
Sample records for blast pressure waves
-
Blast wave parameters at diminished ambient pressure
Silnikov, M. V.; Chernyshov, M. V.; Mikhaylin, A. I.
2015-04-01
Relation between blast wave parameters resulted from a condensed high explosive (HE) charge detonation and a surrounding gas (air) pressure has been studied. Blast wave pressure and impulse differences at compression and rarefaction phases, which traditionally determine damage explosive effect, has been analyzed. An initial pressure effect on a post-explosion quasi-static component of the blast load has been investigated. The analysis is based on empirical relations between blast parameters and non-dimensional similarity criteria. The results can be directly applied to flying vehicle (aircraft or spacecraft) blast safety analysis.
-
High-speed measurement of firearm primer blast waves
Courtney, Michael; Daviscourt, Joshua; Eng, Jonathan; Courtney, Amy
2012-01-01
This article describes a method and results for direct high-speed measurements of firearm primer blast waves employing a high-speed pressure transducer located at the muzzle to record the blast pressure wave produced by primer ignition. Key findings are: 1) Most of the lead styphnate based primer models tested show 5.2-11.3% standard deviation in the magnitudes of their peak pressure. 2) In contrast, lead-free diazodinitrophenol (DDNP) based primers had standard deviations of the peak blast p...
-
Newman, Andrew J; Hayes, Sarah H; Rao, Abhiram S; Allman, Brian L; Manohar, Senthilvelan; Ding, Dalian; Stolzberg, Daniel; Lobarinas, Edward; Mollendorf, Joseph C; Salvi, Richard
2015-03-15
Military personnel and civilians living in areas of armed conflict have increased risk of exposure to blast overpressures that can cause significant hearing loss and/or brain injury. The equipment used to simulate comparable blast overpressures in animal models within laboratory settings is typically very large and prohibitively expensive. To overcome the fiscal and space limitations introduced by previously reported blast wave generators, we developed a compact, low-cost blast wave generator to investigate the effects of blast exposures on the auditory system and brain. The blast wave generator was constructed largely from off the shelf components, and reliably produced blasts with peak sound pressures of up to 198dB SPL (159.3kPa) that were qualitatively similar to those produced from muzzle blasts or explosions. Exposure of adult rats to 3 blasts of 188dB peak SPL (50.4kPa) resulted in significant loss of cochlear hair cells, reduced outer hair cell function and a decrease in neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Existing blast wave generators are typically large, expensive, and are not commercially available. The blast wave generator reported here provides a low-cost method of generating blast waves in a typical laboratory setting. This compact blast wave generator provides scientists with a low cost device for investigating the biological mechanisms involved in blast wave injury to the rodent cochlea and brain that may model many of the damaging effects sustained by military personnel and civilians exposed to intense blasts. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Blast effects physical properties of shock waves
2018-01-01
This book compiles a variety of experimental data on blast waves. The book begins with an introductory chapter and proceeds to the topic of blast wave phenomenology, with a discussion Rankine-Hugoniot equations and the Friedlander equation, used to describe the pressure-time history of a blast wave. Additional topics include arrival time measurement, the initiation of detonation by exploding wires, a discussion of TNT equivalency, and small scale experiments. Gaseous and high explosive detonations are covered as well. The topics and experiments covered were chosen based on the comparison of used scale sizes, from small to large. Each characteristic parameter of blast waves is analyzed and expressed versus scaled distance in terms of energy and mass. Finally, the appendix compiles a number of polynomial laws that will prove indispensable for engineers and researchers.
-
A study on impulsive sound attenuation for a high-pressure blast flow field
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kang, Kuk Jeong; Ko, Sung Ho; Lee, Dong Soo
2008-01-01
The present work addresses a numerical study on impulsive sound attenuation for a complex high-pressure blast flow field; these characteristics are generated by a supersonic propellant gas flow through a shock tube into an ambient environment. A numerical solver for analyzing the high pressure blast flow field is developed in this study. From numerical simulations, wave dynamic processes (which include a first precursor shock wave, a second main propellant shock wave, and interactions in the muzzle blasts) are simulated and discussed. The pressure variation of the blast flow field is analyzed to evaluate the effect of a silencer. A live firing test is also performed to evaluate four different silencers. The results of this study will be helpful in understanding blast wave and in designing silencers
-
A study on impulsive sound attenuation for a high-pressure blast flow field
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kang, Kuk Jeong [Agency for Defence Development, Daejeon (Korea, Republic of); Ko, Sung Ho; Lee, Dong Soo [Chungnam National University, Daejeon (Korea, Republic of)
2008-01-15
The present work addresses a numerical study on impulsive sound attenuation for a complex high-pressure blast flow field; these characteristics are generated by a supersonic propellant gas flow through a shock tube into an ambient environment. A numerical solver for analyzing the high pressure blast flow field is developed in this study. From numerical simulations, wave dynamic processes (which include a first precursor shock wave, a second main propellant shock wave, and interactions in the muzzle blasts) are simulated and discussed. The pressure variation of the blast flow field is analyzed to evaluate the effect of a silencer. A live firing test is also performed to evaluate four different silencers. The results of this study will be helpful in understanding blast wave and in designing silencers
-
Model for small arms fire muzzle blast wave propagation in air
Aguilar, Juan R.; Desai, Sachi V.
2011-11-01
Accurate modeling of small firearms muzzle blast wave propagation in the far field is critical to predict sound pressure levels, impulse durations and rise times, as functions of propagation distance. Such a task being relevant to a number of military applications including the determination of human response to blast noise, gunfire detection and localization, and gun suppressor design. Herein, a time domain model to predict small arms fire muzzle blast wave propagation is introduced. The model implements a Friedlander wave with finite rise time which diverges spherically from the gun muzzle. Additionally, the effects in blast wave form of thermoviscous and molecular relaxational processes, which are associated with atmospheric absorption of sound were also incorporated in the model. Atmospheric absorption of blast waves is implemented using a time domain recursive formula obtained from numerical integration of corresponding differential equations using a Crank-Nicholson finite difference scheme. Theoretical predictions from our model were compared to previously recorded real world data of muzzle blast wave signatures obtained by shooting a set different sniper weapons of varying calibers. Recordings containing gunfire acoustical signatures were taken at distances between 100 and 600 meters from the gun muzzle. Results shows that predicted blast wave slope and exponential decay agrees well with measured data. Analysis also reveals the persistency of an oscillatory phenomenon after blast overpressure in the recorded wave forms.
-
Simulation and scaling analysis of a spherical particle-laden blast wave
Ling, Y.; Balachandar, S.
2018-05-01
A spherical particle-laden blast wave, generated by a sudden release of a sphere of compressed gas-particle mixture, is investigated by numerical simulation. The present problem is a multiphase extension of the classic finite-source spherical blast-wave problem. The gas-particle flow can be fully determined by the initial radius of the spherical mixture and the properties of gas and particles. In many applications, the key dimensionless parameters, such as the initial pressure and density ratios between the compressed gas and the ambient air, can vary over a wide range. Parametric studies are thus performed to investigate the effects of these parameters on the characteristic time and spatial scales of the particle-laden blast wave, such as the maximum radius the contact discontinuity can reach and the time when the particle front crosses the contact discontinuity. A scaling analysis is conducted to establish a scaling relation between the characteristic scales and the controlling parameters. A length scale that incorporates the initial pressure ratio is proposed, which is able to approximately collapse the simulation results for the gas flow for a wide range of initial pressure ratios. This indicates that an approximate similarity solution for a spherical blast wave exists, which is independent of the initial pressure ratio. The approximate scaling is also valid for the particle front if the particles are small and closely follow the surrounding gas.
-
Simulation and scaling analysis of a spherical particle-laden blast wave
Ling, Y.; Balachandar, S.
2018-02-01
A spherical particle-laden blast wave, generated by a sudden release of a sphere of compressed gas-particle mixture, is investigated by numerical simulation. The present problem is a multiphase extension of the classic finite-source spherical blast-wave problem. The gas-particle flow can be fully determined by the initial radius of the spherical mixture and the properties of gas and particles. In many applications, the key dimensionless parameters, such as the initial pressure and density ratios between the compressed gas and the ambient air, can vary over a wide range. Parametric studies are thus performed to investigate the effects of these parameters on the characteristic time and spatial scales of the particle-laden blast wave, such as the maximum radius the contact discontinuity can reach and the time when the particle front crosses the contact discontinuity. A scaling analysis is conducted to establish a scaling relation between the characteristic scales and the controlling parameters. A length scale that incorporates the initial pressure ratio is proposed, which is able to approximately collapse the simulation results for the gas flow for a wide range of initial pressure ratios. This indicates that an approximate similarity solution for a spherical blast wave exists, which is independent of the initial pressure ratio. The approximate scaling is also valid for the particle front if the particles are small and closely follow the surrounding gas.
-
An ultra-fast fiber optic pressure sensor for blast event measurements
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wu, Nan; Tian, Ye; Wang, Xingwei; Zou, Xiaotian; Fitek, John; Maffeo, Michael; Niezrecki, Christopher; Chen, Julie
2012-01-01
Soldiers who are exposed to explosions are at risk of suffering traumatic brain injury (TBI). Since the causal relationship between a blast and TBI is poorly understood, it is critical to have sensors that can accurately quantify the blast dynamics and resulting wave propagation through a helmet and skull that are imparted onto and inside the brain. To help quantify the cause of TBI, it is important to record transient pressure data during a blast event. However, very few sensors feature the capabilities of tracking the dynamic pressure transients due to the rapid change of the pressure during blast events, while not interfering with the physical material layers or wave propagation. In order to measure the pressure transients efficiently, a pressure sensor should have a high resonant frequency and a high spatial resolution. This paper describes an ultra-fast fiber optic pressure sensor based on the Fabry–Perot principle for the application of measuring the rapid pressure changes in a blast event. A shock tube experiment performed in US Army Natick Soldier Research, Development and Engineering Center has demonstrated that the resonant frequency of the sensor is 4.12 MHz, which is relatively close to the designed theoretical value of 4.113 MHz. Moreover, the experiment illustrated that the sensor has a rise time of 120 ns, which demonstrates that the sensor is capable of observing the dynamics of the pressure transient during a blast event. (paper)
-
Dynamics and stability of relativistic gamma-ray-bursts blast waves
Meliani, Z.; Keppens, R.
2010-09-01
Aims: In gamma-ray-bursts (GRBs), ultra-relativistic blast waves are ejected into the circumburst medium. We analyse in unprecedented detail the deceleration of a self-similar Blandford-McKee blast wave from a Lorentz factor 25 to the nonrelativistic Sedov phase. Our goal is to determine the stability properties of its frontal shock. Methods: We carried out a grid-adaptive relativistic 2D hydro-simulation at extreme resolving power, following the GRB jet during the entire afterglow phase. We investigate the effect of the finite initial jet opening angle on the deceleration of the blast wave, and identify the growth of various instabilities throughout the coasting shock front. Results: We find that during the relativistic phase, the blast wave is subject to pressure-ram pressure instabilities that ripple and fragment the frontal shock. These instabilities manifest themselves in the ultra-relativistic phase alone, remain in full agreement with causality arguments, and decay slowly to finally disappear in the near-Newtonian phase as the shell Lorentz factor drops below 3. From then on, the compression rate decreases to levels predicted to be stable by a linear analysis of the Sedov phase. Our simulations confirm previous findings that the shell also spreads laterally because a rarefaction wave slowly propagates to the jet axis, inducing a clear shell deformation from its initial spherical shape. The blast front becomes meridionally stratified, with decreasing speed from axis to jet edge. In the wings of the jetted flow, Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities occur, which are of negligible importance from the energetic viewpoint. Conclusions: Relativistic blast waves are subject to hydrodynamical instabilities that can significantly affect their deceleration properties. Future work will quantify their effect on the afterglow light curves.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Ford, Corey C. (University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM); Taylor, Paul Allen
2008-02-01
The objective of this modeling and simulation study was to establish the role of stress wave interactions in the genesis of traumatic brain injury (TBI) from exposure to explosive blast. A high resolution (1 mm{sup 3} voxels), 5 material model of the human head was created by segmentation of color cryosections from the Visible Human Female dataset. Tissue material properties were assigned from literature values. The model was inserted into the shock physics wave code, CTH, and subjected to a simulated blast wave of 1.3 MPa (13 bars) peak pressure from anterior, posterior and lateral directions. Three dimensional plots of maximum pressure, volumetric tension, and deviatoric (shear) stress demonstrated significant differences related to the incident blast geometry. In particular, the calculations revealed focal brain regions of elevated pressure and deviatoric (shear) stress within the first 2 milliseconds of blast exposure. Calculated maximum levels of 15 KPa deviatoric, 3.3 MPa pressure, and 0.8 MPa volumetric tension were observed before the onset of significant head accelerations. Over a 2 msec time course, the head model moved only 1 mm in response to the blast loading. Doubling the blast strength changed the resulting intracranial stress magnitudes but not their distribution. We conclude that stress localization, due to early time wave interactions, may contribute to the development of multifocal axonal injury underlying TBI. We propose that a contribution to traumatic brain injury from blast exposure, and most likely blunt impact, can occur on a time scale shorter than previous model predictions and before the onset of linear or rotational accelerations traditionally associated with the development of TBI.
-
Investigation of shock waves in explosive blasts using fibre optic pressure sensors
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Watson, S [School of Engineering and Physical Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh EH14 4AS (United Kingdom); MacPherson, W N [School of Engineering and Physical Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh EH14 4AS (United Kingdom); Barton, J S [School of Engineering and Physical Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh EH14 4AS (United Kingdom); Jones, J D C [School of Engineering and Physical Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh EH14 4AS (United Kingdom); Tyas, A [Department of Civil and Structural Engineering, University of Sheffield, Sheffield S1 3JD (United Kingdom); Pichugin, A V [Department of Civil and Structural Engineering, University of Sheffield, Sheffield S1 3JD (United Kingdom); Hindle, A [Department of Civil and Structural Engineering, University of Sheffield, Sheffield S1 3JD (United Kingdom); Parkes, W [Scottish Microelectronics Centre, Kings Buildings, West Mains Road, Edinburgh EH9 3JF (United Kingdom); Dunare, C [Scottish Microelectronics Centre, Kings Buildings, West Mains Road, Edinburgh EH9 3JF (United Kingdom); Stevenson, T [Scottish Microelectronics Centre, Kings Buildings, West Mains Road, Edinburgh EH9 3JF (United Kingdom)
2005-01-01
We describe miniature all-optical pressure sensors, fabricated by wafer etching techniques, less than 1mm{sup 2} in overall cross-section with rise times in the {mu}s regime and pressure ranges typically 600 kPa. Their performance is suitable for experimental studies of the pressure-time history for test models exposed to shocks initiated by an explosive charge. The small size and fast response of the sensors promises higher quality data than has been previously available from conventional electrical sensors, with potential improvements to numerical models of blast effects. Provisional results from blast tests will be presented in which up to 6 sensors were multiplexed, embedded within test models in a range of orientations relative to the shock front.
-
Investigation of shock waves in explosive blasts using fibre optic pressure sensors
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Watson, S; MacPherson, W N; Barton, J S; Jones, J D C; Tyas, A; Pichugin, A V; Hindle, A; Parkes, W; Dunare, C; Stevenson, T
2005-01-01
We describe miniature all-optical pressure sensors, fabricated by wafer etching techniques, less than 1mm 2 in overall cross-section with rise times in the μs regime and pressure ranges typically 600 kPa. Their performance is suitable for experimental studies of the pressure-time history for test models exposed to shocks initiated by an explosive charge. The small size and fast response of the sensors promises higher quality data than has been previously available from conventional electrical sensors, with potential improvements to numerical models of blast effects. Provisional results from blast tests will be presented in which up to 6 sensors were multiplexed, embedded within test models in a range of orientations relative to the shock front
-
Blast-Wave Generation and Propagation in Rapidly Heated Laser-Irradiated Targets
Ivancic, S. T.; Stillman, C. R.; Nilson, P. M.; Solodov, A. A.; Froula, D. H.
2017-10-01
Time-resolved extreme ultraviolet (XUV) spectroscopy was used to study the creation and propagation of a >100-Mbar blast wave in a target irradiated by an intense (>1018WWcm2 cm2) laser pulse. Blast waves provide a platform to generate immense pressures in the laboratory. A temporal double flash of XUV radiation was observed when viewing the rear side of the target, which is attributed to the emergence of a blast wave following rapid heating by a fast-electron beam generated from the laser pulse. The time-history of XUV emission in the photon energy range of 50 to 200 eV was recorded with an x-ray streak camera with 7-ps temporal resolution. The heating and expansion of the target was simulated with an electron transport code coupled to 1-D radiation-hydrodynamics simulations. The temporal delay between the two flashes measured in a systematic study of target thickness and composition was found to evolve in good agreement with a Sedov-Taylor blast-wave solution. This material is based upon work supported by the Department of Energy National Nuclear Security Administration under Award Number DE-NA0001944 and Department of Energy Office of Science Award Number DE-SC-0012317.
-
Courtney, Elya; Courtney, Amy; Summer, Peter David; Courtney, Michael
2014-01-01
Results are presented for lead free primers based on diazodinitrophenol (DDNP)compared with tests on lead styphnate based primers. First, barrel friction measurements in 5.56 mm NATO are presented. Second, shot to shot variations in blast waves are presented as determined by detonating primers in a 7.62x51mm rifle chamber with a firing pin, but without any powder or bullet loaded and measuring the blast wave at the muzzle with a high speed pressure transducer. Third, variations in primer blas...
-
A Blast Wave Model With Viscous Corrections
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yang, Z; Fries, R J
2017-01-01
Hadronic observables in the final stage of heavy ion collision can be described well by fluid dynamics or blast wave parameterizations. We improve existing blast wave models by adding shear viscous corrections to the particle distributions in the Navier-Stokes approximation. The specific shear viscosity η/s of a hadron gas at the freeze-out temperature is a new parameter in this model. We extract the blast wave parameters with viscous corrections from experimental data which leads to constraints on the specific shear viscosity at kinetic freeze-out. Preliminary results show η/s is rather small. (paper)
-
A Blast Wave Model With Viscous Corrections
Yang, Z.; Fries, R. J.
2017-04-01
Hadronic observables in the final stage of heavy ion collision can be described well by fluid dynamics or blast wave parameterizations. We improve existing blast wave models by adding shear viscous corrections to the particle distributions in the Navier-Stokes approximation. The specific shear viscosity η/s of a hadron gas at the freeze-out temperature is a new parameter in this model. We extract the blast wave parameters with viscous corrections from experimental data which leads to constraints on the specific shear viscosity at kinetic freeze-out. Preliminary results show η/s is rather small.
-
Blast wave interaction with a rigid surface
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Josey, T.; Whitehouse, D.R.; Ripley, R.C.; Dionne, J.P.
2004-01-01
A simple model used to investigate blast wave interactions with a rigid surface is presented. The model uses a constant volume energy source analogue to predict pressure histories at gauges located directly above the charge. A series of two-dimensional axi-symmetric CFD calculations were performed, varying the height of the charge relative to the ground. Pressure histories, along with isopycnic plots are presented to evaluate the effects of placing a charge in close proximity to a rigid surface. When a charge is placed near a solid surface the pressure histories experienced at gauges above the charge indicate the presence of two distinct pressure peaks. The first peak is caused by the primary shock and the second peak is a result of the wave reflections from the rigid surface. As the distance from the charge to the wall is increased the magnitude of the second pressure peak is reduced, provided that the distance between the charge and the gauge is maintained constant. The simple model presented is able to capture significant, predictable flow features. (author)
-
Effects of blast wave to main steam piping under high energy line break condition by TNT model
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kim, Seung Hyun; Lee, Eung Seok; Chang, Yoon Suk [Kyung Hee University, Yongin (Korea, Republic of)
2016-05-15
The aim of this study is to examine effect of the blast wave according to pipe break position through FE (Finite Element) analyses. If HELB (High Energy Line Break) accident occurs in nuclear power plants, not only environmental effect such as release of radioactive material but also secondary structural defects should be considered. Sudden pipe rupture causes ejection of high temperature and pressure fluid, which acts as a blast wave around the break location. The blast wave caused by the HELB has a possibility to induce structural defects around the components such as safe-related injection pipes and other structures.
-
Computational Study of Thrust Generation from Laser-Driven Blast Wave
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ohnishi, Naofumi; Ogino, Yousuke
2008-01-01
We have performed axisymmetric simulations in order to investigate the thrust generation resulting from the interference between the projectile and the blast wave produced by a pulsed laser. The results obtained by our numerical code well agree for the pressure history and the momentum coupling coefficient with the experimental data. In such analysis, it is found that the approximate impulse estimated only by the pressure history at the projectile base is difficult to predict the actual one. Since the shock wave rapidly attenuates in low fill pressure, and the interaction with the projectile almost finishes in the shroud, a high momentum coupling coefficient can be achieved unlike the case of high fill pressure in which the projectile experiences the subsequent negative thrust
-
Pontalier, Q.; Loiseau, J.; Goroshin, S.; Frost, D. L.
2018-04-01
The attenuation of a blast wave from a high-explosive charge surrounded by a layer of inert material is investigated experimentally in a spherical geometry for a wide range of materials. The blast wave pressure is inferred from extracting the blast wave velocity with high-speed video as well as direct measurements with pressure transducers. The mitigant consists of either a packed bed of particles, a particle bed saturated with water, or a homogeneous liquid. The reduction in peak blast wave overpressure is primarily dependent on the mitigant to explosive mass ratio, M/C, with the mitigant material properties playing a secondary role. Relative peak pressure mitigation reduces with distance and for low values of M/C (pressure levels in the mid-to-far field. Solid particles are more effective at mitigating the blast overpressure than liquids, particularly in the near field and at low values of M/C, suggesting that the energy dissipation during compaction, deformation, and fracture of the powders plays an important role. The difference in scaled arrival time of the blast and material fronts increases with M/C and scaled distance, with solid particles giving the largest separation between the blast wave and cloud of particles. Surrounding a high-explosive charge with a layer of particles reduces the positive-phase blast impulse, whereas a liquid layer has no influence on the impulse in the far field. Taking the total impulse due to the blast wave and material impact into account implies that the damage to a nearby structure may actually be augmented for a range of distances. These results should be taken into consideration in the design of explosive mitigant systems.
-
PRESSURE-IMPULSE DIAGRAM OF MULTI-LAYERED ALUMINUM FOAM PANELS UNDER BLAST PRESSURE
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
CHANG-SU SHIM
2013-06-01
Full Text Available Anti-terror engineering has increasing demand in construction industry, but basis of design (BOD is normally not clear for designers. Hardening of structures has limitations when design loads are not defined. Sacrificial foam claddings are one of the most efficient methods to protect blast pressure. Aluminum foam can have designed yield strength according to relative density and mitigate the blast pressure below a target transmitted pressure. In this paper, multi-layered aluminum foam panels were proposed to enhance the pressure mitigation by increasing effective range of blast pressure. Through explicit finite element analyses, the performance of blast pressure mitigation by the multi-layered foams was evaluated. Pressure-impulse diagrams for the foam panels were developed from extensive analyses. Combination of low and high strength foams showed better applicability in wider range of blast pressure.
-
Pontalier, Q.; Loiseau, J.; Goroshin, S.; Frost, D. L.
2018-05-01
The attenuation of a blast wave from a high-explosive charge surrounded by a layer of inert material is investigated experimentally in a spherical geometry for a wide range of materials. The blast wave pressure is inferred from extracting the blast wave velocity with high-speed video as well as direct measurements with pressure transducers. The mitigant consists of either a packed bed of particles, a particle bed saturated with water, or a homogeneous liquid. The reduction in peak blast wave overpressure is primarily dependent on the mitigant to explosive mass ratio, M/ C, with the mitigant material properties playing a secondary role. Relative peak pressure mitigation reduces with distance and for low values of M/ C (compaction, deformation, and fracture of the powders plays an important role. The difference in scaled arrival time of the blast and material fronts increases with M/ C and scaled distance, with solid particles giving the largest separation between the blast wave and cloud of particles. Surrounding a high-explosive charge with a layer of particles reduces the positive-phase blast impulse, whereas a liquid layer has no influence on the impulse in the far field. Taking the total impulse due to the blast wave and material impact into account implies that the damage to a nearby structure may actually be augmented for a range of distances. These results should be taken into consideration in the design of explosive mitigant systems.
-
Numerical Study on Blast Wave Propagation Driven by Unsteady Ionization Plasma
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ogino, Yousuke; Sawada, Keisuke; Ohnishi, Naofumi
2008-01-01
Understanding the dynamics of laser-produced plasma is essential for increasing the available thrust and energy conversion efficiency from a pulsed laser to a blast wave in a gas-driven laser-propulsion system. The performance of a gas-driven laser-propulsion system depends heavily on the laser-driven blast wave dynamics as well as on the ionizing and/or recombining plasma state that sustains the blast wave. In this study, we therefore develop a numerical simulation code for a laser-driven blast wave coupled with time-dependent rate equations to explore the formation of unsteady ionizing plasma produced by laser irradiation. We will also examine the various properties of blast waves and unsteady ionizing plasma for different laser input energies
-
The tank's dynamic response under nuclear explosion blast wave
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Xu Mei; Wang Lianghou; Li Xiaotian; Yu Suyuan; Zhang Zhengming; Wan Li
2005-01-01
To weapons and equipment, blast wave is the primary destructive factor. In this paper, taken the real model-59 tank as an example, we try to transform the damage estimation problem into computing a fluid structure interaction problem with finite element method. The response of tank under nuclear explosion blast wave is computed with the general-coupling algorithm. Also, the dynamical interaction of blast wave and tank is reflected in real time. The deformation of each part of the tank is worked out and the result corresponds to the real-measured data. (authors)
-
The Air Blast Wave from a Nuclear Explosion
Reines, Frederick
The sudden, large scale release of energy in the explosion of a nuclear bomb in air gives rise, in addition to nuclear emanations such as neutrons and gamma rays, to an extremely hot, rapidly expanding mass of air.** The rapidly expanding air mass has an initial temperature in the vicinity of a few hundred thousand degrees and for this reason it glows in its early stages with an intensity of many suns. It is important that the energy density in this initial "ball of fire" is of the order of 3 × 103 times that found in a detonating piece of TNT and hence that the initial stages of the large scale air motion produced by a nuclear explosion has no counterpart in an ordinary. H. E. explosion. Further, the relatively low temperatures ˜2,000°C associated with the initial stages of an H. E. detonation implies that the thermal radiation which it emits is a relatively insignificant fraction of the total energy involves. This point is made more striking when it is remembered that the thermal energy emitted by a hot object varies directly with the temperature in the Rayleigh Jeans region appropriate to the present discussion. The expansion of the air mass heated by the nuclear reaction produces, in qualitatively the same manner as in an H.E. explosion or the bursting of a high pressure balloon, an intense sharp pressure pulse, a shock wave, in the atmosphere. As the pressure pulse spreads outward it weakens due to the combined effects of divergence and the thermodynamically irreversible nature of the shock wave. The air comprising such a pressure pulse or blast wave moves first radially outward and then back towards the center as the blast wave passes. Since a permanent outward displacement of an infinite mass of air would require unlimited energy, the net outward displacement of the air distant from an explosion must approach zero with increasing distance. As the distance from the explosion is diminished the net outward displacement due to irreversible shock heating of
-
Effect of surface conditions on blast wave propagation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Song, Seung Ho; Li, Yi Bao; Lee, Chang Hoon; Choi, Jung Il
2016-01-01
We performed numerical simulations of blast wave propagations on surfaces by solving axisymmetric two-dimensional Euler equations. Assuming the initial stage of fireball at the breakaway point after an explosion, we investigated the effect of surface conditions considering surface convex or concave elements and thermal conditions on blast wave propagations near the ground surface. Parametric studies were performed by varying the geometrical factors of the surface element as well as thermal layer characteristics. We found that the peak overpressure near the ground zero was increased due to the surface elements, while modulations of the blast wave propagations were limited within a region for the surface elements. Because of the thermal layer, the precursor was formed in the propagations, which led to the attenuation of the peak overpressure on the ground surface
-
Experimental Study and Engineering Practice of Pressured Water Coupling Blasting
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
J. X. Yang
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Overburden strata movement in large space stope is the major reason that induces the appearance of strong mining pressure. Presplitting blasting for hard coal rocks is crucial for the prevention and control of strong pressure in stope. In this study, pressured water coupling blasting technique was proposed. The process and effect of blasting were analyzed by orthogonal test and field practice. Results showed that the presence of pressure-bearing water and explosive cartridges in the drill are the main influence factors of the blasting effect of cement test block. The high load-transmitting performance of pore water and energy accumulation in explosive cartridges were analyzed. Noxious substances produced during the blasting process were properly controlled because of the moistening, cooling, and diluting effect of pore water. Not only the goal of safe and static rock fragmentation by high-explosive detonation but also a combination of superdynamic blast loading and static loading effect of the pressured water was achieved. Then the practice of blasting control of hard coal rocks in Datong coal mine was analyzed to determine reasonable parameters of pressured water coupling blasting. A good presplitting blasting control effect was achieved for the hard coal rocks.
-
Time development of a blast wave with shock heated electrons
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Edgar, R.J.; Cox, D.P.
1983-01-01
Accurate approximations are presented for the time development of both edge conditions and internal structures of a blast wave with shock heated electrons, and equal ion and electron temperatures at the shock. The cases considered evolve in cavities with power law ambient densities (including the uniform ambient density case) and have negligible external pressure. Account is taken of possible saturation of the thermal conduction flux. The structures evolve smoothly to the adiabatic structures
-
Modelling human eye under blast loading.
Esposito, L; Clemente, C; Bonora, N; Rossi, T
2015-01-01
Primary blast injury (PBI) is the general term that refers to injuries resulting from the mere interaction of a blast wave with the body. Although few instances of primary ocular blast injury, without a concomitant secondary blast injury from debris, are documented, some experimental studies demonstrate its occurrence. In order to investigate PBI to the eye, a finite element model of the human eye using simple constitutive models was developed. The material parameters were calibrated by a multi-objective optimisation performed on available eye impact test data. The behaviour of the human eye and the dynamics of mechanisms occurring under PBI loading conditions were modelled. For the generation of the blast waves, different combinations of explosive (trinitrotoluene) mass charge and distance from the eye were analysed. An interpretation of the resulting pressure, based on the propagation and reflection of the waves inside the eye bulb and orbit, is proposed. The peculiar geometry of the bony orbit (similar to a frustum cone) can induce a resonance cavity effect and generate a pressure standing wave potentially hurtful for eye tissues.
-
Effectiveness of eye armor during blast loading.
Bailoor, Shantanu; Bhardwaj, Rajneesh; Nguyen, Thao D
2015-11-01
Ocular trauma is one of the most common types of combat injuries resulting from the interaction of military personnel with improvised explosive devices. Ocular blast injury mechanisms are complex, and trauma may occur through various injury mechanisms. However, primary blast injuries (PBI) are an important cause of ocular trauma that may go unnoticed and result in significant damage to internal ocular tissues and visual impairment. Further, the effectiveness of commonly employed eye armor, designed for ballistic and laser protection, in lessening the severity of adverse blast overpressures (BOP) is unknown. In this paper, we employed a three-dimensional (3D) fluid-structure interaction computational model for assessing effectiveness of the eye armor during blast loading on human eyes and validated results against free field blast measurements by Bentz and Grimm (2013). Numerical simulations show that the blast waves focused on the ocular region because of reflections from surrounding facial features and resulted in considerable increase in BOP. We evaluated the effectiveness of spectacles and goggles in mitigating the pressure loading using the computational model. Our results corroborate experimental measurements showing that the goggles were more effective than spectacles in mitigating BOP loading on the eye. Numerical results confirmed that the goggles significantly reduced blast wave penetration in the space between the armor and the eyes and provided larger clearance space for blast wave expansion after penetration than the spectacles. The spectacles as well as the goggles were more effective in reducing reflected BOP at higher charge mass because of the larger decrease in dynamic pressures after the impact. The goggles provided greater benefit of reducing the peak pressure than the spectacles for lower charge mass. However, the goggles resulted in moderate, sustained elevated pressure loading on the eye, that became 50-100% larger than the pressure loading
-
Ultrafast Fabry-Perot fiber-optic pressure sensors for multimedia blast event measurements.
Zou, Xiaotian; Wu, Nan; Tian, Ye; Zhang, Yang; Fitek, John; Maffeo, Michael; Niezrecki, Christopher; Chen, Julie; Wang, Xingwei
2013-02-20
A shock wave (SW) is characterized as a large pressure fluctuation that typically lasts only a few milliseconds. On the battlefield, SWs pose a serious threat to soldiers who are exposed to explosions, which may lead to blast-induced traumatic brain injuries. SWs can also be used beneficially and have been applied to a variety of medical treatments due to their unique interaction with tissues and cells. Consequently, it is important to have sensors that can quantify SW dynamics in order to better understand the physical interaction between body tissue and the incident acoustic wave. In this paper, the ultrafast fiber-optic sensor based on the Fabry-Perot interferometric principle was designed and four such sensors were fabricated to quantify a blast event within different media, simultaneously. The compact design of the fiber-optic sensor allows for a high degree of spatial resolution when capturing the wavefront of the traveling SW. Several blast event experiments were conducted within different media (e.g., air, rubber membrane, and water) to evaluate the sensor's performance. This research revealed valuable knowledge for further study of SW behavior and SW-related applications.
-
Study of Perturbations on High Mach Number Blast Waves in Various Gasses
Edens, A.; Adams, R.; Rambo, P.; Shores, J.; Smith, I.; Atherton, B.; Ditmire, T.
2006-10-01
We have performed a series of experiments examining the properties of high Mach number blast waves. Experiments were conducted on the Z-Beamlet^1 laser at Sandia National Laboratories. We created blast waves in the laboratory by using 10 J- 1000 J laser pulses to illuminate millimeter scale solid targets immersed in gas. Our experiments studied the validity of theories forwarded by Vishniac and Ryu^2-4 to explain the dynamics of perturbations on astrophysical blast waves. These experiments consisted of an examination of the evolution of perturbations of known primary mode number induced on the surface of blast waves by means of regularly spaced wire arrays. The temporal evolution of the amplitude of the induced perturbations relative to the mean radius of the blast wave was fit to a power law in time. Measurements were taken for a number of different mode numbers and background gasses and the results show qualitative agreement with previously published theories for the hydrodynamics of thin shell blast wave. The results for perturbations on nitrogen gas have been recently published^5. .^1 P. K. Rambo, I. C. Smith, J. L. Porter, et al., Applied Optics 44, 2421 (2005). ^2 D. Ryu and E. T. Vishniac, Astrophysical Journal 313, 820 (1987). ^3 D. Ryu and E. T. Vishniac, Astrophysical Journal 368, 411 (1991). ^4 E. T. Vishniac, Astrophysical Journal 274, 152 (1983). ^5 A. D. Edens, T. Ditmire, J. F. Hansen, et al., Physical Review Letters 95 (2005).
-
Blast Shock Wave Mitigation Using the Hydraulic Energy Redirection and Release Technology
Chen, Yun; Huang, Wei; Constantini, Shlomi
2012-01-01
A hydraulic energy redirection and release technology has been developed for mitigating the effects of blast shock waves on protected objects. The technology employs a liquid-filled plastic tubing as a blast overpressure transformer to transfer kinetic energy of blast shock waves into hydraulic energy in the plastic tubings. The hydraulic energy is redirected through the plastic tubings to the openings at the lower ends, and then is quickly released with the liquid flowing out through the openings. The samples of the specifically designed body armor in which the liquid-filled plastic tubings were installed vertically as the outer layer of the body armor were tested. The blast test results demonstrated that blast overpressure behind the body armor samples was remarkably reduced by 97% in 0.2 msec after the liquid flowed out of its appropriate volume through the openings. The results also suggested that a volumetric liquid surge might be created when kinetic energy of blast shock wave was transferred into hydraulic energy to cause a rapid physical movement or displacement of the liquid. The volumetric liquid surge has a strong destructive power, and can cause a noncontact, remote injury in humans (such as blast-induced traumatic brain injury and post-traumatic stress disorder) if it is created in cardiovascular system. The hydraulic energy redirection and release technology can successfully mitigate blast shock waves from the outer surface of the body armor. It should be further explored as an innovative approach to effectively protect against blast threats to civilian and military personnel. PMID:22745740
-
Investigations of primary blast-induced traumatic brain injury
Sawyer, T. W.; Josey, T.; Wang, Y.; Villanueva, M.; Ritzel, D. V.; Nelson, P.; Lee, J. J.
2018-01-01
The development of an advanced blast simulator (ABS) has enabled the reproducible generation of single-pulse shock waves that simulate free-field blast with high fidelity. Studies with rodents in the ABS demonstrated the necessity of head restraint during head-only exposures. When the head was not restrained, violent global head motion was induced by pressures that would not produce similar movement of a target the size and mass of a human head. This scaling artefact produced changes in brain function that were reminiscent of traumatic brain injury (TBI) due to impact-acceleration effects. Restraint of the rodent head eliminated these, but still produced subtle changes in brain biochemistry, showing that blast-induced pressure waves do cause brain deficits. Further experiments were carried out with rat brain cell aggregate cultures that enabled the conduct of studies without the gross movement encountered when using rodents. The suspension nature of this model was also exploited to minimize the boundary effects that complicate the interpretation of primary blast studies using surface cultures. Using this system, brain tissue was found not only to be sensitive to pressure changes, but also able to discriminate between the highly defined single-pulse shock waves produced by underwater blast and the complex pressure history exposures experienced by aggregates encased within a sphere and subjected to simulated air blast. The nature of blast-induced primary TBI requires a multidisciplinary research approach that addresses the fidelity of the blast insult, its accurate measurement and characterization, as well as the limitations of the biological models used.
-
Spalling of concrete walls under blast load
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kot, C.A.
1977-01-01
A common effect of the detonation of explosives in close proximity of concrete shield walls is the spalling (scabbing) of the back face of the wall. Spalling is caused by the free surface reflection of the shock wave induced in the wall by high pressure air blast and occurs whenever the dynamic tensile rupture strength is exceeded. While a complex process, reasonable analytical spall estimates can be obtained for brittle materials with low tensile strengths, such as concrete, by assuming elastic material behavior and instantaneous spall formation. Specifically, the spall thicknesses and velocities for both normal and oblique incidence of the shock wave on the back face of the wall are calculated. The complex exponential decay wave forms of the air blast are locally approximated by simple power law expressions. Variations of blast wave strength with distance to the wall, charge weight and angle of incidence are taken into consideration. The shock wave decay in the wall is also accounted for by assuming elastic wave propagation. For explosions close-in to the wall, where the reflected blast wave pressures are sufficiently high, multiple spall layers are formed. Successive spall layers are of increasing thickness, at the same time the spall velocities decrease. The spall predictions based on elastic theory are in overall agreement with experimntal results and provide a rapid means of estimating spalling trends of concrete walls subjected to air blast. (Auth.)
-
Prediction of Near-Field Wave Attenuation Due to a Spherical Blast Source
Ahn, Jae-Kwang; Park, Duhee
2017-11-01
Empirical and theoretical far-field attenuation relationships, which do not capture the near-field response, are most often used to predict the peak amplitude of blast wave. Jiang et al. (Vibration due to a buried explosive source. PhD Thesis, Curtin University, Western Australian School of Mines, 1993) present rigorous wave equations that simulates the near-field attenuation to a spherical blast source in damped and undamped media. However, the effect of loading frequency and velocity of the media have not yet been investigated. We perform a suite of axisymmetric, dynamic finite difference analyses to simulate the propagation of stress waves induced by spherical blast source and to quantify the near-field attenuation. A broad range of loading frequencies, wave velocities, and damping ratios are used in the simulations. The near-field effect is revealed to be proportional to the rise time of the impulse load and wave velocity. We propose an empirical additive function to the theoretical far-field attenuation curve to predict the near-field range and attenuation. The proposed curve is validated against measurements recorded in a test blast.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Maciej Skotak
2018-02-01
Full Text Available Measurement issues leading to the acquisition of artifact-free shock wave pressure-time profiles are discussed. We address the importance of in-house sensor calibration and data acquisition sampling rate. Sensor calibration takes into account possible differences between calibration methodology in a manufacturing facility, and those used in the specific laboratory. We found in-house calibration factors of brand new sensors differ by less than 10% from their manufacturer supplied data. Larger differences were noticeable for sensors that have been used for hundreds of experiments and were as high as 30% for sensors close to the end of their useful lifetime. These observations were despite the fact that typical overpressures in our experiments do not exceed 50 psi for sensors that are rated at 1,000 psi maximum pressure. We demonstrate that sampling rate of 1,000 kHz is necessary to capture the correct rise time values, but there were no statistically significant differences between peak overpressure and impulse values for low-intensity shock waves (Mach number <2 at lower rates. We discuss two sources of experimental errors originating from mechanical vibration and electromagnetic interference on the quality of a waveform recorded using state-of-the-art high-frequency pressure sensors. The implementation of preventive measures, pressure acquisition artifacts, and data interpretation with examples, are provided in this paper that will help the community at large to avoid these mistakes. In order to facilitate inter-laboratory data comparison, common reporting standards should be developed by the blast TBI research community. We noticed the majority of published literature on the subject limits reporting to peak overpressure; with much less attention directed toward other important parameters, i.e., duration, impulse, and dynamic pressure. These parameters should be included as a mandatory requirement in publications so the results can be properly
-
Study of blast wave overpressures using the computational fluid dynamics
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
M. L. COSTA NETO
Full Text Available ABSTRACT The threats of bomb attacks by criminal organizations and accidental events involving chemical explosives are a danger to the people and buildings. Due the severity of these issues and the need of data required for a safety design, more research is required about explosions and shock waves. This paper presents an assessment of blast wave overpressures using a computational fluid dynamics software. Analyses of phenomena as reflection of shock waves and channeling effects were done and a comparison between numerical results and analytical predictions has been executed, based on the simulation on several models. The results suggest that the common analytical predictions aren’t accurate enough for an overpressure analysis in small stand-off distances and that poorly designed buildings may increase the shock wave overpressures due multiple blast wave reflections, increasing the destructive potential of the explosions.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Xin Liu
2018-01-01
Full Text Available During the first-stage project of the main channel of Ningbo-Zhoushan Port’s Shipu Harbor, underwater shock waves were monitored. By analyzing a typical measured pressure time history curve, the characteristics of underwater shock waves in an engineering context were obtained. We obtained a traditional exponential attenuation formula for underwater shock waves based on the measured data, simplified the model of underwater drilling blasting based on engineering practice, deduced a revised formula for underwater shock wave peak overpressure on the basis of dimensional analysis, established a linear fitting model, and obtained the undetermined coefficients of the revised formula using a linear regression analysis. In addition, the accuracies of the two formulas used to predict underwater shock wave peak overpressure and the significance order of influence and influence mechanism of factors included in the revised formula on the underwater shock wave peak overpressure were discussed.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Moss, W C; King, M J; Blackman, E G
2011-01-21
In their Contributed Article, Nyein et al. (1,2) present numerical simulations of blast waves interacting with a helmeted head and conclude that a face shield may significantly mitigate blast induced traumatic brain injury (TBI). A face shield may indeed be important for future military helmets, but the authors derive their conclusions from a much smaller explosion than typically experienced on the battlefield. The blast from the 3.16 gm TNT charge of (1) has the following approximate peak overpressures, positive phase durations, and incident impulses (3): 10 atm, 0.25 ms, and 3.9 psi-ms at the front of the head (14 cm from charge), and 1.4 atm, 0.32 ms, and 1.7 psi-ms at the back of a typical 20 cm head (34 cm from charge). The peak pressure of the wave decreases by a factor of 7 as it traverses the head. The blast conditions are at the threshold for injury at the front of the head, but well below threshold at the back of the head (4). The blast traverses the head in 0.3 ms, roughly equal to the positive phase duration of the blast. Therefore, when the blast reaches the back of the head, near ambient conditions exist at the front. Because the headform is so close to the charge, it experiences a wave with significant curvature. By contrast, a realistic blast from a 2.2 kg TNT charge ({approx} an uncased 105 mm artillery round) is fatal at an overpressure of 10 atm (4). For an injury level (4) similar to (1), a 2.2 kg charge has the following approximate peak overpressures, positive phase durations, and incident impulses (3): 2.1 atm, 2.3 ms, and 18 psi-ms at the front of the head (250 cm from charge), and 1.8 atm, 2.5 ms, and 16.8 psi-ms at the back of the head (270 cm from charge). The peak pressure decreases by only a factor of 1.2 as it traverses the head. Because the 0.36 ms traversal time is much smaller than the positive phase duration, pressures on the head become relatively uniform when the blast reaches the back of the head. The larger standoff implies
-
Codina, R.; Ambrosini, D.
2018-03-01
For the last few decades, the effects of blast loading on structures have been studied by many researchers around the world. Explosions can be caused by events such as industrial accidents, military conflicts or terrorist attacks. Urban centers have been prone to various threats including car bombs, suicide attacks, and improvised explosive devices. Partially vented constructions subjected to external blast loading represent an important topic in protective engineering. The assessment of blast survivability inside structures and the development of design provisions with respect to internal elements require the study of the propagation and leakage of blast waves inside buildings. In this paper, full-scale tests are performed to study the effects of the leakage of blast waves inside a partially vented room that is subjected to different external blast loadings. The results obtained may be useful for proving the validity of different methods of calculation, both empirical and numerical. Moreover, the experimental results are compared with those computed using the empirical curves of the US Defense report/manual UFC 3-340. Finally, results of the dynamic response of the front masonry wall are presented in terms of accelerations and an iso-damage diagram.
-
Viscoelastic Materials Study for the Mitigation of Blast-Related Brain Injury
Bartyczak, Susan; Mock, Willis, Jr.
2011-06-01
Recent preliminary research into the causes of blast-related brain injury indicates that exposure to blast pressures, such as from IED detonation or multiple firings of a weapon, causes damage to brain tissue resulting in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Current combat helmets are not sufficient to protect the warfighter from this danger and the effects are debilitating, costly, and long-lasting. Commercially available viscoelastic materials, designed to dampen vibration caused by shock waves, might be useful as helmet liners to dampen blast waves. The objective of this research is to develop an experimental technique to test these commercially available materials when subject to blast waves and evaluate their blast mitigating behavior. A 40-mm-bore gas gun is being used as a shock tube to generate blast waves (ranging from 1 to 500 psi) in a test fixture at the gun muzzle. A fast opening valve is used to release nitrogen gas from the breech to impact instrumented targets. The targets consist of aluminum/ viscoelastic polymer/ aluminum materials. Blast attenuation is determined through the measurement of pressure and accelerometer data in front of and behind the target. The experimental technique, calibration and checkout procedures, and results will be presented.
-
CHALLENGING SOME CONTEMPORARY VIEWS OF CORONAL MASS EJECTIONS. I. THE CASE FOR BLAST WAVES
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Howard, T. A.; Pizzo, V. J.
2016-01-01
Since the closure of the “solar flare myth” debate in the mid-1990s, a specific narrative of the nature of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) has been widely accepted by the solar physics community. This narrative describes structured magnetic flux ropes at the CME core that drive the surrounding field plasma away from the Sun. This narrative replaced the “traditional” view that CMEs were blast waves driven by solar flares. While the flux rope CME narrative is supported by a vast quantity of measurements made over five decades, it does not adequately describe every observation of what have been termed CME-related phenomena. In this paper we present evidence that some large-scale coronal eruptions, particularly those associated with EIT waves, exhibit characteristics that are more consistent with a blast wave originating from a localized region (such as a flare site) rather than a large-scale structure driven by an intrinsic flux rope. We present detailed examples of CMEs that are suspected blast waves and flux ropes, and show that of our small sample of 22 EIT-wave-related CMEs, 91% involve a blast wave as at least part of the eruption, and 50% are probably blast waves exclusively. We conclude with a description of possible signatures to look for in determining the difference between the two types of CMEs and with a discussion on modeling efforts to explore this possibility.
-
CHALLENGING SOME CONTEMPORARY VIEWS OF CORONAL MASS EJECTIONS. I. THE CASE FOR BLAST WAVES
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Howard, T. A. [Southwest Research Institute, 1050 Walnut Street, Suite 300, Boulder, CO 80302 (United States); Pizzo, V. J., E-mail: howard@boulder.swri.edu [NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center, Boulder, CO (United States)
2016-06-20
Since the closure of the “solar flare myth” debate in the mid-1990s, a specific narrative of the nature of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) has been widely accepted by the solar physics community. This narrative describes structured magnetic flux ropes at the CME core that drive the surrounding field plasma away from the Sun. This narrative replaced the “traditional” view that CMEs were blast waves driven by solar flares. While the flux rope CME narrative is supported by a vast quantity of measurements made over five decades, it does not adequately describe every observation of what have been termed CME-related phenomena. In this paper we present evidence that some large-scale coronal eruptions, particularly those associated with EIT waves, exhibit characteristics that are more consistent with a blast wave originating from a localized region (such as a flare site) rather than a large-scale structure driven by an intrinsic flux rope. We present detailed examples of CMEs that are suspected blast waves and flux ropes, and show that of our small sample of 22 EIT-wave-related CMEs, 91% involve a blast wave as at least part of the eruption, and 50% are probably blast waves exclusively. We conclude with a description of possible signatures to look for in determining the difference between the two types of CMEs and with a discussion on modeling efforts to explore this possibility.
-
Nineteen-Foot Diameter Explosively Driven Blast Simulator; TOPICAL
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
VIGIL, MANUEL G.
2001-01-01
This report describes the 19-foot diameter blast tunnel at Sandia National Laboratories. The blast tunnel configuration consists of a 6 foot diameter by 200 foot long shock tube, a 6 foot diameter to 19 foot diameter conical expansion section that is 40 feet long, and a 19 foot diameter test section that is 65 feet long. Therefore, the total blast tunnel length is 305 feet. The development of this 19-foot diameter blast tunnel is presented. The small scale research test results using 4 inch by 8 inch diameter and 2 foot by 6 foot diameter shock tube facilities are included. Analytically predicted parameters are compared to experimentally measured blast tunnel parameters in this report. The blast tunnel parameters include distance, time, static, overpressure, stagnation pressure, dynamic pressure, reflected pressure, shock Mach number, flow Mach number, shock velocity, flow velocity, impulse, flow duration, etc. Shadowgraphs of the shock wave are included for the three different size blast tunnels
-
A computational model of blast loading on the human eye.
Bhardwaj, Rajneesh; Ziegler, Kimberly; Seo, Jung Hee; Ramesh, K T; Nguyen, Thao D
2014-01-01
Ocular injuries from blast have increased in recent wars, but the injury mechanism associated with the primary blast wave is unknown. We employ a three-dimensional fluid-structure interaction computational model to understand the stresses and deformations incurred by the globe due to blast overpressure. Our numerical results demonstrate that the blast wave reflections off the facial features around the eye increase the pressure loading on and around the eye. The blast wave produces asymmetric loading on the eye, which causes globe distortion. The deformation response of the globe under blast loading was evaluated, and regions of high stresses and strains inside the globe were identified. Our numerical results show that the blast loading results in globe distortion and large deviatoric stresses in the sclera. These large deviatoric stresses may be indicator for the risk of interfacial failure between the tissues of the sclera and the orbit.
-
Simulation of detonation cell kinematics using two-dimensional reactive blast waves
Thomas, G. O.; Edwards, D. H.
1983-10-01
A method of generating a cylindrical blast wave is developed which overcomes the disadvantages inherent in the converging-diverging nozzle technique used by Edwards et al., 1981. It is demonstrated than an exploding wire placed at the apex of a two-dimensional sector provides a satisfactory source of the generation of blast waves in reactive systems. The velocity profiles of the blast waves are found to simulate those in freely propagating detonations very well, and this method does not suffer from the disadvantage of having the mass flow at the throat as in the nozzle method. The density decay parameter is determined to have a constant value of 4 in the systems investigated, and it is suggested that this may be a universal value. It is proposed that suitable wedges could be used to create artificial Mach stems in the same manner as Strehlow and Barthel (1971) without the attendant disadvantages of the nozzle method.
-
Zuckerman, Amitai; Ram, Omri; Ifergane, Gal; Matar, Michael A; Sagi, Ram; Ostfeld, Ishay; Hoffman, Jay R; Kaplan, Zeev; Sadot, Oren; Cohen, Hagit
2017-01-01
The intense focus in the clinical literature on the mental and neurocognitive sequelae of explosive blast-wave exposure, especially when comorbid with post-traumatic stress-related disorders (PTSD) is justified, and warrants the design of translationally valid animal studies to provide valid complementary basic data. We employed a controlled experimental blast-wave paradigm in which unanesthetized animals were exposed to visual, auditory, olfactory, and tactile effects of an explosive blast-wave produced by exploding a thin copper wire. By combining cognitive-behavioral paradigms and ex vivo brain MRI to assess mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) phenotype with a validated behavioral model for PTSD, complemented by morphological assessments, this study sought to examine our ability to evaluate the biobehavioral effects of low-intensity blast overpressure on rats, in a translationally valid manner. There were no significant differences between blast- and sham-exposed rats on motor coordination and strength, or sensory function. Whereas most male rats exposed to the blast-wave displayed normal behavioral and cognitive responses, 23.6% of the rats displayed a significant retardation of spatial learning acquisition, fulfilling criteria for mTBI-like responses. In addition, 5.4% of the blast-exposed animals displayed an extreme response in the behavioral tasks used to define PTSD-like criteria, whereas 10.9% of the rats developed both long-lasting and progressively worsening behavioral and cognitive "symptoms," suggesting comorbid PTSD-mTBI-like behavioral and cognitive response patterns. Neither group displayed changes on MRI. Exposure to experimental blast-wave elicited distinct behavioral and morphological responses modelling mTBI-like, PTSD-like, and comorbid mTBI-PTSD-like responses. This experimental animal model can be a useful tool for elucidating neurobiological mechanisms underlying the effects of blast-wave-induced mTBI and PTSD and comorbid mTBI-PTSD.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gwen B. Effgen
2012-02-01
Full Text Available Due to the prominent role of improvised explosive devices (IEDs in wounding patterns of U.S. war-fighters in Iraq and Afghanistan, blast injury has risen to a new level of importance and is recognized to be a major cause of injuries to the brain. However, an injury risk-function for microscopic, macroscopic, behavioral, and neurological deficits has yet to be defined. While operational blast injuries can be very complex and thus difficult to analyze, a simplified blast injury model would facilitate studies correlating biological outcomes with blast biomechanics to define tolerance criteria. Blast-induced traumatic brain injury (bTBI results from the translation of a shock wave in air, such as that produced by an IED, into a pressure wave within the skull-brain complex. Our blast injury methodology recapitulates this phenomenon in vitro, allowing for control of the injury biomechanics via a compressed-gas shock tube used in conjunction with a custom-designed, fluid-filled receiver that contains the living culture. The receiver converts the air shock wave into a fast-rising pressure transient with minimal reflections, mimicking the intracranial pressure history in blast. We have developed an organotypic hippocampal slice culture model that exhibits cell death when exposed to a 530 17.7 kPa peak overpressure with a 1.026 ± 0.017 ms duration and 190 ± 10.7 kPa-ms impulse in-air. We have also injured a simplified in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier, which exhibits disrupted integrity immediately following exposure to 581 10.0 kPa peak overpressure with a 1.067 ms ± 0.006 ms duration and 222 ± 6.9 kPa-ms impulse in-air. To better prevent and treat bTBI, both the initiating biomechanics and the ensuing pathobiology must be understood in greater detail. A well-characterized, in vitro model of bTBI, in conjunction with animal models, will be a powerful tool for developing strategies to mitigate the risks of bTBI.
-
Spike morphology in blast-wave-driven instability experiments
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kuranz, C. C.; Drake, R. P.; Grosskopf, M. J.; Fryxell, B.; Budde, A.; Hansen, J. F.; Miles, A. R.; Plewa, T.; Hearn, N.; Knauer, J.
2010-01-01
The laboratory experiments described in the present paper observe the blast-wave-driven Rayleigh-Taylor instability with three-dimensional (3D) initial conditions. About 5 kJ of energy from the Omega laser creates conditions similar to those of the He-H interface during the explosion phase of a supernova. The experimental target is a 150 μm thick plastic disk followed by a low-density foam. The plastic piece has an embedded, 3D perturbation. The basic structure of the pattern is two orthogonal sine waves where each sine wave has an amplitude of 2.5 μm and a wavelength of 71 μm. In some experiments, an additional wavelength is added to explore the interaction of modes. In experiments with 3D initial conditions the spike morphology differs from what has been observed in other Rayleigh-Taylor experiments and simulations. Under certain conditions, experimental radiographs show some mass extending from the interface to the shock front. Current simulations show neither the spike morphology nor the spike penetration observed in the experiments. The amount of mass reaching the shock front is analyzed and potential causes for the spike morphology and the spikes reaching the shock are discussed. One such hypothesis is that these phenomena may be caused by magnetic pressure, generated by an azimuthal magnetic field produced by the plasma dynamics.
-
Blast wave injury prediction models for complex scenarios
Teland, J.A.; Doormaal, J.C.A.M. van
2012-01-01
Blast waves from explosions can cause lethal injuries to humans. Development of injury criteria has been ongoing for many years, but with the main focus on free field conditions. However, with terrorist actions as a new threat, explosions in urban areas have become of much more interest. Urban areas
-
Numerical study of laser-induced blast wave coupled with unsteady ionization processes
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ogino, Y; Ohnishi, N; Sawada, K
2008-01-01
We present the results of the numerical simulation of laser-induced blast wave coupled with rate equations to clarify the unsteady property of ionization processes during pulse heating. From comparison with quasi-steady computations, the plasma region expands more widely, which is sustained by the inverse-bremsstrahlung since an ionization equilibrium does not establish at the front of the plasma region. The delayed relaxation leads to the rapid expansion of the driving plasma and enhances the energy conversion efficiency from a pulse heating laser to the blast wave
-
Gas explosion characterization, wave propagation (small scale experiments)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Larsen, G.C.
1985-08-01
A number of experiments have been performed with blast waves arising from the ignition of homogeneous and well defined mixtures of methane, oxygen and nitrogen, contained within spherical balloons with controlled initial dimensions. The pressure characteristics has been studied for blast waves with and without influence from reflected waves. The influence of obstacles in the flow field has also been treated. Both configuration with one box and two closely spaced boxes have been considered, and a wave-wave interaction phenomenon was observed in the case of closely spaced obstacles. Moreover reflection coefficients have been established and some pressure variations over the surfaces have been observed. An acoustic appriximation has been used to model the blast wave originating from an expanding sphere. It has been demonstrated, that the generated pressure pulse is very sensitive to the expansion rate. Calculated and measured data have been compared, and a reasonable agreement has been found. (author)
-
Pontalier, Q.; Lhoumeau, M.; Milne, A. M.; Longbottom, A. W.; Frost, D. L.
2018-04-01
Experiments show that when a high-explosive charge with embedded particles or a charge surrounded by a layer of liquid or granular material is detonated, the flow generated is perturbed by the motion of the particles and the blast wave profile differs from that of an ideal Friedlander form. Initially, the blast wave overpressure is reduced due to the energy dissipation resulting from compaction, fragmentation, and heating of the particle bed, and acceleration of the material. However, as the blast wave propagates, particle-flow interactions collectively serve to reduce the rate of decay of the peak blast wave overpressure. Computations carried out with a multiphase hydrocode reproduce the general trends observed experimentally and highlight the transition between the particle acceleration/deceleration phases, which is not accessible experimentally, since the particles are obscured by the detonation products. The dependence of the particle-blast interaction and the blast mitigation effectiveness on the mitigant to explosive mass ratio, the particle size, and the initial solid volume fraction is investigated systematically. The reduction in peak blast overpressure is, as in experiments, primarily dependent on the mass ratio of material to explosive, with the particle size, density, and initial porosity of the particle bed playing secondary roles. In the near field, the blast overpressure decreases sharply with distance as the particles are accelerated by the flow. When the particles decelerate due to drag, energy is returned to the flow and the peak blast overpressure recovers and reaches values similar to that of a bare explosive charge for low mass ratios. Time-distance trajectory plots of the particle and blast wave motion with the pressure field superimposed, illustrate the weak pressure waves generated by the motion of the particle layer which travel upstream and perturb the blast wave motion. Computation of the particle and gas momentum flux in the multiphase
-
Pontalier, Q.; Lhoumeau, M.; Milne, A. M.; Longbottom, A. W.; Frost, D. L.
2018-05-01
Experiments show that when a high-explosive charge with embedded particles or a charge surrounded by a layer of liquid or granular material is detonated, the flow generated is perturbed by the motion of the particles and the blast wave profile differs from that of an ideal Friedlander form. Initially, the blast wave overpressure is reduced due to the energy dissipation resulting from compaction, fragmentation, and heating of the particle bed, and acceleration of the material. However, as the blast wave propagates, particle-flow interactions collectively serve to reduce the rate of decay of the peak blast wave overpressure. Computations carried out with a multiphase hydrocode reproduce the general trends observed experimentally and highlight the transition between the particle acceleration/deceleration phases, which is not accessible experimentally, since the particles are obscured by the detonation products. The dependence of the particle-blast interaction and the blast mitigation effectiveness on the mitigant to explosive mass ratio, the particle size, and the initial solid volume fraction is investigated systematically. The reduction in peak blast overpressure is, as in experiments, primarily dependent on the mass ratio of material to explosive, with the particle size, density, and initial porosity of the particle bed playing secondary roles. In the near field, the blast overpressure decreases sharply with distance as the particles are accelerated by the flow. When the particles decelerate due to drag, energy is returned to the flow and the peak blast overpressure recovers and reaches values similar to that of a bare explosive charge for low mass ratios. Time-distance trajectory plots of the particle and blast wave motion with the pressure field superimposed, illustrate the weak pressure waves generated by the motion of the particle layer which travel upstream and perturb the blast wave motion. Computation of the particle and gas momentum flux in the multiphase
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kim, I.; Quevedo, H. J.; Feldman, S.; Bang, W.; Serratto, K.; McCormick, M.; Aymond, F.; Dyer, G.; Bernstein, A. C.; Ditmire, T. [Center for High Energy Density Science, Department of Physics, The University of Texas at Austin, C1510, Austin, Texas 78712 (United States)
2013-12-15
Radiative blast waves were created by irradiating a krypton cluster source from a supersonic jet with a high intensity femtosecond laser pulse. It was found that the radiation from the shock surface is absorbed in the optically thick upstream medium creating a radiative heat wave that travels supersonically ahead of the main shock. As the blast wave propagates into the heated medium, it slows and loses energy, and the radiative heat wave also slows down. When the radiative heat wave slows down to the transonic regime, a secondary shock in the ionization precursor is produced. This paper presents experimental data characterizing both the initial and secondary shocks and numerical simulations to analyze the double-shock dynamics.
