids between the MnO{sub 2} nano-flakes is obtained. In contrast, by increasing the PAA concentration, dense and spherical MnO{sub 2} nanostructures have been deposited. These results may be caused by initiation of different kinetics and orientation of nucleation of MnO{sub 2} deposits on ITO surface in presence of different types of polyelectrolytes. Cyclic voltammetry study of these films shows the supercapacitor behavior. The porous MnO{sub 2} films grown from the SPAN containing electrolyte demonstrates a specific capacitance of 368.53 F/g at scan rate of 10 mV/s, which is approximately 10 times higher (i.e., 30.29 F/g) than that of the spherical MnO{sub 2} dense films grown from PAA containing electrolyte. - Highlights: • Conjugated/non-conjugated polyelectrolytes were used in deposition of MnO{sub 2}. • The two kinds of MnO{sub 2} film showed entirely different morphology. • Conjugated polyelectrolyte worked as template and also affected the growth rate. • Non-conducting polyelectrolyte could work as template but hindered MnO{sub 2} growth. • The specific capacitance of MnO{sub 2}–S was 10 times higher than MnO{sub 2}–P.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kong, Hong Jin
2008-01-01
Laser fusion energy (LFE) is well known as one of the promising sources if clean energy for mankind. Laser fusion researches have been actively progressed, since Japan and the Soviet Union as well as USA developed ultrahigh power lasers at the beginning of 1970s. At present in USA, NIF (National Ignition Facility), which is the largest laser fusion facility in the world, is under construction and will be completed in 2008. Japan as a leader of the laser fusion research has developed a high energy and high power laser system, Gekko XII, and is under contemplation of FIREX projects for the fast ignition. China also has SG I, II lasers for performing the fusion research, and SG III is under construction as a next step. France is also constructing LMJ (Laser countries, many other developed countries in Europe, such as Russia, Germany, UK, and so on, have their own high energy laser systems for the fusion research. In Korea, the high power laser development started with SinMyung laser in KAIST in 1994, and KLF (KAERI Laser Facility) of KAERI was recently completed in 2007. For the practical use of laser fusion energy, the laser driver should be operated with a high repetition rate around 10Hz. Yet, current high energy laser systems, Such as NIF, Gekko XII, and etc., can be operated with only several shots per day. Some researchers have developed their own techniques to reduce the thermal loads of the laser material, by using laser diodes as pump sources and ceramic laser materials with high thermal energy scaling up for the real fusion driver. For this reason, H. J. Kong et al. proposed the beam combination laser system using stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugate mirrors (SBS PCMs) for a fusion driver. Proposed beam combination has many advantages for energy scaling up; it is composed by simple optical systems with small amount of components, there is no interaction between neighbored sub beams, the SBS PCMs can be used for a high energy beam reflection with
-
Peptide- and saccharide-conjugated dendrimers for targeted drug delivery: a concise review
Liu, Jie; Gray, Warren D.; Davis, Michael E.; Luo, Ying
2012-01-01
Dendrimers comprise a category of branched materials with diverse functions that can be constructed with defined architectural and chemical structures. When decorated with bioactive ligands made of peptides and saccharides through peripheral chemical groups, dendrimer conjugates are turned into nanomaterials possessing attractive binding properties with the cognate receptors. At the cellular level, bioactive dendrimer conjugates can interact with cells with avidity and selectivity, and this function has particularly stimulated interests in investigating the targeting potential of dendrimer materials for the design of drug delivery systems. In addition, bioactive dendrimer conjugates have so far been studied for their versatile capabilities to enhance stability, solubility and absorption of various types of therapeutics. This review presents a brief discussion on three aspects of the recent studies to use peptide- and saccharide-conjugated dendrimers for drug delivery: (i) synthesis methods, (ii) cell- and tissue-targeting properties and (iii) applications of conjugated dendrimers in drug delivery nanodevices. With more studies to elucidate the structure–function relationship of ligand–dendrimer conjugates in transporting drugs, the conjugated dendrimers hold promise to facilitate targeted delivery and improve drug efficacy for discovery and development of modern pharmaceutics. PMID:23741608
-
Rapid modification of retroviruses using lipid conjugates
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mukherjee, Nimisha G; Le Doux, Joseph M; Andrew Lyon, L
2009-01-01
Methods are needed to manipulate natural nanoparticles. Viruses are particularly interesting because they can act as therapeutic cellular delivery agents. Here we examine a new method for rapidly modifying retroviruses that uses lipid conjugates composed of a lipid anchor (1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine), a polyethylene glycol chain, and biotin. The conjugates rapidly and stably modified retroviruses and enabled them to bind streptavidin. The implication of this work for modifying viruses for gene therapy and vaccination protocols is discussed.
-
CONJUGATED POLYMERS AND POLYELECTROLYTES IN SOLAR PHOTOCONVERSION, Final Technical Report
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Schanze, Kirk S [University of Florida
2014-08-05
This DOE-supported program investigated the fundamental properties of conjugated polyelectrolytes, with emphasis placed on studies of excited state energy transport, self-assembly into conjugated polyelectroyte (CPE) based films and colloids, and exciton transport and charge injection in CPE films constructed atop wide bandgap semiconductors. In the most recent grant period we have also extended efforts to examine the properties of low-bandgap donor-acceptor conjugated polyelectrolytes that feature strong visible light absorption and the ability to adsorb to metal-oxide interfaces.
-
He, Jiao; Li, Jing; Sun, Wenji; Zhang, Tianyou; Ito, Yoichiro
2012-01-01
Coupled with evaporative light scattering detection, a high-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) method was developed for preparative isolation and purification of three glycine-conjugated cholic acids, glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA), glycohyodeoxycholic acid (GHDCA) and glycohyocholic acid (GHCA) from Pulvis Fellis Suis (Pig gallbladder bile) for the first time. The separation was performed with a two-phase solvent system consisted of chloroform-methanol-water-acetic acid (65:30:10:1.5, v/v/v/v) by eluting the lower phase in the head-to-tail elution mode. The revolution speed of the separation column, flow rate of the mobile phase and separation temperature were 800 rpm, 2 ml/min and 25 °C, respectively. In a single operation, 33 mg of GCDCA, 38 mg of GHDCA and 23 mg of GHCA were obtained from 200 mg of crude extract with the purity of 95.65%, 96.72% and 96.63%, respectively, in one step separation. The HSCCC fractions were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and the structures of the three glycine-conjugated cholic acids were identified by ESI-MS, (1)H NMR and (13)C NMR.
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Water-soluble Conjugates of Cabazitaxel Hemiesters-Dextran.
Parhizkar, Elahehnaz; Ahmadi, Fatemeh; Daneshamouz, Saeid; Mohammadi-Samani, Soliman; Sakhteman, Amirhossein; Parhizkar, Golnaz
2017-11-24
Cabazitaxel (CTX) is a second- generation taxane derivative, a class of potent anticancer drugs with very low water solubility. CTX is used in patients with resistant prostate cancer unresponsive to the first generation taxane, docetaxel. Currently marketed formulations of CTX contain high concentrations of surfactant and ethanol, which cause severe hypersensitivity reactions in patients. In order to increase its solubility, two hemiester analogs; CTX-succinate and CTX-glutarate were synthesized and characterized. To improve the solubility of hemiesters even more, dextran as a biocompatible polymer was also conjugated to hemiester analogs. MTT assay was performed on MCF-7 cell line to evaluate the cytotoxicity effect of hemiesters and conjugates. Based on the results, hemiester analogs increased water solubility of the drug up to about 3 and 8 fold. Conjugation to dextran enhanced the CTX solubility to more than 1500 fold. These conjugates released the conjugated CTX in less than 24 hours in a pH dependent manner and showed proper hemocompatibility characteristics. The hemiesters had approximately similar cytotoxicity in comparison with CTX and the dextran conjugates showed higher cytotoxicity effect on MCF-7 cell line. Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
-
Hemoglobin Detection on a Microfluidic Sensor Chip with a Partially Conjugated Polymer
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Eo, Soo Han; Won, Kwang Jae; Song, Simon; Yoon, Bora; Kim, Jong Man
2010-01-01
The development of efficient chemosensors based on the conjugated polymers has been the central focus of a large number of recent research programs. The presence of extensively delocalized electrons and conformational restrictions of the backbone structures make conjugated polymers attractive sensory materials. In these polymers, molecular recognition events influence electronic absorption and emission properties. Thus, a wide variety of conjugated polymer-based sensors have been investigated. However, the majority of the conjugated polymer sensors described to date have been explored in the form of solutions or thin films. Most biologically interesting target molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, or ions, are only soluble in water. Thus, it is desirable to use water-soluble conjugated polymers as sensor matrices. In general, in order to make water-soluble conjugated polymers tedious procedures are required since most synthetic methods developed for this purpose are incompatible with sidechain functionalities. Accordingly, protecting group strategies are required to prepare polymers with requisite functional groups that foster water solubility
-
Baek, Tae Hyun
Photoelasticity is one of the most widely used whole-field optical methods for stress analysis. The technique of birefringent coatings, also called the method of photoelastic coatings, extends the classical procedures of model photoelasticity to the measurement of surface strains in opaque models made of any structural material. Photoelastic phase-shifting method can be used for the determination of the phase values of isochromatics and isoclinics. In this paper, photoelastic phase-shifting technique and conventional Babinet-Soleil compensation method were utilized to analyze a specimen with a triangular hole and a circular hole under bending. Photoelastic phase-shifting technique is whole-field measurement. On the other hand, conventional compensation method is point measurement. Three groups of results were obtained by phase-shifting method with reflective polariscope arrangement, conventional compensation method and FEM simulation, respectively. The results from the first two methods agree with each other relatively well considering experiment error. The advantage of photoelastic phase-shifting method is that it is possible to measure the stress distribution accurately close to the edge of holes.
-
Conjugate Meningococcal Vaccines Development: GSK Biologicals Experience
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jacqueline M. Miller
2011-01-01
Full Text Available Meningococcal diseases are serious threats to global health, and new vaccines specifically tailored to meet the age-related needs of various geographical areas are required. This paper focuses on the meningococcal conjugate vaccines developed by GSK Biologicals. Two combined conjugate vaccines were developed to help protect infants and young children in countries where the incidence of meningococcal serogroup C or serogroup C and Y disease is important: Hib-MenC-TT vaccine, which offers protection against Haemophilus influenzae type b and Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C diseases, is approved in several countries; and Hib-MenCY-TT vaccine, which adds N. meningitidis serogroup Y antigen, is currently in the final stages of development. Additionally, a tetravalent conjugate vaccine (MenACWY-TT designed to help protect against four meningococcal serogroups is presently being evaluated for global use in all age groups. All of these vaccines were shown to be highly immunogenic and to have clinically acceptable safety profiles.
-
Conjugate Meningococcal Vaccines Development: GSK Biologicals Experience
Miller, Jacqueline M.; Mesaros, Narcisa; Van Der Wielen, Marie; Baine, Yaela
2011-01-01
Meningococcal diseases are serious threats to global health, and new vaccines specifically tailored to meet the age-related needs of various geographical areas are required. This paper focuses on the meningococcal conjugate vaccines developed by GSK Biologicals. Two combined conjugate vaccines were developed to help protect infants and young children in countries where the incidence of meningococcal serogroup C or serogroup C and Y disease is important: Hib-MenC-TT vaccine, which offers protection against Haemophilus influenzae type b and Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C diseases, is approved in several countries; and Hib-MenCY-TT vaccine, which adds N. meningitidis serogroup Y antigen, is currently in the final stages of development. Additionally, a tetravalent conjugate vaccine (MenACWY-TT) designed to help protect against four meningococcal serogroups is presently being evaluated for global use in all age groups. All of these vaccines were shown to be highly immunogenic and to have clinically acceptable safety profiles. PMID:21991444
-
Degradable conjugated polymers for the selective sorting of semiconducting carbon nanotubes
Gopalan, Padma; Arnold, Michael Scott; Kansiusarulsamy, Catherine Kanimozhi; Brady, Gerald Joseph; Shea, Matthew John
2018-04-10
Conjugated polymers composed of bi-pyridine units linked to 9,9-dialkyl fluorenyl-2,7-diyl units via imine linkages along the polymer backbone are provided. Also provided are semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes coated with the conjugated polymers and methods of sorting and separating s-SWCNTs from a sample comprising a mixture of s-SWCNTs and metallic single-walled carbon nanotubes using the conjugated polymers.
-
Firth, David; Bell, Leonard; Squires, Martin; Estdale, Sian; McKee, Colin
2015-09-15
We present the demonstration of a rapid "middle-up" liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS)-based workflow for use in the characterization of thiol-conjugated maleimidocaproyl-monomethyl auristatin F (mcMMAF) and valine-citrulline-monomethyl auristatin E (vcMMAE) antibody-drug conjugates. Deconvoluted spectra were generated following a combination of deglycosylation, IdeS (immunoglobulin-degrading enzyme from Streptococcus pyogenes) digestion, and reduction steps that provide a visual representation of the product for rapid lot-to-lot comparison-a means to quickly assess the integrity of the antibody structure and the applied conjugation chemistry by mass. The relative abundance of the detected ions also offer information regarding differences in drug conjugation levels between samples, and the average drug-antibody ratio can be calculated. The approach requires little material (<100 μg) and, thus, is amenable to small-scale process development testing or as an early component of a complete characterization project facilitating informed decision making regarding which aspects of a molecule might need to be examined in more detail by orthogonal methodologies. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Experimental study on the phase equilibria of the Ag-Ti system
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fu Xiaoliang; Li Changrong; Wang Fuming; Li Mei; Zhang Weijing
2005-01-01
The Ag-Ti diffusion couples were prepared by small pure silver plates closely packed in pure titanium powder, sealed in quartz tube, and annealed at 750 deg. C, 980 deg. C, 1100 deg. C and 1200 deg. C, respectively. The phase equilibrium relationship and the conjugate phase compositions in the Ag-Ti system were determined by means of the metallographic microscope and the electron probe microanalysis. Partial liquidus and solidus for the two-phase equilibrium, liquid + (βTi), were obtained. The narrow solution range for the intermediate phase (TiAg) was determined
-
Non-Andersonian conjugate strike-slip faults: Observations, theory, and tectonic implications
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yin, A; Taylor, M H
2008-01-01
Formation of conjugate strike-slip faults is commonly explained by the Anderson fault theory, which predicts a X-shaped conjugate fault pattern with an intersection angle of ∼30 degrees between the maximum compressive stress and the faults. However, major conjugate faults in Cenozoic collisional orogens, such as the eastern Alps, western Mongolia, eastern Turkey, northern Iran, northeastern Afghanistan, and central Tibet, contradict the theory in that the conjugate faults exhibit a V-shaped geometry with intersection angles of 60-75 degrees, which is 30-45 degrees greater than that predicted by the Anderson fault theory. In Tibet and Mongolia, geologic observations can rule out bookshelf faulting, distributed deformation, and temporal changes in stress state as explanations for the abnormal fault patterns. Instead, the GPS-determined velocity field across the conjugate fault zones indicate that the fault formation may have been related to Hagen-Poiseuille flow in map view involving the upper crust and possibly the whole lithosphere based on upper mantle seismicity in southern Tibet and basaltic volcanism in Mongolia. Such flow is associated with two coeval and parallel shear zones having opposite shear sense; each shear zone produce a set of Riedel shears, respectively, and together the Riedel shears exhibit the observed non-Andersonian conjugate strike-slip fault pattern. We speculate that the Hagen-Poiseuille flow across the lithosphere that hosts the conjugate strike-slip zones was produced by basal shear traction related to asthenospheric flow, which moves parallel and away from the indented segment of the collisional fronts. The inferred asthenospheric flow pattern below the conjugate strike-slip fault zones is consistent with the magnitude and orientations of seismic anisotropy observed across the Tibetan and Mongolian conjugate fault zones, suggesting a strong coupling between lithospheric deformation and asthenospheric flow. The laterally moving
-
Non-Andersonian conjugate strike-slip faults: Observations, theory, and tectonic implications
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Yin, A [Department of Earth and Space Sciences and Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA 90025-1567 (United States); Taylor, M H [Department of Geology, University of Kansas, 1475 Jayhawk Blvd., Lawrence, KS 66044 (United States)], E-mail: yin@ess.ucla.edu
2008-07-01
Formation of conjugate strike-slip faults is commonly explained by the Anderson fault theory, which predicts a X-shaped conjugate fault pattern with an intersection angle of {approx}30 degrees between the maximum compressive stress and the faults. However, major conjugate faults in Cenozoic collisional orogens, such as the eastern Alps, western Mongolia, eastern Turkey, northern Iran, northeastern Afghanistan, and central Tibet, contradict the theory in that the conjugate faults exhibit a V-shaped geometry with intersection angles of 60-75 degrees, which is 30-45 degrees greater than that predicted by the Anderson fault theory. In Tibet and Mongolia, geologic observations can rule out bookshelf faulting, distributed deformation, and temporal changes in stress state as explanations for the abnormal fault patterns. Instead, the GPS-determined velocity field across the conjugate fault zones indicate that the fault formation may have been related to Hagen-Poiseuille flow in map view involving the upper crust and possibly the whole lithosphere based on upper mantle seismicity in southern Tibet and basaltic volcanism in Mongolia. Such flow is associated with two coeval and parallel shear zones having opposite shear sense; each shear zone produce a set of Riedel shears, respectively, and together the Riedel shears exhibit the observed non-Andersonian conjugate strike-slip fault pattern. We speculate that the Hagen-Poiseuille flow across the lithosphere that hosts the conjugate strike-slip zones was produced by basal shear traction related to asthenospheric flow, which moves parallel and away from the indented segment of the collisional fronts. The inferred asthenospheric flow pattern below the conjugate strike-slip fault zones is consistent with the magnitude and orientations of seismic anisotropy observed across the Tibetan and Mongolian conjugate fault zones, suggesting a strong coupling between lithospheric deformation and asthenospheric flow. The laterally moving
-
Functional properties of nisin-carbohydrate conjugates formed by radiation induced Maillard reaction
Muppalla, Shobita R.; Sonavale, Rahul; Chawla, Surinder P.; Sharma, Arun
2012-12-01
Nisin-carbohydrate conjugates were prepared by irradiating nisin either with glucose or dextran. Increase in browning and formation of intermediate products was observed with a concomitant decrease in free amino and reducing sugar groups indicating occurrence of the Maillard reaction catalyzed by irradiation. Nisin-carbohydrate conjugates showed a broad spectrum antibacterial activity against Gram negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fluorescence) as well as Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus). Results of antioxidant assays, including that of DPPH radical-scavenging activity and reducing power, showed that the nisin-dextran conjugates possessed better antioxidant potential than nisin-glucose conjugate. These results suggested that it was possible to enhance the functional properties of nisin by preparing radiation induced conjugates suitable for application in food industry.
-
Perry, Caroline M
2013-05-01
The meningococcal groups C and Y and Haemophilus b (Hib) tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine (HibMenCY-TT) contains Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C and Y capsular polysaccharide antigens, and Hib capsular polysaccharide [polyribosyl-ribitol-phosphate (PRP)]. The HibMenCY-TT vaccine is available in the USA for use as active immunization to prevent invasive disease caused by N. meningitidis serogroups C (MenC) and Y (MenY), and Hib in children 6 weeks-18 months of age. HibMenCY-TT is the first meningococcal vaccine available for use in the USA that can be administered to infants as young as 6 weeks of age. In a randomized, controlled, phase III clinical trial, the HibMenCY-TT vaccine, administered to infants at 2, 4, 6 and 12-15 months of age, was immunogenic against MenC and MenY, and met the prespecified criteria for immunogenicity. Anti-PRP antibodies, which have been shown to correlate with protection against Hib invasive disease, were also induced in the infants who received the HibMenCY-TT vaccine, with induced levels of this antibody noninferior to those occurring in the control group of infants who received a Hib tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine at 2, 4, and 6 months and a single dose of Hib conjugated to N. meningitidis outer membrane protein at 12-15 months. In several randomized, controlled clinical trials, HibMenCY-TT was coadministered with vaccines that are routinely administered to infants and toddlers in the USA. These vaccines included: diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis adsorbed, hepatitis B (recombinant) and inactivated poliovirus vaccine combined; 7-valent Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharide conjugate vaccine; measles, mumps and rubella vaccine; and varicella vaccine. Coadministration of these vaccines did not interfere with the immunogenicity of the HibMenCY-TT vaccine. Similarly, immune responses to the coadministered vaccines were not affected by the HibMenCY-TT vaccine. The tolerability profile of the Hib
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Li, Nan-Nan; Zheng, Bing-Na [DSAPM Lab and PCFM Lab, Institute of Polymer Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275 (China); Lin, Jian-Tao [DSAPM Lab and PCFM Lab, Institute of Polymer Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275 (China); Guangdong Medical College, Dongguan 523808 (China); Zhang, Li-Ming, E-mail: ceszhlm@mail.sysu.edu.cn [DSAPM Lab and PCFM Lab, Institute of Polymer Science, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275 (China)
2014-01-01
New heparin–indomethacin conjugate with an ester linkage was prepared by the carbodiimide-mediated condensation reaction, and then characterized by FTIR and {sup 1}HNMR analyses. Due to its amphiphilic character, such a conjugate could self-aggregate into spherical nanoparticles in aqueous system, as confirmed by fluorescence spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy. By the in vitro drug release tests, the resultant conjugate nanoparticles were found to have a sustained and esterase-sensitive release behavior for conjugated indomethacin. In addition, the uptake of these conjugate nanoparticles into human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE1 cells was confirmed by fluorescence microscopy. - Highlights: • New heparin–indomethacin conjugate with an ester linkage was prepared. • Such a conjugate could self-aggregate into spherical nanoparticles in aqueous system. • The resultant conjugate nanoparticles exhibited an esterase-sensitive drug release behavior. • The resultant conjugate nanoparticles showed the cellular uptake ability in CNE1 cells.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
G, Radha [National Centre for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, University of Madras, Guindy Campus, Chennai 600025 (India); S, Balakumar, E-mail: balasuga@yahoo.com [National Centre for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, University of Madras, Guindy Campus, Chennai 600025 (India); Venkatesan, Balaji; Vellaichamy, Elangovan [Department of Biochemistry, University of Madras, Guindy Campus, Chennai 600025 (India)
2017-06-01
In this study, we report the preparation of nano-hydroxyapatite (nHAp) incorporated poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) scaffolds by conjugated thermal induced phase separation (TIPS) and wet-chemical approach, which essentially facilitates the enhancement of both mechanical as well as biological properties of the scaffolds. The dissolution of PMMA was accomplished by acetone (Ace scaffold), ethanol-water (E-W scaffold) and isopropanol-water (I-W scaffold) mixtures as solvents. The existence of nHAp in PMMA matrix was investigated systematically. The higher degree of porous architecture was achieved from Ace scaffolds compared to both I-W and E-W scaffolds. On the other hand, the dense porous architecture of the I-W scaffold exhibited superior hardness and compressive strength than that of the Ace and E-W scaffolds. All the fabricated samples demonstrated enhanced in vitro bioactivity with respect to increasing immersion period as a result of flower-like in vitro apatite layer formation. The MTT assay was carried out for 1 day and 3 day culture using Saos-2 osteoblast-like cells, which showed better cell proliferation with increasing culture period owing to the interconnected pore architecture of scaffolds and the rational hemocompatibility as per the ASTM standard F756-00. - Highlights: • Conjugated TIPS – wet chemical derived strategy was adopted for PMMA-nHAp composite scaffolds preparation. • TIPS method was carried out by varying solvents such as acetone, isopropanol-water and ethanol-water mixtures. • The impact of solvents on porosity and mechanical properties has been explored. • The existence of nHAp in PMMA has improved in-vitro bioactivity through apatitic-flowers formation. • Hemocompatibility of the scaffolds are in agreement with ASTM standards.
-
/sup 125/I Radioimmunoassay of serum ursodeoxycholyl conjugates
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hill, A.; Ross, P.E.; Bouchier, I.A.D. (Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, Dundee (UK))
1983-02-07
A radioimmunoassay for serum ursodeoxycholic conjugates using an iodine-125 ligand has been developed. The bile acid was present in normal fasting serum (0.19 +- SD 0.19 ..mu..mol/l, n=24) and 2-hour post-prandial serum (0.8 +- SD 0.8 ..mu..mol/l, n=16). Gallstone patients undergoing oral ursodeoxycholic acid therapy had significantly higher post-prandial serum levels (21.5 +- SD 14.0 ..mu..mol/l, n=15) by radioimmunoassay. Gas liquid chromatography analysis indicated that in normal serum ursodeoxycholic acid was totally conjugated, whereas sera from gallstone patients contained a proportion as the free bile acid (10.2 +- SD 8.1 ..mu..mol/l, n=15). Following an oral dose of ursodeoxycholic acid, both unconjugated and conjugated forms of the bile acid appeared in the serum of healthy individuals.