-
Numerical simulation of blast wave propagation in vicinity of standalone prism on flat plate
Valger, Svetlana; Fedorova, Natalya; Fedorov, Alexander
2018-03-01
In the paper, numerical simulation of shock wave propagation in the vicinity of a standalone prism and a prism with a cavity in front of it was carried out. The modeling was based on the solution of 3D Euler equations and Fluent software was used as a main computational tool. The algorithm for local dynamic mesh adaptation to high gradients of pressure was applied. The initial stage of the explosion of condensed explosive was described with the help of "Compressed balloon method". The research allowed describing the characteristic stages of the blast in a semi-closed space, the structure of secondary shock waves and their interaction with obstacles. The numerical approach in Fluent based on combining inviscid gas dynamics methods and "Compressed balloon method" was compared with the method which had been used by the authors earlier with the help of AUTODYN and which is based on the use of the hydrodynamic model of a material to describe state of detonation products. For the problem of shock wave propagation in the vicinity of standalone prism the comparison of the simulation results obtained using both the methods with the experimental data was performed on the dependence of static pressure and effective momentum on time for the characteristic points located on prism walls.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Liying eZhang
2013-08-01
Full Text Available Blast-induced traumatic brain injury has emerged as a signature injury in combat casualty care. Present combat helmets are designed primarily to protect against ballistic and blunt impacts, but the current issue with helmets is protection concerning blasts. In order to delineate the blast wave attenuating capability of the Advanced Combat Helmet (ACH, a finite element (FE study was undertaken to evaluate the head response against blast loadings with and without helmet using a partially validated FE model of the human head and ACH. Four levels of overpressures (0.27-0.66 MPa from the Bowen’s lung iso-damage threshold curves were used to simulate blast insults. Effectiveness of the helmet with respect to head orientation was also investigated. The resulting biomechanical responses of the brain to blast threats were compared for human head with and without the helmet. For all Bowen’s cases, the peak intracranial pressures (ICP in the head ranged from 0.68-1.8 MPa in the coup cortical region. ACH was found to mitigate ICP in the head by 10-35%. Helmeted head resulted in 30% lower average peak brain strains and product of strain and strain rate. Among three blast loading directions with ACH, highest reduction in peak ICP (44% was due to backward blasts whereas the lowest reduction in peak ICP and brain strains was due to forward blast (27%. The biomechanical responses of a human head to primary blast insult exhibited directional sensitivity owing to the different geometry contours and coverage of the helmet construction and asymmetric anatomy of the head. Thus, direction-specific tolerances are needed in helmet design in order to offer omni-directional protection for the human head. The blasts of varying peak overpressures and durations that are believed to produce the same level of lung injury produce different levels of mechanical responses in the brain, and hence "iso-damage" curves for brain injury are likely different than the Bowen curves
-
Seismic-safe conditions of blasting near pressure pipe-lines during power installation construction
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Smolij, N.I.; Nikitin, A.S.
1980-01-01
Seismic-safe conditions for performing drill-blasting operations in the vicinity of underground gas pipelines when constructing thermal- or nuclear power plants are discussed. It is shown that, for the determination of seismic-safe parameters, of drill-blasting operations, the maximum permissible level of seismic loads should be specified taking into account the mechanical properties of the pipeline.metal, structural parameters of the gas pipeline and the pressure of the medium transported. Besides, the seismic effect of the blast should be considered with regard to particular conditions of blasting and rock properties. The equations and diagrams used in the calculation are given
-
Bomb blast mass casualty incidents: initial triage and management of injuries.
Goh, S H
2009-01-01
Bomb blast injuries are no longer confined to battlefields. With the ever present threat of terrorism, we should always be prepared for bomb blasts. Bomb blast injuries tend to affect air-containing organs more, as the blast wave tends to exert a shearing force on air-tissue interfaces. Commonly-injured organs include the tympanic membranes, the sinuses, the lungs and the bowel. Of these, blast lung injury is the most challenging to treat. The clinical picture is a mix of acute respiratory distress syndrome and air embolism, and the institution of positive pressure ventilation in the presence of low venous pressures could cause systemic arterial air embolism. The presence of a tympanic membrane perforation is not a reliable indicator of the presence of a blast injury in the other air-containing organs elsewhere. Radiological imaging of the head, chest and abdomen help with the early identification of blast lung injury, head injury, abdominal injury, eye and sinus injuries, as well as any penetration by foreign bodies. In addition, it must be borne in mind that bomb blasts could also be used to disperse radiological and chemical agents.
-
Design of a Simple Blast Pressure Gauge Based on a Heterodyne Velocimetry Measuring Technique
2016-08-01
intensity of the blast being measured. For relatively low-pressure fields, such as that generated by release of compressed air from a standard shop ...unlimited. 13 4. References 1. Walter PL. Air-blast and the science of dynamic pressure measurements. Depew (NY): PCB Piezotronics; Fort Worth (TX...ALEGRA: An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian multimaterial, multiphysics code. 46th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit; 2008 Jan 7–10; Reno (NV
-
Lo, Kam W; Ferguson, Brian G
2012-11-01
The accurate localization of small arms fire using fixed acoustic sensors is considered. First, the conventional wavefront-curvature passive ranging method, which requires only differential time-of-arrival (DTOA) measurements of the muzzle blast wave to estimate the source position, is modified to account for sensor positions that are not strictly collinear (bowed array). Second, an existing single-sensor-node ballistic model-based localization method, which requires both DTOA and differential angle-of-arrival (DAOA) measurements of the muzzle blast wave and ballistic shock wave, is improved by replacing the basic external ballistics model (which describes the bullet's deceleration along its trajectory) with a more rigorous model and replacing the look-up table ranging procedure with a nonlinear (or polynomial) equation-based ranging procedure. Third, a new multiple-sensor-node ballistic model-based localization method, which requires only DTOA measurements of the ballistic shock wave to localize the point of fire, is formulated. The first method is applicable to situations when only the muzzle blast wave is received, whereas the third method applies when only the ballistic shock wave is received. The effectiveness of each of these methods is verified using an extensive set of real data recorded during a 7 day field experiment.
-
Teland, J.A.; Doormaal, J.C.A.M. van; Horst, M.J. van der; Svinsås, E.
2010-01-01
Blast injury models, like Axelsson and Stuhmiller, require four pressure signals as input. Those pressure signals must be acquired by a Blast Test Device (BTD) that has four pressure transducers placed in a horizontal plane at intervals of 90 degrees. This can be either in a physical test setup or
-
Testing and modeling the dynamic response of foam materials for blast protection
Fitek, John H.
The pressure wave released from an explosion can cause injury to the lungs. A personal armor system concept for blast lung injury protection consists of a polymer foam layer behind a rigid armor plate to be worn over the chest. This research develops a method for testing and modeling the dynamic response of foam materials to be used for down-selection of materials for this application. Constitutive equations for foam materials are incorporated into a lumped parameter model of the combined armor plate and foam system. Impact testing and shock tube testing are used to measure the foam model parameters and validate the model response to a pressure wave load. The plate and foam armor model is then coupled to a model of the human thorax. With a blast pressure wave input, the armor model is evaluated based on how it affects the injury-causing mechanism of chest wall motion. Results show that to reduce chest wall motion, the foam must compress at a relatively constant stress level, which requires a sufficient foam thickness.
-
Blast Testing Issues and TBI; Experimental Models that Lead to Wrong Conclusions
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Charles E. Needham
2015-04-01
Full Text Available Over the past several years we have noticed an increase in the number of blast injury studies published in peer-reviewed biomedical journals that have utilized improperly conceived experiments. Data from these studies will lead to false conclusions and more confusion than advancement in the understanding of blast injury, particularly blast neurotrauma. Computational methods to properly characterize the blast environment have been available for decades. These methods, combined with a basic understanding of blast wave phenomena enable researchers to extract useful information from well documented experiments. This basic understanding must include the differences and interrelationships of static pressure, dynamic pressure, reflected pressure, and total or stagnation pressure in transient shockwave flows, how they relate to loading of objects, and how they are properly measured. However, it is critical that the research community effectively overcomes the confusion that has been compounded by a misunderstanding of the differences between the loading produced by a free field explosive blast and loading produced by a conventional shock tube. The principles of blast scaling have been well established for decades and when properly applied will do much to repair these problems.This paper provides guidance regarding proper experimental methods and offers insights into the implications of improperly designed and executed tests. Through application of computational methods, useful data can be extracted from well documented historical tests, and future work can be conducted in a way to maximize the effectiveness and use of valuable biological test data.
-
Gas explosion characterization, wave propagation (small-scale experiments)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Larsen, G.C.
1985-01-01
A number of experiments have been performed with blast waves arising from the ignition of homogeneous and well defined mixtures of methane, oxygen and nitrogen, contained within spherical balloons with controlled initial dimensions. In the initial small scale experiments pressure characteristics, ground reflection phenomena and pressure distribution on box like obstacles were studied. Both configurations with one box and two closely spaced boxes have been considered, and a wave-wave interaction phenomenom was observed in the case of closely spaced obstacles. Main emphasis has been placed on the half scale field experiments. In these, the maximum flame speed has been of the order of 100 m/s, resulting in positive peak pressures of 50-100.10 2 Pa in 5 - 10 m distance from the source. The explosion process was found to be reasonable symmetric. The attenuation of the blast wave due to vegetation and the influence of obstacles as banks, walls and houses on the pressure field have been investigated. The presence of the bank and the house was felt in a zone with a length corresponding to a typical dimension of the obstacles, whereas the overall pressure field is shown to be unaffected by the type of obstacles and vegetation investigated. For the wall and house, reflection factors have been established, and some variation over the surface has been measured. The scatter of the pressure measurements is estimated for stable, neutral and unstable atmospheric conditions, and an attempt to determine the ground reflection factor has been performed. Finally the accelerations of a house exposed to the blast wave have been examined
-
Field of infrasound wave on the earth from blast wave, produced by supersonic flight of a rocket
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Drobzheva, Ya.V.; Krasnov, V.M.
2006-01-01
It was developed a physical model, which allowed calculating a field of infrasound wave on the earth from blast wave, produced by supersonic flight of a rocket. For space launching site Baikonur it is shown that the nearest horizontal distance from launching site of rocket up to which arrive infrasound waves, produced by supersonic flight of a rocket, is 56 km. Amplitude of acoustic impulse decreases in 5 times on distance of 600 km. Duration of acoustic impulse increases from 1.5 to 3 s on the same distance. Values of acoustic field parameters on the earth surface, practically, do not depend from season of launching of rocket. (author)
-
Blast-Induced Acceleration in a Shock Tube: Distinguishing Primary and Tertiary Blast Injury
2016-10-01
injury conditions (blast and acceleration vs acceleration alone) undergo neurobehavioral and histopathological assessments to comprehensively... reversal . To facilitate mid-air blasts, a release mechanism was devised. Balls were attached to the bail of the mechanism. The blast wave would cause
-
Primary blast-induced traumatic brain injury: lessons from lithotripsy
Nakagawa, A.; Ohtani, K.; Armonda, R.; Tomita, H.; Sakuma, A.; Mugikura, S.; Takayama, K.; Kushimoto, S.; Tominaga, T.
2017-11-01
Traumatic injury caused by explosive or blast events is traditionally divided into four mechanisms: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary blast injury. The mechanisms of blast-induced traumatic brain injury (bTBI) are biomechanically distinct and can be modeled in both in vivo and in vitro systems. The primary bTBI injury mechanism is associated with the response of brain tissue to the initial blast wave. Among the four mechanisms of bTBI, there is a remarkable lack of information regarding the mechanism of primary bTBI. On the other hand, 30 years of research on the medical application of shock waves (SWs) has given us insight into the mechanisms of tissue and cellular damage in bTBI, including both air-mediated and underwater SW sources. From a basic physics perspective, the typical blast wave consists of a lead SW followed by shock-accelerated flow. The resultant tissue injury includes several features observed in primary bTBI, such as hemorrhage, edema, pseudo-aneurysm formation, vasoconstriction, and induction of apoptosis. These are well-described pathological findings within the SW literature. Acoustic impedance mismatch, penetration of tissue by shock/bubble interaction, geometry of the skull, shear stress, tensile stress, and subsequent cavitation formation are all important factors in determining the extent of SW-induced tissue and cellular injury. In addition, neuropsychiatric aspects of blast events need to be taken into account, as evidenced by reports of comorbidity and of some similar symptoms between physical injury resulting in bTBI and the psychiatric sequelae of post-traumatic stress. Research into blast injury biophysics is important to elucidate specific pathophysiologic mechanisms of blast injury, which enable accurate differential diagnosis, as well as development of effective treatments. Herein we describe the requirements for an adequate experimental setup when investigating blast-induced tissue and cellular injury; review SW physics
-
Sarvghad-Moghaddam, Hesam; Jazi, Mehdi Salimi; Rezaei, Asghar; Karami, Ghodrat; Ziejewski, Mariusz
2015-01-01
A parametric study was conducted to delineate the efficacy of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as ballistic faceshields and advanced combat helmets, in the case of a blast. The propagations of blast waves and their interactions with an unprotected head, a helmeted one, and a fully protected finite element head model (FEHM) were modeled. The biomechanical parameters of the brain were recorded when the FEHM was exposed to shockwaves from the front, back, top, and bottom. The directional dependent tissue response of the brain and the variable efficiency of PPE with respect to the blast orientation were two major results of this study.
-
Effects of low-level blast exposure on the nervous system: Is there really a controversy?
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gregory A Elder
2014-12-01
Full Text Available High-pressure blast waves can cause extensive CNS injury in humans. However, in combat settings such as Iraq and Afghanistan, lower level exposures associated with mild TBI (mTBI or subclinical exposure have been much more common. Yet controversy exists concerning what traits can be attributed to low-level blast, in large part due to the difficulty of distinguishing blast-related mTBI from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD. We describe how TBI is defined in humans and the problems posed in using current definitions to recognize blast-related mTBI. We next consider the problem of applying definitions of human mTBI to animal models, in particular that TBI severity in humans is defined in relation to alteration of consciousness at the time of injury, which typically cannot be assessed in animals. However, based on outcome assessments a condition of low-level blast exposure can be defined in animals that likely approximates human mTBI or subclinical exposure. We review blast injury modeling in animals noting that inconsistencies in experimental approach have contributed to uncertainty over the effects of low-level blast. Yet animal studies show that low-level blast pressure waves are transmitted to the brain. In brain low-level blast exposures cause behavioral, biochemical, pathological and physiological effects on the nervous system including the induction of PTSD-related behavioral traits in the absence of a psychological stressor. We review the relationship of blast exposure to chronic neurodegenerative diseases noting the paradoxical lowering of Abeta by blast, which along with other observations suggest that blast-related TBI is pathophysiologically distinct from non-blast TBI. Human neuroimaging studies show that blast-related mTBI is associated with a variety of chronic effects that are unlikely to be explained by co-morbid PTSD. We conclude that abundant evidence supports low-level blast as having long-term effects on the nervous system.
-
Modeling of Combined Impact and Blast Loading on Reinforced Concrete Slabs
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Del Linz
Full Text Available Abstract Explosive devices represent a significant threat to military and civilian structures. Specific design procedures have to be followed to account for this and ensure buildings will have the capacity to resist the imposed pressures. Shrapnel can also be produced during explosions and the resulting impacts can weaken the structure, reducing its capacity to resist the blast pressure wave and potentially causing failures to occur. Experiments were performed by the Defence Science and Technology Agency (DSTA of Singapore to study this combined loading phenomenon. Slabs were placed on the ground and loaded with approximately 9 kg TNT charges at a standoff distance of 2.1 m. Spherical steel ball bearings were used to reproduce the shrapnel loading. Loading and damage characteristics were recorded from the experiments. A finite element analysis (FEA model was then created which could simulate the effect of combined shrapnel impacts and blast pressure waves in reinforced concrete slabs, so that its results could be compared to experimental data from the blast tests. Quarter models of the experimental concrete slabs were built using LS-Dyna. Material models available in the software were employed to represent all the main components, taking into account projectile deformations. The penetration depth and damage areas measured were then compared to the experimental data and an analytical solution to validate the models.
-
Experimental Study of Bilinear Initiating System Based on Hard Rock Pile Blasting
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yusong Miao
2017-01-01
Full Text Available It is difficult to use industrial explosives to excavate hard rock and achieve suitable blasting effect due to the low energy utilization rate resulting in large rocks and short blasting footage. Thus, improving the utilization ratio of the explosive energy is important. In this study, a novel bilinear initiation system based on hard rock blasting was proposed to improve the blasting effects. Furthermore, on the basis of the detonation wave collision theory, frontal collision, oblique reflection, and Mach reflection during detonation wave propagation were studied. The results show that the maximum detonation pressure at the Mach reflection point where the incident angle is 46.9° is three times larger than the value of the explosive complete detonation. Then, in order to analyze the crack propagation in different initiation forms, a rock fracture test slot was designed, and the results show that bilinear initiating system can change the energy distribution of explosives. Finally, field experiment was implemented at the hard rock pile blasting engineering, and experimental results show that the present system possesses high explosive energy utilization ratio and low rock fragments size. The results of this study can be used to improve the efficiency in hard rock blasting.
-
A Numerical Method for Blast Shock Wave Analysis of Missile Launch from Aircraft
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sebastian Heimbs
2015-01-01
Full Text Available An efficient empirical approach was developed to accurately represent the blast shock wave loading resulting from the launch of a missile from a military aircraft to be used in numerical analyses. Based on experimental test series of missile launches in laboratory environment and from a helicopter, equations were derived to predict the time- and position-dependent overpressure. The method was finally applied and validated in a structural analysis of a helicopter tail boom under missile launch shock wave loading.
-
Morrissey, M. M.; Savage, W. Z.; Wieczorek, G. F.
1999-10-01
The July 10, 1996, Happy Isles rockfall in Yosemite National Park, California, released 23,000 to 38,000 m3 of granite in four separate events. The impacts of the first two events which involved a 550-m free fall, generated seismic waves and atmospheric pressure waves (air blasts). We focus on the dynamic behavior of the second air blast that downed over 1000 trees, destroyed a bridge, demolished a snack bar, and caused one fatality and several injuries. Calculated velocities for the air blast from a two-phase, finite difference model are compared to velocities estimated from tree damage. From tornadic studies of tree damage, the air blast is estimated to have traveled <108-120 m/s within 50 m from the impact and decreased to <10-20 m/s within 500 m from the impact. The numerical model simulates the two-dimensional propagation of an air blast through a dusty atmosphere with initial conditions defined by the impact velocity and pressure. The impact velocity (105-107 m/s) is estimated from the Colorado Rockfall Simulation Program that simulates rockfall trajectories. The impact pressure (0.5 MPa) is constrained by the kinetic energy of the impact (1010-1012 J) estimated from the seismic energy generated by the impact. Results from the air blast simulations indicate that the second Happy Isles air blast (weak shock wave) traveled with an initial velocity above the local sound speed. The size and location of the first impact are thought to have injected <50 wt% dust into the atmosphere. This amount of dust lowered the local atmospheric sound speed to ˜220 m/s. The discrepancy between calculated velocity data and field estimated velocity data (˜220 m/s versus ˜110 m/s) is attributed to energy dissipated by the downing of trees and additional entrainment of debris into the atmosphere not included in the calculations.
-
Computer Simulation of Blast Waves in a Tunnel with Sudden Decrease in Cross Section
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Glenn, L. A. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Neuscamman, S. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
2011-08-22
The case of an explosion in a tunnel where the blast wave encounters a sudden decrease in cross section is studied with quasi-one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional axisymmetric codes (2D) and the results are compared to experimental data. It is found that the numerical results from both codes are in good agreement until the interface at the change in cross section is encountered. Thereafter, however, the peak pressure derived with the codes is found to be significantly higher than the experimental results although the agreement between the 2D result and the experiment improves with increasing distance down the tunnel. Peak pressure and impulse per unit area obtained downstream of the interface with the 1D analysis are found to be substantially higher than with either the experiment or the 2D results. The reason for this is the time delay for the shock reflecting off the (vertical) rigid wall between the inner and outer tunnel radii to interact with the (supersonic) core flow into the decreased cross section. In the 1D case the reflected and transmitted shocks are formed instantaneously across the entire cross section resulting in higher pressure and increased shock speed downstream of the interface.
-
Numerical simulation of the fluid-structure interaction between air blast waves and soil structure
Umar, S.; Risby, M. S.; Albert, A. Luthfi; Norazman, M.; Ariffin, I.; Alias, Y. Muhamad
2014-03-01
Normally, an explosion threat on free field especially from high explosives is very dangerous due to the ground shocks generated that have high impulsive load. Nowadays, explosion threats do not only occur in the battlefield, but also in industries and urban areas. In industries such as oil and gas, explosion threats may occur on logistic transportation, maintenance, production, and distribution pipeline that are located underground to supply crude oil. Therefore, the appropriate blast resistances are a priority requirement that can be obtained through an assessment on the structural response, material strength and impact pattern of material due to ground shock. A highly impulsive load from ground shocks is a dynamic load due to its loading time which is faster than ground response time. Of late, almost all blast studies consider and analyze the ground shock in the fluid-structure interaction (FSI) because of its influence on the propagation and interaction of ground shock. Furthermore, analysis in the FSI integrates action of ground shock and reaction of ground on calculations of velocity, pressure and force. Therefore, this integration of the FSI has the capability to deliver the ground shock analysis on simulation to be closer to experimental investigation results. In this study, the FSI was implemented on AUTODYN computer code by using Euler-Godunov and the arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE). Euler-Godunov has the capability to deliver a structural computation on a 3D analysis, while ALE delivers an arbitrary calculation that is appropriate for a FSI analysis. In addition, ALE scheme delivers fine approach on little deformation analysis with an arbitrary motion, while the Euler-Godunov scheme delivers fine approach on a large deformation analysis. An integrated scheme based on Euler-Godunov and the arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian allows us to analyze the blast propagation waves and structural interaction simultaneously.
-
The importance of systemic response in the pathobiology of blast-induced neurotrauma
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ibolja eCernak
2010-12-01
Full Text Available Due to complex injurious environment where multiple blast effects interact with the body, parallel blast-induced neurotrauma is a unique clinical entity induced by systemic, local, and cerebral responses. Activation of autonomous nervous system; sudden pressure-increase in vital organs such as lungs and liver; and activation of neuroendocrine-immune system are among the most important mechanisms that contribute significantly to molecular changes and cascading injury mechanisms in the brain. It has been hypothesized that vagally mediated cerebral effects play a vital role in the early response to blast: this assumption has been supported by experiments where bilateral vagotomy mitigated bradycardia, hypotension, and apnea, and also prevented excessive metabolic alterations in the brain of animals exposed to blast. Clinical experience suggests specific blast-body-nervous system interactions such as 1 direct interaction with the head either through direct passage of the blast wave through the skull or by causing acceleration and/or rotation of the head; and 2 via hydraulic interaction, when the blast overpressure compresses the abdomen and chest, and transfers its kinetic energy to the body’s fluid phase, initiating oscillating waves that traverse the body and reach the brain. Accumulating evidence suggests that inflammation plays important role in the pathogenesis of long-term neurological deficits due to blast. These include memory decline, motor function and balance impairments, and behavioral alterations, among others. Experiments using rigid body- or head protection in animals subjected to blast showed that head protection failed to prevent inflammation in the brain or reduce neurological deficits, whereas body protection was successful in alleviating the blast-induced functional and morphological impairments in the brain.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Віктор Петрович Кравченко
2016-07-01
Full Text Available The article presents the analysis of two methods of control over hot blast supply into a blast furnace with constant pressure and constant amount (consumption. The analysis of these two methods was performed with the aim of determining their influence upon changes in gas pressure in the blast furnace top. The blast furnace was considered as a unity of vessels (furnace hearth, the top and gas-dynamic resistance (a column of charge materials. A differential equation was obtained, with regard to the dynamic balance of gas flow at the inlet and outlet of the top; the equation relates the pressure and gas consumption at the top to the pressure and hot blast consumption at the inlet and outlet of the furnace and to the resistance of the column of charge materials. The column of charge materials is considered as n-th number of channels through which gas flow inside the furnace moves and which resist to the flow. By the analysis of this equation at steady state (automatic stabilization of gas pressure in the top, the conditions were obtained to be satisfied with the specified value of gas pressure in the top. This value is equal to a half of the sum of the value of hot blast pressure at the inlet into the furnace and the value of pressure inside the collector of blast furnace gas. This conclusion is verified by the operation practice of blast furnaces in Ukraine. While analyzing the second method of controlling the supply of blast supply-stabilization of consumption (amount of hot blast supplied into the furnace it has been shown that the method could be realized in condition of stabilization of the amount of blast furnace gas, going out of the furnace. As the resistance of the column of charge materials constantly changes it is necessary to change the hot blast pressure in order to ensure the constant amount of blast, supplied into the furnace. It is often connected with possible substantial pressure fluctuations of hot blast at the inlet of the
-
Maasberg, Wolfgang
2012-01-01
Commercial-Industrial Cleaning, by Pressure-Washing, Hydro-Blasting and UHP-Jetting is the first proprietary manual for cleaning and rehabilitation through pressure-washing, hydro-blasting and ultra high pressure water jetting (UHP). It examines the cleaning, restoration and rehabilitation of statuary and historical structures; manufacturing hardware; and application technologies for residential, commercial and industrial areas, structures and buildings. Commercial-Industrial Cleaning, by Pressure-Washing, Hydro-Blasting and UHP-Jetting contains over 450 applications from agricultural, marine, municipal, food processing, paper-pulp, pharmaceutical and cosmetic, industrial and power generating maintenance areas. It includes gear lists to help readers easily identify the appropriate tooling and equipment for each specific application and industry. Commercial-Industrial Cleaning, by Pressure-Washing, Hydro-Blasting and UHP-Jetting supplies readers with the tools to create a successful business model for re...
-
Tan, X. G.; Przekwas, A. J.; Gupta, R. K.
2017-11-01
The modeling of human body biomechanics resulting from blast exposure poses great challenges because of the complex geometry and the substantial material heterogeneity. We developed a detailed human body finite element model representing both the geometry and the materials realistically. The model includes the detailed head (face, skull, brain and spinal cord), the neck, the skeleton, air cavities (lungs) and the tissues. Hence, it can be used to properly model the stress wave propagation in the human body subjected to blast loading. The blast loading on the human was generated from a simulated C4 explosion. We used the highly scalable solvers in the multi-physics code CoBi for both the blast simulation and the human body biomechanics. The meshes generated for these simulations are of good quality so that relatively large time-step sizes can be used without resorting to artificial time scaling treatments. The coupled gas dynamics and biomechanics solutions were validated against the shock tube test data. The human body models were used to conduct parametric simulations to find the biomechanical response and the brain injury mechanism due to blasts impacting the human body. Under the same blast loading condition, we showed the importance of inclusion of the whole body.
-
Primary blast survival and injury risk assessment for repeated blast exposures.
Panzer, Matthew B; Bass, Cameron R Dale; Rafaels, Karin A; Shridharani, Jay; Capehart, Bruce P
2012-02-01
The widespread use of explosives by modern insurgents and terrorists has increased the potential frequency of blast exposure in soldiers and civilians. This growing threat highlights the importance of understanding and evaluating blast injury risk and the increase of injury risk from exposure to repeated blast effects. Data from more than 3,250 large animal experiments were collected from studies focusing on the effects of blast exposure. The current study uses 2,349 experiments from the data collection for analysis of the primary blast injury and survival risk for both long- and short-duration blasts, including the effects from repeated exposures. A piecewise linear logistic regression was performed on the data to develop survival and injury risk assessment curves. New injury risk assessment curves uniting long- and short-duration blasts were developed for incident and reflected pressure measures and were used to evaluate the risk of injury based on blast over pressure, positive-phase duration, and the number of repeated exposures. The risk assessments were derived for three levels of injury severity: nonauditory, pulmonary, and fatality. The analysis showed a marked initial decrease in injury tolerance with each subsequent blast exposure. This effect decreases with increasing number of blast exposures. The new injury risk functions showed good agreement with the existing experimental data and provided a simplified model for primary blast injury risk. This model can be used to predict blast injury or fatality risk for single exposure and repeated exposure cases and has application in modern combat scenarios or in setting occupational health limits. .Copyright © 2012 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
-
Attenuation of blast pressure behind ballistic protective vests.
Wood, Garrett W; Panzer, Matthew B; Shridharani, Jay K; Matthews, Kyle A; Capehart, Bruce P; Myers, Barry S; Bass, Cameron R
2013-02-01
Clinical studies increasingly report brain injury and not pulmonary injury following blast exposures, despite the increased frequency of exposure to explosive devices. The goal of this study was to determine the effect of personal body armour use on the potential for primary blast injury and to determine the risk of brain and pulmonary injury following a blast and its impact on the clinical care of patients with a history of blast exposure. A shock tube was used to generate blast overpressures on soft ballistic protective vests (NIJ Level-2) and hard protective vests (NIJ Level-4) while overpressure was recorded behind the vest. Both types of vest were found to significantly decrease pulmonary injury risk following a blast for a wide range of conditions. At the highest tested blast overpressure, the soft vest decreased the behind armour overpressure by a factor of 14.2, and the hard vest decreased behind armour overpressure by a factor of 56.8. Addition of body armour increased the 50th percentile pulmonary death tolerance of both vests to higher levels than the 50th percentile for brain injury. These results suggest that ballistic protective body armour vests, especially hard body armour plates, provide substantial chest protection in primary blasts and explain the increased frequency of head injuries, without the presence of pulmonary injuries, in protected subjects reporting a history of blast exposure. These results suggest increased clinical suspicion for mild to severe brain injury is warranted in persons wearing body armour exposed to a blast with or without pulmonary injury.
-
Experiments on cylindrically converging blast waves in atmospheric air
Matsuo, Hideo; Nakamura, Yuichi
1980-06-01
Cylindrically converging blast waves have been produced in normal atmospheric conditions by the detonation of the explosives, pentaerythritoltetranitrate, (PETN), over cylindrical surfaces. The shocks generated in this way are so strong that the fronts propagating through the air become luminous of themselves. The production and the propagation of the shocks have been monitored with a framing camera and a streak camera, and the time-space relations of the shock propagations have been determined using an electrical ionization probing system. The results have shown that the trajectory of the shock fronts near the axis of the cylinder can be approximately represented by the Guderley's formula.
-
Supernova blast wave within a stellar cluster outflow
Rodríguez-Ramírez, J. C.; Raga, A. C.; Velázquez, P. F.; Rodríguez-González, A.; Toledo-Roy, J. C.
2014-11-01
In this paper, we develop a semi-analytic model of a supernova which goes off in the centre of a stellar cluster. The supernova remnant interacts with a stratified, pre-existent outflow produced by the winds of the cluster stars. We compare our semi-analytic model with numerical simulations using the spherically symmetric Euler equations with appropriate mass and energy source terms. We find good agreement between these two approaches, and we find that for typical parameters the blast wave is likely to reach the Taylor-Sedov regime outside the cluster radius. We also calculate the predicted X-ray luminosity of the flow as a function of time, and we obtain its dependence on the outer radius and the number of stars of the cluster.
-
A Numerical Study on the Screening of Blast-Induced Waves for Reducing Ground Vibration
Park, Dohyun; Jeon, Byungkyu; Jeon, Seokwon
2009-06-01
Blasting is often a necessary part of mining and construction operations, and is the most cost-effective way to break rock, but blasting generates both noise and ground vibration. In urban areas, noise and vibration have an environmental impact, and cause structural damage to nearby structures. Various wave-screening methods have been used for many years to reduce blast-induced ground vibration. However, these methods have not been quantitatively studied for their reduction effect of ground vibration. The present study focused on the quantitative assessment of the effectiveness in vibration reduction of line-drilling as a screening method using a numerical method. Two numerical methods were used to analyze the reduction effect toward ground vibration, namely, the “distinct element method” and the “non-linear hydrocode.” The distinct element method, by particle flow code in two dimensions (PFC 2D), was used for two-dimensional parametric analyses, and some cases of two-dimensional analyses were analyzed three-dimensionally using AUTODYN 3D, the program of the non-linear hydrocode. To analyze the screening effectiveness of line-drilling, parametric analyses were carried out under various conditions, with the spacing, diameter of drill holes, distance between the blasthole and line-drilling, and the number of rows of drill holes, including their arrangement, used as parameters. The screening effectiveness was assessed via a comparison of the vibration amplitude between cases both with and without screening. Also, the frequency distribution of ground motion of the two cases was investigated through fast Fourier transform (FFT), with the differences also examined. From our study, it was concluded that line-drilling as a screening method of blast-induced waves was considerably effective under certain design conditions. The design details for field application have also been proposed.
-
High resolution imaging of colliding blast waves in cluster media
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Smith, Roland A [Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom); Lazarus, James [Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom); Hohenberger, Matthias [Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom); Marocchino, Alberto [Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom); Robinson, Joseph S [Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom); Chittenden, Jeremy P [Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom); Moore, Alastair S [Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom); Gumbrell, Edward T [Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2AZ (United Kingdom); Dunne, Mike [Central Laser Facility, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Chilton, Didcot OX11 OQX (United Kingdom)
2007-12-15
Strong shocks and blast wave collisions are commonly observed features in astrophysical objects such as nebulae and supernova remnants. Numerical simulations often underpin our understanding of these complex systems, however modelling of such extreme phenomena remains challenging, particularly so for the case of radiative or colliding shocks. This highlights the need for well-characterized laboratory experiments both to guide physical insight and to provide robust data for code benchmarking. Creating a sufficiently high-energy-density gas medium for conducting scaled laboratory astrophysics experiments has historically been problematic, but the unique ability of atomic cluster gases to efficiently couple to intense pulses of laser light now enables table top scale (1 J input energy) studies to be conducted at gas densities of >10{sup 19} particles cm{sup -3} with an initial energy density >5 x 10{sup 9} J g{sup -1}. By laser heating atomic cluster gas media we can launch strong (up to Mach 55) shocks in a range of geometries, with and without radiative precursors. These systems have been probed with a range of optical and interferometric diagnostics in order to retrieve electron density profiles and blast wave trajectories. Colliding cylindrical shock systems have also been studied, however the strongly asymmetric density profiles and radial and longitudinal mass flow that result demand a more complex diagnostic technique based on tomographic phase reconstruction. We have used the 3D magnetoresistive hydrocode GORGON to model these systems and to highlight interesting features such as the formation of a Mach stem for further study.
-
Porcine head response to blast.
Shridharani, Jay K; Wood, Garrett W; Panzer, Matthew B; Capehart, Bruce P; Nyein, Michelle K; Radovitzky, Raul A; Bass, Cameron R 'dale'
2012-01-01
Recent studies have shown an increase in the frequency of traumatic brain injuries related to blast exposure. However, the mechanisms that cause blast neurotrauma are unknown. Blast neurotrauma research using computational models has been one method to elucidate that response of the brain in blast, and to identify possible mechanical correlates of injury. However, model validation against experimental data is required to ensure that the model output is representative of in vivo biomechanical response. This study exposes porcine subjects to primary blast overpressures generated using a compressed-gas shock tube. Shock tube blasts were directed to the unprotected head of each animal while the lungs and thorax were protected using ballistic protective vests similar to those employed in theater. The test conditions ranged from 110 to 740 kPa peak incident overpressure with scaled durations from 1.3 to 6.9 ms and correspond approximately with a 50% injury risk for brain bleeding and apnea in a ferret model scaled to porcine exposure. Instrumentation was placed on the porcine head to measure bulk acceleration, pressure at the surface of the head, and pressure inside the cranial cavity. Immediately after the blast, 5 of the 20 animals tested were apneic. Three subjects recovered without intervention within 30 s and the remaining two recovered within 8 min following respiratory assistance and administration of the respiratory stimulant doxapram. Gross examination of the brain revealed no indication of bleeding. Intracranial pressures ranged from 80 to 390 kPa as a result of the blast and were notably lower than the shock tube reflected pressures of 300-2830 kPa, indicating pressure attenuation by the skull up to a factor of 8.4. Peak head accelerations were measured from 385 to 3845 G's and were well correlated with peak incident overpressure (R(2) = 0.90). One SD corridors for the surface pressure, intracranial pressure (ICP), and head acceleration are
-
Blast from pressurized carbon dioxide released into a vented atmospheric chamber
Hansen, P. M.; Gaathaug, A. V.; Bjerketvedt, D.; Vaagsaether, K.
2018-03-01
This study describes the blast from pressurized carbon dioxide (CO2) released from a high-pressure reservoir into an openly vented atmospheric chamber. Small-scale experiments with pure vapor and liquid/vapor mixtures were conducted and compared with simulations. A motivation was to investigate the effects of vent size and liquid content on the peak overpressure and impulse response in the atmospheric chamber. The comparison of vapor-phase CO2 test results with simulations showed good agreement. This numerical code described single-phase gas dynamics inside a closed chamber, but did not model any phase transitions. Hence, the simulations described a vapor-only test into an unvented chamber. Nevertheless, the simulations reproduced the incident shock wave, the shock reflections, and the jet release inside the atmospheric chamber. The rapid phase transition did not contribute to the initial shock strength in the current test geometry. The evaporation rate was too low to contribute to the measured peak overpressure that was in the range of 15-20 kPa. The simulation results produced a calculated peak overpressure of 12 kPa. The liquid tests showed a significantly higher impulse compared to tests with pure vapor. Reducing the vent opening from 0.1 to 0.01 m2 resulted in a slightly higher impulse calculated at 100 ms. The influence of the vent area on the calculated impulse was significant in the vapor-phase tests, but not so clear in the liquid/vapor mixture tests.
-
COLLIMATION AND ASYMMETRY OF THE HOT BLAST WAVE FROM THE RECURRENT NOVA V745 Sco
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Drake, Jeremy J.; Kashyap, Vinay [Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge, MA 02138 (United States); Delgado, Laura; Hernanz, M. [Institute of Space Sciences, ICE (CSIC-IEEC), E-08193 Cerdanyola del Vallés, Barcelona (Spain); Laming, J. Martin [Space Science Division, Naval Research Laboratory, Code 7674L, Washington, DC 20375 (United States); Starrfield, Sumner [School of Earth and Space Exploration, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287-1404 (United States); Orlando, Salvatore [INAF—Osservatorio Astronomico di Palermo G. S. Vaiana, Piazza del Parlamento 1, I-90134 Palermo (Italy); Page, Kim L. [Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, Leicester, LE1 7RH (United Kingdom); Ness, J.-U. [Science Operations Division, Science Operations Department of ESA, ESAC, E-28691 Villanueva de la Cañada (Madrid) (Spain); Gehrz, R. D.; Woodward, Charles E. [Minnesota Institute for Astrophysics, School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Minnesota, 116 Church Street SE, Minneapolis, MN 55455 (United States); Van Rossum, Daan [Flash Center for Computational Science, Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637 (United States)
2016-07-10
The recurrent symbiotic nova V745 Sco exploded on 2014 February 6 and was observed on February 22 and 23 by the Chandra X-ray Observatory Transmission Grating Spectrometers. By that time the supersoft source phase had already ended, and Chandra spectra are consistent with emission from a hot, shock-heated circumstellar medium with temperatures exceeding 10{sup 7} K. X-ray line profiles are more sharply peaked than expected for a spherically symmetric blast wave, with a full width at zero intensity of approximately 2400 km s{sup 1}, an FWHM of 1200 ± 30 km s{sup 1}, and an average net blueshift of 165 ± 10 km s{sup 1}. The red wings of lines are increasingly absorbed toward longer wavelengths by material within the remnant. We conclude that the blast wave was sculpted by an aspherical circumstellar medium in which an equatorial density enhancement plays a role, as in earlier symbiotic nova explosions. Expansion of the dominant X-ray-emitting material is aligned close to the plane of the sky and is most consistent with an orbit seen close to face-on. Comparison of an analytical blast wave model with the X-ray spectra, Swift observations, and near-infrared line widths indicates that the explosion energy was approximately 10{sup 43} erg and confirms an ejected mass of approximately 10{sup 7} M {sub ⊙}. The total mass lost is an order of magnitude lower than the accreted mass required to have initiated the explosion, indicating that the white dwarf is gaining mass and is a Type Ia supernova progenitor candidate.
-
DIRECT AIR BLAST EXPOSURE EFFECTS IN ANIMALS, OPERATION UPSHOT-KNOTHOLE, PROJECT 4.2
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
DRAEGER, R.H. (UNITED STATES NAVY - DEPARTMENT OF); LEE, R.H. (UNITED STATES NAVY - DEPARTMENT OF)
1953-12-31
tube. The agreement between the estimated pressures and the recorded pressures in the containers were good in some instances but not in others. Discounting the initial pressure rise, it was thought that the records represent the pressure changes in the exposure containers. The individual records exhibited rather wide variations in recorded pressures indicating a complex pressure field. The attempt to compare levels of direct air blast in small and large animals, and thereby to extrapolate to man, was not accomplished due to the lack of statistically reliable data on the dogs. The lapse of time between the death of the dogs and autopsy reduced the interpretable findings below the level required for statistical significance. Laboratory studies are planned to evaluate the relative importance of the several blast wave parameters in the production of injury, Recommendations for future field test studies will depend upon the outcome of this laboratory work.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jianguo Ning
2016-01-01
Full Text Available Artificial explosions are commonly used to prevent rockburst in deep roadways. However, the dissipation of the impact stress wave within the artificial blasting damage zone (ABDZ of the rocks surrounding a deep roadway has not yet been clarified. The surrounding rocks were divided into the elastic zone, blasting damage zone, plastic zone, and anchorage zone in this research. Meanwhile, the ABDZ was divided into the pulverizing area, fractured area, and cracked area from the inside out. Besides, the model of the normal incidence of the impact stress waves in the ABDZ was established; the attenuation coefficient of the amplitude of the impact stress waves was obtained after it passed through the intact rock mass, and ABDZ, to the anchorage zone. In addition, a numerical simulation was used to study the dynamic response of the vertical stress and impact-induced vibration energy in the surrounding rocks. By doing so, the dissipation of the impact stress waves within the ABDZ of the surrounding rocks was revealed. As demonstrated in the field application, the establishment of the ABDZ in the surrounding rocks reduced the effect of the impact-induced vibration energy on the anchorage support system of the roadway.
-
Air blast effects on nuclear power plants from vapor cloud explosions
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wiedermann, A.H.; Eichler, T.V.; Kot, C.A.
1981-01-01
To assess the hazards arising from the explosion of a large flammable vapor cloud a method was developed for estimating the air blast field assuming a detonation wave is established. The actual 'pancake' like geometry typical for negatively buoyant vapor clouds is taken into account. The cloud height and other characteristics are generated by a global cloud dynamics model for negatively buoyant clouds. This model provides the cloud height as a function of fuel vapor concentration and other pertinent variables. A two-dimensional Eulerian shock hydrodynamic computer code is utilized to compute the blast environment in the neighborhood of the end of the cloud. The initial field is taken to be a quasi-steady explosion field calculated by the method of characteristics for a thin Prandtl-Meyer expansion wave, and the upward driven air shock representing the combustion and pressure relief processes inherent in the pancake geometry. This initial fields is established in the 2-D hydrocode at a time corresponding to the arrival of the detonation front at the cloud edge. It is to be noted that the local blast environment scales with respect to the cloud height. The computational results indicate that it is essential to include the influence of cloud geometry for the realistic prediction of the air blast hazard arising from the explosion of a negatively buoyant vapor cloud. (orig./HP)
-
Numerical Derivation of Iso-Damaged Curve for a Reinforced Concrete Beam Subjected to Blast Loading
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Temsah Yehya
2018-01-01
Full Text Available Many engineering facilities are severely damaged by blast loading. Therefore, many manufacturers of sensitive, breakable, and deformed structures (such as facades of glass buildings carry out studies and set standards for these installations to withstand shock waves caused by explosions. Structural engineers also use these standards in their designs for various structural elements by following the ISO Damage Carve, which links pressure and Impulse. As all the points below this curve means that the structure is safe and will not exceed the degree of damage based on the various assumptions made. This research aims to derive the Iso-Damage curve of a reinforced concrete beam exposed to blast wave. An advanced volumetric finite element program (ABAQUS will be used to perform the derivation.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Adel M.E. Mohamed
2013-06-01
Full Text Available Ground vibrations induced by blasting in the cement quarries are one of the fundamental problems in the quarrying industry and may cause severe damage to the nearby utilities and pipelines. Therefore, a vibration control study plays an important role in the minimization of environmental effects of blasting in quarries. The current paper presents the influence of the quarry blasts at the National Cement Company (NCC on the two oil pipelines of SUMED Company southeast of Helwan City, by measuring the ground vibrations in terms of Peak Particle Velocity (PPV. The seismic refraction for compressional waves deduced from the shallow seismic survey and the shear wave velocity obtained from the Multi channel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW technique are used to evaluate the closest site of the two pipelines to the quarry blasts. The results demonstrate that, the closest site of the two pipelines is of class B, according to the National Earthquake Hazard Reduction Program (NEHRP classification and the safe distance to avoid any environmental effects is 650 m, following the deduced Peak Particle Velocity (PPV and scaled distance (SD relationship (PPV = 700.08 × SD−1.225 in mm/s and the Air over Pressure (air blast formula (air blast = 170.23 × SD−0.071 in dB. In the light of prediction analysis, the maximum allowable charge weight per delay was found to be 591 kg with damage criterion of 12.5 mm/s at the closest site of the SUMED pipelines.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hristov Nebojša
2015-02-01
Full Text Available Simulation and measurements of muzzle blast overpressure and its physical manifestations are studied in this paper. The use of a silencer can have a great influence on the overpressure intensity. A silencer is regarded as an acoustic transducer and a waveguide. Wave equations for an acoustic dotted source of directed effect are used for physical interpretation of overpressure as an acoustic phenomenon. Decomposition approach has proven to be suitable to describe the formation of the output wave of the wave transducer. Electroacoustic analogies are used for simulations. A measurement chain was used to compare the simulation results with the experimental ones.
-
EVOLUTION of the Pressure Wave Supercharger Concept
Costiuc, Iuliana; Chiru, Anghel
2017-10-01
Born more than a century ago, the concept of exploiting the pressure wave phenomenon has evolved with rather small steps, experiencing an accelerated progress over the past decades. This paper aims an overview on the researchers’ results over time regarding the pressure wave technology and its applications, pointing out on the internal combustion engine’s supercharging application. This review complements the past reports on the subject, presenting the evolution of the concept and technology, as well as the researcher’s efforts on solving the specific shortcomings of this pressure wave technology. Undoubtedly, the pressure wave rotors have been a research goal over the years. At first, most of the researches were experimental and the theoretical calculations required to improve the technology were too arduous. Recently, new computer software dedicated to accurate simulation of the processes governing the wave rotor operation, altogether with modern experimental measurement instruments and well-developed diagnostic techniques have opened wide possibilities to innovate the pressure wave supercharging technology. This paper also highlights the challenges that specialists still have to overcome and aspects to become future preoccupations and research directions.
-
Feddema, Rick
Feddema, Rick T. M.S.M.E., Purdue University, December 2013. Effect of Aviation Fuel Type and Fuel Injection Conditions on the Spray Characteristics of Pressure Swirl and Hybrid Air Blast Fuel Injectors. Major Professor: Dr. Paul E. Sojka, School of Mechanical Engineering Spray performance of pressure swirl and hybrid air blast fuel injectors are central to combustion stability, combustor heat management, and pollutant formation in aviation gas turbine engines. Next generation aviation gas turbine engines will optimize spray atomization characteristics of the fuel injector in order to achieve engine efficiency and emissions requirements. Fuel injector spray atomization performance is affected by the type of fuel injector, fuel liquid properties, fuel injection pressure, fuel injection temperature, and ambient pressure. Performance of pressure swirl atomizer and hybrid air blast nozzle type fuel injectors are compared in this study. Aviation jet fuels, JP-8, Jet A, JP-5, and JP-10 and their effect on fuel injector performance is investigated. Fuel injector set conditions involving fuel injector pressure, fuel temperature and ambient pressure are varied in order to compare each fuel type. One objective of this thesis is to contribute spray patternation measurements to the body of existing drop size data in the literature. Fuel droplet size tends to increase with decreasing fuel injection pressure, decreasing fuel injection temperature and increasing ambient injection pressure. The differences between fuel types at particular set conditions occur due to differences in liquid properties between fuels. Liquid viscosity and surface tension are identified to be fuel-specific properties that affect the drop size of the fuel. An open aspect of current research that this paper addresses is how much the type of aviation jet fuel affects spray atomization characteristics. Conventional aviation fuel specifications are becoming more important with new interest in alternative
-
A coupling of empirical explosive blast loads to ALE air domains in LS-DYNA (registered)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Slavik, Todd P
2010-01-01
A coupling method recently implemented in LS-DYNA (registered) allows empirical explosive blast loads to be applied to air domains treated with the multi-material arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) formulation. Previously, when simulating structures subjected to blast loads, two methods of analysis were available: a purely Lagrangian approach or one involving the ALE and Lagrangian formulations coupled with a fluid-structure interaction (FSI) algorithm. In the former, air blast pressure is computed with empirical equations and directly applied to Lagrangian elements of the structure. In the latter approach, the explosive as well as the air are explicitly modeled and the blast wave propagating through the ALE air domain impinges on the Lagrangian structure through FSI. Since the purely Lagrangian approach avoids modeling the air between the explosive and structure, a significant computational cost savings can be realized - especially so when large standoff distances are considered. The shortcoming of the empirical blast equations is their inability to account for focusing or shadowing of the blast waves due to their interaction with structures which may intervene between the explosive and primary structure of interest. The new method presented here obviates modeling the explosive and air leading up the structure. Instead, only the air immediately surrounding the Lagrangian structures need be modeled with ALE, while effects of the far-field blast are applied to the outer face of that ALE air domain with the empirical blast equations; thus, focusing and shadowing effects can be accommodated yet computational costs are kept to a minimum. Comparison of the efficiency and accuracy of this new method with other approaches shows that the ability of LS-DYNA (registered) to model a variety of new blast scenarios has been greatly extended.
-
Simulating geometrically complex blast scenarios
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ian G. Cullis
2016-04-01
Full Text Available The effects of blast waves generated by energetic and non-energetic sources are of continuing interest to the ballistics research community. Modern conflicts are increasingly characterised by asymmetric urban warfare, with improvised explosive devices (IEDs often playing a dominant role on the one hand and an armed forces requirement for minimal collateral effects from their weapons on the other. These problems are characterised by disparate length- and time-scales and may also be governed by complex physics. There is thus an increasing need to be able to rapidly assess and accurately predict the effects of energetic blast in topologically complex scenarios. To this end, this paper presents a new QinetiQ-developed advanced computational package called EAGLE-Blast, which is capable of accurately resolving the generation, propagation and interaction of blast waves around geometrically complex shapes such as vehicles and buildings. After a brief description of the numerical methodology, various blast scenario simulations are described and the results compared with experimental data to demonstrate the validation of the scheme and its ability to describe these complex scenarios accurately and efficiently. The paper concludes with a brief discussion on the use of the code in supporting the development of algorithms for fast running engineering models.
-
Characteristics of laser-induced shock wave injury to the inner ear of rats
Kurioka, Takaomi; Matsunobu, Takeshi; Niwa, Katsuki; Tamura, Atsushi; Kawauchi, Satoko; Satoh, Yasushi; Sato, Shunichi; Shiotani, Akihiro
2014-12-01
Recently, the number of blast injuries of the inner ear has increased in the general population. In blast-induced inner ear injury, a shock wave (SW) component in the blast wave is considered to play an important role in sensorineural hearing loss. However, the mechanisms by which an SW affects inner ear tissue remain largely unknown. We aimed to establish a new animal model for SW-induced inner ear injury by using laser-induced SWs (LISWs) on rats. The LISWs were generated by irradiating an elastic laser target with 694-nm nanosecond pulses of a ruby laser. After LISW application to the cochlea through bone conduction, auditory measurements revealed the presence of inner ear dysfunction, the extent of which depended on LISW overpressure. A significantly lower survival rate of hair cells and spiral ganglion neurons, as well as severe oxidative damage, were observed in the inner ear exposed to an LISW. Although considerable differences in the pressure characteristics exist between LISWs and SWs in real blast waves, the functional and morphological changes shown by the present LISW-based model were similar to those observed in real blast-induced injury. Thus, our animal model is expected to be useful for laboratory-based research of blast-induced inner ear injury.
-
Characteristics of laser-induced shock wave injury to the inner ear of rats.
Kurioka, Takaomi; Matsunobu, Takeshi; Niwa, Katsuki; Tamura, Atsushi; Kawauchi, Satoko; Satoh, Yasushi; Sato, Shunichi; Shiotani, Akihiro
2014-12-01
Recently, the number of blast injuries of the inner ear has increased in the general population. In blast-induced inner ear injury, a shock wave (SW) component in the blast wave is considered to play an important role in sensorineural hearing loss. However, the mechanisms by which an SW affects inner ear tissue remain largely unknown. We aimed to establish a new animal model for SW-induced inner ear injury by using laser-induced SWs (LISWs) on rats. The LISWs were generated by irradiating an elastic laser target with 694-nm nanosecond pulses of a ruby laser. After LISW application to the cochlea through bone conduction, auditory measurements revealed the presence of inner ear dysfunction, the extent of which depended on LISW overpressure. A significantly lower survival rate of hair cells and spiral ganglion neurons, as well as severe oxidative damage, were observed in the inner ear exposed to an LISW. Although considerable differences in the pressure characteristics exist between LISWs and SWs in real blast waves, the functional and morphological changes shown by the present LISW-based model were similar to those observed in real blast-induced injury. Thus, our animal model is expected to be useful for laboratory-based research of blast-induced inner ear injury.
-
Chen, Yun; Huang, Wei; Constantini, Shlomi
2013-01-01
After exposure of the human body to blast, kinetic energy of the blast shock waves might be transferred into hydraulic energy in the cardiovascular system to cause a rapid physical movement or displacement of blood (a volumetric blood surge). The volumetric blood surge moves through blood vessels from the high-pressure body cavity to the low-pressure cranial cavity, causing damage to tiny cerebral blood vessels and the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Large-scale cerebrovascular insults and BBB damage that occur globally throughout the brain may be the main causes of non-impact, blast-induced brain injuries, including the spectrum of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The volumetric blood surge may be a major contributor not only to blast-induced brain injuries resulting from physical trauma, but may also be the trigger to psychiatric disorders resulting from emotional and psychological trauma. Clinical imaging technologies, which are able to detect tiny cerebrovascular insults, changes in blood flow, and cerebral edema, may help diagnose both TBI and PTSD in the victims exposed to blasts. Potentially, prompt medical treatment aiming at prevention of secondary neuronal damage may slow down or even block the cascade of events that lead to progressive neuronal damage and subsequent long-term neurological and psychiatric impairment.
-
Simulation of crack propagation in rock in plasma blasting technology
Ikkurthi, V. R.; Tahiliani, K.; Chaturvedi, S.
Plasma Blasting Technology (PBT) involves the production of a pulsed electrical discharge by inserting a blasting probe in a water-filled cavity drilled in a rock, which produces shocks or pressure waves in the water. These pulses then propagate into the rock, leading to fracture. In this paper, we present the results of two-dimensional hydrodynamic simulations using the SHALE code to study crack propagation in rock. Three separate issues have been examined. Firstly, assuming that a constant pressure P is maintained in the cavity for a time τ , we have determined the P- τ curve that just cracks a given rock into at least two large-sized parts. This study shows that there exists an optimal pressure level for cracking a given rock-type and geometry. Secondly, we have varied the volume of water in which the initial energy E is deposited, which corresponds to different initial peak pressures Ppeak. We have determined the E- Ppeak curve that just breaks the rock into four large-sized parts. It is found that there must be an optimal Ppeak that lowers the energy consumption, but with acceptable probe damage. Thirdly, we have attempted to identify the dominant mechanism of rock fracture. We also highlight some numerical errors that must be kept in mind in such simulations.
-
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Roux, A
2009-09-01
Full Text Available of an optical sensor constructed to measure the light flash of an underwater blast to determine the moment of explosion. By measurement of the time taken between this moment and the time when the shock wave reaches the pressure sensors, accurate measurements...
-
Characterization of viscoelastic materials for low-magnitude blast mitigation
Bartyczak, S.; Mock, W.
2014-05-01
Recent research indicates that exposure to low amplitude blast waves, such as IED detonation or multiple firings of a weapon, causes damage to brain tissue resulting in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Current combat helmets are not sufficiently protecting warfighters from this danger and the effects are debilitating, costly, and long-lasting. The objective of the present work is to evaluate the blast mitigating behavior of current helmet materials and new materials designed for blast mitigation using a test fixture recently developed at the Naval Surface Warfare Center Dahlgren Division for use with an existing gas gun. The 40-mm-bore gas gun was used as a shock tube to generate blast waves (ranging from 0.5 to 2 bar) in the test fixture mounted on the gun muzzle. A fast opening valve was used to release helium gas from the breech which formed into a blast wave and impacted instrumented targets in the test fixture. Blast attenuation of selected materials was determined through the measurement of stress data in front of and behind the target. Materials evaluated in this research include polyurethane foam from currently fielded US Army and Marine Corps helmets, polyurea 1000, and three hardnesses of Sorbothane (48, 58, and 70 durometer, Shore 00). Polyurea 1000 and 6061-T6 aluminum were used to calibrate the stress gauges.
-
Plateau Waves of Intracranial Pressure and Partial Pressure of Cerebral Oxygen.
Lang, Erhard W; Kasprowicz, Magdalena; Smielewski, Peter; Pickard, John; Czosnyka, Marek
2016-01-01
This study investigates 55 intracranial pressure (ICP) plateau waves recorded in 20 patients after severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) with a focus on a moving correlation coefficient between mean arterial pressure (ABP) and ICP, called PRx, which serves as a marker of cerebrovascular reactivity, and a moving correlation coefficient between ABP and cerebral partial pressure of oxygen (pbtO2), called ORx, which serves as a marker for cerebral oxygen reactivity. ICP and ICPamplitude increased significantly during the plateau waves, whereas CPP and pbtO2 decreased significantly. ABP, ABP amplitude, and heart rate remained unchanged. In 73 % of plateau waves PRx increased during the wave. ORx showed an increase during and a decrease after the plateau waves, which was not statistically significant. Our data show profound cerebral vasoparalysis on top of the wave and, to a lesser extent, impairment of cerebral oxygen reactivity. The different behavior of the indices may be due to the different latencies of the cerebral blood flow and oxygen level control mechanisms. While cerebrovascular reactivity is a rapidly reacting mechanism, cerebral oxygen reactivity is slower.
-
Assessment of the Effectiveness of Combat Eyewear Protection Against Blast Overpressure.
Sundaramurthy, A; Skotak, M; Alay, E; Unnikrishnan, G; Mao, H; Duan, X; Williams, S T; Harding, T H; Chandra, N; Reifman, J
2018-07-01
It is unclear whether combat eyewear used by U. S. Service members is protective against blast overpressures (BOPs) caused by explosive devices. Here, we investigated the mechanisms by which BOP bypasses eyewear and increases eye surface pressure. We performed experiments and developed three-dimensional (3D) finite element (FE) models of a head form (HF) equipped with an advanced combat helmet (ACH) and with no eyewear, spectacles, or goggles in a shock tube at three BOPs and five head orientations relative to the blast wave. Overall, we observed good agreement between experimental and computational results, with average discrepancies in impulse and peak-pressure values of less than 15% over 90 comparisons. In the absence of eyewear and depending on the head orientation, we identified three mechanisms that contributed to pressure loading on the eyes. Eyewear was most effective at 0 deg orientation, with pressure attenuation ranging from 50 (spectacles) to 80% (goggles) of the peak pressures observed in the no-eyewear configuration. Spectacles and goggles were considerably less effective when we rotated the HF in the counter-clockwise direction around the superior-inferior axis of the head. Surprisingly, at certain orientations, spectacles yielded higher maximum pressures (80%) and goggles yielded larger impulses (150%) than those observed without eyewear. The findings from this study will aid in the design of eyewear that provides better protection against BOP.
-
Pressure wave propagation in sodium loop
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Botelho, D.A.
1989-01-01
A study was done on the pressure wave propagation within the pipes and mixture vessel of a termohydraulic loop for thermal shock with sodium. It was used the characteristic method to solve the one-dimensional continuity and momentum equations. The numerical model includes the pipes and the effects of valves and other accidents on pressure losses. The study was based on designer informations and engineering tables. It was evaluated the pressure wave sizes, parametrically as a function of the draining valve closure times. (author) [pt
-
Higher-order anisotropies in the blast-wave model: Disentangling flow and density field anisotropies
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Cimerman, Jakub [Czech Technical University in Prague, FNSPE, Prague (Czech Republic); Comenius University, FMPI, Bratislava (Slovakia); Tomasik, Boris [Czech Technical University in Prague, FNSPE, Prague (Czech Republic); Univerzita Mateja Bela, FPV, Banska Bystrica (Slovakia); Csanad, Mate; Loekoes, Sandor [Eoetvoes Lorand University, Budapest (Hungary)
2017-08-15
We formulate a generalisation of the blast-wave model which is suitable for the description of higher-order azimuthal anisotropies of the hadron production. The model includes anisotropy in the density profile as well as an anisotropy in the transverse expansion velocity field. We then study how these two kinds of anisotropies influence the single-particle distributions and the correlation radii of two-particle correlation functions. Particularly we focus on the third-order anisotropy and consideration is given averaging over different orientations of the event plane. (orig.)
-
Gvaramadze, V. V.
Most of middle-aged supernova remnants (SNRs) have a distorted and complicated appearance which cannot be explained in the framework of the Sedov-Taylor model. We consider three typical examples of such SNRs (Vela SNR, MSH15-52, G309.2-00.6) and show that their structure could be explained as a result of interaction of a supernova (SN) blast wave with the ambient medium preprocessed by the action of the SN progenitor's wind and ionized emission.
-
Blast-wave analysis of strange particle $m_{T}$ spectra in Pb-Pb collisions at the SPS
Bruno, Giuseppe E
2005-01-01
The transverse mass spectra of high statistics, high purity samples of K/sup 0//sub S/, Lambda , Xi and Omega particles produced in Pb-Pb collisions at SPS energy have been studied in the framework of the blast-wave model. The dependence of the freezeout parameters on particle species and event centrality is discussed. Results at 40 A GeV/c are presented here for the first time.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Clare, P.M.