-
The Solution of Two-Phase Inverse Stefan Problem Based on a Hybrid Method with Optimization
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yang Yu
2015-01-01
Full Text Available The two-phase Stefan problem is widely used in industrial field. This paper focuses on solving the two-phase inverse Stefan problem when the interface moving is unknown, which is more realistic from the practical point of view. With the help of optimization method, the paper presents a hybrid method which combines the homotopy perturbation method with the improved Adomian decomposition method to solve this problem. Simulation experiment demonstrates the validity of this method. Optimization method plays a very important role in this paper, so we propose a modified spectral DY conjugate gradient method. And the convergence of this method is given. Simulation experiment illustrates the effectiveness of this modified spectral DY conjugate gradient method.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. Raath
2008-07-01
Full Text Available At the advent of the Reformation, the institution of marriage, with particular emphasis on the marriage of priests and the degeneration of married life in Germany, proved to be a contentious matter in the discourse on marriage between Martin Luther and his colleague Melanchthon on the one hand and the papal authorities on the other. Although Luther subscribed to the basic definition of marriage postulated by the classical Roman jurists, he placed the issue of man’s “de facto” conjugal union in a broader perspective of moral-jural right as the foundation of the spouses’ duties and rights in marriage. Hence the distinction between “de facto” and “de jure” conjugal union enabled Luther and Melanchthon to develop a broader natural law-inspired view on marital dignity and the right thereto. In this article the origin, content and some implications of Luther’s reformational perspectives on the dignity of marriage are investigated.
-
Wen, Kun Hua; Yan, Lian Shan; Pan, Wei; Luo, Bin; Zou, Xi Hua; Ye, Jia; Ma, Ya Nan
2009-10-10
An analytical expression for calculating the reflection-peak wavelengths (RPWs) of a uniform sampled fiber Bragg grating (SFBG) with the multiple-phase-shift (MPS) technique is derived through Fourier transform of the index modulation. The new expression can accurately depict the RPWs incorporating various parameters such as the duty cycle and the DC index change. The effectiveness of the derived expression is further confirmed by comparing the RPWs estimated from the expression with the simulated reflective spectra using the piecewise uniform method. And the reflective spectrum has been well optimized by introducing the Gaussian apodization function to suppress the sidelobes without any wavelength shift on the RPWs. Then, a high-channel-count comb filter based on MPS is proposed by cascading two or more SFBGs with different Bragg periods but with the same RPWs. Noticeably, the RPWs of the new structured SFBG can also be accurately calculated through the expression. Furthermore, the number of spectral channels can be controlled by choosing gratings with specified difference Bragg periods.
-
Magnetic catechin-dextran conjugate as targeted therapeutic for pancreatic tumour cells.
Vittorio, Orazio; Voliani, Valerio; Faraci, Paolo; Karmakar, Biswajit; Iemma, Francesca; Hampel, Silke; Kavallaris, Maria; Cirillo, Giuseppe
2014-06-01
Catechin-dextran conjugates have recently attracted a lot of attention due to their anticancer activity against a range of cancer cells. Magnetic nanoparticles have the ability to concentrate therapeutically important drugs due to their magnetic-spatial control and provide opportunities for targeted drug delivery. Enhancement of the anticancer efficiency of catechin-dextran conjugate by functionalisation with magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Modification of the coating shell of commercial magnetic nanoparticles (Endorem) composed of dextran with the catechin-dextran conjugate. Catechin-dextran conjugated with Endorem (Endo-Cat) increased the intracellular concentration of the drug and it induced apoptosis in 98% of pancreatic tumour cells placed under magnetic field. The conjugation of catechin-dextran with Endorem enhances the anticancer activity of this drug and provides a new strategy for targeted drug delivery on tumour cells driven by magnetic field. The ability to spatially control the delivery of the catechin-dextran by magnetic field makes it a promising agent for further application in cancer therapy.
-
Fused thiophene-based conjugated polymers and their use in optoelectronic devices
Facchetti, Antonio; Marks, Tobin J.; Takai, Atsuro; Seger, Mark; Chen; , Zhihua
2017-07-18
The present teachings relate to polymeric compounds and their use as organic semiconductors in organic and hybrid optical, optoelectronic, and/or electronic devices such as photovoltaic cells, light emitting diodes, light emitting transistors, and field effect transistors. The disclosed compounds generally include as repeating units at least one annulated thienyl-vinylene-thienyl (TVT) unit and at least one other pi-conjugated unit. The annulated TVT unit can be represented by the formula: ##STR00001## where Cy.sup.1 and Cy.sup.2 can be a five- or six-membered carbocyclic ring. The annulated TVT unit can be optionally substituted at any available ring atom(s), and can be covalently linked to the other pi-conjugated unit via either the thiophene rings or the carbocyclic rings Cy.sup.1 and Cy.sup.2. The other pi-conjugated unit can be a conjugated linear linker including one or more unsaturated bonds, or a conjugated cyclic linker including one or more carbocyclic and/or heterocyclic rings.
-
Shin, I. S.; Lee, S.-M.; Kim, H. S.; Yao, Z.; Regino, C.; Sato, N.; Cheng, K. T.; Hassan, R.; Campo, M. F.; Albone, E. F.; Choyke, P. L.; Pastan, I.; Paik, C. H.
2012-01-01
Introduction Radiolabeling of a monoclonal antibody (mAb) with a metallic radionuclide requires the conjugation of a bifunctional chelator to the mAb. The conjugation, however, can alter the physical and immunological properties of the mAb, consequently affecting its tumor targeting pharmacokinetics. In this study, we investigated the effect of the amount of 2-(p-isothiocyanatobenzyl)-cyclohexyl-diethylenetriamine-pentaacetic acid (CHX-A″) conjugated to MORAb-009, a mAb directed against mesothelin and the effect of MORAb dose on the biodistribution of 111In labeled MORAb-009. Methods We used nude mice bearing A431/K5 tumor as a mesothelin-positive tumor model and A431 tumor as a mesothelin-negative control. To find the optimal level of CHX-A″ conjugation, CHX-A″-MORAb-009 conjugates with 2.4, 3.5, and 5.5 CHX-A″ molecules were investigated. To investigate the effect of injected MORAb-009 dose on neutralizing the shed-mesothelin in the circulation, the biodistribution studies were performed after the i.v. co-injection of the 111In labeled MORAb-009 (2.4 CHX-A″/MORAb-009) with three different doses, 0.2, 2, and 30 μg of MORAb-009. Results The tumor uptake in A431/K5 tumor was 4 times higher than that in A431 tumor, indicating that the tumor uptake in A431/K5 was mesothelin-mediated. The conjugate with 5.5 CHX-A″ showed a lower isoelectric point (pI) and lower immunoreactivity (IR) than the 2.4 CHX-A″ conjugate. These differences were reflected in biodistribution of the 111In label. The 111In labeled MORAb-009 conjugated with 2.4 CHX-A″ produced higher tumor uptake, and lower liver and spleen uptakes than the 5.5 CHX-A″ conjugate. The biodistribution studies also revealed that the tumor uptake was significantly affected by the injected MORAb-009 dose and tumor size. The 30 μg dose produced higher tumor uptake than the 0.2 and 2 μg doses whereas the 30 μg dose produced lower liver and spleen uptakes than the 0.2 μg dose. Conclusion This study
-
Miranda, Jonatan; Arias, Noemi; Fernández-Quintela, Alfredo; del Puy Portillo, María
2014-04-01
Despite its benefits, conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) may cause side effects after long-term administration. Because of this and the controversial efficacy of CLA in humans, alternative biomolecules that may be used as functional ingredients have been studied in recent years. Thus, conjugated linolenic acid (CLNA) has been reported to be a potential anti-obesity molecule which may have additional positive effects related to obesity. According to the results reported in obesity, CLNA needs to be given at higher doses than CLA to be effective. However, because of the few studies conducted so far, it is still difficult to reach clear conclusions about the potential use of these CLNAs in obesity and its related changes (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, or inflammation). Copyright © 2012 SEEN. Published by Elsevier Espana. All rights reserved.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Christian W. Huck
2016-05-01
Full Text Available A review with more than 100 references on the principles and recent developments in the solid-phase extraction (SPE prior and for in situ near and attenuated total reflection (ATR infrared spectroscopic analysis is presented. New materials, chromatographic modalities, experimental setups and configurations are described. Their advantages for fast sample preparation for distinct classes of compounds containing different functional groups in order to enhance selectivity and sensitivity are discussed and compared. This is the first review highlighting both the fundamentals of SPE, near and ATR spectroscopy with a view to real sample applicability and routine analysis. Most of real sample analyses examples are found in environmental research, followed by food- and bioanalysis. In this contribution a comprehensive overview of the most potent SPE-NIR and SPE-ATR approaches is summarized and provided.
-
Yu, Songcheng; Yu, Fei; Zhang, Hongquan; Qu, Lingbo; Wu, Yongjun
2014-06-01
In this study, in order to find out a proper method for conjugation of enrofloxacin to label enzymes, two methods were compared and carbodiimide condensation was proved to be better. The results showed that the binding ratio of enrofloxacin and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) was 8:1 and that of enrofloxacin and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was 5:1. This indicated that conjugate synthesized by carbodiimide condensation was fit for chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA). Furthermore, data revealed that dialysis time was an important parameter for conjugation and 6 days was best. Buffer to dilute conjugate had little effect on CLEIA. The storage condition for conjugates was also studied and it was shown that the conjugate was stable at 4 °C with no additive up to 30 days. These data were valuable for establishing CLEIA to quantify enrofloxacin.
-
Feng, Lan; Wu, Huali; Ma, Ping; Mumper, Russell J; Benhabbour, S Rahima
2011-01-01
THREE DOCETAXEL (DX) LIPID CONJUGATES: 2'-lauroyl-docetaxel (C12-DX), 2'-stearoyl-docetaxel (C18-DX), and 2'-behenoyl-docetaxel (C22-DX) were synthesized to enhance drug loading, entrapment, and retention in liquid oil-filled lipid nanoparticles (NPs). The three conjugates showed ten-fold higher solubility in the liquid oil phase Miglyol 808 than DX. To further increase the drug entrapment efficiency in NPs, orthogonal design was performed. The optimized formulation was composed of Miglyol 808, Brij 78, and Vitamin E tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate (TPGS). The conjugates were successfully entrapped in the reduced-surfactant NPs with entrapment efficiencies of about 50%-60% as measured by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) at a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. All three conjugates showed 45% initial burst release in 100% mouse plasma. Whereas C12-DX showed another 40% release over the next 8 hours, C18-DX and C22-DX in NPs showed no additional release after the initial burst of drug. All conjugates showed significantly lower cytotoxicity than DX in human DU-145 prostate cancer cells. The half maximal inhibitory concentration values (IC(50)) of free conjugates and conjugate NPs were comparable except for C22-DX, which was nontoxic in the tested concentration range and showed only vehicle toxicity when entrapped in NPs. In vivo, the total area under the curve (AUC(0-∞)) values of all DX conjugate NPs were significantly greater than that of Taxotere, demonstrating prolonged retention of drug in the blood. The AUC(0-∞) value of DX in Taxotere was 8.3-fold, 358.0-fold, and 454.5-fold lower than that of NP-formulated C12-DX, C18-DX, and C22-DX, respectively. The results of these studies strongly support the idea that the physical/chemical properties of DX conjugates may be fine-tuned to influence the affinity and retention of DX in oil-filled lipid NPs, which leads to very different pharmacokinetic profiles and blood exposure of an otherwise potent chemo
-
Combining CPT-conjugate neutrino channels at Fermilab
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jansson, Andreas; Parke, Stephen; Saoulidou, Niki; Mena, Olga
2008-01-01
We explore an alternative strategy to determine the neutrino mass hierarchy by making use of possible future neutrino facilities at Fermilab. Here, we use CPT-conjugate neutrino channels, exploiting a ν μ beam from the NuMI beamline and a ν e beam from a beta-beam experimental setup. Both experiments are performed at approximately the same /L. We present different possible accelerator scenarios for the beta-beam neutrino setup and fluxes. This CPT-conjugate neutrino channel scenario can extract the neutrino mass hierarchy down to sin 2 2θ 13 ≅0.02.
-
Homology among tet determinants in conjugative elements of streptococci
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Smith, M.D.; Hazum, S.; Guild, W.R.
1981-10-01
A mutation to tetracycline sensitivity in a resistant strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae was shown by several criteria to be due to a point mutation in the conjugative o(cat-tet) element found in the chromosomes of strains derived from BM6001, a clinical strain resistant to tetracycline and chloramphenicol. Strains carrying the mutation were transformed back to tetracycline resistance with the high efficiency of a point marker by donor deoxyribonucleic acids from its ancestral strain and from nine other clinical isolates of pneumococcus and by deoxyribonucleic acids from Group D Streptococcus faecalis and Group B Streptococcus agalactiae strains that also carry conjugative tet elements in their chromosomes. It was not transformed to resistance by tet plasmid deoxyribonucleic acids from either gram-negative or gram-positive species, except for one that carried transposon TN916, the conjugative tet element present in the chromosomes of some S. faecalis strains. The results showed that the tet determinants in conjugative elements of several streptococcal species share a high degree of deoxyribonucleic acid sequence homology and suggested that they differ from other tet genes.
-
Issues in reflection and debriefing: how nurse educators structure experiential activities.
Brackenreg, Jenni
2004-12-01
Experiential learning is particularly useful in vocational education programs where theory needs to be linked to practice. Although experiential learning is often advocated in nursing education and the importance of debriefing and reflection is almost always espoused, the focus in the literature has tended to be on detailed descriptions of the action phase with little close analysis of how the reflective phase is facilitated. The Lewinian model described by Kolb [Experiential Learning. Experience as Source of Learning and Development, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 1984] and the structuring approach suggested by Thiagarajan [Experiential Learning Packages, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1980] have been used as the theoretical context for an exploration of how nurse teachers describe their facilitation of the debriefing and reflective phases of experiential learning activities. Explication of the entire planned experiential learning experience is important for increasing the chances of the student being able to close the experiential learning loop. The more covert reflective phases for facilitating experiential learning are crucial and if neglected, or inexpertly and insensitively handled, may at best lead to poor learning outcomes or at worst lead to emotional damage and ;unfinished business' for the student. Interviews with eight experienced university educators elicited descriptions of how they constructed experiential activities with special reference to their descriptions of how the debriefing or reflective phases were structured.
-
Parallel conjugate gradient algorithms for manipulator dynamic simulation
Fijany, Amir; Scheld, Robert E.
1989-01-01
Parallel conjugate gradient algorithms for the computation of multibody dynamics are developed for the specialized case of a robot manipulator. For an n-dimensional positive-definite linear system, the Classical Conjugate Gradient (CCG) algorithms are guaranteed to converge in n iterations, each with a computation cost of O(n); this leads to a total computational cost of O(n sq) on a serial processor. A conjugate gradient algorithms is presented that provide greater efficiency using a preconditioner, which reduces the number of iterations required, and by exploiting parallelism, which reduces the cost of each iteration. Two Preconditioned Conjugate Gradient (PCG) algorithms are proposed which respectively use a diagonal and a tridiagonal matrix, composed of the diagonal and tridiagonal elements of the mass matrix, as preconditioners. Parallel algorithms are developed to compute the preconditioners and their inversions in O(log sub 2 n) steps using n processors. A parallel algorithm is also presented which, on the same architecture, achieves the computational time of O(log sub 2 n) for each iteration. Simulation results for a seven degree-of-freedom manipulator are presented. Variants of the proposed algorithms are also developed which can be efficiently implemented on the Robot Mathematics Processor (RMP).
-
Target binding improves relaxivity in aptamer-gadolinium conjugates.
Bernard, Elyse D; Beking, Michael A; Rajamanickam, Karunanithi; Tsai, Eve C; Derosa, Maria C
2012-12-01
MRI contrast agents (CA) have been heavily used over the past several decades to enhance the diagnostic value of the obtained images. From a design perspective, two avenues to improve the efficacy of contrast agents are readily evident: optimization of magnetic properties of the CA, and optimization of the pharmacokinetics and distribution of the CA in the patient. Contrast agents consisting of DNA aptamer-gadolinium(III) conjugates provide a single system in which these factors can be addressed simultaneously. In this proof-of-concept study, the 15mer thrombin aptamer was conjugated to diethylenetriaminepentaacetic (DTPA) dianhydride to form a monoamide derivative of the linear open-chain chelate present in the commonly used contrast agent Magnevist(®). The stability of the conjugated DNA aptamer-DTPA-Gd(III) chelate in a transmetallation study using Zn(II) was found to be similar to that reported for DTPA-Gd(III). Relaxivity enhancements of 35 ± 4 and 20 ± 1 % were observed in the presence of thrombin compared to a control protein at fields of 9.4 and 1.5 T, respectively. The inclusion of spacers between the aptamer and the DTPA to eliminate possible steric effects was also investigated but not found to improve the relaxation enhancement achieved in comparison to the unaltered aptamer conjugate.
-
Yardley, Denise A; Weaver, Robert; Melisko, Michelle E; Saleh, Mansoor N; Arena, Francis P; Forero, Andres; Cigler, Tessa; Stopeck, Alison; Citrin, Dennis; Oliff, Ira; Bechhold, Rebecca; Loutfi, Randa; Garcia, Agustin A; Cruickshank, Scott; Crowley, Elizabeth; Green, Jennifer; Hawthorne, Thomas; Yellin, Michael J; Davis, Thomas A; Vahdat, Linda T
2015-05-10
Glycoprotein NMB (gpNMB), a negative prognostic marker, is overexpressed in multiple tumor types. Glembatumumab vedotin is a gpNMB-specific monoclonal antibody conjugated to the potent cytotoxin monomethyl auristatin E. This phase II study investigated the activity of glembatumumab vedotin in advanced breast cancer by gpNMB expression. Patients (n = 124) with refractory breast cancer that expressed gpNMB in ≥ 5% of epithelial or stromal cells by central immunohistochemistry were stratified by gpNMB expression (tumor, low stromal intensity, high stromal intensity) and were randomly assigned 2:1 to glembatumumab vedotin (n = 83) or investigator's choice (IC) chemotherapy (n = 41). The study was powered to detect overall objective response rate (ORR) in the glembatumumab vedotin arm between 10% (null) and 22.5% (alternative hypothesis) with preplanned investigation of activity by gpNMB distribution and/or intensity (Stratum 1 to Stratum 3). Glembatumumab vedotin was well tolerated as compared with IC chemotherapy (less hematologic toxicity; more rash, pruritus, neuropathy, and alopecia). ORR was 6% (five of 83) for glembatumumab vedotin versus 7% (three of 41) for IC, without significant intertreatment differences for predefined strata. Secondary end point revealed ORR of 12% (10 of 83) versus 12% (five of 41) overall, and 30% (seven of 23) versus 9% (one of 11) for gpNMB overexpression (≥ 25% of tumor cells). Unplanned analysis showed ORR of 18% (five of 28) versus 0% (0 of 11) in patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), and 40% (four of 10) versus 0% (zero of six) in gpNMB-overexpressing TNBC. Glembatumumab vedotin is well tolerated in heavily pretreated patients with breast cancer. Although the primary end point in advanced gpNMB-expressing breast cancer was not met for all enrolled patients (median tumor gpNMB expression, 5%), activity may be enhanced in patients with gpNMB-overexpressing tumors and/or TNBC. A pivotal phase II trial (METRIC
-
HER2 specific delivery of methotrexate by dendrimer conjugated anti-HER2 mAb
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shukla, Rameshwer; Thomas, Thommey P; Desai, Ankur M; Kotlyar, Alina; Park, Steve J; Baker, James R Jr
2008-01-01
Herceptin, a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to human growth factor receptor-2 (HER2), was covalently attached to a fifth-generation (G5) polyamidoamine dendrimer containing the cytotoxic drug methotrexate. The specific binding and internalization of this conjugate labeled with FITC was clearly demonstrated in cell lines overexpressing HER2 by flow cytometry as well as confocal microscopic analysis. In addition, binding and uptake of antibody conjugated dendrimers was completely blocked by excess non-conjugated herceptin. The dendrimer conjugate was also shown to inhibit the dihydrofolate reductase with similar activity to methotrexate. Co-localization experiments with lysotracker red indicate that antibody conjugate, although internalized efficiently into cells, has an unusually long residence time in the lysosome. Somewhat lower cytotoxicity of the conjugate in comparison to free methotrexate was attributed to the slow release of methotrexate from the conjugate and its long retention in the lysosomal pocket
-
Clarke, Christopher; Bakaletz, Lauren O; Ruiz-Guiñazú, Javier; Borys, Dorota; Mrkvan, Tomas
2017-07-01
Protein D-containing vaccines may decrease acute otitis media (AOM) burden and nasopharyngeal carriage of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi). Protein D-containing pneumococcal conjugate vaccine PHiD-CV (Synflorix, GSK Vaccines) elicits robust immune responses against protein D. However, the phase III Clinical Otitis Media and PneumoniA Study (COMPAS), assessing PHiD-CV efficacy against various pneumococcal diseases, was not powered to demonstrate efficacy against NTHi; only trends of protective efficacy against NTHi AOM in children were shown. Areas covered: This review aims to consider all evidence available to date from pre-clinical and clinical phase III studies together with further evidence emerging from post-marketing studies since PHiD-CV has been introduced into routine clinical practice worldwide, to better describe the clinical utility of protein D in preventing AOM due to NTHi and its impact on NTHi nasopharyngeal carriage. Expert commentary: Protein D is an effective carrier protein in conjugate vaccines and evidence gathered from pre-clinical, clinical and observational studies suggest that it also elicits immune response that can help to reduce the burden of AOM due to NTHi. There remains a need to develop improved vaccines for prevention of NTHi disease, which could be achieved by combining protein D with other antigens.
-
Tudela, Eva; Deventer, Koen; Geldof, Lore; Van Eenoo, Peter
2015-02-01
Anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS) are an important class of doping agents. The metabolism of these substances is generally very extensive and includes phase-I and phase-II pathways. In this work, a comprehensive detection of these metabolites is described using a 2-fold dilution of urine and subsequent analysis by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS). The method was applied to study 32 different metabolites, excreted free or conjugated (glucuronide or sulfate), which permit the detection of misuse of at least 21 anabolic steroids. The method has been fully validated for 21 target compounds (8 glucuronide, 1 sulfate and 12 free steroids) and 18 out of 21 compounds had detection limits in the range of 1-10 ng mL(-1) in urine. For the conjugated compounds, for which no reference standards are available, metabolites were synthesized in vitro or excretion studies were investigated. The detection limits for these compounds ranged between 0.5 and 18 ng mL(-1) in urine. The simple and straightforward methodology complements the traditional methods based on hydrolysis, liquid-liquid extraction, derivatization and analysis by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
-
Molecules with linear pi-conjugated pathways between all substituents : Omniconjugation
van der Veen, M.H.; Rispens, M.T; Jonkman, H.T.; Hummelen, J.C.
In this paper, omniconjugation is introduced as a topological phenomenon in pi-conjugated systems. Omniconjugated molecules are defined by the fact that they provide direct and fully pi-conjugated pathways between all subdstituents attached to them. Surprisingly, until now such topologies have never
-
Molecules with Linear π-Conjugated Pathways between All Substituents : Omniconjugation
Veen, Marleen H. van der; Rispens, Minze T.; Jonkman, Harry T.; Hummelen, Jan C.
2004-01-01
In this paper, omniconjugation is introduced as a topological phenomenon in π-conjugated systems. Omniconjugated molecules are defined by the fact that they provide direct and fully π-conjugated pathways between all substituents attached to them. Surprisingly, until now such topologies have never
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ishizuka, T.; Komiya, I.; Hiratsuka, A.; Watabe, T.
1990-01-01
Rats orally given radioactive Clebopride [[14C]CP; N-(1'-benzyl-4'-piperidyl)-2-[14C]methoxy-4-amino-5-chlorobenzamide++ +], an antiulcer agent, excreted a novel type of ornithine (Orn)-GSH double conjugate in the bile as a major metabolite [(14C]BMCP), corresponding to 18% of the dose. The present study provides the first evidence for Orn conjugation of a xenobiotic in mammals and demonstrates that the structure of the radioactive conjugate differs fundamentally from those known in birds and reptiles. The structure of the biliary metabolite, [14C]BMCP, purified to homogeneity by silica gel thin layer and reverse phase high pressure liquid chromatography, was elucidated as S-[2-ornithylamino-4-[14C]methoxy-5-(1'-methyl-4'-piperidylamin o) carboxyphenyl]glutathione, based mainly on the following facts: (1) BMCP showed a protonated molecular ion (M + H)+ peak at m/z 683 in the secondary ion mass spectrum and (2) [14C]BMCP afforded Orn, glutamic acid, glycine, S-(2-amino-4-[14C]methoxy-5-carboxyphenyl)cysteine [( 14C]AMCC), and 1-methyl-4-aminopiperidine (MAP) quantitatively, in an equal molar ratio, by complete hydrolysis with peptidase. Thus, BMCP was a metabolite with three enzymatically hydrolyzable amide bonds in addition to the one existing originally in the parent structure of the drug, which produces MAP by peptic digestion. Of the three additional amide bonds of BMCP, one was a novel type of bond formed by condensation of the alpha-carboxylic acid group of Orn with the primary aromatic amino group of the drug and the other two were in the S-glutathionyl residue, substituted for the chlorine atom vicinal to the Orn-conjugating primary amino group in the aromatic ring and affording glutamic acid, glycine, and the S-cysteine conjugate AMCC by hydrolysis of BMCP with the peptidase
-
Umachandran, Meera; Ioannides, Costas
2006-07-05
The objective of the present study was to evaluate the stability of cytochrome P450 enzymes and of the conjugation enzyme systems epoxide hydrolase, glucuronosyl transferase, sulphotransferase and glutathione S-transferase in precision-cut rat lung slices incubated in RPMI media for different time periods up to 72 h. Moreover, the effect of culturing of lung slices on total glutathione levels and glutathione reductase was also investigated. Monitoring of cytochrome P450 activity was achieved using established diagnostic probes, but when activity in the lung was low the maintenance of the various enzymes in culture was determined immunologically using Western blotting. The dealkylation of pentoxyresorufin declined markedly during the first 4h of incubation but in the case of ethoxyresorufin loss of activity was more gradual and less severe. Western blot analysis revealed that the rate of decrease in cytochrome P450 apoprotein levels was isoform-specific with CYP2E1 being the most stable and CYP3A the least stable. Generally, phase II activities, especially cytosolic sulphotransferase, were relatively more stable throughout the incubation period compared with cytochromes P450. Finally, glutathione reductase activity and total glutathione levels were maintained throughout the 72 h incubation. The present studies indicate that xenobiotic-metabolising enzymes in precision-cut rat lung slices decline in culture, but the rate of loss differs and depends on the nature of the enzyme.