1978-02-01
The gun-driven facility for simulating nuclear air blast has been described in Part 1 (AWRE Report 031/74). It was, however, subject to certain limitations in providing the requisite blast parameters for nuclear hardening. The efficiency of the simulator has been improved beyond that of the gun-driven facility to produce blast waves of higher peak overpressure, longer positive duration and greater equivalent yield. This has been done by firing in the 1.8 m (6 ft) diameter section of the tunnel instead of in the guns. Various line charge arrangements were investigated and the pressures and strains developed in the 1.8 m (6 ft) diameter section were measured. The shock loading on the tube walls was less than that produced by firing in the guns and consisted of a short duration shock decaying to a lower amplitude pressure pulse of longer duration (1 ms), followed by a few reflected shocks which the tube walls were well able to withstand. The equipment is described and results discussed. (author)
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Li Ma
2016-01-01
Full Text Available The impact energy produced by blast casting is able to break and cast rocks, yet the strong vibration effects caused at the same time would threaten the safety of mines. Based on the theory of Janbu’s Limit Equilibrium Method (LEM, pseudo-static method has been incorporated to analyze the influence of dynamic loads of blasting on slope stability. The horizontal loads produced by blast vibrations cause an increase in sliding forces, and this leads to a lower slope stability coefficient. When the tensile stresses of the two adjacent blast holes are greater than the tensile strength of rock mass, the radical oriented cracks are formed, which is the precondition for the formation of presplit face. Thus, the formula for calculating the blast hole spacing of presplit blasting can be obtained. Based on the analysis of the principles of vibration tester and vibration pick-up in detecting blast vibrations, a detection scheme of blast vibration is worked out by taking the blast area with precrack rear and non-precrack side of the detection object. The detection and research results of blast vibration show that presplit blasting can reduce the attenuation coefficient of stress wave by half, and the vibration absorption ratio could reach 50.2%; the impact of dynamic loads on the end-wall slope stability coefficient is 1.98%, which proves that presplit blasting plays an important role in shock absorption of blast casting.
-
Pressure waves in a supersaturated bubbly magma
Kurzon, I.; Lyakhovsky, V.; Navon, O.; Chouet, B.
2011-01-01
We study the interaction of acoustic pressure waves with an expanding bubbly magma. The expansion of magma is the result of bubble growth during or following magma decompression and leads to two competing processes that affect pressure waves. On the one hand, growth in vesicularity leads to increased damping and decreased wave amplitudes, and on the other hand, a decrease in the effective bulk modulus of the bubbly mixture reduces wave velocity, which in turn, reduces damping and may lead to wave amplification. The additional acoustic energy originates from the chemical energy released during bubble growth. We examine this phenomenon analytically to identify conditions under which amplification of pressure waves is possible. These conditions are further examined numerically to shed light on the frequency and phase dependencies in relation to the interaction of waves and growing bubbles. Amplification is possible at low frequencies and when the growth rate of bubbles reaches an optimum value for which the wave velocity decreases sufficiently to overcome the increased damping of the vesicular material. We examine two amplification phase-dependent effects: (1) a tensile-phase effect in which the inserted wave adds to the process of bubble growth, utilizing the energy associated with the gas overpressure in the bubble and therefore converting a large proportion of this energy into additional acoustic energy, and (2) a compressive-phase effect in which the pressure wave works against the growing bubbles and a large amount of its acoustic energy is dissipated during the first cycle, but later enough energy is gained to amplify the second cycle. These two effects provide additional new possible mechanisms for the amplification phase seen in Long-Period (LP) and Very-Long-Period (VLP) seismic signals originating in magma-filled cracks.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Qingwen Li
2015-01-01
Full Text Available In the tunnel and underground space engineering, the blasting wave will attenuate from shock wave to stress wave to elastic seismic wave in the host rock. Also, the host rock will form crushed zone, fractured zone, and elastic seismic zone under the blasting loading and waves. In this paper, an accurate mathematical dynamic loading model was built. And the crushed zone as well as fractured zone was considered as the blasting vibration source thus deducting the partial energy for cutting host rock. So this complicated dynamic problem of segmented differential blasting was regarded as an equivalent elastic boundary problem by taking advantage of Saint-Venant’s Theorem. At last, a 3D model in finite element software FLAC3D accepted the constitutive parameters, uniformly distributed mutative loading, and the cylindrical attenuation law to predict the velocity curves and effective tensile curves for calculating safety criterion formulas of surrounding rock and tunnel liner after verifying well with the in situ monitoring data.
-
Ion time-of-flight study of laser ablation of silver in low pressure gases
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Hansen, T.N.; Schou, Jørgen; Lunney, J.G.
1999-01-01
The dynamics of ions from a laser-ablated silver target in low pressure background atmospheres have been investigated in a simple geometry using an electrical probe. A simple scattering picture for the first transmitted peak of the observed plume splitting has been used to calculate cross section...... of the ablated silver ions in oxygen (sigma{O(2)} = 4.8 x 10(-16) cm(2)) and in argon (sigma{Ar} = 6.7 x 10(-16) cm(2)). The dynamics of the blast wave is well described by blast wave theory. (C) 1999 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved....
-
Starling, R. L. C.; vanderHorst, A. J.; Rol, E.; Wijers, R. A. M. J.; Kouveliotou, C.; Wiersema, K.; Curran, P. A.; Weltervrede, P.
2008-01-01
We constrain blast wave parameters and the circumburst media ofa subsample of 10 BeppoSAX gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). For this sample we derive the values of the injected electron energy distribution index, p, and the density structure index of the circumburst medium, k, from simultaneous spectral fits to their X-ray, optical, and NIR afterglow data. The spectral fits have been done in count space and include the effects ofmetallicity, and are compared with the previously reported optical and X-ray temporal behavior. Using the blast wave model and some assumptions which include on-axis viewing and standard jet structure, constant blast wave energy, and no evolution of the microphysical parameters, we find a mean value ofp for the sample as a whole of 9.... oa -0.003.0" 2 a_ statistical analysis of the distribution demonstrates that the p-values in this sample are inconsistent with a single universal value forp at the 3 _ level or greater, which has significant implications for particle acceleration models. This approach provides us with a measured distribution ofcircumburst density structures rather than considering only the cases of k ----0 (homogeneous) and k - 2 (windlike). We find five GRBs for which k can be well constrained, and in four of these cases the circumburst medium is clearly windlike. The fifth source has a value of 0 medium.
-
Numerical analysis of blast flow-field of baffle type muzzle brake
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kim, D.H. [Graduate School, Chungnam National University, Taejon (Korea); Ko, S. [Chungnam National University, Taejon (Korea)
1998-11-01
A three-dimensional unsteady, inviscid blast flow-field of a baffle type muzzle brake has been simulated by solving the Euler equation. The blast flow-field includes the effect of the free air blast, precursor blast flow and the propellant blast gas flow. Chimera grid scheme was used to generate 9 multi-block volume grids for the complex geometry. The evolution of the blast flow-field is presented by showing the contours of pressure, density and Mach number for certain time step. The comparison of the calculated and measured peak pressures on the surfaces of the muzzle brake is also presented. (author). 4 refs., 5 figs., 1 tab.
-
Scale testing of a partially confined blast chamber
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Grundling, W
2012-10-01
Full Text Available in pressure readings. A scale model of the blast chamber, Emily, was constructed with the addition of a pendulum plate hanging concentrically covering 65% of the open area. PURPOSE OF SCALED BLAST CHAMBER The purpose of this particular test is to evaluate... PHASE Illustrated in Figure 3 and 4 are the results obtained during testing of the scaled blast chamber. In both cases the pressure dissipates over time, showing pulsating behaviour as the shockwaves reflect off the chamber walls. By looking...
-
Wave effects on a pressure sensor
Digital Repository Service at National Institute of Oceanography (India)
Joseph, A.; DeSa, E; Desa, E; McKeown, J.; Peshwe, V.B.
Wave flume experiments indicated that for waves propagating on quiescent waters the sensor's performance improved (i.e. the difference Delta P between the average hydrostatic and measured pressures was small and positive) when the inlet...
-
Wan, Sheng; Li, Hui
2018-03-01
Though the test of blasting vibration, the blasting seismic wave propagation laws in southern granite pumped storage power project are studied. Attenuation coefficient of seismic wave and factors coefficient are acquired by the method of least squares regression analysis according to Sadaovsky empirical formula, and the empirical formula of seismic wave is obtained. This paper mainly discusses on the test of blasting vibration and the procedure of calculation. Our practice might as well serve as a reference for similar projects to come.
-
Bhagwat, Vaibhab Pramod; Dey, Kaushik
2016-04-01
Drilling and blasting are the most economical excavation techniques in underground drifts driven through hard rock formation. Burn cut is the most popular drill pattern, used in this case, to achieve longer advance per blast round. The ground vibration generated due to the propagation of blast waves on the detonation of explosive during blasting is the principal cause for structural and rock damage. Thus, ground vibration is a point of concern for the blasting engineers. The ground vibration from a blast is measured using a seismograph placed at the blast monitoring station. The measured vibrations, in terms of peak particle velocity, are related to the maximum charge detonated at one instant and the distance of seismograph from the blast point. The ground vibrations from a number of blast rounds of varying charge/delay and distances are monitored. A number of scaling factors of these dependencies (viz. Distance and maximum charge/delay) have been proposed by different researchers, namely, square root, cube root, CMRI, Langefors and Kihlstrom, Ghosh-Daemon, Indian standard etc. Scaling factors of desired type are computed for all the measured blast rounds. Regression analysis is carried out between the scaling factors and peak particle velocities to establish the coefficients of the vibration predictor equation. Then, the developed predictor equation is used for designing the blast henceforth. Director General of Mine Safety, India, specified that ground vibrations from eight to ten blast rounds of varying charge/delay and distances should be monitored to develop a predictor equation; however, there is no guideline about the type of scaling factor to be used. Further to this, from the statistical point of view, a regression analysis on a small sample population cannot be accepted without the testing of hypothesis. To show the importance of the above, in this paper, seven scaling factors are considered for blast data set of a hard-rock underground drift using burn
-
Mathematical models of blast induced TBI: current status, challenges and prospects
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Raj K Gupta
2013-05-01
Full Text Available Blast induced traumatic brain injury (TBI has become a signature wound of recent military activities and is the leading cause of death and long-term disability among U.S. soldiers. The current limited understanding of brain injury mechanisms impedes the development of protection, diagnostic and treatment strategies. We believe mathematical models of blast wave brain injury biomechanics and neurobiology, complemented with in vitro and in vivo experimental studies, will enable a better understanding of injury mechanisms and accelerate the development of both protective and treatment strategies. The goal of this paper is to review the current state of the art in mathematical and computational modeling of blast induced TBI, identify research gaps and recommend future developments. A brief overview of blast wave physics, injury biomechanics and the neurobiology of brain injury is used as a foundation for a more detailed discussion of multiscale mathematical models of primary biomechanics and secondary injury and repair mechanisms. The paper also presents a discussion of model development strategies, experimental approaches to generate benchmark data for model validation and potential applications of the model for prevention and protection against blast wave TBI.
-
Corotating pressure waves without streams in the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Burlaga, L.F.
1983-01-01
Voyager 1 and 2 magnetic field and plasma data are presented which demonstrate the existence of large scale, corotating, non-linear pressure waves between 2 AU and 4 AU that are not accompanied by fast streams. The pressure waves are presumed to be generated by corotating streams near the Sun. For two of the three pressure waves that are discussed, the absence of a stream is probably a real, physical effect, viz., a consequence of deceleration of the stream by the associated compression wave. For the third pressure wave, the apparent absence of a stream may be a geometrical effect it is likely that the stream was at latitudes just above those of the spacecraft, while the associated shocks and compression wave extended over a broader range of latitudes so that they could be observed by the spacecraft. It is suggested that the development of large-scale non-linear pressure waves at the expense of the kinetic energy of streams produces a qualitative change in the solar wind in the outer heliosphere. Within a few AU the quasi-stationary solar wind structure is determined by corotating streams whose structure is determined by the boundary conditions near the Sun
-
Pneumatic pressure wave generator provides economical, simple testing of pressure transducers
Gaal, A. E.; Weldon, T. P.
1967-01-01
Testing device utilizes the change in pressure about a bias or reference pressure level produced by displacement of a center-driven piston in a closed cylinder. Closely controlled pneumatic pressure waves allow testing under dynamic conditions.
-
Influence of Plasma Pressure Fluctuation on RF Wave Propagation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Liu Zhiwei; Bao Weimin; Li Xiaoping; Liu Donglin; Zhou Hui
2016-01-01
Pressure fluctuations in the plasma sheath from spacecraft reentry affect radio-frequency (RF) wave propagation. The influence of these fluctuations on wave propagation and wave properties is studied using methods derived by synthesizing the compressible turbulent flow theory, plasma theory, and electromagnetic wave theory. We study these influences on wave propagation at GPS and Ka frequencies during typical reentry by adopting stratified modeling. We analyzed the variations in reflection and transmission properties induced by pressure fluctuations. Our results show that, at the GPS frequency, if the waves are not totally reflected then the pressure fluctuations can remarkably affect reflection, transmission, and absorption properties. In extreme situations, the fluctuations can even cause blackout. At the Ka frequency, the influences are obvious when the waves are not totally transmitted. The influences are more pronounced at the GPS frequency than at the Ka frequency. This suggests that the latter can mitigate blackout by reducing both the reflection and the absorption of waves, as well as the influences of plasma fluctuations on wave propagation. Given that communication links with the reentry vehicles are susceptible to plasma pressure fluctuations, the influences on link budgets should be taken into consideration. (paper)
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Di Stefano, C. A.; Kuranz, C. C.; Klein, S. R.; Drake, R. P.; Malamud, G.; Henry de Frahan, M. T.; Johnsen, E.; Shimony, A.; Shvarts, D.; Smalyuk, V. A.; Martinez, D.
2014-01-01
In this work, we examine the hydrodynamics of high-energy-density (HED) shear flows. Experiments, consisting of two materials of differing density, use the OMEGA-60 laser to drive a blast wave at a pressure of ∼50 Mbar into one of the media, creating a shear flow in the resulting shocked system. The interface between the two materials is Kelvin-Helmholtz unstable, and a mixing layer of growing width develops due to the shear. To theoretically analyze the instability's behavior, we rely on two sources of information. First, the interface spectrum is well-characterized, which allows us to identify how the shock front and the subsequent shear in the post-shock flow interact with the interface. These observations provide direct evidence that vortex merger dominates the evolution of the interface structure. Second, simulations calibrated to the experiment allow us to estimate the time-dependent evolution of the deposition of vorticity at the interface. The overall result is that we are able to choose a hydrodynamic model for the system, and consequently examine how well the flow in this HED system corresponds to a classical hydrodynamic description
-
Wave Shape and Impact Pressure Measurements at a Rock Coast Cliff
Varley, S. J.; Rosser, N. J.; Brain, M.; Vann Jones, E. C.
2016-02-01
Rock coast research focuses largely on wave behaviour across beaches and shore platforms but rarely considers direct wave interaction with cliffs. Hydraulic action is one of the most important drivers of erosion along rock coasts. The magnitude of wave impact pressure has been shown by numerical and laboratory studies to be related to the wave shape. In deep water, a structure is only subjected to the hydrostatic pressure due to the oscillating clapotis. Dynamic pressures, related to the wave celerity, are exerted in shallower water when the wave is breaking at the point of impact; very high magnitude, short duration shock pressures are theorised to occur when the approaching wavefront is vertical. As such, wave shape may directly influence the potential of the impact to weaken rock and cause erosion. Measurements of impact pressure at coastal cliffs are limited, and the occurrence and influence of this phenomenon is currently poorly constrained. To address this, we have undertaken a field monitoring study on the magnitude and vertical distribution of wave impact pressures at the rocky, macro-tidal coastline of Staithes, North Yorkshire, UK. A series of piezo-resistive pressure transducers and a camera were installed at the base of the cliff during low tide. Transducers were deployed vertically up the cliff face and aligned shore-normal to capture the variation in static and dynamic pressure with height during a full spring tidal cycle. Five minute bursts of 5 kHz pressure readings and 4 Hz wave imaging were sampled every 30 minutes for six hours during high tide. Pressure measurements were then compensated for temperature and combined with wave imaging to produce a pressure time series and qualitative wave shape category for each wave impact. Results indicate the presence of a non-linear relationship between pressure impact magnitude, the occurrence of shock pressures, wave shape and tidal stage, and suggest that breaker type on impact (and controls thereof) may
-
Blast densification trials for oilsands tailings
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Port, A. [Klohn Crippen Berger Ltd., Vancouver, BC (Canada); Martens, S. [Klohn Crippen Berger Ltd., Calgary, AB (Canada); Eaton, T. [Shell Canada Ltd., Calgary, AB (Canada)
2010-07-01
The Shell Canada Muskeg River Mine External Tailings Facility (ETF) is an upstream constructed tailings facility located near Fort McMurray, Alberta. Raises have incrementally stepped out over the beach since construction of the starter dam and deposition within standing water has left some parts of the beach in a loose state. In order to assess the effectiveness of blast densification, a blast densification trial program that was conducted in 2006 at the ETF. The primary purpose of the test program was to determine the effectiveness of blast densification in tailings containing layers and zones of bitumen. The paper described the site characterization and explosive compaction trial program, with particular reference to test layout; drilling methodology; and blasting and timing sequence. The paper also described the instrumentation, including the seismographs; high pressure electric piezometers; low pressure electric piezometers; vibrating wire piezometers; inclinometers; settlement gauges; and surveys. Trial observations and post-trial observations were also presented. It was concluded that controlled blasting techniques could be used to safely induce liquefaction in localized areas within the tailings deposit, with a resulting increase in the tailings density. 5 refs., 1 tab., 14 figs.
-
Lang, Erhard W; Kasprowicz, Magdalena; Smielewski, Peter; Pickard, John; Czosnyka, Marek
2015-08-01
Plateau waves in intracranial pressure (ICP) are frequently recorded in neuro intensive care and are not yet fully understood. To further investigate this phenomenon, we analyzed partial pressure of cerebral oxygen (pbtO2) and a moving correlation coefficient between ICP and mean arterial blood pressure (ABP), called PRx, along with the cerebral oxygen reactivity index (ORx), which is a moving correlation coefficient between cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) and pbtO2 in an observational study. We analyzed 55 plateau waves in 20 patients after severe traumatic brain injury. We calculated ABP, ABP pulse amplitude (ampABP), ICP, CPP, pbtO2, heart rate (HR), ICP pulse amplitude (ampICP), PRx, and ORx, before, during, and after each plateau wave. The analysis of variance with Bonferroni post hoc test was used to compare the differences in the variables before, during, and after the plateau wave. We considered all plateau waves, even in the same patient, independent because they are separated by long intervals. We found increases for ICP and ampICP according to our operational definitions for plateau waves. PRx increased significantly (p = 0.00026), CPP (p pressure remains stable in ICP plateau waves, while cerebral autoregulatory indices show distinct changes, which indicate cerebrovascular reactivity impairment at the top of the wave. PbtO2 decreases during the waves and may show a slight overshoot after normalization. We assume that this might be due to different latencies of the cerebral blood flow and oxygen level control mechanisms. Other factors may include baseline conditions, such as pre-plateau wave cerebrovascular reactivity or pbtO2 levels, which differ between studies.
-
Nonlinear Modeling and Analysis of Pressure Wave inside CEUP Fuel Pipeline
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Qaisar Hayat
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Operating conditions dependent large pressure variations are one of the working characteristics of combination electronic unit pump (CEUP fuel injection system for diesel engines. We propose a precise and accurate nonlinear numerical model of pressure inside HP fuel pipeline of CEUP using wave equation (WE including both viscous and frequency dependent frictions. We have proved that developed hyperbolic approximation gives more realistic description of pressure wave as compared to classical viscous damped wave equation. Frictional effects of various frequencies on pressure wave have been averaged out across valid frequencies to represent the combined effect of all frequencies on pressure wave. Dynamic variations of key fuel properties including density, acoustic wave speed, and bulk modulus with varying pressures have also been incorporated. Based on developed model we present analysis on effect of fuel pipeline length on pressure wave propagation and variation of key fuel properties with both conventional diesel and alternate fuel rapeseed methyl ester (RME for CEUP pipeline.
-
Disintegration of liquid metals by low pressure water blasting
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Heshmatpour, B.; Copeland, G.L.
1981-01-01
The feasibility of disintegrating metals by a low cost system and subsequently incorporating them into grout mixtures has been demonstrated. A low pressure water blasting technique consisting of multiple nozzles and a converging-line jet stream was developed to disintegrate liquid metals and produce coarse metal powder and shot. Molten iron resulted in spherical shot, while copper, aluminum, and tin produced irregular shaped particles. The particle size was between 0.05 and 3 mm (0.002 and 0.1 in.), and about half the particles were smaller than 1 mm (0.04 in.) in all cases. The water consumption was rather low, while the production rate was relatively high. The method proved to be simple and reliable. The coarse metal powders were suspendable in grout fluids, indicating that they are probably disposable by the shale hydrofracture technique
-
Sedman, Andrew; Hepper, A
2018-03-19
This paper outlines aspects of UK Ministry of Defence's research and development of blast overpressure protection technologies appropriate for use in body armour, with the aim of both propagating new knowledge and updating existing information. Two simple models are introduced not only to focus the description of the mechanism by which the lungs can be protected, but also to provide a bridge between fields of research that may hold the key to further advances in protection technology and related body armour. Protection can be provided to the lungs by decoupling the stress wave transmission into the thorax by managing the blast energy imparted through the protection system. It is proposed that the utility of the existing 'simple decoupler' blast overpressure protection is reviewed in light of recent developments in the treatment of those sustaining both overpressure and fragment injuries. It is anticipated that further advances in protection technology may be generated by those working in other fields on the analogous technologies of 'buffer plates' and 'sandwich panels'. © Crown copyright (2018), Dstl. This material is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: psi@nationalarchives.gsi.gov.uk.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jingxuan Yang
2017-11-01
Full Text Available In extra-thick coal seams, mining operations can lead to large-scale disturbances, complex overburden structures, and frequent and strong strata behavior in the stope, which are serious threats to mine safety. This study analyzed the overburden structure and strata behavior and proposed the technique of confined blasting in water-filled deep holes as a measure to prevent strong rock pressure. It found that there are two primary reasons for the high effectiveness of the proposed technique in presplitting hard coal and rock. First, the fracture water enables much more efficient transfer of dynamic load due to its incompressibility. Second, the subsequent expansion of water can further split the rock by compression. A mechanical model was used to reveal how the process of confined blasting in water-filled deep holes presplit roof. Moreover, practical implementation of this technique was found to improve the structure of hard, thick roof and prevent strong rock pressure, demonstrating its effectiveness in roof control.
-
Lappa, Marcello; Drikakis, Dimitris; Kokkinakis, Ioannis
2017-03-01
This paper concerns the propagation of shock waves in an enclosure filled with dusty gas. The main motivation for this problem is to probe the effect on such dynamics of solid particles dispersed in the fluid medium. This subject, which has attracted so much attention over recent years given its important implications in the study of the structural stability of systems exposed to high-energy internal detonations, is approached here in the framework of a hybrid numerical two-way coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian methodology. In particular, insights are sought by considering a relatively simple archetypal setting corresponding to a shock wave originating from a small spherical region initialized on the basis of available analytic solutions. The response of the system is explored numerically with respect to several parameters, including the blast intensity (via the related value of the initial shock Mach number), the solid mass fraction (mass load), and the particle size (Stokes number). Results are presented in terms of pressure-load diagrams. Beyond practical applications, it is shown that a kaleidoscope of fascinating patterns is produced by the "triadic" relationships among multiple shock reflection events and particle-fluid and particle-wall interaction dynamics. These would be of great interest to researchers and scientists interested in fundamental problems relating to the general theory of pattern formation in complex nonlinear multiphase systems.
-
Modeling blast waves, gas and particles dispersion in urban and hilly ground areas
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hank, S.; Saurel, R.; Le Metayer, O.; Lapebie, E.
2014-01-01
The numerical simulation of shock and blast waves as well as particles dispersion in highly heterogeneous media such as cities, urban places, industrial plants and part of countries is addressed. Examples of phenomena under study are chemical gas products dispersion from damaged vessels, gas dispersion in urban places under explosion conditions, shock wave propagation in urban environment. A three-dimensional simulation multiphase flow code (HI2LO) is developed in this aim. To simplify the consideration of complex geometries, a heterogeneous discrete formulation is developed. When dealing with large scale domains, such as countries, the topography is considered with the help of elevation data. Meteorological conditions are also considered, in particular regarding complex temperature and wind profiles. Heat and mass transfers on sub-scale objects, such as buildings, trees and other obstacles are considered as well. Particles motion is addressed through a new turbulence model involving a single parameter to describe accurately plumes. Validations against experiments in basic situations are presented as well as examples of industrial and environmental computations. (authors)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Mogi, Gento; Adachi, Tsuyoshi; Yamatomi, Jiro [The University of Tokyo School of Engineering Department of Geosystem Engineering, Tokyo (Japan); Hoshino, Tatsuya [Mitsui Mining and Smelting Corp., Tokyo (Japan)
1999-10-31
In this research, local blast vibration control based on the theory of superposition of waves was investigated. Firstly, the influence of delay time errors of conventional electric detonators upon the level of local blast vibration was examined. Secondly, for a further effective local blast vibration control, a new delay blasting design concept 'combined delay blasting' that postulates the use of electronic detonators, which virtually have no delay time errors, is proposed. For a delay blasting with uniform detonation time intervals, an optimum time interval to minimize the local PPV (Peak Particle Velocity) is obtained based on the relationship between the PPV and the time interval, which is derived by superposing identical vibration time histories of each single hole shot. However, due to the scattering of the actual delay time caused by errors, PPV of a production blast seldom coincides with the estimated one. Since the expected value and the variance of PPV mainly depend on sensitivity of PPV around the nominal delay time, it is proposed that not only the optimum but also several sub-optimum candidates of delay time should be examined taking error into consideration. Concerning the 'combined delay blasting', its concept and some simulation results are presented. The estimated reduction effect of blast vibration of a delay blast based on this concept was quite favorable, indicating a possibility for further effective local blast vibration control. (author)
-
Turbulent Spot Pressure Fluctuation Wave Packet Model
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Dechant, Lawrence J. [Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States)
2017-05-01
Wave packet analysis provides a connection between linear small disturbance theory and subsequent nonlinear turbulent spot flow behavior. The traditional association between linear stability analysis and nonlinear wave form is developed via the method of stationary phase whereby asymptotic (simplified) mean flow solutions are used to estimate dispersion behavior and stationary phase approximation are used to invert the associated Fourier transform. The resulting process typically requires nonlinear algebraic equations inversions that can be best performed numerically, which partially mitigates the value of the approximation as compared to a more complete, e.g. DNS or linear/nonlinear adjoint methods. To obtain a simpler, closed-form analytical result, the complete packet solution is modeled via approximate amplitude (linear convected kinematic wave initial value problem) and local sinusoidal (wave equation) expressions. Significantly, the initial value for the kinematic wave transport expression follows from a separable variable coefficient approximation to the linearized pressure fluctuation Poisson expression. The resulting amplitude solution, while approximate in nature, nonetheless, appears to mimic many of the global features, e.g. transitional flow intermittency and pressure fluctuation magnitude behavior. A low wave number wave packet models also recover meaningful auto-correlation and low frequency spectral behaviors.
-
Design of air blast pressure sensors based on miniature silicon membrane and piezoresistive gauges
Riondet, J.; Coustou, A.; Aubert, H.; Pons, P.; Lavayssière, M.; Luc, J.; Lefrançois, A.
2017-11-01
Available commercial piezoelectric pressure sensors are not able to accurately reproduce the ultra-fast transient pressure occurring during an air blast experiment. In this communication a new pressure sensor prototype based on a miniature silicon membrane and piezoresistive gauges is reported for significantly improving the performances in terms of time response. Simulation results demonstrate the feasibility of a pressure transducer having a fundamental resonant frequency almost ten times greater than the commercial piezoelectric sensors one. The sensor uses a 5μm-thick SOI membrane and four P-type silicon gauges (doping level ≅ 1019 at/cm3) in Wheatstone bridge configuration. To obtain a good trade-off between the fundamental mechanical resonant frequency and pressure sensitivity values, the typical dimension of the rectangular membrane is fixed to 30μm x 90μm with gauge dimension of 1μm x 5μm. The achieved simulated mechanical resonant frequency of these configuration is greater than 40MHz with a sensitivity of 0.04% per bar.
-
Proceedings of the fourteenth annual symposium on explosives and blasting research
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
1998-12-31
Subjects covered include: ground vibration effects on structures; open-pit blast vibration prediction; effects of velocity of detonation and gas pressurization on fragmentation in layered rock; thermal ignition for emulsion powder explosives and emulsion matrix; effect of cut-off pressure on energy partition and blast design; new burden and spacing formulae for optimum blasting; calculated risk of experiencing lightning caused unplanned detonation; predicting explosive toxic fumes; and stemming techniques for loading angled holes charged with Anfo.
-
DYNAMIC TIME HISTORY ANALYSIS OF BLAST RESISTANT DOOR USING BLAST LOAD MODELED AS IMPACT LOAD
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Y. A. Pranata
2012-06-01
Full Text Available A blast resistant single door was designed to withstand a 0.91 bar blast pressure and 44 ms blast duration. The analysis was done using Dynamic Time History Analysis using Blast Load modeled as Impact Load for given duration. The material properties used have been modified to accommodate dynamic effects. The analysis was done using dynamic finite element method (fem for time of the blast duration, and the maximum/minimum internal forces and displacement were taken from the time history output, in order to know the behavior under blast load and estimate the safety margin of the door. Results obtained from this research indicated that the maximum z-displacement is 1.709 mm, while in the term of serviceability, the permitted is 25 mm. The maximum reaction force is 73,960 N, while the maximum anchor capacity is 82,069 N. On blast condition, the maximum frame stress is 71.71 MPa, the maximum hinge shear stress is 45.28 MPa. While on rebound condition, the maximum frame stress is 172.11 MPa, the maximum hinge shear stress is 29.46 MPa. The maximum door edge rotation is 0.44 degree, which is not exceed the permitted boundary (1.2 degree. Keywords: Dynamic time history, blast resistant door, single door, finite element method.
-
Haniff, S.; Taylor, P. A.
2017-11-01
We conducted computational macroscale simulations predicting blast-induced intracranial fluid cavitation possibly leading to brain injury. To further understanding of this problem, we developed microscale models investigating the effects of blast-induced cavitation bubble collapse within white matter axonal fiber bundles of the brain. We model fiber tracks of myelinated axons whose diameters are statistically representative of white matter. Nodes of Ranvier are modeled as unmyelinated sections of axon. Extracellular matrix envelops the axon fiber bundle, and gray matter is placed adjacent to the bundle. Cavitation bubbles are initially placed assuming an intracranial wave has already produced them. Pressure pulses, of varied strengths, are applied to the upper boundary of the gray matter and propagate through the model, inducing bubble collapse. Simulations, conducted using the shock wave physics code CTH, predict an increase in pressure and von Mises stress in axons downstream of the bubbles after collapse. This appears to be the result of hydrodynamic jetting produced during bubble collapse. Interestingly, results predict axon cores suffer significantly lower shear stresses from proximal bubble collapse than does their myelin sheathing. Simulations also predict damage to myelin sheathing, which, if true, degrades axonal electrical transmissibility and general health of the white matter structures in the brain.
-
On the pressure field of nonlinear standing water waves
Schwartz, L. W.
1980-01-01
The pressure field produced by two dimensional nonlinear time and space periodic standing waves was calculated as a series expansion in the wave height. The high order series was summed by the use of Pade approximants. Calculations included the pressure variation at great depth, which was considered to be a likely cause of microseismic activity, and the pressure distribution on a vertical barrier or breakwater.
-
Particle image velocimetry investigation of a finite amplitude pressure wave
Thornhill, D.; Currie, T.; Fleck, R.; Chatfield, G.
2006-03-01
Particle image velocimetry is used to study the motion of gas within a duct subject to the passage of a finite amplitude pressure wave. The wave is representative of the pressure waves found in the exhaust systems of internal combustion engines. Gas particles are accelerated from stationary to 150 m/s and then back to stationary in 8 ms. It is demonstrated that gas particles at the head of the wave travel at the same velocity across the duct cross section at a given point in time. Towards the tail of the wave viscous effects are plainly evident causing the flow profile to tend towards parabolic. However, the instantaneous mean particle velocity across the section is shown to match well with the velocity calculated from a corresponding measured pressure history using 1D gas dynamic theory. The measured pressure history at a point in the duct was acquired using a high speed pressure transducer of the type typically used for engine research in intake and exhaust systems. It is demonstrated that these are unable to follow the rapid changes in pressure accurately and that they are prone to resonate under certain circumstances.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Dworak, B.; Gajek, Sz.
1980-01-01
The results of sintered iron and of blast-furnace slag examination obtained by X-ray fluorescent analyses of energy and of wave dispersion are compared. They show that the methods are comparable for such elements as Ca and Fe, whereas for Mn (in sinter) the X-ray fluorescent analysis of wave dispersion is less precise. (author)
-
Starling, R.L.C.; van der Horst, A.J.; Rol, E.; Wijers, R.A.M.J.; Kouveliotou, C.; Wiersema, K.; Curran, P.A.; Weltevrede, P.
2008-01-01
We constrain blast wave parameters and the circumburst media of a subsample of 10 BeppoSAX gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). For this sample we derive the values of the injected electron energy distribution index, p, and the density structure index of the circumburst medium, k, from simultaneous spectral
-
Measurements of Pressure of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripter Using Pressure-Sensitive Papers
Inose, Naoto; Ide, Masao
1993-05-01
This paper describes measurements of pressures at the focal region of the extracorporeal shock wave lithotripter (ESWL) using pressure-sensitive papers. At the focal region of ESWL, ordinary hydrophones are quickly damaged, because of very high pressures. Recently, measurements of pressure at the focal region of ESWL using pressure-sensitive paper have been advised. Therefore, we have studied the effectiveness of pressure-sensitive papers in the measurement of high acoustic pressures at the focal region of ESWL.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
1997-10-08
In order to perform efficient and safe controlled blasting, attaining sufficient detonation from explosive is important. Therefore, a mechanism of detonation in a bore hole was studied. Two detonation phenomenon measuring methods were established: one is a continuous detonation speed measuring method by using a resistance wire probe, and another is a detonation mark observing and evaluating method using aluminum and metallic lead plates. Assuming delay blastings in multiple bore holes used practically, discussions were given on detonation phenomena of explosives under pressurized condition. Under dynamic pressure condition, size of the pressurization and delay time of the detonations affected largely the detonation. Discussions were given on blasting effect and safety according to difference in forward initiation and reverse initiation. The reverse initiation method was verified to have excellent blasting effect, maintain good face conditions, and assure safety against inflammable gases. A precision initiation method was developed, which can control the initiation time of a detonator more precisely. The initiation accuracy is more than 1000 times greater than the ordinary instantaneously detonating electric detonator. The precision control of the initiation time proved to develop greater crack propagation. Vibration and stone scattering were also controlled. This paper also describes application of the method to a rock elastic wave exploration technique. 136 refs., 99 figs., 13 tabs.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2000-03-01
For the purpose of reducing greenhouse effect gas emissions, a feasibility study was conducted on the energy conservation at Panzhihua Iron and Steel Company in Sichuan Province, China. In this project, the pressure energy of blast furnace is to be recovered in the form of electric power by installing the blast furnace top pressure recovery turbine (TRT). In the project, the pressure-reducing valve was removed, and the dry dust collector/dry TRT were installed to make the scale of electric power production largest. A model of TRT was installed at No. 4 blast furnace and is now in operation. In this project, TRTs are to be installed at Nos. 1, 2 and 3 blast furnaces. As a result of the study, the investment totaled 5.46 billion yen. The capacity of power generation by TRT is 16,890 kW, and the generated output is 137,822 MWh/y. Moreover, the amount of energy conservation is 36,467 toe/y, and the reduction amount of greenhouse effect gas emissions is 112,830 CO2-ton/y. The term of investment recovery is 8.3 years. The effect of reduction in greenhouse effect gas emissions is 20.66 CO2-ton/y/million yen. (NEDO)
-
Conversion of piston-driven shocks from powerful solar flares to blast wave shocks in the solar wind
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pinter, S.
1990-01-01
It was suggested by Smart and Shea (1985) that the time of arrival of solar-flare-generated shock waves at any point in space may be predicted by assuming that they are first driven from the Sun after which they decay into blast shocks. Their study was extended by using the duration of the Type IV radio emission as a phenomenological symptom of the piston-driven phase of these shocks. Using a sample of 39 cases of combined Type II/Type IV observations from 1972 to 1982 solar flares, it was found that the average predicted times-of-arrival of these shocks to Earth (and elsewhere) deviate from the actual times by 1.40 hr with a standard deviation of 1.25 hr. On the average, a representative shock from this sample is emitted from a powerful flare with a velocity of 1,560 km sec -1 ; moves at a constant inertial velocity to a distance of 0.12 AU after which it begins to decelerate as a classical (Sedov-type) blast shock that is convected by the ambient solar wind as suggested by Smart and Shea; and arrives to Earth 45.8 hr after its initiation in the Sun. Shocks that appear to deviate from this phenomenological scenario by virtue of lack of detection on Earth are assumed to decay into fast mode MHD waves. (author). 7 figs., 1 tab., 53 refs
-
Blast overpressure after tire explosion: a fatal case.
Pomara, Cristoforo; D'Errico, Stefano; Riezzo, Irene; Perilli, Gabriela; Volpe, Umberto; Fineschi, Vittorio
2013-12-01
Fatal blast injuries are generally reported in literature as a consequence of the detonation of explosives in war settings. The pattern of lesion depends on the position of the victim in relation to the explosion, on whether the blast tracks through air or water, and whether it happens in the open air or within an enclosed space and the distance from the explosion. Tire explosion-related injuries are rarely reported in literature. This study presents a fatal case of blast overpressure due to the accidental explosion of a truck tire occurring in a tire repair shop. A multidisciplinary approach to the fatality involving forensic pathologists and engineers revealed that the accidental explosion, which caused a series of primary and tertiary blast wave injuries, was due to tire deterioration.
-
A Phased Array Approach to Rock Blasting
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Leslie Gertsch; Jason Baird
2006-07-01
A series of laboratory-scale simultaneous two-hole shots was performed in a rock simulant (mortar) to record the shock wave interference patterns produced in the material. The purpose of the project as a whole was to evaluate the usefulness of phased array techniques of blast design, using new high-precision delay technology. Despite high-speed photography, however, we were unable to detect the passage of the shock waves through the samples to determine how well they matched the expected interaction geometry. The follow-up mine-scale tests were therefore not conducted. Nevertheless, pattern analysis of the vectors that would be formed by positive interference of the shockwaves from multiple charges in an ideal continuous, homogeneous, isotropic medium indicate the potential for powerful control of blast design, given precise characterization of the target rock mass.
-
Blast Impact Prediction Studies at Ghana Manganese Company ...
African Journals Online (AJOL)
Michael
2015-06-01
Jun 1, 2015 ... Keywords: Blast impact, Environment, Prediction, Regulatory threshold. 1 Introduction ... Noise is an environmental nuisance. .... explosion energy released into the ground generates vibration waves within the rock. Several.
-
Atmospheric particulate emissions from dry abrasive blasting using coal slag
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bhaskar Kura; Kalpalatha Kambham; Sivaramakrishnan Sangameswaran; Sandhya Potana [University of New Orleans, New Orleans, LA (United States). Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
2006-08-15
Coal slag is one of the widely used abrasives in dry abrasive blasting. Atmospheric emissions from this process include particulate matter (PM) and heavy metals, such as chromium, lead, manganese, nickel. Quantities and characteristics of PM emissions depend on abrasive characteristics and process parameters. Emission factors are key inputs to estimate emissions. Experiments were conducted to study the effect of blast pressure, abrasive feed rate, and initial surface contamination on total PM (TPM) emission factors for coal slag. Rusted and painted mild steel surfaces were used as base plates. Blasting was carried out in an enclosed chamber, and PM was collected from an exhaust duct using U.S. Environment Protection Agency source sampling methods for stationary sources. Results showed that there is significant effect of blast pressure, feed rate, and surface contamination on TPM emissions. Mathematical equations were developed to estimate emission factors in terms of mass of emissions per unit mass of abrasive used, as well as mass of emissions per unit of surface area cleaned. These equations will help industries in estimating PM emissions based on blast pressure and abrasive feed rate. In addition, emissions can be reduced by choosing optimum operating conditions. 40 refs., 5 figs., 2 tabs.
-
Rigby, S. E.; Fay, S. D.; Tyas, A.; Clarke, S. D.; Reay, J. J.; Warren, J. A.; Gant, M.; Elgy, I.
2017-06-01
The spatial and temporal distribution of pressure and impulse from explosives buried in saturated cohesive and cohesionless soils has been measured experimentally for the first time. Ten experiments have been conducted at quarter-scale, where localised pressure loading was measured using an array of 17 Hopkinson pressure bars. The blast pressure measurements are used in conjunction with high-speed video filmed at 140,000 fps to investigate in detail the physical processes occurring at the loaded face. Two coarse cohesionless soils and one fine cohesive soil were tested: a relatively uniform sand, a well-graded sandy gravel, and a fine-grained clay. The results show that there is a single fundamental loading mechanism when explosives are detonated in saturated soil, invariant of particle size and soil cohesion. It is also shown that variability in localised loading is intrinsically linked to the particle size distribution of the surrounding soil.
-
Rigby, S. E.; Fay, S. D.; Tyas, A.; Clarke, S. D.; Reay, J. J.; Warren, J. A.; Gant, M.; Elgy, I.
2018-05-01
The spatial and temporal distribution of pressure and impulse from explosives buried in saturated cohesive and cohesionless soils has been measured experimentally for the first time. Ten experiments have been conducted at quarter-scale, where localised pressure loading was measured using an array of 17 Hopkinson pressure bars. The blast pressure measurements are used in conjunction with high-speed video filmed at 140,000 fps to investigate in detail the physical processes occurring at the loaded face. Two coarse cohesionless soils and one fine cohesive soil were tested: a relatively uniform sand, a well-graded sandy gravel, and a fine-grained clay. The results show that there is a single fundamental loading mechanism when explosives are detonated in saturated soil, invariant of particle size and soil cohesion. It is also shown that variability in localised loading is intrinsically linked to the particle size distribution of the surrounding soil.
-
Proceedings of the seventh annual symposium on explosives and blasting research
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Anon.
1991-01-01
Papers from this symposium dealt with the following topics: advanced primer designs, seismic effects of blasting, systems for velocity of detonation measurement and pressure measurement, toxic fumes from explosions, blast performance, blasting for rock fragmentation, computer-aided blast design, characteristics of liquid oxygen explosives, and correlations of performance of explosives with ground vibration, partitioning of energy, and firing time scatter effects. Papers have been indexed separately for inclusion on the data base
-
Investigation of density-wave oscillation in parallel boiling channels under high pressure
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Ming Xiao; Xuejun Chen; Mingyuan Zhang
1992-01-01
This paper presents experimental results on density-wave instability in parallel boiling channels. Experiments have been done in a high pressure steam-water loop. Different types of two-phase flow instabilities have been observed, including density-wave oscillation, pressure-drop type oscillation, thermal oscillation and secondary density-wave oscillation. The secondary density-wave oscillation appears at very low exit steam quality (less than 0.1) and at the positive portion of Δ P-G curves with both channels' flow rate oscillating in phase. Density-wave oscillation can appear at pressure up to 192 bar and disappear over 207 bar. (6 figures) (Author)
-
Influence of ambient air pressure on impact pressure caused by breaking waves
Moutzouris, C.
1979-01-01
Engineers are interested in the dynamics of the interface waterstructure. In case of breaking of water waves on a structure high positive and sometimes negative pressures of very short duration occur. Not only the maxima and minima of the pressures on the structure are important to a designing
-
Song, Hailong; Cui, Jiankun; Simonyi, Agnes; Johnson, Catherine E; Hubler, Graham K; DePalma, Ralph G; Gu, Zezong
2018-03-15
Blast exposures are associated with traumatic brain injury (TBI) and blast-induced TBIs are common injuries affecting military personnel. Department of Defense and Veterans Administration (DoD/VA) reports for TBI indicated that the vast majority (82.3%) has been mild TBI (mTBI)/concussion. mTBI and associated posttraumatic stress disorders (PTSD) have been called "the invisible injury" of the current conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan. These injuries induce varying degrees of neuropathological alterations and, in some cases, chronic cognitive, behavioral and neurological disorders. Appropriate animal models of blast-induced TBI will not only assist the understanding of physical characteristics of the blast, but also help to address the potential mechanisms. This report provides a brief overview of physical principles of blast, injury mechanisms related to blast exposure, current blast animal models, and the neurological behavioral and neuropathological findings related to blast injury in experimental settings. We describe relationships between blast peak pressures and the observed injuries. We also report preliminary use of a highly reproducible and intensity-graded blast murine model carried out in open-field with explosives, and describe physical and pathological findings in this experimental model. Our results indicate close relationships between blast intensities and neuropathology and behavioral deficits, particularly at low level blast intensities relevant to mTBI. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
The coexistence of pressure waves in the operation of quartz-crystal shear-wave sensors
Reddy, SM; Jones, JP; Lewis, TJ
1998-01-01
It is demonstrated that an AT-cut quartz crystal driven in the thickness-shear-wave mode and typically used as a sensor to monitor the viscoelastic shear-wave properties of a fluid also produce longitudinal pressure waves. Unlike the shear wave, these waves are capable of long-range propagation through the fluid and of reflection at its boundaries, notably at an outer fluid–air interface. They introduce a component into the measured electrical impedance and resonance frequency shift of the cr...
-
Surface acoustic wave oxygen pressure sensor
Oglesby, Donald M. (Inventor); Upchurch, Billy T. (Inventor); Leighty, Bradley D. (Inventor)
1994-01-01
A transducer for the measurement of absolute gas-state oxygen pressure from pressures of less than 100 Pa to atmospheric pressure (1.01 x 10(exp 5) Pa) is based on a standard surface acoustic wave (SAW) device. The piezoelectric material of the SAW device is coated with a compound which will selectively and reversibly bind oxygen. When oxygen is bound by the coating, the mass of the coating increases by an amount equal to the mass of the bound oxygen. Such an increase in the mass of the coating causes a corresponding decrease in the resonant frequency of the SAW device.
-
On propagation of axisymmetric waves in pressurized functionally graded elastomeric hollow cylinders
Wu, Bin; Su, Yipin; Liu, Dongying; Chen, Weiqiu; Zhang, Chuanzeng
2018-05-01
Soft materials can be designed with a functionally graded (FG) property for specific applications. Such material inhomogeneity can also be found in many soft biological tissues whose functionality is only partly understood to date. In this paper, we analyze the axisymmetric guided wave propagation in a pressurized FG elastomeric hollow cylinder. The cylinder is subjected to a combined action of axial pre-stretch and pressure difference applied to the inner and outer cylindrical surfaces. We consider both torsional waves and longitudinal waves propagating in the FG cylinder made of incompressible isotropic elastomer, which is characterized by the Mooney-Rivlin strain energy function but with the material parameters varying with the radial coordinate in an affine way. The pressure difference generates an inhomogeneous deformation field in the FG cylinder, which dramatically complicates the superimposed wave problem described by the small-on-large theory. A particularly efficient approach is hence employed which combines the state-space formalism for the incremental wave motion with the approximate laminate or multi-layer technique. Dispersion relations for the two types of axisymmetric guided waves are then derived analytically. The accuracy and convergence of the proposed approach is validated numerically. The effects of the pressure difference, material gradient, and axial pre-stretch on both the torsional and the longitudinal wave propagation characteristics are discussed in detail through numerical examples. It is found that the frequency of axisymmetric waves depends nonlinearly on the pressure difference and the material gradient, and an increase in the material gradient enhances the capability of the pressure difference to adjust the wave behavior in the FG cylinder. This work provides a theoretical guidance for characterizing FG soft materials by in-situ ultrasonic nondestructive evaluation and for designing tunable waveguides via material tailoring along
-
Forced wave induced by an atmospheric pressure disturbance moving towards shore
Chen, Yixiang; Niu, Xiaojing
2018-05-01
Atmospheric pressure disturbances moving over a vast expanse of water can induce different wave patterns, which can be determined by the Froude number Fr. Generally, Fr = 1 is a critical value for the transformation of the wave pattern and the well-known Proudman resonance happens when Fr = 1. In this study, the forced wave induced by an atmospheric pressure disturbance moving over a constant slope from deep sea to shore is numerically investigated. The wave pattern evolves from a concentric-circle type into a triangular type with the increase of the Froude number, as the local water depth decreases, which is in accord with the analysis in the unbounded flat-bottom cases. However, a hysteresis effect has been observed, which implies the obvious amplification of the forced wave induced by a pressure disturbance can not be simply predicted by Fr = 1. The effects of the characteristic parameters of pressure disturbances and slope gradient have been discussed. The results show that it is not always possible to observe significant peak of the maximum water elevation before the landing of pressure disturbances, and a significant peak can be generated by a pressure disturbance with small spatial scale and fast moving velocity over a milder slope. Besides, an extremely high run-up occurs when the forced wave hits the shore, which is an essential threat to coastal security. The results also show that the maximum run-up is not monotonously varying with the increase of disturbance moving speed and spatial scale. There exists a most dangerous speed and scale which may cause disastrous nearshore surge.
-
THE EFFECTS OF AREA CONTRACTION ON SHOCK WAVE STRENGTH AND PEAK PRESSURE IN SHOCK TUBE
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
A. M. Mohsen
2012-06-01
Full Text Available This paper presents an experimental investigation into the effects of area contraction on shock wave strength and peak pressure in a shock tube. The shock tube is an important component of the short duration, high speed fluid flow test facility, available at the Universiti Tenaga Nasional (UNITEN, Malaysia. The area contraction was facilitated by positioning a bush adjacent to the primary diaphragm section, which separates the driver and driven sections. Experimental measurements were performed with and without the presence of the bush, at various diaphragm pressure ratios, which is the ratio of air pressure between the driver (high pressure and driven (low pressure sections. The instantaneous static pressure variations were measured at two locations close to the driven tube end wall, using high sensitivity pressure sensors, which allow the shock wave strength, shock wave speed and peak pressure to be analysed. The results reveal that the area contraction significantly reduces the shock wave strength, shock wave speed and peak pressure. At a diaphragm pressure ratio of 10, the shock wave strength decreases by 18%, the peak pressure decreases by 30% and the shock wave speed decreases by 8%.
-
Pressure waves in bubble, two-component, two-phase flows. Theoretical approach
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Micaelli, J.C.
1982-05-01
Common methods of modelling pressure waves (global or acoustic) and their inadequacy are described. A model is proposed, based on a stochastic treatment of the gaseous phase. Different mechanisms which affect pressure wave propagation are analysed. The importance of interfacial momentum and heat transfer is confirmed [fr
-
Electromagnetic Wave Attenuation in Atmospheric Pressure Plasma
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Zhang Shu; Hu Xiwei; Liu Minghai; Luo Fang; Feng Zelong
2007-01-01
When an electromagnetic (EM) wave propagates in an atmospheric pressure plasma (APP) layer, its attenuation depends on the APP parameters such as the layer width, the electron density and its profile and collision frequency between electrons and neutrals. This paper proposes that a combined parameter-the product of the line average electron density n-bar and width d of the APP layer (i.e., the total number of electrons in a unit volume along the wave propagation path) can play a more explicit and decisive role in the wave attenuation than any of the above individual parameters does. The attenuation of the EM wave via the product of n-bar and d with various collision frequencies between electrons and neutrals is presented
-
Investigation on seismic signals for blasting in quarries
Czech Academy of Sciences Publication Activity Database
Pandula, B.; Kondela, J.; Holub, Karel
2012-01-01
Roč. 19, č. 1 (2012), s. 41-59 ISSN 1803-1447 Institutional support: RVO:68145535 Keywords : blasting operations * seismic safety * seismic waves Subject RIV: DC - Siesmology, Volcanology, Earth Structure http://www.caag.cz/egrse/2012-1/04_pandula-r.pdf
-
Calculation of driling and blasting parameters in blasting performance
Dambov, Risto; Karanakova Stefanovska, Radmila; Dambov, Ilija
2015-01-01
In all mining technology drilling and blasting parameters and works are one of the main production processes at each mine. The parameters of drilling and blasting and explosives consumption per ton of blasting mass are define economic indicators of any blasting no matter for what purpose and where mining is performed. The calculation of rock blasting should always have in mind that the methodology of calculation of all drilling and blasting parameters in blasting performance are performed for...
-
LTC vacuum blasting machine (concrete): Baseline report
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
1997-01-01
The LTC shot blast technology was tested and is being evaluated at Florida International University (FIU) as a baseline technology. In conjunction with FIU's evaluation of efficiency and cost, this report covers the evaluation conducted for safety and health issues. It is a commercially available technology and has been used for various projects at locations throughout the country. The LTC 1073 Vacuum Blasting Machine uses a high-capacity, direct-pressure blasting system which incorporates a continuous feed for the blast media. The blast media cleans the surface within the contained brush area of the blast. It incorporates a vacuum system which removes dust and debris from the surface as it is blasted. The safety and health evaluation during the testing demonstration focused on two main areas of exposure: dust and noise. Dust exposure during maintenance activities was minimal, but due to mechanical difficulties dust monitoring could not be conducted during operation. Noise exposure was significant. Further testing for each of these exposures is recommended because of the outdoor environment where the testing demonstration took place. This may cause the results to be inaccurate. It is feasible that the dust and noise levels will be higher in an enclosed environment. In addition, other safety and health issues found were ergonomics, heat stress, tripping hazards, electrical hazards, lockout/tagout, and arm-hand vibration
-
Oscillations in the wake of a flare blast wave
Tothova, D.; Innes, D. E.; Stenborg, G.
2011-04-01
Context. Oscillations of coronal loops in the Sun have been reported in both imaging and spectral observations at the onset of flares. Images reveal transverse oscillations, whereas spectra detect line-of-sight velocity or Doppler-shift oscillations. The Doppler-shift oscillations are commonly interpreted as longitudinal modes. Aims: Our aim is to investigate the relationship between loop dynamics and flows seen in TRACE 195 Å images and Doppler shifts observed by SUMER in Si iii 1113.2 Å and FeXIX 1118.1 Å at the time of a C.8-class limb flare and an associated CME. Methods: We carefully co-aligned the sequence of TRACE 195 Å images to structures seen in the SUMER Si iii, CaX, and FeXIX emission lines. Additionally, Hα observations of a lifting prominence associated with the flare and the coronal mass ejection (CME) are available in three bands around 6563.3 Å. They give constraints on the timing and geometry. Results: Large-scale Doppler-shift oscillations in FeXIX and transverse oscillations in intensity images were observed over a large region of the corona after the passage of a wide bright extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) disturbance, which suggests ionization, heating, and acceleration of hot plasma in the wake of a blast wave. The online movie associated to Fig. 2 is available at http://www.aanda.org and at http://www.mps.mpg.de/data/outgoing/tothova/movie.gif
-
Chen, Wei; Wang, Jianmin; Chen, Jing; Chen, Jichuan; Chen, Zhiqiang
2013-01-01
The auditory system is the most susceptible to damages from blast waves. Blast injuries always lead to varying degrees of hearing impairment. Although a disorder of the cochlear blood flow (CoBF) has been considered to be related to many pathological processes of the auditory system and to contribute to various types of hearing loss, changes in the CoBF induced by blast waves and the relationship between such changes and hearing impairment are undefined. To observe the changes in the cochlear microcirculation after exposure to an explosion blast, investigate the relationship between changes in the CoBF and hearing impairment and subsequently explore the mechanism responsible for the changes in the CoBF, we detected the perfusion of the cochlear microcirculation and hearing threshold shift after exposure to an explosion blast. Then, an N-nitro-L-arginine-methyl ester (L-NAME, NO synthase inhibitor) solution and artificial perilymph were applied to the round window (RW) of the cochlea before the blast exposure, followed by an evaluation of the CoBF and hearing function. The results indicated that the changes in the CoBF were correlated to the strength of the blast wave. The cochlear blood flow significantly increased when the peak value of the blast overpressure was greater than approximately 45 kPa, and there was no significant change in the cochlear blood flow when the peak value of the blast overpressure was less than approximately 35 kPa. Following local administration of the NO synthase inhibitor L-NAME, the increase in the CoBF induced by the blast was inhibited, and this reduction was significantly associated with the hearing threshold.
-
Mataradze, Edgar; Chikhradze, Nikoloz; Bochorishvili, Nika; Akhvlediani, Irakli; Tatishvili, Dimitri
2017-12-01
Explosion protection technologies are based on the formation of a shock wave mitigation barrier between the protection site and the explosion site. Contemporary protective systems use water mist as an extinguishing barrier. To achieve high effectiveness of the protective system, proper selection of water mist characteristics is important. The main factors defining shock wave attenuation in water mist include droplet size distribution, water concentration in the mist, droplet velocity and geometric properties of mist. This paper examines the process of attenuation of shock waves in mist with droplets ranging from 25 to 400 microns under different conditions of water mist location. Experiments were conducted at the Mining Institute with the use of a shock tube to study the processes of explosion suppression by a water mist barrier. The shock tube consists of a blast chamber, a tube, a system for the dosed supply of water, sensors, data recording equipment, and a process control module. Shock wave overpressure reduction coefficient was studied in the shock tube under two different locations of water mist: a) when water mist is created in direct contact with blast chamber and b) the blast chamber and the mist are separated by air space. It is established that in conditions when the air space distance between the blast chamber and the mist is 1 meter, overpressure reduction coefficient is 1.5-1.6 times higher than in conditions when water mist is created in direct contact with blast chamber.
-
Acoustic Pressure Waves in Vibrating 3-D Laminated Beam-Plate Enclosures
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Charles A. Osheku
2009-01-01
Full Text Available The effect of structural vibration on the propagation of acoustic pressure waves through a cantilevered 3-D laminated beam-plate enclosure is investigated analytically. For this problem, a set of well-posed partial differential equations governing the vibroacoustic wave interaction phenomenon are formulated and matched for the various vibrating boundary surfaces. By employing integral transforms, a closed form analytical expression is computed suitable for vibroacoustic modeling, design analysis, and general aerospace defensive applications. The closed-form expression takes the form of a kernel of polynomials for acoustic pressure waves showing the influence of linear interface pressure variation across the axes of vibrating boundary surfaces. Simulated results demonstrate how the mode shapes and the associated natural frequencies can be easily computed. It is shown in this paper that acoustic pressure waves propagation are dynamically stable through laminated enclosures with progressive decrement in interfacial pressure distribution under the influence of high excitation frequencies irrespective of whether the induced flow is subsonic, sonic , supersonic, or hypersonic. Hence, in practice, dynamic stability of hypersonic aircrafts or jet airplanes can be further enhanced by replacing their noise transmission systems with laminated enclosures.
-
Ignition systems and blasting accessories; L'amorcage et les accessoires de tir
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Du Mouza, J. [Ecole Nationale Superieure des Mines, 75 - Paris (France); Monnery, J. [SFEPA, 92 - Puteaux (France); Vuillaume, P. [Institut National de l' Environnement Industriel et des Risques, 60 - Verneuil en Halatte (INERIS) (France); Cervellera, St. [Titanite SA, 21 - Pontailler sur Saone (France); Houeix, T.
2002-03-01
1. General: Blasting caps or detonators are the main elements of the pyrotechnical sequence. They should be reliable in order to guaranty the quality, the safety and the energy liberated by the explosive. They transmit to the explosive the minimum required energy to initiate the detonation. The pyrotechnical sequence comprises a mechanical or electrical device, the blasting cap able to produce a shock or a spark initiating the explosion directly or through a primary explosive more sensible than the main one. 2. Initiation systems: Various types of systems are described determining the way the shock wave is propagated within the explosive. Initiation may be made punctually, by means of a detonator or laterally by means of a cord. Detonators may be operated electrically, non-electrically or electronically. Special devices allow for the retardation of the initiation. 3. Retardation reliability and accuracy: Some points about the consequences of dispersions in lengths of retardation of detonators such as the possible overlapping of explosive loads and combination of vibration trains in the environment are discussed. A smaller dispersion offered by electronic detonators, which are by far the most frequently used, should be able to overcome these difficulties. 4. Impact of the initiation on the explosive yield: The way the ignition is performed has a direct consequence on the yield of the explosive. When a primer explosive is utilised as a booster, various factors (weight, position and diameter) play an important role on the detonation pressure and speed. A chart indicates the explosive energy liberated depending on the way ignition is performed. 5. Blasting accessories: Dynamos were largely used in the past to generate the electric current required to actuate blasting caps. Now this electric current is generated by the discharge of capacitors associated with electronic devices to control the blasting sequence. Ohmmeters are also used to check the electric circuits
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Chen, J. H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Y. G.; Zhong, C.
2015-01-01
The particle production of Kaon and Λ is studied in nucleus-nucleus collisions at relativistic energy based on a chemical equilibrium blast-wave model. The transverse momentum spectra of Kaon and Λ at the kinetic freeze-out stage from our model are in good agreement with the experimental results. The kinetic freeze-out parameters of temperature (T kin ) and radial flow parameter ρ 0 are presented for the FOPI, RHIC, and LHC energies. And the resonance decay effect is also discussed. The systematic study for beam energy dependence of the strangeness particle production will help us to better understand the properties of the matter created in heavy-ion collisions at the kinetic freeze-out stage
-
Sachdev, PL
2004-01-01
Understanding the causes and effects of explosions is important to experts in a broad range of disciplines, including the military, industrial and environmental research, aeronautic engineering, and applied mathematics. Offering an introductory review of historic research, Shock Waves and Explosions brings analytic and computational methods to a wide audience in a clear and thorough way. Beginning with an overview of the research on combustion and gas dynamics in the 1970s and 1980s, the author brings you up to date by covering modeling techniques and asymptotic and perturbative methods and ending with a chapter on computational methods.Most of the book deals with the mathematical analysis of explosions, but computational results are also included wherever they are available. Historical perspectives are provided on the advent of nonlinear science, as well as on the mathematical study of the blast wave phenomenon, both when visualized as a point explosion and when simulated as the expansion of a high-pressure ...
-
Lv, Dongwei; Zhang, Jian; Yu, Xinhai
2018-05-01
In this paper, a fluid-structure interaction dynamic simulation method of spring-loaded pressure relief valve was established. The dynamic performances of the fluid regions and the stress and strain of the structure regions were calculated at the same time by accurately setting up the contact pairs between the solid parts and the coupling surfaces between the fluid regions and the structure regions. A two way fluid-structure interaction dynamic simulation of a simplified pressure relief valve model was carried out. The influence of vertical sinusoidal seismic waves on the performance of the pressure relief valve was preliminarily investigated by loading sine waves. Under vertical seismic waves, the pressure relief valve will flutter, and the reseating pressure was affected by the amplitude and frequency of the seismic waves. This simulation method of the pressure relief valve under vertical seismic waves can provide effective means for investigating the seismic performances of the valves, and make up for the shortcomings of the experiment.