-
Sequence-specific DNA alkylation by tandem Py-Im polyamide conjugates.
Taylor, Rhys Dylan; Kawamoto, Yusuke; Hashiya, Kaori; Bando, Toshikazu; Sugiyama, Hiroshi
2014-09-01
Tandem N-methylpyrrole-N-methylimidazole (Py-Im) polyamides with good sequence-specific DNA-alkylating activities have been designed and synthesized. Three alkylating tandem Py-Im polyamides with different linkers, which each contained the same moiety for the recognition of a 10 bp DNA sequence, were evaluated for their reactivity and selectivity by DNA alkylation, using high-resolution denaturing gel electrophoresis. All three conjugates displayed high reactivities for the target sequence. In particular, polyamide 1, which contained a β-alanine linker, displayed the most-selective sequence-specific alkylation towards the target 10 bp DNA sequence. The tandem Py-Im polyamide conjugates displayed greater sequence-specific DNA alkylation than conventional hairpin Py-Im polyamide conjugates (4 and 5). For further research, the design of tandem Py-Im polyamide conjugates could play an important role in targeting specific gene sequences. © 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Lectins as carriers: preparation and purification of a concanavalin A-trypsin conjugate
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shier, W.T.
1985-01-01
The scheme for the preparation and purification of Con A-trypsin demonstrates the presence of Con A in the conjugate by affinity purification and by hemagglutination. The presence of Con A was demonstrated in two additional ways. The conjugate was prepared using trypsin labeled with iodine 125 and unlabeled Con A. The resulting conjugate containing 42,800 cpm/mg protein was used to demonstrate prolonged retention of the conjugated trypsin in mouse footpads. The presence of trypsin was also demonstrated in the conjugate by affinity chromatography and by the esterase activity characteristic of trypsin with tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester as substrate. Con A-trypsin was also assayed for proteolytic activity with a macromolecular substrate azocasein. A comparison of proteolytic activities with these two substrates indicated that 50-80% of the proteolytic activity observed with the small substrate is retained with macromolecular substrates
-
Enhancing the Photoluminescence Emission of Conjugated MEH-PPV by Light Processing
Botiz, Ioan
2014-04-09
We show here that treatment of thin films of conjugated polymers by illumination with light leads to an increase of the intensity of their photoluminescence by up to 42%. The corresponding enhancement of absorbance was much less pronounced. We explain this significant enhancement of photoluminescence by a planarization of the conjugated polymer chains induced by photoexcitations even below the glass transition temperature, possibly due to an increased conjugation length. Interestingly, the photoluminescence remains at the enhanced level for more than 71 h after treatment of the films by illumination with light, likely due to the fact that below the glass transition temperature no restoring force could return the conjugated chains into their initial conformational state. © 2014 American Chemical Society.
-
Conjugation of Inulin Improves Anti-Biofilm Activity of Chitosan.
Zhang, Guiqiang; Liu, Jing; Li, Ruilian; Jiao, Siming; Feng, Cui; Wang, Zhuo A; Du, Yuguang
2018-05-04
Bacteria biofilm helps bacteria prevent phagocytosis during infection and increase resistance to antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive pathogenic bacterium and is tightly associated with biofilm-related infections, which have led to great threat to human health. Chitosan, the only cationic polysaccharide in nature, has been demonstrated to have antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activities, which, however, require a relative high dosage of chitosan. Moreover, poor water solubility further restricts its applications on anti-infection therapy. Inulins are a group of polysaccharides produced by many types of plants, and are widely used in processed foods. Compared to chitosan, inulin is very soluble in water and possesses a mild antibacterial activity against certain pathogenic bacteria. In order to develop an effective strategy to treat biofilm-related infections, we introduce a method by covalent conjugation of inulin to chitosan. The physicochemical characterization of the inulin⁻chitosan conjugate was assayed, and the anti-biofilm activity was evaluated against S. aureus biofilm. The results indicated that, as compared to chitosan, this novel polysaccharide⁻polysaccharide conjugate significantly enhanced activities against S. aureus either in a biofilm or planktonic state. Of note, the conjugate also showed a broad spectrum anti-biofilm activity on different bacteria strains and low cellular toxicity to mammalian cells. These results suggested that chitosan conjugation of inulin was a viable strategy for treatment against biofilm-related infections. This finding may further spread the application of natural polysaccharides on treatments of infectious disease.
-
[Relationship between family variables and conjugal adjustment].
Jiménez-Picón, Nerea; Lima-Rodríguez, Joaquín-Salvador; Lima-Serrano, Marta
2018-04-01
To determine whether family variables, such as type of relationship, years of marriage, existence of offspring, number of members of family, stage of family life cycle, transition between stages, perceived social support, and/or stressful life events are related to conjugal adjustment. A cross-sectional and correlational study using questionnaires. Primary care and hospital units of selected centres in the province of Seville, Spain. Consecutive stratified sampling by quotas of 369 heterosexual couples over 18years of age, who maintained a relationship, with or without children, living in Seville. A self-report questionnaire for the sociodemographic variables, and the abbreviated version of the Dyadic Adjustment Scale, Questionnaire MOS Perceived Social Support, and Social Readjustment Rating Scale, were used. Descriptive and inferential statistics were performed with correlation analysis and multivariate regression. Statistically significant associations were found between conjugal adjustment and marriage years (r=-10: Pfamily life cycle (F=2.65; Pfamily life cycle stage (mature-aged stage) on conjugal adjustment (R2=.21; F=9.9; df=356; Prelationship. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
-
New preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithms for nonlinear unconstrained optimization problems
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Al-Bayati, A.; Al-Asadi, N.
1997-01-01
This paper presents two new predilection conjugate gradient algorithms for nonlinear unconstrained optimization problems and examines their computational performance. Computational experience shows that the new proposed algorithms generally imp lone the efficiency of Nazareth's [13] preconditioned conjugate gradient algorithm. (authors). 16 refs., 1 tab
-
Orderings for conjugate gradient preconditionings
Ortega, James M.
1991-01-01
The effect of orderings on the rate of convergence of the conjugate gradient method with SSOR or incomplete Cholesky preconditioning is examined. Some results also are presented that help to explain why red/black ordering gives an inferior rate of convergence.
-
alpha-Glucosidase-albumin conjugates: effect of chronic administration in mice
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Allen, T.M.; Murray, L.; Bhardwaj, D.; Poznansky, M.J.
1985-01-01
Enzyme albumin conjugates have been proposed as a means of increasing the efficacy of enzyme use in vivo and decreasing immune response to the enzyme. Particulate drug carriers, however, have a pronounced tendency to localize in the mononuclear phagocyte (reticuloendothelial) system. The authors have examined in mice the effect on phagocytic index, tissue distribution and organ size of continued administration of conjugates of alpha-glucosidase with either homologous or heterologous albumin. Mice received 10 X 2-mg injections of bovine serum albumin (BSA) or mouse serum albumin (MSA), either free, polymerized or conjugated with alpha-glucosidase. Experiments involving BSA had to be terminated before the end of the experiment because of anaphylaxis, but these reactions were less severe to the polymerized albumin than to free albumin. Free BSA, BSA polymer and BSA-enzyme conjugates all caused a decrease in phagocytic index after six injections. Mice receiving MSA showed no evidence of anaphylaxis, but mice receiving six or more injections of free MSA, MSA polymer or MSA-enzyme conjugate had significantly decreased phagocytic indices as compared to controls. Phagocytic indices had returned to normal by 7 days after the final injection. Tissue distribution of 125 I-labeled albumin preparations was determined in either naive or chronically injected mice
-
Effects of conjugated estrogens/bazedoxifene on lipid and coagulation variables
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Skouby, Sven O; Pan, Kaijie; Thompson, John R
2015-01-01
OBJECTIVE: This study aims to evaluate the effects of conjugated estrogens (CE)/bazedoxifene (BZA) on lipid and coagulation variables in a randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled phase 3 study of nonhysterectomized postmenopausal women. METHODS: The Selective estrogens, Menopause......, And Response to Therapy (SMART)-5 trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of CE/BZA in postmenopausal women (N = 1,843) with menopausal symptoms. Lipid (N = 1,843) and coagulation (N = 590) variables were assessed in women receiving daily CE 0.45 mg/BZA 20 mg, CE 0.625 mg/BZA 20 mg, BZA 20 mg, CE 0.45 mg...... reassurance that CE/BZA does not adversely affect lipid metabolism or hemostatic balance. In accordance, the incidences of venous thromboembolic events and cardiovascular events in postmenopausal women are similar to those observed with placebo....
-
Quantification of residual solvents in antibody drug conjugates using gas chromatography
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Medley, Colin D., E-mail: medley.colin@gene.com [Genentech Inc., Small Molecule Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080 (United States); Kay, Jacob [Research Pharmaceutical Services, 520 Virginia Dr. Fort, Washington, PA (United States); Li, Yi; Gruenhagen, Jason; Yehl, Peter; Chetwyn, Nik P. [Genentech Inc., Small Molecule Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1 DNA Way, South San Francisco, CA 94080 (United States)
2014-11-19
Highlights: • Sensitive residual solvents detection in ADCs. • 125 ppm QL for common conjugation solvents. • Generic and validatable method. - Abstract: The detection and quantification of residual solvents present in clinical and commercial pharmaceutical products is necessary from both patient safety and regulatory perspectives. Head-space gas chromatography is routinely used for quantitation of residual solvents for small molecule APIs produced through synthetic processes; however residual solvent analysis is generally not needed for protein based pharmaceuticals produced through cultured cell lines where solvents are not introduced. In contrast, antibody drug conjugates and other protein conjugates where a drug or other molecule is covalently bound to a protein typically use solvents such as N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA), N,N‑dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), or propylene glycol (PG) to dissolve the hydrophobic small molecule drug for conjugation to the protein. The levels of the solvent remaining following the conjugation step are therefore important to patient safety as these parental drug products are introduced directly into the patients bloodstream. We have developed a rapid sample preparation followed by a gas chromatography separation for the detection and quantification of several solvents typically used in these conjugation reactions. This generic method has been validated and can be easily implemented for use in quality control testing for clinical or commercial bioconjugated products.
-
A Dual-Wavelength Radar Technique to Detect Hydrometeor Phases
Liao, Liang; Meneghini, Robert
2016-01-01
This study is aimed at investigating the feasibility of a Ku- and Ka-band space/air-borne dual wavelength radar algorithm to discriminate various phase states of precipitating hydrometeors. A phase-state classification algorithm has been developed from the radar measurements of snow, mixed-phase and rain obtained from stratiform storms. The algorithm, presented in the form of the look-up table that links the Ku-band radar reflectivities and dual-frequency ratio (DFR) to the phase states of hydrometeors, is checked by applying it to the measurements of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Airborne Precipitation Radar Second Generation (APR-2). In creating the statistically-based phase look-up table, the attenuation corrected (or true) radar reflectivity factors are employed, leading to better accuracy in determining the hydrometeor phase. In practice, however, the true radar reflectivities are not always available before the phase states of the hydrometeors are determined. Therefore, it is desirable to make use of the measured radar reflectivities in classifying the phase states. To do this, a phase-identification procedure is proposed that uses only measured radar reflectivities. The procedure is then tested using APR-2 airborne radar data. Analysis of the classification results in stratiform rain indicates that the regions of snow, mixed-phase and rain derived from the phase-identification algorithm coincide reasonably well with those determined from the measured radar reflectivities and linear depolarization ratio (LDR).