-
Radio controlled detonators and sequential real time blast applications
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Bernard, T.; Laboz, J.M. [Delta Caps International, Nice (France)
1995-12-31
Among the numerous technical evolutions in the blasting environment the authors are going to describe below the concept of electronic detonator sequenced by radio waves, and also its numerous applications. Three major technologies are used in the initiation environment: fused-initiated detonators; electric detonators; and non-electric detonators. The last two technologies were made available under multiple variants. Two major innovations are going to substantially change the way traditional detonators operate: pyrotechnic delays are replaced by electronic delays (greater accuracy); and triggering orders, passing through a cable, is now replaced by radio-waves transmission (possibility to do real time delay pattern). Such a new product provided all the features offered by current detonators, but also allows mastering specific cases that were difficult to control with the current technology, such as: vibration control; underground blast; and building demolition.
-
Myocardial preload alters central pressure augmentation through changes in the forward wave
van de Velde, Lennart; Eeftinck Schattenkerk, Daan W.; Venema, Pascale A. H. T.; Best, Hendrik J.; van den Bogaard, Bas; Stok, Wim J.; Westerhof, Berend E.; van den Born, Bert Jan H.
2018-01-01
Augmentation index (AIx) is often used to quantify the contribution of wave reflection to central pulse pressure. Recent studies have challenged this view by showing how contractility-induced changes in the forward pressure wave can markedly impact AIx. We hypothesized that changes in preload will
-
Myocardial preload alters central pressure augmentation through changes in the forward wave
Van De Velde, Lennart; Eeftinck Schattenkerk, Daan W.; Venema, Pascale A.H.T.; Best, Hendrik J.; Van Den Bogaard, Bas; Stok, Wim J.; Westerhof, Berend E.; Van Den Born, Bert Jan H.
2018-01-01
Objective: Augmentation index (AIx) is often used to quantify the contribution of wave reflection to central pulse pressure. Recent studies have challenged this view by showing how contractility-induced changes in the forward pressure wave can markedly impact AIx. We hypothesized that changes in
-
Blast wave protection of aqueous foams
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Britan, Alexander; Ben-Dor, M. Liverts G. [Shock tube Laboratory of Protective Technologies R and D Center, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering Sciences, Ben Gurion University, Beer-Sheva (Israel)
2011-07-01
The primary intention of the present study is to present new contribution of shock tube tests to the problem of particle related stabilization and enhanced mitigation action of the wet particulate foams. The experiments reported were designed to examine (i) the reflection of a shock wave from an air/foam face, (ii) the transmission of the shock wave through the air/foam face and (iii) propagation and dispersion of the transmitted shock wave inside the foam column. Because wet aqueous foam of desired specification is difficult to reproduce, handle and quantitatively characterize the fact that experiments on all the above aspects were conducted in a single facility is a potentially important consideration. Moreover vertical position of shock tube simplified the issues since the gradient of the liquid fraction in draining foam coincides with the shock wave propagation. Under these, much simplified test conditions resulted flows could be treated as one-dimensional and the shock wave mitigation depends on three parameters: the intensity of the incident shock wave, s M , the duration of the foam decay, ∆t and on the particle concentration, n.
-
Time-resolved wave profile measurements in copper to Megabar pressures
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Chhabildas, L C; Asay, J R
1981-01-01
Many time-resolved techniques have been developed which have greatly aided in the understanding of dynamic material behavior such as the high pressure-dynamic strength of materials. In the paper, time-resolved measurements of copper (at shock-induced high pressures and temperatures) are used to illustrate the capability of using such techniques to investigate high pressure strength. Continuous shock loading and release wave profiles have been made in copper to 93 GPa using velocity interferometric techniques. Fine structure in the release wave profiles from the shocked state indicates an increase in shear strength of copper to 1.5 GPa at 93 GPa from its ambient value of 0.08 GPa.
-
Remote operated vehicle with carbon dioxide blasting (ROVCO2)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Resnick, A.M.
1995-01-01
The Remote Operated Vehicle with Carbon Dioxide Blasting (ROVCO 2 ), as shown in a front view, is a six-wheeled remote land vehicle used to decontaminate concrete floors. The remote vehicle has a high pressure Cryogenesis blasting subsystem, Oceaneering Technologies (OTECH) developed a CO 2 xY Orthogonal Translational End Effector (COYOTEE) subsystem, and a vacuum/filtration and containment subsystem. Figure 2 shows a block diagram with the various subsystems labeled
-
Study of the action of blast deck charge in rocky soils
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Boiko V.V.
2017-04-01
Full Text Available Blasting (B in the industry, including the mining extraction of minerals, are carried out mostly with the use of blasthole charges that systematically distributed on the block that is undermined, by individual groups. The latter are blasted according to the scheme of short-delay firing (SDF through the intervals that are accepted not less than 20 Ms. Thus, the seismic effect of group charge explosion, consisting of individual blasthole charges and that actually is a group located charge determined by the formula of concentrated charge. Blast deck charges are effectively used in the driving of the trenches in the mining, formation of screens and cracks near the security objects. Only this method of performing blasting allows to define seismic effect in the transition from one diameter of a charge to another, as well as to determine the actual number of detonated charges in one group, which may differ from the calculated in drilling and blasting project. The work analyzes the physical essence of processes happened while blasting of blast deck charges. The effect of the orientation of the seismic action of blasting of blast deck charges towards the allocation line of charges is investigated. The results of generalized dependence of the speed of the displacement of the ground by the blast parameters and epicentral distance are obtained. We demonstrate with specific examples that blast deck charges that blasting simultaneously make a major chain of the career massive explosions at mining. Keywords: seismic fluctuations; the number of charges; the interaction of charges; the distance between the charges; the coefficients of the seismicity and the attenuation of the intensity of the waves; the unit charge; blast deck and blasthole charges; phase shifting; effective charge.
-
Spectrum of abdominal organ injury in a primary blast type
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Amin Abid
2009-12-01
Full Text Available Abstract Introduction Abdominal organ injury in a primary blast type is always challenging for diagnosis. Air containing abdominal viscera is most vulnerable to effects of primary blast injury. In any patient exposed to a primary blast wave who presents with an acute abdomen, an abdominal organ injury is to be kept in a clinical suspicion. Aim Study various abdominal organ injuries occurring in a primary type of blast injury. Material and methods: All those who had exploratory laparotomy for abdominal organ injuries after a primary blast injury for a period of 10 years from January 1998 - January 2008 were included in this retrospective study. Results Total 154 patients had laparotomy for abdominal organ injuries with a primary blast type of injury. Small intestine was damaged in 48 patients (31.1% followed by spleen in 22.7% cases. 54 patients (35.06% had more than one organ injured. Liver laceration was present in 30 patients (19.48%. Multiple small gut perforations were present in 37 patients (77.08%. Negative laparotomy was found in 5 patients (3.24% whereas 3 (1.94% had re-exploration. Mortality was present in 6 patients (3.89%. Conclusions Primary blast injury causes varied abdominal organ injuries. Single or multiple organ damage can be there. Small intestine is commonest viscera injured. Laparotomy gives final diagnosis.
-
Experimental methods of shock wave research
Seiler, Friedrich
2016-01-01
This comprehensive and carefully edited volume presents a variety of experimental methods used in Shock Waves research. In 14 self contained chapters this 9th volume of the “Shock Wave Science and Technology Reference Library” presents the experimental methods used in Shock Tubes, Shock Tunnels and Expansion Tubes facilities. Also described is their set-up and operation. The uses of an arc heated wind tunnel and a gun tunnel are also contained in this volume. Whenever possible, in addition to the technical description some typical scientific results obtained using such facilities are described. Additionally, this authoritative book includes techniques for measuring physical properties of blast waves and laser generated shock waves. Information about active shock wave laboratories at different locations around the world that are not described in the chapters herein is given in the Appendix, making this book useful for every researcher involved in shock/blast wave phenomena.
-
Interaction of EM Waves with Atmospheric Pressure Plasmas
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Laroussi, Mounir
2000-01-01
.... The focus of the main activities is the generation of large volume, non-thermal, atmospheric pressure plasmas, their diagnostics, and their interactions with EM waves and with the cells of microorganism...
-
Variation of Pressure Waveforms in Measurements of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripter
Inose, Naoto; Ide, Masao
1993-05-01
In this paper, we describe measurement of variation in pressure waveforms of the acoustic field of an extra-corporeal shock-wave lithotripter (ESWL). Variations in the measured acoustic fields and pressure waveform of an underwater spark-gap-type ESWL with an exhausted spark plug electrode have been reported by researchers using crystal sensors. If the ESWL spark plugs become exhausted, patients feel pain during kidney, biliary stone disintegration. We studied the relationship between exhaustion of electrodes and the variation of pressure waveforms and shock-wave fields of the ESWL using a newly developed hydrophone.
-
Modeling and simulations of radiative blast wave driven Rayleigh-Taylor instability experiments
Shimony, Assaf; Huntington, Channing M.; Trantham, Matthew; Malamud, Guy; Elbaz, Yonatan; Kuranz, Carolyn C.; Drake, R. Paul; Shvarts, Dov
2017-10-01
Recent experiments at the National Ignition Facility measured the growth of Rayleigh-Taylor RT instabilities driven by radiative blast waves, relevant to astrophysics and other HEDP systems. We constructed a new Buoyancy-Drag (BD) model, which accounts for the ablation effect on both bubble and spike. This ablation effect is accounted for by using the potential flow model ]Oron et al PoP 1998], adding another term to the classical BD formalism: βDuA / u , where β the Takabe constant, D the drag term, uA the ablation velocity and uthe instability growth velocity. The model results are compared with the results of experiments and 2D simulations using the CRASH code, with nominal radiation or reduced foam opacity (by a factor of 1000). The ablation constant of the model, βb / s, for the bubble and for the spike fronts, are calibrated using the results of the radiative shock experiments. This work is funded by the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under subcontract B614207, and was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC52-07NA27344.
-
Belousov, Alexander; Voight, Barry; Belousova, Marina
2007-01-01
We compare eruptive dynamics, effects and deposits of the Bezymianny 1956 (BZ), Mount St Helens 1980 (MSH), and Soufrière Hills volcano, Montserrat 1997 (SHV) eruptions, the key events of which included powerful directed blasts. Each blast subsequently generated a high-energy stratified pyroclastic density current (PDC) with a high speed at onset. The blasts were triggered by rapid unloading of an extruding or intruding shallow magma body (lava dome and/or cryptodome) of andesitic or dacitic composition. The unloading was caused by sector failures of the volcanic edifices, with respective volumes for BZ, MSH, and SHV c. 0.5, 2.5, and 0.05 km3 . The blasts devastated approximately elliptical areas, axial directions of which coincided with the directions of sector failures. We separate the transient directed blast phenomenon into three main parts, the burst phase, the collapse phase, and the PDC phase. In the burst phase the pressurized mixture is driven by initial kinetic energy and expands rapidly into the atmosphere, with much of the expansion having an initially lateral component. The erupted material fails to mix with sufficient air to form a buoyant column, but in the collapse phase, falls beyond the source as an inclined fountain, and thereafter generates a PDC moving parallel to the ground surface. It is possible for the burst phase to comprise an overpressured jet, which requires injection of momentum from an orifice; however some exploding sources may have different geometry and a jet is not necessarily formed. A major unresolved question is whether the preponderance of strong damage observed in the volcanic blasts should be attributed to shock waves within an overpressured jet, or alternatively to dynamic pressures and shocks within the energetic collapse and PDC phases. Internal shock structures related to unsteady flow and compressibility effects can occur in each phase. We withhold judgment about published shock models as a primary explanation for the
-
Blast Load Response of Steel Sandwich Panels with Liquid Encasement
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Dale Karr; Marc Perlin; Benjamin Langhorst; Henry Chu
2009-10-01
We describe an experimental investigation of the response of hybrid blast panels for protection from explosive and impact forces. The fundamental notion is to dissipate, absorb, and redirect energy through plastic collapse, viscous dissipation, and inter-particle forces of liquid placed in sub-structural compartments. The panels are designed to absorb energy from an impact or air blast by elastic-plastic collapse of the panel substructure that includes fluid-filled cavities. The fluid contributes to blast effects mitigation by providing increased initial mass and resistance, by dissipation of energy through viscosity and fluid flow, and by redirecting the momentum that is imparted to the system from the impact and blast impulse pressures. Failure and deformation mechanisms of the panels are described.
-
Experimental Study on Peak Pressure of Shock Waves in Quasi-Shallow Water
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zhenxiong Wang
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Based on the similarity laws of the explosion, this research develops similarity requirements of the small-scale experiments of underwater explosions and establishes a regression model for peak pressure of underwater shock waves under experimental condition. Small-scale experiments are carried out with two types of media at the bottom of the water and for different water depths. The peak pressure of underwater shock waves at different measuring points is acquired. A formula consistent with the similarity law of explosions is obtained and an analysis of the regression precision of the formula confirms its accuracy. Significance experiment indicates that the influence of distance between measuring points and charge on peak pressure of underwater shock wave is the greatest and that of water depth is the least within the range of geometric parameters. An analysis of data from experiments with different media at the bottom of the water reveals an influence on the peak pressure, as the peak pressure of a shock wave in a body of water with a bottom soft mud and rocks is about 1.33 times that of the case where the bottom material is only soft mud.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Scott A Heldt
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Emotional disorders are a common outcome from mild traumatic brain injury (TBI in humans, but their pathophysiological basis is poorly understood. We have developed a mouse model of closed-head blast injury using an air pressure wave delivered to a small area on one side of the cranium, which we have used to create mild TBI. We found that 20-psi blasts in 3-month old C57BL/6 male mice yielded no obvious behavioral or histological evidence of brain injury, while 25-40 psi blasts produced transient anxiety in an open field arena but little histological evidence of brain damage. By contrast, 50-60 psi blasts resulted in anxiety-like behavior in an open field arena that became more evident with time after blast. In additional behavioral tests conducted 2-8 weeks after blast, 50-60 psi mice also demonstrated increased acoustic startle, perseverance of learned fear, and enhanced contextual fear, as well as depression-like behavior and diminished prepulse inhibition. We found no evident cerebral pathology, however, and only scattered axonal degeneration in brain sections from 50-60 psi mice 3-8 weeks after blast. Thus, the TBI caused by single 50-60 psi blasts in mice exhibits the minimal neuronal loss coupled to diffuse axonal injury characteristic of human mild TBI. A reduction in the abundance of a subpopulation of excitatory projection neurons in basolateral amygdala enriched in Thy1 was, however, observed. The reported link of this neuronal population to fear suppression suggests their damage by mild TBI may contribute to the heightened anxiety and fearfulness observed after blast in our mice. Our overpressure air blast model of concussion in mice will enable further studies of the mechanisms underlying the diverse emotional deficits seen after mild TBI.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Han, L-L; Tsung, T-T; Chen, L-C; Chang Ho; Jwo, C-S
2005-01-01
Piezoelectric pressure sensors are commonly used to measuring the dynamic characteristics in a hydraulic system. The dynamic measurements require a pressure sensor which has a high response rate. In this paper, we proposed use of a pressure square wave to excite the piezoelectric pressure sensor. Experimental frequencies are 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 kHz at 10, 15, 20 bar, respectively. Results show that the waveform of time-domain and frequencydomain response are quite different under above testing conditions. The higher the frequencies tested, the faster the pressure-rise speeds obtained. Similarly, the higher the testing pressure, the shorter the rise time attained
-
Analysis of MINIE2013 Explosion Air-Blast Data
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Schnurr, Julie M. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Univ. of Hawaii, Manoa, HI (United States); Rodgers, Arthur J. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Kim, Keehoon [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Ford, Sean R. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Ramirez, Abelardo L. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
2016-10-14
We report analysis of air-blast overpressure measurements from the MINIE2013 explosive experiments. The MINIE2013 experiment involved a series of nearly 70 near-surface (height-ofburst, HOB, ranging from -1 to +4 m) low-yield (W=2-20 kg TNT equivalent) chemical highexplosives tests that were recorded at local distances (230 m – 28.5 km). Many of the W and HOB combinations were repeated, allowing for quantification of the variability in air-blast features and corresponding yield estimates. We measured canonical signal features (peak overpressure, impulse per unit area, and positive pulse duration) from the air-blast data and compared these to existing air-blast models. Peak overpressure measurements showed good agreement with the models at close ranges but tended to attenuate more rapidly at longer range (~ 1 km), which is likely caused by upward refraction of acoustic waves due to a negative vertical gradient of sound speed. We estimated yields of the MINIE2013 explosions using the Integrated Yield Determination Tool (IYDT). Errors of the estimated yields were on average within 30% of the reported yields, and there were no significant differences in the accuracy of the IYDT predictions grouped by yield. IYDT estimates tend to be lower than ground truth yields, possibly because of reduced overpressure amplitudes by upward refraction. Finally, we report preliminary results on a development of a new parameterized air-blast waveform.
-
Models of brachial to finger pulse wave distortion and pressure decrement.
Gizdulich, P; Prentza, A; Wesseling, K H
1997-03-01
To model the pulse wave distortion and pressure decrement occurring between brachial and finger arteries. Distortion reversion and decrement correction were also our aims. Brachial artery pressure was recorded intra-arterially and finger pressure was recorded non-invasively by the Finapres technique in 53 adult human subjects. Mean pressure was subtracted from each pressure waveform and Fourier analysis applied to the pulsations. A distortion model was estimated for each subject and averaged over the group. The average inverse model was applied to the full finger pressure waveform. The pressure decrement was modelled by multiple regression on finger systolic and diastolic levels. Waveform distortion could be described by a general, frequency dependent model having a resonance at 7.3 Hz. The general inverse model has an anti-resonance at this frequency. It converts finger to brachial pulsations thereby reducing average waveform distortion from 9.7 (s.d. 3.2) mmHg per sample for the finger pulse to 3.7 (1.7) mmHg for the converted pulse. Systolic and diastolic level differences between finger and brachial arterial pressures changed from -4 (15) and -8 (11) to +8 (14) and +8 (12) mmHg, respectively, after inverse modelling, with pulse pressures correct on average. The pressure decrement model reduced both the mean and the standard deviation of systolic and diastolic level differences to 0 (13) and 0 (8) mmHg. Diastolic differences were thus reduced most. Brachial to finger pulse wave distortion due to wave reflection in arteries is almost identical in all subjects and can be modelled by a single resonance. The pressure decrement due to flow in arteries is greatest for high pulse pressures superimposed on low means.
-
Models of brachial to finger pulse wave distortion and pressure decrement
Gizdulich, P.; Prentza, A.; Wesseling, K.H.
1997-01-01
Objective: To model the pulse wave distortion and pressure decrement occurring between brachial and finger arteries. Distortion reversion and decrement correction were also our aims. Methods: Brachial artery pressure was recorded intra-arterially and finger pressure was recorded non-invasively by
-
Magnetosheath waves under very low solar wind dynamic pressure: Wind/Geotail observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. J. Farrugia
2005-06-01
Full Text Available The expanded bow shock on and around "the day the solar wind almost disappeared" (11 May 1999 allowed the Geotail spacecraft to make a practically uninterrupted 54-h-long magnetosheath pass near dusk (16:30-21:11 magnetic local time at a radial distance of 24 to 30 RE (Earth radii. During most of this period, interplanetary parameters varied gradually and in such a way as to give rise to two extreme magnetosheath structures, one dominated by magnetohydrodynamic (MHD effects and the other by gas dynamic effects. We focus attention on unusual features of electromagnetic ion wave activity in the former magnetosheath state, and compare these features with those in the latter. Magnetic fluctuations in the gas dynamic magnetosheath were dominated by compressional mirror mode waves, and left- and right-hand polarized electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EIC waves transverse to the background field. In contrast, the MHD magnetosheath, lasting for over one day, was devoid of mirror oscillations and permeated instead by EIC waves of weak intensity. The weak wave intensity is related to the prevailing low solar wind dynamic pressures. Left-hand polarized EIC waves were replaced by bursts of right-hand polarized waves, which remained for many hours the only ion wave activity present. This activity occurred when the magnetosheath proton temperature anisotropy (= became negative. This was because the weakened bow shock exposed the magnetosheath directly to the (negative temperature anisotropy of the solar wind. Unlike the normal case studied in the literature, these right-hand waves were not by-products of left-hand polarized waves but derived their energy source directly from the magnetosheath temperature anisotropy. Brief entries into the low latitude boundary layer (LLBL and duskside magnetosphere occurred under such inflated conditions that the magnetospheric magnetic pressure was insufficient to maintain pressure balance. In these crossings, the inner edge of
-
SIMULATION OF NEGATIVE PRESSURE WAVE PROPAGATION IN WATER PIPE NETWORK
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Tang Van Lam
2017-11-01
Full Text Available Subject: factors such as pipe wall roughness, mechanical properties of pipe materials, physical properties of water affect the pressure surge in the water supply pipes. These factors make it difficult to analyze the transient problem of pressure evolution using simple programming language, especially in the studies that consider only the magnitude of the positive pressure surge with the negative pressure phase being neglected. Research objectives: determine the magnitude of the negative pressure in the pipes on the experimental model. The propagation distance of the negative pressure wave will be simulated by the valve closure scenarios with the help of the HAMMER software and it is compared with an experimental model to verify the quality the results. Materials and methods: academic version of the Bentley HAMMER software is used to simulate the pressure surge wave propagation due to closure of the valve in water supply pipe network. The method of characteristics is used to solve the governing equations of transient process of pressure change in the pipeline. This method is implemented in the HAMMER software to calculate the pressure surge value in the pipes. Results: the method has been applied for water pipe networks of experimental model, the results show the affected area of negative pressure wave from valve closure and thereby we assess the largest negative pressure that may appear in water supply pipes. Conclusions: the experiment simulates the water pipe network with a consumption node for various valve closure scenarios to determine possibility of appearance of maximum negative pressure value in the pipes. Determination of these values in real-life network is relatively costly and time-consuming but nevertheless necessary for identification of the risk of pipe failure, and therefore, this paper proposes using the simulation model by the HAMMER software. Initial calibration of the model combined with the software simulation results and
-
Effect of pressurization on helical guided wave energy velocity in fluid-filled pipes.
Dubuc, Brennan; Ebrahimkhanlou, Arvin; Salamone, Salvatore
2017-03-01
The effect of pressurization stresses on helical guided waves in a thin-walled fluid-filled pipe is studied by modeling leaky Lamb waves in a stressed plate bordered by fluid. Fluid pressurization produces hoop and longitudinal stresses in a thin-walled pipe, which corresponds to biaxial in-plane stress in a plate waveguide model. The effect of stress on guided wave propagation is accounted for through nonlinear elasticity and finite deformation theory. Emphasis is placed on the stress dependence of the energy velocity of the guided wave modes. For this purpose, an expression for the energy velocity of leaky Lamb waves in a stressed plate is derived. Theoretical results are presented for the mode, frequency, and directional dependent variations in energy velocity with respect to stress. An experimental setup is designed for measuring variations in helical wave energy velocity in a thin-walled water-filled steel pipe at different levels of pressure. Good agreement is achieved between the experimental variations in energy velocity for the helical guided waves and the theoretical leaky Lamb wave solutions. Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Numerical Simulation of Blast Action on Civil Structures in Urban Environment
Valger, Svetlana A.; Fedorova, Natalya N.; Fedorov, Alexander V.
2017-10-01
Nowadays, a lot of industrial accidents accompanied by explosions are happening throughout the world. Also, increase in the number of terrorist acts committed by means of explosions is observed. For improving safety of buildings and structures it is necessary to raise their resistance to explosive effects, as well as to be able to predict degree of potential damage upon explosive loads of various intensities. One of the principal goals in designing the structure resistant to explosive effects is to determine the dynamic response of structures to the impact of the blast wave. To this end, the transient pressure loads on the walls of the civil engineering structures are to be determined. The simulation of explosion is highly complicated, involving an explosion causing the shock wave propagation in air and then interaction with a structure. The engineering-level techniques permit one to estimate an explosive shock impact only for isolated buildings. The complexity of the building, the presence of nearby structures and the surrounding environment cannot be taken into account. Advanced computer aid engineering (CAE) software techniques combined with the latest methods of discrete three-dimensional city modelling permits one to simulate and analyse the effects of explosions in urban areas with a precision which previously was not possible. In the paper, the simulation results are presented of shock wave forming due to a spherical explosive charge and its propagation in the vicinity of geometrical configuration imitating an urban environment. The numerical simulation of a flow in the vicinity of prisms of different cross-sections and heights located on a flat plate was performed. The calculations are carried out in a three-dimensional non-viscous formulation using ANSYS software. On a basis of simulation results, a complex wave structures were analysed, and all the peculiarities of flows and pressure history records on building walls were described and explained. The
-
CMOS-compatible ruggedized high-temperature Lamb wave pressure sensor
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kropelnicki, P; Mu, X J; Randles, A B; Cai, H; Ang, W C; Tsai, J M; Muckensturm, K-M; Vogt, H
2013-01-01
This paper describes the development of a novel ruggedized high-temperature pressure sensor operating in lateral field exited (LFE) Lamb wave mode. The comb-like structure electrodes on top of aluminum nitride (AlN) were used to generate the wave. A membrane was fabricated on SOI wafer with a 10 µm thick device layer. The sensor chip was mounted on a pressure test package and pressure was applied to the backside of the membrane, with a range of 20–100 psi. The temperature coefficient of frequency (TCF) was experimentally measured in the temperature range of −50 °C to 300 °C. By using the modified Butterworth–van Dyke model, coupling coefficients and quality factor were extracted. Temperature-dependent Young's modulus of composite structure was determined using resonance frequency and sensor interdigital transducer (IDT) wavelength which is mainly dominated by an AlN layer. Absolute sensor phase noise was measured at resonance to estimate the sensor pressure and temperature sensitivity. This paper demonstrates an AlN-based pressure sensor which can operate in harsh environment such as oil and gas exploration, automobile and aeronautic applications. (paper)
-
Remote operated vehicle with carbon dioxide blasting (ROVCO{sub 2})
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Resnick, A.M. [Oceaneering International, Inc., Upper Marlboro, MD (United States)
1995-10-01
The Remote Operated Vehicle with Carbon Dioxide Blasting (ROVCO{sub 2}), as shown in a front view is a six-wheeled remote land vehicle used to decontaminate concrete floors. The remote vehicle has a high pressure Cryogenesis blasting subsystem, Oceaneering Technologies (OTECH) developed a CO{sub 2} xY Orthogonal Translational End Effector (COYOTEE) subsystem, and a vacuum/filtration and containment subsystem. The cryogenesis subsystem performs the actual decontamination work and consists of the dry ice supply unit, the blasting nozzle, the remotely controlled electric and pneumatic valves, and the vacuum work-head. The COYOTEE subsystem positions the blasting work-head within a planar work space and the vacuum subsystem provides filtration and containment of the debris generated by the CO{sub 2} blasting. It employs a High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filtration unit to separate contaminants for disposal. All of the above systems are attached to the vehicle subsystem via the support structure.
-
Small-scale tunnel test for blast performance
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Felts, J E; Lee, R J
2014-01-01
The data reported here provide a validation of a small-scale tunnel test as a tool to guide the optimization of new explosives for blast performance in tunnels. The small-scale arrangement consisted of a 2-g booster and 10-g sample mounted at the closed end of a 127 mm diameter by 4.6-m long steel tube with pressure transducers along its length. The three performance characteristics considered were peak pressure, initial energy release, and impulse. The relative performance from five explosives was compared to that from a 1.16-m diameter by 30-m long tunnel that used 2.27-kg samples. The peak pressure values didn't correlate between the tunnels. Partial impulse for the explosives did rank similarly. The initial energy release was determined from a one-dimensional point-source analysis, which nearly tracked with impulse suggesting additional energy released further down the tunnel for some explosives. This test is a viable tool for optimizing compositional variations for blast performance in target scenarios of similar geometry.
-
Transcriptional Changes in the Mouse Retina after Ocular Blast Injury: A Role for the Immune System.
Struebing, Felix L; King, Rebecca; Li, Ying; Chrenek, Micah A; Lyuboslavsky, Polina N; Sidhu, Curran S; Iuvone, P Michael; Geisert, Eldon E
2018-01-01
Ocular blast injury is a major medical concern for soldiers and explosion victims due to poor visual outcomes. To define the changes in gene expression following a blast injury to the eye, we examined retinal ribonucleic acid (RNA) expression in 54 mouse strains 5 days after a single 50-psi overpressure air wave blast injury. We observe that almost 40% of genes are differentially expressed with a false discovery rate (FDR) of immune system are activated. Accompanied by lymphocyte invasion into the inner retina, blast injury also results in progressive loss of visual function and retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). Collectively, these data demonstrate how systems genetics can be used to put meaning to the transcriptome changes following ocular blast injury that eventually lead to blindness.
-
Blasting Damage Predictions by Numerical Modeling in Siahbishe Pumped Storage Powerhouse
Eslami, Majid; Goshtasbi, Kamran
2018-04-01
One of the popular methods of underground and surface excavations is the use of blasting. Throughout this method of excavation, the loading resulted from blasting can be affected by different geo-mechanical and structural parameters of rock mass. Several factors affect turbulence in underground structures some of which are explosion, vibration, and stress impulses caused by the neighbouring blasting products. In investigating the blasting mechanism one should address the processes which expand with time and cause seismic events. To protect the adjoining structures against any probable deconstruction or damage, it is very important to model the blasting process prior to any actual operation. Efforts have been taken in the present study to demonstrate the potentiality of numerical methods in predicting the specified parameters in order to prevent any probable destruction. For this purpose the blasting process was modeled, according to its natural implementation, in one of the tunnels of Siahbishe dam by the 3DEC and AUTODYN 3D codes. 3DEC was used for modeling the blasting environment as well as the blast holes and AUTODYN 3D for modeling the explosion process in the blast hole. In this process the output of AUTODYN 3D, which is a result of modeling the blast hole and is in the form of stress waves, is entered into 3DEC. For analyzing the amount of destruction made by the blasting operation, the key parameter of Peak Particle Velocity was used. In the end, the numerical modeling results have been compared with the data recorded by the seismographs planted through the tunnel. As the results indicated 3DEC and AUTODYN 3D proved appropriate for analyzing such an issue. Therefore, by means of these two softwares one can analyze explosion processes prior to their implementation and make close estimation of the damage resulting from these processes.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Dong, S.N.; Wu, L.; Paterson, N.; Herod, A.A.; Dugwell, D.R.; Kandiyoti, R. [University of London Imperial College of Science & Technology, London (United Kingdom). Dept. of Chemical Engineering
2005-07-01
The aim of the work was to investigate the fate of injectant coal in blast furnaces and the origin of extractable materials in blast furnace carryover dusts. Two sets of samples including injectant coal and the corresponding carryover dusts from a full sized blast furnace and a pilot scale rig have been examined. The samples were extracted using 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP) solvent and the extracts studied by size exclusion chromatography (SEC). The blast furnace carryover dust extracts contained high molecular weight carbonaceous material, of apparent mass corresponding to 10{sup 7}-10{sup 8} u, by polystyrene calibration. In contrast, the feed coke and char prepared in a wire mesh reactor under high temperature conditions did not give any extractable material. Meanwhile, controlled combustion experiments in a high-pressure wire mesh reactor suggest that the extent of combustion of injectant coal in the blast furnace tuyeres and raceways is limited by time of exposure and very low oxygen concentration. It is thus likely that the extractable, soot-like material in the blast furnace dust originated in tars is released by the injectant coal. Our results suggest that the unburned tars were thermally altered during the upward path within the furnace, giving rise to the formation of heavy molecular weight (soot-like) materials.
-
Xu, Kai; Deng, Qingshan; Cai, Lujun; Ho, Siuchun; Song, Gangbing
2018-04-28
Some of the most severe structural loadings come in the form of blast loads, which may be caused by severe accidents or even terrorist activities. Most commonly after exposure to explosive forces, a structure will suffer from different degrees of damage, and even progress towards a state of collapse. Therefore, damage detection of a structure subject to explosive loads is of importance. This paper proposes a new approach to damage detection of a concrete column structure subjected to blast loads using embedded piezoceramic smart aggregates (SAs). Since the sensors are embedded in the structure, the proposed active-sensing based approach is more sensitive to internal or through cracks than surface damage. In the active sensing approach, the embedded SAs act as actuators and sensors, that can respectively generate and detect stress waves. If the stress wave propagates across a crack, the energy of the wave attenuates, and the reduction of the energy compared to the healthy baseline is indicative of a damage. With a damage index matrix constructed by signals obtained from an array of SAs, cracks caused by blast loads can be detected throughout the structure. Conventional sensing methods such as the measurement of dynamic strain and acceleration were included in the experiment. Since columns are critical elements needed to prevent structural collapse, knowledge of their integrity and damage conditions is essential for safety after exposure to blast loads. In this research, a concrete column with embedded SAs was chosen as the specimen, and a series of explosive tests were conducted on the column. Experimental results reveal that surface damages, though appear severe, cause minor changes in the damage index, and through cracks result in significant increase of the damage index, demonstrating the effectiveness of the active sensing, enabled by embedded SAs, in damage monitoring of the column under blast loads, and thus providing a reliable indication of structural
-
Bass, Cameron R; Panzer, Matthew B; Rafaels, Karen A; Wood, Garrett; Shridharani, Jay; Capehart, Bruce
2012-01-01
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) from blast produces a number of conundrums. This review focuses on five fundamental questions including: (1) What are the physical correlates for blast TBI in humans? (2) Why is there limited evidence of traditional pulmonary injury from blast in current military field epidemiology? (3) What are the primary blast brain injury mechanisms in humans? (4) If TBI can present with clinical symptoms similar to those of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), how do we clinically differentiate blast TBI from PTSD and other psychiatric conditions? (5) How do we scale experimental animal models to human response? The preponderance of the evidence from a combination of clinical practice and experimental models suggests that blast TBI from direct blast exposure occurs on the modern battlefield. Progress has been made in establishing injury risk functions in terms of blast overpressure time histories, and there is strong experimental evidence in animal models that mild brain injuries occur at blast intensities that are similar to the pulmonary injury threshold. Enhanced thoracic protection from ballistic protective body armor likely plays a role in the occurrence of blast TBI by preventing lung injuries at blast intensities that could cause TBI. Principal areas of uncertainty include the need for a more comprehensive injury assessment for mild blast injuries in humans, an improved understanding of blast TBI pathophysiology of blast TBI in animal models and humans, the relationship between clinical manifestations of PTSD and mild TBI from blunt or blast trauma including possible synergistic effects, and scaling between animals models and human exposure to blasts in wartime and terrorist attacks. Experimental methodologies, including location of the animal model relative to the shock or blast source, should be carefully designed to provide a realistic blast experiment with conditions comparable to blasts on humans. If traditional blast scaling is
-
Dixon, C. Edward
2011-06-01
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) resulting from exposure to blast energy released by Improvised Explosive Devices (IEDs) has been recognized as the "signature injury" of Operation Iraqi Freedom and Operation Enduring Freedom. Repeated exposure to mild blasts may produce subtle deficits that are difficult to detect and quantify. Several techniques have been used to detect subtle brain dysfunction including neuropsychological assessments, computerized function testing and neuroimaging. Another approach is based on measurement of biologic substances (e.g. proteins) that are released into the body after a TBI. Recent studies measuring biomarkers in CSF and serum from patients with severe TBI have demonstrated the diagnostic, prognostic, and monitoring potential. Advancement of the field will require 1) biochemical mining for new biomarker candidates, 2) clinical validation of utility, 3) technical advances for more sensitive, portable detectors, 4) novel statistical approach to evaluate multiple biomarkers, and 5) commercialization. Animal models have been developed to simulate elements of blast-relevant TBI including gas-driven shock tubes to generate pressure waves similar to those produced by explosives. These models can reproduce hallmark clinical neuropathological responses such as neuronal degeneration and inflammation, as well as behavioral impairments. An important application of these models is to screen novel therapies and conduct proteomic, genomic, and lipodomic studies to mine for new biomarker candidates specific to blast relevant TBI.
-
Proceedings of the twenty-fourth annual conference on explosives and blasting technique
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
1998-01-01
Papers of interest to the coal industry include: death of a coal shovel; deep hole blasting with SMS (site-mix slurry system); trend of bulk explosives in India; bottomhole annular pressure - a theoretical problem with real effects; maximizing rotary blast hole drills; explosive energy concept for drill productivity and higher overall productivity at reduced excavation costs; large diameter presplitting improved through two novel techniques; avoiding tragedy - lessons to be learned from a flyrock fatality; and an economic analysis of cast blasting compared to other stripping alternatives.
-
CrocoBLAST: Running BLAST efficiently in the age of next-generation sequencing.
Tristão Ramos, Ravi José; de Azevedo Martins, Allan Cézar; da Silva Delgado, Gabrielle; Ionescu, Crina-Maria; Ürményi, Turán Peter; Silva, Rosane; Koca, Jaroslav
2017-11-15
CrocoBLAST is a tool for dramatically speeding up BLAST+ execution on any computer. Alignments that would take days or weeks with NCBI BLAST+ can be run overnight with CrocoBLAST. Additionally, CrocoBLAST provides features critical for NGS data analysis, including: results identical to those of BLAST+; compatibility with any BLAST+ version; real-time information regarding calculation progress and remaining run time; access to partial alignment results; queueing, pausing, and resuming BLAST+ calculations without information loss. CrocoBLAST is freely available online, with ample documentation (webchem.ncbr.muni.cz/Platform/App/CrocoBLAST). No installation or user registration is required. CrocoBLAST is implemented in C, while the graphical user interface is implemented in Java. CrocoBLAST is supported under Linux and Windows, and can be run under Mac OS X in a Linux virtual machine. jkoca@ceitec.cz. Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online. © The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com
-
Qualitative Resting Coronary Pressure Wave Form Analysis to Predict Fractional Flow Reserve.
Matsumura, Mitsuaki; Maehara, Akiko; Johnson, Nils P; Fearon, William F; De Bruyne, Bernard; Oldroyd, Keith G; Pijls, Nico H J; Jenkins, Paul; Ali, Ziad A; Mintz, Gary S; Stone, Gregg W; Jeremias, Allen
2018-03-27
To evaluate the predictability of resting distal coronary pressure wave forms for fractional flow reserve (FFR). Resting coronary wave forms were qualitatively evaluated for the presence of (i) dicrotic notch; (ii) diastolic dipping; and (iii) ventricularization. In a development cohort (n=88) a scoring system was developed that was then applied to a validation cohort (n=428) using a multivariable linear regression model to predict FFR and receiver operating characteristics (ROC) to predict FFR ≤0.8. In the development cohort, all 3 qualitative parameters were independent predictors of FFR. However, in a multivariable linear regression model in the validation cohort, qualitative wave form analysis did not further improve the ability of resting distal coronary to aortic pressure ratio (Pd/Pa) (p=0.80) or instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) (p=0.26) to predict FFR. Using ROC, the area under the curve of resting Pd/Pa (0.86 versus 0.86, P=0.08) and iFR (0.86 versus 0.86, P=0.26) did not improve by adding qualitative analysis. Qualitative coronary wave form analysis showed moderate classification agreement in predicting FFR but did not add substantially to the resting pressure gradients Pd/Pa and iFR; however, when discrepancies between quantitative and qualitative analyses are observed, artifact or pressure drift should be considered.
-
Magnetosheath waves under very low solar wind dynamic pressure: Wind/Geotail observations
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
C. J. Farrugia
2005-06-01
Full Text Available The expanded bow shock on and around "the day the solar wind almost disappeared" (11 May 1999 allowed the Geotail spacecraft to make a practically uninterrupted 54-h-long magnetosheath pass near dusk (16:30-21:11 magnetic local time at a radial distance of 24 to 30 RE (Earth radii. During most of this period, interplanetary parameters varied gradually and in such a way as to give rise to two extreme magnetosheath structures, one dominated by magnetohydrodynamic (MHD effects and the other by gas dynamic effects. We focus attention on unusual features of electromagnetic ion wave activity in the former magnetosheath state, and compare these features with those in the latter. Magnetic fluctuations in the gas dynamic magnetosheath were dominated by compressional mirror mode waves, and left- and right-hand polarized electromagnetic ion cyclotron (EIC waves transverse to the background field. In contrast, the MHD magnetosheath, lasting for over one day, was devoid of mirror oscillations and permeated instead by EIC waves of weak intensity. The weak wave intensity is related to the prevailing low solar wind dynamic pressures. Left-hand polarized EIC waves were replaced by bursts of right-hand polarized waves, which remained for many hours the only ion wave activity present. This activity occurred when the magnetosheath proton temperature anisotropy (=
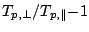 became negative. This was because the weakened bow shock exposed the magnetosheath directly to the (negative temperature anisotropy of the solar wind. Unlike the normal case studied in the literature, these right-hand waves were not by-products of left-hand polarized waves but derived their energy source directly from the magnetosheath temperature anisotropy. Brief entries into the
became negative. This was because the weakened bow shock exposed the magnetosheath directly to the (negative temperature anisotropy of the solar wind. Unlike the normal case studied in the literature, these right-hand waves were not by-products of left-hand polarized waves but derived their energy source directly from the magnetosheath temperature anisotropy. Brief entries into the -
Prevention of Blast-Related Injuries
2017-09-01
in a canvas harness. The harness was further supported by a steel frame which was suspended from a metal beam (3.7 m off the ground) mounted on...direction of the wave propagation (Figure 5). After proper alignment of the head with respect to the center of the C4 charge, the steel frame was...further tied to four hooks cemented to the concrete ground with straps to prevent excessive motion during the blast exposure. The intensity of the two
-
Pressure wave propagation in the discharge piping with water pool
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Bang, Young S.; Seul, Kwang W.; Kim, In Goo
2004-01-01
Pressure wave propagation in the discharge piping with a sparger submerged in a water pool, following the opening of a safety relief valve, is analyzed. To predict the pressure transient behavior, a RELAP5/MOD3 code is used. The applicability of the RELAP5 code and the adequacy of the present modeling scheme are confirmed by simulating the applicable experiment on a water hammer with voiding. As a base case, the modeling scheme was used to calculate the wave propagation inside a vertical pipe with sparger holes and submerged within a water pool. In addition, the effects on wave propagation of geometric factors, such as the loss coefficient, the pipe configuration, and the subdivision of sparger pipe, are investigated. The effects of inflow conditions, such as water slug inflow and the slow opening of a safety relief valve are also examined
-
A numerical technique to design blast noise mitigation measures
Berg, F. van den; Eerden, F.J.M. van der
2007-01-01
Large weapons, such as armor, artillery or demolitions, create a high-energy blast wave. It has a low frequency content, typically between 15 and 125 Hz, and can propagate over large distances. As a result it is a relative important cause for annoyance. Mitigation measures need to be close to the
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Donghui Yang
2018-01-01
Full Text Available Drilling and blasting technology is one of the main methods for pressure relief in deep mining. The traditional method for blasting hole blockage with clay stemming has many problems, which include a large volume of transportation, excess loading time, and high labor intensity. An environmentally friendly blast hole plug was designed and developed. This method is cheap, closely blocks the hole, is quickly loaded, and is convenient for transportation. The impact test on the plug was carried out using an improved split Hopkinson pressure bar test system, and the industrial test was carried out in underground tunnel of coal mine. The tests results showed that, compared with clay stemming, the new method proposed in this paper could prolong the action time of the detonation gas, prevent premature detonation gas emissions, reduce the unit consumption of explosives, improve the utilization ratio, reduce the labor intensity of workers, and improve the effect of rock blasting with low cost of rock breaking.
-
Oil injection into the blast furnace
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Dongsheng Liao; Mannila, P.; Haerkki, J.
1997-12-31
Fuel injection techniques have been extensively used in the commercial blast furnaces, a number of publications concerning the fuels injection have been reported. This present report only summarizes the study achievements of oil injection due to the research need the of authors, it includes the following parts: First, the background and the reasons reducing coke rate of oil injection are analyzed. Reducing coke rate and decreasing the ironmaking costs are the main deriving forces, the contents of C, H and ash are direct reasons reducing coke rate. It was also found that oil injection had great effects on the state of blast furnace, it made operation stable, center gas flow develop fully, pressure drop increase, descent speed of burden materials decrease and generation of thermal stagnation phenomena, the quality of iron was improved. Based on these effects, as an ideal mean, oil injection was often used to adjust the state of blast furnace. Secondly, combustion behavior of oil in the raceway and tuyere are discussed. The distribution of gas content was greatly changed, the location of CO, H{sub 2} generation was near the tuyere; the temperature peak shifts from near the raceway boundary to the tuyere. Oxygen concentration and blast velocity were two important factors, it was found that increasing excess oxygen ratio 0.9 to 1.3, the combustion time of oil decreases 0.5 msec, an increase of the blast velocity results in increasing the flame length. In addition, the nozzle position and oil rate had large effects on the combustion of oil. Based on these results, the limit of oil injection is also discussed, soot formation is the main reason limiting to further increase oil injection rate, it was viewed that there were three types of soot which were generated under blast furnace operating conditions. The reason generating soot is the incomplete conversion of the fuel. Finally, three methods improving combustion of oil in the raceway are given: Improvement of oil
-
Blast tests of expedient shelters in the DICE THROW event
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kearny, C.H.; Chester, C.V.
1978-03-01
To determine the worst blast environments that eight types of expedient shelters can withstand, we subjected a total of 18 shelters to the 1-kiloton blast effects of Defense Nuclear Agency's DICE THROW main event. These expedient shelters included two Russian and two Chinese types. The best shelter tested was a Small-Pole Shelter that had a box-like room of Russian design with ORNL-designed expedient blast entries and blast doors added. It was undamaged at the 53-psi peak overpressure range; the pressure rise inside was only 1.5 psi. An unmodified Russian Pole-Covered Trench Shelter was badly damaged at 6.8 psi. A Chinese ''Man'' Shelter, which skillfully uses very small poles to attain protective earth arching, survived 20 psi, undamaged. Two types of expedient shelters built of materials found in and around most American homes gave good protection at overpressures up to about 6 psi. Rug-Covered Trench Shelters were proved unsatisfactory. Water storage pits lined with ordinary plastic trash bags were proven practical at up to 53 psi, as were triangular expedient blast doors made of poles
-
The influence of different auto-ignition modes on the behavior of pressure waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Xu, Han; Yao, Anren; Yao, Chunde
2015-01-01
Highlights: • Modes of pressure oscillations in knocking, HCCI and super knock are recognized. • Three representative auto-ignition modes in engines are proposed. • A new method of “Energy Injected” is brought into understanding pressure wave. • Simulation results revealed the decisive factors for these three auto-ignition modes. • Different modes lead to different pressure wave behaviors damaging engines. - Abstract: For internal combustion engines, the knock of Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition engines, the conventional knock of gasoline engines and the super knock are all caused by the auto-ignition of unburned mixture which leads to the oscillation burning, but their Maximal Pressure Oscillation Amplitude (MPOA) and Maximum Pressure Rising Rate (MPRR) are totally different. In order to explore the reason, we propose three typical auto-ignition modes and then bring up the method of “Energy Injected” (EI) which is based on the experiment measured heat release rate. Through changing the heat source term in the energy equation for different auto-ignition modes, we conducted a series of numerical simulations for these three modes. After that, the following pressure oscillations can be compared and analyzed. The numerical simulation results show that different combustion pressure waves with different oscillation characteristics come from different auto-ignition modes, thus the macroscopic MPRR and MPOA are totally different. Furthermore, the method of “EI” based on the experiment measured heat release rate can accurately and rapidly help to research the formation and propagation of pressure waves in the engine combustion chamber.
-
Estimation of excitation forces for wave energy converters control using pressure measurements
Abdelkhalik, O.; Zou, S.; Robinett, R.; Bacelli, G.; Wilson, D.
2017-08-01
Most control algorithms of wave energy converters require prediction of wave elevation or excitation force for a short future horizon, to compute the control in an optimal sense. This paper presents an approach that requires the estimation of the excitation force and its derivatives at present time with no need for prediction. An extended Kalman filter is implemented to estimate the excitation force. The measurements in this approach are selected to be the pressures at discrete points on the buoy surface, in addition to the buoy heave position. The pressures on the buoy surface are more directly related to the excitation force on the buoy as opposed to wave elevation in front of the buoy. These pressure measurements are also more accurate and easier to obtain. A singular arc control is implemented to compute the steady-state control using the estimated excitation force. The estimated excitation force is expressed in the Laplace domain and substituted in the control, before the latter is transformed to the time domain. Numerical simulations are presented for a Bretschneider wave case study.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Arimitsu, Tsuyoshi; Ooe, Kazuya; Kawasaki, Koji
2012-01-01
Hydraulic experiments were conducted to estimate tsunami wave pressure acting on several different types of land structures and examine the influence of a seawall in front of the structure on tsunami wave pressure. Wave pressures were measured at some points on the structure. The existing hydrostatic formula tended to underestimate tsunami wave pressure under the condition of inundation flow with large Froude number. Estimation method of tsunami wave pressure using inundation depth and horizontal velocity at the front of the structure was proposed based on the experimental results. It was confirmed from comparison with the experiments that the vertical distribution of the maximum tsunami wave pressure can be reproduced by employing the proposed method in this study. (author)
-
Prevention of Blast-Related Injuries
2013-07-01
influence of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) on the shock wave response 3. Development of the geometric model for the head of a 23 55-kg Yucatan pig 4...of Tissue-Tek® optimum cutting compound and 20% sucrose (w/v) and frozen in a stream of liquid nitrogen (Saljo et al, 2008). The frozen blocks will...review of current models of the pig head under air blast loading 2. Development of a 2-D pig head FE model to study the influence of cerebrospinal fluid
-
Vortex, ULF wave and Aurora Observation after Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Change
Shi, Q.
2017-12-01
Here we will summarize our recent study and show some new results on the Magnetosphere and Ionosphere Response to Dynamic Pressure Change/disturbances in the Solar Wind and foreshock regions. We study the step function type solar wind dynamic pressure change (increase/decrease) interaction with the magnetosphere using THEMIS satellites at both dayside and nightside in different geocentric distances. Vortices generated by the dynamic pressure change passing along the magnetopause are found and compared with model predictions. ULF waves and vortices are excited in the dayside and nightside plasma sheet when dynamic pressure change hit the magnetotail. The related ionospheric responses, such as aurora and TCVs, are also investigated. We compare Global MHD simulations with the observations. We will also show some new results that dayside magnetospheric FLRs might be caused by foreshock structures.Shi, Q. Q. et al. (2013), THEMIS observations of ULF wave excitation in the nightside plasma sheet during sudden impulse events, J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics, 118, doi:10.1029/2012JA017984. Shi, Q. Q. et al. (2014), Solar wind pressure pulse-driven magnetospheric vortices and their global consequences, J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics, 119, doi:10.1002/2013JA019551. Tian, A.M. et al.(2016), Dayside magnetospheric and ionospheric responses to solar wind pressure increase: Multispacecraft and ground observations, J. Geophys. Res., 121, doi:10.1002/2016JA022459. Shen, X.C. et al.(2015), Magnetospheric ULF waves with increasing amplitude related to solar wind dynamic pressure changes: THEMIS observations, J. Geophys. Res., 120, doi:10.1002/2014JA020913Zhao, H. Y. et al. (2016), Magnetospheric vortices and their global effect after a solar wind dynamic pressure decrease, J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics, 121, doi:10.1002/2015JA021646. Shen, X. C., et al. (2017), Dayside magnetospheric ULF wave frequency modulated by a solar wind dynamic pressure negative impulse, J. Geophys. Res
-
Conditions for sustaining low-pressure plasma columns by travelling electromagnetic UHF waves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Benova, E.; Zhelyazkov, I.
1997-01-01
The paper considers the conditions for sustaining low-pressure plasma columns by travelling electromagnetic waves in symmetric and dipolar modes, respectively. The treatment is fully electrodynamic. It is shown that the wave energy flux along the plasma column determines the conditions for sustaining the discharge. In particular as the plasma is sustained by a symmetric wave whose flux depends mainly on the radial distribution of the wave electric field whilst for a dipolar wave sustained plasma the flux is specified by the magnitude of the axial wave field component at the plasma-dielectric interface. (orig.)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Leslie, I.R.M.; Birk, A.M.
1989-08-01
A study was carried out to investigate the state of knowledge about the failure of pressure liquified gas transport and storage tanks. A comprehensive literature search and review was carried out to assess the level of knowledge relating to the causes and characteristics of vessel ruptures. Specific parameters of interest were: the effect of vessel initial conditions (fill level, initial temperature, etc.) on rupture severity; the ability to predict the occurrence of boiling liquid expanding vapor explosions (BLEVE); and the effects of explosions such as blast waves and missile generation. The review revealed that there are several areas where knowledge is weak. These areas include: the effects of blast on structures, the prediction of hazards from, and size of, fireballs, and the understanding of failure modes of pressure liquified gas containers. It was concluded that an experimental program should be initiated to investigate the effects of container size, shape and loading conditions on the consequences of vessel rupture. 68 refs., 16 figs., 10 tabs.
-
Zuo, Weiguang; Liu, Ming; Fan, Tianhui; Wang, Pengtao
2018-06-01
This paper presents the probability distribution of the slamming pressure from an experimental study of regular wave slamming on an elastically supported horizontal deck. The time series of the slamming pressure during the wave impact were first obtained through statistical analyses on experimental data. The exceeding probability distribution of the maximum slamming pressure peak and distribution parameters were analyzed, and the results show that the exceeding probability distribution of the maximum slamming pressure peak accords with the three-parameter Weibull distribution. Furthermore, the range and relationships of the distribution parameters were studied. The sum of the location parameter D and the scale parameter L was approximately equal to 1.0, and the exceeding probability was more than 36.79% when the random peak was equal to the sample average during the wave impact. The variation of the distribution parameters and slamming pressure under different model conditions were comprehensively presented, and the parameter values of the Weibull distribution of wave-slamming pressure peaks were different due to different test models. The parameter values were found to decrease due to the increased stiffness of the elastic support. The damage criterion of the structure model caused by the wave impact was initially discussed, and the structure model was destroyed when the average slamming time was greater than a certain value during the duration of the wave impact. The conclusions of the experimental study were then described.
-
Design of a Continuous Blood Pressure Measurement System Based on Pulse Wave and ECG Signals.
Li, Jian-Qiang; Li, Rui; Chen, Zhuang-Zhuang; Deng, Gen-Qiang; Wang, Huihui; Mavromoustakis, Constandinos X; Song, Houbing; Ming, Zhong
2018-01-01
With increasingly fierce competition for jobs, the pressures on people have risen in recent years, leading to lifestyle and diet disorders that result in significantly higher risks of cardiovascular disease. Hypertension is one of the common chronic cardiovascular diseases; however, mainstream blood pressure measurement devices are relatively heavy. When multiple measurements are required, the user experience and the measurement results may be unsatisfactory. In this paper, we describe the design of a signal collection module that collects pulse waves and electrocardiograph (ECG) signals. The collected signals are input into a signal processing module to filter the noise and amplify the useful physiological signals. Then, we use a wavelet transform to eliminate baseline drift noise and detect the feature points of the pulse waves and ECG signals. We propose the concept of detecting the wave shape associated with an instance, an approach that minimizes the impact of atypical pulse waves on blood pressure measurements. Finally, we propose an improved method for measuring blood pressure based on pulse wave velocity that improves the accuracy of blood pressure measurements by 58%. Moreover, the results meet the american medical instrument promotion association standards, which demonstrate the feasibility of our measurement system.
-
On the excitation of ULF waves by solar wind pressure enhancements
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. T. I. Eriksson
2006-11-01
Full Text Available We study the onset and development of an ultra low frequency (ULF pulsation excited by a storm sudden commencement. On 30 August 2001, 14:10 UT, the Cluster spacecraft are located in the dayside magnetosphere and observe the excitation of a ULF pulsation by a threefold enhancement in the solar wind dynamic pressure. Two different harmonics are observed by Cluster, one at 6.8 mHz and another at 27 mHz. We observe a compressional wave and the development of a toroidal and poloidal standing wave mode. The toroidal mode is observed over a narrow range of L-shells whereas the poloidal mode is observed to have a much larger radial extent. By looking at the phase difference between the electric and magnetic fields we see that for the first two wave periods both the poloidal and toroidal mode are travelling waves and then suddenly change into standing waves. We estimate the azimuthal wave number for the 6.8 mHz to be m=10±3. For the 27 mHz wave, m seems to be several times larger and we discuss the implications of this. We conclude that the enhancement in solar wind pressure excites eigenmodes of the geomagnetic cavity/waveguide that propagate tailward and that these eigenmodes in turn couple to toroidal and poloidal mode waves. Thus our observations give firm support to the magnetospheric waveguide theory.
-
Pressure broadening measurement of submillimeter-wave lines of O3
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yamada, M.M.; Amano, T.
2005-01-01
The pressure broadening coefficients and their temperature dependences for two submillimeter-wave transitions of ozone, one being monitored with Odin and the other to be monitored with JEM/SMILES and EOS-MLS, have been determined by using a BWO based submillimeter-wave spectrometer. The measurements have also been extended to one of the symmetric isotopic species, 16 O 18 O 16 O. The isotopic species is observed in natural abundance and as a consequence the temperature dependence is not determined due to weak signal intensity. The pressure broadening parameters are determined with better than 1% accuracy, while the temperature dependence exponents are obtained within 1.5-3% accuracy for the normal species transitions
-
Constructal design of a blast furnace iron-making process based on multi-objective optimization
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Liu, Xiong; Chen, Lingen; Feng, Huijun; Qin, Xiaoyong; Sun, Fengrui
2016-01-01
For the fixed total raw material cost and based on constructal theory and finite time thermodynamics, a BFIM (blast furnace iron-making) process is optimized by taking a complex function as optimization objective. The complex function is integrated with HM (hot metal) yield and useful energy of the BF (blast furnace). The optimal cost distribution of raw materials (namely “generalized optimal construct”) is obtained. The effects of some parameters, such as oxygen enrichment, blast temperature and pulverized coal dosage, on the optimization results are analyzed. The results show that the HM yield, useful energy and complex function are, respectively, increased by 3.13%, 2.66% and 2.90% after generalized constructal optimization. The utilization efficiencies of the BFG (blast furnace gas) and slag are 41.3% and 57.1%, respectively, which means that the utilization potentials of the BFG and slag can be further exploited. Increasing pulverized coal dosage and decreasing the agglomerate ratio can increase the complex function. The performance the BFIM process can be improved by adjusting the oxygen enrichment, blast temperature, blast dosage, pressure ratio of the Brayton cycle's air compressor and relative pressure drop of the air compressor inlet to their optimal values, respectively, which are new findings of this paper. - Highlights: • Constructal optimization of a blast furnace iron-making process is performed. • Finite time thermodynamic model of open Brayton cycle is adopted. • Weighting function is taken as optimization objective. • Optimal cost distribution of the raw materials is obtained.
-
Calais, Eric; Bernard Minster, J.; Hofton, Michelle; Hedlin, Michael
1998-01-01
Sources such as atmospheric or buried explosions and shallow earthquakes are known to produce infrasonic pressure waves in the atmosphere Because of the coupling between neutral particles and electrons at ionospheric altitudes, these acoustic and gravity waves induce variations of the ionospheric electron density. The Global Positioning System (GPS) provides a way of directly measuring the total electron content in the ionosphere and, therefore, of detecting such perturbations in the upper atmosphere. In July and August 1996, three large surface mine blasts (1.5 Kt each) were detonated at the Black Thunder coal mine in eastern Wyoming. As part of a seismic and acoustic monitoring experiment, we deployed five dual-frequency GPS receivers at distances ranging from 50 to 200 km from the mine and were able to detect the ionospheric perturbation caused by the blasts. The perturbation starts 10 to 15 min after the blast, lasts for about 30 min, and propagates with an apparent horizontal velocity of 1200 m s- 1. Its amplitude reaches 3 × 1014 el m- 2 in the 7-3 min period band, a value close to the ionospheric perturbation caused by the M=6.7 Northridge earthquake (Calais & Minster 1995). The small signal-to-noise ratio of the perturbation can be improved by slant-stacking the electron content time-series recorded by the different GPS receivers taking into account the horizontal propagation of the perturbation. The energy of the perturbation is concentrated in the 200 to 300 s period band, a result consistent with previous observations and numerical model predictions. The 300 s band probably corresponds to gravity modes and shorter periods to acoustic modes, respectively. Using a 1-D stratified velocity model of the atmosphere we show that linear acoustic ray tracing fits arrival times at all GPS receivers. We interpret the perturbation as a direct acoustic wave caused by the explosion itself. This study shows that even relatively small subsurface events can produce
-
Cylindrically converging blast waves in air
Matsuo, H.; Nakamura, Y.
1981-07-01
Cylindrically converging shock waves are produced by utilizing the detonation of cylindrical explosive shells. The production and the propagation of shock waves are observed by framing and streak camera photographs, and the trajectory of shock propagations is determined by using an electrical ionization probing system. The effect of the quantity of explosives on the stability, or the axial symmetry, of shock fronts and on the strength of shocks produced is investigated. It has been shown that, for practical purposes, the approximation of shock trajectories by Guderley's formulas would be sufficiently acceptable in an unexpectedly wide region near the implosion center, and that the axial symmetry of the shock front is improved by increasing the quantity of explosives, and thus, strong shocks are produced by merely increasing the quantity of explosives. The reflected diverging shock seems to be very stable. Piezoelectric elements have also been used to detect reflected diverging waves.
-
Water in blast holes can improve blasting efficiency and cut costs
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
O' Regan, G.
1983-08-01
Water in blast holes has been a traditional problem faced by blasting engineers and foremen in surface mining. Presently accepted techniques for blasting in water-filled holes include the use of more expensive water-gel explosives which are denser than water, dewatering of holes by pumping, and blowing out the water with a small charge before loading the main ANFO charge column. These methods involve considerable expense and delay to the normal charge-loading procedure. The author describes a method of using the water in blast holes to improve blasting efficiency and reduce the consumption of explosive.
-
Radiative energy losses from a high-current air-blast arc
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Strachan, D.C.; Lidgate, D.; Jones, G.R.
1977-01-01
The importance of total radiation losses from high-current arcs burning in highly accelerated air flows representative of conditions existing in commercial gas-blast switchgear has been investigated. Such losses have been measured both in the high-pressure region upstream of a shaped orifice, where gas velocities are low, and in the region downstream where velocities become supersonic and pressure conditions approach ambient. The dominance of upstream electrode vapor as the source of plasma radiation losses is demonstrated and the importance of radiated losses within the arc energy balance is examined using measured values of axial electric field. For upstream electrodes of elkonite (sintered copper/tungsten) as used in high-power gas-blast circuit breakers, it is shown that some 30--40% of the electrical energy input upstream of the orifice is lost as radiation, while downstream this figure becomes 10--20%. The effect of reservoir pressure on arc electric fields is examined and the contribution to this effect of radiation losses is quantified
-
Blasting activity of the mining industry in the United States
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Richards, P.G. [Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Palisades, NY (United States)
1994-12-31
About 2 megatons of chemcial explosives are used annually in the U.S., principally in mining for coal and metal ores. Most of this explosive is used in surface mines rather than underground mines. On a typical work day there are about 30 explosions greater than 50 tons, including one shot greater than 200 tons. Shots in underground mines are typically much smaller, because of safety considerations. Almost all chemical explosions above 1 ton in the U.S. are ripple-fired and almost all above 10 tons are also shallow. Almost all are intended to break rock or to remove overburden, and are therefore very inefficient, relative to contained single shots, in generating seismic signals at regional ore teleseismic distances. These attributes make explosions used in industry quite different from the Non-Proliferation Experiment. There is very little correlation between the total amount of explosive used in a ripple-fired blast, and the seismic magnitude. Statistics on blasting magnitudes are of interest in the context of monitoring network. There is a blast reported with regional (or duration) magnitude 3.5 or above, in the U.S., a few tens of times a year; but it would appear that the teleseismic magnitude (m{sub b}) of such events are significantly lower than 3.5. Only about 10 to 30 chemical explosions per year in the U.S. are detected teleseismically with m{sub b}>3. Methods of routinely discriminating most chemical explosions from other seismic sources use spectra of regional phases at frequencies up to about 30 Hz, which is significantly higher than frequencies needed for recording teleseismic signals. The best discriminants appear to be the high-frequency spectral ratio of waves with P-wave energy (e.g. Pn or Pg) to waves with S-wave energy (Sn or Lg); and the use of spectrograms, which can be particularly useful in identifying ripple-firing.
-
Optimizing cast blasting efficiency using ANFO with liners
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Madsen, A.
2007-01-15
As part of a five research project funded by the National Science Foundation, Peabody Energy studied three experimental cast blasts conducted at the North Antelope Rochelle mine site on July 24,28 and 31 2005. The initial purpose of this research project was to determine the influence that blast initiation sequence have on: NOx production; Face Displacement; Highwall damage; Explosive performance; Vibration emissions; Displacement; Surface swell; and Cast benefit. Two new discoveries on velocity of detonation (VoD) and pressure of detonation (PoD) were made as a result of this research project. Furthermore, a relationship between surface swell velocity and face velocity was also noted. 7 figs., 3 tabs.
-
Spencer, J. W., Jr.; Nur, A. M.
1976-01-01
A description is presented of an experimental assembly which has been developed to conduct concurrent measurements of compressional and shear wave velocities in rocks at high temperatures and confining pressures and with independent control of the pore pressure. The apparatus was used in studies of the joint effects of temperature, external confining pressure, and internal pore water on sonic velocities in Westerly granite. It was found that at a given temperature, confining pressure has a larger accelerating effect on compressional waves in dry rock, whereas at a given confining pressure, temperature has a larger retarding effect on shear waves.
-
Transient response of a liquid injector to a steep-fronted transverse pressure wave
Lim, D.; Heister, S.; Stechmann, D.; Kan, B.
2017-12-01
Motivated by the dynamic injection environment posed by unsteady pressure gain combustion processes, an experimental apparatus was developed to visualize the dynamic response of a transparent liquid injector subjected to a single steep-fronted transverse pressure wave. Experiments were conducted at atmospheric pressure with a variety of acrylic injector passage designs using water as the working fluid. High-speed visual observations were made of the injector exit near field, and the extent of backflow and the time to refill the orifice passage were characterized over a range of injection pressures. A companion transient one-dimensional model was developed for interpretation of the results and to elucidate the trends with regard to the strength of the transverse pressure wave. Results from the model were compared with the experimental observations.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Jixue Zhou
2017-01-01
Full Text Available In Southwest China, most regions are mountainous, where traditional drill-and-blast method is adopted to excavate relatively harder rocks. However, blasting would cause vibration to adjacent structures and might result in damage or even failure. This paper considers a case where subway tunnel is overlying an existing railway tunnel, while the excavation requires blasting method. Vibration and stress distribution are calculated via Dynamic Finite Element Method (DFEM for both full-face excavation and CD method. Result shows that vibration induced by CD method is only 28% of that caused by full-face blasting with same distance. Peak vibration is located on the lining facing the blasting source, while peak tensile stress is on the other side of the contour due to the reflection of stress wave on strata boundary. And peak value of tensile stress induced by full-face blasting is capable of causing lining failure; thus full-face blasting is not suggested within 40 m beyond the underlying tunnel axis. However, CD method has shown much advantage, since blasting within 25 m is also considered safe to the underlying tunnel. But when the blasting source is as near as 12 m within the underlying tunnel, the CD method is no longer safe.
-
Observations of wave-induced pore pressure gradients and bed level response on a surf zone sandbar
Anderson, Dylan; Cox, Dan; Mieras, Ryan; Puleo, Jack A.; Hsu, Tian-Jian
2017-06-01
Horizontal and vertical pressure gradients may be important physical mechanisms contributing to onshore sediment transport beneath steep, near-breaking waves in the surf zone. A barred beach was constructed in a large-scale laboratory wave flume with a fixed profile containing a mobile sediment layer on the crest of the sandbar. Horizontal and vertical pore pressure gradients were obtained by finite differences of measurements from an array of pressure transducers buried within the upper several centimeters of the bed. Colocated observations of erosion depth were made during asymmetric wave trials with wave heights between 0.10 and 0.98 m, consistently resulting in onshore sheet flow sediment transport. The pore pressure gradient vector within the bed exhibited temporal rotations during each wave cycle, directed predominantly upward under the trough and then rapidly rotating onshore and downward as the wavefront passed. The magnitude of the pore pressure gradient during each phase of rotation was correlated with local wave steepness and relative depth. Momentary bed failures as deep as 20 grain diameters were coincident with sharp increases in the onshore-directed pore pressure gradients, but occurred at horizontal pressure gradients less than theoretical critical values for initiation of the motion for compact beds. An expression combining the effects of both horizontal and vertical pore pressure gradients with bed shear stress and soil stability is used to determine that failure of the bed is initiated at nonnegligible values of both forces.type="synopsis">type="main">Plain Language SummaryThe pressure gradient present within the seabed beneath breaking waves may be an important physical mechanism transporting sediment. A large-scale laboratory was used to replicate realistic surfzone conditions in controlled tests, allowing for horizontal and vertical pressure gradient magnitudes and the resulting sediment bed response to be observed with precise instruments
-
The use of computer blast simulations to improve blast quality
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Favreau, R.F.; Kuzyk, G.W.; Babulic, P.J.; Tienkamp, N.J.
1989-01-01
Atomic Energy of Canada Limited is constructing an Underground Research Laboratory (URL) as part of a comprehensive program to evaluate the concept of nuclear fuel waste disposal deep in crystalline rock formations. Careful blasting methods have been used to minimize damage to the excavation surfaces. Good wall quality is desirable in any excavation. In excavations required for nuclear waste disposal, the objective will be to minimize blast-induced fractures which may complicate the sealing requirements necessary to control subsequent movement of groundwater around a sealed disposal vault. The construction of the URL has provided an opportunity for the development of controlled blasting methods, especially for drilling accuracy and optimization of explosive loads in the perimeter and cushion holes. The work has been assisted by the use of blast simulations with the mathematical model Blaspa. This paper reviews the results of a recent project to develop a controlled method of full-face blasting, and compares the observed field results with the results of a blast simulator called Blaspa. Good agreement is found between the two, and the Blaspa results indicate quantitatively how the blasting may induce damage in the final excavation surface. In particular, the rock in the final wall may be stressed more severely by the cushion holes than by the perimeter holes. Bootleg of the rock between the perimeter and cushion rows occurs when the burst-out velocity imparted to it by the explosive loads in the perimeter holes is inadequate. In practice, these findings indicate that quantitative rock stress and rock burst-out velocity criteria can be established to minimize wall damage and bootleg. Thus, blast simulations become an efficient way to design controlled blasting and to optimize quality of the excavation surface
-
Thalen, E; Wit, H; Segenhout, H; Albers, F
Inner ear pressure was measured in scala tympani with a micropipette during square wave pressure manipulation of the intracranial compartment and, subsequently, of the external ear canal (EEC) in the same guinea pig. As expected, the combination of the cochlear aqueduct and the inner ear behaves as
-
Microstructural Consequences of Blast Lung Injury Characterized with Digital Volume Correlation
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hari Arora
2017-12-01
Full Text Available This study focuses on microstructural changes that occur within the mammalian lung when subject to blast and how these changes influence strain distributions within the tissue. Shock tube experiments were performed to generate the blast injured specimens (cadaveric Sprague-Dawley rats. Blast overpressures of 100 and 180 kPa were studied. Synchrotron tomography imaging was used to capture volumetric image data of lungs. Specimens were ventilated using a custom-built system to study multiple inflation pressures during each tomography scan. These data enabled the first digital volume correlation (DVC measurements in lung tissue to be performed. Quantitative analysis was performed to describe the damaged architecture of the lung. No clear changes in the microstructure of the tissue morphology were observed due to controlled low- to moderate-level blast exposure. However, significant focal sites of injury were observed using DVC, which allowed the detection of bias and concentration in the patterns of strain level. Morphological analysis corroborated the findings, illustrating that the focal damage caused by a blast can give rise to diffuse influence across the tissue. It is important to characterize the non-instantly fatal doses of blast, given the transient nature of blast lung in the clinical setting. This research has highlighted the need for better understanding of focal injury and its zone of influence (alveolar interdependency and neighboring tissue burden as a result of focal injury. DVC techniques show great promise as a tool to advance this endeavor, providing a new perspective on lung mechanics after blast.
-
Vasomotor origin of intracranial pressure waves in hydrocephalic infants
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Barritault, L; Rimbert, J N; Hirsch, J F; Pierr-Kahn, A; Lacombe, J; Zouaoui, A; Mises, J; Gabersek, V
1980-12-01
By measuring cerebral blood volume (CBV) and intracranial pressure (ICP) variations at the same running time during sleep, it has been demonstrated that the ICP wave which appears during the REM sleep in hydrocephalic infants is produced by intracerebral vaso-dilatation. Nine infants with stabilized hydrocephalus were investigated by non-invasive means: REM phases were distinguished with the usual polysomnographic electrodes. Intracranial pressure was measured with a fontanel palpation transducer and CBV variations were obtained by recording /sup 99/sup(m)Tc activity at the head level after in vivo labelling of red cells with /sup 99/sup(m)Tc-pertechnetate. The time activity curves, obtained from regions of interest and selected on the sequential radioisotope images, show that an increased ICP wave, occurring during the REM period, is related to a simultaneous increase in the blood volume, limited to the cerebral sector and not to the area of the external carotid artery.
-
Elastic Wave Velocity Measurements on Mantle Peridotite at High Pressure and Temperature
Mistler, G. W.; Ishikawa, M.; Li, B.
2002-12-01
With the success of conducting ultrasonic measurements at high pressure and high temperature in large volume high pressure apparatus with in-situ measurement of the sample length by X-ray imaging, it is now possible to measure elastic wave velocities on aggregate samples with candidate compositions of the mantle to the conditions of the Earth's transition zone in the laboratory. These data can be directly compared with seismic data to distinguish the compositional models in debate. In this work, we carried out velocity measurements on natural peridotite KLB-1 at the conditions of the Earth's upper mantle. Fine powered sample of natural KLB-1 was used as starting material. Specimens for ultrasonic measurements were hot-pressed and equilibrated at various pressure and temperature conditions along geotherm up to the transition zone. The recovered samples were characterized with density measurement, X-ray diffraction and microprobe analysis. Bench top P and S wave velocities of KLB-1 sample sintered at 3-4 GPa and 1400 degree centigrade showed a very good agreement with the VRH average of pyrolite. High pressure and high temperature measurements was conducted up to 7 GPa and 800 degree centigrade using ultrasonic interferometric method in a DIA-type high pressure apparatus in conjunction with X-ray diffraction and X-ray imaging. The utilization of X-ray imaging technique provides direct measurements of sample lengths at high pressure and high temperature, ensuring a precise determination of velocities. The results of P and S wave velocities at high pressure and high temperature as well as their comparison with calculated pyrolite model will be presented.
-
Modeling and simulation of explosion effectiveness as a function of blast and crowd characteristics
Usmani, Zeeshan-Ul-Hassan
Suicide bombing has become one of the most lethal and favorite modus operandi of terrorist organizations around the world. On average, there is a suicide bombing attack every six days somewhere in the world. While various attempts have been made to assess the impact of explosions on structures and military personnel, little has been done on modeling the impact of a blast wave on a crowd in civilian settings. The assessment of an explosion's effect on a crowd can lead to better management of disasters, triage of patients, locating blast victims under the debris, development of protective gear, and safe distance recommendations to reduce the casualties. The overall goal of this work is to predict the magnitude of injuries and lethality on humans from a blast-wave with various explosive and crowd characteristics, and to compare, contrast, and analyze the performance of explosive and injury models against the real-life data of suicide bombing incidents. This thesis introduces BlastSim---a physics based stationary multi-agent simulation platform to model and simulate a suicide bombing event. The agents are constrained by the physical characteristics and mechanics of the blast wave. The BlastSim is programmed to test, analyze, and validate the results of different model combinations under various conditions with different sets of parameters, such as the crowd and explosive characteristics, blockage and human shields, fragmentation and the bomber's position, in 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional environments. The suicide bombing event can be re-created for forensic analysis. The proposed model combinations show a significant performance---the Harold Brode explosive model with Catherine Lee injury model using the blockage stands out consistently to be the best with an overall cumulative accuracy of 87.6%. When comparing against actual data, overall, prediction accuracy can be increased by 71% using this model combination. The J. Clutter with Reflection explosive model using
-
Korshunov, G. I.; Afanasev, P. I.; Bulbasheva, I. A.
2017-10-01
The monitoring and survey results of drilling and blasting operations are specified during the development of Afanasyevsky deposit of cement raw materials for a 110 kV electricity power lines structure. Seismic explosion waves and air shock waves were registered in the course of monitoring. The dependency of peak particle velocities on the scaled distance and explosive weight by the delay time was obtained.
-
Lower blasthole pressures: a means of reducing costs when blasting rocks of low to moderate strength
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hagan, T.N.; Gibson, I.M.
1988-03-01
From a purely mechanical viewpoint, each explosive charge should produce a peak blasthole pressure (P/sub b/) that just fails to crush (i.e. pulverise or plastically deform) the rock which surrounds it. Where P/sub b/ exceeds a critical value, some explosion energy is wasted in crushing an annular section of rock immediately around each charge. As a rock's dynamic compressive breaking strain decreases, so should P/sub b/ (Hagan, 1977b). This paper reviews information on, and anticipates the blasting performance of, bulk charges having effective densities which are as low as about 40% of that for ammonium nitrate fuel oil (ANFO). It also outlines the potential advantages of extending the reaction periods of charges, even to the extent that explosive reactions continue after the blasthole wall and stemming have started to move. The paper then proceeds to define situations in which the use of such lower-pressure charges is likely to result in greatest reductions in mining costs. Some methods of applying bulk charges having effective densities in the 0.3-0.8 g cm/sup -3/ range and/or lower reaction rates are suggested. 15 refs., 3 figs.
-
Inverting Coseismic TEC Disturbances for Neutral Atmosphere Pressure Wave
Lee, R. F.; Mikesell, D.; Rolland, L.
2017-12-01
Research from the past 20 years has shown that we can detect coseismic disturbances in the total electron content (TEC) using global navigation space systems (GNSS). In the near field, TEC disturbances are created by the direct wave from rupture on the surface. This pressure wave travels through the neutral atmosphere to the ionosphere within about 10 minutes. This provides the opportunity to almost immediately characterize the source of the acoustic disturbance on the surface using methods from seismology. In populated areas, this could provide valuable information to first responders. To retrieve the surface motion amplitude information we must account for changes in the waveform caused by the geomagnetic field, motion of the satellites and the geometry of the satellites and receivers. One method is to use a transfer function to invert for the neutral atmosphere pressure wave. Gómez et al (2015) first employed an analytical model to invert for acoustic waves produced by Rayleigh waves propagating along the Earth's surface. Here, we examine the same model in the near field using the TEC disturbances from the direct wave produced by rupture at the surface. We compare results from the forward model against a numerical model that has been shown to be in good agreement with observations from the 2011 Van (Turkey) earthquake. We show the forward model predictions using both methods for the Van earthquake. We then analyze results for hypothetical events at different latitudes and discuss the reliability of the analytical model in each scenario. Gómez, D., R. Jr. Smalley, C. A. Langston, T. J. Wilson, M. Bevis, I. W. D. Dalziel, E. C. Kendrick, S. A. Konfal, M. J. Willis, D. A. Piñón, et al. (2015), Virtual array beamforming of GPS TEC observations of coseismic ionospheric disturbances near the Geomagnetic South Pole triggered by teleseismic megathrusts, J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics, 120, 9087-9101, doi:10.1002/2015JA021725.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Cardoso, E.R.; Piatek, D.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Stambrook, M.; Sutherland, J.B.
1989-01-01
Nineteen consecutive patients with suspected occult communicating hydrocephalus were investigated by means of clinical evaluation, neuropsychological testing, isotope cisternography, computed tomography scanning, and continuous intracranial pressure monitoring. Semi-quantitative grading systems were used in the evaluation of the clinical, neuropsychological, and cisternographic assessments. Clinical examination, neuropsychological testing, and computed tomography scanning were repeated 3 months after ventriculoperitoneal shunting. All patients showed abnormal intracranial pressure waves and all improved after shunting. There was close correlation between number, peak, and pulse pressures of B waves and the mean intracranial pressure. However, quantification of B waves by means of number, frequency, and amplitude did not help in predicting the degree of clinical improvement postshunting. The most sensitive predictor of favorable response to shunting was enlargement of the temporal horns on computed tomography scan. Furthermore, the size of temporal horns correlated with mean intracranial pressure. There was no correlation between abnormalities on isotope cisternography and clinical improvement
-
Placement of the dam for the no. 2 kambaratinskaya HPP by large-scale blasting: some observations
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shuifer, M. I.; Argal, É. S.
2011-01-01
Results of complex instrument observations of large-scale blasting during construction of the dam for the No. 2 Kambaratinskaya HPP on the Naryn River in the Republic of Kirgizia are analyzed. The purpose of these observations was: to determine the actual parameters of the seismic process, evaluate the effect of air and acoustic shock waves, and investigate the kinematics of the surface formed by the blast in its core region within the mass of fractured rocks.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hirata, A. [Kumamoto Industries Univ, Kumamoto (Japan); Yamamoto, M. [Asahi Chemical Industry Co. Ltd., Tokyo (Japan); Inaba, C. [Nishimatsu Construction Co. Ltd., Kanagawa (Japan); Kaneko, K. [Hokkaido Univ (Japan)
1997-08-01
For avoiding the generation of public hazard due to ground vibration causes by blasting in tunneling, it is important to devise a blasting method for ensuring the level of the ground vibration caused thereby under a limit, and an exact predication of ground vibration before blasting is desirable. In this study, the characteristics of the ground vibration caused by tunnel blasting are analyzed, and a summary of amplitude spectra calculating method is described. A theoretical analysis method for predicting the vibration level is proposed based on spectrum-multiplicative method. Vibration caused by multistage blasting in tunneling is most strong and deemed as important. When observing the process of elastic wave motion caused by multistage blasting being measured, the process can be divided into three element processes in frequency area as vibration source spectrum, transmission attenuation spectrum and frequency response function vibrating test, and, with the multiplication of them, the amplitude spectra at an observation portion can be estimated. 12 refs., 12 figs.
-
Skull Flexure from Blast Waves: A Mechanism for Brain Injury with Implications for Helmet Design
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Moss, W C; King, M J; Blackman, E G
2009-04-30
Traumatic brain injury [TBI] has become a signature injury of current military conflicts, with debilitating, costly, and long-lasting effects. Although mechanisms by which head impacts cause TBI have been well-researched, the mechanisms by which blasts cause TBI are not understood. From numerical hydrodynamic simulations, we have discovered that non-lethal blasts can induce sufficient skull flexure to generate potentially damaging loads in the brain, even without a head impact. The possibility that this mechanism may contribute to TBI has implications for injury diagnosis and armor design.
-
Calculation models of pressure wave propagation within the WWER-440 primary circulating loop
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Adamik, V.; Tkach, A.
1982-01-01
Computer codes SHOCK, LOVE, BAREL are described that can be used for the study of pressure wave propagation within the reactor and pipeline system during a LOCA as well as for mechanical loads identification in various parts of the system. SHOCK code is applicable to one-dimensional pressure wave propagation analysis in any hydraulic network containing a compressible nonviscous liquid with a constant (within the considered transient process period) density. LOVE code allows to calculate non-symmetrical mechanical loads on the WWER shaft in case of the main circulation pipeline cold branch rupture. BAREL code is an advanced modification of SHOCK code. It is fitted for two-dimensional pressure wave propagation analysing in the downstream section of a pressurised water reactor in case of the main circulation pipeline cold branch rupture. The calculation results for B-213 type WWER-440 reactor are presented that have been obtained under the assumption of perfect structure rigidity [ru
-
Primary Blast-Induced Changes in Akt and GSK3β Phosphorylation in Rat Hippocampus
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yushan Wang
2017-08-01
Full Text Available Traumatic brain injury (TBI due to blast from improvised explosive devices has been a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in recent conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan. However, the mechanisms of primary blast-induced TBI are not well understood. The Akt signal transduction pathway has been implicated in various brain pathologies including TBI. In the present study, the effects of simulated primary blast waves on the phosphorylation status of Akt and its downstream effector kinase, glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β, in rat hippocampus, were investigated. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD rats (350–400 g were exposed to a single pulse shock wave (25 psi; ~7 ms duration and sacrificed 1 day, 1 week, or 6 weeks after exposure. Total and phosphorylated Akt, as well as phosphorylation of its downstream effector kinase GSK3β (at serine 9, were detected with western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry. Results showed that Akt phosphorylation at both serine 473 and threonine 308 was increased 1 day after blast on the ipsilateral side of the hippocampus, and this elevation persisted until at least 6 weeks postexposure. Similarly, phosphorylation of GSK3β at serine 9, which inhibits GSK3β activity, was also increased starting at 1 day and persisted until at least 6 weeks after primary blast on the ipsilateral side. In contrast, p-Akt was increased at 1 and 6 weeks on the contralateral side, while p-GSK3β was increased 1 day and 1 week after primary blast exposure. No significant changes in total protein levels of Akt and GSK were observed on either side of the hippocampus at any time points. Immunohistochemical results showed that increased p-Akt was mainly of neuronal origin in the CA1 region of the hippocampus and once phosphorylated, the majority was translocated to the dendritic and plasma membranes. Finally, electrophysiological data showed that evoked synaptic N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA receptor activity was
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Gu Wenbin
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Due to the lack of proper instrumentations and the difficulties in underwater measurements, the studies about water bottom vibration induced by underwater drilling blasting are seldom reported. In order to investigate the propagation and attenuation laws of blasting induced water bottom vibration, a water bottom vibration monitor was developed with consideration of the difficulties in underwater measurements. By means of this equipment, the actual water bottom vibration induced by underwater drilling blasting was measured in a field experiment. It shows that the water bottom vibration monitor could collect vibration signals quite effectively in underwater environments. The followed signal analysis shows that the characteristics of water bottom vibration and land ground vibration induced by the same underwater drilling blasting are quite different due to the different geological environments. The amplitude and frequency band of water bottom vibration both exceed those of land ground vibration. Water bottom vibration is mainly in low-frequency band that induced by blasting impact directly acts on rock. Besides the low-frequency component, land vibration contains another higher frequency band component that induced by followed water hammer wave acts on bank slope.
-
Tilted c-Axis Thin-Film Bulk Wave Resonant Pressure Sensors With Improved Sensitivity
Anderås, Emil; Katardjiev, Ilia; Yantchev, Ventsislav
2012-01-01
Aluminum nitride thin film bulk wave resonant pressure sensors employing c- and tilted c-axis texture, have been fabricated and tested for their pressure sensitivities. The c-axis tilted FBAR pressure sensors demonstrate substantially higher pressure sensitivity compared to its c-axis oriented counterpart. More specifically the thickness plate quasi-shear resonance has demonstrated the highest pressure sensitivity while further being able to preserve its performance in liquid environment.
-
Samsom, M.; Fraser, R.; Smout, A. J.; Verhagen, M. A.; Adachi, K.; Horowitz, M.; Dent, J.
1999-01-01
The organization of lumen-occlusive pressure waves is believed to be an important determinant of luminal flow. At present, little is known about the organization of small intestinal pressure waves in humans. The aim of the present study was to characterize the spatiotemporal organization of small
-
Lateral blasts at Mount St. Helens and hazard zonation
Crandell, D.R.; Hoblitt, R.P.
1986-01-01
Lateral blasts at andesitic and dacitic volcanoes can produce a variety of direct hazards, including ballistic projectiles which can be thrown to distances of at least 10 km and pyroclastic density flows which can travel at high speed to distances of more than 30 km. Indirect effect that may accompany such explosions include wind-borne ash, pyroclastic flows formed by the remobilization of rock debris thrown onto sloping ground, and lahars. Two lateral blasts occurred at a lava dome on the north flank of Mount St. Helens about 1200 years ago; the more energetic of these threw rock debris northeastward across a sector of about 30?? to a distance of at least 10 km. The ballistic debris fell onto an area estimated to be 50 km2, and wind-transported ash and lapilli derived from the lateral-blast cloud fell on an additional lobate area of at least 200 km2. In contrast, the vastly larger lateral blast of May 18, 1980, created a devastating pyroclastic density flow that covered a sector of as much as 180??, reached a maximum distance of 28 km, and within a few minutes directly affected an area of about 550 km2. The May 18 lateral blast resulted from the sudden, landslide-induced depressurization of a dacite cryptodome and the hydrothermal system that surrounded it within the volcano. We propose that lateral-blast hazard assessments for lava domes include an adjoining hazard zone with a radius of at least 10 km. Although a lateral blast can occur on any side of a dome, the sector directly affected by any one blast probably will be less than 180??. Nevertheless, a circular hazard zone centered on the dome is suggested because of the difficulty of predicting the direction of a lateral blast. For the purpose of long-term land-use planning, a hazard assessment for lateral blasts caused by explosions of magma bodies or pressurized hydrothermal systems within a symmetrical volcano could designate a circular potential hazard area with a radius of 35 km centered on the volcano
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hendijanifard, Mohammad; Willis, David A
2011-01-01
Laser-matter interactions are frequently studied by measuring the propagation of shock waves caused by the rapid laser-induced material removal. An improved method for calculating the thermo-fluid parameters behind shock waves is introduced in this work. Shock waves in ambient air, induced by pulsed Nd : YAG laser ablation of aluminium films, are measured using a shadowgraph apparatus. Normal shock solutions are applied to experimental data for shock wave positions and used to calculate pressure, temperature, and velocity behind the shock wave. Non-dimensionalizing the pressure and temperature with respect to the ambient values, the dimensionless pressure and temperature are estimated to be as high as 90 and 16, respectively, at a time of 10 ns after the ablation pulse for a laser fluence of F = 14.5 J cm -2 . The results of the normal shock solution and the Taylor-Sedov similarity solution are compared to show that the Taylor-Sedov solution under-predicts pressure when the Mach number of the shock wave is small. At a fluence of 3.1 J cm -2 , the shock wave Mach number is less than 3, and the Taylor-Sedov solution under-predicts the non-dimensional pressure by as much as 45%.
-
Computational Fluid Dynamics Application to Gun Muzzle Blast - A Validation Case Study
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Cler, Daniel
2003-01-01
...) simulations of these flow-fields a viable alternative. Techniques and specialized CFD codes are being developed in order to properly model the unsteady, very high-pressure flows of gun muzzle blast...
-
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Cervenansky, F
2001-01-01
...), and arterial blood pressure (ABP). To clarify the links, we compared two frequency methods based on coherence function to estimate the influence of ICP, ABP, and CBV on couples, respectively CBV-ABP, ICP-CBV and ICP-ABP, of slow waves...
-
Experimental study on pressure wave propagation through the open end of pipe
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yoshida, K.; Kumagai, H.
1994-01-01
The steam generators of a double pool type liquid metal fast breeder reactor (LMFBR) are used in a large sodium pool which is formed between the primary vessel and the secondary vessel and accommodates the entire secondary heat transport system. Therefore, if there is a sodium-water reaction event in the steam generator, it becomes important to evaluate the pressure rises at the walls of the primary and secondary vessels as well as those at the other secondary components. An experimental study was performed, focusing on the propagation of the initial pressure spike of the-sodium-water reaction from the bottom end of the steam generator to the sodium pool. Pressure wave propagation from inside of a pipe to an open space through the pipe end was measured. Two kinds of pressure propagation media, water and air, ensured a wide range of experimental conditions. The experimental results revealed that the pressure attenuation at the open end of a pipe can be put in order using the concept of inertial length, and that the dimensionless inertial length, i.e., the inertial length divided by the half wave length of the pressure pulse, is proportional to the square of the dimensionless diameter. These results provide a prediction method for a pressure rise by the initial pressure spike in the secondary sodium pool of the Double Pool LMFBR
-
Schmied, S.A.
2014-01-01
The aim of the research presented in this work was to investigate the novel idea to produce continuous breaking waves, whereby a pressure source was rotated within an annular wave pool. The concept was that the pressure source generates non-breaking waves that propagate inward to the inner ring of
-
The Mechanism and Application of Deep-Hole Precracking Blasting on Rockburst Prevention
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zhenhua Ouyang
2015-01-01
Full Text Available The mechanism of preventing rockburst through deep-hole precracking blasting was studied based on experimental test, numerical simulation, and field testing. The study results indicate that the deep-hole precracking could change the bursting proneness and stress state of coal-rock mass, thereby preventing the occurrence of rockburst. The bursting proneness of the whole composite structure could be weakened by the deep-hole precracking blasting. The change of stress state in the process of precracking blasting is achieved in two ways: (1 artificially break the roof apart, thus weakening the continuity of the roof strata, effectively inducing the roof caving while reducing its impact strength; and (2 the dynamic shattering and air pressure generated by the blasting can structurally change the properties of the coal-rock mass by mitigating the high stress generation and high elastic energy accumulation, thus breaking the conditions of energy transfer and rock burst occurrence.
-
Identification of Standing Pressure Waves Sources in Primary Loops of NPP with WWER and PWR
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
K.N. Proskuriakov
2016-05-01
Full Text Available Results of measurement and calculation of Eigen frequencies of coolant pressure oscillations in primary loops of NPP are presented. The simple calculation model based on equivalence of electric circuit with elastic wave propagation in liquids and gases, which gives a sensible interpretation of standing pressure waves sources is developed. It is shown, that pressurizer manifest itself as managed Helmholtz resonator generating a number of SPW (with Eigen frequencies of steam volume, water volume and their combination with coolant volume of respiratory line.
-
Anatomical manifestations of primary blast ocular trauma observed in a postmortem porcine model.
Sherwood, Daniel; Sponsel, William E; Lund, Brian J; Gray, Walt; Watson, Richard; Groth, Sylvia L; Thoe, Kimberly; Glickman, Randolph D; Reilly, Matthew A
2014-02-24
We qualitatively describe the anatomic features of primary blast ocular injury observed using a postmortem porcine eye model. Porcine eyes were exposed to various levels of blast energy to determine the optimal conditions for future testing. We studied 53 enucleated porcine eyes: 13 controls and 40 exposed to a range of primary blast energy levels. Eyes were preassessed with B-scan and ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) ultrasonography, photographed, mounted in gelatin within acrylic orbits, and monitored with high-speed videography during blast-tube impulse exposure. Postimpact photography, ultrasonography, and histopathology were performed, and ocular damage was assessed. Evidence for primary blast injury was obtained. While some of the same damage was observed in the control eyes, the incidence and severity of this damage in exposed eyes increased with impulse and peak pressure, suggesting that primary blast exacerbated these injuries. Common findings included angle recession, internal scleral delamination, cyclodialysis, peripheral chorioretinal detachments, and radial peripapillary retinal detachments. No full-thickness openings of the eyewall were observed in any of the eyes tested. Scleral damage demonstrated the strongest associative tendency for increasing likelihood of injury with increased overpressure. These data provide evidence that primary blast alone (in the absence of particle impact) can produce clinically relevant ocular damage in a postmortem model. The blast parameters derived from this study are being used currently in an in vivo model. We also propose a new Cumulative Injury Score indicating the clinical relevance of observed injuries.
-
The effect of convection and shear on the damping and propagation of pressure waves
Kiel, Barry Vincent
Combustion instability is the positive feedback between heat release and pressure in a combustion system. Combustion instability occurs in the both air breathing and rocket propulsion devices, frequently resulting in high amplitude spinning waves. If unchecked, the resultant pressure fluctuations can cause significant damage. Models for the prediction of combustion instability typically include models for the heat release, the wave propagation and damping. Many wave propagation models for propulsion systems assume negligible flow, resulting in the wave equation. In this research the effect of flow on wave propagation was studied both numerically and experimentally. Two experiential rigs were constructed, one with axial flow to study the longitudinal waves, the other with swirling flow to study circumferential waves. The rigs were excited with speakers and the resultant pressure was measured simultaneously at many locations. Models of the rig were also developed. Equations for wave propagation were derived from the Euler Equations. The resultant resembled the wave equation with three additional terms, two for the effect of the convection and a one for the effect of shear of the mean flow on wave propagation. From the experimental and numerical data several conclusions were made. First, convection and shear both act as damping on the wave propagation, reducing the magnitude of the Frequency Response Function and the resonant frequency of the modes. Second, the energy extracted from the mean flow as a result of turbulent shear for a given condition is frequency dependent, decreasing with increasing frequency. The damping of the modes, measured for the same shear flow, also decreased with frequency. Finally, the two convective terms cause the anti-nodes of the modes to no longer be stationary. For both the longitudinal and circumferential waves, the anti-nodes move through the domain even for mean flow Mach numbers less than 0.10. It was concluded that convection
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2000-03-01
From the viewpoint of energy utilization stated above, blast furnace top pressure recovery turbine (TRT) unit installability was studied at Bhilai Steel Works of Steel Authority of India, Ltd., Bokaro Steel Works of Steel Authority of India, Ltd., and Visakhapatnum Steel Works of Rashtriya Ispat Nigem. The energy consumption rate at an Indian steelmaking plant is 8Gcal/t-steel, which is larger than 5-6Gcal/t-steel of Japan and therefore needs improvement. Out of the blast furnaces in India, 26 are larger than 1,000m{sup 3}, and two of them are provided with a TRT device of now-defunct Soviet Union manufacture. The blast furnaces were examined for pressure at the top, amount of gas at the top, amount of dust, and safeness in operation. The No. 2 blast furnace of the Borkaro plant was selected for the project, and studies were made for a wet type TRT device. Improvements to be achieved by TRT device installation were calculated to be a TRT output of 5,900kW, power output of 49,100MWh/year, saved crude oil amount of 12,990toe/year, and CO2 reduction of 40,200 tons-CO2/year. (NEDO)
-
Wave-induced stresses and pore pressures near a mudline
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Andrzej Sawicki
2008-12-01
Full Text Available Conventional methods for the determination of water-wave induced stresses inseabeds composed of granular soils are based on Biot-type models, in which the soilskeleton is treated as an elastic medium. Such methods predict effective stressesin the soil that are unacceptable from the physical point of view, as they permittensile stresses to occur near the upper surface of the seabed. Therefore, in thispaper the granular soil is assumed to behave as an elastic-ideally plastic material,with the Coulomb-Mohr yield criterion adopted to bound admissible stress states inthe seabed. The governing equations are solved numerically by a~finite differencemethod. The results of simulations, carried out for the case of time-harmonicwater waves, illustrate the depth distributions of the excess pore pressures and theeffective stresses in the seabed, and show the shapes of zones of soil in the plastic state.~In particular, the effects on the seabed behaviour of suchparameters as the degree of pore water saturation, the soil permeability, and theearth pressure coefficient, are illustrated.
-
Degenerate pressure driven modified nucleus-acoustic waves in degenerate plasmas
Mamun, A. A.
2018-02-01
The existence of degenerate pressure driven modified nucleus-acoustic (DPDMNA) waves propagating in a cold degenerate quantum plasma (DQP) system [containing cold inertialess degenerate electron species (DES), cold inertial non-degenerate light nucleus species (LNS), and stationary heavy nucleus species (HNS)] is predicted for the first time. The DPDMNA waves (in which the mass density of the cold LNS provides the inertia and the cold inertialess DES gives rise to the restoring force) are new since they completely disappear if the degenerate pressure of the cold DES is neglected. It is found that the phase speed (Vp) of the DPDMNA waves decreases with the rise of the charge number density of the stationary HNS for both non-relativistic and ultra-relativistic DES, and that the ultra-relativistic DES does not have any effect on Vp when β = 1, where β = Λc/Λe with Λ e = ne 0 - 1 / 3 being the average inter-electron distance in the DQP system and Λc being the constant (˜10-10 cm) for the DES. However, the ultra-relativistic DES does have quite a significant effect on Vp for β ≫ 1 and β ≪ 1, and the ultra-relativistic effect significantly enhances (reduces) Vp for β ≫ 1 (β ≪ 1). The DPDMNA waves and their dispersion properties are expected to be useful in understanding the basic features of the electrostatic perturbation mode in space and laboratory DQP systems.
-
Vasomotor wave and blood pressure response to erect posture after operation for aortic coarctation.
Sehested, J; Schultze, G
1982-01-01
Low frequency fluctuations (five to 10/min) in blood pressure, that is vasomotor waves, were recorded in the erect position in 18 patients operated upon for an isolated aortic coarctation six to eight and a half years previously, and compared with vasomotor waves in six age matched normotensive controls with respect to frequency and amplitude. The investigation was carried out by simultaneous intra-arterial blood pressure radiotelemetry recordings from the brachial and femoral arteries in all...
-
Chávez-González, Elibet; González-Rodríguez, Emilio; Llanes-Camacho, María Del Carmen; Garí-Llanes, Merlin; García-Nóbrega, Yosvany; García-Sáez, Julieta
2014-01-01
Increased P wave dispersion are identified as a predictor of atrial fibrillation. There are associations between hypertension, P wave dispersion, constitutional and echocardiographic variables. These relationships have been scarcely studied in pediatrics. The aim of this study was to determine the relationship between P wave dispersion, blood pressure, echocardiographic and constitutional variables, and determine the most influential variables on P wave dispersion increases in pediatrics. In the frame of the PROCDEC II project, children from 8 to 11 years old, without known heart conditions were studied. Arterial blood pressure was measured in all the children; a 12-lead surface electrocardiogram and an echocardiogram were done as well. Left ventricular mass index mean values for normotensive (25.91±5.96g/m(2.7)) and hypertensive (30.34±8.48g/m(2.7)) showed significant differences P=.000. When we add prehypertensive and hypertensive there are 50.38% with normal left ventricular mass index and P wave dispersion was increased versus 13.36% of normotensive. Multiple regression demonstrated that the mean blood pressure, duration of A wave of mitral inflow, weight and height have a value of r=0.88 as related to P wave dispersion. P wave dispersion is increased in pre- and hypertensive children compared to normotensive. There are pre- and hypertensive patients with normal left ventricular mass index and increased P wave dispersion. Mean arterial pressure, duration of the A wave of mitral inflow, weight and height are the variables with the highest influence on increased P wave dispersion. Copyright © 2013 Instituto Nacional de Cardiología Ignacio Chávez. Published by Masson Doyma México S.A. All rights reserved.
-
Improvement of worker safety through the investigation of the site response to rockbursts.
CSIR Research Space (South Africa)
Hagan, TO
1998-12-01
Full Text Available : − A ML = 1,3 rockburst was successfully simulated using explosives and provided new insights into the seismic wave intensities and damage mechanisms involved. The distance of the blast holes from the tunnel wall ensured that no gas pressure....6 Maximum velocities at near tunnel wall for the post-blast model source #4. Maximum velocity for a blast pressure of 1 GPa is much lower than that recorded. Position of maximum velocity is now opposite the blast holes, due to the relatively long...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nara, N.; McCulloch, E.A.
1985-01-01
The blast cells of acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML) may be considered as a renewal population, maintained by blast stem cells capable of both self-renewal and the generation of progeny with reduced or absent proliferative potential. This growth requires that two conditions be met: first, the cultures must contain growth factors in media conditioned either by phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-stimulated mononuclear leukocytes (PHA-LCM), or by cells of the continuous bladder carcinoma line HTB9 (HTB9-CM). Second, the cell density must be maintained at 10(6) blasts/ml; this may be achieved by adding irradiated cells to smaller numbers of intact blasts. The authors are concerned with the mechanism of the feeding function. They present evidence that (a) cell-cell contact is required. (b) Blasts are heterogeneous in respect to their capacity to support growth. (c) Fractions containing membranes from blast cells will substitute for intact cells in promoting the generation of new blast progenitors in culture. (d) This membrane function may be specific for AML blasts, since membranes from blasts of lymphoblastic leukemia or normal marrow cells were inactive
-
Low-pressure degenerate four-wave mixing spectroscopy with flam atomization
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nolan, T.G.; Koutny, L.B.; Blazewicz, P.R.; Whitten, W.B.; Ramsey, J.M.
1988-01-01
A combination of degenerate four-wave mixing spectroscopy and a low-pressure sampling technique has been studied for isotopic analysis in an air-acetylene flame. Hyperfine spectra of D lines of sodium and several mixtures of lithium isotopes obtained in this way are presented
-
Design of blast simulators for nuclear testing
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mark, A.; Opalka, K.O.; Kitchens, C.W. Jr.
1983-01-01
A quasi-one-dimensional computational technique is used to model the flow of a large, complicated shock tube. The shock tube, or Large Blast Simulator, is used to simulate conventional or nuclear explosions by shaping the pressure history. Results from computations show favorable agreement when compared with data taken in the facility at Gramat, France. Such future shock tubes will include a thermal irradiation capability to better simulate a nuclear event. The computations point to the need for venting of the combustion products since the pressure history will be considerably altered as the shock propagates through these hot gases
-
Two-material optimization of plate armour for blast mitigation using hybrid cellular automata
Goetz, J.; Tan, H.; Renaud, J.; Tovar, A.
2012-08-01
With the increased use of improvised explosive devices in regions at war, the threat to military and civilian life has risen. Cabin penetration and gross acceleration are the primary threats in an explosive event. Cabin penetration crushes occupants, damaging the lower body. Acceleration causes death at high magnitudes. This investigation develops a process of designing armour that simultaneously mitigates cabin penetration and acceleration. The hybrid cellular automaton (HCA) method of topology optimization has proven efficient and robust in problems involving large, plastic deformations such as crash impact. Here HCA is extended to the design of armour under blast loading. The ability to distribute two metallic phases, as opposed to one material and void, is also added. The blast wave energy transforms on impact into internal energy (IE) inside the solid medium. Maximum attenuation occurs with maximized IE. The resulting structures show HCA's potential for designing blast mitigating armour structures.
-
Experimental simulation of gas cloud explosion effects on a reactor containment
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Thor, H.J.
1983-01-01
The loading of a nuclear power plant by pressure waves from an exploding gas cloud involves problems of large complexity. Therefore guidelines have been issued, containing conservative estimates, for the case of a deflagrating gas cloud to facilitate the design praxis. The actual load due to pressure waves depends on the type of the explosion. A deflagration with its slow burning speed is characterized by a pressure pulse with relatively long duration and low amplitude, whereas a detonation causes a blast wave with a sudden pressure rise and high peak value but short period. In the deflagration process turbulent flame acceleration also may lead to a blast wave type pressure pulse. Results of experiments are presented carried out to evaluate the loading of a nuclear power plant by pressure pulses of both characteristics. The configuration of the model and the pulse duration are scaled 1/200. An intricate wave pattern is caused by the reflections and diffractions of the pressure waves due to the complex layout. Many parameters are involved which depend on the type of explosion, e.g. peak pressure, duration of positive and negative phase, rise time. (orig./WL)
-
Present state of Ancit hot briquetting. Pt. 2. Blast furnace trials
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Limpach, R; Hermann, W; Schmit, R; Heusbourg, J; Poos, A
1980-09-01
During the last years three long-time blast furnace tests have been run with Ancit formed coke as partial solid fuel. Each trial covered the charging of 8 000 tons of Ancit. Three different kinds of sinter burden were charged: hematite, rich P-ores, low-Fe Minette ores. The three blast furnaces were differentiated as well in hearth diameters as in pig iron productivity; the larger blast furnace was operated on high top pressure. The Ancit formed cokes replacing partially the slot-oven coke had different characteristics; two tests were run on Ancit of 70 ccm and one with 90 ccm unit briquette volume. According to the blast furnace burdening and driving conditions, up to 58% by weight of slot-oven coke could be replaced by formed coke. The Ancit formed cokes proved to have adequate mechanical properties, but the regular briquette shape and comparatively lower voidage of formed coke layers limited the replacement ratio versus oven coke. All tests showed that the permeability, mainly in the bosh, decreased when charging formed coke. The resulting decrease in productivity could be neutralised by increasing the high top pressure. Generally, the dry fuel rate per ton of pig iron increased somewhat; this was due to the higher volatiles content of formed cokes. On the other hand, these volatiles raised the lower calorific value of the top gas; no tar deposits were ever noticed. As a result of these trial, partial replacements of slot-oven coke by Ancit formed cokes can be recommended.
-
Thermal-hydraulic behaviors of vapor-liquid interface due to arrival of a pressure wave
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Inoue, Akira; Fujii, Yoshifumi; Matsuzaki, Mitsuo [Tokyo Institute of Technology (Japan)
1995-09-01
In the vapor explosion, a pressure wave (shock wave) plays a fundamental role for triggering, propagation and enhancement of the explosion. Energy of the explosion is related to the magnitude of heat transfer rate from hot liquid to cold volatile one. This is related to an increasing rate of interface area and to an amount of transient heat flux between the liquids. In this study, the characteristics of transient heat transfer and behaviors of vapor film both on the platinum tube and on the hot melt tin drop, under same boundary conditions have been investigated. It is considered that there exists a fundamental mechanism of the explosion in the initial expansion process of the hot liquid drop immediately after arrival of pressure wave. The growth rate of the vapor film is much faster on the hot liquid than that on the solid surface. Two kinds of roughness were observed, one due to the Taylor instability, by rapid growth of the explosion bubble, and another, nucleation sites were observed at the vapor-liquid interface. Based on detailed observation of early stage interface behaviors after arrival of a pressure wave, the thermal fragmentation mechanism is proposed.
-
Ouyang, Jessica; Pace, Edward; Lepczyk, Laura; Kaufman, Michael; Zhang, Jessica; Perrine, Shane A; Zhang, Jinsheng
2017-07-07
Blast-induced tinitus is the number one service-connected disability that currently affects military personnel and veterans. To elucidate its underlying mechanisms, we subjected 13 Sprague Dawley adult rats to unilateral 14 psi blast exposure to induce tinnitus and measured auditory and limbic brain activity using manganese-enhanced MRI (MEMRI). Tinnitus was evaluated with a gap detection acoustic startle reflex paradigm, while hearing status was assessed with prepulse inhibition (PPI) and auditory brainstem responses (ABRs). Both anxiety and cognitive functioning were assessed using elevated plus maze and Morris water maze, respectively. Five weeks after blast exposure, 8 of the 13 blasted rats exhibited chronic tinnitus. While acoustic PPI remained intact and ABR thresholds recovered, the ABR wave P1-N1 amplitude reduction persisted in all blast-exposed rats. No differences in spatial cognition were observed, but blasted rats as a whole exhibited increased anxiety. MEMRI data revealed a bilateral increase in activity along the auditory pathway and in certain limbic regions of rats with tinnitus compared to age-matched controls. Taken together, our data suggest that while blast-induced tinnitus may play a role in auditory and limbic hyperactivity, the non-auditory effects of blast and potential traumatic brain injury may also exert an effect.
-
Enhancing cuttings removal with gas blasts while drilling on Mars
Zacny, K. A.; Quayle, M. C.; Cooper, G. A.
2005-04-01
Future missions to Mars envision use of drills for subsurface exploration. Since the Martian atmosphere precludes the use of liquids for cuttings removal, proposed drilling machines utilize mechanical cuttings removal systems such as augers. However, an auger can substantially contribute to the total power requirements, and in the worst scenario it can choke. A number of experiments conducted under Martian pressures showed that intermittent blasts of gas at low differential pressures can effectively lift the cuttings out of the hole. A gas flushing system could be incorporated into the drill assembly for assistance in clearing the holes of rock cuttings or for redundancy in case of auger jamming. A number of variables such as the particle size distribution of the rock powder, the type of gas used, the bit and auger side clearances, the initial mass of cuttings, and the ambient pressure were investigated and found to affect the efficiency. In all tests the initial volume of gas was close to 1 L and the differential pressure was varied to achieve desired clearing efficiencies. Particles were being lifted out of the hole at a maximum speed of 6 m/s at a differential pressure of 25 torr and ambient pressure of 5 torr. Flushing tests lasted on average for 2 s. The power required to compress the thin Martian atmosphere to achieve a sufficient gas blast every minute or so at 10% efficiency was calculated to be of the order of a few watts.
-
Castelain, V; Hervé, P; Lecarpentier, Y; Duroux, P; Simonneau, G; Chemla, D
2001-03-15
The purpose of this time-domain study was to compare pulmonary artery (PA) pulse pressure and wave reflection in chronic pulmonary thromboembolism (CPTE) and primary pulmonary hypertension (PPH). Pulmonary artery pressure waveform analysis provides a simple and accurate estimation of right ventricular afterload in the time-domain. Chronic pulmonary thromboembolism and PPH are both responsible for severe pulmonary hypertension. Chronic pulmonary thromboembolism and PPH predominantly involve proximal and distal arteries, respectively, and may lead to differences in PA pressure waveform. High-fidelity PA pressure was recorded in 14 patients (7 men/7 women, 46 +/- 14 years) with CPTE (n = 7) and PPH (n = 7). We measured thermodilution cardiac output, mean PA pressure (MPAP), PA pulse pressure (PAPP = systolic - diastolic PAP) and normalized PAPP (nPAPP = PPAP/MPAP). Wave reflection was quantified by measuring Ti, that is, the time between pressure upstroke and the systolic inflection point (Pi), deltaP, that is, the systolic PAP minus Pi difference, and the augmentation index (deltaP/PPAP). At baseline, CPTE and PPH had similar cardiac index (2.4 +/- 0.4 vs. 2.5 +/- 0.5 l/min/m2), mean PAP (59 +/- 9 vs. 59 +/- 10 mm Hg), PPAP (57 +/- 13 vs. 53 +/- 13 mm Hg) and nPPAP (0.97 +/- 0.16 vs. 0.89 +/- 0.13). Chronic pulmonary thromboembolism had shorter Ti (90 +/- 17 vs. 126 +/- 16 ms, p PPAP (0.26 +/- 0.01 vs. 0.09 +/- 0.07, p < 0.01). Our study indicated that: 1) CPTE and PPH with severe pulmonary hypertension had similar PA pulse pressure, and 2) wave reflection is elevated in both groups, and CPTE had increased and anticipated wave reflection as compared with PPH, thus suggesting differences in the pulsatile component of right ventricular afterload.
-
NOBLAST and JAMBLAST: New Options for BLAST and a Java Application Manager for BLAST results.
Lagnel, Jacques; Tsigenopoulos, Costas S; Iliopoulos, Ioannis
2009-03-15
NOBLAST (New Options for BLAST) is an open source program that provides a new user-friendly tabular output format for various NCBI BLAST programs (Blastn, Blastp, Blastx, Tblastn, Tblastx, Mega BLAST and Psi BLAST) without any use of a parser and provides E-value correction in case of use of segmented BLAST database. JAMBLAST using the NOBLAST output allows the user to manage, view and filter the BLAST hits using a number of selection criteria. A distribution package of NOBLAST and JAMBLAST including detailed installation procedure is freely available from http://sourceforge.net/projects/JAMBLAST/ and http://sourceforge.net/projects/NOBLAST. Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
-
Development of a Strategy for Simulating Blast-Vehicle Interactions
2010-09-01
Magnus effect . Although large rotational speeds were measured, it was concluded that the Magnus force had little influence and did not significantly...CHEM (rigid flat-plate). 104 Figure 5.3: Geometry used for blast wave interacting with a cylinder (Ofengeim and Drikakis 1997). 105 Figure 5.4: CFD...their effects on vehicles and their human occupants. The framework couples the MPMICE CFD code with DYNA3D and LS-DYNA finite element codes
-
Two Dimensional Finite Element Analysis for the Effect of a Pressure Wave in the Human Brain
Ponce L., Ernesto; Ponce S., Daniel
2008-11-01
Brain injuries in people of all ages is a serious, world-wide health problem, with consequences as varied as attention or memory deficits, difficulties in problem-solving, aggressive social behavior, and neuro degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Brain injuries can be the result of a direct impact, but also pressure waves and direct impulses. The aim of this work is to develop a predictive method to calculate the stress generated in the human brain by pressure waves such as high power sounds. The finite element method is used, combined with elastic wave theory. The predictions of the generated stress levels are compared with the resistance of the arterioles that pervade the brain. The problem was focused to the Chilean mining where there are some accidents happen by detonations and high sound level. There are not formal medical investigation, however these pressure waves could produce human brain damage.
-
Evaluation of refractory lining wear of Companhia Siderurgica Nacional (CSN) blast furnaces
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Santos, N.J. dos; Mello, A.H.B. de; Pereira, C.L.; Paula Sarkis, D. de; Martins Filho, D.I.; Banados Perez, H.E.; Carvalho, G.; Daltro, T.F.L.
1984-01-01
The blast furnace refractory linings are submitted to unfavourable conditions such as alkalis attack, temperature, top pressure, abrasion and so forth... After studies on distribution and installation of radioactive sources with low activities in the refractory lining, it was possible to develop a new technique of thickness evaluation and attendance of wearing in the furnace lining. The viability analysis, simulated laboratory tests, localization, identification, installations and periodical measurements of the radioactive sources are described, as well the results obtained on the present campaign of CSN Blast Furnaces. (Author) [pt
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Vassout, P.; Franke, R.; Parmentier, G.; Evrard, G.; Dancer, A.
1987-01-01
A theoretical study on the propagation of a pressure wave in a diphasic medium, when compared to the onset mechanism of pulmonary lesions in subjects exposed to strong shock waves, shows an increase in the incident overpressure at the interface level. Using hydrophones, intracorporal pressure was measured in pigs. The authors recorded the costal wall acceleration on the side directly exposed to the shock wave and calculated the displacement of the costal wall after a shock wave passed by. These experiments were conducted for shock waves in a free field, at an overpressure peak level ranging from 26 kFPa to 380 kPa and for a first positive phase lasting 2 ms. Sensors placed in an intracorporal position detected no increase of the overpressure level for any value of the incident pressure. A comparison of the costal wall displacement, measured experimentally, relative to the theoretical displacement of the entire animal mass indicates that the largest relative displacement of the costal wall could be the origin of the pulmonary lesions found. 5 refs., 13 figs
-
High resolution seismic tomography imaging of Ireland with quarry blast data
Arroucau, P.; Lebedev, S.; Bean, C. J.; Grannell, J.
2017-12-01
Local earthquake tomography is a well established tool to image geological structure at depth. That technique, however, is difficult to apply in slowly deforming regions, where local earthquakes are typically rare and of small magnitude, resulting in sparse data sampling. The natural earthquake seismicity of Ireland is very low. That due to quarry and mining blasts, on the other hand, is high and homogeneously distributed. As a consequence, and thanks to the dense and nearly uniform coverage achieved in the past ten years by temporary and permanent broadband seismological stations, the quarry blasts offer an alternative approach for high resolution seismic imaging of the crust and uppermost mantle beneath Ireland. We detected about 1,500 quarry blasts in Ireland and Northern Ireland between 2011 and 2014, for which we manually picked more than 15,000 P- and 20,000 S-wave first arrival times. The anthropogenic, explosive origin of those events was unambiguously assessed based on location, occurrence time and waveform characteristics. Here, we present a preliminary 3D tomographic model obtained from the inversion of 3,800 P-wave arrival times associated with a subset of 500 events observed in 2011, using FMTOMO tomographic code. Forward modeling is performed with the Fast Marching Method (FMM) and the inverse problem is solved iteratively using a gradient-based subspace inversion scheme after careful selection of damping and smoothing regularization parameters. The results illuminate the geological structure of Ireland from deposit to crustal scale in unprecedented detail, as demonstrated by sensitivity analysis, source relocation with the 3D velocity model and comparisons with surface geology.
-
Divide and Conquer (DC BLAST: fast and easy BLAST execution within HPC environments
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Won Cheol Yim
2017-06-01
Full Text Available Bioinformatics is currently faced with very large-scale data sets that lead to computational jobs, especially sequence similarity searches, that can take absurdly long times to run. For example, the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST and BLAST+ suite, which is by far the most widely used tool for rapid similarity searching among nucleic acid or amino acid sequences, is highly central processing unit (CPU intensive. While the BLAST suite of programs perform searches very rapidly, they have the potential to be accelerated. In recent years, distributed computing environments have become more widely accessible and used due to the increasing availability of high-performance computing (HPC systems. Therefore, simple solutions for data parallelization are needed to expedite BLAST and other sequence analysis tools. However, existing software for parallel sequence similarity searches often requires extensive computational experience and skill on the part of the user. In order to accelerate BLAST and other sequence analysis tools, Divide and Conquer BLAST (DCBLAST was developed to perform NCBI BLAST searches within a cluster, grid, or HPC environment by using a query sequence distribution approach. Scaling from one (1 to 256 CPU cores resulted in significant improvements in processing speed. Thus, DCBLAST dramatically accelerates the execution of BLAST searches using a simple, accessible, robust, and parallel approach. DCBLAST works across multiple nodes automatically and it overcomes the speed limitation of single-node BLAST programs. DCBLAST can be used on any HPC system, can take advantage of hundreds of nodes, and has no output limitations. This freely available tool simplifies distributed computation pipelines to facilitate the rapid discovery of sequence similarities between very large data sets.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Keller, M.D.; Khan, P.K.
1997-12-01
An explosion is the result of a rapid chemical reaction which generates transient air pressure waves called blast waves. There has been much research on the processes of blast wave formation, propagation of blast waves, and quantification of the incident and reflected blast overpressures. The magnitude of blast overpressure, in a partially vented environment, is mainly a function of the type and quantity of detonating material, the amount of available venting, and the orientation and configuration of the reflecting surfaces. In addition to blast overpressure, an explosion can also generate high energy missiles (such as fragments), shock loads, and rapid rise of temperature in the confined space. This study concentrates on the effects of blast overpressure on a 40 feet diameter reinforced concrete cylinder with a hemispherical dome roof, supported on a 3 feet thick reinforced concrete pad, and buried under a minimum of 15 feet of soil used for radiation shielding at the top of the dome. The scope of this study is to determine whether the structure can withstand the blast overpressure generated by the postulated explosion without exceeding allowable design criteria
-
An oxygen pressure sensor using surface acoustic wave devices
Leighty, Bradley D.; Upchurch, Billy T.; Oglesby, Donald M.
1993-01-01
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) piezoelectric devices are finding widespread applications in many arenas, particularly in the area of chemical sensing. We have developed an oxygen pressure sensor based on coating a SAW device with an oxygen binding agent which can be tailored to provide variable sensitivity. The coating is prepared by dissolving an oxygen binding agent in a toluene solution of a copolymer which is then sprayed onto the surface of the SAW device. Experimental data shows the feasibility of tailoring sensors to measure the partial pressure of oxygen from 2.6 to 67 KPa (20 to 500 torr). Potential applications of this technology are discussed.
-
Pressure and tension waves from bubble collapse near a solid boundary: A numerical approach.
Lechner, Christiane; Koch, Max; Lauterborn, Werner; Mettin, Robert
2017-12-01
The acoustic waves being generated during the motion of a bubble in water near a solid boundary are calculated numerically. The open source package OpenFOAM is used for solving the Navier-Stokes equation and extended to include nonlinear acoustic wave effects via the Tait equation for water. A bubble model with a small amount of gas is chosen, the gas obeying an adiabatic law. A bubble starting from a small size with high internal pressure near a flat, solid boundary is studied. The sequence of events from bubble growth via axial microjet formation, jet impact, annular nanojet formation, torus-bubble collapse, and bubble rebound to second collapse is described. The different pressure and tension waves with their propagation properties are demonstrated.
-
Troitskaya, Yuliya; Kandaurov, Alexander; Sergeev, Daniil; Bopp, Maximilian; Caulliez, Guillemette
2017-04-01
Air-sea coupling in general is important for weather, climate, fluxes. Wind wave source is crucially important for surface waves' modeling. But the wind-wave growth rate is strongly uncertain. Using direct measurements of pressure by wave-following Elliott probe [1] showed, weak and indefinite dependence of wind-wave growth rate on the wave steepness, while Grare et.al. [2] discuss the limitations of direct measurements of pressure associated with the inability to measure the pressure close to the surface by contact methods. Recently non-invasive methods for determining the pressure on the basis of technology of time-resolved PIV are actively developed [3]. Retrieving air flow velocities by 2D PIV techniques was started from Reul et al [4]. The first attempt for retrieving wind pressure field of waves in the laboratory tank from the time-resolved PIV measurements was done in [5]. The experiments were performed at the Large Air-Sea Interaction Facility (LASIF) - MIO/Luminy (length 40 m, cross section of air channel 3.2 x 1.6 m). For 18 regimes with wind speed up to 14 m/s including presence of puddle waves, a combination of time resolved PIV technique and optical measurements of water surface form was applied to detailed investigation of the characteristics of the wind flow over the water surface. Ammonium chloride smoke was used for flow visualization illuminated by two 6 Wt blue diode lasers combined into a vertical laser plane. Particle movement was captured with high-speed camera using Scheimpflug technique (up to 20 kHz frame rate with 4-frame bursts, spatial resolution about 190 μm, field of view 314x12 mm). Velocity air flow field was retrieved by PIV images processing with adaptive cross-correlation method on the curvilinear grid following surface wave form. The resulting time resolved instantaneous velocity fields on regular grid allowed us to obtain momentum fluxes directly from measured air velocity fluctuations. The average wind velocity patterns were
-
Novel method to dynamically load cells in 3D-gel culture for primary blast injury studies
Sory, David; Cepa-Areias, Anabela; Overby, Darryl; Proud, William; Institute of Shock Physics, Department of Bioengineering; Royal British Legion CentreBlast I Collaboration
2015-06-01
For at least a century explosive devices have been reported as one of the most important causes of injuries on battlefield in military conflicts as well as in terrorist attacks. Although significant experimental and modelling efforts have been focussed on blast injury at the organ or tissue level, few studies have investigated the mechanism of blast injury at the cellular level. This paper introduces an in vitro method compatible with living cells to examine the effects of high stress and short-duration pulses similar to those observed in blast waves. The experimental phase involved high strain rate axial compression of biological cylindrical specimens within a hermetically sealed sample holder made of a biocompatible polymer. Numerical simulations were performed in order to characterize the loading path within the sample and assess the loading conditions. A proof of concept is presented so as to establish a new window to address fundamental questions regarding primary blast injury at the cellular level. The Institute of Shock Physics acknowledges the support of AWE, Aldermaston, UK and Imperial College London. The Centre for Blast Injury Studies acknowledges the support of the Royal British Legion and Imperial College London.