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Jalvandi, Javid; White, Max; Gao, Yuan; Truong, Yen Bach; Padhye, Rajiv; Kyratzis, Ilias Louis
2017-01-01
A range of biodegradable drug-nanofibres composite mats have been reported as drug delivery systems. However, their main disadvantage is the rapid release of the drug immediately after application. This paper reports an improved system based on the incorporation of drug conjugated-chitosan into polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers. The results showed that controlled release of levofloxacin (LVF) could be achieved by covalently binding LVF to low molecular weight chitosan (CS) via a cleavable amide bond and then blending the conjugated CS with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibres prior to electrospinning. PVA/LVF and PVA-CS/LVF nanofibres were fabricated as controls. The conjugated CS-LVF was characterized by FTIR, DSC, TGA and 1 H NMR. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the blended CS-PVA nanofibres had a reduced fibre diameter compared to the controls. Drug release profiles showed that burst release was decreased from 90% in the control PVA/LVF electrospun mats to 27% in the PVA/conjugated CS-LVF mats after 8 h in phosphate buffer at 37 °C. This slower release is due to the cleavable bond between LVF and CS that slowly hydrolysed over time at neutral pH. The results indicate that conjugation of the drug to the polymer backbone is an effective way of minimizing burst release behaviour and achieving sustained release of the drug, LVF. - Highlights: • A novel drug delivery system for controlled release of drug was designed. • Composite PVA/conjugated CS-LVF nanofibres was fabricated by electrospinning. • Conjugated chitosan and composite nanofibres were characterized by various techniques. • Release profiles of drug were significantly improved in composite nanofibres containing drug conjugated chitosan.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jalvandi, Javid, E-mail: Javid.jlv@gmail.com [CSIRO, Manufacturing Flagship, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168 (Australia); School of Fashion and Textiles, College of Design and Social Context, RMIT University, 25 Dawson Street, Brunswick, Victoria 3056 (Australia); White, Max, E-mail: tamrak@bigpond.com [School of Fashion and Textiles, College of Design and Social Context, RMIT University, 25 Dawson Street, Brunswick, Victoria 3056 (Australia); Gao, Yuan, E-mail: Yuan.Gao@csiro.au [CSIRO, Manufacturing Flagship, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168 (Australia); Truong, Yen Bach, E-mail: Yen.truong@csiro.au [CSIRO, Manufacturing Flagship, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168 (Australia); Padhye, Rajiv, E-mail: rajiv.padhye@rmit.edu.au [School of Fashion and Textiles, College of Design and Social Context, RMIT University, 25 Dawson Street, Brunswick, Victoria 3056 (Australia); Kyratzis, Ilias Louis, E-mail: Louis.kyratzis@csiro.au [CSIRO, Manufacturing Flagship, Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168 (Australia)
2017-04-01
A range of biodegradable drug-nanofibres composite mats have been reported as drug delivery systems. However, their main disadvantage is the rapid release of the drug immediately after application. This paper reports an improved system based on the incorporation of drug conjugated-chitosan into polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers. The results showed that controlled release of levofloxacin (LVF) could be achieved by covalently binding LVF to low molecular weight chitosan (CS) via a cleavable amide bond and then blending the conjugated CS with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibres prior to electrospinning. PVA/LVF and PVA-CS/LVF nanofibres were fabricated as controls. The conjugated CS-LVF was characterized by FTIR, DSC, TGA and {sup 1}H NMR. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the blended CS-PVA nanofibres had a reduced fibre diameter compared to the controls. Drug release profiles showed that burst release was decreased from 90% in the control PVA/LVF electrospun mats to 27% in the PVA/conjugated CS-LVF mats after 8 h in phosphate buffer at 37 °C. This slower release is due to the cleavable bond between LVF and CS that slowly hydrolysed over time at neutral pH. The results indicate that conjugation of the drug to the polymer backbone is an effective way of minimizing burst release behaviour and achieving sustained release of the drug, LVF. - Highlights: • A novel drug delivery system for controlled release of drug was designed. • Composite PVA/conjugated CS-LVF nanofibres was fabricated by electrospinning. • Conjugated chitosan and composite nanofibres were characterized by various techniques. • Release profiles of drug were significantly improved in composite nanofibres containing drug conjugated chitosan.
-
Multiphoton- and simultaneous conjugate Ramsey-Borde atom interferometers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mueller, Holger; Chiow, Sheng-wey; Herrmann, Sven; Chu, Steven
2008-01-01
We report on our experiment to measure h/M, the ratio of the Planck constant to the mass of Cs atoms, and thereby the fine-structure constant. The target accuracy is 1 part per billion or better. We focus on two recent milestones: (i) The first realization of atom interferometers based on light-pulse beam splitters that transfer the momentum of up to 12 photon pairs, which increases the useful signal (matter wave phase shift) by a factor of 144 compared to the beam splitters used in the best present atom interferometers. Moreover, they lead to a cancellation of important systematic effects. (ii) The first realization of a simultaneous pair of conjugate Ramsey-Borde interferometers. In these, the relative sign of the inertial term is reversed so that it can be cancelled. Simultaneous operation means that this holds for a time-dependent inertial term (vibrations) too, which promises a substantial improvement in the signal to noise ratio
-
Measurement range of phase retrieval in optical surface and wavefront metrology
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Brady, Gregory R.; Fienup, James R.
2009-01-01
Phase retrieval employs very simple data collection hardware and iterative algorithms to determine the phase of an optical field. We have derived limitations on phase retrieval, as applied to optical surface and wavefront metrology, in terms of the speed of beam (i.e., f-number or numerical aperture) and amount of aberration using arguments based on sampling theory and geometrical optics. These limitations suggest methodologies for expanding these ranges by increasing the complexity of the measurement arrangement, the phase-retrieval algorithm, or both. We have simulated one of these methods where a surface is measured at unusual conjugates
-
Enzymatic synthesis of tRNA-peptide conjugates and spectroscopic studies of fluorine-modified RNA
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Graber, D.
2010-01-01
The research presented in this thesis concerns the enzymatic synthesis of artificially modified tRNA, in particular the preparation of non-hydrolysable tRNA-peptide conjugates. Another focus is on NMR-spectroscopic investigations of fluorine-modified RNA. In both projects, chemical methods were developed to address specific RNA-biological research questions. In the first part of this thesis the preparation of tRNA-peptide conjugates with a non-hydrolysable 3'-amide linkage is presented. These molecules are of high relevance for the characterization of ribosomal processes that occur in the peptidyl transferase center (such as peptide bond formation, peptide release, or translocation) using X-ray crystallography and biochemical methods. First, a novel concept to prepare chemically modified ('labeled') tRNA was elaborated based on the combination of solid-phase synthesis and enzymatic ligation. Thereby, a variety of differently labeled tRNAs was achieved. Moreover, the most successful high-yield ligation sites were identified to be situated within the TΨ C-loop. Optimization of the synthesis and the corresponding HPLC-purification of the conjugates were initially conducted with puromycin derivatized tRNA. In the course of this project, also two tRNAs with a ribose 3'-amino group at the terminal adenosine A76 were synthesized. For that purpose a protection group pattern had to be developed to obtain a functionalized solid-support bound to 3'-amino-3'-deoxyadenosine which was appropriate for RNA solid-phase synthesis. The successful preparation of tRNA-peptide conjugates was accomplished in cooperation with Holger Moroder and Jessica Steger (Micura group) who contributed short synthetic RNA-peptide conjugates. These fragments represented the tRNA 3'-termini that were required for exploring the new ligation strategies for non-hydrolisable tRNA - a main aim of this thesis. If the 5'-fragments are synthesized by solid-phase synthesis or in vitro transcription they do not
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rekova, M.; Jedinakova-Krizova, V.
2010-01-01
The aim of the study of labeling of ligand-antibody conjugates was to find optimal conditions of preparing of these conjugates and appropriate radioactivity of selected nuclide for applications in nuclear medicine. Conjugation of the γ-immunoglobulin G (human or bovine IgG, polyclonal antibodies) and bifunctional chelating agent, diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid dianhydride (cDTPAA), was carried out. Various values of the cDTPAA/antibody ratio, the weight concentration of polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies (MEM-97) and buffers were used. Further, the labeling conditions of the DTPA-IgG conjugate by radionuclides 90 Y and 177 Lu were optimized, and the labeling yield and the conjugation ratio of prepared radionuclide-DTPA-IgG conjugates was determined. Optimal incubation time of the immunoglobulin conjugation was obtained at 30 min from mixing of individual components. The labeling yield of radionuclide-DTPA-antibody conjugate higher than 95% was achieved. Higher values of conjugation ratio of radionuclide-DTPA-antibody conjugate were achieved in 0.1 mol L -1 carbonate buffer, pH 8.5, and the 0.1 mol L -1 carbonate buffer is suitable for studied conjugation systems. This study showed that the labeling yield as well as the conjugation ratio of tested systems depend on the amount of antibody substance, bifunctional chelating agent/antibody molar ratio and pH value of the buffer used. (author)
-
Molecularly precise dendrimer-drug conjugates with tunable drug release for cancer therapy.
Zhou, Zhuxian; Ma, Xinpeng; Murphy, Caitlin J; Jin, Erlei; Sun, Qihang; Shen, Youqing; Van Kirk, Edward A; Murdoch, William J
2014-10-06
The structural preciseness of dendrimers makes them perfect drug delivery carriers, particularly in the form of dendrimer-drug conjugates. Current dendrimer-drug conjugates are synthesized by anchoring drug and functional moieties onto the dendrimer peripheral surface. However, functional groups exhibiting the same reactivity make it impossible to precisely control the number and the position of the functional groups and drug molecules anchored to the dendrimer surface. This structural heterogeneity causes variable pharmacokinetics, preventing such conjugates to be translational. Furthermore, the highly hydrophobic drug molecules anchored on the dendrimer periphery can interact with blood components and alter the pharmacokinetic behavior. To address these problems, we herein report molecularly precise dendrimer-drug conjugates with drug moieties buried inside the dendrimers. Surprisingly, the drug release rates of these conjugates were tailorable by the dendrimer generation, surface chemistry, and acidity. © 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
-
Excitons in conjugated polymers: Do we need a paradigma change?
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Beenken, Wichard J.D. [Department of Theoretical Physics I, Ilmenau University of Thechnology (Germany)
2009-12-15
We have previously shown that both, polymer conformation and dynamics are crucial for the exciton transport in conjugated polymers. Thereby we found that the usual Foerster-type hopping transfer model - even if one applies the line-dipole approximation - falls short in one crucial aspect: the nature of the sites the excitons are transferred between is still unclear. We found that the simple model of spectroscopic units defined as segments of the polymer chains separated by structural defects breaking the {pi}-conjugation is only justified for chemical defects like hydrogenated double bonds, or extreme gauche (90 ) torsions between the monomers. Both defects are far too rare in a well-prepared conjugated polymer to explain the mean spectroscopic-unit length of typically 6-7 monomers. Meanwhile, also the concept of dynamical formation of the spectroscopic units, we had previously suggested, has also failed. Thus the question of a paradigma change concerning the exciton transport in conjugated polymers appears on the agenda. (Abstract Copyright [2009], Wiley Periodicals, Inc.)
-
Conjugated Polymers as Actuators: Modes of Actuation
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Skaarup, Steen
2004-01-01
The physical and chemical properties of conjugated polymers often depend very strongly on the degree of doping with anions or cations. The movement of ions in and out of the polymer matrix as it is redox cycled is also accompanied by mechanical changes. Both the volume and the stiffness can exhibit...... significant differences between the oxidized and reduced states. These effects form the basis of the use of conjugated polymers as actuators (or “artificial muscles”) controllable by a small (1-10 V) voltage. Three basic modes of actuation (bending, linear extension and stiffness change) have been proposed...
-
Conjugated polymers as actuators: modes of actuation
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Skaarup, Steen
2007-01-01
The physical and chemical properties of conjugated polymers often depend very strongly on the degree of doping with anions or cations. The movement of ions in and out of the polymer matrix as it is redox cycled is also accompanied by mechanical changes. Both the volume and the stiffness can exhibit...... significant differences between the oxidized and reduced states. These effects form the basis of the use of conjugated polymers as actuators (or “artificial muscles”) controllable by a small (1-10 V) voltage. Three basic modes of actuation (bending, linear extension and stiffness change) have been proposed...
-
Functionalized conjugated polyelectrolytes design and biomedical applications
Wang, Shu
2014-01-01
Functionalized Conjugated Polyelectrolytes presents a comprehensive review of these polyelectrolytes and their biomedical applications. Basic aspects like molecular design and optoelectronic properties are covered in the first chapter. Emphasis is placed on the various applications including sensing (chemical and biological), disease diagnosis, cell imaging, drug/gene delivery and disease treatment. This book explores a multi-disciplinary topic of interest to researchers working in the fields of chemistry, materials, biology and medicine. It also offers an integrated perspective on both basic research and application issues. Functionalized conjugated polyelectrolyte materials, which have already drawn considerable interest, will become a major new direction for biomedicine development.
-
Persistence Mechanisms of Conjugative Plasmids
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Bahl, Martin Iain; Hansen, Lars H.; Sørensen, Søren Johannes
2009-01-01
Are plasmids selfish parasitic DNA molecules or an integrated part of the bacterial genome? This chapter reviews the current understanding of the persistence mechanisms of conjugative plasmids harbored by bacterial cells and populations. The diversity and intricacy of mechanisms affecting the suc...