-
An analysis of the heap construction by long hole blasting for in-situ leaching of blasted ore
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Yang Shijiao
1999-01-01
The author establishes specific requirements for heap construction by blasting on the basis of the mechanism for in situ leaching of blasted ore, analyses the feasibility of heap construction by long hole blasting, selection of the blast plan and the relevant technological problems, and gives a case of heap construction by long hole blasting in Renhua uranium mine
-
Rock fragmentation control in opencast blasting
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P.K. Singh
2016-04-01
Full Text Available The blasting operation plays a pivotal role in the overall economics of opencast mines. The blasting sub-system affects all the other associated sub-systems, i.e. loading, transport, crushing and milling operations. Fragmentation control through effective blast design and its effect on productivity are the challenging tasks for practicing blasting engineer due to inadequate knowledge of actual explosive energy released in the borehole, varying initiation practice in blast design and its effect on explosive energy release characteristic. This paper describes the result of a systematic study on the impact of blast design parameters on rock fragmentation at three mines in India. The mines use draglines and shovel–dumper combination for removal of overburden. Despite its pivotal role in controlling the overall economics of a mining operation, the expected blasting performance is often judged almost exclusively on the basis of poorly defined parameters such as powder factor and is often qualitative which results in very subjective assessment of blasting performance. Such an approach is very poor substitutes for accurate assessment of explosive and blasting performance. Ninety one blasts were conducted with varying blast designs and charging patterns, and their impacts on the rock fragmentation were documented. A high-speed camera was deployed to record the detonation sequences of the blasts. The efficiency of the loading machines was also correlated with the mean fragment size obtained from the fragmentation analyses.
-
Simulations of nonlinear continuous wave pressure fields in FOCUS
Zhao, Xiaofeng; Hamilton, Mark F.; McGough, Robert J.
2017-03-01
The Khokhlov - Zabolotskaya - Kuznetsov (KZK) equation is a parabolic approximation to the Westervelt equation that models the effects of diffraction, attenuation, and nonlinearity. Although the KZK equation is only valid in the far field of the paraxial region for mildly focused or unfocused transducers, the KZK equation is widely applied in medical ultrasound simulations. For a continuous wave input, the KZK equation is effectively modeled by the Bergen Code [J. Berntsen, Numerical Calculations of Finite Amplitude Sound Beams, in M. F. Hamilton and D. T. Blackstock, editors, Frontiers of Nonlinear Acoustics: Proceedings of 12th ISNA, Elsevier, 1990], which is a finite difference model that utilizes operator splitting. Similar C++ routines have been developed for FOCUS, the `Fast Object-Oriented C++ Ultrasound Simulator' (http://www.egr.msu.edu/˜fultras-web) to calculate nonlinear pressure fields generated by axisymmetric flat circular and spherically focused ultrasound transducers. This new routine complements an existing FOCUS program that models nonlinear ultrasound propagation with the angular spectrum approach [P. T. Christopher and K. J. Parker, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 90, 488-499 (1991)]. Results obtained from these two nonlinear ultrasound simulation approaches are evaluated and compared for continuous wave linear simulations. The simulation results match closely in the farfield of the paraxial region, but the results differ in the nearfield. The nonlinear pressure field generated by a spherically focused transducer with a peak surface pressure of 0.2MPa radiating in a lossy medium with β = 3.5 is simulated, and the computation times are also evaluated. The nonlinear simulation results demonstrate acceptable agreement in the focal zone. These two related nonlinear simulation approaches are now included with FOCUS to enable convenient simulations of nonlinear pressure fields on desktop and laptop computers.
-
Leaching of Carbothermic Reduced Titanium-bearing Blast Furnace Slag by Acid
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China (English)
ZHEN Yulan; ZHANG Guohua; CHOU Kuochih
2016-01-01
The kinetics of the leaching of carbothermic reduced titanium-bearing blast furnace slag in Panzhihua Iron and Steel Company with acid system under atmosphere pressure was studied. The results show that the temperature and concentration have significant influence on leaching of carbothermic reduced titanium-bearing blast furnace slag by ac-id. The experimental data of leaching indicate that the shrinking core model with chemical reaction controlled process is most applicable for the acid leaching. The apparent activation energy can be estimated to be from 23 to 32 kJ/mol. Fur-thermore, the main products are TiC and SiO2 after leaching.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Ming-Xiong Huang
2014-01-01
Full Text Available Traumatic brain injury (TBI is a leading cause of sustained impairment in military and civilian populations. However, mild TBI (mTBI can be difficult to detect using conventional MRI or CT. Injured brain tissues in mTBI patients generate abnormal slow-waves (1–4 Hz that can be measured and localized by resting-state magnetoencephalography (MEG. In this study, we develop a voxel-based whole-brain MEG slow-wave imaging approach for detecting abnormality in patients with mTBI on a single-subject basis. A normative database of resting-state MEG source magnitude images (1–4 Hz from 79 healthy control subjects was established for all brain voxels. The high-resolution MEG source magnitude images were obtained by our recent Fast-VESTAL method. In 84 mTBI patients with persistent post-concussive symptoms (36 from blasts, and 48 from non-blast causes, our method detected abnormalities at the positive detection rates of 84.5%, 86.1%, and 83.3% for the combined (blast-induced plus with non-blast causes, blast, and non-blast mTBI groups, respectively. We found that prefrontal, posterior parietal, inferior temporal, hippocampus, and cerebella areas were particularly vulnerable to head trauma. The result also showed that MEG slow-wave generation in prefrontal areas positively correlated with personality change, trouble concentrating, affective lability, and depression symptoms. Discussion is provided regarding the neuronal mechanisms of MEG slow-wave generation due to deafferentation caused by axonal injury and/or blockages/limitations of cholinergic transmission in TBI. This study provides an effective way for using MEG slow-wave source imaging to localize affected areas and supports MEG as a tool for assisting the diagnosis of mTBI.
-
Treadmill walking with load carriage increases aortic pressure wave reflection.
Ribeiro, Fernando; Oliveira, Nórton L; Pires, Joana; Alves, Alberto J; Oliveira, José
2014-01-01
The study examined the effects of treadmill walking with load carriage on derived measures of central pressure and augmentation index in young healthy subjects. Fourteen male subjects (age 31.0 ± 1.0 years) volunteered in this study. Subjects walked 10 minutes on a treadmill at a speed of 5 km/h carrying no load during one session and a load of 10% of their body weight on both upper limbs in two water carboys with handle during the other session. Pulse wave analysis was performed at rest and immediately after exercise in the radial artery of the right upper limb by applanation tonometry. The main result indicates that walking with load carriage sharply increased augmentation index at 75 bpm (-5.5 ± 2.2 to -1.4 ± 2.2% vs. -5.2 ± 2.8 to -5.5 ± 2.1%, p<0.05), and also induced twice as high increments in central pulse pressure (7.4 ± 1.5 vs. 3.1 ± 1.4 mmHg, p<0.05) and peripheral (20.5 ± 2.7 vs. 10.3 ± 2.5 mmHg, p<0.05) and central systolic pressure (14.7 ± 2.1 vs. 7.4 ± 2.0 mmHg, p<0.05). Walking with additional load of 10% of their body weight (aerobic exercise accompanied by upper limb isometric contraction) increases derived measures of central pressure and augmentation index, an index of wave reflection and arterial stiffness. Copyright © 2013 Sociedade Portuguesa de Cardiologia. Published by Elsevier España. All rights reserved.
-
Sun, Yimin; Verschuur, Eric; van Borselen, Roald
2018-03-01
The Rayleigh integral solution of the acoustic Helmholtz equation in a homogeneous medium can only be applied when the integral surface is a planar surface, while in reality almost all surfaces where pressure waves are measured exhibit some curvature. In this paper we derive a theoretically rigorous way of building propagation operators for pressure waves on an arbitrarily curved surface. Our theory is still based upon the Rayleigh integral, but it resorts to matrix inversion to overcome the limitations faced by the Rayleigh integral. Three examples are used to demonstrate the correctness of our theory - propagation of pressure waves acquired on an arbitrarily curved surface to a planar surface, on an arbitrarily curved surface to another arbitrarily curved surface, and on a spherical cap to a planar surface, and results agree well with the analytical solutions. The generalization of our method for particle velocities and the calculation cost of our method are also discussed.
-
Wohlfahrt, Peter; Krajcoviechová, Alena; Seidlerová, Jitka; Mayer, Otto; Filipovsky, Jan; Cífková, Renata
2014-02-01
Central systolic blood pressure (cSBP) can be derived by the general transfer function of the radial pressure wave, as used in the SphygmoCor device, or by regression equation from directly measured late systolic shoulder of the radial pressure wave (pSBP2), as used in the Omron HEM-9000AI device. The aim of this study was to compare the SphygmoCor estimates of cSBP with 2 estimates of cSBP provided by the Omron HEM-9000AI (cSBP, pSBP2) in a large cohort of the white population. In 391 patients aged 52.3±13.5 years (46% men) from the Czech post-MONICA Study, cSBP was measured using the SphygmoCor and Omron HEM-9000AI devices in random order. Omron cSBP and pSBP2 were perfectly correlated (r = 1.0; P wave provides a comparable accuracy with the validated general transfer function. When comparing Omron HEM-9000AI and SphygmoCor estimates of cSBP, Omron pSBP2 should be used. The difference between both devices in cSBP may be explained by differences in calibration.
-
Design, development and testing of a high speed door for a blast containment fixture
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Shapiro, C.
1991-01-01
This paper reports that the concept of a large door able to close over a three foot diameter hole in less than 50 milliseconds evolved during the design of a test containment fixture at the Idaho National Engineering laboratory (INEL). This facility was designed for use at the Aberdeen Proving Ground (APG) in Aberdeen, Maryland. EPA regulations required new technologies for blast containment at APG, which culminated in the design of the blast chamber with a high speed door at its entrance. The main requirement of the fixture is to contain large explosion pressure pulses and explosive by-products during a variety of test scenarios. The door was designed to allow entrance of test projectiles and then to close over the entrance hole to contain explosive by-products inside the fixture. The speed of the projectile and the resultant blast pressure pulse required door closure within 56 msec. Analytical modelling of the door closure indicated velocities of up to 150 ft/sec before impact, for closure within the required time. Lightweight materials were used for the moving parts to minimize this impact force, including aluminum honeycomb composite panels and energy absorbers. Actuation was accomplished with a standard explosive bolt. High pressure nitrogen accelerated the door during closure. Time measurement for the door closer were obtained using high speed video equipment
-
Blast response of corroded steel plates
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Eslamimajd, Alireza; RahbarRanji, Ahmad [AmirKabir University of Technology, Tehran (Korea, Republic of)
2014-05-15
Numerical results for one- and both-sided corroded steel plates subjected to blast loading are presented. Finite element analysis, with ABAQUS software, is employed to determine the deformation and stress distributions. The results for the case of triangular pulse pressure on un-corroded plates are validated against literature-based data and then, detailed parametric studies are carried-out. The effects of influential parameters including, plate aspect ratio, degree of pit and different ratio of pit depth at each sides of the plate are investigated. The results show that position of pitted surface in respect to applied pressure is the most influential parameter on reduction of dynamic load carrying capacity of pitted plates. By increasing degree of pitting, reduction of dynamic load carrying capacity decrease more.
-
Human Injury Criteria for Underwater Blasts.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Rachel M Lance
Full Text Available Underwater blasts propagate further and injure more readily than equivalent air blasts. Development of effective personal protection and countermeasures, however, requires knowledge of the currently unknown human tolerance to underwater blast. Current guidelines for prevention of underwater blast injury are not based on any organized injury risk assessment, human data or experimental data. The goal of this study was to derive injury risk assessments for underwater blast using well-characterized human underwater blast exposures in the open literature. The human injury dataset was compiled using 34 case reports on underwater blast exposure to 475 personnel, dating as early as 1916. Using severity ratings, computational reconstructions of the blasts, and survival information from a final set of 262 human exposures, injury risk models were developed for both injury severity and risk of fatality as functions of blast impulse and blast peak overpressure. Based on these human data, we found that the 50% risk of fatality from underwater blast occurred at 302±16 kPa-ms impulse. Conservatively, there is a 20% risk of pulmonary injury at a kilometer from a 20 kg charge. From a clinical point of view, this new injury risk model emphasizes the large distances possible for potential pulmonary and gut injuries in water compared with air. This risk value is the first impulse-based fatality risk calculated from human data. The large-scale inconsistency between the blast exposures in the case reports and the guidelines available in the literature prior to this study further underscored the need for this new guideline derived from the unique dataset of actual injuries in this study.
-
Blasting agents and initiation systems
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Fiscor, S.
2000-01-01
Although blasting differs between and within each industry, as a whole, the mines and quarries are making a shift from a purely ammonium nitrate/fuel oil (ANFO) mixture to a blend of emulsion and ANFO on a straight emulsion. Non-electric (shock tube) initiation systems have provided a viable alternative to the electric detonator (blasting cap). Explosives manufacturers are seeing their roles changes to being blasting contractors or consultants rather than just suppliers. The article discusses these trends and gives examples of typical blasting techniques and amounts of blasting agent used at large USA surface coal mines. Electric caps are still used in blasting underground coal. The Ensign Bickford Co. (EBCo) is developing electronic detonators and has been field testing an electronic initiator, the DIGIDET detonator, for the last four years. When commercially available, electronic detonators will be accurate but will come with a hefty price tag. 2 photos.
-
Higuchi, A.; Watanabe, T.
2013-12-01
Pore-fluid pressure in seismogenic zones can play a key role in the occurrence of earthquakes (e.g., Sibson, 2009). Its evaluation via geophysical observations can lead to a good understanding of seismic activities. The evaluation requires a thorough understanding of the influence of the pore-fluid pressure on geophysical observables like seismic velocity and electrical conductivity. We have studied the influence of pore-fluid pressure on elastic wave velocity and electrical conductivity in water-saturated rocks. Fine grained (100-500μm) biotite granite (Aji, Kagawa pref., Japan) was used as rock samples. The density is 2.658-2.668 g/cm3, and the porosity 0.68-0.87%. The sample is composed of 52.8% plagioclase, 36.0% Quartz, 3.0% K-feldspar, 8.2% biotite. SEM images show that a lot of grain boundaries are open. Few intracrystalline cracks were observed. Following the method proposed by David and Zimmerman (2012), the distribution function of crack aspect ratio was evaluated from the pressure dependence of compressional and shear wave velocities in a dry sample. Cylindrical sample has dimensions of 25 mm in diameter and 30 mm in length, and saturated with 0.01 mol/l KCl aqueous solution. Compressional and shear wave velocities were measured with the pulse transmission technique (PZT transducers, f=2 MHz), and electrical conductivity the two-electrode method (Ag-AgCl electrodes, f=1 Hz-100 kHz). Simultaneous measurements of velocities and conductivity were made using a 200 MPa hydrostatic pressure vessel, in which confining and pore-fluid pressures can be separately controlled. The pore-fluid is electrically insulated from the metal work of the pressure vessel by using a newly designed plastic device (Watanabe and Higuchi, 2013). The confining pressure was progressively increased up to 25 MPa, while the pore-fluid pressure was kept at 0.1 MPa. It took five days or longer for the electrical conductivity to become stationary after increasing the confining pressure
-
Assessment of dynamic mechanical behaviour of reinforced concrete beams using a blast simulator
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Peroni Marco
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Critical infrastructures may become the target of terrorist bombing attacks or may have to withstand explosive loads due to accidents. The impulsive load connected to explosions is delivered to the structure in a few milliseconds forcing it to respond or fail in a peculiar mode. With reference to the above scientific framework this work presents an innovative apparatus designed and developed at the European Laboratory for Structural Assessment to reproduce a blast pressure history without using explosives. This apparatus is practically a hybrid nitrogen-spring-driven actuator that accelerates masses of up to 100 kg to a maximum velocity of about 25 m/s that impact against the tested structure. The pressure-load history applied to the structure is modulated and reshaped using appropriate layers of elastic soft materials (such as polymeric foams placed between the specimen and the impacting masses. Specific instrumentation has extensively been utilised to investigate the blast simulator performance and to precisely measure the pressure loads applied to the specimen. A series of tests on real scale reinforced concrete beams/columns (250 × 250 × 2200 mm has been performed to efficiently assess the performance and potentiality of the new blast simulator. Results are under evaluation. In addition to the experimental work, a series of numerical simulations by means of the explicit FEM code EUROPLEXUS have been carried out to support and improve the equipment design.
-
Zeng, Yaping; Deyo, Donald; Parsley, Margaret A.; Hawkins, Bridget E.; Prough, Donald S.; DeWitt, Douglas S.
2018-01-01
Abstract To determine the effects of mild blast-induced traumatic brain injury (bTBI), several groups of rats were subjected to blast injury or sham injury in a compressed air-driven shock tube. The effects of bTBI on relative cerebral perfusion (laser Doppler flowmetry [LDF]), and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) cerebral vascular resistance were measured for 2 h post-bTBI. Dilator responses to reduced intravascular pressure were measured in isolated middle cerebral arterial (MCA) segments, ex vivo, 30 and 60 min post-bTBI. Neuronal injury was assessed (Fluoro-Jade C [FJC]) 24 and 48 h post-bTBI. Neurological outcomes (beam balance and walking tests) and working memory (Morris water maze [MWM]) were assessed 2 weeks post-bTBI. Because impact TBI (i.e., non-blast TBI) is often associated with reduced cerebral perfusion and impaired cerebrovascular function in part because of the generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species such as peroxynitrite (ONOO−), the effects of the administration of the ONOO− scavenger, penicillamine methyl ester (PenME), on cerebral perfusion and cerebral vascular resistance were measured for 2 h post-bTBI. Mild bTBI resulted in reduced relative cerebral perfusion and MCA dilator responses to reduced intravascular pressure, increases in cerebral vascular resistance and in the numbers of FJC-positive cells in the brain, and significantly impaired working memory. PenME administration resulted in significant reductions in cerebral vascular resistance and a trend toward increased cerebral perfusion, suggesting that ONOO− may contribute to blast-induced cerebral vascular dysfunction. PMID:29160141
-
International Symposium on Military Applications of Blast Simulation (5th)
1977-06-22
Centre d’Etudes de Grainat, Gramat , France, de- scribed their work in designing a blast simulator with a test section of 12—rn width and 7—rn height...de Gramat , Gramat , France) on the dynamic behavior of limestone. Through a series of high—pressure experiments of the type developed in the recent
-
Fragment Size Distribution of Blasted Rock Mass
Jug, Jasmin; Strelec, Stjepan; Gazdek, Mario; Kavur, Boris
2017-12-01
Rock mass is a heterogeneous material, and the heterogeneity of rock causes sizes distribution of fragmented rocks in blasting. Prediction of blasted rock mass fragmentation has a significant role in the overall economics of opencast mines. Blasting as primary fragmentation can significantly decrease the cost of loading, transport, crushing and milling operations. Blast fragmentation chiefly depends on the specific blast design (geometry of blast holes drilling, the quantity and class of explosive, the blasting form, the timing and partition, etc.) and on the properties of the rock mass (including the uniaxial compressive strength, the rock mass elastic Young modulus, the rock discontinuity characteristics and the rock density). Prediction and processing of blasting results researchers can accomplish by a variety of existing software’s and models, one of them is the Kuz-Ram model, which is possibly the most widely used approach to estimating fragmentation from blasting. This paper shows the estimation of fragmentation using the "SB" program, which was created by the authors. Mentioned program includes the Kuz-Ram model. Models of fragmentation are confirmed and calibrated by comparing the estimated fragmentation with actual post-blast fragmentation from image processing techniques. In this study, the Kuz-Ram fragmentation model has been used for an open-pit limestone quarry in Dalmatia, southern Croatia. The resulting calibrated value of the rock factor enables the quality prognosis of fragmentation in further blasting works, with changed drilling geometry and blast design parameters. It also facilitates simulation in the program to optimize blasting works and get the desired fragmentations of the blasted rock mass.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Souza, Murilo Alves Tito de; Rosa, Ericson Rimen Ribeiro; Oliveira, Claudiney Freitas de [Usinas Siderurgicas de Minas Gerais S/A (USIMINAS), Ipatinga, MG (Brazil)
2010-07-01
The use of turbine for energy recovery from top gas from blast furnace is aligned with the strategic objectives of USIMINAS Ipatinga to increase their own power generation, reduce environmental impacts and improve operational control of pressure from the top. This study aimed to present the progress in controlling the top pressure and electric power generation using turbine drawing gas kinetic energy. Will be addressed by developing methods used to control the pressure of the top from the start of operation of Blast Furnace 3 to the present day. Will also be discussed operating procedures and expected performance. (author)
-
Effect of the dynamic pressure on the shock wave structure in a rarefied polyatomic gas
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Taniguchi, Shigeru, E-mail: taniguchi@stat.nitech.ac.jp; Sugiyama, Masaru, E-mail: sugiyama@nitech.ac.jp [Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya Institute of Technology, Nagoya 466-8555 (Japan); Arima, Takashi, E-mail: tks@stat.nitech.ac.jp [Center for Social Contribution and Collaboration, Nagoya Institute of Technology, Nagoya 466-8555 (Japan); Ruggeri, Tommaso, E-mail: tommaso.ruggeri@unibo.it [Department of Mathematics and Research Center of Applied Mathematics (CIRAM), University of Bologna, Bologna (Italy)
2014-01-15
We study the shock wave structure in a rarefied polyatomic gas based on a simplified model of extended thermodynamics in which the dissipation is due only to the dynamic pressure. In this case the differential system is very simple because it is a variant of Euler system with a new scalar equation for the dynamic pressure [T. Arima, S. Taniguchi, T. Ruggeri, and M. Sugiyama, Phys. Lett. A 376, 2799–2803 (2012)]. It is shown that this theory is able to describe the three types of the shock wave structure observed in experiments: the nearly symmetric shock wave structure (Type A, small Mach number), the asymmetric structure (Type B, moderate Mach number), and the structure composed of thin and thick layers (Type C, large Mach number)
-
Blast-induced electromagnetic fields in the brain from bone piezoelectricity.
Lee, Ka Yan Karen; Nyein, Michelle K; Moore, David F; Joannopoulos, J D; Socrate, Simona; Imholt, Timothy; Radovitzky, Raul; Johnson, Steven G
2011-01-01
In this paper, we show that bone piezoelectricity-a phenomenon in which bone polarizes electrically in response to an applied mechanical stress and produces a short-range electric field-may be a source of intense blast-induced electric fields in the brain, with magnitudes and timescales comparable to fields with known neurological effects. We compute the induced charge density in the skull from stress data on the skull from a finite-element full-head model simulation of a typical IED-scale blast wave incident on an unhelmeted human head as well as a human head protected by a kevlar helmet, and estimate the resulting electric fields in the brain in both cases to be on the order of 10 V/m in millisecond pulses. These fields are more than 10 times stronger than the IEEE safety guidelines for controlled environments (IEEE Standards Coordinating Committee 28, 2002) and comparable in strength and timescale to fields from repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) that are designed to induce neurological effects (Wagner et al., 2006a). They can be easily measured by RF antennas, and may provide the means to design a diagnostic tool that records a quantitative measure of the head's exposure to blast insult. Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
NCBI BLAST+ integrated into Galaxy.
Cock, Peter J A; Chilton, John M; Grüning, Björn; Johnson, James E; Soranzo, Nicola
2015-01-01
The NCBI BLAST suite has become ubiquitous in modern molecular biology and is used for small tasks such as checking capillary sequencing results of single PCR products, genome annotation or even larger scale pan-genome analyses. For early adopters of the Galaxy web-based biomedical data analysis platform, integrating BLAST into Galaxy was a natural step for sequence comparison workflows. The command line NCBI BLAST+ tool suite was wrapped for use within Galaxy. Appropriate datatypes were defined as needed. The integration of the BLAST+ tool suite into Galaxy has the goal of making common BLAST tasks easy and advanced tasks possible. This project is an informal international collaborative effort, and is deployed and used on Galaxy servers worldwide. Several examples of applications are described here.
-
HIGH PRODUCTIVITY VACUUM BLASTING SYSTEM
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
McPhee, William S.
1999-01-01
The objective of this project is to improve the productivity and lower the expense of existing vacuum blasting technology. This technology is used to remove radioactive contamination, PCBs, and lead-based paint and provides worker protection by continuously recycling the material and dust for the decontamination tasks. The proposed work would increase the cleaning rate and provide safe and cost-effective decontamination of the DOE sites. This work focuses on redesigning and improving existing vacuum blasting technology including blast head nozzles, ergonomic handling of the blast head by reducing its weight; brush-ring design, vacuum level regulator, efficiency of the dust separator, and operational control sensors. The redesign is expected to enhance the productivity and economy of the vacuum blasting system by at least 50% over current vacuum blasting systems. There are three phases in the project. Phase I consists of developing and testing mathematical models. Phase II consists of pre-prototype design and fabrication and pre-prototype unit testing. Phase III consists of prototype design and field verification testing. In phase I, mathematical models are developed and analyzed for the nozzle, blast head, wind curtain, and dust separator, first as individual devices and then combined as an integrated model. This allows study of respective airflow and design parameters. The Contractor shall, based on the results of the mathematical modeling studies, design experimental models of the components and test these models. In addition, the Contractor shall develop sensors to detect the relationship of the blast head to the blast surfaces and controls to minimize the dependency on an operator's skill and judgment to obtain optimum positioning, as well as real-time characterization sensors to determine as the blast head is moving the depth to which coatings must be removed, thereby improving production and minimizing waste. In phase II, the Contractor shall design and
-
Evaluation of high pressure Freon decontamination. I. Preliminary tests
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Rankin, W.N.
1983-01-01
High-pressure Freon blasting techniques are being evaluated for applications involving the removal of non-adherent radioactive particulate contamination at SRP. Very little waste is generated by this technique because the used Freon can be easily distilled and reused. One of the principle advantages of this technique is that decontaminated electrical equipment can be returned to service immediately without drying, unlike high-pressure water blasting techniques. Preliminary scoutin tests evaluating high-pressure Freon blasting for decontamination at SRP were carried out at Quadrex Co., Oak Ridge, TN, October 12 and 13. DWPF-type contamination (raw sludge plus volatiles) and separations area-type contamination (diluted boiling point (47.6 0 C) allow it to rapidly separate from higher boiling contaminants via distillation with filtration to remove particulate material, and distillation with condensation, the solvent may be recovered for indefinite reuse while reducing the radioactive waste to a minimum. 3 references, 5 figures, 6 tables
-
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Burcharth, Hans F.; Andersen, Thomas Lykke; Meinert, Palle
2008-01-01
Wave induced pressures on model scale monolithic structures like caissons and concrete superstructures on rubble mound breakwaters show very peaky variations, even in cases without impacts from slamming waves....
-
Small surface wave discharge at atmospheric pressure
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Kiss' ovski, Zh; Kolev, M; Ivanov, A; Lishev, St; Koleva, I, E-mail: kissov@phys.uni-sofia.b [Faculty of Physics, Sofia University, BG-1164 Sofia (Bulgaria)
2009-09-21
A small surface wave driven source produces plasma at atmospheric pressure. Microwave power at frequency 2.45 GHz is coupled with the source and a discharge is ignited at power levels below 10 W. The coaxial exciter of the surface waves has a length of 10 mm because its dielectric is a high permittivity discharge tube. The plasma source operates as a plasma jet in the case of plasma columns longer than the tube length. The source maintains stable plasma columns over a wide range of neutral gas flow and applied power in continuous and pulse regimes. An additional advantage of this source is the discharge self-ignition. An electron temperature of T{sub e} {approx} 1.9 eV and a density of n{sub e} {approx} 3.9 x 10{sup 14} cm{sup -3} are estimated by the probe diagnostics method. The emission spectra in the wavelength range 200-1000 nm under different experimental conditions are analysed and they prove the applicability of the source for analytical spectroscopy. The dependences of column length, reflected power and plasma parameters on the gas flow and the input power are discussed. (fast track communication)
-
Effects of the loading conditions on fracturing near the shot hole
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nakamura, Yuichi; Tanishi, Hiroyuki; Maruta, Yuji; Nakashima, Yukitoshi; Inoue, Masayasu.
1984-01-01
As the blasting method controlling the energy emission of explosives, there is cushion blasting method, and recently, attention has been paid to it as the dismantling technique in the decommissioning of nuclear reactors. The objective of this method is to obtain smooth finished surfaces by reducing the damage of natural ground behind fracture surfaces, but it is expected that the state of breaking near a shot hole changes largely by the condition of loading explosives. In the cushion blasting method, it is intended to utilize the dynamic effect of stress waves in media and the static effect of explosion gas by the action of the gap provided around a charge, called decoupling effect. In this study, in order to visually grasp the behavior of stress waves near an explosion source and the progress of breaking, experiment was carried out with acrylic blocks, and the explosion phenomena were observed using a high speed camera, at the same time, the pressure history of the stress waves generated during the explosion was measured with piezo-electric gauges. Moreover, pressure measurement was carried out in the blasting of mortar blocks. The form of specimens and the loading condition, the measurement of the pressure history, the measuring system and the experimenal results are reported. (Kako, I.)
-
Blast-induced traumatic brain injury: a new trend of blast injury research.
Zhao, Yan; Wang, Zheng-Guo
2015-01-01
Blast injury has become the major life- and function-threatening injuries in recent warfares. There is increased research interest in the mental disorders caused by blast-induced traumatic brain injury (bTBI), which has been proved as one of the "signature wounds" in modern battlefield. We reviewed the recent progresses in bTBI-related researches and concluded that the new era of blast injury research has shifted from the traditional physical impairments to cognitive dysfunctional/mental disorders that are proved to be more related to the outcome of combat casualty care.
-
Shouraki, Mohammad Kargar; Naserkheil, Ali Asghar
2011-01-01
Blast Management (BM) is composed of the combination of human resources management (HRM) principles and concepts and various methods of quality management (QM) with a financial approach. BM is made up of three aspects: hard, soft and concept and BLAST means an explosive shift in organization's mindset and thought and rapid action against it. The first aspect, hard, includes a set of managerial toots and philosophies to improve the quality and productivity with a financial approach.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Neichev, Z; Benova, E; Gamero, A; Sola, A
2006-01-01
The paper discusses a new configuration of the surface-wave sustained plasma - 'the coaxial structure'. The coaxial structure is investigated on the base of one-dimensional axial fluid model. That model is adequate enough for low pressure plasma, when the main process for charged particles production is the direct ionization from the ground state and the loss of electrons is due to diffusion to the wall. The role of the geometric factors is evaluated and discussed, varying the discharge conditions in the theoretical model. The main equations of the model - the local dispersion relation and the wave energy balance equation are obtained from Maxwell's equations with appropriate boundary conditions. The phase diagrams, the radial profiles of the electric field and the axial profiles of dimensionless electron number density, wave number, wave power are obtained at various plasma radii and dielectric tube thickness. The results are compared with those for the typical cylindrical plasma column at similar conditions. For the purpose of modelling at low pressure of a coaxial discharge sustained by a travelling electromagnetic wave, some important characteristics of the propagation of surface waves have been investigated experimentally. The axial profiles of the propagation coefficient and radial profiles of the electric field at different experimental conditions have been obtained and discussed
-
Polydiagnostic calibration performed on a low pressure surface wave sustained argon plasma
Vries, de N.; Palomares, J.M.; Iordanova, E.I.; Veldhuizen, van E.M.; Mullen, van der J.J.A.M.
2008-01-01
The electron density and electron temperature of a low pressure surface wave sustained argon plasma have been determined using passive and active (laser) spectroscopic methods simultaneously. In this way the validity of the various techniques is established while the plasma properties are determined
-
High-speed photography of dynamic photoelastic experiment with a highly accurate blasting machine
Katsuyama, Kunihisa; Ogata, Yuji; Wada, Yuji; Hashizume, K.
1995-05-01
A high accurate blasting machine which could control 1 microsecond(s) was developed. At first, explosion of a bridge wire in an electric detonator was observed and next the detonations of caps were observed with a high speed camera. It is well known that a compressed stress wave reflects at the free face, it propagates to the backward as a tensile stress wave, and cracks grow when the tensile stress becomes the dynamic tensile strength. The behavior of these cracks has been discussed through the observation of the dynamic photoelastic high speed photography and the three dimensional dynamic stress analysis.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Marpaung, A.M.; Kurniawan, H.; Tjia, M.O.; Kagawa, K.
2001-01-01
An experimental study has been carried out on the dynamical process taking place in the plasma generated by a TEA CO 2 laser (400 mJ, 100 ns) on a zinc target when surrounded by helium gas of pressure ranging from 2 Torr to 1 atm. Plasma characteristics were examined in detail on the emission lines of Zn I 481.0 nm and He I 587.6 nm by means of an unique time-resolved spatial distribution technique in addition to an ordinary time-resolved emission measurement technique. The results reveal, for the first time, persistent shock wave characteristics in all cases throughout the entire pressure range considered. Further analysis of the data has clarified the distinct characteristics of laser plasmas generated in different ranges of gas pressure. It is concluded that three types of shock wave plasma can be identified; namely, a target shock wave plasma in the pressure range from 2 Torr to around 50 Torr; a coupling shock wave plasma in the pressure range from around 50 Torr to 200 Torr and a gas breakdown shock wave plasma in the pressure range from around 200 Torr to 1 atm. These distinct characteristics are found to be ascribable to the different extents of the gas breakdown process taking place at the different gas pressures. These results, obtained for a TEA CO 2 laser, will provide a useful basis for the analyses of plasmas induced by other lasers. (author)
-
Tunnel pressure waves - A smartphone inquiry on rail travel
Müller, Andreas; Hirth, Michael; Kuhn, Jochen
2016-02-01
When traveling by rail, you might have experienced the following phenomenon: The train enters a tunnel, and after some seconds a noticeable pressure change occurs, as perceived by your ears or even by a rapid wobbling of the train windows. The basic physics is that pressure waves created by the train travel down the tunnel, are reflected at its other end, and travel back until they meet the train again. Here we will show (i) how this effect can be well understood as a kind of large-scale outdoor case of a textbook paradigm, and (ii) how, e.g., a prediction of the tunnel length from the inside of a moving train on the basis of this model can be validated by means of a mobile phone measurement.
-
FastBLAST: homology relationships for millions of proteins.
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Morgan N Price
Full Text Available BACKGROUND: All-versus-all BLAST, which searches for homologous pairs of sequences in a database of proteins, is used to identify potential orthologs, to find new protein families, and to provide rapid access to these homology relationships. As DNA sequencing accelerates and data sets grow, all-versus-all BLAST has become computationally demanding. METHODOLOGY/PRINCIPAL FINDINGS: We present FastBLAST, a heuristic replacement for all-versus-all BLAST that relies on alignments of proteins to known families, obtained from tools such as PSI-BLAST and HMMer. FastBLAST avoids most of the work of all-versus-all BLAST by taking advantage of these alignments and by clustering similar sequences. FastBLAST runs in two stages: the first stage identifies additional families and aligns them, and the second stage quickly identifies the homologs of a query sequence, based on the alignments of the families, before generating pairwise alignments. On 6.53 million proteins from the non-redundant Genbank database ("NR", FastBLAST identifies new families 25 times faster than all-versus-all BLAST. Once the first stage is completed, FastBLAST identifies homologs for the average query in less than 5 seconds (8.6 times faster than BLAST and gives nearly identical results. For hits above 70 bits, FastBLAST identifies 98% of the top 3,250 hits per query. CONCLUSIONS/SIGNIFICANCE: FastBLAST enables research groups that do not have supercomputers to analyze large protein sequence data sets. FastBLAST is open source software and is available at http://microbesonline.org/fastblast.
-
Instability waves and transition in adverse-pressure-gradient boundary layers
Bose, Rikhi; Zaki, Tamer A.; Durbin, Paul A.
2018-05-01
Transition to turbulence in incompressible adverse-pressure-gradient (APG) boundary layers is investigated by direct numerical simulations. Purely two-dimensional instability waves develop on the inflectional base velocity profile. When the boundary layer is perturbed by isotropic turbulence from the free stream, streamwise elongated streaks form and may interact with the instability waves. Subsequent mechanisms that trigger transition depend on the intensity of the free-stream disturbances. All evidence from the present simulations suggest that the growth rate of instability waves is sufficiently high to couple with the streaks. Under very low levels of free-stream turbulence (˜0.1 % ), transition onset is highly sensitive to the inlet disturbance spectrum and is accelerated if the spectrum contains frequency-wave-number combinations that are commensurate with the instability waves. Transition onset and completion in this regime is characterized by formation and breakdown of Λ vortices, but they are more sporadic than in natural transition. Beneath free-stream turbulence with higher intensity (1-2 % ), bypass transition mechanisms are dominant, but instability waves are still the most dominant disturbances in wall-normal and spanwise perturbation spectra. Most of the breakdowns were by disturbances with critical layers close to the wall, corresponding to inner modes. On the other hand, the propensity of an outer mode to occur increases with the free-stream turbulence level. Higher intensity free-stream disturbances induce strong streaks that favorably distort the boundary layer and suppress the growth of instability waves. But the upward displacement of high amplitude streaks brings them to the outer edge of the boundary layer and exposes them to ambient turbulence. Consequently, high-amplitude streaks exhibit an outer-mode secondary instability.
-
The use of computer blast simulations to improve blast quality
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Favreau, R.F.; Kuzzyk, G.W.; Babulic, P.J.; Morin, R.A.; Tienkamp, N.J.
1987-01-01
An underground research laboratory (URL) has been constructed as part of a comprehensive program to evaluate the concept of nuclear fuel waste disposal in deep crystalline rock formations. Careful blasting methods have been used to minimize damage to the excavation surfaces. This paper reviews the results of the program to develop controlled blasting for the full-face method, comparing the field observed results achieved with the simulated theoretical results. The simulated results indicate how the blasting may damage the excavation surface. Results suggest that the rock around the final wall is stressed more severely by the cushion holes than by the perimeter holes and that bootleg of the rock between the perimeter and cushion rows occurs when the burst-out velocity imparted to it by the explosive loads in the perimeter holes is inadequate
-
30 CFR 780.13 - Operation plan: Blasting.
2010-07-01
... 30 Mineral Resources 3 2010-07-01 2010-07-01 false Operation plan: Blasting. 780.13 Section 780.13... SURFACE MINING PERMIT APPLICATIONS-MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR RECLAMATION AND OPERATION PLAN § 780.13 Operation plan: Blasting. (a) Blasting plan. Each application shall contain a blasting plan for the proposed...
-
Control blasting of reinforced concrete
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nagase, Tetsuo
1981-01-01
With the need of decommissioning nuclear power plants, it is urgently required to establish its methods and standards. In Shimizu Construction Co., Ltd., experimental feasibility studies have been made on explosive demolition method i.e. the controlled blasting for the massive concrete structures peculiar to nuclear power plants, considering low radiation exposure, safety and high efficiency. As such, four techniques of line drilling, cushion blasting, pre-splitting and guide hole blasting, respectively, are described with photographs. Assuming the selective demolition of activated concrete structures, the series of experiments showed the good results of clear-cut surfaces and the effect of blasting was confined properly. Moreover, the scattering of debris in blasting was able to be entirely prevented by the use of rubber belts. The generation of gas and dust was also little due to the small amount of the charge used. (J.P.N.)
-
Experimental study on brain injury in Beagle dogs caused by adjacent cabin explosion in warship
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yan-teng LI
2017-04-01
Full Text Available Objective Through the establishment of adjacent cabin blast injury model of Beagle dog, to investigate the pathophysiological changes in the experimental animals in this scenario, then speculate on the mechanisms of injury. Methods Several adjacent cabins were built in the same size with the real warship. Seven Beagle dogs were subjected to injuries from the explosion, from whom one was selected randomly to implant intracranial pressure transducers before blast, the others were tested on the pathophysiological changes after blast. The dogs were mounted on the platform of a cabinet in the adjacent cabin, subjected to injury from 650g bare TNT explosive blast. The transducers recorded the value of space and intracranial shock wave pressure. Following blast treatment, the serum levels of IL -6, IL -8, neuron specific enolase (NSE, brain and chest CT and pathological changes of the brain tissue were observed. Results Serum levels of IL-6, IL-8 and NSE were elevated to varying degrees after blast. All of them increased significantly at different time points after blast (P<0.05. Brain and chest CT examinations did not show any significant positive results. Pathological results showed that there was a little necrosis in the brain, some neurons had karyopycnosis, karyolysis or disappearance of the nucleoli, and the cell boundaries were blurred. The blast wave was blocked greatly by the scalp and skull (about 90%, but could still penetrate them and cause brain injuries. Conclusions Explosion in the adjacent cabin causes mainly mild traumatic brain injuries. Blast wave can be blocked by the scalp and skull greatly. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2017.03.11
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wenbin Gu
2017-01-01
Full Text Available Lighthouses are the most important hydraulic structures that should be protected during underwater drilling blasting. Thus, the effect of blasting vibration on lighthouse should be studied. On the basis of the dimensional analysis, we deduced a revised formula for water depth based on Sodev’s empirical formula and established the linear fitting model. During the underwater reef project in the main channel of Shipu Harbor in the Ningbo–Zhoushan Port, the blasting vibration data of the lighthouse near the underwater blasting area were monitored. The undetermined coefficient, resolvable coefficient, and F value of the two formulas were then obtained. The comparison of the data obtained from the two formulas showed that they can effectively predict the blasting vibration on the lighthouse. The correction formula that considers water depth can obviously reduce prediction errors and accurately predict blasting vibration.
-
30th International Symposium on Shock Waves
Sadot, Oren; Igra, Ozer
2017-01-01
These proceedings collect the papers presented at the 30th International Symposium on Shock Waves (ISSW30), which was held in Tel-Aviv Israel from July 19 to July 24, 2015. The Symposium was organized by Ortra Ltd. The ISSW30 focused on the state of knowledge of the following areas: Nozzle Flow, Supersonic and Hypersonic Flows with Shocks, Supersonic Jets, Chemical Kinetics, Chemical Reacting Flows, Detonation, Combustion, Ignition, Shock Wave Reflection and Interaction, Shock Wave Interaction with Obstacles, Shock Wave Interaction with Porous Media, Shock Wave Interaction with Granular Media, Shock Wave Interaction with Dusty Media, Plasma, Magnetohyrdrodynamics, Re-entry to Earth Atmosphere, Shock Waves in Rarefied Gases, Shock Waves in Condensed Matter (Solids and Liquids), Shock Waves in Dense Gases, Shock Wave Focusing, Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability, Shock Boundary Layer Interaction, Multiphase Flow, Blast Waves, Facilities, Flow Visualization, and Numerical Methods. The two volumes serve as a reference ...
-
Blast Induced Thresholds for Neuronal Networks (BITNeT)
2017-06-19
Neurol. 70, 183–191. Garo, a, Hrapko, M., van Dommelen, J. a W., Peters, G.W.M., 2007. Towards a reliable characterisation of the mechanical behaviour of...surface tension, dissolved gas , presence of particles and nucleation sites. Since the constituents of CSF differ from water, the pressure level at which...2011;Rafaels et al., 2011). Much of the BINT research is in the discovery period. Most primary blast models use shock tubes (compressed gas ) or
-
Guala, Andrea; Camporeale, Carlo; Ridolfi, Luca; Mesin, Luca
2017-04-01
Everyday clinical cardiovascular evaluation is still largely based on brachial systolic and diastolic pressures. However, several clinical studies have demonstrated the higher diagnostic capacities of the aortic pressure, as well as the need to assess the aortic mechanical properties (e.g., by measuring the aortic pulse wave velocity). In order to fill this gap, we propose to exploit a set of easy-to-obtain physical characteristics to estimate the aortic pressure and pulse wave velocity. To this aim, a large population of virtual subjects is created by a validated mathematical model of the cardiovascular system. Quadratic regressive models are then fitted and statistically selected in order to obtain reliable estimations of the aortic pressure and pulse wave velocity starting from the knowledge of the subject age, height, weight, brachial pressure, photoplethysmographic measures and either electrocardiogram or phonocardiogram. The results are very encouraging and foster clinical studies aiming to apply a similar technique to a real population. Copyright © 2017 IPEM. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Cavitation inception by the backscattering of pressure waves from a bubble interface
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Takahira, Hiroyuki, E-mail: takahira@me.osakafu-u.ac.jp; Ogasawara, Toshiyuki, E-mail: oga@me.osakafu-u.ac.jp; Mori, Naoto, E-mail: su101064@edu.osakafu-u.ac.jp; Tanaka, Moe [Osaka Prefecture University, 1-1 Gakuen-cho, Naka-ku, Sakai-shi, Osaka 599-8531 (Japan)
2015-10-28
The secondary cavitation that occurs by the backscattering of focused ultrasound from a primary cavitation bubble caused by the negative pressure part of the ultrasound (Maxwell, et al., 2011) might be useful for the energy exchange due to bubble oscillations in High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU). The present study is concerned with the cavitation inception by the backscattering of ultrasound from a bubble. In the present experiment, a laser-induced bubble which is generated by a pulsed focused laser beam with high intensity is utilized as a primary cavitation bubble. After generating the bubble, focused ultrasound is emitted to the bubble. The acoustic field and the bubble motion are observed with a high-speed video camera. It is confirmed that the secondary cavitation bubble clouds are generated by the backscattering from the laser-induced bubble. The growth of cavitation bubble clouds is analyzed with the image processing method. The experimental results show that the height and width of the bubble clouds grow in stepwise during their evolution. The direct numerical simulations are also conducted for the backscattering of incident pressure waves from a bubble in order to evaluate a pressure field near the bubble. It is shown that the ratio of a bubble collapse time t{sub 0} to a characteristic time of wave propagation t{sub S}, η = t{sub 0}/t{sub s}, is an important determinant for generating negative pressure region by backscattering. The minimum pressure location by the backscattering in simulations is in good agreement with the experiment.
-
Effect of Large Negative Phase of Blast Loading on Structural Response of RC Elements
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Syed Zubair Iman
2016-01-01
Full Text Available Structural response of reinforced concrete (RC elements for analysis and design are often obtained using the positive phase of the blast pressure curve disregarding the negative phase assuming insignificant contribution from the negative phase of the loading. Although, some insight on the effect of negative phase of blast pressure based on elastic single-degree-of-freedom (SDOF analysis was presented before, the influence of negative phase on different types of resistance functions of SDOF models and on realistic finite element analysis has not been explored. In this study, the effects of inclusion of pulse negative phase on structural response of RC elements from SDOF analysis and from more detailed finite element analysis have been investigated. Investigation of SDOF part has been conducted using MATLAB code that utilizes non-linear resistance functions of SDOF model. Detailed numerical investigation using finite element code DIANA was conducted on the significance of the negative phase on structural response. In the FE model, different support stiffness was used to explore the effect of support stiffness on the structural response due to blast negative phase. Results from SDOF and FE analyses present specific situations where the effect of large negative phase was found to be significant on the structural response of RC elements.
-
BLEVE blast by expansion-controlled evaporation
Berg, A.C. van den; Voort, M.M. van der; Weerheijm, J.; Versloot, N.H.A.
2006-01-01
This report presents a new method to calculate the blast effects originating from an exploding vessel of liquefied gas. Adequate blast calculation requires full knowledge of the blast source characteristics, that is, the release and subsequent evaporation rate of the flashing liquid. Because the
-
Changqing, Zhao; Kai, Liu; Tong, Zhao; Takei, Masahiro; Weian, Ren
2014-04-01
The mud-pulse logging instrument is an advanced measurement-while-drilling (MWD) tool and widely used by the industry in the world. In order to improve the signal transmission rate, ensure the accurate transmission of information and address the issue of the weak signal on the ground of oil and gas wells, the signal generator should send out the strong mud-pulse signals with the maximum amplitude. With the rotary valve pulse generator as the study object, the three-dimensional Reynolds NS equations and standard k - ɛ turbulent model were used as a mathematical model. The speed and pressure coupling calculation was done by simple algorithms to get the amplitudes of different rates of flow and axial clearances. Tests were done to verify the characteristics of the pressure signals. The pressure signal was captured by the standpiece pressure monitoring system. The study showed that the axial clearances grew bigger as the pressure wave amplitude value decreased and caused the weakening of the pulse signal. As the rate of flow got larger, the pressure wave amplitude would increase and the signal would be enhanced.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Nagel, H.
1986-01-01
The flow induced valve operation is calculated for single and two-phase flow conditions by the fluid dynamic computer code DYVRO and results are compared to experimental data. The analysis show that the operational behaviour of the valves is not only dependent on the condition of the induced flow, but also the pipe flow can cause a feedback as a result of the induced pressure waves. For the calculation of pressure wave propagation in pipes of which the operation of flow induced valves has a considerable influence it is therefore necessary to have a coupled analysis of the pressure wave propagation and the operational behaviour of the valves. The analyses of the fast transient transfer from steam to two-phase flow show a good agreement with experimental data. Hence even these very high loads on pipes resulting from such fluid dynamic transients can be calculated realistically. (orig.)
-
Experimental Study on Environment Friendly Tap Hole Clay for Blast Furnace
Siva kumar, R.; Mohammed, Raffi; Srinivasa Rao, K.
2018-03-01
Blast furnace (BF) is the best possible route of iron production available. Blast furnace is a high pressure vessel where iron ore is melted and liquid iron is produced. The liquid iron is tapped through the hole in Blast Furnace called tap hole. The tapped liquid metal flowing through the tap hole is plugged using a clay called tap hole clay. Tap hole clay (THC) is a unshaped refractory used to plug the tap hole. The tap hole clay extruded through the tap hole using a gun. The tap hole clay is designed to expand and plug the tap hole. The tap hole filled with clay is drilled using drill bit and the hole made through the tap hole to tap the liquid metal accumulated inside the furnace. The number of plugging and drilling varies depending on the volume of the furnace. The tap hole clay need to have certain properties to avoid problems during plugging and drilling. In the present paper tap hole clay properties in industrial use was tested and studied. The problems were identified related to tap hole clay manufacturing. Experiments were conducted in lab scale to solve the identified problems. The present composition was modified with experimental results. The properties of the modified tap hole clay were found suitable and useful for blast furnace operation with lab scale experimental results.
-
Groenig, Hans
Topics discussed in this volume include shock wave structure, propagation, and interaction; shocks in condensed matter, dusty gases, and multiphase media; chemical processes and related combustion and detonation phenomena; shock wave reflection, diffraction, and focusing; computational fluid dynamic code development and shock wave application; blast and detonation waves; advanced shock tube technology and measuring technique; and shock wave applications. Papers are presented on dust explosions, the dynamics of shock waves in certain dense gases, studies of condensation kinetics behind incident shock waves, the autoignition mechanism of n-butane behind a reflected shock wave, and a numerical simulation of the focusing process of reflected shock waves. Attention is also given to the equilibrium shock tube flow of real gases, blast waves generated by planar detonations, modern diagnostic methods for high-speed flows, and interaction between induced waves and electric discharge in a very high repetition rate excimer laser.
-
Interaction of Acoustic Waves with a Cryogenic Nitrogen Jet at Sub- and Supercritical Pressures
National Research Council Canada - National Science Library
Chehroudi, B
2001-01-01
To better understand the nature of the interaction between acoustic waves and liquid fuel jets in rocket engines, cryogenic liquid nitrogen is injected into a room temperature high-pressure chamber...
-
30 CFR 75.1323 - Blasting circuits.
2010-07-01
...) Blasting circuits shall be protected from sources of stray electric current. (b) Detonators made by different manufacturers shall not be combined in the same blasting circuit. (c) Detonator leg wires shall be... used between the blasting cable and detonator circuitry shall— (1) Be undamaged; (2) Be well insulated...
-
Suppressor for reducing the muzzle blast and flash of a firearm
Klett, James W
2014-09-30
Disclosed are several examples of apparatuses for suppressing the blast and flash produced as a projectile is expelled by gases from a firearm. In some examples, gases are diverted away from the central chamber to an expansion chamber by baffles. The gases are absorbed by the expansion chamber and desorbed slowly, thus decreasing pressure and increasing residence time of the gases. In other examples, the gases impinge against a plurality of rods before expanding through passages between the rods to decrease the pressure and increase the residence time of the gases.
-
Dust acoustic waves in complex plasmas at elevated pressure
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Filippov, A.V.; Starostin, A.N.; Tkachenko, I.M.; Fortov, V.E.
2011-01-01
The bi-Yukawa effective interaction potential with different screening constants is employed to calculate dust static correlation functions in the hyper-netted chain approximation and to generalize the theory of dust acoustic waves within the non-perturbative moment approach complemented by hydrodynamic considerations. For the bi-Yukawa interaction potential the sound speed becomes significantly wavenumber-dependent, an additional soft diffusion-like mode is predicted, and the static dielectric function is shown to take negative values. The results can be applied to non-equilibrium dusty plasmas at elevated pressure. -- Highlights: ► Bi-Yukawa interaction potential of dust particles with different screening lengths. ► Dust static correlation functions in the hyper-netted chain approximation. ► The moment and hydrodynamic approaches are in a good agreement at weak non-ideality. ► The dust acoustic wave phase and group velocities depend on the wavenumber. ► The moment approach hints the appearance of the diffusion-like soft mode.
-
2014-04-15
used for advertising or product endorsement purposes. 6.0 REFERENCES [1] McGlaun, J., Thompson, S. and Elrick, M. “CTH: A Three-Dimensional Shock-Wave...Validation of a Loading Model for Simulating Blast Mine Effects on Armoured Vehicles,” 7 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference, Detroit, MI 2002. [14
-
Ultra Safe And Secure Blasting System
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hart, M M
2009-07-27
The Ultra is a blasting system that is designed for special applications where the risk and consequences of unauthorized demolition or blasting are so great that the use of an extraordinarily safe and secure blasting system is justified. Such a blasting system would be connected and logically welded together through digital code-linking as part of the blasting system set-up and initialization process. The Ultra's security is so robust that it will defeat the people who designed and built the components in any attempt at unauthorized detonation. Anyone attempting to gain unauthorized control of the system by substituting components or tapping into communications lines will be thwarted in their inability to provide encrypted authentication. Authentication occurs through the use of codes that are generated by the system during initialization code-linking and the codes remain unknown to anyone, including the authorized operator. Once code-linked, a closed system has been created. The system requires all components connected as they were during initialization as well as a unique code entered by the operator for function and blasting.
-
Laser-induced pressure-wave and barocaloric effect during flash diffusivity measurements
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Wang, Hsin; Porter, Wallace D.; Dinwiddie, Ralph Barton
2017-01-01
We report laser-induced pressure-wave and barocaloric effect captured by an infrared detector during thermal diffusivity measurements. Very fast (< 1 ms) and negative transients during laser flash measurements were captured by the infrared detector on thin, high thermal conductivity samples. Standard thermal diffusivity analysis only focuses the longer time scale thermal transient measured from the back surface due to thermal conduction. These negative spikes are filtered out and ignored as noise or anomaly from instrument. This study confirmed that the initial negative signal was indeed a temperature drop induced by the laser pulse. The laser pulse induced instantaneous volume expansion and the associated cooling in the specimen can be explained by the barocaloric effect. The initial cooling (< 100 microsecond) is also known as thermoelastic effect in which a negative temperature change is generated when the material is elastically deformed by volume expansion. A subsequent temperature oscillation in the sample was observed and only lasted about one millisecond. The pressure-wave induced thermal signal was systematically studied and analyzed. In conclusion, the underlying physics of photon-mechanical-thermal energy conversions and the potential of using this signal to study barocaloric effects in solids are discussed.
-
Kiełczyński, P; Szalewski, M; Balcerzak, A; Rostocki, A J; Tefelski, D B
2011-12-01
Viscosity measurements were carried out on triolein at pressures from atmospheric up to 650 MPa and in the temperature range from 10°C to 40°C using ultrasonic measuring setup. Bleustein-Gulyaev SH surface acoustic waves waveguides were used as viscosity sensors. Additionally, pressure changes occurring during phase transition have been measured over the same temperature range. Application of ultrasonic SH surface acoustic waves in the liquid viscosity measurements at high pressure has many advantages. It enables viscosity measurement during phase transitions and in the high-pressure range where the classical viscosity measurement methods cannot operate. Measurements of phase transition kinetics and viscosity of liquids at high pressures and various temperatures (isotherms) is a novelty. The knowledge of changes in viscosity in function of pressure and temperature can help to obtain a deeper insight into thermodynamic properties of liquids. Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Engine Cycle Analysis of Air Breathing Microwave Rocket with Reed Valves
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Fukunari, Masafumi; Komatsu, Reiji; Yamaguchi, Toshikazu; Komurasaki, Kimiya; Arakawa, Yoshihiro; Katsurayama, Hiroshi
2011-01-01
The Microwave Rocket is a candidate for a low cost launcher system. Pulsed plasma generated by a high power millimeter wave beam drives a blast wave, and a vehicle acquires impulsive thrust by exhausting the blast wave. The thrust generation process of the Microwave Rocket is similar to a pulse detonation engine. In order to enhance the performance of its air refreshment, the air-breathing mechanism using reed valves is under development. Ambient air is taken to the thruster through reed valves. Reed valves are closed while the inside pressure is high enough. After the time when the shock wave exhausts at the open end, an expansion wave is driven and propagates to the thrust-wall. The reed valve is opened by the negative gauge pressure induced by the expansion wave and its reflection wave. In these processes, the pressure oscillation is important parameter. In this paper, the pressure oscillation in the thruster was calculated by CFD combined with the flux through from reed valves, which is estimated analytically. As a result, the air-breathing performance is evaluated using Partial Filling Rate (PFR), the ratio of thruster length to diameter L/D, and ratio of opening area of reed valves to superficial area α. An engine cycle and predicted thrust was explained.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Parichit Sharma
Full Text Available The function of a newly sequenced gene can be discovered by determining its sequence homology with known proteins. BLAST is the most extensively used sequence analysis program for sequence similarity search in large databases of sequences. With the advent of next generation sequencing technologies it has now become possible to study genes and their expression at a genome-wide scale through RNA-seq and metagenome sequencing experiments. Functional annotation of all the genes is done by sequence similarity search against multiple protein databases. This annotation task is computationally very intensive and can take days to obtain complete results. The program mpiBLAST, an open-source parallelization of BLAST that achieves superlinear speedup, can be used to accelerate large-scale annotation by using supercomputers and high performance computing (HPC clusters. Although many parallel bioinformatics applications using the Message Passing Interface (MPI are available in the public domain, researchers are reluctant to use them due to lack of expertise in the Linux command line and relevant programming experience. With these limitations, it becomes difficult for biologists to use mpiBLAST for accelerating annotation. No web interface is available in the open-source domain for mpiBLAST. We have developed WImpiBLAST, a user-friendly open-source web interface for parallel BLAST searches. It is implemented in Struts 1.3 using a Java backbone and runs atop the open-source Apache Tomcat Server. WImpiBLAST supports script creation and job submission features and also provides a robust job management interface for system administrators. It combines script creation and modification features with job monitoring and management through the Torque resource manager on a Linux-based HPC cluster. Use case information highlights the acceleration of annotation analysis achieved by using WImpiBLAST. Here, we describe the WImpiBLAST web interface features and architecture
-
Sharma, Parichit; Mantri, Shrikant S
2014-01-01
The function of a newly sequenced gene can be discovered by determining its sequence homology with known proteins. BLAST is the most extensively used sequence analysis program for sequence similarity search in large databases of sequences. With the advent of next generation sequencing technologies it has now become possible to study genes and their expression at a genome-wide scale through RNA-seq and metagenome sequencing experiments. Functional annotation of all the genes is done by sequence similarity search against multiple protein databases. This annotation task is computationally very intensive and can take days to obtain complete results. The program mpiBLAST, an open-source parallelization of BLAST that achieves superlinear speedup, can be used to accelerate large-scale annotation by using supercomputers and high performance computing (HPC) clusters. Although many parallel bioinformatics applications using the Message Passing Interface (MPI) are available in the public domain, researchers are reluctant to use them due to lack of expertise in the Linux command line and relevant programming experience. With these limitations, it becomes difficult for biologists to use mpiBLAST for accelerating annotation. No web interface is available in the open-source domain for mpiBLAST. We have developed WImpiBLAST, a user-friendly open-source web interface for parallel BLAST searches. It is implemented in Struts 1.3 using a Java backbone and runs atop the open-source Apache Tomcat Server. WImpiBLAST supports script creation and job submission features and also provides a robust job management interface for system administrators. It combines script creation and modification features with job monitoring and management through the Torque resource manager on a Linux-based HPC cluster. Use case information highlights the acceleration of annotation analysis achieved by using WImpiBLAST. Here, we describe the WImpiBLAST web interface features and architecture, explain design
-
A geophysical shock and air blast simulator at the National Ignition Facility
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Fournier, K. B. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Brown, C. G. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); May, M. J. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Compton, S. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Walton, O. R. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Shingleton, N. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Kane, J. O. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Holtmeier, G. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Loey, H. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Mirkarimi, P. B. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Dunlop, W. H. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Guyton, R. L. [National Security Technologies, Livermore, CA (United States); Huffman, E. [National Security Technologies, Livermore, CA (United States)
2014-09-01
The energy partitioning energy coupling experiments at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) have been designed to measure simultaneously the coupling of energy from a laser-driven target into both ground shock and air blast overpressure to nearby media. The source target for the experiment is positioned at a known height above the ground-surface simulant and is heated by four beams from the NIF. The resulting target energy density and specific energy are equal to those of a low-yield nuclear device. The ground-shock stress waves and atmospheric overpressure waveforms that result in our test system are hydrodynamically scaled analogs of full-scale seismic and air blast phenomena. This report summarizes the development of the platform, the simulations, and calculations that underpin the physics measurements that are being made, and finally the data that were measured. Agreement between the data and simulation of the order of a factor of two to three is seen for air blast quantities such as peak overpressure. Historical underground test data for seismic phenomena measured sensor displacements; we measure the stresses generated in our ground-surrogate medium. We find factors-of-a-few agreement between our measured peak stresses and predictions with modern geophysical computer codes.
-
A geophysical shock and air blast simulator at the National Ignition Facility
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Fournier, K. B.; Brown, C. G.; May, M. J.; Compton, S.; Walton, O. R.; Shingleton, N.; Kane, J. O.; Holtmeier, G.; Loey, H.; Mirkarimi, P. B.; Dunlop, W. H. [Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, P.O. Box 808, L-481, Livermore, California 94550 (United States); Guyton, R. L.; Huffman, E. [National Securities Technologies, Vasco Rd., Livermore, California 94551 (United States)
2014-09-15
The energy partitioning energy coupling experiments at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) have been designed to measure simultaneously the coupling of energy from a laser-driven target into both ground shock and air blast overpressure to nearby media. The source target for the experiment is positioned at a known height above the ground-surface simulant and is heated by four beams from the NIF. The resulting target energy density and specific energy are equal to those of a low-yield nuclear device. The ground-shock stress waves and atmospheric overpressure waveforms that result in our test system are hydrodynamically scaled analogs of full-scale seismic and air blast phenomena. This report summarizes the development of the platform, the simulations, and calculations that underpin the physics measurements that are being made, and finally the data that were measured. Agreement between the data and simulation of the order of a factor of two to three is seen for air blast quantities such as peak overpressure. Historical underground test data for seismic phenomena measured sensor displacements; we measure the stresses generated in our ground-surrogate medium. We find factors-of-a-few agreement between our measured peak stresses and predictions with modern geophysical computer codes.
-
A review on the strain rate dependency of the dynamic viscoplastic response of FCC metals
Salvado, F.C.; Teixeira-Dias, Filipe; Walley, S.; Lea, L.J.; Cardoso, J.B.
2017-01-01
The response of structures and materials subject to ballistic impacts or blast loads remains a field of intense research. In a blast or impact load a sharp pressure wave travelling at supersonic speed impinges on the structure surface where deformation will develop at very high strain rates and stress waves may form and travel through the continuum solid. Both the dynamic loading and the temperature increase will significantly affect the mechanical and failure response of the material. This r...
-
Alkaline carbonates in blast furnace process
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
P. Besta
2014-10-01
Full Text Available The production of iron in blast furnaces is a complex of physical, chemical and mechanical processes. The input raw materials contain not only metallic components, but also a number of negative elements. The most important negative elements include alkaline carbonates. They can significantly affect the course of the blast furnace process and thus the overall performance of the furnace. As a result of that, it is essential to accurately monitor the alkali content in the blast furnace raw materials. The article analyzes the alkali content in input and output raw materials and their impact on the blast furnace process.
-
Pressure effects on spin density wave in Cr rich Cr-Al, Si, Mn, Fe and Co alloys
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Mizuki, Jun-ichiro; Endoh, Yasuo; Ishikawa, Yoshikazu
1982-01-01
The effect of pressure on the spin density wave (SDW) state in Cr rich Cr-Al, Si, Nn, Fe and Co alloys has been elucidated by neutron diffraction studies. We found that the change of the SDW wave vector Q, by applying pressure, 1/Q. delta Q/ delta P, is linearly related to the decrease of T sub(N) with increasing pressure 1/T sub(N). delta T sub(N)/ delta P and that all the results from the Cr-Si, Fe and Co alloys fall on a single straight line independent of their concentrations. Their magnetic phase diagrams in a temperature-pressure coordinate system can be related to the alloy phase diagram by employing an empirical rule that applying pressure corresponds to a decrese in the electron to atom ratio. The non transition metal Si impurity has been found to act as an electron donor, while the effect of Al is not interpreted by the two band nesting model. (author)
-
Wave Engine Topping Cycle Assessment
Welch, Gerard E.
1996-01-01
The performance benefits derived by topping a gas turbine engine with a wave engine are assessed. The wave engine is a wave rotor that produces shaft power by exploiting gas dynamic energy exchange and flow turning. The wave engine is added to the baseline turboshaft engine while keeping high-pressure-turbine inlet conditions, compressor pressure ratio, engine mass flow rate, and cooling flow fractions fixed. Related work has focused on topping with pressure-exchangers (i.e., wave rotors that provide pressure gain with zero net shaft power output); however, more energy can be added to a wave-engine-topped cycle leading to greater engine specific-power-enhancement The energy addition occurs at a lower pressure in the wave-engine-topped cycle; thus the specific-fuel-consumption-enhancement effected by ideal wave engine topping is slightly lower than that effected by ideal pressure-exchanger topping. At a component level, however, flow turning affords the wave engine a degree-of-freedom relative to the pressure-exchanger that enables a more efficient match with the baseline engine. In some cases, therefore, the SFC-enhancement by wave engine topping is greater than that by pressure-exchanger topping. An ideal wave-rotor-characteristic is used to identify key wave engine design parameters and to contrast the wave engine and pressure-exchanger topping approaches. An aerodynamic design procedure is described in which wave engine design-point performance levels are computed using a one-dimensional wave rotor model. Wave engines using various wave cycles are considered including two-port cycles with on-rotor combustion (valved-combustors) and reverse-flow and through-flow four-port cycles with heat addition in conventional burners. A through-flow wave cycle design with symmetric blading is used to assess engine performance benefits. The wave-engine-topped turboshaft engine produces 16% more power than does a pressure-exchanger-topped engine under the specified topping
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Miles, A.R.; Blue, B.; Edwards, M.J.; Greenough, J.A.; Hansen, J.F.; Robey, H.F.; Drake, R.P.; Kuranz, C.; Leibrandt, D.R.
2005-01-01
Perturbations on an interface driven by a strong blast wave grow in time due to a combination of Rayleigh-Taylor, Richtmyer-Meshkov, and decompression effects. In this paper, results from three-dimensional (3D) numerical simulations of such a system under drive conditions to be attainable on the National Ignition Facility [E. M. Campbell, Laser Part. Beams 9, 209 (1991)] are presented. Using the multiphysics, adaptive mesh refinement, higher order Godunov Eulerian hydrocode, Raptor [L. H. Howell and J. A. Greenough, J. Comput. Phys. 184, 53 (2003)], the late nonlinear instability evolution, including transition to turbulence, is considered for various multimode perturbation spectra. The 3D post-transition state differs from the 2D result, but the process of transition proceeds similarly in both 2D and 3D. The turbulent mixing transition results in a reduction in the growth rate of the mixing layer relative to its pretransition value and, in the case of the bubble front, relative to the 2D result. The post-transition spike front velocity is approximately the same in 2D and 3D. Implications for hydrodynamic mixing in core-collapse supernovae are discussed
-
BLAST-EXPLORER helps you building datasets for phylogenetic analysis
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Claverie Jean-Michel
2010-01-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background The right sampling of homologous sequences for phylogenetic or molecular evolution analyses is a crucial step, the quality of which can have a significant impact on the final interpretation of the study. There is no single way for constructing datasets suitable for phylogenetic analysis, because this task intimately depends on the scientific question we want to address, Moreover, database mining softwares such as BLAST which are routinely used for searching homologous sequences are not specifically optimized for this task. Results To fill this gap, we designed BLAST-Explorer, an original and friendly web-based application that combines a BLAST search with a suite of tools that allows interactive, phylogenetic-oriented exploration of the BLAST results and flexible selection of homologous sequences among the BLAST hits. Once the selection of the BLAST hits is done using BLAST-Explorer, the corresponding sequence can be imported locally for external analysis or passed to the phylogenetic tree reconstruction pipelines available on the Phylogeny.fr platform. Conclusions BLAST-Explorer provides a simple, intuitive and interactive graphical representation of the BLAST results and allows selection and retrieving of the BLAST hit sequences based a wide range of criterions. Although BLAST-Explorer primarily aims at helping the construction of sequence datasets for further phylogenetic study, it can also be used as a standard BLAST server with enriched output. BLAST-Explorer is available at http://www.phylogeny.fr
-
Raydet non-electric blast initiation system for efficient and environment-friendly surface blasts
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Sarathy, M.O. [IDL Chemicals Ltd., Hyderabad (India). Technical Services Cell
1995-08-01
This paper discusses the advantages of using the Raydet shock tube based blast initiation system and reviews research work carried out on release of explosive energy in the drillhole, effect of stemming retention (stemming effectiveness) and advantages of `true bottom hole initiation` of drillholes in surface blasting. Some case studies are presented. 6 refs., 5 figs., 1 tab.
-
The second generation of electronic blasting systems
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Hammelmann, F.; Petzold, J. [Dynamit Nobel GmbH (Germany)
2001-07-01
8 years after the market introduction of the first commercial electronic detonator - DYNATRONIC - the paper describes a new area of electronic blasting systems Made in Germany: i-kon. The results of a joint development between Dynamit Nobel and Orica is a unique universal electronic detonator, which is as simple to use as a standard non-electric detonator. The delay time or delay interval is not factory preprogrammed and the system is not based on a numbered system like conventional detonators. The miner or Blaster decides on site which delay timing he likes to use and is programming the whole blast on site. The new i-kon system allows delay times between 0 and 8000 ms by increments of 1 ms. With the control equipment it is possible to blast up to 1600 detonators in a single blast. The paper describes the construction and functionality of this new electronic blasting system - manufactured and developed by Precision Blasting Systems, a joint venture between Orica and Dynamic Nobel. (orig.)
-
Soft Computing Approach to Evaluate and Predict Blast-Induced Ground Vibration
Khandelwal, Manoj
2010-05-01
Drilling and blasting is still one of the major economical operations to excavate a rock mass. The consumption of explosive has been increased many folds in recent years. These explosives are mainly used for the exploitation of minerals in mining industry or the removal of undesirable rockmass for community development. The amount of chemical energy converted into mechanical energy to fragment and displace the rockmass is minimal. Only 20 to 30% of this explosive energy is utilized for the actual fragmentation and displacement of rockmass and rest of the energy is wasted in undesirable ill effects, like, ground vibration, air over pressure, fly rock, back break, noise, etc. Ground vibration induced due to blasting is very crucial and critical as compared to other ill effects due to involvement of public residing in the close vicinity of mining sites, regulating and ground vibration standards setting agencies together with mine owners and environmentalists and ecologists. Also, with the emphasis shifting towards eco-friendly, sustainable and geo-environmental activities, the field of ground vibration have now become an important and imperative parameter for safe and smooth running of any mining and civil project. The ground vibration is a wave motion, spreading outward from the blast like ripples spreading outwards due to impact of a stone dropped into a pond of water. As the vibration passes through the surface structures, it induces vibrations in those structures also. Sometimes, due to high ground vibration level, dwellings may get damaged and there is always confrontation between mine management and the people residing in the surroundings of the mine area. There is number of vibration predictors available suggested by different researchers. All the predictors estimate the PPV based on mainly two parameters (maximum charge used per delay and distance between blast face to monitoring point). However, few predictors considered attenuation/damping factor too. For
-
Destabilization of hydromagnetic drift-Alfven waves in a finite pressure collisional plasma
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tang, J.T.
1974-01-01
In a finite beta (β = 8πn 0 kT 0 /B 0 2 ) plasma, where the plasma pressure n 0 kT 0 is an appreciable fraction of the confining magnetic field energy-density B 0 2 /8π, density-gradient driven drift waves couple with Alfven waves when the phase velocities of the two waves become comparable. The resulting hydromagnetic drift-Alfven waves separate into two branches--a drift mode and an Alfven mode, with both modes exhibiting magnetic field and localized density fluctuations near the coupling point. The dispersion relation of the collisional drift-Alfven wave is derived by using a slab-geometry, two-fluid model which includes finite beta, electron-ion collisions, ion-ion collisions, finite ion larmar radius, temperature fluctuations, and an axial electron current. A hydromagnetic drift mode is found to be unstable in a moderately dense plasma. A localized ''Alfven'' mode is destabilized only with the passage of an axial current along the plasma column. In order to check the theoretical predictions an experiment is performed in a finite-beta plasma of density n 0 = 10 13 -10 15 cm -3 and temperature T/sub e/ approximately T/sub i/ = 1-7 eV. (U.S.)
-
30 CFR 75.1316 - Preparation before blasting.
2010-07-01
... two working faces are approaching each other, cutting, drilling and blasting shall be done at only one... 30 Mineral Resources 1 2010-07-01 2010-07-01 false Preparation before blasting. 75.1316 Section 75... HEALTH MANDATORY SAFETY STANDARDS-UNDERGROUND COAL MINES Explosives and Blasting § 75.1316 Preparation...
-
A Fluid Helmet Liner for Protection Against Blast Induced Traumatic Brain Injury
2010-05-01
Xs- V 0 A \\ /I \\ A // ^> cV- if- y1 ^H5^ ay< $? ̂ fta 11 13 1.3 1 d H 1 R 1.7 1 R 1 q Time (ms) Fig. 11 Pressure profiles: Solid... clinical trials. Furthermore, the data obtained can be used in computational validation. The blast mitigation aspect of the study was accomplished
-
Energy absorption capabilities of composite sandwich panels under blast loads
Sankar Ray, Tirtha
As blast threats on military and civilian structures continue to be a significant concern, there remains a need for improved design strategies to increase blast resistance capabilities. The approach to blast resistance proposed here is focused on dissipating the high levels of pressure induced during a blast through maximizing the potential for energy absorption of composite sandwich panels, which are a competitive structural member type due to the inherent energy absorption capabilities of fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) composites. Furthermore, the middle core in the sandwich panels can be designed as a sacrificial layer allowing for a significant amount of deformation or progressive failure to maximize the potential for energy absorption. The research here is aimed at the optimization of composite sandwich panels for blast mitigation via energy absorption mechanisms. The energy absorption mechanisms considered include absorbed strain energy due to inelastic deformation as well as energy dissipation through progressive failure of the core of the sandwich panels. The methods employed in the research consist of a combination of experimentally-validated finite element analysis (FEA) and the derivation and use of a simplified analytical model. The key components of the scope of work then includes: establishment of quantified energy absorption criteria, validation of the selected FE modeling techniques, development of the simplified analytical model, investigation of influential core architectures and geometric parameters, and investigation of influential material properties. For the parameters that are identified as being most-influential, recommended values for these parameters are suggested in conceptual terms that are conducive to designing composite sandwich panels for various blast threats. Based on reviewing the energy response characteristic of the panel under blast loading, a non-dimensional parameter AET/ ET (absorbed energy, AET, normalized by total energy
-
Condition for Contur Blasting use on Openpit Mines
Krsmanovic, I; Dambov, Risto
2010-01-01
For purpose of obtaining a stable final slope in open pit mines practice, the most common approach is the contour blasting method and investigation of possible applications of various primary blasting methods for purpose of gaining the optimal techno-economical effects. This paper presents one of the contour blasting methods, drilling and blasting parameters, construction of explosive charges and method of initiation.
-
Experimental determination of radiated internal wave power without pressure field data
Lee, Frank M.; Paoletti, M. S.; Swinney, Harry L.; Morrison, P. J.
2014-04-01
We present a method to determine, using only velocity field data, the time-averaged energy flux left and total radiated power P for two-dimensional internal gravity waves. Both left and P are determined from expressions involving only a scalar function, the stream function ψ. We test the method using data from a direct numerical simulation for tidal flow of a stratified fluid past a knife edge. The results for the radiated internal wave power given by the stream function method agree to within 0.5% with results obtained using pressure and velocity data from the numerical simulation. The results for the radiated power computed from the stream function agree well with power computed from the velocity and pressure if the starting point for the stream function computation is on a solid boundary, but if a boundary point is not available, care must be taken to choose an appropriate starting point. We also test the stream function method by applying it to laboratory data for tidal flow past a knife edge, and the results are found to agree with the direct numerical simulation. The supplementary material includes a Matlab code with a graphical user interface that can be used to compute the energy flux and power from two-dimensional velocity field data.
-
Experimental determination of radiated internal wave power without pressure field data
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Lee, Frank M.; Morrison, P. J.; Paoletti, M. S.; Swinney, Harry L.
2014-01-01
We present a method to determine, using only velocity field data, the time-averaged energy flux (J) and total radiated power P for two-dimensional internal gravity waves. Both (J) and P are determined from expressions involving only a scalar function, the stream function ψ. We test the method using data from a direct numerical simulation for tidal flow of a stratified fluid past a knife edge. The results for the radiated internal wave power given by the stream function method agree to within 0.5% with results obtained using pressure and velocity data from the numerical simulation. The results for the radiated power computed from the stream function agree well with power computed from the velocity and pressure if the starting point for the stream function computation is on a solid boundary, but if a boundary point is not available, care must be taken to choose an appropriate starting point. We also test the stream function method by applying it to laboratory data for tidal flow past a knife edge, and the results are found to agree with the direct numerical simulation. The supplementary material includes a Matlab code with a graphical user interface that can be used to compute the energy flux and power from two-dimensional velocity field data
-
Development of an analysis code for pressure wave propagation, (1)
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Tanaka, Yoshihisa; Sakano, Kosuke; Shindo, Yoshihisa
1974-11-01
We analyzed the propagation of the pressure-wave in the piping system of SWAT-1B rig by using SWAC-5 Code. We carried out analyses on the following parts. 1) A straight pipe 2) Branches 3) A piping system The results obtained in these analyses are as follows. 1) The present our model simulates well the straight pipe and the branch with the same diameters. 2) The present our model simulates approximately the branch with the different diameters and the piping system. (auth.)
-
Air Blasts from Cased and Uncased Explosives
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Glenn, L. A. [Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
2016-04-12
The problem of a spherical blast in air is solved using the STUN code. For bare charges, the calculations are shown to be in excellent agreement with previous published results. It is demonstrated that, for an unconfined (uncased) chemical explosive, both range and time to effect scale inversely as the cube root of the yield and directly as the cube root of the ambient air density. It is shown that the peak overpressure decays to roughly 1/10 of ambient pressure in a scaled range of roughly 10 m/kg1/3 at sea level. At a height of 30 km, where the ambient density is a factor of 64 less, the range to the same decay increases to 40 m/kg1/3 . As a direct result of the scaling a single calculation suffices for all charge sizes and altitudes. Although the close-in results are sensitive to the nature of the explosive source and the equation of state of the air, this sensitivity is shown to virtually disappear at scaled ranges > 0.5 m/kg1/3 . For cased explosives the case thickness introduces an additional scale factor. Moreover, when the blast wave arrives at the inner case radius the case begins to expand. Fracture occurs when a critical value of the resulting hoop strain is reached, causing the case to shatter into fragments. A model is proposed to describe the size distribution of the fragments and their subsequent motion via drag interaction with the explosion products and ambient air. It is shown that a significant fraction of the charge energy is initially transmitted to the case fragments in the form of kinetic energy; for example, a 1 kg spherical charge with a 5 mm thick steel case has almost 29% of the total charge energy as initial kinetic energy of case fragments. This percentage increases with increasing case thickness and decreases with increasing charge size. The peak overpressure at a given range is 70-85% for cased explosives as compared with uncased and the peak impulse per unit area is 90-95%. The peak overpressure and
-
Wireless device for activation of an underground shock wave absorber
Chikhradze, M.; Akhvlediani, I.; Bochorishvili, N.; Mataradze, E.
2011-10-01
The paper describes the mechanism and design of the wireless device for activation of energy absorber for localization of blast energy in underground openings. The statistics shows that the greatest share of accidents with fatal results associate with explosions in coal mines due to aero-methane and/or air-coal media explosion. The other significant problem is terrorist or accidental explosions in underground structures. At present there are different protective systems to reduce the blast energy. One of the main parts of protective Systems is blast Identification and Registration Module. The works conducted at G. Tsulukidze Mining Institute of Georgia enabled to construct the wireless system of explosion detection and mitigation of shock waves. The system is based on the constant control on overpressure. The experimental research continues to fulfill the system based on both threats, on the constant control on overpressure and flame parameters, especially in underground structures and coal mines. Reaching the threshold value of any of those parameters, the system immediately starts the activation. The absorber contains a pyrotechnic device ensuring the discharge of dispersed water. The operational parameters of wireless device and activation mechanisms of pyrotechnic element of shock wave absorber are discussed in the paper.
-
Dong, Qian
2017-12-01
The study of propagation law of plane stress wave in jointed rock mass under in-situ stress has important significance for safety excavation of underground rock mass engineering. A model test of the blasting stress waves propagating in the intact rock and jointed rock mass under different in-situ stresses was carried out, and the influencing factors on the propagation law, such as the scale of static loads and the number of joints were studied respectively. The results show that the transmission coefficient of intact rock is larger than that of jointed rock mass under the same loading condition. With the increase of confining pressure, the transmission coefficients of intact rock and jointed rock mass both show an trend of increasing first and then decreasing, and the variation of transmission coefficients in intact rock is smaller than that of jointed rock mass. Transmission coefficient of jointed rock mass decreases with the increase of the number of joints under the same loading condition, when the confining pressure is relatively small, the reduction of transmission coefficients decreases with the increasing of the number of joints, and the variation law of the reduction of transmission coefficients is contrary when the confining pressure is large.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Archibald, K.E.
1997-01-01
Initial tests with CO 2 pellet blasting as a decontamination technique were completed in 1993 at the Idaho Chemical Processing Plant (ICPP) at the Idaho National Engineering Laboratory (INEL). During 1996, a number of additional CO 2 pellet blasting studies with Alpheus Cleaning Technologies, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and Pennsylvania State University were conducted. After the testing with Alpheus was complete, an SDI-5 shaved CO 2 blasting unit was purchased by the ICPP to test and determine its capabilities before using in ICPP decontamination efforts. Results of the 1996 testing will be presented in this report
-
Kouznetsov, Igor; Lotko, William
1995-01-01
The 'radial' transport of energy by internal ULF waves, stimulated by dayside magnetospheric boundary oscillations, is analyzed in the framework of one-fluid magnetohydrodynamics. (the term radial is used here to denote the direction orthogonal to geomagnetic flux surfaces.) The model for the inhomogeneous magnetospheric plasma and background magnetic field is axisymmetric and includes radial and parallel variations in the magnetic field, magnetic curvature, plasma density, and low but finite plasma pressure. The radial mode structure of the coupled fast and intermediate MHD waves is determined by numerical solution of the inhomogeneous wave equation; the parallel mode structure is characterized by a Wentzel-Kramer-Brillouin (WKB) approximation. Ionospheric dissipation is modeled by allowing the parallel wave number to be complex. For boudnary oscillations with frequencies in the range from 10 to 48 mHz, and using a dipole model for the background magnetic field, the combined effects of magnetic curvature and finite plasma pressure are shown to (1) enhance the amplitude of field line resonances by as much as a factor of 2 relative to values obtained in a cold plasma or box-model approximation for the dayside magnetosphere; (2) increase the energy flux delivered to a given resonance by a factor of 2-4; and (3) broaden the spectral width of the resonance by a factor of 2-3. The effects are attributed to the existence of an 'Alfven buoyancy oscillation,' which approaches the usual shear mode Alfven wave at resonance, but unlike the shear Alfven mode, it is dispersive at short perpendicular wavelengths. The form of dispersion is analogous to that of an internal atmospheric gravity wave, with the magnetic tension of the curved background field providing the restoring force and allowing radial propagation of the mode. For nominal dayside parameters, the propagation band of the Alfven buoyancy wave occurs between the location of its (field line) resonance and that of the
-
Alay, E.; Skotak, M.; Misistia, A.; Chandra, N.
2018-01-01
Dynamic loads on specimens in live-fire conditions as well as at different locations within and outside compressed-gas-driven shock tubes are determined by both static and total blast overpressure-time pressure pulses. The biomechanical loading on the specimen is determined by surface pressures that combine the effects of static, dynamic, and reflected pressures and specimen geometry. Surface pressure is both space and time dependent; it varies as a function of size, shape, and external contour of the specimens. In this work, we used two sets of specimens: (1) anthropometric dummy head and (2) a surrogate rodent headform instrumented with pressure sensors and subjected them to blast waves in the interior and at the exit of the shock tube. We demonstrate in this work that while inside the shock tube the biomechanical loading as determined by various pressure measures closely aligns with live-fire data and shock wave theory, significant deviations are found when tests are performed outside.
-
Santiago-Sotelo, Perfecto; Ramirez-Prado, Jorge Humberto
2012-11-01
prfectBLAST is a multiplatform graphical user interface (GUI) for the stand-alone BLAST+ suite of applications. It allows researchers to do nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity searches against public (or user-customized) databases that are locally stored. It does not require any dependencies or installation and can be used from a portable flash drive. prfectBLAST is implemented in Java version 6 (SUN) and runs on all platforms that support Java and for which National Center for Biotechnology Information has made available stand-alone BLAST executables, including MS Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. It is free and open source software, made available under the GNU General Public License version 3 (GPLv3) and can be downloaded at www.cicy.mx/sitios/jramirez or http://code.google.com/p/prfectblast/.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Jung, Jong-Kil; Yoon, Jun-Kyu [Gachon Univ., Sungnam (Korea, Republic of); Kim, Kwang-Chu [KEPCO-E& C, Kimchun (Korea, Republic of)
2017-10-15
A rupture in a high-pressure pipe causes the fluid in the pipe to be discharged in the atmosphere at a high speed resulting in a supersonic jet that generates the compressible flow. This supersonic jet may display complicated and unsteady behavior in general . In this study, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis was performed to investigate the compressible flow generated by a supersonic jet ejected from a high-pressure pipe. A Shear Stress Transport (SST) turbulence model was selected to analyze the unsteady nature of the flow, which depends upon the various gases as well as the diameter of the pipe. In the CFD analysis, the basic boundary conditions were assumed to be as follows: pipe of diameter 10 cm, jet pressure ratio of 5, and an inlet gas temperature of 300 K. During the analysis, the behavior of the shockwave generated by a supersonic jet was observed and it was found that the blast wave was generated indirectly. The pressure wave characteristics of hydrogen gas, which possesses the smallest molecular mass, showed the shortest distance to the safety zone. There were no significant difference observed for nitrogen gas, air, and oxygen gas, which have similar molecular mass. In addition, an increase in the diameter of the pipe resulted in the ejected impact caused by the increased flow rate to become larger and the zone of jet influence to extend further.
-
Blasting in hot zone - a case study
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nabiullah, B.M.P.; Pingua, J.; Dhar, B.B. [Central Mining Research Institute, Dhanbad (India)
1997-12-31
A significant quantity of coking coal reserves in the country are under fire particularly in Jharia coalfield. To control the fire and prevent loss of coal, an opencast mining method is adopted. The main problem with these opencast mines is drilling in hot strata and selection of suitable explosives and blasting in the fire zone. Trial blasts were conducted at two open cast mines. The problem was tackled by quenching the hot blast holes with water. Temperature of blast holes were recorded soon after drilling, after quenching with water and just before charging with explosives. The rise in temperature of charged explosives with time was also recorded until blasting. The thermal behaviour of commercially available explosives (including slurry, emulsion, ANFO and detonating cord) was investigated in laboratory and field simulated conditions. Emulsion, slurry compositions and detonating cord were found safe to use in hot holes up to 120{degree}C for duration of two hours. This paper describes the blasting practices adopted in the fire zones. 4 refs., 6 figs., 8 tabs.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Laye epouse Granier, Agnes
1986-01-01
This report deals with the study of microwave discharges produced in argon gas by surface waves in the 20-760 Torr pressure range. Application to chemical analysis by emission optical spectroscopy is also investigated. First of all we study the propagation of a surface wave in a bounded plasma in which the effective collision frequency for momentum transfer ν is higher than the excitation one. The axial electron density profile is determined from two diagnostic techniques, i.e., phase variations of the wave field and Stark broadening of H β line. Then we deduce the discharge characteristics ν, θ (maintaining power of an electron-ion pair) and E eff (effective electric field for discharge sustaining) from the electron density profile. Then an energy balance of the discharge is developed. It explains the change of operating conditions in the 20-50 Torr range. At low pressure the discharge is governed by ambipolar diffusion whereas at high pressure, the electrons are mainly lost by volume recombination of Ar 2 + . Finally, we report on chemical analysis experiment of gases (optimum sensibility in found near 100 Torr) and of metallic solutions sprayed by a graphite oven. Performances of such a design and ICP plasma torches are compared. (author) [fr
-
Acoustic pressure waves induced in human heads by RF pulses from high-field MRI scanners.
Lin, James C; Wang, Zhangwei
2010-04-01
The current evolution toward greater image resolution from magnetic resonance image (MRI) scanners has prompted the exploration of higher strength magnetic fields and use of higher levels of radio frequencies (RFs). Auditory perception of RF pulses by humans has been reported during MRI with head coils. It has shown that the mechanism of interaction for the auditory effect is caused by an RF pulse-induced thermoelastic pressure wave inside the head. We report a computational study of the intensity and frequency of thermoelastic pressure waves generated by RF pulses in the human head inside high-field MRI and clinical scanners. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (U.S. FDA) guides limit the local specific absorption rate (SAR) in the body-including the head-to 8 W kg(-1). We present results as functions of SAR and show that for a given SAR the peak acoustic pressures generated in the anatomic head model were essentially the same at 64, 300, and 400 MHz (1.5, 7.0, and 9.4 T). Pressures generated in the anatomic head are comparable to the threshold pressure of 20 mPa for sound perception by humans at the cochlea for 4 W kg(-1). Moreover, results indicate that the peak acoustic pressure in the brain is only 2 to 3 times the auditory threshold at the U.S. FDA guideline of 8 W kg(-1). Even at a high SAR of 20 W kg(-1), where the acoustic pressure in the brain could be more than 7 times the auditory threshold, the sound pressure levels would not be more than 17 db above threshold of perception at the cochlea.
-
29 CFR 1926.906 - Initiation of explosive charges-electric blasting.
2010-07-01
...) After firing an electric blast from a blasting machine, the leading wires shall be immediately... 29 Labor 8 2010-07-01 2010-07-01 false Initiation of explosive charges-electric blasting. 1926.906... Use of Explosives § 1926.906 Initiation of explosive charges—electric blasting. (a) Electric blasting...
-
Numerical simulation of muzzle blast
Tyler-Street, M.
2014-01-01
Structural design methods for naval ships include environmental, operational and military load cases. One of the operational loads acting on a typical naval vessel is the muzzle blast from a gun. Simulating the muzzle blast load acting on a ship structure with CFD and ALE methods leads to large
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Miles, A.R.; Edwards, M.J.; Greenough, J.A.
2004-01-01
Perturbations on an interface driven by a strong blast wave grow in time due to a combination of Rayleigh-Taylor, Richtmyer-Meshkov, and decompression effects. In this paper, the results from a computational study of such a system under drive conditions to be attainable on the National Ignition Facility [E. M. Campbell, Laser Part. Beams 9, 209 (1991)] are presented. Using the multiphysics, adaptive mesh refinement, higher order Godunov Eulerian hydrocode, Raptor [L. H. Howell and J. A. Greenough, J. Comput. Phys. 184, 53 (2003)], the late nonlinear instability evolution for multiple amplitude and phase realizations of a variety of multimode spectral types is considered. Compressibility effects preclude the emergence of a regime of self-similar instability growth independent of the initial conditions by allowing for memory of the initial conditions to be retained in the mix-width at all times. The loss of transverse spectral information is demonstrated, however, along with the existence of a quasi-self-similar regime over short time intervals. Certain aspects of the initial conditions, including the rms amplitude, are shown to have a strong effect on the time to transition to the quasi-self-similar regime
-
Dust ion acoustic solitary waves in a magnetized dusty plasma with anisotropic ion pressure
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Choi, Cheong Rim; Ryu, Chang-Mo; Lee, D.-Y.; Lee, Nam C.; Kim, Y.-H.
2007-01-01
The influence of anisotropic ion pressure on the dust ion acoustic solitary wave (DIASW) and the double layer (DL) obliquely propagating to a magnetic field are investigated by using the Sagdeev potential. The anisotropic ion pressure is defined by applying the Chew-Goldberger-Low (CGL) theory, p-perpendicular=p-perpendicular 0 n and p-parallel=p-parallel 0 n 3 , where n is the normalized ion density. The solutions of DIASWs and DLs obliquely propagating to an external magnetic field are obtained in the small amplitude limit. It is found that the perpendicular component of anisotropic ion pressure works differently from that of the parallel component on the DIASWs in a magnetized dusty plasma, deviating from a straight extension of the isotropic pressure effect
-
Predictive control of thermal state of blast furnace
Barbasova, T. A.; Filimonova, A. A.
2018-05-01
The work describes the structure of the model for predictive control of the thermal state of a blast furnace. The proposed model contains the following input parameters: coke rate; theoretical combustion temperature, comprising: natural gas consumption, blasting temperature, humidity, oxygen, blast furnace cooling water; blast furnace gas utilization rate. The output parameter is the cast iron temperature. The results for determining the cast iron temperature were obtained following the identification using the Hammerstein-Wiener model. The result of solving the cast iron temperature stabilization problem was provided for the calculated values of process parameters of the target area of the respective blast furnace operation mode.
-
Gu, Wenbin; Wang, Zhenxiong; Liu, Jianqing; Xu, Jinglin; Liu, Xin; Cao, Tao
2017-01-01
Lighthouses are the most important hydraulic structures that should be protected during underwater drilling blasting. Thus, the effect of blasting vibration on lighthouse should be studied. On the basis of the dimensional analysis, we deduced a revised formula for water depth based on Sodev’s empirical formula and established the linear fitting model. During the underwater reef project in the main channel of Shipu Harbor in the Ningbo–Zhoushan Port, the blasting vibration data of the lighthou...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Naoe, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Wakui, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Shoubu, Takahisa; Takeuchi, Hirotsugu; Kawai, Masayoshi
2008-01-01
Liquid-mercury target systems for MW-class spallation neutron sources are being developed in the world. Proton beams will be used to induce the spallation reaction. At the moment the proton beam hits the target, pressure waves are generated in the mercury because of the abrupt heat deposition. The pressure waves interact with the target vessel leading to negative pressure that may cause cavitation along the vessel wall. Localized impacts by microjets and/or shock waves that are caused by cavitation bubble collapse impose pitting damage on the vessel wall. Bubble collapse behavior was observed by using a high-speed video camera, as well as simulated numerically. Localized impact due to cavitation bubble collapse was quantitatively estimated through comparison between numerical simulation and experiment. A novel surface treatment technique that consists of carburizing and nitriding processes was developed and the treatment condition was optimized to mitigate the pitting damage due to localized impacts. (author)
-
Proceedings of the eighteenth annual conference on explosives and blasting technique
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Anon.
1993-01-01
This edition of the Proceedings of the Annual Conference on Explosives and Blasting Techniques is the eighteenth in a series published by the International Society of Explosives Engineers. The papers cover a wide variety of explosives and blasting techniques, including: rock mechanics, rock drilling, perimeter control handling and documenting blasting complaints, blast vibration frequencies, blasting techniques for surface and underground coal mines, explosives for permafrost blasting, lightning detection, use of slow motion video to analyze blasts, tunneling, and close-in blasting control. Papers have been processed individually for inclusion on the data base
-
Laser driven shock wave experiments for equation of state studies at megabar pressures
Pant, H C; Senecha, V K; Bandyopadhyay, S; Rai, V N; Khare, P; Bhat, R K; Gupta, N K; Godwal, B K
2002-01-01
We present the results from laser driven shock wave experiments for equation of state (EOS) studies of gold metal. An Nd:YAG laser chain (2 J, 1.06 mu m wavelength, 200 ps pulse FWHM) is used to generate shocks in planar Al foils and Al + Au layered targets. The EOS of gold in the pressure range of 9-13 Mbar is obtained using the impedance matching technique. The numerical simulations performed using the one-dimensional radiation hydrodynamic code support the experimental results. The present experimental data show remarkable agreement with the existing standard EOS models and with other experimental data obtained independently using laser driven shock wave experiments.
-
Laser driven shock wave experiments for equation of state studies at megabar pressures
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Pant, H C; Shukla, M; Senecha, V K; Bandyopadhyay, S; Rai, V N; Khare, P; Bhat, R K; Gupta, N K; Godwal, B K
2002-01-01
We present the results from laser driven shock wave experiments for equation of state (EOS) studies of gold metal. An Nd:YAG laser chain (2 J, 1.06 μm wavelength, 200 ps pulse FWHM) is used to generate shocks in planar Al foils and Al + Au layered targets. The EOS of gold in the pressure range of 9-13 Mbar is obtained using the impedance matching technique. The numerical simulations performed using the one-dimensional radiation hydrodynamic code support the experimental results. The present experimental data show remarkable agreement with the existing standard EOS models and with other experimental data obtained independently using laser driven shock wave experiments
-
Proposal of evaluation method of tsunami wave pressure using 2D depth-integrated flow simulation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Arimitsu, Tsuyoshi; Ooe, Kazuya; Kawasaki, Koji
2012-01-01
To design and construct land structures resistive to tsunami force, it is most essential to evaluate tsunami pressure quantitatively. The existing hydrostatic formula, in general, tended to underestimate tsunami wave pressure under the condition of inundation flow with large Froude number. Estimation method of tsunami pressure acting on a land structure was proposed using inundation depth and horizontal velocity at the front of the structure, which were calculated employing a 2D depth-integrated flow model based on the unstructured grid system. The comparison between the numerical and experimental results revealed that the proposed method could reasonably reproduce the vertical distribution of the maximum tsunami pressure as well as the time variation of the tsunami pressure exerting on the structure. (author)
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Roy, P.P. [Central Mining Research Institute, Dhanbad (India). Blasting Dept.
1999-02-01
Experimental blasts were conducted for optimisation of blasting parameters using separate technologies involving non-electric initiation systems, air decking accessories in conjunction with different explosive products like emulsion (cartridge and site-mixed), slurries (cartridge and site-mixed) and ANFO. The cost associated with each such technology was then compared with the conventional methods of drilling and blasting operations. The results of cost analyses are given. Theoretical and practical aspects of such technologies and their best possible usage in order to establish the desired fragmentation, muck profile, wall control and ultimately the accepted level of costs are mentioned in subsequent sections. 16 refs., 17 figs., 8 plates, 11 tabs.
-
Blasting at a Superfund chemical waste site
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Burns, D.R.
1991-01-01
During the summer of 1989, Maine Drilling and Blasting of Gardiner, Maine was contracted by Cayer Corporation of Harvard, Massachusetts to drill and blast an interceptor trench at the Nyanza Chemical Superfund Site in Ashland, Massachusetts. The interceptor trench was to be 1,365 feet long and to be blasted out of granite. The trench was to be 12 feet wide at the bottom with 1/1 slopes, the deepest cut being 30 feet deep. A French drain 12 feet wide by 15 to 35 feet deep was blasted below the main trench on a 2% slope from its center to each end. A French drain is an excavation where the rock is blasted but not dug. The trench would be used as a perimeter road with any ground water flow going through the French drain flowing to both ends of the trench. Being a Superfund project turned a simple blasting project into a regulatory nightmare. The US Environmental Protection Agency performed all the chemical related functions on site. The US Army Corps of Engineers was overseeing all related excavation and construction on site, as was the Massachusetts Department of Environmental Quality Engineering, the local Hazardous Wastes Council, and the local Fire Department. All parties had some input with the blasting and all issues had to be addressed. The paper outlines the project, how it was designed and completed. Also included is an outline of the blast plan to be submitted for approval, an outline of the Safety/Hazardous Waste training and a description of all the problems which arose during the project by various regulatory agencies
-
Liu, Lei; zhang, Zhihua; Wang, Ya; Qin, hao
2018-03-01
The study on the pressure resistance performance of emulsion explosives in deep water can provide theoretical basis for underwater blasting, deep-hole blasting and emulsion explosives development. The sensitizer is an important component of emulsion explosives. By using reusable experimental devices to simulate the charge environment in deep water, the influence of the content of chemical sensitizer on the deep-water pressure resistance performance of emulsion explosives was studied. The experimental results show that with the increasing of the content of chemical sensitizer, the deep-water pressure resistance performance of emulsion explosives gradually improves, and when the pressure is fairly large, the effect is particularly pronounced; in a certain range, with the increase of the content of chemical sensitizer, that emulsion explosives’ explosion performance also gradually improve, but when the content reaches a certain value, the explosion properties declined instead; under the same emulsion matrix condition, when the content of NANO2 is 0.2%, that the emulsion explosives has good resistance to water pressure and good explosion properties. The correctness of the results above was testified in model blasting.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Chandra, B.P.; Parganiha, S.; Sonwane, V.D. [School of Studies in Physics and Astrophysics, Pt. Ravishankar Shukla University, Raipur 492010, Chhattisgarh (India); Chandra, V.K. [Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Chhatrapati Shivaji Institute of Technology, Shivaji Nagar, Kolihapuri, Durg 491001, Chhattisgarh (India); Jha, Piyush, E-mail: piyushjha22@rediffmail.com [Department of Applied Physics, Raipur Institute of Technology, Chhatauna, Mandir Hasuad, Raipur 492101, Chhattisgarh (India); Baghel, R.N. [School of Studies in Physics and Astrophysics, Pt. Ravishankar Shukla University, Raipur 492010, Chhattisgarh (India)
2016-10-15
The impact of a projectile propelled to velocities in the range of 0.5–2.5 km/s on to a target (X-cut quartz crystal) produces shock waves travelling at velocity of nearly 10 km/s in target, in which intense mechanoluminescence (ML) pulses of microsecond duration are produced, both in compression and post-compression conditions. The piezoelectric field produced due to surface charges of fractured target, causes band bending and subsequently, the free charge carriers are generated in the respective bands and the emission of ML occurs. The ML appears after a delay time t{sub th} whose value decreases with increasing value of the shock pressure. Initially, the ML intensity increases with the shock pressure because of the creation of more surfaces; however, for higher values of the shock pressure, the ML intensity tends to attain a saturation value because of the hardening of the crystals due to the creation of small crystallites in which the creation of new surfaces becomes difficult. The ratio between peak ML intensity in the uncompressed region and the maximum ML intensity in the compressed region decreases with increasing shock pressure because more defects produced at high pressure generate higher barrier for the relaxation of blocked cracks under compression. The expressions derived for characteristics of shock-induced ML are able to explain satisfactorily the experimental results. Shock-wave velocity, shock pressure, transit time, lifetime of electrons in conduction band, etc. can be determined by the shock-induced ML.As such, the shock-induced ML provides a new optical technique for the studies of materials under shock pressure.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Stephen Thomas Ahlers
2012-03-01
Full Text Available Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI resulting from exposure to improvised explosive devices (IEDs has fueled a requirement to develop animals models that mirror this condition using exposure to blast overpressure (BOP. En route to developing a model of repeated exposure to BOP we sought to initially characterize the effects of acute BOP exposure in rodents, focusing specifically on the levels of BOP exposure that produced clinical mTBI symptoms. We first measured BOP effects on gross motor function on a balance beam. Separate groups of unanesthetized rats were exposed (in different orientations to 40 kPa, 75 kPa and 120 kPa BOP exposure inside a pneumatically driven shock tube. Results demonstrated that rats exposed to 120 kPa demonstrated transient alterations or loss of consciousness indicated by a transient loss of righting and by increased latencies on the balance beam. The 120 kPa exposure was the threshold for overt pathology for acute BOP exposure with approximately 30% of rats presenting with evidence of subdural hemorrhage and cortical contusions. All animals exposed to 120 kPa BOP manifested evidence of significant pulmonary hemorrhage. Anterograde memory deficits were observed in rats exposed to 75 kPa facing the BOP wave and rats exposed to 120 kPa in the lateral (side orientation. We next assessed repeated exposure to either lateral or frontal 40 kPa BOP in anesthetized rats, once per day for 12 days. Results showed that repeated exposure in the frontal, but not side, orientation to the BOP wave produced a transitory learning deficit on a Morris water maze (MWM task as shown by significantly longer latencies to reach the submerged platform in the second and third blocks of a four block session. Implications of these data are discussed in relation to the manifestation of mTBI in military personnel exposed to IEDs. Finally, we suggest that there are multiple types of brain injury from blast.
-
Blasting as a method for abandoned mine land reclamation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Workman, J.L.; Fletcher, L.R.
1991-01-01
Blasting methods have been proposed for reclaiming abandoned underground coal mine sites having unstable conditions. The objective of blasting is twofold: the permanent stabilization of an area by the collapse of underground workings to prevent any future subsidence, and the use of blasting to close existing sinkholes. This paper presents the results of two research projects funded by the Bureau of Mines Abandoned Mine Land Research Program to investigate the feasibility of blasting to assist in the reclamation of shallow abandoned coal mine sites. Blasting tests were conducted at Beulah, North Dakota and at Scobey, Montana, involving different configurations. The first test was a 10-acre site where blasting was used to collapse regular room and pillar panels for which good mine layout information was available. The second test involved a one acre site containing very irregular workings for which there was little available information. Finally, blasting techniques were used to close 13 individual vertical openings. The depths to the coal seams were 60 feet or less at all sites. When blasting for Abandoned Mine Land Reclamation, material must be cast downward into the abandoned developments or laterally into the sinkhole. Designs based on cratering concepts and spherical charges worked well. The blasting techniques successfully collapsed and stabilized the test areas. Cost of reclamation for the two test sites are presented. Data from blast vibration monitoring are presented because control of vibrations is of concern when mitigation efforts are conducted near homes
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Z. M. Jaini
Full Text Available Abstract Numerical modeling of fracture failure is challenging due to various issues in the constitutive law and the transition of continuum to discrete bodies. Therefore, this study presents the application of the combined finite-discrete element method to investigate the fracture failure of reinforced concrete slabs subjected to blast loading. In numerical modeling, the interaction of non-uniform blast loading on the concrete slab was modeled using the incorporation of the finite element method with a crack rotating approach and the discrete element method to model crack, fracture onset and its post-failures. A time varying pressure-time history based on the mapping method was adopted to define blast loading. The Mohr-Coulomb with Rankine cut-off and von-Mises criteria were applied for concrete and steel reinforcement respectively. The results of scabbing, spalling and fracture show a reliable prediction of damage and fracture.
-
29th International Symposium on Shock Waves
Ranjan, Devesh
2015-01-01
This proceedings present the results of the 29th International Symposium on Shock Waves (ISSW29) which was held in Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A., from July 14 to July 19, 2013. It was organized by the Wisconsin Shock Tube Laboratory, which is part of the College of Engineering of the University of Wisconsin-Madison. The ISSW29 focused on the following areas: Blast Waves, Chemically Reactive Flows, Detonation and Combustion, Facilities, Flow Visualization, Hypersonic Flow, Ignition, Impact and Compaction, Industrial Applications, Magnetohydrodynamics, Medical and Biological Applications, Nozzle Flow, Numerical Methods, Plasmas, Propulsion, Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability, Shock-Boundary Layer Interaction, Shock Propagation and Reflection, Shock Vortex Interaction, Shock Waves in Condensed Matter, Shock Waves in Multiphase Flow, as well as Shock Waves in Rarefield Flow. The two Volumes contain the papers presented at the symposium and serve as a reference for the participants of the ISSW 29 and individuals interes...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Arundhati Undurti
2018-02-01
Full Text Available The most frequent injury sustained by US service members deployed to Iraq or Afghanistan is mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBI, or concussion, by far most often caused by blast waves from improvised explosive devices or other explosive ordnance. TBI from all causes gives rise to chronic neuroendocrine disorders with an estimated prevalence of 25–50%. The current study expands upon our earlier finding that chronic pituitary gland dysfunction occurs with a similarly high frequency after blast-related concussions. We measured circulating hormone levels and accessed demographic and testing data from two groups of male veterans with hazardous duty experience in Iraq or Afghanistan. Veterans in the mTBI group had experienced one or more blast-related concussion. Members of the deployment control (DC group encountered similar deployment conditions but had no history of blast-related mTBI. 12 of 39 (31% of the mTBI participants and 3 of 20 (15% veterans in the DC group screened positive for one or more neuroendocrine disorders. Positive screens for growth hormone deficiency occurred most often. Analysis of responses on self-report questionnaires revealed main effects of both mTBI and hypopituitarism on postconcussive and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD symptoms. Symptoms associated with pituitary dysfunction overlap considerably with those of PTSD. They include cognitive deficiencies, mood and anxiety disorders, sleep problems, diminished quality of life, deleterious changes in metabolism and body composition, and increased cardiovascular mortality. When such symptoms are due to hypopituitarism, they may be alleviated by hormone replacement. These findings suggest consideration of routine post-deployment neuroendocrine screening of service members and veterans who have experienced blast-related mTBI and are reporting postconcussive symptoms.
-
Undurti, Arundhati; Colasurdo, Elizabeth A.; Sikkema, Carl L.; Schultz, Jaclyn S.; Peskind, Elaine R.; Pagulayan, Kathleen F.; Wilkinson, Charles W.
2018-01-01
The most frequent injury sustained by US service members deployed to Iraq or Afghanistan is mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBI), or concussion, by far most often caused by blast waves from improvised explosive devices or other explosive ordnance. TBI from all causes gives rise to chronic neuroendocrine disorders with an estimated prevalence of 25–50%. The current study expands upon our earlier finding that chronic pituitary gland dysfunction occurs with a similarly high frequency after blast-related concussions. We measured circulating hormone levels and accessed demographic and testing data from two groups of male veterans with hazardous duty experience in Iraq or Afghanistan. Veterans in the mTBI group had experienced one or more blast-related concussion. Members of the deployment control (DC) group encountered similar deployment conditions but had no history of blast-related mTBI. 12 of 39 (31%) of the mTBI participants and 3 of 20 (15%) veterans in the DC group screened positive for one or more neuroendocrine disorders. Positive screens for growth hormone deficiency occurred most often. Analysis of responses on self-report questionnaires revealed main effects of both mTBI and hypopituitarism on postconcussive and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. Symptoms associated with pituitary dysfunction overlap considerably with those of PTSD. They include cognitive deficiencies, mood and anxiety disorders, sleep problems, diminished quality of life, deleterious changes in metabolism and body composition, and increased cardiovascular mortality. When such symptoms are due to hypopituitarism, they may be alleviated by hormone replacement. These findings suggest consideration of routine post-deployment neuroendocrine screening of service members and veterans who have experienced blast-related mTBI and are reporting postconcussive symptoms. PMID:29515515
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Padhi, S.N. [DGMS, Bhubaneswar (India)
1994-12-31
Blast vibrations may be felt in intensities as small as 1/100 of that required to cause any damage to structures. Therefore, the public response and thus complaints regarding damages are often imaginary. The paper deals with three case studies, involving alleged damage from blasting in surface and underground coal mines where public litigations and agitations resulted due to such apprehensions. The paper is written in simple technical language as the situations warranted that the blast vibration studies should be understood by the general public. 7 tabs.
-
Massive injection of coal and superoxygenated blast into the blast furnace
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Toxopeus, H.L.; Danloy, G.; Franssen, R.; Havelange, O. [Corus, IJmuiden (Netherlands)
2002-07-01
The aim of the present project was to demonstrate the industrial feasibility of a massive injection of coal, {+-}270 kg/tHM, combined with a high O{sub 2} enrichment of the blast. The coke rate would thus be reduced to well below 250 kg/tHM. A reference level of 200-220 kg coal/tHM was successfully accomplished. However, the technical condition of the blast furnace hearths overruled all ambitions, the anticipated trial scheme had to be abandoned and no further trials were performed. A very short trial was aborted shortly after reaching an injection level of around 265 coal/tHM, due to excessive generation of very fine sludge originating from incomplete combustion. This forced the operators to investigate the merits of combustion more in depth. At the aimed low coke-rate detailed information about the gas distribution is of utmost importance. Therefore, in conjunction with the industrial tests, CRM designed a gas tracing method. Measurement of the transfer time between the injection point (a tuyere) and the sampling points (on an above-burden probe) would allow deduction of the radial gas distribution. CRM made the design and the start-up of an installation built by Hoogovens on blast furnace 7 of IJmuiden. Since then, repeated measurements have shown that the gas transfer time profiles are consistent with the data measured at the blast furnace top and at the wall. The modifications of the moveable armour position are reflected better and faster on the gas distribution as measured by helium tracing than on the skin flow temperatures.
-
Time variation in the reaction-zone structure of two-phase spray detonations.
Pierce, T. H.; Nicholls, J. A.
1973-01-01
A detailed theoretical analysis of the time-varying detonation structure in a monodisperse spray is presented. The theory identifies experimentally observed reaction-zone overpressures as deriving from blast waves formed therein by the explosive ignition of the spray droplets, and follows in time the motion, change in strength, and interactions of these blast waves with one another, and with the leading shock. The results are compared with experimental data by modeling the motion of a finite-size circular pressure transducer through the theoretical data field in an x-t space.
-
Blast Resistance of Slurry Infiltrated Fibre Concrete with Waste Steel Fibres from Tires
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Drdlová Martina
2018-01-01
Full Text Available The utilization of waste steel fibres (coming from the recycling process of the old tires in production of blast resistant cement based panels was assessed. Waste fibres were incorporated in slurry infiltrated fibre concrete (SIFCON, which is a special type of ultra-highperformance fibre reinforced concrete with high fibre content. The technological feasibility (i.e. suitability of the waste fibres for SIFCON technology was assessed using homogeneity test. Test specimens were prepared with three volume fractions (5; 7.5 and 10 % by vol. of waste unclassified fibres. SIFCON with industrial steel fibres (10% by vol. and ultra-highperformance fibre concrete with industrial fibres were also cast and tested for comparison purposes. Quasi-static mechanical properties were determined. Real blast tests were performed on the slab specimens (500x500x40 mm according to the modified methodology M-T0-VTU0 10/09. Damage of the slab, the change of the ultrasound wave velocity propagation in the slab specimen before and after the blast load in certain measurement points, the weight of fragments and their damage potential were evaluated and compared. Realized tests confirmed the possibility of using the waste fibres for SIFCON technology. The obtained results indicate, that the usage of waste fibres does not significantly reduce the values of SIFCON flexural and compressive strength at quasi-static load - the values were comparable to the specimens with industrially produced fibres. With increasing fibre content, the mechanical parameters are increasing as well. Using of the waste fibres reduces fragmentation of SIFCON at blast load due to the fibre size parameters. Using of low diameter fibres means more fibres in the matrix and thus better homogeneity of the whole composite with less unreinforced areas. Regarding the blast tests, the specimen with waste steel fibres showed the best resistance and outperformed also the specimen with commercial fibres. Using of
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yue Shen
2013-01-01
Full Text Available The feasibility of applying delay pressure detection method to eliminate mud pump pressure interference on the downhole mud pressure signals is studied. Two pressure sensors mounted on the mud pipe in some distance apart are provided to detect the downhole mud continuous pressure wave signals on the surface according to the delayed time produced by mud pressure wave transmitting between the two sensors. A mathematical model of delay pressure detection is built by analysis of transmission path between mud pump pressure interference and downhole mud pressure signals. Considering pressure signal transmission characteristics of the mud pipe, a mathematical model of ideal low-pass filter for limited frequency band signal is introduced to study the pole frequency impact on the signal reconstruction and the constraints of pressure sensor distance are obtained by pole frequencies analysis. Theoretical calculation and numerical simulation show that the method can effectively eliminate mud pump pressure interference and the downhole mud continuous pressure wave signals can be reconstructed successfully with a significant improvement in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR in the condition of satisfying the constraints of pressure sensor distance.
-
Fluid dynamics of the 1997 Boxing Day volcanic blast on Montserrat, West Indies
Esposti Ongaro, T.; Clarke, A. B.; Neri, A.; Voight, B.; Widiwijayanti, C.
2008-03-01
Directed volcanic blasts are powerful explosions with a significant laterally directed component, which can generate devastating, high-energy pyroclastic density currents (PDCs). Such blasts are an important class of eruptive phenomena, but quantified understanding of their dynamics and effects is still incomplete. Here we use 2-D and 3-D multiparticle thermofluid dynamic flow codes to examine a powerful volcanic blast that occurred on Montserrat in December 1997. On the basis of the simulations, we divide the blast into three phases: an initial burst phase that lasts roughly 5 s and involves rapid expansion of the gas-pyroclast mixture, a gravitational collapse phase that occurs when the erupted material fails to mix with sufficient air to form a buoyant column and thus collapses asymmetrically, and a PDC phase that is dominated by motion parallel to the ground surface and is influenced by topography. We vary key input parameters such as total gas energy and total solid mass to understand their influence on simulations, and we compare the simulations with independent field observations of damage and deposits, demonstrating that the models generally capture important large-scale features of the natural phenomenon. We also examine the 2-D and 3-D model results to estimate the flow Mach number and conclude that the range of damage sustained at villages on Montserrat can be reasonably explained by the spatial and temporal distribution of the dynamic pressure associated with subsonic PDCs.
-
Blast noise classification with common sound level meter metrics.
Cvengros, Robert M; Valente, Dan; Nykaza, Edward T; Vipperman, Jeffrey S
2012-08-01
A common set of signal features measurable by a basic sound level meter are analyzed, and the quality of information carried in subsets of these features are examined for their ability to discriminate military blast and non-blast sounds. The analysis is based on over 120 000 human classified signals compiled from seven different datasets. The study implements linear and Gaussian radial basis function (RBF) support vector machines (SVM) to classify blast sounds. Using the orthogonal centroid dimension reduction technique, intuition is developed about the distribution of blast and non-blast feature vectors in high dimensional space. Recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE) is then used to eliminate features containing redundant information and rank features according to their ability to separate blasts from non-blasts. Finally, the accuracy of the linear and RBF SVM classifiers is listed for each of the experiments in the dataset, and the weights are given for the linear SVM classifier.
-
Propagation of atmospheric-pressure ionization waves along the tapered tube
Xia, Yang; Wang, Wenchun; Liu, Dongping; Yan, Wen; Bi, Zhenhua; Ji, Longfei; Niu, Jinhai; Zhao, Yao
2018-02-01
Gas discharge in a small radius dielectric tube may result in atmospheric pressure plasma jets with high energy and density of electrons. In this study, the atmospheric pressure ionization waves (IWs) were generated inside a tapered tube. The propagation behaviors of IWs inside the tube were studied by using a spatially and temporally resolved optical detection system. Our measurements show that both the intensity and velocity of the IWs decrease dramatically when they propagate to the tapered region. After the taper, the velocity, intensity, and electron density of the IWs are improved with the tube inner diameter decreasing from 4.0 to 0.5 mm. Our analysis indicates that the local gas conductivity and surface charges may play a role in the propagation of the IWs under such a geometrical constraint, and the difference in the dynamics of the IWs after the taper can be related to the restriction in the size of IWs.
-
Pressure-drop and density-wave instability thresholds in boiling channels
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Gurgenci, H.; Yildirim, T.; Kakac, S.; Veziroglu, T.N.
1987-01-01
In this study, a criterion for linearized stability with respect to both the pressure-drop and the density-wave oscillations is developed for a single-channel upflow boiling system operating between constant pressures with upstream compressibility introduced through a surge tank. Two different two-phase flow models, namely a constant-property homogeneous flow model a variable-property drift-flux model, have been employed. The conservation equations for both models and the equations of surge tank dynamics are first linearized for small perturbation and the stability of the resulting set of equations for each model are examined by use of Nyquist plots. As a measure of the relative instability of the system, the amounts of the inlet throttling necessary to stabilize the system at particular operating points have been calculated. The results are compared with experimental findings. Comparisons show that the drift-flux formulation offers a simple and reliable way of determining the instability thresholds
-
Bomb blast imaging: bringing order to chaos.
Dick, E A; Ballard, M; Alwan-Walker, H; Kashef, E; Batrick, N; Hettiaratchy, S; Moran, C G
2018-06-01
Blast injuries are complex, severe, and outside of our everyday clinical practice, but every radiologist needs to understand them. By their nature, bomb blasts are unpredictable and affect multiple victims, yet require an immediate, coordinated, and whole-hearted response from all members of the clinical team, including all radiology staff. This article will help you gain the requisite expertise in blast imaging including recognising primary, secondary, and tertiary blast injuries. It will also help you understand the fundamental role that imaging plays during mass casualty attacks and how to avoid radiology becoming a bottleneck to the forward flow of severely injured patients as they are triaged and treated. Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
-
On firework blasts and qualitative parameter dependency.
Zohdi, T I
2016-01-01
In this paper, a mathematical model is developed to qualitatively simulate the progressive time-evolution of a blast from a simple firework. Estimates are made for the blast radius that one can expect for a given amount of detonation energy and pyrotechnic display material. The model balances the released energy from the initial blast pulse with the subsequent kinetic energy and then computes the trajectory of the material under the influence of the drag from the surrounding air, gravity and possible buoyancy. Under certain simplifying assumptions, the model can be solved for analytically. The solution serves as a guide to identifying key parameters that control the evolving blast envelope. Three-dimensional examples are given.
-
Waibel, Jill S; Rudnick, Ashley; Nousari, Carlos; Bhanusali, Dhaval G
2016-01-01
Topical drug delivery is the foundation of all dermatological therapy. Laser-assisted drug delivery (LAD) using fractional ablative laser is an evolving modality that may allow for a greater precise depth of penetration by existing topical medications, as well as more efficient transcutaneous delivery of large drug molecules. Additional studies need to be performed using energy-driven methods that may enhance drug delivery in a synergistic manner. Processes such as iontophoresis, electroporation, sonophoresis, and the use of photomechanical waves aid in penetration. This study evaluated in vivo if there is increased efficacy of fractional CO2 ablative laser with immediate acoustic pressure wave device. Five patients were treated and biopsied at 4 treatment sites: 1) topically applied aminolevulinic acid (ALA) alone; 2) fractional ablative CO2 laser and topical ALA alone; 3) fractional ablative CO2 laser and transdermal acoustic pressure wave device delivery system; and 4) topical ALA with transdermal delivery system. The comparison of the difference in the magnitude of diffusion with both lateral spread of ALA and depth diffusion of ALA was measured by fluorescence microscopy. For fractional ablative CO2 laser, ALA, and transdermal acoustic pressure wave device, the protoporphyrin IX lateral fluorescence was 0.024 mm on average vs 0.0084 mm for fractional ablative CO2 laser and ALA alone. The diffusion for the acoustic pressure wave device was an order of magnitude greater. We found that our combined approach of fractional ablative CO2 laser paired with the transdermal acoustic pressure wave device increased the depth of penetration of ALA.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Taha, Z.; Ahmad, N.; Ghazilla, R.A.R.; Yap, H.J.; Ya, T.Y.T.; Passarella, R.; Hasanuddin, I.; Yunus, M. [Malaya Univ. (Malaysia). Centre for Product Design and Manufacturing; Sugiyono [Malaya Univ., (Malaysia). Centre for Product Design and Manufacturing; Gadjah Mada Univ. (Indonesia). Dept. of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering
2009-07-01
The use of renewable energy sources as an alternative to conventional fuels was discussed with particular reference to ocean wave energy and its potential to contribute to the energy requirements of coastal nations. Ocean wave energy has been harnessed and converted into electricity using processes and technologies that are environmentally sound. The oscillating water column (OWC) system is considered to be among the most promising technology for harnessing wave energy. This paper presented the results of a study that investigated the pressure drop in an OWC system and the effect of spherical hub-nose position in an annular duct. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis was used under steady flow conditions for several hub-nose positions to determine the characteristic of pressure drop. The study showed that the hub-nose position influenced the pressure drop in the OWC system. The highest value of the pressure drop in this study occurred when the hub-nose was at the position of 0.0 m relative to the end of the converging cone. The pressure drop decreased when the hub-nose position moved away from the end of converging cone. The lowest value occurred at the position of -0.5 m. It was concluded that despite the numerically small change in pressure drop, this phenomenon should be considered in the design process of the OWC system because of the operational condition of the system at low-pressure pneumatic power. The pressure drop actually reduces the amount of energy that will be converted by the air turbine. 9 refs., 2 tabs., 6 figs.