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Radha, G. [National Centre for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, University of Madras, Guindy campus, Chennai 600025 (India); Balakumar, S., E-mail: balasuga@yahoo.com [National Centre for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, University of Madras, Guindy campus, Chennai 600025 (India); Venkatesan, Balaji; Vellaichamy, Elangovan [Department of Biochemistry, University of Madras, Guindy campus, Chennai 600025 (India)
2017-04-01
In this study, we report the preparation of nano-hydroxyapatite (nHAp) incorporated poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) scaffolds by conjugated thermal induced phase separation (TIPS) and wet-chemical approach, which essentially facilitates the enhancement of both mechanical as well as biological properties of the scaffolds. The dissolution of PMMA was accomplished by acetone (Ace scaffold), ethanol-water (E-W scaffold) and isopropanol-water (I-W scaffold) mixtures as solvents. The existence of nHAp in PMMA matrix was investigated systematically. The porosity of ~ 57.89% was achieved from Ace scaffold that was higher degree compared to both I-W and E-W scaffolds. On the other hand, the dense porous architecture of I-W scaffold exhibited superior hardness of ~ 65.6 HR ‘D’ than that of the Ace and E-W scaffolds. All the fabricated samples demonstrated enhanced in vitro bioactivity with respect to increasing immersion period as a result of flower-like in vitro apatite layer formation. The MTT assay was carried out for 1 day and 3 day culture using Saos-2 osteoblast-like cells, which showed better cell proliferation with increasing culture period owing to the interconnected pore architecture of scaffolds and the rational hemocompatibility as per the ASTM standard F756-00. - Highlights: • Conjugated TIPS – wet chemical derived strategy was adopted for PMMA-nHAp composite scaffolds preparation. • TIPS method was carried out by varying solvents such as acetone, isopropanol-water and ethanol-water mixtures. • The impact of solvents on porosity and mechanical properties has been explored. • The existence of nHAp in PMMA has improved in-vitro bioactivity through apatitic-flowers formation. • Hemocompatibility of the scaffolds are in agreement with ASTM standards.
-
Curcumin-albumin conjugates as an effective anti-cancer agent with immunomodulatory properties.
Aravind, S R; Krishnan, Lissy K
2016-05-01
Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) is an active ingredient in turmeric (Curcuma longa) with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, chemopreventive, chemosensitization, and radiosensitization properties. Conjugation of curcumin (Curc) to albumin (Alb) has been found to increase the aqueous solubility of the drug. The current study aimed to prove the safe use of the Curc-Alb conjugate in animals and to demonstrate that it retains drug action both in vitro and in vivo. Dalton's lymphoma ascites (DLA) cell viability was inhibited by the Curc-Alb conjugate in a dose dependent manner in vitro, as evidenced by the MTT assay. Administration of up to 11.4 mg of conjugated curcumin per kg body weight to healthy animals was non-toxic both in terms of lethality and weight loss. Histological analysis of vital organs (kidney, liver and spleen) also did not show toxic effects. Favorable immuno-modulatory activity was observed after continuous administration of sub-acute doses of the conjugate which caused increase in total leukocyte count, platelet count, and viable cell count in bone marrow, and enhanced proliferation of lymphocyte in vitro upon culture. In vivo studies in the DLA tumor model in mice demonstrated that conjugated drug induces tumor reduction and prevention. Significant tumor reduction was observed when the Curc-Alb conjugate was administered intraperitoneally in DLA-induced mice after 1 day (prevention therapy) and 7 days (reduction therapy) of tumor induction. There was significant reduction in both tumor volume and tumor cell numbers in the treated animals as well as a marked increase in their mean survival time and percent increase in life span. The effect was greater when the conjugate was administered soon after inducing the tumor as compared to when treatment was started after allowing tumor to grow for 7 days. Thus, the results of the present study suggest that curcumin albumin conjugate has immunomodulatory and tumor growth inhibition properties. The study postulates
-
Phase conversion for fusion lasers
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kessler, T.; Castle, W.; Sampat, N.; Skupsky, S.; Smith, D.; Swales, S.
1988-01-01
An essential requirement for direct drive laser fusion is the uniform irradiation of spherical targets that are located in the quasi-far field of a laser system. A major impediment to irradiation uniformity with high-power solid-state laser systems is the presence of a hot-spot structure at the target plane. The hot-spot intensity nonuniformities are caused by spatial variations in the near-field phase front of each laser beam. Although for many tabletop applications diffraction-limited laser performance can be obtained through static phase correction, adaptive optics, or phase conjugation, such approaches are either excessively expensive, difficult to implement, or not yet available for large-aperture, high-peak-power laser beams. An alternative to phase correcting a wavefront involves modifying the laser beam's coherence properties thereby changing its focusing characteristics. The method of induced spatial incoherence (ISI) involves a reduction in both spatial and temporal coherence. Other methods are based on modifications of only the spatial coherence of a laser beam. A phase conversion technology which incorporates a distribution of near-field phases to either perform static phase correction or induce spatial incoherence offers a route toward increasingly higher levels of irradiation uniformity
-
Stochastic Spectral and Conjugate Descent Methods
Kovalev, Dmitry
2018-02-11
The state-of-the-art methods for solving optimization problems in big dimensions are variants of randomized coordinate descent (RCD). In this paper we introduce a fundamentally new type of acceleration strategy for RCD based on the augmentation of the set of coordinate directions by a few spectral or conjugate directions. As we increase the number of extra directions to be sampled from, the rate of the method improves, and interpolates between the linear rate of RCD and a linear rate independent of the condition number. We develop and analyze also inexact variants of these methods where the spectral and conjugate directions are allowed to be approximate only. We motivate the above development by proving several negative results which highlight the limitations of RCD with importance sampling.
-
Stochastic Spectral and Conjugate Descent Methods
Kovalev, Dmitry; Gorbunov, Eduard; Gasanov, Elnur; Richtarik, Peter
2018-01-01
The state-of-the-art methods for solving optimization problems in big dimensions are variants of randomized coordinate descent (RCD). In this paper we introduce a fundamentally new type of acceleration strategy for RCD based on the augmentation of the set of coordinate directions by a few spectral or conjugate directions. As we increase the number of extra directions to be sampled from, the rate of the method improves, and interpolates between the linear rate of RCD and a linear rate independent of the condition number. We develop and analyze also inexact variants of these methods where the spectral and conjugate directions are allowed to be approximate only. We motivate the above development by proving several negative results which highlight the limitations of RCD with importance sampling.
-
Swain, Shasank S; Paidesetty, Sudhir K; Padhy, Rabindra N
2017-03-01
To develop 6 conjugate agents of the moribund antibiotic sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) joined to 6 individual monoterpenes, followed by protocols of medicinal chemistry as potent antibacterials, against multidrug resistant (MDR) human gruesome pathogenic bacteria. Antibacterial activities of the proposed conjugates were ascertained by the 'prediction of activity spectra of substances' (PASS) program. Drug-likeness parameters and toxicity profiles of conjugates were standardized with the Lipinski rule of five, using cheminformatic tools, Molsoft, molinspiration, OSIRIS and ProTox. Antibacterial activities of individual chemicals and conjugates were examined by targeting the bacterial folic acid biosynthesis enzyme, dihydropteroate synthases (DHPSs) of bacteria, Bacillus anthracis, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with 3D structures of DHPSs from protein data bank. According to the PASS program, biological spectral values of conjugate-2, conjugate-5 and conjugate-6 were ascertained effective with 'probably active' or 'Pa' value > 0.5, for anti-infective and antituberculosic activities. Using molecular docking against 5 cited bacterial DHPSs, effective docking scores of 6 monoterpenes in the specified decreasing order (kcal/mol): -9.72 (eugenol against B. anthracis), -9.61 (eugenol against S. pneumoniae), -9. 42 (safrol, against B. anthracis), -9.39 (thymol, against M. tuberculosis), -9.34 (myristicin, against S. pneumoniae) and -9.29 (thymol, against B. anthracis); whereas the lowest docking score of SMZ was -8.46kcal/mol against S. aureus DHPS. Similarly, effective docking scores of conjugates were as specified (kcal/mol.): -10.80 (conjugate-4 consisting SMZ+safrol, against M. tuberculosis), -10.78 (conjugate-5 consisting SMZ+thymol, against M. tuberculosis), -10.60 (conjugate-5 against B. anthracis), -10.26 (conjugate-2 consisting SMZ+ eugenol, against M. tuberculosis), -10.25 (conjugate-5, against S
-
Uptake of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Conjugated with DNA by Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Joseph Harvey
2012-01-01
Full Text Available Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs have been proposed to have great therapeutic potential. SWCNTs conjugated with drugs or genes travel in the systemic circulation to reach target cells or tissues following extravasation from microvessels although the interaction between SWCNT conjugates and the microvascular endothelial cells (ECs remains unknown. We hypothesized that SWCNT-DNA conjugates would be taken up by microvascular ECs and that this process would be facilitated by SWCNTs compared to facilitation by DNA alone. ECs were treated with various concentrations of SWCNT-DNA-FITC conjugates, and the uptake and intracellular distribution of these conjugates were determined by a confocal microscope imaging system followed by quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity. The uptake of SWCNT-DNA-FITC conjugates (2 μg/mL by microvascular ECs was significantly greater than that of DNA-FITC (2 μg/mL, observed at 6 hrs after treatment. For the intracellular distribution, SWCNT-DNA-FITC conjugates were detected in the nucleus of ECs, while DNA-FITC was restricted to the cytoplasm. The fluorescence intensity and distribution of SWCNTs were concentration and time independent. The findings demonstrate that SWCNTs facilitate DNA delivery into microvascular ECs, thus suggesting that SWCNTs serving as drug and gene vehicles have therapeutic potential.
-
Several Guaranteed Descent Conjugate Gradient Methods for Unconstrained Optimization
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
San-Yang Liu
2014-01-01
Full Text Available This paper investigates a general form of guaranteed descent conjugate gradient methods which satisfies the descent condition gkTdk≤-1-1/4θkgk2 θk>1/4 and which is strongly convergent whenever the weak Wolfe line search is fulfilled. Moreover, we present several specific guaranteed descent conjugate gradient methods and give their numerical results for large-scale unconstrained optimization.
-
Conjugation of curcumin onto alginate enhances aqueous solubility and stability of curcumin.
Dey, Soma; Sreenivasan, K
2014-01-01
Curcumin is a potential drug for various diseases including cancer. Prime limitations associated with curcumin are low water solubility, rapid hydrolytic degradation and poor bioavailability. In order to redress these issues we developed Alginate-Curcumin (Alg-Ccm) conjugate which was characterized by FTIR and (1)H NMR spectroscopy. The conjugate self-assembled in aqueous solution forming micelles with an average hydrodynamic diameter of 459 ± 0.32 nm and negative zeta potential. The spherical micelles were visualized by TEM. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) of Alg-Ccm conjugate was determined. A significant enhancement in the aqueous solubility of curcumin was observed upon conjugation with alginate. Formation of micelles improved the stability of curcumin in water at physiological pH. The cytotoxic activity of Alg-Ccm was quantified by MTT assay using L-929 fibroblast cells and it was found to be potentially cytotoxic. Hence, Alg-Ccm could be a promising drug conjugate as well as a nanosized delivery vehicle. Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Comparison of linoleic and conjugated linoleic acids in enzymatic acidolysis of tristearin
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Yang, Tiankui; Xu, Xuebing; Li, L.T.
2001-01-01
tristearin (SSS) and linoleic (L) or conjugated linoleic (cL) acids (1:6, mol/mol). The other was between tristearin and the mixture of linoleic and conjugated linoleic acids (1:3:3, mol/mol/mol). Acyl incorporation and migration together with triacylglycerol composition of the products were monitored...... with gas chromatography, pancreatic lipase hydrolysis, and high performance liquid chromatography. Both acyl incorporation and migration of linoleic acid were faster than those of conjugated linoleic acid. At 5 h reaction, there were 13.0% LLL, 46.5% LSL, 27.7% LSS, and 5.6% SSS in the product for a system...... between tristearin and linoleic acid; whereas there were 2.4% cLcLcL, 10.4% cLScL, 50.9% cLSS, and 36.2% SSS in the product for a system between tristearin and conjugated linoleic acid. The results suggest that linoleic acid was more reactive than conjugated linoleic acid in the enzymatic acidolysis...