-
Plastic Deformation of Metal Tubes Subjected to Lateral Blast Loads
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Kejian Song
2014-01-01
Full Text Available When subjected to the dynamic load, the behavior of the structures is complex and makes it difficult to describe the process of the deformation. In the paper, an analytical model is presented to analyze the plastic deformation of the steel circular tubes. The aim of the research is to calculate the deflection and the deformation angle of the tubes. A series of assumptions are made to achieve the objective. During the research, we build a mathematical model for simply supported thin-walled metal tubes with finite length. At a specified distance above the tube, a TNT charge explodes and generates a plastic shock wave. The wave can be seen as uniformly distributed over the upper semicircle of the cross-section. The simplified Tresca yield domain can be used to describe the plastic flow of the circular tube. The yield domain together with the plastic flow law and other assumptions can finally lead to the solving of the deflection. In the end, tubes with different dimensions subjected to blast wave induced by the TNT charge are observed in experiments. Comparison shows that the numerical results agree well with experiment observations.
-
28th International Symposium on Shock Waves
2012-01-01
The University of Manchester hosted the 28th International Symposium on Shock Waves between 17 and 22 July 2011. The International Symposium on Shock Waves first took place in 1957 in Boston and has since become an internationally acclaimed series of meetings for the wider Shock Wave Community. The ISSW28 focused on the following areas: Blast Waves, Chemically Reacting Flows, Dense Gases and Rarefied Flows, Detonation and Combustion, Diagnostics, Facilities, Flow Visualisation, Hypersonic Flow, Ignition, Impact and Compaction, Multiphase Flow, Nozzle Flow, Numerical Methods, Propulsion, Richtmyer-Meshkov, Shockwave Boundary Layer Interaction, Shock Propagation and Reflection, Shock Vortex Interaction, Shockwave Phenomena and Applications, as well as Medical and Biological Applications. The two Volumes contain the papers presented at the symposium and serve as a reference for the participants of the ISSW 28 and individuals interested in these fields.
-
Drilling-and-blasting method of demolition
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Sinitsyn Denis
2018-01-01
Full Text Available This article analyzes the experience and gives the examples of dismantling and demolition of the construction structures of the buildings and facilities using the drilling-and-blasting method. The drilling-and-blasting method is widely used in construction and reconstruction. The demolition means may be classified according to impact on a material of structures to be demolished and to forces application, where, by virtue of an impact energy type, we choose the blasting method. This method is used during the complete demolition or fragmentation of concrete, reinforced concrete, masonry structures, of old buildings and facilities demolition to their base or in the intended direction. Blasting method may be used as well during the steel and reinforced concrete structures demolition to the smaller easy-to-move parts. Reviewed are the organizational-process activities, which are performed during the various structures dismantling. Given are the areas of application for the various methods of structures demolition. Given is the example of demolition of “Sevemaya” boiler house brick chimney at the territory of Murmansk DSK using the blast in confined spaces of the operating company. Subject of research: methods of construction structures demolition in alarm situations and acts of God. Objects: determination of the most efficient demolition methods in the present conditions of construction operations development. Materials and methods: the developed activities on the construction structures dismantling are given. Results: the most efficient methods and ways of construction structures demolition are defined. Conclusions: it is required for improvement of methods and ways of the structures drilling-and-blasting demolition.
-
The effect of pressure on the charge-density wave and superconductivity in ZrTe sub 3
Yamaya, K; Yasuzuka, S; Okajima, Y; Tanda, S
2002-01-01
The charge-density-wave (CDW) transition temperature, T sub C sub D sub W , of ZrTe sub 3 is found to increase for pressures up to 0.6 GPa, while the superconducting transition temperature, T sub c , decreases with increasing pressure. According to a band calculation, it is found that the pressure-induced enhancement of the CDW and suppression of the superconductivity are not simply explained by the effect of nesting of the Fermi surface, suggesting the possibility of a new relation for the competition between the CDW and superconductivity.
-
Body-wave seismic interferometry applied to earthquake- and storm-induced wavefield
Ruigrok, E.N.
2012-01-01
Seismology is the study of the vibration of the Earth. Seismologists pay much attention to the main source of Earth vibration: earthquakes. But also other seismic sources, like mining blasts, ocean storms and windmills, are studied. All these sources induce seismic waves, which can eventually be
-
Proceedings of the twenty-seventh annual conference on explosives and blasting techniques
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
NONE
2001-07-01
Various aspects of explosives and blasting techniques are covered. Those of particular interest to the coal industry buffer blasting versus cast blasting, post-blast cast profile shape prediction, fragmentation model to estimate ROM size distribution of soft rocks, blasting accidents, blast vibrations, ANFO explosives and carbon monoxide poisoning.
-
Blast mitigation experimental and numerical studies
2013-01-01
Presents experimental methods of material and structural response to dynamic blast loads Includes computational analysis of material and structural response to dynamic blast loads Offers mitigation measures for structures in various environments Relates lab experiments to larger field tests Features more than 150 illustrations
-
Efthimion, Philip C.; Helfritch, Dennis J.
1989-11-28
An apparatus and method for creating high temperature plasmas for enhanced chemical processing of gaseous fluids, toxic chemicals, and the like, at a wide range of pressures, especially at atmospheric and high pressures includes an electro-magnetic resonator cavity, preferably a reentrant cavity, and a wave guiding structure which connects an electro-magnetic source to the cavity. The cavity includes an intake port and an exhaust port, each having apertures in the conductive walls of the cavity sufficient for the intake of the gaseous fluids and for the discharge of the processed gaseous fluids. The apertures are sufficiently small to prevent the leakage of the electro-magnetic radiation from the cavity. Gaseous fluid flowing from the direction of the electro-magnetic source through the guiding wave structure and into the cavity acts on the plasma to push it away from the guiding wave structure and the electro-magnetic source. The gaseous fluid flow confines the high temperature plasma inside the cavity and allows complete chemical processing of the gaseous fluids at a wide range of pressures.
-
Model of Draining of the Blast Furnace Hearth with an Impermeable Zone
Saxén, Henrik
2015-02-01
Due to demands of lower costs and higher productivity in the steel industry, the volume of operating blast furnaces has grown during the last decades. As the height is limited by the allowable pressure drop, the hearth diameter has grown considerably and, along with this, also draining-related problems. In this paper a mathematical model is developed for simulating the drainage in the case where an impermeable region exists in the blast furnace hearth. The model describes the quasi-stationary drainage process of a hearth with two operating tapholes, where the communication between the two pools of molten slag and iron can be controlled by parameterized expressions. The model also considers the case where the buoyancy of the liquids is sufficient for lifting the coke bed. The implications of different size of the liquid pools, communication between the pools, bed porosity, etc. are studied by simulation, and conclusions concerning their effect on the drainage behavior and evolution of the liquid levels in the hearth are drawn. The simulated liquid levels are finally demonstrated to give rise to a pressure profile acting on the hearth which agrees qualitatively with signals from strain gauges mounted in the hearth wall of an industrial ironmaking process.
-
Pressure Wave Measurements from Thermal Cook-Off of an HMX Based High Explosive PBX 9501
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Garcia, F.; Forbes, J.W.; Tarver, C.M.; Urtiew, P.A.; Greenwood, D.W.; Vandersall, K.S.
2001-01-01
A better understanding of thermal cook-off is important for safe handling and storing explosive devices. A number of safety issues exist about what occurs when a cased explosive thermally cooks off. For example, violence of the events as a function of confinement are important for predictions of collateral damage. This paper demonstrates how adjacent materials can be gauged to measure the resulting pressure wave and how this wave propagates in this adjacent material. The output pulse from the thermal cook-off explosive containing fixture is of obvious interest for assessing many scenarios
-
Effect of blasting on output increase of bucket wheel excavators
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Musil, P.
1987-12-01
In brown coal surface mines, consolidated sediments become a problem as mining operations advance into greater depth below the original terrain. Owing to higher digging resistance, the output of bucket wheel excavators drops. This problem may be solved by blasting technology and using drilling machines with higher digging force. This paper describes the blasting operations at the Nastup Mines in Tusmice, Czechoslovakia. About 60% of blasting explosives used is a simple mixture of ammonium nitrate and fuel (ANFO), the rest falls on classic blasting gelatines and blasting explosives plasticized by slurry. It is found that blasting improves output by 30% while electric energy consumption is reduced.
-
22 CFR 121.11 - Military demolition blocks and blasting caps.
2010-04-01
... 22 Foreign Relations 1 2010-04-01 2010-04-01 false Military demolition blocks and blasting caps... blasting caps. Military demolition blocks and blasting caps referred to in Category IV(a) do not include the following articles: (a) Electric squibs. (b) No. 6 and No. 8 blasting caps, including electric...
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Valero Martinez, M.
1980-01-01
The increasing demands in the field of ''Nuclear Safety'', obliges to a perfect knowledge of the causes and effects of every possible accident in a nuclear power plant. In this paper will be analysed the effects of the pressure wave appearing in a LOCA (Loss of collant accident). The pressure wave could deform the following structures: core barrel wall, cover and bottom, control rods and safety coolant system. Any change of the geometry of these structures could provoke and incorrect system reaction after the accident has happened. The basis and hypothesis for the theoretical analysis will be exposed. The structures are considered to be rigid. A typical boiling water be analysed and the developed theory will be verified in comparations with experimental results and the results obtained with some others models. Due to the easy application and short calculation time of the created programmes, they are recommended for parametrical calculations in the analysis of the pressurized water reactors and boiling water reactors. (author)
-
Windows .NET Network Distributed Basic Local Alignment Search Toolkit (W.ND-BLAST
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Oliver Melvin J
2005-04-01
Full Text Available Abstract Background BLAST is one of the most common and useful tools for Genetic Research. This paper describes a software application we have termed Windows .NET Distributed Basic Local Alignment Search Toolkit (W.ND-BLAST, which enhances the BLAST utility by improving usability, fault recovery, and scalability in a Windows desktop environment. Our goal was to develop an easy to use, fault tolerant, high-throughput BLAST solution that incorporates a comprehensive BLAST result viewer with curation and annotation functionality. Results W.ND-BLAST is a comprehensive Windows-based software toolkit that targets researchers, including those with minimal computer skills, and provides the ability increase the performance of BLAST by distributing BLAST queries to any number of Windows based machines across local area networks (LAN. W.ND-BLAST provides intuitive Graphic User Interfaces (GUI for BLAST database creation, BLAST execution, BLAST output evaluation and BLAST result exportation. This software also provides several layers of fault tolerance and fault recovery to prevent loss of data if nodes or master machines fail. This paper lays out the functionality of W.ND-BLAST. W.ND-BLAST displays close to 100% performance efficiency when distributing tasks to 12 remote computers of the same performance class. A high throughput BLAST job which took 662.68 minutes (11 hours on one average machine was completed in 44.97 minutes when distributed to 17 nodes, which included lower performance class machines. Finally, there is a comprehensive high-throughput BLAST Output Viewer (BOV and Annotation Engine components, which provides comprehensive exportation of BLAST hits to text files, annotated fasta files, tables, or association files. Conclusion W.ND-BLAST provides an interactive tool that allows scientists to easily utilizing their available computing resources for high throughput and comprehensive sequence analyses. The install package for W.ND-BLAST is
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Smith, P.R.; Gregory, W.S.
1985-04-01
Pressure transients in nuclear facility air cleaning systems can originate from natural phenomena such as tornadoes or from accident-induced explosive blast waves. This study was concerned with the effective efficiency of high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters during pressure surges resulting from simulated tornado and explosion transients. The primary objective of the study was to examine filter efficiencies at pressure levels below the point of structural failure. Both standard and high-capacity 0.61-m by 0.61-m HEPA filters were evaluated, as were several 0.2-m by 0.2-m HEPA filters. For a particular manufacturer, the material release when subjected to tornado transients is the same (per unit area) for both the 0.2-m by 0.2-m and the 0.61-m by 0.61-m filters. For tornado transients, the material release was on the order of micrograms per square meter. When subjecting clean HEPA filters to simulated tornado transients with aerosol entrained in the pressure pulse, all filters tested showed a degradation of filter efficiency. For explosive transients, the material release from preloaded high-capacity filters was as much as 340 g. When preloaded high-capacity filters were subjected to shock waves approximately 50% of the structural limit level, 1 to 2 mg of particulate was released
-
A Self-similar Flow Behind a Shock Wave in a Gravitating or Non ...
Indian Academy of Sciences (India)
a boundary-layer around the centre of explosion. Gretler & Wehle (1993) ... limits of Rosseland radiative diffusion and Plank radiative emission. In these works, ..... layer theory of blast waves, J. Fluid Mech., 71(1), 65–88. Laumbach, D. D. ...
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
V. Václavík
2012-10-01
Full Text Available The paper presents the results of experimental research that dealt with the substitution of finely ground blast furnace slag for Portland cement in the course of simple concrete manufacturing. Physical and mechanical properties of experimental concrete mixtures based on finely ground blast furnace slag were observed.
-
30 CFR 56.6312 - Secondary blasting.
2010-07-01
... Mineral Resources MINE SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION, DEPARTMENT OF LABOR METAL AND NONMETAL MINE SAFETY AND HEALTH SAFETY AND HEALTH STANDARDS-SURFACE METAL AND NONMETAL MINES Explosives Use § 56.6312 Secondary blasting. Secondary blasts fired at the same time in the same work area shall be initiated from...
-
Safety management system during rock blasting at FRFCF construction site
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Vijayakumaran, C.; Kandasamy, S.; Satpathy, K.K.
2016-01-01
Blasting is an important activity during rock excavation to reach required depth for obtaining stability of the civil structure. For the construction of various Plant Buildings of Fast Reactor Fuel Cycle Facility (FRFCF), IGCAR at Kalpakkam, based on the geological survey it is required to reach a depth of 21.4 meters from existing ground level. This paper details about the procedures and precaution adopted during the rock blasting activities at FRFCF site. The volume of rock removed by blasting was 3 lakh cubic meters. The total number of blasting carried out was 304 using 105.73 tons of blasting material. The entire blasting work could be completed within 174 days without any incident. (author)
-
Application of Carbon Composite Bricks for Blast Furnace Hearth
Zuo, Haibin; Wang, Cong; Zhang, Jianliang; Zhao, Yongan; Jiao, Kexin
Traditional refractory materials for blast furnace hearth lining are mainly composed of carbon bricks and the ceramic cup. However, these materials can't meet the demands for long service life design of blast furnaces. In this paper, a new refractory called carbon composite brick (CCB) was introduced, which combined the advantages of carbon bricks and the ceramic cup. In this case, the resistance of the CCB against corrosion was equal to the ceramic cup and the thermal conductivity of the CCB was equal to carbon bricks. From the results of more than 20 blast furnaces, the CCB could be well used in small blast furnaces and large blast furnaces. In the bad condition of low grade burden and high smelting intensity, the CCB gave full play to the role of cooling system, and effectively resisted the erosion of hot metal to improve the service life of blast furnaces.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
S. N. Raman
2012-01-01
Full Text Available The main distinction of blast load from other types of dynamic loadings is its impulsive nature, where the loads usually act for a very short duration but transmit very high impulsive pressures. This paper presents an overview of the present retrofitting techniques in use to enhance the capacity of structural elements to withstand the effects of blast loads, and introduces an alternative retrofitting approach by utilizing polymer coatings. The authors have demonstrated the positive effects of this approach by conducting a numerical investigation on the behavior of an unretrofitted reinforced concrete panel subjected to the blast load from a 2 kg charge at 1.6 m stand-off distance, and subsequently comparing its performance with several polymer coated panels. The analysis was performed by using an explicit nonlinear finite element (FE code. The results demonstrate the contributions of this technique in terms of panel displacement control and energy dissipation. Considering that the polymer coating can also act as a protective layer in improving the durability of structural materials, this technique can also be optimized favorably to enhance the overall sustainability of structures.
-
Woods, D. Tod; Holzer, Thomas E.; Macgregor, Keith B.
1990-01-01
Lower transition region models with a balance between mechanical heating and radiative losses are expanded to include wave pressure effects. The models are used to study the simple damping length form of the heating function. The results are compared to the results obtained by Woods et al. (1990) for solutions in the lower transition region. The results suggest that a mixture of fast-mode and slow-mode waves may provide the appropriate heating mechanism in the lower transition region, with the decline in effective vertical wave speed caused by the refraction and eventual total reflection of the fast-mode wave resulting from the decreasing atmospheric density.
-
Analysis of stress in reactor core vessel under effect of pressure lose shock wave
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Li Yong; Liu Baoting
2001-01-01
High Temperature gas cooled Reactor (HTR-10) is a modular High Temperature gas cooled Reactor of the new generation. In order to analyze the safety characteristics of its core vessel in case of large rupture accident, the transient performance of its core vessel under the effect of pressure lose shock wave is studied, and the transient pressure difference between the two sides of the core vessel and the transient stresses in the core vessel is presented in this paper, these results can be used in the safety analysis and safety design of the core vessel of HTR-10. (author)
-
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE STABILITY OF SURROUNDING ROCK IN TUNNEL BLASTING CONSTRUCTION
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Hongxian Fu
2018-04-01
Full Text Available In this study, criteria and blasting technologies are introduced in order to control the stability of surrounding rock of tunnel built using drill-and-blast safety. The paper is composed of three parts, namely, a blast vibration propagation law in roof surrounding rock in close proximity to tunnel face, two formulae to calculate particle critical vibration velocity of shotcrete and key structural element at the roof of tunnel, and innovative technologies of tunnel blasting. The blast vibration propagation law is the base to control the stability of surrounding rock during tunnel blasting. Based on Morhr-Coulomb criterion and the dynamic analysis, two formulae to calculate the critical particle vibration velocity are proposed. Based on a series of trial blasts using electronic detonators, two innovative blasting technologies are derived. One is the blast holes detonated one by one by using electronic detonator, and another is the blast holes detonated by combining initiation system of electronic detonators and nonel detonators. The use of electronic detonators in tunnel blasting not only leads to a smaller blast vibration but also to a smaller extent of the EDZ (excavation damaged zone.
-
Chuang, Wei-Liang; Chang, Kuang-An; Mercier, Richard
2018-06-01
Green water kinematics and dynamics due to wave impingements on a simplified geometry, fixed platform were experimentally investigated in a large, deep-water wave basin. Both plane focusing waves and random waves were employed in the generation of green water. The focusing wave condition was designed to create two consecutive plunging breaking waves with one impinging on the frontal vertical wall of the fixed platform, referred as wall impingement, and the other directly impinging on the deck surface, referred as deck impingement. The random wave condition was generated using the JONSWAP spectrum with a significant wave height approximately equal to the freeboard. A total of 179 green water events were collected in the random wave condition. By examining the green water events in random waves, three different flow types are categorized: collapse of overtopping wave, fall of bulk water, and breaking wave crest. The aerated flow velocity was measured using bubble image velocimetry, while the void fraction was measured using fiber optic reflectometry. For the plane focusing wave condition, measurements of impact pressure were synchronized with the flow velocity and void fraction measurements. The relationship between the peak pressures and the pressure rise times is examined. For the high-intensity impact in the deck impingement events, the peak pressures are observed to be proportional to the aeration levels. The maximum horizontal velocities in the green water events in random waves are well represented by the lognormal distribution. Ritter's solution is shown to quantitatively describe the green water velocity distributions under both the focusing wave condition and the random wave condition. A prediction equation for green water velocity distribution under random waves is proposed.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Scott, Edouard
1978-01-01
This research thesis aims at being a contribution to the safety of nuclear facilities by reporting the study of the interaction between nuclear fuel and coolant in simplified conditions. It focuses on the thermal aspect of this interaction between a very hot body and an easily vaporized cold body, which could produce a blast. Thus, this author addresses the field of existence of a thermal blast, and reports the development of a hydrodynamic model which takes the heterogeneous nature of the interacting medium into account, in order to precisely describe the conditions of fuel fragmentation. This model includes the propagation of a shock in a mixture, and the calculation of a multi-phase flow in the reaction zone, and proposes criteria for a self-sustained shock wave propagation in the reactive medium. Results are compared with those obtained with the Bankoff model [fr
-
Comprehensive Numerical Modeling of the Blast Furnace Ironmaking Process
Zhou, Chenn; Tang, Guangwu; Wang, Jichao; Fu, Dong; Okosun, Tyamo; Silaen, Armin; Wu, Bin
2016-05-01
Blast furnaces are counter-current chemical reactors, widely utilized in the ironmaking industry. Hot reduction gases injected from lower regions of the furnace ascend, reacting with the descending burden. Through this reaction process, iron ore is reduced into liquid iron that is tapped from the furnace hearth. Due to the extremely harsh environment inside the blast furnace, it is difficult to measure or observe internal phenomena during operation. Through the collaboration between steel companies and the Center for Innovation through Visualization and Simulation, multiple computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models have been developed to simulate the complex multiphase reacting flow in the three regions of the furnace, the shaft, the raceway, and the hearth. The models have been used effectively to troubleshoot and optimize blast furnace operations. In addition, the CFD models have been integrated with virtual reality. An interactive virtual blast furnace has been developed for training purpose. This paper summarizes the developments and applications of blast furnace CFD models and the virtual blast furnace.
-
Power Tillers for Demining: Blast Test
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Emanuela Elisa Cepolina
2007-06-01
Full Text Available Power tillers are very simple and versatile machines with large scale diffusion in developing countries, where they are commonly used both for agriculture and for transportation purposes. A new integrated participatory approach that makes use of and improves local end-users knowledge has been used to design a new robotic system for humanitarian demining applications in Sri Lanka, using power tiller as core module. A demining machine composed by a tractor unit, a ground processing tool and a vegetation cutting tool is here presented together with results obtained from the first blast test on the preliminary version of tractor unit armouring. Different breakable connections between wheels and axle have been designed to cause physical detachment and interrupt the transmission of the shock wave released by the explosion of a mine under one wheel. Effects of explosions on different types of wheels and on the chassis have been recorded and commented.
-
Power Tillers for Demining: Blast Test
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Emanuela Elisa Cepolina
2008-11-01
Full Text Available Power tillers are very simple and versatile machines with large scale diffusion in developing countries, where they are commonly used both for agriculture and for transportation purposes. A new integrated participatory approach that makes use of and improves local end-users knowledge has been used to design a new robotic system for humanitarian demining applications in Sri Lanka, using power tiller as core module. A demining machine composed by a tractor unit, a ground processing tool and a vegetation cutting tool is here presented together with results obtained from the first blast test on the preliminary version of tractor unit armouring. Different breakable connections between wheels and axle have been designed to cause physical detachment and interrupt the transmission of the shock wave released by the explosion of a mine under one wheel. Effects of explosions on different types of wheels and on the chassis have been recorded and commented.
-
Rice blast disease is a significant threat to stable rice production in the USA and worldwide. The major resistance gene (Pi-ta) located within a cluster of resistance genes on rice chromosome 12 has been demonstrated to confer resistance to the rice blast disease. Katy, a rice cultivar released in ...
-
Akbar, N S; Tripathi, D; Khan, Z H; Bég, O Anwar
2018-04-06
In this paper, we present an analytical study of pressure-driven flow of micropolar non-Newtonian physiological fluids through a channel comprising two parallel oscillating walls. The cilia are arranged at equal intervals and protrude normally from both walls of the infinitely long channel. A metachronal wave is generated due to natural beating of cilia and the direction of wave propagation is parallel to the direction of fluid flow. Appropriate expressions are presented for deformation via longitudinal and transverse velocity components induced by the ciliary beating phenomenon with cilia assumed to follow elliptic trajectories. The conservation equations for mass, longitudinal and transverse (linear) momentum and angular momentum are reduced in accordance with the long wavelength and creeping Stokesian flow approximations and then normalized with appropriate transformations. The resulting non-linear moving boundary value problem is solved analytically for constant micro-inertia density, subject to physically realistic boundary conditions. Closed-form expressions are derived for axial velocity, angular velocity, volumetric flow rate and pressure rise. The transport phenomena are shown to be dictated by several non-Newtonian parameters, including micropolar material parameter and Eringen coupling parameter, and also several geometric parameters, viz eccentricity parameter, wave number and cilia length. The influence of these parameters on streamline profiles (with a view to addressing trapping features via bolus formation and evolution), pressure gradient and other characteristics are evaluated graphically. Both axial and angular velocities are observed to be substantially modified with both micropolar rheological parameters and furthermore are significantly altered with increasing volumetric flow rate. Free pumping is also examined. An inverse relationship between pressure rise and flow rate is computed which is similar to that observed in Newtonian fluids. The
-
Computational modeling of blast induced whole-body injury: a review.
Chanda, Arnab; Callaway, Christian
2018-02-01
Blast injuries affect millions of lives across the globe due to its traumatic after effects on the brain and the whole body. To date, military grade armour materials are designed to mitigate ballistic and shrapnel attacks but are less effective in resisting blast impacts. In order to improve blast absorption characteristics of armours, the first key step is thoroughly understands the effects of blasts on the human body itself. In the last decade, a plethora of experimental and computational work has been carried out to investigate the mechanics and pathophysiology of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). However, very few attempts have been made so far to study the effect of blasts on the various other parts of the body such as the sensory organs (eyes and ears), nervous system, thorax, extremities, internal organs (such as the lungs) and the skeletal system. While an experimental evaluation of blast effects on such physiological systems is difficult, developing finite element (FE) models could allow the recreation of realistic blast scenarios on full scale human models and simulate the effects. The current article reviews the state-of-the-art in computational research in blast induced whole-body injury modelling, which would not only help in identifying the areas in which further research is required, but would also be indispensable for understanding body location specific armour design criteria for improved blast injury mitigation.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Avolio, Alberto P; Butlin, Mark; Walsh, Andrew
2010-01-01
The most common method of clinical measurement of arterial blood pressure is by means of the cuff sphygmomanometer. This instrument has provided fundamental quantitative information on arterial pressure in individual subjects and in populations and facilitated estimation of cardiovascular risk related to levels of blood pressure obtained from the brachial cuff. Although the measurement is taken in a peripheral limb, the values are generally assumed to reflect the pressure throughout the arterial tree in large conduit arteries. Since the arterial pressure pulse becomes modified as it travels away from the heart towards the periphery, this is generally true for mean and diastolic pressure, but not for systolic pressure, and so pulse pressure. The relationship between central and peripheral pulse pressure depends on propagation characteristics of arteries. Hence, while the sphygmomanometer gives values of two single points on the pressure wave (systolic and diastolic pressure), there is additional information that can be obtained from the time-varying pulse waveform that enables an improved quantification of the systolic load on the heart and other central organs. This topical review will assess techniques of pressure measurement that relate to the use of the cuff sphygmomanometer and to the non-invasive registration and analysis of the peripheral and central arterial pressure waveform. Improved assessment of cardiovascular function in relation to treatment and management of high blood pressure will result from future developments in the indirect measurement of arterial blood pressure that involve the conventional cuff sphygmomanometer with the addition of information derived from the peripheral arterial pulse. (topical review)
-
Ice blasting device for washing pump
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Hirose, Yasuo.
1992-01-01
In a nuclear power plant, when the inside of a pump casing such as a recycling pump is scrubbed, since operator's safety should be ensured, it requires a large-scaled operation. Then, a cover is attached to a flange of the pump casing, in which a driving portion is disposed passing through the cover vertically movably and rotatably, an arm is disposed bendably to the top end of the arm, and a blast nozzle is disposed to the top end of the arm for jetting ice particles, with a camera being disposed to the blast nozzle. The inside of the casing can be scrubbed safely and rapidly by an ice blast method by remote operation while monitoring the state of scrubbing for the inside of the casing by a camera. Further, since the flange of the pump casing for installing the ice blast device is covered by the cover, mists are not scattered to the outside. In addition, mists may be sucked and removed by an exhaustion duct. (N.H.)
-
Gardner, J. E.; Andrews, B. J.
2016-12-01
Pyroclastic density currents (flows and surges) are one of the most deadly hazards associated with volcanic eruptions. Understanding what controls how far such currents will travel, and how their dynamic pressure evolves, could help mitigate their hazards. The distance a ground hugging, pyroclastic density current travels is partly limited by when it reverses buoyancy and lifts off into the atmosphere. The 1980 blast surge of Mount St. Helens offers an example of a current seen to lift off. Before lofting, it had traveled up to 20 km and leveled more than 600 km3 of thick forest (the blowdown zone). The outer edge of the devastated area - where burned trees that were left standing (the singe zone) - is where the surge is thought to have lifted off. We recently examined deposits in the outer parts of the blowdown and in the singe zone at 32 sites. The important finding is that the laterally moving surge travelled into the singe zone, and hence the change in tree damage does not mark the run out distance of the ground hugging surge. Eyewitness accounts and impacts on trees and vehicles reveal that the surge consisted of a fast, dilute "overcurrent" and a slower "undercurrent", where most of the mass (and heat) was retained. Reasonable estimates for flow density and velocity show that dynamic pressure of the surge (i.e., its ability to topple trees) peaked near the base of the overcurrent. We propose that when the overcurrent began to lift off, the height of peak dynamic pressure rose above the trees and stopped toppling them. The slower undercurrent continued forward, burning trees but it lacked the dynamic pressure needed to topple them. Grain-size variations argue that it slowed from 30 m/s when it entered the singe zone to 3 m/s at the far end. Buoyancy reversal and liftoff are thus not preserved in the deposits where the surge lofted upwards.
-
ORGANISATIONAL-TECHNOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF BLASTING WORKS ON THE GRIČ TUNNEL
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Zvonimir Deković
2005-12-01
Full Text Available The paper describes organisational-technological characteristics of blasting works during the excavation of the Grič Tunnel. The significance of blasting works during the excavation of the tunnel is shown through adjustment of blasting parameters taking into consideration the dynamics of the works, cost-effectiveness and influence of geological circumstances. Successfulness of blasting directly influences the subsequent tunnel excavation cycle both in terms of duration as well as eventually in terms of influence on the entire tunnel investment. Comparison of changes of basic blasting parameters during tunnel excavation ensured optimal excavation progress with minimal price per meter of tunnel progress.
-
SSS: A code for computing one dimensional shock and detonation wave propagation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Sun Chengwei
1986-01-01
The one-dimensional hydrodynamic code SSS for shock and detonation wave propagation in inert and reactive media is described. The elastic-plastic-hydrodynamic model and four burn techniques (the Arrhenius law, C-J volume, sharp shock and Forest Fire) are used. There are HOM and JWL options for the state equation of detonation products. Comparing with the SIN code published by LANL, the SSS code has several new options: laser effects, blast waves, diverging and instantaneous detonation waves with arbitrary initiation positions. Two examples are given to compare the SSS and SIN calculations with the experimental data
-
Determination of Destress Blasting Effectiveness Using Seismic Source Parameters
Wojtecki, Łukasz; Mendecki, Maciej J.; Zuberek, Wacaław M.
2017-12-01
Underground mining of coal seams in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin is currently performed under difficult geological and mining conditions. The mining depth, dislocations (faults and folds) and mining remnants are responsible for rockburst hazard in the highest degree. This hazard can be minimized by using active rockburst prevention, where destress blastings play an important role. Destress blastings in coal seams aim to destress the local stress concentrations. These blastings are usually performed from the longwall face to decrease the stress level ahead of the longwall. An accurate estimation of active rockburst prevention effectiveness is important during mining under disadvantageous geological and mining conditions, which affect the risk of rockburst. Seismic source parameters characterize the focus of tremor, which may be useful in estimating the destress blasting effects. Investigated destress blastings were performed in coal seam no. 507 during its longwall mining in one of the coal mines in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin under difficult geological and mining conditions. The seismic source parameters of the provoked tremors were calculated. The presented preliminary investigations enable a rapid estimation of the destress blasting effectiveness using seismic source parameters, but further analysis in other geological and mining conditions with other blasting parameters is required.
-
Evaluation of blast-induced vibration effects on structures 1
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lee, Jong Rim; Jeon, Gyu Shick; Lee, Dae Soo; Joo, Kwang Ho; Lee, Woong Keon [Korea Electrotechnology Research Inst., Changwon (Korea, Republic of); Ryu, Chang Ha; Chung, So Keul; Lee, Kyung Won; Shin, Hee Soon; Chun, Sun Woo; Park, Yeon Jun; Synn, Joong Ho; Choi, Byung Hee [Korea Inst. of Geology Mining and Materials, Taejon (Korea, Republic of)
1995-12-31
Due to the difficulties of obtaining construction site for new plants, following ones are inevitably being built in the site adjacent to existing power plants. Therefore considerable thought has been recently given to the dynamic loading generated by blasting works near the plants to maintain the safety of structures and facilities in power plants. Our own standard for safety level of blast vibration is not prepared yet, and foreign standards have been generally employed without theoretical and experimental verification. Safety-related structures of power plants and facilities have to be protected against the effects of possible hazards due to blast vibration. Earthquakes have been considered a major dynamic design loading as a requirement of plant design, but the effects of blast-induced vibration are not. In order to ensure the safety, rational safe criterion should be established and blast design should be satisfy it, which requires the development of a model for prediction of vibration level through more systematic measurement and analysis. The main objectives of the study are : to provide background data for establishing the rational safe vibration limits, to develop models for prediction of blast vibration level, to establish safe blast design criterion, and to accumulate techniques for field measurements, data acquisition and analysis (author). 80 refs., 347 figs.
-
Interactions of Delta Shock Waves for Zero-Pressure Gas Dynamics with Energy Conservation Law
Wei Cai; Yanyan Zhang
2016-01-01
We study the interactions of delta shock waves and vacuum states for the system of conservation laws of mass, momentum, and energy in zero-pressure gas dynamics. The Riemann problems with initial data of three piecewise constant states are solved case by case, and four different configurations of Riemann solutions are constructed. Furthermore, the numerical simulations completely coinciding with theoretical analysis are shown.
-
Biofidelic Three-Dimensional Brain Surrogate Models of mTBI-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology
2016-10-01
Behavioural Brain Research (2016) – Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Behavioural Brain Research journa l homepage: www.e lsev ier...ARTICLEBR-10398; No. of Pages 12 H. Song et al. / Behavioural B eported findings in post-mortem brains of three blast exposed oldiers with no physical...instantaneously filled with gas under high pressure and temperature. The resulting energy expands radially outward as a blast wave moving at
-
High pressure gas scintillation drift chambers with wave-shifter fiber readout
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Parsons, A.; Edberg, T.K.; Sadoulet, B.; Weiss, S.; Wilkerson, J.; Hurley, K.; Lin, R.P.
1990-01-01
The authors present results from a prototype high pressure xenon gas scintillation drift chamber using a novel wave-shifter fiber readout scheme. They have measured the primary scintillation light yield to be one photon per 76 ± 12 eV deposited energy. They present initial results of our chamber for the two-interaction separation (< 4 mm in the drift direction, ∼ 7 mm orthogonal to the drift); for the position resolution (< 400 μm rms in the plane orthogonal to the drift direction); and for the energy resolution (ΔE/E < 6% FWHM at 122 keV)
-
Ultrafast dynamics in CeTe{sub 3} near the pressure-induced charge-density-wave transition
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Tauch, Jonas; Obergfell, Manuel [Department of Physics and Center for Applied Photonics, University of Konstanz (Germany); Schaefer, Hanjo [Department of Physics and Center for Applied Photonics, University of Konstanz (Germany); Institute of Physics, Ilmenau University of Technology (Germany); Demsar, Jure [Department of Physics and Center for Applied Photonics, University of Konstanz (Germany); Institute of Physics, Ilmenau University of Technology (Germany); Institute of Physics, Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz (Germany); Giraldo, Paula; Fisher, Ian R. [Geballe Laboratory for Advanced Materials and Department of Applied Physics, Stanford University (United States); Pashkin, Alexej [Department of Physics and Center for Applied Photonics, University of Konstanz (Germany); Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (Germany)
2015-07-01
Femtosecond pump-probe spectroscopy is an efficient tool for studying ultrafast dynamics in strongly correlated electronic systems, in particular, compounds with a charge-density-wave (CDW) order. Application of external pressure often leads to a suppression of a CDW state due to an impairment of the Fermi surface nesting. We combine time-resolved optical spectroscopy and diamond anvil cell technology to study electron and lattice dynamics in tri-telluride compound CeTe{sub 3}. Around pressures of 4 GPa we observe a gradual vanishing of the relaxation process related to the recombination of the photoexcited quasiparticles. The coherent oscillations of the phonon modes coupled to the CDW order parameter demonstrate even more dramatic suppression with increasing pressure. These observations clearly indicate a transition into the metallic state of CeTe{sub 3} induced by the external pressure.
-
Ligand Effects in Aluminum Cluster based Energetic Materials
2017-09-01
detonation is necessary. Detonation is a process involving a supersonic pressure wave perpetuated by an ongoing chemical reaction . For example, the... chemical reaction and can drive metal, a blast wave or otherwise do work external to the explosive. The detonation wave moves several kilometers per...Electrical Engineering NSWC Indian Head Approved by: Kevin Smith, Chair, Department of Physics Approved by: Douglas Moses, Vice Provost of Academic
-
Blast-Resistant Improvement of Sandwich Armor Structure with Aluminum Foam Composite
Yang, Shu; Qi, Chang
2013-01-01
Sandwich armor structures with aluminum foam can be utilized to protect a military vehicle from harmful blast load such as a landmine explosion. In this paper, a system-level dynamic finite element model is developed to simulate the blast event and to evaluate the blast-resistant performance of the sandwich armor structure. It is found that a sandwich armor structure with only aluminum foam is capable of mitigating crew injuries under a moderate blast load. However, a severe blast load causes...
-
Control of City Shallow Buried Tunnel Blasting Hazard to Surface Buildings
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Yang Deqiang
2015-01-01
Full Text Available Combining with the blasting test of an under-construction tunnel, this paper optimizes the overall blasting construction scheme. The optimized blasting scheme is used in the site construction test and the peak particle vibration velocity is strictly controlled under working conditions through blasting vibration monitoring to ensure the safety of surrounding buildings and structures in the construction process. The corresponding control measures are proposed to reduce the blasting vibration which brings certain guiding significance to the following construction project.
-
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Boergesson, L.; Pusch, R.; Fredriksson, A.; Hoekmark, H.; Karnland, O.; Sanden, R.
1992-01-01
Tests 2 and 3 of the rock sealing project comprised determination of the hydraulic properties of the disturbed rock around tunnels and drifts and the possibilities of decreasing the hydraulic conductivity of the disturbed zones by an attempt to seal the very fine fractures that are causing the increased conductivity. This report deals with the hydraulic testing while the grouting procedures and their effect are described in volume 3. The BMT drift was used for the experiments which basically consisted of measuring the flow of water from an inner pressurized slot and borehole curtain to an outer curtain with zero water pressure (Macro Flow Test). The 12 m long drift was sealed from water inflow by a slurry that filled the entire drift. The slurry was pressurized by a large water filled bladder for eliminating leakage along and through the drift. The flow tests were primarily evaluated by finite element modeling in which the rock was considered an equivalent porous medium. Two possible rock models were developed that satisfied not only the flow and water pressure measurements during the macro flow test but also 3 different flow situations preceding the test. The models imply a shallow blast-disturbed zone with a strongly increased hydraulic conductivity, and a stress disturbed zone with a decreased radial hydraulic conductivity. The main difference between the models is the extension of the blast-damaged zone and the axial hydraulic conductivity of the stress disturbed zone. (au)
-
Tripathi, B. B.; Espíndola, D.; Pinton, G. F.
2017-11-01
The recent discovery of shear shock wave generation and propagation in the porcine brain suggests that this new shock phenomenology may be responsible for a broad range of traumatic injuries. Blast-induced head movement can indirectly lead to shear wave generation in the brain, which could be a primary mechanism for injury. Shear shock waves amplify the local acceleration deep in the brain by up to a factor of 8.5, which may tear and damage neurons. Currently, there are numerical methods that can model compressional shock waves, such as comparatively well-studied blast waves, but there are no numerical full-wave solvers that can simulate nonlinear shear shock waves in soft solids. Unlike simplified representations, e.g., retarded time, full-wave representations describe fundamental physical behavior such as reflection and heterogeneities. Here we present a piecewise parabolic method-based solver for one-dimensional linearly polarized nonlinear shear wave in a homogeneous medium and with empirical frequency-dependent attenuation. This method has the advantage of being higher order and more directly extendable to multiple dimensions and heterogeneous media. The proposed numerical scheme is validated analytically and experimentally and compared to other shock capturing methods. A Riemann step-shock problem is used to characterize the numerical dissipation. This dissipation is then tuned to be negligible with respect to the physical attenuation by choosing an appropriate grid spacing. The numerical results are compared to ultrasound-based experiments that measure planar polarized shear shock wave propagation in a tissue-mimicking gelatin phantom. Good agreement is found between numerical results and experiment across a 40 mm propagation distance. We anticipate that the proposed method will be a starting point for the development of a two- and three-dimensional full-wave code for the propagation of nonlinear shear waves in heterogeneous media.
-
Behavior of coke in large blast furnaces
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Nakamura, N
1978-01-01
Three blast furnaces were quenched in operation and the contents were examined; the temperature distribution was also measured, using Tempil pellets. The furnaces examined included a low productivity one, which was examined to see what was wrong. Changes in the quality of coke as it descends in the furnace, and coke behavior in the raceway and hearth are reported. The functions required of coke, and the effects of poor coke quality, are explained, together with the coke quality required in large blast furnaces. A theoretical study of the role of coke in large blast furnaces is included.
-
Collapse of rocks by blasting. Razrusheniye gornykh porod Vzryvom
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Sukhanov, A F; Kutuzov, B N
1983-01-01
Information is provided about drilling boreholes and wells, explosives and the means for initiating them, storage, transporting and calculation of the explosive materials. Physical essence of the destructive, scientific and air effect of the blast are presented, principles of arrangement and calculation of the charges, reasons for malfunctions and methods of eliminating them, measures for protecting the surrounding objects from harmful effect of the industrial blast. Questions are examined of planning, organization and safety of the blasting operations. The second edition (first edition 1967) has been revised with regard for changes that occurred in the field of blasting operations.
-
Development and Realization of a Shock Wave Test on Expert Flap Qualification Model
De Fruytier, C.; Dell'Orco, F.; Ullio, R.; Gomiero, F.
2012-07-01
This paper presents the methodology and the results of the shock test campaign conducted by TAS-I and TAS ETCA to qualify the EXPERT Flap in regards of shock wave and acoustic load generated by pyrocord detonation at stages 2/3 separation phase of the EXPERT vehicle. The design concept of the open flap (manufactured by MT AEROSPACE) is a fully integral manufactured, four sided control surface, with an additional stiffening rib and flanges to meet the first eigenfrequency and the allowable deformation requirement with a minimum necessary mass. The objectives were to reproduce equivalent loading at test article level in terms of pulse duration, front pressure, front velocity and acoustic emission. The Thales Alenia Space ETCA pyrotechnic shock test device is usually used to produce high level shocks by performing a shock on a test fixture supporting the unit under test. In this case, the facility has been used to produce a shock wave, with different requested physical characteristics, directed to the unit under test. Different configurations have been tried on a dummy of the unit to test, following an empirical process. This unusual work has lead to the definition of a nominal set- up meeting the requested physical parameters. Two blast sensors have been placed to acquire the pressure around the flap. The distance between the two sensors has allowed estimating the front pressure velocity. Then, several locations have been selected to acquire the acceleration responses on the unit when it was submitted to this environment. Additionally, a “standard” shock test has been performed on this model. The qualification of the flap, in regards of shock environment, has been successfully conducted.
-
Impact of Drill and Blast Excavation on Repository Performance Confirmation
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Keller, R.; Francis, N.; Houseworth, J.; Kramer, N.
2000-01-01
There has been considerable work accomplished internationally examining the effects of drill and blast excavation on rock masses surrounding emplacement openings of proposed nuclear waste repositories. However, there has been limited discussion tying the previous work to performance confirmation models such as those proposed for Yucca Mountain, Nevada. This paper addresses a possible approach to joining the available information on drill and blast excavation and performance confirmation. The method for coupling rock damage data from drill and blast models to performance assessment models for fracture flow requires a correlation representing the functional relationship between the peak particle velocity (PPV) vibration levels and the potential properties that govern water flow rates in the host rock. Fracture aperture and frequency are the rock properties which may be most influenced by drill and blast induced vibration. If it can be shown (using an appropriate blasting model simulation) that the effect of blasting is far removed from the waste package in an emplacement drift, then disturbance to the host rock induced in the process of drill and blast excavation may be reasonably ignored in performance assessment calculations. This paper proposes that the CANMET (Canada Center for Mineral and Energy Technology) Criterion, based on properties that determine rock strength, may be used to define a minimum PPV. This PPV can be used to delineate the extent of blast induced damage. Initial applications have demonstrated that blasting models can successfully be coupled with this criterion to predict blast damage surrounding underground openings. The Exploratory Studies Facility at Yucca Mountain has used a blasting model to generate meaningful estimates of near-field vibration levels and damage envelopes correlating to data collected from pre-existing studies conducted. Further work is underway to expand this application over a statistical distribution of geologic
-
Bioeffects on an In Vitro Model by Small-Scale Explosives and Shock Wave Overpressure Impacts
2017-11-01
Many TBIs are associated with blast from improvised explosive devices.2–4 Explosions are physical, chemical , or nuclear reactions involving a rapid...ARL-TR-8210 ● NOV 2017 US Army Research Laboratory Bioeffects on an In Vitro Model by Small-Scale Explosives and Shock Wave...Research Laboratory Bioeffects on an In Vitro Model by Small-Scale Explosives and Shock Wave Overpressure Impacts by Nicole E Zander, Thuvan
-
Seismic safety in conducting large-scale blasts
Mashukov, I. V.; Chaplygin, V. V.; Domanov, V. P.; Semin, A. A.; Klimkin, M. A.
2017-09-01
In mining enterprises to prepare hard rocks for excavation a drilling and blasting method is used. With the approach of mining operations to settlements the negative effect of large-scale blasts increases. To assess the level of seismic impact of large-scale blasts the scientific staff of Siberian State Industrial University carried out expertise for coal mines and iron ore enterprises. Determination of the magnitude of surface seismic vibrations caused by mass explosions was performed using seismic receivers, an analog-digital converter with recording on a laptop. The registration results of surface seismic vibrations during production of more than 280 large-scale blasts at 17 mining enterprises in 22 settlements are presented. The maximum velocity values of the Earth’s surface vibrations are determined. The safety evaluation of seismic effect was carried out according to the permissible value of vibration velocity. For cases with exceedance of permissible values recommendations were developed to reduce the level of seismic impact.
-
Interactions of Delta Shock Waves for Zero-Pressure Gas Dynamics with Energy Conservation Law
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Wei Cai
2016-01-01
Full Text Available We study the interactions of delta shock waves and vacuum states for the system of conservation laws of mass, momentum, and energy in zero-pressure gas dynamics. The Riemann problems with initial data of three piecewise constant states are solved case by case, and four different configurations of Riemann solutions are constructed. Furthermore, the numerical simulations completely coinciding with theoretical analysis are shown.
-
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Shiiba, H; Honda, S; Araki, A [Fukuoka University, Fukuoka (Japan). Faculty of Engineering
1992-09-01
The effect of silica fume and ground blast furnace slag in concrete on the content of superplasticizer, and dynamic properties of hardened mortar with such admixtures were studied experimentally. Although the dependence of a flow value on the superplasticizer was dominated by kinds of superplasticizers, blast furnace slag enhanced the flow value resulting in a high fluidity. Adsorption of superplasticizers onto admixtures was dependent on kinds of superplasticizers, and adsorption onto blast furnace slag was 1.3-2 times that onto normal Portland cement (NPC). The compressive strength of mortar increased by mixing admixtures, while the bending strength was enhanced only by mixing silica fume. Mixing mortar was lower in dynamic elastic modulus than NPC mortar at the same compressive strength, and the velocity of supersonic wave in mortar was scarcely affected by mixing. 11 refs., 14 figs., 3 tabs.
-
Proceedings of the seventeenth annual conference on explosives and blasting technique. Volume 1
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Anon.
1991-01-01
Papers from this conference dealt with the following topics: surface and underground mine blasting, control of blast effects in sensitive areas, blasthole deviation, regulatory impact when blasting at Superfund sites, computer-aided blast design and monitoring, tunneling techniques, shaft excavations, video camera analysis of blasting operations, soil densification, cost optimization, mine blasting accidents, non-electric initiation systems, and delay detonators. Papers have been indexed separately for inclusion on the data base
-
Wave Pressures on Seawave Slot-Cone Generator
DEFF Research Database (Denmark)
Vicinanza, Diego; Kofoed, Jens Peter; Frigaard, Peter
2006-01-01
This paper presents results on loading action on an innovative caisson breakwater for electricity production. The work reported here contributes to the European Union Sixth Framework programme priority 6.1 (Sustainable Energy System), contract 019831, titled "Full- scale demonstration of robust...... and high efficiency energy converter" (WAVESSG). Information on wave loading acting on Wave Energy Convert (WEC) Seawave Slot-Cone GEnerator (SSG) exposed to extreme wave conditions are reported....
-
Interplay of multiple charge-density-waves and superconductivity in DyTe{sub 3} at high pressures
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Zocco, Diego A. [Institute for Solid State Physics, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, D-76021 Karlsruhe (Germany); Department of Physics, University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 (United States); Kapuvari, Andreas; Sauer, Aaron; Weber, Frank [Institute for Solid State Physics, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, D-76021 Karlsruhe (Germany); Paraskevas, Parisiadis; Garbarino, Gaston [European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, F-38043 Grenoble Cedex (France); Fisher, Ian [Department of Applied Physics, Stanford University, CA 94305 (United States); Hamlin, James; Maple, Brian [Department of Physics, University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 (United States)
2015-07-01
DyTe{sub 3} is a quasi-two-dimensional system in which two successive incommensurate charge-density-wave (CDW) states appear upon cooling at ambient pressure (T{sub CDW,1} = 306 K, T{sub CDW,2} = 49 K). The suppression with pressure of the CDW order is followed by the emergence of superconductivity above 1 GPa and below 1.5 K, as shown by our measurements of electrical resistivity and ac-susceptibility. X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiments under pressure indicate that the lower CDW state merges with the upper one at an intermediate pressure, suggesting that the double-CDW state could be accessed directly below a single T{sub CDW}(P) line. The phase diagram obtained from XRD is compared with the results of our recent electrical resistivity experiments.
-
2012-06-29
8217[-·:’ 50 100 150 200 250 300 Time (sec) Mean Peak Shear Stress (Pa) 0.6 ɘ.0001 200 250 300 350 400 Fluid Volume (I- LL ) lack of correlation to...Blood Flow Metab 30: 255–266. 5. Nakagawa A, Manley GT, Gean AD, Ohtani K, Armonda R, et al. (2011) Mechanisms of primary blast-induced traumatic brain
-
Assessment of Blasting Operations Effects During Highway Tunnel Construction
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Valašková Veronika
2015-12-01
Full Text Available Blasting operations are one of the fundamental parts of daily civil engineering. Drilling and blasting still remain the only possible ways of tunnelling in very adverse geological conditions. However, this method is a source of various disadvantages, the main one being tremors propagating through the geological environment which not only affect buildings, but also disturb the comfort of living in the vicinity of the source. Designing this procedure is mostly done using standardized empirical relations. This article shows the possibility of using a FEM technique in predicting blast effects. This approach is demonstrated in a simple case study on the impact of blasting operations on steel pipes.
-
Blast casting requires fresh assessment of methods
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Pilshaw, S.R.
1987-08-01
The article discusses the reasons why conventional blasting operations, mainly that of explosive products, drilling and initiation methods are inefficient, and suggests new methods and materials to overcome the problems of the conventional operations. The author suggests that the use of bulk ANFO for casting, instead of high energy and density explosives with high velocity detonation is more effective in producing heave action results. Similarly the drilling of smaller blast holes than is conventional allows better loading distribution of explosives in the rock mass. The author also suggests that casting would be more efficient if the shot rows were loaded differently to produce a variable burden blasting pattern.
-
Control of blast overpressure and vibrations at the Underground Research Laboratory
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kuzyk, G.W.; Onagi, D.P.; Mohanty, B.
1991-01-01
AECL Research (AECL) has constructed an Underground Research Laboratory (URL) as a facility for research and development in the Canadian Nuclear Fuel Waste Management Program. The objectives of the program are to develop and evaluate the technology to ensure safe, permanent disposal of Canada's nuclear fuel waste. Several multidisciplinary experiments and engineering demonstrations are planned for the URL over the next ten years. In 1989, AECL excavated a test room for the Buffer/Container Experiment at the 240 Level. The blasts were designed to limit vibration and overpressure damage because the excavation was located close to existing furnishings and services that were very susceptible to blast-induced vibration and overpressure. An experimental room, which contained sensitive instrumentation, was located within 30 m of the initial blasts. A concrete floor slab, timber curtains and a bulkhead were installed to protect furnishings and services from fly-rock and overpressure. Five of the initial blasts were monitored. This paper describes the results of the monitoring program and the effectiveness of the blast design, floor slab and timber curtains and bulkhead in reducing blast overpressure and vibrations at the blast site. It is shown that greater than a 20-fold reduction in both blast vibrations and air overpressures can be achieved with specific combinations of blast design, installation of timber curtains and construction of a concrete floor slab
-
Instability of a planar expansion wave
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Velikovich, A.L.; Zalesak, S.T.; Metzler, N.; Wouchuk, J.G.
2005-01-01
An expansion wave is produced when an incident shock wave interacts with a surface separating a fluid from a vacuum. Such an interaction starts the feedout process that transfers perturbations from the rippled inner (rear) to the outer (front) surface of a target in inertial confinement fusion. Being essentially a standing sonic wave superimposed on a centered expansion wave, a rippled expansion wave in an ideal gas, like a rippled shock wave, typically produces decaying oscillations of all fluid variables. Its behavior, however, is different at large and small values of the adiabatic exponent γ. At γ>3, the mass modulation amplitude δm in a rippled expansion wave exhibits a power-law growth with time ∝t β , where β=(γ-3)/(γ-1). This is the only example of a hydrodynamic instability whose law of growth, dependent on the equation of state, is expressed in a closed analytical form. The growth is shown to be driven by a physical mechanism similar to that of a classical Richtmyer-Meshkov instability. In the opposite extreme γ-1 -1/2 , and then starts to decrease. The mechanism driving the growth is the same as that of Vishniac's instability of a blast wave in a gas with low γ. Exact analytical expressions for the growth rates are derived for both cases and favorably compared to hydrodynamic simulation results
-
Evaluation of Blast Resistance of Fiber Reinforced Composite Specimens under Contact Blast Load
Janota, O.; Foglar, M.
2017-09-01
This paper presents results of experimental programme which took place in 2014, 2015 and 2016. Experiments were focused on the resistance of full scale concrete panels subjected to contact blast loading. Specimens were loaded by contact blast by plastic explosive. All specimens were reinforced concrete slabs made of fiber concrete. Basalt mesh and textile sheets were added to some of the experiments for creating more heterogeneous material to achieve better resistance of the specimens. Evaluation of experiments was mainly focused on the damaged area on the contact side and soffit of the specimens. Dependency of the final damage of concrete panels on the weight of explosive and concrete strength was assessed.
-
Decontamination of Steam Generator tube using Abrasive Blasting Technology
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Min, B. Y.; Kim, G. N.; Choi, W. K.; Lee, K. W.; Kim, D. H.; Kim, K. H.; Kim, B. T.
2010-01-01
As a part of a technology development of volume reduction and self disposal for large metal waste project, We at KAERI and our Sunkwang Atomic Energy Safety (KAES) subcontractor colleagues are demonstrating radioactively contaminated steam generator tube by abrasive blasting technology at Kori-1 NPP. A steam generator is a crucial component in a PWR (pressurized Water Reactor). It is the crossing between the primary, contaminated, circuit and the secondary waste-steam circuit. The heat from the primary reactor coolant loop is transferred to the secondary side in thousands of small tubes. Due to several problems in the material of those tube, like SCC (Stress Corrosion Cracking), insufficient control in water chemistry, which can be cause of tube leakage, more and more steam generators are replaced today. Only in Korea, already 2 of them are replaced and will be replaced in the near future. The retired 300 ton heavy Steam generator was stored at the storage waste building of Kori NPP site. The steam generator waste has a large volume, so that it is necessary to reduce its volume by decontamination. A waste reduction effect can be obtained through decontamination of the inner surface of a steam generator. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an optimum method for decontamination of the inner surface of bundle tubes. The dry abrasive blasting is a very interesting technology for the realization of three-dimensional microstructures in brittle materials like glass or silicon. Dry abrasive blasting is applicable to most surface materials except those that might be shattered by the abrasive. It is most effective on flat surface and because the abrasive is sprayed and can also applicable on 'hard to reach' areas such as inner tube ceilings or behind equipment. Abrasive decontamination techniques have been applied in several countries, including Belgium, the CIS, France, Germany, Japan, the UK and the USA
-
Chen, Yongyao; Liu, Haijun; Reilly, Michael; Bae, Hyungdae; Yu, Miao
2014-10-15
Acoustic sensors play an important role in many areas, such as homeland security, navigation, communication, health care and industry. However, the fundamental pressure detection limit hinders the performance of current acoustic sensing technologies. Here, through analytical, numerical and experimental studies, we show that anisotropic acoustic metamaterials can be designed to have strong wave compression effect that renders direct amplification of pressure fields in metamaterials. This enables a sensing mechanism that can help overcome the detection limit of conventional acoustic sensing systems. We further demonstrate a metamaterial-enhanced acoustic sensing system that achieves more than 20 dB signal-to-noise enhancement (over an order of magnitude enhancement in detection limit). With this system, weak acoustic pulse signals overwhelmed by the noise are successfully recovered. This work opens up new vistas for the development of metamaterial-based acoustic sensors with improved performance and functionalities that are highly desirable for many applications.
-
Directory of Open Access Journals (Sweden)
Siu H. Chan
2012-02-01
Full Text Available Vascular stiffness has been proposed as a simple method to assess arterial loading conditions of the heart which induce left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH. There is some controversy as to whether the relationship of vascular stiffness to LVH is independent of blood pressure, and which measurement of arterial stiffness, augmentation index (AI or pulse wave velocity (PWV is best. Carotid pulse wave contor and pulse wave velocity of patients (n=20 with hypertension whose blood pressure (BP was under control (<140/90 mmHg with antihypertensive drug treatment medications, and without valvular heart disease, were measured. Left ventricular mass, calculated from 2D echocardiogram, was adjusted for body size using two different methods: body surface area and height. There was a significant (P<0.05 linear correlation between LV mass index and pulse wave velocity. This was not explained by BP level or lower LV mass in women, as there was no significant difference in PWV according to gender (1140.1+67.8 vs 1110.6+57.7 cm/s. In contrast to PWV, there was no significant correlation between LV mass and AI. In summary, these data suggest that aortic vascular stiffness is an indicator of LV mass even when blood pressure is controlled to less than 140/90 mmHg in hypertensive patients. The data further suggest that PWV is a better proxy or surrogate marker for LV mass than AI and the measurement of PWV may be useful as a rapid and less expensive assessment of the presence of LVH in this patient population.
-
Controlled blasting experiments in a small drift at the CANMET experimental mine
Energy Technology Data Exchange (ETDEWEB)
Lizotte, Y.C.
1994-03-01
Experiments on controlled blasting conducted at the CANMET Experimental Mine to develop suitable controlled blasting techniques for small development headings are described. The methods selected for study must maintain the drill-blast-muck cycle achieved each work shift. The experiments also examine blast damage mechanisms to formulate criteria for dilution minimization with blast designs in stopes. The drift faces are 2.4 m square, with 34 to 43 holes drilled 2.4 m deep. Cartridged water gels, emulsions, and semi-gelatin dynamite were used in the cuts and as primers, ANFO as the main explosive, and semi- gelatin dynamite in 19 mm diameter cartridges was used in perimeter holes. The results of the first set of experiments show the efficiency of controlled blasting techniques to reduce blast damage. 60 refs., 71 figs., 9 tabs.
-
29 CFR 1926.904 - Storage of explosives and blasting agents.
2010-07-01
..., electric blasting caps, detonating primers, and primed cartridges shall not be stored in the same magazine... feet of explosives and detonator storage magazine. (d) No explosives or blasting agents shall be... 29 Labor 8 2010-07-01 2010-07-01 false Storage of explosives and blasting agents. 1926.904 Section...
-
Blasting Impact by the Construction of an Underground Research Tunnel in KAERI
International Nuclear Information System (INIS)
Kwon, S.; Cho, W. J.
2005-12-01
The underground research tunnel, which is under construction in KAERI for the validation of HLW disposal system, is excavated by drill and blasting method using high-explosives. In order not to disturb the operation at the research facilities such as HANARO reactor, it is critical to develop a blasting design , which will not influence on the facilities, even though several tens of explosives are detonated almost simultaneously. To develop a reasonable blasting design, a test blasting at the site should be performed. A preliminary analysis for predicting the expected vibration and noise by the blasting for the construction of the underground research tunnel was performed using a typical empirical equation. From the study, a blasting design could be developed not to influence on the major research facilities in KAERI. For the validation of the blasting design, a test blasting was carried out at the site and the parameters of vibration equation could be determined using the measured data during the test blasting. Using the equation, it was possible to predict the vibration at different locations at KAERI and to conclude that the blasting design would meet the design criteria at the major facilities in KAERI. The study would verify the applicability of blasting method for the construction of a research tunnel in a rock mass and that would help the design and construction of large scale underground research laboratory, which might be carried out in the future. It is also meaningful to accumulate technical experience for enhancing the reliability and effectiveness of the design and construction of the HLW disposal repository, which will be constructed in deep underground by drill and blasting technique
-
Blast resistance behaviour of steel frame structrures
Mediavilla Varas, J.; Soetens, F.
2010-01-01
The effect of a blast explosion on a typical steel frame building is investigated by means of computer simulations. The simulations help to identify possible hot spots that may lead to local or global failure. Since the blast energy is transferred to the structure by means of the façade, it is
-
Blast resistance behaviour of steel frame structures
Varas, J.M.; Soetens, F.
2010-01-01
The effect of a blast explosion on a typical steel frame building is investigated by means of computer simulations. The simulations help to identify possible hot spots that may lead to local or global failure. The blast energy is transferred to the structure by means of the façade. In particular