-
2013-03-28
...-Up Exclusive License: Photosensitizing Antibody-Fluorophore Conjugates for Photoimmunotherapy AGENCY...-205-2010/0-US-01), and entitled ``Photosensitizing Antibody- Fluorophore Conjugates,'' to Aspyrian... invention. The field of use may be limited to ``use of photosensitizing antibody-fluorophore conjugate by...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tom I-P. Shih
2013-03-01
Full Text Available Heat-transfer coefficients (HTC on surfaces exposed to convection environments are often measured by transient techniques such as thermochromic liquid crystal (TLC or infrared thermography. In these techniques, the surface temperature is measured as a function of time, and that measurement is used with the exact solution for unsteady, zero-dimensional (0-D or one-dimensional (1-D heat conduction into a solid to calculate the local HTC. When using the 0-D or 1-D exact solutions, the transient techniques assume the HTC and the free-stream or bulk temperature characterizing the convection environment to be constants in addition to assuming the conduction into the solid to be 0-D or 1-D. In this study, computational fluid dynamics (CFD conjugate analyses were performed to examine the errors that might be invoked by these assumptions for a problem, where the free-stream/bulk temperature and the heat-transfer coefficient vary appreciably along the surface and where conduction into the solid may not be 0-D or 1-D. The problem selected to assess these errors is flow and heat transfer in a channel lined with a staggered array of pin fins. This conjugate study uses three-dimensional (3-D unsteady Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS closed by the shear-stress transport (SST turbulence model for the gas phase (wall functions not used and the Fourier law for the solid phase. The errors in the transient techniques are assessed by comparing the HTC predicted by the time-accurate conjugate CFD with those predicted by the 0-D and 1-D exact solutions, where the surface temperatures needed by the exact solutions are taken from the time-accurate conjugate CFD solution. Results obtained show that the use of the 1-D exact solution for the semi-infinite wall to give reasonably accurate “transient” HTC (less than 5% relative error. Transient techniques that use the 0-D exact solution for the pin fins were found to produce large errors (up to 160% relative error
-
Intini, Francesco Paolo; Zajac, Juraj; Novohradsky, Vojtech; Saltarella, Teresa; Pacifico, Concetta; Brabec, Viktor; Natile, Giovanni; Kasparkova, Jana
2017-02-06
One concept how to improve anticancer effects of conventional metallodrugs consists in conjugation of these compounds with other biologically (antitumor) active agents, acting by a different mechanism. Here, we present synthesis, biological effects, and mechanisms of action of new Pt(II) derivatives containing one or two nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory diclofenac (DCF) ligands also known for their antitumor effects. The antiproliferative properties of these metallic conjugates show that these compounds are potent and cancer cell selective cytotoxic agents exhibiting activity in cisplatin resistant and the COX-2 positive tumor cell lines. One of these compounds, compound 3, in which DCF molecules are coordinated to Pt(II) through their carboxylic group, is more potent than parental conventional Pt(II) drug cisplatin, free DCF and the congeners of 3 in which DCF ligands are conjugated to Pt(II) via a diamine. The potency of 3 is due to several factors including enhanced internalization that correlates with enhanced DNA binding and cytotoxicity. Mechanistic studies show that 3 combines multiple effects. After its accumulation in cells, it releases Pt(II) drug capable of binding/damaging DNA and DCF ligands, which affect distribution of cells in individual phases of the cell cycle, inhibit glycolysis and lactate transport, collapse mitochondrial membrane potential, and suppress the cellular properties characteristic of metastatic progression.
-
Single-particle tracking of quantum dot-conjugated prion proteins inside yeast cells
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tsuji, Toshikazu; Kawai-Noma, Shigeko [Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Graduate School of Biosciences and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, B56, 4259 Nagatsuta, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501 (Japan); Pack, Chan-Gi [Cellular Informatics Laboratory, RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198 (Japan); Terajima, Hideki [Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Graduate School of Biosciences and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, B56, 4259 Nagatsuta, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501 (Japan); Yajima, Junichiro; Nishizaka, Takayuki [Department of Physics, Gakushuin University, 1-5-1 Mejiro, Toshima-ku, Tokyo 171-8588 (Japan); Kinjo, Masataka [Laboratory of Molecular Cell Dynamics, Graduate School of Life Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 001-0021 (Japan); Taguchi, Hideki, E-mail: taguchi@bio.titech.ac.jp [Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Graduate School of Biosciences and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, B56, 4259 Nagatsuta, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501 (Japan)
2011-02-25
Research highlights: {yields} We develop a method to track a quantum dot-conjugated protein in yeast cells. {yields} We incorporate the conjugated quantum dot proteins into yeast spheroplasts. {yields} We track the motions by conventional or 3D tracking microscopy. -- Abstract: Yeast is a model eukaryote with a variety of biological resources. Here we developed a method to track a quantum dot (QD)-conjugated protein in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We chemically conjugated QDs with the yeast prion Sup35, incorporated them into yeast spheroplasts, and tracked the motions by conventional two-dimensional or three-dimensional tracking microscopy. The method paves the way toward the individual tracking of proteins of interest inside living yeast cells.
-
Single-particle tracking of quantum dot-conjugated prion proteins inside yeast cells
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tsuji, Toshikazu; Kawai-Noma, Shigeko; Pack, Chan-Gi; Terajima, Hideki; Yajima, Junichiro; Nishizaka, Takayuki; Kinjo, Masataka; Taguchi, Hideki
2011-01-01
Research highlights: → We develop a method to track a quantum dot-conjugated protein in yeast cells. → We incorporate the conjugated quantum dot proteins into yeast spheroplasts. → We track the motions by conventional or 3D tracking microscopy. -- Abstract: Yeast is a model eukaryote with a variety of biological resources. Here we developed a method to track a quantum dot (QD)-conjugated protein in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We chemically conjugated QDs with the yeast prion Sup35, incorporated them into yeast spheroplasts, and tracked the motions by conventional two-dimensional or three-dimensional tracking microscopy. The method paves the way toward the individual tracking of proteins of interest inside living yeast cells.
-
CP-violating Majorana phases, lepton-conserving processes, and final state interactions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nieves, Jose F.; Pal, Palash B.
2003-01-01
The CP-violating phases associated with Majorana neutrinos can give rise to CP-violating effects even in processes that conserve total lepton number, such as μ→eee-bar, μe→ee, and others. After explaining the reasons that make this happen, we consider the calculation of the rates for a process of the form l a l b →l a l c and its conjugate l-bar a l-bar b →l-bar a l-bar c , where l a ,l b ,l c denote charged leptons of different flavors. In the context of the standard model with Majorana neutrinos, we show that the difference in the rates depends on such phases. Our calculations illustrate in detail the mechanics that operate behind the scene, and set the stage for carrying out the analogous, more complicated (as we explain) calculations for other processes such as μ→eee-bar and its conjugate
-
Storage Conditions of Conjugated Reagents Can Impact Results of Immunogenicity Assays
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Robert J. Kubiak
2016-01-01
Full Text Available Consistent performance of anti-drug antibody (ADA assays through all stages of clinical development is critical for the assessment of immunogenicity and interpretation of PK, PD, safety, and efficacy. The electrochemiluminescent assays commonly employed for ADA measurement use drug conjugated with ruthenium and biotin to bind ADA in samples. Here we report an association between high nonspecific ADA responses in certain drug-naïve individuals and the storage buffer of the conjugated reagents used in a monoclonal antibody ADA assay. Ruthenylated reagents stored in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS buffer had increased levels of aggregate and produced variable and high baseline responses in some subjects. Reagents stored in a histidine-sucrose buffer (HSB had lower aggregate levels and produced low sample responses. In contrast to PBS, conjugated reagents formulated in HSB remained low in aggregate content and in sample response variability after 5 freeze/thaw cycles. A reagent monitoring control (RMC serum was prepared for the real-time evaluation of conjugated reagent quality. Using appropriate buffers for storage of conjugated reagents together with RMCs capable of monitoring of reagent aggregation status can help ensure consistent, long-term performance of ADA methods.
-
Intracellular trafficking of new anticancer therapeutics: antibody–drug conjugates
Kalim, Muhammad; Chen, Jie; Wang, Shenghao; Lin, Caiyao; Ullah, Saif; Liang, Keying; Ding, Qian; Chen, Shuqing; Zhan, Jinbiao
2017-01-01
Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) is a milestone in targeted cancer therapy that comprises of monoclonal antibodies chemically linked to cytotoxic drugs. Internalization of ADC takes place via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-mediated endocytosis, and pinocytosis. Conjugation strategies, endocytosis and intracellular trafficking optimization, linkers, and drugs chemistry present a great challenge for researchers to eradicate tumor cells successfully. This inventiveness of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking has given considerable momentum recently to develop specific antibodies and ADCs to treat cancer cells. It is significantly advantageous to emphasize the endocytosis and intracellular trafficking pathways efficiently and to design potent engineered conjugates and biological entities to boost efficient therapies enormously for cancer treatment. Current studies illustrate endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ADC, protein, and linker strategies in unloading and also concisely evaluate practically applicable ADCs. PMID:28814834
-
Intracellular trafficking of new anticancer therapeutics: antibody-drug conjugates.
Kalim, Muhammad; Chen, Jie; Wang, Shenghao; Lin, Caiyao; Ullah, Saif; Liang, Keying; Ding, Qian; Chen, Shuqing; Zhan, Jinbiao
2017-01-01
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is a milestone in targeted cancer therapy that comprises of monoclonal antibodies chemically linked to cytotoxic drugs. Internalization of ADC takes place via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-mediated endocytosis, and pinocytosis. Conjugation strategies, endocytosis and intracellular trafficking optimization, linkers, and drugs chemistry present a great challenge for researchers to eradicate tumor cells successfully. This inventiveness of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking has given considerable momentum recently to develop specific antibodies and ADCs to treat cancer cells. It is significantly advantageous to emphasize the endocytosis and intracellular trafficking pathways efficiently and to design potent engineered conjugates and biological entities to boost efficient therapies enormously for cancer treatment. Current studies illustrate endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ADC, protein, and linker strategies in unloading and also concisely evaluate practically applicable ADCs.
-
Repercussions of imprisonment for conjugal violence: discourses of men
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Anderson Reis de Sousa
Full Text Available ABSTRACT Objective: to know the consequences that men experience related to incarceration by conjugal violence. Methods: qualitative study on 20 men in jail and indicted in criminal processes related to conjugal violence in a Court specialized in Family and Domestic Violence against women. The interviews were classified based on Collective Subject Discourse method, using NVIVO(r software. Results: the collective discourse shows that the experience of preventive imprisonment starts a process of family dismantling, social stigma, financial hardship and psycho-emotional symptoms such as phobia, depression, hypertension, and headaches. Conclusion: due to the physical, mental and social consequences of the conjugal violence-related imprisonment experience, it is urgent to look carefully into the somatization process as well as to the prevention strategies regarding this process.
-
Droplet generating device for droplet-based μTAS using electro-conjugate fluid
Iijima, Y.; Takemura, K.; Edamura, K.
2017-05-01
Droplet-based μTAS, which carries out biochemical inspection and synthesis by handling samples as droplets on a single chip, has been attracting attentions in recent years. Although miniaturization of a chip is progressed, there are some problems in miniaturization of a whole system because of the necessity to connect syringe pumps to the chip. Thus, this study aims to realize a novel droplets generating device for droplet-based μTAS using electro-conjugate fluid (ECF). The ECF is a dielectric liquid generating a powerful flow when subjected to high DC voltage. The ECF flow generation allows us to realize a tiny hydraulic power source. Using the ECF flow, we can develop a droplet generating device for droplet-based μTAS by placing minute electrode pairs in flow channels. The device contains two channels filled with the ECF, which are dispersed and continuous phases meeting at a T-junction. When a sample in the dispersed phase is injected by the ECF flow to the continuous phase at T-junction, droplets are generated by shearing force between the two phases. We conducted droplet generating experiment and confirmed that droplets are successfully generated when the flow rate of the continuous phase is between 90 and 360 mm3 s-1, and the flow rate of the dispersed phase is between 10 and 40 mm3 s-1. We also confirmed that the droplet diameter and the droplet production rate are controllable by tuning the applied voltage to the electrode pairs.
-
Conjugate heat transfer of laminar film condensation along a horizontal plate
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lee, Euk Soo [Pusan National Univesity, Busan (Korea, Republic of)
2006-03-15
This paper proposes appropriate conjugate parameters and dimensionless temperatures to analysis the conjugate problem of heat conduction in solid wall coupled with laminar film condensation flow adjacent to horizontal flat plate. An efficient methods for some fluids are proposed for its solution. The momentum and energy balance equations are reduced to a nonlinear system of ordinary differential equations with four parameters: the Prandtl number, Pr, Modified Jacob number, Ja{sup *}/Pr, defined by an overall temperature difference, a property ratio {radical}{rho}{sub {iota}}{mu}{sub {iota}} {radical}{rho}{sub {upsilon}}{mu}{sub {upsilon}} and the conjugate parameter {zeta}. The obtained similarity solution reveals the effect of the conjugate parameter, and the results are compared with the simplified solution. The variations of the heat transfer rates as well as the interface temperature and frictions along the plate are shown explicitly.